mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-25 23:11:02 +08:00
[translated] 20170216 Getting Started with PowerShell 6.0 in Linux
This commit is contained in:
parent
b06c2bc380
commit
ea66ed2b74
@ -1,259 +0,0 @@
|
||||
@zijung 翻譯中……
|
||||
|
||||
Getting Started with PowerShell 6.0 in Linux [Beginner Guide]
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
After Microsoft falling in love with Linux (what has popularly come to be known as “Microsoft Loves Linux”), PowerShell which was originally a Windows-only component, was open-sourced and made cross-platform on 18 August 2016, available on Linux and Mac OS.
|
||||
|
||||
PowerShell is a task automation and configuration management system developed by Microsoft. It is made up of a command language interpreter (shell) and scripting language built on the .NET Framework.
|
||||
|
||||
It offers complete access to COM (Component Object Model) and WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation), thereby allowing [system administrators to carry out administrative tasks][1] on both local and remote Windows systems as well as WS-Management and CIM (Common Information Model) enabling administration of remote Linux systems plus network devices.
|
||||
|
||||
Under this framework, administrative tasks are fundamentally carried out by particular .NET classes called cmdlets (pronounced command-lets). Similar to shell scripts in Linux, users can build scripts or executables by storing groups of cmdlets in files by following certain rules. These scripts can be used as independent [command line utilities or tools][2].
|
||||
|
||||
### Install PowerShell Core 6.0 in Linux Systems
|
||||
|
||||
To install PowerShell Core 6.0 in Linux, we will use official Microsoft Ubuntu repository that will allows us to install through most popular Linux package management tools such as [apt-get][3] and [yum][4].
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu 16.04
|
||||
|
||||
First import the public repository GPG keys, then register the Microsoft Ubuntu repository in APT package sources list to install Powershell:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
$ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/16.04/prod.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/microsoft.list
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install -y powershell
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu 14.04
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
$ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/14.04/prod.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/microsoft.list
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install -y powershell
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS 7
|
||||
|
||||
First register the Microsoft RedHat repository in YUM package manager repository list and install Powershell:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/7/prod.repo > /etc/yum.repos.d/microsoft.repo
|
||||
$ sudo yum install -y powershell
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Use Powershell Core 6.0 in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
In this section, we will have a brief introduction to Powershell; where we will see how to start powershell, run some basic commands, look at how to work with files, directories and processes. Then later dive into how to list all available commands, show command help and aliases.
|
||||
|
||||
To start Powershell, type:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ powershell
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][5]
|
||||
|
||||
Start Powershell in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
You can check the Powershell version with the command below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$PSVersionTable
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Check Powershell Version
|
||||
|
||||
Running some basic Powershell commands on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
get-date [# Display current date]
|
||||
get-uptime [# Display server uptime]
|
||||
get-location [# Display present working directory]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Working with Files and Directories in Powershell
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create a new empty file using the two methods below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
new-item tecmint.tex
|
||||
OR
|
||||
“”>tecmint.tex
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
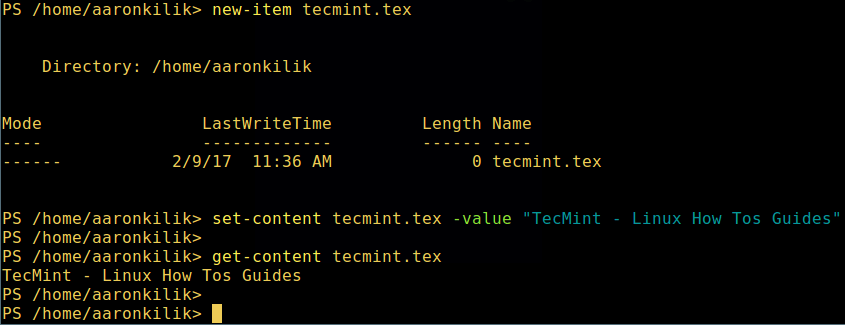
Then add content to it and view the file content.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
set-content tecmint.tex -value "TecMint Linux How Tos Guides"
|
||||
get-content tecmint.tex
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][7]
|
||||
|
||||
Create New File in Powershell
|
||||
|
||||
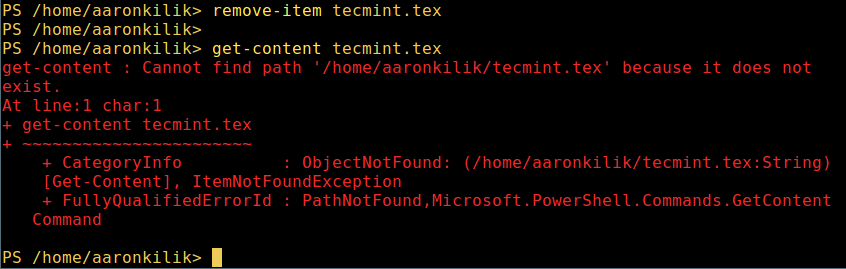
2. Delete a file in powershell.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
remove-item tecmint.tex
|
||||
get-content tecmint.tex
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
Delete File in Powershell
|
||||
|
||||
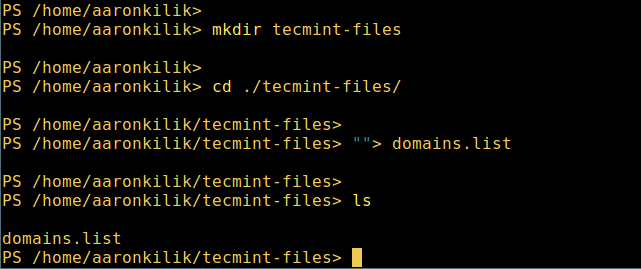
3. Create a new directory.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir tecmint-files
|
||||
cd tecmint-files
|
||||
“”>domains.list
|
||||
ls
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][9]
|
||||
|
||||
Create Directory in Powershell
|
||||
|
||||
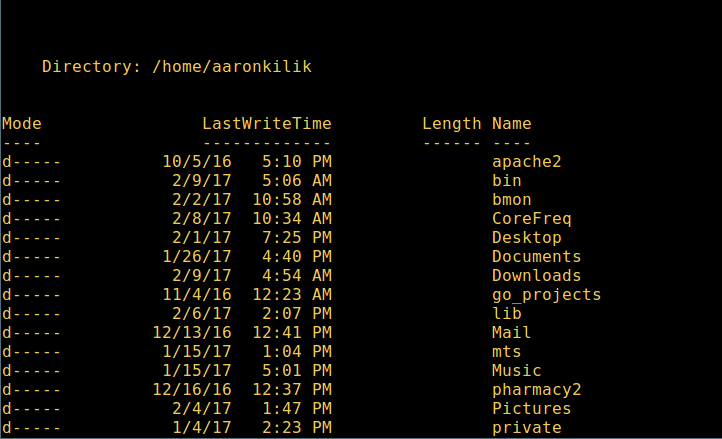
4. To perform a long listing, which displays details of a file/directory including mode (file type), last modification time, type:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dir
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][10]
|
||||
|
||||
Directory Long Listing in Powershell
|
||||
|
||||
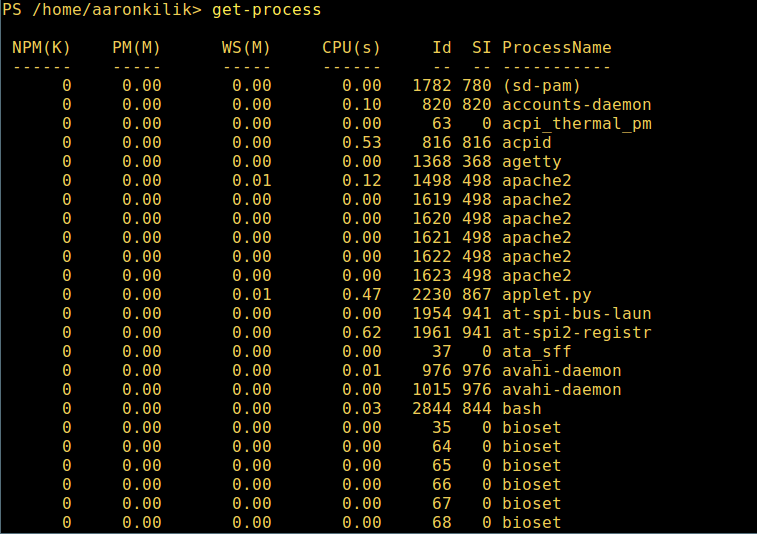
5. View all running processes on your system:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
get-process
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][11]
|
||||
|
||||
View Running Processes in Powershell
|
||||
|
||||
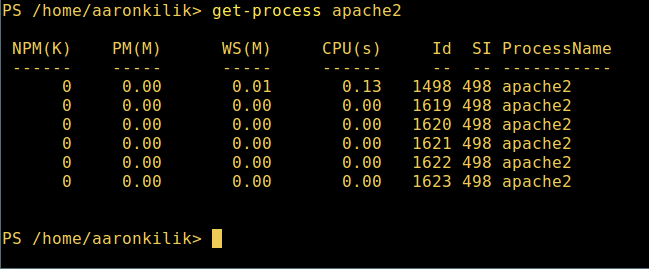
6. To view details of a single/group of running processes with a given name, provide the process name as an argument to the previous command as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
get-process apache2
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][12]
|
||||
|
||||
View Specific Process in Powershell
|
||||
|
||||
Meaning of the units in the output above:
|
||||
|
||||
1. NPM(K) – amount of non-paged memory that the process is using, in kilobytes.
|
||||
2. PM(K) – amount of pageable memory that the process is using, in kilobytes.
|
||||
3. WS(K) – size of the working set of the process, in kilobytes. The working set consists of the pages of memory that were recently referenced by the process.
|
||||
4. CPU(s) – amount of processor time that the process has used on all processors, in seconds.
|
||||
5. ID – process ID (PID).
|
||||
6. ProcessName – name of the process.
|
||||
|
||||
7. To know more, get a list of all Powershell commands for different tasks:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
get-command
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][13]
|
||||
|
||||
List Powershell Commands
|
||||
|
||||
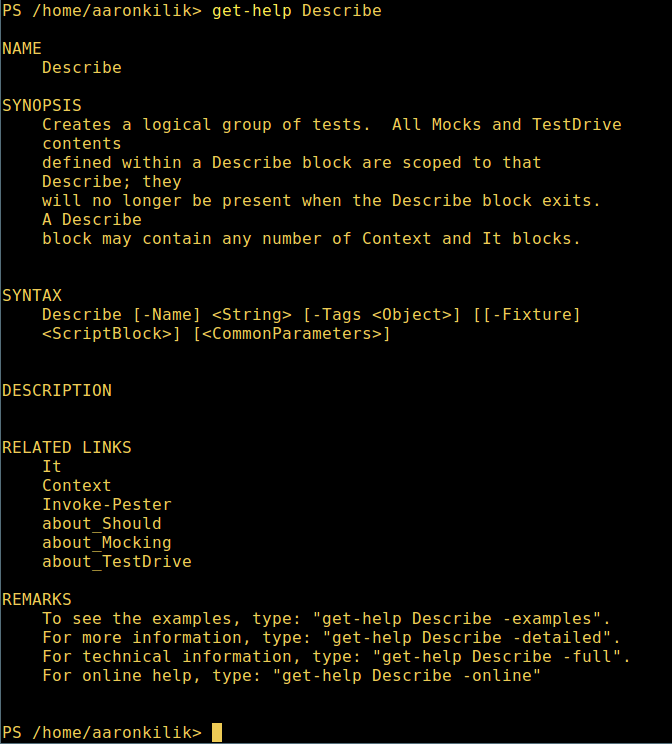
8. To learn how to use a command, view its help page (similar to man page in Unix/Linux); in this example, you can get help for the Describe command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
get-help Describe
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][14]
|
||||
|
||||
Powershell Help Manual
|
||||
|
||||
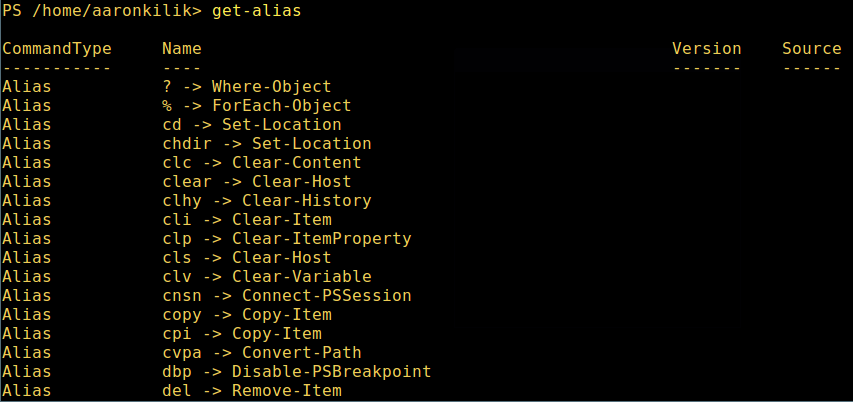
9. view all available command aliases, type:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
get-alias
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][15]
|
||||
|
||||
List Powershell Command Aliases
|
||||
|
||||
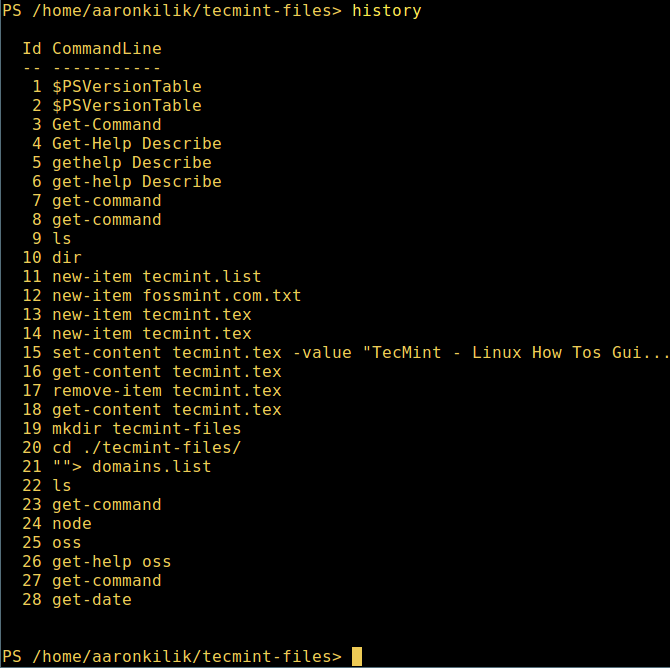
10. Last but not least, display command history (list of commands you had run previously) like so:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
history
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][16]
|
||||
|
||||
List Powershell Commands History
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all! for now, in this article, we showed you how to install Microsoft’s Powershell Core 6.0 in Linux. To me, Powershell still has a very long way to go in comparison to the traditional Unix/Linux shells which offer, by far better, more exciting and productive features to operate a machine from the command line and importantly, for programming (scripting) purposes as well.
|
||||
|
||||
Visit Powershell Github repository: [https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell][17]
|
||||
|
||||
However, you can give it a try and share your views with us in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-powershell-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/using-shell-script-to-automate-linux-system-maintenance-tasks/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/tag/commandline-tools/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/useful-basic-commands-of-apt-get-and-apt-cache-for-package-management/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/start-powershell.png
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/check-powershell-version.png
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Create-New-File-in-Powershell.png
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Delete-File-in-Powershell.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/create-new-directory-in-Powershell.png
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Directory-Long-Listing-in-Powershell.png
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/View-Running-Processes-in-Powershell.png
|
||||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/View-Specific-Process-in-Powershell.png
|
||||
[13]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/List-Powershell-Commands.png
|
||||
[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Powershell-Help-Manual.png
|
||||
[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/List-Powershell-Command-Aliases.png
|
||||
[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/List-Powershell-Command-History.png
|
||||
[17]:https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell
|
||||
[18]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[19]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
|
||||
[20]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,257 @@
|
||||
Linux 使用 PowerShell 6.0 入门 [新手指南]
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
在微软爱上 Linux 之后(众所周知「Microsoft Loves Linux」),PowerShell 从一个原本只有 Windows 才能使用的组件,于2016年8月18日开源并且能够跨平台,已经可以在 Linux 和 macOS 中使用。
|
||||
|
||||
PowerShell 是一个微软开发的自动化任务和配置管理系统。它基于 .NET 框架,由命令行语言解释器(shell)和脚本语言组成。
|
||||
|
||||
PowerShell 提供 COM (Component Object Model) 和 WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation) 的完全访问來在本地或远程 Windows 系统中 [执行系统任务][1],就像 WS-Management 或 CIM (Common Information Model)实现远程 Linux 和网络设备的管理一样。
|
||||
|
||||
通过这个框架,管理任务基本上由称为 cmdlets(发音 command-lets)的 .NET 类执行。就像 Linux 的 shell 脚本一样,用户可以通过按照一定的规则将 cmdlets 写入文件来制作脚本或可执行文件。这些脚本可以独立用作 [命令行程序或工具][2].
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Linux 系统中安装 PowerShell Core 6.0
|
||||
|
||||
要在 Linux 中安装 PowerShell Core 6.0,我们将会用到微软官方的仓库,它允许我们通过 [apt-get][3]、[yum][4] 等最流行的几个包管理器来安装。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Ubuntu 16.04 中安装
|
||||
|
||||
首先,导入 GPG 密钥,然后将微软的 Ubuntu 仓库添加到 APT 的源中来安装 PowerShell:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
$ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/16.04/prod.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/microsoft.list
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install -y powershell
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Ubuntu 14.04 中安裝
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
$ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/14.04/prod.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/microsoft.list
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install -y powershell
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 CentOS 7 中安裝
|
||||
|
||||
首先,将微软的 RedHat 仓库添加到 YUM 源中然后安装 PowerShell:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/7/prod.repo > /etc/yum.repos.d/microsoft.repo
|
||||
$ sudo yum install -y powershell
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在 Linux 中使用 PowerShell Core 6.0
|
||||
|
||||
在这一节中,我们将会简单介绍下 PowerShell;我们将会看到如何启动 PowerShell,如何运行一些基础命令,如何操作文件、目录和进程。然后学习怎样列出所有可用的命令、显示命令帮助和别名。
|
||||
|
||||
输入以下命令来启动 PowerShell:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ powershell
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][5]
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 中开启 PowerShell
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过以下命令来查看 PowerShell 版本:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$PSVersionTable
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][6]
|
||||
|
||||
查看 PowerShell 版本
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 中运行 PowerShell 基础命令。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
get-date [# 显示当前日期]
|
||||
get-uptime [# 显示开机时间]
|
||||
get-location [# 显示当前工作目录]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 PowerShell 中操作文件和目录
|
||||
|
||||
1. 可以通过两种方法创建空文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
new-item tecmint.tex
|
||||
OR
|
||||
"">tecmint.tex
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后往里面添加内容并查看文件内容。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
set-content tecmint.tex -value "TecMint Linux How Tos Guides"
|
||||
get-content tecmint.tex
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][7]
|
||||
|
||||
在 PowerShell 中创建新文件
|
||||
|
||||
2. 在 PowerShell 中删除一个文件
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
remove-item tecmint.tex
|
||||
get-content tecmint.tex
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
在 PowerShell 中删除一个文件
|
||||
|
||||
3. 创建目录
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir tecmint-files
|
||||
cd tecmint-files
|
||||
“”>domains.list
|
||||
ls
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][9]
|
||||
|
||||
在 PowerShell 中创建目录
|
||||
|
||||
4. 列出一个包括文件/目录的权限(文件类型)、最后修改时间等詳細信息的列表,使用以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
dir
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][10]
|
||||
|
||||
列出目录
|
||||
|
||||
5. 显示系统中所有的进程:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
get-process
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][11]
|
||||
|
||||
在 PowerShell 中显示运行中的进程
|
||||
|
||||
6. 通过给定的名称获取正在运行的进程/进程组,将进程名作为参数传给命令,就像这样:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
get-process apache2
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][12]
|
||||
|
||||
在 PowerShell 中查看指定的进程
|
||||
|
||||
输出上方的单位的意思:
|
||||
|
||||
1. NPM(K) – 进程总共使用的非分页内存,单位:K。
|
||||
2. PM(K) – 进程总共使用的可分页内存,单位:K。
|
||||
3. WS(K) – 进程的工作集大小,单位:K,工作集包括进程将要访问的页。
|
||||
4. CPU(s) – 进程所用的总计算时间,单位:秒。
|
||||
5. ID – 进程 ID (PID).
|
||||
6. ProcessName – 进程名称。
|
||||
|
||||
7. 想要了解更多,获取 PowerShell 命令列表:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
get-command
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][13]
|
||||
|
||||
列出 PowerShell 的命令
|
||||
|
||||
8. 想知道如何使用一个命令,查看它的帮助(类似于 Unix/Linux 中的 man);举个例子,你可以这样获取命令「Describe」的帮助:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
get-help Describe
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][14]
|
||||
|
||||
PowerShell 帮助手册
|
||||
|
||||
9. 显示所有命令的别名,輸入:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
get-alias
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][15]
|
||||
|
||||
列出 PowerShell 命令别名
|
||||
|
||||
10. 最后,但并非不重要的,显示命令历史记录(曾运行过的命令的列表):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
history
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][16]
|
||||
|
||||
显示 PowerShell 历史记录
|
||||
|
||||
到此为止!现在,在这篇文章里,我们向你展示了如何在 Linux 中安装微软的 PowerShell Core 6.0。我认为,与拥有更好、更多令人激动和富有成效的特性的,通过命令行和更为重要的编程(脚本)来操作机器的传统 Unix/Linux 的 shell 相比,PowerShell 还有很长的路要走。
|
||||
|
||||
查看 PowerShell 的 GitHub 倉庫:[https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell][17]
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在评论中分享你的观点。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 狂热爱好者,将来的 Linux 系统管理员、web 开发者,目前是 TecMint 的内容编辑,是一个热爱研究计算机与坚定的分享知识的人。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-powershell-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[zijung](https://github.com/zijung)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/using-shell-script-to-automate-linux-system-maintenance-tasks/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/tag/commandline-tools/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/useful-basic-commands-of-apt-get-and-apt-cache-for-package-management/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/start-powershell.png
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/check-powershell-version.png
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Create-New-File-in-Powershell.png
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Delete-File-in-Powershell.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/create-new-directory-in-Powershell.png
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Directory-Long-Listing-in-Powershell.png
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/View-Running-Processes-in-Powershell.png
|
||||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/View-Specific-Process-in-Powershell.png
|
||||
[13]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/List-Powershell-Commands.png
|
||||
[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Powershell-Help-Manual.png
|
||||
[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/List-Powershell-Command-Aliases.png
|
||||
[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/List-Powershell-Command-History.png
|
||||
[17]:https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell
|
||||
[18]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[19]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
|
||||
[20]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user