mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-27 02:30:10 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject
This commit is contained in:
commit
e65e3b72bc
published
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Copy CD & DVD Discs Using Ubuntu.mdHow to Crack a Wi-Fi Network's WEP Password with BackTrack.mdInsights into top 3 IT skill groups in highest demand.mdLinux shell tips and tricks.mdProprietary Unix Continues to Fall.md
The Linux Kernel
11 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 7.md12 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 8.md
UNIGINE Is Probably the Best Gaming Engine on Linux.mdsources
10 Useful Chaining Operators in Linux with Practical Examples.mdGNOME`s File Manager Will Be More User Friendly.mdGnu--toward the post-scarcity world – the Free Software Column.mdHow to Upgrade to GNOME 3.10 in Ubuntu 13.10.mdHow to install and configure Nagios on Linux.mdHow to open a large text file on Linux.mdLinux Mint Respond to Ubuntu Developer’s ‘Vulnerable’ Claim.mdLinux lsusb Command to Print information about USB on System.mdLinux mpstat Command – Reports Processors Related Statistics.mdOpen Source Is Here To Stay On IBM i.mdOracle Linux 6.5 Arrives with Unbreakable Enterprise Linux Kernel 3.8.mdSolving HIPPA, HITECH, SSAE16 Server Compliance Issues with Next Generation Datacenters.mdTeamViewer 9 Released – Install on RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Debian/Ubuntu.md
translated
10 Useful Chaining Operators in Linux with Practical Examples.mdHow to Upgrade to GNOME 3.10 in Ubuntu 13.10.mdLinux whoami command – Knowing Who is Logged In.mdSenior researchers analyzed LibreOffice with interesting conclusions.mdTeamViewer 9 Released – Install on RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Debian/Ubuntu.md
@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
每日Ubuntu小技巧 - 使用Ubuntu拷贝CD和DVD光盘
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ubuntu,一个功能强大的现代操作系统,可以执行很多任务。你可以使用Ubuntu创建文档,浏览网页,聆听音乐,以及烧录或拷贝媒体光盘。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu是一个功能强大的现代操作系统,可以执行很多任务。你可以使用Ubuntu创建文档,浏览网页,聆听音乐,以及烧录或拷贝媒体光盘。
|
||||
|
||||
就像Windows和Max OS X一样,Ubuntu是无所不能的!
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,14 +13,14 @@ Brasero光盘烧录机安装在UBuntu的每一个版本上。它是Ubuntu上默
|
||||
|
||||
下面列出来的是Brasero的一些特性:
|
||||
- 创建数据CD/DVD时自动过滤隐藏和损坏的文件
|
||||
- 同时支持多个绘画,可以执行磁盘文件的完整性
|
||||
- 可以在忙碌中烧录视频CD/DVD[on the fly翻译不合适]
|
||||
- 可以拷贝CD/DVD到系统硬盘
|
||||
- 可以擦除CD/DVD
|
||||
- 同时支持多个会话,可以执行磁盘文件的完整性检查
|
||||
- 可以即时烧录视频CD/DVD
|
||||
- 可以镜像CD/DVD内容到硬盘
|
||||
- 可以擦除可擦写CD/DVD
|
||||
|
||||
还有很多其它的功能。如果你想找一个Ubuntu上简便的磁盘刻录机,在做任何操作前请先检查这个软件。
|
||||
还有很多其它的功能。如果你想找一个Ubuntu上简便的磁盘刻录机,在做任何操作前请先看看这个软件。
|
||||
|
||||
为了开始使用Brasero去烧录CD/DVD光盘,请确保你的电脑安装了CD/DVD烧录机。如果没有,你将无法成功烧录。如果你的电脑符合要求,将你想要翻录的数据插入CD/DVD,然后进入Dash,搜索Brasero。
|
||||
要开始使用Brasero去烧录CD/DVD光盘,请确保你的电脑安装了CD/DVD烧录机。如果没有,显然你无法烧录。如果你的电脑符合要求,将你想要翻录的数据光盘插入CD/DVD,然后进入Dash,搜索Brasero。
|
||||
|
||||
当Brasero打开后,选择磁盘拷贝。这个功能会拷贝一个光盘里的内容,然后将其写入到另一个光盘中。如果这是你想要的,请继续。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,10 +37,11 @@ Brasero光盘烧录机安装在UBuntu的每一个版本上。它是Ubuntu上默
|
||||
安装完成后,Brasero会开始拷贝光盘。如果最终光盘完成拷贝,系统会提示你插入一张空白的可写入的CD/DVD光盘以便写入拷贝。插入它然后等待完成将内容写入光盘的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
当你完成以上操作时,移除光盘,就可以使用烧录好的光盘了!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/12/daily-ubuntu-tips-copy-cd-dvd-discs-using-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,40 +1,42 @@
|
||||
[翻译中]by stduolc
|
||||
如何使用BackTrack破解WIFI无线网络的WEP密钥
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可能已经知道如果你想要加锁自己的WIFI无线网络,你最好选择[WPA加密][3]方式,因为WEP加密很容易被人破解。但是,你知道有多么的容易么?下面我们来看看吧。
|
||||
|
||||
*注意:此帖是验证如何破解使用老的使用较少的WEP加密协议加密的密码。如果你希望破解的网络采用了更受欢迎的WPA加密,请看这篇[使用Reaver(掠夺者)破解WIFI的WPA加密指南][2].*
|
||||
*注意:此帖是验证如何破解很少使用而陈旧的WEP加密协议。如果你希望破解的网络采用了更受欢迎的WPA加密,请看这篇:[如何使用Reaver破解Wi-Fi网络的WPA密码][2]。*
|
||||
|
||||
今天我们来看看如何一步一步的破解采用WEP加密方法加密的WIFI网络。但是,有言在先:知识是一种力量,但是力量并不意味着你应该成为一个混球或者做任何违法的事。知道[如何挑选一把锁具][3]并不会让你成为一个贼。请将此帖看成是教育性质或者概念验证性试验。
|
||||
今天我们来看看如何一步一步的破解采用WEP加密方法加密的WIFI网络。但是,有言在先:知识是一种力量,但是力量并不意味着你应该成为一个混球或者做任何违法的事。知道[如何挑选一把锁具][3]并不会让你成为一个贼。请将此帖用于教育性质或者概念验证性试验。
|
||||
|
||||
关于如何使用这个方案破解WEP加密的教程在互联网上有很多。认认真真的谷歌下。这个并不能被称作新闻。但是,让人惊讶的是如笔者一般的只有很少的网络经验的菜鸟,也可以使用一些免费的软件和廉价的WIFI适配器来完成这个做破解。下面就来看看吧!
|
||||
关于如何使用这个方案破解WEP加密的教程在互联网上有很多。认认真真的谷歌下,这个并不能被称作新闻。但是,让人惊讶的是如笔者一般的只有很少的网络经验的菜鸟,也可以使用一些免费的软件和廉价的WIFI适配器来完成这个做破解。下面就来看看吧!
|
||||
|
||||
### 你需要写什么 ###
|
||||
### 你需要些什么 ###
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
除非你是一个电脑网络安全的忍者,否则你不太可能具有完成实验的所有工具。一下是你需要的:
|
||||
除非你是一个电脑网络安全的忍者,否则你不太可能具有完成实验的所有工具。以下是你需要的:
|
||||
|
||||
- **一个可兼容的无线适配器**.这是最主要的需求。你需要一个无线适配器,能用来完成包注入,你的电脑很可能不具备这个功能。在和我的安全专家邻居讨论了以后,我从亚马逊上花了50美元购买了一个Alfa AWUS050NH适配器,图片如下。更新:别学我,应该买[Alfa AWUS036H][4]而不是US050NH。[视频][5]里的哥们儿用$12美金在Ebay上买了一个解调器(同时可以选择把[自己的路由器][6]卖掉).网上有很多可以[兼容aircrack的适配器][7].
|
||||
- **一个兼容的无线适配器**.这是最主要的需求。你需要一个无线适配器,能用来完成包注入,你的电脑很可能不具备这个功能。在和我的安全专家邻居讨论了以后,我从亚马逊上花了50美元购买了一个Alfa AWUS050NH适配器,图片如上。更新:别学我,其实应该买[Alfa AWUS036H][4]而不是US050NH。[视频][5]里的哥们儿用$12美金在Ebay上买了一个解调器(同时可以选择把[自己的路由器][6]卖掉)。网上有很多可以[兼容aircrack的适配器][7]。
|
||||
|
||||
- **[一个BackTrack Live CD][8]**. 我们已经提供了一个完整的[BackTrack 3的安装使用教程][9],Linux Live CD可以让你完成所有的安全测试和测试工作。请自行下载一个CD,然后刻录或者从VMware中启动它。
|
||||
- **[一个BackTrack Live CD][8]**. 我们已经提供了一个完整的[BackTrack 3的安装使用教程][9],Linux Live CD可以让你完成所有的安全测试和测试工作。请自行下载一个CD镜像,然后刻录或者从VMware中启动它。
|
||||
|
||||
- **一个靠近的WEP加密的WIFI网络**. 信号需要足够的强,理想的情况下最好有用户正在使用、连接和断开设备。越多的人使用网络,你就可以的到更多的破解数据,这样你就更可能成功。
|
||||
|
||||
- **使用命令行的耐心**. 这里总共有10步,总共需要出入很长、很难懂的命令,然后等你的wifi网卡手机足够破解密码的数据。就像一个医生和一个急躁的病人说,有点耐心。
|
||||
- **使用命令行的耐心**. 这里总共有10步,总共需要输入很长、很难懂的命令,然后等你的wifi网卡收集足够破解密码的数据。就像一个医生和一个急躁的病人说,要有点耐心。
|
||||
|
||||
### 破解WEP ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了破解WEP,你需要启动一个Konsole,BackTrack内置的命令行。现在,就剩下命令了。
|
||||
为了破解WEP,你需要启动一个Konsole,它是BackTrack内置的命令行界面,它在任务栏的左下角,从左往右第二个图标。现在,输入命令吧。
|
||||
|
||||
第一步,运行下面的命令,获得你网卡列表:
|
||||
|
||||
airmon-ng
|
||||
|
||||
笔者只看见了一个ra0的结果。你的可能不一样;记录下这些label(找个纸或者截图)。现在开始,更改替换掉命令中每一个包括(interface)的地方。
|
||||
笔者只看见了一个ra0的结果。你的可能不一样;记录下这些内容(找个纸或者截图)。现在开始,更改替换掉命令中每一个包括(interface)的地方。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,运行下面的四个命令。看看截图里的输入结果。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
airmon-ng stop (interface)
|
||||
ifconfig (interface) down
|
||||
macchanger —mac 00:11:22:33:44:55 (interface)
|
||||
@ -42,20 +44,22 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你没有获得截图一样的结果,最可能的情况就是你的无线网卡不能在特殊破解模式下工作。如果你成功了,你应该已经有效的在你的无线网卡上伪造了一个新的MAC地址,00:11:22:33:44:55.
|
||||
如果你没有获得像截图一样的结果,最可能的情况就是你的无线网卡不能在特殊破解模式下工作。如果你成功了,你应该已经成功的在你的无线网卡上伪造了一个新的MAC地址,00:11:22:33:44:55.
|
||||
|
||||
现在,开始使用的你网络接口,运行:(译者注:interface在范例中就是ra0)
|
||||
|
||||
现在,开始使用的你网络接口,运行:(译者注:interface在示范中就是ra0)
|
||||
airodump-ng (interface)
|
||||
|
||||
就可以看见你周围的wifi网络列表了。当你认准了你的目标后,按Ctrl+C结束列表。高亮你感兴趣的网络,同时记录下两样数据:它的BSSID和它的Channel(讯道,标签为CH的那列),就像下面的截图。很明显你想要破解的网络需要是WEP加密的,而不是WPA或者其他加密方式。
|
||||
就可以看见你周围的wifi网络列表了。当你认准了你的目标后,按Ctrl+C结束列表。高亮你感兴趣的网络,同时记录下两样数据:它的BSSID和它的Channel(讯道,标签为CH的那列),就像下面的截图。很明显你想要破解的网络需要是WEP加密的,而不是WPA或者其他加密方式。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
就像我说的,按Ctrl+C来终止列表。(我需要重复一两次来找到我需要的网络)一旦你找到了你需要破解的网络,高亮BSSID然后复制它到你的剪切板来为将要输入的命令做准备。
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们需要观察你选中的目标网络,并捕捉信息存入一个文件里,运行如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
airodump-ng -c (channel) -w (file name) —bssid (bssid) (interface)
|
||||
|
||||
Where (channel) is your network's channel, and (bssid) is the BSSID you just copied to clipboard. You can use the Shift+Insert key combination to paste it into the command. Enter anything descriptive for (file name). I chose "yoyo," which is the network's name I'm cracking.
|
||||
其中,(channel),(bssid)就是你之前获取的那些信息。你可以使用Shift+Insert来将剪切板中的bssid信息粘贴到命令行中。随便给你的文件取个名字。我用的是“YoYo”,我破解的网络的名字。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
@ -72,14 +76,15 @@ Where (channel) is your network's channel, and (bssid) is the BSSID you just cop
|
||||
|
||||
aireplay-ng -3 -b (bssid) -h 00:11:22:33:44:55 (interface)
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们创建了一个路由通路来更快的抓取数据,从而加快我们的破解过程。几分钟以后,前台的窗口会开始疯狂的读写数据包。(同时,我可以利用YoYo的网络在另一台机器上上网)这里,你可以喝杯Java牌儿咖啡,然后出去走走。一般来说,你需要收集到足够的数据后再运行你的破解程序。看着“#Data”列里的数据,你需要它在10,000以上。(图里的数据只有854)
|
||||
现在,我们创建了一个路由通路来更快的抓取数据,从而加快我们的破解过程。几分钟以后,前台的窗口会开始疯狂的读写数据包。(这时,我也不能用YoYo的网络在另一台机器上上网)这里,你可以喝杯Java牌儿咖啡,然后出去走走。一般来说,你需要收集到足够的数据后再运行你的破解程序。看着“#Data”列里的数据,你需要它在10,000以上。(图里的数据只有854)
|
||||
|
||||
这个过程可能需要一些时间,这取决于你的网络信号强度(截图中可以看到,我的信号强度低于-32DB,虽然YoYo的AP和我的适配器在同一间屋里)。等待直到包数据到达10K,因为在此之前破解过程不会成功。实际上,你可能需要超过10K,虽然他可能是大多数情况下都足够了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
一旦你收集了足够多的数据,就是见证奇迹的时刻了。启动第三个终端窗口,同时输入下面的命令来破解你收集到的数据:
|
||||
aircrack-ng -b (bssid) (file name-01.cap)
|
||||
|
||||
aircrack-ng -b (bssid) (filename-01.cap)
|
||||
|
||||
这里的filename就是你在上面输入的文件名。你可以在自己的Home目录下看到。他应该是一个.cap后缀名的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -90,7 +95,7 @@ WEP密钥会接着显示“KEY FOUND”。去掉引号,然后输入他就可
|
||||
|
||||
### 这个过程中的问题 ###
|
||||
|
||||
通过这篇文章,我们可以证明想要破解WEP加密的网络对于任何一个具有硬件和软件人来说是如此简单的过程。我仍然认为是这样的。但是不像下面视频里的伙计,这个过程中我遇到了很多的问题。实际上,你应该可以注意到最后一张截图和其他的不一样,因为它不是我的截图。虽然我破解的AP是我自己的AP,和我的Alfa在同一间屋子里,而且读取的信号强度一直在-30左右,但是数据的收集速度依然很缓慢,而在数据收集完成以前,BackTrack不能破解他。在尝试了各种方案(在我的MAC和PC上),我始终没能抓取到足够的数据量来破解密钥。
|
||||
通过这篇文章,我们可以证明想要破解WEP加密的网络对于任何一个具有硬件和软件人来说是如此简单的过程。我一直认为是这样的,但是不像下面视频里的伙计,这个过程中我遇到了很多的问题。实际上,你应该可以注意到最后一张截图和其他的不一样,因为它不是我的截图。虽然我破解的AP是我自己的AP,和我的Alfa在同一间屋子里,而且读取的信号强度一直在-30左右,但是数据的收集速度依然很缓慢,而在数据收集完成以前,BackTrack不能破解他。在尝试了各种方案(在我的MAC和PC上),我始终没能抓取到足够的数据量来破解密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,这个过程在理论上是很简单的,实际上因为设备、到AP的距离却又因人而异.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -98,18 +103,18 @@ WEP密钥会接着显示“KEY FOUND”。去掉引号,然后输入他就可
|
||||
|
||||
[http://www.youtube.com/embed/kDD9PjiQ2_U?wmode=transparent&rel=0&autohide=1&showinfo=0&enablejsapi=1][10]
|
||||
|
||||
感受到一点使用BackTrack破解WEP加密的作用了么?你想说些什么呢?赶快换掉它把。
|
||||
感受到一点使用BackTrack破解WEP加密的作用了么?你想说些什么呢?赶快换掉它吧。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://lifehacker.com/5305094/how-to-crack-a-wi+fi-networks-wep-password-with-backtrack
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[stduolc](https://github.com/stduolc) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[stduolc](https://github.com/stduolc) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://lifehacker.com/386675/secure-your-home-wi+fi-network
|
||||
[2]:http://lifehacker.com/5873407/how-to-crack-a-wi+fi-networks-wpa-password-with-reaver
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.cn/article-2335-1.html
|
||||
[3]:http://lifehacker.com/399735/how-to-pick-a-lock-with-a-bump-key
|
||||
[4]:http://www.amazon.com/Alfa-AWUS036H-802-11b-Wireless-network/dp/B002WCEWU8?tag=lifehackeramzn-20&ascsubtag=[referrer|lifehacker.com[type|link[postId|5305094[asin|B002WCEWU8[authorId|5774310829120954491
|
||||
[5]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oHq-cKoYcr8
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
洞悉需求最高的三大IT技能组
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
据[IT技能清单][1]调查报告结果显示,雇主所需的Linux人才应具备的IT技能可分成相对独立的组群。本文将着重介绍在上一个季度(2013年7月-9月)需求度最高的3组IT技能,这些技能在包括美国在内的被选国家招聘广告中都有所提及,同时结果表明这三组技能可以和Linux相关的工作领域需求相匹配。
|
||||
|
||||
报告指出在上一季度具有嵌入式开发人员相关技能的人才是Linux专业雇主亟需的一类。排在第二位和第三位涉及的技能领域分别对应虚拟化技术和LAMP管理。本文将基于这三类工作清单涉及到的技能需求加以讨论,并对分析后的三组技能间的依赖结构关系加以洞悉。
|
||||
@ -8,41 +9,52 @@
|
||||
> 如果您尚未阅读[IT技能清单][1],我们强烈建议您在阅读以下内容前先熟悉这篇文章。它详细阐明了本次研究中用到的方法,本文也是基于[IT技能清单][1]的材料才得以进一步分析。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2013年8月IT技能分类更新 ###
|
||||
|
||||
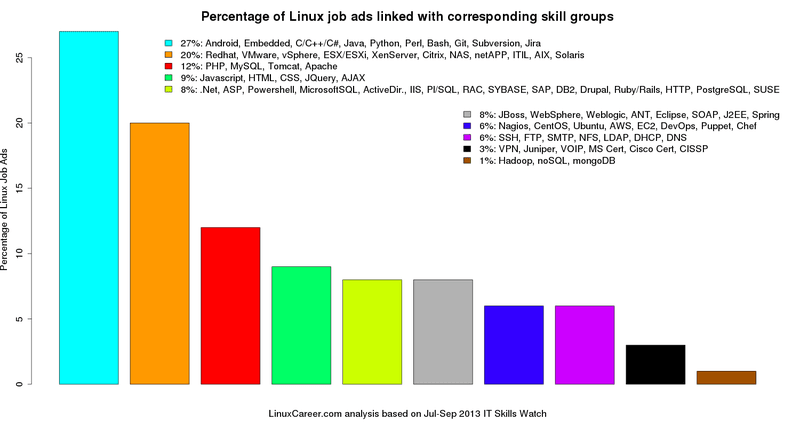
|
||||
|
||||
在IT技能清单这篇文章中,LinuxCareer.com分析了2013年5月到6月底的Linux工作清单,我们在这个基础上将2013年7月到9月底这个时间段的更新也加至分类分析中。10类相关的IT技能在Linux招聘广告中出现的比率列于如上[条形图][1]中。[IT分类][2]图表表明如何基于分类设计出此条形图。我们可以看到,IT技能需求前三组为:占据27%的Linux就业市场份额的嵌入式开发人员需求,占20%就业份额的虚拟化技术工程师和占12%Linux就业份额的LAMP管理员。文章接下来的三部分将围绕这三项IT技能需求组及三者的相互关系展开详细的讨论。例如,MySQL和PHP这两项技能有强关联性,通常雇主都会一起考虑。另外要指出的是,LinuxCareer.com的这项调查里掌握Linux的基础知识已默认存在于任一招聘需求中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 嵌入式开发人员及程序员 ###
|
||||
|
||||
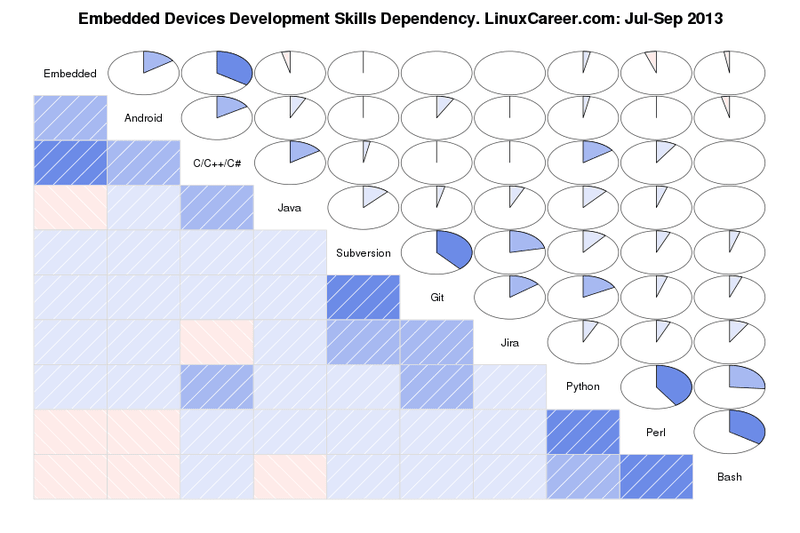
需求最高的第一类技能组是针对嵌入式开发人员及程序员的。如下的[依赖图][2]详细阐明了技能间的关联关系,尤其表明了哪几项技能更可能同时出现在Linux招聘需求中。例如,嵌入式开发非常需要C/C++/C#相关技能,而这些语言要么在图表下部的深色矩形区域,要么在图表上部的对应圆形阴影中聚集。
|
||||
|
||||
总体来说,这组技能可以进一步细分成如下三类:
|
||||
1. **Android, Embedded, C/C++/C# and Java**.如果您准备在嵌入式领域发展,这些是你需要掌握的核心技能,而C/C++/C#或Java掌握其一便可满足雇主需求,因为Java是基于部分C/C++/C#性能的扩展性语言。如果您阅读了8月的IT技能表,就会发现,Java以9513分居于编程语言的榜首,而C/C++/C#是5403分。如果您尚在犹豫是掌握C/C++/C#还是Java,从技能表得分看起来Java应该是更好的选择。但根据如下图表显示,C/C++/C#似乎在嵌入式领域的招聘需求中更受欢迎。总结可得尽管Java在IT技能表中有更高的得分,但在嵌入式开发职位上掌握C/C++/C#会比Java更有用。
|
||||
|
||||
1.** Python, Perl and Bash**.这些是对脚本编程语言技能的补充。对Perl和Python语言的需求经常会在招聘中同时出现,当然,也可以理解成这两种语言技能都是需要掌握的。
|
||||
1. **Android, Embedded, C/C++/C# 和 Java**。如果您准备在嵌入式领域发展,这些是你需要掌握的核心技能,而C/C++/C#或Java掌握其一便可满足雇主需求,因为Java是基于部分C/C++/C#性能的扩展性语言。如果您阅读了8月的IT技能表,就会发现,Java以9513分居于编程语言的榜首,而C/C++/C#是5403分。如果您尚在犹豫是掌握C/C++/C#还是Java,从技能表得分看起来Java应该是更好的选择。但根据如下图表显示,C/C++/C#似乎在嵌入式领域的招聘需求中更受欢迎。总结可得尽管Java在IT技能表中有更高的得分,但在嵌入式开发职位上掌握C/C++/C#会比Java更有用。
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Python, Perl 和 Bash**。这些是对脚本编程语言技能的补充。对Perl和Python语言的需求经常会在招聘中同时出现,当然,也可以理解成这两种语言技能都是需要掌握的。
|
||||
|
||||
3. **Git, Subversion 和 Jira**。这些软件知识会应用到源码管理、调试和项目管理中,同时了解这几个方面的知识对相关项目的编程大有裨益。目前,主流开源项目和大量合作项目都在用类似的软件管理他们的源码。
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Git, Subversion and Jira**.这些软件知识会应用到源码管理、调试和项目管理中,同时了解这几个方面的知识对相关项目的编程大有裨益。目前,主流开源项目和大量合作项目都在用类似的软件管理他们的源码。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
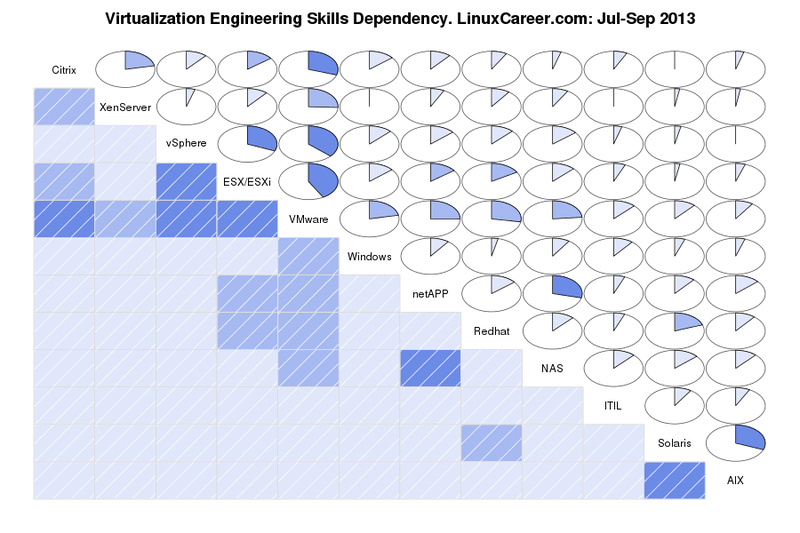
### 涉及数据仓储及管理的虚拟化技术工程师 ###
|
||||
目前第二大需求技能组是如下[依赖图][2]所示与虚拟化技术工程师相关的技能。这一组可进一步细分成两部分,第一部分是Redhat, VMware, vSphere, ESX/ESXi, XenServer and Citrix,这些技能对寻求虚拟化技术工程师的工作很重要;第二部分是同Unix系统、数据仓储及管理相关的技能。同时这两部分是紧密联系的。显然VMware和ESX/ESXi及vSphere是相关的,因为ESX/ESXi是VMware虚拟机下提供的虚拟产品,而vSphere是VMware虚拟机的云端虚拟操作系统。Redhat和VMware、Citrix产品被分到同一部分同样有其原因。这里Solaris和AIX具有密切关系的原因可以理解为它们都是专有的Unix系统,掌握其一便可。
|
||||
|
||||
目前第二大需求技能组是如下[依赖图][2]所示与虚拟化技术工程师相关的技能。这一组可进一步细分成两部分,第一部分是Redhat, VMware, vSphere, ESX/ESXi, XenServer 和 Citrix,这些技能对寻求虚拟化技术工程师的工作很重要;第二部分是同Unix系统、数据仓储及管理相关的技能。同时这两部分是紧密联系的。显然VMware和ESX/ESXi及vSphere是相关的,因为ESX/ESXi是VMware虚拟机下提供的虚拟产品,而vSphere是VMware虚拟机的云端虚拟操作系统。Redhat和VMware、Citrix产品被分到同一部分同样有其原因。这里Solaris和AIX具有密切关系的原因可以理解为它们都是专有的Unix系统,掌握其一便可。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
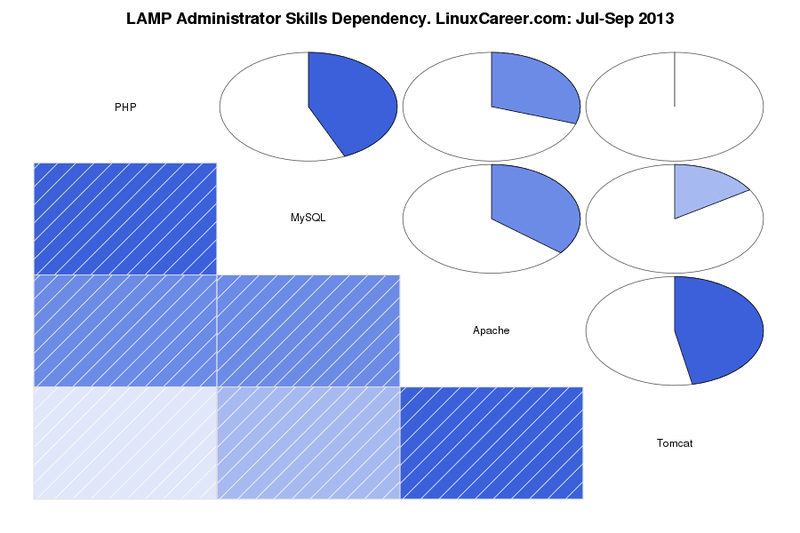
### LAMP管理员 ###
|
||||
|
||||
最后,第三大技能组是如下[依赖图][2]中显示雇主需求的LAMP管理员应具备的技能。LAMP是Linux、Apache、MySQL和PHP的简称,所有这四项内容是作为一名LAMP管理员所要了解的核心。这是一组相对来说小规模却会引领你至在Linux路途中发展更远的技能。实际上,PHP和MySQL的密切关系表明这些技能中的任一项都不能脱离其它技能来单独掌握。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
本文基于就业能力和Linux专业人员需求技能分组阐明了两点。第一点是对经常出现的IT技能通过集群分析划出了10类IT技能组;第二点是基于Linux工作需求与相应技能组的对应结果,嵌入式程序员在Linux招聘需求比率最高,第二及第三技能需求比率最高的领域分别对应虚拟化技术工程师及LAMP管理员领域。这三大技能组即为上一季度分析出的Linux技能需求的核心。
|
||||
|
||||
### 参考 ###
|
||||
[1] Percentage of Linux job ads linked with corresponding skill groups created by [GNU R][3]. Relevant package: graphics.
|
||||
|
||||
[2] Dependency charts created by [GNU R][3]. Relevant package: corrgram.
|
||||
\[1] Percentage of Linux job ads linked with corresponding skill groups created by [GNU R][3]. Relevant package: graphics.
|
||||
|
||||
\[2] Dependency charts created by [GNU R][3]. Relevant package: corrgram.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxcareer.com/insights-into-top-3-it-skills-groups-in-highest-demand
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[icybreaker](https://github.com/icybreaker) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[icybreaker](https://github.com/icybreaker) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,36 +1,38 @@
|
||||
Linux sheel 贴士和技巧
|
||||
Linux shell中的那些小把戏
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
我日常使用Linux shell(Bash),但是我经常忘记一些有用的命令或者shell技巧。是的,我能记住一些命令但是我不能说只在特定的任务上使用一次。那么我就开始在我的Dropbox账号里用文本文件写下这些Linux shell的贴士,现在我决定共享它。这个表我以后还会更新。记住,这里的一些贴士需要在你的Linux发行版上安装额外的软件。
|
||||
我日常使用Linux shell(Bash),但是我经常忘记一些有用的命令或者shell技巧。是的,我能记住一些命令,但是肯定不会只在特定的任务上使用一次,所以我就开始在我的Dropbox账号里用文本文件写下这些Linux shell的小技巧,现在我决定共享它给你。这个表我以后还会更新。记住,这里的一些贴士需要在你的Linux发行版上安装额外的软件。
|
||||
|
||||
在bash中检查远程端口是否打开:
|
||||
|
||||
echo >/dev/tcp/8.8.8.8/53 && echo "open"
|
||||
|
||||
终止进程:
|
||||
将进程挂起:
|
||||
|
||||
Ctrl + z
|
||||
|
||||
将进程移到前台:
|
||||
|
||||
fg
|
||||
|
||||
(译注,挂起的进程是不执行的,如果希望在后台执行,可以使用bg命令,并且指定通过jobs命令获得的任务号。)
|
||||
|
||||
生成随机16进制数字,n是字符的数量:
|
||||
|
||||
openssl rand -hex n
|
||||
|
||||
在当前shell中从一个文件中执行命令:
|
||||
在当前shell中执行一个文件中的命令(译注:这个文件不是一个bash脚本,比如.bashrc、bash_profile等):
|
||||
|
||||
source /home/user/file.name
|
||||
|
||||
提取前5个字符的字串:
|
||||
提取字符串的前5个字符:
|
||||
|
||||
${variable:0:5}
|
||||
|
||||
SSH调试模式:
|
||||
打开SSH调试模式(译注:当你遇到SSH连接问题时很有用):
|
||||
|
||||
ssh -vvv user@ip_address
|
||||
|
||||
带pem key的SSH
|
||||
使用pem key的进行SSH连接:
|
||||
|
||||
ssh user@ip_address -i key.pem
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,11 +40,11 @@ SSH调试模式:
|
||||
|
||||
wget -r --no-parent --reject "index.html*" http://hostname/ -P /home/user/dirs
|
||||
|
||||
创建多个目录:
|
||||
同时创建多个目录:
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir -p /home/user/{test,test1,test2}
|
||||
|
||||
列出带子进程的进程树:
|
||||
以树状列出进程及子进程:
|
||||
|
||||
ps axwef
|
||||
|
||||
@ -58,7 +60,7 @@ SSH调试模式:
|
||||
|
||||
hdparm -Tt /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
从文本中获取md5值:
|
||||
获取文本的md5值:
|
||||
|
||||
echo -n "text" | md5sum
|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,7 +68,7 @@ SSH调试模式:
|
||||
|
||||
xmllint --noout file.xml
|
||||
|
||||
在新的目录中提取tar.gz文件:
|
||||
将tar.gz文件解压到指定目录:
|
||||
|
||||
tar zxvf package.tar.gz -C new_dir
|
||||
|
||||
@ -74,7 +76,7 @@ SSH调试模式:
|
||||
|
||||
curl -I http://www.example.com
|
||||
|
||||
修改一些文件或目录的时间戳 (YYMMDDhhmm):
|
||||
修改一些文件或目录的时间戳 (格式为:YYMMDDhhmm):
|
||||
|
||||
touch -t 0712250000 file
|
||||
|
||||
@ -86,7 +88,7 @@ SSH调试模式:
|
||||
|
||||
LANG=c < /dev/urandom tr -dc _A-Z-a-z-0-9 | head -c${1:-16};echo;
|
||||
|
||||
快速创建一个文件的备份:
|
||||
快速创建一个文件的备份(扩展名是.bkp):
|
||||
|
||||
cp some_file_name{,.bkp}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -94,7 +96,7 @@ SSH调试模式:
|
||||
|
||||
smbclient -U "DOMAIN\user" //dc.domain.com/share/test/dir
|
||||
|
||||
在历史中运行命令 (这里在第100行):
|
||||
运行history中的命令 (这里在history中的第100个):
|
||||
|
||||
!100
|
||||
|
||||
@ -102,11 +104,11 @@ unzip到目录中:
|
||||
|
||||
unzip package_name.zip -d dir_name
|
||||
|
||||
多行文字 (按 CTRL + d 退出):
|
||||
输入多行文字 (按 CTRL + d 退出):
|
||||
|
||||
cat > test.txt
|
||||
|
||||
创建空白的文件或者已存在的文件:
|
||||
创建空白的文件或者清空已存在的文件:
|
||||
|
||||
> test.txt
|
||||
|
||||
@ -114,16 +116,16 @@ unzip到目录中:
|
||||
|
||||
ntpdate ntp.ubuntu.com
|
||||
|
||||
netstat 显示所有tcp4监听的端口:
|
||||
netstat 显示所有IPv4的TCP监听的端口:
|
||||
|
||||
netstat -lnt4 | awk '{print $4}' | cut -f2 -d: | grep -o '[0-9]*'
|
||||
|
||||
将qcow2图像转化成raw:
|
||||
将qcow2的镜像转化成raw格式:
|
||||
|
||||
qemu-img convert -f qcow2 -O raw precise-server-cloudimg-amd64-disk1.img \
|
||||
precise-server-cloudimg-amd64-disk1.raw
|
||||
|
||||
重复运行命令,显示它的输出 (默认2s刷新):
|
||||
重复运行命令并显示它的输出 (默认2秒重复一次):
|
||||
|
||||
watch ps -ef
|
||||
|
||||
@ -131,17 +133,17 @@ netstat 显示所有tcp4监听的端口:
|
||||
|
||||
getent passwd
|
||||
|
||||
以读写模式挂载root:
|
||||
以读写模式挂载根文件系统:
|
||||
|
||||
mount -o remount,rw /
|
||||
|
||||
挂在目录 (适合于符号链接不成功的情况下):
|
||||
挂载目录 (适合于符号链接不能工作的情况下):
|
||||
|
||||
mount --bind /source /destination
|
||||
|
||||
发送动态更新给DNS:
|
||||
发送DNS动态更新给DNS:
|
||||
|
||||
nsupdate < <EOF
|
||||
nsupdate <<EOF
|
||||
update add $HOST 86400 A $IP
|
||||
send
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
@ -150,7 +152,7 @@ netstat 显示所有tcp4监听的端口:
|
||||
|
||||
grep -r "some_text" /path/to/dir
|
||||
|
||||
列出10个最大的已打开的文件:
|
||||
列出10个最大的系统中已打开的文件:
|
||||
|
||||
lsof / | awk '{ if($7 > 1048576) print $7/1048576 "MB "$9 }' | sort -n -u | tail
|
||||
|
||||
@ -162,15 +164,15 @@ netstat 显示所有tcp4监听的端口:
|
||||
|
||||
vim + some_file_name
|
||||
|
||||
git clone特定branch (master):
|
||||
git clone特定branch (本例是master分支):
|
||||
|
||||
git clone git@github.com:name/app.git -b master
|
||||
|
||||
git切换到另外一个branch (develop):
|
||||
git切换到另外一个branch (本例是develop分支):
|
||||
|
||||
git checkout develop
|
||||
|
||||
git删除一个branch(myfeature):
|
||||
git删除一个branch(本例是myfeature):
|
||||
|
||||
git branch -d myfeature
|
||||
|
||||
@ -198,23 +200,23 @@ Git push 新的branch到远程:
|
||||
|
||||
< test.txt sed -n '50,60p'
|
||||
|
||||
运行最后的命令 (如果是: mkdir /root/test, 下面会运行: sudo mkdir /root/test):
|
||||
以sudo权限重新运行上一个执行的命令 (如果是: mkdir /root/test, 下面会运行: sudo mkdir /root/test)(译注:当你执行一个命令忘记sudo时,可以这样重新执行,而不必再把完整命令敲一遍):
|
||||
|
||||
sudo !!
|
||||
|
||||
创建临时RAM文件系统 - ramdisk (首先创建在 /tmpram 目录):
|
||||
创建临时RAM文件系统 - ramdisk (请先创建 /tmpram 目录):
|
||||
|
||||
mount -t tmpfs tmpfs /tmpram -o size=512m
|
||||
|
||||
Grep完整单词:
|
||||
Grep完整的单词(译注:而不是其它单词的一部分):
|
||||
|
||||
grep -w "name" test.txt
|
||||
|
||||
需要特权模式在一个文件后追加文本:
|
||||
提升权限后在一个文件后追加文本:
|
||||
|
||||
echo "some text" | sudo tee -a /path/file
|
||||
|
||||
列出所有的kill信号:
|
||||
列出所有支持的kill信号:
|
||||
|
||||
kill -l
|
||||
|
||||
@ -226,7 +228,7 @@ Grep完整单词:
|
||||
|
||||
kill -9 $$
|
||||
|
||||
扫描网络找出打开的端口:
|
||||
扫描网络来找出开放的端口:
|
||||
|
||||
nmap -p 8081 172.20.0.0/16
|
||||
|
||||
@ -234,15 +236,15 @@ Grep完整单词:
|
||||
|
||||
git config --global user.email "me@example.com"
|
||||
|
||||
如果你有未提交的commit,与master同步:
|
||||
如果你有未提交的commit,与master同步:
|
||||
|
||||
git pull --rebase origin master
|
||||
|
||||
将文件中含有txt的所有文件移动到/home/user:
|
||||
将文件名中含有txt的所有文件移动到/home/user:
|
||||
|
||||
find -iname "*txt*" -exec mv -v {} /home/user \;
|
||||
|
||||
一行行合并文件:
|
||||
按行将两个文件中的对应行合并显示:
|
||||
|
||||
paste test.txt test1.txt
|
||||
|
||||
@ -254,19 +256,19 @@ shell中的进度条:
|
||||
|
||||
echo "hosts.sampleHost 10 `date +%s`" | nc 192.168.200.2 3000
|
||||
|
||||
转换tab到空格:
|
||||
转换tab为空格:
|
||||
|
||||
expand test.txt > test1.txt
|
||||
|
||||
跳过bash历史:
|
||||
|
||||
< <space>>cmd
|
||||
<<空格>>cmd
|
||||
|
||||
回到先前的工作目录:
|
||||
回到之前的工作目录:
|
||||
|
||||
cd -
|
||||
|
||||
切割大的tar.gz文件 (每个 100MB) 并还原:
|
||||
切割大的tar.gz文件为几个文件 (每个100MB),并还原:
|
||||
|
||||
split –b 100m /path/to/large/archive /path/to/output/files
|
||||
cat files* > archive
|
||||
@ -287,7 +289,7 @@ shell中的进度条:
|
||||
|
||||
lsblk -f
|
||||
|
||||
找出末尾空格的文件:
|
||||
找出文件中带有末尾空格的文件:
|
||||
|
||||
find . -type f -exec egrep -l " +$" "{}" \;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -305,6 +307,6 @@ shell中的进度条:
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.techbar.me/linux-shell-tips/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
|
||||
专有 Unix 持续缩减
|
||||
Unix 持有量持续缩减
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
国际数据公司(IDC)的分析师在周三投寄了一篇[新闻稿][1]凸显出IBM 的 AIX 系统和 P-系列的硬件持有量已经快速下降。伴随着专有 Unix 系统下跌的同时,相关的运行着 Linux 系统的 X86 服务器销量却在崛起。IBM 已经明确指出这是一个长期趋势,所以投资了10亿美元用在基于 Power 系统的 Linux 开发。与新闻报道的 AIX 20%销售额下降的同时,我的这篇文章终于发布出来。
|
||||
|
||||
过去数年中,我在管理 AIX 和 Linux 系统上一点都不顺利,如果能让我挑选的话,会选择灵活性和易用性更好的 Linux 系统和稳定性更高的 Power 机器。根据我的经验, AIX 很难设置,在设置好要变动也很困难,但一旦设置好并启动起来,它就会一直很好的运行下去。一台配置合适的 AIX 服务器可以正常运行数年而无需干预,但是需要修改配置的时候,并且经常需要修改配置,就准备好长期的艰苦跋涉吧。相比之下,经过这么多年来,成千上万的开发人员和系统管理员,以及大牌公司的贡献,使得Linux更易于管理。根据[资讯天地][2]报道:
|
||||
国际数据公司(IDC)的分析师在周三投寄了一篇[新闻稿][1]凸显出IBM 的 AIX 系统和 P-系列的硬件持有量已经快速下降。伴随着专有 Unix 系统下跌的同时,相关的运行着 Linux 系统的 X86 服务器销量却在崛起。IBM 已经明确指出这是一个长期趋势,所以投资了10亿美元用在基于 Power 系统的 Linux 开发。与新闻报道的 AIX 20%销售额下降的同时,我的这篇文章终于发布出来了。
|
||||
|
||||
过去数年中,我在管理 AIX 和 Linux 系统上一点都不顺利,如果能让我挑选的话,会选择灵活性和易用性更好的 Linux 系统和稳定性更高的 Power 机器。根据我的经验, AIX 很难设置,在设置好后要变动也很困难,但一旦设置好并启动起来,它就会一直很好的运行下去。一台配置合适的 AIX 服务器可以正常运行数年而无需干预,但是需要修改配置的时候,并且经常需要修改配置,就准备好长期的艰苦跋涉吧。相比之下,经过这么多年来,成千上万的开发人员和系统管理员,以及大牌公司的贡献,使得Linux更易于管理。根据[Infoworld][2]报道:
|
||||
|
||||
> Linux服务器市场正在健步崛起,服务器总销量占总收入的百分比高达28%,所以任何可以提高市场占有率的投资,将会非常有价值,即使大部分份额的Linux服务器仍然是商用 x86 硬件。
|
||||
|
||||
Intel 和 AMD 的硬件也现跨越式发展,正在缩小与 Power 机器的性能差距。当我听到一个新的刀片上配置 10GB 的以太网卡已经成为标准、256GB 的 RAM 已经很正常了以及普通业务需要订购装有 16 核 CPU 的服务器已经成为常态时,吃惊不小。Intel 服务器和 IBM 的 Power 服务器性能差不多,但价格低很多。因为企业的观注点在于是否逃脱“顾问软件”及 IBM 的供应商锁定,所以在行业标准的x86硬件上运行的开源软件正变得越来越有吸引力。然而,IBM已经降低了 Power 系列机器的价格来保持竞争力。
|
||||
Intel 和 AMD 的硬件也现跨越式发展,正在缩小与 Power 机器的性能差距。当我听到一个新的刀片上配置 10GB 的以太网卡已经成为标准、256GB 的 RAM 已经很正常了,以及普通业务需要订购装有 16 核 CPU 的服务器已经成为常态时,吃惊不小。Intel 服务器和 IBM 的 Power 服务器性能差不多,但价格低很多。因为企业的关注点在于是否逃脱“顾问软件”及 IBM 的供应商锁定,所以在行业标准的x86硬件上运行的开源软件正变得越来越有吸引力。不过,IBM已经降低了 Power 系列机器的价格来保持竞争力。
|
||||
|
||||
这说明, IBM 选择投入在基于 Power 机器的 Linux 系统而不是 AIX 系统。 IBM 可能已经开发出现代版的 AIX,并使用通用的开源工具以使交互操作性更好。尽管 IBM 声明 AIX 仍然是重要的,但在 Power 机器的销售额持续下降,伴随的是 Linux 方面的投入,这一切的一切都正在翻开新故事的新篇章。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,7 +17,7 @@ IBM 不可能一切都以 AIX 为核心,但他们可能会无限期的延长
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/proprietary-unix-continues-to-fall
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
11 Linux内核: 配置内核 (Part 7)
|
||||
戴文的Linux内核专题:11 配置内核(7)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -6,11 +6,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
进程地址空间标识符(Process Address Space Identifiers (PASIDs))允许PCI设备同时访问多个IO地址空间(PCI PASID support)。这个特性需要一个支持PASIDs支持的IOMMU。
|
||||
|
||||
下面我们可以启用/禁用"PCI IO-APIC hotplug support"。APIC代表高级可编程中断控制器(Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controllers)。可编程中断控制器(PIC)收集所有来自不同源发给一个或者多个CPU流水线的中断。高级PIC与PIC一样,但是它们有更多的特性像高级中断管理和更多的优先级模型。热插拔一种在系统在运行时加入一件设备的能力并且不需要重启。这个驱动是为了PCI主板能拥有处理输入/输出APIC热插拔的能力。
|
||||
下面我们可以启用/禁用"PCI IO-APIC hotplug support"。APIC代表高级可编程中断控制器(Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controllers)。可编程中断控制器(PIC)收集所有来自不同源发给一个或者多个CPU流水线的中断。高级PIC与PIC一样,但是它们有更多的特性像高级中断管理和更多的优先级模型。热插拔是一种在系统在运行时加入一件设备的能力并且不需要重启。这个驱动是为了PCI主板能拥有处理输入/输出APIC热插拔的能力。
|
||||
|
||||
在这之后,下面的问题询问的是启用"ISA-style DMA support"。在前文中提到过,DMA是直接内存访问,它是一种设备无需借助CPU直接访问内存的能力。ISA代表的是工业标准架构(Industry Standard Architecture),它是一种像PCI的总线标准。这个特性允许在ISA主板上支持DMA。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们可以移步到"PCCard (PCMCIA/CardBus) support"。PCMCIA代表的是个人计算机存储卡国际协会(Personal Computer Memory Card International Association)。PC卡、PCMCIA卡和Cardbus卡都是卡片形状的笔记本外设。
|
||||
现在,我们可以移步到"PC Card (PCMCIA/CardBus) support"。PCMCIA代表的是个人计算机存储卡国际协会(Personal Computer Memory Card International Association)。PC卡、PCMCIA卡和Cardbus卡都是卡片形状的笔记本外设。
|
||||
|
||||
下一个PCMCIA选项处理"16-bit PCMCIA support"。一些旧的计算机使用16位PCMCIA卡。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ CardBus是16位PCMCIA的更新32位版本。这个驱动提供对这类设备的
|
||||
|
||||
对于带有支持CompactPCI热插拔支持的CompactPCI卡的系统,启用"CompactPCI Hotplug driver"。
|
||||
|
||||
下面,我们有一个选项对于另一种COmpactPCI系统卡(Ziatech ZT5550 CompactPCI Hotplug)。
|
||||
下面,我们有一个选项对于另一种CompactPCI系统卡(Ziatech ZT5550 CompactPCI Hotplug)。
|
||||
|
||||
使用#ENUM热插拔信号通过标准IO口作为系统注册位的CompactPCI卡需要这个驱动(Generic port I/O CompactPCI Hotplug)。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -100,15 +100,15 @@ IPsec安全联合定位器可以当这个特性启用时(Transformation migrate
|
||||
|
||||
如果这是一个路由器Linux系统的内核,那就启用这个选项(IP: advanced router)。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的特性启用了,那么IP地址会在启动时自动配置(IP: kernel level autoconfiguration)。当用户希望不用配置就能连接到一个网络时是很有用的。
|
||||
如果下面的特性启用了,那么IP地址会在启动时自动配置(IP: kernel level autoconfiguration)。当用户希望不用配置就能连接到一个网络时是很有用的。
|
||||
|
||||
启用另外DHCP协议支持,那么Linux系统可以通过网络像NFS挂载它的根文件系统并且使用DHCP发现IP地址(IP: DHCP support)。这允许Linux系统通过网络拥有它的远程根文件系统而不必用户在每次系统启动时手动管理进程。
|
||||
启用了DHCP协议支持,那么Linux系统可以通过网络像NFS挂载它的根文件系统并且使用DHCP发现IP地址(IP: DHCP support)。这允许Linux系统通过网络拥有它的远程根文件系统而不必用户在每次系统启动时手动管理进程。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的选项和上面的类似除了使用的是BOOTP而不是DHCP(IP: BOOTP support。BOOTP是自举协议;这个协议使用UDP而不是TCP并且只能使用IPv4网络
|
||||
|
||||
RARP是一个由于BOOTP和DHCP如今已经废除了的旧协议,但是它仍可以加到内核中(IP: RARP support)。
|
||||
RARP是一个被BOOTP和DHCP替代了的旧协议,但是它仍可以加到内核中(IP: RARP support)。
|
||||
|
||||
网络协议可以在另一个概念中使用,称作"隧道"。这个特性可以用在Linux内核中(IP: tunneling)。安全shell协议(The secure shell protocol (SSH))就是隧道协议的一个例子。这个特性需要SSH。
|
||||
网络协议可以在另一个概念中使用,称作"隧道"。这个特性可以用在Linux内核中(IP: tunneling)。安全shell协议(The secure shell protocol (SSH))就是隧道协议的一个例子。SSH需要这个特性。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的驱动可以多路复用通用路由封装包(GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation))(IP: GRE demultiplexer)。多路复用是一个使单个信号进入不同部分的过程(这不会复制消息,只是分解它)。GRE是一种隧道协议。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -122,6 +122,6 @@ RARP是一个由于BOOTP和DHCP如今已经废除了的旧协议,但是它仍
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-7.4490/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
12 Linux内核: 配置内核 (Part 8)
|
||||
戴文的Linux内核专题:12 配置内核(8)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
下一个要配置的网络特性是"ARP daemon support"。这让内核有一张IP地址表以及它们相应的在内部缓存中的硬件地址。ARP代表的是地址解析协议(Address-Resolution-Protocol)。
|
||||
|
||||
为了额外的安全,"TCP syncookie support"应该要启用。这保护计算机免于受到SVN洪水攻击。黑客或者恶意软件可能会发送SVN信息给一台服务器来消耗它的资源,以便让真实的访客无法使用服务器提供的服务。SVN消息会打开一个计算机和服务器之间的连接。Syncookie会阻断不正当的SVN消息。那么,真实的用户可以仍旧访问访问网站而没有黑客消耗带宽。服务器应该启用这个特性。
|
||||
为了额外的安全,"TCP syncookie support"应该要启用。这保护计算机免于受到SYN洪水攻击。黑客或者恶意软件可能会发送SYN信息给一台服务器来消耗它的资源,以便让真实的访客无法使用服务器提供的服务。SYN消息会打开一个计算机和服务器之间的连接。Syncookie会阻断不正当的SYN消息。那么,真实的用户可以仍旧访问访问网站,而黑客则没办法浪费你的带宽。服务器应该启用这个特性。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的特性是用于 "Virtual (secure) IP: tunneling"。隧道是一个网络协议到另外一个网络协议的封装。当在使用虚拟私人网络(VPN)时需要使用安全隧道。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
在这之后,启用"ESP transformation"增加对IPSec封装安全协议的支持。这是加密与可选择的数据验证的安全措施。
|
||||
|
||||
如果启用了这个特性(IP: IPComp transformation),Linux内核会支持IP负载压缩协议。这是一种无损压缩系统。无损指的是数据仍在它的完整形式。在解压缩后,数据在压缩前后没有变化。压缩在加密前先执行。由于更少的数据传输,所以这个压缩协议可以加速网络。
|
||||
如果启用了这个特性(IP: IPComp transformation),Linux内核会支持IP负载压缩协议。这是一种无损压缩系统。无损指的是数据仍会保持完整,在解压缩后,数据在压缩前后没有变化。压缩在加密前先执行。由于更少的数据传输,所以这个压缩协议可以加速网络。
|
||||
|
||||
下面三个设置用于处理不同的IPsec特性("IP: IPsec transport mode"、"IP: IPsec tunnel mode"和"IP: IPsec BEET mode")。IPSec代表的是因特网安全协议(Internet Protocol SECurity).两台计算机之间并且/或者服务器间的传输模式是默认的IPSec模式。传输模式使用AH或者ESP头并且只加密IP头。在隧道模式下,IP头和负载会被加密。隧道模式通常用于连接网关到服务器/服务器或者服务器到服务器。BEET模式(Bound End-to-End Tunnel)不会在IP地址改变时重连。BEET模式下的连接会仍然存在。BEET模式比其他几种模式使用更少的字节。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ TCP连接可以被MD5保护(TCP: MD5 Signature Option support)。这用于保护
|
||||
|
||||
下面的特性是一个特殊的隐私特性(IPv6: Privacy Extensions (RFC 3041) support)。这使得系统在网络接口中生成并使用不同的随即地址。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:没有计算机是真正随机的。计算机中随机数和随机字串通常称为伪随机。
|
||||
注意:计算机中没有数据是真正随机的。计算机中随机数和随机字串通常称为伪随机。
|
||||
|
||||
在多路由的网络中,这个特性允许系统能够更有效地计算出该使用哪一个(IPv6: Router Preference (RFC 4191))。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -132,6 +132,6 @@ LAN仿真(LANE)仿真了ATM网络上的LAN服务(LAN Emulation (LANE) support)
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-8.4525/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ Unigine 引擎正是由 Unigine 公司开发的, 同时这公司还开发了 H
|
||||
- 密杂草丛的高度现已实现同步。
|
||||
- 修复了在渲染非 Flash 闪屏时崩溃的漏洞。
|
||||
|
||||
所有平台的完整新特性列表,可以在官方的[公告]中找到。[1].
|
||||
所有平台的完整新特性列表,可以在官方的[公告][1]中找到。.
|
||||
|
||||
要记住 UNIGINE 引擎只针对商业企业,并不向广大用户提供试用版。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,19 +28,9 @@ Unigine 引擎正是由 Unigine 公司开发的, 同时这公司还开发了 H
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/UNIGINE-Is-Probably-the-Best-Gaming-Engine-on-Linux-404484.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[hyaocuk](https://github.com/hyaocuk) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[hyaocuk](https://github.com/hyaocuk) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unigine.com/devlog/2013/11/27/113
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,162 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating-------------geekpi
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
10 Useful Chaining Operators in Linux with Practical Examples
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Chaining of Linux commands means, combining several commands and make them execute based upon the behaviour of operator used in between them. Chaining of commands in Linux, is something like you are writing [short shell scripts][1] at the shell itself, and executing them from the terminal directly. Chaining makes it possible to automate the process. Moreover, an unattended machine can function in a much systematic way with the help of chaining operators.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*10 Chaining Operators in Linux*
|
||||
|
||||
This Article aims at throwing light on frequently used **command-chaining operators**, with short descriptions and corresponding examples which surely will increase your productivity and lets you write short and meaningful codes beside reducing system load, at times.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Ampersand Operator (&) ###
|
||||
|
||||
The function of ‘**&**‘ is to make the command run in background. Just type the command followed with a white space and ‘**&**‘. You can execute more than one command in the background, in a single go.
|
||||
|
||||
Run one command in the background:
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ ping c5 www.tecmint.com &
|
||||
|
||||
Run two command in background, simultaneously:
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/tecmint# apt-get update & apt-get upgrade &
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. semi-colon Operator (;) ###
|
||||
|
||||
The semi-colon operator makes it possible to run, several commands in a single go and the execution of command occurs sequentially.
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/tecmint# apt-get update ; apt-get upgrade ; mkdir test
|
||||
|
||||
The above command combination will first execute **update** instruction, then **upgrade** instruction and finally will create a ‘**test**‘ directory under the current working directory.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. AND Operator (&&) ###
|
||||
|
||||
The **AND Operator (&&)** would execute the second command only, if the execution of first command fails, i.e., the exit status of the first command is **1**. This command is very useful in checking the execution status of last command.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, I want to visit website **tecmint.com** using **[links command][2]**, in terminal but before that I need to check if the host is **live** or **not**.
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/tecmint# ping -c3 www.tecmint.com && links www.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. OR Operator (||) ###
|
||||
|
||||
The **OR Operator (||)** is much like an ‘**else**‘ statement in programming. The above operator allow you to execute second command only if the execution of first command fails, i.e., the exit status of first command is ‘**1**‘.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, I want to execute ‘**apt-get update**‘ from non-root account and if the first command fails, then the second ‘**links www.tecmint.com**‘ command will execute.
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ apt-get update || links tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
In the above command, since the **user** was not allowed to **update** system, it means that the exit status of first command is ’**1**′ and hence the last command ‘**links tecmint.com**‘ gets executed.
|
||||
|
||||
What if the first command is executed successfully, with an exit status ‘**0**‘? Obviously! Second command won’t execute.
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ mkdir test || links tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
Here, the user creates a folder ‘**test**‘ in his home directory, for which user is permitted. The command executed successfully giving an exit status ‘**0**‘ and hence the last part of the command is not executed.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. NOT Operator (!) ###
|
||||
|
||||
The **NOT Operator (!)** is much like an ‘**except**‘ statement. This command will execute all except the condition provided. To understand this, create a directory ‘**tecmint**‘ in your home directory and ‘**cd**‘ to it.
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ mkdir tecmint
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ cd tecmint
|
||||
|
||||
Next, create several types of files in the folder ‘**tecmint**‘.
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ touch a.doc b.doc a.pdf b.pdf a.xml b.xml a.html b.html
|
||||
|
||||
See we’ve created all the new files within the folder ‘**tecmint**‘.
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ ls
|
||||
|
||||
a.doc a.html a.pdf a.xml b.doc b.html b.pdf b.xml
|
||||
|
||||
Now delete all the files except ‘**html**‘ file all at once, in a smart way.
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ rm -r !(*.html)
|
||||
|
||||
Just to verify, last execution. List all of the available files using [ls command][3].
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ ls
|
||||
|
||||
a.html b.html
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. AND – OR operator (&& – ||) ###
|
||||
|
||||
The above operator is actually a combination of ‘**AND**‘ and ‘**OR**‘ Operator. It is much like an ‘**if-else**‘ statement.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, let’s do ping to **tecmint.com**, if success echo ‘**Verified**‘ else echo ‘**Host Down**‘.
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ ping -c3 www.tecmint.com && echo "Verified" || echo "Host Down"
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sample Output ####
|
||||
|
||||
PING www.tecmint.com (212.71.234.61) 56(84) bytes of data.
|
||||
64 bytes from www.tecmint.com (212.71.234.61): icmp_req=1 ttl=55 time=216 ms
|
||||
64 bytes from www.tecmint.com (212.71.234.61): icmp_req=2 ttl=55 time=224 ms
|
||||
64 bytes from www.tecmint.com (212.71.234.61): icmp_req=3 ttl=55 time=226 ms
|
||||
|
||||
--- www.tecmint.com ping statistics ---
|
||||
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2001ms
|
||||
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 216.960/222.789/226.423/4.199 ms
|
||||
Verified
|
||||
|
||||
Now, disconnect your internet connection, and try same command again.
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ ping -c3 www.tecmint.com && echo "verified" || echo "Host Down"
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sample Output ####
|
||||
|
||||
ping: unknown host www.tecmint.com
|
||||
Host Down
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. PIPE Operator (|) ###
|
||||
|
||||
This **PIPE** operator is very useful where the output of first command acts as an input to the second command. For example, pipeline the output of ‘**ls -l**‘ to ‘**less**‘ and see the output of the command.
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ ls -l | less
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Command Combination Operator {} ###
|
||||
|
||||
Combine two or more commands, the second command depends upon the execution of the first command.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, check if a file ‘**xyz.txt**‘ and ‘**xyz1.txt**‘ is available under my **Downloads** directory or not, and output corresponding output.
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ [ -f /home/tecmint/Downloads/xyz.txt ] || echo “The file does not exist”
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ [ -f /home/tecmint/Downloads/xyz1.txt ] || echo “The file does not exist”
|
||||
|
||||
“The file does not exist”
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Precedence Operator () ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Operator makes it possible to execute command in precedence order.
|
||||
|
||||
Command_x1 &&Command_x2 || Command_x3 && Command_x4.
|
||||
|
||||
In the above pseudo command, what if the **Command_x1** fails? Neither of the **Command_x2**, **Command_x3**, **Command_x4** would executed, for this we use **Precedence Operator**, as:
|
||||
|
||||
(Command_x1 &&Command_x2) || (Command_x3 && Command_x4)
|
||||
|
||||
In the above pseudo command, if **Command_x1** fails, **Command_x2** also fails but Still **Command_x3** and **Command_x4** executes depends upon exit status of **Command_x3**.
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Concatenation Operator (\) ###
|
||||
|
||||
The **Concatenation Operator (\)** as the name specifies, is used to concatenate large commands over several lines in the shell. For example, The below command will open text file **test(1).txt**.
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/Downloads$ nano test\(1\).txt
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I am coming up with another interesting article very soon. Till then Stay tuned, healthy and connected to **Tecmint**. Don’t forget to give your Valuable feedback in our comment section.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/chaining-operators-in-linux-with-practical-examples/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/category/bash-shell/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/command-line-web-browsers/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/15-basic-ls-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
44
sources/GNOME`s File Manager Will Be More User Friendly.md
Normal file
44
sources/GNOME`s File Manager Will Be More User Friendly.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
translating by zsJacky
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME’s File Manager Will Be More User Friendly
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Allan Day, a GNOME designer, posted a few days ago on his blog a very long article about [what’s coming next in the Nautilus (now known as Files) file manager for the GNOME desktop environment][1].**
|
||||
|
||||
What you will read in this article is a short summary of the new design features that will be implemented in upcoming releases of Nautilus, which will be part of the GNOME 3.12 desktop environment.
|
||||
|
||||
Apparently, a team of GNOME developers decided to revamp the default file manager of the controversial desktop environment, and bring some of its background functionality to the spotlight, making them obvious to new users.
|
||||
|
||||
Believe it or not, there are a lot of new users, those who are trying to discover the wonders of the Linux world, that have no idea what to do in Nautilus, how to copy, paste, rename, move or even access their files… and this is a big and embarrassing problem that needs to be fixed!
|
||||
|
||||
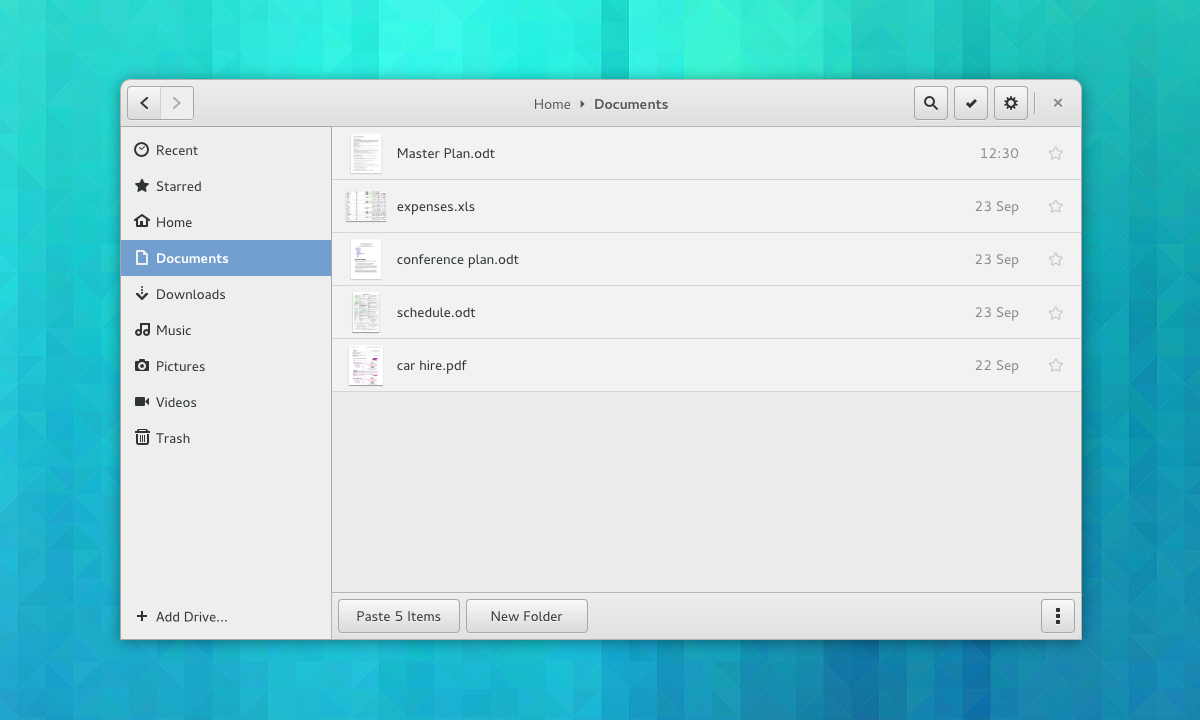
Therefore, future versions of the Nautilus file manager will have improved, responsive grids and lists views with big and clear thumbnails, as well as helpful zoom levels, so you can easily recognize your files. An updated View menu, with nicer controls, will also be implemented.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Nautilus list view*
|
||||
|
||||
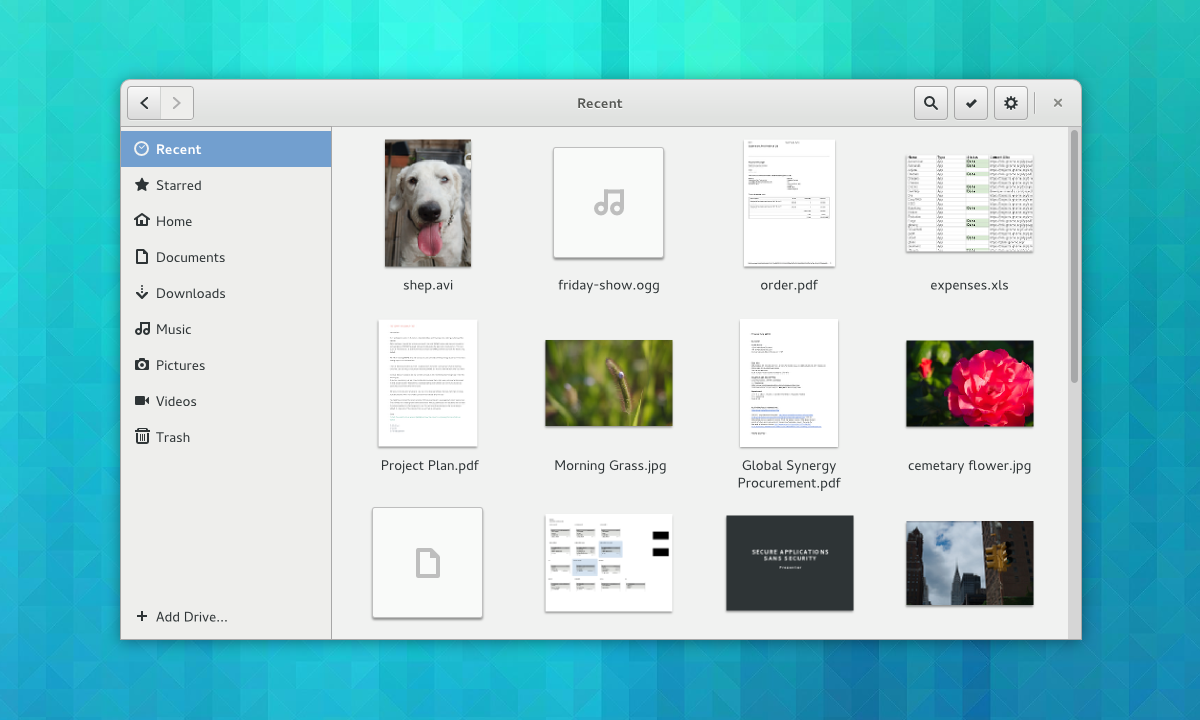
|
||||
*Nautilus grid view*
|
||||
|
||||
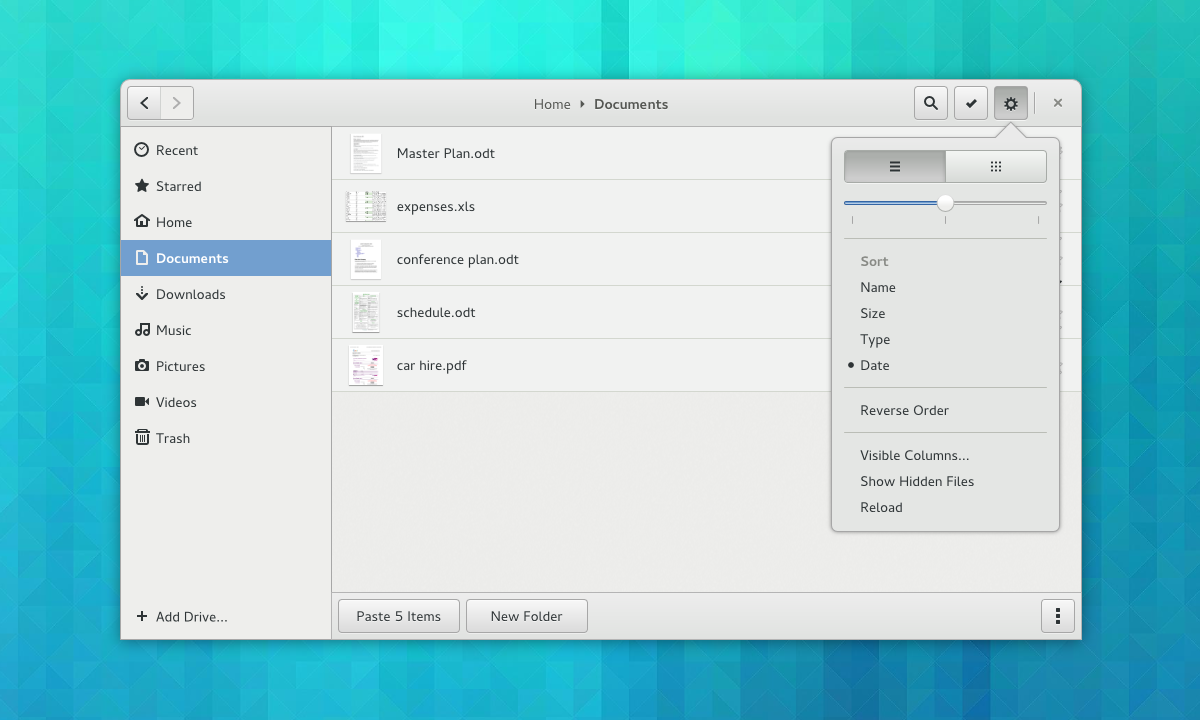
|
||||
Nautilus gear menu
|
||||
|
||||
Another important feature that will be implemented in Nautilus (Files) will be all kind of helpful buttons, such as Copy To, Move To, Create New Folder, or Open With, so it can make file operations more user friendly. Also, previewing files will be more straightforward, including a highly anticipated navigation function, so you can easily browse through multiple photos or documents
|
||||
|
||||
Moreover, the sidebar will be more customizable, allowing users to add or remove network drives, partitions or remote connections from it, making it as uncluttered as possible. A “Starred” entry will also be available for all your favorite files, along with an improved content selection function, allowing users to select items from multiple sources.
|
||||
|
||||
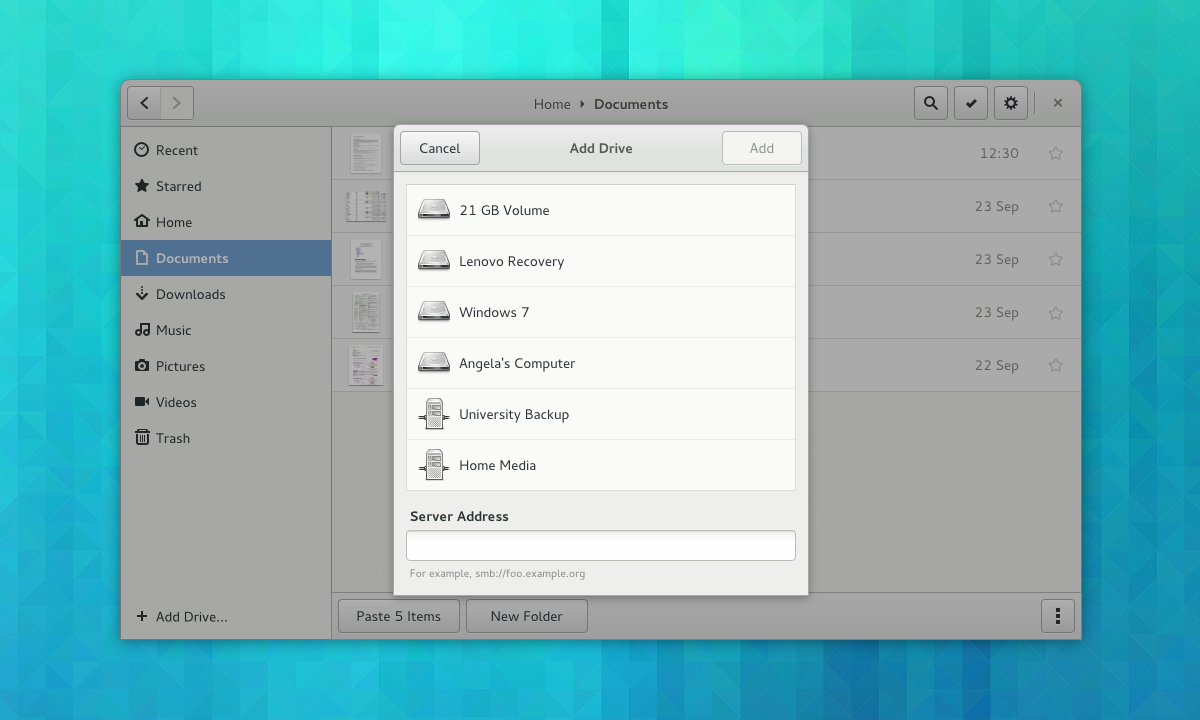
|
||||
*Nautilus add drive dialog*
|
||||
|
||||
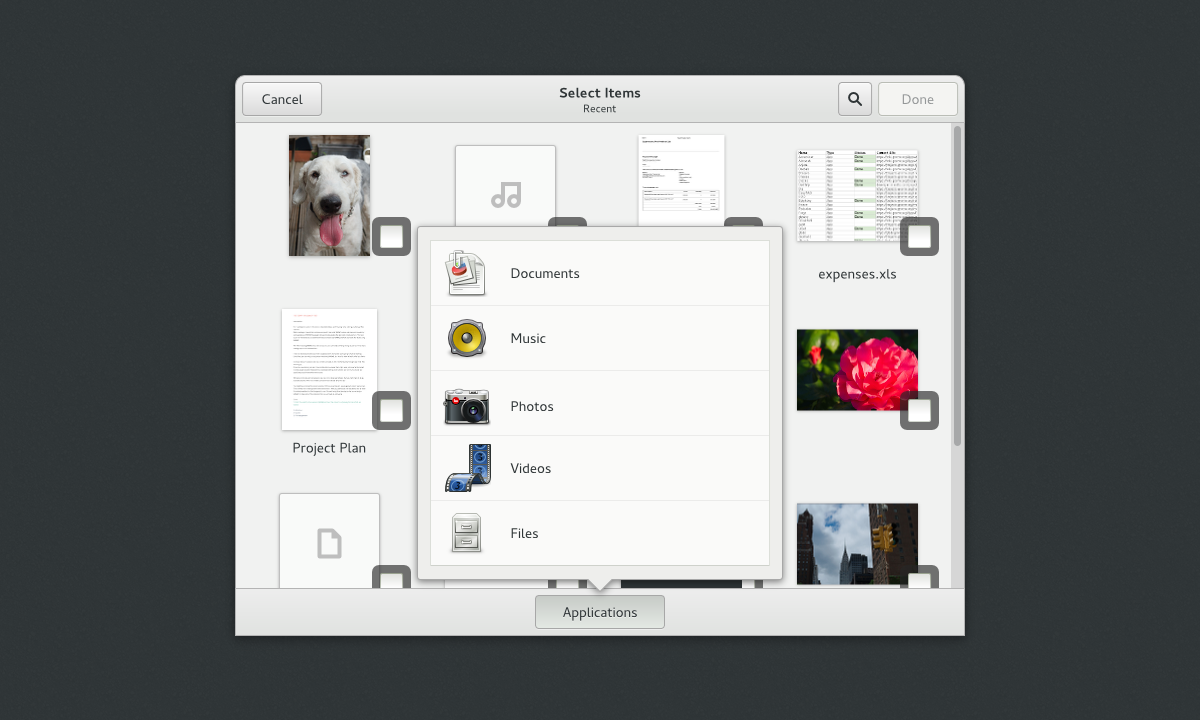
|
||||
*Nautilus content selection*
|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately, there’s no way for us to compile and test the upcoming Nautilus file manager at this moment, but we will let you know when the first development version is out. We remind everyone that Nautilus is also the default file manager for the Ubuntu Linux operating system.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/GNOME-s-File-Manager-Will-Be-More-User-Friendly-409360.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[zsJacky](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://afaikblog.wordpress.com/2013/12/11/nautilus-next/
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
[Translating by SteveArcher]
|
||||
Gnu: toward the post-scarcity world – the Free Software Column
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**It is 30 years since Richard Stallman announced that he was going to write a complete UNIX-compatible software system called GNU, pioneering the idea of free and open source software, but the struggle continues **
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,100 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[翻译中] by KayGuowhu
|
||||
How to Upgrade to GNOME 3.10 in Ubuntu 13.10
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu 13.10 ships with the GNOME 3.8 desktop available in its archives. While a dependable, stable and featured alternative to Unity, it’s also outdated.**
|
||||
|
||||
The newer version of the GNOME desktop was released back in September 2013 and comes with a raft of improved features, apps and usability tweaks. From hi-res screen support to new client-side decoration of app windows, GNOME 3.10 is a compelling upgrade.
|
||||
|
||||
The good news is that – providing you’re running Ubuntu 13.10, have a decent internet connection, and some command line aptitude (pun fully intended) – you don’t have to stick with a stale version of GNOME.
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Upgrade to GNOME 3.10 in Ubuntu 13.10 ###
|
||||
|
||||
For the benefit of the skim readers whose eyes dropped straight to the point I’ll reiterate: you **need to be running Ubuntu 13.10 to install GNOME 3.10**.
|
||||
|
||||
First, let’s add the GNOME 3 PPA to Ubuntu’s Software Sources. This can be done using a GUI but it is far easier to achieve using the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
Open a new *Terminal* window and enter the following command, entering your user password when asked:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3-next && sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
With the PPA added and our package list updated we can move on to installing GNOME 3.10 itself. To do this run the following command, again entering your user password when prompted:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install gnome-shell ubuntu-gnome-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
It can take a while for all the necessary packages and components to be fetched and installed, so try to be patient.
|
||||
|
||||
Midway through the installation a prompt will appear in the Terminal asking you to choose what display manager – aka “login screen” – should be used by default.
|
||||
|
||||
This decision is entirely up to you; both Ubuntu’s Unity Greeter and the **GNOME Display Manager** let you easily switch between desktop sessions (handy if you want to keep Unity or another desktop around) but only GDM offers GNOME-specific features such as lock-screen notifications.
|
||||
|
||||
When you’re ready to decide make your selection using the up/down arrow keys and hit ‘Enter/Return’ to confirm. The installation will then proceed.
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding The Extra Stuff ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME 3.10 comes with some great new features, applications – [including GNOME Weather, Music and Maps][1] – and other miscellaneous changes. Because not all of these are considered ‘stable’ enough to be included in the main GNOME 3 PPA we added earlier, you’ll need to make use of an additional pair of GNOME PPAs if you want to use them.
|
||||
|
||||
Now – and it’s important you’re aware of this – some of the packages in these repositories are reported to have stability issues. Most of these will be minor – i.e., the odd app crash or broken feature – but the potential for more major issues, like making GNOME crash entirely, is possible.
|
||||
|
||||
Warning out of the way, open up a new tab in a Terminal and punch in the following:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3-staging
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
To add some of the cool apps we mentioned earlier run:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gnome-weather gnome-music gnome-maps cheese gnome-documents
|
||||
|
||||
With that we’re done!
|
||||
|
||||
You may wish to log out and back in (remembering to select the ‘GNOME’ session) to ensure that everything takes effect correctly.
|
||||
|
||||
### Minor Differences ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you’ve kept Unity installed alongside GNOME 3.10 then there are a few things you’ll need to note down.
|
||||
|
||||
First off, you’ll find **two entries for ‘Online Accounts’ in System Settings**. The one with the key-themed icon is the Unity version, and the one with the plug emblem is GNOME’s.
|
||||
|
||||
Some apps will require you to add accounts to the Unity version (Shotwell, Gwibber, Empathy) and some to the GNOME one (Evolution, Documents, Contacts).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The ‘Notifications’ and ‘Search’ entries are GNOME-specific, both letting you pick and choose which applications and sources are able to show notifications or appear in the Activities Overlay.
|
||||
|
||||
### Uninstalling GNOME 3.10 ###
|
||||
|
||||
So you’ve tried it and didn’t like it. Now what?
|
||||
|
||||
Removing GNOME 3.10 is a fairly straightforward processing providing we use a command-line tool called ‘PPA Purge’. It can be found in the Ubuntu Software Center and is by far the easiest way to automatically remove and/or downgrade packages installed from PPAs.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Install PPA Purge from Ubuntu Software Center][2]
|
||||
|
||||
To use the tool we’ll need to go back to the terminal and enter the following, taking care to look out for any prompts that may appear during the downgrade process.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ppa-purge ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3-next
|
||||
|
||||
If you also added the optional extra PPAs you will also need to purge those as well:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ppa-purge ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3-staging
|
||||
sudo ppa-purge ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3
|
||||
|
||||
Once completed you should be left with the stock GNOME 3.8 desktop. If you don’t want to keep GNOME Shell around at all you can proceed to remove it:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove gnome-shell ubuntu-gnome-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, manually remove any remaining applications that persist after downgrade (e.g., Epiphany and GNOME Documents), then reboot.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/12/upgrade-gnome-3-10-ubuntu-13-10
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/09/gnome-3-10-released-with-new-apps-experimental-wayland-support
|
||||
[2]:apt:ppa-purge
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Translating by icybreaker
|
||||
How to install and configure Nagios on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[Nagios][1] is one of the most powerful network monitoring systems, which is widely used in the industry. It can actively monitor any network, and generate audio/email warnings and alerts when any problem is detected. The check types and alert timers are fully customizable.
|
||||
|
||||
118
sources/How to open a large text file on Linux.md
Normal file
118
sources/How to open a large text file on Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
|
||||
How to open a large text file on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In the era of "big data", large text files (GB or more) could be commonly encountered around us. Suppose you somehow need to search and edit one of those big text files by hand. Or you could be analyzing multi-GB log files manually for specific troubleshooting purposes. A typical text editor may not be designed to deal with such large text files efficiently, and may simply get choked while attempting to open a big file, due to insufficient memory.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are a savvy system admin, you can probably open or touch an arbitrary text file with a combination of cat, tail, grep, sed, awk, etc. In this tutorial, I will discuss more user-friendly ways to **open (and possibly edit) a large text file on Linux**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Vim with LargeFile Plugin ###
|
||||
|
||||
Vim text editor boasts of various plugins (or scripts) which can extend Vim's functionality. One such Vim plugin is [LargeFile plugin][1].
|
||||
|
||||
The LargeFile plugin allows you to load and edit large files more quickly, by turning off several Vim features such as events, undo, syntax highlighting, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
To install the LargeFile plugin on Vim, first make sure that you have Vim installed.
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install vim
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora, CentOS or RHEL:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install vim-enhanced
|
||||
|
||||
Then download the LargFile plugin from [Vim website][2]. The latest version of the plugin is 5, and it will be saved in Vimball format (.vba extension).
|
||||
|
||||
To install the plugin in your home directory, you can open the .vba file with Vim as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ gunzip LargeFile.vba.gz
|
||||
$ vim LargeFile.vba
|
||||
|
||||
Enter ":so %" and press ENTER within Vim window to install the plugin in your home directory.
|
||||
|
||||
[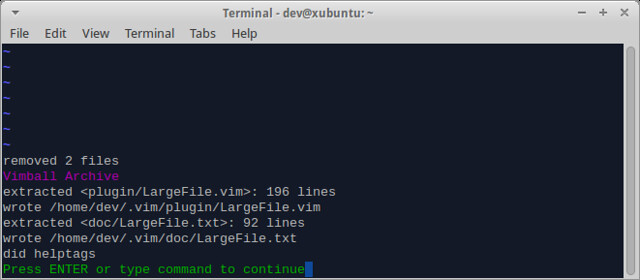][3]
|
||||
|
||||
After this, enter ":q" to quit Vim.
|
||||
|
||||
The plugin will be installed at ~/.vim/plugin/LargeFile.vim. Now you can start using Vim as usual.
|
||||
|
||||
What this plugin does is to turn off events, undo, syntax highlighting, etc. when a "large" file is loaded on Vim. By default, files bigger than 100MB are considered "large" by the plugin. To change this setting, you can edit ~/.vimrc file (create one if it does not exist).
|
||||
|
||||
To change the minimum size of large files to 10MB, add the following entry to ~/.vimrc.
|
||||
|
||||
> let g:LargeFile=10
|
||||
|
||||
While the LargeFile plugin can help you speed up file loading, Vim itself still cannot handle editing an extremely large file very well, because it tries to load the entire file in memory. For example, when a 1GB file is loaded on Vim, it takes as much memory and swap space, as shown in the top output below.
|
||||
|
||||
So if your files are significantly bigger than the physical memory of your Linux system, you can consider other options, as explained below.
|
||||
|
||||
### glogg Log Explorer ###
|
||||
|
||||
If all you need is "read-only" access to a text file, and you don't have to edit it, you can consider [glogg][4], which is a GUI-based standalone log analyzer. The glogg analyzer supports filtered views of an input text file, based on extended regular expressions and wildcards.
|
||||
|
||||
To install glogg on Debian (Wheezy and higher), Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install glogg
|
||||
|
||||
To install glogg on Fedora (17 or higher):
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install glogg
|
||||
|
||||
To open a text file with glogg:
|
||||
|
||||
$ glogg test.log
|
||||
|
||||
glogg can open a large text file pretty fast. It took me around 12 seconds to open a 1GB log file.
|
||||
|
||||
[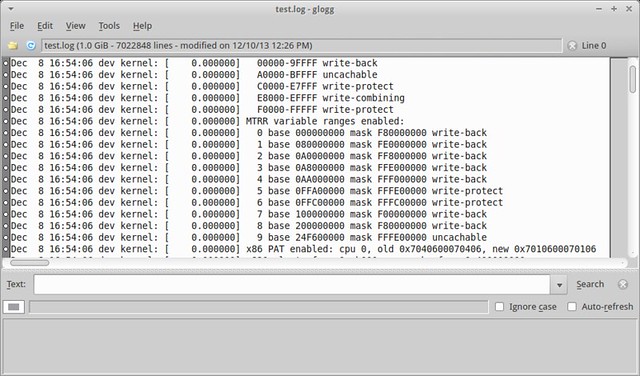][5]
|
||||
|
||||
You can enter a regular expression in the "Text" field, and press "Search" button. It supports case-insensitive search and auto-refresh features. After searching, you will see a filtered view at the bottom window.
|
||||
|
||||
Compared to Vim, glogg is much more lightweight after a file is loaded. It was using only 83MB of physical memory after loading a 1GB log file.
|
||||
|
||||
[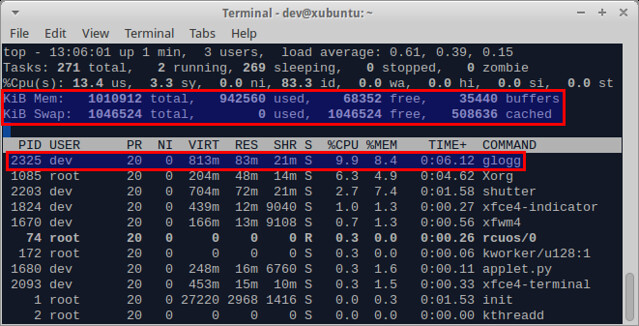][6]
|
||||
|
||||
### JOE Text Editor ###
|
||||
|
||||
[JOE][7] is a light-weight terminal based text editor released under GPL. JOE is one of few text editors with large file support, allows opening and editing files larger than memory.
|
||||
|
||||
Besides, JOE supports various powerful text editing features, such as non-destructive editing, search and replace with regular expression, unlimited undo/redo, syntax highlighting, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
To install JOE on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install joe
|
||||
|
||||
To install JOE on Fedora, CentOS or RHEL:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install joe
|
||||
|
||||
To open a text file for editing, run:
|
||||
|
||||
$ joe test.log
|
||||
|
||||
[][8]
|
||||
|
||||
Loading a large file on JOE is a little bit sluggish, compared to glogg above. It took around 30 seconds to load a 1GB file. Still, that's not too bad, considering that a file is fully editable now. Once a file is loaded, you can start editing a file in terminal mode, which is quite fast.
|
||||
|
||||
The memory consumption of JOE is impressive. To load and edit a 1GB text file, it only takes 47MB of physical memory.
|
||||
|
||||
[][9]
|
||||
|
||||
If you know any other way to open/edit a large text file on Linux, share your knowledge!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/open-large-text-file-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=1506
|
||||
[2]:http://www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=1506
|
||||
[3]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11313669824/
|
||||
[4]:http://glogg.bonnefon.org/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11313640286/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11313594455/
|
||||
[7]:http://joe-editor.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11317402126/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11317483233/
|
||||
@ -1,45 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux Mint Respond to Ubuntu Developer’s ‘Vulnerable’ Claim
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**It’s never a particularly tasty task having to write a news article on something that you know is going to cause headache and upset in the wider community.**
|
||||
|
||||
Earlier today I had to grin and bear it as I did just that in an article relaying comments made by Canonical engineer Oliver Grawert in which he branded Linux Mint a “‘vulnerable’ system” due to the way the distro provides security updates to users.
|
||||
|
||||
*Tl;dr: they don’t. (At least, not automatically.)*
|
||||
|
||||
A Canonical developer highlighting security concerns with another distro might sound like pure click bait on paper, but in practice it has important ramifications for users. Security is important, even on a platform that most perceive as invincible.
|
||||
|
||||
> ‘To put my own Top Trumps cards on the table, I was unaware that Mint held back security updates…’
|
||||
|
||||
Whether you agreed with Oliver’s take on Mint’s approach or not, **his comments were worth relaying**. These weren’t made by someone with an axe to grind.. They were informed by his esteemed position as an Ubuntu engineer. He knows what he’s talking about. Whether correct or misplaced, his comments have resulted in positive discussions about how security update practices should be handled.
|
||||
|
||||
To put my own Top *Trump™* cards on the table, I was unaware that Mint held back security updates for packages like Xorg and the Linux Kernel. So, at the very least, this mini-furore – borne largely out of knee-jerk reaction to the comments rather than their content in intent – has served a purpose.
|
||||
|
||||
### Mint Respond ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux Mint head-honco Clement Lefebvre has since responded to the remarks, saying that he and his team of developers are “very happy with the filtering system” for security updates in Mint.
|
||||
|
||||
> ” We explained why the Ubuntu update policy was not good enough for us and we consequently developed the update manager to solve that particular problem.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Firefox doesn’t come to you later in Mint than it does in Ubuntu (it’s a level 2 update).
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Yes, by default you get updates in Ubuntu for kernels and Xorg and not in Mint. Yes, there’s a very good reason for that.”
|
||||
|
||||
While Lefebvre doesn’t expand on precisely what that “very good reason” is, the general consensus on the web seems to be that Kernel and Xorg updates are held back because of the stability and performance issues that sometimes arise after upgrading.
|
||||
|
||||
Which, in many ways, is understandable.
|
||||
|
||||
Linux Mint don’t prevent their users from installing these updates but they are not enabled by default.
|
||||
|
||||
For further information on Linux Mint’s approach to security refer to the following blog post.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Linux Mint – Security Vs Stability][1]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/11/linux-mint-responds-ubuntu-developers-security-claims
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://segfault.linuxmint.com/2013/11/answering-controversy-stability-vs-security-is-something-you-configure/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,252 @@
|
||||
Linux lsusb Command to Print information about USB on System
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Universal Serial Bus** or **USB** was designed to standardize the connection of computer peripherals such as keyboards, pointing devices, printers, digital cameras, portable media players, disk drives and network adapters) – Source : [Wikipedia][1]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Since it becoming a industry standard, now it’s hard to see a computer without USB port on it. The usage of USB Flashdisk makes it more popular. On Linux, we have **lsusb** to list the USB devices and its properties.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is lsusb ###
|
||||
|
||||
From it’s manual page, lsusb is defined as :
|
||||
|
||||
A utility for displaying information about USB buses in the system and the devices connected to them.
|
||||
|
||||
How to run lsusb
|
||||
|
||||
To run lsusb, you can type lsusb directly from console.
|
||||
|
||||
$ lsusb
|
||||
|
||||
Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
|
||||
Bus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
|
||||
Bus 003 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
|
||||
Bus 004 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
|
||||
Bus 005 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
|
||||
Bus 006 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
|
||||
Bus 007 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
|
||||
Bus 008 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
|
||||
Bus 002 Device 003: ID 17ef:4811 Lenovo Integrated Webcam [R5U877]
|
||||
Bus 008 Device 002: ID 0a5c:217f Broadcom Corp. Bluetooth Controller
|
||||
|
||||
**lsusb** will show you the drivers and device which is internally attach on your system.
|
||||
|
||||
This is how to read the output. I grab the last line from above output :
|
||||
|
||||
#### Bus 008 Device 002 : ID 0a5c:217f Broadcom Corp. Bluetooth Controller ####
|
||||
|
||||
- **Bus 008** : means where the device is attached
|
||||
- **Device 002** : means this is the second device that attach
|
||||
- **ID** : means the ID number of this device
|
||||
- **Broadcom Corp**. Bluetooth Controller : means its manufacture name and device name
|
||||
|
||||
We also see that we also have USB 2.0 root hub drivers and USB 1.1 root hub drivers attach in our system.
|
||||
|
||||
This is also shown using [dmesg][2] command. Here’s an example of it.
|
||||
|
||||
$ dmesg |grep -i usb
|
||||
|
||||
[ 0.353138] usbcore: registered new interface driver usbfs
|
||||
[ 0.353150] usbcore: registered new interface driver hub
|
||||
[ 0.353182] usbcore: registered new device driver usb
|
||||
[ 0.730026] ehci_hcd: USB 2.0 ‘Enhanced’ Host Controller (EHCI) Driver
|
||||
[ 0.730116] ehci_hcd 0000:00:1a.7: new USB bus registered, assigned bus number 1
|
||||
[ 0.748019] ehci_hcd 0000:00:1a.7: USB 2.0 started, EHCI 1.00
|
||||
[ 0.748169] hub 1-0:1.0: USB hub found
|
||||
[ 0.748336] ehci_hcd 0000:00:1d.7: new USB bus registered, assigned bus number 2
|
||||
[ 0.768019] ehci_hcd 0000:00:1d.7: USB 2.0 started, EHCI 1.00
|
||||
[ 0.768147] hub 2-0:1.0: USB hub found
|
||||
[ 0.768236] ohci_hcd: USB 1.1 ‘Open’ Host Controller (OHCI) Driver
|
||||
[ 0.768251] uhci_hcd: USB Universal Host Controller Interface driver
|
||||
|
||||
### How to list USB details ###
|
||||
|
||||
Use **-v** paramater to do it. Here’s a sample of it.
|
||||
|
||||
$ lsusb -v
|
||||
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 1
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 5
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 2
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 224 Wireless
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Radio Frequency
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 1 Bluetooth
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0×83 EP 3 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 1
|
||||
Transfer Type Isochronous
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0×0040 1x 64 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0×03 EP 3 OUT
|
||||
bmAttributes 1
|
||||
Transfer Type Isochronous
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0×0040 1x 64 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
|
||||
### Find how many USB devices are connected ###
|
||||
|
||||
To find it use this command
|
||||
|
||||
$ find /dev/bus
|
||||
|
||||
Then you will have an output like this :
|
||||
|
||||
/dev/bus
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/008
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/008/002
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/008/001
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/007
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/007/001
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/006
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/006/001
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/005
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/005/001
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/004
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/004/001
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/003
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/003/001
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/002
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/002/004
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/002/003
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/002/001
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/001
|
||||
/dev/bus/usb/001/001
|
||||
|
||||
Using **lsusb** command **combine with -D** parameter, you can print the detail of specific device. Here’s a sample to view Broadcom Bluetooth device.
|
||||
|
||||
$ lsusb -D /dev/bus/usb/008/002
|
||||
|
||||
Device: ID 0a5c:217f Broadcom Corp. Bluetooth Controller
|
||||
Couldn’t open device, some information will be missing
|
||||
Device Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 18
|
||||
bDescriptorType 1
|
||||
bcdUSB 2.00
|
||||
bDeviceClass 224 Wireless
|
||||
bDeviceSubClass 1 Radio Frequency
|
||||
bDeviceProtocol 1 Bluetooth
|
||||
bMaxPacketSize0 64
|
||||
idVendor 0x0a5c Broadcom Corp.
|
||||
idProduct 0x217f Bluetooth Controller
|
||||
bcdDevice 3.60
|
||||
iManufacturer 1
|
||||
iProduct 2
|
||||
iSerial 3
|
||||
bNumConfigurations 1
|
||||
Configuration Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 2
|
||||
wTotalLength 216
|
||||
bNumInterfaces 4
|
||||
bConfigurationValue 1
|
||||
iConfiguration 0
|
||||
bmAttributes 0xe0
|
||||
Self Powered
|
||||
Remote Wakeup
|
||||
MaxPower 0mA
|
||||
Interface Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 9
|
||||
bDescriptorType 4
|
||||
bInterfaceNumber 0
|
||||
bAlternateSetting 0
|
||||
bNumEndpoints 3
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 224 Wireless
|
||||
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Radio Frequency
|
||||
bInterfaceProtocol 1 Bluetooth
|
||||
iInterface 0
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0×81 EP 1 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 3
|
||||
Transfer Type Interrupt
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0×0010 1x 16 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0×82 EP 2 IN
|
||||
bmAttributes 2
|
||||
Transfer Type Bulk
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0×0040 1x 64 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
Endpoint Descriptor:
|
||||
bLength 7
|
||||
bDescriptorType 5
|
||||
bEndpointAddress 0×02 EP 2 OUT
|
||||
bmAttributes 2
|
||||
Transfer Type Bulk
|
||||
Synch Type None
|
||||
Usage Type Data
|
||||
wMaxPacketSize 0×0040 1x 64 bytes
|
||||
bInterval 1
|
||||
|
||||
### Find your Mass Storage ###
|
||||
|
||||
Since **lsusb -v** give us a very detail information, you may miss something to read. We can focus to specific information using grep command. Here are some samples.
|
||||
|
||||
Mass storage will have a vendor name and ID. We can use it as a starting point.
|
||||
|
||||
$ lsusb -v |grep -Ei ‘(idVendor|Mass\ Storage)’
|
||||
|
||||
idVendor 0×1005 Apacer Technology, Inc.
|
||||
bInterfaceClass 8 Mass Storage
|
||||
|
||||
You can see, that we have one USB Mass Storage attached on our system from Apacer Technology, Inc.
|
||||
|
||||
### Dump the physical USB device hierarchy as a tree ###
|
||||
|
||||
Use **-t** parameter to fulfill this purpose.
|
||||
|
||||
$ lsusb -t
|
||||
|
||||
/: Bus 08.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=uhci_hcd/2p, 12M
|
||||
/: Bus 07.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=uhci_hcd/2p, 12M
|
||||
/: Bus 06.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=uhci_hcd/2p, 12M
|
||||
/: Bus 05.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=uhci_hcd/2p, 12M
|
||||
/: Bus 04.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=uhci_hcd/2p, 12M
|
||||
/: Bus 03.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=uhci_hcd/2p, 12M
|
||||
/: Bus 02.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=ehci_hcd/6p, 480M
|
||||
|__ Port 1: Dev 4, If 0, Class=stor., Driver=usb-storage, 480M
|
||||
|__ Port 6: Dev 3, If 0, Class=’bInterfaceClass 0x0e not yet handled’, Driver=uvcvideo, 480M
|
||||
|__ Port 6: Dev 3, If 1, Class=’bInterfaceClass 0x0e not yet handled’, Driver=uvcvideo, 480M
|
||||
/: Bus 01.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=ehci_hcd/6p, 480M
|
||||
|
||||
The number **12M and 480M** is **indicate the transfer rate speed** of USB type.
|
||||
|
||||
- 12M means 12Mbit/s which is a USB 1.0 / 1.1 type
|
||||
- 480M means 480Mbit/s which is a USB 2.0 type
|
||||
|
||||
If you found 5.0G, it means that you have USB 3.0 type. It has 5.0Gbit/s transfer rate. Linux recognize the detail of USB devices from **/var/lib/usbutils/usb.ids** . Or you can visit to [Linux-USB.org][3] to get the newest list of USB ID’s.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all about lsusb command on daily basis. You can use lsusb command to do a diagnostic activity about your USB devices on your system. As usual, you can explore more detail by reading lsusb manual page. Just type **man lsusb** to see its manual page.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-lsusb-command-print-usb/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/USB
|
||||
[2]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-dmesg-command/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.linux-usb.org/usb.ids
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
|
||||
Linux mpstat Command – Reports Processors Related Statistics
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Generally today computer is using multiple processors. Or maybe 1 physical processor with 4 cores inside. On server side, more processors or cores means more power. But the other side, application also more power consumption. You may find a situation when your cpu utilization is high but you feel that you don’t running anything. On Linux system, you can monitor this activity using **mpstat**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### What is mpstat ###
|
||||
|
||||
**mpstat** is used to monitor cpu utilization on your system. It will be more usefull if your system has multiple processors. The first processors will signed as CPU 0. The second one will be signed CPU 1 and so on. From its manual page, mpstat is described as :
|
||||
|
||||
> The mpstat command writes to standard output activities for each available processor, processor 0 being the first one. Global average activities among all processors are also reported. The mpstat command can be used both on SMP and UP machines, but in the latter, only global average activities will be printed. If no activity has been selected, then the default report is the CPU utilization report
|
||||
|
||||
### How to run mpstat ###
|
||||
|
||||
Just type **mpstat** on your console to run mpstat.
|
||||
|
||||
$ mpstat
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 3.2.0-57-generic (USERNB01) 12/12/2013 _x86_64_ (2 CPU)
|
||||
|
||||
03:29:29 PM CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %idle
|
||||
03:29:29 PM all 6.30 0.06 1.94 3.75 0.00 0.06 0.00 0.00 87.88
|
||||
|
||||
If you found an error such as : **command not found** or similar you may not install mpstat in your system.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using **CentOS, RedHat or Fedora**, run this command to install mpstat
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install sysstat
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using **Debian, Ubuntu or its derivative**, run this command to install mpstat
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install sysstat
|
||||
|
||||
And here’s how to read the information above.
|
||||
|
||||
- **03:29:29 PM** : means the time that mpstat was run
|
||||
- **all** : means All CPUs
|
||||
- **%usr** : show the percentage of CPU utilization that occurred while executing at the user level (application)
|
||||
- **%nice** : show the percentage of CPU utilization that occurred while executing at the user level with nice priority
|
||||
- **%sys** : show the percentage of CPU utilization that occurred while executing at the system level (kernel)
|
||||
- **%iowait** : show the percentage of time that the CPU or CPUs were idle during which the system had an outstanding disk I/O request
|
||||
- **%irq** : show the percentage of time spent by the CPU or CPUs to service hardware interrupts
|
||||
- **%soft** : show the percentage of time spent by the CPU or CPUs to service software interrupts
|
||||
- **%steal** : show the percentage of time spent in involuntary wait by the virtual CPU or CPUs while the hypervisor was servicing another virtual processor
|
||||
- **%guest** : show the percentage of time spent by the CPU or CPUs to run a virtual processor
|
||||
- **%idle** : show the percentage of time that the CPU or CPUs were idle and the system did not have an outstanding disk I/O equest
|
||||
|
||||
### Print CPU utilization per processors ###
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see above, our system has 2 CPUs. If you want, you can use -P parameter followed by CPU number to see specific CPU utilization.
|
||||
|
||||
$ mpstat -P 0
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 3.2.0-57-generic (USERNB01) 12/12/2013 _x86_64_ (2 CPU)
|
||||
|
||||
03:54:00 PM CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %idle
|
||||
03:54:00 PM 0 3.82 0.01 1.16 3.88 0.00 0.06 0.00 0.00 91.06
|
||||
|
||||
$ mpstat -P 1
|
||||
Linux 3.2.0-57-generic (USERNB01) 12/12/2013 _x86_64_ (2 CPU)
|
||||
|
||||
03:53:58 PM CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %idle
|
||||
03:53:58 PM 1 16.52 0.20 4.48 0.46 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.00 78.30
|
||||
|
||||
### Print all CPU Utilization ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can also print every CPU utilization of processors in a single page. Just use **-P ALL** parameter to do it
|
||||
|
||||
$ mpstat -P ALL
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 3.2.0-57-generic (USERNB01) 12/12/2013 _x86_64_ (2 CPU)
|
||||
|
||||
04:07:36 PM CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %idle
|
||||
04:07:36 PM all 6.02 0.04 1.72 2.99 0.00 0.05 0.00 0.00 89.17
|
||||
04:07:36 PM 0 3.84 0.01 1.15 3.72 0.00 0.06 0.00 0.00 91.21
|
||||
04:07:36 PM 1 13.55 0.15 3.66 0.46 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.00 82.15
|
||||
|
||||
### Print CPU utilization using intervals ###
|
||||
|
||||
You may want to see the CPU utilization movement. To do this, you can use intervals. Here’s an example.
|
||||
|
||||
$ mpstat 3 4
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 3.2.0-57-generic (USERNB01) 12/12/2013 _x86_64_ (2 CPU)
|
||||
|
||||
04:27:11 PM CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %idle
|
||||
04:27:14 PM all 0.67 0.00 0.34 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 98.99
|
||||
04:27:17 PM all 1.17 0.00 0.33 1.33 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 97.17
|
||||
04:27:20 PM all 0.84 0.00 0.17 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 98.99
|
||||
04:27:23 PM all 1.00 0.00 0.17 1.51 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 97.32
|
||||
Average: all 0.92 0.00 0.25 0.71 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 98.12
|
||||
|
||||
The above command is to show you **4 reports** about CPU utilization with **3 seconds intervals**
|
||||
|
||||
### Print mpstat version ###
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, to print mstat version, use -V parameter
|
||||
|
||||
$ mpstat -V
|
||||
|
||||
sysstat version 10.0.3
|
||||
(C) Sebastien Godard (sysstat orange.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s a quick usage of mpstat command in Linux system. You may see msptat manual page by typing **man mpstat** to explore more detail.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-mpstat-command/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,61 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Open Source Is Here To Stay On IBM i
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
For years, open source software has been a bit of a redheaded stepchild in the button-down IBM midrange community. IBM i shops were hesitant to use it, and vendors were afraid to adopt it. But with so much of the computing world now running on open source, the aversion to open source has gradually melted away, and it has steadily crept into use among large corporations, and the IBM i world too.
|
||||
|
||||
It is tough to measure the adoption of open source software, which flows freely across networks by its very nature. Nobody requires you to register to use open source software, and there's no central clearinghouse of information about open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
However, recent surveys and audits point to greater adoption of open source across all industries. Open source software components are widely used in in the financial services industry, according to Julian Brook, associate director at SQS Software, which conducts software quality audits for financial software vendors. "I would say that, arguably, open source is used in every organization that is developing software, especially in the financial services world," Brook [told Out-Law.com recently][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Governmental agencies lead the way in use of open source software, according to [Black Duck Software][2]'s 2013 Future of Open Source survey. More than 35 percent of government representatives queried for the survey say they use open source, followed by medical (15.2 percent), media (13 percent), financial (8.8 percent), and retail (5.9 percent). You can view more of the survey at [Slideshare][3].
|
||||
|
||||
Increasingly, users are adopting open source software because they expect higher software quality and security with open source, according to surveys like those from Black Duck. That's very interesting, because for many years, open source software was largely avoided for those two very reasons.
|
||||
|
||||
These are opinion surveys, mind you. They're not necessarily reflections of actual reality. But it is clear than many of the shortcomings that people previously associated with open source software products are disappearing. And slowly but surely, this trend is bleeding over into the competitive world of IBM i software, too.
|
||||
|
||||
### Open Source Impacts On IBM i ###
|
||||
|
||||
The IBM i server is one of the last great bastions of proprietary technology in a world heading in the direction of open source. IBM does not share with the world the guts of the IBM i OS and the System Licensed Internal Code (SLIC) it runs on. You can take what access IBM provides developers to the machine, or you can leave it, but you can't get access to the internals.
|
||||
|
||||
What goes on above the OS and SLIC layers is another matter entirely. We're not seeing a big influx of open source software in the world of ERP and business applications. But in many other software categories, open source options are proliferating.
|
||||
|
||||
One IBM i proponent of open source software is [Raz-Lee][4]. The security software vendor, which relies on the open source [ClamAV][5] offering to power its IBM i-based anti-virus offering, called iSecurity Anti-Virus, says ClamAV had an update for an evolving security threat--the W32/Autorun.worm.aaeh Trojan Horse--months before its competitor had updated the signature library for its IBM i-based antivirus offering.
|
||||
|
||||
"It turns out that ClamAV has been handling this threat . . . as of about eight to nine months ago," Raz-Lee vice president of business development Eli Spitz wrote in an email to IT Jungle last month. "In fact, one of our technicians here at Raz-Lee actually added his own unofficial signature to ClamAV's database before ClamAV included their formal signature for this virus."
|
||||
|
||||
Another IBM i software vendor using open source tools is [Arpeggio Software][6] . The Atlanta, Georgia-based company uses lots of open source components in its various IBM i utilities, which aren't available under an open source license, but which Arpeggio gives away and then charges customers to get technical support, a common approach taken by commercial open source vendors.
|
||||
|
||||
Arpeggio's latest offering, called ARP-DROP, uses the open source OAuth authentication method to help secure communication channels between IBM i servers and [DropBox][7] service running on the Internet. It also uses the OpenSSH encryption technology with ARP-SFTP client for IBM i. Arpeggio's founders (who also founded Trailblazer Systems, now part of [Liaison Technologies][8]) acknowledge that IBM i professionals could adopt the same open source tools to write similar tools. But they argue that Arpeggio does it better, so why not adopt their free tools and save yourself the time?
|
||||
|
||||
In many cases, an IBM i shop's first conscious exposure to open source is the server side scripting language PHP. IBM and [Zend Technology][9] have worked for years to make PHP run well on IBM i, and Zend's entry-level PHP runtime is shipped along with every Power Systems server and IBM i license.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the most popular PHP applications that run on IBM i servers is [SugarCRM][10]. Representatives with the Cupertino, California, company recently said that it has nearly 1,000 customers running the CRM software on IBM i servers. This includes paid enterprise licenses along with free community edition licenses.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fighting Perceptions ###
|
||||
|
||||
Most IBM i shops are big users of IBM i software, whether they know it or not. Some of the biggest, most important IT infrastructure components come from open source, including the Apache Web server, the Linux OS, the Java and PHP programming languages, the MySQL database, and the Eclipse development environment.
|
||||
|
||||
There's no reason not to call open source "commercial grade" anymore, Raz-Lee's Spitz said. "A few weeks ago Sourcefire, the owners of ClamAV, was purchased by [Cisco Systems][11]. That's obviously a 'certification' by a large commercial organization for open source software. So open source anti-virus software seems to be valuable to a multi-national company."
|
||||
|
||||
While open source software is making inroads in the IBM i community, it still has a ways to go to match the momentum that open source enjoys in the IT market as a whole. "It seems that the IBM i community is often less involved with open source and is not exposed to its importance and prevalence in the current computing area," Spitz said. "In many cases, open source is the 'playground' of very large companies who join to create a better arena for us all."
|
||||
|
||||
As the corporations of the world gradually becomes amenable to open source, the IBM i community will have no choice but to follow.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.itjungle.com/tfh/tfh120213-story01.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.out-law.com/en/articles/2013/september/open-source-code-use-within-financial-services-organisations-visibility-only-50-at-best-says-software-quality-expert/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.blackducksoftware.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.slideshare.net/blackducksoftware/the-2013-future-of-open-source-survey-results
|
||||
[4]:http://www.razlee.com/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.clamav.net/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.arpeggiosoftware.com/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.dropbox.com/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.liaison.com/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.zend.com/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.sugarcrm.com/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.cisco.com/
|
||||
@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Oracle Linux 6.5 Arrives with Unbreakable Enterprise Linux Kernel 3.8
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Oracle has announced a few days ago that its Oracle Linux operating system has reached version 6.5, bringing lots of new features, updated packages and several improvements over previus releases.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
First of all, we should mention that Oracle Linux 6.5 is now powered by three separate kernels, the unbreakable enterprise kernel version 2.6.39-400.211.1.el6uek only for the x86 (32-bit) platform, the unbreakable enterprise kernel version 3.8.13-16.2.1.el6uek for both 64-bit and 32-bit architectures, and the Red Hat compatible kernel 2.6.32-431.el6 for x86 and x86_64.
|
||||
|
||||
Unbreakable Enterprise Kernel Release 3 (UEK R3) introduces major improvements over UEK R2, including integrated DTrace support, device mapper support, Btrfs quota groups, Btrfs send and receive subcommands, support for replacing devices without unmounting in Btrfs, EXT4 quotas, TCP controlled delay management, TCP connection repair, STCP and TCP early retransmit, TCP fast open, and TCP small queue algorithm.
|
||||
|
||||
The loop driver has been update to provide the same I/O functionality as the dm-nfs project, simply by extending the AIO interface to perform direct I/O. Moreover, the secure computing mode feature has been added, and the OpenFabrics Enterprise Distribution (OFED) 2.0 stack supports the following protocols: SRP (SCSI RDMA Protocol), iSER (iSCSI Extensions), RDS (Reliable Datagram Sockets), SDP (Sockets Direct Protocol), EoIB (Ethernet over InfiniBand), IPoIB (IP encapsulation over InfiniBand), and eIPoIB (Ethernet tunneling over InfiniBand).
|
||||
|
||||
The OFED (OpenFabrics Enterprise Distribution) 2.0 stack also supports the following RDS features: AS (Async Send), APM (Automatic Path Migration), QoS (Quality of Service), SRQ (Shared Request Queue), AB (Active Bonding), and NF (Netfilter).
|
||||
|
||||
Last but not least, paravirtualization support has been enabled for Oracle Linux guests on Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V or Windows Server 2008 Hyper-V.
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Oracle Linux 6.5 right now:**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Oracle Enterprise Linux 6.5 (ISO) i386][1][iso] [3 GB]
|
||||
- [Oracle Enterprise Linux 6.5 (ISO) amd64][2][iso] [3.60 GB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Oracle-Linux-6-5-Arrives-with-Unbreakable-Enterprise-Linux-Kernel-3-8-406093.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://mirrors.dotsrc.org/oracle-linux/OL6/U5/i386/OracleLinux-R6-U5-Server-i386-dvd.iso
|
||||
[2]:http://mirrors.dotsrc.org/oracle-linux/OL6/U5/x86_64/OracleLinux-R6-U5-Server-x86_64-dvd.iso
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
|
||||
Solving HIPPA, HITECH, SSAE16 Server Compliance Issues with Next Generation Datacenters
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
HIPPA stands for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, and HITECH stands for Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act. Both acts have to do with how health records and data are handled. SSAE16 is similar. It’s an accounting standard created by the Auditing Standards Board (ASB) of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA). The parameters of all three have enormous implications both for healthcare and for web hosting. Dedicated server and managed hosting services that use next generation datacenters must ensure that they can meet the requirements as outlined in the compliance requirements of each one of them.
|
||||
|
||||
### The Basics ###
|
||||
|
||||
It is important to ensure that you are using a datacenter that will comply with the standards of HIPAA, HITECH and SSAE16. When discussing your needs with a datacenter, such as Atlantic.net, you should confirm that the datacenters conform to the standard contingency plan; data backup plan; disaster recovery plan; emergency mode operation plan; testing and revision procedures and applications; and data criticality analysis. Data servers have their own compliance requirements when it comes to managing your data, and you need to ensure that their performance standards can match up with your compliance requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
Achieving SSAE16 Type II Certification to ensure that SSAE16 will not present a problem for the server in the current time or immediate future is important. If you are in healthcare, you are probably familiar with the increasing demand for server and datacenter compliance. The new generation of data centers has helped to pave the way for many healthcare IT companies that needed to find a rock solid solution for their businesses’ hosting solution needs.
|
||||
|
||||
HIPAA was designed to provide better access to health insurance, reduce the occurrence of fraud and abuse, and lower the cost of obtaining health care in the USA. HITECH further reinforces the HIPAA regulations and provides some additional rules for you to follow. The data center you choose should help make the transition to become a fully compliant business, at least through your online presence. This may raise a few eyebrows and some people are even a bit nervous about whether or not their business can meet the demand in time for compliance testing. With the proper structure completed ahead of time, the hard part is done; all you need to do is plug into the tools and features we have available for you to use.
|
||||
|
||||
### What Does Compliance Involve? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Being HIPPA, SSAE16 and HITECH compliant means going the extra mile in server colocation, delivering dedicated servers, managed server hosting, and compliance through a credible datacenter. A datacenter must be reliable, with certified and trained staff who know how to handle customer problems and inquiries.
|
||||
|
||||
Being HIPPA, HITECH and SSAE16 compliant is vital in today’s environment, and everyone is fully aware of the legal boundaries in which healthcare organizations must operate. More efficient cooling procedures ensure that the compliance sequences are followed without a possibility for failure.
|
||||
|
||||
Dynamic allocation of resources where they are needed helps solve many resource issues. Additionally, the resources are used in the coolest parts of the datacenter, meaning more efficient use of the resources as well.
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizing application performance is one of the main advancements that next generation datacenters do incredibly well. These next generation datacenters that have been brought into operation have data security as one of their incredible strong points.
|
||||
|
||||
The new healthcare reform mandates implement even tighter security with HITECH, and service providers has vested large amounts in these regulations. Ample controls and checks/balances to help the patients and healthcare providers will be ensured for obvious reasons. The government understands that companies need to be encouraged to take things to the next level, and as a result, there are tax incentives to deploy EMR/EHR (Electronic Medical Records and Electronic Health Records).
|
||||
|
||||
Using cloud servers, you are able to scale up and scale out according to what your business needs. Even more so, quality datacenters can keep your healthcare organization safe! Using virtualization, companies have dedicated themselves to the continued success of your business. This means they have left no stone unturned to bring you an unprecedented level of services from which you can choose.
|
||||
|
||||
Being [HIPAA compliant][1] is partly the job of the hosting company and partly yours as well. They provide you with the services – the datacenter, the managed hosting and the tech support to ensure you have what you need to bring your healthcare business to the compliance level. They can only offer you the services that are required by the HIPAA, HITECH and SSAE16 regulations. They need your help to make sure both parties are up to speed in the quest to keep your business in complete compliance.
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud computing is a really big part of next generation datacenters. Virtualization technology has made it possible for everyone to have their resources delivered at the most optimum moment through more efficient handling of server resources. If you are new to cloud computing, you should know that this technology in no way endangers your ability to stay HIPAA, HITECH and SSAE16 compliant. Cloud computing is simply the new way of handling server requests and scaling additional resources up and out.
|
||||
|
||||
Have you ever stopped to consider what would happen if you were tagged with a violation of the HIPAA, HITECH or [SSAE16 compliance][2] standards? It would be a catastrophic blow to your business that would land you in court! Additionally, the people affected by the violation could possibly sue for damages. Quality web hosting services are now structured around ensuring that everything in the facility is certified to the new standards of operation.
|
||||
|
||||
Being in business for over 15 years, since 1994, has given us a chance to really perfect the art of hosting, server virtualization, data security, compliance, and the ability to provide a carrier-neutral datacenter.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusions ###
|
||||
|
||||
Atlantic.Net and other serious hosting companies have been a step ahead of the compliance standards from day one. Business expertise has allowed us to keep the healthcare IT businesses that we already have under our wing and ahead of the flames. We can help your business stay in line with these compliance standards as well.
|
||||
|
||||
All in all, server compliance issues won’t be much of a big deal once you realize what they are all about. The compliance issues would generally arise from a datacenter not having sufficient hardware or software to accommodate regulatory compliance; or the customer themselves may not be able to get the business into a state of compliance. Either way, a next generation datacenter must be able to offer the services in demand to meet the compliance requirements in order to be compliant with the regulations themselves.
|
||||
|
||||
By [Brett Haines][3]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.atlantic.net/blog/2013/12/04/solving-hippa-hitech-ssae16-server-compliance-issues-generation-datacenters/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.atlantic.net/hipaa-compliant-hosting/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.atlantic.net/ssae-16-type-2-compliant/
|
||||
[3]:https://plus.google.com/u/0/100137311390909550920?rel=author
|
||||
@ -1,100 +0,0 @@
|
||||
(翻译中 by runningwater)
|
||||
TeamViewer 9 Released – Install on RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Debian/Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
This guide shows how to install **Teamviewer 9** on **RedHat, CentOS, Fedora** and **Debian**, **Ubuntu**, **Linux Mint**, **Xubuntu** systems. **Teamviewer** is a one of the most popular application for remote assistant, Desktop sharing or transferring files between computers, web conferencing and online meetings etc. Teamviewer is a proprietary application.
|
||||
|
||||
However, it’s a freeware for personal use. Teamviewer is available for **Windows, Linux, Mac OS, Android** and **iPhone**. Teamviewer uses **WINE** application which is integrated within it. We don’t have to [install WINE application][1]separately. **Teamviewer** is not a native **Linux** application.
|
||||
|
||||
Recently, the latest stable version of **TeamViewer 9** released with new features and many improvements. Following are some of the new features are added in **TeamViewer 9** which are highlighted below:
|
||||
|
||||
### Features for Windows, Linux and Mac ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Open multiple connections in different tabs
|
||||
- Support for Wake-on-LAN
|
||||
- Added two factor authentication for TeamViewer accounts
|
||||
- Support for Windows 8.1 and Mac OS X Mavericks
|
||||
- Save custom modules such as QuickSupport, QuickJoin, etc.
|
||||
- API Integration
|
||||
- Stronger security of the Teamviewer account
|
||||
- Quick connection via desktop shortcut
|
||||
- Visual notification
|
||||
- Copy and paste files and text between computers
|
||||
- Initiating file transfers to computers
|
||||
- Quick connection via desktop shortcut
|
||||
- Faster video transfers
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I Install Teamviewer 9 on RedHat, CentOS, Fedora ###
|
||||
|
||||
You may download package for rpm based Linux distributions at [teamviewer_linux.rpm][2].
|
||||
|
||||
Let us start installation. Go to the directory from where you have downloaded package and execute following yum command to install it. It will install missing dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://www.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux.rpm
|
||||
# yum install teamviewer_linux.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
If you get missing public key error, you can download public key and import it using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://www.teamviewer.com/link/?url=354858
|
||||
# rpm --import TeamViewer_Linux_PubKey.asc
|
||||
|
||||
After importing the public key, please run the “**yum install**” command again to install the Teamviewer rpm.
|
||||
|
||||
To start Teamviewer application, run the following command from the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
# teamviewer
|
||||
|
||||
Teamviewer application running on my **Fedora 18** system.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Running TeamViewer in Fedora 18*
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I Install Teamviewer 9 on Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Xubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
You may download teamviewer package for **32-bit** or **64-bit** systems at [teamviewer linux .deb][3] packages. or you can download the package using **wget** command as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
## 32 Bit System ##
|
||||
$ sudo wget http://www.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux.deb
|
||||
|
||||
## 64 Bit System ##
|
||||
$ sudo wget http://www.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux_x64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
Once you’ve downloaded the package, go to the directory where you’ve downloaded Teamviewer package and run the following command to install it.
|
||||
|
||||
## 32 Bit System ##
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_linux.deb
|
||||
|
||||
## 64 Bit System ##
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_linux_x64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
If you get missing dependencies error, please use the following command to install those dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install -f
|
||||
|
||||
Once installation is done. To start Teamviewer package on **Ubuntu** Linux, go to **Dash Home** and type **teamviewer** and click on **teamviewer** icon to run application.
|
||||
|
||||
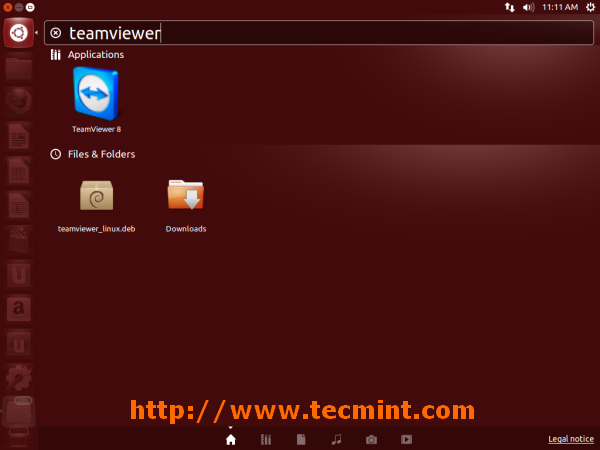
|
||||
*Running TeamViewer in Ubuntu 13.10*
|
||||
|
||||
Teamviewer application running on my **Ubuntu 13.10** system.
|
||||
|
||||
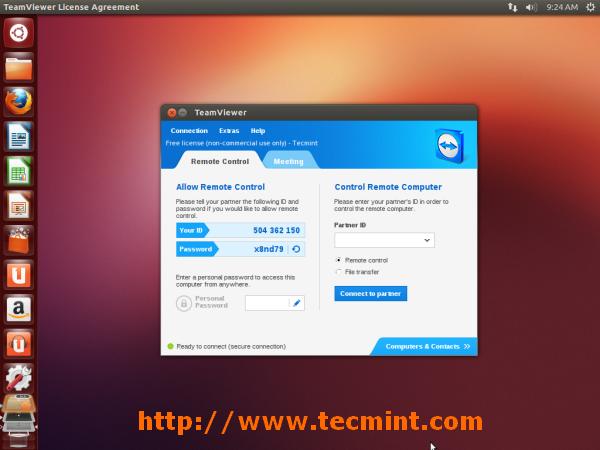
|
||||
*TeamViewer 9 Under Ubuntu 13.10*
|
||||
|
||||
To start on **Linux Mint**, Go to **Menu >> Internet >> Teamviewer** and click on **Accept License Agreement** to run application.
|
||||
|
||||
Teamviewer application running on my **Linux Mint 15**.
|
||||
|
||||
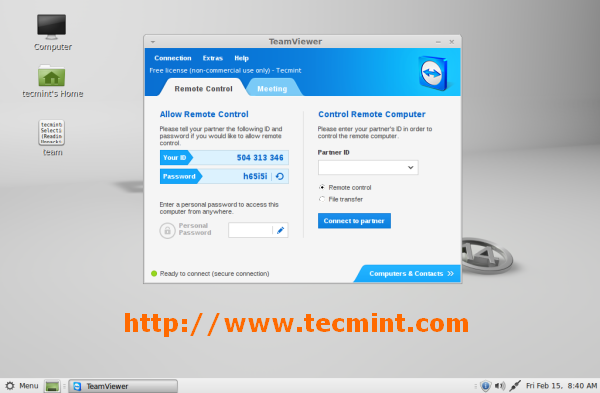
|
||||
*Running TeamViewer in Linux Mint 15*
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-install-teamviewer-on-linux-distributions/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-wine-in-rhel-centos-and-fedora/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux.rpm
|
||||
[3]:http://www.teamviewer.com/hi/download/linux.aspx
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,158 @@
|
||||
示例说明10个Linux中有用打的链接操作符
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux命令中的链接的意思是,结合几个命令并基于它们之间操作符的行为执行。Linux中的链接命令,有些像你在shell中写[短小的shell脚本],并直接在终端中执行。链接使得自动处理变得可能。不仅如此,一个无人看管的机器在链接操作符的帮助下如此有条理地运行。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*Linux中的10个链接操作符*
|
||||
|
||||
本文旨在常用的**链接操作符**,并作简短的描述和相关的肯定能提高你生产力的例子,除了有时能降低系统负载外还能让你写出简短有意义的代码。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 和号操作符 (&) ###
|
||||
|
||||
‘**&**‘的作用是使命令在后台运行。只要在命令后面跟上一个空格和 ‘**&**。你可以一口气在后台运行多个命令。
|
||||
|
||||
在后台运行一个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ ping c5 www.tecmint.com &
|
||||
|
||||
同时在后台运行两个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/tecmint# apt-get update & apt-get upgrade &
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 分号操作符 (;) ###
|
||||
|
||||
分号操作符使你可以一口气运行几个命令,命令顺序执行。
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/tecmint# apt-get update ; apt-get upgrade ; mkdir test
|
||||
|
||||
创建了一个‘**test**‘文件夹
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 与操作符 (&&) ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果第一个命令执行成功(译者注: 原文为“if the execution of first command fails”,译者认为与上下文意思不同),**与操作符 (&&)**会执行第二个命令,也就是说,第一个命令退出状态是**1**。这个命令在检查最后一个命令的执行状态时很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,我想使用**[links command][2]**在终端中访问网站**tecmint.com**,但在这之前我需要检查主机是否**在线**或者**不在线**。
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/tecmint# ping -c3 www.tecmint.com && links www.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 或操作符 (||) ###
|
||||
|
||||
**或操作符 (||)**很像编程中的**else**语句。上面的操作符允许你在第一个命令失败的情况下执行第二个命令,也就是说,第一个命令的退出状态是**1**。
|
||||
|
||||
举例来说,我想要在非root帐户中执行‘**apt-get update**‘,如果第一个命令失败了,接着会执行第二个命令‘**links www.tecmint.com**‘。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ apt-get update || links tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令中,由于**用户**不允许**更新**系统,这意味着第一个命令的退出状态是’**1**′,因此最后一个命令‘**links tecmint.com**‘会执行。
|
||||
|
||||
如果第一个命令成功执行并且退出状态是‘**0**‘呢?很明显的,第二个命令不会执行。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ mkdir test || links tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
这里,用户在家目录创建了一个‘**test**‘文件夹,这是被允许的。命令成功的执行,退出状态是‘**0**‘,因此,最后的命令不会执行。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 非操作符 (!) ###
|
||||
|
||||
**非操作符 (!)**很像**except**语句。这个命令会执行除了提供的条件外的所有的语句。要理解这点,在你的家目录创建一个目录‘**tecmint**‘,并‘**cd**‘到它这里。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ mkdir tecmint
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ cd tecmint
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,在文件夹‘**tecmint**‘下创建不同类型的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ touch a.doc b.doc a.pdf b.pdf a.xml b.xml a.html b.html
|
||||
|
||||
看一下我们在文件夹‘**tecmint**‘创建的新文件。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ ls
|
||||
|
||||
a.doc a.html a.pdf a.xml b.doc b.html b.pdf b.xml
|
||||
|
||||
用一种聪明的办法马上删除除了 ‘**html**‘之外的所有文件。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ rm -r !(*.html)
|
||||
|
||||
验证一下上次的执行结果,使用[ls 命令][3]列出可见所有文件。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ ls
|
||||
|
||||
a.html b.html
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 与 – 或 操作符 (&& – ||) ###
|
||||
|
||||
上面的操作符实际上是‘**与**‘和‘**或**‘操作符的组合。它很像‘**if-else**‘语句。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,让我们ping **tecmint.com**,如果成功打印‘**已验证**‘,否则打印‘**主机故障**‘。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ ping -c3 www.tecmint.com && echo "Verified" || echo "Host Down"
|
||||
|
||||
#### 示例输出 ####
|
||||
|
||||
PING www.tecmint.com (212.71.234.61) 56(84) bytes of data.
|
||||
64 bytes from www.tecmint.com (212.71.234.61): icmp_req=1 ttl=55 time=216 ms
|
||||
64 bytes from www.tecmint.com (212.71.234.61): icmp_req=2 ttl=55 time=224 ms
|
||||
64 bytes from www.tecmint.com (212.71.234.61): icmp_req=3 ttl=55 time=226 ms
|
||||
|
||||
--- www.tecmint.com ping statistics ---
|
||||
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2001ms
|
||||
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 216.960/222.789/226.423/4.199 ms
|
||||
Verified
|
||||
|
||||
现在,断开我们现在的网络连接诶,再试一下相同的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ ping -c3 www.tecmint.com && echo "verified" || echo "Host Down"
|
||||
|
||||
#### 实例输出 ####
|
||||
|
||||
ping: unknown host www.tecmint.com
|
||||
Host Down
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. 管道操作符 (|) ###
|
||||
|
||||
**PIPE**在第一个命令的输出作为第二个命令的输入时很有用。比如,‘**ls -l**‘的输出通过管道到‘**less**‘,并看一下输出。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ ls -l | less
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. 命令合并操作符 {} ###
|
||||
|
||||
合并两个或多个命令,第二个命令依赖于第一个命令的执行。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,检查一下文件‘**xyz.txt**‘和‘**xyz1.txt**‘是否在**Downloads**目录下,并输出相关的输出。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ [ -f /home/tecmint/Downloads/xyz.txt ] || echo “The file does not exist”
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ [ -f /home/tecmint/Downloads/xyz1.txt ] || echo “The file does not exist”
|
||||
|
||||
“The file does not exist”
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. 优先操作符 () ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个操作符可以让命令以优先顺序执行。
|
||||
|
||||
Command_x1 &&Command_x2 || Command_x3 && Command_x4.
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的伪代码中,如果**Command_x1**执行失败了会怎么样,**Command_x2**, **Command_x3**, **Command_x4**没有一个会自行,对于这种,我们使用**优先操作符**。
|
||||
|
||||
(Command_x1 &&Command_x2) || (Command_x3 && Command_x4)
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的伪代码中,如果**Command_x1**执行失败,**Command_x2**同样失败,但是**Command_x3**会继续执行, **Command_x4**会依赖于 **Command_x3**的退出状态。
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. 连接符 (\) ###
|
||||
|
||||
**连接符 (\)**如它名字所说,被用于连接shell中跨越多行的命令。比如,下面的命令会打开文本文件**test(1).txt**。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/Downloads$ nano test\(1\).txt
|
||||
|
||||
今天就到这里,我会近日开始另外一个有趣的文章。不要走开,继续关注**Tecmint**。不要忘记在评论栏里提出有价值的反馈。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/chaining-operators-in-linux-with-practical-examples/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/category/bash-shell/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/command-line-web-browsers/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/15-basic-ls-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
101
translated/How to Upgrade to GNOME 3.10 in Ubuntu 13.10.md
Normal file
101
translated/How to Upgrade to GNOME 3.10 in Ubuntu 13.10.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
How to Upgrade to GNOME 3.10 in Ubuntu 13.10
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu 13.10 在它的归档(archives是这么翻译吗?)中搭载可用的GNOME 3.8桌面。 尽管对于Unity这是一个可靠稳定以及有特色的替代品,但这个版本还是过时了。**
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME桌面的最新版本在2013年9月被发布了,随之而来的是一系列改进的功能、应用程序和可用性的调整。从对高分辨率屏幕的支持到应用窗口上全新的客户端美化,GNOME 3.10是一个引人注目的升级版本。
|
||||
|
||||
好消息是:假设你正在运行Ubuntu 13.10,拥有不错的网络连接和命令行功能(一语双关),那么你无需继续使用一个过时版本的GNOME。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu 13.10 上升级到GNOME 3.10 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了那些关注点在我会重申的地方上的普通读者的利益(skim未翻译),你**需要运行Ubuntu 13.10来安装GNOME 3.10**.
|
||||
|
||||
首先,让我们添加GNOME 3 的PPA到Ubuntu的软件资源中。这个操作可以使用图形界面完成,但使用命令行会更容易归档一些。
|
||||
|
||||
打开一个新的*终端*窗口,键入下列命令,在被要求的时候输入你的用户密码:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3-next && sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
添加完PPA和更新包列表后,我们就可以转向安装GNOME 3.10了。运行下列命令,当弹出提示时再次输入你的用户密码:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install gnome-shell ubuntu-gnome-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
获取并安装所有必要的包和部件会花一点时间,所以请耐心一点。
|
||||
|
||||
在安装过程中,在终端可能会弹出一个提示,要求你选择一种显示管理器,默认使用的是“登录窗口”。
|
||||
|
||||
这个决定完全取决于你;UBuntu的Unity Greeter和**GNOME的显示管理器**都能让你很轻松地在桌面会话之间切换(如果你想保持在Unity界面或者另一个桌面将很方便),但仅仅只有GDM提供给GNOME特定的功能,譬如锁屏通知。
|
||||
|
||||
当你准备好你的选择后,使用上下键选择,然后敲击‘确认\返回’键以确认选择。安装便会继续进行。
|
||||
|
||||
### 增加额外的功能 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
GNOME 3.10还有一些不错的新特性,应用-[包括GNOME天气,音乐盒地图][1] 以及其它各种各样的改变。
|
||||
因为并不是所有的特性都足够稳定以致于可以被包含在我们之前添加的GNOME 3 PPA中,所以如果你想使用它们,就需要利用到一对额外的GNOME PPA。
|
||||
|
||||
现在-你需要意识到很重要的是-在这些仓库里的一些包据说已经有了稳定的发行版。它们中的大部分是次要的,譬如应用程序崩溃和损坏的特性。但对于更多主要的发行版来说,像使得GNOME完全崩溃是有可能的。
|
||||
|
||||
除开这个警告,在终端里打开一个新的选项卡,输入下列命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3-staging
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
为了添加一些之前提到的很酷的应用,运行这个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gnome-weather gnome-music gnome-maps cheese gnome-documents
|
||||
|
||||
这样之后,就搞定了!
|
||||
|
||||
你可能会想先注销然后重新登录(记得选择“GNOME”会话)以确保改动都已经正确生效了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 细小的差别 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在不卸载Unity的情况下安装GNOME 3.10,那么有一些注意事项你需要记下来。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,你会发现**在系统设置里“Online Accounts”有两个入口**。其中,有key-themed(不知道怎么翻译)的图标是Unity版的,另一个有插件符号的是GNOME版的。
|
||||
|
||||
一些应用程序可能会要求你往Unity中添加账户(Shotwell, Gwibber, Empathy),有一些可能是要求往GNOME中添加(Evolution, Documents, Contacts)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
“通知”和“搜索”入口是GNOME指定的,它们让你挑选哪些应用程序和资源能够显示通知或出现在活动区。
|
||||
|
||||
### 卸载GNOME 3.10 ###
|
||||
|
||||
既然你已经尝试了GNOME 3.10,但不喜欢它。这时该怎么办?
|
||||
|
||||
假设我们使用一个叫做“PPA Purge”的命令行工具,那么移除GNOME 3.10 是一个相当简单的过程。这个工具可以在Ubuntu软件中心里找到,是目前为止自动移除或降级从PPA安装的包的最容易的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
- [Install PPA Purge from Ubuntu Software Center][2]
|
||||
|
||||
为了使用这个工具,我们需要返回终端然后键入下面命令,要留意任何出现在降级过程中的提示。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ppa-purge ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3-next
|
||||
|
||||
如果你也添加了其它可选的PPA,你也需要清楚它们:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ppa-purge ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3-staging
|
||||
sudo ppa-purge ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3
|
||||
|
||||
一旦完成,你应该在GNOME 3.8 桌面中离开(stock不知怎么翻译)。如果你不再想保留GNOME Shell了,你可以执行下列命令去卸载它:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove gnome-shell ubuntu-gnome-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
最后,手动移除任何在降级之后可能残留的应用程序(譬如,Epiphany and GNOME Documents),然后重启。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/12/upgrade-gnome-3-10-ubuntu-13-10
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[KAyGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/09/gnome-3-10-released-with-new-apps-experimental-wayland-support
|
||||
[2]:apt:ppa-purge
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
Linux系统 whoami 命令 – 知晓当前登陆用户
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
通常,在控制台的命令提示符下你会发现 **用户名已经被显示出来** 。但有一些 shell, 比如 **csh**, 默认情况下是不会显示你的用户名的。所以这个命令最应该用在那些不能回显用户名的 shell 终端上。
|
||||
|
||||
### 怎么样使用 whoami ###
|
||||
|
||||
要使用这个命令,仅仅只需要输入 whoami 。下面的例子中我们使用的是 chs shell 终端。
|
||||
|
||||
% whoami
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Whoami 的参数选项 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个命令仅仅只有两个参数选项: **–help** 和 **–version**。
|
||||
|
||||
% whoamin –help
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
下面这选项会输出和 **man whoami** 命令一样的信息
|
||||
|
||||
% whoami –version
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
不同的是 **–version** 会显示你系统上的 whoami 命令的版本信息
|
||||
|
||||
### 相似性 ###
|
||||
|
||||
whoami 命令和 **id -un** 有相同的输出。它们都打印出当前用户的用户名。
|
||||
|
||||
% id -un
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
whoami 命令也用于当你使用 su 命令(切换用户)时, 它能让你确认出你登陆的用户是否正确。 whoami 跟 who 命令不相同, who 命令会显示所有已经登陆的用户名,而 whoami 不是。当你切换用户时, whoami 命令会显示会话所属的当前用户,而 who 命令会显示你切换前的那个源用户。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-whoami-command/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
高级研究人员分析 LibreOffice 得出的有趣结论
|
||||
高级研究员分析 LibreOffice 得出有趣结论
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
用户、编辑、国务院、团队和城管都正享用着 [LibreOffice][1] 这样一套免费的开源办公套件。而这套办公套件,也因在全球范围内通过越来越多人的使用和积极的反馈,证明了自身的成功。
|
||||
用户、编辑、国家机关、团队以及城市管理部门都正享用着 [LibreOffice][1] 这样一套免费的开源办公套件。而这款办公套件也通过与日俱增的用户数量和积极的反馈证明了自身的成功。
|
||||
|
||||
不但用户们感到 LibreOffice 的不妥协和强大之外,通过“分支之后开源软件社区的可持续发展:LibreOffice 是如何演变的?为什么?”这一文档,认真的研究人员还似乎发现并且把 LibreOffice 描述为真正的成功。
|
||||
用户们不仅感受到 LibreOffice 的不妥协和强大之处,通过“分支之后开源软件社区的可持续发展:LibreOffice 是如何演变的?为什么?”这一文档,认真的研究人员似乎还发现并且把 LibreOffice 描述为真正的成功。
|
||||
|
||||
本质上来说。“分支之后的开远软件社区的可持续发展:LibreOffice 是如何演变的?为什么?”是一篇研究 LibreOffice 和它的组成的文档,其中涉及研究的组成部分包括从地位到公众的看法、未来的功能、吸引支持者和参与者的能力。
|
||||
本质上来说。“分支之后开源软件社区的可持续发展:LibreOffice 是如何演变的?为什么?”是一篇研究 LibreOffice 和它的组成的文档,其中涉及研究的组成部分包括从有声望者到公众的看法、未来的功能、吸引支持者和参与者的能力。
|
||||
|
||||
上述提到的文档得到的结论,自然而然地谈到 LibreOffice 在各个方面的成功,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,16 +15,16 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这份由 Skövde 大学信息研究中心高级研究人员编写的正经的长达60页的文档(可以在[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0164121213002744/pdfft...][3]下载)为 LibreOffice 这套健壮的办公套件提供了详尽的、深入且精准的分析。
|
||||
这份由 Skövde 大学信息研究中心高级研究人员编写的长达60页的文档(可以在[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0164121213002744/pdfft...][3]下载)为 LibreOffice 这套强大的办公套件提供了详尽的、深入且精准的分析。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/senior-researchers-analyzed-libreoffice-interesting-conclusions
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[hyaocuk](https://github.com/hyaocuk) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[hyaocuk](https://github.com/hyaocuk) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.libreoffice.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0164121213002744
|
||||
[3]:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0164121213002744/pdfft?md5=4b986a117fb06cc127b854cb5f622bec&pid=1-s2.0-S0164121213002744-main.pdf
|
||||
[3]:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0164121213002744/pdfft?md5=4b986a117fb06cc127b854cb5f622bec&pid=1-s2.0-S0164121213002744-main.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
|
||||
TeamViewer 9发布-基于RHEL/CentOS/Fedora和Debian/Ubuntu的安装
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
这篇指南介绍了怎么样在 **RedHat、 CentOS、 Fedora** 和 **Debian**、 **Ubuntu**、 **Linux Mint**、 **Xubuntu** 等这些系统中安装 **Teamviewer 9**。**Teamviewer** 是一款用于远程助理、桌面共享、计算机之间互传文件、网络会议及在线会议等方面的流行应用软件,并且他是一款专业应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,个人用户可以免费使用。Teamviewer可以运行在 **Windows、Linux、Mac OS、Android** 系统以及 **iPhone** 设备上,它使用 **WINE** 应用程序来运行,并且他们已经集成在一起,所以我们用的时候不需单独[安装 WINE 程序][1]了。 **Teamviewer** 并不是原生的 **Linux** 应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
最近,最新的稳定版本 **TeamViewer 9** 已经发布了,有了些新的功能和很多性能的改进。在 **TeamViewer 9** 中增加的一些新功能特性,其要点如下:
|
||||
|
||||
### Windows、Linux 和 Mac 系统下的功能特性 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 在不同的选项卡中打开多个连接
|
||||
- 支持局域网唤醒
|
||||
- 支持为 TeamViewer 帐户添加双重身份验证
|
||||
- 支持 Windows 8.1 和 Mac OS X Mavericks 系统
|
||||
- 能保存自定义模块,如uickSupport、QuickJoin等等
|
||||
- 集成了应用程序编程接口(API)
|
||||
- 更强的 Teamviewer 账户安全
|
||||
- 通过桌面快捷方式快速连接
|
||||
- 可视化通知信息
|
||||
- 不同计算机间复制和粘贴文件和文本
|
||||
- 不同计算机间的初始化文件传输
|
||||
- 视频传输更快
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 RedHat、 CentOS、 Fedora 上安装 Teamviewer 9 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在 [teamviewer_linux.rpm][2] 上下载到基于 Linux 发行版本的 rpm 包。
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://www.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
让我们开始安装吧。进入你的下载包所在的目录,执行如下的 yum 命令来安装,它将会自动安装需要的依赖包。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install teamviewer_linux.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
如果出现公钥缺失错误,你可以用如下命令来下载,并导入之。
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://www.teamviewer.com/link/?url=354858
|
||||
# rpm --import TeamViewer_Linux_PubKey.asc
|
||||
|
||||
在导入公钥后,请再一次运行 “**yum install*” 命令来安装 Teamviewer rpm 包。
|
||||
|
||||
要启动运行 Teamviewer 应用,从终端中运行如下命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# teamviewer
|
||||
|
||||
Teamviewer 应用程序正运行在我的 **Fedora 18** 系统上。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*Fedora 18 系统上运行的 TeamViewer*
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Xubuntu 上安装 Teamviewer 9 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在 [teamviewer linux .deb][3] 上下载到基于 **32-位** 系统或 **64-位** 系统的 teamviewer 安装包,或者你可以用如下所示的 **wget** 命令来下载安装包。
|
||||
|
||||
## 32 位系统 ##
|
||||
$ sudo wget http://www.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux.deb
|
||||
|
||||
## 64 位系统 ##
|
||||
$ sudo wget http://www.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux_x64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
一旦下载好,就可以进入你下载的 Teamviewer 包所在的目录,然后运行如下命令来安装。
|
||||
|
||||
## 32 位系统 ##
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_linux.deb
|
||||
|
||||
## 64 位系统 ##
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_linux_x64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
如果出现有缺失依赖包错误这种情况,请使用如下命令来安装这些依赖包。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install -f
|
||||
|
||||
一旦全部都安装成功,在 **Ubuntu** 系统中要启动 Teamviewer,打开 **Dash 主窗口**,输入 **teamviewer** ,然后点击出现的 **teamviewer** 图标,程序就启动运行了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*Ubuntu 13.10 系统上运行的 TeamViewer*
|
||||
|
||||
Teamviewer 应用程序正运行在我的 **Ubuntu 13.10** 系统上。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*在 Ubuntu 13.10 下的 TeamViewer 9*
|
||||
|
||||
要在 **Linux Mint** 上启动,进入 **菜单 >> 网络 >> Teamviewer**, 并点击 **接受许可协议** 来启动运行 TeamViewer。
|
||||
|
||||
Teamviewer 应用程序正运行在我的 **Linux Mint 15** 系统上。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*Linux Mint 15 系统上运行的 TeamViewer*
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-install-teamviewer-on-linux-distributions/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-wine-in-rhel-centos-and-fedora/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux.rpm
|
||||
[3]:http://www.teamviewer.com/hi/download/linux.aspx
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user