mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-13 22:30:37 +08:00
Merge pull request #10465 from HankChow/master
翻译完成 20180823 How To Easily And Safely Manage Cron Jobs In Linux
This commit is contained in:
commit
f0ea26b8aa
@ -1,133 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
HankChow translating
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
How To Easily And Safely Manage Cron Jobs In Linux
|
|
||||||
======
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
When it comes to schedule tasks in Linux, which utility comes to your mind first? Yeah, you guessed it right. **Cron!** The cron utility helps you to schedule commands/tasks at specific time in Unix-like operating systems. We already published a [**beginners guides to Cron jobs**][1]. I have a few years experience in Linux, so setting up cron jobs is no big deal for me. But, it is not piece of cake for newbies. The noobs may unknowingly do small mistakes while editing plain text crontab and bring down all cron jobs. Just in case, if you think you might mess up with your cron jobs, there is a good alternative way. Say hello to **Crontab UI** , a web-based tool to easily and safely manage cron jobs in Unix-like operating systems.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You don’t need to manually edit the crontab file to create, delete and manage cron jobs. Everything can be done via a web browser with a couple mouse clicks. Crontab UI allows you to easily create, edit, pause, delete, backup cron jobs, and even import, export and deploy jobs on other machines without much hassle. Error log, mailing and hooks support also possible. It is free, open source and written using NodeJS.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Installing Crontab UI
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Installing Crontab UI is just a one-liner command. Make sure you have installed NPM. If you haven’t install npm yet, refer the following link.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Next, run the following command to install Crontab UI.
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
$ npm install -g crontab-ui
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
It’s that simple. Let us go ahead and see how to manage cron jobs using Crontab UI.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Easily And Safely Manage Cron Jobs In Linux
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To launch Crontab UI, simply run:
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
$ crontab-ui
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You will see the following output:
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
Node version: 10.8.0
|
|
||||||
Crontab UI is running at http://127.0.0.1:8000
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now, open your web browser and navigate to **<http://127.0.0.1:8000>**. Make sure the port no 8000 is allowed in your firewall/router.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Please note that you can only access Crontab UI web dashboard within the local system itself.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If you want to run Crontab UI with your system’s IP and custom port (so you can access it from any remote system in the network), use the following command instead:
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
$ HOST=0.0.0.0 PORT=9000 crontab-ui
|
|
||||||
Node version: 10.8.0
|
|
||||||
Crontab UI is running at http://0.0.0.0:9000
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now, Crontab UI can be accessed from the any system in the nework using URL – **http:// <IP-Address>:9000**.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
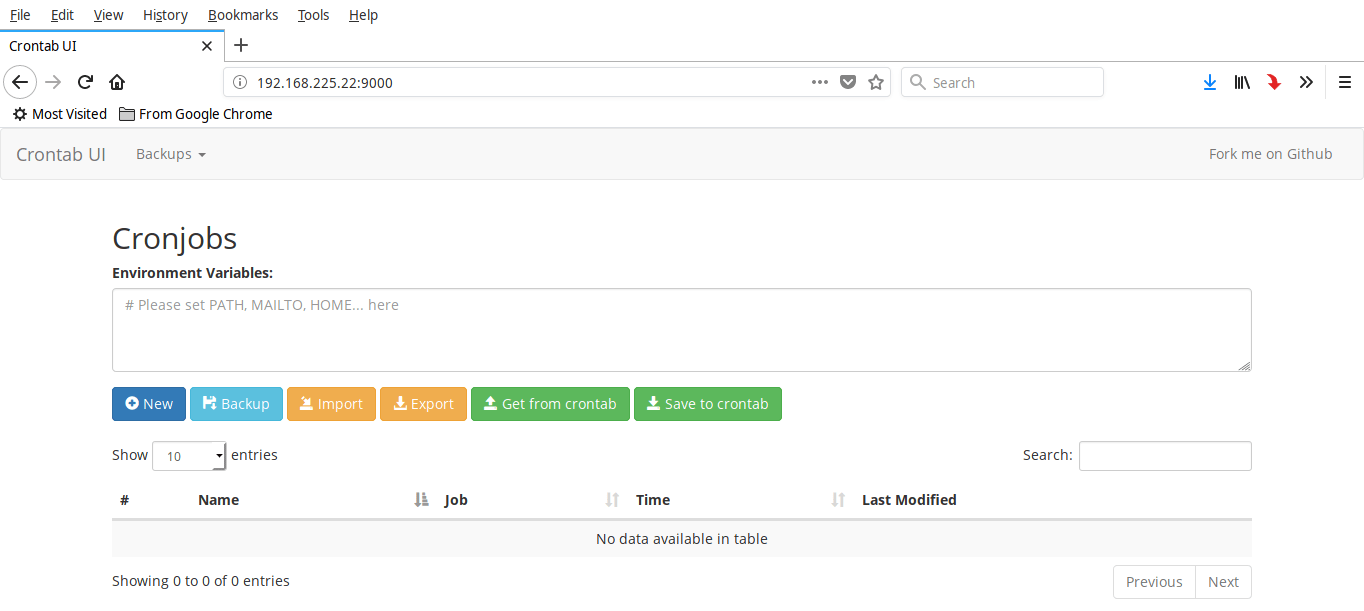
This is how Crontab UI dashboard looks like.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
As you can see in the above screenshot, Crontab UI dashbaord is very simply. All options are self-explanatory.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To exit Crontab UI, press **CTRL+C**.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Create, edit, run, stop, delete a cron job**
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To create a new cron job, click on “New” button. Enter your cron job details and click Save.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. Name the cron job. It is optional.
|
|
||||||
2. The full command you want to run.
|
|
||||||
3. Choose schedule time. You can either choose the quick schedule time, (such as Startup, Hourly, Daily, Weekly, Monthly, Yearly) or set the exact time to run the command. After you choosing the schedule time, the syntax of the cron job will be shown in **Jobs** field.
|
|
||||||
4. Choose whether you want to enable error logging for the particular job.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
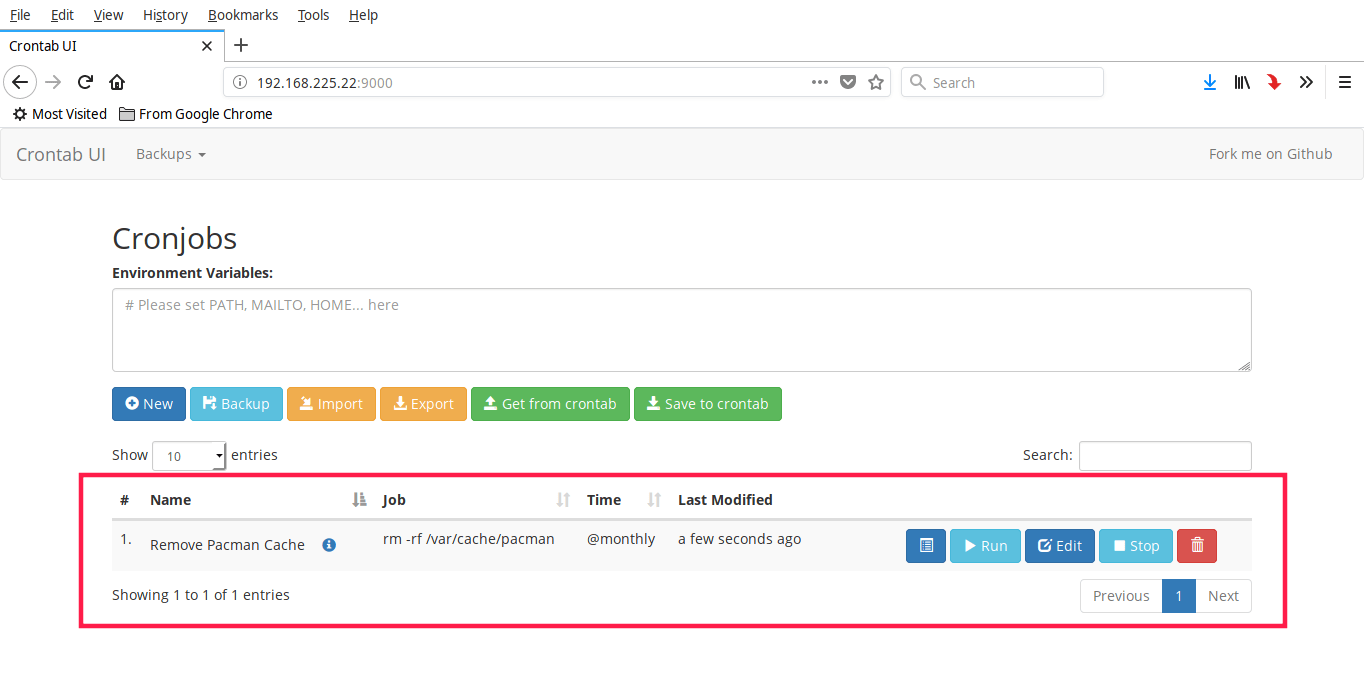
Here is my sample cron job.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
As you can see, I have setup a cron job to clear pacman cache at every month.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Similarly, you can create any number of jobs as you want. You will see all cron jobs in the dashboard.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If you wanted to change any parameter in a cron job, just click on the **Edit** button below the job and modify the parameters as you wish. To run a job immediately, click on the button that says **Run**. To stop a job, click **Stop** button. You can view the log details of any job by clicking on the **Log** button. If the job is no longer required, simply press **Delete** button.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Backup cron jobs**
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To backup all cron jobs, press the Backup from main dashboard and choose OK to confirm the backup.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You can use this backup in case you messed with the contents of the crontab file.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Import/Export cron jobs to other systems**
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Another notable feature of Crontab UI is you can import, export and deploy cron jobs to other systems. If you have multiple systems on your network that requires the same cron jobs, just press **Export** button and choose the location to save the file. All contents of crontab file will be saved in a file named **crontab.db**.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Here is the contents of the crontab.db file.
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
$ cat Downloads/crontab.db
|
|
||||||
{"name":"Remove Pacman Cache","command":"rm -rf /var/cache/pacman","schedule":"@monthly","stopped":false,"timestamp":"Thu Aug 23 2018 10:34:19 GMT+0000 (Coordinated Universal Time)","logging":"true","mailing":{},"created":1535020459093,"_id":"lcVc1nSdaceqS1ut"}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Then you can transfer the entire crontab.db file to some other system and import its to the new system. You don’t need to manually create cron jobs in all systems. Just create them in one system and export and import all of them to every system on the network.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Get the contents from or save to existing crontab file**
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
There are chances that you might have already created some cron jobs using **crontab** command. If so, you can retrieve contents of the existing crontab file by click on the **“Get from crontab”** button in main dashboard.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Similarly, you can save the newly created jobs using Crontab UI utility to existing crontab file in your system. To do so, just click **Save to crontab** option in the dashboard.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
See? Managing cron jobs is not that complicated. Any newbie user can easily maintain any number of jobs without much hassle using Crontab UI. Give it a try and let us know what do you think about this tool. I am all ears!
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
And, that’s all for now. Hope this was useful. More good stuffs to come. Stay tuned!
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Cheers!
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
via: https://www.ostechnix.com/how-to-easily-and-safely-manage-cron-jobs-in-linux/
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
|
||||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
|
||||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
|
||||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[a]:https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
|
|
||||||
[1]:https://www.ostechnix.com/a-beginners-guide-to-cron-jobs/
|
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
|
|||||||
|
在 Linux 中安全轻松地管理 Cron 定时任务
|
||||||
|
======
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在 Linux 中遇到计划任务的时候,你首先会想到的大概就是 Cron 定时任务了。Cron 定时任务能帮助你在类 Unix 操作系统中计划性地执行命令或者任务。也可以参考一下我们之前的一篇[《关于 Cron 定时任务的新手指导》][1]。对于有一定 Linux 经验的人来说,设置 Cron 定时任务不是什么难事,但对于新手来说就不一定了,他们在编辑 Crontab 文件的时候不知不觉中犯的一些小错误,也有可能把整个 Cron 定时任务搞挂了。如果你在处理 Cron 定时任务的时候为了以防万一,可以尝试使用 **Crontab UI**,它是一个可以在类 Unix 操作系统上安全轻松管理 Cron 定时任务的页面工具。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Crontab UI 是使用 NodeJS 编写的免费开源软件。有了 Crontab UI,你在创建、删除和修改 Cron 定时任务的时候就不需要手工编辑 Crontab 文件了,只需要打开浏览器稍微操作一下,就能完成上面这些工作。你可以用 Crontab UI 轻松创建、编辑、暂停、删除、备份 Cron 定时任务,甚至还可以简单做到导入、导出、部署其它机器上的 Cron 定时任务,它还支持错误日志、邮件发送和钩子。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 安装 Crontab UI
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
只需要一条命令就可以安装好 Crontab UI,但前提是已经安装好 NPM。如果还没有安装 NPM,可以参考[《如何在 Linux 上安装 NodeJS》][2]这篇文章。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
执行这一条命令来安装 Crontab UI。
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
$ npm install -g crontab-ui
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
就是这么简单,下面继续来看看在 Crontab UI 上如何管理 Cron 定时任务。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 在 Linux 上安全轻松管理 Cron 定时任务
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
执行这一条命令启动 Crontab UI:
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
$ crontab-ui
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
你会看到这样的输出:
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
Node version: 10.8.0
|
||||||
|
Crontab UI is running at http://127.0.0.1:8000
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
首先在你的防火墙和路由器上放开 8000 端口,然后打开浏览器访问 **<http://127.0.0.1:8000>**。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
注意,默认只有在本地才能访问到 Crontab UI 的控制台页面。但如果你想让 Crontab UI 使用系统的 IP 地址和自定义端口,也就是想让其它机器也访问到本地的 Crontab UI,你需要使用以下这个命令:
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
$ HOST=0.0.0.0 PORT=9000 crontab-ui
|
||||||
|
Node version: 10.8.0
|
||||||
|
Crontab UI is running at http://0.0.0.0:9000
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Crontab UI 就能够通过 <http://IP-Address>:9000 这样的 URL 被远程机器访问到了。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Crontab UI 的控制台页面长这样:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
从上面的截图就可以看到,Crontab UI 的界面非常简洁,所有选项的含义都能不言自明。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
输入 `Ctrl + C` 就可以关闭 Crontab UI。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**创建、编辑、运行、停止、删除 Cron 定时任务**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
点击“New”,输入 Cron 定时任务的信息并点击“Save”保存,就可以创建一个新的 Cron 定时任务了。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. 为 Cron 定时任务命名,这是可选的;
|
||||||
|
2. 你想要执行的完整命令;
|
||||||
|
3. 设定计划执行的时间。你可以按照启动、每时、每日、每周、每月、每年这些指标快速指定计划任务,也可以明确指定任务执行的具体时间。指定好计划时间后,**Jobs** 区域就会显示 Cron 定时任务的句式。
|
||||||
|
4. 选择是否为某个 Cron 定时任务记录错误日志。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
这是我的一个 Cron 定时任务样例。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
如你所见,我设置了一个每月清理 `pacman` 缓存的 Cron 定时任务。你也可以设置多个 Cron 定时任务,都能在控制台页面看到。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
如果你需要更改 Cron 定时任务中的某些参数,只需要点击 **Edit** 按钮并按照你的需求更改对应的参数。点击 **Run** 按钮可以立即执行 Cron 定时任务,点击 **Stop** 则可以立即停止 Cron 定时任务。如果想要查看某个 Cron 定时任务的详细日志,可以点击 **Log** 按钮。对于不再需要的 Cron 定时任务,就可以按 **Delete** 按钮删除。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**备份 Cron 定时任务**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
点击控制台页面的 **Backup** 按钮并确认,就可以备份所有 Cron 定时任务。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
备份之后,一旦 Crontab 文件出现了错误,就可以使用备份来恢复了。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**导入/导出其它机器上的 Cron 定时任务**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Crontab UI 还有一个令人注目的功能,就是导入、导出、部署其它机器上的 Cron 定时任务。如果同一个网络里的多台机器都需要执行同样的 Cron 定时任务,只需要点击 **Export** 按钮并选择文件的保存路径,所有的 Cron 定时任务都会导出到 `crontab.db` 文件中。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
以下是 `crontab.db` 文件的内容:
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
$ cat Downloads/crontab.db
|
||||||
|
{"name":"Remove Pacman Cache","command":"rm -rf /var/cache/pacman","schedule":"@monthly","stopped":false,"timestamp":"Thu Aug 23 2018 10:34:19 GMT+0000 (Coordinated Universal Time)","logging":"true","mailing":{},"created":1535020459093,"_id":"lcVc1nSdaceqS1ut"}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
导出成文件以后,你就可以把这个 `crontab.db` 文件放置到其它机器上并导入成 Cron 定时任务,而不需要在每一台主机上手动设置 Cron 定时任务。总之,在一台机器上设置完,导出,再导入到其他机器,就完事了。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**在 Crontab 文件获取/保存 Cron 定时任务**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
你可能在使用 Crontab UI 之前就已经使用 `crontab` 命令创建过 Cron 定时任务。如果是这样,你可以点击控制台页面上的 **Get from crontab** 按钮来获取已有的 Cron 定时任务。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
同样地,你也可以使用 Crontab UI 来将新的 Cron 定时任务保存到 Crontab 文件中,只需要点击 **Save to crontab** 按钮就可以了。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
管理 Cron 定时任务并没有想象中那么难,即使是新手使用 Crontab UI 也能轻松管理 Cron 定时任务。赶快开始尝试并发表一下你的看法吧。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
via: https://www.ostechnix.com/how-to-easily-and-safely-manage-cron-jobs-in-linux/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||||
|
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||||
|
译者:[HankChow](https://github.com/HankChow)
|
||||||
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[a]:https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
|
||||||
|
[1]:https://www.ostechnix.com/a-beginners-guide-to-cron-jobs/
|
||||||
|
[2]:https://www.ostechnix.com/install-node-js-linux/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user