mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-26 21:30:55 +08:00
20170411-2 选题
This commit is contained in:
parent
f5febb6599
commit
e5f9bf2a34
@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
|
||||
How to Add a New Disk Larger Than 2TB to An Existing Linux
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Have you ever tried to do the partitioning of hard disk larger than 2TB using [fdisk utility][1] and wondered why you end up getting a warning to use GPT? Yes, you got that right. We cannot partition a hard disk larger than 2TB using fdisk tool.
|
||||
|
||||
In such cases, we can use parted command. The major difference lies in the partitioning formats that fdisk uses DOS partitioning table format and parted uses GPT format.
|
||||
|
||||
TIP: You can use gdisk as well instead of parted tool.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, we will show you to add a new disk larger than 2TB to an existing Linux server such as RHEL/CentOS or Debian/Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
I am using fdisk and parted utilities to do this configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
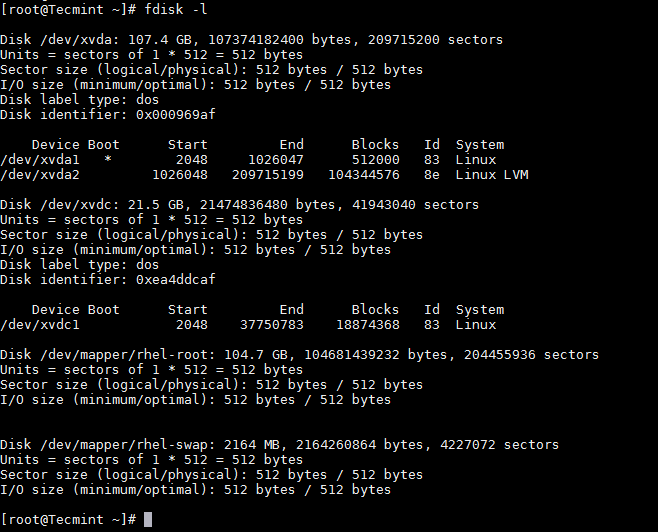
First list the current partition details using fdisk command as shown.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fdisk -l
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][2]
|
||||
|
||||
List Linux Partition Table
|
||||
|
||||
For the purpose of this article, I am attaching a hard disk of 20GB capacity, which can be followed for disk larger than 2TB as well. Once you added a disk, verify the partition table using same fdisk command as shown.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fdisk -l
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][3]
|
||||
|
||||
List New Partition Table
|
||||
|
||||
Tip: If you are adding a physical hard disk, you may find that partitions already created. In such cases, you can use fdsik to delete the same before using parted.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fdisk /dev/xvdd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use `d` switch for the command to delete the partition and `w` to write the changes and quit.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Delete Linux Partition
|
||||
|
||||
Important: You need to be careful while deleting the partition. This will erase the data on the disk.
|
||||
|
||||
Now its time to partition a new hard disk using parted command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# parted /dev/xvdd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Set the partition table format to GPT
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(parted) mklabel gpt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create the Primary partition and assign the disk capacity, here I am using 20GB (in your case it would be 2TB).
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(parted) mkpart primary 0GB 20GB
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][5]
|
||||
|
||||
Create Partition using Parted
|
||||
|
||||
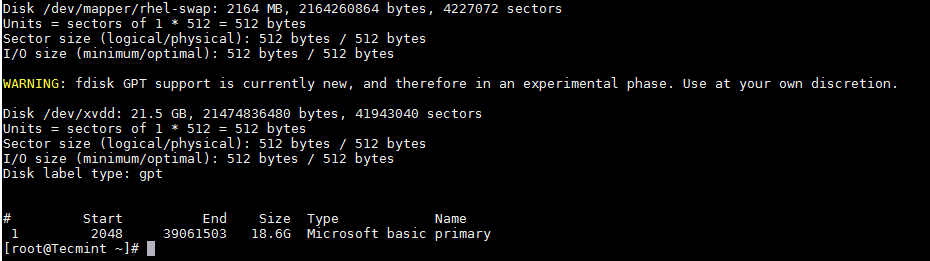
Just for curiosity, let’s see how this new partition is listed in fdisk.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fdisk /dev/xvdd
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Verify Partition Details
|
||||
|
||||
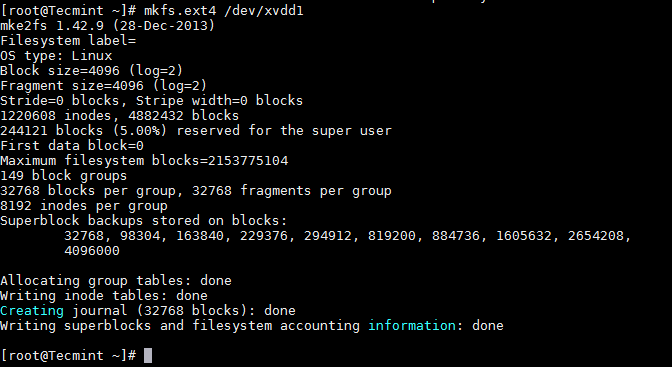
Now format and then mount the partition and add the same in /etc/fstab which controls the file systems to be mounted when the system boots.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/xvdd1
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][7]
|
||||
|
||||
Format Linux Partition
|
||||
|
||||
Once partition has been formatted, now it’s time mount the partition under /data1.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mount /dev/xvdd1 /data1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For permanent mounting add the entry in /etc/fstab file.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/dev/xvdd1 /data1 ext4 defaults 0 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Important: Kernel should support GPT in order to partition using GPT format. By default RHEL/CentOS have Kernel with GPT support, but for Debian/Ubuntu you need to recompile the kernel after changing the config.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it! In this article, we have shown you how to use the parted command. Share your comments and feedback with us.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
I work on various platforms including IBM-AIX, Solaris, HP-UX, and storage technologies ONTAP and OneFS and have hands on experience on Oracle Database.
|
||||
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/add-disk-larger-than-2tb-to-an-existing-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Lakshmi Dhandapani][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/lakshmi/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/fdisk-commands-to-manage-linux-disk-partitions/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/List-Linux-Partition-Table.png
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/List-New-Partition-Table.png
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Delete-Linux-Partition.png
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Create-Partition-using-Parted.png
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Verify-Partition-Details.png
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Format-Linux-Partition.png
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/lakshmi/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user