mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
commit
faaae1caf2
69
published/20210228 What is GNU-Linux Copypasta.md
Normal file
69
published/20210228 What is GNU-Linux Copypasta.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: (What is GNU/Linux Copypasta?)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://itsfoss.com/gnu-linux-copypasta/)
|
||||
[#]: author: (Abhishek Prakash https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/)
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: (wxy)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
|
||||
[#]: publisher: (wxy)
|
||||
[#]: url: (wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
谈谈 GNU/Linux 口水话
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
作为一个 Linux 用户,你可能遇到过以这样开头的一大段文字:“我想插一句话。你所说的 Linux,实际上是指 GNU/Linux。”
|
||||
|
||||
这让一些人对什么是 “Linux” 和什么是 “GNU/Linux” 感到困惑。对此,我在关于 [Linux 发行版的概念][1] 的文章中已经解释过。
|
||||
|
||||
基本上,[Linux 是一个内核][2],加上 [GNU 软件][3],它就可以以操作系统的形式使用。
|
||||
|
||||
许多纯粹主义者和拥趸们不希望人们忘记 GNU 对基于 Linux 的操作系统的贡献。因此,他们经常在各种论坛和社区发布这篇长文(被称为 GNU Linux <ruby>口水话<rt>copypaste</rt></ruby>)。
|
||||
|
||||
我不清楚这些 GNU/Linux 口水话的起源,也不清楚它是从什么时候开始出现的。有些人把它归功于 Richard Stallman 的 [2011 年在 GNU 博客上的文章][4]。我无法证实或否认这一点。
|
||||
|
||||
### 完整的 GNU/Linux 口水话
|
||||
|
||||
> 我只想插一句话。你所说的 Linux,实际上是 GNU/Linux,或者正如我最近所称,是 GNU + Linux。Linux 本身并不是一个操作系统,而是功能齐全的 GNU 系统的另一个自由组件,这个系统是由 GNU 核心库、shell 实用程序和重要的系统组件组成的、按 POSIX 定义构成的完整操作系统。
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 许多计算机用户每天都在运行着一个修改过的 GNU 系统,却没有意识到这一点。通过一个奇特的转折,这个今天被广泛使用的 GNU 版本通常被称为 Linux,而它的许多用户并不知道它基本上是由 GNU 项目开发的 GNU 系统。
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Linux 倒也真的是存在,这些人也在使用它,但它只是他们使用的系统的一部分罢了。Linux 是内核:在系统中该程序将机器的资源分配给你运行的其他程序。内核是操作系统的一个重要部分,但它本身是无用的;它只能在一个完整的操作系统的环境下发挥作用。Linux 通常与 GNU 操作系统结合使用:整个系统基本上是添加了 Linux 的 GNU,或者叫 GNU/Linux。所有所谓的 Linux 发行版实际上都是 GNU/Linux 的发行版!
|
||||
|
||||
### 到底什么是口水话?
|
||||
|
||||
![][7]
|
||||
|
||||
你是否注意到,我使用了“Copypasta”(LCTT 译注:译者选择翻译为“口水话”,或许有更贴合中文的译法,请大家指正)这个术语。它与<ruby>意大利面<rt>pasta</rt></ruby>毫无关系。
|
||||
|
||||
[口水话][8] 是在互联网上复制和粘贴的文本块,通常是为了嘲弄或取笑别人。它是“<ruby>复制-粘贴<rt>copy-paste</rt></ruby>”一词的变种。
|
||||
|
||||
口水话也被认为是垃圾内容,因为它们被重复了一次又一次。以 GNU Linux 口水话为例。如果每次有人在讨论区中使用 Linux 这个词而不是 GNU/Linux 时,总会有几个人不断地粘贴这些大段的文本,那么就会惹恼其他成员。
|
||||
|
||||
### 你有没有贴过 GNU/Linux 口水话?
|
||||
|
||||
就个人而言,我从来没有这样做过。但是,说实话,当我还是一个新的 Linux 用户,在浏览一些 Linux 论坛时,我就是这样知道 GNU/Linux 这个术语的。
|
||||
|
||||
你呢?你有没有在 Linux 论坛上复制粘贴过“我想插一句话……”?你认为它是“嘲弄”工具,还是让人们了解 GNU 项目的必要之举?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://itsfoss.com/gnu-linux-copypasta/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://itsfoss.com/what-is-linux-distribution/
|
||||
[2]: https://itsfoss.com/what-is-linux/
|
||||
[3]: https://www.gnu.org/
|
||||
[4]: https://www.gnu.org/gnu/linux-and-gnu.html
|
||||
[5]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/what-is-foss.png?fit=800%2C450&ssl=1
|
||||
[6]: https://itsfoss.com/what-is-foss/
|
||||
[7]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/copypasta.png?resize=800%2C450&ssl=1
|
||||
[8]: https://www.makeuseof.com/what-is-a-copypasta/
|
||||
@ -4,21 +4,19 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: "geekpi"
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: "turbokernel"
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: "wxy"
|
||||
[#]: url: "https://linux.cn/article-13771-1.html"
|
||||
|
||||
日常需求应用之四:音频编辑器
|
||||
满足日常需求的应用(四):音频编辑器
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
![][1]
|
||||
|
||||
图片由 [Brooke Cagle][2] 在 [Unsplash][3] 上发布。
|
||||
|
||||
在过去,音频编辑应用或数字音频工作站(DAW)只提供给专业人士使用,如唱片制作人、音响工程师和音乐家。但现在很多不是专业人士的人也需要它们。这些工具被用于演示文稿解说、视频博客,甚至只是作为一种爱好。现在尤其如此,因为有这么多的在线平台,方便大家分享音频作品,如音乐、歌曲、播客等。本文将介绍一些你可以在 Fedora Linux 上使用的开源音频编辑器或 DAW。你可能需要安装提到的软件。如果你不熟悉如何在 Fedora Linux 中添加软件包,请参阅我之前的文章[安装 Fedora 34 工作站后要做的事情][4]。这里列出了音频编辑器或 DAW 类的一些日常需求的应用。
|
||||
在过去,音频编辑应用或<ruby>数字音频工作站<rt>digital audio workstation</rt></ruby>(DAW)只提供给专业人士使用,如唱片制作人、音响工程师和音乐家。但现在很多不是专业人士的人也需要它们。这些工具被用于演示文稿解说、视频博客,甚至只是作为一种爱好。现在尤其如此,因为有这么多的在线平台,方便大家分享音频作品,如音乐、歌曲、播客等。本文将介绍一些你可以在 Fedora Linux 上使用的开源音频编辑器或 DAW。你可能需要安装提到的软件。如果你不熟悉如何在 Fedora Linux 中添加软件包,请参阅我之前的文章[安装 Fedora 34 工作站后要做的事情][4]。这里列出了音频编辑器或 DAW 类的一些日常需求的应用。
|
||||
|
||||
### Audacity
|
||||
|
||||
我相信很多人已经知道 Audacity 了。它是一个流行的多轨音频编辑器和录音机,可用于对所有类型的音频进行后期处理。大多数人使用 Audacity 来记录他们的声音,然后进行编辑,使其结果更好。其结果可以作为播客或视频博客的解说词。此外,人们还用 Audacity 来创作音乐和歌曲。你可以通过麦克风或调音台录制现场音频。它还支持 32 位的声音质量。
|
||||
我相信很多人已经知道 Audacity 了。它是一个流行的多轨音频编辑器和录音机,可用于对所有类型的音频进行后期处理。大多数人使用 Audacity 来记录他们的声音,然后进行编辑,使其成品更好。其成品可以作为播客或视频博客的解说词。此外,人们还用 Audacity 来创作音乐和歌曲。你可以通过麦克风或调音台录制现场音频。它还支持 32 位的声音质量。
|
||||
|
||||
Audacity 有很多功能,可以支持你的音频作品。它有对插件的支持,你甚至可以自己编写插件。Audacity 提供了许多内置效果,如降噪、放大、压缩、混响、回声、限制器等。你可以利用实时预览功能在直接聆听音频的同时尝试这些效果。内置的插件管理器可以让你管理经常使用的插件和效果。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,18 +24,14 @@ Audacity 有很多功能,可以支持你的音频作品。它有对插件的
|
||||
|
||||
详情请参考此链接: <https://www.audacityteam.org/>
|
||||
|
||||
* * *
|
||||
|
||||
### LMMS
|
||||
|
||||
LMMS 或 Linux MultiMedia Studio 是一个全面的音乐创作应用。你可以从头使用 LMMS 用你的电脑开始制作你的音乐。你可以根据自己的创意创造旋律和节拍,并通过选择声音乐器和各种效果使其更加完美。有几个与乐器和效果有关的内置功能,如 16 个内置合成器、嵌入式 ZynAddSubFx、支持插入式 VST 效果插件、捆绑图形和参数均衡器、内置分析器等等。LMMS 还支持 MIDI 键盘和其他音频外围设备。
|
||||
LMMS(即 <ruby>Linux 多媒体工作室<rt>Linux MultiMedia Studio</rt></ruby>)是一个全面的音乐创作应用。你可以从头使用 LMMS 用你的电脑开始制作你的音乐。你可以根据自己的创意创造旋律和节拍,并通过选择声音乐器和各种效果使其更加完美。有几个与乐器和效果有关的内置功能,如 16 个内置合成器、嵌入式 ZynAddSubFx、支持插入式 VST 效果插件、捆绑图形和参数均衡器、内置分析器等等。LMMS 还支持 MIDI 键盘和其他音频外围设备。
|
||||
|
||||
![][6]
|
||||
|
||||
详情请参考此链接: <https://lmms.io/>
|
||||
|
||||
* * *
|
||||
|
||||
### Ardour
|
||||
|
||||
Ardour 作为一个全面的音乐创作应用,其功能与 LMMS 相似。它在其网站上说,Ardour 是一个 DAW 应用,是来自世界各地的音乐家、程序员和专业录音工程师合作的结果。Ardour 拥有音频工程师、音乐家、配乐编辑和作曲家需要的各种功能。
|
||||
@ -48,8 +42,6 @@ Ardour 提供了完整的录音、编辑、混音和输出功能。它有无限
|
||||
|
||||
详情请参考此链接: <https://ardour.org/>
|
||||
|
||||
* * *
|
||||
|
||||
### TuxGuitar
|
||||
|
||||
TuxGuitar 是一款指法谱和乐谱编辑器。它配备了指法编辑器、乐谱查看器、多轨显示、拍号管理和速度管理。它包括弯曲、滑动、颤音等各种效果。虽然 TuxGuitar 专注于吉他,但它也可以为其他乐器写乐谱。它也能够作为一个基本的 MIDI 编辑器。你需要对指法谱和乐谱有一定的了解才能使用它。
|
||||
@ -58,11 +50,9 @@ TuxGuitar 是一款指法谱和乐谱编辑器。它配备了指法编辑器、
|
||||
|
||||
详情请参考此链接: <http://www.tuxguitar.com.ar/>
|
||||
|
||||
* * *
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
本文章介绍了四款音频编辑器,满足您在 Fedora Linux 上日常使用的需求。其实,在 Fedora Linux 上还有很多音频编辑器或者 DAW 供您选择。您也可以使用 Mixxx、Rosegarden、Kwave、Qtractor、MuseScore、musE 等等。希望本文为您调查和选择合适的音频编辑器或者 DAW 提供帮助。如您有使用这些应用的经验,请在评论中分享您的经验。
|
||||
本文章介绍了四款音频编辑器,可以满足你在 Fedora Linux 上日常使用的需求。其实,在 Fedora Linux 上还有很多音频编辑器或者 DAW 供你选择。你也可以使用 Mixxx、Rosegarden、Kwave、Qtractor、MuseScore、musE 等等。希望本文为你调查和选择合适的音频编辑器或者 DAW 提供帮助。如你有使用这些应用的经验,请在评论中分享你的经验。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
92
published/20210901 What are container runtimes.md
Normal file
92
published/20210901 What are container runtimes.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "What are container runtimes?"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://opensource.com/article/21/9/container-runtimes"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Nived V https://opensource.com/users/nivedv"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: "geekpi"
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: "turbokernel"
|
||||
[#]: publisher: "wxy"
|
||||
[#]: url: "https://linux.cn/article-13772-1.html"
|
||||
|
||||
什么是容器运行时?
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
> 通过深入了解容器运行时,理解容器环境是如何建立的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在学习 [容器镜像][2] 时,我们讨论了容器的基本原理,但现在是深入研究容器<ruby>运行时<rt>runtime</rt></ruby>的时候了,从而了解容器环境是如何构建的。本文的部分信息摘自 <ruby>开放容器计划<rt>Open Container Initiative</rt></ruby>(OCI)的 [官方文档][3],所以无论使用何种容器引擎,这些信息都是一致的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 容器运行机制
|
||||
|
||||
那么,当你运行 `podman run` 或 `docker run` 命令时,在后台到底发生了什么?一个分步的概述如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 如果本地没有镜像,则从镜像<ruby>登记仓库<rt>registry</rt></ruby>拉取镜像
|
||||
2. 镜像被提取到一个写时复制(COW)的文件系统上,所有的容器层相互堆叠以形成一个合并的文件系统
|
||||
3. 为容器准备一个挂载点
|
||||
4. 从容器镜像中设置元数据,包括诸如覆盖 `CMD`、来自用户输入的 `ENTRYPOINT`、设置 SECCOMP 规则等设置,以确保容器按预期运行
|
||||
5. 提醒内核为该容器分配某种隔离,如进程、网络和文件系统(<ruby>命名空间<rt>namespace</rt></ruby>)
|
||||
6. 提醒内核为改容器分配一些资源限制,如 CPU 或内存限制(<ruby>控制组<rt>cgroup</rt></ruby>)
|
||||
7. 传递一个<ruby>系统调用<rt>syscall</rt></ruby>给内核用于启动容器
|
||||
8. 设置 SELinux/AppArmor
|
||||
|
||||
容器运行时负责上述所有的工作。当我们提及容器运行时,想到的可能是 runc、lxc、containerd、rkt、cri-o 等等。嗯,你没有错。这些都是容器引擎和容器运行时,每一种都是为不同的情况建立的。
|
||||
|
||||
<ruby>容器运行时<rt>Container runtime</rt></ruby>更侧重于运行容器,为容器设置命名空间和控制组(cgroup),也被称为底层容器运行时。高层的容器运行时或容器引擎专注于格式、解包、管理和镜像共享。它们还为开发者提供 API。
|
||||
|
||||
### 开放容器计划(OCI)
|
||||
|
||||
<ruby>开放容器计划<rt>Open Container Initiative</rt></ruby>(OCI)是一个 Linux 基金会的项目。其目的是设计某些开放标准或围绕如何与容器运行时和容器镜像格式工作的结构。它是由 Docker、rkt、CoreOS 和其他行业领导者于 2015 年 6 月建立的。
|
||||
|
||||
它通过两个规范来完成如下任务:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1、镜像规范
|
||||
|
||||
该规范的目标是创建可互操作的工具,用于构建、传输和准备运行的容器镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
该规范的高层组件包括:
|
||||
|
||||
* [镜像清单][4] — 一个描述构成容器镜像的元素的文件
|
||||
* [镜像索引][5] — 镜像清单的注释索引
|
||||
* [镜像布局][6] — 一个镜像内容的文件系统布局
|
||||
* [文件系统布局][7] — 一个描述容器文件系统的变更集
|
||||
* [镜像配置][8] — 确定镜像层顺序和配置的文件,以便转换成 [运行时捆包][9]
|
||||
* [转换][10] — 解释应该如何进行转换的文件
|
||||
* [描述符][11] — 一个描述被引用内容的类型、元数据和内容地址的参考资料
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2、运行时规范
|
||||
|
||||
该规范用于定义容器的配置、执行环境和生命周期。`config.json` 文件为所有支持的平台提供了容器配置,并详细定义了用于创建容器的字段。在详细定义执行环境时也描述了为容器的生命周期定义的通用操作,以确保在容器内运行的应用在不同的运行时环境之间有一个一致的环境。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 容器规范使用了各种内核特性,包括<ruby>命名空间<rt>namespace</rt></ruby>、<ruby>控制组<rt>cgroup</rt></ruby>、<ruby>权能<rt>capability</rt></ruby>、LSM 和文件系统<ruby>隔离<rt>jail</rt></ruby>等来实现该规范。
|
||||
|
||||
### 小结
|
||||
|
||||
容器运行时是通过 OCI 规范管理的,以提供一致性和互操作性。许多人在使用容器时不需要了解它们是如何工作的,但当你需要排除故障或优化时,了解容器是一个宝贵的优势。
|
||||
|
||||
本文基于 [techbeatly][12] 的文章,并经授权改编。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/21/9/container-runtimes
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Nived V][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[turbokernel](https://github.com/turbokernel)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/nivedv
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/kubernetes_containers_ship_lead.png?itok=9EUnSwci (Ships at sea on the web)
|
||||
[2]: https://opensource.com/article/21/8/container-fundamentals-2
|
||||
[3]: https://github.com/opencontainers
|
||||
[4]: https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/master/manifest.md
|
||||
[5]: https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/master/image-index.md
|
||||
[6]: https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/master/image-layout.md
|
||||
[7]: https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/master/layer.md
|
||||
[8]: https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/master/config.md
|
||||
[9]: https://github.com/opencontainers/runtime-spec
|
||||
[10]: https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/master/conversion.md
|
||||
[11]: https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/master/descriptor.md
|
||||
[12]: https://medium.com/techbeatly/container-runtimes-deep-dive-77eb0e511939
|
||||
@ -3,16 +3,18 @@
|
||||
[#]: author: "Abhishek Prakash https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: "geekpi"
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: "wxy"
|
||||
[#]: publisher: "wxy"
|
||||
[#]: url: "https://linux.cn/article-13773-1.html"
|
||||
|
||||
如何在 Ubuntu Linux 上安装 Dropbox
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
Dropbox 是[最受欢迎的云存储服务之一,可用于 Linux][1] 和其他操作系统。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
事实上,Dropbox 是最早提供原生 Linux 应用的服务之一。它仍然[支持 32 位 Linux 系统][2],这也是一项值得称赞的工作。
|
||||
Dropbox 是 [最受欢迎的云存储服务之一,可用于 Linux][1] 和其他操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
事实上,Dropbox 是最早提供原生 Linux 应用的服务之一。它仍然 [支持 32 位 Linux 系统][2],这也是一项值得称赞的工作。
|
||||
|
||||
在这个初学者的教程中,我将展示在 Ubuntu 上安装 Dropbox 的步骤。这些步骤其实很简单,但有些网站把它弄得不必要的复杂。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,9 +24,9 @@ Dropbox 是[最受欢迎的云存储服务之一,可用于 Linux][1] 和其他
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第一步:获取 Ubuntu 的 Dropbox 安装程序
|
||||
|
||||
Dropbox 为其安装程序提供 DEB文 件。进入网站的下载页面:
|
||||
Dropbox 为其安装程序提供 DEB 文件。进入网站的下载页面:
|
||||
|
||||
[Dropbox Download][3]
|
||||
- [下载 Dropbox][3]
|
||||
|
||||
下载相应的 DEB 文件。考虑到你使用的是 64 位的 Ubuntu,请获取 64 位版本的 DEB 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -32,9 +34,9 @@ Dropbox 为其安装程序提供 DEB文 件。进入网站的下载页面:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第二步:安装 Dropbox 安装程序
|
||||
|
||||
你下载的 deb 文件只是 Dropbox 的一个安装程序。实际的 Dropbox 安装稍后开始,类似于[在 Ubuntu 上安装 Steam][5]。
|
||||
你下载的 deb 文件只是 Dropbox 的一个安装程序。实际的 Dropbox 安装稍后开始,类似于 [在 Ubuntu 上安装 Steam][5]。
|
||||
|
||||
要[安装下载的 deb 文件][6],可以双击它,或者右击并选择用软件安装打开。
|
||||
要 [安装下载的 deb 文件][6],可以双击它,或者右击并选择用软件安装打开。
|
||||
|
||||
![Installing the downloaded Dropbox deb file][7]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -46,7 +48,7 @@ Dropbox 为其安装程序提供 DEB文 件。进入网站的下载页面:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第三步:开始安装 Dropbox
|
||||
|
||||
现在 Dropbox 安装程序已经安装完毕。按 Windows 键(也叫 super 键),搜索 Dropbox 并点击它。
|
||||
现在 Dropbox 安装程序已经安装完毕。按 `Windows` 键(也叫 `Super` 键),搜索 Dropbox 并点击它。
|
||||
|
||||
![Start Dropbox for installation][9]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,9 +56,9 @@ Dropbox 为其安装程序提供 DEB文 件。进入网站的下载页面:
|
||||
|
||||
![Starting Dropbox installation][10]
|
||||
|
||||
点击 Restart Nautilus/Close(在 Nautilus 弹出窗口)或 OK(在安装弹出窗口),开始实际的 Dropbox 客户端下载和安装。如果 “Nautilus Restart” 在点击关闭按钮时没有关闭,请点击 x 按钮。
|
||||
点击 “Restart Nautilus” -> “Close”(在 Nautilus 弹出窗口)或 “OK”(在安装弹出窗口),开始实际的 Dropbox 客户端下载和安装。如果 “Nautilus Restart” 在点击关闭按钮时没有关闭,请点击 “X” 按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
等待Dropbox的安装完成。
|
||||
等待 Dropbox 的安装完成。
|
||||
|
||||
![Installing Dropbox][11]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -78,7 +80,7 @@ Dropbox 为其安装程序提供 DEB文 件。进入网站的下载页面:
|
||||
|
||||
![Dropbox folder is created under home directory][14]
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想节省磁盘空间或带宽,你可以进入偏好设置并选择选择性同步选项。选择性同步选项允许你只在本地系统上同步来自 Dropbox 云的选定文件夹。
|
||||
如果你想节省磁盘空间或带宽,你可以进入偏好设置并选择<ruby>选择性同步<rt>Selective Sync</rt></ruby>选项。该选项允许你只在本地系统上同步来自 Dropbox 云的选定文件夹。
|
||||
|
||||
![Using selective sync in Dropbox][15]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -93,7 +95,7 @@ via: https://itsfoss.com/install-dropbox-ubuntu/
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,62 +3,58 @@
|
||||
[#]: author: "Jim Hall https://opensource.com/users/jim-hall"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: "geekpi"
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: "wxy"
|
||||
[#]: publisher: "wxy"
|
||||
[#]: url: "https://linux.cn/article-13779-1.html"
|
||||
|
||||
从 Linux 终端调整图像的大小
|
||||
在 Linux 终端调整图像的大小
|
||||
======
|
||||
用 ImageMagick 的转换命令从你的终端收缩一张图像。
|
||||
![Old camera blue][1]
|
||||
|
||||
> 用 ImageMagick 的转换命令从你的终端缩放一张图像。
|
||||
|
||||
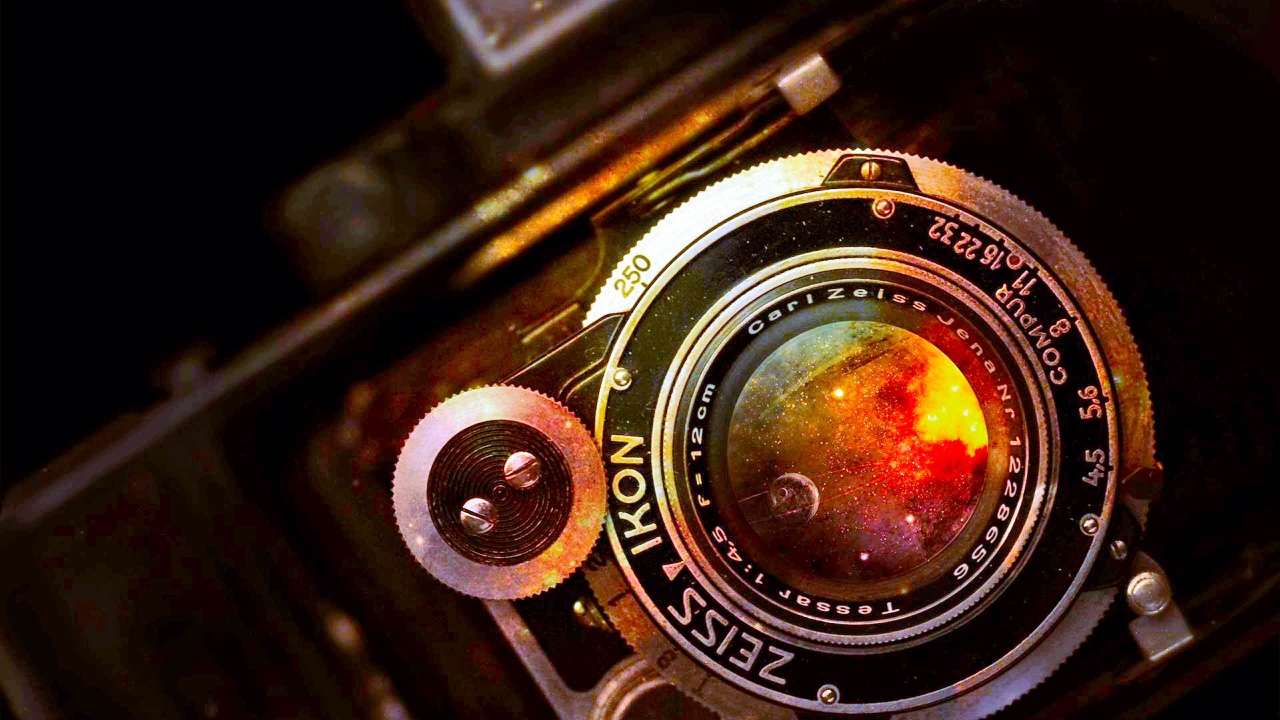
|
||||
|
||||
ImageMagick 是一个方便的多用途命令行工具,它能满足你所有的图像需求。ImageMagick 支持各种图像类型,包括 JPG 照片和 PNG 图形。
|
||||
|
||||
### 调整图像大小
|
||||
|
||||
我经常在我的网络服务器上使用 ImageMagick 来调整图像大小。例如,假设我想在我的个人网站上发一张我的猫的照片。我手机里的照片非常大,大约 4000x3000 像素,有 3.3MB。这对一个网页来说太大了。我使用 ImageMagick 转换工具来改变照片的大小,这样我就可以把它放在我的网页上。ImageMagick 是一套完整的工具,其中最常用的是 `convert` 命令。
|
||||
我经常在我的 Web 服务器上使用 ImageMagick 来调整图像大小。例如,假设我想在我的个人网站上发一张我的猫的照片。我手机里的照片非常大,大约 4000x3000 像素,有 3.3MB。这对一个网页来说太大了。我使用 ImageMagick 转换工具来改变照片的大小,这样我就可以把它放在我的网页上。ImageMagick 是一套完整的工具,其中最常用的是 `convert` 命令。
|
||||
|
||||
ImageMagick 的 `convert` 命令使用这样的一般语法:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
`convert {input} {actions} {output}`
|
||||
convert {input} {actions} {output}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
要将一张名为 `PXL_20210413_015045733.jpg` 的照片调整到一个更容易管理的 500 像素宽度,请输入:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
`$ convert PXL_20210413_015045733.jpg -resize 500x sleeping-cats.jpg`
|
||||
$ convert PXL_20210413_015045733.jpg -resize 500x sleeping-cats.jpg
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在新图片的大小只有 65KB。
|
||||
|
||||
![Sleeping cats][2]
|
||||
|
||||
Jim Hall,[CC BY-SA 4.0][3]
|
||||
|
||||
你可以用 `-resize` 选项同时提供宽度和高度尺寸。但是,如果只提供宽度,ImageMagic 就会为你做计算,并通过调整输出图像的高度比例来自动保留长宽比。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Linux 上安装 ImageMagick
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 上,你可以使用你的包管理器安装 ImageMagick。例如,在 Fedora 或类似系统上:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
`$ sudo dnf install imagemagick`
|
||||
$ sudo dnf install imagemagick
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 Debian 和类似系统上:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
`$ sudo apt install imagemagick`
|
||||
$ sudo apt install imagemagick
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 macOS 上,使用 [MacPorts][4] 或 [Homebrew][5]。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Windows 上,使用 [Chocolatey][6]。
|
||||
在 Windows 上,使用 [Chocolatey][6] 即可。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -67,7 +63,7 @@ via: https://opensource.com/article/21/9/resize-image-linux
|
||||
作者:[Jim Hall][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,32 +3,32 @@
|
||||
[#]: author: "Ankush Das https://itsfoss.com/author/ankush/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: "anine09"
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: "wxy"
|
||||
[#]: publisher: "wxy"
|
||||
[#]: url: "https://linux.cn/article-13777-1.html"
|
||||
|
||||
使用 Tangram Browser 在 Linux 中运行 Web 应用
|
||||
使用 Tangram 浏览器在 Linux 中运行 Web 应用
|
||||
=======
|
||||
|
||||
_**导语:**Tangram 是一个旨在帮助你在 Linux 中运行和管理 Web 应用的浏览器_。_一起来看看它是如何使用的吧。_
|
||||
> Tangram 是一个旨在帮助你在 Linux 中运行和管理 Web 应用的浏览器。一起来看看它是如何使用的吧。
|
||||
|
||||
即使我们有许多本地的工具类 Linux 本地应用,但是许多人最终还是选择使用 Web 应用。
|
||||
对于一些工具来说,即使我们有许多 Linux 原生应用,但是许多人最终还是选择使用 Web 应用。
|
||||
|
||||
他们也许是使用 Electron 构建的应用或是直接在浏览器中打开网页,使用本地应用正在成为一种比较“传统”的做法。
|
||||
他们也许是使用 Electron 构建的应用,或是直接在浏览器中打开的网页,使用原生应用正在成为一种比较“传统”的做法。
|
||||
|
||||
当然,运行 Web 应用,不管是什么平台,都会占用更多的系统资源。而且,考虑到每一个服务都是基于 Web 端而不是本地,我们就需要一种有效管理 Web 应用的解决方案。
|
||||
当然,不管在什么平台运行 Web 应用都会占用更多的系统资源。而且,考虑到每一个服务都正在提供基于 Web 的方式,而不是原生体验,我们就需要一种有效管理 Web 应用的解决方案。
|
||||
|
||||
因此,我为你介绍一款开源的 Linux 应用,Tangram。
|
||||
一款开源的 Linux 应用 Tangram 或许就是这个解决方案。
|
||||
|
||||
### Tangram:专为 Web 应用设计的浏览器
|
||||
|
||||
![][1]
|
||||
|
||||
你可以选择其他[优秀的浏览器][2]来运行 Web 应用,但是如果你想完全专注于 Web 应用体验的浏览器,Tangram 是个不错的选择。
|
||||
你可以选择其他 [优秀的浏览器][2] 来运行 Web 应用,但是如果你想完全专注于 Web 应用体验的浏览器,Tangram 是个不错的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
Tangram 的开发者从 GNOME Web,[Franz][3],和 [Rambox][4] 中获得的灵感。
|
||||
Tangram 的开发者从 GNOME Web、[Franz][3] 和 [Rambox][4] 中获得了灵感。
|
||||
|
||||
没有其他花里胡哨的功能, Tangram 能帮助你改变你的用户代理( User Agent )和管理那些你已经登陆的 Web 应用。
|
||||
没有其他花里胡哨的功能,只是能更改你的<ruby>用户代理<rt>User Agent</rt></ruby>和管理你所登录的 Web 应用。
|
||||
|
||||
它可以用于访问多个社交媒体,聊天工具,工作协同应用等等。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,16 +36,15 @@ Tangram 的开发者从 GNOME Web,[Franz][3],和 [Rambox][4] 中获得的
|
||||
|
||||
![][5]
|
||||
|
||||
考虑到 Tangram 是基于 WebKitGTK 的精简化浏览器,它拥有的功能不算很多,下面是一些功能要点:
|
||||
考虑到 Tangram 是一个基于 WebKitGTK 的精简化浏览器,它拥有的功能不算很多,下面是一些功能要点:
|
||||
|
||||
* 重新排列的侧边栏选项卡
|
||||
* 方便地添加任何一个 Web 服务作为一个 Web 应用程序
|
||||
* 在桌面端和移动端调整用户代理(User Agent)
|
||||
* 重新排列侧边栏的标签
|
||||
* 方便地将任何一个 Web 服务添加为 Web 应用程序
|
||||
* 调整用户代理(桌面端和移动端)
|
||||
* 使用键盘快捷键
|
||||
* 改变侧边栏和选项卡的位置
|
||||
* 改变侧边栏(标签栏)的位置
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
你所需要做的就是加载一个 Web 服务,登陆,然后点击**“完成”**,将其添加为 Web 应用程序。
|
||||
你所需要做的就是加载一个 Web 服务,登录,然后点击“完成”,将其添加为 Web 应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
![][6]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -63,9 +62,9 @@ flatpak install flathub re.sonny.Tangram
|
||||
|
||||
想要了解更多信息,请访问 [Tangram 的 Github 页面][9]。
|
||||
|
||||
[Tangram Browser][10]
|
||||
- [Tangram Browser][10]
|
||||
|
||||
你试过 Tangram 吗?你更喜欢 Web 应用还是本地应用?欢迎在下面的评论中分享你的想法。
|
||||
你试过 Tangram 吗?你更喜欢 Web 应用还是原生应用?欢迎在下面的评论中分享你的想法。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -74,7 +73,7 @@ via: https://itsfoss.com/tangram/
|
||||
作者:[Ankush Das][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[anine09](https://github.com/anine09)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,9 +24,9 @@ rule_bypass_check() {
|
||||
[ -f /tmp/bypass ] && echo "匹配规则:绕过检查"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# 添加原文:添加至少一篇原文
|
||||
# 添加原文:只能添加一篇原文
|
||||
rule_source_added() {
|
||||
[ "$SRC_A" -ge 1 ] \
|
||||
[ "$SRC_A" -eq 1 ] \
|
||||
&& check_category SRC A \
|
||||
&& [ "$TOTAL" -eq "$SRC_A" ] && echo "匹配规则:添加原文 ${SRC_A} 篇"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: (PDF Mix Tool 1.0.1 Now Lets You Edit Metadata with an Improved UI & Qt 6 Support)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://news.itsfoss.com/pdf-mix-tool-1-0-1-release/)
|
||||
[#]: author: (Omar Maarof https://news.itsfoss.com/author/omar/)
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: ( )
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
|
||||
PDF Mix Tool 1.0.1 Now Lets You Edit Metadata with an Improved UI & Qt 6 Support
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
[PDF Mix Tool][1] is one of the [best PDF editors for Linux][2] and an alternative to [PDF Arranger][3].
|
||||
It is a neat and simple GUI tool for manipulating pdf files and allows you to modify your files (rotating, splitting, extracting from files), not their content, however.
|
||||
|
||||
Although this application does not come with a lot of tools, it provides a concise toolset so you can manipulate your documents.
|
||||
|
||||
After a year of no new releases, the developer is back with another release (1.0.1) with some significant improvements.
|
||||
|
||||
Let us discover what features this release has to offer.
|
||||
|
||||
### Improved User Interface (UI)
|
||||
|
||||
There is now a left sidebar containing icons for all the operations you might need to perform. Each one of the icons has a respective function and its name below it.
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
This is not a big makeover but helps enhancing the user experience, which should be the focus for a useful tool like PDF Mix Tool.
|
||||
|
||||
### PDF Metadata Editing
|
||||
|
||||
![][5]
|
||||
|
||||
You can now modify your document’s title, author, subject, keywords, creator, producer, and creation and modification dates. Thus, you can edit your document’s metadata easily.
|
||||
|
||||
### Support for Qt 6.0
|
||||
|
||||
PDF Mix Tool is written in C++, and it relies on **qpdf** and the **Qt** library to make its magic work. It supports [Qt 6.0][6] now, which will affect the UX positively.
|
||||
|
||||
### Other Improvements
|
||||
|
||||
* PDF Mix Tool now adds right-to-left support in page composition.
|
||||
* Links, annotations, and outlines are preserved as much as possible in all operations.
|
||||
* This version fixed some bugs.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You can check out the [official changelog][7] in their GitLab page.
|
||||
|
||||
### Summing Up
|
||||
|
||||
Despite its reputation for being a lightweight, PDF Mix Tool is a handy application that delivers essential capabilities to the user.
|
||||
|
||||
You can get it from [Flathub][8] or [Snap store][9]. For Arch Linux users, you may not find the latest release in the repositories or the [AUR][10]. In either case, you can build it from source that can be found on [GitLab][11].
|
||||
|
||||
You may want to go through our [Flatpak guide][12] or the tutorial for [using Snaps in Linux][13] to get help with installation.
|
||||
|
||||
[Download PDFMixTool][14]
|
||||
|
||||
_What do you think about this release? I’m also curious to know what PDF editor do you happen to use?_
|
||||
|
||||
#### Big Tech Websites Get Millions in Revenue, It's FOSS Got You!
|
||||
|
||||
If you like what we do here at It's FOSS, please consider making a donation to support our independent publication. Your support will help us keep publishing content focusing on desktop Linux and open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not interested
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.itsfoss.com/pdf-mix-tool-1-0-1-release/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Omar Maarof][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://news.itsfoss.com/author/omar/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://scarpetta.eu/pdfmixtool/
|
||||
[2]: https://itsfoss.com/pdf-editors-linux/
|
||||
[3]: https://news.itsfoss.com/pdf-arranger-1-7-release/
|
||||
[4]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjUyMyIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[5]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjU3MiIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[6]: https://news.itsfoss.com/qt-6-released/
|
||||
[7]: https://gitlab.com/scarpetta/pdfmixtool/-/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md
|
||||
[8]: https://flathub.org/apps/details/eu.scarpetta.PDFMixTool
|
||||
[9]: https://snapcraft.io/pdfmixtool
|
||||
[10]: https://itsfoss.com/aur-arch-linux/
|
||||
[11]: https://gitlab.com/scarpetta/pdfmixtool
|
||||
[12]: https://itsfoss.com/flatpak-guide/
|
||||
[13]: https://itsfoss.com/use-snap-packages-ubuntu-16-04/
|
||||
[14]: https://scarpetta.eu/pdfmixtool/#download
|
||||
@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: (Edward Snowden Thinks GIMP Needs a Major UI Overhaul)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://news.itsfoss.com/gimp-ui-edward-snowden/)
|
||||
[#]: author: (Ankush Das https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/)
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: ( )
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
|
||||
Edward Snowden Thinks GIMP Needs a Major UI Overhaul
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
Edward Snowden’s recent tweet praised what free and open-source software can achieve.
|
||||
|
||||
In the tweet, he highlights that every time he uses Blender (an open-source 3D software suite), it reminds him of the advantages of FOSS and the growth of the ecosystem.
|
||||
|
||||
He did not just limit to that, in a follow-up reply to the same thread, he also tagged **GIMP** and added, “**I’m really hoping for a major UI overhaul. You guys could be eating Adobe’s lunch.**“
|
||||
|
||||
> P.S. [@GIMP_Official][1], I'm really hoping for a major UI overhaul. You guys could be eating Adobe's lunch.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> — Edward Snowden (@Snowden) [July 18, 2021][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### Does GIMP Require a Major UI Overhaul?
|
||||
|
||||
![][3]
|
||||
|
||||
[GIMP][4] is one of the most effective free and open-source image manipulation tools available.
|
||||
|
||||
It is actively used by professionals and all kinds of individuals to get a variety of things done.
|
||||
|
||||
You can even [make a GIF in GIMP][5]. Hence, it is tailored for simple and advanced tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
While it offers a learning curve to get used to its UI, it is good enough functionality-wise.
|
||||
|
||||
Does it require a UI overhaul?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, as per the trends, all kinds of designing/editing tools are working to improve the user-friendliness factor, GIMP may have missed out on this front.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, a sudden UI change may affect the workflow for a lot of veteran users. But, it does require a UI overhaul to beat its competitors like Adobe’s tools.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, with an easy-to-use interface, it will attract more users, potentially helping it grow and monetize the project even further.
|
||||
|
||||
And, it is also clear that Snowden thinks the same way, which is why he is hoping for a major UI overhaul while expecting GIMP to challenge Adobe tools in a big way.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why is GIMP Not Working on a Major User Experience Overhaul Yet?
|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately, GIMP does not have regular UX contributors or developers to work on a major overhaul.
|
||||
|
||||
They mentioned it as a reply to one of the tweets in Snowden’s tweet thread:
|
||||
|
||||
> “We worked with a UX architect between 2005 and 2012. Good things came out of it. We make small UX improvements in almost every update now that point releases (e.g. 2.10.24) are allowed to have new stuff. But we don’t have a regular UX contributor or devs for a huge overhaul”
|
||||
|
||||
Well, this is definitely a sad thing for such a popular project that gets immense love from thousands of users.
|
||||
|
||||
And, I hope, after Snowden’s tweet, the GIMP project gets more traction and we see regular contributors to help evolve GIMP with the love it deserves.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to help, you can explore [GIMP’s contribution page][6] to learn more about helping the project.
|
||||
|
||||
_Feel free to let me know your thoughts on GIMP and if you find it useful. Do you think that it needs a major UI overhaul, comments section is all yours!_
|
||||
|
||||
**Image Credits (Snowden’s image)**: [TheGuardian][7]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Big Tech Websites Get Millions in Revenue, It's FOSS Got You!
|
||||
|
||||
If you like what we do here at It's FOSS, please consider making a donation to support our independent publication. Your support will help us keep publishing content focusing on desktop Linux and open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not interested
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.itsfoss.com/gimp-ui-edward-snowden/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ankush Das][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://twitter.com/GIMP_Official?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw
|
||||
[2]: https://twitter.com/Snowden/status/1416778909358731266?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw
|
||||
[3]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQzMCIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[4]: https://www.gimp.org
|
||||
[5]: https://itsfoss.com/make-gif-in-gimp/
|
||||
[6]: https://www.gimp.org/develop/
|
||||
[7]: https://www.theguardian.com/books/2019/aug/01/edward-snowden-memoir-to-reveal-whistleblowers-secrets-permanent-record
|
||||
@ -1,91 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: (You Can Now Use KDE Connect in Windows as Well)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-connect-windows/)
|
||||
[#]: author: (Ankush Das https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/)
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: (imgradeone)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
|
||||
You Can Now Use KDE Connect in Windows as Well
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
KDE Connect is a popular open-source tool that lets you share a connection between a phone and your computer.
|
||||
|
||||
While it was always limited to the Linux platform, it looks like that it is coming to Windows after all.
|
||||
|
||||
And, cross-platform availability of software is always a good thing.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is KDE Connect?
|
||||
|
||||
In case you are coming across it for the first time—KDE connect lets you share files, links, sync notifications, gives you the ability to reply to messages, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also choose to control your desktop and perform some custom commands remotely. And, you can also use your phone to control the volume/skip the music playing on your computer.
|
||||
|
||||
### KDE Connect Available as Beta in Microsoft Store
|
||||
|
||||
![][1]
|
||||
|
||||
As per a Reddit thread posted a few weeks back, a KDE contributor mentions that the beta version is available from the [Microsoft Store][2].
|
||||
|
||||
However, it is only accessible through the private link and cannot be found when you search for it in the Microsoft Store.
|
||||
|
||||
This also marks official support for Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
![][3]
|
||||
|
||||
### KDE Connect for Windows: Here’s How it Looks
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
You just need to make sure that both of your devices are connected to the same network.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, all you have to do is pair them and then start sharing files/links, browse your phone, and also get notifications.
|
||||
|
||||
You can choose to tweak some of the options that include storage paths for shared images or change the sound to play when you try to ring the device.
|
||||
|
||||
![][5]
|
||||
|
||||
As you can notice here, you have a variety of options to make use of.
|
||||
|
||||
I tried connecting my Android device for a while, and it worked just fine. You may want to explore more to learn what else you can do with it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why is it Good News for Windows Users?
|
||||
|
||||
Undoubtedly Windows users already had plenty of options to achieve the same functions without KDE Connect. But with KDE connect onboard, it will finally provide the opportunity to use an open-source and privacy-friendly tool that they can pair their devices with.
|
||||
|
||||
After all, you would not want your notifications, and links/files that you share to be spied upon by a shoddy third-party application.
|
||||
|
||||
In that case, KDE Connect is your friend.
|
||||
|
||||
Even though it is in beta right now. You can try it out by visiting the link and installing it from the Microsoft store.
|
||||
|
||||
[KDE Connect on Microsoft Store][2]
|
||||
|
||||
**Via**: [Omg!Ubuntu!][6]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Big Tech Websites Get Millions in Revenue, It's FOSS Got You!
|
||||
|
||||
If you like what we do here at It's FOSS, please consider making a donation to support our independent publication. Your support will help us keep publishing content focusing on desktop Linux and open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not interested
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.itsfoss.com/kde-connect-windows/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ankush Das][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjIyOCIgd2lkdGg9Ijc2MyIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[2]: https://www.microsoft.com/en-gb/p/kde-connect/9n93mrmsxbf0?&activetab=pivot:overviewtab
|
||||
[3]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjI4NyIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[4]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQ2NiIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[5]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQ2MyIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[6]: https://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2021/07/kde-connect-windows-app
|
||||
@ -1,126 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "Top 9 Features in the Newly Released Zorin OS 16 Linux Distribution"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://news.itsfoss.com/zorin-os-16-features/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Ankush Das https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
Top 9 Features in the Newly Released Zorin OS 16 Linux Distribution
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
Zorin OS 16 is a gorgeous Linux distribution. With the latest release, there are several helpful feature additions to the distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
While we have [highlighted the key updates in our release coverage][1], I shall focus on some of the best features you can find in Zorin OS 16.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1\. Jelly Mode
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
Jelly Mode adds an engaging animation when you minimize or move the window on your screen.
|
||||
|
||||
It is more like a wobble effect when you move the windows and a fluid effect when you minimize or launch an app.
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike other animation improvements, this is quite a pleasing effect to enhance the user experience.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2\. Windows 11-like Layout
|
||||
|
||||
![][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Considering that Windows 11 made a lot of buzz for its launch, it only makes sense for Zorin OS to offers a familiar layout.
|
||||
|
||||
After all, it is one of the best Windows-like Linux distributions out there.
|
||||
|
||||
The Windows 11-like layout is only available in the Zorin Appearance settings for Pro users. So, get the Pro edition if you want to support the development and get access to some extra layouts.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3\. Touchpad Gestures
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to get a seamless touch experience with your laptop/touchpad, Zorin OS 16 is here to the rescue.
|
||||
|
||||
A simple three-finger pinch would help you navigate to the activity overview and dabble between active windows.
|
||||
|
||||
And a four-finger swipe up/down will let you switch between workspaces.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4\. Windows Software Detection
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Zorin OS 16 utilizes a database of popular Windows software to detect if you download a .exe file and want to install it.
|
||||
|
||||
This is incredibly useful for beginners considering that it also informs the alternative or the correct way to install the software on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
Even if it does not have exact instructions for the Windows software you downloaded, it prompts you to install “**Windows App Support**” when trying to access the .exe file.
|
||||
|
||||
![][5]
|
||||
|
||||
### 5\. New Photos App
|
||||
|
||||
![][6]
|
||||
|
||||
The default photos or image viewer is often untouched when a distribution is updated. But, with Zorin OS 16, you get a more straightforward and clean photo management app.
|
||||
|
||||
You get essential options like cropping, adding filters, enhancing the image, and screencasting to the devices connected to your network.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6\. Flathub Apps
|
||||
|
||||
![][7]
|
||||
|
||||
You no longer need to install Flatpak applications from the terminal separately. Flathub is now included with the Software center.
|
||||
|
||||
So, you can effortlessly search for Flatpak applications right from the Software app.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7\. Taskbar and Dash Customization
|
||||
|
||||
With Zorin OS 16, you get a variety of customization options to tweak the appearance of the taskbar, panel, and dock.
|
||||
|
||||
![][8]
|
||||
|
||||
Starting from the transparency to its position, behavior, size, and more. These options should let you tweak your user experience.
|
||||
|
||||
### 8\. Taskbar Unread Icons and Progress bar
|
||||
|
||||
The taskbar is usually static for most of the Linux distributions. Here, you finally get an unread badge counter in the taskbar, and it also supports a new progress bar for tasks like file transfer.
|
||||
|
||||
The progress bar is a helpful addition, given that you do not have to open the app repeatedly to watch the progress.
|
||||
|
||||
### 9\. New Sound Recorder App
|
||||
|
||||
![][9]
|
||||
|
||||
You do not have to opt for a third-party application to record basic voice-overs, podcasts, or voice notes.
|
||||
|
||||
The built-in sound record app offers a clean and easy-to-use interface. So, it should be a breeze to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Wrapping Up
|
||||
|
||||
Have you tried Zorin OS 16 yet? What feature did you find the most useful? Let me know your thoughts in the comments down below.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Big Tech Websites Get Millions in Revenue, It's FOSS Got You!
|
||||
|
||||
If you like what we do here at It's FOSS, please consider making a donation to support our independent publication. Your support will help us keep publishing content focusing on desktop Linux and open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not interested
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.itsfoss.com/zorin-os-16-features/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ankush Das][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://news.itsfoss.com/zorin-os-16-release/
|
||||
[2]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjM0MyIgd2lkdGg9Ijc1MiIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[3]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQzOSIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[4]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjM2MSIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[5]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQyMiIgd2lkdGg9IjYxNCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[6]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjUyMSIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[7]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjIzMCIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[8]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQ4NSIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[9]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQ4MCIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
@ -1,144 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "Zorin OS 16 is a Visual Spectacle! You Can Download This New Linux Release Right Now"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://news.itsfoss.com/zorin-os-16-release/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Ankush Das https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
Zorin OS 16 is a Visual Spectacle! You Can Download This New Linux Release Right Now
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
Zorin OS 16, one of the most anticipated Linux distros, based on Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS, has arrived.
|
||||
|
||||
With the latest release, they now offer a new “Pro” edition replacing the “Ultimate” edition that comes loaded with a few applications pre-installed and a couple of extra layouts.
|
||||
|
||||
Moreover, you get technical support for installation if you get the Zorin OS 16 Pro to support the developers.
|
||||
|
||||
The base edition is Zorin OS 16 “Core,” is free, which includes all the essentials.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, I shall highlight the key new additions along with my initial impressions of Zorin OS 16.
|
||||
|
||||
### Zorin OS 16: What’s New?
|
||||
|
||||
Zorin OS 16 may not be as big of an upgrade compared to [elementary OS 6][1], but there are significant improvements across the board. Let us take a look at them.
|
||||
|
||||
### Refined User Interface
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
The user interface remains familiar, but they have revamped the default theme and worked on the animations to present a polished look.
|
||||
|
||||
Subtle differences to the default transparency setting, theme, icons, and animations impact the overall user experience.
|
||||
|
||||
While you can notice the differences with Zorin OS 16 Core, the Pro edition takes it up a notch with the stunning new wallpapers and premium layouts available out-of-the-box.
|
||||
|
||||
### Flatpak Enabled
|
||||
|
||||
![][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Previously, Zorin OS supported snap right out of the box with its Software center. Now, with Zorin OS 16, Flathub has been enabled by default.
|
||||
|
||||
So, you can find plenty of applications available, including Flatpak packages in the Software manager.
|
||||
|
||||
You can even select a different package (if it is available) from the dropdown menu available in the top-right corner (as shown in the screenshot above).
|
||||
|
||||
### Improved Tour Screen
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
They have also revamped their welcome screen to help you set up all the important things right from the start.
|
||||
|
||||
You get to configure online accounts, connect your smartphone with Zorin Connect, and get a head start on the available layouts to choose from.
|
||||
|
||||
### Windows 11-like Layout
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
In my previous [Zorin OS 16 beta][5] coverage, I mentioned a potential Windows 10X-like layout was in the works.
|
||||
|
||||
Considering that Windows 10X no longer exists, the new layout is an alternative to Windows 11 experience.
|
||||
|
||||
Do note that you need to purchase the Zorin OS 16 Pro if you want to access Windows 11-like layout on your system.
|
||||
|
||||
### New Touchpad Gestures
|
||||
|
||||
For laptop or touchpad users, you can now swipe up/down with four fingers to move between workspaces and pinch using three fingers to open the activities overview.
|
||||
|
||||
### New Sound Recorder App
|
||||
|
||||
![][6]
|
||||
|
||||
A clean sound recording app to help you quickly record voice notes or podcasts without worrying about 3rd party applications.
|
||||
|
||||
### Performance Improvements
|
||||
|
||||
Even though I don’t have a figure, I observed some noticeable performance improvements compared to my experience with Zorin OS 15.
|
||||
|
||||
For instance, switching between different layouts is an entirely seamless experience.
|
||||
|
||||
As a side note, I tested Zorin OS 16 Pro on my desktop with **i5-7400, 16 GB RAM,** and **a GTX 1050ti** graphics card.
|
||||
|
||||
I always have my doubts when it comes to Nvidia driver compatibility. But it worked like a charm.
|
||||
|
||||
The boot menu when installing Zorin OS 16 offered a different option for modern NVIDIA drivers, which is what I chose to install.
|
||||
|
||||
So, yes, **Zorin OS 16’s ISO comes with Nvidia driver support out-of-the-box.**
|
||||
|
||||
### Other Improvements
|
||||
|
||||
![][7]
|
||||
|
||||
There are several other additions to the animation, customization settings, and more with Zorin OS 16. Some of them are:
|
||||
|
||||
* Jelly mode to enable a macOS-like animation when minimizing or opening applications.
|
||||
* Improved taskbar
|
||||
* Introduction of fractional scaling
|
||||
* Active directory domain option in the installer
|
||||
* New photos app
|
||||
* Disabled telemetry and tracking in Firefox browser for better privacy
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To explore more, you can check out [our Zorin OS 16 features list][8] or go through the [official announcement][9].
|
||||
|
||||
### Get Zorin OS 16
|
||||
|
||||
You can download Zorin OS 16 Core for free. If you opt for the Pro edition at **$39**, you also get access to a Pro-lite edition, which will be available to install for old computers.
|
||||
|
||||
The free lite edition and the pro lite version is not yet available and should be coming soon.
|
||||
|
||||
[Zorin OS 16 Download][10]
|
||||
|
||||
What do you think about Zorin OS 16? Share your thoughts in the comments down below.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Big Tech Websites Get Millions in Revenue, It's FOSS Got You!
|
||||
|
||||
If you like what we do here at It's FOSS, please consider making a donation to support our independent publication. Your support will help us keep publishing content focusing on desktop Linux and open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not interested
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.itsfoss.com/zorin-os-16-release/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ankush Das][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://news.itsfoss.com/elementary-os-6-release/
|
||||
[2]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQzOSIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[3]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjIzMCIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[4]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjUzNiIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[5]: https://news.itsfoss.com/zorin-os-16-beta/
|
||||
[6]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQ4MCIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[7]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQxNSIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[8]: https://news.itsfoss.com/zorin-os-16-features/
|
||||
[9]: https://blog.zorin.com/2021/08/17/2021-08-17-zorin-os-16-is-released/
|
||||
[10]: https://zorin.com/os/download/
|
||||
@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "KaOS 2021.08 Release Focuses on Visual Changes and Package Updates"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://news.itsfoss.com/kaos-2021-08-release/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Rishabh Moharir https://news.itsfoss.com/author/rishabh/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
KaOS 2021.08 Release Focuses on Visual Changes and Package Updates
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
The built-from-scratch Linux distribution KaOS — which uses KDE, Qt, and [pacman][1] as a package manager, has finally received its fifth update this year. This article will highlight the significant changes that have been brought to the distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
Let us get to know about what this new release brings!
|
||||
|
||||
### Desktop Environment Update
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
The new Application Launcher, introduced in Plasma 5.22, is now the new home for accessing apps while the traditional cascading app menu is abandoned.
|
||||
|
||||
The default Midna theme has been given a slightly different look, which can be easily noticed from the boot-up to the logout screen. This includes a darker look for the logout screen, combined with a transparent sidebar for the lockscreen and SDDM, and a minimal look for the splash screen. The icon themes have also been customized accordingly for both the light and dark versions of the theme.
|
||||
|
||||
The desktop environment is now based on Plasma 5.22.4 and the latest Frameworks 5.85.0; both are built on Qt 5.15.2+.
|
||||
|
||||
### Application Updates
|
||||
|
||||
#### KDE Apps
|
||||
|
||||
This update brings the latest KDE Gear 21.08. This includes animated previews of folders and an easy method of renaming folders using F2 and TAB in Dolphin file manager, color and image previews, along with an SSH plugin in Konsole. And, a keyframeable effect for altering the speed of clips in Kdenlive, and a party mode in Elisa.
|
||||
|
||||
Plasma mobile apps are now available on KaOS and are promised to be suitable for desktop use. These apps include Angelfish — web browser, Koko – image viewer, Kalk – calculator, and Kasts – podcasts.
|
||||
|
||||
#### System Apps
|
||||
|
||||
Some Calligra users may be disappointed to learn that LibreOffice is now the default office application. Moreover, other applications like bibletime, speedtest-CLI, and mauikit-accounts have also been added.
|
||||
|
||||
### Calamares installer
|
||||
|
||||
Calamares is now built on QML modules designed specifically for KaOS. This gives it an even and modern look with other apps. This also includes an all-new Users and Summary page.
|
||||
|
||||
![Calamares Summary Page][3]
|
||||
|
||||
You can now select your preferred file system while opting for automated partitioning.
|
||||
|
||||
A handy feature allows the transfer of network settings from the Live system to the newly installed system. Thus, you don’t need to connect your PC to your Wi-Fi again.
|
||||
|
||||
### Other Package Updates
|
||||
|
||||
Several other systems packages have been updated. This should improve the overall compatibility and stability as well. Some package updates include:
|
||||
|
||||
* Systemd 249.3
|
||||
* Curl 7.78.0
|
||||
* NetworkManager 1.32.8
|
||||
* Mesa 21.1.7
|
||||
* Vulkan packages 1.2.187
|
||||
* Udisks 2.9.3, MLT 7.0.1
|
||||
* Openexr 3.1.1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Do note that this release does not support installation in systems with RAID set up as of now.
|
||||
|
||||
To explore more about the changes, you can refer to the [official announcement][4].
|
||||
|
||||
With this release, KaOS is focused on giving KDE users a streamlined experience. In addition, the installation has been made easier, and power users can definitely make use of the new apps.
|
||||
|
||||
[Download KaOS 2021.08][5]
|
||||
|
||||
What do you think about the latest KaOS release? Is it turning out to be a promising Linux distribution? Let me know your thoughts in the comments below.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Big Tech Websites Get Millions in Revenue, It's FOSS Got You!
|
||||
|
||||
If you like what we do here at It's FOSS, please consider making a donation to support our independent publication. Your support will help us keep publishing content focusing on desktop Linux and open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not interested
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.itsfoss.com/kaos-2021-08-release/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Rishabh Moharir][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://news.itsfoss.com/author/rishabh/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://itsfoss.com/pacman-command/
|
||||
[2]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQ0NCIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[3]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQ4NSIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[4]: https://kaosx.us/news/2021/kaos08/
|
||||
[5]: https://kaosx.us/pages/download/
|
||||
@ -1,123 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "Intel’s XeSS Could be the Open-Source Alternative to Nvidia’s DLSS"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://news.itsfoss.com/intel-xess-open-source/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Jacob Crume https://news.itsfoss.com/author/jacob/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
Intel’s XeSS Could be the Open-Source Alternative to Nvidia’s DLSS
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
Over the past year, everyone in the PC gaming community has been talking about DLSS and FidelityFX. However, it seems that Linux gamers have been missing out, with DLSS only working through Proton when combined with a beta Nvidia driver and FidelityFX leaving much to be desired in terms of graphics.
|
||||
|
||||
Fortunately, Intel appears to want to change that with their new XeSS frame rate boosting technology. Launching alongside their upcoming Alchemist range of GPUs, it promises the ease of implementation of FidelityFX while competing in terms of image quality with DLSS.
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we will be exploring how this technology works and the incredible impact it will have on gaming on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### Is it like Nvidia’s DLSS?
|
||||
|
||||
![][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling), XeSS stands for Xe Super Sampling. AMD’s FidelityFX is a collection of technologies that enable games to run at a much higher frame rate than traditional rendering with minimal loss to visual quality.
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, two different technologies are used to achieve this. These are AI and traditional upscaling, both with various drawbacks and advantages.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Traditional Upscaling
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike AI, this approach has been worked on for many years. Previously, we have seen it being used in many TVs, computer monitors, and even some games to make a lower resolution image (or frame) appear clearer, with decent results.
|
||||
|
||||
This is the technology that AMD has chosen for their FidelityFX. They did this for several reasons; some possible ones include:
|
||||
|
||||
* Easier implementation by game developers
|
||||
* The capability to run on almost any GPU
|
||||
* Proven technology
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
That isn’t to say that it is without its disadvantages, some being:
|
||||
|
||||
* Reduced visual quality compared to AI-based solutions
|
||||
* More limited in opportunities to improve it in the future
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
AMD is currently the only major company using this technology for game upscaling. That means that we must move on to the other major upscaling technology: AI.
|
||||
|
||||
#### AI Upscaling
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
It is the latest advancement in upscaling technology used by DLSS and XeSS.
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike traditional upscaling, this approach typically depends on some special hardware to run.
|
||||
|
||||
Specifically, it would help if you had a GPU with dedicated AI cores. On Nvidia’s cards, these come in the form of Tensor cores.
|
||||
|
||||
Because these cores are new, they are only available on 20 and 30 series GPUs, meaning that older cards are stuck with traditional upscaling. Additionally, it is much harder for developers to implement as the AI needs to be “trained,” involving feeding the AI thousands of hours of gameplay.
|
||||
|
||||
Yet, these trade-offs are worth it for many people, as AI provides better image quality and performance.
|
||||
|
||||
This is the route Intel has taken for its solution.
|
||||
|
||||
### Open Source and Upscaling
|
||||
|
||||
DLSS is completely closed source in true Nvidia style, like the drivers that annoyed Linus Torvalds so much.
|
||||
|
||||
Fortunately, Intel is following in the footsteps of AMD, and they plan to open-source XeSS once it’s ready for prime time.
|
||||
|
||||
While there is no significant commitment made by them, but multiple reports suggest that they plan to eventually open-source it.
|
||||
|
||||
This allows them to take advantage of the numerous contributions the open-source community will (hopefully) make. The result should be a fascinating GPU landscape with many different technologies and companies constantly fight for the top spot in upscaling.
|
||||
|
||||
### Intel XeSS
|
||||
|
||||
![][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Compared to Nvidia’s DLSS (XeSS’s main competitor), XeSS promises better performance, visual quality, and ease of implementation.
|
||||
|
||||
So far, we have seen demos running at as much as double the native performance, backing up the performance claims. But that’s press material for now.
|
||||
|
||||
As I mentioned, Intel is planning to make it open-source.
|
||||
|
||||
While it may not be open-source at launch, they intend on open-sourcing once it matures.
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
If Intel is to be believed, this could be the killer feature of their upcoming Alchemy GPUs, putting them ahead of both AMD and Nvidia in one single scoop.
|
||||
|
||||
### Final Thoughts
|
||||
|
||||
I am incredibly excited about this feature, more so than I was about DLSS and FidelityFX combined. It should be noted that this is still some time away, with it expected to release in early 2022.
|
||||
|
||||
Overall, it looks like a significant step forward for Intel and maybe the key to them coming back from behind AMD and Nvidia.
|
||||
|
||||
_Are you excited about XeSS? Let me know in the comments below!_
|
||||
|
||||
**Via**: [Videocardz][5]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Big Tech Websites Get Millions in Revenue, It's FOSS Got You!
|
||||
|
||||
If you like what we do here at It's FOSS, please consider making a donation to support our independent publication. Your support will help us keep publishing content focusing on desktop Linux and open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not interested
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.itsfoss.com/intel-xess-open-source/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jacob Crume][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://news.itsfoss.com/author/jacob/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjM4MSIgd2lkdGg9IjY3OCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[2]: https://i2.wp.com/i.ytimg.com/vi/-Dp61_bM948/hqdefault.jpg?w=780&ssl=1
|
||||
[3]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQzMiIgd2lkdGg9Ijc2OCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[4]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQzOSIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[5]: https://videocardz.com/newz/intel-xess-ai-based-super-sampling-technology-will-be-open-source-once-it-matures
|
||||
@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "SparkyLinux 6.0 Release is based on Debian 11 and Includes a Built-in VPN"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://news.itsfoss.com/sparkylinux-6-0-release/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Ankush Das https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
SparkyLinux 6.0 Release is based on Debian 11 and Includes a Built-in VPN
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
SparkyLinux 6.0 is a major stable update that utilizes Debian 11 ‘Bullseye’ as its base now.
|
||||
|
||||
While you can go through the [features of Debian 11][1], SparkyLinux 6.0 should reflect some of the perks associated with it.
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we shall take a quick look at what SparkyLinux 6.0 has to offer.
|
||||
|
||||
### SparkyLinux 6.0 “Po Tolo”: What’s New?
|
||||
|
||||
The major highlight of the release is the latest Debian 11 ‘Bullseye’ as its base. The repositories have also been updated to get the latest packages.
|
||||
|
||||
SparkyAPTus AppCenter has replaced the original SparkyAPTus, which is no longer developed.
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
You can install, reinstall, and remove applications easily. Not just limited to the applications, but you also get the ability to tweak the pre-configured desktops using it.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to that, you can remove and install Linux Kernels as well. You can choose from Debian Kernel, Liquorix, Sparky, and XanMod.
|
||||
|
||||
![][3]
|
||||
|
||||
It is worth noting that you will still be able to access all the tools from the old APTus.
|
||||
|
||||
To enhance privacy and security, SparkyLinux has decided to include the non-profit [RiseUp VPN][4] application pre-installed.
|
||||
|
||||
It is a VPN service that relies on donations to keep the network alive and comes with cross-platform support. You can also find it available for Android devices.
|
||||
|
||||
So, this makes it an interesting addition to the distribution. If you are not using any VPN service, this should make things easy.
|
||||
|
||||
The FirstRun app has been replaced with an improved welcome app that guides you through some basic pointers.
|
||||
|
||||
![][5]
|
||||
|
||||
### Other Improvements
|
||||
|
||||
With the latest release, you can also find new wallpapers and updated application packages that include:
|
||||
|
||||
* Thunderbird 78.13.0
|
||||
* VLC 3.0.16
|
||||
* LibreOffice 7.0.4
|
||||
* Calamares Installer 3.2.41.1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To know more about the release, you can refer to the [official announcement][6].
|
||||
|
||||
### Download Sparky 6.0
|
||||
|
||||
SparkyLinux 6.0 is available to download with Xfce and KDE Plasma desktop environments. It supports 32-bit systems as well, which is a good thing.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are already running SparkLinux “Po Tolo” rolling release, you need to update your system to get Sparky 6.0.
|
||||
|
||||
Do note that the rolling version will switch to a stable release. So, if you want to stay on the rolling release, you need to wait for a few days.
|
||||
|
||||
[SparkyLinux 6.0][7]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Big Tech Websites Get Millions in Revenue, It's FOSS Got You!
|
||||
|
||||
If you like what we do here at It's FOSS, please consider making a donation to support our independent publication. Your support will help us keep publishing content focusing on desktop Linux and open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not interested
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.itsfoss.com/sparkylinux-6-0-release/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ankush Das][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://news.itsfoss.com/debian-11-feature/
|
||||
[2]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjU4NyIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[3]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjU4NSIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[4]: https://riseup.net/en/vpn
|
||||
[5]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjU2MyIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[6]: https://sparkylinux.org/sparky-6-0-po-tolo/
|
||||
[7]: https://sparkylinux.org/download/
|
||||
@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "“Apps for GNOME” is a New Web Portal to Showcase Best Linux Apps for GNOME"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://news.itsfoss.com/apps-for-gnome-portal/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Ankush Das https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
“Apps for GNOME” is a New Web Portal to Showcase Best Linux Apps for GNOME
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
There are several apps built for GNOME. Most of the stock (default) GNOME apps do not get enough spotlight as a separate mention.
|
||||
|
||||
While Flathub as a platform helps highlight some fantastic applications for GNOME, it limits to Flatpak apps only.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, it is not just dedicated to GNOME, of course.
|
||||
|
||||
Hence, there is a new website to focus more on the GNOME ecosystem and highlight the best GNOME apps.
|
||||
|
||||
### Apps for GNOME
|
||||
|
||||
![][1]
|
||||
|
||||
A [blog post][2] by Sophie Herold on Planet GNOME announced the availability of the platform.
|
||||
|
||||
[apps.gnome.org][3] is where you can find all the GNOME apps, both default and third-party applications tailored primarily for the GNOME environment.
|
||||
|
||||
With this portal, they aim to encourage users to participate and contribute to the development of such applications.
|
||||
|
||||
When you head to explore an app on the platform, you will be presented with plenty of information that includes where to submit feedback for the app, help translate, and contribute financially.
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
It is not something out-of-the-box, but it presents all the information related to a GNOME app in a single place.
|
||||
|
||||
You get a complete picture for a GNOME app starting with the description, screenshots, latest version, information about the maintainers, and translation status.
|
||||
|
||||
![][5]
|
||||
|
||||
Not just limited to desktop GNOME apps, but you will also find applications marked with a mobile icon if it is supported on GNOME mobile devices.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the key GNOME apps, it also aims to feature applications that do not offer a flatpak package but suits well for the GNOME platform.
|
||||
|
||||
[Apps for GNOME][3]
|
||||
|
||||
### Making Information More Accessible
|
||||
|
||||
I find it much more insightful than what Flathub seems to provide. And, I think this is not just going to help highlight GNOME apps, but it should help new users get to know more about the applications they use.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, it should also encourage users to get involved, which is the primary focus.
|
||||
|
||||
While KDE already had an [application portal][6], it might need an upgrade if they take Apps for GNOME as an example to improve.
|
||||
|
||||
_What do you think about the Apps for GNOME initiative?_ _Feel free to share your thoughts in the comments._
|
||||
|
||||
#### Big Tech Websites Get Millions in Revenue, It's FOSS Got You!
|
||||
|
||||
If you like what we do here at It's FOSS, please consider making a donation to support our independent publication. Your support will help us keep publishing content focusing on desktop Linux and open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not interested
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.itsfoss.com/apps-for-gnome-portal/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ankush Das][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjU2MiIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[2]: https://blogs.gnome.org/sophieh/2021/08/26/apps-gnome-org-is-online/
|
||||
[3]: https://apps.gnome.org
|
||||
[4]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjI4MiIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[5]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQ3OSIgd2lkdGg9Ijc0NCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[6]: https://apps.kde.org
|
||||
@ -1,122 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "Open Source Video Editor OpenShot 2.6 Released With AI Effects & Major Improvements"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://news.itsfoss.com/openshot-2-6-release/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Ankush Das https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
Open Source Video Editor OpenShot 2.6 Released With AI Effects & Major Improvements
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
OpenShot is one of the most popular [open-source video editors][1] out there.
|
||||
|
||||
It is not just for Linux, but it is an impressive free video editor for Windows and Mac users as well.
|
||||
|
||||
While it was already a functional, easy-to-use, feature-rich video editor, it stepped up a notch with the latest release.
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we discuss some key additions in OpenShot 2.6.0 release.
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenShot 2.6.0 Released: What’s New?
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
The primary highlight of this release is the inclusion of AI and computer vision effects. But, there is more to it than meets the eye.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the highlights for OpenShot 2.6.0 changes:
|
||||
|
||||
* New AI and computer vision effects
|
||||
* New audio effects
|
||||
* New zoom slider
|
||||
* Improved transform tool
|
||||
* Improved video effects
|
||||
* Improved snapping
|
||||
* More emoji support
|
||||
* Improved performance
|
||||
* Bug fixes
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Considering the fundamental changes, OpenShot is now a more compelling option for professional video editors.
|
||||
|
||||
![Official YouTube video for OpenShot 2.6][3]
|
||||
|
||||
### AI Effects
|
||||
|
||||
Taking the help of an AI to process images/videos is becoming increasingly common these days.
|
||||
|
||||
Hence, OpenShot adds the support for AI effects to make it easier to enhance and edit videos.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the features includes eliminating any shake/motion in a video by calculating it.
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
You can also track particular objects in a video. This is undoubtedly helpful for animation or any other creative work where you need to follow a specific element of the video.
|
||||
|
||||
Like a real-time feed where the camera detects vehicles, it can also identify objects in the video. While this feature is in beta, it should be fun to experiment with it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Audio Effects
|
||||
|
||||
OpenShot video editor featured most of the essential audio effects. And, in this release, some more important audio effects have been added that include:
|
||||
|
||||
* Compressor
|
||||
* Expander
|
||||
* Echo
|
||||
* Delay
|
||||
* Distortion
|
||||
* Noise
|
||||
* EQ
|
||||
* Robotic voice and whispering voice effects
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### New & Improved Tools
|
||||
|
||||
![][5]
|
||||
|
||||
Vital tools in snapping and transform mode have been improved.
|
||||
|
||||
The improved transform tool lets you resize, rotate, and work seamlessly to create complex animations.
|
||||
|
||||
Furthermore, when trimming the clip, the snapping tool allows you better align the edges of the clips.
|
||||
|
||||
A new zoom slider tool has been added to give you better control over the timeline. You can easily drag and work with a specific portion of the timeline as needed.
|
||||
|
||||
### Other Improvements
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the essential changes, you can find performance improvements and numerous bug fixes.
|
||||
|
||||
You can find the latest version as an AppImage file as of now. It should reflect soon in the Flathub repository and other sources as well. Consider reading [how to use AppImage files][6] if you are not aware of it.
|
||||
|
||||
[Download OpenShot 2.6.0][7]
|
||||
|
||||
To explore more about the release, you may refer to the [official release announcement][8].
|
||||
|
||||
#### Big Tech Websites Get Millions in Revenue, It's FOSS Got You!
|
||||
|
||||
If you like what we do here at It's FOSS, please consider making a donation to support our independent publication. Your support will help us keep publishing content focusing on desktop Linux and open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not interested
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.itsfoss.com/openshot-2-6-release/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ankush Das][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://itsfoss.com/open-source-video-editors/
|
||||
[2]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjYwOSIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[3]: https://i0.wp.com/i.ytimg.com/vi/06sgvsYB378/hqdefault.jpg?w=780&ssl=1
|
||||
[4]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQzOCIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[5]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjM2MSIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[6]: https://itsfoss.com/use-appimage-linux/
|
||||
[7]: https://www.openshot.org/download/
|
||||
[8]: https://www.openshot.org/blog/2021/08/25/new_openshot_release_260/
|
||||
@ -1,154 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "Linux Kernel 5.14 Released Right After the 30th Anniversary of Linux"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://news.itsfoss.com/kernel-5-14-release/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Jacob Crume https://news.itsfoss.com/author/jacob/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
Linux Kernel 5.14 Released Right After the 30th Anniversary of Linux
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
Back in June, I looked at [Linux Kernel 5.13][1], where we received preliminary support for the M1, RISC-V improvements, and support for new GPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, Linux kernel 5.14 is here! Linus Torvalds just [announced it on the kernel mailing list][2]:
|
||||
|
||||
![Kernel 5.14 announcement mail][3]
|
||||
|
||||
While this release is not quite as large as the aforementioned one, it still has many improvements, especially for ARM devices.
|
||||
|
||||
Let us take a quick look at the key highlights of this release.
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux Kernel 5.14: What’s New?
|
||||
|
||||
Linux kernel 5.14 contains a wide variety of new features, especially for ARM-based systems. This is all happening despite Linus Torvalds claiming that this is a relatively small release in the initial [kernel announcement][4].
|
||||
|
||||
Fast forward to its release candidate v7 before its final release, Linus mentioned:
|
||||
|
||||
> Most of the changes here are drivers (GPU and networking stand out),
|
||||
>
|
||||
> and the rest is pretty random stuff: arch, tracing, core networking, a
|
||||
>
|
||||
> couple of VM fixes..
|
||||
|
||||
Linus Torvalds, Linux kernel 5.14 RC7 announcement
|
||||
|
||||
This release contains a variety of new features. Here is a list of the key new features present in Linux kernel 5.14:
|
||||
|
||||
* The [Raspberry Pi 400][5] can now work completely with this kernel, thanks to the work done for the past couple of months.
|
||||
* The [Rockchip RK3568 SoC][6] is now supported
|
||||
* Initial support for the Sony Xperia 1/1II and 5/5II
|
||||
* Various updates added for Microsoft Surface Duo
|
||||
* Updates to DIY BananaPi M5 board added
|
||||
* [Important updates][7] for RISC-V
|
||||
* Improved support for Intel Alder Lake P and Alder Lake M graphics cards
|
||||
* New hot-unplug support on AMD Radeon graphics cards
|
||||
* ‘Secret’ memory areas introduced with a new system called ‘memfd_secret’
|
||||
* Improvements to [lower the latency of its USB audio driver][8]s
|
||||
* Improved support for USB4
|
||||
* Initial groundwork to support Intel Alder lake processors
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, we will be looking at what these features are, and what they mean for the end user.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Raspberry Pi 400
|
||||
|
||||
Last year, the Raspberry Pi Foundation launched the [Raspberry Pi 400][5], a keyboard computer similar to those of the 1980s. Unfortunately, this computer requires a custom kernel version to function due to non-mainline drivers.
|
||||
|
||||
However, with the kernel 5.14 release, this appears to have changed. After months of development, the Raspberry Pi 400 can now be booted using the Linux kernel 5.14. While it is unfortunate for support to take this long, it is much better late than never.
|
||||
|
||||
#### RK35xx SoC Support
|
||||
|
||||
This year has truly been a glorious year for [Rockchip][9]. They started off by launching their rk35xx series of SoCs, with many manufacturers integrating the newly-released SoCs into their products.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the most notable uses of the RK35xx series is in the Quartz64, an SBC developed by [Pine64][10] (which I am currently helping mainline). And Linux 5.14 brings support for one of these SoCs, the RK3568.
|
||||
|
||||
For all the upcoming boards based on this SoC, this inclusion is extremely important as it greatly simplifies distro porting.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Initial Support for Sony Xperia 1/1II and 5/5II
|
||||
|
||||
[Sony][11] is one of the few mobile phone manufacturers that actively support running Linux on their phones. This is demonstrated through their compatibility with operating systems such as [Sailfish OS][12] and [Ubuntu Touch][13].
|
||||
|
||||
Now, with the Sony Xperia 1/1II and 5/5II being mainlined, it should be much easier to get an even wider variety of distributions booted. However, it should be also be kept in mind that this is only initial support, much like Linux 5.13’s M1 support.
|
||||
|
||||
#### RISC-V Updates
|
||||
|
||||
One of the trends I have noticed over the past few kernel updates is the ever-improving support for [RISC-V][14] processors. Last update, we got some significant build system improvements, a re-arranged kernel memory map, and support for the kernel debugging module KProbes.
|
||||
|
||||
This time, it appears that this trend is continuing, with the addition of a few RISC-V-specific improvements. These include:
|
||||
|
||||
* Support for transparent huge pages
|
||||
* An optimized copy_{to,from}_user.
|
||||
* Generic PCI resources mapping support
|
||||
* Support for KFENCE (Kernel Electric Fence) for memory safety error detection/validation
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
While mostly minor, these updates should pave the way for future RISC-V based devices.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Radeon Hot-Unplug
|
||||
|
||||
Perhaps my favorite feature of this release, AMD Radeon cards are getting a new hot-unplug feature. Previously, ripping your GPU out while your system was running would result in a kernel panic. Now, you can remove your (Radeon) GPU at any time and your system will continue to function normally, at least in theory.
|
||||
|
||||
I just hope that this feature works better on Linux than my experience with it on Windows. While I wouldn’t recommend randomly pulling your GPU out of your system mid-update, it is still a nice feature to see, and it will be interesting to see what people do with it.
|
||||
|
||||
#### USB 4 Support
|
||||
|
||||
As we see an increasing number of new laptops shipping with USB 4, it has become more and more important for Linux to start supporting it. Fortunately, the Linux kernel 5.14 has a wide variety of improvements for USB 4 users.
|
||||
|
||||
These include:
|
||||
|
||||
* More USB 4 support added to the thunderbolt core
|
||||
* Build warning fixes all over the place
|
||||
* USB-serial driver updates and new device support
|
||||
* A wide variety of driver updates
|
||||
* Lots of other tiny things
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
While not game-changing, these improvements should help many current and future users of USB 4.
|
||||
|
||||
### Wrapping Up
|
||||
|
||||
Between the improved USB support, multitude of updates for ARM and RISC-V devices, and minor GPU upgrades, this release is looking pretty good. As I mentioned before, I am most excited about the Radeon hot-unplug support, as this should make GPU swapping that little bit easier.
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly to last time, I’d recommend waiting for your distribution to offer official updates before upgrading to Linux kernel 5.14. Fortunately, users of distributions such as Arch and Manjaro should receive the updates very shortly. [Advanced Ubuntu users can install the latest mainline Kernel][15] with some effort though it should be avoided.
|
||||
|
||||
_What do you think about the improvements in Linux Kernel 5.14? Let me know down in the comments!_
|
||||
|
||||
#### Big Tech Websites Get Millions in Revenue, It's FOSS Got You!
|
||||
|
||||
If you like what we do here at It's FOSS, please consider making a donation to support our independent publication. Your support will help us keep publishing content focusing on desktop Linux and open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not interested
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.itsfoss.com/kernel-5-14-release/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jacob Crume][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://news.itsfoss.com/author/jacob/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-kernel-5-13-release/
|
||||
[2]: https://lkml.org/lkml/2021/8/29/382
|
||||
[3]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQ1NiIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[4]: http://lkml.iu.edu/hypermail/linux/kernel/2107.1/02943.html
|
||||
[5]: https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-400/
|
||||
[6]: https://www.96rocks.com/blog/2020/11/28/introduce-rockchip-rk3568/
|
||||
[7]: https://lore.kernel.org/lkml/mhng-423e8bdb-977e-4b99-a1bb-b8c530664a51@palmerdabbelt-glaptop/
|
||||
[8]: http://lkml.iu.edu/hypermail/linux/kernel/2107.1/00919.html
|
||||
[9]: https://www.rock-chips.com/a/en/index.html
|
||||
[10]: http://pine64.org
|
||||
[11]: https://electronics.sony.com/c/mobile
|
||||
[12]: https://sailfishos.org/
|
||||
[13]: https://ubuntu-touch.io/
|
||||
[14]: https://riscv.org/
|
||||
[15]: https://itsfoss.com/upgrade-linux-kernel-ubuntu/
|
||||
@ -1,76 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "Ransomware Disguised as Open-Source Krita Painting App Promo Video"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://news.itsfoss.com/krita-email-scam/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Ankush Das https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
Ransomware Disguised as Open-Source Krita Painting App Promo Video
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
Ransomware attacks are exponentially increasing. And, the way it gets distributed evolves every day.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the most effective ways is by using reputable brand names to lure users into downloading malicious files that may end up encrypting your files and demand a ransom.
|
||||
|
||||
And, in this case, some scammers have started using Krita’s name to deceive users through email.
|
||||
|
||||
### Spreading Malware via Email as Krita Officials
|
||||
|
||||
The attackers disguise themselves as the team for Krita, one of the best [digital open-source painting app][1].
|
||||
|
||||
The email mentions that Krita wants to collaborate with your YouTube channel or your social media space to share promotional videos about their software/product.
|
||||
|
||||
And, they mention that this is a paid advertising campaign, so you think you are getting a reward for promoting Krita.
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s how the email looks like (as shared by [Krita on Twitter][2]):
|
||||
|
||||
![][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Once you show interest in promoting Krita, they send you a follow-up mail instructing you to download a press kit containing screenshots, videos, and other materials.
|
||||
|
||||
The link may look similar to the official one like _krita.io, krita.net_, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
In a detailed video shared by a Twitter user, you can see that the link they share is malicious and sometimes goes undetected by Google’s safe browsing feature:
|
||||
|
||||
> Recently, I received the same email. Though I know this is likely a scam, I decided to proceed further just to see how far will they take us. They asked me to download some files and you can watch the full video here: <https://t.co/Mv2p9z3HCa> [pic.twitter.com/P1K2tlHiT4][4]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> — Inside Electronics (@InsideElectro) [August 29, 2021][5]
|
||||
|
||||
While I agree that this is not the best attempt to distribute malware, not everyone is as attentive as this user here.
|
||||
|
||||
### Never Trust an Email Without Proper Verification
|
||||
|
||||
It is easy for attackers to send you emails that you expect or something that may spark an interest in your work.
|
||||
|
||||
Scammers do their homework to know what you like, but always stay cautious no matter what or who appears to be sending the email.
|
||||
|
||||
If an email explicitly asks to enter your personal information, download an attachment, or visit a website to download a file, you need to double-check if it comes from an official source.
|
||||
|
||||
Generally, officials do not ask you to download any file or personal information unless you took action first. So, it is always wise to think twice and run a background check for what you interact with via emails.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Big Tech Websites Get Millions in Revenue, It's FOSS Got You!
|
||||
|
||||
If you like what we do here at It's FOSS, please consider making a donation to support our independent publication. Your support will help us keep publishing content focusing on desktop Linux and open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not interested
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.itsfoss.com/krita-email-scam/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ankush Das][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://news.itsfoss.com/author/ankush/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://itsfoss.com/open-source-paint-apps/
|
||||
[2]: https://twitter.com/Krita_Painting/status/1432295734074880003
|
||||
[3]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjI3OSIgd2lkdGg9IjU4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[4]: https://t.co/P1K2tlHiT4
|
||||
[5]: https://twitter.com/InsideElectro/status/1431938502862663680?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw
|
||||
@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "Linux Lite Moves to Pay What You Want Model With Version 5.6 Release"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-lite-5-6-release/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Jacob Crume https://news.itsfoss.com/author/jacob/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
Linux Lite Moves to Pay What You Want Model With Version 5.6 Release
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
[Linux Lite][1] has just announced Linux lite 5.6, the fourth installment in their 5.x series of releases. This release brings some major changes, especially in the download process. Other, more subtle tweaks are also shown throughout the OS.
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we will be looking at what is new, what has changed, and how these changes may affect the future of Linux Lite.
|
||||
|
||||
### What Has Changed in Linux Lite 5.6?
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
Alongside the new download model, there a few key changes. These include:
|
||||
|
||||
* New features in the Lite Tweaks app
|
||||
* Updated icon theme
|
||||
* New wallpapers
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
While this list is relatively short, there are a couple of meaningful changes.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pay Want You Want Download Model
|
||||
|
||||
Definitely the most impactful change, Linux Lite has moved to a “Pay what you want” download model. For those not familiar with the term, it is a system where the user is encouraged to pay to obtain a download link. Users can still enter $0 to get the download link for free, but it is not immediately clear and does not support the distro.
|
||||
|
||||
This move follows the footsteps of other popular distros, including ElementryOS. While I can see many users being annoyed at this change, it has also been made clear that Linux Lite would die without this change.
|
||||
|
||||
> “This is a road I’d never thought I’d go down, but we have no choice. Either we stagnate and accept the big G’s ever-changing algorithms, or we boldly go where others have dared.”
|
||||
|
||||
Jerry Bezencon
|
||||
|
||||
In hindsight, this change was inevitable, as there is almost no other way for distributions to reasonably sustain themselves (aside from donations). Now we need to see how this change pays off for the developers of Linux Lite.
|
||||
|
||||
### Updated Lite Tweaks App
|
||||
|
||||
With this update, the Lite Tweaks app gets a few improvements. One of these is the ability to completely clear the cache of the Brave web browser. It also has a new option to set Brave as the default web browser.
|
||||
|
||||
The second update within the Lite Tweaks app is a fix for GRUB. This tweak changes the grub entry from “Ubuntu” to “Linux Lite”. However, it should be noted that this option is only available when GRUB is controlled by Linux Lite.
|
||||
|
||||
### Wrapping Up
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to try Linux Lite for yourself, you can [download it from its website][3]. If you are already running Linux Lite, you can update to version 5.6 using the instructions found on the [release announcement][4].
|
||||
|
||||
While minor, this release does have a few improvements scattered around the OS. Most importantly, however, is the fact that Linux Lite can now be self-sustaining, meaning that we will continue to see more features added with every release. I think this is much better that the distro dying, don’t you?
|
||||
|
||||
#### Big Tech Websites Get Millions in Revenue, It's FOSS Got You!
|
||||
|
||||
If you like what we do here at It's FOSS, please consider making a donation to support our independent publication. Your support will help us keep publishing content focusing on desktop Linux and open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not interested
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.itsfoss.com/linux-lite-5-6-release/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jacob Crume][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://news.itsfoss.com/author/jacob/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://www.linuxliteos.com/
|
||||
[2]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjQ0MCIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[3]: https://www.linuxliteos.com/download.php
|
||||
[4]: https://www.linuxliteos.com/forums/release-announcements/linux-lite-5-6-final-released/
|
||||
@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "Lakka Linux 3.4 Brings Fidelity FX Support With the New RetroArch 1.9.9"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://news.itsfoss.com/lakka-retroarch-release/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Jacob Crume https://news.itsfoss.com/author/jacob/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
Lakka Linux 3.4 Brings Fidelity FX Support With the New RetroArch 1.9.9
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
For years now, [RetroArch][1] has been the gold standard in emulation, thanks to its ease of use and simplicity. Similarly, [Lakka][2] has gotten a name by using RetroArch to create an incredibly smooth and straightforward experience for its users.
|
||||
|
||||
Hence, we have recommended it in the past to [turn your old PC into a retrogaming console][3].
|
||||
|
||||
It is always a great day when these two large projects announce new releases, and it looks like we have some exciting news with Lakka 3.4 and RetroArch 1.9.9 release.
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we will be looking at some of the new features announced in RetroArch 1.9.9 and Lakka 3.4 and the significant impact on the future of emulation.
|
||||
|
||||
### What’s New?
|
||||
|
||||
With this release, RetroArch has introduced some useful and impactful new features. These include:
|
||||
|
||||
* AMD FidelityFX support for all games
|
||||
* Windows users can now use HDR on many games
|
||||
* New touchscreen menu for the Nintendo DS
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Lakka (which includes RetroArch) has also received some welcome improvements.
|
||||
|
||||
* Improved stability
|
||||
* 3 new cores for the PS1, PS2, and DOS
|
||||
* Updated Mesa to version 21.2.1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Here we focus on the key highlights and, primarily, Integrated FidelityFX.
|
||||
|
||||
#### FidelityFX For Retro Games
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
When AMD announced its open-source alternative to DLSS back in June, we could never have predicted the incredible impact it would have on emulation.
|
||||
|
||||
For those not aware, [FidelityFX][5] allows games to run at a lower resolution while retaining the same image quality, dramatically improving the performance.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, with the RetroArch 1.9.9 release, this technology is being brought to RetroArch and Lakka. This is great because it allows older games designed to run at a low resolution to look much better without resorting to mods or texture packs.
|
||||
|
||||
Overall, I expect this addition to be widely appreciated, especially by people looking for a more modern version of their favorite retro games.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to learn more about FidelityFX and upscaling, I’d highly suggest you check out [our article on Intel’s XeSS where we explain all this][6] and how it impacts you.
|
||||
|
||||
#### New Touchscreen Menu For Nintendo 3DS
|
||||
|
||||
One of the more interesting ports of RetroArch, the Nintendo 3DS, has also gotten a cool new feature. This comes in the form of a touchscreen menu for the bottom screen, which shows a few useful shortcuts without covering the game.
|
||||
|
||||
While this doesn’t apply to Lakka, users of RetroArch running on top of another distribution should receive this change once RetroArch 1.9.9 lands in the repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
### Wrapping Up
|
||||
|
||||
Overall, [RetroArch 1.9.9][7] and [Lakka 3.4][8] are looking to be significant upgrades, especially with the new integration with FidelityFX.
|
||||
|
||||
As we have already seen, with emulators such as [RPCS3][9], FidelityFX can provide significant graphical improvements on older games, so it is exciting to see this come to RetroArch.
|
||||
|
||||
_What do you think about FidelityFX being used for retro games? Let me know in the comments below!_
|
||||
|
||||
#### Big Tech Websites Get Millions in Revenue, It's FOSS Got You!
|
||||
|
||||
If you like what we do here at It's FOSS, please consider making a donation to support our independent publication. Your support will help us keep publishing content focusing on desktop Linux and open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not interested
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.itsfoss.com/lakka-retroarch-release/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jacob Crume][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://news.itsfoss.com/author/jacob/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://www.retroarch.com/
|
||||
[2]: http://lakka.tv
|
||||
[3]: https://itsfoss.com/lakka-retrogaming-linux/
|
||||
[4]: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyBoZWlnaHQ9IjIzMCIgd2lkdGg9Ijc4MCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=
|
||||
[5]: https://www.amd.com/en/technologies/radeon-software-fidelityfx-super-resolution
|
||||
[6]: https://news.itsfoss.com/intel-xess-open-source/
|
||||
[7]: https://www.libretro.com/index.php/retroarch-1-9-9-released/
|
||||
[8]: http://lakka.tv/articles/2021/09/06/lakka-3.4/
|
||||
[9]: http://rpcs3.net
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "Here’s Why Firefox is Seeing a Continuous Decline for Last 12 Years"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://news.itsfoss.com/firefox-continuous-decline/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Community https://news.itsfoss.com/author/team/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s Why Firefox is Seeing a Continuous Decline for Last 12 Years
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
There has been a lot of discussion lately about the decline of the Firefox browser and numerous articles about it [losing 50 Million users in the last two years][1].
|
||||
|
||||
But the _**real decline has been over 12 years with a total loss of half a Billion users**_ and 75% of the market share it once held.
|
||||
|
||||
It all started in 2009 Q3 with the fateful decision to force…
|
||||
|
||||
### Tabs-On-Top
|
||||
|
||||
As soon as [this decision was made][2], Firefox starting losing market share. Every other program on a PC uses tabs against the active window. Proprietary software like MS Office and Adobe, FOSS software like Notepad++ and GIMP, 3D design, video editors, hex editors, you name it: It is the standard, logical design.
|
||||
|
||||
Then Google decided to make the tabs on top standard for its Chrome browser, which was designed for mobile devices not desktops. On a smartphone it may make sense, as there isn’t room for a full desktop style menu layout. On a desktop it is counterintuitive and breaks workflow with all other programs. The code for desktops is different from phones so there was no rational reason to try and force a mobile UI onto desktop users who were Firefox’s primary userbase. The argument that it was “too hard to maintain” a single setting enacted by 2 lines of code in a 4 Million line codebase is just insulting to the intelligence of users. Code isn’t a lawn. It doesn’t change if you leave it alone for a few weeks.
|
||||
|
||||
When inundated with user complaints about the change, the response I received from a lead developer who shall remain nameless was “We have hundreds of millions of users. 5000 people complaining doesn’t represent the majority of users”. Those complaints had one common sentiment, “If I wanted my browser to look like Chrome I’d just use Chrome”. And so they did.
|
||||
|
||||
### Constant removal of features “that no-one uses”
|
||||
|
||||
Every change made to Firefox had the same pattern. The default feature was changed, but there was a menu setting to revert it. Then the menu setting was removed and you could only change it via about:config. Then the about:config option was removed. Every protest from the userbase met the same response “You’re just a tiny minority, most people like the change”.
|
||||
|
||||
75% is not a minority. Almost everyone hated the changes and each change pushed more users away, and the arrogant, condescending responses from Mozilla staff left a bitter taste in their mouth ensuring they would never return. Looking closely at the user numbers you could see a visible drop with every removal, only stabilising when a third party add-on or CSS would revert the change. Over and over, year after year. No lessons were learnt.
|
||||
|
||||
Removing settings wasn’t enough. Firefox went on to neuter add-ons and themes, forcing centralised signing and ultimately deprecating XUL without adequate webextension api’s to replace lost functionality. Complaining about this change I again spoke to one of the lead developers (same guy). His response was (exact quote) “People don’t use Firefox because of add-ons. Our telemetry shows 80% of users never install any add-ons” i.e. the telemetry that any tech savvy person immediately turns off because they don’t want their browser spying on them and about which we have also complained numerous times.
|
||||
|
||||
Even the one great move they made in UI design, the drag and drop customisable Australis interface, alienated more users because of the horrible default layout and lack of options that didn’t need CSS. The awful angled tabs (copied from chrome) is the only UI change Mozilla has admitted was terrible and they only did so, surprise surpise, AFTER chrome did away with them.
|
||||
|
||||
To this day, Mozilla still claims to want to hear from their users and after 12 years they still keep ignoring us, the awful default Proton UI being the latest foolish choice forced upon an unwilling userbase. (Type in “Firefox Proton” on Google to look at the most commonly searched suggestions if you think I’m in the minority). Fortunately it can still be mostly fixed with userChrome.css but even I’m getting sick of having to repeatedly patch together new code to keep up with constant deprecation and format changes.
|
||||
|
||||
### Bad coding paradigms
|
||||
|
||||
Mozilla’s source code is a nightmare. For example, default profile location is defined 3 times, using different variables, in 3 different languages, one of which is generated by combining multiple variables located in separate files. Another example I saw was another global variable being defined in 6 different files.
|
||||
|
||||
Post compiling, history for downloads, visited pages, bookmarks etc, are all shoved together into obfuscated files. The end result? Try deleting 400 entries from your history and watch how long it takes. Deleting that many lines from a separate text file would take a split second. Want to change the appearance of an icon or add a new one for a custom search? They’re mostly just PNGs, but they are obfuscated and sealed into the omni.ja file. Could otherwise be changed in seconds with your editor of choice, instead you need to install and learn a program like Eclipse and recompile the file with every change. The list goes on and on.
|
||||
|
||||
It is no wonder Mozilla’s coders have such trouble finding and fixing bugs. This led to an even worse coding paradigm, logging everything for the purpose of bugfixes. This is one of the culprits of…
|
||||
|
||||
### Poor memory management
|
||||
|
||||
If a program is sitting there doing nothing, its memory usage should not change. Looking at my memory manager I have 40 processes obeying this principle. What is the only program constantly reading and writing to disk despite doing nothing? Firefox. It is running 13 processes and all of them are constantly doing both. I’ve been coding for 40 years and building PC’s for 30 so I do know a thing or two about how computing works. This is just awful design at the base level and no amount of tinkering on the surface will fix that.
|
||||
|
||||
The code paradigm is the root of Mozilla’s performance issues and they won’t address it. I’ll wager that’s also the reason for the failure of FirefoxOS, which was a great idea but failed because of poor execution and coding practices resulting in too many bugs to fix.
|
||||
|
||||
### Invading your privacy at the same time as telling us “we value your privacy”
|
||||
|
||||
Telemetry. Hidden telemetry that isn’t disabled when you click “disable telemetry”. Firstrun pings. Forced signing of add-ons. Auto-updates you can’t switch off, pinging every 10 minutes. “Experiments” which require a separate opt out. Now the latest offence is enforcing app based 2FA to login to a Firefox Add-on account just to make a custom theme, which you wouldn’t need in the first place if not for forced add-on signing.
|
||||
|
||||
Mozilla has as little respect for their users privacy as they do for our opinions.
|
||||
|
||||
### Final thoughts
|
||||
|
||||
It didn’t have to be this way. It still doesn’t, but the mind that is incapable of admitting when it is wrong, or of considering differing opinions is doomed to stagnation and decay. The decision makers of Mozilla appear to have such minds so I do not hold out much hope for the future. Hopefully some of you out there can at least learn from their mistakes and succeed where they are failing. You succeed by giving users what they want, not telling them what they should want. By providing what is missing in the market, not blindly trying to copy your competitors.
|
||||
|
||||
_The views and opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of It’s FOSS._
|
||||
|
||||
Author info: From Melbourne Australia, Dan has been coding for about 40 years and doing graphic design for 25 years. He also works on open source mechanical designs based on 3D printer kits.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Big Tech Websites Get Millions in Revenue, It's FOSS Got You!
|
||||
|
||||
If you like what we do here at It's FOSS, please consider making a donation to support our independent publication. Your support will help us keep publishing content focusing on desktop Linux and open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not interested
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.itsfoss.com/firefox-continuous-decline/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Community][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://news.itsfoss.com/author/team/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://news.itsfoss.com/firefox-decline/
|
||||
[2]: https://www.wired.com/2009/07/mozilla-considers-copying-chrome-for-firefox-4dot0/
|
||||
@ -1,73 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: (What is GNU/Linux Copypasta?)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://itsfoss.com/gnu-linux-copypasta/)
|
||||
[#]: author: (Abhishek Prakash https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/)
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: ( )
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
|
||||
What is GNU/Linux Copypasta?
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
As a Linux user, you might have come across a long text that starts with “I’d like to interject for a moment. What you are referring to as Linux, is in fact, GNU/Linux”.
|
||||
|
||||
It makes some people confused about what is Linux and what is GNU/Linux. I have explained it in the article about the [concept of Linux distributions][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Basically, [Linux is a kernel][2] and with [GNU softwares][3], it becomes usable in the form of an operating system.
|
||||
|
||||
Many purists and enthusiasts don’t want people to forget the contribution of GNU to the Linux-based operating systems. Hence, they often post this long text (known as GNU Linux copypasta) in various forums and communities.
|
||||
|
||||
I am not sure of the origin of the GNU/Linux copypasta and since when it came into existence. Some people attribute it to Richard Stallman’s [article on GNU blog in 2011][4]. I cannot confirm or deny that.
|
||||
|
||||
### Complete GNU/Linux Copypasta
|
||||
|
||||
I’d just like to interject for a moment. What you’re refering to as Linux, is in fact, GNU/Linux, or as I’ve recently taken to calling it, GNU plus Linux. Linux is not an operating system unto itself, but rather another free component of a fully functioning GNU system made useful by the GNU corelibs, shell utilities and vital system components comprising a full OS as defined by POSIX.
|
||||
|
||||
Many computer users run a modified version of the GNU system every day, without realizing it. Through a peculiar turn of events, the version of GNU which is widely used today is often called Linux, and many of its users are not aware that it is basically the GNU system, developed by the GNU Project.
|
||||
|
||||
There really is a Linux, and these people are using it, but it is just a part of the system they use. Linux is the kernel: the program in the system that allocates the machine’s resources to the other programs that you run. The kernel is an essential part of an operating system, but useless by itself; it can only function in the context of a complete operating system. Linux is normally used in combination with the GNU operating system: the whole system is basically GNU with Linux added, or GNU/Linux. All the so-called Linux distributions are really distributions of GNU/Linux!
|
||||
|
||||
**Recommended Read:**
|
||||
|
||||
![][5]
|
||||
|
||||
#### [Linux Jargon Buster: What is FOSS (Free and Open Source Software)? What is Open Source?][6]
|
||||
|
||||
### What is a Copypasta, again?
|
||||
|
||||
![][7]
|
||||
|
||||
Did you notice that I used the term ‘copypasta’. It has nothing to do with Italian dish pasta.
|
||||
|
||||
[Copypasta][8] is a block of text which is copied and pasted across the internet, often to troll or poke fun at people. It is a degeneration of the term ‘copy-paste’.
|
||||
|
||||
Copypasta is also considered spam because they are repeated as it is a number of times. Take the example of GNU Linux copypasta. If a few people keep on pasting the huge text block every time someone uses Linux instead of GNU/Linux in a discussion forum, it would annoy other members.
|
||||
|
||||
### Have you ever used GNU/Linux Copypasta?
|
||||
|
||||
Personally, I have never done that. But, to be honest, that’s how I come to know about the term GNU/Linux when I was a new Linux users and was browsing through some Linux forum.
|
||||
|
||||
How about you? Have you ever copy-pasted the “I would like to interject for a moment” in a Linux forum? Do you think it’s a tool for ‘trolls’ or is it the necessary evil to make people aware of the GNU project?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://itsfoss.com/gnu-linux-copypasta/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://itsfoss.com/what-is-linux-distribution/
|
||||
[2]: https://itsfoss.com/what-is-linux/
|
||||
[3]: https://www.gnu.org/
|
||||
[4]: https://www.gnu.org/gnu/linux-and-gnu.html
|
||||
[5]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/what-is-foss.png?fit=800%2C450&ssl=1
|
||||
[6]: https://itsfoss.com/what-is-foss/
|
||||
[7]: https://i0.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/copypasta.png?resize=800%2C450&ssl=1
|
||||
[8]: https://www.makeuseof.com/what-is-a-copypasta/
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: ( )
|
||||
[#]: translator: (runningwater)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
@ -221,7 +221,7 @@ via: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3543232/how-to-examine-processes-runni
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sandra Henry-Stocker][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,101 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "elementary OS 6 ODIN Released. This is What’s New."
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/08/elementary-os-6/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Arindam https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
elementary OS 6 ODIN Released. This is What’s New.
|
||||
======
|
||||
The team announced the release of elementary OS 6 ODIN, and it is
|
||||
immediately available for download. We recap the release in this post.
|
||||
![elementary OS 6 ODIN Desktop][1]
|
||||
|
||||
The elementary OS 6 code named “ODIN” was a long due. This release coming after more than two years since its predecessor, [elementary OS 5.1 Hera][2]. A lot had happened in the last two years, that includes a full-fledged pandemic. Despite all the challenges, roadblocks – a brand new and much awaited release is here.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s take a look at what’s new.
|
||||
|
||||
### elementary OS 6 Odin – What’s New
|
||||
|
||||
The team promises the following items in a nutshell in this release:
|
||||
|
||||
> Empowering you to be in control and express yourself,
|
||||
> Continuing to innovate with new features, and
|
||||
> Making elementary OS easier to get and more inclusive
|
||||
|
||||
* This release is based on Ubuntu 20.04 and Linux Kernel 5.8. If you ask me, it’s late at this moment to have a new version of a distro based on Ubuntu 20.04 whereas next LTS is due in 2022.
|
||||
* Dark theme and new ascent color is introduced in this release. With the dark theme enabled, all the default applications, windows automatically adapt to dark mode. This mode also can be set based on sunset and sunrise at your location.
|
||||
* The ascent colors applied across the system when chosen. A fair and nice list of assent colors are available.
|
||||
* The new dark theme is designed such as way that third party app developers can easily integrate their application to follow elementary OS stylesheet.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
![Dark and Light theme][3]
|
||||
|
||||
* All apps in AppCenter are now Flatpak apps which runs in their separate sandbox. This is one of the best move by elementary team and all the Flatpak apps requires separate permission controls via settings.
|
||||
* If you are a touchpad/touch device fan, then you are in for a treat. Three finger swipe up gestures brings up the activities overview.
|
||||
* Three finger left and right – swap between dynamic workspaces.
|
||||
* And all the applicable apps uses two finger gestures.
|
||||
* Notifications are revamped with new look and can follow dark theme.
|
||||
* A new task application introduced to track your tasks and can sync with online accounts.
|
||||
* elementary OS 6 comes with firmware updates built in, powered by the Linux Vendor Firmware Service. Firmware updates are provided for supported devices by hardware manufacturers like Star Labs, Dell, Lenovo, HP, Intel, Logitech, Wacom, 8bitdo, and many more—now supported devices can get the latest updates for security and stability straight from System Settings → System → Firmware or by searching the Applications Menu for “Firmware.”
|
||||
* Native applications are updated and redesigned completely. Epiphany browser is renamed as Web. Mail is completely rewritten with tighter integration with online accounts.
|
||||
* Files introduces a different behavioral change. You need to single click to browse folders, but double click for files. This can not be changed via gsettings.
|
||||
* And many more updates, which you can read in the [change log][4] here.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
SEE ALSO: elementary OS 6 Beta Released. Download and Test Now!
|
||||
|
||||
### Minimum System Requirement for elementary OS 6
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a system specification for this version, before you hit download.
|
||||
|
||||
* Recent Intel i3 or comparable dual-core 64-bit processor
|
||||
* 4 GB of system memory (RAM)
|
||||
* Solid state drive (SSD) with 15 GB of free space
|
||||
* Internet access
|
||||
* Built-in or wired mouse/touchpad and keyboard
|
||||
* 1024×768 minimum resolution display
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### elementary OD 6 Odin – Download
|
||||
|
||||
The .iso files for the new release is available in below link. Due to rush, the servers might be busy, hence it is recommended to use torrents if possible.
|
||||
|
||||
[Download elementary OS 6 ODIN][6]
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
There is no upgrade path available at the moment to upgrade to elementary 6 from elementary 5.1. Hence, you need to take backups and do a fresh installation via .iso available in above link.
|
||||
|
||||
### Closing Notes
|
||||
|
||||
There is no question that elementary OS is a one-of-a-kind Linux Distribution today. And its popularity is increasing everyday due to the awesome Pantheon desktop. It is one of the rare Linux distribution which appeals both macOS and Windows users. That said, I think the development process requires a bit faster and two years of the wait between versions is too long for IT. This release is based on Ubuntu 20.04 which is already two years old, and we have a new LTS coming up on 2022. And of course there is no upgrade path. I believe if the team work on these aspects, considering dedicated developers, donations, I think it would be one of the best Linux distro.
|
||||
|
||||
* * *
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/08/elementary-os-6/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arindam][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://www.debugpoint.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/elementary-OS-6-ODIN-Desktop-1024x576.jpg
|
||||
[2]: https://www.debugpoint.com/2019/12/elementary-os-hera-released/
|
||||
[3]: https://www.debugpoint.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Dark-and-Light-theme-1024x692.png
|
||||
[4]: https://blog.elementary.io/elementary-os-6-odin-released/
|
||||
[5]: https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/05/elementary-os-6-beta/
|
||||
[6]: https://elementary.io/
|
||||
@ -1,118 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "SparkyLinux 6.0 “Po-Tolo” Released Based on Debian 11 Bullseye"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/08/sparky-linux-6-review/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Arindam https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
SparkyLinux 6.0 “Po-Tolo” Released Based on Debian 11 Bullseye
|
||||
======
|
||||
We review the SparkyLinux 6 “Po-Tolo” and round up the release.
|
||||
[SparkyLinux][1] is a desktop-based Linux distribution based on Debian and provides almost all major desktop flavors. It is a unique distribution in the sense that it provides both Debian Stable and Debian Testing editions with the latest desktop packages. SparkyLinux also provides a collection of curated applications, with some special editions as well. For example, if you are a Game lover, then the SparkyLinux GameOver edition is there. For system admins, there is a Rescue Edition as well to fix broken systems. All these special editions come with pre-loaded games, utilities with some proprietary packages as well.
|
||||
|
||||
The latest release of SparkyLinux 6 brings the packages from [Debian 11 Bullseye][2], which released a while back. Let’s take a look at what’s new.
|
||||
|
||||
![SparkyLinux 6 desktop \(Xfce\)][3]
|
||||
|
||||
### SparkyLinux 6 – What’s New
|
||||
|
||||
* SparkyLinux 6 is based on Debian 11 Bullseye.
|
||||
* Powered by Linux Kernel 5.10.x LTS
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* This distribution maintains its own repo, and it is now updated with Bullseye packages.
|
||||
* The default and necessary applications are updated to their respective Debian stable version. Here’s a quick update:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
– Firefox 78.13.0ESR instead of Firefox (latest)
|
||||
– Thunderbird 78.13.0
|
||||
– VLC 3.0.16
|
||||
– LibreOffice 7.0.4
|
||||
– Calamares 3.2.41.1
|
||||
|
||||
* The default AppCenter – APTUS is included in this release which provides you curated 2000+ applications which can be installed via a simple GUI with one-click. This is one of the best feature of SparkyLinux, specially for new users or large deployments.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* The APTUS – AppCenter also provides one-click features for the followings –
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
System upgrade
|
||||
Search packages
|
||||
Fix broken packages
|
||||
Edit repo
|
||||
Clean up cache
|
||||
…and more
|
||||
|
||||
* Desktop environments retain their current stable versions with Sparky flavors –
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Xfce 4.16
|
||||
KDE Plasma 5.22
|
||||
LXQt 0.17
|
||||
|
||||
* Other changes include, the MinimalGUI version changed file manager to PCManFM and browser to Firefox ESR.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Detailed changes with information is available [here][4].
|
||||
|
||||
### Download, Upgrade and Install
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using an earlier version of SparkyLinux, simple making a system upgrade takes you to SparkyLinux 6.0. No additional steps are required.
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
SEE ALSO: SparkyLinux 2021.03 Gets First-Ever KDE Plasma Edition with Debian 11
|
||||
|
||||
For fresh installation with respective Desktop environments – refer below link for download. You can use [Etcher][6] or similar utility to create LIVE usb for fresh installation. Do not forget to turn off secure boot if you are installing in UEFI systems.
|
||||
|
||||
[download sparkylinux stable][7]
|
||||
|
||||
### Sparky Linux 6 – Quick Review
|
||||
|
||||
* I ran SparkyLinux in a virtual machine and native install, both with Xfce desktop edition for a quick test. The installation went smooth, thanks to the awesome Calamares installer. No surprises there.
|
||||
* After initial boot, a welcome screen guides you to go over the important items if you may want to read. SparkyLinux takes care of system configurations based on GUI based utility. For example, you do not need to open terminal and run “sudo apt upgrade” to update your system. It’ll prompt you that an upgrade is available, you give admin password, and it takes care of it.
|
||||
* SparkyLinux is super stable thanks to Debian and very lightweight. In idle scenario, the Xfce desktop with SparkyLinux was consuming around 600 MB of memory and most of the CPU is used by respective desktop window manager which is at around 5%.
|
||||
* If you are using KDE Plasma or LXQt – the memory and CPU usage should vary, but they would not fluctuate much.
|
||||
* The APTUS – AppCenter plus system administration utility is one of the best feature which makes it stand apart among other distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
![APTus APPCENTER in SparkyLinux][8]
|
||||
|
||||
* And the good thing is, it gives you flavors of Debian Rolling and Debian Stable both. If you want to use Debian Rolling packages in SparkyLinux, then you can get it out-of-the-box.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
That said, it’s a simple, stable and user-friendly distribution. Give it a try if you have not yet; It is a perfect and suitable daily-usage distro.
|
||||
|
||||
Cheers.
|
||||
|
||||
* * *
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/08/sparky-linux-6-review/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arindam][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.debugpoint.com/author/admin1/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://sparkylinux.org
|
||||
[2]: https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/05/debian-11-features/
|
||||
[3]: https://www.debugpoint.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/SparkyLinux-6-desktop-Xfce-1024x764.jpeg
|
||||
[4]: https://sparkylinux.org/sparky-6-0-po-tolo/
|
||||
[5]: https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/03/sparkylinux-2021-03-release/
|
||||
[6]: https://www.debugpoint.com/2021/01/etcher-bootable-usb-linux/
|
||||
[7]: https://sparkylinux.org/download/stable/
|
||||
[8]: https://www.debugpoint.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/APTus-APPCENTER-in-SparkyLinux-1024x781.jpeg
|
||||
@ -1,25 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: ""
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://www.2daygeek.com/upgrade-opensuse-from-15-2-to-15-3/"
|
||||
[#]: author: " "
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.2daygeek.com/upgrade-opensuse-from-15-2-to-15-3/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
@ -1,82 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "Getting the Top Indicator Panel Back in GNOME"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://itsfoss.com/enable-applet-indicator-gnome/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Abhishek Prakash https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
Getting the Top Indicator Panel Back in GNOME
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME is the popular desktop environment that thrives to give Linux a modern desktop experience.
|
||||
|
||||
While it works for the most part, some of their decisions has left the user fuming and questioning.
|
||||
|
||||
You cannot have icons and files on the desktop, [new document option has been removed][1] from the right click context menu. In addition to that, GNOME has also removed the applet indicator functionality.
|
||||
|
||||
You know what indicator applets are, don’t you? Those little icons that let you access additional features of the given application. I have plenty of them in my Ubuntu system.
|
||||
|
||||
![Indicator applets][2]
|
||||
|
||||
And this creates a problem, specially for applications that rely completely on these applet indicators to function. Take [Dropbox][3] for example. The only way to access Dropbox settings is through the app-indicator and you won’t find it in GNOME.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s a problem, but thankfully, there is a workaround for that.
|
||||
|
||||
### Enabling applet indicator in GNOME via extension
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using GNOME, you probably already know what GNOME Extension is. These are basically small add-ons developed by enthusiastic, independent developers.
|
||||
|
||||
If not done already, [enable GNOME extensions][4]. It’s actually quite simple. Go to any GNOME extension’s page using Firefox or Chrome and it will suggest downloading a browser extension. Install it and you are good to go.
|
||||
|
||||
![Enabling GNOME Extension browser add-on][5]
|
||||
|
||||
Now, there are several GNOME extensions available that allow adding applet indicators in the top panel. At the time of writing this tutorial, [AppIndicator and KStatusNotifierItem Support][6] extension is well developed and supported for the recent GNOME versions.
|
||||
|
||||
Go to its webpage:
|
||||
|
||||
[AppIndicator Extension][6]
|
||||
|
||||
On the page, you should see a toggle button. Click it to install it.
|
||||
|
||||
![][7]
|
||||
|
||||
There will be a pop-up. Hit install when you see it.
|
||||
|
||||
![Install the extension][8]
|
||||
|
||||
The results won’t be seen immediately. You’ll have to restart GNOME. On Xorg, you could just use Alt+F2 and enter r but that does not work in Wayland.
|
||||
|
||||
Log out of the system and log back in. Applet indicator should be activated now. If you have any applications installed that provides an indicator applet, you should see it on the top panel.
|
||||
|
||||
In my case, I had Dropbox already installed and hence it started showing the icon in the top panel.
|
||||
|
||||
![Dropbox indicator working in GNOME][9]
|
||||
|
||||
I hope this little tip help you gain access to the app indicators in the top panel of GNOME again.
|
||||
|
||||
I do not know why the GNOME developers though that dropping this essential feature was a good idea. Anyway, if one door closes, another opens (usually). Enjoy GNOME to your liking.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://itsfoss.com/enable-applet-indicator-gnome/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://itsfoss.com/add-new-document-option/
|
||||
[2]: https://itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/indicator-applet-linux.webp
|
||||
[3]: https://www.dropbox.com
|
||||
[4]: https://itsfoss.com/gnome-shell-extensions/
|
||||
[5]: https://itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/installing-gnome-extension-add-on-800x355.webp
|
||||
[6]: https://extensions.gnome.org/extension/615/appindicator-support/
|
||||
[7]: https://itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/appindicator-extension-800x329.webp
|
||||
[8]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/installing-appindicator-extension.png?resize=800%2C269&ssl=1
|
||||
[9]: https://itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/gnome-dropbox-indicator-800x561.webp
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "Building an open source community health analytics platform"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://opensource.com/article/21/9/openrit-mystic"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Quinn Foster https://opensource.com/users/quinn-foster"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
Building an open source community health analytics platform
|
||||
======
|
||||
An academic OSPO is working with CHAOSS software to build a community
|
||||
health analytics platform.
|
||||
![metrics and data shown on a computer screen][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Rochester Institute of Technology (RIT) has made considerable strides in increasing its presence in the open source world lately. RIT's _Free and Open Source Software and Free Culture_ minor is the first of its kind in academia. For example, its open source programs office, Open @ RIT, has begun helping RIT faculty and staff fellows build and maintain communities for their open source projects.
|
||||
|
||||
These strides are driven by the students, faculty, and staff at RIT. Already, a growing number of people at the university are heading their own open projects. However, running an entirely open source project can be cumbersome. Much of this comes from maintaining a community for the project and managing data such as the project's code, issue tracking, and repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
To help these people, Open @ RIT is creating a system called Mystic, a community health analytics platform that utilizes [GrimoireLab][2], an open source toolkit developed by [CHAOSS][3] software that provides metrics and analytics for open source projects. GrimoireLab allows users to gather, enrich, filter, and visualize a project's data, such as the time it takes a reported issue to be solved, contributor affiliations, and much more.
|
||||
|
||||
Mystic will act as a front-end portal where anybody can submit their project. From there, the project will be sent directly to GrimoireLab, which will compute and publish the project's metrics for the submitter after only a few minutes.
|
||||
|
||||
> "Our hope is that anyone at RIT who is managing, leading, or participating in an open source project will be able to submit that project to Mystic and have any metrics they need provided to them," says Emi Simpson, full-stack developer at Open @ RIT and head developer of Mystic.
|
||||
|
||||
The process is straightforward. After logging into Mystic, the user uploading their project opens up a pop-up window where they enter details about the project and links to data sources like GitLab, RSS feed, and an Open Software Foundation (OSF) project. Once the details and project are saved, Mystic uses GrimoireLab to automatically retrieve metrics from the project source and render graphs for each source. The project and its metrics will then be displayed on its own dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||
![Mystic statistics page][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Screenshot by Quinn Foster, [CC-BY SA 4.0][5]
|
||||
|
||||
These dashboards will also be displayed and listed on a single page for others to see, encouraging cooperative development and interaction between open source communities within RIT worldwide. Simpson and Open @ RIT hope this will increase participation in open work at RIT and further cement the university as an open work hub.
|
||||
|
||||
> "If somebody asks what is RIT doing for open source software, my hope is that people will be able to point to Mystic and GrimoireLab and say 'here's what,'" says Simpson. "By building that metric of 'here's what we're doing, here's what we've contributed, here are the projects that people are working on,' we can build a community at RIT centered around the work that we're doing in open source."
|
||||
|
||||
At the moment, Mystic is still under development and not ready for a production environment, but its potential for both RIT and open source as a whole remains well in sight. Future goals include implementing easy integration with the university's reporting tools and comprehensive dashboards at the project level and in aggregate.
|
||||
|
||||
Are you interested in contributing to Mystic? [Get in touch with us][6] to get started.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/21/9/openrit-mystic
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Quinn Foster][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/quinn-foster
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/metrics_data_dashboard_system_computer_analytics.png?itok=oxAeIEI- (metrics and data shown on a computer screen)
|
||||
[2]: https://chaoss.github.io/grimoirelab/
|
||||
[3]: https://chaoss.community/
|
||||
[4]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/mystic_statistics_page.png (Mystic statistics page)
|
||||
[5]: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/
|
||||
[6]: https://opensource.ieee.org/rit/mystic
|
||||
212
sources/tech/20210910 MAKE MORE with Inkscape - Ink-Stitch.md
Normal file
212
sources/tech/20210910 MAKE MORE with Inkscape - Ink-Stitch.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,212 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "MAKE MORE with Inkscape – Ink/Stitch"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://fedoramagazine.org/make-more-with-inkscape-ink-stitch/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Sirko Kemter https://fedoramagazine.org/author/gnokii/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
MAKE MORE with Inkscape – Ink/Stitch
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
![MAKE more with Inkscape - Ink/Stitch][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Inkscape, the most used and loved tool of Fedora’s Design Team, is not just a program for doing nice vector graphics. With vector graphics (in our case SVG) a lot more can be done. Many programs can import this format. Also, Inkscape can do a lot more than just graphics. The first article of this [series][2] showed how to [produce GCode with Inkscape][3]. This article will examine another Inkscape extension – [Ink/Stitch][4]. Ink/Stitch is an extension for designing embroidery with Inkscape.
|
||||
|
||||
### DIY Embroidery
|
||||
|
||||
In the last few years the do-it-yourself or maker scene has experienced a boom. You could say it all began with the inexpensive option of [3D printing][5]; followed by also not expensive [CNC][6] machines and laser cutters/engravers. Also the prices for more _“_traditional_”_ machines such as embroidery machines have fallen during recent years. [Home embroidery machines are now available for 500 US dollars][7].
|
||||
|
||||
If you don’t want to or can’t buy one yourself, the nearest [MakerSpace][8] often has one. Even the prices for commercial single-head embroidery machines are down to 5,000 US dollars. They are an investment that can pay off quickly.
|
||||
|
||||
### Software for Embroidery Design
|
||||
|
||||
Some of the home machines include their own software for designing embroidery. But most, if not all, of these applications are Windows-only. Also, the most used manufacturer-independent software of this area – [Embird][9] – is only available for Windows. But you could run it in Wine.
|
||||
|
||||
Another solution for Linux – [Embroidermodde][10] – is not really developed anymore. And this is after having had a fundraising campaign.
|
||||
|
||||
Today, only one solution is left – [Ink/Stitch][4]
|
||||
|
||||
![The logo of the Ink/Stitch project][11]
|
||||
|
||||
### Open Source and Embroidery Design
|
||||
|
||||
Ink/Stitch started out using [libembroidery][12]. Today [pyembroidery][13] is used. The manufacturers can’t be blamed for the prices of these machines and the number of Linux users. It is hardly worthwhile to develop applications for Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
#### The Embroidery File Format Problem
|
||||
|
||||
There is a problem with the proliferation of file formats for embroidery machines; especially among manufacturers that cook their own file format for their machines. In some cases, even a single manufacturer may use several different file formats.
|
||||
|
||||
* **.10o** – Toyota embroidery machines
|
||||
* **.100** – Toyota embroidery machines
|
||||
* **.CSD** – Poem, Huskygram, and Singer EU embroidery home sewing machines.
|
||||
* **.DSB** – Baruda embroidery machines
|
||||
* **.JEF** – MemoryCraft 10000 machines.
|
||||
* **.SEW** – MemoryCraft 5700, 8000, and 9000 machines.
|
||||
* **.PES** – Brother and Babylock embroidery home sewing machines.
|
||||
* **.PEC** – Brother and Babylock embroidery home sewing machines.
|
||||
* **.HUS** – Husqvarna/Viking embroidery home sewing machines.
|
||||
* **.PCS** – Pfaff embroidery home sewing machines.
|
||||
* **.VIP** – old Pfaff format also used by Husqvarna machines.
|
||||
* **.VP3** – newer Pfaff embroidery home sewing machines.
|
||||
* **.DST** – Tajima commercial embroidery sewing machines.
|
||||
* **.EXP** – Melco commercial embroidery sewing machines.
|
||||
* **.XXX** – Compucon, Singer embroidery home sewing machines.
|
||||
* **.ZSK** – ZSK machines on the american market
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This is just a small selection of the file formats that are available for embroidery. You can find a more complete list [here][14]. If you are interested in [deeper knowledge about these file formats, see here for more information][15].
|
||||
|
||||
#### File Formats of Ink/Stitch
|
||||
|
||||
Ink/Stitch can currently read the following file formats: 100, 10o, BRO, DAT, DSB, DST, DSZ, EMD, EXP, EXY, FXY, GT, INB, JEF, JPX, KSM, MAX, MIT, NEW, PCD, PCM, PCQ, PCS, PEC, PES, PHB, PHC, SEW, SHV, STC, STX, TAP, TBF, U01, VP3, XXX, ZXY and also GCode as TXT file.
|
||||
|
||||
For the more important task of writing/saving your work, Ink/Stitch supports far fewer formats: DST, EXP, JEF, PEC, PES, U01, VP3 and of course SVG, CSV and GCode as TXT
|
||||
|
||||
Besides the problem of all these file formats, there are other problems that a potential stitch program has to overcome.
|
||||
|
||||
Working with the different kinds of stitches is one difficulty. The integration of tools for drawing and lettering is another. But why invent such a thing from scratch? Why not take an existing vector program and just add the functions for embroidery to it? That was the idea behind the [Ink/Stitch project][4] over three years ago.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Ink/Stitch
|
||||
|
||||
Ink/Stitch is an [extension for Inkscape][16]. Inkscape’s new functionality for downloading and installing extensions is still experimental. And you will not find Ink/Stitch among the extensions that are offered there. You must [download][17] the extension manually. After it is downloaded, unzip the package into your directory for Inkscape extensions. The default location is _~/.config/Inkscape/extensions_ (or _/usr/share/inkscape/extensions_ for system-wide availability). If you have changed the defaults, you may need to check Inkscape’s settings to find the location of the extensions directory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Customization – Install Add-ons for Ink/Stitch
|
||||
|
||||
The Ink/Stitch extension provides a function called Install Add-Ons for Inkscape, which you should run first.
|
||||
|
||||
The execution of this function – _Extensions > Ink/Stitch > Thread Color Management > Install thread color palettes for Inkscape_ – will take a while.
|
||||
|
||||
Do not become nervous as there is no progress bar or a similar thing to see.
|
||||
|
||||
This function will install 70 color palettes of various yarn manufacturers and a symbol library for Ink/Stitch.
|
||||
|
||||
![Inkscape with the swatches dialogue open, which shows the Madeira Rayon color palette][18]
|
||||
|
||||
If you use the download from Github version 2.0.0, the ZIP-file contains the color palette files. You only need to unpack them into the right directory (_~/.config/inkscape/palettes/_). If you need a [hoop template, you can download][19] one and save it to _~/.config/inkscape/templates_.
|
||||
|
||||
The next time you start Inkscape, you will find it under _File > New From Template_.
|
||||
|
||||
### Lettering with Ink/Stitch
|
||||
|
||||
The way that is by far the easiest and most widely used, is to get a embroidery design using the _Lettering_ function of Ink/Stitch. It is located under _Extensions > Ink/Stitch > Lettering_. Lettering for embroidery is not simple. What you expect are so called satin stitched letters. For this, special font settings are needed.
|
||||
|
||||
![Inkscape with a “Chopin” glyph for satin stitching defined for the Lettering function][20]
|
||||
|
||||
You can convert paths to satin stitching. But this is more work intensive than using the Lettering function. Thanks to the work of an active community, the May 2021 release of Ink/Stitch 2.0 brought more predefined fonts for this. An English tutorial on how to create such fonts can be found [here][21].
|
||||
|
||||
Version 2.0 also brings functions (_Extensions > Ink/Stitch > Font Management_) to make managing these kinds of fonts easier. There are also functions for creating these kinds of fonts. But you will need knowledge about font design with Inkscape to do so. First, you create an an entire SVG font. It is then feed through a JSON script which converts the SVG font into the type of files that Ink/Stitch’s font management function works with.
|
||||
|
||||
![On the left side the Lettering dialogue and on the right the preview of this settings][22]
|
||||
|
||||
The function will open a dialogue window where you just have to put in your text, choose the size and font, and then it will render a preview.
|
||||
|
||||
### Embroider Areas/Path-Objects
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest thing with Ink/Stitch, is to embroider areas or paths. Just draw your path. When you use shapes then you have to convert them and then run _Extensions > Ink/Stitch > Fill Tools > Break Apart Fill Objects…_
|
||||
|
||||
This breaks apart the path into its different parts. You have to use this function. The _Path > Break apart_ function of Inkscape won’t work for this.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, you can run Ink/Stitch’s built-in simulator: _Extensions > Ink/Stitch > Visualise and Export > Simulator/Realistic Preview_.
|
||||
|
||||
![The new Fedora logo as Stitch Plan Preview][23]
|
||||
|
||||
Be careful with the simulator. It takes a lot system resources and it will take a while to start. You may find it easier to use the function _Extensions > Ink/Stitch > Visualise and Export > Stitch Plan Preview_. The latter renders the threading of the embroidery outside of the document.
|
||||
|
||||
![Nicubunu’s Fedora hat icon as embroidery. The angles for the stitches of the head part and the brim are different so that it looks more realistic. The outline is done in Satin stitching][24]
|
||||
|
||||
### Simple Satin and Satin Embroidery
|
||||
|
||||
Ink/Stitch will convert each stroke with a continuous line (no dashes) to what they call Zig-Zag or Simple Satin. Stitches are created along the path using the stroke width you have specified. This will work as long there aren’t too many curves on the path.
|
||||
|
||||
![Parameter setting dialogue and on the right the Fedora logo shape embroidered as Zig-Zag line][25]
|
||||
|
||||
This is simple. But it is by far not the best way. It is better to use the Satin Tools for this. The functions for the Satin embroidery can be found under _Extensions > Satin Tools_. The most important is the conversion function which converts paths to satin strokes.
|
||||
|
||||
![Fedora logo shape as Satin Line embroidery][26]
|
||||
|
||||
You can also reverse the stitch direction using _Extensions > Satin Tools > Flip Satin Column Rails_. This underlines the 3D effect satin embroidery gets, especially when you make puff embroidery. For machines that have this capability, you can also set the markings for the trims of jump stitches. To visualize these trims, Ink/Stitch uses the symbols that where installed from its own symbol library.
|
||||
|
||||
### The Ink/Stitch Stitch Library
|
||||
|
||||
What is called the stitch library is simply the kind of stitches that Ink/Stitch can create. The Fill Stitch and Zig-Zag/Satin Stitch have already been introduced. But there are more.
|
||||
|
||||
* **Running Stitches**: These are used for doing outline designs. The running stitch produces a series of small stitches following a line or curve. Each dashed line will be converted into a Running Stitch. The size of the dashes does not matter.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
![A running stitch – each dashed line will be converted in such one][27]
|
||||
|
||||
* **Bean Stitches**: These can also be used for outline designs or add details to a design. The bean stitch describes a repetition of running stitches back and forth. This results in thicker threading.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
![Bean Stitches – creating a thicker line][28]
|
||||
|
||||
* **Manual Stitch**: In this mode, Ink/Stitch will use each node of a path as a needle penetration point; exactly as they are placed.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
![In manual mode – each node will be the needle penetration point][29]
|
||||
|
||||
* **E-Stitch**: The main use for e-stitch is a simple but strong cover stitch for applique items. It is often used for baby cloths because their skin tends to be more sensitive.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
![E-Stitch mostly used for applications on baby cloths, soft but strong connection][30]
|
||||
|
||||
### Embroidery Thread List
|
||||
|
||||
Some embroidery machines (especially those designed for commercial use) allow different threads to be fitted in advance according to what will be needed for the design. These machines will automatically switch to the right thread when needed. Some file formats for embroidery support this feature. But some do not. Ink/Stitch can apply custom thread lists to an embroidery design.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to work on an existing design, you can import a thread list: _Extensions > Ink/Stitch > Import Threadlist_. Thread lists can also be exported: _Save As different file formats as *.zip_. You can also print them: _Extensions > Ink/Stitch > Visualise and Export > Print PDF_.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion
|
||||
|
||||
Writing software for embroidery design is not easy. Many functions are needed and diverse (sometimes closed-source) file formats make the task difficult. Ink/Stitch has managed to create a useful tool with many functions. It enables the user to get started with basic embroidery design. Some things could be done a little better. But it is definitely a good tool as-is and I expect that it will become better over time. Machine embroidery can be an interesting hobby and with Ink/Stitch the Fedora Linux user can begin designing breathtaking things.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://fedoramagazine.org/make-more-with-inkscape-ink-stitch/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sirko Kemter][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://fedoramagazine.org/author/gnokii/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/drawing2-816x345.png
|
||||
[2]: https://fedoramagazine.org/series/make-more/
|
||||
[3]: https://fedoramagazine.org/make-more-with-inkscape-g-code-tools/
|
||||
[4]: https://inkstitch.org/
|
||||
[5]: https://fedoramagazine.org/3d-printing-in-fedora-from-an-idea-to-the-thing/
|
||||
[6]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Numerical_control
|
||||
[7]: https://www.amazon.com/-/de/dp/B07VZ2YBLL/ref=sr_1_11?__mk_de_DE=%C3%85M%C3%85%C5%BD%C3%95%C3%91&crid=1MFJJWXMKQD6R&dchild=1&keywords=home+embroidery+machine&qid=1628388092&rnid=2941120011&s=arts-crafts&sprefix=home+embroider+%2Caps%2C-1&sr=1-11
|
||||
[8]: https://www.fablabs.io/labs/map
|
||||
[9]: https://www.embird.net/
|
||||
[10]: https://embroidermodder.org/
|
||||
[11]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/inkstitch_logo.png
|
||||
[12]: https://github.com/Embroidermodder/libembroidery
|
||||
[13]: https://github.com/inkstitch/pyembroidery
|
||||
[14]: http://www.needlework.ru/page/embroidery.htm
|
||||
[15]: http://edutechwiki.unige.ch/en/Embroidery_format
|
||||
[16]: https://inkscape.org/~wwderw/%E2%98%85inkstitch-embroidery-extension
|
||||
[17]: https://github.com/inkstitch/inkstitch/releases/tag/v2.0.0
|
||||
[18]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/swatches-1024x556.png
|
||||
[19]: https://inkstitch.org/assets/images/tutorials/templates/hoop-template.svg
|
||||
[20]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/satinfont-1024x556.png
|
||||
[21]: https://inkstitch.org/tutorials/font-creation/
|
||||
[22]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/lettering-1024x523.png
|
||||
[23]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/stitch-preview-1024x556.png
|
||||
[24]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/nicu-stitch.gif
|
||||
[25]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/zigzag-1024x463.png
|
||||
[26]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/satin.png
|
||||
[27]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/running-stitch-detail.jpg
|
||||
[28]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/bean-stitch-detail.jpg
|
||||
[29]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/manual-stitch-detail.png
|
||||
[30]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/e-stitch-detail.jpg
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,257 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "Quadratic algorithms are slow (and hashmaps are fast)"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://jvns.ca/blog/2021/09/10/hashmaps-make-things-fast/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Julia Evans https://jvns.ca/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: "unigeorge"
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
Quadratic algorithms are slow (and hashmaps are fast)
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
Hello! I was talking to a friend yesterday who was studying for a programming interview and trying to learn some algorithms basics.
|
||||
|
||||
The topic of quadratic-time vs linear-time algorithms came up, I thought this would be fun to write about here because avoiding quadratic-time algorithms isn’t just important in interviews – it’s sometimes good to know about in real life too! I’ll explain what a “quadratic-time algorithm is” in a minute :)
|
||||
|
||||
here are the 3 things we’ll talk about:
|
||||
|
||||
1. quadratic time functions are WAY WAY WAY slower than linear time functions
|
||||
2. sometimes you can make a quadratic algorithm into a linear algorithm by using a hashmap
|
||||
3. this is because hashmaps lookups are very fast (instant!)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
I’m going to try to keep the math jargon to a minimum and focus on real code examples and how fast/slow they are.
|
||||
|
||||
### our problem: intersect two lists
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s talk about a simple interview-style problem: getting the intersection of 2 lists of numbers. For example, `intersect([1,2,3], [2,4,5])` should return `[2]`.
|
||||
|
||||
This problem is also somewhat realistic – you could imagine having a real program where you need to take the intersection of 2 lists of IDs.
|
||||
|
||||
### the “obvious” solution:
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s write some code to take the intersection of 2 lists. Here’s a program that does it, called `quadratic.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
# the actual code
|
||||
def intersection(list1, list2):
|
||||
result = []
|
||||
for x in list1:
|
||||
for y in list2:
|
||||
if x == y:
|
||||
result.append(y)
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
# some boilerplate so that we can run it from the command line on lists of
|
||||
# different sizes
|
||||
def run(n):
|
||||
# make 2 lists of n+1 elements
|
||||
list1 = list(range(3, n)) + [2]
|
||||
list2 = list(range(n+1, 2*n)) + [2]
|
||||
# intersect them and print out the result
|
||||
print(list(intersection(list1, list2)))
|
||||
|
||||
# Run with the program's first command line argument
|
||||
run(int(sys.argv[1]))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The reason it’s called `quadratic.py` is that if `list1` and `list2` have size `n`, then the inner loop (`if x == y`) will run `n^2` times. And in math, functions like `x^2` are called “quadratic” functions.
|
||||
|
||||
### how slow is `quadratic.py`?
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s run this program with a bunch of lists of different lengths. The intersection of the two lists is always the same: `[2]`.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ time python3 quadratic.py 10
|
||||
[2]
|
||||
|
||||
real 0m0.037s
|
||||
$ time python3 quadratic.py 100
|
||||
[2]
|
||||
|
||||
real 0m0.053s
|
||||
$ time python3 quadratic.py 1000
|
||||
[2]
|
||||
|
||||
real 0m0.051s
|
||||
$ time python3 quadratic.py 10000 # 10,000
|
||||
[2]
|
||||
|
||||
real 0m1.661s
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
So far none of this is too bad – it’s still taking less than 2 seconds.
|
||||
|
||||
Then I ran it on two lists with 100,000 elements, and I had to wait a LONG time. Here’s the result:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ time python3 quadratic.py 100000 # 100,000
|
||||
[2]
|
||||
|
||||
real 2m41.059s
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This is very slow! It’s 160 seconds, which is almost exactly 100x longer than it did to run on 10,000 elements (which was 1.6 seconds). So we can see that after a certain point, every time we make the list 10x bigger, the program takes about 100x longer to run.
|
||||
|
||||
I didn’t try to run this program on 1,000,000 elements, because I knew it would take 100x longer again – probably about 3 hours. I don’t have time for that!
|
||||
|
||||
You can probably see now why quadratic time algorithms can be a problem – even this very simple program starts getting very slow pretty quickly.
|
||||
|
||||
### let’s write a fast version: `linear.py`
|
||||
|
||||
Okay, so let’s write a fast version of the program. First I’ll show you the program, then I’ll explain it.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
# the actual algorithm
|
||||
def intersection(list1, list2):
|
||||
set1 = set(list1) # this is a hash set
|
||||
result = []
|
||||
for y in list2:
|
||||
if y in set1:
|
||||
result.append(y)
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
# some boilerplate so that we can run it from the command line on lists of
|
||||
# different sizes
|
||||
def run(n):
|
||||
# make 2 lists of n+1 elements
|
||||
list1 = range(3, n) + [2]
|
||||
list2 = range(n+1, 2*n) + [2]
|
||||
# print out the intersection
|
||||
print(intersection(list1, list2))
|
||||
|
||||
run(int(sys.argv[1]))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(this isn’t the most idiomatic Python, but I wanted to write it without using too many python-isms so that people who don’t know Python could understand it more easily)
|
||||
|
||||
We’ve done 2 things differently here than our slow program:
|
||||
|
||||
1. convert `list1` into a set called `set1`
|
||||
2. only use one for loop instead of two for loops
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### let’s see how fast this `linear.py` program is
|
||||
|
||||
Before we talk about _why_ this program is fast, let’s first prove that it’s fast by running it on some big lists. Here it is running on lists of size 10 to 10,000,000. (remember that our original program started getting SUPER slow when run on 100,000 elements)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ time python3 linear.py 100
|
||||
[2]
|
||||
|
||||
real 0m0.056s
|
||||
$ time python3 linear.py 1000
|
||||
[2]
|
||||
|
||||
real 0m0.036s
|
||||
$ time python3 linear.py 10000 # 10,000
|
||||
[2]
|
||||
|
||||
real 0m0.028s
|
||||
$ time python3 linear.py 100000 # 100,000
|
||||
[2]
|
||||
|
||||
real 0m0.048s <-- quadratic.py took 2 minutes in this case! we're doing it in 0.04 seconds now!!! so fast!
|
||||
$ time python3 linear.py 1000000 # 1,000,000
|
||||
[2]
|
||||
|
||||
real 0m0.178s
|
||||
$ time python3 linear.py 10000000 # 10,000,000
|
||||
[2]
|
||||
|
||||
real 0m1.560s
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### running `linear.py` on an extremely big list
|
||||
|
||||
If we try to run it on a very very big list (10 billion / 10,000,000,000 elements), then actually we run into a different problem: it’s _fast_ enough (that list is only 100x bigger than the list that took 4.2 seconds, so we could probably do it in 420 seconds), but my computer doesn’t have enough memory to store all of the elements of the list and so the program crashes before it gets there.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ time python3 linear.py 10000000000
|
||||
Traceback (most recent call last):
|
||||
File "/home/bork/work/homepage/linear.py", line 18, in <module>
|
||||
run(int(sys.argv[1]))
|
||||
File "/home/bork/work/homepage/linear.py", line 13, in run
|
||||
list1 = [1] * n + [2]
|
||||
MemoryError
|
||||
|
||||
real 0m0.090s
|
||||
user 0m0.034s
|
||||
sys 0m0.018s
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We’re not talking about memory usage in this blog post though, so let’s ignore that.
|
||||
|
||||
### okay, why is `linear.py` fast?
|
||||
|
||||
Now I’ll try to explain why `linear.py` is fast.
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s the code again:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
def intersection(list1, list2):
|
||||
set1 = set(list1) # this is a hash set
|
||||
result = []
|
||||
for y in list2:
|
||||
if y in set1:
|
||||
result.append(y)
|
||||
return result
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s say that `list1` and `list2` are both lists of about 10,000,000 different elements. That’s kind of a lot of elements!
|
||||
|
||||
So why is this able to run so fast? HASHMAPS!!!
|
||||
|
||||
### hashmap lookups are instant (“constant time”)
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s look at this if statement from our fast program:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
if y in set1:
|
||||
result.append(y)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You might think that this check – `if y in set1` – would be slower if the `set1` contains 10 million elements than it is if `set1` contains 1000 elements. But it’s not! It always takes basically the same amount of time (SUPER FAST), no matter how big `set1` gets.
|
||||
|
||||
This is because `set1` is a hash set, which is a type of hashmap/hashtable which only has keys and no values.
|
||||
|
||||
I’m not going to explain _why_ hashmap lookups are instant in this post, but the amazing Vaidehi Joshi’s [basecs][1] series has explanations of [hash tables][2] and [hash functions][3] which talk about it.
|
||||
|
||||
### accidentally quadratic: real life quadratic algorithms!
|
||||
|
||||
This issue that we saw where quadratic time algorithms are really slow is actually a problem that shows up in real life – Nelson Elhage has a great blog called [accidentally quadratic][4] with stories about performance problems caused by code that accidentally ran in quadratic time.
|
||||
|
||||
### quadratic time algorithms can kind of sneak up on you
|
||||
|
||||
The weird thing about quadratic time algorithms is that when you run them on a small number of elements (like 1000), it doesn’t seem so bad! It’s not that slow! But then if you throw 1,000,000 elements at it, it can really take hours to run.
|
||||
|
||||
So I think it’s worth being broadly aware of them, so you can avoid writing them by accident. Especially if there’s an easy way to write a linear-time algorithm instead (like using a hashmap).
|
||||
|
||||
### hashmaps always feel a little magical to me
|
||||
|
||||
Hashmaps aren’t magic of course (you can learn the math behind why hashmap lookups are instant! it’s cool!), but it always _feels_ a little magical to me, and every time I use hashmaps in a program to speed things up it makes me happy :)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://jvns.ca/blog/2021/09/10/hashmaps-make-things-fast/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Julia Evans][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[unigeorge](https://github.com/unigeorge)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://jvns.ca/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://medium.com/basecs
|
||||
[2]: https://medium.com/basecs/taking-hash-tables-off-the-shelf-139cbf4752f0
|
||||
[3]: https://medium.com/basecs/hashing-out-hash-functions-ea5dd8beb4dd
|
||||
[4]: https://accidentallyquadratic.tumblr.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,157 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "How to Set JAVA_HOME Variable in Ubuntu Linux Correctly"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://itsfoss.com/set-java-home-ubuntu/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Abhishek Prakash https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
How to Set JAVA_HOME Variable in Ubuntu Linux Correctly
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
If you are [running Java programs on Ubuntu][1] using Eclipse, [Maven][2] or Netbeans etc, you’ll need to set JAVA_HOME to your path. Otherwise, your system will complain that “java_home environment variable is not set”.
|
||||
|
||||
In this beginner’s tutorial, I’ll show the steps to correctly set Java Home variable on Ubuntu. The steps should be valid for most other Linux distributions as well.
|
||||
|
||||
The process consists of these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
* Making sure Java Development Kit (JDK) is installed.
|
||||
* Finding the correct location of JDK executable.
|
||||
* Setting the JAVA_HOME variable and making the change permanent.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Check if JDK is installed
|
||||
|
||||
The simplest way to check if Java Development Kit (JDK) is installed on your Linux system is by running this command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
javac --version
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The above command checks the version of Java compiler. If it is installed, it will show the Java version.
|
||||
|
||||
![Java Compiler is installed][3]
|
||||
|
||||
If the command shows an error like javac command not found, you’ll have to install JDK.
|
||||
|
||||
![Java Compiler is not installed][4]
|
||||
|
||||
If Java Compiler is not installed on your system, install Java Development Kit using this command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt install default-jdk
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will install the default Java version in your current Ubuntu version. If you need some other specific Java version, you’ll have to specify it while [installing Java on Ubuntu][5].
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have made sure that Java Compiler is present on your system, it’s time to find its location.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Get the location of JDK executable (Java Compiler)
|
||||
|
||||
The executable is usually located in the /usr/lib/jvm directory. I won’t left you on your own for a guessing game. Instead, let’s find out the path of the Java executable.
|
||||
|
||||
[Use the which command][6] to get the location of Java Compiler executable:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
which javac
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The problem here is that the location it gives is actually a [symbolic link][7]. You’ll have to follow it a couple of times:
|
||||
|
||||
![][8]
|
||||
|
||||
An easier method is to follow the symbolic link and get to the actual executable file directly using this command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
readlink -f `which java`
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The readlink command follows a symbolic link. I have used ` around _which java_. This is called command substitution and it replaces the command with its output. So basically, the above command is equivalent to _readlink -f /usr/bin/java_ in this case.
|
||||
|
||||
In my example, the location of the executable file is **/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/java**. It could be different for you. Copy the correct path you got from the above command in your system. You know, you can [copy paste in the Ubuntu terminal][9].
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Setting JAVA_HOME variable
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you have got the location, use it to set the JAVA_HOME environment variable:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/java
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Check the value of JAVA_HOME directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
echo $JAVA_HOME
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
![][10]
|
||||
|
||||
Try to run your program or project in the SAME TERMINAL and see if it works.
|
||||
|
||||
This is not over yet. The JAVA_HOME variable you just declared is temporary. If you close the terminal or start a new session, it will be empty again.
|
||||
|
||||
To set JAVA_HOME variable ‘permanently’, you should add it to the bashrc file in your home directory.
|
||||
|
||||
You can [use the Nano editor for editing files in the Linux terminal][11]. If you do not want that and take a simple copy-paste approach, use the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
Back up your bashrc file (in case you mess it, you can get it back):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cp ~/.bashrc ~/.bashrc.bak
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, [use the echo command to append][12] the export command you used at the beginning of this section. _**Change the command below to use the correct path as displayed by your system in**_.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
echo "export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/java" >> ~/.bashrc
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Verify that it has been correctly added to the end of the file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
tail -3 ~/.bashrc
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The above [tail command][13] will show the last 3 lines of the specified file.
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s the entire output of the above three commands.
|
||||
|
||||
![][14]
|
||||
|
||||
Now, even if you exit the session or restart the system, the JAVA_HOME variable will still be set to the value you specified. That’s what you want, right?
|
||||
|
||||
Do note that if you change the default Java version in the future, you’ll have to change the value of JAVA_HOME and point it to the correct executable path.
|
||||
|
||||
I hope this tutorial not only helped you to set Java Home, it also taught you how you are doing it.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are still facing issues or have any questions or suggestions, please let me know in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://itsfoss.com/set-java-home-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://itsfoss.com/run-java-program-ubuntu/
|
||||
[2]: https://maven.apache.org/
|
||||
[3]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/check-java-compiler-ubuntu.png?resize=750%2C310&ssl=1
|
||||
[4]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/java-compiler-check-ubuntu.png?resize=732%2C300&ssl=1
|
||||
[5]: https://itsfoss.com/install-java-ubuntu/
|
||||
[6]: https://linuxhandbook.com/which-command/
|
||||
[7]: https://linuxhandbook.com/symbolic-link-linux/
|
||||
[8]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/get-java-home-path-ubuntu.png?resize=800%2C283&ssl=1
|
||||
[9]: https://itsfoss.com/copy-paste-linux-terminal/
|
||||
[10]: https://i1.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/setting-java-home-ubuntu.png?resize=800%2C268&ssl=1
|
||||
[11]: https://itsfoss.com/nano-editor-guide/
|
||||
[12]: https://linuxhandbook.com/echo-command/
|
||||
[13]: https://linuxhandbook.com/tail-command/
|
||||
[14]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/set-java-home-bashrc-ubuntu.png?resize=786%2C348&ssl=1
|
||||
206
sources/tech/20210911 Play with model trains in OpenTTD.md
Normal file
206
sources/tech/20210911 Play with model trains in OpenTTD.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,206 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "Play with model trains in OpenTTD"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://opensource.com/article/21/9/model-trains-openttd"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Seth Kenlon https://opensource.com/users/seth"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: " "
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
Play with model trains in OpenTTD
|
||||
======
|
||||
Don't have room for a physical model train set? Try virtual trains with
|
||||
OpenTTD.
|
||||
![Old train][1]
|
||||
|
||||
My father has always been fond of model trains, and I remember watching him building a track around the Christmas tree when I was young. When [Lego][2] train sets were released, he and I transitioned to them for their convenience and inherent extensibility. We built and operated Lego trains and monorail tracks over the course of many years. I've often imagined a possible future in which I have a garage or a basement dedicated to miniature landscapes and electric whistling trains. Then again, the probability of me diving that severely into yet another hobby is pretty low, so I was very happy to discover that _virtual_ model railways can provide me with much of the same satisfaction. The engine for my virtualized hobby is [OpenTTD][3], an open source simulation game based on an old '90s game called **Transport Tycoon Deluxe**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing OpenTTD
|
||||
|
||||
You can download OpenTTD for Linux, macOS, and Windows from [openttd.org/downloads][4].
|
||||
|
||||
If you're running Debian Linux or one of its derivatives, or even [running it on a Chromebook][5], you can download the `.deb` package. Install it with `apt`:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
`$ sudo apt install ./openttd*deb`
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you're using any other Linux distribution, download the generic installer and extract the package with [the `tar command`][6]:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
`$ tar xvf openttd-x.yy.z-linux*.tar.xz`
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
OpenTTD is also available on [Steam][7] for Linux, macOS, and Windows (Steam isn't open source, but it's a common cross-platform gaming client).
|
||||
|
||||
### Launch OpenTTD
|
||||
|
||||
If you installed OpenTTD, you can launch it from your application menu.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're downloaded the generic package, change into the directory and launch the game using the local `openttd` command:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cd openttd*
|
||||
$ ./openttd &
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The first time you launch OpenTTD, it alerts you that you must download a graphic set. This is automatically installed in the Steam edition, but it's a single-click in the stand-alone app. And anyway, because OpenTTD is open source, it's well modded, so you'll end up downloading a lot more than just the default graphics.
|
||||
|
||||
After the graphics have been downloaded, you're presented with the quaintly diminutive interface. I find a 640x480 interface a little small, and while the old graphics do hearken back to simpler computing days, a slight upgrade for modern screens is helpful. For that reason, your first stop is the **Check online content** button.
|
||||
|
||||
### Loading mods
|
||||
|
||||
The **Content downloading** screen provides you with a window to approved OpenTTD mods, giving improved graphics, new music, train models, and map names appropriate to your location or interests. I use the New Zealand set, so all of my generated cities sound familiar, although, since 2020, I've started using the Fallout 3 set. There are _a lot_ of mods, so use the search bar in the top right to narrow your choices.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the mods I consider essential:
|
||||
|
||||
* **abase** \- High res graphics. At nearly 300 MB, this is the largest download you're likely to need (the game itself is barely 50 MB).
|
||||
* **OpenSFX** \- A sound set so you can hear the traffic in cities, the horns of the boating industry, and the very satisfying whistles of trains.
|
||||
* **Town names** \- The default names of cities are fun, but I find it easier to remember names that feel local.
|
||||
* **Trains** \- OpenTTD has a default set of train models that work perfectly well, but if you're a trainspotter already, then you might enjoy downloading some additional train sets. I use the NZR set, but there are many trains available, including trains from the UK, the USA, Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, and on and on down the alphabet.
|
||||
* **Beginner tutorial** \- A scenario to help you learn the game and its interface.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Game engine defaults
|
||||
|
||||
Once you download your new assets, you must set them as your defaults. There are two places for this: Game engine defaults and in-game scripts and assets.
|
||||
|
||||
![OpenTTD main menu][8]
|
||||
|
||||
The OpenTTD menu (Seth Kenlon, [CC BY-SA 4.0][9])
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Game Options** button. In the **Game Options** screen, adjust these settings:
|
||||
|
||||
* Set the **screen resolution** to your preferred interface size.
|
||||
* Set **base graphics set** to **abase.**
|
||||
* Set **base sounds set** to **OpenSFX.**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Close the **Game Options** screen. Your changes are saved automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
### Game options
|
||||
|
||||
From the main menu screen, click the **NewGRF Settings** button.
|
||||
|
||||
![NewGRF settings window][10]
|
||||
|
||||
The NewGRF settings menu (Seth Kenlon, [CC BY-SA 4.0][9])
|
||||
|
||||
Inactive mods are listed at the bottom of the **NewGRF Settings** window. To activate one, select it and click the **Add** button in the bottom left. Once you've chosen the mods to activate, click the **Apply** button.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tutorial
|
||||
|
||||
If you downloaded the **Beginner tutorial** scenario, you could learn OpenTTD by playing through it. To start the tutorial, click the **Play scenario** button near the top of the main menu screen. Select the tutorial and begin.
|
||||
|
||||
The tutorial gives you a full tour of the game's interface, and it takes some time to get through it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
By way of a quicker introduction, here's what you need to know: vehicles come from depots, and everything needs a schedule. By remembering those two rules, you can start building trains (and roads and seaports and airports) right away.
|
||||
|
||||
#### **Build stations**
|
||||
|
||||
To build a simple rail line between two cities, click the railway track icon in the top icon bar.
|
||||
|
||||
![New icon bar - railway option][11]
|
||||
|
||||
The new icon bar - railway option (Seth Kenlon, [CC BY-SA 4.0][9])
|
||||
|
||||
Railways start and end with stations, so I usually place a station at each end of my intended line. Click the train station icon (mouse over it to see its label). For a train station to serve a region, its area of effect must overlap with as much of the region as possible. To see a station's coverage, enable **Coverage area highlight** by clicking the **On** button at the bottom of the station dialog box.
|
||||
|
||||
![Station coverage window][12]
|
||||
|
||||
Station coverage information window (Seth Kenlon, [CC BY-SA 4.0][9])
|
||||
|
||||
The dark grid overlay represents coverage, while the white grid overlay shows the physical footprint of the station. As you hover over an area, the supplies that a station's coverage enables are listed in the station popup window. Start simple and create a single-track, 4-car platform. Do this twice between two cities on the map.
|
||||
|
||||
![create station menu][13]
|
||||
|
||||
The create station menu (Seth Kenlon, [CC BY-SA 4.0][9])
|
||||
|
||||
### Lay the rails
|
||||
|
||||
Next, connect the stations with rails. The isometric view of OpenTTD takes some getting used to, but after clicking on the rail icons and clicking and dragging on the map, you start to get a feel for it. The X-rail icon provides an "autorail" mode, which aligns the track based on where in a square you click.
|
||||
|
||||
Be careful as you lay your rails. OpenTTD is rather unforgiving, so once you click in a square, rails are constructed. You must use the dynamite icon to remove rails. Just like in real life, there's no undo button.
|
||||
|
||||
### Train depot
|
||||
|
||||
Trains come from a depot. So to add a train to your railway, you must add a depot somewhere along the line. Click the depot icon and place a depot near an existing rail. Connect the depot to an existing track to ensure your trains can get from the depot to the appropriate (in this simple example, the only) line.
|
||||
|
||||
![create depot menu][14]
|
||||
|
||||
The create depot menu (Seth Kenlon, [CC BY-SA 4.0][9])
|
||||
|
||||
### Model trains
|
||||
|
||||
At long last, you get to add a virtual model train to your virtual railway. To create a train, click on your depot.
|
||||
|
||||
Click the **New Vehicle** button at the bottom of the depot window to list available train engines and cars. The list you get depends partly on what models you've added from the downloadable content. Generally, there are three types of engines: Steam, diesel, and electric. Early in the game, which starts in the year 1950, you have only steam. As the years progress, you get innovative new models you can use as upgrades.
|
||||
|
||||
![create train menu][15]
|
||||
|
||||
The create train menu (Seth Kenlon, [CC BY-SA 4.0][9])
|
||||
|
||||
For now, create a simple train that includes an engine, a passenger car, and a mail car. If you want to add other kinds of cars, click on your stations to confirm the types of supplies they're able to accept (as determined by its area of coverage).
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a train schedule
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you have a railway and a train, you must create a train schedule. Schedules are attached to vehicles, so any time you add a new vehicle of any kind, you must add a schedule for it to be useful.
|
||||
|
||||
To add a schedule to your train, click the number to the left of the train in its depot listing. This opens a viewport for the train, with buttons along the right side of the window. Click the arrow icon to see that train's schedule.
|
||||
|
||||
![create schedule menu][16]
|
||||
|
||||
The create schedule menu (Seth Kenlon, [CC BY-SA 4.0][9])
|
||||
|
||||
To create a schedule, click the **Go To** button at the bottom of the schedule window, and then click on the station you want to set as the first destination. Then click the next station. You can adjust loading and unloading requirements by selecting a stop in the schedule and browsing the options in the **Full load** and **Unload** drop-down menus, and you can adjust routes (should you develop new routes) in the **Non-stop** drop-down menu. The options are plentiful, and as cities grow and your map becomes more developed, you may have to adjust your strategy.
|
||||
|
||||
But for now, click the red **Stopped** button at the bottom of your train viewport to put your train into service!
|
||||
|
||||
![train moving from station to station][17]
|
||||
|
||||
Train in service (Seth Kenlon, [CC BY-SA 4.0][9])
|
||||
|
||||
### Try OpenTTD
|
||||
|
||||
OpenTTD is a simulator, but it's also a game, so you do have constraints, including a budget and parameters you might want to optimize. For instance, you can click on a city, farm, or factory to discover what kind of imports and exports are acceptable to it. You can borrow money by clicking the budget button in the bottom right corner of the OpenTTD window. And it's not just a virtual train set. You can build roads, airports, seaports, and more. Just remember that all vehicles need depots and schedules, and you're halfway to a successful virtual enterprise.
|
||||
|
||||
OpenTTD has an active and enthusiastic community, [an extensive wiki][18], and there are lots of resources and tutorials available online. Download the game and give it a try!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/21/9/model-trains-openttd
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Seth Kenlon][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/seth
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/train-plane-speed-big-machine.png?itok=f377dXKs (Old train)
|
||||
[2]: https://opensource.com/article/20/6/open-source-virtual-lego
|
||||
[3]: http://openttd.org
|
||||
[4]: https://www.openttd.org/downloads/openttd-releases/latest.html
|
||||
[5]: https://opensource.com/article/21/2/chromebook-linux
|
||||
[6]: https://opensource.com/article/17/7/how-unzip-targz-file
|
||||
[7]: https://store.steampowered.com/app/1536610/OpenTTD/
|
||||
[8]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/openttd-menu.jpg (OpenTTD menu)
|
||||
[9]: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/
|
||||
[10]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/openttd-newgrf.jpg (The NewGRF settings menu)
|
||||
[11]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/openttd-iconbar-railway.jpg (The new icon bar - railway option)
|
||||
[12]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/openttd-window-station.jpg (Station coverage information window)
|
||||
[13]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/openttd-create-station.jpg (The create station menu)
|
||||
[14]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/openttd-create-depot.jpg (Create depot menu)
|
||||
[15]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/openttd-create-train.jpg (The create train menu)
|
||||
[16]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/openttd-create-schedule.png (The create schedule menu)
|
||||
[17]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/openttd-train.jpg (Train in service)
|
||||
[18]: https://wiki.openttd.org/en/
|
||||
@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "What are container runtimes?"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://opensource.com/article/21/9/container-runtimes"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Nived V https://opensource.com/users/nivedv"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: "geekpi"
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
什么是容器运行时?
|
||||
======
|
||||
深入了解容器运行时,你就可以理解容器环境是如何建立的。
|
||||
![Ships at sea on the web][1]
|
||||
|
||||
在对[容器镜像][2]的检查中,我讨论了容器的基本原理,但现在是时候深入研究容器运行时了,这样你就可以了解容器环境是如何构建的。本文的部分信息摘自 Open Container Initiative (OCI)(容器的开放标准)的[官方文档][3],所以无论你的容器引擎如何,这些信息都是相关的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 容器运行机制
|
||||
|
||||
那么,当你运行 `podman run` 或 `docker run` 命令时,在后台到底发生了什么?这里为你提供一个逐步的概述:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 如果本地没有镜像,则从镜像注册处拉取镜像
|
||||
2. 镜像被提取到一个写时拷贝的文件系统上,所有的容器层相互叠加以创建一个合并的文件系统
|
||||
3. 准备一个容器挂载点
|
||||
4. 从容器镜像中设置元数据,包括诸如覆盖 CMD、来自用户输入的 ENTRYPOINT、设置 SECCOMP 规则等设置,以确保容器按预期运行
|
||||
5. 提醒内核为该容器分配某种隔离,如进程、网络和文件系统(命名空间)
|
||||
6. 内核还被提醒为这个容器分配一些资源限制,如 CPU 或内存限制(cgroups)
|
||||
7. 一个系统调用(syscall)被传递给内核以启动容器
|
||||
8. 设置 SELinux/AppArmor
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
容器运行时负责上述所有的工作。当我们想到容器运行时,想到的可能是 runc、lxc、containerd、rkt、cri-o 等等。嗯,你没有错。这些都是容器引擎和容器运行时,每一种都是为不同的情况建立的。
|
||||
|
||||
_容器运行时_更侧重于运行容器,为容器设置命名空间和 cgroups,也被称为底层容器运行时。高层的容器运行时或容器引擎专注于格式、解包、管理和镜像共享。它们还为开发者提供 API。
|
||||
|
||||
### Open Container Initiative (OCI)
|
||||
|
||||
Open Container Initiative(OCI)是一个 Linux 基金会项目。其目的是设计某些开放标准或围绕如何与容器运行时和容器镜像格式工作的结构。它是由 Docker、rkt、CoreOS 和其他行业领导者于 2015 年 6 月建立的。
|
||||
|
||||
它使用两个规范来做这件事:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1\. 镜像规范(image-spec)
|
||||
|
||||
该规范的目标是创建可互操作的工具,用于构建、传输和准备运行的容器镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
该规范的高层组件包括:
|
||||
|
||||
* [Image Manifest][4] — 一个描述构成容器镜像的元素的文件
|
||||
* [Image Index][5] — 镜像清单的注释索引
|
||||
* [Image Layout][6] — 一个代表镜像内容的文件系统布局
|
||||
* [Filesystem Layer][7] — 一个描述容器文件系统的变化集
|
||||
* [Image Configuration][8] — 确定镜像层排序和配置的文件,适合转换成[运行时包][9]。
|
||||
* [Conversion][10] — 解释应该如何进行转换的文件
|
||||
* [Descriptor][11] — 一个描述被引用内容的类型、元数据和内容地址的参考资料
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2\. 运行时规范(runtime-spec)
|
||||
|
||||
该规范旨在定义容器的配置、执行环境和生命周期。config.json 文件为所有支持的平台提供了容器配置,并详细说明了能够创建容器的地方。执行环境与为容器的生命周期定义的通用操作一起被详细说明,以确保在容器内运行的应用在不同的运行时之间有一个一致的环境。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 容器规范使用了各种内核功能,包括命名空间、cgroups、capabilities、LSM 和文件系统监牢来实现该规范。
|
||||
|
||||
### 现在你知道了
|
||||
|
||||
容器运行时是由 OCI 规范管理的,以提供一致性和互操作性。许多人在使用容器时不需要了解它们是如何工作的,但当你需要排除故障或优化使用方法时,了解容器是一个宝贵的优势。
|
||||
|
||||
* * *
|
||||
|
||||
_本文基于 [techbeatly][12] 的文章,并经授权改编。_
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/21/9/container-runtimes
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Nived V][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/nivedv
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/image-full-size/public/lead-images/kubernetes_containers_ship_lead.png?itok=9EUnSwci (Ships at sea on the web)
|
||||
[2]: https://opensource.com/article/21/8/container-fundamentals-2
|
||||
[3]: https://github.com/opencontainers
|
||||
[4]: https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/master/manifest.md
|
||||
[5]: https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/master/image-index.md
|
||||
[6]: https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/master/image-layout.md
|
||||
[7]: https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/master/layer.md
|
||||
[8]: https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/master/config.md
|
||||
[9]: https://github.com/opencontainers/runtime-spec
|
||||
[10]: https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/master/conversion.md
|
||||
[11]: https://github.com/opencontainers/image-spec/blob/master/descriptor.md
|
||||
[12]: https://medium.com/techbeatly/container-runtimes-deep-dive-77eb0e511939
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
|
||||
[#]: subject: "Getting the Top Indicator Panel Back in GNOME"
|
||||
[#]: via: "https://itsfoss.com/enable-applet-indicator-gnome/"
|
||||
[#]: author: "Abhishek Prakash https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/"
|
||||
[#]: collector: "lujun9972"
|
||||
[#]: translator: "imgradeone"
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: " "
|
||||
[#]: publisher: " "
|
||||
[#]: url: " "
|
||||
|
||||
恢复 GNOME 顶栏的托盘图标
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME 是一款流行的 Linux 桌面环境,致力于为 Linux 用户提供现代化的桌面体验。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然这款桌面绝大部分功能都是可用的,但 GNOME 团队的某些决定确实也让许多用户恼火、质疑。
|
||||
|
||||
前脚不能在桌面摆放图标和文件,后脚将右键菜单中的 [新建文档选项移除][1],现在,除此之外,GNOME 同样也移除了托盘图标栏功能。
|
||||
|
||||
怎么说,你总得知道托盘图标栏是什么吧?这些小图标允许你使用相应应用程序的额外功能。我自己的 Ubuntu 系统里就有许多托盘图标。
|
||||
|
||||
![托盘图标栏][2]
|
||||
|
||||
这一砍就砍出了大问题,尤其是针对那些完全依赖托盘图标的软件的致命打击。就拿 [Dropbox][3] 举例子吧,你只能通过 Dropbox 的托盘图标菜单来访问 Dropbox 的设置页面,很不幸,你在 GNOME 中就完全找不到这个图标。
|
||||
|
||||
这确实是个大问题,好在,我们还是有解决办法的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 借助插件来重新启用 GNOME 的托盘图标栏
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在用 GNOME,想必你已经知道 GNOME 插件是什么了。这些小插件基本上是由热心的独立开发者开发的。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你没有准备好,那么就去 [启用 GNOME 插件][4] 吧。这一步其实非常简单,使用 Chrome 或 Firefox 打开任意一个插件的页面,然后页面会提示你安装浏览器扩展。安装这个扩展,然后就可以启程了。
|
||||
|
||||
![启用 GNOME 插件的浏览器扩展][5]
|
||||
|
||||
现在,这里有一些可以向顶栏增加托盘图标的 GNOME 插件。在撰写本篇教程的时候,[AppIndicator and KStatusNotifierItem Support][6] 这款插件在 GNOME 的较新版本中已经有良好的开发优化与支持。、
|
||||
|
||||
前往插件的页面:
|
||||
|
||||
[AppIndicator 插件][6]
|
||||
|
||||
在这个页面中,你应该能看到一个开关按钮。点击这个按钮即可安装该插件。
|
||||
|
||||
![][7]
|
||||
|
||||
接下来会有一个弹窗,弹出后请点击“安装”。
|
||||
|
||||
![安装插件][8]
|
||||
|
||||
也许安装插件后,插件不会立即生效。此时,你必须重启 GNOME。在 Xorg 会话中,你只需要按下 Alt + F2 并输入 `r` 即可重启 GNOME,但这个操作不支持 Wayland 会话。
|
||||
|
||||
注销当前会话,并且重新登录,此后托盘图标应该就能成功启用了。如果你安装了任何一款带托盘图标的软件,那么你应该可以在顶栏上看见这些图标的身影了。
|
||||
|
||||
于我而言,我已经安装了 Dropbox,因此托盘图标就直接出现在顶栏上了。
|
||||
|
||||
![Dropbox 托盘图标在 GNOME 下可用的截图][9]
|
||||
|
||||
希望这个小提示能帮助你恢复 GNOME 顶栏中的托盘图标。
|
||||
|
||||
我完全不理解,为什么 GNOME 的开发者会认为把这种实用性极强的功能删除会是个好主意。不过,上帝关上了一扇门,却(通常)会再打开一扇窗。好好享受按你的偏好运作的 GNOME 吧。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://itsfoss.com/enable-applet-indicator-gnome/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[imgradeone](https://github.com/imgradeone)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://itsfoss.com/add-new-document-option/
|
||||
[2]: https://itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/indicator-applet-linux.webp
|
||||
[3]: https://www.dropbox.com
|
||||
[4]: https://itsfoss.com/gnome-shell-extensions/
|
||||
[5]: https://itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/installing-gnome-extension-add-on-800x355.webp
|
||||
[6]: https://extensions.gnome.org/extension/615/appindicator-support/
|
||||
[7]: https://itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/appindicator-extension-800x329.webp
|
||||
[8]: https://i2.wp.com/itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/installing-appindicator-extension.png?resize=800%2C269&ssl=1
|
||||
[9]: https://itsfoss.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/gnome-dropbox-indicator-800x561.webp
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user