mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-25 00:50:15 +08:00
commit
eb8c85e5ed
@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
|
||||
如何在 Linux 上检查用户所属组
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
将用户添加到现有组是 Linux 管理员的常规活动之一。这是一些在大环境中工作的管理员的日常活动。
|
||||
|
||||
即使我因为业务需求而在我的环境中每天都在进行这样的活动。它是帮助你识别环境中现有组的重要命令之一。
|
||||
甚至我会因为业务需求而在我的环境中每天都在进行这样的活动。它是帮助你识别环境中现有组的重要命令之一。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,这些命令还可以帮助你识别用户所属的组。所有用户都列在 `/etc/passwd` 中,组列在 `/etc/group` 中。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,61 +12,60 @@
|
||||
### 什么是 /etc/passwd?
|
||||
|
||||
`/etc/passwd` 是一个文本文件,其中包含登录 Linux 系统所必需的每个用户信息。它维护有用的用户信息,如用户名、密码、用户 ID、组 ID、用户 ID 信息、家目录和 shell。passwd 每行包含了用户的详细信息,共有如上所述的 7 个字段。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ grep "daygeek" /etc/passwd
|
||||
daygeek:x:1000:1000:daygeek,,,:/home/daygeek:/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 /etc/group?
|
||||
|
||||
`/etc/group` 是一个文本文件,用于定义用户所属的组。我们可以将多个用户添加到单个组中。它允许用户访问其他用户文件和文件夹,因为 Linux 权限分为三类,用户、组和其他。它维护有关组的有用信息,例如组名、组密码,组 ID(GID)和成员列表。每个都在一个单独的行。组文件每行包含了每个组的详细信息,共有 4 个如上所述字段。
|
||||
`/etc/group` 是一个文本文件,用于定义用户所属的组。我们可以将多个用户添加到单个组中。它允许用户访问其他用户文件和文件夹,因为 Linux 权限分为三类:用户、组和其他。它维护有关组的有用信息,例如组名、组密码,组 ID(GID)和成员列表。每个都在一个单独的行。组文件每行包含了每个组的详细信息,共有 4 个如上所述字段。
|
||||
|
||||
这可以通过使用以下方法来执行。
|
||||
|
||||
* `groups:` 显示一个组的所有成员。
|
||||
* `id:` 打印指定用户名的用户和组信息。
|
||||
* `lid:` 显示用户的组或组的用户。
|
||||
* `getent:` 从 Name Service Switch 库中获取条目。
|
||||
* `grep:` 代表“全局正则表达式打印”(global regular expression print),它能打印匹配的模式。
|
||||
* `groups`: 显示一个组的所有成员。
|
||||
* `id`: 打印指定用户名的用户和组信息。
|
||||
* `lid`: 显示用户的组或组的用户。
|
||||
* `getent`: 从 Name Service Switch 库中获取条目。
|
||||
* `grep`: 代表“<ruby>全局正则表达式打印<rt>global regular expression print</rt></ruby>”,它能打印匹配的模式。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 groups 命令?
|
||||
|
||||
`groups` 命令打印每个给定用户名的主要组和任何补充组的名称。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是组命令?
|
||||
|
||||
groups 命令打印每个给定用户名的主要组和任何补充组的名称。
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ groups daygeek
|
||||
daygeek : daygeek adm cdrom sudo dip plugdev lpadmin sambashare
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果要检查与当前用户关联的组列表。只需运行 **“group”** 命令,无需带任何用户名。
|
||||
如果要检查与当前用户关联的组列表。只需运行 `groups` 命令,无需带任何用户名。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ groups
|
||||
daygeek adm cdrom sudo dip plugdev lpadmin sambashare
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 id 命令?
|
||||
|
||||
id 代表身份。打印真实有效的用户和组 ID。打印指定用户或当前用户的用户和组信息。
|
||||
id 代表 “<ruby>身份<rt>identity</rt></ruby>”。它打印真实有效的用户和组 ID。打印指定用户或当前用户的用户和组信息。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ id daygeek
|
||||
uid=1000(daygeek) gid=1000(daygeek) groups=1000(daygeek),4(adm),24(cdrom),27(sudo),30(dip),46(plugdev),118(lpadmin),128(sambashare)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果要检查与当前用户关联的组列表。只运行 **“id”** 命令,无需带任何用户名。
|
||||
如果要检查与当前用户关联的组列表。只运行 `id` 命令,无需带任何用户名。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ id
|
||||
uid=1000(daygeek) gid=1000(daygeek) groups=1000(daygeek),4(adm),24(cdrom),27(sudo),30(dip),46(plugdev),118(lpadmin),128(sambashare)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 lid 命令?
|
||||
|
||||
它显示用户的组或组的用户。显示有关包含用户名的组或组名称中包含的用户的信息。此命令需要管理员权限。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo lid daygeek
|
||||
adm(gid=4)
|
||||
@ -76,12 +76,12 @@ $ sudo lid daygeek
|
||||
lpadmin(gid=108)
|
||||
daygeek(gid=1000)
|
||||
sambashare(gid=124)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 getent 命令?
|
||||
|
||||
getent 命令显示 Name Service Switch 库支持的数据库中的条目,它们在 /etc/nsswitch.conf 中配置。
|
||||
`getent` 命令显示 Name Service Switch 库支持的数据库中的条目,它们在 `/etc/nsswitch.conf` 中配置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ getent group | grep daygeek
|
||||
adm:x:4:syslog,daygeek
|
||||
@ -92,10 +92,10 @@ plugdev:x:46:daygeek
|
||||
lpadmin:x:118:daygeek
|
||||
daygeek:x:1000:
|
||||
sambashare:x:128:daygeek
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你只想打印关联的组名称,请在上面的命令中使用 **“awk”**。
|
||||
如果你只想打印关联的组名称,请在上面的命令中使用 `awk`。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ getent group | grep daygeek | awk -F: '{print $1}'
|
||||
adm
|
||||
@ -106,10 +106,10 @@ plugdev
|
||||
lpadmin
|
||||
daygeek
|
||||
sambashare
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
运行以下命令仅打印主群组信息。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ getent group daygeek
|
||||
daygeek:x:1000:
|
||||
@ -118,7 +118,8 @@ daygeek:x:1000:
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 grep 命令?
|
||||
|
||||
grep 代表“全局正则表达式打印”(global regular expression print),它能打印文件匹配的模式。
|
||||
`grep` 代表 “<ruby>全局正则表达式打印<rt>global regular expression print</rt></ruby>”,它能打印文件匹配的模式。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ grep "daygeek" /etc/group
|
||||
adm:x:4:syslog,daygeek
|
||||
@ -129,10 +130,10 @@ plugdev:x:46:daygeek
|
||||
lpadmin:x:118:daygeek
|
||||
daygeek:x:1000:
|
||||
sambashare:x:128:daygeek
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你只想打印关联的组名称,请在上面的命令中使用 **“awk”**。
|
||||
如果你只想打印关联的组名称,请在上面的命令中使用 `awk`。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ grep "daygeek" /etc/group | awk -F: '{print $1}'
|
||||
adm
|
||||
@ -143,8 +144,8 @@ plugdev
|
||||
lpadmin
|
||||
daygeek
|
||||
sambashare
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.2daygeek.com/how-to-check-which-groups-a-user-belongs-to-on-linux/
|
||||
@ -152,7 +153,7 @@ via: https://www.2daygeek.com/how-to-check-which-groups-a-user-belongs-to-on-lin
|
||||
作者:[Prakash Subramanian][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
|
||||
如何在 Linux 系统中使用 dd 命令而不会损毁你的磁盘
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
||||
> 使用 Linux 中的 dd 工具安全、可靠地制作一个驱动器、分区和文件系统的完整镜像。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*这篇文章节选自 Manning 出版社出版的图书 [Linux in Action][1]的第 4 章。*
|
||||
|
||||
你是否正在从一个即将损坏的存储驱动器挽救数据,或者要把本地归档进行远程备份,或者要把一个别处的活动分区做个完整的副本,那么你需要懂得如何安全而可靠的复制驱动器和文件系统。幸运的是,`dd` 是一个可以使用的简单而又功能强大的镜像复制命令,从现在到未来很长的时间内,也许直到永远都不会出现比 `dd` 更好的工具了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 对驱动器和分区做个完整的副本
|
||||
|
||||
仔细研究后,你会发现你可以使用 `dd` 做各种任务,但是它最重要的功能是处理磁盘分区。当然,你可以使用 `tar` 命令或者 `scp` 命令从一台计算机复制整个文件系统的文件,然后把这些文件原样粘贴在另一台刚刚安装好 Linux 操作系统的计算机中。但是,因为那些文件系统归档不是完整的映像文件,所以在复制文件的过程中需要计算机操作系统的运行作为基础。
|
||||
|
||||
另一方面,使用 `dd` 可以对任何数字信息完美的进行逐个字节的镜像。但是不论何时何地,当你要对分区进行操作时,我要告诉你早期的 Unix 管理员曾开过这样的玩笑:“ dd 的意思是<ruby>磁盘毁灭者<rt>disk destroyer</rt></ruby>”(LCTT 译注:`dd` 原意是<ruby>磁盘复制<rt>disk dump</rt></ruby>)。 在使用 `dd` 命令的时候,如果你输入了哪怕是一个字母,也可能立即永久性的擦除掉整个磁盘驱动器里的所有重要的数据。因此,一定要注意命令的拼写格式规范。
|
||||
|
||||
**记住:** 在按下回车键执行 `dd` 命令之前,暂时停下来仔细的认真思考一下。
|
||||
|
||||
### dd 命令的基本操作
|
||||
|
||||
现在你已经得到了适当的提醒,我们将从简单的事情开始。假设你要对代号为 `/dev/sda` 的整个磁盘数据创建精确的映像,你已经插入了一块空的磁盘驱动器 (理想情况下具有与代号为 `/dev/sda` 的磁盘驱动器相同的容量)。语法很简单: `if=` 定义源驱动器,`of=` 定义你要将数据保存到的文件或位置:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=/dev/sda of=/dev/sdb
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来的例子将要对 `/dev/sda` 驱动器创建一个 .img 的映像文件,然后把该文件保存的你的用户帐号家目录:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=/dev/sda of=/home/username/sdadisk.img
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令针对整个驱动器创建映像文件,你也可以针对驱动器上的单个分区进行操作。下面的例子针对驱动器的单个分区进行操作,同时使用了一个 `bs` 参数用于设置单次拷贝的字节数量 (此例中是 4096)。设定 `bs` 参数值可能会影响 `dd` 命令的整体操作速度,该参数的理想设置取决于你的硬件配置和其它考虑。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=/dev/sda2 of=/home/username/partition2.img bs=4096
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
数据的恢复非常简单:通过颠倒 `if` 和 `of` 参数可以有效的完成任务。在此例中,`if=` 使用你要恢复的映像,`of=` 使用你想要写入映像的目标驱动器:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=sdadisk.img of=/dev/sdb
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以在一条命令中同时完成创建和拷贝任务。下面的例子中将使用 SSH 从远程驱动器创建一个压缩的映像文件,并把该文件保存到你的本地计算机中:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ssh username@54.98.132.10 "dd if=/dev/sda | gzip -1 -" | dd of=backup.gz
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你应该经常测试你的归档,确保它们可正常使用。如果它是你创建的启动驱动器,将它粘贴到计算机中,看看它是否能够按预期启动。如果它是普通分区的数据,挂载该分区,确保文件都存在而且可以正常的访问。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 dd 擦除磁盘数据
|
||||
|
||||
多年以前,我的一个负责政府海外大使馆安全的朋友曾经告诉我,在他当时在任的时候, 政府会给每一个大使馆提供一个官方版的锤子。为什么呢? 一旦大使馆设施可能被不友善的人员侵占,就会使用这个锤子毁坏所有的硬盘.
|
||||
|
||||
为什么要那样做?为什么不是删除数据就好了?你在开玩笑,对吧?所有人都知道从存储设备中删除包含敏感信息的文件实际上并没有真正移除这些数据。除非使用锤子彻底的毁坏这些存储介质,否则,只要有足够的时间和动机, 几乎所有的内容都可以从几乎任何数字存储介质重新获取。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,你可以使用 `dd` 命令让坏人非常难以获得你的旧数据。这个命令需要花费一些时间在 `/dev/sda1` 分区的每个扇区写入数百万个 `0`(LCTT 译注:是指 0x0 字节,意即 NUL ,而不是数字 0 ):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
还有更好的方法。通过使用 `/dev/urandom` 作为源文件,你可以在磁盘上写入随机字符:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/sda1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 监控 dd 的操作
|
||||
|
||||
由于磁盘或磁盘分区的归档可能需要很长的时间,因此你可能需要在命令中添加进度查看器。安装管道查看器(在 Ubuntu 系统上安装命令为 `sudo apt install pv`),然后把 `pv` 命令和 `dd` 命令结合在一起。使用 `pv`,最终的命令是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=/dev/urandom | pv | dd of=/dev/sda1
|
||||
|
||||
4,14MB 0:00:05 [ 98kB/s] [ <=> ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
想要推迟备份和磁盘管理工作?有了 `dd` 工具,你不会有太多的借口。它真的非常简单,但是要小心。祝你好运!
|
||||
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:https://opensource.com/article/18/7/how-use-dd-linux
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[David Clinton][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[SunWave](https://github.com/SunWave)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/remyd
|
||||
[1]: https://www.manning.com/books/linux-in-action?a_aid=bootstrap-it&a_bid=4ca15fc9&chan=opensource
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,149 @@
|
||||
Arch Linux Applications Automatic Installation Script
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Howdy Archers! Today, I have stumbled upon an useful utility called **“ArchI0”** , a CLI menu-based Arch Linux applications automatic installation script. This script provides an easiest way to install all essential applications for your Arch-based distribution. Please note that **this script is meant for noobs only**. Intermediate and advanced users can easily figure out [**how to use pacman**][1] to get things done. If you want to learn how Arch Linux works, I suggest you to manually install all software one by one. For those who are still noobs and wanted an easy and quick way to install all essential applications for their Arch-based systems, make use of this script.
|
||||
|
||||
### ArchI0 – Arch Linux Applications Automatic Installation Script
|
||||
|
||||
The developer of this script has created two scripts namely **ArchI0live** and **ArchI0**. You can use ArchI0live script to test without installing it. This might be helpful to know what actually is in this script before installing it on your system.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install ArchI0
|
||||
|
||||
To install this script, Git cone the ArchI0 script repository using command:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/SifoHamlaoui/ArchI0.git
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will clone the ArchI0 GtiHub repository contents in a folder called ArchI0 in your current directory. Go to the directory using command:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cd ArchI0/
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Make the script executable using command:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ chmod +x ArchI0live.sh
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run the script with command:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo ./ArchI0live.sh
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We need to run this script as root or sudo user, because installing applications requires root privileges.
|
||||
|
||||
> **Note:** For those wondering what all are those commands for at the beginning of the script, the first command downloads **figlet** , because the script logo is shown using figlet. The 2nd command install **Leafpad** which is used to open and read the license file. The 3rd command install **wget** to download files from sourceforge. The 4th and 5th commands are to download and open the License File on leafpad. And, the final and 6th command is used to close the license file after reading it.
|
||||
|
||||
Type your Arch Linux system’s architecture and hit ENTER key. When it asks to install the script, type y and hit ENTER.
|
||||
|
||||
![][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Once it is installed, you will be redirected to the main menu.
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
As you see in the above screenshot, ArchI0 has 13 categories and contains 90 easy-to-install programs under those categories. These 90 programs are just enough to setup a full-fledged Arch Linux desktop to perform day-to-day activities. To know about this script, type **a** and to exit this script type **q**.
|
||||
|
||||
After installing it, you don’t need to run the ArchI0live script. You can directly launch it using the following command:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo ArchI0
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It will ask you each time to choose your Arch Linux distribution architecture.
|
||||
```
|
||||
This script Is under GPLv3 License
|
||||
|
||||
Preparing To Run Script
|
||||
Checking For ROOT: PASSED
|
||||
What Is Your OS Architecture? {32/64} 64
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
From now on, you can install the program of your choice from the categories listed in the main menu. To view the list of available programs under a specific category, enter the category number. Say for example, to view the list of available programs under **Text Editors** category, type **1** and hit ENTER.
|
||||
```
|
||||
This script Is under GPLv3 License
|
||||
|
||||
[ R00T MENU ]
|
||||
Make A Choice
|
||||
1) Text Editors
|
||||
2) FTP/Torrent Applications
|
||||
3) Download Managers
|
||||
4) Network managers
|
||||
5) VPN clients
|
||||
6) Chat Applications
|
||||
7) Image Editors
|
||||
8) Video editors/Record
|
||||
9) Archive Handlers
|
||||
10) Audio Applications
|
||||
11) Other Applications
|
||||
12) Development Environments
|
||||
13) Browser/Web Plugins
|
||||
14) Dotfiles
|
||||
15) Usefull Links
|
||||
------------------------
|
||||
a) About ArchI0 Script
|
||||
q) Leave ArchI0 Script
|
||||
|
||||
Choose An Option: 1
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, choose the application you want to install. To return to main menu, type **q** and hit ENTER.
|
||||
|
||||
I want to install Emacs, so I type **3**.
|
||||
```
|
||||
This script Is under GPLv3 License
|
||||
|
||||
[ TEXT EDITORS ]
|
||||
[ Option ] [ Description ]
|
||||
1) GEdit
|
||||
2) Geany
|
||||
3) Emacs
|
||||
4) VIM
|
||||
5) Kate
|
||||
---------------------------
|
||||
q) Return To Main Menu
|
||||
|
||||
Choose An Option: 3
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, Emacs will be installed on your Arch Linux system.
|
||||
|
||||
![][5]
|
||||
|
||||
Press ENTER key to return to main menu after installing the applications of your choice.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion
|
||||
|
||||
Undoubtedly, this script makes the Arch Linux user’s life easier, particularly the beginner’s. If you are looking for a fast and easy way to install applications without using pacman, then this script might be a good choice. Give it a try and let us know what you think about this script in the comment section below.
|
||||
|
||||
And, that’s all. Hope this tool helps. We will be posting useful guides every day. If you find our guides useful, please share them on your social, professional networks and support OSTechNix.
|
||||
|
||||
Cheers!!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.ostechnix.com/archi0-arch-linux-applications-automatic-installation-script/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ostechnix.com/getting-started-pacman/
|
||||
[2]:data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7
|
||||
[3]:http://www.ostechnix.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/sk@sk-ArchI0_003.png
|
||||
[4]:http://www.ostechnix.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/sk@sk-ArchI0_004-1.png
|
||||
[5]:http://www.ostechnix.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/pacman-as-superuser_005.png
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,159 @@
|
||||
How To Force User To Change Password On Next Login In Linux
|
||||
======
|
||||
When you created the users account with a default password, you have to force the users to change their password on next login.
|
||||
|
||||
This option is mandatory when you were working in organization because old employees might know the default password and they may or may not try to malpractices.
|
||||
|
||||
This is one of the security complaint so, make sure you have to take care this in the proper way without any fail. Even your team members can do the same.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of the users are lazy and they don’t change their password until you force them to do so, make this practices.
|
||||
|
||||
For security reason you need to change your password frequently, or at-least once in a month.
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure you are using hard and guess password (The combination of Upper and Lower alphabets, Numbers, and Special characters) . It should be at-least 10-15 characters.
|
||||
|
||||
We have ran a shell script to create a user account in Linux server which automatically append a password for user, with combination of actual username followed by few numeric values.
|
||||
|
||||
We can achieve this by using the below two methods.
|
||||
|
||||
* passwd command
|
||||
* chage command
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Suggested Read :**
|
||||
**(#)** [How To Check Which Groups A User Belongs To On Linux][1]
|
||||
**(#)** [How To Check User Created Date On Linux][2]
|
||||
**(#)** [How To Reset/Change User Password In Linux][3]
|
||||
**(#)** [How To Manage Password Expiration & Aging Using passwd Command][4]
|
||||
|
||||
### Method-1: Using passwd Command
|
||||
|
||||
passwd stands for password. It updates user’s authentication tokens. The passwd command/utility is used to set or modify or change users password.
|
||||
|
||||
Normal users are only allowed to change their own account but super users can change the password for any account.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, we can use an additional options which allows user to perform other activities such as deleting password for the user, lock/unlock the user account, set the password expiry for given user account, etc,.
|
||||
|
||||
This can be performed in Linux by calling the Linux-PAM and Libuser API.
|
||||
|
||||
Users details will be stored in /etc/passwd file when you created a user in Linux. The passwd file contain each/every user details as a single line with seven fields.
|
||||
|
||||
Also below four files will be updated while creating a new users in the Linux system.
|
||||
|
||||
* `/etc/passwd:` User details will be updated in this file.
|
||||
* `/etc/shadow:` User password info will be updated in this file.
|
||||
* `/etc/group:` Group details will be updated of the new user in this file.
|
||||
* `/etc/gshadow:` Group password info will be updated of the new user in the file.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### How To Perform This With passwd Command
|
||||
|
||||
We can perform this with passwd command by adding the `-e` option.
|
||||
|
||||
To test this, let’s create a new user account and see how it’s working.
|
||||
```
|
||||
# useradd -c "2g Admin - Magesh M" magesh && passwd magesh
|
||||
Changing password for user magesh.
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
Retype new password:
|
||||
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Expire the password for the given user account. The user will be forced to change the password during the next login attempt.
|
||||
```
|
||||
# passwd -e magesh
|
||||
Expiring password for user magesh.
|
||||
passwd: Success
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It’s asking me to set a new password when i’m trying to login to the system at first time.
|
||||
```
|
||||
login as: magesh
|
||||
[email protected]'s password:
|
||||
You are required to change your password immediately (root enforced)
|
||||
WARNING: Your password has expired.
|
||||
You must change your password now and login again!
|
||||
Changing password for user magesh.
|
||||
Changing password for magesh.
|
||||
(current) UNIX password:
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
Retype new password:
|
||||
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
|
||||
Connection to localhost closed.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Method-2: Using chage Command
|
||||
|
||||
chage stands for change age. It changes user password expiry information.
|
||||
|
||||
The chage command changes the number of days between password changes and the date of the last password change. This information is used by the system to determine when a user must change his/her password.
|
||||
|
||||
This allows user to perform other activities such as set account expiration date, set password inactive after expiration, show account aging information, set minimum & maximum number of days before password change and set expiration warning days.
|
||||
|
||||
#### How To Perform This With chage Command
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s perform this with help of chage command by adding the `-d` option.
|
||||
|
||||
To test this, let’s create a new user account and see how it’s working. We are going to create a user account called `thanu`.
|
||||
```
|
||||
# useradd -c "2g Editor - Thanisha M" thanu && passwd thanu
|
||||
Changing password for user thanu.
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
Retype new password:
|
||||
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To achieve this, set a user’s date of last password change to “0” with the chage command.
|
||||
```
|
||||
# chage -d 0 thanu
|
||||
|
||||
# chage -l thanu
|
||||
Last password change : Jul 18, 2018
|
||||
Password expires : never
|
||||
Password inactive : never
|
||||
Account expires : never
|
||||
Minimum number of days between password change : 0
|
||||
Maximum number of days between password change : 99999
|
||||
Number of days of warning before password expires : 7
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It’s asking me to set a new password when i’m trying to login to the system at first time.
|
||||
```
|
||||
login as: thanu
|
||||
[email protected]'s password:
|
||||
You are required to change your password immediately (root enforced)
|
||||
WARNING: Your password has expired.
|
||||
You must change your password now and login again!
|
||||
Changing password for user thanu.
|
||||
Changing password for thanu.
|
||||
(current) UNIX password:
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
Retype new password:
|
||||
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
|
||||
Connection to localhost closed.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.2daygeek.com/how-to-force-user-to-change-password-on-next-login-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Prakash Subramanian][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.2daygeek.com/author/prakash/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.2daygeek.com/how-to-check-which-groups-a-user-belongs-to-on-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.2daygeek.com/how-to-check-user-created-date-on-linux/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.2daygeek.com/passwd-command-examples/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.2daygeek.com/passwd-command-examples-part-l/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
How to check free disk space in Linux
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Keeping track of disk utilization information is on system administrators' (and others') daily to-do list. Linux has a few built-in utilities that help provide that information.
|
||||
|
||||
### df
|
||||
|
||||
The `df` command stands for "disk-free," and shows available and used disk space on the Linux system.
|
||||
|
||||
`df -h` shows disk space in human-readable format
|
||||
|
||||
`df -a` shows the file system's complete disk usage even if the Available field is 0
|
||||
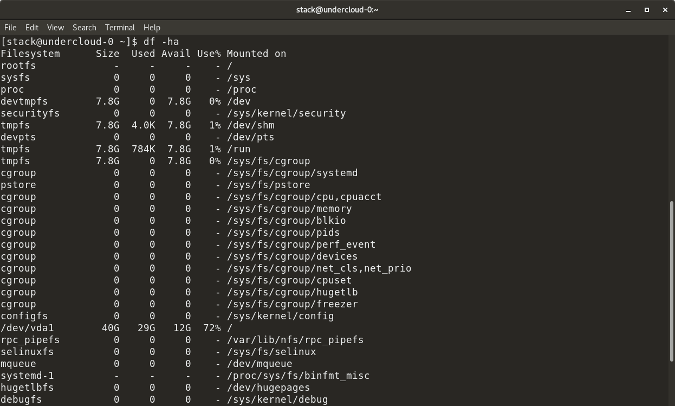
|
||||
`df -T` shows the disk usage along with each block's filesystem type (e.g., xfs, ext2, ext3, btrfs, etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
`df -i` shows used and free inodes
|
||||
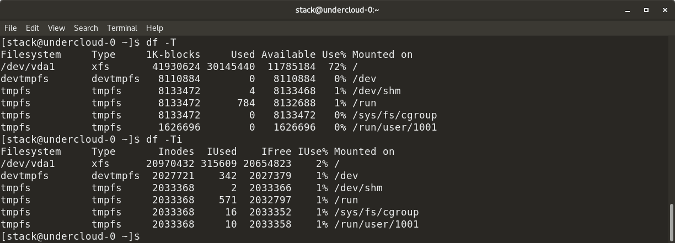
|
||||
|
||||
### du
|
||||
|
||||
`du` shows the disk usage of files, folders, etc. in the default kilobyte size
|
||||
|
||||
`du -h` shows disk usage in human-readable format for all directories and subdirectories
|
||||
|
||||
`du -a` shows disk usage for all files
|
||||
|
||||
`du -s` provides total disk space used by a particular file or directory
|
||||
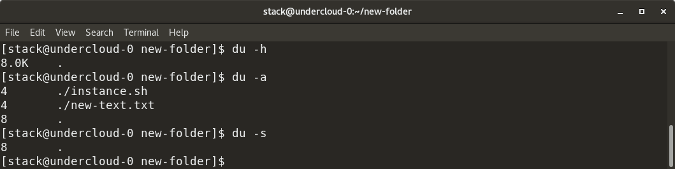
|
||||
|
||||
The following commands will check your total space and your utilized space.
|
||||
|
||||
### ls -al
|
||||
|
||||
`ls -al` lists the entire contents, along with their size, of a particular directory
|
||||
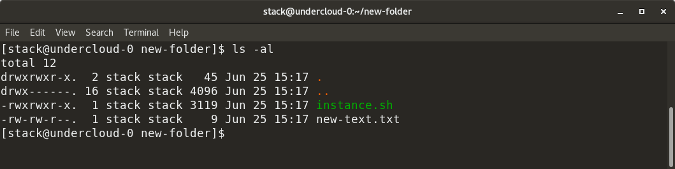
|
||||
|
||||
### stat
|
||||
|
||||
`stat <file/directory> `displays the size and other stats of a file/directory or a filesystem.
|
||||
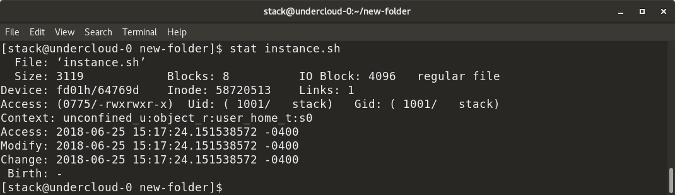
|
||||
|
||||
### fdisk -l
|
||||
|
||||
`fdisk -l` shows disk size along with disk partitioning information
|
||||
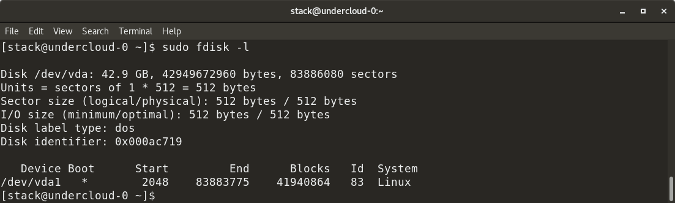
|
||||
|
||||
These are most of the built-in utilities for checking file space in Linux. There are many similar tools, like [Disks][1] (GUI), [Ncdu][2], etc., that also show disk space utilization. Do you have a favorite tool that's not on this list? Please share in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/7/how-check-free-disk-space-linux
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Archit Modi][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://opensource.com/users/architmodi
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Disks
|
||||
[2]:https://dev.yorhel.nl/ncdu
|
||||
@ -1,29 +1,34 @@
|
||||
streams:一个新的 Redis 通用数据结构
|
||||
==================================
|
||||
|
||||
直到几个月以前,对于我来说,在消息传递的环境中,streams 只是一个有趣且相对简单的概念。在 Kafka 流行这个概念之后,我主要研究它们在 Disque 实例中的用途。Disque 是一个将会转化为 Redis 4.2 的模块的消息队列。后来我发现 Disque 全都是 AP 消息,它将在不需要客户端过多参与的情况下实现容错和保证送达,因此,我认为 streams 的概念在那种情况下并不适用。
|
||||
直到几个月以前,对于我来说,在消息传递的环境中,streams 只是一个有趣且相对简单的概念。在 Kafka 流行这个概念之后,我主要研究它们在 Disque 实例中的用途。Disque 是一个将会转变为 Redis 4.2 模块的消息队列。后来我发现 Disque 全都是 AP 消息,它将在不需要客户端过多参与的情况下实现容错和保证送达,因此,我认为 streams 的概念在那种情况下并不适用。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,在 Redis 中有一个问题,那就是缺省情况下导出数据结构并不轻松。它在 Redis 列表、排序集和发布/订阅(Pub/Sub)能力上有某些缺陷。你可以合适地使用这些工具去模拟一个消息或事件的序列,而有所权衡。排序集是大量耗费内存的,不能自然的模拟一次又一次的相同消息的传递,客户端不能阻塞新消息。因为一个排序集并不是一个序列化的数据结构,它是一个根据它们量的变化而移动的元素集:它不是很像时间系列一样的东西。列表有另外的问题,它在某些特定的用例中产生类似的适用性问题:你无法浏览列表中部是什么,因为在那种情况下,访问时间是线性的。此外,没有任何的指定输出功能,列表上的阻塞操作仅为单个客户端提供单个元素。列表中没有固定的元素标识,也就是说,不能指定从哪个元素开始给我提供内容。对于一到多的工作负载,这里有发布/订阅,它在大多数情况下是非常好的,但是,对于某些不想“即发即弃”的东西:保留一个历史是很重要的,而不是断开之后重新获得消息,也因为某些消息列表,像时间系列,在用范围查询浏览时,是非常重要的:在这 10 秒范围内我的温度读数是多少?
|
||||
然而同时,在 Redis 中有一个问题,那就是缺省情况下导出数据结构并不轻松。它在 Redis 列表、排序集和发布/订阅(Pub/Sub)能力之间有某些缺陷。你可以权衡使用这些工具去模拟一个消息或事件的序列。
|
||||
|
||||
排序集是大量耗费内存的,不能自然的模拟一次又一次的相同消息的传递,客户端不能阻塞新消息。因为一个排序集并不是一个序列化的数据结构,它是一个元素可以根据它们量的变化而移动的集合:它不是很像时间系列一样的东西。
|
||||
|
||||
列表有另外的问题,它在某些特定的用例中产生类似的适用性问题:你无法浏览列表中部是什么,因为在那种情况下,访问时间是线性的。此外,没有任何的指定输出功能,列表上的阻塞操作仅为单个客户端提供单个元素。列表中没有固定的元素标识,也就是说,不能指定从哪个元素开始给我提供内容。
|
||||
|
||||
对于一到多的工作任务,有发布/订阅机制,它在大多数情况下是非常好的,但是,对于某些不想“即发即弃”的东西:保留一个历史是很重要的,而不是断开之后重新获得消息,也因为某些消息列表,像时间系列,用范围查询浏览是非常重要的:在这 10 秒范围内我的温度读数是多少?
|
||||
|
||||
这有一种方法可以尝试处理上面的问题,我计划对排序集进行通用化,并列入一个唯一的、更灵活的数据结构,然而,我的设计尝试最终以生成一个比当前的数据结构更加矫揉造作的结果而结束。一个关于 Redis 数据结构导出的更好的想法是,让它更像天然的计算机科学的数据结构,而不是,“Salvatore 发明的 API”。因此,在最后我停止了我的尝试,并且说,“ok,这是我们目前能提供的”,或许,我将为发布/订阅增加一些历史信息,或者将来对列表访问增加一些更灵活的方式。然而,每次在会议上有用户对我说“你如何在 Redis 中模拟时间系列” 或者类似的问题时,我的脸就绿了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 起源
|
||||
|
||||
在将 Redis 4.0 中的模块介绍完之后,用户开始去看他们自己怎么去修复这些问题。他们之一,Timothy Downs,通过 IRC 写信给我:
|
||||
在 Redis 4.0 中引入模块之后,用户开始去看他们自己怎么去修复这些问题。他们中的一个,Timothy Downs,通过 IRC 写信给我:
|
||||
|
||||
<forkfork> 这个模块,我计划去增加一个事务日志式的数据类型 - 这意味着大量的订阅者可以在没有大量的内存增加的情况下做一些像发布/订阅那样的事情
|
||||
<forkfork> 订阅者保持他在消息队列中的位置,而不是在 Redis 上维护每个客户和复制消息的每个订阅者
|
||||
\<forkfork> 这个模块,我计划去增加一个事务日志式的数据类型 —— 这意味着大量的订阅者可以在没有大量增加 redis 内存使用的情况下做一些像发布/订阅那样的事情
|
||||
\<forkfork> 订阅者保持它在消息队列中的位置,而不是让 Redis 必须维护每个消费者的位置和为每个订阅者复制消息
|
||||
|
||||
这激发了我的想像力。我想了几天,并且意识到这可能是我们立刻同时解决上面的问题的契机。我需要去重新想像 “日志” 的概念是什么。它是个基本的编程元素,每个人都使用到它,因为它是非常简单地在追加模式中打开一个文件并以一定的格式写入数据,数据结构必须是抽象的。然而 Redis ,它们在内存中,并且我们使用 RAM 并不是因为我们懒,但是,因为使用一些指针,我们可以概念化数据结构并让他们抽象,并允许他们去摆脱明显的限制。对于实例,正常的日志有几个问题:偏移不是逻辑的,但是,它是一个真实的字节偏移,如果你想逻辑偏移是什么,那是与条目插入的时间相关的,我们有范围查询可用。同样的,一个日志通常很难收集:在一个只追加的数据结构中怎么去删除旧的元素?好吧,在我们理想的日志中,我们只是说,我想要最大的条目数,而旧的元素一个也不要,等等。
|
||||
这激发了我的想像力。我想了几天,并且意识到这可能是我们立刻同时解决上面所有问题的契机。我需要去重新构想 “日志” 的概念是什么。它是个基本的编程元素,每个人都使用过它,因为它只是简单地以追加模式打开一个文件,并以一定的格式写入数据。然而 Redis 数据结构必须是抽象的。它们在内存中,并且我们使用内存并不是因为我们懒,而是因为使用一些指针,我们可以概念化数据结构并把它们抽象,以允许它们摆脱明显的限制。对于正常的例子来说,日志有几个问题:偏移不是逻辑的,而是真实的字节偏移,如果你想要与条目插入的时间相关的逻辑偏移,我们有范围查询可用。同样的,日志通常很难进行垃圾收集:在一个只追加的数据结构中怎么去删除旧的元素?好吧,在我们理想的日志中,我们只是说,我想要编号最大的那个条目,而旧的元素一个也不要,等等。
|
||||
|
||||
当我从 Timothy 的想法,去尝试着写一个规范的时候,我使用了 radix 树去实现,它是用于 Redis 集群的,去优化它内部的某些部分。这为实现一个有效的空间日志提供了基础。它在对数的时间(logarithmic time)内得到范围是仍然可访问的。同时,我开始去读关于 Kafka 流,去得到另外的创意,它也非常适合我的设计,并且产生了一个 Kafka 客户组的概念,并且,将它理想化用于 Redis 和内存中(in-memory)使用的案例。然而,该规范仅保留了几个月,在一段时间后,我积累了与别人讨论的即将增加到 Redis 中的内容,为了升级它,使用了许多提示(hint)几乎从头到尾重写了一遍。我想 Redis 流尤其对于时间系列是非常有用的,而不仅是用于事件和消息类的应用程序。
|
||||
当我从 Timothy 的想法萌芽,去尝试着写一个规范的时候,我使用了我用于 Redis 集群中的 radix 树实现,优化了它内部的某些部分。这为实现一个有效利用空间的日志提供了基础,而仍然可以用对数时间来访问范围。同时,我开始去读关于 Kafka 流以获得另外的灵感,它也非常适合我的设计,并且产生了一个 Kafka 消费组的概念,并且,理想化的话,它可以用于 Redis 和内存用例。然而,该规范仅维持了几个月,在一段时间后我几乎把它从头到尾重写了一遍,以便将我与别人讨论的即将增加到 Redis 中的内容所得到的许多建议一起升级。我希望 Redis 流是非常有用的,尤其对于时间序列,而不仅是用于事件和消息类的应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们写一些代码
|
||||
=====================
|
||||
### 让我们写一些代码
|
||||
|
||||
从 Redis 会议回来后,在整个夏天,我实现了一个称为 “listpack” 的库。这个库是 ziplist.c 的继承者,那是一个表示在单个分配中字符串元素的列表的数据结构。它是一个非常专业的序列化格式,有在相反的顺序中可解析的特性,从右到左: 在所有的用户案例中用于替代 ziplists 中所需的某些东西。
|
||||
从 Redis 大会回来后,在整个夏天,我实现了一个称为 “listpack” 的库。这个库是 ziplist.c 的继任者,那是一个表示在单个分配中的字符串元素列表的数据结构。它是一个非常特殊的序列化格式,其特点在于也能够以逆序(从右到左)解析:需要它以便在各种用例中替代 ziplists。
|
||||
|
||||
结合 radix 树 + listpacks,它可以很容易地去构建一个日志,它同时也是非常高效的,并且是索引化的,意味着,允许通过 IDs 和时间进行随机访问。自从实现这个方法后,为了实现流数据结构,我开始去写一些代码。我直到完成实现,不管怎样,在这个时候,在 Github 上的 Redis 内部的 “streams” 分支,去启动共同开发并接受订阅已经足够了。我并没有声称那个 API 是最终版本,但是,这有两个有趣的事实:一是,在那时,仅客户组是缺失的,加上一些不那么重要的命令去操作流,但是,所有的大的方面都已经实现了。二是,一旦各个方面比较稳定了之后 ,决定将所有的流的工作移植到 4.0 分支,它大约两个月后发布。这意味着 Redis 用户为了使用流,不用等待 Redis 4.2,它们将对生产使用的 ASAP 可用。这是可能的,因为有一个新的数据结构,几乎所有的代码改变都是独立于新代码的。除了阻塞列表操作之外 :代码都重构了,因此,我们和流共享了相同的代码,并且,列表阻塞操作在 Redis 内部进行了大量的简化。
|
||||
结合 radix 树和 listpacks,它可以很容易地去构建一个日志,它同时也是非常空间高效的,并且是索引化的,这意味着允许通过 ID 和时间进行随机访问。自从这些就绪后,我开始去写一些代码以实现流数据结构。我最终完成了该实现,不管怎样,现在,在 Github 上的 Redis 的 “streams” 分支里面,它已经可以跑起来了。我并没有声称那个 API 是 100% 的最终版本,但是,这有两个有趣的事实:一是,在那时,只有消费组是缺失的,加上一些不那么重要的命令去操作流,但是,所有的大的方面都已经实现了。二是,一旦各个方面比较稳定了之后 ,决定大概用两个月的时间将所有的流的工作向后移植到 4.0 分支。这意味着 Redis 用户为了使用流,不用等待 Redis 4.2,它们在生产环境马上就可用了。这是可能的,因为作为一个新的数据结构,几乎所有的代码改变都出现在新的代码里面。除了阻塞列表操作之外:该代码被重构了,我们对于流和列表阻塞操作共享了相同的代码,而极大地简化了 Redis 内部。
|
||||
|
||||
教程:欢迎使用 Redis 流
|
||||
==================================
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## 如何在linux系统中使用dd命令而不会损毁你的磁盘
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章节选自 Manning 出版社出版的图书[Linux in Action](https://www.manning.com/books/linux-in-action?a_aid=bootstrap-it&a_bid=4ca15fc9&chan=opensource)的第4章.
|
||||
|
||||
你是否正在从一个即将损坏的存储驱动器挽救数据,把本地文件进行远程备份,或者把一个活动分区的数据完整的复制到别处,那么你需要懂得如何安全而可靠的复制驱动器和文件系统数据.幸运的是,dd 是一个可以使用的简单而又功能强大的镜像复制命令,从现在到未来很长的时间内,也许直到永远都不会出现比 dd 更好的工具了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 完整的复制驱动器和分区中的数据
|
||||
|
||||
仔细研究后,你会发现你可以使用 dd 做各种任务,但是它最重要的功能是处理磁盘分区。当然,你可以使用 tar 命令或者 scp 命令从一台计算机复制整个文件系统的文件, 然后把这些文件原样粘贴在另一台刚刚安装好 linux 操作系统的计算机中。但是,因为文件系统的文件不是映像文件,所以在复制文件的过程中需要计算机操作系统的运行作为基础。
|
||||
|
||||
另一方面,使用 dd 可以对任何数字信息完美的进行逐个字节的镜像。但是不论何时何地,当你要对分区进行操作时,我要告诉你早期的Unix管理员曾开过这样的玩笑: " dd 象征着磁盘毁灭者"。 在使用 dd 命令的时候,如果你输入了哪怕是一个字母,也可能立即永久性的擦除掉整个磁盘驱动器里的所有重要的数据。因此,一定要注意命令的拼写格式规范。
|
||||
|
||||
**记住:** 在按下 Enter 键执行 dd 命令之前,暂时停下来仔细的认真思考一下。
|
||||
|
||||
### dd 命令的基本操作
|
||||
|
||||
现在你已经得到了适当的提醒,我们将从简单的事情开始。假设你要对代号为 /dev/sda 的整个磁盘数据创建精确的映像,你已经插入了一张空的磁盘驱动器 (理想情况下具有与代号为 /dev/sda 的磁盘驱动器相同的容量)。语法很简单: if = 定义源驱动器 `of =` 定义你要将数据保存到的文件或位置:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=/dev/sda of=/dev/sdb
|
||||
```
|
||||
接下来的例子将要对 /dev/sda 驱动器创建一个 .img 的映像文件,然后把该文件保存的你的用户帐号家目录:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=/dev/sda of=/home/username/sdadisk.img
|
||||
```
|
||||
上面的命令针对整个驱动器创建映像文件,你也可以针对驱动器上的单个分区进行操作。 下面的例子针对驱动器的单个分区进行操作,同时使用了一个 bs 参数用于设置单次拷贝的字节数量 (此例中是 4096)。设定 bs 参数值可能会影响 dd 命令的整体操作速度,但理想的设置取决于你的硬件配置和其它考虑。
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=/dev/sda2 of=/home/username/partition2.img bs=4096
|
||||
```
|
||||
数据的恢复非常简单:通过颠倒 if 和 of 参数可以有效的完成任务。在此例中,if = 使用你要恢复的映像,of = 使用你想要写入映像的目标驱动器:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=sdadisk.img of=/dev/sdb
|
||||
```
|
||||
你也可以在一条命令中同时完成创建和拷贝任务。下面的例子中将从支持 SSH 的远程驱动器创建一个压缩的映像文件并把该文件保存到你的本地计算机中:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ssh username@54.98.132.10 "dd if=/dev/sda | gzip -1 -" | dd of=backup.gz
|
||||
```
|
||||
你应该经常测试你的档案,确保它们可正常使用。如果它是你创建的启动驱动器,将它粘贴到计算机中,看看它是否能够按预期启动。如果它是普通分区的数据,挂载该分区,确保文件都存在而且可以正常的访问。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 dd 擦除磁盘数据
|
||||
|
||||
多年以前,我的一个负责政府海外大使馆安全的朋友曾经告诉我,在他当时在任的时候, 政府会给每一个大使馆提供一个官方版的锤子。为什么呢? 一旦大使馆设施可能被不友善的人员侵占,就会使用这个锤子毁坏所有的硬盘.
|
||||
|
||||
为什么要那样做?为什么不仅仅删除数据?你在开玩笑,对吧?所有人都知道从存储设备中删除包含敏感信息的文件实际上并没有真正移除这些数据。除非使用锤子彻底的毁坏这些存储介质,否则,只要有足够的时间和动机, 几乎所有的内容都可以从几乎任何数字存储介质重新获取。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,你可以使用 dd 命令让坏人非常难以获得你的旧数据。这个命令需要花费一些时间在 `/dev/sda1` 分区的每个扇区写入数百万个 zero:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda1
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
还有更好的方法。通过使用 /dev/urandom 作为源文件,你可以在磁盘上写入随机字符:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/sda1
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 监控 dd 的操作
|
||||
|
||||
由于磁盘或磁盘分区的存档可能需要很长的时间,因此你可能需要在命令中添加进度查看器。安装 Pipe Viewer(在Ubuntu系统上安装命令为 sudo apt install pv),然后把 pv 命令和 dd 命令结合在一起。使用 pv,最终的命令是这样的:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# dd if=/dev/urandom | pv | dd of=/dev/sda1
|
||||
|
||||
4,14MB 0:00:05 [ 98kB/s] [ <=> ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
想要推迟备份和磁盘管理工作?有了 dd 工具,你不会有太多的借口。它真的非常简单,但是要小心。祝你好运!
|
||||
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
编译自:https://opensource.com/article/18/7/how-use-dd-linux
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[David Clinton](https://opensource.com/users/remyd)
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[SunWave](https://github.com/SunWave)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,17 +1,15 @@
|
||||
Translating by Auk7F7
|
||||
|
||||
Install Microsoft Windows Fonts In Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 上安装 Microsoft Windows 字体
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Most of the educational institutions are still using Microsoft Fonts. I am not sure about other countries. But, in Tamilnadu (An Indian state), **Times New Roman** and **Arial** fonts are being mostly used by almost all sorts of documentation works, projects, and assignments in colleges and schools. Not only the educational institutions, some small organizations, offices, and shops are still using MS Windows Fonts. Just in case, if you are in a situation where you need to use Microsoft fonts in your Ubuntu Linux desktop, here is how to do it.
|
||||
大多数教育机构仍在使用 Microsoft 字体, 我不清楚其他国家是什么情况。但在泰米尔纳德邦(印度的一个州), **Times New Roman** 和 **Arial** 字体主要被用于大学和学校的几乎所有文档工作,项目和作业。不仅是教育机构,而且一些小型组织,办公室和商店仍在使用 MS Windows 字体。以防万一,如果你需要在 Ubuntu 桌面版上使用 Microsoft 字体,请按照以下步骤安装。
|
||||
|
||||
**Disclaimer:** Microsoft has released its core fonts for free. However, **Please be aware that usage of Microsoft fonts is prohibited in other operating systems**. Read the EULA carefully before installing MS Fonts in any Linux operating system. We (OSTechNix) are not responsible for any kind of piracy act.
|
||||
**免责声明**: Microsoft 已免费发布其核心字体。 但**请不要在其他操作系统中禁止使用 Microsoft 字体**。在任何 Linux 操作系统中安装 MS 字体之前请仔细阅读 EULA 。我们(OSTechNix)不负责这种任何种类的盗版行为。
|
||||
|
||||
### Install MS Fonts in Ubuntu 18.04 LTS desktop
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 桌面版上安装 MS 字体
|
||||
|
||||
Install MS TrueType Fonts as shown below:
|
||||
如下所示安装 MS TrueType 字体:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt update
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,21 +17,21 @@ $ sudo apt install ttf-mscorefonts-installer
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Microsoft’s End user agreement wizard will appear. Click **OK** to continue.
|
||||
然后将会出现 Microsoft 的最终用户协议向导,点击 **OK** 以继续。
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
Click **Yes** to accept the Microsoft agreement:
|
||||
点击 **Yes** 已接受 Microsoft 的协议:
|
||||
|
||||
![][3]
|
||||
|
||||
After installing the fonts, we need to update the font cache using command:
|
||||
安装字体之后, 我们需要使用命令行来更新字体缓存:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo fc-cache -f -v
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample output:**
|
||||
**示例输出:**
|
||||
```
|
||||
/usr/share/fonts: caching, new cache contents: 0 fonts, 6 dirs
|
||||
/usr/share/fonts/X11: caching, new cache contents: 0 fonts, 4 dirs
|
||||
@ -111,25 +109,26 @@ fc-cache: succeeded
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Install MS Fonts in Dual boot with Linux and Windows
|
||||
### 在 Linux 和 Windows 双启动的机器上安装 MS 字体
|
||||
|
||||
If you have dual boot system with Linux and Windows operating system, you can easily install the MS fonts from Windows C drive. All you have to do is mount the Windows partition (C:/Windows).
|
||||
如果你有 Linux 和 Windows 的双启动系统,你可以轻松地从 Windows C 驱动器上安装 MS 字体。
|
||||
你所要做的就是挂载 Windows 分区(C:/windows)。
|
||||
|
||||
I assume you have mounted the **C:\Windows** partition at **/Windowsdrive** directory in linux.
|
||||
我假设你已经在 Linux 中将 **C:\Windows** 分区挂载在了 **/Windowsdrive** 目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
Now, link the fonts location to your Linux system’s fonts folder as shown below.
|
||||
现在,将字体位置链接到你的 Linux 系统的字体文件夹,如下所示。
|
||||
```
|
||||
ln -s /Windowsdrive/Windows/Fonts /usr/share/fonts/WindowsFonts
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After linking the fonts folder, regenerate the fontconfig cache using command:
|
||||
链接字体文件之后,使用命令行重新生成 fontconfig 缓存::
|
||||
```
|
||||
fc-cache
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, copy all Windows fonts to **/usr/share/fonts** directory and install the fonts using the following commands:
|
||||
或者,将所有的 Windows 字体复制到 **/usr/share/fonts** 目录下并使用一下命令安装字体:
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir /usr/share/fonts/WindowsFonts
|
||||
|
||||
@ -139,23 +138,25 @@ chmod 755 /usr/share/fonts/WindowsFonts/*
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, regenerate the fontconfig cache using command:
|
||||
最后,使用命令行重新生成 fontconfig 缓存:
|
||||
```
|
||||
fc-cache
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Test Windows font
|
||||
|
||||
Open LibreOffice or GIMP after installing MS Fonts. Now, you will see there the Microsoft coretype fonts.
|
||||
### 测试 Windows 字体
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
安装 MS 字体后打开 LibreOffice 或 GIMP。 现在,你将会看到 Microsoft coretype 字体。
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it. Hope this guide useful. Again, I warn you usage of MS fonts in other operating system is prohibited. Please read the Microsoft License agreement before installing the MS fonts.
|
||||
就是这样, 希望这本指南有用。我再次警告你,在其他操作系统中使用 MS 字体是被禁止的。在安装 MS 字体之前请先阅读 Microsoft 许可协议。
|
||||
|
||||
If you find our guides useful, please share them on your social, professional networks and support OSTechNix. More good stuffs to come. Keep visiting!
|
||||
如果你觉得我们的指南有用,请在你的社区、专业网络上分享并支持 OSTechNix。还有更多好东西在等着我们。持续访问!
|
||||
|
||||
Cheers!!
|
||||
庆祝吧!!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -165,7 +166,7 @@ via: https://www.ostechnix.com/install-microsoft-windows-fonts-ubuntu-16-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
译者:[Auk7F7](https://github.com/Auk7F7)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user