mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-27 02:30:10 +08:00
commit
f1a67d67dd
published
20141217 Centralized Secure Storage (iSCSI)-- 'Initiator Client' Setup on RHEL or CentOS or Fedora -Part III.md20141217 Create Centralized Secure Storage using iSCSI Target on RHEL or CentOS or Fedora Part -I.md20141217 How to Create and Setup LUNs using LVM in 'iSCSI Target Server' on RHEL or CentOS or Fedora -Part II.md20150115 How To Run Linux Applications From The Terminal In Background Mode.md
201502
20140819 Top 4 Linux download managers.md20140821 What is a good EPUB reader on Linux.md20140917 How to create a software RAID-1 array with mdadm on Linux.md20141029 How to Install and Setup My Weather Indicator in Ubuntu 14.10.md20141030 Test drive Linux with nothing but a flash drive.md20141108 Adding Ubuntu 14.10, Ubuntu 14.04 and Debian 7 to PXE Network Boot Environment Setup on RHEL or CentOS 7.md20141114 How To Use Emoji Anywhere With Twitter's Open Source Library.md20141120 How to install Xen hypervisor on unused old hardware.md20141203 Undelete Files on Linux Systems.md20141204 The Easy Way to Keep Track of Multiple Time Zones in Ubuntu.md20141205 What is a good free control panel for VPS.md20141210 How to configure rsyslog client for remote logging on CentOS.md20141211 How to use matplotlib for scientific plotting on Linux.md20141219 How to block unwanted IP addresses on Linux efficiently.md20141219 How to schedule appointments and to-do tasks in a Linux terminal.md20141223 20 Linux Commands Interview Questions & Answers.md20141223 Setting up a 'PXE Network Boot Server' for Multiple Linux Distribution Installations in RHEL or CentOS 7.md20141224 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install Kingsoft Office on Linux.md20141224 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to rename multiple files on Linux.md20141226 How to Download Music from Grooveshark with a Linux OS.md20141229 4 Steps to Setup Local Repository in Ubuntu using APT-mirror.md20141229 How to Create Btrfs Filesystem in Linux and its Features.md20150104 Auditd--Tool for Security Auditing on Linux Server.md20150104 How To Install Websvn In CentOS 7.md20150105 How To Install Kodi 14 (XBMC) In Ubuntu 14.04 and Linux Mint 17.md20150105 How To Install Winusb In Ubuntu 14.04.md20150105 Ubuntu apt-get and apt-cache commands with practical examples.md20150106 How to deduplicate files on Linux with dupeGuru.md20150106 Managing Linux server configs with the SaltStack.md20150108 How to Install SSL on Apache 2.4 in Ubuntu 14.0.4.md20150112 Best GNOME Shell Themes For Ubuntu 14.04.md20150114 How to Configure Chroot Environment in Ubuntu 14.04.md20150114 How to Install Ghost on Ubuntu Server 14.04 LTS (Trusty).md20150114 How to Manage Network using nmcli Tool in RedHat or CentOS 7.x.md20150114 Installing Telnet In CentOS or RHEL or Scientific Linux 6 & 7.md20150114 Why Mac users don't switch to Linux.md20150115 Configure Mate Desktop With Mate Tweak.md20150115 How To Extract a Tar Files To a Different Directory on a Linux or Unix-like Systems.md20150115 Tips for Apache Migration From 2.2 to 2.4 on Ubuntu 14.04.md20150116 A Step By Step Guide To Installing Xubuntu Linux.md20150119 3 Ways To Create A Lightweight And Persistent Xubuntu Linux USB Drive.md20150119 Cutegram--A Better Telegram Client For GNU or Linux.md20150119 How To Disable IPv6 In CentOS 7.md20150119 Quick Tip--How To Restart Cinnamon After Crash.md20150121 If a 32-bit integer overflows.md20150121 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to check disk space on Linux with df command.md20150122 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to add a cron job on Linux.md20150122 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to check memory usage on Linux.md20150122 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to set a custom HTTP header in curl.md20150125 4 Best Modern Open Source Code Editors For Linux.md20150126 Ubuntu 15.04 to Integrate Linux Kernel 3.19 Branch Soon.md20150127 Bug in Wi-Fi Direct Android Implementation Causes Denial of Service.md20150127 Install Jetty Web Server On CentOS 7.md20150128 Meet Vivaldi--A New Web Browser Built for Power Users.md20150130 OpenJDK 7 Vulnerabilities Closed in Ubuntu 14.04 and Ubuntu 14.10.md20150202 How to create and show a presentation from the command line on Linux.md20150203 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix 'Your profile could not be opened correctly' on Google Chrome.md20150205 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install Go language on Linux.md20150205 LinuxQuestions Survey Results Surface Top Open Source Projects.md20150209 CrunchBang Linux Is Dead.md20150209 Non-Linux FOSS--Homebrew.md20150215 Get Rid Of Two Google Chrome Icons From Dock In Elementary OS Freya.md
20150215 How To Make GDebi Default Instead of Ubuntu Software Center.mdsources
news
20150130 LibreOffice 4.4 Released as the Most Beautiful LibreOffice Ever.md20150130 OpenJDK 7 Vulnerabilities Closed in Ubuntu 14.04 and Ubuntu 14.10.md20150202 The Pirate Bay Is Now Back Online.md20150205 Debian Forked over systemd--Birth of Devuan GNU or Linux Distribution.md20150207 BQ and Canonical Officially Launch Aquaris E4.5 Ubuntu Edition, the First Ubuntu Phone.md20150209 CrunchBang Linux Is Dead.md20150225 Italian Region Emilia-Romagna Is Switching To OpenOffice.md
share
20141127 11 Useful Utilities To Supercharge Your Ubuntu Experience.md20150119 Cutegram--A Better Telegram Client For GNU or Linux.md20150209 Non-Linux FOSS--Homebrew.md20150225 Install Google's Material Design Inspired GTK And Icon Theme Paper in Linux.md20150227 Chess in a Few Bytes.md
talk
20141211 Open source all over the world.md20141217 Docker and the Integrated Open Source Company.md20141219 2015 will be the year Linux takes over the enterprise and other predictions.md20150112 Linus Tells Wired Leap Second Irrelevant.md20150119 Linus Torvalds responds to Ars about diversity niceness in open source.md20150122 Top 10 FOSS legal developments of 2014.md20150122 Top 10 open source projects of 2014.md20150205 LinuxQuestions Survey Results Surface Top Open Source Projects.md20150215 A Look At What Linux Games We Will See In 2015 And Beyond.md20150225 Torvalds--'People who start writing kernel code get hired really quickly'.md20150304 No reboot patching comes to Linux 4.0.md
tech
20130315 How to protect SSH server from brute force attacks using fail2ban.md20141203 Undelete Files on Linux Systems.md20141205 How to configure a syslog server with rsyslog on Linux.md20141229 4 Steps to Setup Local Repository in Ubuntu using APT-mirror.md20150104 How to set up a cross-platform backup server on Linux with BackupPC.md20150112 What are useful command-line network monitors on Linux.md20150115 Get back your privacy and control.md20150121 How to Monitor Network Usage with nload in Linux.md20150121 How to apply image effects to pictures on Raspberry Pi.md20150126 Improve system performance by moving your log files to RAM Using Ramlog.md
@ -1,33 +1,33 @@
|
||||
中心化存储(iSCSI)- “初始器客户端” 在RHEL/CentOS/Fedora上的设置 - 第三部分
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
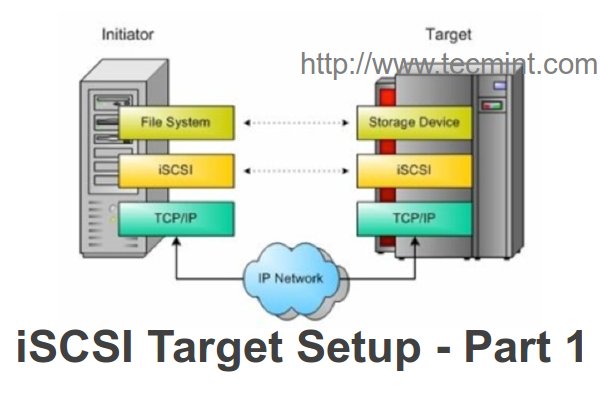
**iSCSI** 初始化器是一种用于与iSCSI target服务器认证并访问服务器上共享的的LUN的客户端。我们可以在本地挂载的硬盘上部署任何操作系统,只需要安装一个包来与target服务器验证。
|
||||
设置iSCSI的发起程序(客户端)(三)
|
||||
============================
|
||||
|
||||
**iSCSI** 发起程序是一种用于同 iSCSI 目标器认证并访问服务器上共享的LUN的客户端。我们可以在本地挂载的硬盘上部署任何操作系统,只需要安装一个包来与目标器验证。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
初始器客户端设置
|
||||
*初始器客户端设置*
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能 ####
|
||||
### 功能 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 可以处理本地挂载磁盘上的任意文件系统
|
||||
- 在使用fdisk命令后不需要重启系统
|
||||
- 在使用fdisk命令分区后不需要重启系统
|
||||
|
||||
#### 要求 ####
|
||||
### 前置阅读 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- [使用iSCSI Target创建集中化安全存储- 第一部分][1]
|
||||
- [在Target服务器中使用LVM创建LUN - 第二部分][2]
|
||||
- [使用iSCSI Target创建集中式安全存储(一)][1]
|
||||
- [在 iSCSI Target 服务器中使用LVM创建和设置LUN(二)][2]
|
||||
|
||||
#### 我的客户端设置 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 操作系统 – CentOS release 6.5 (最终版)
|
||||
- iSCSI Target IP – 192.168.0.50
|
||||
- 操作系统 – CentOS 6.5 (Final)
|
||||
- iSCSI 目标器 IP – 192.168.0.50
|
||||
- 使用的端口 : TCP 3260
|
||||
|
||||
**Warning**: Never stop the service while LUNs Mounted in Client machines (Initiator).
|
||||
**Warning**:永远不要在使用LUN的时候在客户端中(初始化器)停止服务。
|
||||
**警告**:永远不要在LUN还挂载在客户端(发起程序)时停止服务。
|
||||
|
||||
### 客户端设置 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**1.** 在客户端,我们需要安装包‘**iSCSI-initiator-utils**‘,用下面的命令搜索包。
|
||||
**1.** 在客户端,我们需要安装包‘**iSCSI-initiator-utils**’,用下面的命令搜索包。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum search iscsi
|
||||
|
||||
@ -37,29 +37,29 @@
|
||||
iscsi-initiator-utils.x86_64 : iSCSI daemon and utility programs
|
||||
iscsi-initiator-utils-devel.x86_64 : Development files for iscsi-initiator-utils
|
||||
|
||||
**2.** 一旦定位了包,就用下面的yum命令安装初始化包。
|
||||
**2.** 找到了包,就用下面的yum命令安装初始化包。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install iscsi-initiator-utils.x86_64
|
||||
|
||||
**3.** 安装完毕后,我们需要发现**Target 服务器**上的共享。客户端的命令有点难记,因此我们使用man来的到需要运行的命令列表
|
||||
**3.** 安装完毕后,我们需要发现**目标器**上的共享。客户端的命令有点难记,因此我们使用man找到需要运行的命令列表。
|
||||
|
||||
# man iscsiadm
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
man iscsiadm
|
||||
*man iscsiadm*
|
||||
|
||||
**4.** 按下**SHIFT+G** 进入man页的底部并且稍微向上滚动来的到登录的示例命令。下面的发现命令中,需要用我们的**服务器IP地址**来替换。
|
||||
**4.** 按下**SHIFT+G** 进入man页的底部并且稍微向上滚动找到示例的登录命令。下面的发现命令中,需要用我们的**服务器IP地址**来替换。
|
||||
|
||||
# iscsiadm --mode discoverydb --type sendtargets --portal 192.168.0.200 --discover
|
||||
|
||||
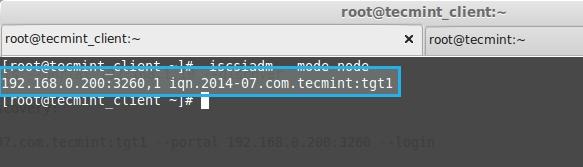
**5.** 这里我们从下面的命令中得到了iSCSIi限定名(iqn)。
|
||||
**5.** 这里我们从下面的命令输出中找到了iSCSI的限定名(iqn)。
|
||||
|
||||
192.168.0.200:3260,1 iqn.2014-07.com.tecmint:tgt1
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
发现服务器
|
||||
*发现服务器*
|
||||
|
||||
**6.** 要登录就用下面的命令来连接一台LUN到我们本地系统中,这会与服务器验证并允许我们登录LUN。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -67,7 +67,7 @@ man iscsiadm
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
登录到服务器
|
||||
*登录到服务器*
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:登出使用登录命令并在命令的最后使用logout来替换。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -75,15 +75,15 @@ man iscsiadm
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
等出服务器
|
||||
*登出服务器*
|
||||
|
||||
**7.** 登录服务器后,使用下面的命令列出节点的记录。
|
||||
**7.** 登录服务器后,使用下面的命令列出节点的记录行。
|
||||
|
||||
# iscsiadm --mode node
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
列出节点
|
||||
*列出节点*
|
||||
|
||||
**8.** 显示特定节点的所有数据
|
||||
|
||||
@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ man iscsiadm
|
||||
iface.linklocal_autocfg = <empty>
|
||||
....
|
||||
|
||||
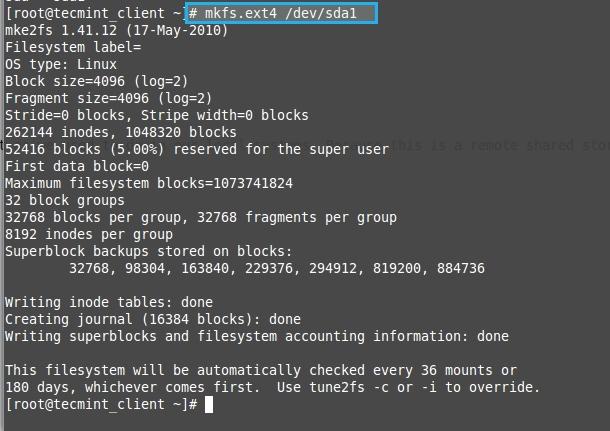
**9.** 接着列出使用的磁盘,fdisk会列出所有的认证过的磁盘。
|
||||
**9.** 接着列出使用的磁盘,fdisk会列出所有的登录认证过的磁盘。
|
||||
|
||||
# fdisk -l /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
@ -123,7 +123,7 @@ man iscsiadm
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建新分区
|
||||
*创建新分区*
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:在使用fdisk创建新分区之后,我们无需重启,就像使用我们本地的文件系统一样就行。因为这个将远程共享存储挂载到本地了。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -133,7 +133,7 @@ man iscsiadm
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
格式化新分区
|
||||
*格式化新分区*
|
||||
|
||||
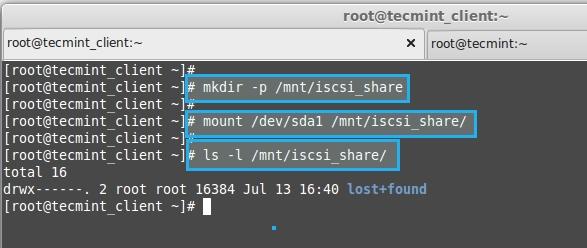
**12.** 创建一个目录来挂载新创建的分区
|
||||
|
||||
@ -143,20 +143,20 @@ man iscsiadm
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
挂载新分区
|
||||
*挂载新分区*
|
||||
|
||||
**13.** 列出挂载点
|
||||
|
||||
# df -Th
|
||||
|
||||
- **-T** – Prints files system types.
|
||||
- **-h** – Prints in human readable format eg : Megabyte or Gigabyte.
|
||||
- **-T** – 输出文件系统类型
|
||||
- **-h** – 以易读的方式显示大小
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列出新分区
|
||||
*列出新分区*
|
||||
|
||||
**14.** 如果需要永久挂在使用fdtab文件
|
||||
**14.** 如果需要永久挂载,使用fdtab文件
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/fstab
|
||||
|
||||
@ -168,18 +168,18 @@ man iscsiadm
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
自动挂载分区
|
||||
*自动挂载分区*
|
||||
|
||||
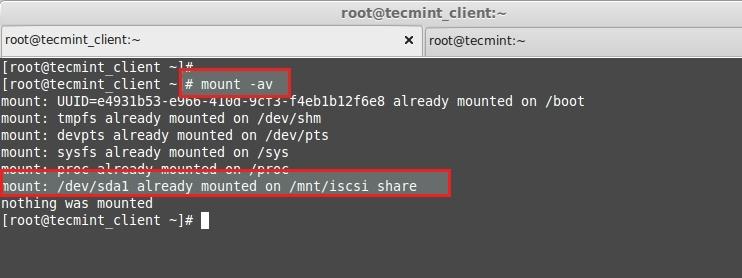
**16.** 最后检查我们fstab文件是否有错误。
|
||||
|
||||
# mount -av
|
||||
|
||||
- **-a** – 所有挂载点
|
||||
- **-v** – 繁琐模式
|
||||
- **-v** – 冗余模式
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
验证fstab文件
|
||||
*验证fstab文件*
|
||||
|
||||
我们已经成功完成了我们的客户端配置。现在让我们像本地磁盘一样使用它吧。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -189,10 +189,10 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/iscsi-initiator-client-setup/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Babin Lonston][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/babinlonston/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/create-centralized-secure-storage-using-iscsi-targetin-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/create-luns-using-lvm-in-iscsi-target/
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-4971-1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.cn/article-4972-1.html
|
||||
@ -1,46 +1,47 @@
|
||||
在RHEL/CentOS/Fedora上使用iSCSI Target创建集中式安全存储 - 第一部分
|
||||
使用iSCSI Target创建集中式安全存储(一)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**iSCSI** 是一种就块级别协议,用于通过TCP/IP网络共享**原始存储设备**,可以用已经存在的IP和以太网如网卡、交换机、路由器等通过iSCSI协议共享和访问存储。iSCSI target是一种远程iSCSI服务器或者taget上的远程硬盘。
|
||||
**iSCSI** 是一种块级别的协议,用于通过TCP/IP网络共享**原始存储设备**,可以用已经存在的IP和以太网如网卡、交换机、路由器等通过iSCSI协议共享和访问存储。iSCSI target是一种由远程iSCSI服务器(target)提供的远程硬盘。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux中安装iSCSI Target
|
||||
|
||||
我们不需要在客户端为了稳定的连接和性能而占用很大的资源。iSCSI服务器称为Target,它共享存储。iSCSI客户端称为Initiator,它访问Target服务器行的存储。市场中有用于大型存储服务如SAN的iSCSI适配器。
|
||||
*在Linux中安装iSCSI Target*
|
||||
|
||||
我们不需要占用很大的资源就可以为客户端提供稳定的连接和性能。iSCSI服务器称为“Target(目标器)”,它提供服务器上的存储共享。iSCSI客户端称为“Initiator(发起程序)”,它访问目标器共享的存储。市场中有卖的用于大型存储服务如SAN的iSCSI适配器。
|
||||
|
||||
**我们为什么要在大型存储领域中使用iSCSI适配器**
|
||||
|
||||
以太网适配器(NIC)被设计用于在系统、服务器和存储设备如NAS间传输分组数据,它不适合在Internet中传输块级别数据。
|
||||
以太网适配器(NIC)被设计用于在系统、服务器和存储设备如NAS间传输分组数据,它不适合在Internet中传输块级数据。
|
||||
|
||||
### iSCSI Target的功能 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 可以在一台机器上运行几个iSCSI target
|
||||
- 一台机器的多个iSCSI target可以在iSCSI中访问
|
||||
- 一个target就是一块存储,并且可以通过网络被初始化器(客户端)访问
|
||||
- 可以在一台机器上运行几个iSCSI 目标器
|
||||
- 一台机器可以提供多个iSCSI 目标器用于iSCSI SAN访问
|
||||
- 一个目标器就是一块存储,并且可以通过网络被发起程序(客户端)访问
|
||||
- 把这些存储汇聚在一起让它们在网络中可以访问的是iSCSI LUN(逻辑单元号)
|
||||
- iSCSI支持在同一个会话中含有多个连接
|
||||
- iSCSI初始化器在网络中发现目标接着用LUN验证并登录,这样就可以本地访问远程存储。
|
||||
- 我们了一在本地挂载的LUN上安装任何操作系统,就像我们安装我们本地的操作系统一样。
|
||||
- iSCSI支持在同一个会话中使用多个连接
|
||||
- iSCSI发起程序在网络中发现目标接着用LUN验证并登录,这样就可以本地访问远程存储。
|
||||
- 我们可以在本地挂载的LUN上安装任何操作系统,就像我们安装我们本地的操作系统一样。
|
||||
|
||||
### 为什么需要iSCSI? ###
|
||||
|
||||
在虚拟化中,我们需要存储拥有高度的冗余性、稳定性,iSCSI以低成本的方式提供了这些特性。与使用光纤通道的SAN比起来,我们可以使用已经存在的设备比如NIC、以太网交换机等建造一个低成本的SAN。
|
||||
|
||||
现在我开始使用iSCSI Target安装并配置安全存储。本篇中,我们遵循下面的步骤
|
||||
现在我开始使用iSCSI 目标器安装并配置安全存储。本篇中,我们遵循下面的步骤:
|
||||
|
||||
- 我们需要隔离一个系统来设置iSCSI Target服务器和初始化器(客户端)。
|
||||
- 可以在大型存储环境中添加多个硬盘,但是我们除了基本的安装盘之外只使用一个额外的驱动器。
|
||||
- 现在我们只使用2块硬盘,一个用于基本的服务器安装,另外一个用于存储(LUN),这个我们会在这个系列的第二篇描述。
|
||||
- 我们需要隔离一个系统来设置iSCSI Target服务器和发起程序(客户端)。
|
||||
- 在大型存储环境中可以添加多个硬盘,但是这里我们除了基本的安装盘之外只使用了一个额外的驱动器。
|
||||
- 这里我们只使用了2块硬盘,一个用于基本的服务器安装,另外一个用于存储(LUN),这个我们会在这个系列的第二篇描述。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 主服务器设置 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 操作系统 – CentOS release 6.5 (最终版)
|
||||
- iSCSI Target IP – 192.168.0.200
|
||||
- 操作系统 – CentOS 6.5 (Final)
|
||||
- iSCSI 目标器 IP – 192.168.0.200
|
||||
- 使用的端口 : TCP 860, 3260
|
||||
- 配置文件 : /etc/tgt/targets.conf
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装 iSCSI Target ##
|
||||
### 安装 iSCSI Target ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端并使用yum命令来搜索我们需要在iscsi target上安装的包名。
|
||||
打开终端并使用yum命令来搜索需要在iscsi 目标器上安装的包名。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum search iscsi
|
||||
|
||||
@ -52,21 +53,21 @@
|
||||
lsscsi.x86_64 : List SCSI devices (or hosts) and associated information
|
||||
scsi-target-utils.x86_64 : The SCSI target daemon and utility programs
|
||||
|
||||
We got the search result as above, choose the **Target** package and install to play around.
|
||||
你会的到上面的那些结果,选择**Target**包来安装
|
||||
你会的到上面的那些结果,选择**Target**包来安装。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install scsi-target-utils -y
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
安装iSCSI工具
|
||||
|
||||
列出安装的包来了解默认的配置、服务和man页面的位置
|
||||
*安装iSCSI工具*
|
||||
|
||||
列出安装的包里面的内容来了解默认的配置、服务和man页面的位置。
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -ql scsi-target-utils.x86_64
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列出所有的iSCSI文件
|
||||
*列出所有的iSCSI包里面的文件*
|
||||
|
||||
让我们启动iSCSI服务,并检查服务运行的状态,iSCSI的服务名是**tgtd**。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -75,7 +76,7 @@ We got the search result as above, choose the **Target** package and install to
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
启动iSCSI服务
|
||||
*启动iSCSI服务*
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们需要配置开机自动启动。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -87,53 +88,53 @@ We got the search result as above, choose the **Target** package and install to
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
开机启动iSCSI
|
||||
*开机启动iSCSI*
|
||||
|
||||
现在使用**tgtadm**来列出在我们的服务器上已经配置了哪些target和LUN。
|
||||
现在使用**tgtadm**来列出在我们的服务器上已经配置了哪些目标器和LUN。
|
||||
|
||||
# tgtadm --mode target --op show
|
||||
|
||||
**tgtd**已经安装并在运行了,但是上面的命令没有**输出**因为我们还没有在Target服务器上定义LUN。要查看手册,运行‘**man**‘命令。
|
||||
**tgtd**已经安装并在运行了,但是上面的命令没有**输出**因为我们还没有在目标器上定义LUN。要查看手册,可以运行‘**man**‘命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# man tgtadm
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
iSCSI Man 页面
|
||||
*iSCSI Man 页面*
|
||||
|
||||
最终我们需要为iSCSI添加iptable规则,如果你的target服务器上存在iptable的话。首先使用netstat命令找出iscsi target的端口号,target总是监听TCP端口3260。
|
||||
如果你的target服务器上有iptable的话,那么我们需要为iSCSI添加iptable规则。首先使用netstat命令找出iscsi target的端口号,target总是监听TCP端口3260。
|
||||
|
||||
# netstat -tulnp | grep tgtd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
找出iSCSI端口
|
||||
*找出iSCSI端口*
|
||||
|
||||
下面加入如下规则让iptable允许广播iSCSI target发现包。
|
||||
下面加入如下规则让iptable允许广播iSCSI 目标器发现包。
|
||||
|
||||
# iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 860 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
|
||||
# iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 3260 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
打开iSCSI端口
|
||||
*打开iSCSI端口*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
添加iSCSI端口到iptable中
|
||||
*添加iSCSI端口到iptable中*
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 规则可能根据你的 **默认链策略**而不同。接着保存iptable并重启。
|
||||
**注意**: 规则可能根据你的 **默认链策略**而不同。接着保存iptable并重启该服务。
|
||||
|
||||
# iptables-save
|
||||
# /etc/init.d/iptables restart
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
重启iptable
|
||||
*重启iptable*
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们已经部署了一个target服务器来共享LUN给通过TCP/IP认证的初始化器。这也适用于从小到大规模的生产环境。
|
||||
现在我们已经部署了一个目标器来共享LUN给通过TCP/IP认证的发起程序。这也适用于从小到大规模的生产环境。
|
||||
|
||||
在我的下篇文章中,我会展示如何[在Target服务器中使用LVM创建LUN][1],并且如何在客户端中共享LUN,在此之前请继续关注TecMint获取更多的更新,并且不要忘记留下有价值的评论。
|
||||
在我的下篇文章中,我会展示如何[在目标器中使用LVM创建LUN][1],并且如何在客户端中共享LUN,不要忘记留下有价值的评论。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -141,7 +142,7 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/create-centralized-secure-storage-using-iscsi-target
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Babin Lonston][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,47 +1,47 @@
|
||||
如何在RHEL/CentOS/Fedora中使用LVM创建和设置LUN- 第二部分
|
||||
在 iSCSI Target 服务器中使用LVM创建和设置LUN(二)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
LUN是逻辑单元号,它与iSCSI存储服务器共享。物理iSCSI target服务器共享它的驱动器来初始化TCP/IP网络。驱动器的集合称作LUN来幸存一个大型存储也就是SAN(Storage Area Network)。在真实环境中LUN在LVM中定义,因此它可以按需扩展。
|
||||
LUN是逻辑单元号,它与iSCSI存储服务器共享。iSCSI 目标器通过TCP/IP网络共享它的物理驱动器给发起程序(initiator)。这些来自一个大型存储(SAN:Storage Area Network)的驱动器集合称作LUN。在真实环境中LUN是在LVM中定义的,因为它可以按需扩展。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Create LUNS using LVM in Target Server
|
||||
|
||||
*在目标器中使用 LVM 创建 LUN*
|
||||
|
||||
### 为什么使用LUN? ###
|
||||
|
||||
LUN用于存储,SAN存储大多数有LUN的集群来组成池,LUN由几块物理驱动器组成。我们可以使用LUN作为系统物理驱动器来安装操作系统,LUN在集群、虚拟服务器、SAN中使用。在虚拟服务器中使用LUN的目的是作为系统存储。LUN的性能和可靠性根据在创建目标存储服务器时所使用的驱动器决定。
|
||||
LUN用于存储,SAN存储大多数由LUN的集群来组成存储池,LUN由目标器的几块物理驱动器组成。我们可以使用LUN作为系统物理驱动器来安装操作系统,LUN可以用在集群、虚拟服务器、SAN中。在虚拟服务器中使用LUN的主要用途是作为操作系统的存储。LUN的性能和可靠性根据在创建目标存储服务器时所使用的驱动器决定。
|
||||
|
||||
### 需求 ###
|
||||
### 前置阅读 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要了解创建iSCSI target服务器点击下面的链接。
|
||||
要了解创建iSCSI 目标器,点击下面的链接。
|
||||
|
||||
- [使用iSCSI target创建爱你集中话安全存储][1]
|
||||
- [使用iSCSI Target创建集中式安全存储(一)][1]
|
||||
|
||||
#### 主服务器设置 ####
|
||||
|
||||
系统信息和网络设置部分与已经写的iSCSI Target服务相同 - 我们在相同的服务器上定义LUN。
|
||||
系统信息和网络设置部分与前文的iSCSI 目标器相同 - 我们在相同的服务器上定义LUN。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 操作系统 – CentOS release 6.5 (最终版)
|
||||
- iSCSI Target IP – 192.168.0.200
|
||||
- 操作系统 – CentOS 6.5 (Final)
|
||||
- iSCSI 目标器 IP – 192.168.0.200
|
||||
- 使用的端口 : TCP 860, 3260
|
||||
- 配置文件 : /etc/tgt/targets.conf
|
||||
|
||||
## 在iSCSI Target Server使用LVM创建LUN ##
|
||||
### 在iSCSI 目标器使用LVM创建LUN ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,用**fdisk -l**命令找出驱动器的列表,这会列出系统中所有分区的列表。
|
||||
|
||||
# fdisk -l
|
||||
|
||||
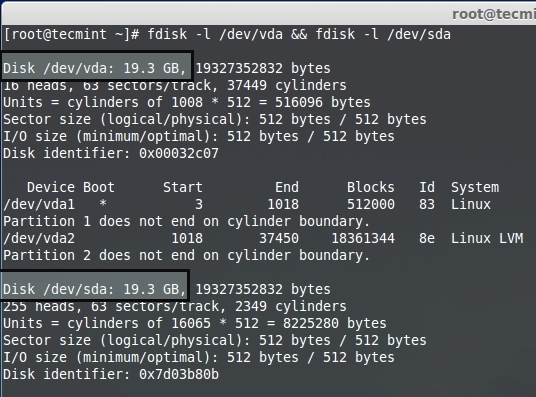
上面的命令只会给出基本系统的驱动器信息。为了个到存储设备的信息,使用下面的命令来的到存储设备的列表。
|
||||
上面的命令只会给出基本系统的驱动器信息。为了得到存储设备的信息,使用下面的命令来得到存储设备的列表。
|
||||
|
||||
# fdisk -l /dev/vda && fdisk -l /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
列出存储设备
|
||||
*列出存储设备*
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:这里**vda**是虚拟机硬盘,因为我使用的是虚拟机来用于演示,**/dev/sda** 是额外加入的存储。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一步: 创建用于LUN的LVM ###
|
||||
### 第一步: 创建用于LUN的LVM驱动器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用**/dev/sda**驱动器来创建LVM。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -49,14 +49,14 @@ LUN用于存储,SAN存储大多数有LUN的集群来组成池,LUN由几块
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列出LVM驱动器
|
||||
*列出LVM驱动器*
|
||||
|
||||
现在让我们如下使用fdisk命令列出驱动器分区。
|
||||
现在让我们使用如下fdisk命令列出驱动器分区。
|
||||
|
||||
# fdisk -cu /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
- The option ‘**-c**‘ 关闭DOS兼容模式。
|
||||
- The option ‘**-u**‘ 用于列出分区表,给出扇区而不是柱面的大小。
|
||||
- 选项 ‘**-c**’ 关闭DOS兼容模式。
|
||||
- 选项 ‘**-u**’ 用于列出分区表时给出扇区而不是柱面的大小。
|
||||
|
||||
使用**n**创建新的分区。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ LUN用于存储,SAN存储大多数有LUN的集群来组成池,LUN由几块
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建LVM分区
|
||||
*创建LVM分区*
|
||||
|
||||
系统重启后,使用fdisk命令列出分区表。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -117,7 +117,7 @@ LUN用于存储,SAN存储大多数有LUN的集群来组成池,LUN由几块
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
验证LVM分区
|
||||
*验证LVM分区*
|
||||
|
||||
### 第二步: 为LUN创建逻辑卷 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -125,7 +125,7 @@ LUN用于存储,SAN存储大多数有LUN的集群来组成池,LUN由几块
|
||||
|
||||
# pvcreate /dev/sda1
|
||||
|
||||
用iSCSI的名字创建卷组来区分组。
|
||||
用iSCSI的名字创建卷组来区分这个卷组。
|
||||
|
||||
# vgcreate vg_iscsi /dev/sda1
|
||||
|
||||
@ -148,17 +148,17 @@ LUN用于存储,SAN存储大多数有LUN的集群来组成池,LUN由几块
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建LVM逻辑卷
|
||||
*创建LVM逻辑卷*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
验证LVM逻辑卷
|
||||
*验证LVM逻辑卷*
|
||||
|
||||
### 第三步: 在Target Server中定义LUN ###
|
||||
### 第三步: 在目标器中定义LUN ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们已经创建了逻辑卷并准备使用LUN,现在我们在target配置中定义LUN,如果这样那么它只能用在客户机中(启动器)。
|
||||
我们已经创建了逻辑卷并准备使用LUN,现在我们在目标器配置中定义LUN,只有这样做它才能用在客户机中(发起程序)。
|
||||
|
||||
用你选择的编辑器打开位于‘/etc/tgt/targets.conf’的target配置文件。
|
||||
用你选择的编辑器打开位于‘/etc/tgt/targets.conf’的目标器配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/tgt/targets.conf
|
||||
|
||||
@ -179,20 +179,22 @@ LUN用于存储,SAN存储大多数有LUN的集群来组成池,LUN由几块
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在target中配置LUN
|
||||
*在target中配置LUN*
|
||||
|
||||
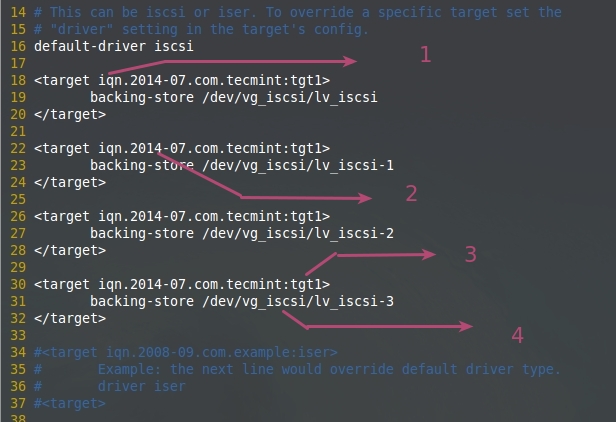
- iSCSI 限定名 (iqn.2014-07.com.tecmint:tgt1).
|
||||
- 随你怎么使用
|
||||
- 确定使用目标, 这台服务器中的第一个目标
|
||||
- 4. LVM共享特定的LUN。
|
||||
上图的解释:
|
||||
|
||||
接下来使用下面命令重载**tgd**服务配置。
|
||||
1. iSCSI 采取限定名 (iqn.2014-07.com.tecmint:tgt1).
|
||||
2. 名称随便你
|
||||
3. 用于确定目标名, 这是这台服务器中的第一个目标
|
||||
4. LVM共享特定的LUN。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来使用下面的命令重载**tgd**服务配置。
|
||||
|
||||
# /etc/init.d/tgtd reload
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
重载配置
|
||||
*重载配置*
|
||||
|
||||
接下来使用下面的命令验证可用的LUN。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -200,23 +202,22 @@ LUN用于存储,SAN存储大多数有LUN的集群来组成池,LUN由几块
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
列出可用LUN
|
||||
*列出可用LUN*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
LUN信息
|
||||
*LUN信息*
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will give long list of available LUNs with following information.
|
||||
上面的命令会列出可用LUN的下面这些信息
|
||||
|
||||
- iSCSI 限定名
|
||||
- iSCSI 准备使用
|
||||
- 默认LUN 0被控制器保留
|
||||
- LUN 1是我们定义的target服务器
|
||||
- 这里我为每个LUN都定义了4GB
|
||||
- 在线: 是的,这就是可以使用的LUN
|
||||
1. iSCSI 限定名
|
||||
2. iSCSI 已经准备好
|
||||
3. 默认LUN 0被控制器所保留
|
||||
4. LUN 1是我们定义的目标器
|
||||
5. 这里我为每个LUN都定义了4GB
|
||||
6. 在线: 是的,这就是可以使用的LUN
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们已经使用LVM为target服务器定义了LUN,这可扩展并且支持很多特性,如快照。我们将会在第三部分了解如何用target服务器授权,并且本地挂载远程存储。
|
||||
现在我们已经使用LVM为目标器定义了LUN,这可扩展并且支持很多特性,如快照。我们将会在第三部分了解如何用目标器授权,并且本地挂载远程存储。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -224,9 +225,9 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/create-luns-using-lvm-in-iscsi-target/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Babin Lonston][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/babinlonston/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/create-centralized-secure-storage-using-iscsi-targetin-linux/
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-4971-1.html
|
||||
@ -1,17 +1,16 @@
|
||||
Translated By H-mudcup
|
||||
|
||||
Linux排名前四的下载管理器
|
||||
Linux下的四大下载管理器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**改善并更好的管理你的网页下载,不论是镜像、抓取数据包还是仅仅更好的掌控你的文件。**
|
||||
**改善你的网页下载,以便更好的管理文件镜像、批量下载还是仅仅希望更好的管理你的文件。**
|
||||
|
||||
下载管理器现在似乎已经是旧闻了,但是他们仍然非常有用。我们来比较一下Linux上排名前四的下载管理器。
|
||||
下载管理器现在似乎已经不新鲜了,但是他们仍然非常有用。我们来比较一下Linux上排名前四的下载管理器。
|
||||
|
||||
### [uGet][1] ###
|
||||
|
||||
如同很多其他的Linux应用一样uGet把体积轻巧和功能全面作为宣传亮点。它能处理有着过滤器的多线程数据流,还能与任何网络浏览器进行整合。它从当初的UrlGet开始,如今已经经过了十年。它还能在Windows上运行。
|
||||
如同很多其他的Linux应用一样,uGet把体积轻巧和功能全面作为宣传亮点。它能处理多线程下载,支持过滤器,还能与任何网络浏览器进行整合。它从当初的UrlGet开始,如今已经经过了十年。它还能在Windows上运行。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
uGet的功能其实非常全面,有很多先进的BT下载客户端所拥有的功能
|
||||
|
||||
*uGet的功能其实非常全面,有很多先进的BT下载客户端所拥有的功能*
|
||||
|
||||
#### 界面 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,40 +22,41 @@ uGet让我们想起了许多BT下载客户端的界面:有着活跃、结束
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能 ####
|
||||
|
||||
成熟的uGet完备了各种功能,包括按计划进行下载任务的启动和终止的高级功能,通过剪贴板批量下载,还能改变它在剪贴板里查找的文件的类型。虽然有插件选项,但不多。
|
||||
成熟的uGet完备了各种功能,包括按计划启动和终止下载任务的高级功能,通过剪贴板批量下载,还能改变它在剪贴板里查找的文件的类型。虽然有插件选项,但不多。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 可得性 ####
|
||||
#### 可获得性 ####
|
||||
|
||||
虽然在多数主要的发行版的软件库中都能得到它,但uGet网站上有着定期更新的适用于各种流行的发行版的二进制安装文件,还能轻易获得源代码。它的运行基于GTK 3+的图形库,所以它在某些桌面环境上的封装要比其他的小,然而我们得说,在KDE或其他Qt桌面上值得有这么一个额外的从属。
|
||||
虽然在多数主要的发行版的软件库中都能得到它,但uGet网站上有着定期更新的适用于各种流行的发行版的二进制安装文件,还能轻易获得源代码。它的运行基于GTK 3+的图形库,所以它在某些桌面环境上的封装要比其他的小,然而我们得说,在KDE或其他Qt桌面上值得为此添加额外的依赖库。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 总体评价 ####
|
||||
|
||||
8/10
|
||||
|
||||
我们非常喜欢uGet——它种类繁多的功能和极高的人气,让它成为了能与Linux浏览器优雅结合的,万能的下载管理器。
|
||||
我们非常喜欢uGet——它种类繁多的功能和极高的人气,让它成为了能与Linux浏览器优雅结合的万能下载管理器。
|
||||
|
||||
### [KGet][2] ###
|
||||
|
||||
KDE自家的下载管理器貌似原本是设计成与KDE的网页浏览器,Konqueror,一同工作的。它带来了我们这次测试中所期待的功能:多下载控制和对下载完成的文件计算校验和的能力。
|
||||
KDE自家的下载管理器貌似原本是设计成与KDE的网页浏览器 Konqueror 一同工作的。它带来了我们这次测试中所期待的功能:多下载控制和对下载完成的文件计算校验和的能力。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
你需要手动激活查看剪贴板中下载链接的功能
|
||||
|
||||
*你需要手动激活查看剪贴板中下载链接的功能*
|
||||
|
||||
#### 界面 ####
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个备受期待的KDE应用软件,KGet用一贯的图标和线条,与桌面环境的审美风格完美融合。它的设计也相当简洁,在主工具栏里只显示最必要的功能,当前下载也以最小界面显示。
|
||||
作为一个备受期待的KDE应用软件,KGet采用一贯的图标和线条,与桌面环境的审美风格完美融合。它的设计也相当简洁,在主工具栏里只显示最必要的功能,当前下载也以最小界面显示。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 集成 ####
|
||||
|
||||
KGet会集成到本地的KDE的Konqueror浏览器里,虽然它并不是最流行的浏览器。Firefox对KGet的支持是一如往常的是通过FlashGot完成的,但是在Chromium里并没有任何一种方法能真正的将它集成进去。你可以打开一个询问你是否想下载已复制的URL的功能,然而KGet对于剪贴板的分析并不是很好,有的时候会把文本下载下来。
|
||||
KGet会集成到本地的KDE的Konqueror浏览器里,虽然它并不是最流行的浏览器。Firefox对KGet的支持是一如既往的是通过FlashGot完成的,但是在Chromium里并没有任何一种方法能真正的将它集成进去。你可以打开一个“询问你是否想下载已复制好的URL”的功能,然而KGet对于剪贴板的分析并不是很好,有的时候会把文本下载下来。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能 ####
|
||||
|
||||
能够选择的功能并不多。没有计划任务,没有批量下载,而且通常情况下,下载功能的数量几乎是光秃秃的。剪贴板扫描功能,想法很不错就是有点问题。设置菜单看起来有点怪怪的,因为它看起来应该设计有更多的功能。
|
||||
能够选择的功能并不多。没有计划任务,没有批量下载,基本上没有什么特色的下载功能。剪贴板扫描功能,想法很不错就是有点问题。设置菜单看起来有点怪怪的,因为它看起来应该设计有更多的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 可得性 ####
|
||||
#### 可获得性 ####
|
||||
|
||||
虽然它不会随着KDE默认安装,但可以在任何支持KDE的发行版里得到它。虽然它的运行需要几个KDE库,找到它的源代码也很困难。支持如此少的发行版,二进制安装文件也没什么可选的。
|
||||
虽然它不会随着KDE默认安装,但可以在任何支持KDE的发行版里得到它。虽然它的运行需要几个KDE库,找到它的源代码也很困难。除了少数几个发行版之外也没有什么二进制安装文件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 总体评价 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,14 +66,15 @@ KGet并没有真正的给予用户比大多数主流浏览器内置下载管理
|
||||
|
||||
### [DownThemAll!][3] ###
|
||||
|
||||
经由Firefox的附件进入Linux的DownThemAll某种程度上可以说是跨平台。这让它只能通过Firefox使用,然而作为世界上最流行的浏览器之一,它这更加紧凑的集成也许正是某些人对下载管理器所期望的。
|
||||
经由Firefox的附属组件进入Linux的DownThemAll从某种程度上可以说是跨平台。这让它只能通过Firefox使用,然而作为世界上最流行的浏览器之一,它这更加紧凑的集成也许正是某些人对下载管理器所期望的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
其实在DownThemALL!上有很多选项可以设置,这让它非常的灵活
|
||||
|
||||
*其实在DownThemALL!上有很多选项可以设置,这让它非常的灵活*
|
||||
|
||||
#### 界面 ####
|
||||
|
||||
与Firefox的集成使得DownThemAll!的风格符合浏览器的审美标准,右键单击可以唤出普通下载和DownThemAll选项。额外的对话框菜单通常和Firefox使用相同的主题,然而主下载窗口则非常整洁并且是基于它本身的设计。
|
||||
与Firefox的集成使得DownThemAll!的风格符合浏览器的审美标准,右键单击可以唤出普通下载和DownThemAll选项。额外的对话框菜单通常和Firefox的主题风格一致,然而主下载窗口则非常整洁并采用了它自己的设计。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 集成 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -81,11 +82,11 @@ KGet并没有真正的给予用户比大多数主流浏览器内置下载管理
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能 ####
|
||||
|
||||
拥有着能同时控制多个下载任务的能力,限制而不荒废带宽以及先进的自动或手动过滤功能,DownThemAll!有着一大堆有助于大规模下载的优秀功能。“一键”功能还让它能非常迅速的启动到预定的文件夹中的下载。这比普通下载功能快多了。
|
||||
拥有着能同时控制多个下载任务的能力,限制而不浪费带宽以及先进的自动或手动过滤功能,DownThemAll!有着一大堆有助于大规模下载的优秀功能。“一键”功能还让它能非常迅速的启动预定文件夹的下载。这比普通下载功能快多了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 可得性 ####
|
||||
#### 可获得性 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Firefox几乎能在所有的发行版和Linux以外的操作系统中获得。这让DownThemAll!也和它一样多产。不幸的是,这是一把双刃剑,因为Firefox可能不是你喜欢的浏览器。它还给浏览器增加了一些负担,让它的启动不再那么轻松。
|
||||
Firefox几乎能在所有的发行版和Linux以外的操作系统中获得。这让DownThemAll!也和它一样多能。不幸的是,这是一把双刃剑,因为Firefox可能不是你喜欢的浏览器。它还给浏览器增加了一些负担,让它的启动不再那么轻松。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 总体评价 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -95,10 +96,11 @@ DownThemAll!是很优秀的,如果你使用Firefox你也许就不再需要用
|
||||
|
||||
### [Steadyflow][4] ###
|
||||
|
||||
Steadyflow很容易在Ubuntu和一些基于Debian的发行版中获得,获取到它的方式可能受到了限制,但它在某些圈子里一直被认为是你能得到的任何发行版里最好的管理器。它能查找剪贴板里的URL,使用GNOME的预设代理,还有许多其他的功能。
|
||||
Steadyflow很容易在Ubuntu和一些基于Debian的发行版中获得,获取它的方式可能受到了一些制约,但它在某些圈子里一直被认为是你能得到的任何发行版里最好的管理器。它能查找剪贴板里的URL,使用GNOME的预设代理,还有许多其他的功能。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Steady flow里的设置非常受限,而且有点难以使用。
|
||||
|
||||
*Steady flow里的设置非常少,而且有点难以使用。*
|
||||
|
||||
#### 界面 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -112,7 +114,7 @@ Steadyflow的形象相当简洁,令人愉悦的、干净的界面并没有让
|
||||
|
||||
极度缺少功能,选项菜单也受到很大限制。暂停和恢复功能看起来也不怎么好使——这是任何浏览器文件下载功能的最基本的部分。文件下载结束的通知和默认行为是可以设置的,还可以选择在文件下载完成之后运行脚本。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 可得性 ####
|
||||
#### 可获得性 ####
|
||||
|
||||
只能在Ubuntu上获取,还不容易得到这个应用的源代码。这意味着虽然在所有基于Ubuntu的发行版中都能很容易的得到它,但也仅限于这些发行版。由于它不是Linux上能得到的最好的下载管理器,所以也不用想太多。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -126,7 +128,7 @@ Steadyflow的形象相当简洁,令人愉悦的、干净的界面并没有让
|
||||
|
||||
#### uGet ####
|
||||
|
||||
在此次测试中,我们已经证明了现代电脑中还是有下载管理器的一席之地的,即便它们中的佼佼者们从BT下载客户端中抄袭了某些功能,貌似侵犯了他们的权益。对于某些人来说BT下载可能是个更有效率的方式,随着ISP们对待BT流量越来越机智,一些人可能用一个好的下载管理器就得到更好的效果。大多数主流ISP不仅仅强加了数据转移标记,在高峰时段他们中的一些甚至开始减慢或封掉BT流量——甚至连发行版的ISO文件和其他免费软件的合法数据流都被限制了。
|
||||
在此次测试中,我们已经证明了现代电脑中还是有下载管理器的一席之地的,即便它们中的佼佼者们从BT下载客户端中抄袭了某些功能,貌似侵犯了他们的权益。对于某些人来说BT下载可能是个更有效率的方式,随着ISP们对待BT流量越来越机智,一些人可能用一个好的下载管理器就得到更好的效果。大多数主流ISP不仅仅强加了数据传输限额,在高峰时段他们中的一些甚至开始减慢或封掉BT流量——甚至连发行版的ISO文件和其他免费软件的合法数据流都被限制了。
|
||||
|
||||
对于这类问题Steadyflow看起来是非常受欢迎的解决方式,但我们的使用和测试显示出,它是一个未完成的简陋的产品。更加古老的uGet则是这场表演的明星,有着惊人数量的可选功能,这些功能既能在下载单一文件中有所帮助,还能在整个网页里过滤出相关元素进行抓取。DownThemAll!与之类似,优秀的Firefox有加分,但它也离不开Firefox,有着几乎同级别的功能,但集成效果更好。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -140,7 +142,7 @@ via: http://www.linuxuser.co.uk/reviews/top-4-linux-download-managers
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Rob Zwetsloot
|
||||
译者:[H-mudcup](https://github.com/H-mudcup)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,25 +1,25 @@
|
||||
Linux版EPUB阅读器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
如果说用平板电脑看书尚属主流的话,那么在电脑上读书就非常少见了。专注阅读16世纪的书是非常困难的了,没人希望后台蹦出Facebook聊天窗口。但是如果你非要在电脑上打开电子书的话,那么你需要一个电子书阅读软件。大多数编辑支持使用EPUB格式来存放电子书(电子出版物)。幸运的书,linux上从不缺乏此类软件。以下书一些Linux上比较好的EPUB阅读软件。
|
||||
如果说用平板电脑看书尚属主流的话,那么在电脑上读书就非常少见了。专注阅读16世纪的书是非常困难的了,没人希望后台蹦出QQ聊天窗口。但是如果你非要在电脑上打开电子书的话,那么你需要一个电子书阅读软件。大多数出版物支持使用EPUB格式的电子书(电子出版物)。幸运的是,linux上从不缺乏EPUB阅读器类的软件。以下是一些Linux上不错的EPUB阅读软件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Calibre ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
先从列表中最有名的软件开始: [Calibre][1]。Calibre 不仅仅是个阅读器,他还是个电子图书馆。软件支持几乎所有的格式,集成了阅读器,管理器,一个可以从互联网下载书籍封面的元数据编辑器,一个EPUB编辑器,新闻阅读器和一个用来下载电子书的搜索引擎。可喜的是,界面丝毫不逊色专业的阅读软件。唯一的缺点书如果你只想要一个EPUB阅读器的话,这个软件还是太大了。
|
||||
先从列表中最有名的软件开始: [Calibre][1]。Calibre 不仅仅是个阅读器,它还是个电子图书馆。软件支持几乎所有的格式,集成了阅读器、管理器、一个可以从互联网下载书籍封面的元数据编辑器、一个EPUB编辑器、新闻阅读器和一个用来下载电子书的搜索引擎。可喜的是,界面丝毫不逊色专业的阅读软件。唯一的缺点是如果你只想要一个EPUB阅读器的话,这个软件还是太大了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. FBReader ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[FBReader][2] 也是一个图书馆管理软件,但是比Calibre小。界面简洁分为两个部分:左边书文件管理、元数据编辑、和下载新书等功能;右边书阅读区。如果你喜欢简洁,这个软件挺不错。我个人非常喜欢这类直观标记书籍和分类的做法。
|
||||
[FBReader][2] 也是一个图书馆管理软件,但是比Calibre小。界面简洁分为两个部分:左边是文件管理、元数据编辑和下载新书等功能;右边是阅读区。如果你喜欢简洁,这个软件挺不错。我个人非常喜欢这类直观标记书籍和分类的做法。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Cool Reader ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
对于那些只想想看EPUB书内容的用户,我推荐 [Cool Reader][5]。遵循Linux应用程序的规则,Cool Reader 做了优化,每次只打开一个EPUB文件,可以使用简单的快捷键进行阅读和导航。由于程序书基于Qt开发的,所以他也遵循Qt的规则,需要大量的设置项。
|
||||
对于那些只想想看EPUB书内容的用户,我推荐 [Cool Reader][5]。遵循Linux应用程序的文化,Cool Reader 做了优化,每次只打开一个EPUB文件,可以使用简单的快捷键进行阅读和导航。由于程序书基于Qt开发的,所以他也遵循Qt的风格,需要大量的设置项。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Okular ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -31,19 +31,19 @@ Linux版EPUB阅读器
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[pPub][4]是个老项目,Github上可以找到这个项目,他最后的更新已经是在两年前了。尽管如此,这个软件还是值得使用的,pPub是用Python编写的,基于GTK3和WebKit,是个简单轻量的软件。界面可能需要一些更新,不够简洁,但是内部却非常好。软件支持JavaScript。所以,谁来捡起这个项目呢?
|
||||
[pPub][4]是个老项目,Github上可以找到这个项目,它最后的更新已经是在两年前了。尽管如此,这个软件还是值得使用的,pPub是用Python编写的,基于GTK3和WebKit,是个简单轻量的软件。界面可能需要一些更新,不够简洁,但是内部却非常好。软件支持JavaScript。所以,谁来捡起这个项目呢?
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. epub ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你只是想快速简单的查看EPUB文件的内容,不关心任何图形化界面功能的话,最好使用命令行模式打开EPUB。[epub][6] 是一个用Python编写的阅读器,可以在终端环境读取EPUB文件的内容。软件可以在章节、页面见切换,没有其他的功能。这是最简洁的EPUB阅读器了。
|
||||
如果你只是想快速简单的查看EPUB文件的内容,不关心任何图形化界面功能的话,最好使用命令行模式打开EPUB。[epub][6] 是一个用Python编写的阅读器,可以在终端环境读取EPUB文件的内容。软件可以在章节、页面间切换,没有其他的功能。这是最简洁的EPUB阅读器了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Sigil ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最后介绍的这个实际上不是个EPUB阅读器,应该是个独立的编辑器。[Sigil][7] 可以提取EPUB文件的内容并转换成其他格式:xhtml文本,图像,格式,还有其他的内容,比如音频等。界面比基本的阅读器复杂,但是功能还是比较丰富的。我很喜欢他的标签体系,如果你对网页比较熟悉的话,这个软件书很好使用的。
|
||||
最后介绍的这个实际上不是个EPUB阅读器,应该是个独立的编辑器。[Sigil][7] 可以提取EPUB文件的内容并将其分离成其他格式:xhtml文本、图像、css,及其他的内容比如音频等。界面比基本的阅读器复杂,但是功能还是比较丰富的。我很喜它的标签体系,如果你对网页比较熟悉的话,这个软件是很好使用的。
|
||||
|
||||
总结,有很多的开源的EPUB阅读器,有一些只有最基本的功能, 另外一些功能却太多了。一般来说,我建议你选择一个最合适的使用。如果你有更好的EPUB阅读器,请在评论里告诉我们!
|
||||
|
||||
@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/good-epub-reader-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrien Brochard][a]
|
||||
译者:[shipsw](https://github.com/shipsw)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
如何使用linux程序mdadm创建软件RAID1软阵列
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
磁盘冗余阵列(RAID)是将多个物理磁盘结合成一个逻辑磁盘的技术,该技术可以提高磁盘容错性能,提高磁盘的读写速度。根据数据存储的排列(如 条带存储,镜像存储,奇偶或者他们的组合),定义了几个不同级别的RAID(RAID-0,RAID-1,RAID-5 等等)。磁盘阵列可以使用软件或者硬件方式实现。现代Linux操作系统中,基本的软件RAID功能是默认安装的。
|
||||
磁盘冗余阵列(RAID)是将多个物理磁盘结合成一个逻辑磁盘的技术,该技术可以提高磁盘容错性能,提高磁盘的读写速度。根据数据存储的排列(如:条带存储,镜像存储,奇偶或者他们的组合),定义了几个不同级别的RAID(RAID-0,RAID-1,RAID-5 等等)。磁盘阵列可以使用软件或者硬件方式实现。现代Linux操作系统中,基本的软件RAID功能是默认安装的。
|
||||
|
||||
本文中,我们将介绍软件方式构建RAID-1阵列(镜像阵列),RAID-1将相同的数据写到不同的设备中。虽然可以使用同一个磁盘的两个分区实现RAID-1,但是如果磁盘坏了的话数据就都丢了,所以没什么意义。实际上,这也是为什么大多数RAID级别都使用多个物理磁盘提供冗余。当单盘失效后不影响整个阵列的运行,并且可以在线更换磁盘,最重要的是数据不会丢失。尽管如此,阵列不能取代外部存储的定期备份。
|
||||
|
||||
由于RAID-1阵列的大小是最小磁盘的大小,一般来说应该使用两个大小相同的磁盘来组建RAID-1。
|
||||
由于RAID-1阵列的大小是阵列中最小磁盘的大小,一般来说应该使用两个大小相同的磁盘来组建RAID-1。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装mdadm ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,7 +28,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# aptitude install mdadm
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu系统中,会要求为电子邮件通知配置后缀MTA。你可以跳过去。
|
||||
Ubuntu系统中,会要求配置Postfix MTA 以发送电子邮件通知。你可以跳过去。
|
||||
|
||||
Debian系统中,安装程序会显示以下解释信息,用来帮助我们去判断是否将根目录安装到RAID阵列中。下面的所有操作都有赖于这一步,所以应该仔细阅读他。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,13 +38,13 @@ Debian系统中,安装程序会显示以下解释信息,用来帮助我们
|
||||
|
||||
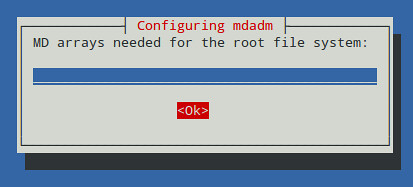
|
||||
|
||||
提示是否开机启动阵列的时候,选择是。注意,这里需要往/etc/fstab 文件中添加一个条目使得系统启动的时候正确挂载阵列。
|
||||
提示是否开机启动阵列的时候,选择“是”。注意,这里需要往/etc/fstab 文件中添加一个条目使得系统启动的时候正确挂载阵列。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 硬盘分区 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在开始准备建立阵列需要的硬盘。这里往插入两个8GB的usb磁盘,使用dmesg命令设备显示设备 /dev/sdb 和 /dev/sdc
|
||||
现在开始准备建立阵列需要的硬盘。这里插入两个8GB的usb磁盘,使用dmesg命令设备显示设备 /dev/sdb 和 /dev/sdc
|
||||
|
||||
# dmesg | less
|
||||
|
||||
@ -107,7 +107,7 @@ Debian系统中,安装程序会显示以下解释信息,用来帮助我们
|
||||
|
||||
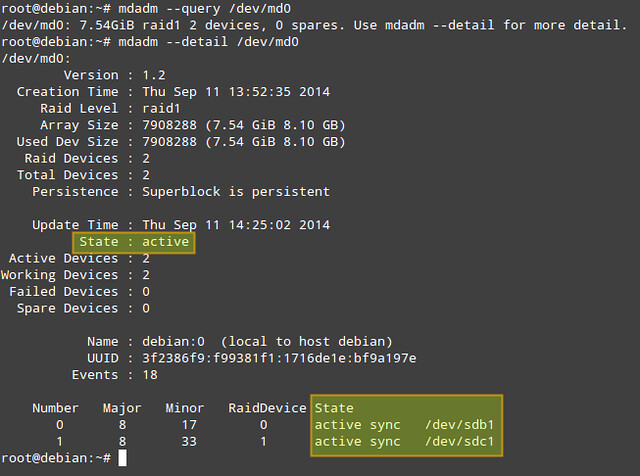
|
||||
|
||||
'mdadm -D'命令提供的信息中,最重要就是阵列状态类。激活状态说明阵列正在进行读写操作。其他几个状态分别为 完成(读写完成)、降级(有一块磁盘失效或丢失)或者恢复中(一张新盘已插入,系统正在写入数据)。这几个状态涵盖类大多数情况。
|
||||
'mdadm -D'命令提供的信息中,最重要就是阵列状态类。激活状态说明阵列正在进行读写操作。其他几个状态分别为:完成(读写完成)、降级(有一块磁盘失效或丢失)或者恢复中(一张新盘已插入,系统正在写入数据)。这几个状态涵盖了大多数情况。
|
||||
|
||||
### 格式化或加载磁盘阵列 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -128,7 +128,7 @@ Debian系统中,安装程序会显示以下解释信息,用来帮助我们
|
||||
|
||||
mdadm工具内置有磁盘阵列监控功能。当mdadm作为守护程序运行的时候(就像我们上文那样),会周期性的检测阵列运行状态,将检测到的信息通过电子邮件或者系统日志报告上来。当然,也可以配置其在发生致命性错误的时候调用紧急命令。
|
||||
|
||||
mdadm默认会记录所有已知分区和阵列的事件,并将他们记录到 /var/log/syslog中。或者你可以在配置文件中(/etc/mdadm/mdadm.conf debian系统 /etc/mdadm.conf 红帽子系统)以以下格式指定监控设备或者阵列。如果mdadm.conf文件不存在,你可以创建一个。
|
||||
mdadm默认会记录所有已知分区和阵列的事件,并将他们记录到 /var/log/syslog中。或者你可以在配置文件中(debian系统:/etc/mdadm/mdadm.conf ,红帽子系统:/etc/mdadm.conf )用以下格式指定监控设备或者阵列。如果mdadm.conf文件不存在,你可以创建一个。
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE /dev/sd[bcde]1 /dev/sd[ab]1
|
||||
|
||||
@ -169,7 +169,7 @@ CentOS或者RHEL 6:
|
||||
|
||||
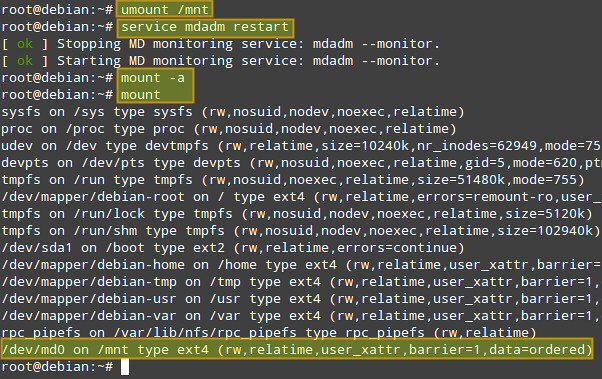
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们的阵列已经可以访问类,拷贝文件/etc/passwd到/mnt中测试一下:
|
||||
现在我们的阵列已经可以访问了,拷贝文件/etc/passwd到/mnt中测试一下:
|
||||
|
||||
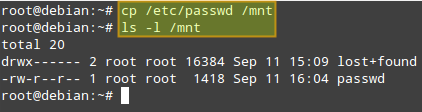
|
||||
|
||||
@ -179,7 +179,7 @@ Debian系统中,需要在/etc/default/mdadm 设置 AUTOSTART 变量为 true
|
||||
|
||||
### 模拟磁盘丢失故障 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们将使用以下命令卸载磁盘来模拟磁盘故障。注意,在实际应用中,磁盘已经上故障状态了,不需要卸载。
|
||||
我们将使用以下命令卸载磁盘来模拟磁盘故障。注意,在实际应用中,磁盘如果已经是故障状态了,不需要卸载。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,卸载阵列:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -190,7 +190,7 @@ Debian系统中,需要在/etc/default/mdadm 设置 AUTOSTART 变量为 true
|
||||
# mdadm /dev/md0 --fail /dev/sdb1 #Marks /dev/sdb1 as faulty
|
||||
# mdadm --remove /dev/md0 /dev/sdb1 #Removes /dev/sdb1 from the array
|
||||
|
||||
然后,如果你有个备用盘的话,重新添加以下:
|
||||
然后,如果你有个备用盘的话,重新添加一下:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm /dev/md0 --add /dev/sdb1
|
||||
|
||||
@ -208,7 +208,7 @@ Debian系统中,需要在/etc/default/mdadm 设置 AUTOSTART 变量为 true
|
||||
# mdadm /dev/md0 --add /dev/sdb1
|
||||
# mdadm --assemble /dev/md0 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1
|
||||
|
||||
希望本文对你有所帮助
|
||||
希望本文对你有所帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -216,7 +216,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/09/create-software-raid1-array-mdadm-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[shipsw](https://github.com/shipsw)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,7 +1,5 @@
|
||||
试试只用U盘加载Linux系统
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
图片来源:Opensource.com
|
||||
|
||||
也许你听过Linux并对它有点好奇,终于想要实际体验一下,但可能不知道从哪儿开始。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,25 +7,27 @@
|
||||
|
||||
如果你手上正好有个U盘的话,那就可以试试做一个USB Linux启动盘。它是一个包含了整个操作系统并可以直接引导开机的U盘。创建它并不需要什么专业技术能力,让我们来看看怎么做,以及如何从USB引导进入Linux系统。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 你需要准备的 ###
|
||||
|
||||
除了一台台式机或笔记本电脑外,你还需要:
|
||||
|
||||
- 一个空白的U盘-最好容量能有4GB或更多。
|
||||
- 一个你想尝试的Linux发行版[ISO镜像][1](一种把所有磁盘内容打包起来的档案文件)。待会再详细介绍。
|
||||
- 一个叫[Unetbootin][2]的应用程序,它是一个开源的,跨平台的工具,用来创建USB启动盘。运行它并不需要启动Linux。在下面的教程中,我是在MacBook上运行的Unetbootiin。
|
||||
- 一个叫[Unetbootin][2]的应用程序,它是一个开源的,跨平台的工具,用来创建USB启动盘。运行它并不需要启动Linux。在下面的教程中,我是在MacBook上运行的Unetbootiin(LCTT 译注:它还有 Windows 和 Linux 版本)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 开始干活 ###
|
||||
|
||||
把U盘插到你电脑的USB端口上,然后启动Unetbootin。然后会要求你输入电脑的登录密码。
|
||||
把U盘插到你电脑的USB端口上,然后启动Unetbootin。然后会要求你输入当前电脑的登录密码。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
还记得之前提到的ISO镜像文件吗?有两种方式可以获得:要么自己从你想尝试的Linux发行版网站上下载,或者让Unetbootin帮你下载。还是选后者,在窗口顶部点击**选择发行版**,选择你想下载的发行版,然后点击**选择版本**来选择你希望尝试的发行版版本。
|
||||
还记得之前提到的ISO镜像文件吗?有两种方式可以获得:要么自己从你想尝试的Linux发行版网站上下载,或者让Unetbootin帮你下载。如果选后者,在窗口顶部点击**选择发行版**,选择你想下载的发行版,然后点击**选择版本**来选择你希望尝试的发行版版本。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
或者,你也可以自己下载发行版。通常,我想尝试的Linux发行版都没有在列表中。如果选择另一个方向,点击**磁盘镜像**,然后点击按钮来选择你下载好的.iso文件。
|
||||
或者,你也可以自己下载发行版。通常,我想尝试的Linux发行版都没有在列表中。如果选择自己下载,那么点击**磁盘镜像**,然后点击按钮来选择你下载好的.iso文件。
|
||||
|
||||
注意到下面的选项**预留每次重新启动后保存文件的空间(仅Ubuntu有效)**吗?如果你尝试的是Ubuntu或它的任一个衍生版(比如Lubuntu或Xubuntu),你可以在U盘上留出几M空间用来保存文件,比如网页书签或你自己创建的文档。当用这个U盘下次启动Ubuntu的时候,你可以继续使用这些文件。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,21 +39,21 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 检验USB启动盘 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个时候,你需要拥抱一下自己内在的极客精神。不会太难,不过你将需要进入[BIOS][3]去偷看一下你电脑内部空间。你的电脑的BIOS会加载各种硬件,并控制电脑操作系统的引导或启动。
|
||||
这个时候,你需要拥抱一下自己内在的极客精神。这不会太难,不过你将需要进入[BIOS][3]去偷看一下你的电脑内部空间。你的电脑的BIOS会加载各种硬件,并控制电脑操作系统的引导或启动。
|
||||
|
||||
BIOS通常会按这个顺序搜索操作系统(或者类似的顺序):硬盘,然后是CD/DVD光驱,然后是外部存储设备。你需要调整这个顺序,让外部存储设备(在这里,意味着你的U盘启动盘)成为BIOS第一个搜索的设备。
|
||||
BIOS通常会按这个顺序搜索操作系统(或者类似的顺序):硬盘,然后是CD/DVD光驱,然后是外部存储设备。你需要调整这个顺序,让外部存储设备(在这里,指的是你的U盘启动盘)成为BIOS第一个搜索的设备。
|
||||
|
||||
要做到这个,把U盘插到电脑上再重启电脑。在看到提示信息**Press F2 to enter setup**之后,按它要求的做。在有的电脑上,这个键可能是F10。
|
||||
要做到这一点,请把U盘插到电脑上再重启电脑。在看到提示信息**Press F2 to enter setup**之后,按它要求的做。在有的电脑上,这个键可能是F10。
|
||||
|
||||
在BIOS里,用键盘上的向右方向键切换到**Boot**菜单。然后你将看到你电脑上的驱动器列表。使用键盘上的向下方向键选中名字为**USB HDD**的选项,然后按下**F6**移动这个选项到列表的顶部。
|
||||
|
||||
完成后,按下**F10**来保存改动。然后你会从BIOS里被踢出来,然后电脑会自己启动。等一小会,你就会看到一个你正在尝试的Linux发行版的启动菜单。选择**Run without installing**(或者最接近的选项)。
|
||||
完成后,按下**F10**来保存改动。然后你会从BIOS里被踢出来,然后电脑会自己启动。等一小会,你就会看到一个你正在尝试的Linux发行版的启动菜单。选择**Run without installing**(或者最类似的选项)。
|
||||
|
||||
在进入桌面后,你可以连接上无线或有线网络,看看网页,试一试预装的软件。你还可以看看,比如说,你的打印机或扫描仪是否能在你试的这个发行版下正常工作。你要是真的想不开,也可以去摸一下命令行。
|
||||
|
||||
### 能干什么 ###
|
||||
|
||||
根据你尝试的Linux发行版和你使用的U盘的速度,操作系统可能会需要更长的时间来加载,而且很可能比直接装到硬盘上会慢一点。
|
||||
根据你尝试的Linux发行版和你使用的U盘的速度,操作系统可能会需要较长的时间来加载,而且很可能比直接装到硬盘上会慢一点。
|
||||
|
||||
还有,你也只能运行Linux发行版里预装好的基本软件。通常会有网页浏览器,一个文字处理软件,一个文本编辑器,一个媒体播放器,一个相片浏览器,以及一套实用工具。这些应该足够给你使用Linux的感觉了。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -65,7 +65,7 @@ via: https://opensource.com/life/14/10/test-drive-linux-nothing-flash-drive
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Scott Nesbitt][a]
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,24 +1,26 @@
|
||||
添加Ubuntu 14.10,Ubuntu 14.04和Debian 7到RHEL/CentOS 7的PXE网络启动环境
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
本教程将指引你添加**Ubuntu 14.10 Server, Ubuntu 14.04 Server**和**Debian 7 Wheezy**发行版到**RHEL/CentOS 7**的PXE网络启动环境中。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
添加Ubuntu和Debian到PXE网络
|
||||
|
||||
*添加Ubuntu和Debian到PXE网络*
|
||||
|
||||
虽然对于本教程,我只会演示怎样来添加**64位**网络安装镜像,但对于Ubuntu或者Debian的**32位**系统,或者其它架构的镜像,操作步骤也基本相同。同时,就我而言,我会解释添加Ubuntu 32位源的方法,但不会演示配置。
|
||||
|
||||
从PXE服务器安装 **Ubuntu**或者**Debian**要求你的客户机必须激活网络连接,最好是使用**DHCP**通过**NAT**来进行动态分配地址。以便安装器拉取所需的包并完成安装过程。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 需求 ####
|
||||
#### 前置阅读 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- [在RHEL/CentOS 7中为多种Linux发行版安装PXE网络启动服务器][1]
|
||||
|
||||
## 步骤 1: 添加Ubuntu 14.10和Ubuntu 14.04服务器到PXE菜单 ##
|
||||
|
||||
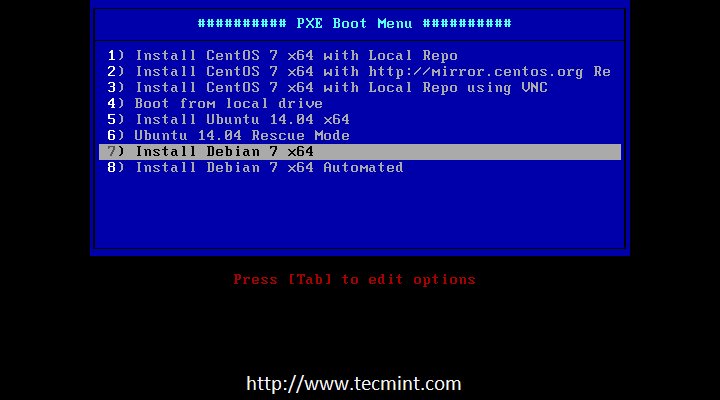
**1.** 为**Ubuntu 14.10**和**Ubuntu 14.04**添加网络安装源到PXE菜单可以通过两种方式实现:其一是通过下载Ubuntu CD ISO镜像并挂载到PXE服务器机器上以便可以读取Ubuntu网络启动文件,其二是通过直接下载Ubuntu网络启动归档包并将其解压缩到系统中。下面,我将进一步讨论这两种方法:
|
||||
**1.** 要将**Ubuntu 14.10**和**Ubuntu 14.04**添加网络安装源到PXE菜单可以通过两种方式实现:其一是通过下载Ubuntu CD ISO镜像并挂载到PXE服务器机器上,以便可以读取Ubuntu网络启动文件,其二是通过直接下载Ubuntu网络启动归档包并将其解压缩到系统中。下面,我将进一步讨论这两种方法:
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用Ubuntu 14.10和Ubuntu 14.04 CD ISO镜像 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了能使用此方法,你的PXE服务器需要有一台可工作的CD/DVD驱动器。在一台专有计算机上,转到[Ubuntu 14.10下载][2]和[Ubuntu 14.04 下载][3]页,获取64位**服务器安装镜像**,将它烧录到CD,并将CD镜像放到PXE服务器DVD/CD驱动器,然后使用以下命令挂载到系统。
|
||||
为了能使用此方法,你的PXE服务器需要有一台可工作的CD/DVD驱动器(LCTT 译注:也可以不用,参考下面内容)。在一台专用的计算机上,转到[Ubuntu 14.10下载][2]和[Ubuntu 14.04 下载][3]页,获取64位**服务器安装镜像**,将它烧录到CD,并将CD镜像放到PXE服务器DVD/CD驱动器,然后使用以下命令挂载到系统。
|
||||
|
||||
# mount /dev/cdrom /mnt
|
||||
|
||||
@ -160,16 +162,20 @@
|
||||
下面是**Ubuntu 14.04**PXE客户端安装测试的截图。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
从PXE菜单选择Ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
*从PXE菜单选择Ubuntu*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
选择Ubuntu安装语言
|
||||
|
||||
*选择Ubuntu安装语言*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
选择Ubuntu救援模式
|
||||
|
||||
*选择Ubuntu救援模式*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Ubuntu救援模式Shell
|
||||
|
||||
*Ubuntu救援模式Shell*
|
||||
|
||||
## 步骤 2: 添加Debian 7 Wheezy到PXE菜单 ##
|
||||
|
||||
@ -184,7 +190,8 @@ Ubuntu救援模式Shell
|
||||
# wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-amd64/current/images/netboot/netboot.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
下载Debian 7网络启动包
|
||||
|
||||
*下载Debian 7网络启动包*
|
||||
|
||||
**6.** 在**wget**下载完成**netboot.tar.gz**文件后,请将其解压缩并运行以下命令拷贝**debian-installer**目录到tftp服务器默认路径。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -192,10 +199,12 @@ Ubuntu救援模式Shell
|
||||
# cp -rf debian-installer/ /var/lib/tftpboot/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
解压缩Debian 7网络启动包
|
||||
|
||||
*解压缩Debian 7网络启动包*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
拷贝Debian 7网络启动文件到FTP
|
||||
|
||||
*拷贝Debian 7网络启动文件到FTP*
|
||||
|
||||
**7.** 要添加**Debian Wheezy**标签到**PXE菜单**,请用你最喜爱的文本编辑器打开PXE服务器默认配置文件并添加以下标签。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -214,7 +223,8 @@ Debian Wheezy 64位的PXE标签菜单。
|
||||
append auto=true priority=critical vga=788 initrd=debian-installer/amd64/initrd.gz -- quiet
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
添加Debian到PXE启动
|
||||
|
||||
*添加Debian到PXE启动*
|
||||
|
||||
**注**:如果你想要添加其它Debian架构,请重复上述步骤,并相应替换PXE默认菜单配置文件中的标签号和**debian-installer/$architecture_name/**目录。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -225,10 +235,12 @@ Debian Wheezy 64位的PXE标签菜单。
|
||||
**9.** 然后通过网络启动一台客户机,选择从PXE菜单安装Debian,并像正常安装一样进一步下去。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
选择从PXE安装Debian
|
||||
|
||||
*选择从PXE安装Debian*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
选择Debian安装语言
|
||||
|
||||
*选择Debian安装语言*
|
||||
|
||||
以上是要求添加并从RHEL/CentOS 7 PXE服务器安装**Ubuntu**或**Debian**到客户机上的全部步骤。在我的下一篇文章中,我将讨论一种更为复杂的方法,如何使用RHEL/CentOS 7 PXE网络启动服务器来安装**Windows 7**到客户机。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -243,7 +255,7 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/add-ubuntu-to-pxe-network-boot/
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-pxe-network-boot-server-in-centos-7/
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-4902-1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/14.10/
|
||||
[3]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/14.04/
|
||||
[4]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/netboot/14.10/
|
||||
@ -1,36 +1,36 @@
|
||||
怎样通过 Twitter 的开源库来随处使用 Emoji 表情符号
|
||||
怎样通过 Twitter 的开源库来随处使用 Emoji 表情符号
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 通过 GitHub 将它们嵌入到网页和其他项目中。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Emoji, 来自日本的小巧符号,通过图像表达感情,已经征服了手机文字信息的世界。
|
||||
Emoji, 来自日本的小巧符号,通过图像表达感情,已经征服了移动互联网的信息世界。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你可以在虚拟世界中随处使用它们了。 Twitter 最近[开源了][1]他们的 emoji 符号库,使得你可以在你自己的网站,应用,和项目中使用它们。
|
||||
|
||||
但这需要一点体力活。 Unicode 已经识别甚至标准化了 emoji 字母表, 然而 emoji 仍然[不能完全与所有的网络浏览器相兼容][2],这意味着大多数情况下,它们将呈现为 “豆腐块”或 空白盒子。当 Twitter 想使得 emoji 可用时,社交网络联合一家名为[Icon Factory][3]的公司共同渲染浏览器以模仿 文本信息符号的效果。结果,Twiter 说道 人们对他们的 emoji 库有很大的需求。
|
||||
但这需要一点体力活。 Unicode 已经识别甚至标准化了 emoji 字母表, 然而 emoji 仍然[不能完全与所有的网络浏览器相兼容][2],这意味着大多数情况下,它们将呈现为 “豆腐块”或“空白盒子”。当 Twitter 想使得 emoji 到处可用时,这家社交网络联合了一家名为[Icon Factory][3]的公司来渲染浏览器以模仿文本信息符号的效果。Twiter 认为人们对他们的 emoji 库有很大的需求。
|
||||
|
||||
现在, 你可以从 [GitHub][4] 上克隆 Twitter 的整个库,从而在你的开发项目中使用它们。 下面将为你介绍如何达到上面的目的以及如何使得 emoji 更容易被使用。
|
||||
|
||||
### 为 Emoji 得到 Unicode 支持 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Unicode 是国际编码标准,它为任意的符号,字母或人们想在网络上使用的数字配置了一串符号。换句话说,它是 你如何在计算机上阅读文本 与 计算机如何读取文本 之间的缺失环节。例如,对于你正看到的位于这些句子中的`空白`,计算机读取为 “&mbsp”。
|
||||
Unicode 是国际编码标准,它为任意的符号、字母或人们想在网络上使用的数字配置了一串编码。换句话说,它是你如何在计算机上阅读文本与计算机如何读取文本之间的缺失环节。例如,对于你正看到的位于这些句子中的`空格`(LCTT 译注:英文分词中间的空格),计算机读取为 “ ”。
|
||||
|
||||
Unicode 甚至拥有其自己的 [原始 emoji][5],它们可以 在没有你的任何努力的情况下在浏览器中被阅读。例如,当你看到了 一个 ❤ 符号,你的计算机正在解码字符串 “2665” 。
|
||||
Unicode 甚至拥有其自己的[原始 emoji][5],它们可以在没有你的任何努力的情况下在浏览器中被阅读。例如,当你看到了 一个 ❤ 符号,你的计算机正在解码字符串 “2665” 。
|
||||
|
||||
要在大多数情况下使用 Twitter 的 emoji 库,你只需在你的 HTML 网页中的 `<head>`块中添加如下脚本:
|
||||
|
||||
<script src="//twemoji.maxcdn.com/twemoji.min.js"></script>
|
||||
|
||||
这样就使得你的项目可以访问 包含有已经在 Twitter 中可使用的数以百计的 Emoji 符号的 JavaScript 库。然而,创建一个仅仅包含这个脚本的文档并不能使得在你的网站中呈现出 emoji 符号,实际上,你仍需要嵌入一些 emoji 符号!
|
||||
这样就使得你的项目可以访问包含有已经在 Twitter 中可使用的数以百计的 Emoji 符号的 JavaScript 库。然而,创建一个仅仅包含这个脚本的文档并不能使得在你的网站中呈现出 emoji 符号,实际上,你仍需要嵌入这些 emoji 符号!
|
||||
|
||||
在 `<body>`块中,粘贴一些可以在 Twitter 的[preview.html 文件源代码][6] 中找到的 emoji 字符串。我使用了 🎹 和 🏁,当然我并不知道在浏览器窗口中它们的样子。是的,你必须粘贴并猜测它们。你已经看出了问题,我们将在 第二小节中予以解决。
|
||||
在 `<body>`块中,粘贴一些可以在 Twitter 的[preview.html 文件源代码][6] 中找到的 emoji 字符串。我使用了 🎹 和 🏁,当然我并不知道在浏览器窗口中它们的样子。是的,你必须粘贴并猜测它们。你已经看出了问题,我们将在第二小节中予以解决。
|
||||
|
||||
无论如何,通过一些尝试,你可以将一个如下图的原始 HTML 文件---
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
---转变成如下图的网页:
|
||||
---显示为如下图的网页:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -52,11 +52,11 @@ Unicode 甚至拥有其自己的 [原始 emoji][5],它们可以 在没有你
|
||||
|
||||
<link rel="stylesheet" href="twemoji-awesome.css">
|
||||
|
||||
一旦你将上面的代码添加了进去,你便可以删除先前添加的 Twitter 的脚本链接。
|
||||
一旦你将上面的代码添加了进去,你便可以删除先前添加的 Twitter 的脚本链接。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,找到 `body` 块部分的代码,然后添加一些 emoji 符号。我使用了 `<i class="twa twa-sparkling-heart"></i>`, `<i class="twa twa-exclamation"></i>`, `<i class="twa twa-lg twa-sparkles"></i>` 和 `<i class="twa twa-beer"></i>`。
|
||||
现在,找到 `body` 块部分的代码,然后添加一些 emoji 符号。我使用了 `<i class="twa twa-sparkling-heart"></i>`, `<i class="twa twa-exclamation"></i>`, `<i class="twa twa-lg twa-sparkles"></i>` 和 `<i class="twa twa-beer"></i>`。
|
||||
|
||||
最终,你将得到如下的代码:
|
||||
最终,你将得到如下的代码:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -64,9 +64,9 @@ Unicode 甚至拥有其自己的 [原始 emoji][5],它们可以 在没有你
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当当!这样你不仅得到了一个可以在浏览器中支持 emoji 符号的基本网页,而且还知道了如何简单地实现它。你可以随意的在[我的 GitHub][9] 中查看这个教程,并且可以克隆这些实际的文件而不只是看看这些截图。
|
||||
Duang!这样你不仅得到了一个可以在浏览器中支持 emoji 符号的基本网页,而且还知道了如何简单地实现它。你可以随意的在[我的 GitHub][9] 中查看这个教程,并且可以克隆这些实际的文件而不只是看看这些截图。
|
||||
|
||||
来自于[得到 Emoji][10]的引导图像; Lauren Orsini 截图。
|
||||
题图来自于[得到 Emoji][10]; Lauren Orsini 截图。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -74,7 +74,7 @@ via: http://readwrite.com/2014/11/12/how-to-use-emoji-in-the-browser-window
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Lauren Orsini][a]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
怎样在废旧的硬件上安装 Xen 虚拟机监视器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Xen 是一个直接运行在硬件上的虚拟机监视器,这意味着你必须准备一个裸机来安装和运行 Xen。KVM 和 Xen 有一些不同 —— 你可以把它安装在任何已经正在运行 Linux 的机器上。本教程描述了如何在废旧的硬件上安装和配置 Xen 虚拟机监视器。
|
||||
Xen 是一个直接运行在硬件上的虚拟机监视器,这意味着你必须准备一个裸机来安装和运行 Xen。而 KVM 则和 Xen 有一些不同 —— 你可以把它添加到任何已经正在运行 Linux 的机器上。本教程描述了如何在废旧的硬件上安装和配置 Xen 虚拟机监视器。
|
||||
|
||||
整个安装过程使用 Debian Jessie(Debian 的测试发行版)作为宿主机操作系统(也称作 [Dom0][1])。Jessie 并不是唯一的选择 —— Xen 的支持是内建在 Linux 内核中的,[许多 Linux 发行版][2] 都包含支持 Xen 的内核。
|
||||
|
||||
### 找点废旧的硬件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,找一个可以格式化的合适的工作站,比如一台旧的笔记本或者台式机。旧的硬件可能不适合玩游戏,但是足够安装一个宿主机和一些客户机了。一个满足下面这些要求的 PC 机就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
- 一个双核 CPU(64 位)
|
||||
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ Xen 是一个直接运行在硬件上的虚拟机监视器,这意味着你必
|
||||
- 能够从 CD,DVD 或者 USB 引导启动
|
||||
- 一块网卡
|
||||
|
||||
注意 CPU 必须是 64 位的,因为 Debian 已经不再支持 32 位的 Xen 安装包。如果你没有空余的硬件,你可以花点钱投资一台旧机器。2010 年值 $1000 的旗舰级笔记本现在只需要 $100。从 eBay 买台二手笔记本并升级下内存也可以满足需求。
|
||||
注意 **CPU 必须是 64 位的,因为 Debian 已经不再支持 32 位的 Xen 安装包**。如果你没有空余的硬件,你可以花点钱买一台旧机器。2010 年值 $1000 的旗舰级笔记本现在只需要 $100。从 eBay 买台二手笔记本并升级下内存也可以满足需求。
|
||||
|
||||
### 刻录一个引导 CD/USB ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,19 +41,19 @@ Xen 是一个直接运行在硬件上的虚拟机监视器,这意味着你必
|
||||
这里的设置使用了四个分区。自动安装时通常会创建一个包含逻辑分区的扩展分区。像下面这样给硬盘分四个区。
|
||||
|
||||
- sda1 挂载至 /boot,200MB
|
||||
- sda2 /, 20GB, Ubuntu 占用 4GB
|
||||
- sda3 swap, 6GB (4GB x 1.5 = 6)
|
||||
- sda2 做为 /, 20GB, Ubuntu 占用 4GB
|
||||
- sda3 做为 swap, 6GB (4GB x 1.5 = 6)
|
||||
- sda4 保留用作 LVM, 不挂载,大小为剩余的硬盘大小
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装基本的系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这里尽可能的让系统的安装更简单快速一些。一个基本的工作用系统可以稍后再添加。Debian 的 APT(Advanced Package Tool)使得添加软件非常的简单。在一个工作站上安装 Deibian 可能会有一些很浪费时间的问题。可能显卡驱动与内核不监控或者可能老旧的 CD-ROM 驱动器只能间歇性的工作。
|
||||
这里尽可能的让系统的安装更简单快速一些。一个基本的工作用系统可以稍后再添加。Debian 的 APT(Advanced Package Tool)使得添加软件非常的简单。在机器上安装 Debian 可能会有一些很浪费时间的问题。可能显卡驱动与内核不监控或者可能老旧的 CD-ROM 驱动器只能间歇性的工作。
|
||||
|
||||
当选择安装软件时,选择安装一个 SSH 服务器,不要安装桌面环境如 Gnome。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
安装一个图形桌面需要安装成百上千的包 —— 这些额外的工作可以稍后再进行。如果你遇到问题了,等到图形桌面的安装会浪费很多事件。同时,没有桌面组件,系统的启动可以更快一些 —— 只需要几十秒而不是几分钟。整个安装过程会需要重启几次,因此这样做可以节省不少时间。
|
||||
安装一个图形桌面需要安装成百上千的包 —— 这些额外的工作可以稍后再进行。如果你遇到问题了,等待图形桌面的安装会浪费很多时间。同时,没有桌面组件,系统的启动可以更快一些 —— 只需要几十秒而不是几分钟。整个安装过程会需要重启几次,因此这样做可以节省不少时间。
|
||||
|
||||
一个 SSH 服务器可以让你从另一台电脑来配置这台工作站。这可以避免一些旧硬件的问题 —— 可能旧机器的键盘少了几个键,LCD 屏幕有坏点或者触摸板没有反应等等。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -79,9 +79,9 @@ Xen 是一个直接运行在硬件上的虚拟机监视器,这意味着你必
|
||||
|
||||
检查 LVM 状态。
|
||||
|
||||
# pvs (to view information about physical volumes)
|
||||
# vgs (to view information about volume groups)
|
||||
# lvs (to view information about logical volumes)
|
||||
# pvs (查看物理卷的信息)
|
||||
# vgs (查看卷组的信息)
|
||||
# lvs (查看逻辑卷的信息)
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加一个 Linux 网桥 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -92,7 +92,6 @@ Xen 是一个直接运行在硬件上的虚拟机监视器,这意味着你必
|
||||
# apt-get install bridge-utils
|
||||
|
||||
查看在哪块网卡配置桥接。
|
||||
See what interfaces are configured.
|
||||
|
||||
# ip addr
|
||||
|
||||
@ -156,13 +155,13 @@ See what interfaces are configured.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
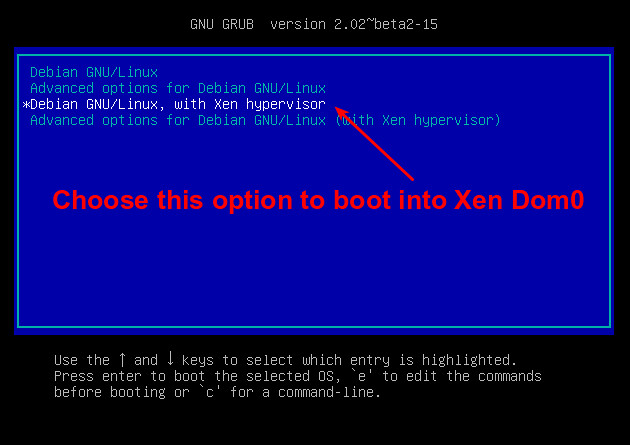
第一个选项会在 5 秒钟内自动启动(在 /etc/default/grub 的 GRUB_TIMEOUT 这行设置),因此这点时间还来不及喝咖啡的。
|
||||
第一个选项会在 5 秒钟内自动启动(在 /etc/default/grub 的 GRUB_TIMEOUT 这行设置),因此这点时间可来不及喝咖啡。
|
||||
|
||||
按下方向键选择 "Debian GNU/Linux, with Xen hypervisor" 这个选项,然后按回车。这时屏幕会出现很多行信息,接着是正常的登录界面。
|
||||
|
||||
### 检查 Xen 工作是否正常 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Xen 虚拟机监视器嗲有一个管理 Xen 的命令行工序叫做 xl,可以用来创建和管理 Xen 虚拟机。使用 xl 命令来检查 Xen 是否成功安装了。
|
||||
Xen 虚拟机监视器带有一个管理 Xen 的命令行程序叫做 xl,可以用来创建和管理 Xen 虚拟机。使用 xl 命令来检查 Xen 是否成功安装了。
|
||||
|
||||
以 root 用户登录,执行:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -206,9 +205,11 @@ Xen 虚拟机监视器嗲有一个管理 Xen 的命令行工序叫做 xl,可
|
||||
|
||||
### 最后 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你使用这台主机作为你的工作站,可以安装一个图形桌面。Debian 包好几种[桌面环境][6]。如果你想要一个包含所有东西的图形桌面,那么安装 Gnome 吧。如果图形效果并不是你的菜,试试 Awesome 吧。
|
||||
如果你使用这台主机作为你的工作站,可以安装一个图形桌面。Debian 包括好几种[桌面环境][6]。如果你想要一个包含所有东西的图形桌面,那么安装 Gnome 吧。如果它的图形效果并不是你的菜,试试 Awesome 吧。
|
||||
|
||||
注意 Debian 的默认 Gnome 环境有大量的额外应用程序包括办公套件 LibreOffice,Iceweasel 浏览器和 Rhythmbox 音乐播放器。安装命令 "apt-get install gnome" 会安装 1,000 多个包并需要将近 2GB 的硬盘空间。运行这个重量级的桌面环境需要占用 1GB 的内存。
|
||||
注意 Debian 的默认 Gnome 环境有大量的额外应用程序包括办公套件 LibreOffice,Iceweasel 浏览器和 Rhythmbox 音乐播放器。安装命令 "apt-get install gnome" 会安装 1,000 多个包并需要将近 2GB 的硬盘空间。运行这个重量级的桌面环境需要占用 1GB 的内存。
|
||||
|
||||
(LCTT 译注:本文没有涉及如何安装 guest 虚拟机,请关注后继文章)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -216,7 +217,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/install-xen-hypervisor.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Nick Hardiman][a]
|
||||
译者:[Liao](https://github.com/liaoishere)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
127
published/201502/20141203 Undelete Files on Linux Systems.md
Normal file
127
published/201502/20141203 Undelete Files on Linux Systems.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
|
||||
怎样在 Linux 系统中恢复已删除文件
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
当用户意外地删除了一个仍然需要的文件时,大多数情况下,是没有简便的方法可以重新找回或重建这个文件。不过,幸运的是文件是可以通过一些方法恢复的。当用户删除了一个文件,该文件并没有消失,只是被隐藏了一段时间。
|
||||
|
||||
这里将解释它是如何工作的。在一个文件系统中,有一个叫做 `文件分配表` 的东西,这个表跟踪文件在存储单元(如硬盘, MicroSD 卡,闪存驱动器等等)中的位置。当一个文件被删除,文件系统将会在`文件分配表`中执行以下两个任务之一:这个文件在`文件分配表`上的条目被标记为 “自由空间” 或删除`文件分配表`里这个文件的条目,且将相应的空间被标记为自由空间 。现在,如果有一个新的文件需要被放置在一个存储单元上,操作系统将会把这个文件放置到标记为空位的地方。在新文件被写入到这个空位后,被删除的文件就彻底消失了。当需要恢复一个已经删除的文件时,用户绝对不能再对任何文件进行操作,因为假如该文件对应的“空位”被占用,这个文件就永远也不能恢复了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 恢复软件是如何工作的? ###
|
||||
|
||||
大多数的文件系统(在删除文件时)只是标记空间为空白。在这些文件系统下,恢复软件查看`文件分配表`这个文件,然后复制被删除的文件到另外的存储单元中。假如该文件被复制到其它需要恢复的被删除的存储单元中,那么用户将有可能会失去那个所需的删除文件。
|
||||
|
||||
文件系统很少会擦除`文件分配表`中的条目。假如文件系统真的这样做了, 这便是恢复软件在恢复文件了。恢复软件在存储单元中扫描文件头,所有文件都拥有一个特殊的编码字符串,它们位于文件的最前面,也被叫做 `魔法数字`。例如,一个编译的 JAVA 类文件的魔法数字在十六进制中是“CAFEBABE”。所以,假如要恢复该类型的文件,恢复软件会查找 “CAFEBABE” 然后复制文件到另一个存储单元。一些恢复软件可以查找某种特殊的文件类型。若用户想恢复一个 PDF 文件,则恢复软件将会查找十六进制的魔法数字 “25504446”,这恰恰是 ASCII 编码中的 “%PDF”。恢复软件将会查找所有的魔法数字,然后用户可以选择恢复哪个已删除的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
假如一个文件的部分被覆写了,则整个文件就会被损坏。通常这个文件可以被恢复,但是其中的内容可能已经没有什么用处。例如,恢复一个已损坏的 JPEG 文件将会是无意义的,因为图片查看器不能从这个损坏的文件产生一幅图片。因此,即使用户拥有了这个文件,该文件也将毫无用处。
|
||||
|
||||
### 设备的位置:###
|
||||
|
||||
在我们继续之前,下面的一些信息将会对指引恢复软件找到正确的存储单元起到一定的帮助。所有的设备均挂载在 `/dev/` 目录下。操作系统赋予每个设备的名称(并不是管理员给予每个分区或设备的名称)遵循一定的命名规律。
|
||||
|
||||
第一个 SATA 硬盘的第二个分区的名称将会是 sda2。名称的第一个字母暗示了存储类型,在这里指的是 SATA,但字母 “s” 也可能指的是 SCSI、 FireWire(火线端口)或 USB。第二个字母 “d” 指的是 disk(硬盘)。第三个字母指的是设备序数,即字母 “a” 指的是第一个 SATA 而 “b” 指的是第二个。最后的数字代表分区。没有分区数字的设备名代表该设置的所有分区。对于上面的例子,对应的名称为 sda 。作为命名的第一个字母还可能是 “h” ,这对应 PATA 硬盘(IDE)。
|
||||
|
||||
以下为命名规律的一些例子。假如一个用户有一个 SATA 硬盘(sda),这个设备有 4 个分区- sda1、 sda2、 sda3 和 sda4 。该用户删除了第三个分区,但直到格式化第四个分区之前,第四个分区名 sda4 都将保留不变。然后该用户插入了一个带有一个分区 - 即sdb1- 的 usb 存储卡(sdb),又增加了一个带有一个分区 -hda1- 的 IDE 硬盘 ,接着该用户又增加了一个 SCSI 硬盘 - sdc1 。接着用户移除了 USB 存储卡(sdb)。现在,SCSI 硬盘的名称仍然为 sdc,但如果这个 SCSI 被移除接着再被插入,则它的名称将变为 sdb。虽然还有其他的存储设备存在, 那个 IDE 硬盘的名称仍会有一个 “a”, 因为它是第一个 IDE 硬盘,IDE 设备的命名与 SCSI、 SATA、 FireWire 和 USB 设备要分开计数。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 TestDisk 进行恢复:###
|
||||
|
||||
每个恢复软件有其不同的功能,特征及支持的不同文件系统。下面是一些关于 使用 TestDisk 在各种文件系统中恢复文件的指南。
|
||||
|
||||
####FAT16、 FAT32、 exFAT (FAT64)、 NTFS 以及 ext2/3/4:####
|
||||
|
||||
TestDisk 是一个运行在 Linux、 *BSD、 SunOS、 Mac OS X、 DOS 和 Windows 等操作系统下的开源的自由软件。 TestDisk 可以从下面的链接中找到 :[http://www.cgsecurity.org/wiki/TestDisk][1]。TestDisk 也可以通过键入 `sudo apt-get install testdisk` 来安装。TestDisk 有着许多的功能,但这篇文章将只关注恢复文件这个功能。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 root 权限从终端中打开 TestDisk 可以通过键入 `sudo testdisk` 命令。
|
||||
|
||||
现在, TestDisk 命令行应用将会被执行。终端的显示将会改变。TestDisk 询问用户它是否可以保留日志,这完全由用户决定。假如一个用户正从系统存储中恢复文件,则不必保留日志。可选择的选项有“生成”、 “追加” 和 “无日志”。假如用户想保留日志,则日志将会保留在该用户的主目录。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在接着的屏幕中,存储设备以 `/dev/*`的方式被罗列出来。对于我的系统,系统的存储单元为 `/dev/sda`,这意味着我的存储单元为 一个 SATA硬盘(sd)且它是第一个硬盘(a)。每个存储单元的容量以 Gigabyte(千兆字节)为单位显示的。使用上下键来选择一个存储设备然后点击进入。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
下一屏显示出一个列有分区表(也叫做分区映射表)的清单。正如文件有`文件配置表`,分区有着分区表。分区是存储设备上的分段。例如在几乎所有的 Linux 系统中,至少存在两种分区类型 - EXT3/4 和 Swap 。每一个分区表将会在下面被简要地描述。TestDisk 并不支持所有类型的分区表,所以这并不是完整的列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **Intel** - 这类分区表在 Windows 系统和许多的 Linux 系统中非常普遍,它也常常称作 MBR 分区表。
|
||||
- **EFI GPT** - 这种类型的分区表通常用在 Linux 系统中。对于 Linux 系统,这种分区表是最为推荐的, 因为逻辑分区或扩展分区的概念并不适用于 GPT (GUID Partition Table) 分区表。 这意味着,如果每个分区中有一个 Linux 系统,一个 Linux 用户可以从多种类型的 Linux 系统中进行多重启动。当然使用 GPT 分区表还有其他的优势,但那些已超出了本文的讨论范围。
|
||||
- **Humax** - Humax 分区映射表适用于韩国公司 Humax 生产的设备。
|
||||
- **Mac** - Apple 分区映射表 (APM) 适用于 Apple 的设备。
|
||||
- **None** - 某些设备并没有分区表。例如,许多 Subor 游戏控制台不使用分区映射表。如果一个用户试图以其它分区表类型从这类设备中恢复文件,用户就会困扰 TestDisk 为何找卟到任何的文件系统或者文件。
|
||||
- **Sun** - Sun 分区表适用于 Sun 系统。
|
||||
- **Xbox** -Xbox 适用于使用 Xbox 分区映射表的存储设备。
|
||||
|
||||
假如用户选择了 “Xbox” ,尽管他的系统使用了 GPT 分区表, 那么 TestDisk 将不能找到任何分区或文件系统。假如 TestDisk 按照用户的选择执行,则它可能猜测错误。(下面的图片显示的是当分区表类型错误时的输出)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当用户为他们的设备选择了正确的选项,则在下一屏中,选择 “高级” 选项。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在,用户将看到一个列有用户存储设备中所有的文件系统或分区的列表。假如用户选择了错误的分区映射表,则在这一步中用户就将会知道他们做出了错误的选择。假如没有错误,通过移动文字光标来高亮选择含有被删除文件的分区。使用 左右键来高亮位于终端底部的 “列表”。接着,按下回车确认。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
新的一屏便会呈现出列有文件和目录的列表。那些白色的文件名就是未被删除的文件,而红色的文件名是那些已被删除的文件。最右边的一列是文件的名称,从右到左方向的接着一列是文件的创建日期,再往左的一列是文件的大小(以 byte/ 比特为单位),最左边带有“-”,“d” ,“r”, “w” 和"x"的一列则代表的是文件的权限情况。“d” 表示该文件为一个目录,其他的权限术语与本文关系不大。在列表的最顶端以“.”代表的一项表示当前目录,第二行以".."代表的一项表示当前目录的上级目录,所以用户可以通过选择目录所在行到达该目录。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
举个例子,我想进入"Xaiml\_Dataset" 目录,该目录基本上由被删除的文件组成。通过按键盘上的 "c"键,我将恢复文件 "computers.xaiml",接着我被询问选择一个目标目录,当然,我应该放置该文件到另一个分区中。现在,当我在我的家目录时,按下了“c”键。(选择目标目录时)哪个目录被高亮并没有什么影响,当前目录就是目标目录,在屏幕的上方,将会显示“复制完成”的消息。在我的家目录中便会有一个名为"Xaiml_Dataset"的目录,里面里有一个 Xaiml 文件。 假如我在更多的已删除文件上按“c” 键,则这些文件将会被放置到新的文件夹中而无需再向我询问目标目录。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当这些步骤完成后,重复按“q”键直到看到正常的终端模样。目录"Xaiml_Dataset" 只能被 root 用户访问。为了解决这个问题,使用 root 权限改变该目录及其子目录的权限。做完这些后,文件便被恢复了且用户可以访问它们。
|
||||
|
||||
### 特别的 ReiserFS:###
|
||||
|
||||
为了从 ReiserFS 文件系统中恢复一个文件,首先需将分区中的所有文件做一个备份。因为如果发生某些错误, 这个方法可能会引起文件丢失。接着执行下面的命令,其中 `DEVICE`指的是那些以 sda2 形式命名的设备。一些文件将被放入 lost+found 目录而其他则会保存到原先被删除的位置。
|
||||
|
||||
reiserfsck --rebuild-tree --scan-whole-partition /dev/DEVICE
|
||||
|
||||
### 恢复被某个程序打开的删除文件: ###
|
||||
|
||||
假设用户意外地删除了一个文件,且该文件被某个程序打开。虽然在硬盘中该文件被删除了,但这个程序正使用着位于 RAM 中的该文件的副本。幸好,我们有两种简单的解决方法来恢复该文件。
|
||||
|
||||
假如这个软件有保存功能,如文本编辑器,则用户可以重新保存该文件,这样,文本编辑器可以将该文件写入硬盘中。
|
||||
|
||||
假设在音乐播放器中有一个 MP3 文件,而该音乐播放器并不能保存该 MP3 文件,则这种情形下需要比先前花更多的时间来恢复文件。不幸的是,这种方法并不能保证在所有的系统和应用中有效。首先,键入下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
lsof -c smplayer | grep mp3
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令会列出所有由 smplayer 使用的文件,这个列表由 `grep` 命令通过管道搜索 mp3 。命令的输入类似于下面:
|
||||
|
||||
smplayer 10037 collier mp3 169r 8,1 676376 1704294 /usr/bin/smplayer
|
||||
|
||||
现在,键入下面的命令来直接从 RAM(在 Linux 系统中,`/proc/`映射到 RAM)中恢复文件,并复制该文件到选定的文件夹中。其中 `cp` 指的是复制命令,输出中的数字 10037 来自于进程数,输出中的数字 169 指的是文件描述符,"~/Music/"为目标目录,最后的 "music.mp3" 为用户想恢复的文件的名称。
|
||||
|
||||
cp /proc/10037/fd/169 ~/Music/music.mp3
|
||||
|
||||
### 真正的删除: ###
|
||||
|
||||
为确保一个文件不能被恢复,可以使用一个命令来 “擦除” 硬盘。擦除硬盘实际上是向硬盘中写入无意义的数据。例如,许多擦除程序向硬盘中写入零,随机字母或随机数据。不会有空间被占用或丢失,擦除程序只是对空位进行重写覆盖。假如存储单元被文件占满而没有空余空间,则所有先前被删除的文件将会消失而不能恢复。
|
||||
|
||||
擦除硬盘的目的是确保隐私数据不被他人看见。举个例子,一个公司可能预订了一些新的电脑,总经理决定将旧的电脑卖掉,然而,新的电脑拥有者可能会看到公司的一些机密或诸如信用卡号码,地址等顾客信息。幸好,公司的电脑技术人员可以在卖掉这些旧电脑之前,擦除这些硬盘。
|
||||
|
||||
为了安装擦除程序 secure-delete,键入 `sudo apt-get install secure-delete`,这个命令将会安装一个包含 4 个程序的程序集,用以确保被删除的文件不能被恢复。
|
||||
|
||||
- srm - 永久删除一个文件。使用方法: `srm -f ./secret_file.txt`
|
||||
- sfill - 擦除空白空间。使用方法: `sfill -f /mount/point/of/partition`
|
||||
- sswap - 擦除 swap 空间。使用方法: `sswap -f /dev/SWAP_DEVICE`
|
||||
|
||||
假如电脑实际去清除那些删除的文件,那么就需要花费更长的时间去执行删除任务。将某些空间标记为空位是快速且容易的,但使得文件永远消失需要花费一定的时间。例如,擦除一个存储单元,可能需要花费几个小时的时间(根据磁盘容量大小)。总之,现在的系统工作的就挺好,因为即便用户清空了垃圾箱,他们仍然有另一次机会来改变他们当初的想法(或错误)。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/undelete-files-on-linux-systems.4316/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[DevynCJohnson][a]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linux.org/members/devyncjohnson.4843/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cgsecurity.org/wiki/TestDisk
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux有效地屏蔽不需要的IP
|
||||
如何在 Linux 下大量屏蔽恶意 IP 地址
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
你可能需要在Linux的不同的环境下屏蔽IP地址。比如,作为一个终端用户,你可能想要免受间谍软件或者IP追踪的困扰。或者当你在运行P2P软件时。你可能想要过滤反P2P活动的网络链接。如果你是一名系统管理员,你可能想要禁止垃圾IP地址访问你们的生产邮件服务器。或者你因一些原因想要禁止某些国家访问web服务。在许多情况下,然而,你的IP地址屏蔽列表可能会很快地增长到几万的IP。该如何处理这个?
|
||||
|
||||
很多情况下,你可能需要在Linux下屏蔽IP地址。比如,作为一个终端用户,你可能想要免受间谍软件或者IP追踪的困扰。或者当你在运行P2P软件时。你可能想要过滤反P2P活动的网络链接。如果你是一名系统管理员,你可能想要禁止垃圾IP地址访问你们的公司邮件服务器。或者你因一些原因想要禁止某些国家访问你的web服务。在许多情况下,然而,你的IP地址屏蔽列表可能会很快地增长到几万的IP。该如何处理这个?
|
||||
|
||||
### Netfilter/IPtables 的问题 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,11 +9,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -A INPUT -s 1.1.1.1 -p TCP -j DROP
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要完全屏蔽一个IP地址,你可以用下面的命令很简单地做到:
|
||||
如果你想要完全屏蔽一个IP地址段,你可以用下面的命令很简单地做到:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -A INPUT -s 1.1.2.0/24 -p TCP -j DROP
|
||||
|
||||
然而,当你有1000个独立IP地址,且不带CIDR(无类别域间路由)前缀,你该怎么做?你要有1000条iptable规则!这显然无法扩展。
|
||||
然而,当你有1000个独立IP地址,且不带CIDR(无类别域间路由)前缀,你该怎么做?你要有1000条iptable规则!这显然这并不适于大规模屏蔽。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -A INPUT -s 1.1.1.1 -p TCP -j DROP
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -A INPUT -s 2.2.2.2 -p TCP -j DROP
|
||||
@ -21,13 +22,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是IP集? ###
|
||||
|
||||
这时候就是[IP集][1]登场了。IP集是一个内核特性,它允许多个(独立)IP地址、MAC地址或者甚至是端口号编码并有效地存储在位图/哈希内核数据结构中。一旦IP集创建之后,你可以创建一条iptable规则来匹配这个集合。
|
||||
这时候就是[IP集][1]登场了。IP集是一个内核特性,它允许多个(独立)IP地址、MAC地址或者甚至是端口号被编码和有效地存储在位图/哈希内核数据结构中。一旦IP集创建之后,你可以创建一条iptables规则来匹配这个集合。
|
||||
|
||||
你应该马上看见IP集合的好处了,它可以让你用一条iptable规则匹配多个ip地址!你可以用多个IP地址和端口号的方式来构造IP集,并且可以动态地更新规则而没有请能影响。
|
||||
你马上就会看见IP集合的好处了,它可以让你用一条iptable规则匹配多个ip地址!你可以用多个IP地址和端口号的方式来构造IP集,并且可以动态地更新规则而没有性能影响。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Linux中安装IPset工具 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了创建和管理IP集,你需要使用成为ipset的用户空间工具。
|
||||
为了创建和管理IP集,你需要使用称为ipset的用户空间工具。
|
||||
|
||||
要在Debian、Ubuntu或者Linux Mint上安装:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -45,7 +46,7 @@ Fedora或者CentOS/RHEL 7上安装:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ipset create banthis hash:net
|
||||
|
||||
第二个参数(hash:net)是必须的,代表的是集合的类型。IP集有[多个类型][2]。hash:net类型的IP集使用哈希来存储多个CIDR块。如果你想要在一个集合中存储独立的IP地址,你可以使用hash:ip类型。
|
||||
第二个参数(hash:net)是必须的,代表的是集合的类型。IP集有[多个类型][2]。hash:net类型的IP集使用哈希来存储多个CIDR块。如果你想要在一个集合中存储单独的IP地址,你可以使用hash:ip类型。
|
||||
|
||||
一旦创建了一个IP集之后,你可以用下面的命令来检查:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -70,25 +71,25 @@ Fedora或者CentOS/RHEL 7上安装:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
现在是时候去创建一个使用IP集的iptable规则了。这里的关键是使用"-m set --match-set <name>"选项。
|
||||
现在是时候去创建一个使用IP集的iptables规则了。这里的关键是使用"-m set --match-set <name>"选项。
|
||||
|
||||
现在让我们创建一条让之前那些IP块不能通过80端口访问web服务的iptable规则。可以通过下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -I INPUT -m set --match-set banthis src -p tcp --destination-port 80 -j DROP
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想,你可以保存特定的IP集到一个文件中,以后可以从文件中还原:
|
||||
如果你愿意,你可以保存特定的IP集到一个文件中,以后可以从文件中还原:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ipset save banthis -f banthis.txt
|
||||
$ sudo ipset destroy banthis
|
||||
$ sudo ipset restore -f banthis.txt
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令中,我使用了destory选项来删除一个已有的IP集来见证我可以还原它。
|
||||
上面的命令中,我使用了destory选项来删除一个已有的IP集来看看我是否可以还原它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 自动IP地址禁用 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在你应该看到了IP集合的强大了。维护IP黑名单是一件繁琐和费时的工作。实际上,有很多免费或者收费的服务可以来帮你完成这个。一个额外的好处是,让我们看看如何自动将IP黑名单家到IP集中。
|
||||
现在你应该看到了IP集合的强大了。维护IP黑名单是一件繁琐和费时的工作。实际上,有很多免费或者收费的服务可以来帮你完成这个。一个额外的好处是,让我们看看如何自动将IP黑名单加到IP集中。
|
||||
|
||||
首先让我们从[iblocklist.com][3]抓取免费的黑名单,这个网站u有不同的免费和收费的名单。免费的版本是P2P格式。
|
||||
首先让我们从[iblocklist.com][3]得到免费的黑名单,这个网站有不同的免费和收费的名单。免费的版本是P2P格式。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来我要使用一个名为iblocklist2ipset的开源Python工具来将P2P格式的黑名单转化成IP集。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -131,14 +132,13 @@ Fedora或者CentOS/RHEL 7上安装:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ipset list banthis
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在写这篇文章时候,“level1”类表包含了237,000个屏蔽的IP列表。你可以看到很多IP地址已经加入到IP集中了。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,创建一条iptable命令来屏蔽它们!
|
||||
最后,创建一条iptables命令来屏蔽这些坏蛋!
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章中,我描述了你该如何用强大的ipset来·屏蔽不想要的IP地址。同时结合了第三方工具iblocklist2ipset,这样你就可以流畅地维护你的IP屏蔽列表了。对于那些对于ipset的速度提升好奇的人来说,下图显示了iptables在使用和不使用ipset的基准测试结果。
|
||||
这篇文章中,我描述了你该如何用强大的ipset来屏蔽不想要的IP地址。同时结合了第三方工具iblocklist2ipset,这样你就可以流畅地维护你的IP屏蔽列表了。那些对ipset的性能提升好奇的人,下图显示了iptables在使用和不使用ipset的基准测试结果。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -150,7 +150,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/block-unwanted-ip-addresses-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
RHEL/CentOS 7中配置用于多版本Linux安装的“PXE网络启动服务器”
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**PXE服务器**——预启动执行环境——指示客户端计算机直接从网络接口启动、运行或安装操作系统,而不需要烧录CD/DVD或使用某个物理介质,它也可以减轻你网络中多台机器同时安装Linux发行版的工作。
|
||||
**PXE服务器**——预启动执行环境——指示客户端计算机直接从网络接口启动、运行或安装操作系统,而不需要烧录CD/DVD或使用某个物理介质,它可以减轻你网络中多台机器同时安装Linux发行版的工作。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
在RHEL/CentOS 7中设置PXE网络启动
|
||||
|
||||
#### 需求 ####
|
||||
*在RHEL/CentOS 7中设置PXE网络启动*
|
||||
|
||||
#### 前置阅读 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- [CentOS 7最小化安装步骤][1]
|
||||
- [RHEL 7最小化安装步骤][2]
|
||||
@ -14,7 +15,7 @@ RHEL/CentOS 7中配置用于多版本Linux安装的“PXE网络启动服务器
|
||||
- [移除RHEL/CentOS 7中不要的服务][4]
|
||||
- [安装NTP服务器以设置RHEL/CentOS 7的正确时间][5]
|
||||
|
||||
本文将介绍如何在配置有本地镜像安装仓库的**RHEL/CentOS 7** 64位上安装并配置一台**PXE服务器**,仓库源由CentOS 7 DVD ISO镜像提供,并由**DNSMASQ**服务器提供解析。
|
||||
本文将介绍如何在配置有本地镜像安装仓库的**RHEL/CentOS 7** 64位上安装并配置一台**PXE服务器**,仓库源由CentOS 7 DVD 的 ISO镜像提供,并由**DNSMASQ**服务器提供解析。
|
||||
|
||||
该机器提供了**DNS**和**DHCP**服务,用于网络启动引导的**Syslinux**包,**TFTP-Server**——提供了可通过网络使用**小文件传输协议**下载的可启动镜像,以及提供本地挂载DVD镜像的**VSFTPD**服务器——它将扮演官方RHEL/CentOS 7镜像安装仓库的角色,安装器将从这里提取所需的包。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,11 +28,12 @@ RHEL/CentOS 7中配置用于多版本Linux安装的“PXE网络启动服务器
|
||||
# yum install dnsmasq
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
安装dnsmasq包
|
||||
|
||||
**2.** DNSMASQ的默认主配置文件位于**/etc**目录中,虽然不需要任何说明就能看懂,但编辑起来确实相当困难的,即使有很详细的说明性注释。
|
||||
*安装dnsmasq包*
|
||||
|
||||
首先,确保你备份了该文件,以便你需要在以后对它进行恢复。然后使用你喜爱的文本编辑器创建一个新的空配置文件,命令如下。
|
||||
**2.** DNSMASQ的默认的主配置文件位于**/etc**目录中,虽然不需要任何说明就能看懂,但编辑起来确实相当困难的,即使有很详细的说明性注释。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,确保你备份了该文件,以便你需要在以后对它进行恢复。然后使用你爱用的文本编辑器创建一个新的空配置文件,命令如下。
|
||||
|
||||
# mv /etc/dnsmasq.conf /etc/dnsmasq.conf.backup
|
||||
# nano /etc/dnsmasq.conf
|
||||
@ -61,7 +63,8 @@ RHEL/CentOS 7中配置用于多版本Linux安装的“PXE网络启动服务器
|
||||
tftp-root=/var/lib/tftpboot
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Dnsmasq配置
|
||||
|
||||
*Dnsmasq配置*
|
||||
|
||||
你需要修改的声明有以下这些:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -89,14 +92,16 @@ Dnsmasq配置
|
||||
# yum install syslinux
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
安装Syslinux启动加载器
|
||||
|
||||
*安装Syslinux启动加载器*
|
||||
|
||||
**5.** PXE启动加载器文件位于**/usr/share/syslinux**系统绝对路径下,你可以通过列出该路径下的内容来查看。该步骤不是必须的,但你可能需要知道该路径,因为在下一步中,我们将拷贝该路径下的所有内容到**TFTP服务器**路径下。
|
||||
|
||||
# ls /usr/share/syslinux
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Syslinux文件
|
||||
|
||||
*Syslinux文件*
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤3: 安装TFTP-Server并加入SYSLINUX加载启动器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -106,7 +111,8 @@ Syslinux文件
|
||||
# cp -r /usr/share/syslinux/* /var/lib/tftpboot
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
安装TFTP服务器
|
||||
|
||||
*安装TFTP服务器*
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤4: 设置PXE服务器配置文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -117,13 +123,13 @@ Syslinux文件
|
||||
# mkdir /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg
|
||||
# touch /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
|
||||
|
||||
**8.** 现在,该来编辑**PXE服务器**配置文件了,为它添加合法的Linux发行版安装选项。请注意,该文件中使用的所有路径必须是相对于**/var/lib/tftpboot**目录的。
|
||||
**8.** 现在,该来编辑**PXE服务器**配置文件了,为它添加合理的Linux发行版安装选项。请注意,该文件中使用的所有路径必须是相对于**/var/lib/tftpboot**目录的。
|
||||
|
||||
下面,你可以看到配置文件的样例,你可以使用该模板,但请修改安装镜像(kernel和initrd文件)、协议(FTP、HTTP、HTTPS、NFS)以及映射你网络安装源仓库和路径的IP地址。
|
||||
下面,你可以看到配置文件的样例,你可以使用该模板,但请修改安装镜像(kernel和initrd文件)、协议(FTP、HTTP、HTTPS、NFS)以及映射你网络安装源仓库和路径的IP地址等参数。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
|
||||
|
||||
添加一下整个节录到文件中。
|
||||
添加以下整个节录到文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
default menu.c32
|
||||
prompt 0
|
||||
@ -151,17 +157,18 @@ Syslinux文件
|
||||
menu label ^4) Boot from local drive
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
配置PXE服务器
|
||||
|
||||
*配置PXE服务器*
|
||||
|
||||
正如你所见,CentOS 7启动镜像(kernel和initrd)位于名为**centos7**的目录,该目录是**/var/lib/tftpboot**目录的相对路径(其系统绝对路径为**/var/lib/tftpboot/centos7**),而安装器仓库位于可通过FTP协议访问的**192.168.1.20/pub**网络位置中——在本例中,这些仓库位于本地,因为IP地址和PXE服务器地址相同。
|
||||
|
||||
同时,菜单**label 3**指定客户端安装应该通过**VNC**从一个远程位置实现(这里替换VNC密码为一个健壮的密码),如果你在一台没有输入输出的客户端上安装,菜单**label 2**指定了作为安装源的一个CentOS 7官方互联网镜像(这种情况要求客户端通过DHCP和NAT连接到互联网)。
|
||||
|
||||
**重要**:正如你在上述配置中说看到的,我们使用了CentOS 7进行演示,但是你也可以定义RHEL 7镜像。而下面的完整说明和配置都只是基于CentOS 7的,所以在选在发行版时要当心。
|
||||
**重要**:正如你在上述配置中所看到的,我们使用了CentOS 7进行演示,但是你也可以定义一个 RHEL 7镜像。而下面的整个的说明和配置都只是基于CentOS 7的,所以在选发行版时要注意一下。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤5: 添加CentOS 7启动镜像到PXE服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**9.** 对于此步骤,需要用到CentOS的kernel和initrd文件。要获取这些文件,你需要**CentOS 7 DVD ISO**镜像。所以,去下载CentOS DVD镜像吧,然后把它放入你的DVD驱动器并挂载镜像到**/mnt**路径,命令见下面。
|
||||
**9.** 对于此步骤,需要用到CentOS的kernel和initrd文件。要获取这些文件,你需要**CentOS 7 DVD ISO**镜像。所以,去下载CentOS DVD镜像吧,然后把它(刻录成光盘)放入你的DVD驱动器并挂载镜像到**/mnt**路径,命令见下面。
|
||||
|
||||
使用DVD,而不是最小化CD镜像的原因在于,在后面我们将使用该DVD的内容为**FTP**源创建本地安装器仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -169,27 +176,29 @@ Syslinux文件
|
||||
# ls /mnt
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
挂载CentOS DVD
|
||||
|
||||
*挂载CentOS DVD*
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的机器没有DVD驱动器,你也可以使用**wget**或**curl**工具从[CentOS镜像站][7]下载**CentOS 7 DVD ISO**到本地并挂载。
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://mirrors.xservers.ro/centos/7.0.1406/isos/x86_64/CentOS-7.0-1406-x86_64-DVD.iso
|
||||
# mount -o loop /path/to/centos-dvd.iso /mnt
|
||||
|
||||
**10.** 在DVD内容可供使用后,创建**centos7**目录并将CentOS 7可启动kernel和initrd映像文件从DVD挂载位置拷贝到centos7文件夹。
|
||||
**10.** 在DVD内容可供使用后,创建**centos7**目录并将CentOS 7 的可启动的 kernel和initrd映像文件从DVD挂载位置拷贝到centos7文件夹。
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir /var/lib/tftpboot/centos7
|
||||
# cp /mnt/images/pxeboot/vmlinuz /var/lib/tftpboot/centos7
|
||||
# cp /mnt/images/pxeboot/initrd.img /var/lib/tftpboot/centos7
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
拷贝CentOS可启动文件
|
||||
|
||||
*拷贝CentOS可启动文件*
|
||||
|
||||
使用该方法的原因在于,今后你可能会在**/var/lib/tftpboot**路径中创建新的独立的目录,并添加其它Linux发行版到PXE菜单中,你就不会将整个目录结构弄得一团糟了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤6: 创建CentOS 7本地镜像安装源 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**11.** 虽然你可以通过多种协议设置**安装源镜像**,如HTTP、HTTPS或NFS,但对于本指南,我选择使用**FTP**协议。因为通过**vsftpd**,你可以很便捷地配置,而且它也很稳定。
|
||||
**11.** 虽然你可以通过多种协议设置**安装源镜像**,如HTTP、HTTPS或NFS,但对于本指南,我选择了使用**FTP**协议。因为通过**vsftpd**,你可以很便捷地配置,而且它也很稳定。
|
||||
|
||||
接下里,安装vsftpd进程,然后复制所有DVD挂载目录中的内容到**vsftpd**默认服务器路径下(**/var/ftp/pub**)——这会花费一些时间,这取决于你的系统资源。然后为该路径设置可读权限,命令如下。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -198,17 +207,20 @@ Syslinux文件
|
||||
# chmod -R 755 /var/ftp/pub
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
安装Vsftpd服务器
|
||||
|
||||
*安装Vsftpd服务器*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
拷贝Files到FTP路径
|
||||
|
||||
*拷贝Files到FTP路径*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
设置FTP路径的权限
|
||||
|
||||
*设置FTP路径的权限*
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤7: 在系统范围内启动并启用进程 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**12.** 既然PXE服务器配置已经完成,那么就来启动**DNSMASQ**和**VSFTPD**服务器吧。验证它们的状况并在系统范围内启用,以便让这些服务在每次系统重启后都能随系统启动,命令如下。
|
||||
**12.** 既然PXE服务器配置已经完成,那么就来启动**DNSMASQ**和**VSFTPD**服务器吧。验证它们的状况并在系统上启用,以便让这些服务在每次系统重启后都能随系统启动,命令如下。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start dnsmasq
|
||||
# systemctl status dnsmasq
|
||||
@ -218,10 +230,12 @@ Syslinux文件
|
||||
# systemctl enable vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
启动Dnsmasq服务
|
||||
|
||||
*启动Dnsmasq服务*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
启动Vsftpd服务
|
||||
|
||||
*启动Vsftpd服务*
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤8: 打开防火墙并测试FTP安装源 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -236,53 +250,62 @@ Syslinux文件
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload ## Apply rules
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
检查监听端口
|
||||
|
||||
*检查监听端口*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
在防火墙上开启端口
|
||||
|
||||
*在防火墙上开启端口*
|
||||
|
||||
**14.** 要测试FTP安装源网络路径,请在本地或另外一台计算机上打开浏览器([**lynx**][8]就可以做此事),然后输入你架设有FTP服务的PXE服务器的IP地址,并在填入的URL后面加上**/pub**网络位置,结果应该和截图中看到的一样。
|
||||
|
||||
ftp://192.168.1.20/pub
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
通过浏览器访问FTP文件
|
||||
|
||||
*通过浏览器访问FTP文件*
|
||||
|
||||
**15.** 要解决PXE服务器最终的配置或其它信息产生的问题,请在live模式下诊断,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# tailf /var/log/messages
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
检查PXE日志错误
|
||||
|
||||
**16.** 最后,最后所需的步骤就是卸载CentOS 7 DVD,并移除物理介质。
|
||||
*检查PXE日志错误*
|
||||
|
||||
**16.** 最后,最终所需的步骤就是卸载CentOS 7 DVD,并移除物理介质。
|
||||
|
||||
# umount /mnt
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤9: 配置客户端从网络启动 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**17.** 现在,你的客户端可以通过它们的系统BIOS或在**BIOS开机自检**时按指定键来配置网络启动作为**首要启动设备**,具体方法见主板说明手册。
|
||||
**17.** 现在,你的客户端可以通过它们的系统BIOS或在**BIOS开机自检**时按指定键来配置网络启动作为**首选启动设备**,具体方法见主板说明手册。
|
||||
|
||||
为了选择网络启动,在第一次PXE提示符出现时,请按下**F8**键进入到PXE安装界面,然后敲**回车**键继续进入PXE菜单。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
PXE网络启动
|
||||
|
||||
*PXE网络启动*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
PXE网络OS启动
|
||||
|
||||
*PXE网络OS启动*
|
||||
|
||||
**18.** 一旦你进入PXE菜单,请选择你的CentOS 7安装类型,敲**回车**键继续安装过程,就像你使用本地启动介质安装一样。
|
||||
|
||||
请记下这一点,使用菜单中的变体2需要激活目标客户端上的互联网连接。在下面的屏幕截图中,你可以通过VNC看到远程安装的实例。
|
||||
请记住这一点,使用菜单中的变体2需要激活目标客户端上的互联网连接。在下面的屏幕截图中,你可以通过VNC看到远程安装的实例。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PXE菜单
|
||||
|
||||
*PXE菜单*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
通过VNC远程安装Linux
|
||||
|
||||
*通过VNC远程安装Linux*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
远程安装CentOS
|
||||
|
||||
*远程安装CentOS*
|
||||
|
||||
以上是**CentOS 7**上配置最小化**PXE服务器**的所有内容。在我的本系列下一篇文章中,我将讨论其它PXE服务器配置过程中的其它问题,如怎样使用**Kickstart**文件来配置自动化安装**CentOS 7**,以及添加其它Linux发行版到PXE菜单——**Ubuntu Server**和**Debian 7**。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -292,14 +315,14 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-pxe-network-boot-server-in-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matei Cezar][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/centos-7-installation/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/redhat-enterprise-linux-7-installation/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/configure-network-interface-in-rhel-centos-7-0/
|
||||
[3]:http://linux.cn/article-3977-1.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/remove-unwanted-services-in-centos-7/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-ntp-server-in-centos/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.thekelleys.org.uk/dnsmasq/docs/dnsmasq-man.html
|
||||
@ -1,21 +1,20 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答-- 如何在Linux重命名多个文件
|
||||
Linux有问必答:如何在Linux下重命名多个文件
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **提问**:我知道我可以用mv命令重命名文件。但是当我想重命名很多文件怎么办?如果为每个文件都这么做将会是很乏味的。有没有办法一次性重命名多个文件?
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux中,当你想要改变一个文件名,使用mv命令就好了。然而mv不能使用通配符重命名多个文件。可以用sed、awk或者与[xargs][1]结合使用来处理多个文件的情况。然而,这些命令行即繁琐u又不友好,并且如果不小心的话还很容易出错。你不会想要撤销1000个文件的错误名的。
|
||||
在Linux中,当你想要改变一个文件名,使用mv命令就好了。然而mv不能使用通配符重命名多个文件。可以用sed、awk或者与[xargs][1]结合使用来处理多个文件的情况。然而,这些命令行即繁琐又不友好,并且如果不小心的话还很容易出错。你不会想要撤销1000个文件的错误名吧!
|
||||
|
||||
When it comes to renaming multiple files, the rename utility is probably the easiest, the safest, and the most powerful command-line tool. The rename command is actually a Perl script, and comes pre-installed on all modern Linux distributions.
|
||||
当你想要重命名多个文件的时候,重命名的工具或许是最简单、最安全和最强大的命令行工具。重命名命令实际上是一个Perl脚本,它预安装在所有的现在Linux发行班上
|
||||
当你想要重命名多个文件的时候,rename 工具或许是最简单、最安全和最强大的命令行工具。这个rename命令实际上是一个Perl脚本,它预安装在所有的现在Linux发行版上。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是重命名命令的基本语法。
|
||||
|
||||
rename [-v -n -f] <pcre> <files>
|
||||
|
||||
<pcre> 是Perl兼容正则表达式,它表示的是要重命名的文件和该怎么做。正则表达式的形式是‘s/old-name/new-name/’。
|
||||
\<pcre> 是Perl兼容正则表达式,它表示的是要重命名的文件和该怎么做。正则表达式的形式是‘s/old-name/new-name/’。
|
||||
|
||||
‘-v’选项会显示文件名改变的细节(比如:XXX重命名成YYY)。
|
||||
|
||||
‘-n’选项告诉rename会在不实际改变名称的情况下显示文件将会重命名的情况。这个选项在你想要在不改变文件名的情况下模拟改变文件名的情况下很有用。
|
||||
‘-n’选项告诉rename命令在不实际改变名称的情况下显示文件将会重命名的情况。这个选项在你想要在不改变文件名的情况下模拟改变文件名的情况下很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
‘-f’选项强制覆盖存在的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -43,7 +42,7 @@ When it comes to renaming multiple files, the rename utility is probably the eas
|
||||
|
||||
### 更改文件名模式 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在让我们考虑包含子模式的更复杂的正则表达式。在PCRE中,子模式包含在圆括号中,$符后接上数字(比如$1,$2)。
|
||||
现在让我们考虑更复杂的包含子模式的正则表达式。在PCRE中,子模式包含在圆括号中,$符后接上数字(比如$1,$2)。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,下面的命令会将‘img_NNNN.jpeg’变成‘dan_NNNN.jpg’。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,7 +56,7 @@ When it comes to renaming multiple files, the rename utility is probably the eas
|
||||
img_5420.jpeg renamed as dan_5420.jpg
|
||||
img_5421.jpeg renamed as dan_5421.jpg
|
||||
|
||||
比如,下面的命令会将‘img_000NNNN.jpeg’变成‘dan_NNNN.jpg’。
|
||||
比如,下面的命令会将‘img\_000NNNN.jpeg’变成‘dan\_NNNN.jpg’。
|
||||
|
||||
# rename -v 's/img_\d{3}(\d{4})\.jpeg$/dan_$1\.jpg/' *jpeg
|
||||
|
||||
@ -76,7 +75,7 @@ When it comes to renaming multiple files, the rename utility is probably the eas
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/rename-multiple-files-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
**Grooveshark 对于喜欢音乐的人来说是一个不错的在线平台,同时有多种从上面下载音乐的方法。Groovesquid 是众多允许用户从 Grooveshark 上下载音乐的应用之一,并且是支持多平台的。**
|
||||
|
||||
只要有在线流媒体服务,就一定有方法从获取你之前看过或听过的视频及音乐。即使下载接口关闭了,也不是什么大不了的事,因为还有很多种解决方法,无论你用的什么操作系统。比如,网络上就有许多种 YouTube 下载器,同样的道理,从 Grooveshark 上下载音乐也并非难事。
|
||||
只要有在线流媒体服务,就一定有方法将你看过或听过的视频及音乐保存到本地。即使下载接口关闭了,也不是什么大不了的事,因为还有很多种解决方法,无论你用的什么操作系统。比如,网络上就有许多种 YouTube 下载器,同样的道理,从 Grooveshark 上下载音乐也并非难事。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,得考虑合法性的问题。与许多其他应用一样,Groovesquid 并非是完全不合法的。如果有用户使用应用去做一些非法的事情,那责任应归咎于用户。同样的道理也适用于 utorrent 或者 Bittorrent。只要你不触及版权问题,那你就可以无所顾忌的使用 Groovesquid 了。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
你能够找到的 Groovesquid 的唯一缺点是,它是基于 Java 而编写的,这从来都不是一个好的兆头。虽然为了确保应用的可移植性这样做确实是一个好方法,但这样做的结果导致了其糟糕的界面。确实是非常糟糕的的界面,不过这一点并不会影响到用户的使用体验,特别是这款应用所完成的工作时如此的有用。
|
||||
|
||||
有一点需要注意的地方。Groovesquid 是一款免费的应用,但为了将免费保持下去,它会在菜单栏的右侧显示一则广告。这对大多数人来说都应该不是问题,不过最好在打开应用后注意下菜单栏右侧。
|
||||
有一点需要注意的地方。Groovesquid 是一款免费的应用,但为了将免费保持下去,它会在菜单栏的右侧显示一则广告。这对大多数人来说都应该不是问题,不过最好在打开应用后注意下菜单栏右侧(那不是应用的一部分)。
|
||||
|
||||
从易用性的角度来看,这款应用非常简洁。用户可以通过在顶部地址栏里输入链接直接下载单曲,地址栏的位置可以通过其左侧的下拉菜单进行修改。在下拉菜单中,也可以修改为歌曲名称、流行度、专辑名称、播放列表以及艺术家。有些选项向你提供了诸如查看 Grooveshark 上最流行的音乐,或者下载整个播放列表等。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Download-Music-from-Grooveshark-with-
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[Stevearzh](https://github.com/Stevearzh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
|
||||
使用 APT-mirror 四步配置 Ubuntu 本地软件仓库
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
今天,我们将向你展示如何在你的 Ubuntu 个人电脑或 Ubuntu 服务器中,直接通过 Ubuntu 官方软件仓库来配置本地软件仓库。在你的电脑中创建一个本地软件仓库有着许多的好处。假如你有许多电脑需要安装软件 、安全升级和修复补丁,那么配置一个本地软件仓库是一个做这些事情的高效方法。因为,所有需要安装的软件包都可以通过快速的局域网连接从你的本地服务器中下载,这样可以节省你的网络带宽,降低互联网接入的年度开支 ...
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用多种工具在你的本地个人电脑或服务器中配置一个 Ubuntu 的本地软件仓库,但在本教程中,我们将为你介绍 APT-Mirror。这里,我们将把默认的镜像包镜像到我们本地的服务器或个人电脑中,并且在你的本地或外置硬盘中,我们至少需要 **120 GB** 或更多的可用空间才行。 我们可以通过配置一个 **HTTP** 或 **FTP** 服务器来与本地系统客户端共享这个软件仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
我们需要安装 Apache 网络服务器和 APT-Mirror 来使得我们的工作得以开始。下面是配置一个可工作的本地软件仓库的步骤:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 安装需要的软件包 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们需要从 Ubuntu 的公共软件包仓库中取得所有的软件包,然后在我们本地的 Ubuntu 服务器硬盘中保存它们。
|
||||
|
||||
首先我们安装一个Web 服务器来承载我们的本地软件仓库。这里我们将安装 Apache Web 服务器,但你可以安装任何你中意的 Web 服务器。对于 http 协议,Web 服务器是必须的。假如你需要配置 ftp 协议 及 rsync 协议,你还可以再分别额外安装 FTP 服务器,如 proftpd, vsftpd 等等 和 Rsync 。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install apache2
|
||||
|
||||
然后我们需要安装 apt-mirror:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install apt-mirror
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**注: 正如我先前提到的,我们需要至少 120 GB 的可用空间来使得所有的软件包被镜像或下载。**
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 配置 APT-Mirror ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在,在你的硬盘上创建一个目录来保存所有的软件包。例如,我们创建一个名为 `/linoxide`的目录,我们将在这个目录中保存所有的软件包:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir /linoxide
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在,打开文件 **/etc/apt/mirror.list** :
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /etc/apt/mirror.list
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
复制下面的命令行配置到 `mirror.list`文件中并按照你的需求进行修改:
|
||||
|
||||
############# config ##################
|
||||
#
|
||||
set base_path /linoxide
|
||||
#
|
||||
# set mirror_path $base_path/mirror
|
||||
# set skel_path $base_path/skel
|
||||
# set var_path $base_path/var
|
||||
# set cleanscript $var_path/clean.sh
|
||||
# set defaultarch <running host architecture>
|
||||
# set postmirror_script $var_path/postmirror.sh
|
||||
# set run_postmirror 0
|
||||
set nthreads 20
|
||||
set _tilde 0
|
||||
#
|
||||
############# end config ##############
|
||||
|
||||
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-security main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-updates main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
#deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
#deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-backports main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
|
||||
deb-src http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
deb-src http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-security main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
deb-src http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-updates main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
#deb-src http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
#deb-src http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-backports main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
|
||||
clean http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**注: 你可以将上面的官方镜像服务器网址更改为离你最近的服务器的网址,可以通过访问 [Ubuntu Mirror Server][1]来找到这些服务器地址。假如你并不太在意镜像完成的时间,你可以沿用默认的官方镜像服务器网址。**
|
||||
|
||||
这里,我们将要镜像最新和最大的 Ubuntu LTS 发行版 --- 即 Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (Trusty Tahr) --- 的软件包仓库,所以在上面的配置中发行版本号为 trusty 。假如我们需要镜像 Saucy 或其他的 Ubuntu 发行版本,请修改上面的 trusy 为相应的代号。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们必须运行 apt-mirror 来下载或镜像官方仓库中的所有软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-mirror
|
||||
|
||||
从 Ubuntu 服务器中下载所有的软件包所花费的时间取决于你和镜像服务器之间的网络连接速率和性能。这里我中断了下载,因为我已经下载好了 ...
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3.配置网络服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了使得其他的电脑能够访问这个软件仓库,你需要一个Web服务器。你也可以通过 ftp 来完成这件事,但我选择使用一个Web服务器因为在上面的步骤 1 中我提及到使用Web服务器。因此,我们现在要对 Apache 服务器进行配置:
|
||||
|
||||
我们将为我们本地的软件仓库目录 建立一个到 Apache 托管目录 --- 即 `/var/www/ubuntu` --- 的符号链接。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ln -s /linoxide /var/www/ubuntu
|
||||
$ sudo service apache2 start
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令将允许我们从本地主机(localhost) --- 即 http://127.0.0.1(默认情况下) --- 浏览我们的镜像软件仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 配置客户端 ###
|
||||
|
||||
最后,我们需要在其他的电脑中添加软件源,来使得它们可以从我们的电脑中取得软件包或软件仓库。为达到此目的,我们需要编辑 `/etc/apt/sources.list` 文件并添加下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list
|
||||
|
||||
添加下面的一行到` /etc/apt/sources.list`中并保存。
|
||||
|
||||
deb http://192.168.0.100/ubuntu/ trusty main restricted universe
|
||||
|
||||
**注: 这里的 192.168.0.100 是我们的服务器电脑的局域网 IP 地址,你需要替换为你的服务器电脑的局域网 IP 地址**
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
最终,我们完成了任务。现在,你可以使用`sudo apt-get install packagename` 命令来从你的本地 Ubuntu 软件仓库中安装所需的软件包,这将会是高速的且消耗很少的带宽。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/setup-local-repository-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+archivemirrors
|
||||
@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ Btrfs文件系统在Linux中的创建及其特性
|
||||
|
||||
### 转换到Btrfs ###
|
||||
|
||||
**警告:在尝试转换文件系统前,请务必备份数据。虽然此操作很稳定,也很安全,但它仍然可能导致数据丢失,而防止此情况发生的唯一途径就是进行数据备份。**
|
||||
**警告:在尝试转换文件系统前,请务必备份数据!虽然此操作很稳定,也很安全,但它仍然可能导致数据丢失,而防止此情况发生的唯一途径就是进行数据备份。**
|
||||
|
||||
将现存的ext4文件系统转换到btrfs是相当简单而易懂的。你首先需要使用fsck来检查你现存分区上是否存在错误,然后使用btrfs-convert命令进行转换。如果你想要对/dev/sda3分区进行转换,你可以进行以下操作:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ Btrfs文件系统在Linux中的创建及其特性
|
||||
|
||||
### 转换根分区 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要对你系统上的根分区进行转换,你首先需要使用Live CD启动。对于Ubuntu,你可以使用Ubuntu安装CD来完成此操作,在启动后第一个屏幕选择“尝试Ubuntu”。对于其它系统,你同样可以使用Live CD镜像,操作类似。
|
||||
如果你想要对你系统上的根分区进行转换,你首先需要使用Live CD启动。对于Ubuntu,你可以使用Ubuntu安装盘来完成此操作,在启动后第一个屏幕选择“尝试Ubuntu”。对于其它系统,你同样可以使用Live CD镜像,操作类似。
|
||||
|
||||
在启动后,打开终端,使用下面的命令来转换文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ Btrfs文件系统在Linux中的创建及其特性
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在来编辑fstab,并根据blkid输出的结果来修改当前/文件系统的UUID,并将它的文件系统类型修改为btrfs,修改后的行如下:
|
||||
现在来编辑fstab,并根据blkid输出的结果来修改当前“/”文件系统的UUID,并将它的文件系统类型修改为btrfs,修改后的行如下:
|
||||
|
||||
UUID=8e7e80aa-337e-4179-966d-d60128bd3714 / btrfs defaults 0 1
|
||||
|
||||
@ -74,7 +74,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/file-system/create-btrfs-features/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrian Dinu][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
|
||||
Auditd - Linux 服务器安全审计工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
首先,Linoxide组祝读者 **2015新年快乐万事如意!** 。下面开始这个新年版审计工具的介绍。
|
||||
首先,Linux中国祝贺读者 **2015羊年春节快乐,万事如意!** 。下面开始这个新年版审计工具的介绍。
|
||||
|
||||
安全防护是首先要考虑的问题。为了避免别人盗取我们的数据,我们需要维护它。安全防护包括很多东西,审计是其中一个。
|
||||
安全防护是首先要考虑的问题。为了避免别人盗取我们的数据,我们需要时刻关注它。安全防护包括很多东西,审计是其中之一。
|
||||
|
||||
我们知道Linux系统上有一个叫 **auditd** 的审计工具。这个工具在大多数Linux操作系统中是默认安装的。审计工具是什么?如何使用?下面我们开始介绍。
|
||||
我们知道Linux系统上有一个叫 **auditd** 的审计工具。这个工具在大多数Linux操作系统中是默认安装的。那么auditd 是什么?如何使用呢?下面我们开始介绍。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是审计? ###
|
||||
|
||||
审计(或审计监控)是Linux审计系统中用户部分的一个组件,负责将审计记录写入磁盘。
|
||||
auditd(或 auditd 守护进程)是Linux审计系统中用户空间的一个组件,其负责将审计记录写入磁盘。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,16 +20,17 @@ Ubuntu系统中,我们可以使用 [wajig][1] 工具或者 **apt-get 工具**
|
||||
|
||||
按照下面的说明安装auditd,安装完毕后将自动安装以下auditd和相关的工具:
|
||||
|
||||
- **auditctl ;** 运行过程中控制守护进程的工具,比如如添加规则等等。
|
||||
- **/etc/audit/audit.rules ;** 记录审计规则的文件。
|
||||
- **aureport ;** 查看和生成审计报告的工具。
|
||||
- **ausearch ;** 查找审计事件的工具
|
||||
- **auditspd ;** 转发事件通知给其他应用程序,不写审计日志文件。
|
||||
- **autrace ;** 跟踪处理过程的命令。
|
||||
- **/etc/audit/auditd.conf ;** auditd工具的配置文件。
|
||||
- 首次安装 **auditd** 后, 审计规则是空的。
|
||||
- **auditctl :** 即时控制审计守护进程的行为的工具,比如如添加规则等等。
|
||||
- **/etc/audit/audit.rules :** 记录审计规则的文件。
|
||||
- **aureport :** 查看和生成审计报告的工具。
|
||||
- **ausearch :** 查找审计事件的工具
|
||||
- **auditspd :** 转发事件通知给其他应用程序,而不是写入到审计日志文件中。
|
||||
- **autrace :** 一个用于跟踪进程的命令。
|
||||
- **/etc/audit/auditd.conf :** auditd工具的配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
可以使用以下命令查看
|
||||
首次安装 **auditd** 后, 审计规则是空的。
|
||||
|
||||
可以使用以下命令查看:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo auditctl -l
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,7 +42,7 @@ Ubuntu系统中,我们可以使用 [wajig][1] 工具或者 **apt-get 工具**
|
||||
|
||||
#### Audit 文件和目录访问审计 ####
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用审计工具的一个目的是监控文件和目录的更改。对于auditd工具,我们可使用命令来配置(注意,以下命令需要root权限)。
|
||||
我们使用审计工具的一个基本的需求是监控文件和目录的更改。使用auditd工具,我们可通过如下命令来配置(注意,以下命令需要root权限)。
|
||||
|
||||
**文件审计**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,9 +52,9 @@ Ubuntu系统中,我们可以使用 [wajig][1] 工具或者 **apt-get 工具**
|
||||
|
||||
**选项 :**
|
||||
|
||||
- **-w path ;** 监控指定的路径,上面的命令指定监控路径 /etc/passwd
|
||||
- **-p ; ** 指定触发审计的文件和目录的访问权限
|
||||
- **rwxa ;** 指定的触发条件,r 读取权限,w 写入权限,x 执行权限
|
||||
- **-w path :** 指定要监控的路径,上面的命令指定了监控的文件路径 /etc/passwd
|
||||
- **-p :** 指定触发审计的文件/目录的访问权限
|
||||
- **rwxa :** 指定的触发条件,r 读取权限,w 写入权限,x 执行权限,a 属性(attr)
|
||||
|
||||
#### 目录审计 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -79,31 +80,41 @@ Ubuntu系统中,我们可以使用 [wajig][1] 工具或者 **apt-get 工具**
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ausearch -f /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
- **-f** 设定ausearch审计/etc/passwd文件
|
||||
- 下面是输出 :
|
||||
- **-f** 设定ausearch 调出 /etc/passwd文件的审计内容
|
||||
|
||||
下面是输出 :
|
||||
|
||||
> **time**->Mon Dec 22 09:39:16 2014
|
||||
|
||||
> type=PATH msg=audit(1419215956.471:194): item=0 **name="/etc/passwd"** inode=142512 dev=08:01 mode=0100644 ouid=0 ogid=0 rdev=00:00 nametype=NORMAL
|
||||
|
||||
> type=CWD msg=audit(1419215956.471:194): **cwd="/home/pungki"**
|
||||
|
||||
> type=SYSCALL msg=audit(1419215956.471:194): arch=40000003 **syscall=5** success=yes exit=3 a0=b779694b a1=80000 a2=1b6 a3=b8776aa8 items=1 ppid=2090 pid=2231 **auid=4294967295 uid=1000 gid=1000** euid=0 suid=0 fsuid=0 egid=1000 sgid=1000 fsgid=1000 tty=pts0 ses=4294967295 **comm="sudo" exe="/usr/bin/sudo"** key=(null)
|
||||
|
||||
下面开始解读输出结果。
|
||||
|
||||
- **time ;** 审计时间。
|
||||
- **name ;** 审计对象
|
||||
- **cwd ;** 当前路径
|
||||
- **syscall ;** 相关的系统调用
|
||||
- **auid ;** 审计用户ID
|
||||
- **uid and gid ;** 访问文件的用户ID和用户组ID
|
||||
- **comm ;** 用户访问文件的命令
|
||||
- **exe ;** 上面命令的可执行文件路径
|
||||
- 以上审计日志显示文件未被改动。
|
||||
- **time :** 审计时间。
|
||||
- **name :** 审计对象
|
||||
- **cwd :** 当前路径
|
||||
- **syscall :** 相关的系统调用
|
||||
- **auid :** 审计用户ID
|
||||
- **uid 和 gid :** 访问文件的用户ID和用户组ID
|
||||
- **comm :** 用户访问文件的命令
|
||||
- **exe :** 上面命令的可执行文件路径
|
||||
|
||||
以下我们将要添加一个用户,看看auditd如何记录文件 /etc/passwd的改动的。
|
||||
以上审计日志显示文件未被改动。
|
||||
|
||||
以下我们将要添加一个用户,看看auditd如何记录文件 /etc/passwd的改动的。
|
||||
|
||||
> **time->**Mon Dec 22 11:25:23 2014
|
||||
|
||||
> type=PATH msg=audit(1419222323.628:510): item=1 **name="/etc/passwd.lock"** inode=143992 dev=08:01 mode=0100600 ouid=0 ogid=0 rdev=00:00 nametype=DELETE
|
||||
|
||||
> type=PATH msg=audit(1419222323.628:510): item=0 **name="/etc/"** inode=131073 dev=08:01 mode=040755 ouid=0 ogid=0 rdev=00:00 nametype=PARENT
|
||||
|
||||
> type=CWD msg=audit(1419222323.628:510): **cwd="/root"**
|
||||
|
||||
> type=SYSCALL msg=audit(1419222323.628:510): arch=40000003 **syscall=10** success=yes exit=0 a0=bfc0ceec a1=0 a2=bfc0ceec a3=897764c items=2 ppid=2978 pid=2994 **auid=4294967295 uid=0 gid=0** euid=0 suid=0 fsuid=0 egid=0 sgid=0 fsgid=0 tty=pts0 ses=4294967295 **comm="chfn" exe="/usr/bin/chfn"** key=(null)
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以看到,在指定的时间,**/etc/passwd ** 被root用户(uid =0, gid=0)在/root目录下修改。/etc/passwd 文件是使用**/usr/bin/chfn** 访问的。
|
||||
@ -133,7 +144,7 @@ Ubuntu系统中,我们可以使用 [wajig][1] 工具或者 **apt-get 工具**
|
||||
|
||||
一旦定义审计规则后,它会自动运行。过一段时间后,我们可以看看auditd是如何帮我们跟踪审计的。
|
||||
|
||||
Auditd提供了另一个工具叫 **aureport** 。从名字上可以猜到, **aureport** 是使用系统日志生成简要报告的工具。
|
||||
Auditd提供了另一个工具叫 **aureport** 。从名字上可以猜到, **aureport** 是使用系统审计日志生成简要报告的工具。
|
||||
|
||||
我们已经配置auditd去跟踪/etc/passwd文件。auditd参数设置后一段时间后,audit.log 文件就创建出来了。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -155,7 +166,7 @@ Auditd提供了另一个工具叫 **aureport** 。从名字上可以猜到, *
|
||||
|
||||
从上图可以看出,由两个用户在特定的时间授权失败。
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们想看所有相关账户修改的事件,可以使用-m参数。
|
||||
如果我们想看所有账户修改相关的事件,可以使用-m参数。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo aureport -m
|
||||
|
||||
@ -165,8 +176,10 @@ Auditd提供了另一个工具叫 **aureport** 。从名字上可以猜到, *
|
||||
|
||||
我们已经添加如下规则:
|
||||
|
||||
- $ sudo auditctl -w /etc/passwd -p rwxa
|
||||
- $ sudo auditctl -w /production/
|
||||
- 现在,如果确信这些规则正常,我们可以将其添加到**/etc/audit/audit.rules**中使得规则永久有效。以下介绍如何将他们添加到/etc/audit/audit.rules中去。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,如果确信这些规则可以正常工作,我们可以将其添加到**/etc/audit/audit.rules**中使得规则永久有效。以下介绍如何将他们添加到/etc/audit/audit.rules中去。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -192,7 +205,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/how-tos/auditd-tool-security-auditing/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Pungki Arianto][a]
|
||||
译者:[shipsw](https://github.com/shipsw)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
如何在 Ubuntu 14.04 和 Linux Mint 17 中安装 Kodi14(XBMC)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Kodi][1],原名就是大名鼎鼎的XBMC,发布了开发代号为Helix的[最新版本14][2]。感谢官方XMBC提供的PPA,现在可以很简单地在Ubuntu14.04中安装了。
|
||||
|
||||
有些人可能还不了解Kodi,它是一个媒体中心软件,支持所有平台,如Windows、Linux、 Mac, Android等。此软件拥有全屏的媒体中心,可以管理所有音乐和视频,不单支持本地文件还支持网络播放,如Tube、[Netflix][3]、 Hulu, Amazon Prime和其他流媒体服务商。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 14.04 和 Linux Mint 17 中安装 XBMC 14 Kodi Helix ###
|
||||
|
||||
再次感谢官方的PPA,让我们可以轻松安装Kodi 14。支持Ubuntu 14.04、Ubuntu 12.04、Linux Mint 17、Pinguy OS 14.04、Deepin 2014、LXLE 14.04、Linux Lite 2.0, Elementary OS 以及其他基于 Ubuntu 的 Linux 发行版。
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端(Ctrl+Alt+T)然后使用下列命令。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:team-xbmc/ppa
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install kodi
|
||||
|
||||
需要下载大约100MB,在我看来,这不是很大。若需安装解码插件,使用下列命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install kodi-audioencoder-* kodi-pvr-*
|
||||
|
||||
#### 从 Ubuntu 中移除 Kodi 14 ####
|
||||
|
||||
从系统中移除 Kodi 14,使用下列命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove kodi
|
||||
|
||||
同样也应该移除PPA软件源:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:team-xbmc/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
我希望这篇简单的文章可以帮助到你在Ubuntu、Linux Mint 和其他 Linux 版本中轻松安装 Kodi 14。你是怎么发现 Kodi 14 Helix 的?
|
||||
|
||||
你有没有使用其他的媒体中心来作为 XBMC 的替代?可以在下面的评论区分享你的观点。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/install-kodi-14-xbmc-in-ubuntu-14-04-linux-mint-17/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[Vic020/VicYu](http://www.vicyu.net)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://kodi.tv/
|
||||
[2]:http://kodi.tv/kodi-14-0-helix-unwinds/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/watch-netflix-in-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
如何在 Ubuntu 14.04 中安装 Winusb
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[WinUSB][1]是一款即简单又有用的工具,可以让你从 Windows ISO 镜像或者 DVD 中创建 USB 安装盘(LCTT译注:支持将 Windows Vista/7/8/PE 制作成 USB 安装盘)。它支持 GUI 和命令行,你可以根据你的喜好决定使用哪种。
|
||||
|
||||
在本文中我们会展示**如何在 Ubuntu 14.04、14.10 和 Linux Mint 17 中安装 WinUSB**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 14.04、14.10 和 Linux Mint 17 中安装 WinUSB ###
|
||||
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 13.10 之前, WinUSB 一直都在积极开发,且在官方 PPA 中可以找到。但这个 PPA 还没有为 Ubuntu 14.04 和 14.10 更新,不过其二进制文件仍旧可在更新版本的 Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 中运行。基于[你使用的系统是32位还是64位][2],使用下面的命令来下载二进制文件:
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端,32位的系统下使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
wget https://launchpad.net/~colingille/+archive/freshlight/+files/winusb_1.0.11+saucy1_i386.deb
|
||||
|
||||
对于64位的系统,使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
wget https://launchpad.net/~colingille/+archive/freshlight/+files/winusb_1.0.11+saucy1_amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
当你下载了正确的二进制包,你可以用下面的命令安装WinUSB:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg -i winusb*
|
||||
|
||||
不要担心在你安装WinUSB时看到的错误。使用这条命令修复依赖错误:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get -f install
|
||||
|
||||
之后,你就可以在 Unity Dash 中查找 WinUSB 并且用它在 Ubuntu 14.04 中创建 Windows 的 live USB 了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我希望这篇文章能够帮到你**在 Ubuntu 14.04、14.10 和 Linux Mint 17 中安装 WinUSB**。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/install-winusb-in-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://en.congelli.eu/prog_info_winusb.html
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-know-ubuntu-unity-version/
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
实例展示Ubuntu中apt-get和apt-cache命令的使用
|
||||
apt-get 和 apt-cache 命令实例展示
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
apt-get和apt-cache是**Ubuntu Linux**中的命令行下的**包管理**工具。 apt-get的GUI版本是Synaptic包管理器,本篇中我们会讨论apt-get和apt-cache命令的不同。
|
||||
apt-get和apt-cache是**Ubuntu Linux**中的命令行下的**包管理**工具。 apt-get的GUI版本是Synaptic包管理器。本篇中我们会展示apt-get和apt-cache命令的15个不同例子。
|
||||
|
||||
### 示例:1 列出所有可用包 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ apt-get和apt-cache是**Ubuntu Linux**中的命令行下的**包管理**工具
|
||||
|
||||
### 示例:2 用关键字搜索包 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个命令在你不确定包名时很有用,只要在apt-cache(这里原文是apt-get,应为笔误)后面输入与包相关的关键字即可/
|
||||
这个命令在你不确定包名时很有用,只要在apt-cache(LCTT 译注:这里原文是apt-get,应为笔误)后面输入与包相关的关键字即可。
|
||||
|
||||
linuxtechi@localhost:~$ apt-cache search "web server"
|
||||
apache2 - Apache HTTP Server
|
||||
@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ apt-get和apt-cache是**Ubuntu Linux**中的命令行下的**包管理**工具
|
||||
pnp4nagios-bin: /etc/pnp4nagios/nagios.cfg
|
||||
pnp4nagios-bin: /usr/share/doc/pnp4nagios/examples/nagios.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
### 示例:3 显示特定包的基本信息 ###
|
||||
### 示例:3 显示特定包的基本信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
linuxtechi@localhost:~$ apt-cache show postfix
|
||||
Package: postfix
|
||||
@ -92,7 +92,7 @@ apt-get和apt-cache是**Ubuntu Linux**中的命令行下的**包管理**工具
|
||||
|
||||
### 示例:6 使用 “apt-get update” 更新仓库 ###
|
||||
|
||||
使用命令“apt-get update”, 我们可以重新从源仓库中同步文件索引。包的索引从“/etc/apt/sources.list”中检索
|
||||
使用命令“apt-get update”, 我们可以重新从源仓库中同步文件索引。包的索引从“/etc/apt/sources.list”中检索。
|
||||
|
||||
linuxtechi@localhost:~$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
Ign http://extras.ubuntu.com utopic InRelease
|
||||
@ -106,7 +106,7 @@ apt-get和apt-cache是**Ubuntu Linux**中的命令行下的**包管理**工具
|
||||
Ign http://in.archive.ubuntu.com utopic-backports InRelease
|
||||
................................................................
|
||||
|
||||
### 示例:7 使用apt-get安装包 ###
|
||||
### 示例:7 使用apt-get安装包 ###
|
||||
|
||||
linuxtechi@localhost:~$ sudo apt-get install icinga
|
||||
|
||||
@ -140,15 +140,15 @@ apt-get和apt-cache是**Ubuntu Linux**中的命令行下的**包管理**工具
|
||||
Get:1 http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ utopic/universe icinga amd64 1.11.6-1build1 [1,474 B]
|
||||
Fetched 1,474 B in 1s (1,363 B/s)
|
||||
|
||||
上面的目录会从你当前的目录下载icinga包。
|
||||
上面的目录会把icinga包下载到你的当前工作目录。
|
||||
|
||||
### 示例:12 清理本地包占用的磁盘空间 ###
|
||||
|
||||
linuxtechi@localhost:~$ sudo apt-get clean
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令会清零apt-get在下载包时占用的磁盘空间。
|
||||
上面的命令会清空apt-get所下载的包占用的磁盘空间。
|
||||
|
||||
我们也可以使用“**autoclean**”选项来代替“**clean**“,两者之间主要的区别是autoclean清理不再使用且没用的下载。
|
||||
我们也可以使用“**autoclean**”选项来代替“**clean**”,两者之间主要的区别是autoclean清理不再使用且没用的下载。
|
||||
|
||||
linuxtechi@localhost:~$ sudo apt-get autoclean
|
||||
Reading package lists... Done
|
||||
@ -167,9 +167,9 @@ apt-get和apt-cache是**Ubuntu Linux**中的命令行下的**包管理**工具
|
||||
Get:1 Changelog for apache2 (http://changelogs.ubuntu.com/changelogs/pool/main/a/apache2/apache2_2.4.10-1ubuntu1/changelog) [195 kB]
|
||||
Fetched 195 kB in 3s (60.9 kB/s)
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令会下载apache2的更新日志,并在你屏幕上显示。
|
||||
上面的命令会下载apache2的更新日志,并在你屏幕上分页显示。
|
||||
|
||||
### 示例15 使用 “check” 选项显示损坏的依赖 ###
|
||||
### 示例:15 使用 “check” 选项显示损坏的依赖关系 ###
|
||||
|
||||
linuxtechi@localhost:~$ sudo apt-get check
|
||||
Reading package lists... Done
|
||||
@ -182,7 +182,7 @@ via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/ubuntu-apt-get-apt-cache-commands-examples/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux上使用dupeGuru删除重复文件
|
||||
删除重复文件的神器:dupeGuru
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
最近,我被要求清理我父亲的文件和文件夹。有一个难题是,里面存在很多不正确的名字的重复文件。有移动硬盘的备份,同时还为同一个文件编辑了多个版本,甚至改变的目录结构,同一个文件被复制了好几次,改变名字,改变位置等,这些挤满了磁盘空间。追踪每一个文件成了一个最大的问题。万幸的是,有一个小巧的软件可以帮助你省下很多时间来找到删除你系统中重复的文件:[dupeGuru][1]。它用Python写成,这个去重软件几个小时钱前切换到了GPLv3许可证。因此是时候用它来清理你的文件了!
|
||||
最近,我需要清理我父亲的文件和文件夹。有一个难题是,里面存在很多不正确的名字的重复文件。有移动硬盘的备份,同时还为同一个文件编辑了多个版本,甚至改变的目录结构,同一个文件被复制了好几次,名字改变,位置改变等,这些文件挤满了磁盘空间。追踪每一个文件成了一个最大的问题。万幸的是,有一个小巧的软件可以帮助你省下很多时间来找到删除你系统中重复的文件:[dupeGuru][1]。它用Python写成,这个去重软件几个小时前切换到了GPLv3许可证。因此是时候用它来清理你的文件了!
|
||||
|
||||
### dupeGuru的安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu上, 你可以加入Hardcoded的软件PPA:
|
||||
在Ubuntu上, 你可以加入如下硬编码的软件PPA:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-add-repository ppa:hsoft/ppa
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
@ -33,29 +33,29 @@ DupeGuru的构想是既快又安全。这意味着程序不会在你的系统上
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
注意的是默认上dupeGuru基于文件的内容匹配,而不是他们的名字。为了防止意外地删除了重要的文件,匹配那列列出了使用的匹配算法。在这里,你可以选择你想要删除的匹配文件,并按下“Action” 按钮来看到可用的操作。
|
||||
注意的是默认上dupeGuru基于文件的内容匹配,而不是他们的名字。为了防止意外地删除了重要的文件,匹配列列出了其使用的匹配算法。在这里,你可以选择你想要删除的匹配文件,并按下“Action” 按钮来看到可用的操作。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
可用的选项是相当广泛的。简而言之,你可以删除重复、移动到另外的位置、忽略它们、打开它们、重命名它们甚至用自定义命令运行它们。如果你选择删除重复文件,你可能会像我一样非常意外竟然还有删除选项。
|
||||
可用的选项相当广泛。简而言之,你可以删除重复、移动到另外的位置、忽略它们、打开它们、重命名它们甚至用自定义命令运行它们。如果你希望删除重复文件,你可能会像我一样非常意外竟然有这么多种删除方式。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你不及可以将删除文件移到垃圾箱或者永久删除,还可以选择留下指向原文件的链接(软链接或者硬链接)。也就是说,重复文件按将会删除但是会保留下指向原文件的链接。这将会省下大量的磁盘空间。如果你将这些文件导入到工作空间或者它们有一些依赖时很有用。
|
||||
你不仅可以将删除的文件移到垃圾箱或者永久删除,还可以选择留下指向原文件的链接(软链接或者硬链接)。也就是说,重复文件将会删除文件存储,但是会保留下一个指向原文件的链接。这将会省下大量的磁盘空间。如果你将这些文件导入到工作空间或者它们有一些依赖时很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
还有一个奇特的选项:你可以用HTML或者CSV文件导出结果。不确定你会不会这么做,但是我假设你想追踪重复文件而不是想让dupeGuru处理它们时会有用。
|
||||
还有一个奇特的选项:你可以用HTML或者CSV文件导出结果。我不确定你会不会需要这么做,但是我假设你想追踪重复文件而不是想让dupeGuru处理它们时会有用。
|
||||
|
||||
最后但并不是最不重要的是,偏好菜单可以让你对去重的想法成真。
|
||||
最后但并不是最不重要的是,偏好菜单可以让你按照你的想法来操作去重这件事。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这里你可以选择扫描的标准,基于内容还是基于文字,并且有一个阈值来控制结果的数量。这里同样可以定义自定义在执行中可以选择的命令。在无数其他小的选项中,要注意的是dupeGuru默认忽略小于10KB的文件。
|
||||
这里你可以选择扫描的标准,基于内容还是基于名字,并且有一个阈值来控制结果的数量。这里同样可以定义自定义在执行中可以选择的命令。混在其他那些小的选项中,要注意的是dupeGuru默认忽略小于10KB的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
要了解更多的信息,我建议你到[official website][4]官方网站看下,这里有很多文档、论坛支持和其他好东西。
|
||||
要了解更多的信息,我建议你到[官方网站][4]看下,这里有很多文档、论坛支持和其他好东西。
|
||||
|
||||
总结一下,dupeGuru是我无论何时准备备份或者释放空间时想到的软件。我发现这对高级用户而言也足够强大了,对新人而言也很直观。锦上添花的是:dupeGuru是跨平台的额,这意味着你可以在Mac或者在Windows PC上都可以使用。如果你有特定的需求,想要清理音乐或者图片。这里有两个变种:[dupeguru-me][5]和 [dupeguru-pe][6], 相应地可以清理音频和图片文件。与常规版本的不同是它不仅比较文件格式还比较特定的媒体数据像质量和码率。
|
||||
总结一下,dupeGuru是我无论何时准备备份或者释放空间时所想到的软件。我发现这对高级用户而言也足够强大了,对新人而言也很直观。锦上添花的是:dupeGuru是跨平台的,这意味着你可以在Mac或者在Windows PC上都可以使用。如果你有特定的需求,想要清理音乐或者图片。这里有两个变种:[dupeguru-me][5]和 [dupeguru-pe][6], 相应地可以清理音频和图片文件。与常规版本的不同是它不仅比较文件格式还比较特定的媒体数据像质量和码率。
|
||||
|
||||
你dupeGuru怎么样?你会考虑使用它么?或者你有任何可以替代的软件的建议么?让我在评论区知道你们的想法。
|
||||
你觉得dupeGuru怎么样?你会考虑使用它么?或者你有任何可以替代的软件的建议么?让我在评论区知道你们的想法。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/dupeguru-deduplicate-files-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrien Brochard][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,20 +1,21 @@
|
||||
SaltStack:Linux服务器配置管理神器
|
||||
通过 SaltStack 管理服务器配置
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我在搜索[Puppet][1]的替代品时,偶然间碰到了Salt。我喜欢puppet,但是我又爱上Salt了:)。我发现Salt在配置和使用上都要比Puppet简单,当然这只是一家之言,你大可不必介怀。另外一个爱上Salt的理由是,它可以让你从命令行管理服务器配置,比如:
|
||||
|
||||
要通过Salt来更新所有服务器,你只需运行以下命令
|
||||
要通过Salt来更新所有服务器,你只需运行以下命令即可
|
||||
|
||||
salt ‘*’ pkg.upgrade
|
||||
salt '*' pkg.upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
**安装SaltStack到Linux上。**
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是在CentOS 6/7上安装的话,那么Salt可以通过EPEL仓库获取到。而对于Pi和Ubuntu Linux用户,你可以从[这里][2]添加Salt仓库。Salt是基于python的,所以你也可以使用‘pip’来安装,但是你得用yum-utils或是其它包管理器来自己处理它的依赖关系哦。
|
||||
##安装SaltStack到Linux上##
|
||||
|
||||
Salt遵循服务器-客户端模式,服务器端称为领主,而客户端则称为下属。
|
||||
如果你是在CentOS 6/7上安装的话,那么Salt可以通过EPEL仓库获取到。而对于Pi和Ubuntu Linux用户,你可以从[这里][2]添加Salt仓库。Salt是基于python的,所以你也可以使用‘pip’来安装,但是你得用yum-utils或是其它包管理器来自己处理它的依赖关系。
|
||||
|
||||
**安装并配置Salt领主**
|
||||
Salt采用服务器-客户端模式,服务器端称为领主,而客户端则称为下属。
|
||||
|
||||
###安装并配置Salt领主###
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master~]# yum install salt-master
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,7 +28,7 @@ Salt配置文件位于/etc/salt和/srv/salt。Salt虽然可以开箱即用,但
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master ~]# systemctl start salt-master
|
||||
|
||||
**安装并配置Salt下属**
|
||||
###安装并配置Salt下属###
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-minion~]#yum install salt-minion
|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,7 +40,7 @@ Salt配置文件位于/etc/salt和/srv/salt。Salt虽然可以开箱即用,但
|
||||
|
||||
在启动时,下属客户机会生成一个密钥和一个id。然后,它会连接到Salt领主服务器并验证自己的身份。Salt领主服务器在允许下属客户机下载配置之前,必须接受下属的密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
**在Salt领主服务器上列出并接受密钥**
|
||||
###在Salt领主服务器上列出并接受密钥###
|
||||
|
||||
# 列出所有密钥
|
||||
[root@salt-master~] salt-key -L
|
||||
@ -59,7 +60,7 @@ Salt配置文件位于/etc/salt和/srv/salt。Salt虽然可以开箱即用,但
|
||||
|
||||
在接受下属客户机的密钥后,你可以使用‘salt’命令来立即获取信息。
|
||||
|
||||
**Salt命令行实例**
|
||||
##Salt命令行实例##
|
||||
|
||||
# 检查下属是否启动并运行
|
||||
[root@salt-master~] salt 'minion.com' test.ping
|
||||
@ -75,15 +76,15 @@ Salt配置文件位于/etc/salt和/srv/salt。Salt虽然可以开箱即用,但
|
||||
# 安装/更新所有服务器上的软件
|
||||
[root@salt-master ~]# salt '*' pkg.install git
|
||||
|
||||
salt命令需要一些组件来发送信息,其中之一是mimion id,而另一个是下属客户机上要调用的函数。
|
||||
salt命令需要一些组件来发送信息,其中之一是下属客户机的id,而另一个是下属客户机上要调用的函数。
|
||||
|
||||
在第一个实例中,我使用‘test’模块的‘ping’函数来检查系统是否启动。该函数并不是真的实施一次ping,它仅仅是在下属客户机作出回应时返回‘真’。
|
||||
|
||||
‘cmd.run’用于执行远程命令,而‘pkg’模块包含了包管理的函数。本文结尾提供了全部内建模块的列表。
|
||||
|
||||
**颗粒实例**
|
||||
###颗粒实例###
|
||||
|
||||
Salt使用一个名为**颗粒**的界面来获取系统信息。你可以使用颗粒在指定属性的系统上运行命令。
|
||||
Salt使用一个名为**颗粒(Grains)**的界面来获取系统信息。你可以使用颗粒在指定属性的系统上运行命令。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@vps4544 ~]# salt -G 'os:Centos' test.ping
|
||||
minion:
|
||||
@ -91,11 +92,11 @@ Salt使用一个名为**颗粒**的界面来获取系统信息。你可以使用
|
||||
|
||||
更多颗粒实例,请访问http://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/targeting/grains.html
|
||||
|
||||
**通过状态文件系统进行包管理。**
|
||||
##通过状态文件系统进行包管理##
|
||||
|
||||
为了是软件配置自动化,你需要使用状态系统,并创建状态文件。这些文件使用YAML格式和python字典、列表、字符串以及编号来构成数据结构。将这些文件从头到尾研读一遍,这将有助于你更好地理解它的配置。
|
||||
为了使软件配置自动化,你需要使用状态系统,并创建状态文件。这些文件使用YAML格式和python字典、列表、字符串以及编号来构成数据结构。将这些文件从头到尾研读一遍,这将有助于你更好地理解它的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
**VIM状态文件实例**
|
||||
###VIM状态文件实例###
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master~]# vim /srv/salt/vim.sls
|
||||
vim-enhanced:
|
||||
@ -107,7 +108,7 @@ Salt使用一个名为**颗粒**的界面来获取系统信息。你可以使用
|
||||
- group: root
|
||||
- mode: 644
|
||||
|
||||
该文件的第一和第三行成为状态id,它们必须包含有需要管理的包或文件的确切名称或路径。在状态id之后是状态和函数声明,‘pkg’和‘file’是状态声明,而‘installed’和‘managed’是函数声明。函数接受参数,用户、组、模式和源都是函数‘managed’的参数。
|
||||
该文件的第一和第三行称为状态id,它们必须包含有需要管理的包或文件的确切名称或路径。在状态id之后是状态和函数声明,‘pkg’和‘file’是状态声明,而‘installed’和‘managed’是函数声明。函数接受参数,用户、组、模式和源都是函数‘managed’的参数。
|
||||
|
||||
要将该配置应用到下属客户端,请移动你的‘vimrc’文件到‘/src/salt’,然后运行以下命令。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -253,7 +254,7 @@ Salt使用一个名为**颗粒**的界面来获取系统信息。你可以使用
|
||||
[root@vps4544 ssh]# cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config /srv/salt/ssh/
|
||||
[root@vps4544 ssh]# salt 'minion.com' state.sls ssh
|
||||
|
||||
**Top文件和环境。**
|
||||
###Top文件和环境###
|
||||
|
||||
top文件(top.sls)是用来定义你的环境的文件,它允许你映射下属客户机到包,默认环境是‘base’。你需要定义在基本环境下,哪个包会被安装到哪台服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -268,7 +269,7 @@ top文件(top.sls)是用来定义你的环境的文件,它允许你映射
|
||||
dev:
|
||||
- /srv/salt/dev
|
||||
|
||||
现在,添加一个top.sls文件到/src/salt
|
||||
现在,添加一个top.sls文件到/src/salt。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master ~]# vim /srv/salt/top.sls
|
||||
base:
|
||||
@ -299,7 +300,9 @@ top文件(top.sls)是用来定义你的环境的文件,它允许你映射
|
||||
|
||||
下属客户机将下载top文件并搜索用于它的配置,领主服务器也会将配置应用到所有下属客户机。
|
||||
|
||||
这仅仅是一个Salt的简明教程,如果你想要深入学习并理解,你可以访问以下链接。如果你已经在使用Salt,那么请告诉我你的建议和意见吧。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
这仅仅是一个Salt的简明教程,如果你想要深入学习并理解,你可以访问下面的链接。如果你已经在使用Salt,那么请告诉我你的建议和意见吧。
|
||||
|
||||
更新: [Foreman][3] 已经通过[插件][4]支持salt。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -329,7 +332,7 @@ via: http://techarena51.com/index.php/getting-started-with-saltstack/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Leo G][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,15 +1,14 @@
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu 14.04 上为Apache 2.4 安装SSL
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu 14.04 上为Apache 2.4 安装SSL支持
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
今天我会站如如何为你的个人网站或者博客安装**SSL 证书**,来保护你的访问者和网站之间通信的安全。
|
||||
今天我会讲述如何为你的个人网站或者博客安装**SSL 证书**,来保护你的访问者和网站之间通信的安全。
|
||||
|
||||
安全套接字层或称SSL,是一种加密网站和浏览器之间连接的标准安全技术。这确保服务器和浏览器之间传输的数据保持隐私和安全。这被成千上万的人使用来保护他们与客户的通信。要启用SSL链接,web服务器需要安装SSL证书。
|
||||
安全套接字层或称SSL,是一种加密网站和浏览器之间连接的标准安全技术。这确保服务器和浏览器之间传输的数据保持隐私和安全。它被成千上万的人使用来保护他们与客户的通信。要启用SSL链接,Web服务器需要安装SSL证书。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以创建你自己的SSL证书,但是这默认不会被浏览器信任,要修复这个问题,你需要从受信任的证书机构(CA)处购买证书,我们会向你展示如何
|
||||
或者证书并在apache中安装。
|
||||
你可以创建你自己的SSL证书,但是这默认不会被浏览器所信任,要解决这个问题,你需要从受信任的证书机构(CA)处购买证书,我们会向你展示如何获取证书并在apache中安装。
|
||||
|
||||
### 生成一个证书签名请求 ###
|
||||
|
||||
证书机构(CA)会要求你在你的服务器上生成一个证书签名请求(CSR)。这是一个很简单的过程,只需要一会就行,你需要运行下面的命令并输入需要的信息:
|
||||
证书机构(CA)会要求你在你的服务器上生成一个证书签名请求(CSR)。这是一个很简单的过程,只需要一会儿就行,你需要在你的服务器上运行下面的命令并输入需要的信息:
|
||||
|
||||
# openssl req -new -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout yourdomainname.key -out yourdomainname.csr
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,13 +16,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这一步会生成两个文件按:一个用于解密SSL证书的私钥文件,一个证书签名请求(CSR)文件(用于申请你的SSL证书)。
|
||||
这一步会生成两个文件:一个用于解密SSL证书的私钥文件,一个证书签名请求(CSR)文件(用于申请你的SSL证书)。
|
||||
|
||||
根据你申请的机构,你会需要上传csr文件或者在网站表格中粘帖他的内容。
|
||||
根据你申请的机构,你会需要上传csr文件或者在网站表格中粘帖该文件内容。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Apache中安装实际的证书 ###
|
||||
|
||||
生成步骤完成之后,你会收到新的数字证书,本篇教程中我们使用[Comodo SSL][1]并在一个zip文件中收到了证书。要在apache中使用它,你首先需要用下面的命令为收到的证书创建一个组合的证书:
|
||||
生成步骤完成之后,你会收到新的数字证书。本篇教程中我们使用[Comodo SSL][1],并在一个它发给我们的zip文件中收到了证书。要在apache中使用它,你首先需要用下面的命令用收到的证书创建一个组合的证书:
|
||||
|
||||
# cat COMODORSADomainValidationSecureServerCA.crt COMODORSAAddTrustCA.crt AddTrustExternalCARoot.crt > bundle.crt
|
||||
|
||||
@ -48,12 +47,12 @@
|
||||
|
||||
你现在应该可以用https://YOURDOMAIN/(注意使用‘https’而不是‘http’)来访问你的网站了,并可以看到SSL的进度条了(通常在你浏览器中用一把锁来表示)。
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE:** All the links must now point to https, if some of the content on the website (like images or css files) still point to http links you will get a warning in the browser, to fix this you have to make sure that every link points to https.
|
||||
**注意:** 现在所有的链接都必须指向https,如果网站上的一些内容(像图片或者css文件等)仍旧指向http链接的话,你会在浏览器中得到一个警告,要修复这个问题,请确保每个链接都指向了https。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:** 现在所有的内容链接都必须指向https,如果网站上的一些内容(像图片或者css文件等)仍旧指向http链接的话,你会在浏览器中得到一个警告,要修复这个问题,请确保每个链接都指向了https。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在你的网站上重定向HTTP请求到HTTPS中 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你希望重定向常规的HTTP请求到HTTPS,添加下面的文本到你希望的虚拟主机或者如果希望给服务器上所有网站都添加的话就加入到apache.conf中:
|
||||
如果你希望重定向常规的HTTP请求到HTTPS,添加下面的文本到你希望修改的虚拟主机,或者如果希望给服务器上所有网站都添加的话就加入到apache.conf中:
|
||||
|
||||
RewriteEngine On
|
||||
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} off
|
||||
@ -65,7 +64,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/install-ssl-apache-2-4-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrian Dinu][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@ Ubuntu 14.04 上 最好的 GNOME Shell 主题
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
自定义主题是自定义你的 Linux 桌面的最好方式。假如你在 [Ubuntu 14.04 中安装 GNOME][1] 或 在 Ubuntu 14.10 中安装了 GNOME,你或许想改变默认的主题以呈现出不同的外观。在这里,为帮助你完成该任务,我已经编制好了一个 **Ubuntu 或其他已经安装了 GNOME shell 的 Linux 操作系统中,最好的 GNOME Shell 主题** 的清单 。但在我们揭晓这份清单之前, 让我们先了解如何在 GNOME shell 中安装和应用新的主题。
|
||||
最好的方式来自定义你的 Linux 桌面就是使用自定义主题。假如你在 [Ubuntu 14.04 中安装 GNOME][1] 或 在 Ubuntu 14.10 中安装了 GNOME,你或许想改变默认的主题以呈现出不同的外观。在这里,为了帮助你完成该任务,我已经编制好了一个列表—— **Ubuntu 或其他已经安装了 GNOME shell 的 Linux 操作系统中,最好的 GNOME Shell 主题** 。但在我们揭晓这份列表之前, 让我们先了解如何在 GNOME shell 中安装和应用新的主题。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 GNOME Shell 中安装主题 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ Ubuntu 14.04 上 最好的 GNOME Shell 主题
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gnome-tweak-tool
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
或者,你可以使用新主题通过把它们放置到 `~/.themes` 目录中。如果你需要,我已经写了一个关于 [如何安装和使用 GNOME shell][2]的具体教程。
|
||||
或者,你可以通过把主题放置到 `~/.themes` 目录中来使用。如果你需要,我已经写了一个关于 [如何安装和使用 GNOME shell][2]的具体教程。
|
||||
|
||||
### 最好的 GNOME Shell 主题 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ sudo apt-get install gnome-tweak-tool
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
任何没有提到 [Numix 主题][3] 的清单都是不完整的。这个主题是如此地受欢迎以至于 [Numix 团队开发出一个新的 Linux 操作系统, Ozon][4]。考虑到他们的设计作品 Numix 主题,称在不久的将来发行的 `Ozon` 为 [最美丽的 Linux 操作系统][5] 也不为过。
|
||||
任何没有提到 [Numix 主题][3] 的列表都是不完整的。这个主题是如此地受欢迎以至于 [Numix 团队开发出一个新的 Linux 操作系统, Ozon][4]。考虑到他们的设计作品 Numix 主题,把不久将发行的 `Ozon` 称为 [最美丽的 Linux 操作系统][5] 也不为过。
|
||||
|
||||
使用下面的命令,在基于 Ubuntu 的发行版本中安装 Numix 主题:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ sudo apt-get install numix-icon-theme-circle
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
另一个来自 Numix 团队的成员之一的 Satyajit Sahoo 的美丽主题 。[Elegance Colors][6] 拥有自己的 PPA (译者注: 即 Personal Package Archive 的缩写) 使得你可以轻易地安装它:
|
||||
另一个美丽主题来自 Numix 团队成员之一 Satyajit Sahoo。[Elegance Colors][6] 拥有自己的 PPA (译者注: 即 Personal Package Archive 的缩写) 使得你可以轻松安装它:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:satyajit-happy/themes
|
||||
@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ sudo apt-get install gnome-shell-theme-elegance-colors
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Moka][7] 是另一个迷人的主题,它总是位于美丽的主题的清单之中。它是由给我们带来 Unity Tweak Tool 的开发者所设计。 Moka 是你绝对要尝试的主题之一:
|
||||
[Moka][7] 是另一个迷人的主题,它总是位于美丽的主题列表之中。它是由 Unity Tweak Tool 的开发者所设计。 Moka 是你一定要尝试的主题:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:moka/stable
|
||||
@ -68,7 +68,7 @@ sudo apt-get install moka-gnome-shell-theme
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
以前它以 Zukitwo Dark 的名字为人们熟知, Ciliora-Prima 是一个拥有方块图标的主题,可得到的三种版本之间相互略有不同。你可以从下面的链接中下载它们:
|
||||
以前它以 Zukitwo Dark 的名字为人们熟知, Ciliora-Prima 是一个拥有方块图标的主题,可使用的三种版本之间彼此略有不同。你可以从下面的链接中下载它们:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Ciliora-Prima GNOME Shell Theme][9]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ sudo apt-get install moka-gnome-shell-theme
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Faience 作为一个受欢迎的主题已经有一段时间了。你可以通过下面的 PPA 为 GNOME 3.10 及更高版本 安装 Faience:
|
||||
Faience 作为一个受欢迎的主题已经有一段时间了。你可以通过下面的 PPA 为 GNOME 3.10 及更高版本安装 Faience:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:tiheum/equinox
|
||||
@ -88,7 +88,7 @@ sudo apt-get install faience-theme
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
自从 Google 提出 `Material Design`,人们一直为之疯狂。Paper GTK 主题受 Google Material design 启发, 作者为 Sam Hewitt( Moka 项目开发者之一); 它正处于开发中,这意味着当前你将不能对 Paper 拥有最好的体验。假如你和我一样,具有一点实验精神,你绝对可以试一试。
|
||||
自从 Google 提出 `Material Design`,人们一直为之疯狂。Paper GTK 主题受 Google Material design 启发,作者为 Sam Hewitt( Moka 项目开发者之一);它正处于开发中,这意味着当前你还不能拥有 Paper 的最好体验。假如你和我一样,具有一点实验精神,你绝对可以试一试。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:snwh/pulp
|
||||
@ -96,9 +96,9 @@ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install paper-gtk-theme
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
以上就是我的清单。假如你正试着给你的 Ubuntu 换一个不同的模样,你也应该试试这个清单: [Ubuntu 14.04 中最好的图标主题][10]。
|
||||
以上就是我的列表。如果你正试着给你的 Ubuntu 换一个不同的模样,你也应该试试这个列表: [Ubuntu 14.04 中最好的图标主题][10]。
|
||||
|
||||
你是怎样找到这份 **最好的 GNOME shell 主题** 清单的呢?在上面列举的主题中,哪个是你最中意的呢? 如果它没有在这里列出,请一定让我们知道那个你心目中最好的 GNOME shell 主题 。
|
||||
你是怎样找到这份 **最好的 GNOME shell 主题** 列表的呢?在上面列举的主题中,哪个是你最中意的? 如果它没有在这里列出,请一定在评论中告诉我们哪个是你心目中最好的 GNOME shell 主题 。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -106,7 +106,7 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/gnome-shell-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
你可能会有很多理由想要把一个应用、一个用户或者一个环境与你的 linux 系统隔离开来。不同的操作系统有不同的实现方式,而在 linux 中,一个典型的方式就是 chroot 环境。
|
||||
|
||||
在这份教程中,我会一步一步指导你怎么使用 chroot 命令去配置一个与真实系统分离出来的独立环境。这个功能主要可以用于测试项目,这些步骤都在 **Ubuntu 14.04** 虚拟专用服务器(VPS)上执行。
|
||||
在这份教程中,我会一步一步指导你怎么使用 chroot 命令去配置一个与真实系统分离出来的独立环境。这个功能主要可以用于测试项目,以下这些步骤都在 **Ubuntu 14.04** 虚拟专用服务器(VPS)上执行。
|
||||
|
||||
学会快速搭建一个简单的 chroot 环境是一项非常实用的技能,绝大多数系统管理员都能从中受益。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
举个例子,你可以在 chroot 环境中编译、安装、测试软件,而不去动真实的系统。你也可以**在64位环境下使用 chroot 创建一个32位环境,然后运行一个32位的程序**(LCTT泽注:如果你的真实环境是32位的,那就不能 chroot 一个64位的环境了)。
|
||||
|
||||
但是 为了安全考虑,chroot 环境为非特权用户设立了非常严格的限制,而不是提供完整的安全策略。如果你需要的是有完善的安全策略的隔离方案,可以考虑下 LXC、Docker、vservers等等。
|
||||
但是为了安全考虑,chroot 环境为非特权用户设立了非常严格的限制,而不是提供完整的安全策略。如果你需要的是有完善的安全策略的隔离方案,可以考虑下 LXC、Docker、vservers等等。
|
||||
|
||||
### Debootstrap 和 Schroot ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -138,7 +138,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/configure-chroot-environment-ubuntu-14-04
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
今天我们将会在Ubuntu Server 14.04 LTS (Trusty)上安装一个博客平台Ghost。
|
||||
|
||||
Ghost是一款设计优美的发布平台,很容易使用且对任何人都免费。它是免费的开源软件(FOSS),它的源码在Github上。截至2014年1月,它的界面很简单还有分析面板。编辑使用的是分屏显示。
|
||||
Ghost是一款设计优美的发布平台,很容易使用且对任何人都免费。它是免费的开源软件(FOSS),它的源码在Github上。截至2015年1月(LCTT 译注:原文为2014,应为2015),它的界面很简单还有分析面板。编辑使用的是很便利的分屏显示。
|
||||
|
||||
因此有了这篇步骤明确的在Ubuntu Server上安装Ghost的教程:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -52,12 +52,12 @@ Ghost是一款设计优美的发布平台,很容易使用且对任何人都免
|
||||
sudo adduser --shell /bin/bash --gecos 'Ghost application' ghost
|
||||
sudo chown -R ghost:ghost /var/www/ghost/
|
||||
|
||||
现在启动Ghost,你需要以“ghsot”用户登录。
|
||||
现在启动Ghost,你需要以“ghost”用户登录。
|
||||
|
||||
su - ghost
|
||||
cd /var/www/ghost/
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你已经以“ghsot”用户登录,并可启动Ghost:
|
||||
现在,你已经以“ghost”用户登录,并可启动Ghost:
|
||||
|
||||
npm start --production
|
||||
|
||||
@ -67,7 +67,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/install-ghost-ubuntu-server-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ nmcli的通常语法是:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli [ OPTIONS ] OBJECT { COMMAND | help }
|
||||
|
||||
一件很酷的事情是你可以使用tab键来补全操作,这样你在何时忘记了语法你都可以用tab来看到可用的选项了。
|
||||
一件很酷的事情是你可以使用tab键来补全操作,这样你在何时忘记了语法你都可以按下tab来看到可用的选项了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -46,33 +46,33 @@ nmcli通常用法的一些例子:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli device connect eno16777736
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用静态IP添加一个以太网连接 ###
|
||||
### 添加一个使用静态IP的以太网连接 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要用静态IP添加一个以太网连接可以使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection add type ethernet con-name NAME_OF_CONNECTION ifname interface-name ip4 IP_ADDRESS gw4 GW_ADDRESS
|
||||
# nmcli connection add type ethernet con-name NAME_OF_CONNECTION ifname INTERFACE-NAME ip4 IP_ADDRESS gw4 GW_ADDRESS
|
||||
|
||||
将NAME_OF_CONNECTION替换成新的连接名,IP_ADDRESS替换成你要的IP地址,GW_ADDRESS替换成你使用的网关地址(如果你并不使用网关,你可以忽略这部分)。
|
||||
将NAME_OF_CONNECTION替换成新的连接名(LCTT 译注:这个名字以后可以用来对其操作,可以使用任何简单明了的名称),INTERFACE-NAME 替换成你的接口名,IP_ADDRESS替换成你要的IP地址,GW_ADDRESS替换成你使用的网关地址(如果你并不使用网关,你可以忽略这部分)。
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection add type ethernet con-name NEW ifname eno16777736 ip4 192.168.1.141 gw4 192.168.1.1
|
||||
# nmcli connection add type ethernet con-name NEW_STATIC ifname eno16777736 ip4 192.168.1.141 gw4 192.168.1.1
|
||||
|
||||
=要设置这个连接的DNS服务器使用下面的命令:
|
||||
要设置这个连接所使用的DNS服务器使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection modify NEW ipv4.dns "8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4"
|
||||
# nmcli connection modify NEW_STATIC ipv4.dns "8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4"
|
||||
|
||||
要启用新的以太网连接,使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection up NEW ifname eno16777736
|
||||
# nmcli connection up NEW_STATIC ifname eno16777736
|
||||
|
||||
要查看新配置连接的详细信息,使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli -p connection show NEW
|
||||
# nmcli -p connection show NEW_STATIC
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 添加一个使用DHCP的连接 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要添加一个使用DHCP来配置接口IP地址、网关地址和dns服务器地址的新的连接,你要做的就是忽略命令中的ip/gw部分,NetworkManager会自动使用DHCP来获取配置细节。
|
||||
如果你想要添加一个使用DHCP来配置接口IP地址、网关地址和dns服务器地址的新的连接,你要做的就是忽略上述命令中的ip/gw部分,NetworkManager会自动使用DHCP来获取配置细节。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,要创建一个新的叫NEW_DHCP的DHCP连接,在设备eno16777736上你可以使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -84,7 +84,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/nmcli-tool-red-hat-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrian Dinu][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -65,7 +65,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
|
||||
|
||||
加入红色显示的行:
|
||||
加入如下行“-A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW --dport 23 -j ACCEPT”:
|
||||
|
||||
# Firewall configuration written by system-config-firewall
|
||||
# Manual customization of this file is not recommended.
|
||||
@ -151,7 +151,7 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/installing-telnet-centosrhelscientific-linux-6-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
[在Ubuntu中安装Mate桌面][1]是一码事但是你或许想要知道如何**配置Mate桌面**? 大多数桌面环境都有它们自己的调整工具。比如Unity有Unity Tweak,Gnome有Gnome Tweak,Elementary OS有 Elementary OS Teweak。好消息是Mate桌面也有它自己的调整工具,叫Mate Tweak][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
Mate Tweak是[mintDesktop][3]的克隆分支,一款Linux Mint的配置工具。
|
||||
Mate Tweak是[mintDesktop][3]的克隆分支,那是一款Linux Mint的配置工具。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装Mate Tweak来配置Mate桌面 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/configure-mate-desktop-mate-tweak/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,17 +5,17 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这个教程会一步一步的教你如何安装Xubuntu Linux。
|
||||
这个教程会一步步教你如何安装Xubuntu Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
为什么你会想要安装Xubuntu呢?这里有三个原因:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 你有一台安装Windows XP的计算机,但是微软已经不再对Windows XP提供支持
|
||||
2. 你的[电脑运行很慢][1],并且你想要一个轻量级并且跟得上时代潮流的操作系统
|
||||
3. 你想要增加一些DIY经验
|
||||
2. 你的[电脑运行很慢][1],你想要一个轻量级并且跟得上时代潮流的操作系统
|
||||
3. 你想要自定义你的电脑使用体验
|
||||
|
||||
首先,你需要[下载Xubuntu,并且创建一个启动优盘][2]。
|
||||
首先,你需要[下载Xubuntu,并且创建一个可启动的USB驱动器][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
完成以后,用优盘启动到Xubuntu,然后点击安装Xubuntu图标。
|
||||
完成以后,用优盘启动到当前版本的Xubuntu,然后点击安装Xubuntu图标。
|
||||
|
||||
### 选择你的安装语言 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -29,9 +29,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
第二步,需要你来选择你的网络链接。这个步骤不是必须的。
|
||||
第二步,需要你来选择你的网络链接。这个步骤不是必须的,你在这个阶段可能会选择不设置网络链接是有原因的。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你[网络状况十分糟糕][3],直接跳过是一个明智的选择,因为安装程序会在安装过程中从网络上下载一些更新包。那么可想而知,你的安装过程就会花费很长的时间。
|
||||
如果你的[网络状况十分糟糕][3],不选无线网络是一个明智的选择,因为安装程序会在安装过程中从网络上下载一些更新包。那么可想而知,你的安装过程就会花费很长的时间。
|
||||
|
||||
当然,如果你的[网速很快][4],选择一个无线网,然后输入密码就行了。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,17 +51,19 @@
|
||||
|
||||
安装过程中,如果电池电量耗完的话,你才必须要链接到到电源。
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,如果你连网了,这里有一个关闭安装过程中下载更新包的复选框。
|
||||
|
||||
这里还有一个复选框,提示你是否安装用于[播放MP3][5]或者[Flash视频][6]的第三方软件,当然,这些内容也可以在安装完成以后进行。
|
||||
|
||||
### 选择安装类型 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
接下来的步骤是选择安装类型。显示那些选项,取决于之前电脑上安装了什么系统。
|
||||
接下来的步骤是选择安装类型。显示哪些选项,取决于之前电脑上安装了什么系统。
|
||||
|
||||
在我的示例中,我已经安装了[Ubuntu MATE][7],所以,我的选项是重装Ubuntu、删除并且重装、Xubuntu和Ubuntu双系统、以及其他。
|
||||
在我的示例中,我已经安装了[Ubuntu MATE][7],所以,我的选项是重装Ubuntu、删除并且重装、安装Xubuntu和Ubuntu双系统,或者其它。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的计算机上安装了Windows,那么你得到的选项就是,安装双系统、使用Xubuntu替换Windows以及其他。
|
||||
如果你的计算机上安装了Windows,那么你得到的选项就是,安装双系统,使用Xubuntu替换Windows或者其他。
|
||||
|
||||
这个教程只是用来说明如何在计算机上安装Xubuntu,而不是怎么安装双系统,那将是一个完全不同的教程。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -73,11 +75,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
选择你要在那个磁盘上安装的Xubuntu。
|
||||
选择你要安装Xubuntu的磁盘。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“Install Now”。
|
||||
|
||||
这时候会弹出一个警告窗口,会提示你,选择的磁盘驱动器会被完全清除,然后会显示一个新创建的分区列表。
|
||||
这时候会弹出一个警告窗口,会提示你选择的磁盘驱动器会被完全清除,然后会显示一个新创建的分区列表。
|
||||
|
||||
> 备注:这是你改变主意的最后一个机会,如果你点击继续,磁盘就会被完全清除,然后开始安装Xubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -103,7 +105,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
如果你需要确认键盘布局是否正确,可以在“Type here to test your keyboard”输入字符。你需要特别注意fn键和一些符号,例如英镑和美元符号。
|
||||
|
||||
如果在安装过程中没有设对也没关系,安装完成以后在Xubuntu系统设置中也可以进行调整。
|
||||
如果在安装过程中没有设置正确也没关系,安装完成以后在Xubuntu系统设置中也可以进行调整。
|
||||
|
||||
### 新增用户 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -115,9 +117,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
为用户选择一个用户名并且[创建一个密码][8]。为了保证你的密码输入正确,你需要输入两遍。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要系统自动登入,而不是在每次启动的时候输入密码,选择“Log in automatically”。尽管对于我来说,我肯定不会选择这个选项。
|
||||
如果你想要系统自动登入,而不是在每次启动的时候输入密码,选择“Log in automatically”。对于我来说,我肯定不会选择这个选项。
|
||||
|
||||
更好的选项是“Require my password to log in”,并且如果你想要更高的安全等级,勾选“Encrypt my home fodler”选项。
|
||||
更好的选项是“Require my password to log in”,并且如果你想要更高的安全等级,勾选“Encrypt my home folder”选项。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“Continue”然后继续。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -125,9 +127,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这个步骤中,将会会拷贝文件到你的电脑,并且安装Xubuntu。
|
||||
这个步骤中,将会拷贝文件到你的电脑,并且安装Xubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
在这个过程中,你会看到一个简短的幻灯片。在这个时候你可以去[泡一杯咖啡][9]或者放松一下什么的。
|
||||
在这个过程中,你会看到一个简短的幻灯片。在这个时候你可以去[泡一杯咖啡][9]或者放松一下。
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成以后,会弹出提示告诉你是否重新启动,并且开始体验一下新安装的Xubuntu系统。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -139,7 +141,7 @@ via : http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/A-Step-By-Step-Guide-To-Installing-Xu
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gary Newell][a]
|
||||
译者:[zhouj-sh](https://github.com/zhouj-sh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -152,4 +154,4 @@ via : http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/A-Step-By-Step-Guide-To-Installing-Xu
|
||||
[6]:http://animation.about.com/od/2danimationtutorials/ss/2d_fla_lesson1.htm
|
||||
[7]:http://www.everydaylinuxuser.com/2014/11/ubuntu-mate-vs-lubuntu-on-old-netbook.html
|
||||
[8]:http://netsecurity.about.com/cs/generalsecurity/a/aa112103b.htm
|
||||
[9]:http://coffeetea.about.com/od/preparationandrecipes/
|
||||
[9]:http://coffeetea.about.com/od/preparationandrecipes/
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
3种创建轻量、持久化的Xubuntu Linux USB系统盘的方法
|
||||
3种方法来创建轻量、持久化的Xubuntu Linux USB系统盘
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用Universal USB Install创建持久化USB Xubuntu系统盘 ###
|
||||
@ -9,13 +9,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
> 译者注:持久化Linux USB系统盘(Persistent Linux USB drive),安装在优盘的Linux系统,允许用户保存数据到优盘而不是仅仅将这些修改留在内存中。这些数据可以在重启后恢复并且重新使用,甚至是在其他的机器上面启动也没有关系。一般情况下,持久化系统盘会安装一个压缩过的Linux操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
为什么你需要做这些事情呢,这里有5个很好的理由:
|
||||
为什么要这样做呢,这里有5个很好的理由:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 你想要在你的电脑上安装一个轻量的并且功能完善的Linux版本。
|
||||
1. 你想要在你的电脑上安装一个轻量并且功能完善的Linux版本。
|
||||
2. 你的电脑没有硬盘,那么一个Linux USB系统盘就可以让这台电脑摆脱被扔到垃圾堆的命运。
|
||||
3. 你想体验一下Linux,但是你却不想花太多的时间去准备。
|
||||
4. 你想创建一个USB系统恢复盘,并且在优盘上安装一些特定的应用程序。
|
||||
5. 你想要一个可以装在屁股口袋或者可以挂在钥匙圈上面的可定制的Linux版本。
|
||||
5. 你想要一个可定制的Linux版本,能装在后兜或者挂在钥匙圈上。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们有了充足的理由,那么开始做一些准备工作吧。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
14.04版是一个长期维护的版本,维护周期会持续3年。14.10是最新版本,但是只提供9个月的维护。
|
||||
|
||||
你选择了下载站点以后,会提示你选择32位版本或者64位版本。如果你的电脑是32位,就选32位版本,同样,如果你的电脑是64位选64位版本就行了。
|
||||
你选择了下载站点以后,会提示你选择32位版本或者64位版本。如果你的电脑是32位,就选32位版本,同样,如果你的电脑是64位,那就选64位版本。
|
||||
|
||||
[点击这里,有一个教程来教你辨别你的电脑是32位还是64位][5]。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -105,7 +105,7 @@ Universal USB Installer主界面出现以后,从下拉列表中选择你想要
|
||||
|
||||
Startup Disk Creator使用起来很简单。
|
||||
|
||||
界面被划分成两个部分。在上面部分指定下载的系统盘路径,在下面指定安装的优盘。
|
||||
界面被划分成两个部分。上部分指定下载的系统盘路径,下部分指定安装的优盘。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,点击“Other”按钮,第二步,选择你所下载的Xubuntu ISO文件。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -119,7 +119,7 @@ Startup Disk Creator使用起来很简单。
|
||||
|
||||
你创建的过程中,你可能需要输入几次你的系统密码,USB系统盘创建完成以后,你就可以使用它启动到Xubuntu了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用UNetbootin创建持久化Xubuntu系统盘 ###
|
||||
### 使用UNetbootin创建持久化的Xubuntu系统盘 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -127,7 +127,7 @@ Startup Disk Creator使用起来很简单。
|
||||
|
||||
个人来说,在Windows系统上面我喜欢用Universal USB Installer,但Linux的话,UNetbootin更合适一些。
|
||||
|
||||
> 注:UNetbootin并不是100%完美的,它并不支持所有的Linux发行版。
|
||||
> 注:UNetbootin并不是100%完美的,不是所有的Linux发行版都支持。
|
||||
|
||||
Windows平台可以点击[这里][8]下载UNetbootin。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -141,11 +141,11 @@ Linux平台可以使用package manager安装UNetbootin。
|
||||
|
||||
> sudo unetbootin
|
||||
|
||||
UNetbootin的界面分为两个部分。你可以在上面的部分选择一个Linux发行版,然后下载它,如果已经下载了某个发行版,可以在下半部分选择已经下载的系统盘。
|
||||
UNetbootin的界面分为两个部分。你可以在上半部分选择一个Linux发行版,然后下载它,如果已经下载了某个发行版,可以在下半部分选择已经下载的系统盘。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“Diskimage”单选框,然后点击三个点的按钮。找到已经下载的Xubuntu ISO文件。路径会显示到按钮旁边的文本框里面。
|
||||
|
||||
修改“Space used to preserve files across reboots”的值,来指定你想要用来存储“持久化”数据的空间大小。
|
||||
设置“Space used to preserve files across reboots”的值,来指定你想要用来存储“持久化”数据的空间大小。
|
||||
|
||||
类型选择USB drive,然后选择优盘的盘符。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -159,7 +159,7 @@ via : http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/How-To-Create-A-Persistent-Bootable-Xu
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gary Newell][a]
|
||||
译者:[zhouj-sh](https://github.com/Zhouj-sh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -171,4 +171,4 @@ via : http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/How-To-Create-A-Persistent-Bootable-Xu
|
||||
[5]:http://pcsupport.about.com/od/fixtheproblem/f/32-bit-64-bit-windows.htm
|
||||
[6]:http://www.pendrivelinux.com/universal-usb-installer-easy-as-1-2-3/
|
||||
[7]:http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/fl/Learn-Ubuntu-The-Unity-Dash.htm
|
||||
[8]:http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/How-To-Create-A-UEFI-Bootable-Ubuntu-USB-Drive-Using-Windows.htm
|
||||
[8]:http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/How-To-Create-A-UEFI-Bootable-Ubuntu-USB-Drive-Using-Windows.htm
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
Cutegram: 一个GNU/Linux下不错的Telegram客户端
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
不需要再介绍**Telegram**了,对吧。Telegram是一款流行的免费即时通信工具,帮助你在全球与朋友聊天。不像Whatsapp,Telegram是永久免费、没有广告、没有订阅费用的。并且Telegram客户端也是开源的。Telegram在许多不同的平台中都有,包括Linux、Android、iOS、Windows Phone和Mac OS X。使用telegram发送的消息是高度加密且会自我销毁。它很安全,并且没有对你的多媒体和聊天的大小作限制。
|
||||
|
||||
在[先前的教程][1]中我们已经提到你可以在Ubuntu/Debian中安装Telegram。然而,有一个新的Telegram客户端叫**Cutegram**出现了,可以使你的聊天体验更加有趣和简单。
|
||||
|
||||
### Cutegram是什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cutegram是一款专注于用户友好、与Linux桌面环境兼容和易于使用的开源 telegram 的 GNU/Linux客户端。Cutegram使用Qt5、QML、libqtelegram、libappindication、AsemanQtTools技术和Faenzatu图标和Twitter emojie图片集。它在GPLv3许可证下免费发布。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 Cutegram ###
|
||||
|
||||
进入Cutegrm的首页病根据你的发行版版本选择最新的版本。我使用的是Ubuntu 64位版,所以我下载的是.deb文件。
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://aseman.co/downloads/cutegram/cutegram_1.0.2-1-amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
现在,如下安装Cutegram:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gdebi
|
||||
sudo gdebi cutegram_1.0.2-1-amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
对于其他发行版,运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
**64位:**
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://aseman.co/downloads/cutegram/cutegram-1.0.2-linux-x64-installer.run
|
||||
|
||||
**32位:**
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://aseman.co/downloads/cutegram/cutegram-1.0.2-linux-installer.run
|
||||
|
||||
设置执行权限:
|
||||
|
||||
chmod a+x cutegram-1.0.2-linux*.run
|
||||
|
||||
如下进行安装。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ./cutegram-1.0.2-linux*.run
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在菜单或者Unity dash中启动Cutegram。在登录界面,选择你的国家并输入电话号码,最好点击**Login**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
一个验证码将会发送到你手机上。输入验证码并点击**Sign in**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你会看到
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
开始聊天吧!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
接着,你可以设置头像,开始新的聊天/群聊,或者使用左边面板的按钮开始秘密聊天。
|
||||
|
||||
玩得开心!干杯!!
|
||||
|
||||
更多细节,请关注[Cutegram 网站][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/cutegram-better-telegram-client-gnulinux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/install-telegram-desktop-via-ppa/
|
||||
[2]:http://aseman.co/en/products/cutegram/
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
如何在CentOS 7中禁止IPv6
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
最近,我的一位朋友问我该如何禁止IPv6。在搜索了一番之后,我找到了下面的方案。下面就是我在CentOS 7迷你版中禁止IPv6的方法。
|
||||
最近,我的一位朋友问我该如何禁止IPv6。在搜索了一番之后,我找到了下面的方案。下面就是在我的CentOS 7 迷你服务器禁止IPv6的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以用两个方法做到这个。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,7 +41,6 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 我在禁止IPv6后遇到问题怎么办 ###
|
||||
|
||||
You may get problems after disabling IPv6.
|
||||
你可能在禁止IPv6后遇到一些问题
|
||||
|
||||
#### 问题1: ####
|
||||
@ -60,9 +59,7 @@ vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||
|
||||
AddressFamily inet
|
||||
|
||||
或者,
|
||||
|
||||
在这行的前面去掉注释**(#)**:
|
||||
或者,在这行的前面去掉注释**(#)**:
|
||||
|
||||
#ListenAddress 0.0.0.0
|
||||
|
||||
@ -89,7 +86,7 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/disable-ipv6-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
如何在崩溃后重启Cinnamon
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Cinnamon是一个提供了高级创新特性和传统用户体验的Linux桌面环境。桌面布局和Gnome 2相似。底层的技术与Gnome Shell相似。它的重点是让用户有宾至如归的感觉并提供一个简单和舒适的桌面体验。
|
||||
Cinnamon是一个提供了高级创新特性和传统用户体验的Linux桌面环境。桌面布局和Gnome 2相似。底层的技术与Gnome Shell相似。它的重点是让用户以熟悉的方式得到简单和舒适的桌面体验。
|
||||
|
||||
本篇中我们会展示一个快速的方法来重启Cinnamon而不用在崩溃后登出或者重启。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,15 +18,15 @@ Cinnamon应该会重新在面板和菜单中显示图标和文本了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
享受吧!
|
||||
试试吧!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/quick-tip-restart-cinnamon-crash/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Enock Seth Nyamador][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,17 @@
|
||||
如果使用32位整型会溢出,那么是否可以使用一个40位结构体代替64位长整型?
|
||||
---------
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
###问题:
|
||||
|
||||
#问题:
|
||||
假如说,使用32位的整型会溢出,在不考虑使用长整型的情况下,如果我们只需要表示2的40次方范围内的数,是否可以利用某些40位长的数据类型来表示呢?这样的话,每个整型数就可以节省24位的空间。
|
||||
|
||||
如果可以,该怎么做?
|
||||
|
||||
需求是:我现在必须处理数以亿计的数字,所以在存储空间上受到了很大的限制。
|
||||
|
||||
#回答:
|
||||
###回答:
|
||||
|
||||
##可以是可以,但是……
|
||||
可以是可以,但是……
|
||||
|
||||
这种方法的确可行,但这么做通常没什么意义(因为几乎没有程序需要处理多达十亿的数字):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,14 +23,15 @@ struct bad_idea
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在这里,变量var占据40位大小,但是以生成代码时拥有非常低的运行效率来换取的(事实证明“非常”二字言过其实了——测试中程序开销仅仅增加了1%到2%,正如下面的测试时间所示),而且这么做通常没什么用。除非你还需要保存一个24位的值(或者是8位、16位的值),这样你皆可以它们放到同一个结构中。不然的话,因为对齐内存地址产生的开销会抵消这么做带来的好处。
|
||||
在这里,变量var占据40位大小,但是这是以生成代码时拥有非常低的运行效率来换取的(事实证明“非常”二字言过其实了——测试中程序开销仅仅增加了1%到2%,正如下面的测试时间所示),而且这么做通常没什么用。除非你还需要保存一个24位的值(或者是8位、16位的值),这样你皆可以它们放到同一个结构中。不然的话,因为对齐内存地址产生的开销会抵消这么做带来的好处。
|
||||
|
||||
在任何情况下,除非你是真的需要保存数以亿计的数字,否则这样做给内存消耗带来的好处是可以忽略不计的(但是为了处理这些位字段的额外代码量是不可忽略的!)。
|
||||
|
||||
###说明:
|
||||
|
||||
在此期间,这个问题已经被更新了,是为了说明实际上确实有需要处理数以亿计数字的情况。假设,采取某些措施来防止因为结构体对齐和填充抵消好处(比如在后24位中存储其它的内容,或者使用多个8位来存储40位),那么这么做就变得有意义了。
|
||||
如果有十亿个数,每个数都节省三个字节的空间,那么这么做就非常有用了。因为使用更小的空间存储要求更少的内存页,也就会产生更少的cache和TLB不命中和内存缺页(单个缺页会产生数以千万计的指令(译者注:直译是这样,但语义说不通!))。
|
||||
|
||||
如果有十亿个数,每个数都节省三个字节的空间,那么这么做就非常有用了。因为使用更小的空间存储要求更少的内存页,也就会产生更少的cache和TLB不命中和内存缺页(单个缺页会产生数以千万计的指令 [译者注:直译是这样,但语义说不通!])。
|
||||
|
||||
尽管上面提到的情况不足以充分利用到剩余的24位(它仅仅使用了40位部分),如果确实在剩余位中放入了有用的数据,那么使用类似下面的方法会使得这种思路就管理内存而言显得非常有用。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -43,9 +45,10 @@ struct using_gaps
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
结构体大小和对齐长度等于64位整型的大小,所以只要使用得当就不会浪费空间,比如对一个保存10亿个数的数组使用这个结构(不考虑使用指定编译器的扩展)。如果你不会用到一个8位的值,那么你可以使用一个48位和16位的值(giving a bigger overflow margin)。
|
||||
|
||||
或者以牺牲可用性为代价,把8个64位的值放入这样的结构体中(或者使用40和64的组合使得其和满足320)。当然,在这种情况下,通过代码去访问数组结构体中的元素会变得非常麻烦(尽管一种方法是实现一个operator[]在功能上还原线性数组,隐藏结构体的复杂性)。
|
||||
|
||||
更新:
|
||||
###更新:
|
||||
|
||||
我写了一个快速测试工具,只是为了获得位字段的开销(以及伴随位字段引用的重载操作)。由于长度限制将代码发布在gcc.godbolt.org上,在本人64位Win7上的测试结果如下:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -85,7 +88,7 @@ via:[stackoverflow](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/27705409/if-a-32-bit-inte
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Damon][a][Michael Kohne][b]
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@ Linux 有问必答: 如何在Linux中加入cron任务
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **提问**: 我想在我的Linux中安排一个计划任务,该任务在固定时间周期性地运行。我该如何在Linux中添加一个cron任务?
|
||||
|
||||
cron是Linux中默认的计划任务。使用cron,你可以安排一个计划(比如:命令或者shell脚本)周期性地运行或者在指定的小时、天、周、月等特定时间运行。cron在你安排不同的常规维护任务时是很有用的,比如周期性地备份、日志循环、检查文件系统、监测磁盘空间等等。
|
||||
cron是Linux中默认的计划任务。使用cron,你可以安排一个计划(比如:命令或者shell脚本)周期性地运行或者在指定的分钟、小时、天、周、月等特定时间运行。cron在你安排不同的常规维护任务时是很有用的,比如周期性地备份、日志循环、检查文件系统、监测磁盘空间等等。
|
||||
|
||||
### 从命令行中添加cron任务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ cron是Linux中默认的计划任务。使用cron,你可以安排一个计划
|
||||
|
||||
每个cron任务的格式如下。
|
||||
|
||||
<minute> <hour> <day-of-month> <month-of-year> <day-of-week> <command>
|
||||
<分钟> <小时> <日> <月> <星期> <命令>
|
||||
|
||||
前5个元素定义了任务的计划,最后一个元素是命令或者脚本的完整路径。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,13 +30,13 @@ cron是Linux中默认的计划任务。使用cron,你可以安排一个计划
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一些cron任务示例。
|
||||
|
||||
- *** * * * * /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 每分钟运行。
|
||||
- **\* * * * * /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 每分钟运行。
|
||||
- **0 * * * * /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 每小时运行。
|
||||
- **0 0 * * * /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 每12小时运行。
|
||||
- **0 0 * * * /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 每天零点运行。
|
||||
- **0 9,18 * * * /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 在每天的9AM和6PM运行。
|
||||
- **0 9-18 * * * /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 在9AM到6PM的每个小时运行。
|
||||
- **0 9-18 * * 1-5 /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 周一到周五的9AM到6PM每小时运行。
|
||||
- ***/10 * * * * /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 每10分钟运行。
|
||||
- **\*/10 * * * * /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 每10分钟运行。
|
||||
|
||||
一旦完成上面的设置步骤后,按下Ctrl+X来保存并退出编辑器。此时,新增的计划任务应该已经激活了。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -61,6 +61,6 @@ cron是Linux中默认的计划任务。使用cron,你可以安排一个计划
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/add-cron-job-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ curl是一个强大的命令行工具,它可以通过网络将信息传递给
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在一些个例中,或许你想要在一个HTTP请求中覆盖掉默认的HTTP头或者添加一个新的自定义头部字段。例如,你或许想要重写“HOST”字段来测试一个[负载均衡][1],或者通过重写"User-Agent"字符串来欺骗特定浏览器以解决其访问限制的问题。
|
||||
在一些个例中,或许你想要在一个HTTP请求中覆盖掉默认的HTTP头或者添加一个新的自定义头部字段。例如,你或许想要重写“HOST”字段来测试一个[负载均衡][1],或者通过重写"User-Agent"字符串来假冒特定浏览器以解决一些访问限制的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
为了解决所有这些问题,curl提供了一个简单的方法来完全控制传出HTTP请求的HTTP头。你需要的这个参数是“-H” 或者 “--header”。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ wget是另外一个类似于curl,可以用来获取URL的命令行工具。并
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/custom-http-header-curl.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Ping](http://mr-ping.com)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,18 +1,18 @@
|
||||
有请Vivaldi——全新网页浏览器,为高手级用户而生
|
||||
认识Vivaldi——一款为高手级用户定制的全新网页浏览器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**这一周一个为了满足高手级用户的需要而制造出来的全新网页浏览器已然来临——而且它已经可以在Linux上使用了。**
|
||||
**这周一个为了满足高手级用户的需要而定制的全新网页浏览器已然来临——而且它已经可以在Linux上使用了。**
|
||||
|
||||
Vivaldi就是这个新浏览器的名字,而且它还面向64位Linux,Windows和Mac机的技术预览版(请读:无责任测试)发行。它是在 — 震惊 — 尝试且已测试过的Chromium开源框架,Blink和Google的开源V8 JavaScript引擎(以及其他项目)的基础上制造的。
|
||||
Vivaldi就是这个新浏览器的名字,而且它还面向64位Linux、Windows 和 Mac 机发布了技术预览版(注解:无责任测试版)。它是建立在已测试过的Chromium开源框架,Blink和Google的开源V8 JavaScript引擎(以及其他项目)的基础上。
|
||||
|
||||
这个世界真的想要再有一个浏览器吗?Vivaldi——出自Opera软件前首席执行官Jon S.von Tetzchner的想法——不怎么关注所要,更关注所需。
|
||||
这个世界真的还需要一个浏览器吗?Opera软件前首席执行官Jon S.von Tetzchner的构想——Vivaldi不怎么关注所要,更关注所需。
|
||||
|
||||
Vivaldi被制造成带有着偏向于键盘操作的tab键瘾君子所需的那种功能。并没有为那些认为Firefox复杂或是对Chrome的唯一批评是它改动了书签按钮的用户而进行修改。
|
||||
Vivaldi被制造成带有着偏向于键盘操作的tab键痴迷者所需的那种功能。并没有为那些认为Firefox复杂或是批评Chrome改动了书签按钮的用户而进行修改。
|
||||
|
||||
这也不是什么俗气的营销噱头。不去看它所戴的‘技术预览版’标签,Vivaldi已经有了明显偏向于高手级用户们的功能。
|
||||
这也并不是什么俗气的营销噱头。尽管它带有‘技术预览版’标签,Vivaldi已经有了明显偏向于高手级用户们的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
相当多的人觉得自己被其他软件公司所生产的简化的,配对后发行的产品遗弃了、糊弄了。Vivaldi——即使在这个过渡期的早期——看起来适逢其会以至于打败了其他产品。
|
||||
相当多的人觉得自己被其他软件公司所生产的简化的,配对后发行的产品遗弃了、糊弄了。Vivaldi——即使在这个过渡期的早期——看起来适逢其会,可以打败其他产品。
|
||||
|
||||
### Vivaldi功能###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,13 +20,13 @@ Vivaldi被制造成带有着偏向于键盘操作的tab键瘾君子所需的那
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**快捷命令** (Ctrl + Q)是个内置的HUD应用,他可以让你快速的滤过设置,选项和功能,用它打开一个书签或是隐藏状态栏,只需用你的键盘。无需点击。
|
||||
**快捷命令** (Ctrl + Q)是个内置的HUD应用,它可以让你快速过滤设置、选项和功能,用它打开一个书签或是隐藏状态栏,只需用你的键盘,无需鼠标点击。
|
||||
|
||||
**标签堆** 让你可以通过把多个不同标签分到一组来清理你的工作区,然后可以通过键盘命令或者可预览标签选择器在标签组之间进行切换。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
一个可折叠的**侧边栏**藏有额外功能(就像旧Opera)包括一个(目前还不能工作的)邮箱客户端,链接,书签浏览器和可以让你截屏并做注释的笔记专区
|
||||
一个可折叠的**侧边栏**藏有额外功能(就像旧Opera)包括一个(目前还不能工作的)邮箱客户端,链接,书签浏览器和可以让你截屏并做注释的笔记专区。
|
||||
|
||||
还提供了一大堆其他的功能,包括设置键盘快捷键,一个可以被设置在浏览器任何一个边(或完全隐藏)的标签栏,隐私选项和一个快速打开文件夹的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -34,9 +34,9 @@ Vivaldi被制造成带有着偏向于键盘操作的tab键瘾君子所需的那
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
把Vivaldi当作Opera post-Presto(Opera旧的拥有版权的引擎)的真正继承者并不是什么值得惊奇的事。当Opera(今天也推出了一个小更新)追求一个更轻、更好管理的一套功能时,已经剔除了它很多“高手级用户”功能。
|
||||
把Vivaldi当作Opera post-Presto(Opera拥有版权的旧引擎)的真正继承者并不是什么值得惊奇的事。当Opera(今天也推出了一个小更新)追求一个更轻、更好管理的一套功能时,已经剔除了它很多“高手级用户”功能。
|
||||
|
||||
Vivaldi想要捡起Opera曾急于脱手的负担。虽然这么做没有帮他抓到什么预期的市场份额,但是它抓住了高手级用户的眼球。他们大多数无疑已经在使用Linux了。
|
||||
Vivaldi想要捡起Opera曾急于脱手的负担。虽然这么做没有帮它抓住什么预期的市场份额,但是它吸引了高手级用户的眼球。他们大多数无疑已经在使用Linux了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 下载 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/01/vivaldi-web-browser-linux-download-power
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[H-mudcup](https://github.com/H-mudcup)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
OpenJDK 7的漏洞已经在Ubuntu 14.04 和Ubuntu 14.10中解决了
|
||||
----
|
||||
*建议用户尽快升级*
|
||||
|
||||
**Canonical发布新 OpenJDK 7 的安全公告,它已经提交到Ubuntu 14.04 LTS和Ubuntu 14.10 的仓库中。该更新修复了大量的问题和漏洞。**
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu维护者已经升级了仓库中的OpenJDK包,并且含有大量的修复。这是一个重要的更新,其涵盖了少量的库。
|
||||
|
||||
安全公告中说“OpenJDK JRE中发现了一些信息泄露、数据完整性和可用性的漏洞。攻击者可以利用这些通过网络执行拒绝服务或者泄露信息。”
|
||||
|
||||
同样,“OpenJDK JRE中发现了关于信息泄露和完整性的漏洞。攻击者可以利用这点通过网络泄露敏感信息。”
|
||||
|
||||
这里有几个漏洞被开发者确认,并且由维护人员解决。关于该问题的详细描述,你可以参考Canonical的安全通告。建议用户尽快升级系统。
|
||||
|
||||
这个漏洞只要你升级到最新的openjdk 7相关的包就可以修复。要应用该补丁,用户需要运行升级管理程序。通常上,一个标准系统更新就会安装必要的更新。所有java相关的程序需要重新启动。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linux.softpedia.com/blog/OpenJDK-7-Vulnerabilities-Closed-in-Ubuntu-14-04-and-Ubuntu-14-10-471605.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文发布时间:29 Jan 2015, 16:53 GMT
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答--如果修复Google Chrome 的 ‘Your profile could not be opened correctly’错误
|
||||
Linux有问必答——如何修复Google Chrome 的“Your profile could not be opened correctly”错误
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **提问**:当我在linux打开Google Chrome 浏览器时,我已经几次收到弹出窗口,提示我的档案文件没有被正确打开(Your profile could not be opened correctly.)。每次我打开Chrome都要弹出来,我应该如何修复这个问题?
|
||||
|
||||
当你在你的Chrome上看见"Your profile could not be opened correctly"错误信息时,那是因为你的Chrome档案数据已经损坏。这个问题经常发生在手动升级Google Chrome时候。
|
||||
当你在你的Chrome上看见"Your profile could not be opened correctly"错误信息时,从某种程度上讲,那是因为你的Chrome配置文件数据已经损坏。这个问题经常发生在手动升级Google Chrome的时候。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ Linux有问必答--如果修复Google Chrome 的 ‘Your profile could not be op
|
||||
|
||||
### 方法一 ###
|
||||
|
||||
关掉所有Chrome窗口和子窗口。
|
||||
关掉所有Chrome窗口和标签页。
|
||||
|
||||
进入~/.config/google-chrome/Default,移除或者重命名"Web Data"文件。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,9 +21,9 @@ Linux有问必答--如果修复Google Chrome 的 ‘Your profile could not be op
|
||||
|
||||
### 方法二 ###
|
||||
|
||||
关掉所有Chrome窗口和子窗口。
|
||||
关掉所有Chrome窗口和标签页。
|
||||
|
||||
进入~/.config/google-chrome/"Profile 1", 并重命名"History"文件。
|
||||
进入~/.config/google-chrome/"Profile 1",并重命名"History"文件。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd ~/.config/google-chrome/"Profile 1"
|
||||
$ mv History History.bak
|
||||
@ -32,9 +32,9 @@ Linux有问必答--如果修复Google Chrome 的 ‘Your profile could not be op
|
||||
|
||||
### 方法三 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果依然没有解决,你可以试试移除所有默认档案文件夹(~/.config/google-chrome/Default)。注意:如果这样做,你将会遗失所有之前打开的Google子窗口,导入的书签,浏览记录和登录数据等。
|
||||
如果依然没有解决,你可以试试移除所有默认配置文件夹(~/.config/google-chrome/Default)。注意:如果这样做,你将会遗失所有之前打开的Google标签、导入的书签,浏览记录和登录数据等。
|
||||
|
||||
在移除之前,先关掉所有Chrome窗口和子窗口
|
||||
在移除之前,先关掉所有Chrome窗口和标签页
|
||||
|
||||
$ rm -rf ~/.config/google-chrome/Default
|
||||
|
||||
@ -45,6 +45,6 @@ Linux有问必答--如果修复Google Chrome 的 ‘Your profile could not be op
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/your-profile-could-not-be-opened-correctly-google-chrome.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[VicYu/Vic020](http://vicyu.net)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
LinuxQuestions 问卷调查揭晓最佳开源项目
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在Linux用户社区中, 很多人每年都会期待来自 LinuxQuestions.org 细致可靠的年度问卷调查报告。如同[Susan在她的报告][1]中指出的那样, 今年的[结果][2]着重于调查网站读者心中最棒的开源项目。 这份报告目前已经完成。 在LinuxQuestions的大多数人都是“专家级”的用户, 他们经常在网站上在线回答Linux新手们的提问。
|
||||
|
||||
在Susan所作的报告的附加内容里, 你可以看到由“专家”们对开源世界的关注点分布。
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以在[这里][3]找到一份较为精美的调查问卷总结图.这里呈现了网站投票得出的最佳Linux发行版, 可以看到Mint和Slackwaer平分了半壁江山:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
而下图则是网站票选出的得出的最佳云项目。值得注意的是, LinuxQuestions的用户群体给予了ownCloud项目极高的评价。 你一定得亲自去看看调查结果的详情, 也看看 [Susan 关于各项目“赢家”][4]的总结, 还有[一堆精美的图表][5]。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/linuxquestions-survey-results-surface-top-open-source-projects
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sam Dean][a]
|
||||
译者:[jerryling315](https://github.com/jerryling315)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ostatic.com/member/samdean
|
||||
[1]:http://ostatic.com/blog/lq-members-choice-award-winners-announced
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/linux-news-59/2014-linuxquestions-org-members-choice-award-winners-4175532948/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/2014mca.php
|
||||
[4]:http://ostatic.com/blog/lq-members-choice-award-winners-announced
|
||||
[5]:http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/2014mca.php
|
||||
32
published/201502/20150209 CrunchBang Linux Is Dead.md
Normal file
32
published/201502/20150209 CrunchBang Linux Is Dead.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
CrunchBang Linux 已死!!!
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
是的,你没看错。最小的Linux发行版**CrunchBang Linux 已经消失了**。
|
||||
|
||||
CrunchBang Linux,被大家所熟知的缩写标志“#!”,其基于Debian和[Openbox][1]窗口管理器。这个黑色主题的 Linux 发行版是许多资深 Linux用户的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
### CrunchBang 因为 “不再有继续下去的价值” 而消失了 ###
|
||||
|
||||
其[公告][2]称,CrunchBang将不在继续开发,项目的领头人Philip Newborough说他在开始这个项目的时候,Linux 世界和现在不同。他指出那时在这种发行版还没有‘竞争’,但是随着Linux发行版的进步,如Lubuntu,Crunchbang这样的发行版就不具备原来的价值了。
|
||||
|
||||
> 对于任何十年前使用Linux的人而言,我想他们都会看到事物在不断发展。虽然一些事情一直保持不变,还有一些的变化超出了认知。这称之为进步。对于大部分事物而言,进步是一件好事。也就是说当进步发生时,一些事物落后了。对于我而言,CrunchBang就是我需要抛弃的东西。我抛弃它的原因是我真的认为它不再具有任何价值了,虽然我还可以因为一些多愁善感的原因把它留下来,但是我不认为那些使用原生Debian用户还有兴趣了。
|
||||
|
||||
### CrunchBang消失之后会怎么样? ###
|
||||
|
||||
就像[Pear OS][3]那样,CrunchBang论坛仍将在线。现在仍可以下载但是不久的将来就会停止。Philip对他即将面对的新的项目和工作感到很激动。我希望他今后工作顺利。很难过见到一个像CrunchBang这样好的Linux发行版的消失。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/crunchbang-linux-dead/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Openbox
|
||||
[2]:http://crunchbang.org/forums/viewtopic.php?id=38916
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/pear-os-history/
|
||||
24
published/201502/20150209 Non-Linux FOSS--Homebrew.md
Normal file
24
published/201502/20150209 Non-Linux FOSS--Homebrew.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
||||
非Linux的自由开源软件:Homebrew
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
我日常工作中使用的是OS X。我能容忍它很大程序上是因为它的终端。如果我不能在黑色背景绿色文字的终端下工作,我想我会疯了。不幸的是,OS X 没有我需要的全部命令行工具。Homebrew的到来拯救了我。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Homebrew扮演了OS X中所缺乏的包管理器的角色。命令的使用很像apt-get,它能够安装无数的应用。一个最好的例子是wget。我很惊讶OS X中没有包含wget,但是homebrew中有,很简单就安装上了。
|
||||
|
||||
最棒的是homebrew在/usr/local文件夹下安装软件。你不必担心homebrew会破坏你的系统,因为它不会访问/usr/local之外的其他文件。OSX系统更新不会覆盖你的程序,并且/usr/local/bin已经在PATH中,使用homebrew安装的程序可以直接工作。
|
||||
|
||||
homebrew使用ruby管理它的包和功能,但是使用它不需要任何编程知识。并且安装过程只需要在命令行中复制粘贴就好了。如果你使用的是OS X,但是你希望像在Linux中那样方便地安装,就试一试homrbrew吧:[http://brew.sh][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/non-linux-foss-homebrew
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Shawn Powers][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxjournal.com/users/shawn-powers
|
||||
[1]:http://brew.sh/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
||||
如何避免在ELemetary OS Freya中出现两个Google Chrome 图标
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章会教你**如何避免在ELemetary OS Freya中出现两个Google Chrome 图标**。
|
||||
|
||||
Chrome才是我在所有系统中使用的主浏览器。[Modori][2] 是默认放在dock中的浏览器,所以你每次使用Chrome时都需要在Slingshot中搜索Google Chrome,而为了节省时间,我通常会将它“保持在dock”中。
|
||||
|
||||
这里的问题是当你点击dock中的Chrome图标时,它会创建另外一个Google Chrome的实例。这就在dock中留下两个Chrome图标,这或许你可以不在意,但是很显然处女座不能忍!如果你有相同的感受,让我们看下如何移除这第二个Google Chrome图标。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Elementary OS Freya的dock中删除第二个Google Chrome 图标 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第一步: ####
|
||||
|
||||
从dock中删除Google Chrome。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第二步: ####
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端并使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
cp /usr/share/applications/google-chrome.desktop ~/.local/share/applications
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第三步: ####
|
||||
|
||||
接下来我们要编辑google-chrome.destop文件。使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
scratch-text-editor ~/.local/share/applications/google-chrome.desktop
|
||||
|
||||
这会用Scratch打开google-chrome.destop文件。在[Desktop Entry]段落下,加入下面的行:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
StartupWMClass=Google-chrome-stable
|
||||
|
||||
看上去像这样:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 第四步: ####
|
||||
|
||||
进入Slingshot并且再次打开Google Chrome。再次选择“keep in dock”。关闭并重新打开它来验证它是否在dock中打开了另外一个新的Chrome图标。这里不需要重启系统。
|
||||
|
||||
我希望这篇提示能够帮助你删除Elementary OS Freya中多出的Chrome图标。有任何问题或建议让我在评论区中知道。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/rid-google-chrome-icons-dock-elementary-os-freya/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://elementary.io/
|
||||
[2]:http://midori-browser.org/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
如何使 GDebi 默认代替 Ubuntu 软件中心
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你使用 Ubuntu 或基于 Ubuntu 的 Linux 发行版本,比如Elementary OS Freya,也许你使用 Ubuntu 软件中心来安装 `.deb` 可执行文件。对于查找和安装应用,Ubuntu 软件中心是一个很好的应用,但它会消耗很多资源且运行速度缓慢。这就是为什么我更偏爱使用 [一个 Ubuntu 软件中心的轻量级替代品——App Grid][1] 的原因。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,假如你只是尝试安装一个 `.deb` 文件,我不会向你推荐 Ubuntu 软件中心或 App Grid ,我的建议为 GDebi,一个安装 Debian 可执行文件的专用程序。它极其轻量,且专注于安装 `.deb` 文件。GDebi 最有用的功能是它也可以为你展示出将要安装的程序的依赖。
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中,我们将看一看 **如何安装 GDebi 以及使用它代替 Ubuntu 软件中心作为默认的安装器**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 和其他 Linux 发行版本中安装 GDebi ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端并使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gdebi
|
||||
|
||||
### 使得 GDebi 成为默认的 `.deb`包安装器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
一旦你安装了 GDebi,就是时候来看看如何使它成为安装 `.deb` 文件的默认应用了。请读者注意在这篇教程中我使用的是 Elementary OS Freya ,但下面的步骤对于所有基于 Ubuntu 的发行版本都是适用的。可能截屏显示会有点不同。
|
||||
|
||||
首先下载一个 `.deb`文件。例如你已经下载了一个 Google Chrome 的 `.deb`包。进入下载目录并右击该 `.deb`文件。在这里,接着选择 **属性**选项。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在属性中,你应该可以看到 **打开方式** 选项。点击它并选择为 GDebi。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这样下次你双击一个 `.deb` 文件,便会自动打开 GDebi 来安装这个`.deb` 文件。使用这样轻量级的应用的确是一个[加速 Ubuntu][2] 或其他 Linux 系统的好方法。
|
||||
|
||||
你怎么看呢?对于安装应用,你仍然偏爱 Ubuntu 软件中心还是 GDebi 呢?如果你是一个守旧派,也许你更喜欢 [新立得软件包管理器(Synaptic Package Manager)][3]?那么,哪一个是你的最爱?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/gdebi-default-ubuntu-software-center/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/app-grid-lighter-alternative-ubuntu-software-center/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/speed-up-ubuntu-1310/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.nongnu.org/synaptic/
|
||||
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
||||
LibreOffice 4.4 Released as the Most Beautiful LibreOffice Ever
|
||||
----
|
||||
*The developer has made a lot of UI improvements*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The Document Foundation has just announced that a new major update has been released for LibreOffice and it brings important UI improvements, enough for them to call this the most beautiful version ever.
|
||||
|
||||
The Document Foundation doesn't usually make the UI the main focus of an update, but now the developers are saying that this is the most beautiful release made so far and that says a lot. Fortunately, this version is not just about interface fixes and there are plenty of other major improvements that should really provide a very good reason to get LibreOffice 4.4.
|
||||
|
||||
LibreOffice has been gaining quite a lot of fans and users, and the past couple of years have been very successful. The office suite is implemented by default in most of the important Linux distributions out there and it was adopted by numerous administrations and companies across the world. LibreOffice is proving to be a difficult adversary for Microsoft's Office and each new version makes it even better.
|
||||
LibreOffice 4.4 brings a lot of new features
|
||||
|
||||
If we move aside all the improvements made to the interface, we're still left with a ton of fixes and changes. The Document Foundation takes its job very seriously and all upgrades really improve the users' experience tremendously.
|
||||
|
||||
"LibreOffice 4.4 has got a lot of UX and design love, and in my opinion is the most beautiful ever. We have completed the dialog conversion, redesigned menu bars, context menus, toolbars, status bars and rulers to make them much more useful. The Sifr monochrome icon theme is extended and now the default on OS X. We also developed a new Color Selector, improved the Sidebar to integrate more smoothly with menus, and reworked many user interface details to follow today’s UX trends," [says Jan "Kendy" Holesovsky](1), a member of the Membership Committee and the leader of the design team.
|
||||
|
||||
Some of the other improvements include much better support for OOXML file formats, the source code has been "groomed" and cleaned after a Coverity Scan analysis, digital signatures for exported PDF files, improved import filters for Microsoft Visio, Microsoft Publisher and AbiWord files, and Microsoft Works spreadsheets, and much more.
|
||||
|
||||
For now, the PPA doesn't have the latest version, but that should change soon. For the time being, you can download the [LibreOffice 4.4](2) source packages from Softpedia, if you want to compile them yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://news.softpedia.com/news/LibreOffice-4-4-Releases-As-the-Most-Beautiful-LibreOffice-Ever-471575.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文发布时间:29 Jan 2015, 14:16 GMT
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://blog.documentfoundation.org/2015/01/29/libreoffice-4-4-the-most-beautiful-libreoffice-ever/
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.softpedia.com/get/Office/Office-Suites/LibreOffice-60713.shtml
|
||||
@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
||||
OpenJDK 7 Vulnerabilities Closed in Ubuntu 14.04 and Ubuntu 14.10
|
||||
----
|
||||
*Users have been advised to upgrade as soon as possible*
|
||||
|
||||
##Canonical published details about a new OpenJDK 7 version has been pushed to the Ubuntu 14.04 LTS and Ubuntu 14.10 repositories. This update fixes a number of problems and various vulnerabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
The Ubuntu maintainers have upgraded the OpenJDK packages in the repositories and numerous fixes have been implemented. This is an important update and it covers a few libraries.
|
||||
|
||||
"Several vulnerabilities were discovered in the OpenJDK JRE related to information disclosure, data integrity and availability. An attacker could
|
||||
exploit these to cause a denial of service or expose sensitive data over the network,” reads the security notice.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, "a vulnerability was discovered in the OpenJDK JRE related to information disclosure and integrity. An attacker could exploit this to
|
||||
expose sensitive data over the network."
|
||||
|
||||
These are just a couple of the vulnerabilities identified and corrected by the developer and implemented by the maintainers/., and for a more detailed description of the problems, you can see Canonical's security notification. Users have been advised to upgrade their systems as soon as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
The flaws can be fixed if you upgrade your system to the latest openjdk-7-related packages specific to each distribution. To apply the patch, users will have to run the Update Manager application. In general, a standard system update will make all the necessary changes. All Java-related applications will have to be restarted.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://linux.softpedia.com/blog/OpenJDK-7-Vulnerabilities-Closed-in-Ubuntu-14-04-and-Ubuntu-14-10-471605.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文发布时间:29 Jan 2015, 16:53 GMT
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
||||
The Pirate Bay Is Now Back Online
|
||||
------
|
||||
*The website was closed for about seven weeks*
|
||||

|
||||
##After being [raided](1) by the police almost two months ago, (in)famous torrent website The Pirate Bay is now back online. Those who thought the website will never return will be either disappointed or happy given that The Pirate Bay seems to live once again.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to celebrate its coming back, The Pirate Bay admins have posted a Phoenix bird on the front page, which signifies the fact that the website can't be killed only damaged.
|
||||
|
||||
About two weeks after The Pirate Bay was raided the domain miraculously came back to life. Soon after a countdown appeared on the temporary homepage of The Pirate Bay indicating that the website is almost ready for a comeback.
|
||||
|
||||
The countdown hinted to February 1, as the possible date for The Pirate Bay's comeback, but it looks like those who manage the website manage to pull it out one day earlier.
|
||||
|
||||
Beginning today, those who have accounts on The Pirate Bay can start downloading the torrents they want. Other than the Phoenix on the front page there are no other messages that might point to the resurrection The Pirate Bay except for the fact that it's now operational.
|
||||
|
||||
Admins of the website said a few weeks ago they will find ways to manage and optimize The Pirate Bay, so that there will be minimal chances for the website to be closed once again. Let's see how it lasts this time.
|
||||
|
||||
##Another version of The Pirate Bay may be launched soon
|
||||
|
||||
In related news, one of the members of the original staff was dissatisfied with the decisions made by the majority regarding some of the changes made in the way admins interact with the website.
|
||||
|
||||
He told [Torrentfreak](2) earlier this week that he, along with a few others, will open his version of The Pirate Bay, which they claim will be the "real" one.
|
||||
|
||||
------
|
||||
via:http://news.softpedia.com/news/The-Pirate-Bay-Is-Now-Back-Online-471802.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文发布时间:31 Jan 2015, 22:49 GMT
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Cosmin Vasile][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/cosmin-vasile
|
||||
[1]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/The-Pirate-Bay-Is-Down-December-9-2014-466987.shtml
|
||||
[2]:http://torrentfreak.com/pirate-bay-back-online-150131/
|
||||
@ -1,98 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Debian Forked over systemd: Birth of Devuan GNU/Linux Distribution
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Debian GNU/Linux distribution is one of the oldest Linux distribution that is currently in working state. init used to be the default central management and configuration platform for Linux operating system before systemd emerged. Systemd from the date of its release has been very much controversial.
|
||||
|
||||
Sooner or later it has replaced init on most of the Linux distribution. Debian remained no exception and Debian 8 codename JESSIE will be having systemd by default. The Debian adaptation of systemd in replacement of init caused polarization. This led to forking of Debian and hence Devuan GNU/Linux distribution born.
|
||||
|
||||
Devuan project started with the primary goal to put back nit and remove controversial systemd. A lot of Linux Distribution are based on Debian or a derivative of Debian and one does not simply fork Debian. Debian will always attract developers.
|
||||
|
||||
### What Devuan is all About? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Devuan in Italian (pronounced Devone in English) suggests “Don’t panic and keep forking Debian”, for Init-Freedom lovers. Developers see Devuan as the beginning of a process which aims at base distribution and is able to protect the freedom of developers and community.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Debian Forked over systemd: Birth of Devuan Linux
|
||||
|
||||
Devuan project priority includes – interoperability, diversity and backward compatibility. It will derive its own installer and repos from Debian and modify where ever required. If everything works smooth by the mid of 2015 users can switch to Devuan from Debian 7 and start using devuan repos.
|
||||
|
||||
The process of switching will fairly remain as simple as upgrading a Debian installation. The project will be as minimal as possible and completely in accordance of UNIX philosophy – “Doing one thing and doing it well”. The targeted users of Devuan will be System Admins, Developers and users having experience of Debian.
|
||||
|
||||
The project started by italian developers has raised a fund of 4.5k€ (EUR) in the year 2014. They have moved distro infrastructure from GitHub to GitLab, progress on Loginkit (systemd Logind replaced), discussing Logo and other important aspects useful in long run.
|
||||
|
||||
A few of the Logos are in discussion now are shown in the picture.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Devuan Logo Proposals
|
||||
|
||||
Have a look at them here at: [http://without-systemd.org/wiki/index.php/Category:Logo][1]
|
||||
|
||||
The unrest over systemd that gave birth to Devuan is good or bad? Lets have a look.
|
||||
|
||||
### Is Devuan fork a good thing? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Well! difficult to answer that forking such a huge distro is really going to be of any good. A (group of) developer(s) who initially were working with Debian got unsatisfied with systemd and forked it.
|
||||
|
||||
Now the actual number of developers working on Debian/Systemd decreased which is going to affect the productivity of both the projects. Now the same number of developers are working on two different projects.
|
||||
|
||||
What you think would be the fate of Devuan as well as Debian project? Won’t it hinder the progress of either distro and Linux in the long run?
|
||||
|
||||
Please give your [comments][2] about Devuan project.
|
||||
|
||||
注:如果可以在发布文章的时候发布一个调查,就把下面这段发成一个调查,如果不行,就直接嵌入js代码
|
||||
|
||||
<script type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8" src="http://static.polldaddy.com/p/8629256.js"></script>
|
||||
|
||||
Do you think systemd for Debian is
|
||||
|
||||
Good
|
||||
Bad
|
||||
Don't Know
|
||||
Don't Care
|
||||
Other:
|
||||
|
||||
VoteView ResultsPolldaddy.com
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Do you really feel that Debian with systemd will have a bad fate as depicted below**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Strip SystmeD
|
||||
|
||||
Time to wait for Devuan 1.0 and lets see what it could contain.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
All the major Linux Distributions Like Fedora, RedHat, openSUSE, SUSE Enterprise, Arch, Megia have already switched to Systemd, Ubuntu and Debian are in the way to replace init with systemd. Only Gentoo and Slack till date have shown no interest in systemd but who knows someday even Gentoo and slack too started moving in the same direction.
|
||||
|
||||
The reputation of Debian as a Linux Distro is something very few have reached the mark. It is blessed by some hundreds of developers and millions of users. The actual question is what percentage of users and developers were not comfortable with systemd. If the percentage is really high then what led debian to switch to systemd. Had it moved against the wishes of its users and developers. If this is the case the chance of success of devuan is pretty fair. Well how many developers put long hours of code punching for the project.
|
||||
|
||||
Hope the fate of this project will not be something like those distros which once was started with high degree of passion and enthusiasm and later the developers got uninterested.
|
||||
|
||||
Post Script : Linus Torvalds do not mind systemd that much.
|
||||
|
||||
**If you need Devuan, then join and support it now!**
|
||||
|
||||
Development : [https://git.devuan.org][3]
|
||||
Donations : [https://devuan.org/donate.html][4]
|
||||
Discussions : [https://mailinglists.dyne.org/cgi-bin/mailman/listinfo/dng][5]
|
||||
Devuan Developers : onelove@devuan.org
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/debian-forked-over-systemd-birth-of-devuan-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://without-systemd.org/wiki/index.php/Category:Logo
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/debian-forked-over-systemd-birth-of-devuan-linux/#comments
|
||||
[3]:https://git.devuan.org/
|
||||
[4]:https://devuan.org/donate.html
|
||||
[5]:https://mailinglists.dyne.org/cgi-bin/mailman/listinfo/dng
|
||||
@ -1,45 +0,0 @@
|
||||
BQ and Canonical Officially Launch Aquaris E4.5 Ubuntu Edition, the First Ubuntu Phone
|
||||
------
|
||||
*Everything you need to know about Aquaris E4.5*
|
||||
|
||||
##BQ and Canonical have officially announced the new Aquaris E4.5 Ubuntu Edition and the fact that the phone will be available in the coming weeks through a series of flash sales.
|
||||
|
||||
Information about the imminent launch of BQ Ubuntu phone has been around for some time and now it the two companies seem to have decided to make it official. This is the first device powered by Ubuntu Touch and a lot of people will be paying very close attention to what is happening in the mobile world.
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Touch is the latest operating system from Canonical and it's a brand new experience that aims to be very different from what users can find right now on the market, and that includes systems like Jola or Firefox OS. The OS has been in the works for more than two years and it's a system designed to work on all kind of devices, across the hardware spectrum.
|
||||
|
||||
##Who is BQ and why has Canonical chosen them?
|
||||
|
||||
When Mark Shuttleworth announced the two partners for the launch of Ubuntu Touch, BQ and Meizu, most of the people watching asked the same question. Who? BQ is not a very big company, but it's a young company and it has already started to penetrate the European market with some interesting devices. In many ways, they are doing the same thing companies like Meizu or Xiaomi are trying and succeeded in China: to offer devices that are interesting and different from what everyone else is doing.
|
||||
|
||||
Many Ubuntu fans have questioned Canonical’s decision of choosing small companies and not big ones, but they are trying to do the same thing as the just-mentioned hardware makers. They want to offer an operating system radically different from what everyone else is doing. It's easy to understand why the goals of Canonical and BQ are actually one and the same.
|
||||
|
||||
##What is Ubuntu Touch?
|
||||
|
||||
The new operating system developed by Canonical embraces the fact that people are now swiping a lot more than they are tapping. Smartphones are no longer something new and everyone can understand how to swipe and get things done on a phone. Ubuntu devs have taken this to a whole new level. The operating system has no buttons, with the exception of the regular power and volume buttons. Everything is done with swiped gestures, from all sides of the screen.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, Ubuntu Touch brings a new concept to the market, that of scopes. There is no longer a home screen, just scopes defined by the user to expand the experience. For example, you can have a Music scope that aggregates all your music sources on a single screen. It's a different way of looking at your smartphone, but this is built for people who crave a new experience. Don't worry, regular apps still exist, but they are differently integrated.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
"As any kind of content can be presented via Scopes - they provide developers an easy path for their creations to be integral to the device experience. It is simple to create new Scopes via an easy to use UI toolkit with much lower development and maintenance costs than traditional apps. Canonical and BQ have worked with a host of partners to ensure that there is a wealth of interesting, relevant and dynamic content available at launch, with more content partners to follow," said Cristian Parrino, VP Mobile at Canonical.
|
||||
|
||||
##BQ’s Aquaris E4.5 Ubuntu Edition hardware specs
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, it's important to know that Aquaris E4.5 Ubuntu Edition is a dual-sim phone and it comes unlocked so that everyone can use it with their network. It boasts a MediaTek Quad-Core Cortex A7 processor running at up to 1.3 GHz, a 4.5-inch screen, 1GB RAM, rear camera with high-quality BSI sensors, Largan lens, and autofocus with dual flash(8MP), and front camera with 5MP.
|
||||
|
||||
It's also worth mentioning that several operators in Europe, including 3 Sweden, amena.com, giffgaff, and Portugal Telecom have decided to provide SIM bundles at purchase. The price is €169.90 ($191).
|
||||
|
||||
So, are you ready to buy the Aquaris E4.5 Ubuntu Edition?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/BQ-and-Canonical-Officially-Launch-Aquaris-E4-5-Ubuntu-Edition-472397.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
|
||||
CrunchBang Linux Is Dead!!!
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Yes! You read it correct. The minimalist Linux distribution **CrunchBang Linux has been discontinued**.
|
||||
|
||||
CrunchBang Linux, popularly known for its abbreviated symbol #!, is based on Debian and comes with [Openbox][1] window manager. The dark themed Linux was/is a popular Linux choice for many experience Linux users.
|
||||
|
||||
### CrunchBang discontinued for “it no longer holds any value” ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Announcing][2] that CrunchBang will no longer be developed, head of the project Philip Newborough said that when he started the project, Linux world was different place. He mentioned that there was no ‘competition’ in the same ilk at that time but with the advancement of Linux distros like Lubuntu, Crunchbang doesn’t hold the same value.
|
||||
|
||||
> For anyone who has been involved with Linux for the past ten years or so, I’m sure they’ll agree that things have moved on. Whilst some things have stayed exactly the same, others have changed beyond all recognition. It’s called progress, and for the most part, progress is a good thing. That said, when progress happens, some things get left behind, and for me, CrunchBang is something that I need to leave behind. I’m leaving it behind because I honestly believe that it no longer holds any value, and whilst I could hold on to it for sentimental reasons, I don’t believe that would be in the best interest of its users, who would benefit from using vanilla Debian.
|
||||
|
||||
### What after CrunchBang demise? ###
|
||||
|
||||
As happened in case of [Pear OS][3], CrunchBang forums will stay online. Downloads are available for now but will be removed in near future. Philip mentioned that he was excited about some of his incoming projects and his day job. I wish him luck in his future endeavors. It is sad to see the death of a nice Linux distribution like CrunchBang.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/crunchbang-linux-dead/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Openbox
|
||||
[2]:http://crunchbang.org/forums/viewtopic.php?id=38916
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/pear-os-history/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
Italian Region Emilia-Romagna Is Switching To OpenOffice
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Italy seems to be winning the race to Open Source adoption, it seems. We have learned about how various Italian cities like [Udine][1], [Turin][2], [Todi and Turni][3] opted for [open source alternatives of Microsoft office][4] in the past. Now the news comes that [Emilia-Romagna][5] region in northern Italy is about to complete its switch to [Apache OpenOffice][6] next month.
|
||||
|
||||
### Switching to OpenOffice ###
|
||||
|
||||
The migration to OpenOffice will be complete by next month and will cover 4200 workstations, across 10 departments and 5 agencies. In addition, Open Document Format (ODF) will be the default document format. The initiative to switch to OpenOffice was approved in late 2013 and was originally planned to be completed by end of 2014. The move to OpenOffice from proprietary office product is believed to [save around 2 million euro][8] in licensing fee.
|
||||
|
||||
To ease this migration and improve interoperability, several custom tools and plugins are also being developed by the team in charge of the migration.
|
||||
|
||||
Head of the project, Giovanni Grazia is enthusiastic about the migration but he is prepared for the brickbats as well.
|
||||
|
||||
> “Changing office suite is hard work, and we use the occasion to advocate for free and open source software. Some of the region’s civil servants are keen to switch, and some are very annoyed, as they have been using the proprietary alternative for 20 years. To deal with any issues during the transition, a team of five support staffers is backed up by three IT specialists. Department by department, one at a time, we’re completing the switch. Step by step, change is coming.”
|
||||
|
||||
#### Best wishes ####
|
||||
|
||||
I wish good luck to Grazia and hope that other administrative regions in Italy will follow the suit. I also hope that neighboring countries like [France will also speed up the open source adoption process][8].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/emiliaromagna-completes-switch-openoffice/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/udine-open-source/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/italian-city-turin-open-source/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/italian-cities-switch-libreoffice/
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/best-free-open-source-alternatives-microsoft-office/
|
||||
[5]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emilia-Romagna
|
||||
[6]:https://www.openoffice.org/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.slwoods.co.uk/?p=2886
|
||||
[8]:http://itsfoss.com/french-city-toulouse-saved-1-million-euro-libreoffice/
|
||||
@ -1,154 +0,0 @@
|
||||
11 Useful Utilities To Supercharge Your Ubuntu Experience
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Whether you’re a relative novice or a seasoned pro, we all want to get the most from our operating system. Ubuntu, like most modern OSes, has more to offer than what is presented at first blush.**
|
||||
|
||||
From tweaking and refining the look, behaviour and performance of the Unity desktop to performing system maintenance, there are a huge array of useful utilities and apps that can help **tune Ubuntu to meet your needs in no time**.
|
||||
|
||||
Caveat time: Ubuntu has always shipped with ‘sane defaults’ — options that just work — out of the box. These defaults are well suited for the majority of people. They’re tested, accepted and recommended.
|
||||
|
||||
But one size doesn’t fit all. For the tinkerers and experimenters among us the default experience is a starting point from which to tailor.
|
||||
|
||||
So, without any more waffle, here is a set of 11 nifty utilities to help you supercharge your Ubuntu experience.
|
||||
|
||||
### Unity Tweak Tool ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
I’ll kick off this list with the big one: **Unity Tweak** Tool. The kitchen sink of customisation, Unity Tweak Tool offers a comprehensive set of system tweaks tuned for Ubuntu and the Unity desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s stuffed full of switches, toggles and control, letting you configure everything from the way Unity looks to the way it behaves. Use it to **quickly and easily change the GTK theme and icon set**, set up hot corners, adjust launcher size, add or remove workspaces, and — notably — enable Unity’s elusive ‘minimise on click’ feature.
|
||||
|
||||
Free and readily available from the Software Center, Unity Tweak Tool is one well worth keeping in your back pocket.
|
||||
|
||||
### Unity Privacy Indicator ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Privacy. A big, big issue and rightly so. But the topic is often shaded rather than binary; you may be happy to let some data or habits, say apps you frequently open, be logged locally, but not be ok with the searches you make in the Dash being ferried to a third-party server (however anonymous that data may be).
|
||||
|
||||
[Privacy Indicator][1] is a useful tool to help you stay abreast of what files, folders and services are being accessed, logged and recce’d on the Ubuntu desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
With a quick click on the ‘eye’ icon added to the desktop panel you can:
|
||||
|
||||
- Toggle Online Search Results, Zeitgeist, HUD Logging & GeoIP
|
||||
- Quick access to clean Zeitgeist, F2, Recent Files, etc.
|
||||
- Options to show/hide desktop icons and name in the panel
|
||||
|
||||
The latter two options may seem a little misplaced in this app but have less obvious privacy implications for those who take screenshots or screen share.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Indicator Privacy (.deb)][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### Unity Folders ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Android, iOS, OS X, Chrome OS, and GNOME Shell have app folders, and so can Unity with a nifty third-party app. **
|
||||
|
||||
“Unity Folders” allows you to organise apps on the Unity Launcher into handy folders — think ‘games’, ‘office’, ‘social‘, etc. You get quick access to your favourite apps without needing to open the Dash, which may suit your workflow.
|
||||
|
||||
Each ‘folder’ is, actually, an application that opens up and positions itself near the origin point. But the overall effect is one that looks like an OS X style stack or an Android folder popover.
|
||||
|
||||
Folder icons can be customised or auto-generated based on the applications tucked up inside. Existing folders can be edited, rearranged, rename and re-other stuff, too.
|
||||
|
||||
- Create as many folders as you like
|
||||
- Choose custom or auto-generated folder icon
|
||||
- 3 folder layouts to choose from
|
||||
- Set custom icons for apps added to folders
|
||||
- Edit existing folders
|
||||
|
||||
- Unity Folders Website
|
||||
|
||||
### Caffeine ###
|
||||
|
||||
A staple for many of us, and not just in our drinks, Caffeine offers a fast, silent way to stop your screensaver or lock-screen kicking in. The degree of usefulness will depend on your circumstances (read: quirks of your system), and though it’s not quite as user friendly as it once was, it’s still worth [checking out][3].
|
||||
|
||||
### System Monitor Indicator ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you’re a stat hound who likes to keep tabs on apps, processes and hardware status, Linux makes it easy. From Conky Configs to Terminal Commands — there’s no shortage of ways to monitor your CPU usage, network traffic or GPU temperature.
|
||||
|
||||
But by far my favourite is System **Monitor Indicator** – also known as indicator-multiload — available from the Ubuntu Software Center. It has a host of configuration options, too.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Click to Install ‘System Load Indicator’ on Ubuntu][4]
|
||||
|
||||
### Power Saving Tools for Linux Laptops ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**TLP**
|
||||
|
||||
Linux distributions don’t have the best reputation when it comes to power efficiency on portable devices.
|
||||
|
||||
If your own Linux laptop can barely get you from the sofa to the kitchen before needing a recharge, there are some tools you can try.
|
||||
|
||||
TLP is one of the most popular automated background tool promising to prolong battery life of laptops running Linux. It does this by adjusting the settings and behaviour of system processes and hardware, such as enabling Wi-Fi power saving mode, runtime power management of PCI bus devices, and processor frequency scaling.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s available to [install on Ubuntu 14.04 LTS and later using the dedicated TLP PPA][5] and comes with a ‘catch-all’ config to get you started. The more advanced users among you can dive in and manually adjust the settings to suit your own hardware, something that a [thorough guide on the TLP wiki][6] makes easy.
|
||||
|
||||
**Laptop Mode Tools**
|
||||
|
||||
If TLP sounds a little too complex — and there’s no shame if it does — there’s a simpler alternative: **Laptop Mode Tools**. This package is available to install from the Ubuntu Software Center and keeps the tweaks made to a set of sane defaults (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, etc.).
|
||||
|
||||
Laptop Mode Tools cannot be installed at the same time as TLP.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Laptop Mode Tools in Ubuntu Software Center][7]
|
||||
|
||||
### Intel Graphics Installer ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The Intel Graphics Installer tool is a must-have for those running Intel graphics hardware who want the best performance they can get. It makes finding and installing the latest Intel GPU drivers a painless, fuss-free affair — no PPAs or Terminal kung foo needed.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Intel Graphics Installer for Linux 0.7][8]
|
||||
|
||||
### Hardware Stats ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
If you plan on upgrading your PC or replacing a worn-out part you’ll need to get some specific hardware details, such as RAM type, CPU socket set or what PCI slots are available.
|
||||
|
||||
**I-Nex** makes unearthing this, and host of other detailed system stats, easy. Use it to find your motherboard model number, RAM stepping, S.M.A.R.T. status and…well, pretty much anything else you can think of!
|
||||
|
||||
- [Learn More About I-Nex on Launchpad][9]
|
||||
|
||||
### Disk Space Visualizer ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
In this age of 1TB hard drives we might not need to be as prudent with disk space as we once were. But for those of using a smallish SSD, running multiple partitions or working in a virtual machine with a fixed-size virtual disk, there’ll be times when freeing up a bit of extra space is required.
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME Disks, installed in Ubuntu by default, makes finding the biggest space-gobbling culprits easy. Ideal for locating hidden logs, caches, and media files.
|
||||
|
||||
### BleachBit (Cruft Cleaner) ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Windows users will be familiar with applications like CCleaner, which scan for and clean out junk files, empty folders, bloated caches, and obsolete packages. For a a similarly quick and effortless click n’ clean solution on Ubuntu try **BleachBit**.
|
||||
|
||||
It is a powerful tool, so do pay attention to what you’re cleaning. Don’t aimlessly check every box; not everything that it can clean needs to be. Play it smart; when in doubt, leave it out.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Install BleachBit from Ubuntu Software Center][10]
|
||||
|
||||
Got a favourite system utility of your own? Let others know about it in the comments.
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/11/useful-tools-for-ubuntu-do-you-use-them
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.florian-diesch.de/software/indicator-privacy/index.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.florian-diesch.de/software/indicator-privacy/dist/indicator-privacy_0.04-1_all.deb
|
||||
[3]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/05/stop-ubuntu-sleeping-caffeine
|
||||
[4]:apt://indicator-mulitload
|
||||
[5]:https://launchpad.net/~linrunner/+archive/ubuntu/tlp/+packages
|
||||
[6]:http://linrunner.de/en/tlp/docs/tlp-configuration.html
|
||||
[7]:https://apps.ubuntu.com/cat/applications/laptop-mode-tools/
|
||||
[8]:https://01.org/linuxgraphics/downloads/2014/intelr-graphics-installer-linux-1.0.7
|
||||
[9]:https://launchpad.net/i-nex
|
||||
[10]:https://apps.ubuntu.com/cat/applications/bleachbit/
|
||||
@ -1,76 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Cutegram: A Better Telegram Client For GNU/Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
No need for a introduction to **Telegram**, right? Telegram is a popular free Instant messenger application that can be used to chat with your friends all over the world. Unlike Whatsapp, Telegram is free forever, no ads, no subscription fees. And, the Telegram client is open source too. Telegram is available for many different platforms, including Linux, Android, iOS, Windows Phone, Windows, and Mac OS X. The messages which are sending using telegram are highly encrypted and self-destructive. It is very secure, and there is no limit on the size of your media and chats.
|
||||
|
||||
You can install and use Telegram desktop on your Debian/Ubuntu systems as mentioned in [our previous tutorial][1]. However, a new telegram client called **Cutegram** is available now to make your chat experience more fun and easy.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is Cutegram? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cutegram is a free and opensource telegram clients for GNU/Linux focusing on user friendly, compatibility with Linux desktop environments and easy to use. Cutegram using Qt5, QML, libqtelegram, libappindication, AsemanQtTools technologies and Faenza icons and Twitter emojies graphic sets. It’s free and released under GPLv3 license.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Cutegram ###
|
||||
|
||||
Head over to the Cutegram homepage and download the latest version of your distribution’s choice. As I use Ubuntu 64 bit, I downloaded the .deb file.
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://aseman.co/downloads/cutegram/cutegram_1.0.2-1-amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
Now, Install Cutegram as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gdebi
|
||||
sudo gdebi cutegram_1.0.2-1-amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
For other distributions, run the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
**64bit:**
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://aseman.co/downloads/cutegram/cutegram-1.0.2-linux-x64-installer.run
|
||||
|
||||
**32 bit:**
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://aseman.co/downloads/cutegram/cutegram-1.0.2-linux-installer.run
|
||||
|
||||
Set executable permission:
|
||||
|
||||
chmod + cutegram-1.0.2-linux*.run
|
||||
|
||||
And, install it as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ./cutegram-1.0.2-linux*.run
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage ###
|
||||
|
||||
Launch Cutegram either from Menu or Unity dash. From the login screen, select your country, and enter your mobile number, finally click **Login**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
A code will be sent to your mobile number. Enter the code and click **Sign in**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
There you go.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Start Chatting!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
And, you can set a profile picture, start new chat/group chat, or secret chat from using the buttons on the left pane.
|
||||
|
||||
Stay happy! Cheers!!
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, check the [Cutegram website][2].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/cutegram-better-telegram-client-gnulinux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/install-telegram-desktop-via-ppa/
|
||||
[2]:http://aseman.co/en/products/cutegram/
|
||||
@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Non-Linux FOSS: Homebrew
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
I use OS X quite often during my day job. I'm able to tolerate it largely due to the terminal. If I couldn't do my work with green text on a black background, I think I'd go crazy (or crazier). Unfortunately, OS X doesn't come with all the command-line tools I need. That's where Homebrew comes in to save the day.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Homebrew acts like the package management system OS X is lacking. Using commands very similar to apt-get, it allows the installation of hundreds of applications. A perfect example is the wget program. I was surprised to find that OS X doesn't include wget, but with Homebrew, it's a simple one-liner away.
|
||||
|
||||
The best part is that Homebrew installs everything in the /usr/local file space. There's no reason to worry about Homebrew corrupting your system, because it doesn't touch anything outside of /usr/local. OS X system updates won't overwrite your programs, and because /usr/local/bin is already in the PATH, installed Homebrew apps just work!
|
||||
|
||||
Homebrew uses Ruby to manage its packages and functions, but it doesn't require any programming knowledge to use. And the installation procedure is literally a copy/paste on the command line. If you use OS X, but you wish you could install packages as easily as in Linux, give Homebrew a try: [http://brew.sh][1].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/non-linux-foss-homebrew
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Shawn Powers][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxjournal.com/users/shawn-powers
|
||||
[1]:http://brew.sh/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
Install Google’s Material Design Inspired GTK And Icon Theme Paper in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Paper][1] is a new upcoming GTK and icon theme inspired by Google’s [Material design][2] guidelines. It is developed by Sam Hewitt, the man behind [Moka Project][3]. Moka has always been in the list of [best themes for Ubuntu][4] and looking at Paper, I can say that once it is developed completely, it will surely be listed as one of the [best GTK themes][5].
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you heard it right. The theme is still under development. Therefore I suggest that if you want to install Paper theme in Ubuntu or any other Linux distributions, do it only for experimentation purpose. You may see some broken icons here and there but the over all experience is nice.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Paper theme in Ubuntu based distributions via PPA ###
|
||||
|
||||
Sam has a dedicated PPA for Ubuntu based distributions. I recommend that you use this PPA instead of downloading the theme because you’ll be getting the updates on the themes regularly. This PPA is available for Ubuntu 15.04, Ubuntu 14.10, Ubuntu 14.04, Elementary OS Freya, Elementary OS Luna, Linux Mint 17, Linux Mint 16 and other Linux distributions based on Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
Open a terminal and use the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:snwh/pulp
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install paper-gtk-theme paper-icon-theme
|
||||
|
||||
### Download Paper GTK and icon theme ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you do not want to use the PPA, you can download the themes and icons manually. As I said previously, you won’t get the updates automatically this way.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Paper icon themes][6]
|
||||
- [Download Paper GTK themes][7]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using Paper themes and icons ####
|
||||
|
||||
I hope that you know how to change or install themes in your respective Linux distributions. If you are not unaware of it, below are few tutorials that could help you to install new themes:
|
||||
|
||||
- [How to change themes in Ubuntu Unity][8]
|
||||
- [How to change themes in GNOME Shell][9]
|
||||
- [How to change themes in Linux Mint][10]
|
||||
- [How to change theme in Elementary OS Freya][11]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Here is what Paper theme looks like ####
|
||||
|
||||
Since I am using [Elementary OS Freya][12] these days, here are some of the screenshots of how Paper theme and icons look like in Elementary OS Freya. I have used a wallpaper with Material design look so that it blends well with the icon and themes.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
How do you find this Material design inspired theme? If you did use it, do share the screenshot of your desktop with rest of us here.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/install-paper-theme-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://snwh.org/paper/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.google.fr/design/spec/material-design/introduction.html
|
||||
[3]:http://mokaproject.com/moka-icon-theme/
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/gnome-shell-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
[6]:https://github.com/snwh/paper-icon-theme
|
||||
[7]:https://github.com/snwh/paper-gtk-theme
|
||||
[8]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-install-themes-in-ubuntu-13-10/
|
||||
[9]:http://itsfoss.com/install-switch-themes-gnome-shell/
|
||||
[10]:http://itsfoss.com/install-icon-linux-mint/
|
||||
[11]:http://itsfoss.com/install-themes-icons-elementary-os-freya/
|
||||
[12]:http://itsfoss.com/tag/elementary-os-freya/
|
||||
114
sources/share/20150227 Chess in a Few Bytes.md
Normal file
114
sources/share/20150227 Chess in a Few Bytes.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,114 @@
|
||||
Chess in a Few Bytes
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
I am showing my age by mentioning that my introduction to computing was a ZX81, a home computer produced by a UK developer (Sinclair Research) which had a whopping 1KB of RAM. The 1KB is not a typographical error, the home computer really shipped with a mere 1KB of onboard memory. But this memory limitation did not prevent enthusiasts producing a huge variety of software. In fact the machine sparked a generation of programming wizards who were forced to get to grips with its workings. The machine was upgradable with a 16KB RAM pack which offered so many more coding possibilities. But the unexpanded 1KB machine still inspired programmers to release remarkable software.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
My favourite ZX81 games were Flight Simulation, 3D Monster Maze, Galaxians, and above all 1K ZX Chess. Only the latter was written for the unexpanded ZX81. In fact, David Horne's 1K ZX Chess was coded in a mere 672 bytes of RAM. However, the game managed to implement most chess rules, and offer a computer opponent. While some important rules were omitted (castling, pawn promotion, and en passant capture), it was still amazing to be able to play against artificial intelligence. The game took up a fair chunk of my misspent youth.
|
||||
|
||||
1K ZX Chess remained the smallest implementation of chess on any computer for 33 years until the record was broken by BootChess this year, and subsequently by Toledo AtomChess. These three games do not implement all of the chess rules, so for completeness I have included my favourite small implementation of chess that implements a complete set of chess rules.
|
||||
|
||||
Linux has a good range of extremely strong chess engines such as Stockfish, Critter, Togo II, Crafty, GNU Chess, and Komodo. The chess engines featured in this article offer no match to a good chess engine, but they show how much can be achieved with a minuscule codebase.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You may have seen a considerable amount of press coverage about BootChess, a chess program written in 487 bytes of code, smashing the record of the then smallest chess program, 1K ZX Chess. Óscar Toledo Gutiérrez took up the mantle and decided to code an even more compact chess game. Toledo Atomchess is a mere 481 bytes of x86 assembly code which fits in a boot sector. The engine plays a reasonable game of chess given the limitations of its incredibly small codebase.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Basic chess movements
|
||||
- ASCII text representation of chess board
|
||||
- Moves are entered in algebraic form
|
||||
- Search depth of 3-ply
|
||||
|
||||
Obviously, to fit the chess of game into 481 bytes, the author had to make some sacrifices. These limitations include:
|
||||
|
||||
- No promotion of pawns
|
||||
- No castling
|
||||
- No en passant
|
||||
- No move validation
|
||||
|
||||
The author has also written chess programs in C, JavaScript and Java; each are very small implementations of chess.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [nanochess.org/chess6.html][1]
|
||||
- Developer: Óscar Toledo Gutiérrez
|
||||
- License: Free for non-commercial use
|
||||
- Version Number: -
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
BootChess is an extremely small computer implementation of chess. The game is crammed into a mere 487 bytes and runs on Windows, Mac OS X and Linux operating systems. The board and pieces of BootChess are represented by text alone, with P representing pawns, Q used for the queens and full stops entered for empty squares.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Graphic text representation of chess board and use input
|
||||
- Bootsector sized (512 bytes) with a playable chess game
|
||||
- x86 bios hardware only bootstrap (no software dependencies)
|
||||
- All main legal moves including double square pawn start
|
||||
- Pawn promotion to queen (contrary to 1k ZX Chess)
|
||||
- CPU artificial intelligence called taxiMax > minMax half-ply
|
||||
- Hard-coded Spanish white pieces opening
|
||||
|
||||
Again, there are some important limitations. Omissions include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Under-promotion
|
||||
- En passant pawn capture
|
||||
- No castling
|
||||
- 3-repetition rule
|
||||
- 50 move draw rule
|
||||
- No opening or closing books
|
||||
- One or more minMax/negaMax full plies for artificial intelligence
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [www.pouet.net/prod.php?which=64962][2]
|
||||
- Developer: Olivier "Baudsurfer/RSi" Poudade
|
||||
- License: WTFPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: .02
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Micro-Max is a 133-line chess source which is written in C
|
||||
|
||||
The author has implemented a (hash) transposition table, the engine checks the legality of the input moves, and full FIDE rules except for for under-promotions.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Recursive negamax search
|
||||
- Quiescence search with recaptures
|
||||
- Recapture extensions
|
||||
- Iterative deepening
|
||||
- Best-move-first 'sorting'
|
||||
- Hash table storing score and best move
|
||||
- Full FIDE rules (except under promotion) and move-legality checking
|
||||
|
||||
There is also a stripped-down 1433-character version, but allowing you to play under-promotions for full FIDE-rule compliance.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [home.hccnet.nl/h.g.muller/max-src2.html][3]
|
||||
- Developer: Harm Geert Muller
|
||||
- License: The MIT License
|
||||
- Version Number: 3.2
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20150222033906262/ChessBytes.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://nanochess.org/chess6.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.pouet.net/prod.php?which=64962
|
||||
[3]:http://home.hccnet.nl/h.g.muller/max-src2.html
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,3 @@
|
||||
////translating by yupmoon
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Open source all over the world
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Docker and the Integrated Open Source Company
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
It’s been a long time since an open source project has gotten as much buzz and attention as Docker. The easiest way to explain the concept is, well, to look at the logo of the eponymous1 company that created and manages the project:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The reference in the logo is to shipping containers, one of the most important inventions of the 20th century. Actually, the word “invention” is not quite right: the idea of putting bulk goods into consistently-sized boxes goes back at least a few hundred years.[2][1] What changed the world was the standardization of containers by a trucking magnate named Malcom McLean and Keith Tantlinger, his head engineer. Tantlinger developed much of the technology undergirding the intermodal container, especially its corner casting and Twistlock mechanism that allowed the containers to be stacked on ships, transported by trucks, and moved by crane. More importantly, Tantlinger convinced McLean to release the patented design for anyone to copy without license, knowing that the technology would only be valuable if it were deployed in every port and on every transport ship in the world. Tantlinger, to put it in software terms, open-sourced the design.
|
||||
|
||||
Shipping containers really are a perfect metaphor for what Docker is building: standardized containers for applications.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Just as the idea of a container wasn’t invented by Tantlinger, Docker is building on a concept that has been around for quite a while. Companies like Oracle, HP, and IBM have used containers for many years, and Google especially has a very similar implementation to Docker that they use for internal projects. Docker, though, by being open source and [community-centric][2], offers the promise of standardization
|
||||
- It doesn’t matter what is inside of a shipping container; the container itself will fit on any ship, truck, or crane in the world. Similarly, it doesn’t matter what app (and associated files, frameworks, dependencies, etc.) is inside of a docker container; the container will run on any Linux distribution and, more importantly, just about every cloud provider including AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform, Rackspace, etc.
|
||||
- When you move abroad, you can literally have a container brought to your house, stick in your belongings, and then have the entire thing moved to a truck to a crane to a ship to your new country. Similarly, containers allow developers to build and test an application on their local machine and have confidence that the application will behave the exact same way when it is pushed out to a server. Because everything is self-contained, the developer does not need to worry about there being different frameworks, versions, and other dependencies in the various places the application might be run
|
||||
|
||||
The implications of this are far-reaching: not only do containers make it easier to manage the lifecycle of an application, they also (theoretically) commoditize cloud services through the age-old hope of “write once run anywhere.” More importantly, at least for now, docker containers offer the potential of being far more efficient than virtual machines. Relative to a container, using virtual machines is like using a car transport ship to move cargo: each unique entity on the ship is self-powered, which means a lot of wasted resources (those car engines aren’t very useful while crossing the ocean). Similarly, each virtual machine has to deal with the overhead of its own OS; containers, on the other hand, all share the same OS resulting in huge efficiency gains.[3][4]
|
||||
|
||||
In short, Docker is a really big deal from a technical perspective. What excites me, though, is that the company is also innovating when it comes to their business model.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
The problem with monetizing open source is self-evident: if the software is freely available, what exactly is worth paying for? And, unlike media, you can’t exactly stick an advertisement next to some code!
|
||||
|
||||
For many years the default answer has been to “be like Red Hat.” Red Hat is the creator and maintainer of the Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) distribution, which, like all Linux distributions, is freely available.[4][5] Red Hat, however, makes money by offering support, training, a certification program, etc. for enterprises looking to use their software. It is very much a traditional enterprise model – make money on support! – just minus the up-front license fees.
|
||||
|
||||
This sort of business is certainly still viable; Hortonworks is [set to IPO][3] with a similar model based on Hadoop, albeit at a much lower valuation than it received during its last VC round. That doesn’t surprise me: I don’t think this is a particularly great model from a business perspective.
|
||||
|
||||
To understand why it’s useful to think about there being three distinct parts of any company that is based on open source: the open source project itself, any value-added software built on top of that project, and the actual means of making money:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*There are three parts of an open source business: the project itself, the value-added software on top of that project, and the means of monetization*
|
||||
|
||||
The problem with the “Red Hat” model is the complete separation of all three of these parts: Red Hat doesn’t control the core project (Linux), and their value-added software (RHEL) is free, leaving their money-making support program to stand alone. To the company’s credit they have pulled this model off, but I think a big reason is because utilizing Linux was so much more of a challenge back in the 90s.[5][11] I highly doubt Red Hat could successfully build a similar business from scratch today.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*The three parts of Red Hat’s business are separate and more difficult for the company to control and monetize*
|
||||
|
||||
GitHub, the repository hosting service, is exploring what is to my mind a more compelling model. GitHub’s value-added software is a hosting service based on Git, an open-source project designed by Linux creator Linus Torvalds. Crucially, GitHub is seeking to monetize that hosting service directly, both through a SaaS model and through an on-premise enterprise offering[6][6]. This means that, in comparison to Red Hat, there is one less place to disintermediate GitHub: you can’t get their value-added software (for private projects – public is free) unless you’re willing to pay.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*While GitHub does not control Git, their value-added software and means of monetization are unified, making the latter much easier and more sustainable*
|
||||
|
||||
Docker takes the GitHub model a step further: the company controls everything from the open source project itself to the value-added software (DockerHub) built on top of that, and, just last week, [announced a monetization model][7] that is very similar to GitHub’s enterprise offering. Presuming Docker continues its present momentum and finds success with this enterprise offering, they have the potential to be a fully integrated open source software company: project, value-added software, and monetization all rolled into one.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Docker controls all the parts of their business: they are a fully integrated open source company.*
|
||||
|
||||
This is exciting, and, to be honest, a little scary. What is exciting is that very few movements have had such a profound effect as open source software, and not just on the tech industry. Open source products are responsible for end user products like this blog; more importantly, open source technologies have enabled exponentially more startups to get off the ground with minimal investment, vastly accelerating the rate of innovation and iteration in tech.[7][8] The ongoing challenge for any open source project, though, is funding, and Docker’s business model is a potentially sustainable solution not just for Docker but for future open source technologies.
|
||||
|
||||
That said, if Docker is successful, over the long run commercial incentives will steer the Docker open source project in a way that benefits Docker the company, which may not be what is best for the community broadly. That is what is scary about this: might open source in the long run be subtly corrupted by this business model? The makers of CoreOS, a stripped-down Linux distribution that is a perfect complement for Docker, [argued that was the case][9] last week:
|
||||
|
||||
> We thought Docker would become a simple unit that we can all agree on. Unfortunately, a simple re-usable component is not how things are playing out. Docker now is building tools for launching cloud servers, systems for clustering, and a wide range of functions: building images, running images, uploading, downloading, and eventually even overlay networking, all compiled into one monolithic binary running primarily as root on your server. The standard container manifesto was removed. We should stop talking about Docker containers, and start talking about the Docker Platform. It is not becoming the simple composable building block we had envisioned.
|
||||
|
||||
This, I suppose, is the beauty of open source: if you disagree, fork, which is essentially what CoreOS did, launching their own “Rocket” container.[8][10] It also shows that Docker’s business model – and any business model that contains open source – will never be completely defensible: there will always be a disintermediation point. I suspect, though, that Rocket will fail and Docker’s momentum will continue: the logic of there being one true container is inexorable, and Docker has already built up quite a bit of infrastructure and – just maybe – a business model to make it sustainable.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://stratechery.com/2014/docker-integrated-open-source-company/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ben Thompson][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://stratechery.com/category/about/
|
||||
[1]:http://stratechery.com/2014/docker-integrated-open-source-company/#fn:1:1300
|
||||
[2]:https://github.com/docker/docker
|
||||
[3]:http://blogs.wsj.com/digits/2014/12/01/ipo-bound-hortonworks-drops-out-of-billion-dollar-startup-club/
|
||||
[4]:http://stratechery.com/2014/docker-integrated-open-source-company/#fn:2:1300
|
||||
[5]:http://stratechery.com/2014/docker-integrated-open-source-company/#fn:3:1300
|
||||
[6]:http://stratechery.com/2014/docker-integrated-open-source-company/#fn:5:1300
|
||||
[7]:http://blog.docker.com/2014/12/docker-announces-docker-hub-enterprise/
|
||||
[8]:http://stratechery.com/2014/docker-integrated-open-source-company/#fn:6:1300
|
||||
[9]:https://coreos.com/blog/rocket/
|
||||
[10]:http://stratechery.com/2014/docker-integrated-open-source-company/#fn:7:1300
|
||||
[11]:http://stratechery.com/2014/docker-integrated-open-source-company/#fn:4:1300
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
|
||||
translating by barney-ro
|
||||
|
||||
2015 will be the year Linux takes over the enterprise (and other predictions)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Jack Wallen removes his rose-colored glasses and peers into the crystal ball to predict what 2015 has in store for Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,29 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linus Tells Wired Leap Second Irrelevant
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Two larger publications today featured Linux and the effect of the upcoming leap second. The Register today said that the leap second effects of the past are no longer an issue. Coincidentally, Wired talked to Linus Torvalds about the same issue today as well.
|
||||
|
||||
**Linus Torvalds** spoke with Wired's Robert McMillan about the approaching leap second due to be added in June. The Register said the last leap second in 2012 took out Mozilla, StumbleUpon, Yelp, FourSquare, Reddit and LinkedIn as well as several major airlines and travel reservation services that ran Linux. Torvalds told Wired today that the kernel is patched and he doesn't expect too many issues this time around. [He said][1], "Just take the leap second as an excuse to have a small nonsensical party for your closest friends. Wear silly hats, get a banner printed, and get silly drunk. That’s exactly how relevant it should be to most people."
|
||||
|
||||
**However**, The Register said not everyone agrees with Torvalds' sentiments. They quote Daily Mail saying, "The year 2015 will have an extra second — which could wreak havoc on the infrastructure powering the Internet," then remind us of the Y2K scare that ended up being a non-event. The Register's Gavin [Clarke concluded][2]:
|
||||
|
||||
> No reason the Penguins were caught sans pants.
|
||||
|
||||
> Now they've gone belt and braces.
|
||||
|
||||
The take-away is: move along, nothing to see here.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/linus-tells-wired-leap-second-irrelevant
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Susan Linton][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ostatic.com/member/susan-linton
|
||||
[1]:http://www.wired.com/2015/01/torvalds_leapsecond/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.theregister.co.uk/2015/01/09/leap_second_bug_linux_hysteria/
|
||||
@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linus Torvalds responds to Ars about diversity, niceness in open source
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Acknowledges diversity factors, says "we're different in so many other ways."
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
See, sometimes Linus isn't flicking people off.
|
||||
|
||||
Athanasios Kasampalis
|
||||
|
||||
On Thursday, Linux legend Linus Torvalds sent a lengthy statement to Ars Technica responding to [statements he made in Auckland, New Zealand earlier that day about diversity and "niceness"][2] in the open source sector.
|
||||
|
||||
"What I wanted to say [at the keynote]—and clearly must have done very badly—is that one of the great things about open source is exactly the fact that different people are so different," Torvalds wrote via e-mail. "I think people sometimes look at it as being just 'programmers,' which is not true. It's about all the people who are more oriented toward commercial things, too. It's about all those people who are interested in legal issues—and the social ones, too!"
|
||||
|
||||
Torvalds spoke to what he thought was a larger concept of "diversity" than what has been mentioned a lot in recent stories on the topic, including economic disparity, language, and culture (even between neighboring European countries). "There's a lot of talk about gender and sexual preferences and race, but we're different in so many other ways, too," he wrote.
|
||||
|
||||
"'Open source' as a term and as a movement hasn't been about 'you have to be a believer,'" Torvalds added. "It's not a religion. It's not an 'us vs them' thing. We've been able to work with all those 'evil commercial interests' and companies who also do proprietary software. And I think that was one of the things that the Linux community (and others—don't get me wrong, it's not unique to us) did and does well."
|
||||
|
||||
Torvalds also talked about progress since the GPL vs. BSD "flame wars" from the '80s and early '90s, saying that the open source movement brought more technology and less "ideology" to the sector. "Which is not to say that a lot of people aren't around because they believe it's the 'ethical' thing to do (I do myself too)," Torvalds added, "but you don't have to believe that, and you can just do it because it's the most fun, or the most efficient way to do technology development."
|
||||
|
||||
### “This ‘you have to be nice’ seems very popular in the US” ###
|
||||
|
||||
He then sent a second e-mail to Ars about the topic of "niceness" that came up during the keynote. He said that his return to his Auckland hotel was delayed by "like three hours" because of hallway conversations about this very topic.
|
||||
|
||||
"I don't know where you happen to be based, but this 'you have to be nice' seems to be very popular in the US," Torvalds continued, calling the concept an "ideology."
|
||||
|
||||
"The same way we have developers and marketing people and legal people who speak different languages, I think we can have some developers who are used to—and prefer—a more confrontational style, and still **also** have people who don't," he wrote.
|
||||
|
||||
He lambasted the "brainstorming" model of having a criticism-free bubble to bounce ideas off of. "Maybe it works for some people, but I happen to simply not believe in it," he said. "I'd rather be really confrontational, and bad ideas should be [taken] down aggressively. Even good ideas need to be vigorously defended."
|
||||
|
||||
"Maybe it's just because I like arguing," Torvalds added. "I'm just not a huge believer in politeness and sensitivity being preferable over bluntly letting people know your feelings. But I also understand that other people are driven away by cursing and crass language when it all gets a bit too carried away." To that point, Torvalds said that the open source movement might simply need more "people who are good at mediating," as opposed to asking developers to calm their own tone or attitude.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://arstechnica.com/business/2015/01/linus-torvalds-responds-to-ars-about-diversity-niceness-in-open-source/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sam Machkovech][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/samred/
|
||||
[1]:https://secure.flickr.com/photos/12693492@N04/1338136415/in/photolist-33fikv-3jXFce-3ALpLy-4m6Shj-4pADUg-4pHwcW-4rNTR7-4GMhKc-4HM2qp-4JSHKa-4PomQo-4SKxMo-58LBYf-5iVNX6-5tXbB8-5xi67A-5A8rRc-5C8fAT-5Ccxjw-5EcYvx-5UoNTc-5UoVJK-5Uti6q-5UuiX2-5UuE2B-5UyEJu-5UyHMf-5UyJ2G-5UFbXP-5UFg8Z-5UFhwV-5UKDkG-5UKDP9-5UTHGv-5XM2s2-5YFmLu-65N31L-6pSwh7-6trmfx-6H2uZP-6JVV4V-71qkot-71BBbk-72vuYo-73j9yB-79aQ2a-79bfqe-79EKPH-79EXvD-79PuG5-7a4BxF
|
||||
[2]:http://arstechnica.com/business/2015/01/linus-torvalds-on-why-he-isnt-nice-i-dont-care-about-you/
|
||||
@ -1,72 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Top 10 FOSS legal developments of 2014
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Image by : opensource.com
|
||||
|
||||
The year 2014 continued the trend of the increasing importance of legal issues for the FOSS community. Continuing [the tradition of looking back][1] over the top ten legal developments in FOSS, my selection of the top ten issues for 2014 is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Courts interpret General Public License version 2 (GPLv2) ###
|
||||
|
||||
The GPLv2 continues to be the most widely used and most important license for free and open source software. Black Duck Software estimates that 16 billion lines of code are licensed under the GPLv2. Despite its importance, the GPLv2 has been the subject of very few court decisions, and virtually all of the most important terms of the GPLv2 have not been interpreted by courts. This lack of court decisions is about to change due to the five interrelated cases arising from an attempt by Versata Software, Inc. (Versata) to terminate its software license to Ameriprise Financial, Inc. Versata’s product included software licensed by Ximpleware, Inc. (Ximpleware) under the GPLv2, but Versata had not complied with the terms of the GPLv2. Ximpleware sued Versata and eight of its customers for both copyright and patent infringement. (For a more detailed description of the facts [read this article][2].) This dispute is important because Ximpleware is the first commercial enforcer of the GPLv2 in which the courts are likely to issue decisions and Ximpleware is seeking monetary damages rather than compliance.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. GPL guides ###
|
||||
|
||||
Two of the most important organizations enforcing the GPL family of licenses recently provided [guidance on compliance][3]: On October 31, the Software Freedom Law Center published the second version of their Practical Guide to GPL Compliance. Several days later, the Software Conservancy and the Free Software Foundation published the first version of their guide, the Copyleft, and the GNU General Public License: [A Comprehensive Tutorial and Guide][4]. These guides are required reading for anyone managing FOSS.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. EU Commission (EC) to revise FOSS policy ###
|
||||
|
||||
Governments are one of the most important users of software but have had a mixed record in using and contributing to FOSS (free and open source software). The EC recently announced that it intends to remove the barriers that may hinder code contributions to FOSS projects. In particular, the EC wants to clarify legal aspects, including intellectual property rights, copyright, and which author or authors to name when submitting code to the upstream repositories. Pierre Damas, Head of Sector at the Directorate General for IT, [hopes that such clarification][5] will motivate many of the EC’s software developers and functionaries to promote the use of FOSS at the EC.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Validation of FOSS business model by Hortonworks IPO ###
|
||||
|
||||
Hortonworks provides services and support for the Hadoop data analysis software managed by the Apache Software Foundation. Hortonworks is one of three venture backed companies based on the Hadoop software. Hortonworks went public this fall and immediately rose 65% in share price, valuing the company at over $1 billion. The market for Hadoop products, software, and services is projected to reach $50.2 billion in 2020, up from $1.5 billion in 2012.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Core Infrastructure Initiative ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Linux Foundation put together [a consortium of companies][6] to support the many smaller open source projects that are critical to software ecosystem, such as OpenSSL. This effort was a response to the Heartbleed problem with OpenSSL in 2013, which I described in last year’s summary. This consortium is a great example of the ability of the FOSS community to come together to solve community problems.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Linux SCO case terminated again ###
|
||||
|
||||
The lawsuit by Santa Cruz Operations, Inc. (SCO) against IBM claiming that Linux includes Unix code was once a potentially major challenge to FOSS. Despite losing its suit against Novell, the bankruptcy court allowed SCO to continue its suit against IBM. I thought this case [had been concluded in 2008][7], but Judge Nuffer appears to have put the case to rest on December 15, 2014. He dismissed the case against IBM based on the decisions in the Novell case (although SCO could still appeal once again):
|
||||
|
||||
*It is further ORDERED that, with respect to all remaining claims and counterclaims, SCO is bound by, and may not here re-litigate, the rulings in the Novell Judgment that Novell (not SCO) owns the copyrights to the pre-1996 UNIX source code, and that Novell waived SCO’s contract claims against IBM for alleged breaches of the licensing agreements pursuant to which IBM licensed such source code.*
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. FOSS trademark issues ###
|
||||
|
||||
The use of trademarks in FOSS projects continues to raise issues. This year brought the settlement of the dispute over the “Python” mark between the Python Software Foundation and Veber, a small hosting company in the UK. Veber had decided to use "Python" in branding certain of its products and services. In addition, the OpenStack Foundation is working through the application of trademarks to the OpenStack project through its [DefCore committee][8].
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Use of FOSS by commercial companies expands ###
|
||||
|
||||
We have discussed in the past how many large companies are using FOSS as an explicit strategy to build their software. Jim Zemlin, Executive Director of the Linux Foundation, has described this strategic use of FOSS as external “research and development.” His conclusions are supported by Gartner who noted that “the top tech companies are still spending tens of billions of dollars on software research and development, the smart ones are leveraging open source for 80 percent of the code and spending their money on the remaining 20 percent, which represents their program’s ‘special sauce.’” The scope of this trend was emphasized by Microsoft’s announcement that it was “open sourcing” the .NET software framework (this software is used by millions of developers to build and operate websites and other large online applications).
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Rockstar Consortium threat evaporates ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Rockstar Consortium was formed by Microsoft, Blackberry, Ericsson, Sony, and Apple to exploit the 6,000 patents from Nortel Networks. The Rockstar Consortium sued Google for infringement of the Android operating system. This litigation was aimed at fundamental functions of the Android operating system and could have had a significant effect on the Android ecosystem. The Rockstar Consortium settled its litigation with Google this year, but then sold 4,000 of its patents to RPX, the patent defense firm (financed by a number of companies as well as RPX). The remaining patents were distributed to the members of the Rockstar Consortium.
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Android litigation ###
|
||||
|
||||
The litigation surrounding Android continued this year, with significant developments in the patent litigation between Apple Computer, Inc. (Apple) and Samsung Electronics, Inc. (Samsung) and the copyright litigation over the Java APIs between Oracle Corporation (Oracle) and Google, Inc. (Google). Apple and Samsung have agreed to end patent disputes in nine countries, but they will continue the litigation in the US. As I stated last year, the Rockstar Consortium was a wild card in this dispute. However, the Rockstar Consortium settled its litigation with Google this year and sold off its patents, so it will no longer be a risk to the Android ecosystem.
|
||||
|
||||
The copyright litigation regarding the copyrightability of the Java APIs was brought back to life by the Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit (CAFC) decision which overturned [the District Court decision][9]. The District Court had found that Google was not liable for copyright infringement for its admitted copying of the Java APIs: the court found that the Java APIs were either not copyrightable or their use by Google was protected by various defenses to copyright. The CAFC overturned both the decision and the analysis and remanded the case to the District Court for a review of the fair use defense raised by Google. Subsequently, Google filed an appeal to the Supreme Court. The impact of a finding that Google was liable for copyright infringement in this case would have a dramatic effect on Android and, depending on the reasoning, would have a ripple effect across the interpretation of the scope of the “copyleft” terms of the GPL family of licenses which use APIs.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://opensource.com/law/15/1/top-foss-legal-developments-2014
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Mark Radcliffe][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://opensource.com/users/mradcliffe
|
||||
[1]:http://lawandlifesiliconvalley.com/blog/?p=853
|
||||
[2]:http://opensource.com/law/14/12/gplv2-court-decisions-versata
|
||||
[3]:http://www.softwarefreedom.org/resources/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.copyleft.org/guide/
|
||||
[5]:https://joinup.ec.europa.eu/community/osor/news/european-commission-update-its-open-source-policy
|
||||
[6]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/programs/core-infrastructure-initiative
|
||||
[7]:http://lawandlifesiliconvalley.com/blog/?m=200812
|
||||
[8]:https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Governance/CoreDefinition
|
||||
[9]:http://law.justia.com/cases/federal/appellate-courts/cafc/13-1021/13-1021-2014-05-09.html
|
||||
@ -1,126 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Top 10 open source projects of 2014
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Image credits : [CC0 Public Domain][1], modifications by Jen Wike Huger
|
||||
|
||||
Every year we collect the best of the best open source projects covered on Opensource.com. [Last year's list of 10 projects][2] guided people working and interested in tech throughout 2014. Now, we're setting you up for 2015 with a brand new list of accomplished open source projects.
|
||||
|
||||
Some faces are new. Some have been around and just keep rocking it. Let's dive in!
|
||||
|
||||
## Top 10 open source projects in 2014 ##
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker ###
|
||||
|
||||
[application container platform][3]
|
||||
|
||||
"In the same way that power management and virtualisation has allowed us to get maximum engineering benefit from our server utilisation, the problem of how to really solve first world problems in virtualisation has remained prevalent. Docker's open sourcing in 2013 can really align itself with these pivotal moments in the evolution of open source—providing the extensible building blocks allowing us as engineers and architects to extend distributed platforms like never before." —Richard Morrell, [Senior software engineer Petazzoni on the breathtaking growth of Docker][4].
|
||||
|
||||
**Interview**: VP of Services for Docker talks to Jodi Biddle in [Why is Docker the new craze in virtualization and cloud computing?][5] "I think it's the lightweight nature of Docker combined with the workflow. It's fast, easy to use and a developer-centric DevOps-ish tool. Its mission is basically: make it easy to package and ship code." —James Turnbull.
|
||||
|
||||
### Kubernetes ###
|
||||
|
||||
[orchestration system for containers][6]
|
||||
|
||||
"One of the projects you're starting to hear a lot about in the orchestration space is [Kubernetes][7], which came out of Google's internal container work. It aims to provide features such as high availability and replication, service discovery, and service aggregation." —Gordon Haff, [Open source accelerating the pace of software][8].
|
||||
|
||||
### Taiga ###
|
||||
|
||||
[project management platform][9]
|
||||
|
||||
"It’s almost always the case that the project management tool doesn’t reflect the actual project scenario. One solution to this is using a tool that is intuitive and fits alongside the developer's normal workflow. Additionally, a tool that is quick to update and attracts users to use it. [Taiga][10] is an open source project management tool that aims to solve the basic problem of software usability." —Nitish Tiwari, [Taiga, a new open source project management tool with focus on usability][11].
|
||||
|
||||
### Apache Mesos ###
|
||||
|
||||
[cluster manager][12]
|
||||
|
||||
"[Apache Mesos][13] is a cluster manager that provides efficient resource isolation and sharing across distributed applications or frameworks. It sits between the application layer and the operating system and makes it easier to deploy and manage applications in large-scale clustered environments more efficiently. It can run many applications on a dynamically shared pool of nodes. Prominent users of Mesos include Twitter, Airbnb, MediaCrossing, Xogito and Categorize. —Sachin P Bappalige, [Open source datacenter computing with Apache Mesos][14].
|
||||
|
||||
Interview: Head of Open Source at Twitter talks to Jason Hibbets in [Scale like Twitter with Apache Mesos][15]. "As of today, Twitter has over 270 million active users which produces 500+ million tweets a day, up to 150k+ tweets per second, and more than 100TB+ of compressed data per day. Architecturally, Twitter is mostly composed of services, mostly written in the open source project [Finagle][16], representing the core nouns of the platform such as the user service, timeline service, and so on. Mesos allows theses services to scale to tens of thousands of bare-metal machines and leverage a shared pool of servers across data centers." —Chris Aniszczyk
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenStack ###
|
||||
|
||||
[cloud computing platform][17]
|
||||
|
||||
"As OpenStack continues to mature and slowly make its way into production environments, the focus on the user is continuing to grow. And so, to better meet the needs of users, the community is working hard to get users to meet the next step of engagement by highlighting those users who are change agents both in their organization and within the OpenStack community at large: the superusers." —Jason Baker, [What is an OpenStack superuser][18]?
|
||||
|
||||
**Interview**: Infrastructure manager at CERN talks to Jason Hibbets in [How OpenStack powers the research at CERN][19]. "At CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research physicists and engineers are probing the fundamental structure of the universe. In order to do this, we use some of the world's largest and most complex scientific instruments such as the Large Hadron Collider, a 27 KM ring 100m underground on the border between France and Switzerland. OpenStack provides the infrastructure cloud which is used to provide much of the compute resources for this processing." —Tim Bell.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ansible ###
|
||||
|
||||
[IT automation tool][20]
|
||||
|
||||
"A lot of what I want to do is enable people to not only have more free time for beer, but to have more free time for their own projects, their own ideas, and to do new an interesting things." —[Michael DeHaan, Making your IT infrastructure boring with Ansible][21].
|
||||
|
||||
**Interview**: CTO of Ansible talks to Jen Krieger in [Behind the scenes with CTO Michael DeHaan of Ansible][22]. "I like to quote Star Trek 2 a lot. We definitely optimize for 'the needs of the many'. I know Spock dies after he says that, but he does get to come back." —Michael DeHaan
|
||||
|
||||
### ownCloud ###
|
||||
|
||||
[cloud storage tool][23]
|
||||
|
||||
"I was looking for an easy way how to have all my online storage services, such as Google Drive and Dropbox, integrated with my Linux desktop without using some nasty hack, and I finally have a solution that works. I'm here to share it with you. This is not rocket science really, all I did was a little bit of documentation reading, and a couple of clicks." —Jiri Folta, [Using ownCloud to integrate Dropbox, Google Drive, and more in Gnome][24].
|
||||
|
||||
**Listed**: Top 5 open source alternatives: "ownCloud does most everything that the proprietary names do and it keeps control of your information in your hands." —Scott Nesbitt, [Five open source alternatives to popular web apps][25].
|
||||
|
||||
### Apache Hadoop ###
|
||||
|
||||
[framework for big data][26]
|
||||
|
||||
"Apache Hadoop is an open source software framework for storage and large scale processing of data-sets on clusters of commodity hardware. Hadoop is an Apache top-level project being built and used by a global community of contributors and users. It is licensed under the Apache License 2.0." —Sachin P Bappalige, [An introduction to Apache Hadoop for big data][27].
|
||||
|
||||
### Drupal ###
|
||||
|
||||
[content management system (CMS)][28]
|
||||
|
||||
"When it was released in 2011, Drupal 7 was the most accessible open source content management system (CMS) available. I expect that this will be true until the release of Drupal 8. Web accessibility requires constant vigilance and will be something that will always need attention in any piece of software striving to meet the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0 guidelines." —Mike Gifford, [Drupal 8's accessibility advantage][29].
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenDaylight ###
|
||||
|
||||
[foundation for software defined networking][30]
|
||||
|
||||
"We are seeing more and more that the networking functions traditionally done in the datacenter by dedicated, almost exclusively proprietary hardware and software combinations, are now being defined through software. Leading that charge within the open source community has been the [OpenDaylight Project][31], a collaborative project through the [Linux Foundation][32] working to define the needs which software defined networking may fill and coordinating the efforts of individuals and companies worldwide to create an open source solution to software defined networking (SDN)." —Jason Baker, [Define your network in software with OpenDaylight][33].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://opensource.com/business/14/12/top-10-open-source-projects-2014
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jen Wike Huger][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://opensource.com/users/jen-wike
|
||||
[1]:http://pixabay.com/en/lightbulb-lamp-light-hotspot-336193/
|
||||
[2]:http://opensource.com/life/13/12/top-open-source-projects-2013
|
||||
[3]:https://www.docker.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://opensource.com/business/14/7/interview-jerome-petazzoni-docker
|
||||
[5]:https://opensource.com/business/14/7/why-docker-new-craze-virtualization-and-cloud-computing
|
||||
[6]:http://kubernetes.io/
|
||||
[7]:https://cloud.google.com/compute/docs/containers
|
||||
[8]:http://opensource.com/business/14/11/open-source-accelerating-pace-software
|
||||
[9]:https://taiga.io/
|
||||
[10]:https://github.com/taigaio
|
||||
[11]:https://opensource.com/business/14/10/taiga-open-source-project-management-tool
|
||||
[12]:http://mesos.apache.org/
|
||||
[13]:http://mesos.apache.org/
|
||||
[14]:https://opensource.com/business/14/9/open-source-datacenter-computing-apache-mesos
|
||||
[15]:https://opensource.com/business/14/8/interview-chris-aniszczyk-twitter-apache-mesos
|
||||
[16]:https://twitter.github.io/finagle/
|
||||
[17]:http://www.openstack.org/
|
||||
[18]:https://opensource.com/business/14/5/what-is-openstack-superuser
|
||||
[19]:https://opensource.com/business/14/10/interview-tim-bell-cern-it-operating-systems
|
||||
[20]:http://www.ansible.com/home
|
||||
[21]:https://opensource.com/business/14/12/ansible-it-infrastructure
|
||||
[22]:https://opensource.com/business/14/10/interview-michael-dehaan-ansible
|
||||
[23]:http://owncloud.org/
|
||||
[24]:https://opensource.com/life/14/12/using-owncloud-integrate-dropbox-google-drive-gnome
|
||||
[25]:https://opensource.com/life/14/10/five-open-source-alternatives-popular-web-apps
|
||||
[26]:http://hadoop.apache.org/
|
||||
[27]:http://opensource.com/life/14/8/intro-apache-hadoop-big-data
|
||||
[28]:https://www.drupal.org/
|
||||
[29]:http://opensource.com/business/14/5/new-release-drupal-8-accessibility-advantage
|
||||
[30]:http://www.opendaylight.org/
|
||||
[31]:http://www.opendaylight.org/
|
||||
[32]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[33]:http://opensource.com/business/14/5/defining-your-network-software-opendaylight
|
||||
@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
|
||||
LinuxQuestions Survey Results Surface Top Open Source Projects
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Many people in the Linux community look forward to the always highly detailed and reliable results of the annual surveys from LinuxQuestions.org. As [Susan covered in detail in this post][1], this year's [results][2], focused on what readers at the site deem to be the best open source projects, are now available. Most of the people at LinuxQuestions are expert-level users who are on the site to answer questions from newer Linux users.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the summary results that Susan provided in her post, below you'll find a graphical snapshot of what the experts took note of on the open source front.
|
||||
|
||||
You can get a very nice graphical summary of the findings from the LinuxQuestions survey [here][3]. Here is a snapshot of the site's determination of the best Linux distributions, where Mint and Slackware fare quite well:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
And below is a snapshot of the site's determination of the best cloud projects. Notably, the LinuxQuestions crowd gives very high praise to ownCloud. Definiitely check into the full results of the survey at the site, see [Susan's summary][4] of winners, and check out all the good graphics [here][5].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/linuxquestions-survey-results-surface-top-open-source-projects
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sam Dean][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ostatic.com/member/samdean
|
||||
[1]:http://ostatic.com/blog/lq-members-choice-award-winners-announced
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/linux-news-59/2014-linuxquestions-org-members-choice-award-winners-4175532948/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/2014mca.php
|
||||
[4]:http://ostatic.com/blog/lq-members-choice-award-winners-announced
|
||||
[5]:http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/2014mca.php
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
||||
A Look At What Linux Games We Will See In 2015 And Beyond
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux Gaming is dead they said, Linux Gaming is pointless they said...ah whatever. Here’s a look at what’s to come for us in 2015 and beyond.
|
||||
|
||||
It's pretty hard to keep up with everything that's going on for us, but here's a quick look at what we could see soon.
|
||||
|
||||
### Confirmed Games ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Adventure Games ####
|
||||
|
||||
- [Firewatch][1]
|
||||
- [Paradise Lost: First Contact][2]
|
||||
- [SteamWorld Heist][3]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Action Games ####
|
||||
|
||||
- [Darksiders][4]
|
||||
- [Darksiders II][5]
|
||||
- [Ray's The Dead][6]
|
||||
- [Skullgirls][7]
|
||||
|
||||
#### FPS Games ####
|
||||
|
||||
- [Bioshock Infinite][8]
|
||||
- Half Life 3 /troll
|
||||
- [Homefront: The Revolution][9]
|
||||
- [Killing Floor 2][10]
|
||||
- Serious Sam 4 (No official site for it yet)
|
||||
- [Storm United][11]
|
||||
- [SUPERHOT][12]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Platformers ####
|
||||
|
||||
- [Broforce][13]
|
||||
- [Chasm][14]
|
||||
- [Giana Sisters][15]
|
||||
- [Heart Forth, Alicia][16]
|
||||
- [Hot Tin Roof][17]
|
||||
- [Infinifactory][18]
|
||||
- [Mighty No. 9][19]
|
||||
- [Night in the Woods][20]
|
||||
- [Noct][21]
|
||||
- [Oddworld: New 'N' Tasty][22]
|
||||
- [Red Goddess][23]
|
||||
|
||||
#### RPG Games ####
|
||||
|
||||
- [Divinity: Original Sin][24]
|
||||
- [Pillars Of Eternity][25]
|
||||
- [Shadowrun: Hong Kong][26]
|
||||
- [The Banner Saga][27]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Strategy Games ####
|
||||
|
||||
- [Age of Wonders III][28]
|
||||
- [Banished][29]
|
||||
- [Cities: Skylines][30]
|
||||
- [Clockwork Empires][31]
|
||||
- [Parkitect][32]
|
||||
- [Scrolls][33]
|
||||
- [Space Pirates And Zombies 2][34]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sandbox Games ####
|
||||
|
||||
- [Terraria][35]
|
||||
- [X Rebirth][36]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Unconfirmed, but highly likely ####
|
||||
|
||||
- [Company of Heroes 2][37]
|
||||
- [Outlast][38]
|
||||
- [Shadow Warrior][39]
|
||||
- [Torchlight II][40]
|
||||
|
||||
Then there’s the [two ports teased from Feral Interactive][41], we can’t let them be left out just because we don’t know what they are.
|
||||
|
||||
We imagine Aspyr Media are also working on new bigger ports, but they have only just released their latest game, so it may be a few months until we see anything.
|
||||
|
||||
**This isn't a complete list** of course, as we can easily forget with the sheer amount of games heading our way, and wow what a list!
|
||||
|
||||
We have GDC next month, and we are expecting a few announcements too. While we don't have anything solid, with Valve's big presence with Steam Machines we are expecting at least some more Linux games, otherwise it we fear it may be a little lacklustre for Valve to only show off older existing games for Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
What did we miss that you’re excited about for Linux?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/a-look-at-what-linux-games-we-will-see-in-2015-and-beyond.4963
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[liamdawe][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.gamingonlinux.com/profiles/1
|
||||
[1]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/category/17/articles/firewatch-a-first-person-mystery-game-finally-reveals-itself-in-a-trailer.4231
|
||||
[2]:http://www.asthreeworks.com/games/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/category/17/articles/image-form-announces-steamworld-heist.4304
|
||||
[4]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/darksiders-linux-port-looks-like-it-is-still-happening.4893
|
||||
[5]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/darksiders-2-confirmed-for-linux.4154
|
||||
[6]:http://ragtagstudio.com/?page_id=457
|
||||
[7]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/editorial-skullgirls-on-linux-finally-shows-some-progress.4789
|
||||
[8]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/bioshock-infinite-looks-set-for-a-linux-release-confirmed.4668
|
||||
[9]:http://www.homefront-game.com/
|
||||
[10]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/category/17/articles/killing-floor-2-fps-has-a-new-trailer.4676
|
||||
[11]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/storm-united-online-fps-shows-first-real-gameplay-video-first-alpha-due-soon.4872
|
||||
[12]:http://superhotgame.com/
|
||||
[13]:http://steamcommunity.com/app/274190/discussions/0/540738051503306548/#c540738051518330743
|
||||
[14]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/category/17/articles/chasm-rpg-platformer-will-have-a-same-day-linux-release.4266
|
||||
[15]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/linux-port-of-platformer-giana-sisters-brought-inhouse-sequel-might-get-sameday-release.4913
|
||||
[16]:http://www.alonsomartin.mx/hfa/
|
||||
[17]:http://www.hottinroofgame.com/
|
||||
[18]:https://twitter.com/zachtronics/status/566016742825005057
|
||||
[19]:http://www.mightyno9.com/
|
||||
[20]:http://www.nightinthewoods.com/
|
||||
[21]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/category/17/articles/noct-a-fantastic-top-down-thermal-image-survival-horror-game.4783
|
||||
[22]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/puzzle-platformer-oddworld-new-n-tasty-will-release-for-linux-next-month.4836
|
||||
[23]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/new-trailer-for-platformer-red-goddesss-looks-really-good.4939
|
||||
[24]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/divinity-original-sin-is-pushing-ahead-for-the-linux-release.4938
|
||||
[25]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/pillars-of-eternity-the-rpg-aims-for-a-sameday-linux-release-on-march-26th.4834
|
||||
[26]:https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/webeharebrained/shadowrun-hong-kong
|
||||
[27]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/the-banner-saga-rpg-looks-close-to-a-linux-version.4862
|
||||
[28]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/the-linux-port-of-age-of-wonders-iii-is-progressing-a-bit-too-explosive-right-now.4857
|
||||
[29]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/banished-survival-city-building-sim-is-being-ported-to-linux.4813
|
||||
[30]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/city-builder-game-cities-skylines-now-has-a-release-date.4954
|
||||
[31]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/clockwork-empires-still-pushing-towards-a-linux-version-suffering-delays.4734
|
||||
[32]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/category/17/articles/parkitect-what-roller-coaster-tycoon-should-have-grown-into.4528
|
||||
[33]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/mojangs-scrolls-now-has-an-experimental-linux-build.4450
|
||||
[34]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/space-pirates-and-zombies-2-reveals-the-zombies-in-a-brand-new-video.4759
|
||||
[35]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/terraria-officially-confirmed-to-be-in-development-for-linux-finally.4299
|
||||
[36]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/egosofts-x-rebirth-actively-being-ported-to-linux.4822
|
||||
[37]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/company-of-heroes-2-looks-like-it-is-heading-to-linux.4199
|
||||
[38]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/outlast-that-really-scary-game-looks-like-its-still-heading-to-linux.4896
|
||||
[39]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/shadow-warrior-looks-like-it-will-come-to-linux.4859
|
||||
[40]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/torchlight-ii-has-even-more-positive-signs-for-linux.4817
|
||||
[41]:http://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/feralinteractive.com/en/upcoming/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
Torvalds: 'People who start writing kernel code get hired really quickly'
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Now more than ever, the development of the Linux kernel is a matter for the professionals, as unpaid volunteer contributions to the project reached their lowest recorded levels in the latest "Who Writes Linux" report, which was released today.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the report, which is compiled by the Linux Foundation, just 11.8 percent of kernel development last year was done by unpaid volunteers -- a 19 percent downturn from the 2012 figure of 14.6 percent. The foundation says that the downward trend in volunteer contributions has been present for years.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Even so, unpaid contributors were still the single biggest source of commits in the latest Who Writes Linux, at 11,968 total changes -- good for 12.4 percent of the whole. However, corporate contributors collectively account for much, much more. The Linux Foundation said that more than 80 percent of all work on the kernel is done by paid professional developers.
|
||||
|
||||
According to Linus Torvalds, the shift towards paid developers hasn't changed much about kernel development on its own.
|
||||
|
||||
"I think one reason it hasn't changed things all that much is that it's not so much 'unpaid volunteers are going away' as 'people who start writing kernel code get hired really quickly,'" he told Network World.
|
||||
|
||||
Torvalds said that, while Linux development has changed for plenty of other reasons -- and that, naturally, new contributors pop up all the time -- many of the original developers, with decades of experience, have simply been snapped up by companies with an interest in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
"We may have started as volunteers, but we're happily employed doing Linux these days," he said.
|
||||
|
||||
Torvalds' own role in development has become increasingly hands-off, according to the report -- he has personally signed off on 329 patches since version 3.10 of kernel was released, or 0.4 percent. Increasingly, subsystem maintainers do their own reviews and merges of code.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.infoworld.com/article/2885339/application-development/torvalds-people-who-start-writing-kernel-code-get-hired-really-quickly.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jon Gold][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.infoworld.com/author/Jon-Gold/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
No reboot patching comes to Linux 4.0
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Summary**:With the new Linux 4.0 kernel, you'll need to reboot Linux less often than ever.
|
||||
|
||||
With [Linux 4.0][1], you may never need to reboot your operating system again.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Using Linux means never having to reboot. -- SUSE
|
||||
|
||||
One reason to love Linux on your servers or in your data-center is that you so seldom needed to reboot it. True, critical patches require a reboot, but you could go months without rebooting. Now, with the latest changes to the Linux kernel you may be able to go years between reboots.
|
||||
|
||||
This is actually a feature that was available in Linux in 2009 thanks to a program called [Ksplice][2]. This program compares the original and patched kernels and then uses a customized kernel module to patch the new code into the running kernel. Each Ksplice-enabled kernel comes with a special set of flags for each function that will be patched. The [Ksplice process][3] then watches for a moment when the code for the function being patched isn't in use, and ta-da, the patch is made and your server runs on.
|
||||
|
||||
[Oracle acquired Ksplice][4] in 2011, and kept it just for its own [Oracle Linux][5], a [Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)][6] clone, and as a RHEL subscription service. That left all the other enterprise and server Linux back where they started.
|
||||
|
||||
Then [KernelCare released a service that could provide bootless patches][7] for most enterprise Linux distros. This program use proprietary software and is only available as a service with a monthly fee. That was a long way from satisfying many Linux system administrators.
|
||||
|
||||
So, [Red Hat][8] and [SUSE][9] both started working on their own purely open-source means of giving Linux the ability to keep running even while critical patches were being installed. Red Hat's program was named [kpatch][10], while SUSE' is named [kGraft][11].
|
||||
|
||||
The two companies took different approaches. Kpatch issues a stop_machine() command. After that it looks at the stack of existing processes using [ftrace][12] and, if the patch can be made safely, it redirects the running code to the patched functions and then removes the now outdated code.
|
||||
|
||||
Kgraft also uses ftrace, but it works on the thread level. When an old function is called it makes sure the thread reaches a point that it can switch to the new function.
|
||||
|
||||
While the end result is the same, the operating system keeps running while patches are made, there are significant differences in performance. Kpatch takes from one to forty milliseconds, while kGraft might take several minutes but there's never even a millisecond of down time.
|
||||
|
||||
At the Linux Plumbers Conference in October 2014, the two groups got together and started work on a way to [patch Linux without rebooting that combines the best of both programs][13]. Essentially, what they ended up doing was putting both kpatch and kGraft in the 4.0 Linux kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
Jiri Kosina, a SUSE software engineer and Linux kernel developer, explained, that live-patching in the Linux kernel will "provides a basic infrastructure for function "live patching" (i.e. code redirection), including API [application programming interface] for kernel modules containing the actual patches, and API/ABI [application binary interface] for userspace to be able to operate on the patches. This is "relatively simple and minimalistic, as it's making use of existing kernel infrastructure (namely ftrace) as much as possible. It's also self-contained, in a sense that it doesn't hook itself in any other kernel subsystem (it doesn't even touch any other code)."
|
||||
|
||||
The release candidate for Linux 4.0 is now out. Kosina stated that "It's now implemented for x86 only as a reference architecture, but support for powerpc, s390 and arm is already in the works." And, indeed, the source code for these architectures is already in the [Live Patching Git code][14].
|
||||
|
||||
Simply having the code in there is just the start. Your Linux distribution will have to support it with patches that can make use of it. With both Red Hat and SUSE behind it, live patching will soon be the default in all serious business Linux distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.zdnet.com/article/no-reboot-patching-comes-to-linux-4-0/#ftag=RSSbaffb68
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.zdnet.com/meet-the-team/us/sjvn/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/linux-kernel-turns-over-release-odometer-to-4-0/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.computerworld.com/article/2466389/open-source-tools/never-reboot-again-with-linux-and-ksplice.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.ksplice.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/oracle-acquires-zero-downtime-linux-upgrade-software/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.oracle.com/us/technologies/linux/overview/index.html
|
||||
[6]:http://www.redhat.com/en/technologies/linux-platforms/enterprise-linux
|
||||
[7]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/kernelcare-new-no-reboot-linux-patching-system/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.redhat.com/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.suse.com/
|
||||
[10]:http://rhelblog.redhat.com/2014/02/26/kpatch/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/suse-gets-live-patching/
|
||||
[12]:http://elinux.org/Ftrace
|
||||
[13]:http://linuxplumbersconf.org/2014/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/LPC2014_LivePatching.txt
|
||||
[14]:https://kernel.googlesource.com/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/jikos/livepatching/+/9ec0de0ee0c9f0ffe4f72da9158194121cc22807
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,170 @@
|
||||
How to protect SSH server from brute force attacks using fail2ban
|
||||
================
|
||||
|
||||
One common attack on SSH service is brute force attacks where a remote attacker indefinitely attempts to log in with different passwords. Of course there are arguments against password authentication for SSH, and alternative authentication mechanisms such as [public key authentication][1] or [two-factor authentication][2] exist to obsolete such attacks. Putting aside pros and cons of different authentication methods, let's consider the situation where password authentication is required. How would you protect your SSH server against brute-force attacks?
|
||||
|
||||
[fail2ban][3] is a well-known open-source intrusion prevention framework on Linux that monitors various system log files (e.g., /var/log/auth.log or /var/log/secure) and automatically triggers various defensive actions upon detecting any suspicious activities. In fact, fail2ban can be quite useful to defend against brute force password guessing attacks on an SSH server.
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, I will demonstrate **how to install and configure fail2ban to protect an SSH server against brute force attacks from a remote IP address**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Fail2ban on Linux
|
||||
|
||||
To install fail2ban on CentOS or RHEL, first [set up EPEL repository][4], and then run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install fail2ban
|
||||
|
||||
To install fail2ban on Fedora, simply run:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install fail2ban
|
||||
|
||||
To install fail2ban on Ubuntu, Debian or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install fail2ban
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure Fail2ban for SSH Server
|
||||
|
||||
Now you are ready to configure fail2ban to harden your SSH server. You need to edit the configuration file at /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf. The configuration file contains "DEFAULT" section where you define default parameters for all monitored services, and service-specific sections where you define any service-specific jails (e.g., SSH, Apache, etc) to overwrite default parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
In the service-specific jail sections (somewhere after [DEFAULT] section), you need to define [ssh-iptables] section, where you define SSH-specific jail configurations. Actual IP address banning is done by iptables.
|
||||
|
||||
The following is an example of /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf which contains "ssh-iptables" jail configuration. Of course there could be other application-specific jails depending on your needs.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[DEFAULT]
|
||||
# a space delimited list of IP addresses, CIDR prefixes, or DNS hostnames
|
||||
# to bypass fail2ban protection
|
||||
ignoreip = 127.0.0.1 172.31.0.0/24 10.10.0.0/24 192.168.0.0/24
|
||||
|
||||
# number of seconds during which a client host is blocked
|
||||
bantime = 86400
|
||||
|
||||
# number of failures before a client host is blocked
|
||||
maxretry = 5
|
||||
|
||||
# number of seconds within which "maxentry" failures result in banning
|
||||
findtime = 600
|
||||
|
||||
mta = sendmail
|
||||
|
||||
[ssh-iptables]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
filter = sshd
|
||||
action = iptables[name=SSH, port=ssh, protocol=tcp]
|
||||
sendmail-whois[name=SSH, dest=your@email.com, sender=fail2ban@email.com]
|
||||
# for Debian-based distros
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/auth.log
|
||||
# for Red Hat-based distros
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/secure
|
||||
# ssh-specific max-retry threshold
|
||||
maxretry = 3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
According to the above configuration, fail2ban will automatically ban any remote IP address from which there have been at least 3 failed login attempts within the last 10 minutes. Once banned, the offending IP address will remain blocked for 24 hours. Such an event will be notified by sendemail to a recipient email address.
|
||||
|
||||
Once the configuration file is ready, restart fail2ban service as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, Ubuntu or CentOS/RHEL 6:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service fail2ban restart
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora or CentOS/RHEL 7:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart fail2ban
|
||||
|
||||
To verify fail2ban is running successfully, run fail2ban-client command with "ping" argument. If fail2ban service is running okay, you should see "pong" as a response.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo fail2ban-client ping
|
||||
Server replied: pong
|
||||
|
||||
### Test Protection against SSH Brute-Force Attacks with Fail2ban
|
||||
|
||||
To test whether fail2ban works, try to SSH to the server using incorrect passwords to simulate a brute-force attack. In the mean time, monitor /var/log/fail2ban.log, which is logging any interesting events that are happening in fail2ban.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo tail -f /var/log/fail2ban.log
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
According to the log file above, fail2ban has banned an IP address 192.168.1.8, upon detecting multiple failed SSH login attempts from the IP address.
|
||||
|
||||
### Check Fail2ban Status and Unban Blocked IP Addresses
|
||||
|
||||
As fail2ban's "ssh-iptables" jail uses iptables to block offending IP addresses, you can easily verify the ban by checking current iptables rules as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables --list -n
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
|
||||
target prot opt source destination
|
||||
fail2ban-SSH tcp -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:22
|
||||
|
||||
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
|
||||
target prot opt source destination
|
||||
|
||||
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
|
||||
target prot opt source destination
|
||||
|
||||
Chain fail2ban-SSH (1 references)
|
||||
target prot opt source destination
|
||||
DROP all -- 192.168.1.8 0.0.0.0/0
|
||||
RETURN all -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to unblock the IP address from fail2ban, you can also use iptables command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -D fail2ban-SSH -s 192.168.1.8 -j DROP
|
||||
|
||||
While you can check and manage fail2ban's IP blocklist manually with iptables command like above, a proper way is in fact to use fail2ban-client command-line tool. This tool allows you to manage not only "ssh-iptables" jail, but also any other types of fail2ban jails in a unified command-line interface.
|
||||
|
||||
To check fail2ban status (which will show a list of currently active jails):
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo fail2ban-client status
|
||||
|
||||
To check the status of a particular jail (e.g., ssh-iptables):
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo fail2ban-client status ssh-iptables
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will show a list of banned IP addresses.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To unban a particular IP address:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo fail2ban-client set ssh-iptables unbanip 192.168.1.8
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Note that if you stop fail2ban, all blocked IP addresses will be unblocked. When you restart fail2ban, it will find a list of offending IP addresses from /var/log/secure (or /var/log/auth.log), and re-ban those IP addresses if the elapsed time of the offenses are still within ban time.
|
||||
|
||||
### Set Fail2ban to Auto-start on Boot
|
||||
|
||||
Once you haved tested fail2ban successfully, the last step is to enable fail2ban to launch automatically upon powering on your server. On Debian-based distributions, fail2ban auto-start is enabled by default. On Red Hat-based distributions, enable auto-start as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
On CentOS/RHEL 6:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chkconfig fail2ban on
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora or CentOS/RHEL 7:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl enable fail2ban
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I demonstrated how to install and configure fail2ban to protect an SSH server. While fail2ban can mitigate brute-force password guessing attacks, please note that it cannot protect SSH servers against sophisticated distributed brute-force campaigns, where an attacker bypasses fail2ban by using many thousands of bot-controlled IP addresses.
|
||||
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/tools/linux-compress-decompress-tools/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-force-ssh-login-via-public-key-authentication.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/two-factor-authentication-ssh-login-linux.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.fail2ban.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
@ -1,120 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by FSSlc
|
||||
|
||||
Undelete Files on Linux Systems
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Often times, a computer user will delete a needed file accidentally and not have an easy way to regain or recreate the file. Thankfully, files can be undeleted. When a user deletes a file, it is not gone, only hidden for some time. Here is how it all works. On a filesystem, the system has what is called a file allocation list. This list keeps track of what files are where on the storage unit (hard-drive, MicroSD card, flash-drive, etc.). When a file is deleted, the filesystem will perform one of two tasks on the allocation table. The file's entry on the file allocation table marked as "free space" or the file's entry on the list is erased and then the space is marked as free. Now, if a file needs to be placed on the storage unit, the operating system will put the file in the space marked as empty. After the new file is written to the "empty space", the deleted file is now gone forever. When a deleted file is to be recovered, the user must not manipulate any files because if the "empty space" is used, then the file can never be retrieved.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do undelete programs work? ###
|
||||
|
||||
The majority of filesystems only mark the space as empty. With these filesystems, the undelete program looks at the file allocation list and copies the deleted file to another storage unit. If the files were copied to the same storage unit, then the user could lose other deleted files that are needed.
|
||||
|
||||
Rarely do filesystems erase the allocation table entry. If a filesystem does, this is how an undelete program undeletes the file. The program searches the storage unit for file headers. All files have a specific string of code that is at the very beginning of the file. This is called a magic number. For example, the magic number of a compiled JAVA class is the hex number "CAFEBABE". So, an undelete program would find "CAFEBABE" and copy that file to another storage unit. Some undelete programs can look for a specific file type. The user may want a PDF, so the program searches for the hex magic number "25504446" which is the ASCII code for "%PDF". Other undelete programs search for all magic numbers. Then, the user can select which deleted files to recover.
|
||||
|
||||
If a part of the file has been written over, then the whole file will be corrupted. The file can usually be recovered, but the contents will be useless. For instance, recovering a corrupted JPEG file will be pointless because the image viewer will not be able to generate an image from the file. So, the user has the file, but the file is useless.
|
||||
|
||||
### Device Locations: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Before we continue, here is some information that will aid in directing the undelete utilities to the correct storage unit. All devices are in the /dev/ folder. The name of each device (not the name that the admin gave each partition or device) that is given by the system follows a predictable scheme. The second partition on the first SATA hard-drive would be sda2. The first letter indicates the storage type, in this case SATA, but an "s" could also mean SCSI, FireWire, or USB. The second letter "d" means disk. The third letter indicates the device number, so an "a" would be the first SATA and a "b" would be the second. The number displays the partition. To name the whole device with all partitions type the letters without the number. For this example that would be sda. Other possible letters "h" as the first letter. This means PATA hard-drive (IDE). As some examples of this scheme, a user has a computer with one SATA hard-drive (sda). The drive has four partitions - sda1, sda2, sda3, and sda4. The user deletes the third one, but sda4 remains sda4 until sda4 is reformatted. The user then plugs in a usb memory card (sdb) with one partition - sdb1. The user then adds a IDE hard-drive with one partition - hda1. Next, the user adds a SCSI hard-drive - sdc1. Then, the user removes the USB memory card (sdb). Now, the SCSI remains sdc, but if the SCSI is removed and added back, it will be sdb. Even though other storage device existed, the IDE drive will have the "a" because it is the first IDE drive. IDE devices are numbered separately from SCSI, SATA, FireWire, and USB devices.
|
||||
|
||||
### Recovery: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Each undelete program has different abilities, features, and support for various filesystems. Below are some instructions for using TestDisk to recover files on a set of filesystems.
|
||||
|
||||
**FAT16, FAT32, exFAT (FAT64), NTFS, and ext2/3/4:**
|
||||
|
||||
TestDisk is an open-source, free program that works on Linux, *BSD, SunOS, Mac OS X, DOS, and Windows. TestDisk can be found here: [http://www.cgsecurity.org/wiki/TestDisk][1]. TestDisk can also be installed by typing "sudo apt-get install testdisk". TestDisk has many abilities, but this article is concerned with undeleting files.
|
||||
|
||||
Open TestDisk in a terminal using root privileges by typing “sudo testdisk”.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, the TestDisk command-line application will execute. The terminal appearance will change. TestDisk asks the user if it can keep logs. This is entirely up to the user. If the user is recovering files from the system storage, then do not keep a log. The choices are "Create", "Append", and "No Log". If the user wants a log, it is kept in that user's home folder.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the following screen, the storage devices are listed using the /dev/* method. For my system, the system's storage unit is /dev/sda. This means that my storage unit is a SATA hard-drive (sd) and it is the first hard-drive (a). The size of each storage unit is displayed in Gigabytes. Use the up and down arrows to select a storage device and hit enter.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The next screen displays a list of partition table (also called partition map) types. Just as there is the file allocation table for files, there is a table for the partitions. Partitions are dividers on a storage device. For instance, on almost all Linux systems there is at least two partitions - EXT3/4 and Swap. Each partition table will be briefly described. TestDisk does not support all partition tables, so this is not a complete list.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **Intel** - This partition table is very common on Windows systems and many Linux systems. This table is also know as MBR.
|
||||
- **EFI GPT** - This is usually used with Linux systems. This partition map is most recommended for Linux because the concept of logical/extended partitions does not apply to GPT (GUID Partition Table) tables. This means that a Linux user can multiboot many forms of Linux with one Linux OS on each partition. There are other advantages to using GPT, but that is beyond this article.
|
||||
- **Humax** - Humax maps are used with device made by the South Korean company Humax.
|
||||
- **Mac** - The Apple Partition Map (APM) is used by Apple devices.
|
||||
- **None** - Some devices do not have a partition table. For instance, many Subor game consoles do not use a partition map. If a user tried to undelete a file on these devices thinking that the partition map was one of the other choices, the user will be confused by the fact that TestDisk does not find any filesystem or files.
|
||||
- **Sun** - The Sun partition table is used by Sun systems.
|
||||
- **Xbox** - The Xbox uses the Xbox partition map for its storage devices.
|
||||
|
||||
If a user selects "Xbox" even though their system uses GPT, TestDisk will not be able to find a partition or filesystem. If it does, then it will guess incorrectly. (The image below displays the output when the incorrect partition type)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once the user picks the correct choice for their device, on the next screen, select "Advanced".
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, the user should see a list of all of their filesystems/partitions on the storage unit. If the user had chosen the wrong partition map, then here is where they will know if they made the incorrect selection. If there are no errors, highlight the partition that contains the deleted file by placing the text-based cursor on it. Use the left and right arrows to highlight "List" on the bottom of the terminal. Now, hit enter.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
A new screen is displayed with a list of files and folders. The whitish files are current files that are not deleted. The red files have been deleted. On the far right column is the files' names. The next column over to the left is the creation date of the file. One column over to the left again is the files' sizes in bytes. To the far left is a column with dashes, "d"s, "r"s, "w"s, and "x"s. These are the file permissions. A "d" indicates that the item is a directory. The rest of the permission syntax is irrelevant to this article. The item on the top of the file list titled "." means the current directory. The second object titled ".." means go up one directory, so a user can move up a directory by selecting this line. For an example, I will go into the directory "Xaiml_Dataset". The folder is nearly full of deleted files. I will undelete "computers.xaiml" by pressing "c" on the keyboard. I am now asked to select a destination directory. Of course, I will put it on another partition. I am in my home folder, and I press "c". It does not matter what folder is highlighted. The current folder is the destination directory. Now, I am back to the list of files. At the top of the screen is a message that says "Copy Done!". In my home folder is a folder called "Xaiml_Dataset", and inside is the Xaiml file. If I press "c" on more deleted files, they will be placed in the new folder without a****g me for a destination.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
When finished press "q" repeatedly until the normal terminal is seen. The folder "Xaiml_Dataset" can only be accessed by the root. To fix this, use root privileges to change the folder permissions and the contained files. After that, the files have been recovered and accessible to the user.
|
||||
|
||||
### ReiserFS: ###
|
||||
|
||||
To undelete a file from a ReiserFS filesystem, make a backup of all of the files on the partition because this method can cause the file to be lost if something goes wrong. Next, execute the following command where DEVICE is the device in the form sda2. Some files will be put in the lost+found directory and other will remain where they were before deletion.
|
||||
|
||||
reiserfsck --rebuild-tree --scan-whole-partition /dev/DEVICE
|
||||
|
||||
### Recover Deleted File that is Open in a Program: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Assume a user accidentally deletes a file that a program has open. The file of the hard-drive was deleted, but the program is using a copy of the file that is on the RAM. Thankfully, there are two easy solutions.
|
||||
|
||||
If the program has save capabilities like a text editor, the user can resave the file. Thus, the file editor will write the file to the hard-drive.
|
||||
|
||||
Assume that this is an MP3 file in a music player. The music player cannot save the MP3 file. This task requires a little more time than the previous situation. Unfortunately, this method does not work on all systems and applications. To begin, type the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
lsof -c smplayer | grep mp3
|
||||
|
||||
This command LiSts all of the Open Files used by Smplayer. This list is piped (given) to grep which searches for mp3. The output looks like the following.
|
||||
|
||||
smplayer 10037 collier mp3 169r 8,1 676376 1704294 /usr/bin/smplayer
|
||||
|
||||
Now, type the following command to recover the file directly from the RAM (on Linux systems, /proc/ is the RAM) and copy it to a folder of choice. The "cp" is the copy command. The 10037 number comes from the process number given in the output. The 169 is the file descriptor shown in the output. The "~/Music/" is the destination directory. Lastly, "music.mp3" is the file name that the user wants for the file.
|
||||
|
||||
cp /proc/10037/fd/169 ~/Music/music.mp3
|
||||
|
||||
### Real Deletion: ###
|
||||
|
||||
To make for sure that a file can never be recovered, use a command that "wipes" the hard-drive. Wiping the hard-drive means writing meaningless data to the disk. For example, many wiping programs write zeros, random letters, or random data to the hard-drive. No space is taken up or lost. The wiping program just overwrites the "empty space". If the storage unit is ever full of files with no free space remaining, then all of the previously deleted files will be gone.
|
||||
|
||||
The purpose of wiping hard-drives is to make sure that private data is never seen. For illustration, a company may order new computers. The manager decides to sell the old computers. However, there is concern that the new owners may view company secrets or customer information like credit card numbers and addresses. Thankfully, a computer technician in the company can wipe the hard-drives before selling the old computers.
|
||||
|
||||
To install secure-delete, a wiping program, type "sudo apt-get install secure-delete". This installs a set of four commands that make sure that deleted files are never recovered.
|
||||
|
||||
- srm - permanently delete a file. Usage: srm -f ./secret_file.txt
|
||||
- sfill - wipe the free space. Usage: sfill -f /mount/point/of/partition
|
||||
- sswap - wipe swap space. Usage: sswap -f /dev/SWAP_DEVICE
|
||||
|
||||
If computers were to truly delete a file selected for deletion, then more time would be required to perform the task. It is quick and easy to mark some space as free, but to make the file gone forever requires time. Wiping a storage unit, for instance, takes a few hours to complete (depending on storage size). Overall, the current system works well because even when a user empties the recycle bin, they still have another chance to change their mind.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/undelete-files-on-linux-systems.4316/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[DevynCJohnson][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linux.org/members/devyncjohnson.4843/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cgsecurity.org/wiki/TestDisk
|
||||
@ -1,156 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by coloka...
|
||||
|
||||
How to configure a syslog server with rsyslog on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A syslog server represents a central log monitoring point on a network, to which all kinds of devices including Linux or Windows servers, routers, switches or any other hosts can send their logs over network. By setting up a syslog server, you can filter and consolidate logs from different hosts and devices into a single location, so that you can view and archive important log messages more easily.
|
||||
|
||||
On most Linux distributions, **rsyslog** is the standard syslog daemon that comes pre-installed. Configured in a client/server architecture, **rsyslog** can play both roles; as a syslog server **rsyslog** can gather logs from other devices, and as a syslog client, **rsyslog** can transmit its internal logs to a remote syslog server.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, we cover how to configure a centralized syslog server using **rsyslog** on Linux. Before we go into the details, it is instructive to go over syslog standard first.
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic of Syslog Standard ###
|
||||
|
||||
When logs are collected with syslog mechanism, three important things must be taken into consideration:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Facility level**: what type of processes to monitor
|
||||
- **Severity (priority) level**: what type of log messages to collect
|
||||
- **Destination**: where to send or record log messages
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take a look at how the configuration is defined in more detail.
|
||||
|
||||
The facility levels define a way to categorize internal system processes. Some of the common standard facilities in Linux are:
|
||||
|
||||
- **auth**: messages related to authentication (login)
|
||||
- **cron**: messages related to scheduled processes or applications
|
||||
- **daemon**: messages related to daemons (internal servers)
|
||||
- **kernel**: messages related to the kernel
|
||||
- **mail**: messages related to internal mail servers
|
||||
- **syslog**: messages related to the syslog daemon itself
|
||||
- **lpr**: messages related to print servers
|
||||
- **local0 - local7**: messages defined by user (local7 is usually used by Cisco and Windows servers)
|
||||
|
||||
The severity (priority) levels are standardized, and defined by using standard abbreviation and an assigned number with number 7 being the highest level of all. These levels are:
|
||||
|
||||
- emerg: Emergency - 0
|
||||
- alert: Alerts - 1
|
||||
- crit: Critical - 2
|
||||
- err: Errors - 3
|
||||
- warn: Warnings - 4
|
||||
- notice: Notification - 5
|
||||
- info: Information - 6
|
||||
- debug: Debugging - 7
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, the destination statement enforces a syslog client to perform one of three following tasks: (1) save log messages on a local file, (2) route them to a remote syslog server over TCP/UDP, or (3) send them to stdout such as a console.
|
||||
|
||||
In rsyslog, syslog configuration is structured based on the following schema.
|
||||
|
||||
[facility-level].[severity-level] [destination]
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure Rsyslog on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we understand syslog, it's time to configure a Linux server as a central syslog server using rsyslog. We will also see how to configure a Windows based system as a syslog client to send internal logs to the syslog server.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step One: Initial System Requirements ####
|
||||
|
||||
To set up a Linux host as a central log server, we need to create a separate /var partition, and allocate a large enough disk size or create a LVM special volume group. That way, the syslog server will be able to sustain the exponential growth of collected logs over time.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Two: Enable Rsyslog Daemon ####
|
||||
|
||||
rsyslog daemon comes pre-installed on modern Linux distributions, but is not enabled by default. To enable rsyslog daemon to receive external messages, edit its configuration file located in /etc/rsyslog.conf.
|
||||
|
||||
Once the file is opened for editing, search and uncomment the below two lines by removing the # sign from the beginning of lines.
|
||||
|
||||
$ModLoad imudp
|
||||
$UDPServerRun 514
|
||||
|
||||
This will enable rsyslog daemon to receive log messages on UDP port 514. UDP is way faster than TCP, but does not provide reliability on data flow the same way as TCP does. If you need to reliable delivery, you can enable TCP by uncommenting the following lines.
|
||||
|
||||
$ModLoad imtcp
|
||||
$InputTCPServerRun 514
|
||||
|
||||
Note that both TCP and UDP can be set on the server simultaneously to listen on TCP/UDP connections.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Three: Create a Template for Log Receipt ####
|
||||
|
||||
In the next step we need to create a template for remote messages, and tell rsyslog daemon how to record messages received from other client machines.
|
||||
|
||||
Open /etc/rsyslog.conf with a text editor, and append the following template before the GLOBAL DIRECTIVES block:
|
||||
|
||||
$template RemoteLogs,"/var/log/%HOSTNAME%/%PROGRAMNAME%.log" *
|
||||
*.* ?RemoteLogs
|
||||
& ~
|
||||
|
||||
This template needs a little explanation. The $template RemoteLogs directive ("RemoteLogs" string can be changed to any other descriptive name) forces rsyslog daemon to write log messages to separate local log files in /var/log/, where log file names are defined based on the hostname of the remote sending machine as well as the remote application that generated the logs. The second line ("*.* ?RemoteLogs") implies that we apply RemoteLogs template to all received logs.
|
||||
|
||||
The "& ~" sign represents a redirect rule, and is used to tell rsyslog daemon to stop processing log messages further, and not write them locally. If this redirection is not used, all the remote messages would be also written on local log files besides the log files described above, which means they would practically be written twice. Another consequence of using this rule is that the syslog server's own log messages would only be written to dedicated files named after machine's hostname.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want, you can direct log messages with a specific facility or severity level to this new template using the following schema.
|
||||
|
||||
[facility-level].[severity-level] ?RemoteLogs
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
Direct all internal authentication messages of all priority levels to RemoteLogs template:
|
||||
|
||||
authpriv.* ?RemoteLogs
|
||||
|
||||
Direct informational messages generated by all system processes, except mail, authentication and cron messages to RemoteLogs template:
|
||||
|
||||
*.info,mail.none,authpriv.none,cron.none ?RemoteLogs
|
||||
|
||||
If we want all received messages from remote clients written to a single file named after their IP address, you can use the following template. We assign a new name "IpTemplate" to this template.
|
||||
|
||||
$template IpTemplate,"/var/log/%FROMHOST-IP%.log"
|
||||
*.* ?IpTemplate
|
||||
& ~
|
||||
|
||||
After we have enabled rsyslog daemon and edited its configuration file, we need to restart the daemon.
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, Ubuntu or CentOS/RHEL 6:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service rsyslog restart
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora or CentOS/RHEL 7:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart rsyslog
|
||||
|
||||
We can verify that rsyslog daemon is functional by using netstat command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo netstat -tulpn | grep rsyslog
|
||||
|
||||
The output should look like the following in case rsyslog daemon listens on UDP port.
|
||||
|
||||
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:514 0.0.0.0:* 551/rsyslogd
|
||||
udp6 0 0 :::514 :::* 551/rsyslogd
|
||||
|
||||
If rsyslog daemon is set up to listen on TCP connections, the output should look like this.
|
||||
|
||||
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:514 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1891/rsyslogd
|
||||
tcp6 0 0 :::514 :::* LISTEN 1891/rsyslogd
|
||||
|
||||
#### Send Windows Logs to a Remote Rsyslog Server ####
|
||||
|
||||
To forward a Windows based client's log messages to our rsyslog server, we need a Windows syslog agent. While there are a multitude of syslog agents that can run on Windows, we can use [Datagram SyslogAgent][1], which is a freeware program.
|
||||
|
||||
After downloading and installing the syslog agent, we need to configure it to run as a service. Specify the protocol though which it will send data, the IP address and port of a remote rsyslog server, and what type of event logs should be transmitted as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
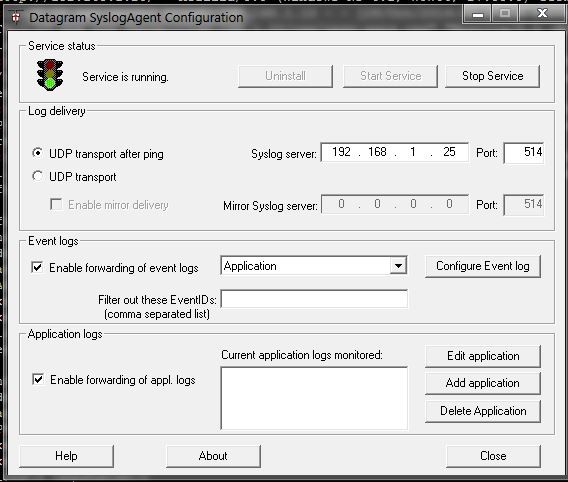
|
||||
|
||||
After we have set up all the configurations, we can start the service and watch the log files on the central rsyslog server using tailf command line utility.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
By creating a central rsyslog server that can collect log files of local or remote hosts, we can get a better idea on what is going on internally in their systems, and can debug their problems more easily should any of them become unresponsive or crash.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/configure-syslog-server-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Caezsar M][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/caezsar
|
||||
[1]:http://www.syslogserver.com/download.html
|
||||
@ -1,126 +0,0 @@
|
||||
ideas4u is translating!
|
||||
4 Steps to Setup Local Repository in Ubuntu using APT-mirror
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Today we will show you how to setup a local repository in your Ubuntu PC or Ubuntu Server straight from the official Ubuntu repository. There are a lot benefit of creating a local repository in your computer if you have a lot of computers to install software, security updates and fixes often in all systems, then having a local Ubuntu repository is an efficient way. Because all required packages are downloaded over the fast LAN connection from your local server, so that it will save your Internet bandwidth and reduces the annual cost of Internet..
|
||||
|
||||
You can setup a local repository of Ubuntu in your local PC or server using many tools, but we'll featuring about APT-Mirror in this tutorial. Here, we'll be mirroring packages from the default mirror to our Local Server or PC and we'll need at least **120 GB** or more free space in your local or external hard drive. It can be configured through a **HTTP** or **FTP** server to share its software packages with local system clients.
|
||||
|
||||
We'll need to install Apache Web Server and APT-Mirror to get our stuffs working out of the box. Here are the steps below to configure a working local repository:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Installing Required Packages ###
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, we are going to pull whole packages from the public repository of Ubuntu package server and save them in our local Ubuntu server hard disk.
|
||||
|
||||
We'll first install a web server to host our local repository. We'll install Apache web server but you can install any web server you wish, web server are necessary for the http protocol. You can additionally install FTP servers like proftpd, vsftpd,etc if you need to configure for ftp protocols and Rsync for rsync protocols.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install apache2
|
||||
|
||||
And then we'll need to install apt-mirror:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install apt-mirror
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Note: As I have already mentioned that we'll need at least 120 GBs free space to get all the packages mirrored or download.**
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Configuring APT-Mirror ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now create a directory on your harddisk to save all packages. For example, let us create a directory called “/linoxide”. We are going to save all packages in this directory:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir /linoxide
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, open the file **/etc/apt/mirror.list** file
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /etc/apt/mirror.list
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Copy the below lines of configuration to mirror.list and edit as your requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
############# config ##################
|
||||
#
|
||||
set base_path /linoxide
|
||||
#
|
||||
# set mirror_path $base_path/mirror
|
||||
# set skel_path $base_path/skel
|
||||
# set var_path $base_path/var
|
||||
# set cleanscript $var_path/clean.sh
|
||||
# set defaultarch <running host architecture>
|
||||
# set postmirror_script $var_path/postmirror.sh
|
||||
# set run_postmirror 0
|
||||
set nthreads 20
|
||||
set _tilde 0
|
||||
#
|
||||
############# end config ##############
|
||||
|
||||
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-security main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-updates main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
#deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
#deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-backports main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
|
||||
deb-src http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
deb-src http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-security main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
deb-src http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-updates main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
#deb-src http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
#deb-src http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-backports main restricted universe multiverse
|
||||
|
||||
clean http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Note: You can replace the above official mirror server url by the nearest one, you can get your nearest server by visiting the page [Ubuntu Mirror Server][1]. If you are not in hurry and can wait for the mirroring, you can go with the default official one.**
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we are going to mirror package repository of the latest and greatest LTS release of Ubuntu ie. Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (Trusty Tahr) so, we have configured trusty. If you need to mirror of Saucy or other version of Ubuntu, please edit it as its codename.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll have to run apt-mirror which will now get/mirror all the packages in the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-mirror
|
||||
|
||||
It will take time to download all the packages from the Ubuntu Server which depends upon the connection speed and performance with respect to you and the mirror server. I have interrupted the download as I have already done that...
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3.Configuring Web Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
To be able to access the repo from other computers you need a webserver. You can also do it via ftp but I choose to use a webserver as I mentioned in above step 1. So, we are now gonna configure Apache Server:
|
||||
|
||||
We will create a symlink from our local repo's directory to a directory ubuntu in the hosting directory of Apache ie /var/www/ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ln -s /linoxide /var/www/ubuntu
|
||||
$ sudo service apache2 start
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The above command will allow us to browse our Mirrored Repo from our localhost ie http://127.0.0.1 by default.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Configuring Client Side ###
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, we need to add repository source in other computers which will fetch the packages and repository from our computer. To do that, we'll need to edit /etc/apt/sources.list and add the following lines.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list
|
||||
|
||||
Add this line in /etc/apt/sources.list and save.
|
||||
|
||||
deb http://192.168.0.100/ubuntu/ trusty main restricted universe
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: here 192.168.0.100 is the LAN IP address of our server computer, you need to replace that with yours.**
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, we are done. Now you can install the required packages using sudo apt-get install packagename from your local Ubuntu repository with high speed download and with low bandwidth.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/setup-local-repository-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+archivemirrors
|
||||
@ -1,134 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to set up a cross-platform backup server on Linux with BackupPC
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Just in case you haven't been able to tell from my earlier posts on [backupninja][1] and [backup-manager][2], I am a big backup fan. When it comes to backup, I'd rather have too much than not enough, because if the need arises, you will be grateful that you took the time and effort to generate extra copies of your important data.
|
||||
|
||||
In this post, I will introduce you to [BackupPC][3], a cross-platform backup server software which can perform pull backup of Linux, Windows and MacOS client hosts over network. BackupPC adds a number of features that make managing backups an almost fun thing to do.
|
||||
|
||||
### Features of BackupPC ###
|
||||
|
||||
BackupPC comes with a robust web interface that allows you to collect and manage backups of other remote client hosts in a centralized fashion. Using the web interface, you can examine logs and configuration files, start/cancel/schedule backups of other remote hosts, and visualize current status of backup tasks. You can also browse through archived files and restore individual files or entire jobs from backup archives very easily. To restore individual single files, you can download them from any previous backup directly from the web interface. As if this weren't enough, no special client-side software is needed for client hosts. On Windows clients, the native SMB protocol is used, whereas on *nix clients, you will use `rsync` or tar over SSH, RSH or NFS.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing BackupPC ###
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, Ubuntu and their derivatives, run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# aptitude install backuppc
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora, use `yum` command. Note the case sensitive package name.
|
||||
|
||||
On CentOS/RHEL 6, first enable [EPEL repository][4]. On CentOS/RHEL 7, enable [Nux Dextop][5] repository instead. Then go ahead with `yum` command:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install BackupPC
|
||||
|
||||
As usual, both package management systems will take care of dependency resolution automatically. In addition, as part of the installation process, you may be asked to configure, or reconfigure the web server that will be used for the graphical user interface. The following screenshot is from a Debian system:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Select your choice by pressing the space bar, and then move to Ok with the tab key and hit ENTER.
|
||||
|
||||
You will then be presented with the following screen informing you that an administrative user account 'backuppc', along with its corresponding password (which can be changed later if desired), has been created to manage BackupPC. Note that both a HTTP user account and a regular Linux account of the same name 'backuppc' will be created with an identical password. The former is needed to access BackupPC's protected web interface, while the latter is needed to perform backup using rsync over SSH.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You can change the default password for the HTTP user 'backuppc' with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# htpasswd /path/to/hash/file backuppc
|
||||
|
||||
As for a regular 'backuppc' [Linux][6] user account, use passwd command to change its default password.
|
||||
|
||||
# passwd backuppc
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the installation process creates the web and the program's configuration files automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
### Launching BackupPC and Configuring Backups ###
|
||||
|
||||
To start, open a browser window and point to http://<server's FQDN or IP address>/backuppc/. When prompted, enter the default HTTP user credentials that were supplied to you earlier. If the authentication succeeds, you will be taken to the main page of the web interface.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Most likely the first thing that you will want to do is add a new client host to back up. Go to "Edit Hosts" in the Task pane. We will add two client hosts:
|
||||
|
||||
- Host #1: CentOS 7 [IP 192.168.0.17]
|
||||
- Host #2: Windows 7 [IP 192.168.0.103]
|
||||
|
||||
We will back up the CentOS host using rsync over SSH and the Windows host using SMB. Prior to performing the backup, we need to set up [key-based authentication][7] to our CentOS host and a shared folder in our Windows machine.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the instructions for setting up key-based authentication for a remote CentOS host. We create the 'backuppc' user's RSA key pair, and transfer its public key to the root account of the CentOS host.
|
||||
|
||||
# usermod -s /bin/bash backuppc
|
||||
# su - backuppc
|
||||
# ssh-keygen -t rsa
|
||||
# ssh-copy-id root@192.168.0.17
|
||||
|
||||
When prompted, type yes and enter root's password for 192.168.0.17.
|
||||
|
||||
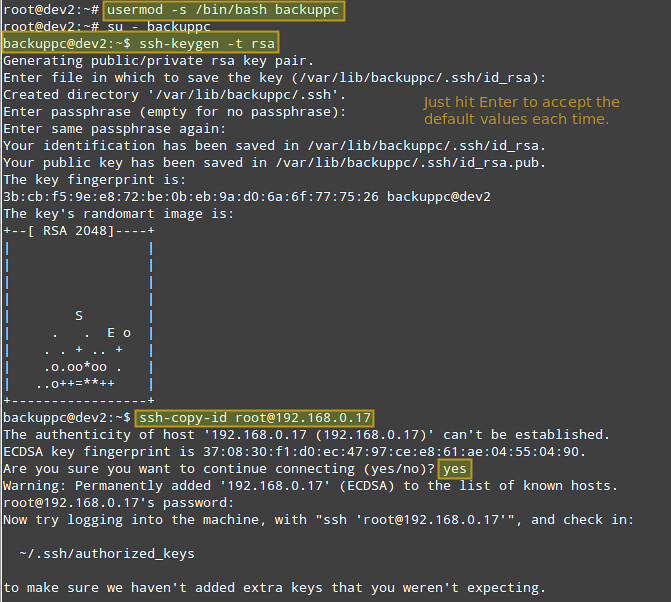
|
||||
|
||||
You will need root access for a remote CentOS host to grant write access to all its file system in case of restoring a backup of files or directories owned by root.
|
||||
|
||||
Once the CentOS and Windows hosts are ready, add them to BackupPC using the web interface:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The next step consists of modifying each host's backup settings:
|
||||
|
||||
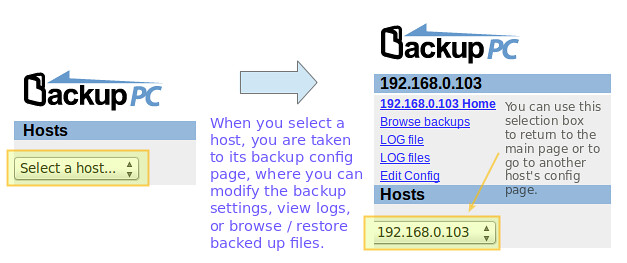
|
||||
|
||||
The following image shows the configuration for the backup of the Windows machine:
|
||||
|
||||
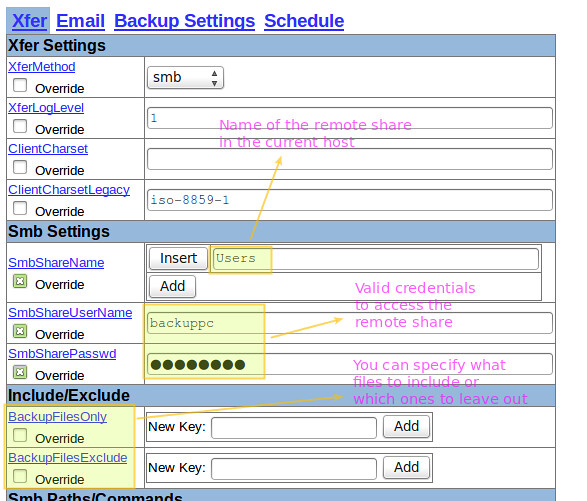
|
||||
|
||||
And the following screenshot shows the settings for the backup of the CentOS box:
|
||||
|
||||
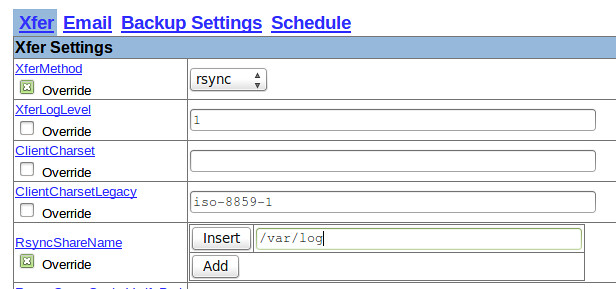
|
||||
|
||||
### Starting a Backup ###
|
||||
|
||||
To start each backup, go to each host's settings, and then click "Start Full Backup":
|
||||
|
||||
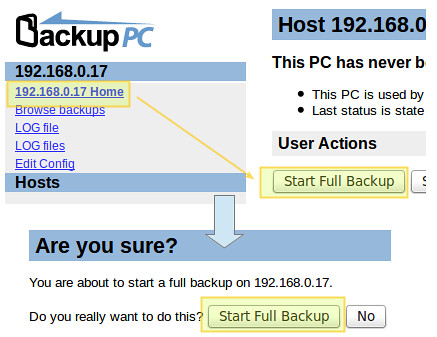
|
||||
|
||||
At any time, you can view the status of the process by clicking on the host's home as shown in the image above. If it fails for some reason, a link to a page with the error message(s) will appear in the host menu as well. When a backup completes successfully, a directory with the host's name or IP address is created under /var/lib/backuppc/pc in the server:
|
||||
|
||||
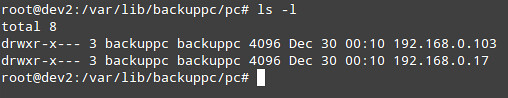
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to browse those directories for the files from the command line, but there is an easier way to look for those files and restore them.
|
||||
|
||||
### Restoring Backup ###
|
||||
|
||||
To view the files that have been saved, go to "Browse backups" under each host's main menu. You can visualize the directories and files at a glance, and select those that you want to restore. Alternatively, you can click on files to open them with the default program, or right click and choose Save link as to download it to the machine where you're working at the time:
|
||||
|
||||
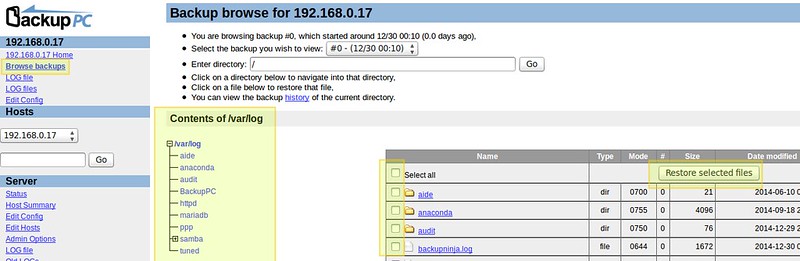
|
||||
|
||||
If you want, you can download a zip or tar file containing the backup's contents:
|
||||
|
||||
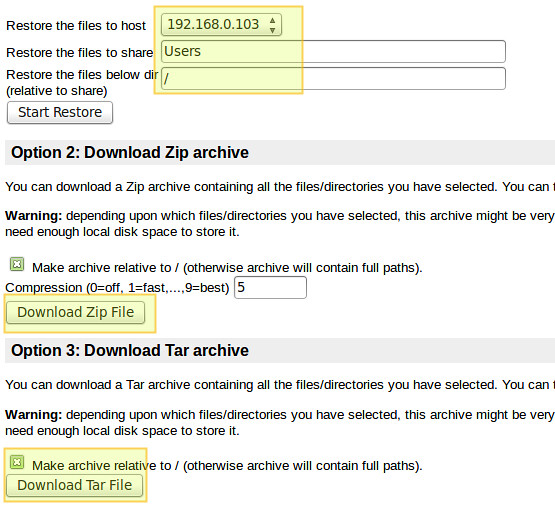
|
||||
|
||||
or just restore the file(s):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
There is a saying that goes, "the simpler, the better", and that is just what BackupPC has to offer. In BackupPC, you will not only find a backup tool but also a very versatile interface to manage your backups of several operating systems without needing any client-side application. I believe that's more than reason enough for you to give it at least a try.
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to leave your comments and questions, if you have any, using the form below. I am always happy to hear what readers have to say!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/backuppc-cross-platform-backup-server-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/gabriel
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/backup-debian-system-backupninja.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/linux-backup-manager.html
|
||||
[3]:http://backuppc.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[5]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/enable-nux-dextop-repository-centos-rhel.html
|
||||
[6]:http://xmodulo.com/recommend/linuxguide
|
||||
[7]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-enable-ssh-login-without.html
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
translating by coloka
|
||||
What are useful command-line network monitors on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Network monitoring is a critical IT function for businesses of all sizes. The goal of network monitoring can vary. For example, the monitoring activity can be part of long-term network provisioning, security protection, performance troubleshooting, network usage accounting, and so on. Depending on its goal, network monitoring is done in many different ways, such as performing packet-level sniffing, collecting flow-level statistics, actively injecting probes into the network, parsing server logs, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
theo-l translating
|
||||
How to Monitor Network Usage with nload in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
nload is a free linux utility that can help the linux user or sysadmin to monitor network traffic and bandwidth usage in real time by providing two simple graphs: one per incoming traffic and one for outgoing traffic.
|
||||
@ -203,4 +204,4 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/monitor-network-usage-nload/
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/oltjano/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.roland-riegel.de/nload/nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||
[1]:http://www.roland-riegel.de/nload/nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to apply image effects to pictures on Raspberry Pi
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Like a common pocket camera which has a built-in function to add various effects on captured photos, [Raspberry Pi camera board][1] ("raspi cam") can actually do the same. With the help of raspistill camera control options, we can add the image effects function like we have in a pocket camera.
|
||||
|
||||
There are [three comman-line applications][2] which can be utilized for [taking videos or pictures][3] with raspi cam, and one of them is the raspistill application. The raspistill tool offers various camera control options such as sharpness, contrast, brightness, saturation, ISO, exposure, automatic white balance (AWB), image effects.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article I will show how to apply exposure, AWB, and other image effects with raspistill while capturing pictures using raspi cam. To automate the process, I wrote a simple Python script which takes pictures and automatically applies a series of image effects to the pictures. The raspi cam documentation describes available types of the exposure, AWB, and image effects. In total, the raspi cam offers 16 types of image effects, 12 types of exposure, and 10 types of AWB values.
|
||||
|
||||
The simple Python script looks like the following.
|
||||
|
||||
#!/usb/bin/python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
list_ex=['auto','night']
|
||||
list_awb=['auto','cloud',flash']
|
||||
list_ifx=['blur','cartoon','colourswap','emboss','film','gpen','hatch','negative','oilpaint','posterise','sketch','solarise','watercolour']
|
||||
x=0
|
||||
for ex in list_ex:
|
||||
for awb in list_awb:
|
||||
for ifx in list_ifx:
|
||||
x=x+1
|
||||
filename='img_'+ex+'_'+awb+'_'+ifx+'.jpg'
|
||||
cmd='raspistill -o '+filename+' -n -t 1000 -ex '+ex+' -awb '+awb+' -ifx '+ifx+' -w 640 -h 480'
|
||||
pid=subprocess.call(cmd,shell=True)
|
||||
print "["+str(x)+"]-"+ex+"_"+awb+"_"+ifx+".jpg"
|
||||
time.sleep(0.25)
|
||||
print "End of image capture"
|
||||
|
||||
The Python script operates as follows. First, create three array/list variable for the exposure, AWB and image effects. In the example, we use 2 types of exposure, 3 types of AWB, and 13 types of image effects values. Then make nested loops for applying the value of the three variables that we have. Inside the nested loop, execute the raspistill application. We specify (1) the output filename; (2) exposure value; (3) AWB value; (4) image effect value; (5) the time to take a photo, which is set to 1 second; and (6) the size of the photo, which is set to 640x480px. This Python script will create 78 different versions of a captured photo with a combination of 2 types of exposure, 3 types of AWB, and 13 types of image effects.
|
||||
|
||||
To execute the Python script, simply type:
|
||||
|
||||
$ python name_of_this_script.py
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the first round of the sample result.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Bonus ###
|
||||
|
||||
For those who are more interested, there is another way to access and control the raspi cam besides raspistill. [Picamera][4] a pure Python interface which provides APIs for accessing and controlling raspi cam, so that one can build a complex program for utilizing raspi cam according to their needs. If you are skilled at Python, picamera is a good feature-complete interface for implementing your raspi cam project. The picamera interface is included by default in the recent image of Raspbian. If your [Raspberry Pi][5] operating system is not new or not Raspbian, you can install it on your system as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
First, install pip on your system by following [this guideline][6].
|
||||
|
||||
Then, install picamera as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo pip install picamera
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the [official documentation][7] on how to use picamera.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/apply-image-effects-pictures-raspberrypi.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kristophorus Hadiono][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/kristophorus
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/go/picam
|
||||
[2]:http://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/usage/camera/raspicam/
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/install-raspberry-pi-camera-board.html
|
||||
[4]:https://pypi.python.org/pypi/picamera
|
||||
[5]:http://xmodulo.com/go/raspberrypi
|
||||
[6]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-pip-linux.html
|
||||
[7]:http://picamera.readthedocs.org/
|
||||
@ -1,113 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by soooogreen
|
||||
Improve system performance by moving your log files to RAM Using Ramlog
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ramlog act as a system daemon. On startup it creates ramdisk, it copies files from /var/log into ramdisk and mounts ramdisk as /var/log. All logs after that will be updated on ramdisk. Logs on harddrive are kept in folder /var/log.hdd which is updated when ramlog is restarted or stopped. On shutdown it saves log files back to harddisk so logs are consistent. Ramlog 2.x is using tmpfs by default, ramfs and kernel ramdisk are suppored as well. Program rsync is used for log synchronization.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Logs not saved to harddrive are lost in case of power outage or kernel panic.
|
||||
|
||||
Install ramlog if you have enough of free memory and you want to keep your logs on ramdisk. It is good for notebook users, for systems with UPS or for systems running from flash -- to save some write cycles.
|
||||
|
||||
How it works and what it does:
|
||||
|
||||
1.Ramlog starts among the first daemons (it depends on other daemons you have installed).
|
||||
|
||||
2.Directory /var/log.hdd is created and hardlinked to /var/log.
|
||||
|
||||
3.In case tmpfs (default) or ramfs is used, it is mounted over /var/log
|
||||
|
||||
If kernel ramdisk is used, ramdisk created in /dev/ram9 and it is mounted to /var/log, by default ramlog takes all ramdisk memory specified by kernel argument "ramdisk_size".
|
||||
|
||||
5.All other daemons are started and all logs are updated in ramdisk. Logrotate works on ramdisk as well.
|
||||
|
||||
6.In case ramlog is restarted (by default it is one time per day), directory /var/log.hdd is synchronized with /var/log using rsync. Frequency of the automatic log saves can be controller via cron, by default, the ramlog file is placed into /etc/cron.daily
|
||||
|
||||
7.On shutdown ramlog shuts among the last daemons.
|
||||
|
||||
8. During ramlog stop phase files from /var/log.hdd are synchronized with /var/log
|
||||
Then /var/log is unmounted, /var/log.hdd is unmounted as well and empty directory /var/log.hdd is deleted.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:- This article is for advanced users only**
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Ramlog in Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
First you need to download the .deb package from [here][1] using the following command
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://www.tremende.com/ramlog/download/ramlog_2.0.0_all.deb
|
||||
|
||||
Now you should be having ramlog_2.0.0_all.deb package install this package using the following command
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg -i ramlog_2.0.0_all.deb
|
||||
|
||||
This will complete the installation now you need to run the following commands
|
||||
|
||||
sudo update-rc.d ramlog start 2 2 3 4 5 . stop 99 0 1 6 .
|
||||
|
||||
#Now update sysklogd in init levels, so it is stopped properly before ramlog is stopped:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo update-rc.d -f sysklogd remove
|
||||
|
||||
sudo update-rc.d sysklogd start 10 2 3 4 5 . stop 90 0 1 6 .
|
||||
|
||||
Now you need to restart your system
|
||||
|
||||
sudo reboot
|
||||
|
||||
After rebooting you need to run ‘ramlog getlogsize' to determine the size of your actual /var/log.Add about 40% to that number to ensure your ramdisk has sufficient size -- this will be the ramdisk size
|
||||
|
||||
Edit your boot manager config file such as /etc/grub.conf, /boot/grub/menu.lst or /etc/lilo.conf and add update the actual kernel by adding kernel paramter ‘ramdisk_size=xxx' where xxx is calculated ramdisk size
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuring Ramlog ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ramlog configuration file is located in /etc/default/ramlog on deb based systems and you can set there below variables:
|
||||
|
||||
Variable (with default value):
|
||||
|
||||
Description:
|
||||
|
||||
RAMDISKTYPE=0
|
||||
# Values:
|
||||
# 0 -- tmpfs (can be swapped) -- default
|
||||
# 1 -- ramfs (no max size in older kernels,
|
||||
# cannot be swapped, not SELinux friendly)
|
||||
# 2 -- old kernel ramdisk
|
||||
TMPFS_RAMFS_SIZE=
|
||||
#Maximum size of memory to be used by tmpfs or ramfs.
|
||||
# The value can be percentage of total RAM or size in megabytes -- for example:
|
||||
# TMPFS_RAMFS_SIZE=40%
|
||||
# TMPFS_RAMFS_SIZE=100m
|
||||
# Empty value means default tmpfs/ramfs size which is 50% of total RAM.
|
||||
# For more options please check ‘man mount', section ‘Mount options for tmpfs'
|
||||
# (btw -- ramfs supports size limit in newer kernels
|
||||
# as well despite man says there are no mount options)
|
||||
# It has only effect if RAMDISKTYPE=0 or 1
|
||||
KERNEL_RAMDISK_SIZE=MAX
|
||||
#Kernel ramdisk size in kilobytes or MAX to use entire ramdisk.
|
||||
#It has only effect if RAMDISKTYPE=2
|
||||
LOGGING=1
|
||||
# 0=off, 1=on Logs can be found in /var/log/ramdisk
|
||||
LOGNAME=ramlog
|
||||
# name of the ramlog log file (makes sense if LOGGING=1)
|
||||
VERBOSE=1
|
||||
# 0=off, 1=on (if 1, teststartstop puts detials
|
||||
# to the logs and it is called after start or stop fails)
|
||||
|
||||
### How to uninstall Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
Open the terminal and run the following command
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg -P ramlog
|
||||
|
||||
Note: If ramlog was running before you uninstalled it, you should reboot your box to finish uninstallation procedure.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/improve-system-performance-by-moving-your-log-files-to-ram-using-ramlog.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ruchi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tremende.com/ramlog/download/ramlog_2.0.0_all.deb
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user