diff --git a/published/20180926 How to use the Scikit-learn Python library for data science projects.md b/published/20180926 How to use the Scikit-learn Python library for data science projects.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b7ebe9a6bd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20180926 How to use the Scikit-learn Python library for data science projects.md
@@ -0,0 +1,239 @@
+如何将 Scikit-learn Python 库用于数据科学项目
+======
+
+> 灵活多样的 Python 库为数据分析和数据挖掘提供了强力的机器学习工具。
+
+
+
+Scikit-learn Python 库最初于 2007 年发布,通常用于解决各种方面的机器学习和数据科学问题。这个多种功能的库提供了整洁、一致、高效的 API 和全面的在线文档。
+
+### 什么是 Scikit-learn?
+
+[Scikit-learn][1] 是一个开源 Python 库,拥有强大的数据分析和数据挖掘工具。 在 BSD 许可下可用,并建立在以下机器学习库上:
+
+- `NumPy`,一个用于操作多维数组和矩阵的库。它还具有广泛的数学函数汇集,可用于执行各种计算。
+- `SciPy`,一个由各种库组成的生态系统,用于完成技术计算任务。
+- `Matplotlib`,一个用于绘制各种图表和图形的库。
+
+Scikit-learn 提供了广泛的内置算法,可以充分用于数据科学项目。
+
+以下是使用 Scikit-learn 库的主要方法。
+
+#### 1、分类
+
+[分类][2]工具识别与提供的数据相关联的类别。例如,它们可用于将电子邮件分类为垃圾邮件或非垃圾邮件。
+
+Scikit-learn 中的分类算法包括:
+
+- 支持向量机(SVM)
+- 最邻近
+- 随机森林
+
+#### 2、回归
+
+回归涉及到创建一个模型去试图理解输入和输出数据之间的关系。例如,回归工具可用于理解股票价格的行为。
+
+回归算法包括:
+
+- 支持向量机(SVM)
+- 岭回归
+- Lasso(LCTT 译注:Lasso 即 least absolute shrinkage and selection operator,又译为最小绝对值收敛和选择算子、套索算法)
+
+#### 3、聚类
+
+Scikit-learn 聚类工具用于自动将具有相同特征的数据分组。 例如,可以根据客户数据的地点对客户数据进行细分。
+
+聚类算法包括:
+
+- K-means
+- 谱聚类
+- Mean-shift
+
+#### 4、降维
+
+降维降低了用于分析的随机变量的数量。例如,为了提高可视化效率,可能不会考虑外围数据。
+
+降维算法包括:
+
+- 主成分分析(PCA)
+- 功能选择
+- 非负矩阵分解
+
+#### 5、模型选择
+
+模型选择算法提供了用于比较、验证和选择要在数据科学项目中使用的最佳参数和模型的工具。
+
+通过参数调整能够增强精度的模型选择模块包括:
+
+- 网格搜索
+- 交叉验证
+- 指标
+
+#### 6、预处理
+
+Scikit-learn 预处理工具在数据分析期间的特征提取和规范化中非常重要。 例如,您可以使用这些工具转换输入数据(如文本)并在分析中应用其特征。
+
+预处理模块包括:
+
+- 预处理
+- 特征提取
+
+### Scikit-learn 库示例
+
+让我们用一个简单的例子来说明如何在数据科学项目中使用 Scikit-learn 库。
+
+我们将使用[鸢尾花花卉数据集][3],该数据集包含在 Scikit-learn 库中。 鸢尾花数据集包含有关三种花种的 150 个细节,三种花种分别为:
+
+- Setosa:标记为 0
+- Versicolor:标记为 1
+- Virginica:标记为 2
+
+数据集包括每种花种的以下特征(以厘米为单位):
+
+- 萼片长度
+- 萼片宽度
+- 花瓣长度
+- 花瓣宽度
+
+#### 第 1 步:导入库
+
+由于鸢尾花花卉数据集包含在 Scikit-learn 数据科学库中,我们可以将其加载到我们的工作区中,如下所示:
+
+```
+from sklearn import datasets
+iris = datasets.load_iris()
+```
+
+这些命令从 `sklearn` 导入数据集 `datasets` 模块,然后使用 `datasets` 中的 `load_iris()` 方法将数据包含在工作空间中。
+
+#### 第 2 步:获取数据集特征
+
+数据集 `datasets` 模块包含几种方法,使您更容易熟悉处理数据。
+
+在 Scikit-learn 中,数据集指的是类似字典的对象,其中包含有关数据的所有详细信息。 使用 `.data` 键存储数据,该数据列是一个数组列表。
+
+例如,我们可以利用 `iris.data` 输出有关鸢尾花花卉数据集的信息。
+
+```
+print(iris.data)
+```
+
+这是输出(结果已被截断):
+
+```
+[[5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2]
+ [4.9 3. 1.4 0.2]
+ [4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2]
+ [4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2]
+ [5. 3.6 1.4 0.2]
+ [5.4 3.9 1.7 0.4]
+ [4.6 3.4 1.4 0.3]
+ [5. 3.4 1.5 0.2]
+ [4.4 2.9 1.4 0.2]
+ [4.9 3.1 1.5 0.1]
+ [5.4 3.7 1.5 0.2]
+ [4.8 3.4 1.6 0.2]
+ [4.8 3. 1.4 0.1]
+ [4.3 3. 1.1 0.1]
+ [5.8 4. 1.2 0.2]
+ [5.7 4.4 1.5 0.4]
+ [5.4 3.9 1.3 0.4]
+ [5.1 3.5 1.4 0.3]
+```
+
+我们还使用 `iris.target` 向我们提供有关花朵不同标签的信息。
+
+```
+print(iris.target)
+```
+
+这是输出:
+
+```
+[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
+ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
+ 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
+ 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
+ 2 2]
+```
+
+如果我们使用 `iris.target_names`,我们将输出数据集中找到的标签名称的数组。
+
+```
+print(iris.target_names)
+```
+
+以下是运行 Python 代码后的结果:
+
+```
+['setosa' 'versicolor' 'virginica']
+```
+
+#### 第 3 步:可视化数据集
+
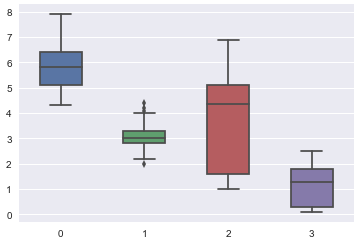
+我们可以使用[箱形图][4]来生成鸢尾花数据集的视觉描绘。 箱形图说明了数据如何通过四分位数在平面上分布的。
+
+以下是如何实现这一目标:
+
+```
+import seaborn as sns
+box_data = iris.data # 表示数据数组的变量
+box_target = iris.target # 表示标签数组的变量
+sns.boxplot(data = box_data,width=0.5,fliersize=5)
+sns.set(rc={'figure.figsize':(2,15)})
+```
+
+让我们看看结果:
+
+
+
+在横轴上:
+
+ * 0 是萼片长度
+ * 1 是萼片宽度
+ * 2 是花瓣长度
+ * 3 是花瓣宽度
+
+垂直轴的尺寸以厘米为单位。
+
+### 总结
+
+以下是这个简单的 Scikit-learn 数据科学教程的完整代码。
+
+```
+from sklearn import datasets
+iris = datasets.load_iris()
+print(iris.data)
+print(iris.target)
+print(iris.target_names)
+import seaborn as sns
+box_data = iris.data # 表示数据数组的变量
+box_target = iris.target # 表示标签数组的变量
+sns.boxplot(data = box_data,width=0.5,fliersize=5)
+sns.set(rc={'figure.figsize':(2,15)})
+```
+
+Scikit-learn 是一个多功能的 Python 库,可用于高效完成数据科学项目。
+
+如果您想了解更多信息,请查看 [LiveEdu][5] 上的教程,例如 Andrey Bulezyuk 关于使用 Scikit-learn 库创建[机器学习应用程序][6]的视频。
+
+有什么评价或者疑问吗? 欢迎在下面分享。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/18/9/how-use-scikit-learn-data-science-projects
+
+作者:[Dr.Michael J.Garbade][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[Flowsnow](https://github.com/Flowsnow)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/drmjg
+[1]: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html
+[2]: https://blog.liveedu.tv/regression-versus-classification-machine-learning-whats-the-difference/
+[3]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iris_flower_data_set
+[4]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Box_plot
+[5]: https://www.liveedu.tv/guides/data-science/
+[6]: https://www.liveedu.tv/andreybu/REaxr-machine-learning-model-python-sklearn-kera/oPGdP-machine-learning-model-python-sklearn-kera/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180926 How to use the Scikit-learn Python library for data science projects.md b/translated/tech/20180926 How to use the Scikit-learn Python library for data science projects.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6f94cb8327..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20180926 How to use the Scikit-learn Python library for data science projects.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,238 +0,0 @@
-如何将Scikit-learn Python库用于数据科学项目
-======
-
-
-
-Scikit-learn Python库最初于2007年发布,从头到尾都通常用于解决机器学习和数据科学问题。 多功能库提供整洁,一致,高效的API和全面的在线文档。
-
-### 什么是Scikit-learn?
-
-[Scikit-learn][1]是一个开源Python库,拥有强大的数据分析和数据挖掘工具。 在BSD许可下可用,并建立在以下机器学习库上:
-
-- **NumPy**,一个用于操作多维数组和矩阵的库。 它还具有广泛的数学函数汇集,可用于执行各种计算。
-- **SciPy**,一个由各种库组成的生态系统,用于完成技术计算任务。
-- **Matplotlib**,一个用于绘制各种图表和图形的库。
-
-Scikit-learn提供了广泛的内置算法,可以充分用于数据科学项目。
-
-以下是使用Scikit-learn库的主要方法。
-
-#### 1. 分类
-
-[分类][2]工具识别与提供的数据相关联的类别。 例如,它们可用于将电子邮件分类为垃圾邮件或非垃圾邮件。
-
-Scikit-learn中的分类算法包括:
-
-- 支持向量机(SVM)
-- 最邻近
-- 随机森林
-
-#### 2. 回归
-
-回归涉及到创建一个模型去试图理解输入和输出数据之间的关系。 例如,回归工具可用于了解股票价格的行为。
-
-回归算法包括:
-
-- SVM
-- 岭回归Ridge regression
-- Lasso(LCTT译者注:Lasso 即 least absolute shrinkage and selection operator,又译最小绝对值收敛和选择算子、套索算法)
-
-#### 3. 聚类
-
-Scikit-learn聚类工具用于自动将具有相同特征的数据分组。 例如,可以根据客户数据的地点对客户数据进行细分。
-
-聚类算法包括:
-
-- K-means
-- 谱聚类Spectral clustering
-- Mean-shift
-
-#### 4. 降维
-
-降维降低了用于分析的随机变量的数量。 例如,为了提高可视化效率,可能不会考虑外围数据。
-
-降维算法包括:
-
-- 主成分分析Principal component analysis(PCA)
-- 功能选择Feature selection
-- 非负矩阵分解Non-negative matrix factorization
-
-#### 5. 模型选择
-
-模型选择算法提供了用于比较,验证和选择要在数据科学项目中使用的最佳参数和模型的工具。
-
-通过参数调整能够增强精度的模型选择模块包括:
-
-- 网格搜索Grid search
-- 交叉验证Cross-validation
-- 指标Metrics
-
-#### 6. 预处理
-
-Scikit-learn预处理工具在数据分析期间的特征提取和规范化中非常重要。 例如,您可以使用这些工具转换输入数据(如文本)并在分析中应用其特征。
-
-预处理模块包括:
-
-- 预处理
-- 特征提取
-
-### Scikit-learn库示例
-
-让我们用一个简单的例子来说明如何在数据科学项目中使用Scikit-learn库。
-
-我们将使用[鸢尾花花卉数据集][3],该数据集包含在Scikit-learn库中。 鸢尾花数据集包含有关三种花种的150个细节,三种花种分别为:
-
-- Setosa-标记为0
-- Versicolor-标记为1
-- Virginica-标记为2
-
-数据集包括每种花种的以下特征(以厘米为单位):
-
-- 萼片长度
-- 萼片宽度
-- 花瓣长度
-- 花瓣宽度
-
-#### 第1步:导入库
-
-由于Iris数据集包含在Scikit-learn数据科学库中,我们可以将其加载到我们的工作区中,如下所示:
-
-```
-from sklearn import datasets
-iris = datasets.load_iris()
-```
-
-这些命令从**sklearn**导入数据集**datasets**模块,然后使用**datasets**中的**load_iris()**方法将数据包含在工作空间中。
-
-#### 第2步:获取数据集特征
-
-数据集**datasets**模块包含几种方法,使您更容易熟悉处理数据。
-
-在Scikit-learn中,数据集指的是类似字典的对象,其中包含有关数据的所有详细信息。 使用**.data**键存储数据,该数据列是一个数组列表。
-
-例如,我们可以利用**iris.data**输出有关Iris花卉数据集的信息。
-
-```
-print(iris.data)
-```
-
-这是输出(结果已被截断):
-
-```
-[[5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2]
- [4.9 3. 1.4 0.2]
- [4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2]
- [4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2]
- [5. 3.6 1.4 0.2]
- [5.4 3.9 1.7 0.4]
- [4.6 3.4 1.4 0.3]
- [5. 3.4 1.5 0.2]
- [4.4 2.9 1.4 0.2]
- [4.9 3.1 1.5 0.1]
- [5.4 3.7 1.5 0.2]
- [4.8 3.4 1.6 0.2]
- [4.8 3. 1.4 0.1]
- [4.3 3. 1.1 0.1]
- [5.8 4. 1.2 0.2]
- [5.7 4.4 1.5 0.4]
- [5.4 3.9 1.3 0.4]
- [5.1 3.5 1.4 0.3]
-```
-
-我们还使用**iris.target**向我们提供有关花朵不同标签的信息。
-
-```
-print(iris.target)
-```
-
-这是输出:
-
-```
-[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
- 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
- 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
- 2 2]
-
-```
-
-如果我们使用**iris.target_names**,我们将输出数据集中找到的标签名称的数组。
-
-```
-print(iris.target_names)
-```
-
-以下是运行Python代码后的结果:
-
-```
-['setosa' 'versicolor' 'virginica']
-```
-
-#### 第3步:可视化数据集
-
-我们可以使用[箱形图][4]来生成鸢尾花数据集的视觉描绘。 箱形图说明了数据如何通过四分位数在平面上分布的。
-
-以下是如何实现这一目标:
-
-```
-import seaborn as sns
-box_data = iris.data # 表示数据数组的变量
-box_target = iris.target # 表示标签数组的变量
-sns.boxplot(data = box_data,width=0.5,fliersize=5)
-sns.set(rc={'figure.figsize':(2,15)})
-```
-
-让我们看看结果:
-
-
-
-在横轴上:
-
- * 0是萼片长度
- * 1是萼片宽度
- * 2是花瓣长度
- * 3是花瓣宽度
-
-垂直轴的尺寸以厘米为单位。
-
-### 总结
-
-以下是这个简单的Scikit-learn数据科学教程的完整代码。
-
-```
-from sklearn import datasets
-iris = datasets.load_iris()
-print(iris.data)
-print(iris.target)
-print(iris.target_names)
-import seaborn as sns
-box_data = iris.data # 表示数据数组的变量
-box_target = iris.target # 表示标签数组的变量
-sns.boxplot(data = box_data,width=0.5,fliersize=5)
-sns.set(rc={'figure.figsize':(2,15)})
-```
-
-Scikit-learn是一个多功能的Python库,可用于高效完成数据科学项目。
-
-如果您想了解更多信息,请查看[LiveEdu][5]上的教程,例如Andrey Bulezyuk关于使用Scikit-learn库创建[机器学习应用程序][6]的视频。
-
-有什么评价或者疑问吗? 欢迎在下面分享。
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/18/9/how-use-scikit-learn-data-science-projects
-
-作者:[Dr.Michael J.Garbade][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[Flowsnow](https://github.com/Flowsnow)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]: https://opensource.com/users/drmjg
-[1]: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html
-[2]: https://blog.liveedu.tv/regression-versus-classification-machine-learning-whats-the-difference/
-[3]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iris_flower_data_set
-[4]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Box_plot
-[5]: https://www.liveedu.tv/guides/data-science/
-[6]: https://www.liveedu.tv/andreybu/REaxr-machine-learning-model-python-sklearn-kera/oPGdP-machine-learning-model-python-sklearn-kera/
\ No newline at end of file