mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-27 02:30:10 +08:00
20150304-2 选题
This commit is contained in:
parent
da22e2769a
commit
f34e78bfa0
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
No reboot patching comes to Linux 4.0
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Summary**:With the new Linux 4.0 kernel, you'll need to reboot Linux less often than ever.
|
||||
|
||||
With [Linux 4.0][1], you may never need to reboot your operating system again.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Using Linux means never having to reboot. -- SUSE
|
||||
|
||||
One reason to love Linux on your servers or in your data-center is that you so seldom needed to reboot it. True, critical patches require a reboot, but you could go months without rebooting. Now, with the latest changes to the Linux kernel you may be able to go years between reboots.
|
||||
|
||||
This is actually a feature that was available in Linux in 2009 thanks to a program called [Ksplice][2]. This program compares the original and patched kernels and then uses a customized kernel module to patch the new code into the running kernel. Each Ksplice-enabled kernel comes with a special set of flags for each function that will be patched. The [Ksplice process][3] then watches for a moment when the code for the function being patched isn't in use, and ta-da, the patch is made and your server runs on.
|
||||
|
||||
[Oracle acquired Ksplice][4] in 2011, and kept it just for its own [Oracle Linux][5], a [Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)][6] clone, and as a RHEL subscription service. That left all the other enterprise and server Linux back where they started.
|
||||
|
||||
Then [KernelCare released a service that could provide bootless patches][7] for most enterprise Linux distros. This program use proprietary software and is only available as a service with a monthly fee. That was a long way from satisfying many Linux system administrators.
|
||||
|
||||
So, [Red Hat][8] and [SUSE][9] both started working on their own purely open-source means of giving Linux the ability to keep running even while critical patches were being installed. Red Hat's program was named [kpatch][10], while SUSE' is named [kGraft][11].
|
||||
|
||||
The two companies took different approaches. Kpatch issues a stop_machine() command. After that it looks at the stack of existing processes using [ftrace][12] and, if the patch can be made safely, it redirects the running code to the patched functions and then removes the now outdated code.
|
||||
|
||||
Kgraft also uses ftrace, but it works on the thread level. When an old function is called it makes sure the thread reaches a point that it can switch to the new function.
|
||||
|
||||
While the end result is the same, the operating system keeps running while patches are made, there are significant differences in performance. Kpatch takes from one to forty milliseconds, while kGraft might take several minutes but there's never even a millisecond of down time.
|
||||
|
||||
At the Linux Plumbers Conference in October 2014, the two groups got together and started work on a way to [patch Linux without rebooting that combines the best of both programs][13]. Essentially, what they ended up doing was putting both kpatch and kGraft in the 4.0 Linux kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
Jiri Kosina, a SUSE software engineer and Linux kernel developer, explained, that live-patching in the Linux kernel will "provides a basic infrastructure for function "live patching" (i.e. code redirection), including API [application programming interface] for kernel modules containing the actual patches, and API/ABI [application binary interface] for userspace to be able to operate on the patches. This is "relatively simple and minimalistic, as it's making use of existing kernel infrastructure (namely ftrace) as much as possible. It's also self-contained, in a sense that it doesn't hook itself in any other kernel subsystem (it doesn't even touch any other code)."
|
||||
|
||||
The release candidate for Linux 4.0 is now out. Kosina stated that "It's now implemented for x86 only as a reference architecture, but support for powerpc, s390 and arm is already in the works." And, indeed, the source code for these architectures is already in the [Live Patching Git code][14].
|
||||
|
||||
Simply having the code in there is just the start. Your Linux distribution will have to support it with patches that can make use of it. With both Red Hat and SUSE behind it, live patching will soon be the default in all serious business Linux distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.zdnet.com/article/no-reboot-patching-comes-to-linux-4-0/#ftag=RSSbaffb68
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.zdnet.com/meet-the-team/us/sjvn/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/linux-kernel-turns-over-release-odometer-to-4-0/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.computerworld.com/article/2466389/open-source-tools/never-reboot-again-with-linux-and-ksplice.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.ksplice.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/oracle-acquires-zero-downtime-linux-upgrade-software/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.oracle.com/us/technologies/linux/overview/index.html
|
||||
[6]:http://www.redhat.com/en/technologies/linux-platforms/enterprise-linux
|
||||
[7]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/kernelcare-new-no-reboot-linux-patching-system/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.redhat.com/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.suse.com/
|
||||
[10]:http://rhelblog.redhat.com/2014/02/26/kpatch/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/suse-gets-live-patching/
|
||||
[12]:http://elinux.org/Ftrace
|
||||
[13]:http://linuxplumbersconf.org/2014/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/LPC2014_LivePatching.txt
|
||||
[14]:https://kernel.googlesource.com/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/jikos/livepatching/+/9ec0de0ee0c9f0ffe4f72da9158194121cc22807
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
How To Fix “Not Enough Free Disk Space On /boot” In Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Question: How To Fix “Not Enough Free Disk Space On /boot” In Ubuntu? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Today, I got the following error, but a simple one, when try to update my Lubuntu 14.04 desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
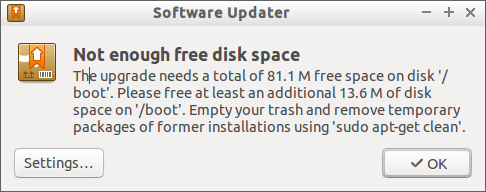
> “Not Enough Free Disk Space On /boot”
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This is because my /boot partition has caught up with unwanted old kernels, packages etc.
|
||||
|
||||
### Answer: ###
|
||||
|
||||
I heard about **Computer Janitor** feature which will remove unwanted old junk files in Ubuntu Tweak tool. Using the Computer Janitor, you can clean up your system like a freshly installed system. Janitor will remove;
|
||||
|
||||
- Apps cache(Firefox/Chrome cache, Software center cache);
|
||||
- Thumbnail cache;
|
||||
- Apt cache;
|
||||
- Old kernels;
|
||||
- Package configs;
|
||||
- And unneeded packages.
|
||||
|
||||
If you haven’t install this tool, look at the following link.
|
||||
|
||||
- **[How To Install And Use Ubuntu Tweak On Ubuntu][1]**
|
||||
|
||||
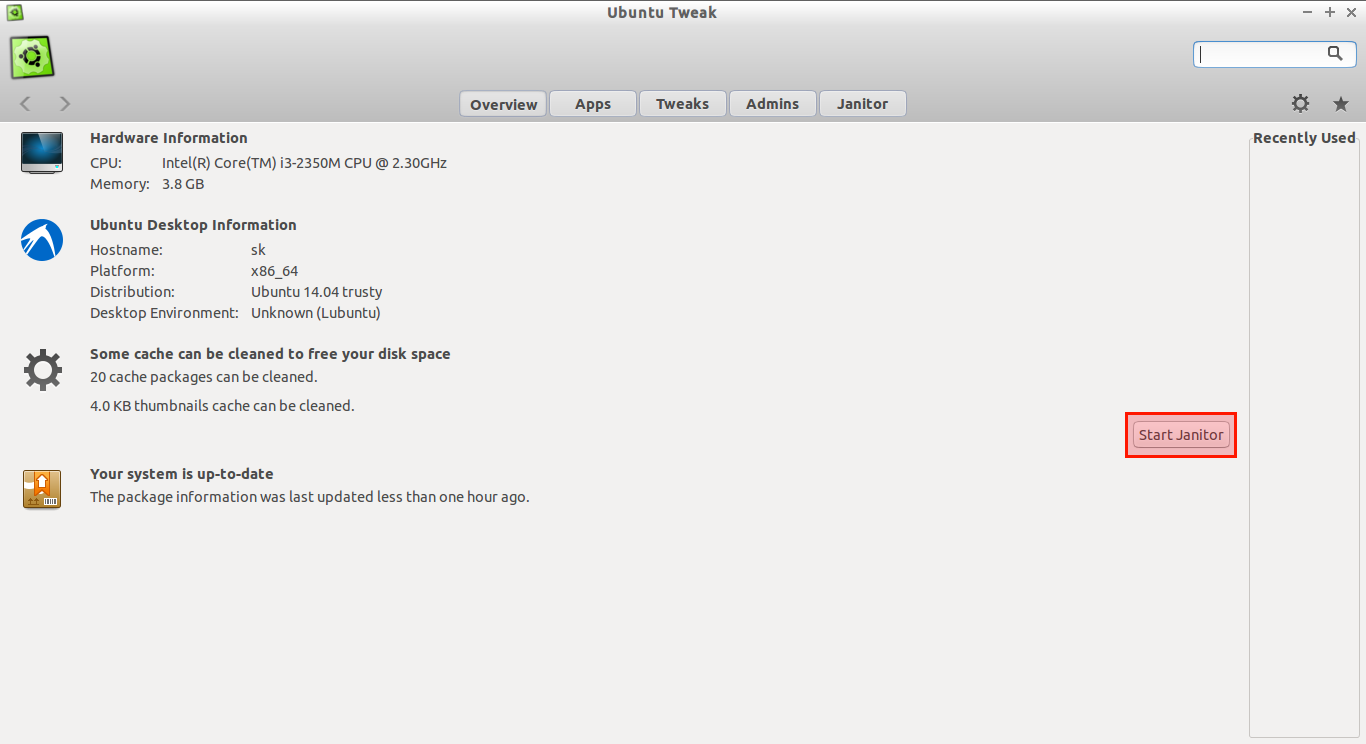
To remove unwanted junk files, open Ubuntu Tweak, and click on the **Janitor** option.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
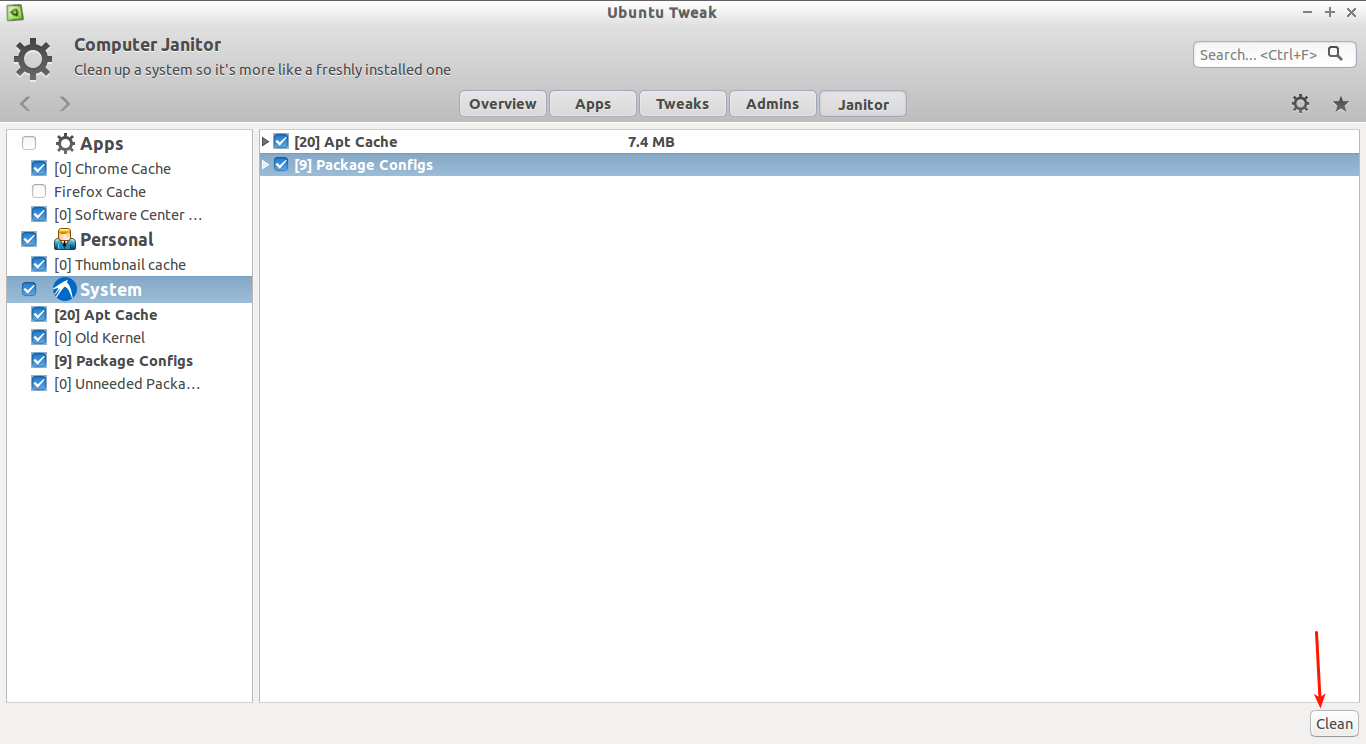
Select the check the boxes to remove unwanted junk from your system, and click **Clean** button.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
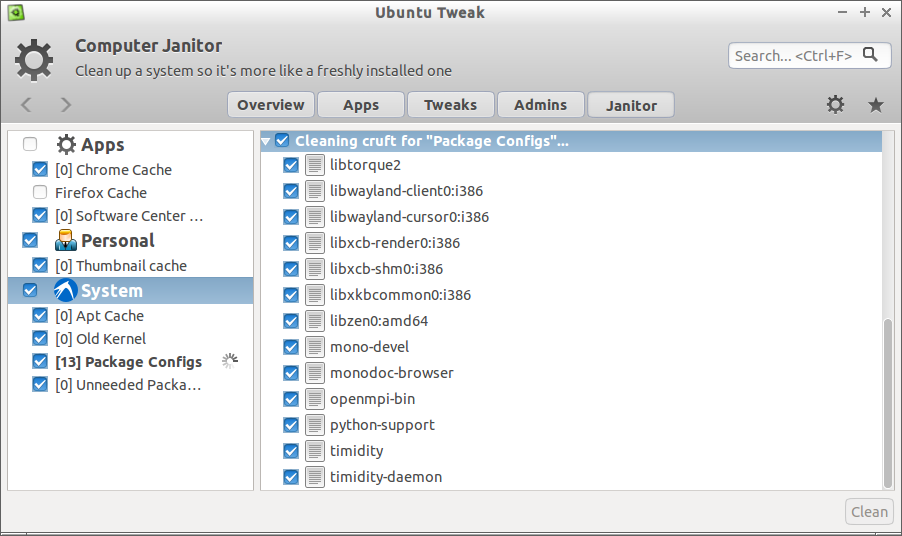
Janitor will now start to clean up your system
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
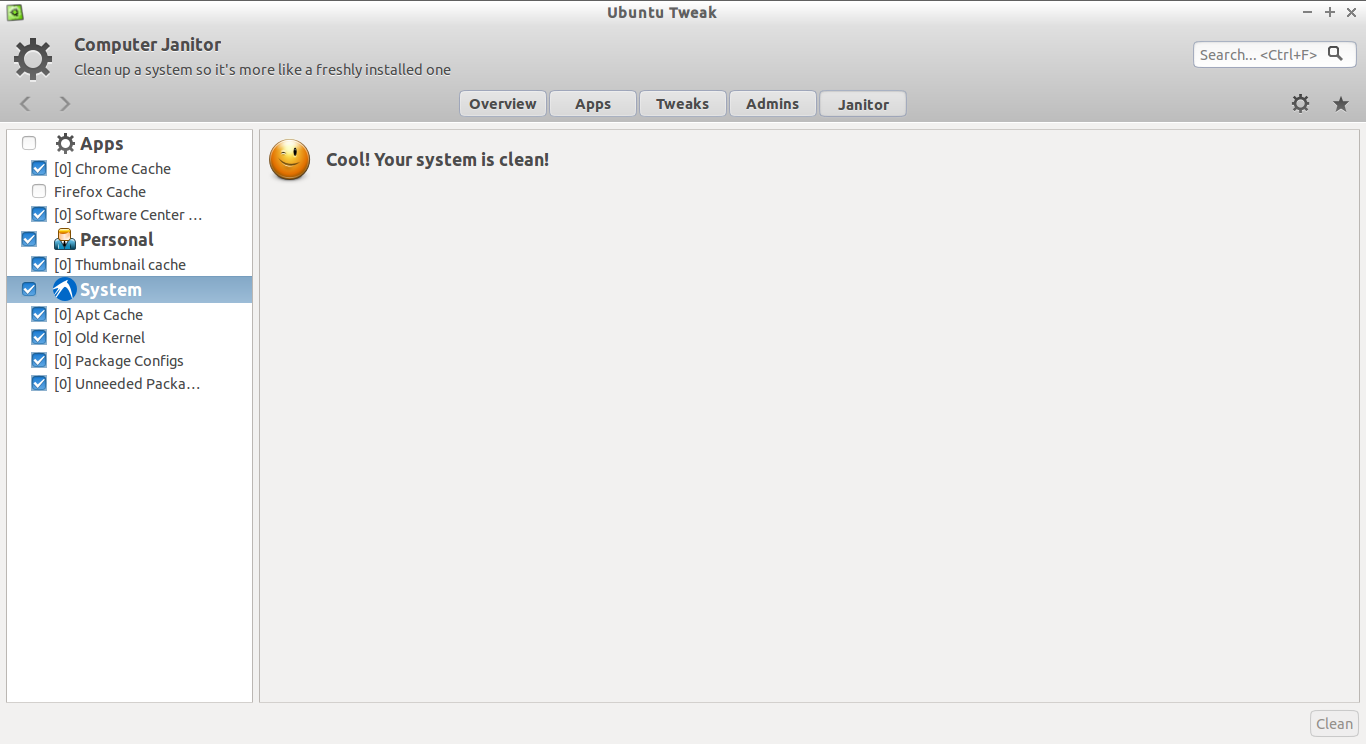
Cool! The system is clean now.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
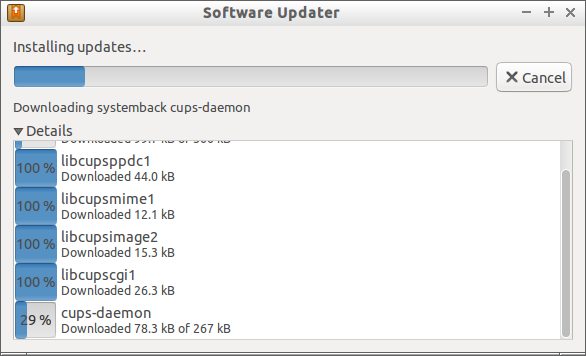
Again I re-launched the software updater. This time it went smoothly without any issues.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all. Enjoy. There are others ways also available to clean up the system. But, this seems very easy to follow. We can do system clean up in few mouse clicks.
|
||||
|
||||
Cheers!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.unixmen.com/how-to-fix-not-enough-free-disk-space-on-boot-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/after-a-fresh-install-of-ubuntu-1010-maverick-meerkat-configuration-made-easy-with-ubuntu-tweak/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
How To Fix Windows Updates Stuck At 0%
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
How do you feel when you log in to Windows after a month, find there are updates to install, you select to install these updates and those **Windows updates stuck at zero percent**?
|
||||
|
||||
Why am I talking about Windows updates on a blog dedicated to Linux and Open Source? Because I prefer to [dual boot Windows with Linux][1]. While I use Linux as my main desktop, once in a while I do log in to Windows. The most annoying thing after logging in Windows is the Windows updates. It has happened to me on several occasions that I found **Windows update not working**. I choose to install the updates and Windows updates get stuck at 0 KB and 0%, like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, we shall see how to make Windows update work again. The tutorial should be applicable for Windows 7, Windows 8 and Windows 8.1.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fix Windows updates stuck at zero percent ###
|
||||
|
||||
Please mind that Windows updates can be stuck at any percent and the trick which we are going to use would require you to install those updates again. I hope you do not find that too inconvenient. If you are ready, let’s see how to fix this Windows update issue.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 1: ####
|
||||
|
||||
Press Windows+R. This will prompt run dialogue box. In here, type services.msc:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2: ####
|
||||
|
||||
Now it brings us to all the services installed in Windows. These services are listed in alphabetical order. Scroll down and look for **Windows Update Service**. Right click on it and stop it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 3: ####
|
||||
|
||||
Now go in **C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution and delete all of its contents**. Actually, this is the folder where downloaded installation files were stored. But since Windows update suck, they somehow have problem with partially downloaded update files.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 4: ####
|
||||
|
||||
Go back to services again (as mentioned in Step 1) and this time start the Windows Update Service, by right clicking on it. Try to update Windows again. It should be working this time.
|
||||
|
||||
So once you have got the updates working, perhaps you will find plenty of updates to install at next reboot. And that moment calls for a meme:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Jokes apart, I hope this tip helps you to get rid of Windows updates hanged at 0%. I wish that Linux like updates are also included in the list of [Windows 10 features copied from Linux][2]. I wish.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-windows-updates-stuck-0/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/install-ubuntu-1404-dual-boot-mode-windows-8-81-uefi/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/windows-10-inspired-linux/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
|
||||
Share Folders On Local Network Between Ubuntu And Windows
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This is a complete tutorial to show you **how to share folders over local network in Ubuntu**.
|
||||
|
||||
Do you have multiple devices in your home? Do you have to use Flash Drive or SD card to transfer data from Ubuntu to another computer? Do you find it annoying? We know you do. Because we don’t want you to waste your precious time while you can transfer your files, documents and other large stuff quickly and easily, over the local network. It’s one time setup and then with some clicks you will be able to **share files between Ubuntu and Windows** or any other Linux system. And don’t worry it’s easy and takes only little time.
|
||||
|
||||
One more thing to add, while we performed this tutorial on Ubuntu, this tutorial should be valid for any other Linux OS.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Share folder on local network in Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using Ubuntu 14.04, 14.10 or 12.04, there are two ways you can share your local files over the local network to access it from Windows or other Linux computers.
|
||||
|
||||
- Share it for everyone’s access on local network, without password
|
||||
- Password protect the folders for restricted access
|
||||
|
||||
We’ll see both methods in this post and will let you decide which one you would prefer to use.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Share folders on local network without password ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 1: ####
|
||||
|
||||
To share a folder on local network in Ubuntu, right click on the desired folder and select Local Network Share:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Possible troubleshoot**: If do not see the option of Local Network Share in right click menu, open a terminal and use the following command to install nautlius-share:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install nautilus-share
|
||||
|
||||
You’ll need to restart Nautilus. Either log out and log in back or use the command below:
|
||||
|
||||
nautilus -q
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2: ####
|
||||
|
||||
When you click on Local Network Share, you will see the option of sharing the folder. Just check the option of Share this folder:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Possible troubleshoot: If you are prompted about Sharing service not being installed, like in the screenshot below, just click on Install service and follow the instructions.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 3: ####
|
||||
|
||||
When you check the option of Share this folder, you’ll see option of Create Share available for you. You can also allow other users to edit the files in the shared folder. Option for guest access can be checked as well.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You’ll see that the folder icon have been changed to show that it has been shared. To stop sharing a folder, just uncheck the Share this folder option.
|
||||
|
||||
Now this was the easy way out. This provides access to anyone on your local network to access these files. In normal condition, you should prefer this. I mean, devices on your home network should be generally know devices. But this could not be the case always. What if you want only certain people to access it? This is where Samba server comes in picture. We’ll see that in the second part of the tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Share the folders on local network in Ubuntu with password protection ###
|
||||
|
||||
To do this, we need to configure Samba server. Actually, we did use Samba in the previous part of this tutorial. We just did not emphasize on it. Before we go on seeing how to set up Samba server for local network sharing in Ubuntu, let’s first have a quick look on what actually is [Samba][1].
|
||||
|
||||
#### What is Samba? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Samba is the software package that allows you to share files, documents and printers across a network, irrespective of whether you are using Linux, Windows and Mac. It’s available for all major platforms and can work tremendously nice in all of them. Quoting from Wikipedia:
|
||||
|
||||
> Samba a free software re-implementation of the SMB/CIFS networking protocol, and was originally developed by Andrew Tridgell. As of version 3, Samba provides file and print services for various Windows Clients and can integrate with a Windows Server domain, either as a Primary Domain Controller (PDC) or as a domain member. It can also be part an Active Directory domain.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install Samba server on Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can easily install Samba on you Ubuntu box. Before installing update your system so that you can install any available updates.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && apt-get upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
Now install Samba serer and few other required stuffs with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install samba samba-common system-config-samba python-glade2 gksu
|
||||
|
||||
Once you’ve installed Samba server, it’s time to configure Samba from the graphical interface window to share files.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Configure Samba server on Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
Open Samba Configuration tool from the dash:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Go to **Preference->Server Settings**. Although the default settings are good and may be same you need. But you may need to make change to it in some cases.
|
||||
|
||||
Now in Server Settings you’ve two tabs, ‘Basic’ and ‘Security’. Under Basic tab you’ve the following options that mean:
|
||||
|
||||
- Workgroup – This is the name of the Workgroup of the computer you want to connect to. For example, if you want to connect to a Windows computer so you will enter the workgroup name of Windows computer, and in Windows you already have the same workgroup name as is set by default in Samba Server Settings. But if you have a different workgroup name on Windows then you will enter that workgroup name in this field. (In Windows 7 to get the workgroup name, right-click Computer icon and go to Properties, there you’ll see Windows Workgroup name.)
|
||||
- Description – This is the name of your computer as seen by others. Don’t use spaces or non-internet friendly characters.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
setting up samba serverAllowing ‘Guests’ is not advisable so there is no reason to change security settings. Keep as it is.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Samba Security security settingsIt is all done! You’ve setup Samba Server. We are not far from sharing our first folder on network.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Create a system user for network file sharing ####
|
||||
|
||||
We will now create a system user for sharing file on network. This is how simple it is.
|
||||
|
||||
- Go to **System Settings**.
|
||||
- Under Systems Settings Click **User Accounts**.
|
||||
- Click **unlock** to Enable + (**plus**) icon.
|
||||
- Click + (plus) icon to create a new system user.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now as you can see the above image, you can enter ‘Full name’. As you enter ‘Full name’ Username will be taken as Full name automatically. Because we are creating this user to share files so we will assign Account Type to ‘**Standard**‘.
|
||||
|
||||
Done above steps? Click add. You have created a system user. The user is not yet activated so we will activate it by setting up password for this account. Make sure Users accounts panel is unlocked. Click Account disabled and type a new password, then confirm password and click Change.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Yipee… Upto now we have installed and configured Samba and We have created a System user to share files on network from the account and we have activated our newly created account, too. Now We will move to Samba for the last step of configuring everything, then we will share a folder.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Add new Samba user ####
|
||||
|
||||
Open Samba and click Samba Users under Preference. Fill up the the simple dialogue. Here are couple of details about the fields:
|
||||
|
||||
**Unix Username** – In this case I am selecting the user that I just created.
|
||||
|
||||
**Windows Username** – You will enter this username when you are accessing from Windows Machine.
|
||||
|
||||
**Samba Password** – You will enter this password when you are accessing from Windows Machine.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once you’ve done click OK. Now take a deep breath. You have successfully created a network with the help of Samba. Now restart the network or Samba services and ready to share files with other machines.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo restart smbd && sudo restart nmbd
|
||||
|
||||
#### Share folders or files over the network ####
|
||||
|
||||
To share files with Samba it’s simple with graphical user interface. Click the Plus icon in Samba and you will get dialogue like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
share files and folders over network with sambaComplete the fields. In ‘Directory‘ browse the folder you want to share. Here are the details about the fields you will see here:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Share name** is the name of the folder that other would see.
|
||||
- **Description** is simply about the content you are sharing on network.
|
||||
- **Writable** You shared folders are ‘read only’ by default. You can set them to writable if you want others on network to change them.
|
||||
- **Visible** As the name suggests when you click Visible, the shared folder will be visible to the people on network.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can set permissions for the folder you are sharing. To do this click ‘Access’ tab and check the users you want to share the folder with. When you select Allow access to everyone, the folder will be accessible to everyone on the network.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Finally click OK to complete the sharing. Now the folder is shared with the people you want. You have completed sharing file on network. Is there everything left? Yes! How to remove the folders from the network?
|
||||
|
||||
#### Remove shared folders ####
|
||||
|
||||
We will also need to remove some of the folders after sometime from network. It is very simple and here is how we can do that.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This is all done! We can also share files over network using terminal but that would not be as easy as this one. If you request for command line sharing then I will write a tutorial on how to share files over network with command line in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
So, how do you find this tutorial to share files on local network in Ubuntu? I hope with this tutorial you can **easily share files between Ubuntu and Windows**. If you have questions or suggestions, feel free to ask it in the comment box below.
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial was requested by Kalc. If you would like, you can [request your own tutorial][2]. We would be happy to help you out along with other readers facing the same issue.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/share-folders-local-network-ubuntu-windows/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Mohd Sohail][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/sohail/
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Samba_%28software%29
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/request-tutorial/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user