mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
[Translated] 20161201 5 Ways to Empty or Delete a Large File Content in Linux.md
This commit is contained in:
parent
f77d927b7a
commit
f788bffcf2
@ -1,158 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FSSlc translating
|
||||
|
||||
5 Ways to Empty or Delete a Large File Content in Linux
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Occasionally, while dealing with files in Linux terminal, you may want to clear the content of a file without necessarily opening it using any [Linux command line editors][1]. How can this be achieved? In this article, we will go through several different ways of emptying file content with the help of some useful commands.
|
||||
|
||||
Caution: Before we proceed to looking at the various ways, note that because in [Linux everything is a file][2], you must always make sure that the file(s) you are emptying are not important user or system files. Clearing the content of a critical system or configuration file could lead to a fatal application/system error or failure.
|
||||
|
||||
With that said, below are means of clearing file content from the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
Important: For the purpose of this article, we’ve used file `access.log` in the following examples.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1\. Empty File Content by Redirecting to Null
|
||||
|
||||
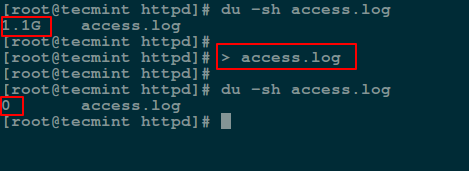
A easiest way to empty or blank a file content using shell redirect `null` (non-existent object) to the file as below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# > access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Empty Large File Using Null Redirect in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
### 2\. Empty File Using ‘true’ Command Redirection
|
||||
|
||||
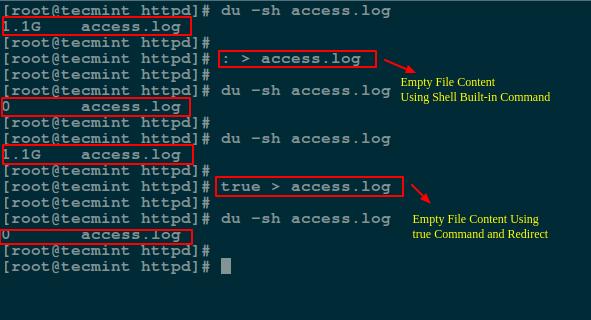
Here we will use a symbol `:` is a shell built-in command that is essence equivalent to the `true`command and it can be used as a no-op (no operation).
|
||||
|
||||
Another method is to redirect the output of `:` or `true` built-in command to the file like so:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# : > access.log
|
||||
OR
|
||||
# true > access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Empty Large File Using Linux Commands
|
||||
|
||||
### 3\. Empty File Using cat/cp/dd utilities with /dev/null
|
||||
|
||||
In Linux, the `null` device is basically utilized for discarding of unwanted output streams of a process, or else as a suitable empty file for input streams. This is normally done by redirection mechanism.
|
||||
|
||||
And the `/dev/null` device file is therefore a special file that writes-off (removes) any input sent to it or its output is same as that of an empty file.
|
||||
|
||||
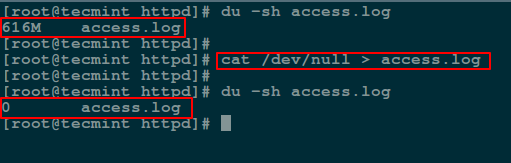
Additionally, you can empty contents of a file by redirecting output of `/dev/null` to it (file) as input using [cat command][5]:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# cat /dev/null > access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Empty File Using cat Command
|
||||
|
||||
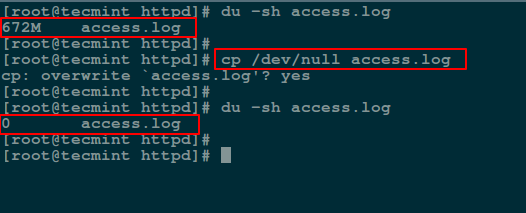
Next, we will use [cp command][7] to blank a file content as shown.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# cp /dev/null access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
Empty File Content Using cp Command
|
||||
|
||||
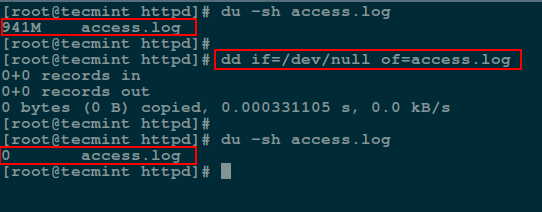
In the following command, `if` means the input file and `of` refers to the output file.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=/dev/null of=access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][9]
|
||||
|
||||
Empty File Content Using dd Command
|
||||
|
||||
### 4\. Empty File Using echo Command
|
||||
|
||||
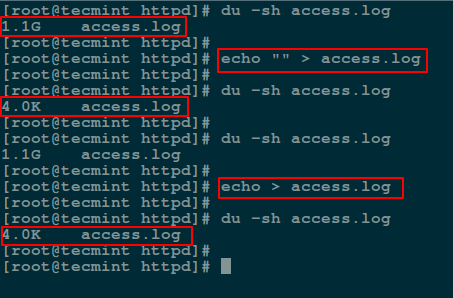
Here, you can use an [echo command][10] with an empty string and redirect it to the file as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# echo "" > access.log
|
||||
OR
|
||||
# echo > access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][11]
|
||||
|
||||
Empty File Using echo Command
|
||||
|
||||
Note: You should keep in mind that an empty string is not the same as null. A string is already an object much as it may be empty while null simply means non-existence of an object.
|
||||
|
||||
For this reason, when you redirect the out of the [echo command][12] above into the file, and view the file contents using the [cat command][13], is prints an empty line (empty string).
|
||||
|
||||
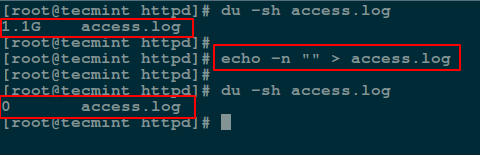
To send a null output to the file, use the flag `-n` which tells echo to not output the trailing newline that leads to the empty line produced in the previous command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# echo -n "" > access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][14]
|
||||
|
||||
Empty File Using Null Redirect
|
||||
|
||||
### 5\. Empty File Using truncate Command
|
||||
|
||||
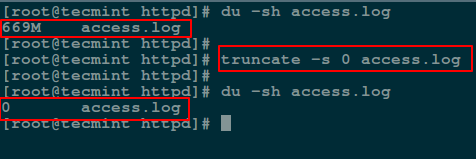
The truncate command helps to [shrink or extend the size of a file][15] to a defined size.
|
||||
|
||||
You can employ it with the `-s` option that specifies the file size. To empty a file content, use a size of 0 (zero) as in the next command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# truncate -s 0 access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][16]
|
||||
|
||||
Truncate File Content in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it for now, in this article we have covered multiple methods of clearing or emptying file content using simple command line utilities and shell redirection mechanism.
|
||||
|
||||
These are not probably the only available practical ways of doing this, so you can also tell us about any other methods not mentioned in this guide via the feedback section below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/empty-delete-file-content-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-command-line-editors/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/explanation-of-everything-is-a-file-and-types-of-files-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-Large-File-in-Linux.png
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-Large-File-Using-Linux-Commands.png
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-File-Using-cat-Command.png
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/progress-monitor-check-progress-of-linux-commands/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-File-Content-Using-cp-Command.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-File-Content-Using-dd-Command.png
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-File-Using-echo-Command.png
|
||||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-File-Using-Null-Redirect.png
|
||||
[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/parted-command-to-create-resize-rescue-linux-disk-partitions/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Truncate-File-Content-in-Linux.png
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
|
||||
Linux 下清空或删除文件内容的 5 种方法
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 终端下处理文件时,有时我们想清空文件的内容但又不想使用任何 [Linux 命令行编辑器][1] 去打开这些文件。那怎样才能达到这个目的呢?在这篇文章中,我们将一一介绍几种借助一些实用的命令来清空文件内容的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:在我们进一步深入了解这些方法之前,请记住: 由于[在 Linux 中一切皆文件][2],你需要时刻注意确保你将要清空的文件不是重要的用户或者系统配置文件。清空重要的系统文件或者配置文件可能会引发严重的应用启动失败错误或者系统错误。
|
||||
|
||||
前面已经说道,下面的这些方法都是从命令行中达到清空文件的目的。
|
||||
|
||||
提示:在下面的示例中,我们将使用名为 `access.log` 的文件来作为示例样本。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1\. 通过重定向到 Null 来清空文件内容
|
||||
|
||||
清空或者让一个文件成为空白的最简单方式是像下面那样通过 shell 重定向 `null` (不存在的事物)到该文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# > access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][3]
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 下使用 Null 和重定向来清空大文件
|
||||
|
||||
### 2\. 使用 ‘true’ 命令重定向来清空文件
|
||||
|
||||
下面我们将使用 `:` 符号,它是 shell 的一个内置命令,等同于 `true` 命令,它可被用来作为一个 no-op(即不进行任何操作)。
|
||||
|
||||
另一种清空文件的方法是将 `:` 或者 `true` 内置命令的输出重定向到文件中,具体如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# : > access.log
|
||||
或
|
||||
# true > access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][4]
|
||||
|
||||
使用 Linux 命令清空大文件
|
||||
|
||||
### 3\. 使用 cat/cp/dd 实用工具及 /dev/null 设备来清空文件
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 中, `null` 设备基本上被用来丢弃某个进程不再需要的输出流,或者作为某个输入流的空白文件,这些通常可以利用重定向机制来达到。
|
||||
|
||||
所以 `/dev/null` 设备文件是一个特殊的文件,它将清空送到它这里来的所有输入,而它的输出则可被视为一个空文件。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,你可以通过使用 [cat 命令][5] 显示 `/dev/null` 的内容然后重定向输出到某个文件,以此来达到清空该文件的目的。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# cat /dev/null > access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][6]
|
||||
|
||||
使用 cat 命令来清空文件
|
||||
|
||||
下面,我们将使用 [cp 命令][7] 复制 `/dev/null` 的内容到某个文件来达到清空该文件的目的,具体如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# cp /dev/null access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
使用 cp 命令来清空文件
|
||||
|
||||
而下面的命令中, `if` 代表输入文件,`of` 代表输出文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=/dev/null of=access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][9]
|
||||
|
||||
使用 dd 命令来清空文件内容
|
||||
|
||||
### 4\. 使用 echo 命令清空文件
|
||||
|
||||
在这里,你可以使用 [echo 命令][10] 将空字符串的内容重定向到文件中,具体如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# echo "" > access.log
|
||||
或者
|
||||
# echo > access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][11]
|
||||
|
||||
使用 echo 命令来清空文件
|
||||
|
||||
注意:你应该记住空字符串并不等同于 null 。字符串表明它是一个具体的事物,只不过它的内容可能是空的,但 null 则意味着某个事物并不存在。
|
||||
|
||||
基于这个原因,当你通过重定向将 [echo 命令][12] 的输出输入到文件后,使用 [cat 命令][13] 来查看该文件的内容时,你将看到一个空白行(即一个空字符串)。
|
||||
|
||||
要将 null 输入到文件中,你应该使用 `-n` 选项,这个选项将告诉 echo 不再像上面的那个命令那样输出结尾的那个新行。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# echo -n "" > access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][14]
|
||||
|
||||
使用 Null 重定向来清空文件
|
||||
|
||||
### 5\. 使用 truncate 命令来清空文件内容
|
||||
|
||||
`truncate` 可被用来[将一个文件缩小或者扩展到某个给定的大小][15]。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以利用它和 `-s` 参数来特别指定文件的大小。要清空文件的内容,则在下面的命令中将文件的大小设定为 0:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# truncate -s 0 access.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][16]
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 中截断文件内容
|
||||
|
||||
我要介绍的就是这么多了。在本文中,我们介绍了几种通过使用一些简单的命令行工具和 shell 重定向机制来清除或清空文件内容的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
上面介绍的这些可能并不是达到清空文件内容这个目的的所有可行的实践方法,所以你也可以通过下面的评论栏告诉我们本文中尚未提及的其他方法。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/empty-delete-file-content-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-command-line-editors/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/explanation-of-everything-is-a-file-and-types-of-files-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-Large-File-in-Linux.png
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-Large-File-Using-Linux-Commands.png
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-File-Using-cat-Command.png
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/progress-monitor-check-progress-of-linux-commands/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-File-Content-Using-cp-Command.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-File-Content-Using-dd-Command.png
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-File-Using-echo-Command.png
|
||||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Empty-File-Using-Null-Redirect.png
|
||||
[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/parted-command-to-create-resize-rescue-linux-disk-partitions/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Truncate-File-Content-in-Linux.png
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user