mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
Translating: How to create a cloud-based encrypted file system on Linux (至L100)
This commit is contained in:
parent
a4883e72a9
commit
f330eb51cc
@ -36,9 +36,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
对于 Arch Linux,使用 [AUR][6]。
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure S3QL for the First Time ###
|
||||
### 首次配置 S3QL ###
|
||||
|
||||
Create authinfo2 file in ~/.s3ql directory, which is a default S3QL configuration file. This file contains information about a required AWS access key, S3 bucket name and encryption passphrase. The encryption passphrase is used to encrypt the randomly-generated master encryption key. This master key is then used to encrypt actual S3QL file system data.
|
||||
在 ~/.s3ql 目录中创建 autoinfo2 文件,它是 S3QL 的一个默认的配置文件。这个文件里的信息包括必须的 AWS access key,S3 bucket 名,以及加密口令。这个加密口令将被用来加密一个随机生成的主密钥,而主密钥将被用来实际地加密 S3QL 文件系统数据。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mkdir ~/.s3ql
|
||||
$ vi ~/.s3ql/authinfo2
|
||||
@ -51,48 +51,48 @@ Create authinfo2 file in ~/.s3ql directory, which is a default S3QL configuratio
|
||||
backend-password: [your-secret-access-key]
|
||||
fs-passphrase: [your-encryption-passphrase]
|
||||
|
||||
The AWS S3 bucket that you specify should be created via AWS management console beforehand.
|
||||
指定的 AWS S3 bucket 需要预先通过 AWS 管理面板来创建。
|
||||
|
||||
Make the authinfo2 file readable to you only for security.
|
||||
为了安全起见,让 authinfo2 文件仅对你可访问。
|
||||
|
||||
$ chmod 600 ~/.s3ql/authinfo2
|
||||
|
||||
### Create an S3QL File System ###
|
||||
### 创建 S3QL 文件系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
You are now ready to create an S3QL file system on top of AWS S3.
|
||||
现在你已经准备好可以在 AWS S3 上创建一个 S3QL 文件系统了。
|
||||
|
||||
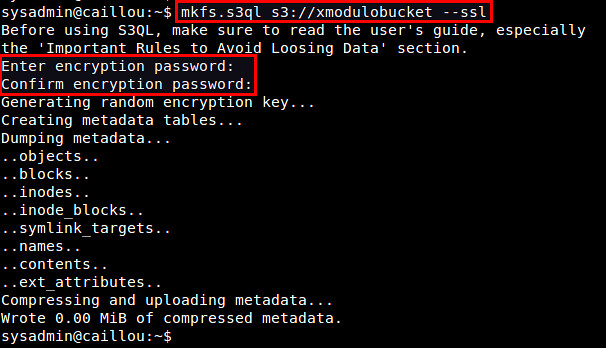
Use mkfs.s3ql command to create a new S3QL file system. The bucket name you supply with the command should be matched with the one in authinfo2 file. The "--ssl" option forces you to use SSL to connect to backend storage servers. By default, the mkfs.s3ql command will enable compression and encryption in the S3QL file system.
|
||||
使用 mkfs.s3ql 工具来创建一个新的 S3QL 文件系统。这个命令中的 bucket 名应该与 authinfo2 文件中所指定的相符。使用“--ssl”参数将强制使用 SSL 连接到后端存储服务器。默认情况下,mkfs.s3ql 命令会在 S3QL 文件系统中启用压缩和加密。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mkfs.s3ql s3://[bucket-name] --ssl
|
||||
|
||||
You will be asked to enter an encryption passphrase. Type the same passphrase as you defined in ~/.s3ql/autoinfo2 (under "fs-passphrase").
|
||||
你会被要求输入一个加密口令。请输入你在 ~/.s3ql/autoinfo2 中通过“fs-passphrase”指定的那个口令。
|
||||
|
||||
If a new file system was created successfully, you will see the following output.
|
||||
如果一个新文件系统被成功创建,你将会看到这样的输出:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Mount an S3QL File System ###
|
||||
### 挂载 S3QL 文件系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once you created an S3QL file system, the next step is to mount it.
|
||||
当你创建了一个 S3QL 文件系统之后,下一步便是要挂载它。
|
||||
|
||||
First, create a local mount point, and then use mount.s3ql command to mount an S3QL file system.
|
||||
首先创建一个本地的挂载点,然后使用 mount.s3ql 命令来挂载 S3QL 文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mkdir ~/mnt_s3ql
|
||||
$ mount.s3ql s3://[bucket-name] ~/mnt_s3ql
|
||||
|
||||
You do not need privileged access to mount an S3QL file system. Just make sure that you have write access to the local mount point.
|
||||
挂载一个 S3QL 文件系统不需要特权用户,只要确定你对该挂载点有写权限即可。
|
||||
|
||||
Optionally, you can specify a compression algorithm to use (e.g., lzma, bzip2, zlib) with "--compress" option. Without it, lzma algorithm is used by default. Note that when you specify a custom compression algorithm, it will apply to newly created data objects, not existing ones.
|
||||
视情况,你可以使用“--compress”参数来指定一个压缩算法(如 lzma、bzip2、zlib)。在不指定的情况下,lzma 将被默认使用。注意如果你指定了一个自定义的压缩算法,它将只会应用到新创建的数据对象上,并不会影响已经存在的数据对象。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mount.s3ql --compress bzip2 s3://[bucket-name] ~/mnt_s3ql
|
||||
|
||||
For performance reason, an S3QL file system maintains a local file cache, which stores recently accessed (partial or full) files. You can customize the file cache size using "--cachesize" and "--max-cache-entries" options.
|
||||
因为性能原因,S3QL 文件系统维护了一份本地文件缓存,里面包括了最近访问的(部分或全部的)文件。你可以通过“--cachesize”和“--max-cache-entries”选项来自定义文件缓存的大小。
|
||||
|
||||
To allow other users than you to access a mounted S3QL file system, use "--allow-other" option.
|
||||
如果想要除你以外的用户访问一个已挂载的 S3QL 文件系统,请使用“--allow-other”选项。
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to export a mounted S3QL file system to other machines over NFS, use "--nfs" option.
|
||||
如果你想通过 NFS 导出已挂载的 S3QL 文件系统到其他机器,请使用“--nfs”选项。
|
||||
|
||||
After running mount.s3ql, check if the S3QL file system is successfully mounted:
|
||||
运行 mount.s3ql 之后,检查 S3QL 文件系统是否被成功挂载了:
|
||||
|
||||
$ df ~/mnt_s3ql
|
||||
$ mount | grep s3ql
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user