mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
[Translated 20150104 How to set up a cross-platform backup server on Linux with BackupPC.md]
This commit is contained in:
parent
a860fb2916
commit
e933a22f48
@ -1,136 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FSSlc translating
|
||||
|
||||
How to set up a cross-platform backup server on Linux with BackupPC
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Just in case you haven't been able to tell from my earlier posts on [backupninja][1] and [backup-manager][2], I am a big backup fan. When it comes to backup, I'd rather have too much than not enough, because if the need arises, you will be grateful that you took the time and effort to generate extra copies of your important data.
|
||||
|
||||
In this post, I will introduce you to [BackupPC][3], a cross-platform backup server software which can perform pull backup of Linux, Windows and MacOS client hosts over network. BackupPC adds a number of features that make managing backups an almost fun thing to do.
|
||||
|
||||
### Features of BackupPC ###
|
||||
|
||||
BackupPC comes with a robust web interface that allows you to collect and manage backups of other remote client hosts in a centralized fashion. Using the web interface, you can examine logs and configuration files, start/cancel/schedule backups of other remote hosts, and visualize current status of backup tasks. You can also browse through archived files and restore individual files or entire jobs from backup archives very easily. To restore individual single files, you can download them from any previous backup directly from the web interface. As if this weren't enough, no special client-side software is needed for client hosts. On Windows clients, the native SMB protocol is used, whereas on *nix clients, you will use `rsync` or tar over SSH, RSH or NFS.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing BackupPC ###
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, Ubuntu and their derivatives, run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# aptitude install backuppc
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora, use `yum` command. Note the case sensitive package name.
|
||||
|
||||
On CentOS/RHEL 6, first enable [EPEL repository][4]. On CentOS/RHEL 7, enable [Nux Dextop][5] repository instead. Then go ahead with `yum` command:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install BackupPC
|
||||
|
||||
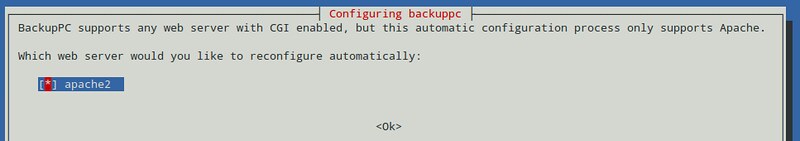
As usual, both package management systems will take care of dependency resolution automatically. In addition, as part of the installation process, you may be asked to configure, or reconfigure the web server that will be used for the graphical user interface. The following screenshot is from a Debian system:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Select your choice by pressing the space bar, and then move to Ok with the tab key and hit ENTER.
|
||||
|
||||
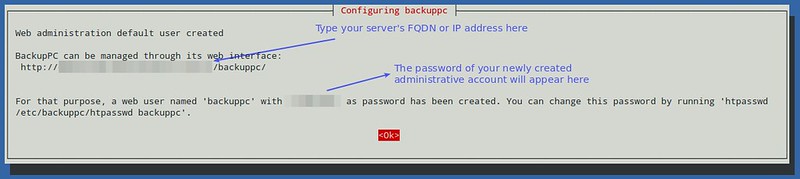
You will then be presented with the following screen informing you that an administrative user account 'backuppc', along with its corresponding password (which can be changed later if desired), has been created to manage BackupPC. Note that both a HTTP user account and a regular Linux account of the same name 'backuppc' will be created with an identical password. The former is needed to access BackupPC's protected web interface, while the latter is needed to perform backup using rsync over SSH.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You can change the default password for the HTTP user 'backuppc' with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# htpasswd /path/to/hash/file backuppc
|
||||
|
||||
As for a regular 'backuppc' [Linux][6] user account, use passwd command to change its default password.
|
||||
|
||||
# passwd backuppc
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the installation process creates the web and the program's configuration files automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
### Launching BackupPC and Configuring Backups ###
|
||||
|
||||
To start, open a browser window and point to http://<server's FQDN or IP address>/backuppc/. When prompted, enter the default HTTP user credentials that were supplied to you earlier. If the authentication succeeds, you will be taken to the main page of the web interface.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Most likely the first thing that you will want to do is add a new client host to back up. Go to "Edit Hosts" in the Task pane. We will add two client hosts:
|
||||
|
||||
- Host #1: CentOS 7 [IP 192.168.0.17]
|
||||
- Host #2: Windows 7 [IP 192.168.0.103]
|
||||
|
||||
We will back up the CentOS host using rsync over SSH and the Windows host using SMB. Prior to performing the backup, we need to set up [key-based authentication][7] to our CentOS host and a shared folder in our Windows machine.
|
||||
|
||||
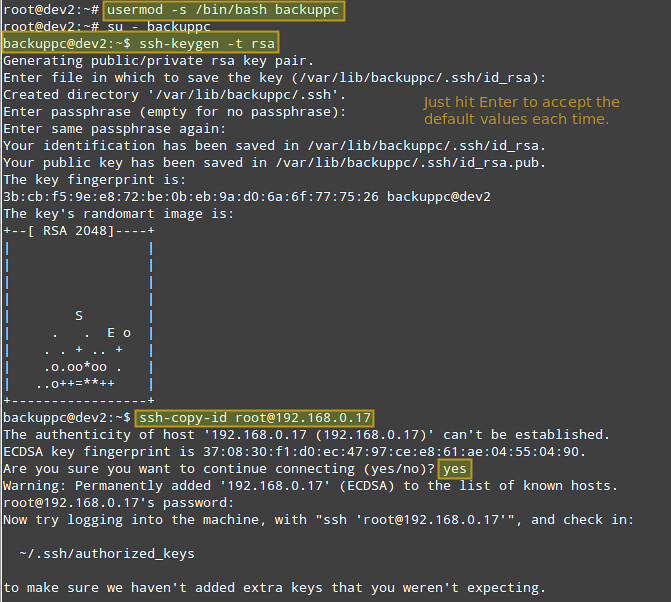
Here are the instructions for setting up key-based authentication for a remote CentOS host. We create the 'backuppc' user's RSA key pair, and transfer its public key to the root account of the CentOS host.
|
||||
|
||||
# usermod -s /bin/bash backuppc
|
||||
# su - backuppc
|
||||
# ssh-keygen -t rsa
|
||||
# ssh-copy-id root@192.168.0.17
|
||||
|
||||
When prompted, type yes and enter root's password for 192.168.0.17.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You will need root access for a remote CentOS host to grant write access to all its file system in case of restoring a backup of files or directories owned by root.
|
||||
|
||||
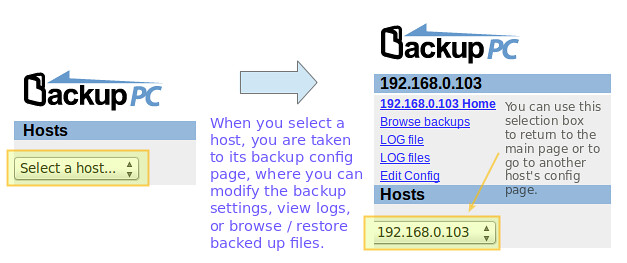
Once the CentOS and Windows hosts are ready, add them to BackupPC using the web interface:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The next step consists of modifying each host's backup settings:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
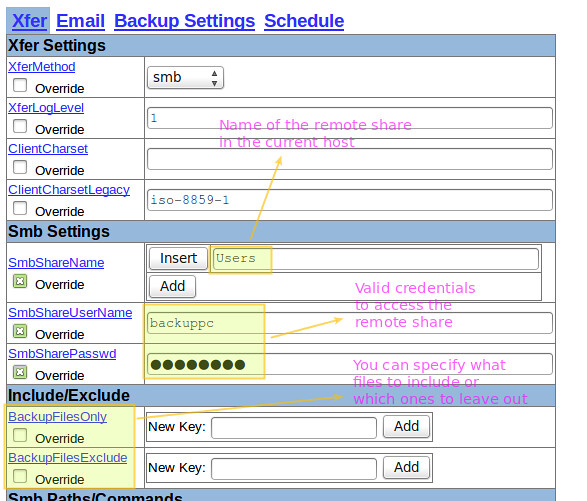
The following image shows the configuration for the backup of the Windows machine:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
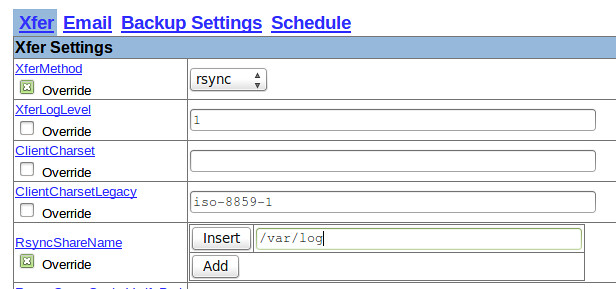
And the following screenshot shows the settings for the backup of the CentOS box:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Starting a Backup ###
|
||||
|
||||
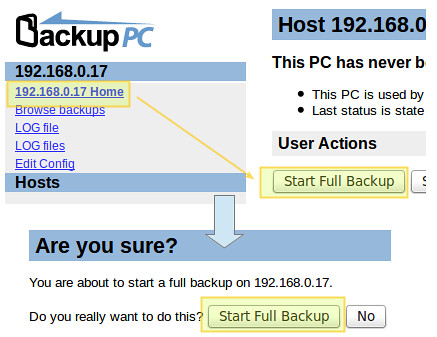
To start each backup, go to each host's settings, and then click "Start Full Backup":
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
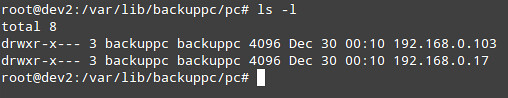
At any time, you can view the status of the process by clicking on the host's home as shown in the image above. If it fails for some reason, a link to a page with the error message(s) will appear in the host menu as well. When a backup completes successfully, a directory with the host's name or IP address is created under /var/lib/backuppc/pc in the server:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to browse those directories for the files from the command line, but there is an easier way to look for those files and restore them.
|
||||
|
||||
### Restoring Backup ###
|
||||
|
||||
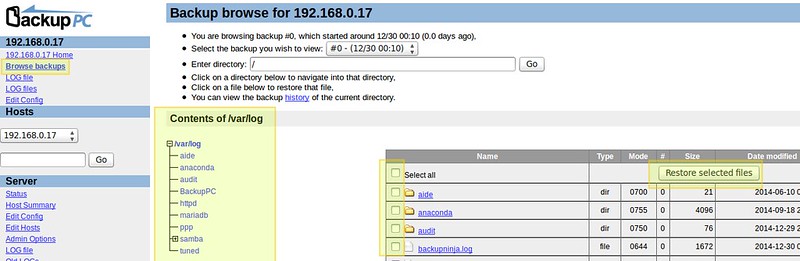
To view the files that have been saved, go to "Browse backups" under each host's main menu. You can visualize the directories and files at a glance, and select those that you want to restore. Alternatively, you can click on files to open them with the default program, or right click and choose Save link as to download it to the machine where you're working at the time:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
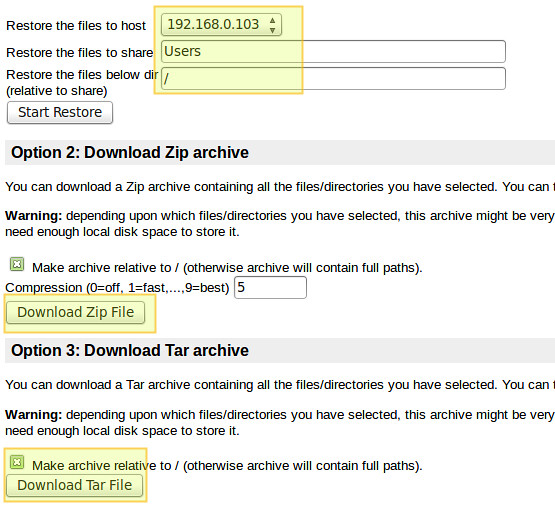
If you want, you can download a zip or tar file containing the backup's contents:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
or just restore the file(s):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
There is a saying that goes, "the simpler, the better", and that is just what BackupPC has to offer. In BackupPC, you will not only find a backup tool but also a very versatile interface to manage your backups of several operating systems without needing any client-side application. I believe that's more than reason enough for you to give it at least a try.
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to leave your comments and questions, if you have any, using the form below. I am always happy to hear what readers have to say!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/backuppc-cross-platform-backup-server-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/gabriel
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/backup-debian-system-backupninja.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/linux-backup-manager.html
|
||||
[3]:http://backuppc.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[5]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/enable-nux-dextop-repository-centos-rhel.html
|
||||
[6]:http://xmodulo.com/recommend/linuxguide
|
||||
[7]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-enable-ssh-login-without.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
|
||||
如何在 Linux 上使用 BackupPC 来设置一个跨平台的备份服务器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
为了防止你不能分辨这篇教程和我先前关于[backupninja][1] 和 [backup-manager][2] 的帖子,=== 我是一个积极的备份迷。当提到备份,我宁愿备份的太多而不希望备份不足,因为如果我们有需要的话,你将会感激你花费了时间和精力来为你的重要数据生成额外的拷贝。
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇帖子中,我将向你介绍[BackupPC][3],一个跨平台的备份服务器软件,它可以通过网络为 Linux,Window 和 MacOS 等系统上的客户端主机拉取备份。BackupPC 添加了一系列的特点使得管理备份变为一件快乐的事。
|
||||
|
||||
### BackupPC 的特点 ###
|
||||
|
||||
BackupPC 自带有一个健壮的 Web 界面,允许你以集中的方式来收集和管理其他远程客户端主机上的备份。通过使用它的 Web 界面,你可以检查日志和配置文件、为其他远程主机启动/取消/安排备份任务以及可视化备份任务的当前状态。你也可以非常容易地浏览归档的文件以及从备份的归档中恢复个人文件或整个作业。为了恢复单一的个人文件,你可以直接通过 Web 界面来下载任何先前备份的文件。若如这还不够,针对客户端主机,没有特别的客户端软件需要安装。在 Windows 客户端上, 本机 SMB 协议将被使用,而对于 *nix 客户端,你将使用 `rsync` 或 通过 SSH, RSH 或 NFS 来使用 `tar` 。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 BackupPC ###
|
||||
|
||||
在 Debian,Ubuntu 和它们的衍生版本上,运行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# aptitude install backuppc
|
||||
|
||||
在 Fedra, 使用 `yum` 命令。请注意软件包名字对大小写敏感。
|
||||
|
||||
在 CentOS/RHEL 6 上,首先要启用 [EPEL 软件仓库][4]。在 CentOS/RHEL 7 上,请替代启用 [Nux Dextop][5] 。然后接着使用 `yum` 命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install BackupPC
|
||||
|
||||
同往常一样,这两种包管理系统都会自动地对依赖问题进行解决。另外,作为安装过程中的一部分,你可能会被要求去配置或重新配置用于图形用户界面的 Web 服务器。下面的截图来自于 Debian 系统:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
通过空格键来确定你的选择,然后使用 tab 键移动到 Ok 选项并敲回车键。
|
||||
|
||||
接着类似于下面的截屏将会呈现在你眼前,通知你一个用来管理 BackupPC 的名为 ‘backuppc’的管理员用户以及相应的密码(这个密码可以在以后被更改,如果你希望的话)已经被创建。这里需要注意的是:同样名为 ‘backuppc’的一个 HTTP 账户和一个常规的 Linux 账户将会被创建,它们使用同一个密码。需要前者的目的是来访问受保护的 BackupPC 的 Web 界面,而后者则是为了通过 SSH 来使用 `rsync` 来执行备份任务。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用下面的命令来更改 HTTP 账户 ‘backuppc’ 的默认密码:
|
||||
|
||||
# htpasswd /path/to/hash/file backuppc
|
||||
|
||||
至于常规的 ‘backuppc’ [Linux][6]账户,可以使用 `passwd`命令来更改它的默认密码:
|
||||
|
||||
# passwd backuppc
|
||||
|
||||
需要提及的是:安装过程中会自动创建 Web 和程序的配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 启动 BackupPC 并设置备份 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,打开一个浏览器窗口并指向 http://<server's FQDN or IP address>/backuppc/ 。当弹出提示框时,输入先前向你提供的默认 HTTP 用户凭据(注:即用户名 backuppc 和相应的默认密码)。假如认证成功,你就会被带入到 Web 界面的主页:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你想做的第一件事最有可能是新增一个客户端主机来备份。进入任务窗格中的 “编辑主机”选项。我们将添加两个客户端主机:
|
||||
|
||||
- Host #1: CentOS 7 [IP 192.168.0.17]
|
||||
- Host #2: Windows 7 [IP 192.168.0.103]
|
||||
|
||||
我们将通过 SSH 使用 `rsync`来备份 CentOS 主机,使用 SMB 来备份 Windows 主机。在执行备份之前,我们需要向我们的 CentOS 主机设置 [基于密码认证][7](注:这里我不知如何翻译,根据链接,感觉是无需密码来连接主机)以及在我们的 Windows 主机中设置一个共享目录。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是关于如何设置为一个远程 CentOS 主机设置 key-based authentication 的指导。我们创建 ‘backuppc’ 用户的 RSA 密钥对,并向 CentOS 主机上的 root 账户传递它的公共密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
# usermod -s /bin/bash backuppc
|
||||
# su - backuppc
|
||||
# ssh-keygen -t rsa
|
||||
# ssh-copy-id root@192.168.0.17
|
||||
|
||||
当弹出提示框时,键入 yes 并为 192.168.0.17 键入 root 用户的密码:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你需要一个远程的 CentOS 主机的 root 权限来在该主机中的文件系统中发放写权限,以防恢复的备份文件或目录的所有者为 root 账户。
|
||||
|
||||
一旦 CentOS 和 Windows 主机都准备完毕,使用 Web 界面将它们添加到 BackupPC:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
下一步的内容由更改每个主机的备份设置组成:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
接下来的图片展示了 Windows 主机的备份设置:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
而接着的截图展示了 CentOS 盒子的备份设置:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 开始一个备份任务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了开始每个备份,到每个主机的设定选项,然后点击“开始全备份”:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在任何时候,你都可以通过点击如上图展示的每个主机的备份主页来查看备份任务的状态。假如因为某些原因备份失败,在主机菜单中将会出现一个指向包含错误信息的网页。当一个备份任务被成功地完成,一个名为主机名或 IP 地址的目录将会在服务器的 /var/lib/backuppc/pc 目录下被创建。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我们也可以随意地在命令行中浏览这个目录中的文件,但存在一个更加简单的方式来查找和恢复这些文件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 恢复备份 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了浏览已经保存过的文件。进入每个主机的主菜单下的 “浏览备份”选项,你可以一目了然地看到目录和文件,并选择那些你想恢复的文件。另外,你还可以通过点击文件来使用默认程序打开文件或右击文件并选择“另存为”来下载该文件到你正工作的机器上:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如若你想,你可以下载一个包含所有你想备份的内容的 zip 或 tar 文件:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
或只是恢复文件:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
有句俗话说,"越简单,越好",而这正是 BackupPC 所提供。在 BackupPC 中,你将不仅找到了一个备份工具,而且还找到了一个无需任何客户端应用来在几个不同的操作系统中管理你的备份的方法。我相信这就有足够的理由让你去尝试一下。
|
||||
|
||||
欢迎使用下面的评论框来留下你的评论和问题,假如你有的话。我总是乐于听取读者想说的话!
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/backuppc-cross-platform-backup-server-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/gabriel
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/backup-debian-system-backupninja.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/linux-backup-manager.html
|
||||
[3]:http://backuppc.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[5]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/enable-nux-dextop-repository-centos-rhel.html
|
||||
[6]:http://xmodulo.com/recommend/linuxguide
|
||||
[7]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-enable-ssh-login-without.html
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user