mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
commit
f86f8e8397
@ -1,212 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating---geekpi
|
||||
|
||||
3 Ways to Permanently and Securely Delete ‘Files and Directories’ in Linux
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
In most cases the means we use to [delete a file from our computers][1] such as using `Delete` key, Trash files or `rm` command, which do not permanently and securely remove the file from the hard disk (or any storage media).
|
||||
|
||||
The file is simply hidden from users and it resides somewhere on the hard disk. It can be recovered by data thieves, law enforcement or other threats.
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming a file contains classified or secret content such as usernames and passwords of a security system, an attacker with the necessary knowledge and skills can easily [recover a deleted copy of the file][2] and access these user credentials (and you can probably guess the aftermath of such as scenario).
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, we will explain a number of command line tools for permanently and securely deleting files in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1\. Shred – Overwrite a File to Hide Content
|
||||
|
||||
shred overwrites a file to hide its contents, and can optionally delete it as well.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
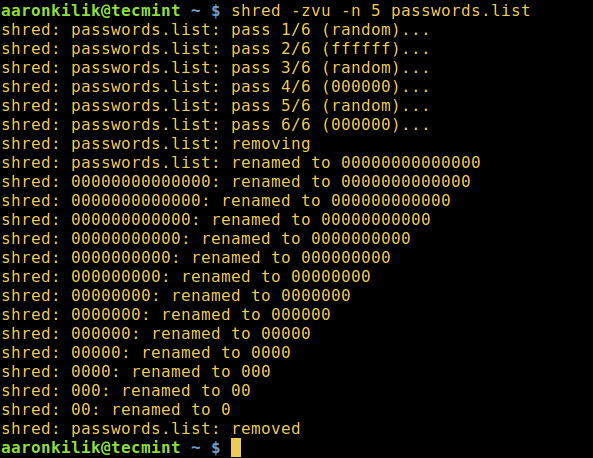
$ shred -zvu -n 5 passwords.list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the command below, the options:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `-z` – adds a final overwrite with zeros to hide shredding
|
||||
2. `-v` – enables display of operation progress
|
||||
3. `-u` – truncates and removes file after overwriting
|
||||
4. `-n` – specifies number of times to overwrite file content (the default is 3)
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][3]
|
||||
|
||||
shred – overwrite a file to hide its contents
|
||||
|
||||
You can find more usage options and information in the shred man page:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man shred
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 2\. Wipe – Securely Erase Files in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
A Linux wipe command securely erases files from magnetic memory and thereby making it impossible to [recover deleted files or directory content][4].
|
||||
|
||||
First, you need to install wipe tool in order to it, run the appropriate command below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install wipe [On Debian and its derivatives]
|
||||
$ sudo yum install wipe [On RedHat based systems]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The following command will destroy everything under the directory private.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
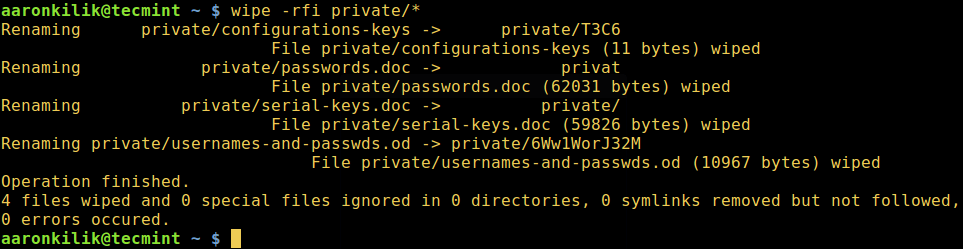
$ wipe -rfi private/*
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
where the flags used:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `-r` – tells wipe to recurse into subdirectories
|
||||
2. `-f` – enables forced deletion and disable confirmation query
|
||||
3. `-i` – shows progress of deletion process
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][5]
|
||||
|
||||
Wipe – Securely Erase Files in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Wipe only works reliably on magnetic memory, therefore use the other methods for solid state disks (memory).
|
||||
|
||||
Read through the wipe man page for additional usage options and instructions:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man wipe
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3\. Secure-deletetion Toolkit for Linux
|
||||
|
||||
Secure-delete is a collection of secure file deletion tools, that contains srm (secure_deletion) tool, which is used to remove files securely.
|
||||
|
||||
First you need to install it using the relevant command below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install secure-delete [On Debian and its derivatives]
|
||||
$ sudo yum install secure-delete [On RedHat based systems]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once installed, you can use srm tool to remove files or directories securely on a Linux system as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
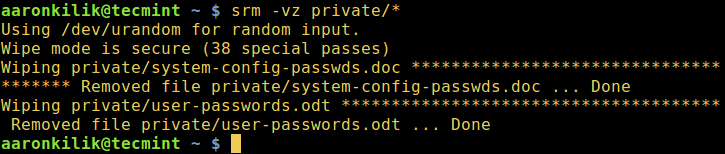
$ srm -vz private/*
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
where the options used:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `-v` – enables verbose mode
|
||||
2. `-z` – wipes the last write with zeros instead of random data
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][6]
|
||||
|
||||
srm – Securely Delete Files in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
Read through the srm man page for more usage options and information:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man srm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 4\. sfill -Secure Free Disk/Inode Space Wiper
|
||||
|
||||
sfill is a part of secure-deletetion toolkit, is a secure free disk and inode space wiper, it deletes files on free disk space in a secure method. sfill [checks the the free space on the specified partition][7] and fills it with random data from /dev/urandom.
|
||||
|
||||
The command below will execute sfill on my root partition, with the `-v` switch enabling verbose mode:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sfill -v /home/aaronkilik/tmp/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming you created a separate partition, `/home` to store normal system users home directories, you can specify a directory on that partition to apply sfill on it:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sfill -v /home/username
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The are a few limitations of sfill that you can read about in the man page, where you can also find additional usage flags and instructions:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man sfill
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note: These following two tools (sswap and sdmem) in the secure-deletetion toolkit are not directly relevant for the scope of this guide, however, we will explain them for knowledge purpose and future use.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5\. sswap – Secure Swap Wiper
|
||||
|
||||
It is a secure partition wiper, sswap deletes data present on your swap partition in a secure manner.
|
||||
|
||||
Caution: remember to unmount your swap partition before using sswap! Otherwise your system might crash!
|
||||
|
||||
Simply determine you swap partition (and check if paging and swapping devices/files are turned on using swapon command), next, disable paging and swapping devices/files with swapoff command (renders swap partition unusable).
|
||||
|
||||
Then run sswap command on the swap partition:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cat /proc/swaps
|
||||
$ swapon
|
||||
$ sudo swapoff /dev/sda6
|
||||
$ sudo sswap /dev/sda6 #this command may take some time to complete with 38 default passes
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
sswap – Secure Swap Wiper
|
||||
|
||||
Make an effort to read through the sswap man page for more usage options and information:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man sswap
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 6\. sdmem – Secure Memory Wiper
|
||||
|
||||
sdmem is a secure memory wiper, it is designed to remove data present in your memory (RAM) in a secure manner.
|
||||
|
||||
It was originally named [smem][9], but because on Debain systems there exists another package called [smem – report memory consumption on per-process and per-user basis][10], the developer decided to rename it sdmem.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sdmem -f -v
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more usage information, read through the sdmem man page:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man sdmem
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Suggested Read:** [PhotoRec – Recover Deleted or Lost Files in Linux][11]
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it! In this article, we reviewed a number command line tools for permanently as well as securely deleting files in Linux. As usual, offer your thoughts or suggestions about the post via the comment form below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
I am Ravi Saive, creator of TecMint. A Computer Geek and Linux Guru who loves to share tricks and tips on Internet. Most Of My Servers runs on Open Source Platform called Linux. Follow Me: Twitter, Facebook and Google+
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/permanently-and-securely-delete-files-directories-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ravi Saive][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/admin/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/delete-all-files-in-directory-except-one-few-file-extensions/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/photorec-recover-deleted-lost-files-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/shred-command-example.png
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/recover-deleted-file-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Wipe-Securely-Erase-Files.png
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/srm-securely-delete-Files-in-Linux.png
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-top-large-directories-and-files-sizes-in-linux/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/sswap-Secure-Swap-Wiper.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/smem-linux-memory-usage-per-process-per-user/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/smem-linux-memory-usage-per-process-per-user/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/photorec-recover-deleted-lost-files-in-linux/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,210 @@
|
||||
3 个在 Linux 中永久并安全删除`文件和目录`的方法
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
在大多数情况下,我们习惯于[从我们的计算机中删除文件][1],例如使用 `Delete` 键、垃圾箱或 `rm` 命令,这不是永久安全地从硬盘中(或任何存储介质)删除文件的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
该文件只是对用户隐藏,它驻留在硬盘上的某个地方。它可以通过数据窃贼、执法或其他威胁来恢复。
|
||||
|
||||
假设文件包含密级或机密内容,例如安全系统的用户名和密码,具有必要知识和技能的攻击者可以轻松地[恢复删除文件的副本][2]并访问这些用户凭证(你可以猜测到这种情况的后果)。
|
||||
|
||||
在本文中,我们将解释一些命令行工具,用于永久并安全地删除 Linux 中的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1\. shred – 覆盖文件来隐藏内容
|
||||
|
||||
shred 会覆盖文件来隐藏它的内容,并且也可以选择删除它。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ shred -zvu -n 5 passwords.list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在下面的命令中,选项有:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `-z` - 用零覆盖以隐藏碎片
|
||||
2. `-v` - 显示操作进度
|
||||
3. `-u` - 在覆盖后截断并删除文件
|
||||
4. `-n` - 指定覆盖文件内容的次数(默认值为3)
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][3]
|
||||
|
||||
shred - 覆盖文件来隐藏它的内容
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在 shred 的帮助页中找到更多的用法选项和信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man shred
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 2\. wipe – 在 Linux 中安全删除文件
|
||||
|
||||
Linux wipe 命令可以安全地擦除磁盘中的文件,从而不可能[恢复删除的文件或目录内容] 4]。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,你需要安装 wipe 工具,运行以下适当的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install wipe [On Debian and its derivatives]
|
||||
$ sudo yum install wipe [On RedHat based systems]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令会摧毁 private 目录下的所有文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ wipe -rfi private/*
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
当使用下面的标志时:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `-r` - 告诉 wipe 递归擦除子目录
|
||||
2. `-f` - 启用强制删除并禁用确认查询
|
||||
3. `-i` - 显示擦除进度
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][5]
|
||||
|
||||
wipe – 在 Linux 中安全擦除文件
|
||||
|
||||
注意:wipe 仅在磁性存储上可以可靠地工作,因此对固态磁盘(内存)请使用其他方法。
|
||||
|
||||
阅读 wipe 手册以获取其他使用选项和说明:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man wipe
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3\. Linux 中的安全删除工具集
|
||||
|
||||
secure-delete 是一个安全文件删除工具的集合,它包含srm(secure_deletion)工具,用于安全删除文件。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,你需要使用以下相关命令安装它:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install secure-delete [On Debian and its derivatives]
|
||||
$ sudo yum install secure-delete [On RedHat based systems]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后,你可以使用 srm 工具在 Linux 中安全地删除文件和目录。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ srm -vz private/*
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下面是使用的选项:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `-v` – 启用 verbose 模式
|
||||
2. `-z` – 用0而不是随机数据来擦除最后的写入
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][6]
|
||||
|
||||
srm – 在 Linux 中安全删除文件
|
||||
|
||||
阅读 srm 手册来获取更多的使用选项和信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man srm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 4\. sfill -安全免费的磁盘/inode 空间擦除器
|
||||
|
||||
sfill 是 secure-deletetion 工具包的一部分,是一个安全免费的磁盘和 inode 空间擦除器,它以安全的方法删除可用磁盘空间中的文件。 sfill 会[检查指定分区上的可用空间][7],并使用来自 /dev/urandom 的随机数据填充它。
|
||||
|
||||
以下命令将在我的根分区上执行 sfill,使用 `-v' 选项启用 verbose 模式:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sfill -v /home/aaronkilik/tmp/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
假设你创建了一个单独的分区 `/home` 来存储正常的系统用户主目录,你可以在该分区上指定一个目录,以便在其上应用 sfill:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sfill -v /home/username
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在 sfill 的手册上看到一些限制,你也可以看到额外的使用标志和命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man sfill
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意:secure-deletetion 工具包中的两个工具(sswap 和 sdmem)与本指南的范围不直接相关,但是,我们会在将来为了传播知识的目的来解释它们。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5\. sswap – 安全 swap 擦除器
|
||||
|
||||
它是一个安全的分区擦除器,sswap以安全的方式删除 swap 分区上存在的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
警告:请记住在使用 sswap 之前卸载 swap 分区! 否则你的系统可能会崩溃!
|
||||
|
||||
只需确定交换分区(并检查分页和交换设备/文件是否使用 swapon 命令打开),接下来,使用 swapoff 命令禁用分页和交换设备/文件(使 swap 分区不可用)。
|
||||
|
||||
然后在 swap 分区上运行 sswap 命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cat /proc/swaps
|
||||
$ swapon
|
||||
$ sudo swapoff /dev/sda6
|
||||
$ sudo sswap /dev/sda6 #this command may take some time to complete with 38 default passes
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
sswap – 安全 swap 擦除器
|
||||
|
||||
阅读 sswap 的手册来获取更多的选项和信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man sswap
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 6\. sdmem – 安全内存擦除器
|
||||
|
||||
sdmem 是一个安全的内存擦除器,它被设计为以安全的方式删除存储器(RAM)中的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
它最初命名为[smem][9],但是因为在 Debain 系统上存在另一个包[smem - 报告每个进程和每个用户的内存消耗][10],开发人员决定将它重命名为 sdmem。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sdmem -f -v
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
关于更多的使用信息,阅读 sdmen 的手册:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man sdmem
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**推荐阅读:** [PhotoRec – 在 Linux 中恢复删除或遗失的文件][11]
|
||||
|
||||
就是这样了!在本文中,我们审查了一系列可以永久安全地删除 Linux 中的文件的工具。像往常一样,通过下面的评论栏发表你对本篇文章的想法或建议。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
我是 Ravi Saive,TecMint 的创建者。 一个计算机 Geek 和 Linux 大师,喜欢在互联网上分享技巧和贴士。我的服务器大多数运行在称为 Linux 的开源平台上。关注我:Twitter、Facebook 和 Google+
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/permanently-and-securely-delete-files-directories-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ravi Saive][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/admin/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/delete-all-files-in-directory-except-one-few-file-extensions/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/photorec-recover-deleted-lost-files-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/shred-command-example.png
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/recover-deleted-file-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Wipe-Securely-Erase-Files.png
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/srm-securely-delete-Files-in-Linux.png
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-top-large-directories-and-files-sizes-in-linux/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/sswap-Secure-Swap-Wiper.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/smem-linux-memory-usage-per-process-per-user/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/smem-linux-memory-usage-per-process-per-user/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/photorec-recover-deleted-lost-files-in-linux/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user