mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-06 01:20:12 +08:00
commit
f5cfd218a9
@ -1,73 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translation by strugglingyouth
|
||||
Install Qmmp 0.9.0 Winamp-like Audio Player in Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
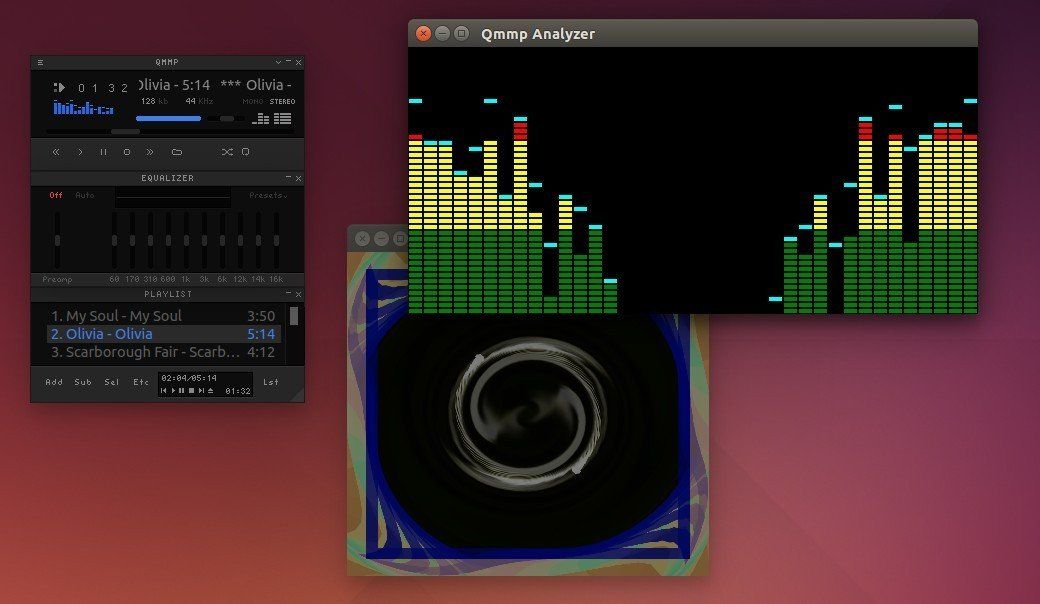
Qmmp, Qt-based audio player with winamp or xmms like user interface, now is at 0.9.0 release. PPA updated for Ubuntu 15.10, Ubuntu 15.04, Ubuntu 14.04, Ubuntu 12.04 and derivatives.
|
||||
|
||||
Qmmp 0.9.0 is a big release with many new features, improvements and some translation updates. It added:
|
||||
|
||||
- audio-channel sequence converter;
|
||||
- 9 channels support to equalizer;
|
||||
- album artist tag support;
|
||||
- asynchronous sorting;
|
||||
- sorting by file modification date;
|
||||
- sorting by album artist;
|
||||
- multiple column support;
|
||||
- feature to hide track length;
|
||||
- feature to disable plugins without qmmp.pri modification (qmake only)
|
||||
- feature to remember playlist scroll position;
|
||||
- feature to exclude cue data files;
|
||||
- feature to change user agent;
|
||||
- feature to change window title;
|
||||
- feature to reset fonts;
|
||||
- feature to restore default shortcuts;
|
||||
- default hotkey for the “Rename List” action;
|
||||
- feature to disable fadeout in the gme plugin;
|
||||
- Simple User Interface (QSUI) with the following changes:
|
||||
- added multiple column support;
|
||||
- added sorting by album artist;
|
||||
- added sorting by file modification date;
|
||||
- added feature to hide song length;
|
||||
- added default hotkey for the “Rename List” action;
|
||||
- added “Save List” action to the tab menu;
|
||||
- added feature to reset fonts;
|
||||
- added feature to reset shortcuts;
|
||||
- improved status bar;
|
||||
|
||||
It also improved playlist changes notification, playlist container, sample rate converter, cmake build scripts, title formatter, ape tags support in the mpeg plugin, fileops plugin, reduced cpu usage, changed default skin (to Glare) and playlist separator.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Qmmp 0.9.0 in Ubuntu: ###
|
||||
|
||||
New release has been made into PPA, available for all current Ubuntu releases and derivatives.
|
||||
|
||||
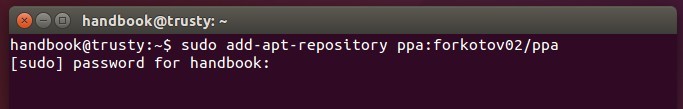
1. To add the [Qmmp PPA][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Open terminal from the Dash, App Launcher, or via Ctrl+Alt+T shortcut keys. When it opens, run command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:forkotov02/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. After adding the PPA, upgrade Qmmp player through Software Updater. Or refresh system cache and install the software via below commands:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install qmmp qmmp-plugin-pack
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it. Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/2015/09/qmmp-0-9-0-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ji m][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/about/
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/~forkotov02/+archive/ubuntu/ppa
|
||||
@ -1,451 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translation by strugglingyouth
|
||||
nstalling NGINX and NGINX Plus With Ansible
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Coming from a production operations background, I have learned to love all things related to automation. Why do something by hand if a computer can do it for you? But creating and implementing automation can be a difficult task given an ever-changing infrastructure and the various technologies surrounding your environments. This is why I love [Ansible][1]. Ansible is an open source tool for IT configuration management, deployment, and orchestration that is extremely easy to use.
|
||||
|
||||
One of my favorite features of Ansible is that it is completely clientless. To manage a system, a connection is made over SSH, using either [Paramiko][2] (a Python library) or native [OpenSSH][3]. Another attractive feature of Ansible is its extensive selection of modules. These modules can be used to perform some of the common tasks of a system administrator. In particular, they make Ansible a powerful tool for installing and configuring any application across multiple servers, environments, and operating systems, all from one central location.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial I will walk you through the steps for using Ansible to install and deploy the open source [NGINX][4] software and [NGINX Plus][5], our commercial product. I’m showing deployment onto a [CentOS][6] server, but I have included details about deploying on Ubuntu servers in [Creating an Ansible Playbook for Installing NGINX and NGINX Plus on Ubuntu][7] below.
|
||||
|
||||
For this tutorial I will be using Ansible version 1.9.2 and performing the deployment from a server running CentOS 7.1.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible --version
|
||||
ansible 1.9.2
|
||||
|
||||
$ cat /etc/redhat-release
|
||||
CentOS Linux release 7.1.1503 (Core)
|
||||
|
||||
If you don’t already have Ansible, you can get instructions for installing it [at the Ansible site][8].
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using CentOS, installing Ansible is easy as typing the following command. If you want to compile from source or for other distributions, see the instructions at the Ansible link provided just above.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install -y epel-release && sudo yum install -y ansible
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on your environment, some of the commands in this tutorial might require sudo privileges. The path to the files, usernames, and destination servers are all values that will be specific to your environment.
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating an Ansible Playbook for Installing NGINX (CentOS) ###
|
||||
|
||||
First we create a working directory for our NGINX deployment, along with subdirectories and deployment configuration files. I usually recommend creating the directory in your home directory and show that in all examples in this tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd $HOME
|
||||
$ mkdir -p ansible-nginx/tasks/
|
||||
$ touch ansible-nginx/deploy.yml
|
||||
$ touch ansible-nginx/tasks/install_nginx.yml
|
||||
|
||||
The directory structure now looks like this. You can check by using the tree command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ tree $HOME/ansible-nginx/
|
||||
/home/kjones/ansible-nginx/
|
||||
├── deploy.yml
|
||||
└── tasks
|
||||
└── install_nginx.yml
|
||||
|
||||
1 directory, 2 files
|
||||
|
||||
If you do not have tree installed, you can do so using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install -y tree
|
||||
|
||||
#### Creating the Main Deployment File ####
|
||||
|
||||
Next we open **deploy.yml** in a text editor. I prefer vim for editing configuration files on the command line, and will use it throughout the tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
$ vim $HOME/ansible-nginx/deploy.yml
|
||||
|
||||
The **deploy.yml** file is our main Ansible deployment file, which we’ll reference when we run the ansible‑playbook command in [Running Ansible to Deploy NGINX][9]. Within this file we specify the inventory for Ansible to use along with any other configuration files to include at runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
In my example I use the [include][10] module to specify a configuration file that has the steps for installing NGINX. While it is possible to create a playbook in one very large file, I recommend that you separate the steps into smaller included files to keep things organized. Sample use cases for an include are copying static content, copying configuration files, or assigning variables for a more advanced deployment with configuration logic.
|
||||
|
||||
Type the following lines into the file. I include the filename at the top in a comment for reference.
|
||||
|
||||
# ./ansible-nginx/deploy.yml
|
||||
|
||||
- hosts: nginx
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- include: 'tasks/install_nginx.yml'
|
||||
|
||||
The hosts statement tells Ansible to deploy to all servers in the **nginx** group, which is defined in **/etc/ansible/hosts**. We’ll edit this file in [Creating the List of NGINX Servers below][11].
|
||||
|
||||
The include statement tells Ansible to read in and execute the contents of the **install_nginx.yml** file from the **tasks** directory during deployment. The file includes the steps for downloading, installing, and starting NGINX. We’ll create this file in the next section.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Creating the Deployment File for NGINX ####
|
||||
|
||||
Now let’s save our work to **deploy.yml** and open up **install_nginx.yml** in the editor.
|
||||
|
||||
$ vim $HOME/ansible-nginx/tasks/install_nginx.yml
|
||||
|
||||
The file is going to contain the instructions – written in [YAML][12] format – for Ansible to follow when installing and configuring our NGINX deployment. Each section (step in the process) starts with a name statement (preceded by hyphen) that describes the step. The string following name: is written to stdout during the Ansible deployment and can be changed as you wish. The next line of a section in the YAML file is the module that will be used during that deployment step. In the configuration below, both the [yum][13] and [service][14] modules are used. The yum module is used to install packages on CentOS. The service module is used to manage UNIX services. The final line or lines in a section specify any parameters for the module (in the example, these lines start with name and state).
|
||||
|
||||
Type the following lines into the file. As with **deploy.yml**, the first line in our file is a comment that names the file for reference. The first section tells Ansible to install the **.rpm** file for CentOS 7 from the NGINX repository. This directs the package manager to install the most recent stable version of NGINX directly from NGINX. Modify the pathname as necessary for your CentOS version. A list of available packages can be found on the [open source NGINX website][15]. The next two sections tell Ansible to install the latest NGINX version using the yum module and then start NGINX using the service module.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** In the first section, the pathname to the CentOS package appears on two lines only for space reasons. Type the entire path on a single line.
|
||||
|
||||
# ./ansible-nginx/tasks/install_nginx.yml
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | Installing NGINX repo rpm
|
||||
yum:
|
||||
name: http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/noarch/RPMS/nginx-release-centos-7-0.el7.ngx.noarch.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | Installing NGINX
|
||||
yum:
|
||||
name: nginx
|
||||
state: latest
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | Starting NGINX
|
||||
service:
|
||||
name: nginx
|
||||
state: started
|
||||
|
||||
#### Creating the List of NGINX Servers ####
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we have our Ansible deployment configuration files all set up, we need to tell Ansible exactly which servers to deploy to. We specify this in the Ansible **hosts** file I mentioned earlier. Let’s make a backup of the existing file and create a new one just for our deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mv /etc/ansible/hosts /etc/ansible/hosts.backup
|
||||
$ sudo vim /etc/ansible/hosts
|
||||
|
||||
Type (or edit) the following lines in the file to create a group called **nginx** and list the servers to install NGINX on. You can designate servers by hostname, IP address, or in an array such as **server[1-3].domain.com**. Here I designate one server by its IP address.
|
||||
|
||||
# /etc/ansible/hosts
|
||||
|
||||
[nginx]
|
||||
172.16.239.140
|
||||
|
||||
#### Setting Up Security ####
|
||||
|
||||
We are almost all set, but before deployment we need to ensure that Ansible has authorization to access our destination server over SSH.
|
||||
|
||||
The preferred and most secure method is to add the Ansible deployment server’s RSA SSH key to the destination server’s **authorized_keys** file, which gives Ansible unrestricted SSH permissions on the destination server. To learn more about this configuration, see [Securing OpenSSH][16] on wiki.centos.org. This way you can automate your deployments without user interaction.
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can request the password interactively during deployment. I strongly recommend that you use this method during testing only, because it is insecure and there is no way to track changes to a destination host’s fingerprint. If you want to do this, change the value of StrictHostKeyChecking from the default yes to no in the **/etc/ssh/ssh_config** file on each of your destination hosts. Then add the --ask-pass flag on the ansible-playbook command to have Ansible prompt for the SSH password.
|
||||
|
||||
Here I illustrate how to edit the **ssh_config** file to disable strict host key checking on the destination server. We manually SSH into the server to which we’ll deploy NGINX and change the value of StrictHostKeyChecking to no.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh kjones@172.16.239.140
|
||||
kjones@172.16.239.140's password:***********
|
||||
|
||||
[kjones@nginx ]$ sudo vim /etc/ssh/ssh_config
|
||||
|
||||
After you make the change, save **ssh_config**, and connect to your Ansible server via SSH. The setting should look as below before you save your work.
|
||||
|
||||
# /etc/ssh/ssh_config
|
||||
|
||||
StrictHostKeyChecking no
|
||||
|
||||
#### Running Ansible to Deploy NGINX ####
|
||||
|
||||
If you have followed the steps in this tutorial, you can run the following command to have Ansible deploy NGINX. (Again, if you have set up RSA SSH key authentication, then the --ask-pass flag is not needed.) Run the command on the Ansible server with the configuration files we created above.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ansible-playbook --ask-pass $HOME/ansible-nginx/deploy.yml
|
||||
|
||||
Ansible prompts for the SSH password and produces output like the following. A recap that reports failed=0 like this one indicates that deployment succeeded.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ansible-playbook --ask-pass $HOME/ansible-nginx/deploy.yml
|
||||
SSH password:
|
||||
|
||||
PLAY [all] ********************************************************************
|
||||
|
||||
GATHERING FACTS ***************************************************************
|
||||
ok: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX | Installing NGINX repo rpm] *************************************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX | Installing NGINX] **********************************************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX | Starting NGINX] ************************************************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************
|
||||
172.16.239.140 : ok=4 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0
|
||||
|
||||
If you didn’t get a successful play recap, you can try running the ansible-playbook command again with the -vvvv flag (verbose with connection debugging) to troubleshoot the deployment process.
|
||||
|
||||
When deployment succeeds (as it did for us on the first try), you can verify that NGINX is running on the remote server by running the following basic [cURL][17] command. Here it returns 200 OK. Success! We have successfully installed NGINX using Ansible.
|
||||
|
||||
$ curl -Is 172.16.239.140 | grep HTTP
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating an Ansible Playbook for Installing NGINX Plus (CentOS) ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now that I’ve shown you how to install the open source version of NGINX, I’ll walk you through the steps for installing NGINX Plus. This requires some additional changes to the deployment configuration and showcases some of Ansible’s other features.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Copying the NGINX Plus Certificate and Key to the Ansible Server ####
|
||||
|
||||
To install and configure NGINX Plus with Ansible, we first need to copy the key and certificate for our NGINX Plus subscription from the [NGINX Plus Customer Portal][18] to the standard location on the Ansible deployment server.
|
||||
|
||||
Access to the NGINX Plus Customer Portal is available for customers who have purchased NGINX Plus or are evaluating it. If you are interested in evaluating NGINX Plus, you can request a 30-day free trial [here][19]. You will receive a link to your trial certificate and key shortly after you sign up.
|
||||
|
||||
On a Mac or Linux host, use the [scp][20] utility as I show here. On a Microsoft Windows host, you can use [WinSCP][21]. For this tutorial, I downloaded the files to my Mac laptop, then used scp to copy them to the Ansible server. These commands place both the key and certificate in my home directory.
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /path/to/nginx-repo-files/
|
||||
$ scp nginx-repo.* user@destination-server:.
|
||||
|
||||
Next we SSH to the Ansible server, make sure the SSL directory for NGINX Plus exists, and move the files there.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh user@destination-server
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir -p /etc/ssl/nginx/
|
||||
$ sudo mv nginx-repo.* /etc/ssl/nginx/
|
||||
|
||||
Verify that your **/etc/ssl/nginx** directory contains both the certificate (**.crt**) and key (**.key**) files. You can check by using the tree command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ tree /etc/ssl/nginx
|
||||
/etc/ssl/nginx
|
||||
├── nginx-repo.crt
|
||||
└── nginx-repo.key
|
||||
|
||||
0 directories, 2 files
|
||||
|
||||
If you do not have tree installed, you can do so using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install -y tree
|
||||
|
||||
#### Creating the Ansible Directory Structure ####
|
||||
|
||||
The remaining steps are very similar to the ones for open source NGINX that we performed in [Creating an Ansible Playbook for Installing NGINX (CentOS)][22]. First we set up a working directory for our NGINX Plus deployment. Again I prefer creating it as a subdirectory of my home directory.
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd $HOME
|
||||
$ mkdir -p ansible-nginx-plus/tasks/
|
||||
$ touch ansible-nginx-plus/deploy.yml
|
||||
$ touch ansible-nginx-plus/tasks/install_nginx_plus.yml
|
||||
|
||||
The directory structure now looks like this.
|
||||
|
||||
$ tree $HOME/ansible-nginx-plus/
|
||||
/home/kjones/ansible-nginx-plus/
|
||||
├── deploy.yml
|
||||
└── tasks
|
||||
└── install_nginx_plus.yml
|
||||
|
||||
1 directory, 2 files
|
||||
|
||||
#### Creating the Main Deployment File ####
|
||||
|
||||
Next we use vim to create the **deploy.yml** file as for open source NGINX.
|
||||
|
||||
$ vim ansible-nginx-plus/deploy.yml
|
||||
|
||||
The only difference from the open source NGINX deployment is that we change the name of the included file to **install_nginx_plus.yml**. As a reminder, the file tells Ansible to deploy NGINX Plus on all servers in the **nginx** group (which is defined in **/etc/ansible/hosts**), and to read in and execute the contents of the **install_nginx_plus.yml** file from the **tasks** directory during deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
# ./ansible-nginx-plus/deploy.yml
|
||||
|
||||
- hosts: nginx
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- include: 'tasks/install_nginx_plus.yml'
|
||||
|
||||
If you have not done so already, you also need to create the hosts file as detailed in [Creating the List of NGINX Servers][23] above.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Creating the Deployment File for NGINX Plus ####
|
||||
|
||||
Open **install_nginx_plus.yml** in a text editor. The file is going to contain the instructions for Ansible to follow when installing and configuring your NGINX Plus deployment. The commands and modules are specific to CentOS and some are unique to NGINX Plus.
|
||||
|
||||
$ vim ansible-nginx-plus/tasks/install_nginx_plus.yml
|
||||
|
||||
The first section uses the [file][24] module, telling Ansible to create the SSL directory for NGINX Plus as specified by the path and state arguments, set the ownership to root, and change the mode to 0700.
|
||||
|
||||
# ./ansible-nginx-plus/tasks/install_nginx_plus.yml
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Creating NGINX Plus ssl cert repo directory
|
||||
file: path=/etc/ssl/nginx state=directory group=root mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
The next two sections use the [copy][25] module to copy the NGINX Plus certificate and key from the Ansible deployment server to the NGINX Plus server during the deployment, again setting ownership to root and the mode to 0700.
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Copying NGINX Plus repository certificate
|
||||
copy: src=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.crt dest=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.crt owner=root group=root mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Copying NGINX Plus repository key
|
||||
copy: src=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.key dest=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.key owner=root group=root mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
Next we tell Ansible to use the [get_url][26] module to download the CA certificate from the NGINX Plus repository at the remote location specified by the url argument, put it in the directory specified by the dest argument, and set the mode to 0700.
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Downloading NGINX Plus CA certificate
|
||||
get_url: url=https://cs.nginx.com/static/files/CA.crt dest=/etc/ssl/nginx/CA.crt mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, we tell Ansible to download the NGINX Plus repo file using the get_url module and copy it to the **/etc/yum.repos.d** directory on the NGINX Plus server.
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Downloading yum NGINX Plus repository
|
||||
get_url: url=https://cs.nginx.com/static/files/nginx-plus-7.repo dest=/etc/yum.repos.d/nginx-plus-7.repo mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
The final two name sections tell Ansible to install and start NGINX Plus using the yum and service modules.
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Installing NGINX Plus
|
||||
yum:
|
||||
name: nginx-plus
|
||||
state: latest
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Starting NGINX Plus
|
||||
service:
|
||||
name: nginx
|
||||
state: started
|
||||
|
||||
#### Running Ansible to Deploy NGINX Plus ####
|
||||
|
||||
After saving the **install_nginx_plus.yml** file, we run the ansible-playbook command to deploy NGINX Plus. Again here we include the --ask-pass flag to have Ansible prompt for the SSH password and pass it to each NGINX Plus server, and specify the path to the main Ansible **deploy.yml** file.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ansible-playbook --ask-pass $HOME/ansible-nginx-plus/deploy.yml
|
||||
|
||||
PLAY [nginx] ******************************************************************
|
||||
|
||||
GATHERING FACTS ***************************************************************
|
||||
ok: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX Plus | Creating NGINX Plus ssl cert repo directory] **************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX Plus | Copying NGINX Plus repository certificate] ****************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX Plus | Copying NGINX Plus repository key] ************************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX Plus | Downloading NGINX Plus CA certificate] ********************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX Plus | Downloading yum NGINX Plus repository] ********************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX Plus | Installing NGINX Plus] ************************************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX Plus | Starting NGINX Plus] **************************************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************
|
||||
172.16.239.140 : ok=8 changed=7 unreachable=0 failed=0
|
||||
|
||||
The playbook recap was successful. Now we can run a quick curl command to verify that NGINX Plus is running. Great, we get 200 OK! Success! We have successfully installed NGINX Plus with Ansible.
|
||||
|
||||
$ curl -Is http://172.16.239.140 | grep HTTP
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating an Ansible Playbook for Installing NGINX and NGINX Plus on Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
The process for deploying NGINX and NGINX Plus on [Ubuntu servers][27] is pretty similar to the process on CentOS, so instead of providing step-by-step instructions I’ll show the complete deployment files and and point out the slight differences from CentOS.
|
||||
|
||||
First create the Ansible directory structure and the main Ansible deployment file, as for CentOS. Also create the **/etc/ansible/hosts** file as described in [Creating the List of NGINX Servers][28]. For NGINX Plus, you need to copy over the key and certificate as described in [Copying the NGINX Plus Certificate and Key to the Ansible Server][29].
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s the **install_nginx.yml** deployment file for open source NGINX. In the first section, we use the [apt_key][30] module to import the NGINX signing key. The next two sections use the [lineinfile][31] module to add the package URLs for Ubuntu 14.04 to the **sources.list** file. Lastly we use the [apt][32] module to update the cache and install NGINX (apt replaces the yum module we used for deploying to CentOS).
|
||||
|
||||
# ./ansible-nginx/tasks/install_nginx.yml
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | Adding NGINX signing key
|
||||
apt_key: url=http://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key state=present
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | Adding sources.list deb url for NGINX
|
||||
lineinfile: dest=/etc/apt/sources.list line="deb http://nginx.org/packages/mainline/ubuntu/ trusty nginx"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Adding sources.list deb-src url for NGINX
|
||||
lineinfile: dest=/etc/apt/sources.list line="deb-src http://nginx.org/packages/mainline/ubuntu/ trusty nginx"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | Updating apt cache
|
||||
apt:
|
||||
update_cache: yes
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | Installing NGINX
|
||||
apt:
|
||||
pkg: nginx
|
||||
state: latest
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | Starting NGINX
|
||||
service:
|
||||
name: nginx
|
||||
state: started
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s the **install_nginx.yml** deployment file for NGINX Plus. The first four sections set up the NGINX Plus key and certificate. Then we use the apt_key module to import the signing key as for open source NGINX, and the get_url module to download the apt configuration file for NGINX Plus. The [shell][33] module evokes a printf command that writes its output to the **nginx-plus.list** file in the **sources.list.d** directory. The final name modules are the same as for open source NGINX.
|
||||
|
||||
# ./ansible-nginx-plus/tasks/install_nginx_plus.yml
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Creating NGINX Plus ssl cert repo directory
|
||||
file: path=/etc/ssl/nginx state=directory group=root mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Copying NGINX Plus repository certificate
|
||||
copy: src=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.crt dest=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.crt owner=root group=root mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Copying NGINX Plus repository key
|
||||
copy: src=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.key dest=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.key owner=root group=root mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Downloading NGINX Plus CA certificate
|
||||
get_url: url=https://cs.nginx.com/static/files/CA.crt dest=/etc/ssl/nginx/CA.crt mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Adding NGINX Plus signing key
|
||||
apt_key: url=http://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key state=present
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Downloading Apt-Get NGINX Plus repository
|
||||
get_url: url=https://cs.nginx.com/static/files/90nginx dest=/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/90nginx mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Adding sources.list url for NGINX Plus
|
||||
shell: printf "deb https://plus-pkgs.nginx.com/ubuntu `lsb_release -cs` nginx-plus\n" >/etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx-plus.list
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Running apt-get update
|
||||
apt:
|
||||
update_cache: yes
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Installing NGINX Plus via apt-get
|
||||
apt:
|
||||
pkg: nginx-plus
|
||||
state: latest
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | Start NGINX Plus
|
||||
service:
|
||||
name: nginx
|
||||
state: started
|
||||
|
||||
We’re now ready to run the ansible-playbook command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ansible-playbook --ask-pass $HOME/ansible-nginx-plus/deploy.yml
|
||||
|
||||
You should get a successful play recap. If you did not get a success, you can use the verbose flag to help troubleshoot your deployment as described in [Running Ansible to Deploy NGINX][34].
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
What I demonstrated in this tutorial is just the beginning of what Ansible can do to help automate your NGINX or NGINX Plus deployment. There are many useful modules ranging from user account management to custom configuration templates. If you are interested in learning more about these, please visit the extensive [Ansible documentation][35 site.
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about Ansible, come hear my talk on deploying NGINX Plus with Ansible at [NGINX.conf 2015][36], September 22–24 in San Francisco.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kevin Jones][a]
|
||||
译者:[struggling](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/author/kjones/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ansible.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.paramiko.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.openssh.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://nginx.org/en/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.nginx.com/products/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.centos.org/
|
||||
[7]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#ubuntu
|
||||
[8]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/intro_installation.html#installing-the-control-machine
|
||||
[9]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#deploy-nginx
|
||||
[10]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/playbooks_roles.html#task-include-files-and-encouraging-reuse
|
||||
[11]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#list-nginx
|
||||
[12]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/YAMLSyntax.html
|
||||
[13]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/yum_module.html
|
||||
[14]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/service_module.html
|
||||
[15]:http://nginx.org/en/linux_packages.html
|
||||
[16]:http://wiki.centos.org/HowTos/Network/SecuringSSH
|
||||
[17]:http://curl.haxx.se/
|
||||
[18]:https://cs.nginx.com/
|
||||
[19]:https://www.nginx.com/#free-trial
|
||||
[20]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/scp
|
||||
[21]:https://winscp.net/eng/download.php
|
||||
[22]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#playbook-nginx
|
||||
[23]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#list-nginx
|
||||
[24]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/file_module.html
|
||||
[25]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/copy_module.html
|
||||
[26]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/get_url_module.html
|
||||
[27]:http://www.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[28]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#list-nginx
|
||||
[29]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#copy-cert-key
|
||||
[30]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/apt_key_module.html
|
||||
[31]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/lineinfile_module.html
|
||||
[32]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/apt_module.html
|
||||
[33]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/shell_module.html
|
||||
[34]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#deploy-nginx
|
||||
[35]:http://docs.ansible.com/
|
||||
[36]:https://www.nginx.com/nginxconf/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 上安装 Qmmp 0.9.0 类似 Winamp 的音频播放器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Qmmp,基于 Qt 的音频播放器,与 Winamp 或 xmms 的用户界面类似,现在最新版本是0.9.0。PPA 已经在 Ubuntu 15.10,Ubuntu 15.04,Ubuntu 14.04,Ubuntu 12.04 和其衍生物中已经更新了。
|
||||
|
||||
Qmmp 0.9.0 是一个较大的版本,有许多新的功能,有许多改进和新的转变。它添加了如下功能:
|
||||
|
||||
- 音频-信道序列转换器;
|
||||
- 9通道支持均衡器;
|
||||
- 艺术家专辑标签支持;
|
||||
- 异步排序;
|
||||
- 通过文件的修改日期排序;
|
||||
- 按艺术家专辑排序;
|
||||
- 支持多专栏;
|
||||
- 有隐藏踪迹长度功能;
|
||||
- 不用修改 qmmp.pri 来禁用插件(仅在 qmake 中)功能
|
||||
- 记住播放列表滚动位置功能;
|
||||
- 排除提示数据文件功能;
|
||||
- 更改用户代理功能;
|
||||
- 改变窗口标题功能;
|
||||
- 复位字体功能;
|
||||
- 恢复默认快捷键功能;
|
||||
- 默认热键为“Rename List”功能;
|
||||
- 功能禁用弹出的 GME 插件;
|
||||
- 简单的用户界面(QSUI)有以下变化:
|
||||
- 增加了多列表的支持;
|
||||
- 增加了按艺术家专辑排序;
|
||||
- 增加了按文件的修改日期进行排序;
|
||||
- 增加了隐藏歌曲长度功能;
|
||||
- 增加了默认热键为“Rename List”;
|
||||
- 增加了“Save List”功能到标签菜单;
|
||||
- 增加了复位字体功能;
|
||||
- 增加了复位快捷键功能;
|
||||
- 改进了状态栏;
|
||||
|
||||
它还改进了播放列表的通知,播放列表容器,采样率转换器,cmake 构建脚本,标题格式,在 mpeg 插件中支持 ape 标签,fileops 插件,降低了 cpu 占用率,改变默认的皮肤(炫光)和分离播放列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 中安装 Qmmp 0.9.0 : ###
|
||||
|
||||
新版本已经制做了 PPA,适用于目前所有 Ubuntu 发行版和衍生版。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 添加 [Qmmp PPA][1].
|
||||
|
||||
从 Dash 中打开终端并启动应用,通过按 Ctrl+Alt+T 快捷键。当它打开时,运行命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:forkotov02/ppa
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2. 在添加 PPA 后,通过更新软件来升级 Qmmp 播放器。刷新系统缓存,并通过以下命令安装软件:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install qmmp qmmp-plugin-pack
|
||||
|
||||
就是这样。尽情享受吧!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/2015/09/qmmp-0-9-0-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ji m][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/about/
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/~forkotov02/+archive/ubuntu/ppa
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,452 @@
|
||||
translation by strugglingyouth
|
||||
nstalling NGINX and NGINX Plus With Ansible
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在生产环境中,我会更喜欢做与自动化相关的所有事情。如果计算机能完成你的任务,何必需要你亲自动手呢?但是,在不断变化并存在多种技术的环境中,创建和实施自动化是一项艰巨的任务。这就是为什么我喜欢[Ansible][1]。Ansible是免费的,开源的,对于 IT 配置管理,部署和业务流程,使用起来非常方便。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我最喜欢 Ansible 的一个特点是,它是完全无客户端。要管理一个系统,通过 SSH 建立连接,也使用了[Paramiko][2](一个 Python 库)或本地的 [OpenSSH][3]。Ansible 另一个吸引人的地方是它有许多可扩展的模块。这些模块可被系统管理员用于执行一些的相同任务。特别是,它们使用 Ansible 这个强有力的工具可以安装和配置任何程序在多个服务器上,环境或操作系统,只需要一个控制节点。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我将带你使用 Ansible 完成安装和部署开源[NGINX][4] 和 [NGINX Plus][5],我们的商业产品。我将在 [CentOS][6] 服务器上演示,但我也写了一个详细的教程关于在 Ubuntu 服务器上部署[在 Ubuntu 上创建一个 Ansible Playbook 来安装 NGINX 和 NGINX Plus][7] 。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中我将使用 Ansible 1.9.2 版本的,并在 CentOS 7.1 服务器上部署运行。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible --version
|
||||
ansible 1.9.2
|
||||
|
||||
$ cat /etc/redhat-release
|
||||
CentOS Linux release 7.1.1503 (Core)
|
||||
|
||||
如果你还没有 Ansible,可以在 [Ansible 网站][8] 查看说明并安装它。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你使用的是 CentOS,安装 Ansible 十分简单,只要输入以下命令。如果你想使用源码编译安装或使用其他发行版,请参阅上面 Ansible 链接中的说明。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install -y epel-release && sudo yum install -y ansible
|
||||
|
||||
根据环境的不同,在本教程中的命令有的可能需要 sudo 权限。文件路径,用户名,目标服务器的值取决于你的环境中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建一个 Ansible Playbook 来安装 NGINX (CentOS) ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们为 NGINX 的部署创建一个工作目录,以及子目录和部署配置文件目录。我通常建议在主目录中创建目录,在文章的所有例子中都会有说明。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd $HOME
|
||||
$ mkdir -p ansible-nginx/tasks/
|
||||
$ touch ansible-nginx/deploy.yml
|
||||
$ touch ansible-nginx/tasks/install_nginx.yml
|
||||
|
||||
目录结构看起来是这样的。你可以使用 tree 命令来查看。
|
||||
|
||||
$ tree $HOME/ansible-nginx/
|
||||
/home/kjones/ansible-nginx/
|
||||
├── deploy.yml
|
||||
└── tasks
|
||||
└── install_nginx.yml
|
||||
|
||||
1 directory, 2 files
|
||||
|
||||
如果你没有安装 tree 命令,使用以下命令去安装。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install -y tree
|
||||
|
||||
#### 创建主部署文件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,我们在文本编辑器中打开 **deploy.yml**。我喜欢在命令行上使用 vim 来编辑配置文件,在整个教程中也都将使用它。
|
||||
|
||||
$ vim $HOME/ansible-nginx/deploy.yml
|
||||
|
||||
**deploy.yml** 文件是 Ansible 部署的主要文件,[ 在使用 Ansible 部署 NGINX][9] 时,我们将运行 ansible‑playbook 命令执行此文件。在这个文件中,我们指定运行时 Ansible 使用的库以及其它配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
在这个例子中,我使用 [include][10] 模块来指定配置文件一步一步来安装NGINX。虽然可以创建一个非常大的 playbook 文件,我建议你将其分割为小文件,以保证其可靠性。示例中的包括复制静态内容,复制配置文件,为更高级的部署使用逻辑配置设定变量。
|
||||
|
||||
在文件中输入以下行。包括顶部参考注释中的文件名。
|
||||
|
||||
# ./ansible-nginx/deploy.yml
|
||||
|
||||
- hosts: nginx
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- include: 'tasks/install_nginx.yml'
|
||||
|
||||
hosts 语句说明 Ansible 部署 **nginx** 组的所有服务器,服务器在 **/etc/ansible/hosts** 中指定。我们将编辑此文件来 [创建 NGINX 服务器的列表][11]。
|
||||
|
||||
include 语句说明 Ansible 在部署过程中从 **tasks** 目录下读取并执行 **install_nginx.yml** 文件中的内容。该文件包括以下几步:下载,安装,并启动 NGINX。我们将创建此文件在下一节。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 为 NGINX 创建部署文件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
现在,先保存 **deploy.yml** 文件,并在编辑器中打开 **install_nginx.yml** 。
|
||||
|
||||
$ vim $HOME/ansible-nginx/tasks/install_nginx.yml
|
||||
|
||||
该文件包含的说明有 - 以 [YAML][12] 格式写入 - 使用 Ansible 安装和配置 NGINX。每个部分(步骤中的过程)起始于一个 name 声明(前面连字符)描述此步骤。下面的 name 字符串:是 Ansible 部署过程中写到标准输出的,可以根据你的意愿来改变。YAML 文件中的下一个部分是在部署过程中将使用的模块。在下面的配置中,[yum][13] 和 [service][14] 模块使将被用。yum 模块用于在 CentOS 上安装软件包。service 模块用于管理 UNIX 的服务。在这部分的最后一行或几行指定了几个模块的参数(在本例中,这些行以 name 和 state 开始)。
|
||||
|
||||
在文件中输入以下行。对于 **deploy.yml**,在我们文件的第一行是关于文件名的注释。第一部分说明 Ansible 从 NGINX 仓库安装 **.rpm** 文件在CentOS 7 上。这说明软件包管理器直接从 NGINX 仓库安装最新最稳定的版本。需要在你的 CentOS 版本上修改路径。可使用包的列表可以在 [开源 NGINX 网站][15] 上找到。接下来的两节说明 Ansible 使用 yum 模块安装最新的 NGINX 版本,然后使用 service 模块启动 NGINX。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:** 在第一部分中,CentOS 包中的路径名是连着的两行。在一行上输入其完整路径。
|
||||
|
||||
# ./ansible-nginx/tasks/install_nginx.yml
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | Installing NGINX repo rpm
|
||||
yum:
|
||||
name: http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/noarch/RPMS/nginx-release-centos-7-0.el7.ngx.noarch.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | Installing NGINX
|
||||
yum:
|
||||
name: nginx
|
||||
state: latest
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | Starting NGINX
|
||||
service:
|
||||
name: nginx
|
||||
state: started
|
||||
|
||||
#### 创建 NGINX 服务器列表 ####
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们有 Ansible 部署所有配置的文件,我们需要告诉 Ansible 部署哪个服务器。我们需要在 Ansible 中指定 **hosts** 文件。先备份现有的文件,并新建一个新文件来部署。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mv /etc/ansible/hosts /etc/ansible/hosts.backup
|
||||
$ sudo vim /etc/ansible/hosts
|
||||
|
||||
在文件中输入以下行来创建一个名为 **nginx** 的组并列出安装 NGINX 的服务器。你可以指定服务器通过主机名,IP 地址,或者在一个区域,例如 **server[1-3].domain.com**。在这里,我指定一台服务器通过 IP 地址。
|
||||
|
||||
# /etc/ansible/hosts
|
||||
|
||||
[nginx]
|
||||
172.16.239.140
|
||||
|
||||
#### 设置安全性 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在部署之前,我们需要确保 Ansible 已通过 SSH 授权能访问我们的目标服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
首选并且最安全的方法是添加 Ansible 所要部署服务器的 RSA SSH 密钥到目标服务器的 **authorized_keys** 文件中,这给 Ansible 在目标服务器上的 SSH 权限不受限制。要了解更多关于此配置,请参阅 [安全的 OpenSSH][16] 在 wiki.centos.org。这样,你就可以自动部署而无需用户交互。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,你也可以在部署过程中需要输入密码。我强烈建议你只在测试过程中使用这种方法,因为它是不安全的,没有办法判断目标主机的身份。如果你想这样做,将每个目标主机 **/etc/ssh/ssh_config** 文件中 StrictHostKeyChecking 的默认值 yes 改为 no。然后在 ansible-playbook 命令中添加 --ask-pass参数来表示 Ansible 会提示输入 SSH 密码。
|
||||
|
||||
在这里,我将举例说明如何编辑 **ssh_config** 文件来禁用在目标服务器上严格的主机密钥检查。我们手动 SSH 到我们将部署 NGINX 的服务器并将StrictHostKeyChecking 的值更改为 no。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh kjones@172.16.239.140
|
||||
kjones@172.16.239.140's password:***********
|
||||
|
||||
[kjones@nginx ]$ sudo vim /etc/ssh/ssh_config
|
||||
|
||||
当你更改后,保存 **ssh_config**,并通过 SSH 连接到你的 Ansible 服务器。保存后的设置应该如下图所示。
|
||||
|
||||
# /etc/ssh/ssh_config
|
||||
|
||||
StrictHostKeyChecking no
|
||||
|
||||
#### 运行 Ansible 部署 NGINX ####
|
||||
|
||||
如果你一直照本教程的步骤来做,你可以运行下面的命令来使用 Ansible 部署NGINX。(同样,如果你设置了 RSA SSH 密钥认证,那么--ask-pass 参数是不需要的。)在 Ansible 服务器运行命令,并使用我们上面创建的配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ansible-playbook --ask-pass $HOME/ansible-nginx/deploy.yml
|
||||
|
||||
Ansible 提示输入 SSH 密码,输出如下。recap 中显示 failed=0 这条信息,意味着部署成功了。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ansible-playbook --ask-pass $HOME/ansible-nginx/deploy.yml
|
||||
SSH password:
|
||||
|
||||
PLAY [all] ********************************************************************
|
||||
|
||||
GATHERING FACTS ***************************************************************
|
||||
ok: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX | Installing NGINX repo rpm] *************************************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX | Installing NGINX] **********************************************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX | Starting NGINX] ************************************************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************
|
||||
172.16.239.140 : ok=4 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0
|
||||
|
||||
如果你没有得到一个成功的 play recap,你可以尝试用 -vvvv 参数(带连接调试的详细信息)再次运行 ansible-playbook 命令来解决部署过程的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
当部署成功(因为我们不是第一次部署)后,你可以验证 NGINX 在远程服务器上运行基本的 [cURL][17] 命令。在这里,它会返回 200 OK。Yes!我们使用Ansible 成功安装了 NGINX。
|
||||
|
||||
$ curl -Is 172.16.239.140 | grep HTTP
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建 Ansible Playbook 来安装 NGINX Plus (CentOS) ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我已经展示了如何安装 NGINX 的开源版本,我将带你完成安装 NGINX Plus。这需要更改一些额外的部署配置,并展示了一些 Ansible 的其他功能。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 复制 NGINX Plus 上的证书和密钥到 Ansible 服务器 ####
|
||||
|
||||
使用 Ansible 安装和配置 NGINX Plus 时,首先我们需要将 [NGINX Plus Customer Portal][18] 的密钥和证书复制到部署 Ansible 服务器上的标准位置。
|
||||
|
||||
购买了 NGINX Plus 或正在试用的客户也可以访问 NGINX Plus Customer Portal。如果你有兴趣测试 NGINX Plus,你可以申请免费试用30天[点击这里][19]。在你注册后不久你将收到一个试用证书和密钥的链接。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Mac 或 Linux 主机上,我在这里演示使用 [scp][20] 工具。在 Microsoft Windows 主机,可以使用 [WinSCP][21]。在本教程中,先下载文件到我的 Mac 笔记本电脑上,然后使用 scp 将其复制到 Ansible 服务器。密钥和证书的位置都在我的家目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /path/to/nginx-repo-files/
|
||||
$ scp nginx-repo.* user@destination-server:.
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,我们通过 SSH 连接到 Ansible 服务器,确保 NGINX Plus 的 SSL 目录存在,移动文件到这儿。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh user@destination-server
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir -p /etc/ssl/nginx/
|
||||
$ sudo mv nginx-repo.* /etc/ssl/nginx/
|
||||
|
||||
验证你的 **/etc/ssl/nginx** 目录包含证书(**.crt**)和密钥(**.key**)文件。你可以使用 tree 命令检查。
|
||||
|
||||
$ tree /etc/ssl/nginx
|
||||
/etc/ssl/nginx
|
||||
├── nginx-repo.crt
|
||||
└── nginx-repo.key
|
||||
|
||||
0 directories, 2 files
|
||||
|
||||
如果你没有安装 tree,可以使用下面的命令去安装。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install -y tree
|
||||
|
||||
#### 创建 Ansible 目录结构 ####
|
||||
|
||||
以下执行的步骤将和开源 NGINX 的非常相似在[创建安装 NGINX 的 Ansible Playbook 中(CentOS)][22]。首先,我们建一个工作目录为部署 NGINX Plus 使用。我喜欢将它创建为我主目录的子目录。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd $HOME
|
||||
$ mkdir -p ansible-nginx-plus/tasks/
|
||||
$ touch ansible-nginx-plus/deploy.yml
|
||||
$ touch ansible-nginx-plus/tasks/install_nginx_plus.yml
|
||||
|
||||
目录结构看起来像这样。
|
||||
|
||||
$ tree $HOME/ansible-nginx-plus/
|
||||
/home/kjones/ansible-nginx-plus/
|
||||
├── deploy.yml
|
||||
└── tasks
|
||||
└── install_nginx_plus.yml
|
||||
|
||||
1 directory, 2 files
|
||||
|
||||
#### 创建主部署文件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,我们使用 vim 为开源的 NGINX 创建 **deploy.yml** 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
$ vim ansible-nginx-plus/deploy.yml
|
||||
|
||||
和开源 NGINX 的部署唯一的区别是,我们将包含文件的名称修改为**install_nginx_plus.yml**。该文件告诉 Ansible 在 **nginx** 组中的所有服务器(**/etc/ansible/hosts** 中定义的)上部署 NGINX Plus ,然后在部署过程中从 **tasks** 目录读取并执行 **install_nginx_plus.yml** 的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
# ./ansible-nginx-plus/deploy.yml
|
||||
|
||||
- hosts: nginx
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- include: 'tasks/install_nginx_plus.yml'
|
||||
|
||||
如果你还没有这样做的话,你需要创建 hosts 文件,详细说明在上面的 [创建 NGINX 服务器的列表][23]。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 为 NGINX Plus 创建部署文件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在文本编辑器中打开 **install_nginx_plus.yml**。该文件在部署过程中使用 Ansible 来安装和配置 NGINX Plus。这些命令和模块仅针对 CentOS,有些是 NGINX Plus 独有的。
|
||||
|
||||
$ vim ansible-nginx-plus/tasks/install_nginx_plus.yml
|
||||
|
||||
第一部分使用 [文件][24] 模块,告诉 Ansible 使用指定的路径和状态参数为 NGINX Plus 创建特定的 SSL 目录,设置根目录的权限,将权限更改为0700。
|
||||
|
||||
# ./ansible-nginx-plus/tasks/install_nginx_plus.yml
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 创建 NGINX Plus ssl 证书目录
|
||||
file: path=/etc/ssl/nginx state=directory group=root mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
接下来的两节使用 [copy][25] 模块从部署 Ansible 的服务器上将 NGINX Plus 的证书和密钥复制到 NGINX Plus 服务器上,再修改权根,将权限设置为0700。
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 复制 NGINX Plus repo 证书
|
||||
copy: src=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.crt dest=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.crt owner=root group=root mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 复制 NGINX Plus 密钥
|
||||
copy: src=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.key dest=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.key owner=root group=root mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,我们告诉 Ansible 使用 [get_url][26] 模块从 NGINX Plus 仓库下载 CA 证书在 url 参数指定的远程位置,通过 dest 参数把它放在指定的目录,并设置权限为 0700。
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 下载 NGINX Plus CA 证书
|
||||
get_url: url=https://cs.nginx.com/static/files/CA.crt dest=/etc/ssl/nginx/CA.crt mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
同样,我们告诉 Ansible 使用 get_url 模块下载 NGINX Plus repo 文件,并将其复制到 **/etc/yum.repos.d** 目录下在 NGINX Plus 服务器上。
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 下载 yum NGINX Plus 仓库
|
||||
get_url: url=https://cs.nginx.com/static/files/nginx-plus-7.repo dest=/etc/yum.repos.d/nginx-plus-7.repo mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
最后两节的 name 告诉 Ansible 使用 yum 和 service 模块下载并启动 NGINX Plus。
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 安装 NGINX Plus
|
||||
yum:
|
||||
name: nginx-plus
|
||||
state: latest
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 启动 NGINX Plus
|
||||
service:
|
||||
name: nginx
|
||||
state: started
|
||||
|
||||
#### 运行 Ansible 来部署 NGINX Plus ####
|
||||
|
||||
在保存 **install_nginx_plus.yml** 文件后,然后运行 ansible-playbook 命令来部署 NGINX Plus。同样在这里,我们使用 --ask-pass 参数使用 Ansible 提示输入 SSH 密码并把它传递给每个 NGINX Plus 服务器,指定路径在 **deploy.yml** 文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ansible-playbook --ask-pass $HOME/ansible-nginx-plus/deploy.yml
|
||||
|
||||
PLAY [nginx] ******************************************************************
|
||||
|
||||
GATHERING FACTS ***************************************************************
|
||||
ok: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX Plus | Creating NGINX Plus ssl cert repo directory] **************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX Plus | Copying NGINX Plus repository certificate] ****************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX Plus | Copying NGINX Plus repository key] ************************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX Plus | Downloading NGINX Plus CA certificate] ********************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX Plus | Downloading yum NGINX Plus repository] ********************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX Plus | Installing NGINX Plus] ************************************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [NGINX Plus | Starting NGINX Plus] **************************************
|
||||
changed: [172.16.239.140]
|
||||
|
||||
PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************
|
||||
172.16.239.140 : ok=8 changed=7 unreachable=0 failed=0
|
||||
|
||||
playbook 的 recap 是成功的。现在,使用 curl 命令来验证 NGINX Plus 是否在运行。太好了,我们得到的是 200 OK!成功了!我们使用 Ansible 成功地安装了 NGINX Plus。
|
||||
|
||||
$ curl -Is http://172.16.239.140 | grep HTTP
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 上创建一个 Ansible Playbook 来安装 NGINX 和 NGINX Plus ###
|
||||
|
||||
此过程在 [Ubuntu 服务器][27] 上部署 NGINX 和 NGINX Plus 与 CentOS 很相似,我将一步一步的指导来完成整个部署文件,并指出和 CentOS 的细微差异。
|
||||
|
||||
首先和 CentOS 一样,创建 Ansible 目录结构和主要的 Ansible 部署文件。也创建 **/etc/ansible/hosts** 文件来描述 [创建 NGINX 服务器的列表][28]。对于 NGINX Plus,你也需要复制证书和密钥在此步中 [复制 NGINX Plus 证书和密钥到 Ansible 服务器][29]。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是开源 NGINX 的 **install_nginx.yml** 部署文件。在第一部分,我们使用 [apt_key][30] 模块导入 Nginx 的签名密钥。接下来的两节使用[lineinfile][31] 模块来添加 URLs 到 **sources.list** 文件中。最后,我们使用 [apt][32] 模块来更新缓存并安装 NGINX(apt 取代了我们在 CentOS 中部署时的 yum 模块)。
|
||||
|
||||
# ./ansible-nginx/tasks/install_nginx.yml
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | 添加 NGINX 签名密钥
|
||||
apt_key: url=http://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key state=present
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | 为 NGINX 添加 sources.list deb url
|
||||
lineinfile: dest=/etc/apt/sources.list line="deb http://nginx.org/packages/mainline/ubuntu/ trusty nginx"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 为 NGINX 添加 sources.list deb-src url
|
||||
lineinfile: dest=/etc/apt/sources.list line="deb-src http://nginx.org/packages/mainline/ubuntu/ trusty nginx"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | 更新 apt 缓存
|
||||
apt:
|
||||
update_cache: yes
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | 安装 NGINX
|
||||
apt:
|
||||
pkg: nginx
|
||||
state: latest
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX | 启动 NGINX
|
||||
service:
|
||||
name: nginx
|
||||
state: started
|
||||
下面是 NGINX Plus 的部署文件 **install_nginx.yml**。前四节设置了 NGINX Plus 密钥和证书。然后,我们用 apt_key 模块为开源的 NGINX 导入签名密钥,get_url 模块为 NGINX Plus 下载 apt 配置文件。[shell][33] 模块使用 printf 命令写下输出到 **nginx-plus.list** 文件中在**sources.list.d** 目录。最终的 name 模块是为开源 NGINX 的。
|
||||
|
||||
# ./ansible-nginx-plus/tasks/install_nginx_plus.yml
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 创建 NGINX Plus ssl 证书 repo 目录
|
||||
file: path=/etc/ssl/nginx state=directory group=root mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 复制 NGINX Plus 仓库证书
|
||||
copy: src=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.crt dest=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.crt owner=root group=root mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 复制 NGINX Plus 仓库密钥
|
||||
copy: src=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.key dest=/etc/ssl/nginx/nginx-repo.key owner=root group=root mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 安装 NGINX Plus CA 证书
|
||||
get_url: url=https://cs.nginx.com/static/files/CA.crt dest=/etc/ssl/nginx/CA.crt mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 添加 NGINX Plus 签名密钥
|
||||
apt_key: url=http://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key state=present
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 安装 Apt-Get NGINX Plus 仓库
|
||||
get_url: url=https://cs.nginx.com/static/files/90nginx dest=/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/90nginx mode=0700
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 为 NGINX Plus 添加 sources.list url
|
||||
shell: printf "deb https://plus-pkgs.nginx.com/ubuntu `lsb_release -cs` nginx-plus\n" >/etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx-plus.list
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 运行 apt-get update
|
||||
apt:
|
||||
update_cache: yes
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 安装 NGINX Plus 通过 apt-get
|
||||
apt:
|
||||
pkg: nginx-plus
|
||||
state: latest
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NGINX Plus | 启动 NGINX Plus
|
||||
service:
|
||||
name: nginx
|
||||
state: started
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们已经准备好运行 ansible-playbook 命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ansible-playbook --ask-pass $HOME/ansible-nginx-plus/deploy.yml
|
||||
|
||||
你应该得到一个成功的 play recap。如果你没有成功,你可以使用 verbose 参数,以帮助你解决在 [运行 Ansible 来部署 NGINX][34] 中出现的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
### 小结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我在这个教程中演示是什么是 Ansible,可以做些什么来帮助你自动部署 NGINX 或 NGINX Plus,这仅仅是个开始。还有许多有用的模块,用户账号管理,自定义配置模板等。如果你有兴趣了解更多关于这些,请访问 [Ansible 官方文档][35]。
|
||||
|
||||
要了解更多关于 Ansible,来听我讲用 Ansible 部署 NGINX Plus 在[NGINX.conf 2015][36],9月22-24日在旧金山。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kevin Jones][a]
|
||||
译者:[strugglingyouth](https://github.com/strugglingyouth)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/author/kjones/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ansible.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.paramiko.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.openssh.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://nginx.org/en/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.nginx.com/products/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.centos.org/
|
||||
[7]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#ubuntu
|
||||
[8]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/intro_installation.html#installing-the-control-machine
|
||||
[9]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#deploy-nginx
|
||||
[10]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/playbooks_roles.html#task-include-files-and-encouraging-reuse
|
||||
[11]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#list-nginx
|
||||
[12]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/YAMLSyntax.html
|
||||
[13]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/yum_module.html
|
||||
[14]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/service_module.html
|
||||
[15]:http://nginx.org/en/linux_packages.html
|
||||
[16]:http://wiki.centos.org/HowTos/Network/SecuringSSH
|
||||
[17]:http://curl.haxx.se/
|
||||
[18]:https://cs.nginx.com/
|
||||
[19]:https://www.nginx.com/#free-trial
|
||||
[20]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/scp
|
||||
[21]:https://winscp.net/eng/download.php
|
||||
[22]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#playbook-nginx
|
||||
[23]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#list-nginx
|
||||
[24]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/file_module.html
|
||||
[25]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/copy_module.html
|
||||
[26]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/get_url_module.html
|
||||
[27]:http://www.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[28]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#list-nginx
|
||||
[29]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#copy-cert-key
|
||||
[30]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/apt_key_module.html
|
||||
[31]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/lineinfile_module.html
|
||||
[32]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/apt_module.html
|
||||
[33]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/shell_module.html
|
||||
[34]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#deploy-nginx
|
||||
[35]:http://docs.ansible.com/
|
||||
[36]:https://www.nginx.com/nginxconf/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user