mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-25 23:11:02 +08:00
Translated by qhwdw
This commit is contained in:
parent
b8d0703921
commit
e9339480df
@ -1,201 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by qhwdw
|
||||
A sysadmin's guide to network management
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you're a sysadmin, your daily tasks include managing servers and the data center's network. The following Linux utilities and commands—from basic to advanced—will help make network management easier.
|
||||
|
||||
In several of these commands, you'll see `<fqdn>`, which stands for "fully qualified domain name." When you see this, substitute your website URL or your server (e.g., `server-name.company.com`), as the case may be.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ping
|
||||
|
||||
As the name suggests, `ping` is used to check the end-to-end connectivity from your system to the one you are trying to connect to. It uses [ICMP][1] echo packets that travel back to your system when a ping is successful. It's also a good first step to check system/network connectivity. You can use the `ping` command with IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. (Read my article "[How to find your IP address in Linux][2]" to learn more about IP addresses.)
|
||||
|
||||
**Syntax:**
|
||||
|
||||
* IPv4: `ping <ip address>/<fqdn>`
|
||||
* IPv6: `ping6 <ip address>/<fqdn>`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
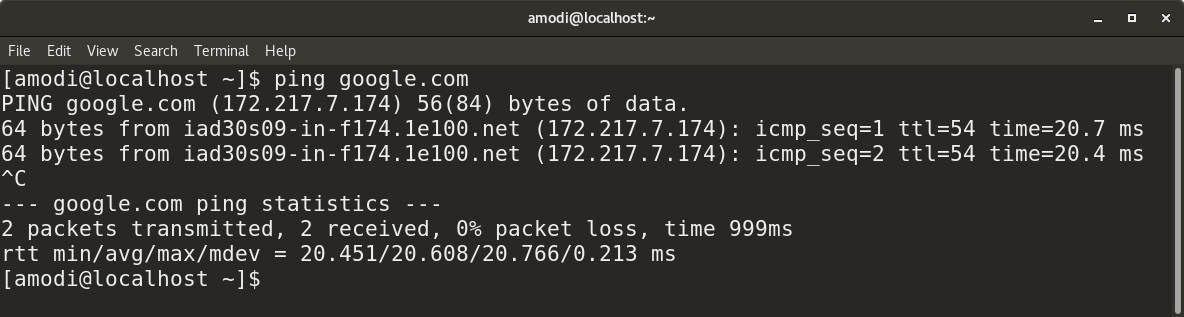
You can also use `ping` to resolve names of websites to their corresponding IP address, as shown below:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Traceroute
|
||||
|
||||
`ping` checks end-to-end connectivity, the `traceroute` utility tells you all the router IPs on the path you travel to reach the end system, website, or server. `traceroute` is usually is the second step after `ping` for network connection debugging.
|
||||
|
||||
This is a nice utility for tracing the full network path from your system to another. Wherechecks end-to-end connectivity, theutility tells you all the router IPs on the path you travel to reach the end system, website, or server.is usually is the second step afterfor network connection debugging.
|
||||
|
||||
**Syntax:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `traceroute <ip address>/<fqdn>`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Telnet
|
||||
|
||||
**Syntax:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `telnet <ip address>/<fqdn>` is used to [telnet][3] into any server.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Netstat
|
||||
|
||||
The network statistics (`netstat`) utility is used to troubleshoot network-connection problems and to check interface/port statistics, routing tables, protocol stats, etc. It's any sysadmin's must-have tool.
|
||||
|
||||
**Syntax:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `netstat -l` shows the list of all the ports that are in listening mode.
|
||||
* `netstat -a` shows all ports; to specify only TCP, use `-at` (for UDP use `-au`).
|
||||
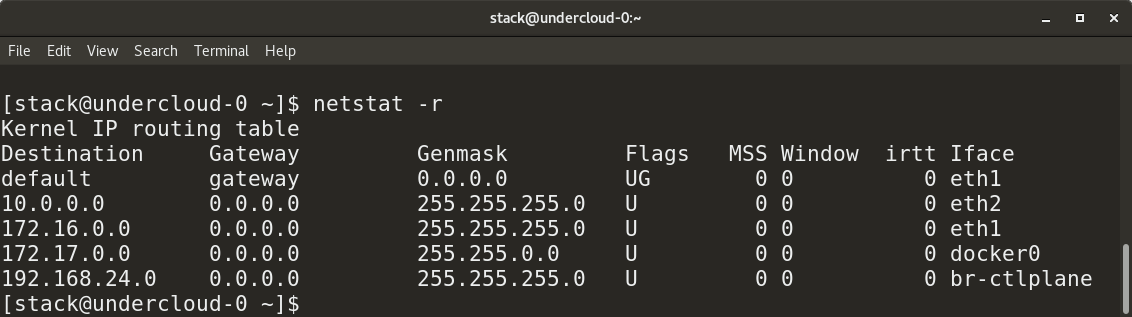
* `netstat -r` provides a routing table.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
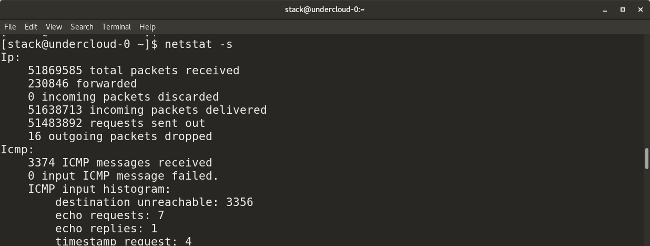
* `netstat -s` provides a summary of statistics for each protocol.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
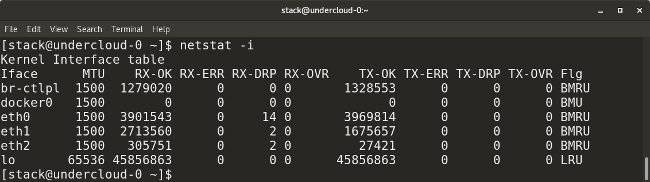
* `netstat -i` displays transmission/receive (TX/RX) packet statistics for each interface.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Nmcli
|
||||
|
||||
`nmcli` is a good utility for managing network connections, configurations, etc. It can be used to control Network Manager and modify any device's network configuration details.
|
||||
|
||||
**Syntax:**
|
||||
|
||||
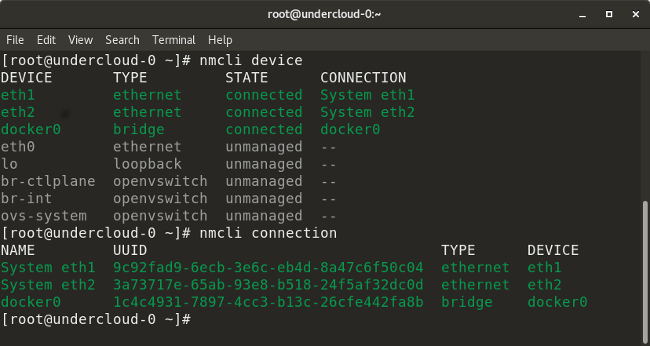
* `nmcli device` lists all devices on the system.
|
||||
|
||||
* `nmcli device show <interface>` shows network-related details of the specified interface.
|
||||
|
||||
* `nmcli connection` checks a device's connection.
|
||||
|
||||
* `nmcli connection down <interface>` shuts down the specified interface.
|
||||
|
||||
* `nmcli connection up <interface>` starts the specified interface.
|
||||
|
||||
* `nmcli con add type vlan con-name <connection-name> dev <interface> id <vlan-number> ipv4 <ip/cidr> gw4 <gateway-ip>` adds a virtual LAN (VLAN) interface with the specified VLAN number, IP address, and gateway to a particular interface.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Routing
|
||||
|
||||
There are many commands you can use to check and configure routing. Here are some useful ones:
|
||||
|
||||
**Syntax:**
|
||||
|
||||
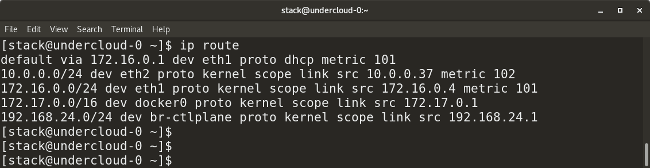
* `ip route` shows all the current routes configured for the respective interfaces.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
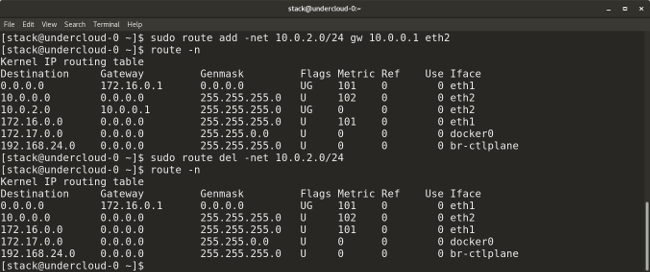
* `route add default gw <gateway-ip>` adds a default gateway to the routing table.
|
||||
* `route add -net <network ip/cidr> gw <gateway ip> <interface>` adds a new network route to the routing table. There are many other routing parameters, such as adding a default route, default gateway, etc.
|
||||
* `route del -net <network ip/cidr>` deletes a particular route entry from the routing table.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
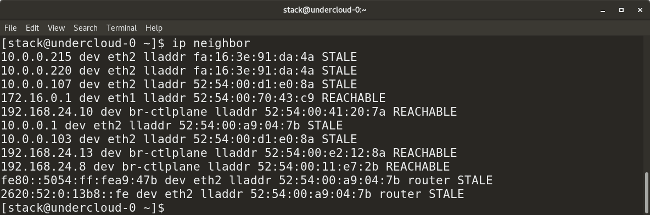
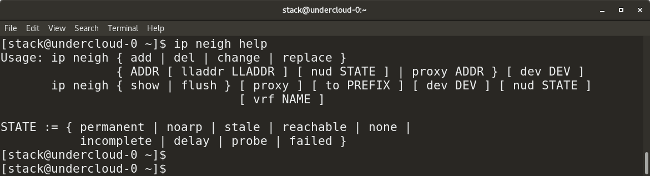
* `ip neighbor` shows the current neighbor table and can be used to add, change, or delete new neighbors.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
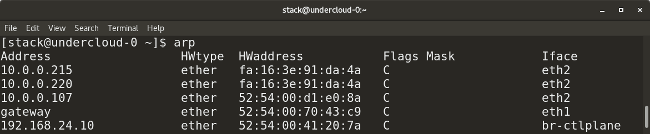
* `arp` (which stands for address resolution protocol) is similar to `ip neighbor`. `arp` maps a system's IP address to its corresponding MAC (media access control) address.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Tcpdump and Wireshark
|
||||
|
||||
Linux provides many packet-capturing tools like `tcpdump`, `wireshark`, `tshark`, etc. They are used to capture network traffic in packets that are transmitted/received and hence are very useful for a sysadmin to debug any packet losses or related issues. For command-line enthusiasts, `tcpdump` is a great tool, and for GUI users, `wireshark` is a great utility to capture and analyze packets. `tcpdump` is a built-in Linux utility to capture network traffic. It can be used to capture/show traffic on specific ports, protocols, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
**Syntax:**
|
||||
|
||||
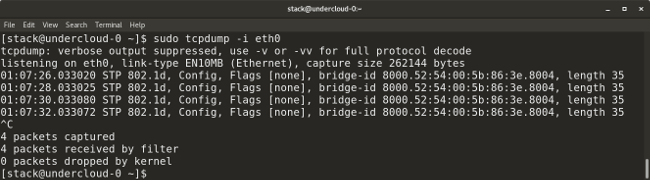
* `tcpdump -i <interface-name>` shows live packets from the specified interface. Packets can be saved in a file by adding the `-w` flag and the name of the output file to the command, for example: `tcpdump -w <output-file.> -i <interface-name>`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* `tcpdump -i <interface> src <source-ip>` captures packets from a particular source IP.
|
||||
* `tcpdump -i <interface> dst <destination-ip>` captures packets from a particular destination IP.
|
||||
* `tcpdump -i <interface> port <port-number>` captures traffic for a specific port number like 53, 80, 8080, etc.
|
||||
* `tcpdump -i <interface> <protocol>` captures traffic for a particular protocol, like TCP, UDP, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Iptables
|
||||
|
||||
`iptables` is a firewall-like packet-filtering utility that can allow or block certain traffic. The scope of this utility is very wide; here are some of its most common uses.
|
||||
|
||||
**Syntax:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `iptables -L` lists all existing `iptables` rules.
|
||||
* `iptables -F` deletes all existing rules.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The following commands allow traffic from the specified port number to the specified interface:
|
||||
|
||||
* `iptables -A INPUT -i <interface> -p tcp –dport <port-number> -m state –state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT`
|
||||
* `iptables -A OUTPUT -o <interface> -p tcp -sport <port-number> -m state – state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The following commands allow loopback access to the system:
|
||||
|
||||
* `iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT`
|
||||
* `iptables -A OUTPUT -o lo -j ACCEPT`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Nslookup
|
||||
|
||||
The `nslookup` tool is used to obtain IP address mapping of a website or domain. It can also be used to obtain information on your DNS server, such as all DNS records on a website (see the example below). A similar tool to `nslookup` is the `dig` (Domain Information Groper) utility.
|
||||
|
||||
**Syntax:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `nslookup <website-name.com>` shows the IP address of your DNS server in the Server field, and, below that, gives the IP address of the website you are trying to reach.
|
||||
* `nslookup -type=any <website-name.com>` shows all the available records for the specified website/domain.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Network/interface debugging
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a summary of the necessary commands and files used to troubleshoot interface connectivity or related network issues.
|
||||
|
||||
**Syntax:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `ss` is a utility for dumping socket statistics.
|
||||
* `nmap <ip-address>`, which stands for Network Mapper, scans network ports, discovers hosts, detects MAC addresses, and much more.
|
||||
* `ip addr/ifconfig -a` provides IP addresses and related info on all the interfaces of a system.
|
||||
* `ssh -vvv user@<ip/domain>` enables you to SSH to another server with the specified IP/domain and username. The `-vvv` flag provides "triple-verbose" details of the processes going on while SSH'ing to the server.
|
||||
* `ethtool -S <interface>` checks the statistics for a particular interface.
|
||||
* `ifup <interface>` starts up the specified interface.
|
||||
* `ifdown <interface>` shuts down the specified interface.
|
||||
* `systemctl restart network` restarts a network service for the system.
|
||||
* `/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/<interface-name>` is an interface configuration file used to set IP, network, gateway, etc. for the specified interface. DHCP mode can be set here.
|
||||
* `/etc/hosts` this file contains custom host/domain to IP mappings.
|
||||
* `/etc/resolv.conf` specifies the DNS nameserver IP of the system.
|
||||
* `/etc/ntp.conf` specifies the NTP server domain.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/7/sysadmin-guide-networking-commands
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Archit Modi][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://opensource.com/users/architmodi
|
||||
[1]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_Control_Message_Protocol
|
||||
[2]:https://opensource.com/article/18/5/how-find-ip-address-linux
|
||||
[3]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telnet
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,200 @@
|
||||
系统管理员的一个网络管理指南
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你是一位系统管理员,那么你的日常工作应该包括管理服务器和数据中心的网络。以下的 Linux 实用工具和命令 —— 从基础的到高级的 —— 将帮你更轻松地管理你的网络。
|
||||
|
||||
在几个命令中,你将会看到 `<fqdn>`,它是“完全合格域名”的全称。当你看到它时,你应该用你的网站 URL 或你的服务器来代替它(比如,`server-name.company.com`),具体要视情况而定。
|
||||
|
||||
### Ping
|
||||
|
||||
正如它的名字所表示的那样,`ping` 是用于去检查从你的系统到你想去连接的系统之间端到端的连通性。当一个 ping 成功时,它使用的 [ICMP][1] 的 echo 包将会返回到你的系统中。它是检查系统/网络连通性的一个良好开端。你可以在 IPv4 和 IPv6 地址上使用 `ping` 命令。(阅读我的文章 "[如何在 Linux 系统上找到你的 IP 地址][2]" 去学习更多关于 IP 地址的知识)
|
||||
|
||||
**语法:**
|
||||
|
||||
* IPv4: `ping <ip address>/<fqdn>`
|
||||
* IPv6: `ping6 <ip address>/<fqdn>`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以使用 `ping` 去解析出网站所对应的 IP 地址,如下图所示:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Traceroute
|
||||
|
||||
`ping` 是用于检查端到端的连通性,`traceroute` 实用工具将告诉你到达对端系统、网站、或服务器所经过的路径上所有路由器的 IP 地址。`traceroute` 在网络连接调试中经常用于在 `ping` 之后的第二步。
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个跟踪从你的系统到其它对端的全部网络路径的非常好的工具。在检查端到端的连通性时,这个实用工具将告诉你到达对端系统、网站、或服务器上所经历的路径上的全部路由器的 IP 地址。通常用于网络连通性调试的第二步。
|
||||
|
||||
**语法:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `traceroute <ip address>/<fqdn>`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Telnet
|
||||
|
||||
**语法:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `telnet <ip address>/<fqdn>` 是用于 [telnet][3] 进入任何支持该协议的服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Netstat
|
||||
|
||||
这个网络统计(`netstat`)实用工具是用于去分析解决网络连接问题和检查接口/端口统计数据、路由表、协议状态等等的。它是任何管理员都应该必须掌握的工具。
|
||||
|
||||
**语法:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `netstat -l` 显示所有处于监听状态的端口列表。
|
||||
* `netstat -a` 显示所有端口;如果去指定仅显示 TCP 端口,使用 `-at`(指定信显示 UDP 端口,使用 `-au`)。
|
||||
* `netstat -r` 显示路由表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* `netstat -s` 显示每个协议的状态总结。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* `netstat -i` 显示每个接口传输/接收(TX/RX)包的统计数据。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Nmcli
|
||||
|
||||
`nmcli` 是一个管理网络连接、配置等工作的非常好的实用工具。它能够去管理网络管理程序和修改任何设备的网络配置详情。
|
||||
|
||||
**语法:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `nmcli device` 列出网络上的所有设备。
|
||||
|
||||
* `nmcli device show <interface>` 显示指定接口的网络相关的详细情况。
|
||||
|
||||
* `nmcli connection` 检查设备的连接情况。
|
||||
|
||||
* `nmcli connection down <interface>` 关闭指定接口。
|
||||
|
||||
* `nmcli connection up <interface>` 打开指定接口。
|
||||
|
||||
* `nmcli con add type vlan con-name <connection-name> dev <interface> id <vlan-number> ipv4 <ip/cidr> gw4 <gateway-ip>` 在特定的接口上使用指定的 VLAN 号添加一个虚拟局域网(VLAN)接口、IP 地址、和网关。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 路由
|
||||
|
||||
检查和配置路由的命令很多。下面是其中一些比较有用的:
|
||||
|
||||
**语法:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `ip route` 显示各自接口上所有当前的路由配置。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* `route add default gw <gateway-ip>` 在路由表中添加一个默认的网关。
|
||||
* `route add -net <network ip/cidr> gw <gateway ip> <interface>` 在路由表中添加一个新的网络路由。还有许多其它的路由参数,比如,添加一个默认路由,默认网关等等。
|
||||
* `route del -net <network ip/cidr>` 从路由表中删除一个指定的路由条目。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* `ip neighbor` 显示当前的邻接表和用于去添加、改变、或删除新的邻居。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* `arp` (它的全称是 “地址解析协议”)类似于 `ip neighbor`。`arp` 映射一个系统的 IP 地址到它相应的 MAC(介质访问控制)地址。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Tcpdump 和 Wireshark
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 提供了许多包捕获工具,比如 `tcpdump`、`wireshark`、`tshark` 等等。它们被用于去捕获传输/接收的网络流量中的数据包,因此它们对于系统管理员去诊断丢包或相关问题时非常有用。对于热衷于命令行操作的人来说,`tcpdump` 是一个非常好的工具,而对于喜欢 GUI 操作的用户来说,`wireshark` 是捕获和分析数据包的不二选择。`tcpdump` 是一个 Linux 内置的用于去捕获网络流量的实用工具。它能够用于去捕获/显示特定端口、协议等上的流量。
|
||||
|
||||
**语法:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `tcpdump -i <interface-name>` 显示指定接口上实时通过的数据包。通过在命令中添加一个 `-w` 标志和输出文件的名字,可以将数据包保存到一个文件中。例如:`tcpdump -w <output-file.> -i <interface-name>`。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* `tcpdump -i <interface> src <source-ip>` 从指定的源 IP 地址上捕获数据包。
|
||||
* `tcpdump -i <interface> dst <destination-ip>` 从指定的目标 IP 地址上捕获数据包。
|
||||
* `tcpdump -i <interface> port <port-number>` 从一个指定的端口号(比如,53、80、8080 等等)上捕获数据包。
|
||||
* `tcpdump -i <interface> <protocol>` 捕获指定协议的数据包,比如:TCP、UDP、等等。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Iptables
|
||||
|
||||
`iptables` 是一个包过滤防火墙工具,它能够允许或阻止某些流量。这个实用工具的应用范围非常广泛;下面是它的其中一些最常用的使用命令。
|
||||
|
||||
**语法:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `iptables -L` 列出所有已存在的 `iptables` 规则。
|
||||
* `iptables -F` 删除所有已存在的规则。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
下列命令允许流量从指定端口到指定接口:
|
||||
|
||||
* `iptables -A INPUT -i <interface> -p tcp –dport <port-number> -m state –state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT`
|
||||
* `iptables -A OUTPUT -o <interface> -p tcp -sport <port-number> -m state – state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
下列命令允许<ruby>环回<rt>loopback</rt></ruby>接口访问系统:
|
||||
|
||||
* `iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT`
|
||||
* `iptables -A OUTPUT -o lo -j ACCEPT`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Nslookup
|
||||
|
||||
`nslookup` 工具是用于去获得一个网站或域名所映射的 IP 地址。它也能用于去获得你的 DNS 服务器的信息,比如,一个网站的所有 DNS 记录(具体看下面的示例)。与 `nslookup` 类似的一个工具是 `dig`(Domain Information Groper)实用工具。
|
||||
|
||||
**语法:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `nslookup <website-name.com>` 显示你的服务器组中 DNS 服务器的 IP 地址,它后面就是你想去访问网站的 IP 地址。
|
||||
* `nslookup -type=any <website-name.com>` 显示指定网站/域中所有可用记录。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 网络/接口调试
|
||||
|
||||
下面是用于接口连通性或相关网络问题调试所需的命令和文件的汇总。
|
||||
|
||||
**语法:**
|
||||
|
||||
* `ss` 是一个转储套接字统计数据的实用工具。
|
||||
* `nmap <ip-address>`,它的全称是 “Network Mapper”,它用于扫描网络端口、发现主机、检测 MAC 地址,等等。
|
||||
* `ip addr/ifconfig -a` 提供一个系统上所有接口的 IP 地址和相关信息。
|
||||
* `ssh -vvv user@<ip/domain>` 允许你使用指定的 IP/域名和用户名通过 SSH 协议登入到其它服务器。`-vvv` 标志提供 SSH 登入到服务器过程中的 "最详细的" 信息。
|
||||
* `ethtool -S <interface>` 检查指定接口上的统计数据。
|
||||
* `ifup <interface>` 启动指定的接口。
|
||||
* `ifdown <interface>` 关闭指定的接口
|
||||
* `systemctl restart network` 重启动系统上的一个网络服务。
|
||||
* `/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/<interface-name>` 是一个对指定的接口设置 IP 地址、网络、网关等等的接口配置文件。DHCP 模式也可以在这里设置。
|
||||
* `/etc/hosts` 这个文件包含自定义的主机/域名到 IP 地址的映射。
|
||||
* `/etc/resolv.conf` 指定系统上的 DNS 服务器的 IP 地址。
|
||||
* `/etc/ntp.conf` 指定 NTP 服务器域名。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/7/sysadmin-guide-networking-commands
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Archit Modi][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[qhwdw](https://github.com/qhwdw)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://opensource.com/users/architmodi
|
||||
[1]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_Control_Message_Protocol
|
||||
[2]:https://opensource.com/article/18/5/how-find-ip-address-linux
|
||||
[3]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telnet
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user