mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-26 21:30:55 +08:00
20150813-1 选题
This commit is contained in:
parent
dd776df276
commit
ed05a3b848
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
How to get Public IP from Linux Terminal?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Public addresses are assigned by InterNIC and consist of class-based network IDs or blocks of CIDR-based addresses (called CIDR blocks) that are guaranteed to be globally unique to the Internet. How to get Public IP from Linux Terminal - blackMORE OpsWhen the public addresses are assigned, routes are programmed into the routers of the Internet so that traffic to the assigned public addresses can reach their locations. Traffic to destination public addresses are reachable on the Internet. For example, when an organization is assigned a CIDR block in the form of a network ID and subnet mask, that [network ID, subnet mask] pair also exists as a route in the routers of the Internet. IP packets destined to an address within the CIDR block are routed to the proper destination. In this post I will show several ways to find your public IP address from Linux terminal. This though seems like a waste for normal users, but when you are in a terminal of a headless Linux server(i.e. no GUI or you’re connected as a user with minimal tools). Either way, being able to getHow to get Public IP from Linux Terminal public IP from Linux terminal can be useful in many cases or it could be one of those things that might just come in handy someday.
|
||||
|
||||
There’s two main commands we use, curl and wget. You can use them interchangeably.
|
||||
|
||||
### Curl output in plain text format: ###
|
||||
|
||||
curl icanhazip.com
|
||||
curl ifconfig.me
|
||||
curl curlmyip.com
|
||||
curl ip.appspot.com
|
||||
curl ipinfo.io/ip
|
||||
curl ipecho.net/plain
|
||||
curl www.trackip.net/i
|
||||
|
||||
### curl output in JSON format: ###
|
||||
|
||||
curl ipinfo.io/json
|
||||
curl ifconfig.me/all.json
|
||||
curl www.trackip.net/ip?json (bit ugly)
|
||||
|
||||
### curl output in XML format: ###
|
||||
|
||||
curl ifconfig.me/all.xml
|
||||
|
||||
### curl all IP details – The motherload ###
|
||||
|
||||
curl ifconfig.me/all
|
||||
|
||||
### Using DYNDNS (Useful when you’re using DYNDNS service) ###
|
||||
|
||||
curl -s 'http://checkip.dyndns.org' | sed 's/.*Current IP Address: \([0-9\.]*\).*/\1/g'
|
||||
curl -s http://checkip.dyndns.org/ | grep -o "[[:digit:].]\+"
|
||||
|
||||
### Using wget instead of curl ###
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://ipecho.net/plain -O - -q ; echo
|
||||
wget http://observebox.com/ip -O - -q ; echo
|
||||
|
||||
### Using host and dig command (cause we can) ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use host and dig command assuming they are available or installed
|
||||
|
||||
host -t a dartsclink.com | sed 's/.*has address //'
|
||||
dig +short myip.opendns.com @resolver1.opendns.com
|
||||
|
||||
### Sample bash script: ###
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
PUBLIC_IP=`wget http://ipecho.net/plain -O - -q ; echo`
|
||||
echo $PUBLIC_IP
|
||||
|
||||
Quite a few to pick from.
|
||||
|
||||
I was actually writing a small script to track all the IP changes of my router each day and save those into a file. I found these nifty commands and sites to use while doing some online research. Hope they help someone else someday too. Thanks for reading, please Share and RT.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.blackmoreops.com/2015/06/14/how-to-get-public-ip-from-linux-terminal/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
438
sources/tech/20150813 Linux file system hierarchy v2.0.md
Normal file
438
sources/tech/20150813 Linux file system hierarchy v2.0.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,438 @@
|
||||
Linux file system hierarchy v2.0
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
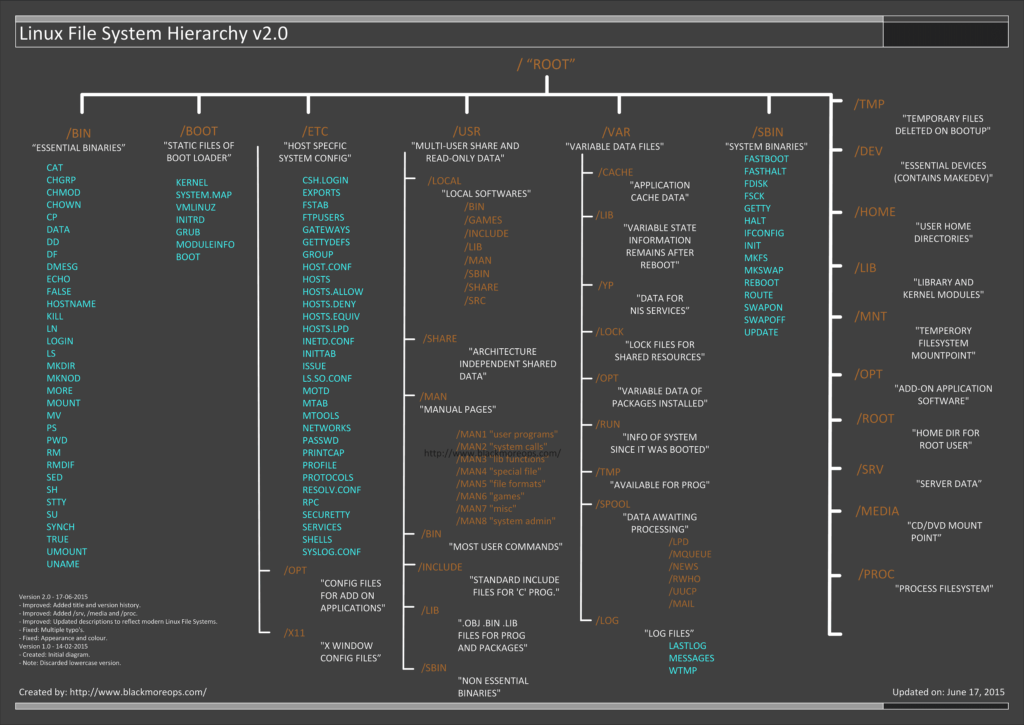
What is a file in Linux? What is file system in Linux? Where are all the configuration files? Where do I keep my downloaded applications? Is there really a filesystem standard structure in Linux? Well, the above image explains Linux file system hierarchy in a very simple and non-complex way. It’s very useful when you’re looking for a configuration file or a binary file. I’ve added some explanation and examples below, but that’s TL;DR.
|
||||
|
||||
Another issue is when you got configuration and binary files all over the system that creates inconsistency and if you’re a large organization or even an end user, it can compromise your system (binary talking with old lib files etc.) and when you do [security audit of your Linux system][1], you find it is vulnerable to different exploits. So keeping a clean operating system (no matter Windows or Linux) is important.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is a file in Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
A simple description of the UNIX system, also applicable to Linux, is this:
|
||||
|
||||
> On a UNIX system, everything is a file; if something is not a file, it is a process.
|
||||
|
||||
This statement is true because there are special files that are more than just files (named pipes and sockets, for instance), but to keep things simple, saying that everything is a file is an acceptable generalization. A Linux system, just like UNIX, makes no difference between a file and a directory, since a directory is just a file containing names of other files. Programs, services, texts, images, and so forth, are all files. Input and output devices, and generally all devices, are considered to be files, according to the system.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Version 2.0 – 17-06-2015
|
||||
- – Improved: Added title and version history.
|
||||
- – Improved: Added /srv, /media and /proc.
|
||||
- – Improved: Updated descriptions to reflect modern Linux File Systems.
|
||||
- – Fixed: Multiple typo’s.
|
||||
- – Fixed: Appearance and colour.
|
||||
- Version 1.0 – 14-02-2015
|
||||
- – Created: Initial diagram.
|
||||
- – Note: Discarded lowercase version.
|
||||
|
||||
### Download Links ###
|
||||
|
||||
Following are two links for download. If you need this in any other format, let me know and I will try to create that and upload it somewhere.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Large (PNG) Format – 2480×1755 px – 184KB][2]
|
||||
- [Largest (PDF) Format – 9919x7019 px – 1686KB][3]
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: PDF Format is best for printing and very high in quality
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux file system description ###
|
||||
|
||||
In order to manage all those files in an orderly fashion, man likes to think of them in an ordered tree-like structure on the hard disk, as we know from `MS-DOS` (Disk Operating System) for instance. The large branches contain more branches, and the branches at the end contain the tree’s leaves or normal files. For now we will use this image of the tree, but we will find out later why this is not a fully accurate image.
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
<table cellspacing="2" border="4" style="border-collapse: collapse; width: 731px; height: 2617px;">
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th scope="col">Directory</th>
|
||||
<th scope="col">Description</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td><i>Primary hierarchy</i> root and root directory of the entire file system hierarchy.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/bin</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Essential command binaries that need to be available in single user mode; for all users, <i>e.g.</i>, cat, ls, cp.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/boot</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Boot loader files, <i>e.g.</i>, kernels, initrd.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/dev</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Essential devices, <i>e.g.</i>, <code>/dev/null</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/etc</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Host-specific system-wide configuration filesThere has been controversy over the meaning of the name itself. In early versions of the UNIX Implementation Document from Bell labs, /etc is referred to as the <i>etcetera directory</i>, as this directory historically held everything that did not belong elsewhere (however, the FHS restricts /etc to static configuration files and may not contain binaries). Since the publication of early documentation, the directory name has been re-designated in various ways. Recent interpretations include backronyms such as “Editable Text Configuration” or “Extended Tool Chest”.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/opt</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Configuration files for add-on packages that are stored in <code>/opt/</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/sgml</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Configuration files, such as catalogs, for software that processes SGML.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/X11</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Configuration files for the X Window System, version 11.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/xml</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Configuration files, such as catalogs, for software that processes XML.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/home</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Users’ home directories, containing saved files, personal settings, etc.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/lib</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Libraries essential for the binaries in <code>/bin/</code> and <code>/sbin/</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/lib<qual></code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Alternate format essential libraries. Such directories are optional, but if they exist, they have some requirements.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/media</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Mount points for removable media such as CD-ROMs (appeared in FHS-2.3).</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/mnt</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Temporarily mounted filesystems.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/opt</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Optional application software packages.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/proc</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Virtual filesystem providing process and kernel information as files. In Linux, corresponds to a procfs mount.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/root</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Home directory for the root user.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/sbin</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Essential system binaries, <i>e.g.</i>, init, ip, mount.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/srv</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Site-specific data which are served by the system.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/tmp</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Temporary files (see also <code>/var/tmp</code>). Often not preserved between system reboots.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/usr</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td><i>Secondary hierarchy</i> for read-only user data; contains the majority of (multi-)user utilities and applications.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/bin</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Non-essential command binaries (not needed in single user mode); for all users.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/include</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Standard include files.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/lib</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Libraries for the binaries in <code>/usr/bin/</code> and <code>/usr/sbin/</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/lib<qual></code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Alternate format libraries (optional).</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/local</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td><i>Tertiary hierarchy</i> for local data, specific to this host. Typically has further subdirectories, <i>e.g.</i>, <code>bin/</code>, <code>lib/</code>, <code>share/</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/sbin</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Non-essential system binaries, <i>e.g.</i>, daemons for various network-services.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/share</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Architecture-independent (shared) data.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/src</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Source code, <i>e.g.</i>, the kernel source code with its header files.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/X11R6</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>X Window System, Version 11, Release 6.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/var</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Variable files—files whose content is expected to continually change during normal operation of the system—such as logs, spool files, and temporary e-mail files.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/cache</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Application cache data. Such data are locally generated as a result of time-consuming I/O or calculation. The application must be able to regenerate or restore the data. The cached files can be deleted without loss of data.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/lib</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>State information. Persistent data modified by programs as they run, <i>e.g.</i>, databases, packaging system metadata, etc.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/lock</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Lock files. Files keeping track of resources currently in use.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/log</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Log files. Various logs.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/mail</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Users’ mailboxes.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/opt</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Variable data from add-on packages that are stored in <code>/opt/</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/run</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Information about the running system since last boot, <i>e.g.</i>, currently logged-in users and running <a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Daemon_%28computing%29">daemons</a>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/spool</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Spool for tasks waiting to be processed, <i>e.g.</i>, print queues and outgoing mail queue.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/mail</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Deprecated location for users’ mailboxes.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/tmp</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Temporary files to be preserved between reboots.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Types of files in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
Most files are just files, called `regular` files; they contain normal data, for example text files, executable files or programs, input for or output from a program and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
While it is reasonably safe to suppose that everything you encounter on a Linux system is a file, there are some exceptions.
|
||||
|
||||
- `Directories`: files that are lists of other files.
|
||||
- `Special files`: the mechanism used for input and output. Most special files are in `/dev`, we will discuss them later.
|
||||
- `Links`: a system to make a file or directory visible in multiple parts of the system’s file tree. We will talk about links in detail.
|
||||
- `(Domain) sockets`: a special file type, similar to TCP/IP sockets, providing inter-process networking protected by the file system’s access control.
|
||||
- `Named pipes`: act more or less like sockets and form a way for processes to communicate with each other, without using network socket semantics.
|
||||
|
||||
### File system in reality ###
|
||||
|
||||
For most users and for most common system administration tasks, it is enough to accept that files and directories are ordered in a tree-like structure. The computer, however, doesn’t understand a thing about trees or tree-structures.
|
||||
|
||||
Every partition has its own file system. By imagining all those file systems together, we can form an idea of the tree-structure of the entire system, but it is not as simple as that. In a file system, a file is represented by an `inode`, a kind of serial number containing information about the actual data that makes up the file: to whom this file belongs, and where is it located on the hard disk.
|
||||
|
||||
Every partition has its own set of inodes; throughout a system with multiple partitions, files with the same inode number can exist.
|
||||
|
||||
Each inode describes a data structure on the hard disk, storing the properties of a file, including the physical location of the file data. When a hard disk is initialized to accept data storage, usually during the initial system installation process or when adding extra disks to an existing system, a fixed number of inodes per partition is created. This number will be the maximum amount of files, of all types (including directories, special files, links etc.) that can exist at the same time on the partition. We typically count on having 1 inode per 2 to 8 kilobytes of storage.At the time a new file is created, it gets a free inode. In that inode is the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
- Owner and group owner of the file.
|
||||
- File type (regular, directory, …)
|
||||
- Permissions on the file
|
||||
- Date and time of creation, last read and change.
|
||||
- Date and time this information has been changed in the inode.
|
||||
- Number of links to this file (see later in this chapter).
|
||||
- File size
|
||||
- An address defining the actual location of the file data.
|
||||
|
||||
The only information not included in an inode, is the file name and directory. These are stored in the special directory files. By comparing file names and inode numbers, the system can make up a tree-structure that the user understands. Users can display inode numbers using the -i option to ls. The inodes have their own separate space on the disk.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.blackmoreops.com/2015/06/18/linux-file-system-hierarchy-v2-0/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.blackmoreops.com/2015/02/15/in-light-of-recent-linux-exploits-linux-security-audit-is-a-must/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.blackmoreops.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/Linux-file-system-hierarchy-v2.0-2480px-blackMORE-Ops.png
|
||||
[3]:http://www.blackmoreops.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/Linux-File-System-Hierarchy-blackMORE-Ops.pdf
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu Want To Make It Easier For You To Install The Latest Nvidia Linux Driver
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
Ubuntu Gamers are on the rise -and so is demand for the latest drivers
|
||||
|
||||
**Installing the latest upstream NVIDIA graphics driver on Ubuntu could be about to get much easier. **
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu developers are considering the creation of a brand new ‘official’ PPA to distribute the latest closed-source NVIDIA binary drivers to desktop users.
|
||||
|
||||
The move would benefit Ubuntu gamers **without** risking the stability of the OS for everyone else.
|
||||
|
||||
New upstream drivers would be installed and updated from this new PPA **only** when a user explicitly opts-in to it. Everyone else would continue to receive and use the more recent stable NVIDIA Linux driver snapshot included in the Ubuntu archive.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why Is This Needed? ###
|
||||
|
||||
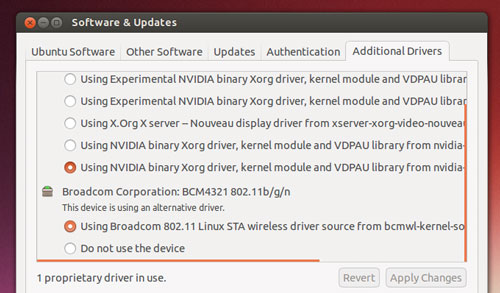
|
||||
Ubuntu provides drivers – but they’re not the latest
|
||||
|
||||
The closed-source NVIDIA graphics drivers that are available to install on Ubuntu from the archive (using the command line, synaptic or through the additional drivers tool) work fine for most and can handle the composited Unity desktop shell with ease.
|
||||
|
||||
For gaming needs it’s a different story.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to squeeze every last frame and HD texture out of the latest big-name Steam game you’ll need the latest binary drivers blob.
|
||||
|
||||
> ‘Installing the very latest Nvidia Linux driver on Ubuntu is not easy and not always safe.’
|
||||
|
||||
The more recent the driver the more likely it is to support the latest features and technologies, or come pre-packed with game-specific tweaks and bug fixes too.
|
||||
|
||||
The problem is that installing the very latest Nvidia Linux driver on Ubuntu is not easy and not always safe.
|
||||
|
||||
To fill the void many third-party PPAs maintained by enthusiasts have emerged. Since many of these PPAs also distribute other experimental or bleeding-edge software their use is **not without risk**. Adding a bleeding edge PPA is often the fastest way to entirely hose a system!
|
||||
|
||||
A solution that lets Ubuntu users install the latest propriety graphics drivers as offered in third-party PPAs is needed **but** with the safety catch of being able to roll-back to the stable archive version if needed.
|
||||
|
||||
### ‘Demand for fresh drivers is hard to ignore’ ###
|
||||
|
||||
> ‘A solution that lets Ubuntu users get the latest hardware drivers safely is coming.’
|
||||
|
||||
‘The demand for fresh drivers in a fast developing market is becoming hard to ignore, users are going to want the latest upstream has to offer,’ Castro explains in an e-mail to the Ubuntu Desktop mailing list.
|
||||
|
||||
‘[NVIDIA] can deliver a kickass experience with almost no effort from the user [in Windows 10]. Until we can convince NVIDIA to do the same with Ubuntu we’re going to have to pick up the slack.’
|
||||
|
||||
Castro’s proposition of a “blessed” NVIDIA PPA is the easiest way to do this.
|
||||
|
||||
Gamers would be able to opt-in to receive new drivers from the PPA straight from Ubuntu’s default proprietary hardware drivers tool — no need for them to copy and paste terminal commands from websites or wiki pages.
|
||||
|
||||
The drivers within this PPA would be packaged and maintained by a select band of community members and receive benefits from being a semi-official option, namely **automated testing**.
|
||||
|
||||
As Castro himself puts it: ‘People want the latest bling, and no matter what they’re going to do it. We might as well put a framework around it so people can get what they want without breaking their computer.’
|
||||
|
||||
**Would you make use of this PPA? How would you rate the performance of the default Nvidia drivers on Ubuntu? Share your thoughts in the comments, folks! **
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/08/ubuntu-easy-install-latest-nvidia-linux-drivers
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user