** with the **id** “screen”: **
.**
+
+4\. Add the following code after the **** tag or at the end of the document:
+
+```
+
+```
+
+In this, **#screen** is the **id** of **
** in which you want to display the temperature. It loads the **temperature.php** file every 1000 milliseconds.
+
+I have used bootstrap to make a beautiful panel for displaying temperature. You can add multiple icons and glyphicons as well to make it more attractive.
+
+This was just a basic system that controls a relay board and displays the temperature. You can develop it even further by creating event-based triggers based on timings, temperature readings from the thermostat, etc.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+
+作者简介:
+
+Abdul Hannan Mustajab - I'm 17 years old and live in India. I am pursuing an education in science, math, and computer science. I blog about my projects at spunkytechnology.com. I've been working on AI based IoT using different micro controllers and boards .
+
+--------
+
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/17/3/operate-relays-control-gpio-pins-raspberry-pi
+
+作者:[ Abdul Hannan Mustajab][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/mustajabhannan
+[1]:http://www.php.net/system
+[2]:http://www.php.net/system
+[3]:http://www.php.net/system
+[4]:http://www.php.net/system
+[5]:http://www.php.net/system
+[6]:http://www.php.net/file
+[7]:http://www.php.net/explode
+[8]:http://www.php.net/number_format
+[9]:https://opensource.com/article/17/3/operate-relays-control-gpio-pins-raspberry-pi?rate=RX8QqLzmUb_wEeLw0Ee0UYdp1ehVokKZ-JbbJK_Cn5M
+[10]:https://opensource.com/user/123336/feed
+[11]:https://opensource.com/users/mustajabhannan
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170317 Join CentOS 7 Desktop to Samba4 AD as a Domain Member – Part 9.md b/sources/tech/20170317 Join CentOS 7 Desktop to Samba4 AD as a Domain Member – Part 9.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..355ffe2e4c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20170317 Join CentOS 7 Desktop to Samba4 AD as a Domain Member – Part 9.md
@@ -0,0 +1,315 @@
+Join CentOS 7 Desktop to Samba4 AD as a Domain Member – Part 9
+============================================================
+
+by [Matei Cezar][23] | Published: March 17, 2017 | Last Updated: March 17, 2017
+
+ Download Your Free eBooks NOW - [10 Free Linux eBooks for Administrators][24] | [4 Free Shell Scripting eBooks][25]
+
+This guide will describe how you can integrate CentOS 7 Desktop to Samba4 Active Directory Domain Controller with Authconfig-gtk in order to authenticate users across your network infrastructure from a single centralized account database held by Samba.
+
+#### Requirements
+
+1. [Create an Active Directory Infrastructure with Samba4 on Ubuntu][1]
+2. [CentOS 7.3 Installation Guide][2]
+
+### Step 1: Configure CentOS Network for Samba4 AD DC
+
+1. Before starting to join CentOS 7 Desktop to a Samba4 domain you need to assure that the network is properly setup to query domain via DNS service.
+
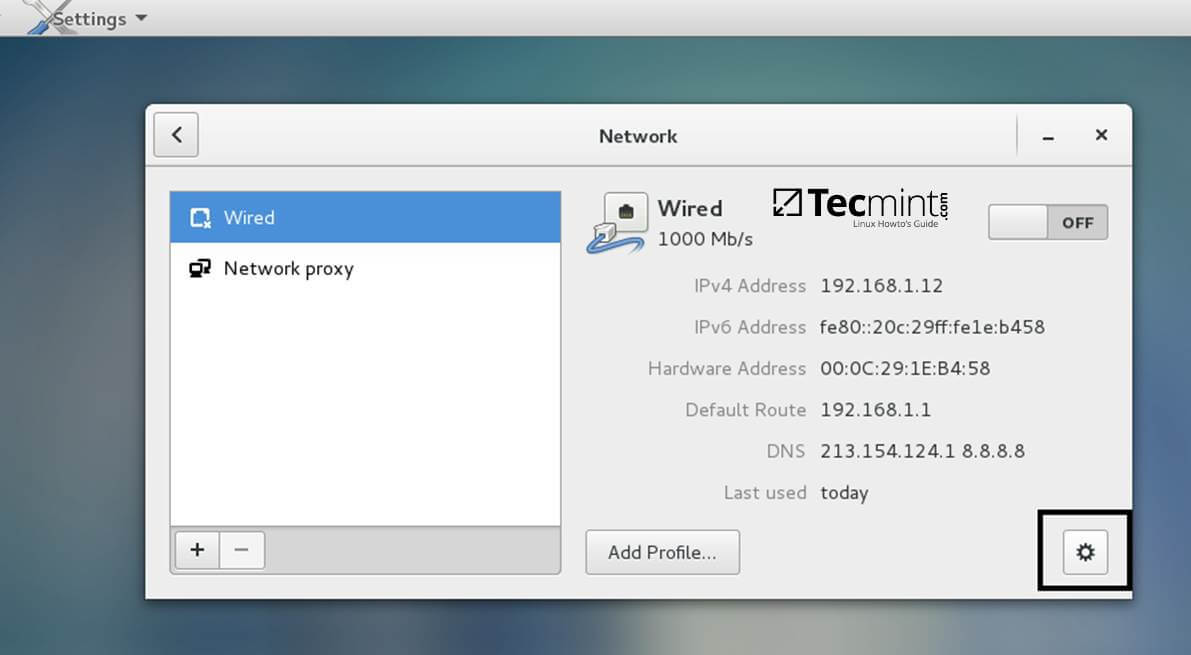
+Open Network Settings and turn off the Wired network interface if enabled. Hit on the lower Settings button as illustrated in the below screenshots and manually edit your network settings, especially the DNS IPs that points to your Samba4 AD DC.
+
+When you finish, Apply the configurations and turn on your Network Wired Card.
+
+[
+ 
+][3]
+
+Network Settings
+
+[
+ 
+][4]
+
+Configure Network
+
+2. Next, open your network interface configuration file and add a line at the end of file with the name of your domain. This line assures that the domain counterpart is automatically appended by DNS resolution (FQDN) when you use only a short name for a domain DNS record.
+
+```
+$ sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eno16777736
+```
+
+Add the following line:
+
+```
+SEARCH="your_domain_name"
+```
+[
+ 
+][5]
+
+Network Interface Configuration
+
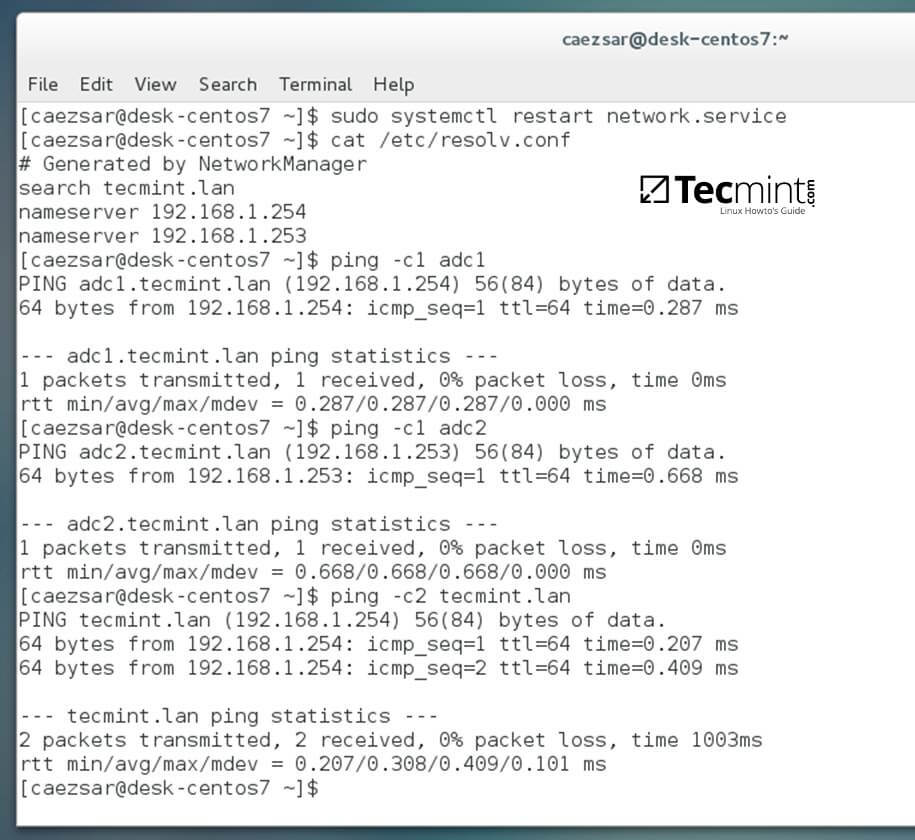
+3. Finally, restart the network services to reflect changes, verify if the resolver configuration file is correctly configured and issue a series of ping commands against your DCs short names and against your domain name in order to verify if DNS resolution is working.
+
+```
+$ sudo systemctl restart network
+$ cat /etc/resolv.conf
+$ ping -c1 adc1
+$ ping -c1 adc2
+$ ping tecmint.lan
+```
+[
+ 
+][6]
+
+Verify Network Configuration
+
+4. Also, configure your machine hostname and reboot the machine to properly apply the settings by issuing the following commands:
+
+```
+$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname your_hostname
+$ sudo init 6
+```
+
+Verify if hostname was correctly applied with the below commands:
+
+```
+$ cat /etc/hostname
+$ hostname
+```
+
+5. The last setting will ensure that your system time is in sync with Samba4 AD DC by issuing the below commands:
+
+```
+$ sudo yum install ntpdate
+$ sudo ntpdate -ud domain.tld
+```
+
+### Step 2: Install Required Software to Join Samba4 AD DC
+
+6. In order to integrate CentOS 7 to an Active Directory domain install the following packages from command line:
+
+```
+$ sudo yum install samba samba samba-winbind krb5-workstation
+```
+
+7. Finally, install the graphical interface software used for domain integration provided by CentOS repos: Authconfig-gtk.
+
+```
+$ sudo yum install authconfig-gtk
+```
+
+### Step 3: Join CentOS 7 Desktop to Samba4 AD DC
+
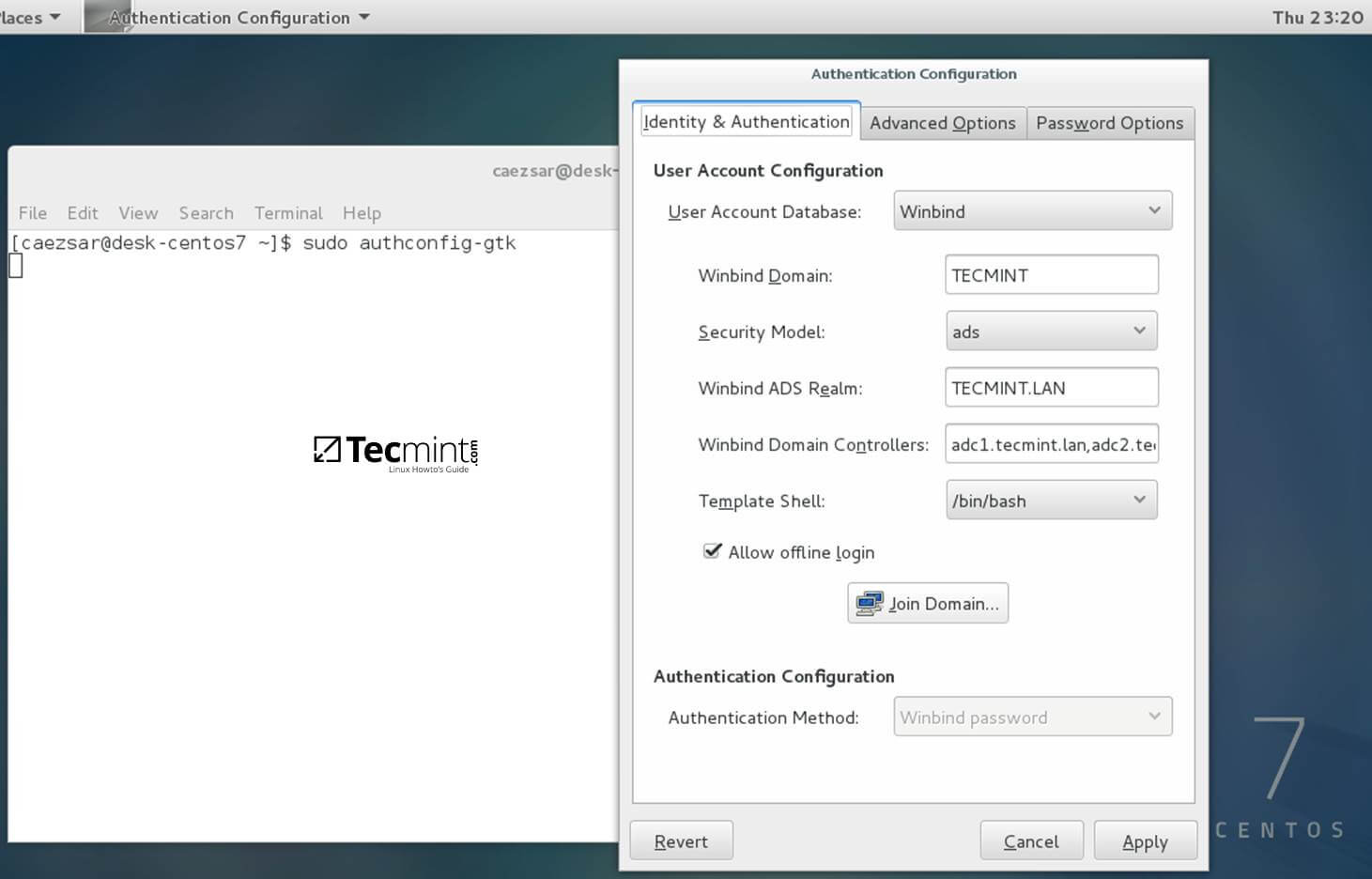
+8. The process of joining CentOS to a domain controller is very straightforward. From command line open Authconfig-gtk program with root privileges and make the following changes as described below:
+
+```
+$ sudo authconfig-gtk
+```
+
+On Identity & Authentication tab.
+
+* User Account Database = select Winbind
+* Winbind Domain = YOUR_DOMAIN
+* Security Model = ADS
+* Winbind ADS Realm = YOUR_DOMAIN.TLD
+* Domain Controllers = domain machines FQDN
+* Template Shell = /bin/bash
+* Allow offline login = checked
+
+[
+ 
+][7]
+
+Authentication Configuration
+
+On Advanced Options tab.
+
+* Local Authentication Options = check Enable fingerprint reader support
+* Other Authentication Options = check Create home directories on the first login
+
+[
+ 
+][8]
+
+Authentication Advance Configuration
+
+9. After you’ve added all required values, return to Identity & Authentication tab and hit on Join Domain button and the Save button from alert window to save settings.
+
+[
+ 
+][9]
+
+Identity and Authentication
+
+[
+ 
+][10]
+
+Save Authentication Configuration
+
+10. After the configuration has been saved you will be asked to provide a domain administrator account in order to join the domain. Supply the credentials for a domain administrator user and hit OK button to finally join the domain.
+
+[
+ 
+][11]
+
+Joining Winbind Domain
+
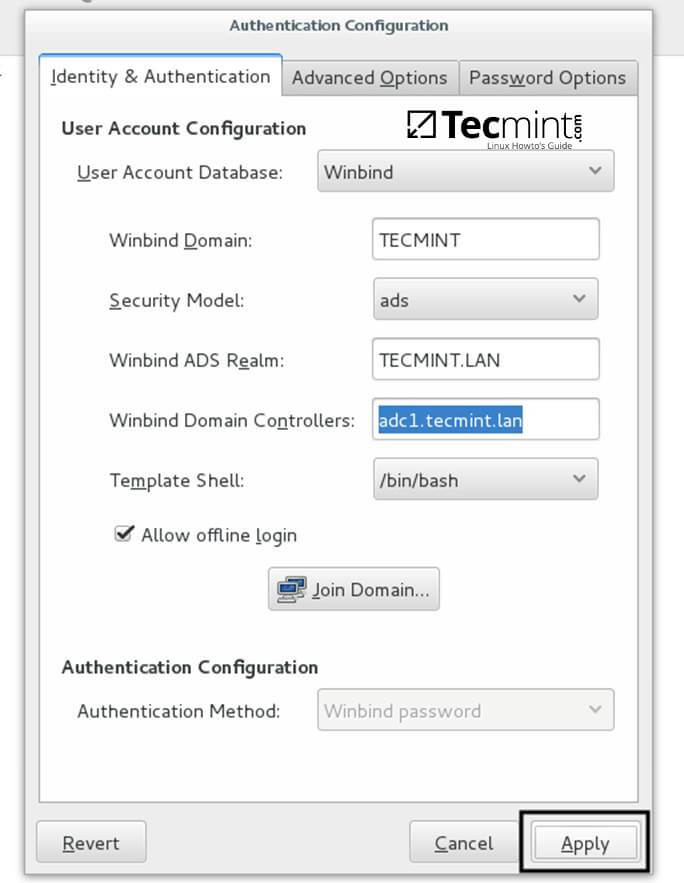
+11. After your machine has been integrated into the realm, hit on Apply button to reflect changes, close all windows and reboot the machine.
+
+[
+ 
+][12]
+
+Apply Authentication Configuration
+
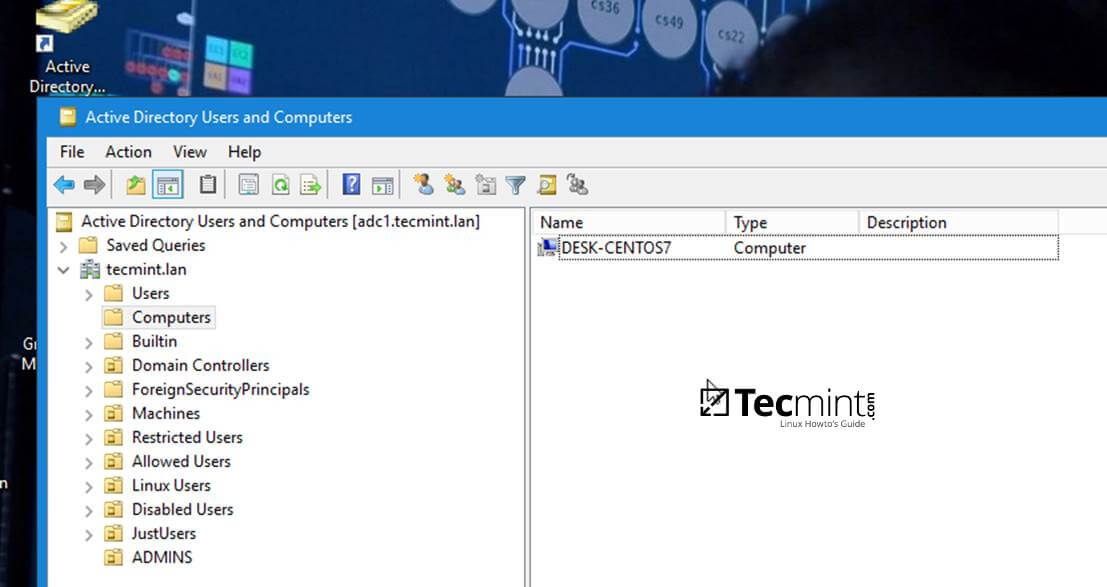
+12. In order to verify if the system has been joined to Samba4 AD DC open AD Users and Computers from a Windows machine with [RSAT tools installed][13] and navigate to your domain Computers container.
+
+The name of your CentOS machine should be listed on the right plane.
+
+[
+ 
+][14]
+
+Active Directory Users and Computers
+
+### Step 4: Login to CentOS Desktop with a Samba4 AD DC Account
+
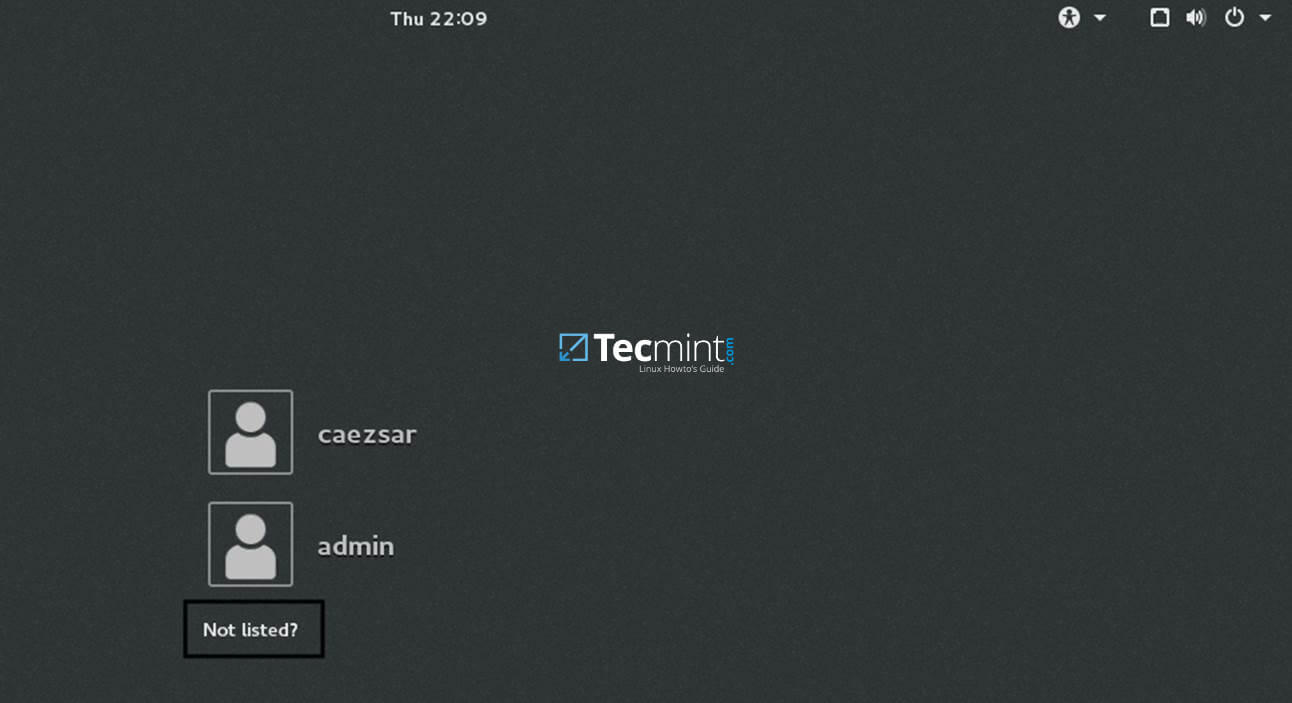
+13. In order to login to CentOS Desktop hit on Not listed? link and add the username of a domain account preceded by the domain counterpart as illustrated below.
+
+```
+Domain\domain_account
+or
+Domain_user@domain.tld
+```
+[
+ 
+][15]
+
+Not listed Users
+
+[
+ 
+][16]
+
+Enter Domain Username
+
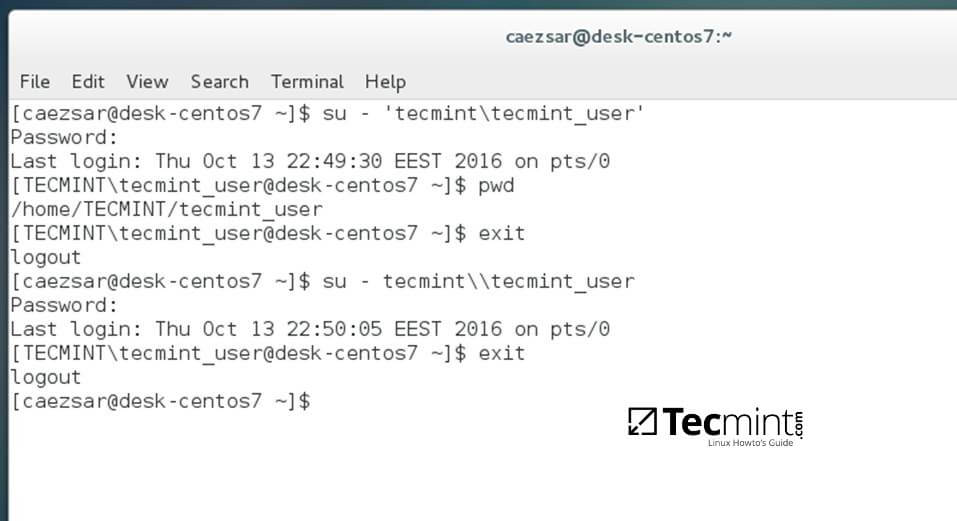
+14. To authenticate with a domain account from command line in CentOS use one of the following syntaxes:
+
+```
+$ su - domain\domain_user
+$ su - domain_user@domain.tld
+```
+[
+ 
+][17]
+
+Authenticate Domain Username
+
+[
+ 
+][18]
+
+Authenticate Domain User Email
+
+15. To add root privileges for a domain user or group, edit sudoers file using visudo command with root powers and add the following lines as illustrated on the below excerpt:
+
+```
+YOUR_DOMAIN\\domain_username ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL #For domain users
+%YOUR_DOMAIN\\your_domain\ group ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL #For domain groups
+```
+[
+ 
+][19]
+
+Assign Permission to User and Group
+
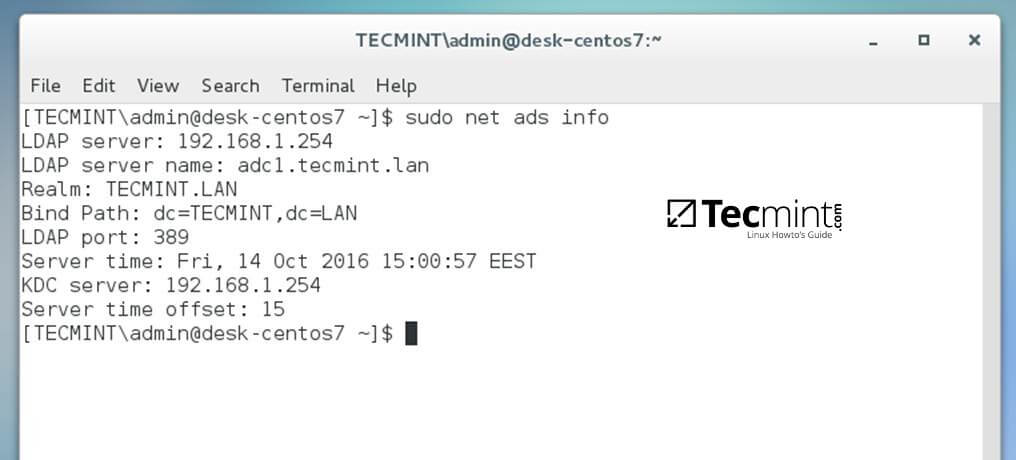
+16. To display a summary about the domain controller use the following command:
+
+```
+$ sudo net ads info
+```
+[
+ 
+][20]
+
+Check Domain Controller Info
+
+17. In order to verify if the trust machine account created when CentOS was added to the Samba4 AD DC is functional and list domain accounts from command line install Winbind client by issuing the below command:
+
+```
+$ sudo yum install samba-winbind-clients
+```
+
+Then issue a series of checks against Samba4 AD DC by executing the following commands:
+
+```
+$ wbinfo -p #Ping domain
+$ wbinfo -t #Check trust relationship
+$ wbinfo -u #List domain users
+$ wbinfo -g #List domain groups
+$ wbinfo -n domain_account #Get the SID of a domain account
+```
+[
+ 
+][21]
+
+Get Samba4 AD DC Details
+
+18. In case you want to leave the domain issue the following command against your domain name by using an domain account with administrator privileges:
+
+```
+$ sudo net ads leave your_domain -U domain_admin_username
+```
+[
+ 
+][22]
+
+Leave Domain from Samba4 AD
+
+That’s all! Although this procedure is focused on joining CentOS 7 to a Samba4 AD DC, the same steps described in this documentation are also valid for integrating a CentOS 7 Desktop machine to a Microsoft Windows Server 2008 or 2012 domain.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+作者简介:
+
+I'am a computer addicted guy, a fan of open source and linux based system software, have about 4 years experience with Linux distributions desktop, servers and bash scripting.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/join-centos-7-to-samba4-active-directory/
+
+作者:[Matei Cezar][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
+
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-samba4-active-directory-ubuntu/
+[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/centos-7-3-installation-guide/
+[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Network-Settings.jpg
+[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Configure-Network.jpg
+[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Network-Interface-Configuration.jpg
+[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Verify-Network-Configuration.jpg
+[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Authentication-Configuration.jpg
+[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Authentication-Advance-Configuration.jpg
+[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Identity-and-Authentication.jpg
+[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Save-Authentication-Configuration.jpg
+[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Joining-Winbind-Domain.jpg
+[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Apply-Authentication-Configuration.jpg
+[13]:http://www.tecmint.com/manage-samba4-ad-from-windows-via-rsat/
+[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Active-Directory-Users-and-Computers.jpg
+[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Not-listed-Users.jpg
+[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Enter-Domain-Username.jpg
+[17]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Authenticate-Domain-User.jpg
+[18]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Authenticate-Domain-User-Email.jpg
+[19]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Assign-Permission-to-User-and-Group.jpg
+[20]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Check-Domain-Controller-Info.jpg
+[21]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Get-Samba4-AD-DC-Details.jpg
+[22]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Leave-Domain-from-Samba4-AD.jpg
+[23]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
+[24]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
+[25]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170317 Kgif – A Simple Shell Script to Create a Gif File from Active Window.md b/sources/tech/20170317 Kgif – A Simple Shell Script to Create a Gif File from Active Window.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0a89669a5e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20170317 Kgif – A Simple Shell Script to Create a Gif File from Active Window.md
@@ -0,0 +1,153 @@
+Kgif – A Simple Shell Script to Create a Gif File from Active Window
+============================================================
+
+[Kgif][2] is a simple shell script which create a Gif file from active window. I felt this app especially designed to capture the terminal activity. I personally used, very often for that purpose.
+
+It captures activity as a series of PNG images, then combines all together to create a animated GIF. The script taking a screenshot of the active window at 0.5s intervals. If you feel, its not matching your requirement, straight away you can modify the script as per your need.
+
+Originally it was created for capturing tty output and creating preview for github projects.
+
+Make sure you have installed scrot and ImageMagick packages before running Kgif.
+
+Suggested Read : [Peek – Create a Animated GIF Recorder in Linux][3]
+
+What’s ImageMagick ImageMagick is a command line tool which used for image conversion and editing. It support all kind of image formats (over 200) such as PNG, JPEG, JPEG-2000, GIF, TIFF, DPX, EXR, WebP, Postscript, PDF, and SVG.
+
+What’s Scrot Scrot stand for SCReenshOT is an open source, command line tool to capture a screen shots of your Desktop, Terminal or a Specific Window.
+
+#### Install Dependencies
+
+Kgif required scrot and ImageMagick to work.
+
+For Debian based Systems
+
+```
+$ sudo apt-get install scrot imagemagick
+```
+
+For RHEL/CentOS based Systems
+
+```
+$ sudo yum install scrot ImageMagick
+```
+
+For Fedora Systems
+
+```
+$ sudo dnf install scrot ImageMagick
+```
+
+For openSUSE Systems
+
+```
+$ sudo zypper install scrot ImageMagick
+```
+
+For Arch Linux based Systems
+
+```
+$ sudo pacman -S scrot ImageMagick
+```
+
+#### Install Kgif & Usage
+
+Installation of Kgif not a big deal because no installation required. Just clone the source file from developer github page wherever you want and run the `kgif.sh` file to capture the active window. By default, it’s sets delay to 1 sec, you can modify this by including `--delay` option with kgif. Finally press `Ctrl+c` to stop capturing.
+
+```
+$ git clone https://github.com/luminousmen/Kgif
+$ cd Kgif
+$ ./kgif.sh
+Setting delay to 1 sec
+
+Capturing...
+^C
+Stop capturing
+Converting to gif...
+Cleaning...
+Done!
+```
+
+Check whether dependencies are presents in system.
+
+```
+$ ./kgif.sh --check
+OK: found scrot
+OK: found imagemagick
+```
+
+Set delay in seconds with script to start capturing, after N seconds.
+
+```
+$ ./kgif.sh --delay=5
+
+Setting delay to 5 sec
+
+Capturing...
+^C
+Stop capturing
+Converting to gif...
+Cleaning...
+Done!
+```
+
+It save the gif file name as a `terminal.gif` and overwrite every time whenever get a new file. So, i advise you to add `--filename`option to save the file in a different name.
+
+```
+$ ./kgif.sh --delay=5 --filename=2g-test.gif
+
+Setting delay to 5 sec
+
+Capturing...
+^C
+Stop capturing
+Converting to gif...
+Cleaning...
+Done!
+```
+
+Set noclean with script to keep the source png screen shots.
+
+```
+$ ./kgif.sh --delay=5 --noclean
+```
+
+To know more all the options.
+
+```
+$ ./kgif.sh --help
+
+usage: ./kgif.sh [--delay] [--filename ] [--gifdelay] [--noclean] [--check] [-h]
+ -h, --help Show this help, exit
+ --check Check if all dependencies are installed, exit
+ --delay= Set delay in seconds to specify how long script will wait until start capturing.
+ --gifdelay= Set delay in seconds to specify how fast images appears in gif.
+ --filename= Set file name for output gif.
+ --noclean Set if you don't want to delete source *.png screenshots.
+```
+
+Default capturing output.
+[
+ 
+][4]
+
+I felt, the default capturing is very fast, then i made few changes and got the proper output.
+[
+ 
+][5]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.2daygeek.com/kgif-create-animated-gif-file-active-window-screen-recorder-capture-arch-linux-mint-fedora-ubuntu-debian-opensuse-centos/
+
+作者:[MAGESH MARUTHAMUTHU][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/
+[1]:http://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/
+[2]:https://github.com/luminousmen/Kgif
+[3]:http://www.2daygeek.com/kgif-create-animated-gif-file-active-window-screen-recorder-capture-arch-linux-mint-fedora-ubuntu-debian-opensuse-centos/www.2daygeek.com/peek-create-animated-gif-screen-recorder-capture-arch-linux-mint-fedora-ubuntu/
+[4]:http://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/kgif-test.gif
+[5]:http://www.2daygeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/kgif-test-delay-modified.gif
diff --git a/sources/tech/20170317 The End of the Line for EPEL-5.md b/sources/tech/20170317 The End of the Line for EPEL-5.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b64729bb6c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20170317 The End of the Line for EPEL-5.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+# [The End of the Line for EPEL-5][1]
+
+
+ 
+
+For the last 10 years, the Fedora Project has been building packages for the same release of another operating system. **However on March 31st, 2017, that will come to an end** when Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) version 5 moves out of production.
+
+### A Short History of EPEL
+
+RHEL is a downstream rebuild of a subset of Fedora releases that Red Hat feels it can adequetely support over a multi-year lifetime. While these packages make for a full operating system, there have always been a need by system administrators for ‘more’ packages. Before RHEL-5, many of these packages would be built and supplied by various rebuilders. With Fedora Extras growing to include many of the packages, and several of the rebuilders having joined Fedora, there was an idea of combining forces and creating a dedicated sub-project who would rebuild Fedora packages with specific RHEL releases and then distribute them from Fedora’s centralized servers.
+
+After much debate and a failure to come up with a catchy name, the Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (or EPEL) sub-project of Fedora was created. While at first rebuilding packages for RHEL-4, the main goal was to have as many packages available for RHEL-5 when it arrived. It took a lot of hard work getting the plague builders in place, but most of the work was in crafting the rules and guidelines that EPEL would use for the next 10 years. [As anyone can see from the old mail archives][2], the debates were fierce from both various Fedora contributors feeling this took away focus from moving Fedora releases forward to outside contributors worried about conflicts with existing installed packages.
+
+In the end, EPEL-5 went live sometime in April of 2007 and over the next 10 years grew to a repository of over 5000 source packages and 200,000 unique ip addresses checking in per day at its peak of 240,000 in early 2013\. While every package built for EPEL is done with the RHEL packages, all of these packages have been useful for the various community rebuilds (CentOS, Scientific Linux, Amazon Linux) of RHEL. This meant that growth in those eco-systems brought more users into using EPEL and helping on packaging as later RHEL releases came out. However as these newer releases and rebuilds grew in usage, the number of EPEL-5 users has gradually fallen to around 160,000 unique ip addresses per day. Also over that time, the number of packages supported by developers has fallen and the repository has shrunk in size to 2000 source packages.<>
+
+Part of the shrinkage was due to the original rules put in place back in 2007\. At that time, Red Hat Enterprise Linux releases were only thought to have an active life time of 6 years before being end of lifed. It was thought that for such a ‘limited’ lifetime, packages could be ‘frozen’ in EPEL like they were in the RHEL release. This meant that whenever possible fixes should be backported and major changes would not be allowed. Time and packaging stands still for no human, and packages would be continually pruned from EPEL-5 as packagers no longer wanted to try and backport fixes. While various rules were loosened to allow for larger changes in packages, the packaging rules that Fedora used have continually moved and improved from 2007\. This has made trying to rebuild a package from newer releases harder and harder with the older operating systems.
+
+### What Happens on March 31st 2017
+
+As stated before, on March 31st Red Hat will end of life and no longer put updates out for RHEL-5 for regular customers. This means that
+Fedora and the various rebuild distributors will start various archive processes. For the EPEL project this means that we will follow the steps that happen every year with Fedora releases.
+
+1. On **March 27th**, no new builds will be allowed to be pushed for EPEL-5 so that the repository is essentially frozen. This will allow mirrors to have a clear tree of all files.
+2. All packages in EPEL-5 will be hardlinked on the master mirror from `/pub/epel/5/` and `/pub/epel/testing/5/` to `/pub/archives/epel/`. **This will start happening on the 27th** so all mirrors of archives can populate their disks.
+3. Because March 31st happens on a Friday, and system administrators do not like Friday surprises, there will be no change then. On **April 3rd**, mirrormanager will be updated to point to the archives.
+4. On **April 6th**, the /pub/epel/5/ trees will be removed and mirrors will update accordingly.
+
+For a system administrator who has cron jobs which do yum updates, there should be minimal hassle. The systems will continue to update and even install any packages which were in the archives at that time. There will be breakage for system administrators who have scripts which directly download files from mirrors. Those scripts will need to change to the new canonical location of /pub/archive/epel/5/.
+
+While irksome, this is a blessing in disguise for many system administrators who will still be using an older Linux. Because packages have been regularly removed from EPEL-5, the various support mailing lists and irc channels have regular requests from system administrators wondering where some package they needed has gone. After the archive is done, this won’t be a problem because no more packages will be removed :).
+
+For system administrators who have been hit by this problem, the older EPEL packages are still available though in a much slower method. All EPEL packages are built in the Fedora Koji system, and so older builds of packages can be found using [Koji search.][3]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://fedoramagazine.org/the-end-of-the-line-for-epel-5/
+
+作者:[smooge][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://smooge.id.fedoraproject.org/
+[1]:https://fedoramagazine.org/the-end-of-the-line-for-epel-5/
+[2]:https://www.redhat.com/archives/epel-devel-list/2007-March/thread.html
+[3]:https://koji.fedoraproject.org/koji/search
diff --git a/translated/comic/20170314 6 The Depressed Developer series.md b/translated/comic/20170314 6 The Depressed Developer series.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 0b4ee74e89..0000000000
--- a/translated/comic/20170314 6 The Depressed Developer series.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
-消沉的程序员系列漫画
-=========================
-### 消沉的程序员 1
-
-
-
-很有意思吧,很多看到这样的漫画对话的程序员,应该感觉似曾相识吧。Bug 出现了?
-
-### 消沉的程序员 2
-
-
-
-有点疑惑,有好像有点眉目,好像是感觉到哪里错了,是不是要重构。
-
-### 消沉的程序员 3
-
-
-
-哎,终于发现错误了,感觉有点可笑,自己居然犯这样的错误,原来是那次急于提交代码造成的。
-
-### 消沉的程序员 4
-
-
-
-是啊,在编程里一生戎马,代码编写无数,各种平台、规范等等,到头来也是满身的错误啊。该是技术不行吧!
-
-### 消沉的程序员 5
-
-
-
-呀,快要消除错误了,可是,不对。相信事后的 Bug 和 Debug 会是程序员生活中的一个部分。
-
-### 消沉的程序员 6
-
-
-
-每个新建的工程都是有美好的设想吧,可后来为什么总是渐行渐远?大多时候的自言自语,总是是有人认为是在和代码对话吧?可没有身在其中,别人有这么懂得!
-
-### 消沉的程序员 7
-
-
-
-好吧,产品的上线,总是要经过无数次的创建分支,Bug 和 Debug 总还是程序员的永恒话题。其中,有些东西总免不了自己推翻自己,感觉要从头再来一样。
-
-### 消沉的程序员 10
-
-
-
-为了某项专门的研究,学习一门相关的语言,不知道是不是值得?是不是先要思考其必要性呢?最后发现自己并不喜欢这么语言,导致怀疑自己的专业技能,这样大概不好吧!
-
-### 消沉的程序员 11
-
-
-
-其实,本来是愉快的蹲个坑,却不自觉的陷入编码的思考。想想,不仅是程序员,很多人有都有类似此景的情况吧,明明在做着某事,却想着另外一件事。
-
-### 后记
-
-看至此处,各位朋友是不是感觉少了系列的第 8 和第 9 篇?起初,译者也这么想,后来问了作者 Daniel Stori 之后,才恍然,原来序号采用了八进制,按照作者说的,一个隐式的玩笑。明白了吗,朋友们?
-
-大伙儿都习惯了日常的十进制。当常态处于优先级的时候,日常一些非常态就如同细枝末节,也就往往容易被人们忽略。大概就是这样吧。
-
--------------------------------
-
-译者简介:
-
-[GHLandy](http://GHLandy.com) —— 生活中所有欢乐与苦闷都应藏在心中,有些事儿注定无人知晓,自己也无从说起。
-
--------------------------------
-
-via:
-- http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer/
-- http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-2/
-- http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-3/
-- http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-4/
-- http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-5/
-- http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-6/
-- http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-7/
-- http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-10/
-- http://turnoff.us/geek/the-depressed-developer-11/
-
-作者:[Daniel Stori][a]
-译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://turnoff.us/about/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20131113 Your visual how-to guide for SELinux policy enforcement.md b/translated/tech/20131113 Your visual how-to guide for SELinux policy enforcement.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b0fe7bbb01
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20131113 Your visual how-to guide for SELinux policy enforcement.md
@@ -0,0 +1,186 @@
+
+看漫画学 SELinux 强制策略
+============================================================
+
+ 
+>图像来自: opensource.com
+
+今年是我们一起庆祝 SELinux 纪念日的第十个年头了。真是太难以置信了!SELinux 最初在 Fedora Core 3 中被引入,随后加入了红帽企业版 Linux 4。从来没有使用过 SELinux 的家伙,你可要好好儿找个理由了……
+
+更多的 Linux 资源
+
+* [Linux 是什么?][1]
+* [Linux 容器是什么?][2]
+* [在 Linux 中操作设备][3]
+* [立刻下载: Linux 命令小抄][4]
+* [我们最新的 Linux 文章][5]
+
+SElinux 是一个标签型系统。每一个进程都有一个标签。操作系统中的每一个文件/目录客体都有一个标签。甚至连网络端口、设备和潜在的主机名称都被分配了标签。我们把控制访问进程标签的规则写入一个类似文件的客体标签中。我们称之为_策略_。内核加强了这些规则。有时候这种加强被称为强制访问控制体系 (MAC)。
+
+一个客体的拥有者在客体的安全属性下没有自主权。标准 Linux 访问控制体系,拥有者/分组 + 权限标志如 rwx,常常被称作自主访问控制(DAC)。SELinux 没有文件 UID 或 拥有权的概念。一切都被标签控制。意味着配置一个 SELinux 系统可以没有一个功能强大的根进程。
+
+**注意:** _SELinux不允许你摒弃 DAC 控制。SELinux 是一个并行的强制模型。一个应用必须同时支持 SELinux 和 DAC 来完成特定的行为。这可能会导致管理员迷惑为什么进程返回拒绝访问。管理员看到拒绝访问是因为 DAC 出了问题,而不是 SELinux标签。
+
+### 类型强制
+
+让我们更深入的研究下标签。SELinux 最主要的模型或强制叫做_类型强制_。基本上这意味着我们通过一个进程的类型来定义它的标签,通过文件系统客体的类型来定义它的标签。
+
+_打个比方_
+
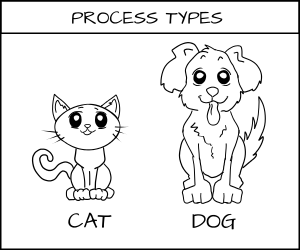
+想象一下在一个系统里定义客体的类型为猫和狗。猫(CAT)和狗(DOG)都是进程类型(PROCESS TYPES)。
+
+_*所有的漫画都来自 [Máirín Duffy][6]_
+
+ 
+
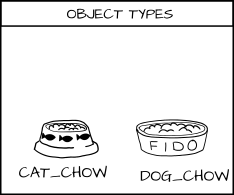
+我们有一类客体希望能够和我们称之为食物的东西交互。而我希望能够为食物增加类型:_cat_food_ (猫粮)和 _dog_food_(狗粮)。
+
+ 
+
+作为一个策略制定者,我可以说一只狗有权限去吃狗粮(DOG_CHOW),而一只猫有权限去吃猫粮(CAT_CHOW)。在 SELinux 中我可以将这条规则写入策略中。
+
+ 
+
+allow cat cat_chow:food eat;
+
+允许 猫 猫粮 吃;
+
+allow dog dog_chow:food eat;
+
+允许 狗 狗粮 吃;
+
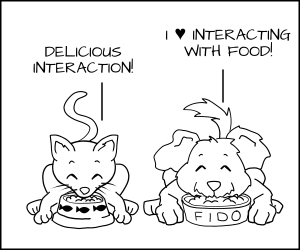
+有了这些规则,内核会允许猫进程去吃打上猫粮标签 _cat_chow_ 的食物,允许狗去吃打上狗粮标签 _dog_chow_ 的食物。
+
+ 
+
+但是在 SELinux 系统中,一切都是默认被禁止的。这意味着,如果狗进程想要去吃猫粮 _cat_chow_,内核会阻止它。
+
+ 
+
+同理,猫也不允许去接触狗粮。
+
+ 
+
+_现实例子_
+
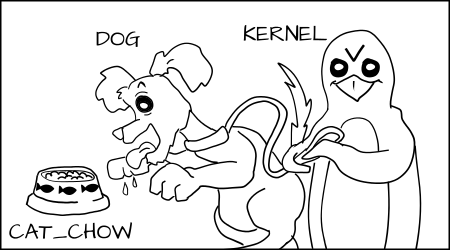
+我们将 Apache 进程标为 _httpd_t_,将 Apache 上下文标为 _httpd_sys_content_t_ 和 _httpdsys_content_rw_t_。想象一下我们把信用卡数据存储在 mySQL 数据库中,其标签为 _msyqld_data_t_。如果一个 Apache 进程被劫持,黑客可以获得 _httpd_t_ 进程的控制权而且允许去读取 _httpd_sys_content_t_ 文件并向 _httpd_sys_content_rw_t_ 执行写操作。但是黑客却不允许去读信用卡数据(_mysqld_data_t_),即使 Apache 进程是在 root 下运行。在这种情况下 SELinux 减轻了这次闯入的后果。
+
+
+
+### 多类别安全强制
+
+_打个比方_
+
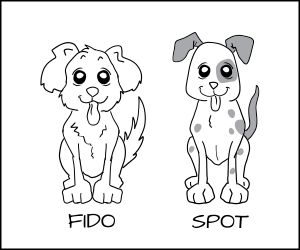
+上面我们定义了狗进程和猫进程,但是如果你有多个狗进程:Fido 和 Spot,而你想要阻止 Fido 去吃 Spot 的狗粮 _dog_chow_ 怎么办呢?
+
+ 
+
+一个解决方式是创建大量的新类型,如 _Fido_dog_ 和 _Fido_dog_chow_。但是这很快会变得难以驾驭因为所有的狗都有差不多相同的权限。
+
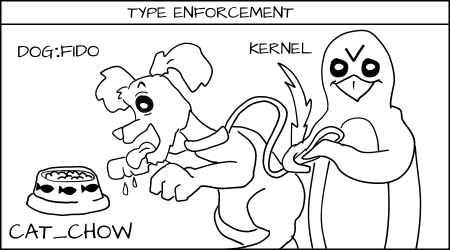
+为了解决这个问题我们发明了一种新的强制形式,叫做多类别安全(MCS)。在 MCS 中,我们在狗进程和狗粮的标签上增加了另外一部分标签。现在我们将狗进程标记为 _dog:random1(Fido)_ 和 _dog:random2(Spot)_。
+
+ 
+
+我们将狗粮标记为_dog_chow:random1(Fido)_ 和 _dog_chow:random2(Spot)_。
+
+ 
+
+MCS 规则声明如果类型强制规则被遵守而且随机 MCS 标签正确匹配,则访问是允许的,否则就会被拒绝。
+
+Fido (dog:random1) 尝试去吃 _cat_chow:food_ 被类型强制拒绝了。
+
+ 
+
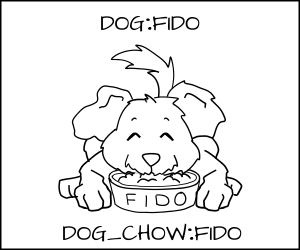
+Fido (dog:random1) 允许去吃 _dog_chow:random1._
+
+ 
+
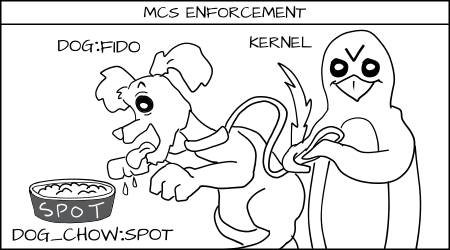
+Fido (dog:random1) 去吃 spot( _dog_chow:random2_ )的食物被拒绝.
+
+ 
+
+_现实例子_
+
+在计算机系统中我们经常有很多具有同样访问权限的进程,但是我们又希望它们各自独立。有时我们称之为_多租户环境_。最好的例子就是虚拟机。如果我有一个运行很多虚拟机的服务器,而其中一个被劫持,我希望能能够阻止它去攻击其它虚拟机和虚拟机镜像。但是在一个类型强制系统中 KVM 虚拟机被标记为 _svirt_t_ 而镜像被标记为 _svirt_image_t_。 我们有权限允许 _svirt_t_ 可以读/写/删除标记为 _svirt_image_t_ 的上下文。通过使用 libvirt 我们不仅实现了类型强制隔离,而且实现了 MCS 隔离。当 libvirt 将要启动一个虚拟机,它会挑选出一个随机 MCS 标签如 _s0:c1,c2_,接着它会将 _svirt_image_t:s0:c1,c2_ 标签分发给虚拟机需要去操作的所有上下文。最终,虚拟机以 _svirt_t:s0:c1,c2_ 为标签启动。因此,SELinux 内核控制 _svirt_t:s0:c1,c2_ 不允许写向 _svirt_image_t:s0:c3,c4_,即使虚拟机被一个黑客劫持并接管。即使它是运行在 root 下。
+
+我们在 OpenShift 中使用[类似的隔离策略][8]。每一个 gear(user/app process)都有相同的 SELinux 类型(openshift_t)(译者注:gear 为 OpenShift 的计量单位)。策略定义的规则控制着 gear 类型的访问权限,而一个独一无二的 MCS 标签确保了一个 gear 不能影响其他 gear。
+
+请观看[这个短视频][9]来看 OpenShift gear 切换到 root 会发生什么。
+
+### MLS enforcement
+
+多级别安全强制
+
+另外一种不经常使用的 SELinux 强制形式叫做 多级别安全(MLS);它于 60 年代被开发并且主要使用在受信的操作系统上如 Trusted Solaris。
+
+核心观点就是通过进程使用的数据等级来控制进程。一个 _secret_ 进程不能读取 _top secret_ 数据。
+
+MLS 很像 MCS,除了它在强制策略中增加了支配概念。MCS 标签必须完全匹配,但 一个 MLS 标签可以支配另一个 MLS 标签并且获得访问。
+
+_打个比方_
+
+不讨论不同名字的狗,我们现在来看不同种类。我们现在有一只灰狗和一只吉娃娃。
+
+ 
+
+我们可能想要允许灰狗去吃任何狗粮,但是吉娃娃如果尝试去吃灰狗的狗粮可能会被呛到。
+
+我们把灰狗标记为 _dog:Greyhound_,把它的狗粮标记为 _dog_chow:Greyhound_,把吉娃娃标记为 _dog:Chihuahua_,把它的狗粮标记为 _dog_chow:Chihuahua_。
+
+ 
+
+使用 MLS 策略,我们可以使 MLS 灰狗标签支配吉娃娃标签。这意味着 _dog:Greyhound_ 允许去吃 _dog_chow:Greyhound_ 和 _dog_chow:Chihuahua_ 。
+
+ 
+
+但是 _dog:Chihuahua_ 不允许去吃 _dog_chow:Greyhound_。
+
+ 
+
+当然,由于类型强制, _dog:Greyhound_ 和 _dog:Chihuahua_ 仍然不允许去吃 _cat_chow:Siamese_,即使 MLS 类型 GreyHound 支配 Siamese。
+
+ 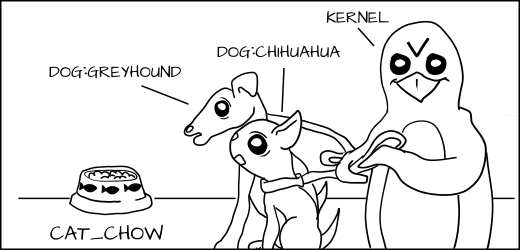
+
+_现实例子_
+
+有两个 Apache 服务器:一个以 _httpd_t:TopSecret_ 运行,一个以 _httpd_t:Secret_ 运行。如果 Apache 进程 _httpd_t:Secret_ 被劫持,黑客可以读取 _httpd_sys_content_t:Secret_ 但会被禁止读取 _httpd_sys_content_t:TopSecret_。
+
+但是如果运行 _httpd_t:TopSecret_ 的 Apache 进程被劫持,它可以读取 _httpd_sys_content_t:Secret_ 数据和 _httpd_sys_content_t:TopSecret_ 数据。
+
+我们在军事系统上使用 MLS,一个用户可能被允许读取 _secret_ 数据,但是另一个用户在同一个系统上可以读取 _top secret_ 数据。
+
+
+
+### 结论
+
+SELinux 是一个功能强大的标签系统,控制内核授予每个进程的访问权限。最主要的特性是类型强制,策略规则定义的进程访问权限基于进程被标记的类型和客体被标记的类型。另外两个控制手段也被引入,来独立有着同样类型进程的叫做 MCS,可以完全独立每个进程,而MLS,允许进程间存在支配等级。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+作者简介:
+
+Daniel J Walsh - Daniel Walsh 已经在计算机安全领域工作了将近 30 年。Daniel 与 2001 年 8 月加入红帽。
+
+-------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/business/13/11/selinux-policy-guide
+
+作者:[Daniel J Walsh ][a]
+译者:[xiaow6](https://github.com/xiaow6)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/rhatdan
+[1]:https://opensource.com/resources/what-is-linux?src=linux_resource_menu
+[2]:https://opensource.com/resources/what-are-linux-containers?src=linux_resource_menu
+[3]:https://opensource.com/article/16/11/managing-devices-linux?src=linux_resource_menu
+[4]:https://developers.redhat.com/promotions/linux-cheatsheet/?intcmp=7016000000127cYAAQ
+[5]:https://opensource.com/tags/linux?src=linux_resource_menu
+[6]:https://opensource.com/users/mairin
+[7]:https://opensource.com/business/13/11/selinux-policy-guide?rate=XNCbBUJpG2rjpCoRumnDzQw-VsLWBEh-9G2hdHyB31I
+[8]:http://people.fedoraproject.org/~dwalsh/SELinux/Presentations/openshift_selinux.ogv
+[9]:http://people.fedoraproject.org/~dwalsh/SELinux/Presentations/openshift_selinux.ogv
+[10]:https://opensource.com/user/16673/feed
+[11]:https://opensource.com/business/13/11/selinux-policy-guide#comments
+[12]:https://opensource.com/users/rhatdan
diff --git a/translated/tech/20170107 Min Browser Muffles the Web Noise.md b/translated/tech/20170107 Min Browser Muffles the Web Noise.md
index 843c3e9f10..81e85b2d97 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20170107 Min Browser Muffles the Web Noise.md
+++ b/translated/tech/20170107 Min Browser Muffles the Web Noise.md
@@ -2,110 +2,110 @@
============================================================

-[Min][1] 是一款具有最小设计的 web 浏览器,可以通过简单的功能提供快速操作。
+[Min][1] 是一款精简设计的 web 浏览器,功能简便,响应迅速。
-当涉及到软件设计时,“最小”并不意味着潜在的低级功能或未开发。如果你喜欢文本编辑器和笔记程序中的最小防干扰工具,那么你会在 Min 浏览器中有同样舒适的感觉。
+在软件设计中,“简单”并不意味着功能低级、有待改进。你如果喜欢花哨工具比较少的文本编辑器和笔记程序,那么在 Min 浏览器中会有同样舒适的感觉。
-我大多在我的台式机和笔记本电脑上使用 Google Chrome、Chromium和 Firefox。我研究了很多它们的附加功能,所以我可以在我的长期研究和工作中可以访问所有的专业服务。
+我经常在台式机和笔记本电脑上使用 Google Chrome、Chromium和 Firefox。我研究了它们的很多附加功能,所以我在长期的研究和工作中可以享用它们的特色服务。
-然而,我有时喜欢一个快速、整洁的替代品来上网。随着多个项目的进行,我可以很快打开一大批选项卡甚至是独立窗口的强大浏览器。
+然而,有时我希望有个快速、整洁的替代品来上网。随着多个项目的进行,我需要很快打开一大批选项卡甚至是独立窗口的强大浏览器。
-我试过其他浏览器选项但很少成功。替代品通常有自己的一套分散注意力的附件和功能,它们会让我开小差。
+我试过其他浏览器但很少能令我满意。替代品通常有一套独特的花哨的附件和功能,它们会让我开小差。
-Min 浏览器不这样做。它是一个易于使用并在 GitHub 开源的 web浏览器,它不会使我分心。
+Min 浏览器就不这样。它是一个易于使用,并在 GitHub 开源的 web 浏览器,不会使我分心。

-Min 浏览器是最小化浏览器,提供了简单的功能以及迅速的操作。只是不要指望马上上手
+Min 浏览器是精简的浏览器,提供了简单的功能以及快速的响应。只是不要指望马上上手。
### 它做些什么
-Min 浏览器提供了 Debian Linux 版本、Windows 和 Mac 机器的版本。它不能与主流跨平台 web 浏览器中的可用功能竞争。
+Min 浏览器提供了 Debian Linux、Windows 和 Mac 机器的版本。它不能与功能众多的主流跨平台 web 浏览器竞争。
-它不必竞争,但是它的声誉非常好,它可能是补充而不是取代它们。
+但它不必竞争,它很有名的原因应该是补充而不是取代那些主流浏览器。
其中一个主要原因是其内置的广告拦截功能。开箱即用的 Min 浏览器不需要配置或寻找兼容的第三方应用程序来拦截广告。
-在 Edit/Preferences 中,关于内容阻止你有三个选项可以点击/取消点击。它很容易修改屏蔽策略来适应你的喜好。阻止跟踪器和广告选项使用 EasyList 和 EasyPrivacy。 如果没有其他原因,请保持此选项选中。
+在 Edit/Preferences 中,你可以通过三个选项来设置阻止的内容。它很容易修改屏蔽策略来满足你的喜好。阻止跟踪器和广告选项使用 EasyList 和 EasyPrivacy。 如果没有其他原因,请保持此选项选中。
-你还可以阻止脚本和图像。这样做可以最大限度地提高网站加载速度,并真正提高你对恶意代码的防御。
+你还可以阻止脚本和图像。这样做可以最大限度地提高网站加载速度,并能有效防御恶意代码。
### 按你的方式搜索
-如果你花费大量时间在搜索上,你会喜欢 Min 处理搜索的方式。这是一个顶级的功能。
+如果你在搜索上花费大量时间,你会喜欢 Min 处理搜索的方式。这是一个顶级的功能。
-可以直接在浏览器的网址栏中访问搜索功能。Min 使用搜索引擎有 DuckDuckGo 和维基百科。你可以直接在 web 地址栏中输入搜索查询。
+可以直接在浏览器的网址栏中使用搜索功能。Min 使用搜索引擎 DuckDuckGo 和维基百科的内容进行搜索。你可以直接在 web 地址栏中输入要搜索的东西。
-这种方法很节省时间,因为你不必先进入搜索引擎窗口。 一个额外的好处是可以搜索你的书签。
+这种方法很节省时间,因为你不必先进入搜索引擎窗口。 还有一个好处是可以搜索你的书签。
在 Edit/Preferences 菜单中,选择默认的搜索引擎。该列表包括 DuckDuckGo、Google、Bing、Yahoo、Baidu、Wikipedia 和 Yandex。
-尝试将 DuckDuckGo 作为默认搜索引擎。 Min 默认使用这个选项,但它不会强加给你。
+尝试将 DuckDuckGo 作为默认搜索引擎。 Min 默认使用这个引擎,但你也能更换。

-Min 浏览器的搜索功能是 URL 栏的一部分。Min 使用 DuckDuckGo 和维基百科作为搜索引擎。你可以直接在 web 地址栏中输入搜索查询。
+Min 浏览器的搜索功能是 URL 栏的一部分。Min 利用搜索引擎 DuckDuckGo 和维基百科的内容。你可以直接在 web 地址栏中输入要搜索的东西。
-搜索栏会非常快速地显示你问题的答案。它会使用 DuckDuckGo 的信息,包括维基百科条目、计算器以及更多。
+搜索栏会非常快速地显示问题的答案。它会使用 DuckDuckGo 的信息,包括维基百科条目、计算器和其它的内容。
-它能提供快速片段、答案和网络建议。它是在基于 Google 环境的一个替代。
+它能快速提供片段、答案和网络建议。它有点像不是基于 Goolge 环境的替代品。
### 导航辅助
-Min 允许你使用模糊搜索快速跳转到任何网站。它几乎能立即向你抛出建议。
+Min 允许你使用模糊搜索快速跳转到任何网站。它能立即向你提出建议。
-我喜欢在当前标签旁边打开标签的方式。你不必设置此选项。它在默认情况下没有其他选择,但它是有道理的。
+我喜欢在当前标签旁边打开标签的方式。你不必设置此选项。它在默认情况下没有其他选择,但这也有道理。
[

][2]
-Min 的一个很酷的操作是将标签整理到任务中,这样你可以随时搜索。(点击图片放大)
+Min 的一个很酷的功能是将标签整理到任务栏中,这样你随时都可以搜索。(点击图片放大)
-你不用一直点击标签。这使你可以专注于当前的任务,而不会分心。
+不点击标签,过一会儿它就会消失。这使你可以专注于当前的任务,而不会分心。
Min 不需要附加工具来控制多个标签。浏览器会显示标签列表,并允许你将它们分组。
### 保持专注
-Min 在“视图”菜单中隐藏了一个可选的“聚焦模式”。启用后,除了你打开的选项卡外,它会隐藏所有选项卡。 你必须返回到菜单以关闭“聚焦模式”,然后才能打开新选项卡。
+Min 在“视图”菜单中有一个可选的“聚焦模式”。启用后,除了你打开的选项卡外,它会隐藏其它所有选项卡。 你必须返回到菜单,关闭“聚焦模式”,才能打开新选项卡。
-任务功能还可以帮助你保持专注。你可以从“文件”菜单或使用 Ctrl+Shift+N 创建任务。如果要打开新选项卡,可以在“文件”菜单中选择该选项,或使用 Control+T。
+任务功能还可以帮助你保持专注。你可以在“文件(File)”菜单或使用 Ctrl+Shift+N 创建任务。如果要打开新选项卡,可以在“文件”菜单中选择该选项,或使用 Control+T。
-调用符合你的风格的新任务。我喜欢能够组织与显示与工作项目或与我的研究的特定部分相关联的所有标签。我可以在任何时间召回整个列表,以轻松快速的方式找到我的浏览记录。
+按照你的风格打开新任务。我喜欢按组来管理和显示标签,这组标签与工作项目或研究的某些部分相关。我可以在任何时间重新打开整个列表,从而轻松快速的方式找到我的浏览记录。
-另一个整洁的功能是在 tab 区域可以找到段落对齐按钮。单击它启用阅读模式。此模式会保存文章以供将来参考,并删除页面上的一切,以便你可以专注于阅读任务。
+另一个好用的功能是可以在 tab 区域找到段落对齐按钮。单击它启用阅读模式。此模式会保存文章以供将来参考,并删除页面上的一切,以便你可以专注于阅读任务。
### 并不完美
-Min 浏览器并不是强大的,功能丰富的完美替代品。它有一些明显的弱点,开发人员花了太长时间而不能改正。
+Min 浏览器并不是强大的,功能丰富的完美替代品。它有一些明显的缺点,开发人员花了很多时间也没有修正。
-例如,它缺乏一个支持论坛和详细用户指南的开发人员网站。可能部分原因是它的官网在 GitHub,而不是一个独立的开发人员网站。尽管如此,对新用户而言这是一个弱点。
+例如,它缺乏一个支持论坛和详细用户指南的开发人员网站。可能部分原因是它的官网在 GitHub,而不是一个独立的开发人员网站。尽管如此,对新用户而言这是一个缺点。
没有网站支持,用户被迫在 GitHub 上寻找自述文件和各种目录列表。你也可以在 Min 浏览器的帮助菜单中访问它们 - 但这没有太多帮助。
-一个例子是当你启动浏览器时,屏幕会显示欢迎界面。它会显示两个按钮,一个人是 “Start Browsing”,另一个是 “Take a Tour.”。但是没有一个按钮可以使用
+一个例子是当你启动浏览器时,屏幕会显示欢迎界面。它会显示两个按钮,一个人是 “Start Browsing”,另一个是 “Take a Tour.”。但是没有一个按钮可以使用。
-但是,你可以通过单击 Min 窗口顶部的菜单栏开始浏览。但是,缺少导览还没有解决办法。
+但是,你可以通过单击 Min 窗口顶部的菜单栏开始浏览。但是,还没有解决缺少概览办法。
### 底线
-Min 并不是一个有完整功能的 web 浏览器。它不是为通常在成熟的 web 浏览器中有的插件和其他许多功能而设计的。然而,Min 通过提供速度和免打扰来达到它重要的目的。
+Min 并不是一个功能完善、丰富的 web 浏览器。你在功能完善的主流浏览器中所用的插件和其它许多功能都不是 Min 的设计目标。然而,Min 在快速响应和免打扰方面很有用。
-我越使用 Min 浏览器,它对我来说越有效率 - 但是当你第一次使用它时要小心。
+我越使用 Min 浏览器,我越觉得它高效 - 但是当你第一次使用它时要小心。
-Min 并不复杂或让人困惑 - 它只是有点古怪。你必须要玩弄一下才能明白它如何使用。
+Min 并不复杂,也不难操作 - 它只是有点古怪。你必须要玩弄一下才能明白它如何使用。
### 想要提建议么?
-有没有一个你想提议 Linux 程序或发行版?有没有你爱的或者想要了解的?
+有没有你建议回顾的 Linux 程序或发行版?有没有你爱的或者想要了解的?
-请[在电子邮件中给我发送你的想法][3],我会考虑将来在 Linux Picks and Pans 专栏上登出。
+请[在电子邮件中给我发送你的想法][3],我会考虑将来在 “Linux Picks and Pans” 专栏上登出。
-并使用下面的读者评论功能提出你的想法!
+可以使用下方的读者评论功能说出你的想法!
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
作者简介:
-Jack M. Germain 从苹果 II 和 PC 的早期起就一直在写关于计算机技术。他仍然有他原来的 IBM PC-Jr 和一些其他遗留的 DOS 和 Windows 盒子。他为 Linux 桌面的开源世界留下过共享软件。他运行几个版本的 Windows 和 Linux 操作系统,还通常不能决定是否用他的平板电脑、上网本或 Android 智能手机,而不是用他的台式机或笔记本电脑。你可以在 Google+ 上与他联系。
+Jack M. Germain 从苹果 II 和 PC 的早期起就一直在写关于计算机技术。他仍然有他原来的 IBM PC-Jr 和一些其他遗留的 DOS 和 Windows 盒子。他为 Linux 桌面的开源世界留下过共享软件。他运行几个版本的 Windows 和 Linux 操作系统,还通常不能决定是否用他的平板电脑、上网本或 Android 智能手机,还是用他的台式机或笔记本电脑。你可以在 Google+ 上与他联系。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ via: http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/84212.html?rss=1
作者:[Jack M. Germain][a]
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[GitFuture](https://github.com/GitFuture)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20170111 NMAP Common Scans – Part One.md b/translated/tech/20170111 NMAP Common Scans – Part One.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0db1c11990
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20170111 NMAP Common Scans – Part One.md
@@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
+NMAP 常用扫描简介 - 第一部分
+========================
+
+我们之前在‘[NMAP 的安装][1]’一文中,列出了 10 种不同的 ZeNMAP 扫描模式(这里将 Profiles 翻译成了模式,不知是否合适)。大多数的模式使用了各种参数。大多数的参数代表了执行不同的扫描模式。这篇文章将介绍其中的四种通用的扫描类型。
+
+**四种通用扫描类型**
+
+下面列出了最常使用的四种扫描类型:
+
+1. PING 扫描 (-sP)
+2. TCP SYN 扫描 (-sS)
+3. TCP Connect() 扫描 (-sT)
+4. UDP 扫描 (-sU)
+
+当我们利用 NMAP 来执行扫描的时候,这四种扫描类型是我们需要熟练掌握的。更重要的是需要知道这些命令做了什么并且需要知道这些命令是怎么做的。本文将介绍 PING 扫描和 UDP 扫描。在之后的文中会介绍 TCP 扫描。
+
+**PING 扫描 (-sP)**
+
+某些扫描会造成网络拥塞,然而 Ping 扫描在网络中最多只会产生两个包。当然这两个包不包括可能需要的 DNS 搜索和 ARP 请求。每个被扫描的 IP 最少只需要一个包来完成 Ping 扫描。
+
+通常 Ping 扫描是用来查看在指定的 IP 地址上是否有在线的主机存在。例如,当我拥有网络连接却联不上一台指定的网络服务器的时候,我就可以使用 PING 来判断这台服务器是否在线。PING 同样也可以用来验证我的当前设备与网络服务器之间的路由是否正常。
+
+**注意:** 当我们讨论 TCP/IP 的时候,相关信息在使用 TCP/IP 协议的英特网与局域网(LAN)中都是相当有用的。这些程序都能工作。同样在广域网(WAN)也能工作得相当好。
+
+当参数给出的是一个域名的时候,我们就需要域名解析服务来找到相对应的 IP 地址,这个时候将会生成一些额外的包。例如,当我们执行 ‘ping linuxforum.com’ 的时候,需要首先请求域名(linuxforum.com)的 IP 地址(98.124.199.63)。当我们执行 ‘ping 98.124.199.63’ 的时候 DNS 查询就不需要了。当 MAC 地址未知的时候,就需要发送 ARP 请求来获取指定 IP 地址的 MAC 地址了(这里的指定 IP 地址,未必是目的 IP)。
+
+Ping 命令会向指定的 IP 地址发送一个英特网信息控制协议(ICMP)包。这个包是需要响应的 ICMP Echo 请求。当服务器系统在线的状态下我们会得到一个响应包。当两个系统之间存在防火墙的时候,PING 请求包可能会被防火墙丢弃。一些服务器也会被配置成不响应 PING 请求来避免可能发生的死亡之 PING。(现在的操作系统似乎不太可能)
+
+**注意:** 死亡之 PING 是一种恶意构造的 PING 包当它被发送到系统的时候,会造成被打开的连接等待一个 rest 包。一旦有一堆这样的恶意请求被系统响应,由于所有的可用连接都已经被打开所以系统将会拒绝所有其它的连接。技术上来说这种状态下的系统就是不可达的。
+
+当系统收到 ICMP Echo 请求后它将会返回一个 ICMP Echo 响应。当源系统收到 ICMP Echo 响应后我们就能知道目的系统是在线可达的。
+
+使用 NMAP 的时候你可以指定单个 IP 地址也可以指定 某个 IP 地址段。当被指定为 PING 扫描(-sP)的时候,PING 命令将会对每一个 IP 地址执行。
+
+在图 1 中你可以看到我执行‘nmap -sP 10.0.0.1-10’命令后的结果。An ARP is sent out, three for each IP Address given to the command. In this case thirty requests went out – two for each of the ten IP Addresses.(这两句话就没有读懂,不清楚具体指的是什么意思,从图2看的话第一句里的三指的是两个 ARP 包和一个 ICMP 包,按照下面一段话的描述的话就是每个 IP 地址会有三个 ARP 请求,但是自己试的时候 Centos6 它发了两个 ARP 请求没获取到 MAC 地址也就就结束了,这里不清楚究竟怎么理解)
+
+ 
+
+**图 1**
+
+图 2 中展示了利用 Wireshark 抓取的从网络上另一台计算机发出的请求-的确是在 Windows 系统下完成这次抓取的。第一行展示了发出的第一条请求,广播请求的是 10.0.0.2 IP 地址对应 MAC 地址。由于 NMAP 是在 10.0.0.1 这台机器上执行的,因此 10.0.0.1 被略过了。由于本机 IP 地址被略过,我们现在可以说总共只发出了 27 个 ARP 请求。第二行展示了 10.0.0.2 这台机器的 ARP 响应。第三行到第十行是其它八个 IP 地址的 ARP 请求。第十一行是由于没有收到请求系统(10.0.0.1)的反馈所以发送的另一个 ARP 响应。(自己试的话它发送一个请求收到一个响应就结束了,也没有搜到相关的重发响应是否存在的具体说明,不是十分清楚)第十二行是源系统向 10.0.0.2 响应的 ‘SYN’ 和 Sequence 0。(这行感觉更像是三次握手里的首包)第十三行和第十四行的两次 Restart(RST)和 Synchronize(SYN)响应是用来关闭第二行和第十一行所打开的连接的。(这个描述似乎有问题 ARP 请求怎么会需要 TCP 来关闭连接呢,感觉像是第十二行的响应)注意 Sequence ID 是 ‘1’ - 是源 Sequence ID + 1。(这个不理解,不是应该 ACK = seq + 1 的么)第十五行开始就是类似相同的内容。
+
+ 
+
+**图 2**
+
+回到图 1 中我们可以看到有两台主机在线。其中一台是本机(10.0.0.1)另一台是(10.0.0.2)。整个扫描花费了 14.40 秒。
+
+PING 扫描是一种用来发现在线主机的快速扫描方式。扫描结果中没有关于网络、系统的其它信息。这是一种较好的初步发现网络上在线主机的方式,接着你就可以针对在线系统执行更加复杂的扫描了。你可能还会发现一些不应该出现在网络上的系统。出现在网络上的流氓软件是很危险的,他们可以很轻易的收集内网信息和相关的系统信息。
+
+一旦你获得了在线系统的列表,你就可以使用 UDP 扫描来查看哪些端口是可能开启了的。
+
+**UDP 扫描 (-sU)**
+
+现在你已经知道了有那些系统是在线的,你的扫描就可以聚焦在这些 IP 地址之上。在整个网络上执行大量的没有针对性的扫描活动可不是一个好主意。系统管理员可以使用程序来监控网络流量当有大量可以活动发生的时候就会触发警报。
+
+用户数据报协议(UDP)在发现在线系统的开放端口方面十分有用。由于 UDP 不是一个面向连接的协议,因此是不需要响应的。这种扫描方式可以向指定的端口发送一个 UDP 包。如果目标系统没有回应那么这个端口可能是关闭的也可能是被过滤了的。如果端口是开放状态的那么应该会有一个响应。在大多数的情况下目标系统会返回一个 ICMP 信息说端口不可达。ICMP 信息让 NMAP 知道端口是被关闭了。如果端口是开启的状态那么目标系统应该响应 ICMP 信息来告知 NMAP 端口可达。
+
+**注意: **只有最前面的1024个常用端口会被扫描。(这里将 1000 改成了1024,因为手册中写的是默认扫描 1 到 1024 端口)在后面的文章中我们会介绍如何进行深度扫描。
+
+由于我知道 10.0.0.2 这个主机是在线的,因此我只会针对这个 IP 地址来执行扫描。扫描过程中总共收发了 3278 个包。‘sudo nmap -sU 10.0.0.2’这个命令的输出结果在图 3 中展现。
+
+ 
+
+**图 3**
+
+在这副图中你可以看见端口 137(netbios-ns)被发现是开放的。在图 4 中展示了 Wireshark 抓包的结果。不能看到所有抓取的包,但是可以看到一长串的 UDP 包。
+
+ 
+
+**图 4**
+
+如果我把目标系统上的防火墙关闭之后会发生什么呢?我的结果有那么一点的不同。NMAP 命令的执行结果在图 5 中展示。
+
+ 
+
+**图 5**
+
+**注意:** 当你执行 UDP 扫描的时候是需要 root 权限的。
+
+会产生大量的包是由于我们使用了 UDP。当 NMAP 发送 UDP 请求时它是不保证数据包会被收到的。因为数据包可能会在中途丢失因此它会多次发送请求。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.linuxforum.com/threads/nmap-common-scans-part-one.3637/
+
+作者:[Jarret][a]
+译者:[wcnnbdk1](https://github.com/wcnnbdk1)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.linuxforum.com/members/jarret.268/
+[1]:https://www.linuxforum.com/threads/nmap-installation.3431/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20170208 free – A Standard Command to Check Memory Usage Statistics in Linux.md b/translated/tech/20170208 free – A Standard Command to Check Memory Usage Statistics in Linux.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 291e4c010f..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20170208 free – A Standard Command to Check Memory Usage Statistics in Linux.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,220 +0,0 @@
-free - 一个在 Linux 中检查内存使用统计(空闲和已用)的标准命令
-============================================================
-
-我们都知道, IT 基础设施方面的大多数服务器(包括世界顶级超级计算机)都运行在 Linux 平台上,因为和其他操作系统相比, Linux 更加灵活。其他操作系统对于一些微乎其微的改动和补丁更新都需要重启,但是 Linux 不需要,只有对于一些关键补丁的更新, Linux 才会需要重启。
-
-Linux 系统管理员面临的一大挑战是如何在没有任何停机时间的情况下维护系统的良好运行。管理内存使用是 Linux 管理员又一个具有挑战性的任务。`free` 是 Linux 中一个标准的并且被广泛使用的命令,它被用来分析内存统计(空闲和已用)。今天,我们将要讨论 `free` 命令以及它的一些有用选项。
-
-推荐文章:
-
-* [smem - Linux 内存报告/统计工具][1]
-* [vmstat - 一个报告虚拟内存统计的标准而又漂亮的工具][2]
-
-#### Free 命令是什么
-
-free 命令能够显示系统中物理上的`空闲`和`已用`内存,还有`交换`内存,同时,也能显示被内核使用的`缓冲`和`缓存`。这些信息是通过解析文件 /proc/meninfo 而收集到的。
-
-#### 显示系统内存
-
-不带任何选项运行 `free` 命令会显示系统内存,包括`空闲`、`已用`、`缓冲`、`缓存`和`交换`的内存总数。
-
-```
-# free
- 总共 已用 空闲 共用 缓冲 缓存大小
-内存: 32869744 25434276 7435468 0 412032 23361716
--/+ 缓冲/缓存: 1660528 31209216
-交换: 4095992 0 4095992
-```
-
-输出有三行:
-
-* 第一行:表明全部内存、已用内存、空闲内存、共用内存(主要被 tmpfs(/proc/meninfo 中的 Shmem 项)使用)、用于缓冲的内存以及缓存内容大小。
-
-* 全部:全部已安装内存(/proc/meminfo 中的 MemTotal 项)
-* 已用:已用内存(全部计算 - 空间+缓冲+缓存)
-* 空闲:未使用内存(/proc/meminfo 中的 MemFree 项)
-* 共用:主要被 tmpfs 使用的内存(/proc/meminfo 中的 Shmem 项)
-* 缓冲:被内核缓冲使用的内存(/proc/meminfo 中的 Buffers 项)
-* 缓存:被页面缓存使用的内存(/proc/meminfo 中的 Cached and SSReclaimable 项)
-
-* 第二行:表明已用和空闲缓冲/缓存
-* 第三行:表明总交换内存(/proc/meminfo 中的 SwapTotal 项)、空闲内存(/proc/meminfo 中的 SwapFree 项)和已用交换内存。
-
-#### 以 MB 为单位显示系统内存
-
-默认情况下, `free` 命令以 `KB - Kilobytes` 为单位输出系统内存,这对于绝大多数管理员来说会有一点迷糊(当系统内存很大的时候,我们中的许多人需要把输出转化为以 MB 为单位,从而才能够理解内存大小)。为了避免这个迷惑,我们在 ‘free’ 命令后面加上 `-m` 选项,就可以立即得到以 ‘MB - Megabytes’ 为单位的输出。
-
-```
-# free -m
- 全部 已用 空闲 公用 缓冲 缓存
-内存: 32099 24838 7261 0 402 22814
--/+ 缓冲/缓存: 1621 30477
-交换: 3999 0 3999
-```
-
-如何从上面的输出中检查剩余多少空闲内存?主要基于`已用`和`空闲`两列。你可能在想,你只有很低的空闲内存,因为它只有 `10%`, 为什么?
-
-全部实际可用内存 = (全部内存 - 第 2 行已用内存)
-全部内存 = 32099
-实际已用内存 = -1621
-
-全部实际可用内存 = 30477
-
-如果你的 Linux 版本是最新的,那么有一个查看实际空闲内存的选项,叫做 `available` ,对于旧的版本,请看显示 `-/+ buffers/cache` 那一行对应的‘空闲’一列。
-
-如何从上面的输出中检查有多少实际已用内存?基于`已用`和`空闲`一列。你可能想,你已经使用了超过 `95%` 的内存。
-
-全部实际已用内存 = 第一列‘已用’ - (第一列‘缓冲’ + ‘第一列缓存’)
-已用内存 = 24838
-已用缓冲 = 402
-已用缓存 = 22814
-
-全部实际已用内存 = 1621
-
-#### 以 GB 为单位显示内存
-
-默认情况下, `free` 命令会以 `KB - kilobytes` 为单位显示输出,这对于大多数管理员来说会有一些迷惑,所以我们使用上面的选项来获得以 `MB - Megabytes` 为单位的输出。但是,当服务器的内存很大(超过 100 GB 或 200 GB)时,上面的选项也会让人很迷惑。所以,在这个时候,我们可以在 `free` 命令后面加上 `-g` 选项,从而立即得到以 `GB - Gigabytes` 为单位的输出。
-
-```
-# free -g
- 全部 已用 空闲 共用 缓冲 缓存
-内存: 31 24 7 0 0 22
--/+ 缓冲/缓存: 1 29
-交换: 3 0 3
-```
-
-#### 显示全部内存线
-
-默认情况下, `free` 命令的输出只有三列(内存、缓冲/缓存以及交换)。为了统一以分割线显示(全部(内存+交换)、已用(内存+(已用-缓冲/缓存)+交换)以及空闲(内存+(已用-缓冲/缓存)+交换),在 ‘free’ 命令后面加上 `-t` 选项
-
-```
-# free -t
- 全部 已用 空闲 共用 缓冲 缓存
-内存: 32869744 25434276 7435468 0 412032 23361716
--/+ 缓冲/缓存: 1660528 31209216
-交换: 4095992 0 4095992
-交换: 36965736 27094804 42740676
-```
-
-#### 伴有延迟运行 free 命令从而更好的统计
-
-默认情况下, free 命令只会显示单一的统计输出,这是不足够进一步排除故障的,所以,可以通过添加延迟(在几秒内更新的延迟)来定期统计内存活动。如果你想以两秒的延迟运行 free 命令,可以使用下面的命令(如果你想要更多的延迟,你可以按照你的意愿更改数值)。
-
-下面的命令将会每 2 秒运行一次直到你退出:
-
-```
-# free -s 2
- 全部 已用 空闲 共用 缓冲 缓存
-内存: 32849392 25935844 6913548 188 182424 24632796
--/+ 缓冲/缓存: 1120624 31728768
-交换: 20970492 0 20970492
-
- 全部 已用 空闲 共用 缓冲 缓存
-内存: 32849392 25935288 6914104 188 182424 24632796
--/+ 缓冲/缓存: 1120068 31729324
-交换: 20970492 0 20970492
-
- 全部 已用 空闲 共用 缓冲 缓存
-内存: 32849392 25934968 6914424 188 182424 24632796
--/+ 缓冲/缓存: 1119748 31729644
-交换: 20970492 0 20970492
-```
-
-#### 伴有延迟和计数运行 free 命令
-
-另外,你可以伴随延迟和具体计数运行 free 命令,一旦达到具体计数,便自动退出
-
-下面的命令将会每 2 秒运行一次 free 命令,计数 5 次以后自动退出
-
-```
-# free -s 2 -c 5
- 全部 已用 空闲 共用 缓冲 缓存
-内存: 32849392 25931052 6918340 188 182424 24632796
--/+ 缓冲/缓存: 1115832 31733560
-交换: 20970492 0 20970492
-
- 全部 已用 空闲 共用 缓冲 缓存
-内存: 32849392 25931192 6918200 188 182424 24632796
--/+ 缓冲/缓存: 1115972 31733420
-Swap: 20970492 0 20970492
-
- 全部 已用 空闲 共用 缓冲 缓存
-内存: 32849392 25931348 6918044 188 182424 24632796
--/+ 缓冲/缓存: 1116128 31733264
-交换: 20970492 0 20970492
-
- 全部 已用 空闲 共用 缓冲 缓存
-内存: 32849392 25931316 6918076 188 182424 24632796
--/+ 缓冲/缓存: 1116096 31733296
-交换: 20970492 0 20970492
-
- 全部 已用 空闲 共用 缓冲 缓存
-内存: 32849392 25931308 6918084 188 182424 24632796
--/+ 缓冲/缓存: 1116088 31733304
-交换: 20970492 0 20970492
-```
-
-#### 人类可读格式
-
-为了以人类可读的格式输出,在 `free` 命令的后面加上 `-h` 选项,和其他选项比如 `-m` 和 `-g` 相比,这将会打印出更多的细节输出。
-
-```
-# free -h
- 全部 已用 空闲 共用
- 缓冲/缓存 可用
-内存: 2.0G 1.6G 138M 20M 188M 161M
-交换: 2.0G 1.8G 249M
-```
-
-#### 分离缓冲区和缓存内存输出
-
-默认情况下, `缓冲/缓存` 内存输出是在一起的。为了分离缓冲和缓存内存输出,可以在 free 命令后面加上 `-w` 选项。(该选项在版本 3.3.12 上可用)
-
-注意:看上面的输出,`缓冲/缓存`是在一起的。
-
-```
-# free -wh
- 全部 已用 空闲 共用 缓冲 缓存 可用
-内存: 2.0G 1.6G 137M 20M 8.1M 183M 163M
-交换: 2.0G 1.8G 249M
-```
-
-#### 显示最低和最高的内存统计
-
-默认情况下, `free` 命令不会显示最低和最高的内存统计。为了显示最低和最高的内存统计,在 free 命令后面加上 `-l` 选项。
-
-```
-# free -l
- 全部 已用 空闲 共用 缓冲 缓存
-内存: 32849392 25931336 6918056 188 182424 24632808
-底: 32849392 25931336 6918056
-高: 0 0 0
--/+ 缓冲/缓存: 1116104 31733288
-交换: 20970492 0 20970492
-```
-
-#### 阅读关于 free 命令的更过信息
-
-如果你想了解 free 命令的更多可用选项,只需查看 man 手册。
-
-
-```
-# free --help
-or
-# man free
-```
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.2daygeek.com/free-command-to-check-memory-usage-statistics-in-linux/
-
-作者:[MAGESH MARUTHAMUTHU][a]
-译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/
-[1]:http://www.2daygeek.com/smem-linux-memory-usage-statistics-reporting-tool/
-[2]:http://www.2daygeek.com/linux-vmstat-command-examples-tool-report-virtual-memory-statistics/
-[3]:http://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20170213 Set Up and Configure a Firewall with FirewallD on CentOS 7.md b/translated/tech/20170213 Set Up and Configure a Firewall with FirewallD on CentOS 7.md
index aef7d7031c..b7878eef22 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20170213 Set Up and Configure a Firewall with FirewallD on CentOS 7.md
+++ b/translated/tech/20170213 Set Up and Configure a Firewall with FirewallD on CentOS 7.md
@@ -4,27 +4,23 @@

-
-
-FirewallD 是 CentOS 7 服务器上的一个默认可用的防火墙管理工具。基本上,它是 iptables 的封装,有图形配置工具 firewall-config 和命令行工具 firewall-cmd。使用 iptables 服务每次改动都要求刷新旧规则,并且从 `/etc/sysconfig/iptables` 读取新规则,然而 firewalld 仅仅会应用改动了的不同部分。
+FirewallD 是 CentOS 7 服务器上的一个默认可用的防火墙管理工具。基本上,它是 iptables 的封装,有图形配置工具 firewall-config 和命令行工具 firewall-cmd。使用 iptables 服务,每次改动都要求刷新旧规则,并且从 `/etc/sysconfig/iptables` 读取新规则,然而 firewalld 仅仅会应用改动了的不同部分。
### FirewallD zones
-
FirewallD 使用 services 和 zones 代替 iptables 的 rules 和 chains 。
默认情况下,有以下的 zones 可用:
-
-* drop – 丢弃所有传入的网络数据包并且无回应,只有传出网络连接可用。
-* block — 拒绝所有传入网络数据包并回应一条主机禁止 ICMP 的消息,只有传出网络连接可用。
-* public — 只接受被选择的传入网络连接,用于公共区域。
-* external — 用于启用伪装的外部网络,只接受被选择的传入网络连接。
-* dmz — DMZ 隔离区,外部受限地访问内部网络,只接受被选择的传入网络连接。
-* work — 对于处在你家庭区域内的计算机,只接受被选择的传入网络连接。
-* home — 对于处在你家庭区域内的计算机,只接受被选择的传入网络连接。
-* internal — 对于处在你内部网络的计算机,只接受被选择的传入网络连接。
-* trusted — 所有网络连接都接受。
+* **drop** – 丢弃所有传入的网络数据包并且无回应,只有传出网络连接可用。
+* **block** — 拒绝所有传入网络数据包并回应一条主机禁止 ICMP 的消息,只有传出网络连接可用。
+* **public** — 只接受被选择的传入网络连接,用于公共区域。
+* **external** — 用于启用伪装的外部网络,只接受被选择的传入网络连接。
+* **dmz** — DMZ 隔离区,外部受限地访问内部网络,只接受被选择的传入网络连接。
+* **work** — 对于处在你家庭区域内的计算机,只接受被选择的传入网络连接。
+* **home** — 对于处在你家庭区域内的计算机,只接受被选择的传入网络连接。
+* **internal** — 对于处在你内部网络的计算机,只接受被选择的传入网络连接。
+* **trusted** — 所有网络连接都接受。
列出所有可用的 zones :
```
@@ -145,7 +141,7 @@ via: https://www.rosehosting.com/blog/set-up-and-configure-a-firewall-with-firew
作者:[rosehosting.com][a]
译者:[Locez](https://github.com/locez)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20170214 How to Install Ubuntu with Separate Root and Home Hard Drives.md b/translated/tech/20170214 How to Install Ubuntu with Separate Root and Home Hard Drives.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b3158d29d8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20170214 How to Install Ubuntu with Separate Root and Home Hard Drives.md
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+
+如何通过分离 Root 目录和 Home 目录安装 Ubuntu
+============================================================
+
+
+
+
+当我们在安装 Linux 系统时,可以有两种不同的方式。第一种方式是在一个超快的固态硬盘上进行安装,这样可以保证迅速开机和高速访问数据。第二种方式是在一个较慢但很强大的普通硬盘驱动上安装,这样的硬盘转速很快并且存储容量很大,从而可以存储大量的应用程序和数据。
+
+然而,一些 Linux 用户都知道,[固态硬盘][10]很棒,但是又很贵,而普通硬盘容量很大但速度较慢。如果我告诉你,可以同时利用两种硬盘来安装 Linux 系统,会怎么样?一个超快、现代化的固态硬盘驱动 Linux 内核,一个容量很大的普通硬盘来存储其他数据。
+
+在这篇文章中,我将阐述如何通过分离 Root 目录和 Home 目录安装 Ubuntu 系统 — Root 目录存于 SSD(固态硬盘)中,Home 目录存于普通硬盘中。
+
+### 没有多余的硬盘驱动?尝试一下 SD 卡(内存卡)!
+
+ 
+
+进行多驱动 Linux 系统安装是很不错的,并且每一个高级用户都应该学会这样做。然而,还有一种情况使得用户应该这样安装 Linux 系统 - 在低存储容量的笔记本电脑上安装系统。可能你有一台很便宜、没有花费太多的笔记本电脑,上面安装了 Linux 系统,电脑上没有多余的硬盘驱动,但有一个 SD 卡插槽。
+
+这篇教程也是针对这种类型的电脑的。跟随这篇教程,为笔记本电脑买一个高速的 SD 卡来存储 Home 目录,而不是使用另一个硬盘驱动。本教程也适用于使用另一个硬盘驱动来存储 Home 目录的情况。
+
+### 制作 USB 启动盘
+
+首先去[网站][11]下载最新的 Ubuntu Linux 版本。然后下载 [Etcher][12]- USB 镜像制作工具。这是一个使用起来很简单的工具,并且支持所有的主流操作系统。你还需要一个至少有 2GB 大小的 USB 驱动。
+
+ 
+
+安装好 Etcher 以后,直接打开。点击 “Select Image” 按钮来制作镜像。这将提示用户浏览、寻找 ISO 镜像,找到前面下载的 Ubuntu ISO 文件并选择。然后,插入 USB 驱动,Etcher 应该会自动选择驱动。之后,点击 “Flash!” 按钮,Ubuntu 启动盘的制作过程就开始了。
+
+为了能够启动 Ubuntu 系统,需要配置 BIOS。这是必需的,这样计算机才能启动新创建的 Ubuntu 启动盘。为了进入 BIOS,在插入 USB 的情况下重启电脑,然后按正确的键(Del、F2 或者任何和你的特定电脑匹配的键)。找到 ‘从 USB 启动’ 选项,然后启用这个选项。
+
+如果你的个人电脑不支持 USB 启动,那么把 Ubuntu 镜像刻入 DVD 中。
+
+### 安装
+
+第一次加载 Ubuntu 时,欢迎界面会出现两个选项。请选择 “安装 Ubuntu” 选项。在下一页中,强大的安装工具会请求用户选择一些选项。这些选项不是强制性的,可以忽略。然而,建议勾选这两个选项,因为这样可以节省安装系统以后的时间,特别是安装 MP3 解码器和更新系统。
+
+ 
+
+勾选了“准备安装 Ubuntu” 页面中的两个选项以后,需要选择安装类型了。有许多种安装类型。然而,这个教程需要选择自定义安装类型。为了进入自定义安装页面,勾选“其他”选项,然后点击“继续”。
+
+这儿将用到 Ubuntu 自定义安装分区工具。它将显示任何/所有能够安装 Ubuntu 系统的磁盘。如果两个硬盘均可用,那么它们都会显示。如果插有 SD 卡,那么它也会显示。
+
+选择用于 Root 文件系统的硬盘驱动。如果上面已经有分区表,请使用分区工具把它们全部删除。如果驱动没有格式化也没有分区,那么使用鼠标选择驱动,然后点击“新分区表”。对所有驱动执行这个操作,从而使它们都有分区表。
+
+ 
+
+现在所有分区都有了分区表(和已删除分区),可以开始进行配置了。在第一个驱动下选择空闲空间,然后点击加号按钮来创建新分区。然后将会出现一个“创建分区窗口”。允许工具使用整个硬盘。然后转到“挂载点”下拉菜单。选择 ‘/’ 作为挂载点,之后点击 OK 按钮确认设置。
+
+对第二个驱动做相同的事,这次选择 ‘/home’ 作为挂载点。两个驱动都设置好以后,选择引导装载器将进入的正确驱动,然后点击 “install now”,安装进程就开始了。
+
+ 
+
+从这以后的安装进程是标准安装。创建用户名、选择时区等。
+
+**注:**你是以 UEFI 模式进行安装吗?如果是,那么需要给 boot 创建一个 512 MB 大小的 FAT32 分区。在创建其他任何分区前做这件事。确保选择 “/boot” 作为这个分区的挂载点。
+
+如果你需要一个交换分区,那么,在创建用于 ‘/’ 的分区前,在第一个驱动上进行创建。可以通过点击 ‘+’ 按钮,然后输入所需大小,选择下拉菜单中的“交换区域”来创建交换分区。
+
+### 结论
+
+Linux 最好的地方就是可以自己按需配置。有多少其他操作系统可以让你把文件系统分割在不同的硬盘驱动上?并不多,这是肯定的。我希望有了这个指南,你将意识到 Ubuntu 能够提供的真正力量。
+
+你是否使用了多重驱动安装 Ubuntu 系统?请在下面的评论中让我们知道。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/install-ubuntu-with-different-root-home-hard-drives/
+
+作者:[Derrik Diener][a]
+译者:[ucasFL](https://github.com/ucasFL)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/derrikdiener/
+[1]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/derrikdiener/
+[2]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/install-ubuntu-with-different-root-home-hard-drives/#respond
+[3]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/category/linux-tips/
+[4]:http://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.maketecheasier.com%2Finstall-ubuntu-with-different-root-home-hard-drives%2F
+[5]:http://twitter.com/share?url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.maketecheasier.com%2Finstall-ubuntu-with-different-root-home-hard-drives%2F&text=How+to+Install+Ubuntu+with+Separate+Root+and+Home+Hard+Drives
+[6]:mailto:?subject=How%20to%20Install%20Ubuntu%20with%20Separate%20Root%20and%20Home%20Hard%20Drives&body=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.maketecheasier.com%2Finstall-ubuntu-with-different-root-home-hard-drives%2F
+[7]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/byb-dimmable-eye-care-desk-lamp/
+[8]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/download-appx-files-from-windows-store/
+[9]:https://support.google.com/adsense/troubleshooter/1631343
+[10]:http://www.maketecheasier.com/tag/ssd
+[11]:http://ubuntu.com/download
+[12]:https://etcher.io/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20170217 Understanding the difference between sudo and su.md b/translated/tech/20170217 Understanding the difference between sudo and su.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5fc1672b00
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20170217 Understanding the difference between sudo and su.md
@@ -0,0 +1,168 @@
+理解 sudo 与 su 之间的区别
+============================================================
+
+### 本文导航
+
+1. [Linux su 命令][7]
+ 1. [su -][1]
+ 2. [su -c][2]
+2. [Sudo vs Su][8]
+2. [Sudo vs Su][8]
+ 1. [关于密码][3]
+ 2. [默认行为][4]
+ 3. [日志记录][5]
+ 4. [灵活性][6]
+3. [Sudo su][9]
+
+在[早前的一篇文章][11]中,我们深入讨论了 `sudo` 命令的相关内容。同时,在该文章的末尾有提到相关的命令 `su` 的部分内容。本文,我们将详细讨论关于 su 命令与 sudo 命令之间的区别。
+
+在开始之前有必要说明一下,文中所涉及到的示例教程都已经在 Ubuntu 14.04 LTS 上测试通过。
+
+### Linux su 命令
+
+su 命令的主要作用是让你可以在已登录的会话中切换到另外一个用户。换句话说,这个工具可以让你在不登出当前用户的情况下登录另外一个用户(以该用户的身份)。
+
+su 命令经常被用于切换到超级用户或 root 用户(因为在命令行下工作,经常需要 root 权限),但是 - 正如前面所提到的 - su 命令也可以用于切换到任意非 root 用户。
+
+如何使用 su 命令切换到 root 用户,如下:
+
+[
+ 
+][12]
+
+如上,su 命令要求输入的密码是 root 用户密码。所以,一般 su 命令需要输入目标用户的密码。在输入正确的密码之后,su 命令会在终端的当前会话中打开一个子会话。
+
+### su -
+
+还有一种方法可以切换到 root 用户:运行 `su -` 命令,如下:
+
+[
+ 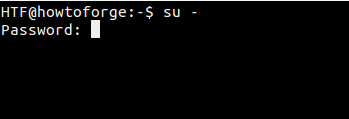
+][13]
+
+那么,`su` 命令与 `su -` 命令之间有什么区别呢?前者在切换到 root 用户之后仍然保持旧的或原始用户的环境,而后者则是创建一个新的环境(由 root 用户 ~/.bashrc 文件所设置的环境),相当于使用 root 用户正常登录(从登录屏幕显示登录)。
+
+`su` 命令手册页很清楚地说明了这一点:
+
+```
+可选参数 `-` 可提供的环境为用户在直接登录时的环境。
+```
+
+因此,你会觉得使用 `su -` 登录更有意义。但是,同时存在 `su` 命令,那么大家可能会想知道它在什么时候用到。以下内容摘自[ArchLinux wiki website][14] - 关于 `su` 命令的好处和坏处:
+
+* 有的时候,对于系统管理员来讲,使用其他普通用户的 Shell 账户而不是自己的 Shell 账户更会好一些。尤其是在处理用户问题时,最有效的方法就是是:登录目标用户以便重现以及调试问题。
+
+* 然而,在多数情况下,当从普通用户切换到 root 用户进行操作时,如果还使用普通用户的环境变量的话,那是不可取甚至是危险的操作。因为是在无意间切换使用普通用户的环境,所以当使用 root 用户进行程序安装或系统更改时,会产生与正常使用 root 用户进行操作时不相符的结果。例如,可以给普通用户安装电源意外损坏系统的程序或获取对某些数据的未授权访问的程序。
+
+注意:如果你想在 `su -` 命令后面传递更多的参数,那么你必须使用 `su -l` 来实现。以下是 `-` 和 `-l` 命令行选项的说明:
+
+```
+-, -l, --login
+提供相当于用户在直接登录时所期望的环境。
+
+当使用 - 时,必须放在 su 命令的最后一个选项。其他选项(-l 和 --login)无此限制。
+```
+
+### su -c
+
+还有一个值得一提的 `su` 命令行选项为:`-c`。该选项允许你提供在切换到目标用户之后要运行的命令。
+
+`su` 命令手册页是这样说明:
+
+```
+-c, --command COMMAND
+使用 -c 选项指定由 Shell 调用的命令。
+
+被执行的命令无法控制终端。所以,此选项不能用于执行需要控制 TTY 的交互式程序。
+```
+
+参考示例:
+
+```
+su [target-user] -c [command-to-run]
+```
+
+示例中,`command-to-run` 将会被这样执行:
+
+```
+[shell] -c [command-to-run]
+```
+
+示例中的 `shell` 类型将会被目标用户在 `/etc/passwd` 文件中定义的登录 shell 类型所替代。
+
+### Sudo vs Su
+
+现在,我们已经讨论了关于 `su` 命令的基础知识,是时候来探讨一下 `sudo` 和 `su` 命令之间的区别了。
+
+### 关于密码
+
+两个命令的最大区别是:`sudo` 命令需要输入当前用户的密码,`su` 命令需要输入 root 用户的密码。
+
+很明显,就安全而言,`sudo` 命令更好。例如,考虑到需要 root 访问权限的多用户使用的计算机。在这种情况下,使用 `su` 意味着需要与其他用户共享 root 用户密码,这显然不是一种好习惯。
+
+此外,如果要撤销特定用户的超级用户/root 用户的访问权限,唯一的办法就是更改 root 密码,然后再告知所有其他用户新的 root 密码。
+
+而使用 `sudo` 命令就不一样了,你可以很好的处理以上的两种情况。鉴于 `sudo` 命令要求输入的是其他用户的密码,所以,不需要共享 root 密码。同时,想要阻止特定用户访问 root 权限,只需要调整 `sudoers` 文件中的相应配置即可。
+
+### 默认行为
+
+两个命令之间的另外一个区别是默认行为。`sudo` 命令只允许使用提升的权限运行单个命令,而 `su` 命令会启动一个新的 shell,同时允许使用 root 权限运行尽可能多的命令,直到显示退出登录。
+
+因此,`su` 命令的默认行为是有风险的,因为用户很有可能会忘记他们正在以 root 用户身份进行工作,于是,无意中做出了一些不可恢复的更改(例如:对错误的目录运行 `rm -rf` 命令)。关于为什么不鼓励以 root 用户身份进行工作的详细内容,请参考[这里][10]
+
+### 日志记录
+
+尽管 `sudo` 命令是以目标用户(默认情况下是 root 用户)的身份执行命令,但是他们会使用 sudoer 所配置的用户名来记录是谁执行命令。而 `su` 命令是无法直接跟踪记录用户切换到 root 用户之后执行了什么操作。
+
+### 灵活性
+
+`sudo` 命令会比 `su` 命令灵活很多,因为你甚至可以限制 sudo 用户可以访问哪些命令。换句话说,用户通过 `sudo` 命令只能访问他们工作需要的命令。而 `su` 命令让用户有权限做任何事情。
+
+### Sudo su
+
+大概是因为使用 `su` 命令或直接以 root 用户身份登录有风险,所以,一些 Linux 发行版(如 Ubuntu)默认禁用 root 用户帐户。鼓励用户在需要 root 权限时使用 `sudo` 命令。
+
+However, you can still do 'su' successfully, i.e, without entering the root password. All you need to do is to run the following command:
+然而,您还是可以成功执行 `su` 命令,即不用输入 root 用户的密码。运行以下命令:
+
+```
+sudo su
+```
+
+由于你使用 `sudo` 运行命令,你只需要输入当前用户的密码。所以,一旦完成操作,`su` 命令将会以 root 用户身份运行,这意味着它不会再要求输入任何密码。
+
+** PS **:如果你想在系统中启用 root 用户帐户(虽然强烈反对,但你还是可以使用 `sudo` 命令或 `sudo su` 命令),你必须手动设置 root 用户密码 可以使用以下命令:
+
+```
+sudo passwd root
+```
+
+### 结论
+
+这篇文章以及之前的教程(其中侧重于 `sudo` 命令)应该能给你一个比较好的建议,当你需要可用的工具来提升(或一组完全不同的)权限来执行任务时。 如果您也想分享关于 `su` 或 `sudo` 的相关内容或者经验,欢迎您在下方进行评论。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-vs-su/
+
+作者:[Himanshu Arora][a]
+译者:[zhb127](https://github.com/zhb127)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-vs-su/
+[1]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-vs-su/#su-
+[2]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-vs-su/#su-c
+[3]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-vs-su/#password
+[4]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-vs-su/#default-behavior
+[5]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-vs-su/#logging
+[6]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-vs-su/#flexibility
+[7]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-vs-su/#the-su-command-in-linux
+[8]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-vs-su/#sudo-vs-su
+[9]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-vs-su/#sudo-su
+[10]:http://askubuntu.com/questions/16178/why-is-it-bad-to-login-as-root
+[11]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/sudo-beginners-guide/
+[12]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/sudo-vs-su/big/su-command.png
+[13]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/sudo-vs-su/big/su-hyphen-command.png
+[14]:https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Su
diff --git a/translated/tech/20170309 How to Change Root Password of MySQL or MariaDB in Linux.md b/translated/tech/20170309 How to Change Root Password of MySQL or MariaDB in Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6f7cd301e1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20170309 How to Change Root Password of MySQL or MariaDB in Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
+在 Linux 中修改 MySQL 或 MariaDB 的 Root 密码
+============================================================
+
+如果你是第一次[安装 MySQL 或 MariaDB][1],你可以执行 `mysql_secure_installation` 脚本来实现基本的安全设置。
+
+其中的一个设置是数据库的 root 密码 —— 该密码必须保密,并且只在必要的时候使用。如果你需要修改它(例如,当数据库管理员换了人 —— 或者被解雇了!)。
+
+**建议阅读:**[在 Linux 中恢复 MySQL 或 MariaDB 的 Root 密码][2]
+
+这篇文章迟早会派上用场的。我们讲说明怎样来在 Linux 中修改 MySQL 或 MariaDB 数据库服务器的 root 密码。
+
+尽管我们会在本文中使用 MariaDB 服务器,但本文中的用法说明对 MySQL 也有效。
+
+### 修改 MySQL 或 MariaDB 的 root 密码
+
+你知道 root 密码,但是想要重置它,对于这样的情况,让我们首先确定 MariaDB 正在运行:
+
+```
+------------- CentOS/RHEL 7 and Fedora 22+ -------------
+# systemctl is-active mariadb
+------------- CentOS/RHEL 6 and Fedora -------------
+# /etc/init.d/mysqld status
+```
+
+[
+ 
+][3]
+
+*检查 MysQL 状态*
+
+如果上面的命令返回中没有 `active` 这个关键词,那么该服务就是停止状态,你需要在进行下一步之前先启动数据库服务:
+
+```
+------------- CentOS/RHEL 7 and Fedora 22+ -------------
+# systemctl start mariadb
+------------- CentOS/RHEL 6 and Fedora -------------
+# /etc/init.d/mysqld start
+```
+
+接下来,我们将以 root 登录进数据库服务器:
+
+```
+# mysql -u root -p
+```
+
+为了兼容不同版本,我们将使用下面的声明来更新 mysql 数据库的用户表。注意,你需要将 `YourPasswordHere` 替换为你为 root 选择的新密码。
+
+```
+MariaDB [(none)]> USE mysql;
+MariaDB [(none)]> UPDATE user SET password=PASSWORD('YourPasswordHere') WHERE User='root' AND Host = 'localhost';
+MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
+```
+
+要验证是否操作成功,请输入以下命令退出当前 MariaDB 会话。
+
+```
+MariaDB [(none)]> exit;
+```
+
+然后,敲回车。你现在应该可以使用新密码连接到服务器了。
+
+[
+ 
+][4]
+
+*修改 MysQL/MariaDB Root 密码*
+
+
+##### 小结
+
+在本文中,我们说明了如何修改 MariaDB / MySQL 的 root 密码 —— 或许你知道当前所讲的这个方法,也可能不知道。
+
+像往常一样,如果你有任何问题或者反馈,请尽管使用下面的评论框来留下你宝贵的意见或建议,我们期待着您的留言。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+作者简介:
+
+Gabriel Cánepa是一位来自阿根廷圣路易斯的 Villa Mercedes 的 GNU/Linux 系统管理员和 web 开发者。他为世界范围内的主要的消费产品公司工作,也很钟情于在他日常工作的方方面面中使用 FOSS 工具来提高生产效率。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/change-mysql-mariadb-root-password/
+
+作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
+
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-mariadb-in-centos-7/
+[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/reset-mysql-or-mariadb-root-password/
+[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Check-MySQL-Status.png
+[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Change-MySQL-Root-Password.png
+[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
+[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
+[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
diff --git a/translated/tech/CentOS-vs-Ubuntu.md b/translated/tech/CentOS-vs-Ubuntu.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8622bd0ac2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/CentOS-vs-Ubuntu.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+# CentOS vs. Ubuntu
+
+[
+][4]
+Linux 的可选项似乎“无穷无尽”,因为每个人都可以通过修改一个已经发行的版本或者新的 [白手起家的版本] [7] (LFS) 来组建 Linux。关于 Linux 发行版的选择,我们关注的因素包括用户接口、文件系统、包分配、新的特征选项以及更新周期和可维护性等。
+
+在这篇文章中,我们会讲到两个较为熟知的 Linux 发行版,实际山,更多的是介绍两者之间的不同,以及在哪些角度一方比另一方更好。
+
+### 什么是 CentOS?
+
+CentOS ( _Community Enterprise Operating System_ ) 是脱胎于
+红帽企业 Linux (RHEL) 并与之兼容的 Linux 克隆社区支持的发行版,所以我们可以认为 CentOS 是 RHEL 的一个免费版。CentOS 的没一套发行版都有 10 年的维护期,每个新版本的释出周期为 2 年。在 1 月 14 日,CentOS 声明正式加入红帽,为新的 CentOS 董事会所管理,但仍然保持与 RHEL 的独立性。
+
+扩展阅读——[如何安装 CentOS?][1]
+
+### CentOS 的历史和第一次释出
+
+[CentOS][8] 第一次释出是在 2004 年,当时名叫 cAOs Linux;它是由社区维护和管理的一套基于 RPM 的发行版。
+
+CentOS 结合了包括 Debian、Red Hat Linux/Fedora 和 FreeBSD等在内的许多方面,使其能够令服务器和集群稳定工作 3 到 5 年的时间。它有一群开源软件开发者作为拥趸,但只是一个大型组织(CAO 组织)的一部分[1]。
+
+在 2006 年 6 月,David Parsley宣布由他开发的 TAO Linux,另一个 RHEL 克隆版本,退出历史舞台并全力转入 CentOS 的开发工作。不过,他的领域转移并不会影响之前的 TAO 用户, 因为他们可以通过使用 yum update 来更新他们的系统。
+
+2014 年 1 月,红帽开始赞助 CentOS 项目,并移交了所有权和商标。
+
+[[1\. 开源软件][9]]
+
+### CentOS 设计
+确切地说,CentOS 是付费 RHEL (Red Had Enterprise Edition) 版本的克隆。RHEL 提供源码以供之后为 CentOS 修改和变更(移除商标和logo)并完善为最终的成品。
+
+### Ubuntu
+Ubuntu 是一个 基于 Debian 的 Linux 操作系统,应用于桌面、服务器、智能手机和平板电脑等多个领域。Ubuntu 是由一个叫做 Canonical Ltd 的公司发行的,南非的 Mark Shuttleworth 给予赞助。
+
+扩展阅读—— [安装完 Ubuntu 16.10 必须做的 10 件事][2]
+
+### Ubuntu Design
+
+### Ubuntu 设计
+
+Ubuntu 是一个在全世界的开发者共同努力下生成的开源发行版。在这些年的悉心经营下,Ubuntu 变得越来越现代化和人性化,整个系统运行也更加流畅、安全,并且有成千上万的应用可供下载。
+
+由于它是基于 [Debian][10] 的,因此它也支持 .deb 包、最近 post 包系统和更为安全的 [snap 包格式 (snappy)][11].
+
+这种新的打包系统允许应用能够满足所有的依赖性进而传送。
+
+扩展阅读——[Ubuntu 16.10 中的 Linux 及 Ubuntu 回顾][3]
+
+## CentOS 与 Ubuntu 的区别
+
+* Ubuntu 基于 Debian, CentOS 基于 RHEL;
+* Ubuntu 使用 .deb and .snap 的包,CentOS 使用 .rpm 和 flatpak 包;
+* Ubuntu 使用 apt 来更新,CentOS 使用 yum;
+* CentOS 看起来会更稳定,因为它不会像 Ubuntu 那样对包做常规性更新,但这并不意味着 Ubuntu 就不比 CentOS 安全;
+* Ubuntu 有更多的文档和免费的问题、信息支持;
+* Ubuntu 服务器版本有更多的云服务和容器部署上的支持。
+
+### 结论
+
+不论你的选择如何,**是 Ubuntu 还是 CentOS**,两者都是非常优秀稳定的发行版。如果你想要一个释出周期更短的版本,那么就选 Ubuntu;如果你想要一个不经常变更包的版本,那么就选 CentOS。在下方留下的评论,说出你更钟爱哪一个吧!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/centos-vs-ubuntu
+
+作者:[linuxandubuntu.com][a]
+译者:[Meditator-hkx](http://www.kaixinhuang.com)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/centos-vs-ubuntu
+[1]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/how-to-install-centos
+[2]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/10-things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-16-04-xenial-xerus
+[3]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/linuxandubuntu-review-of-unity-8-preview-in-ubuntu-1610
+[4]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/centos-vs-ubuntu
+[5]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/centos-vs-ubuntu
+[6]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/centos-vs-ubuntu#comments
+[7]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/how-to-create-a-linux-distro
+[8]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/10-things-to-do-after-installing-centos
+[9]:https:]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/linuxandubuntu-review-of-unity-8-preview-in-ubuntu-1610
+[10]:https://www.debian.org/
+[11]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Snappy_(package_manager)