mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
[Translated] How to set up Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE) in Linux
This commit is contained in:
parent
24e73478bf
commit
e5a3196e73
@ -1,238 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[felixonmars translating...]
|
||||
|
||||
How to set up Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE) in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
As far as network management is concerned, Nagios is one of the most powerful tools. Nagios can monitor the reachability of remote hosts, as well as the state of services running on them. However, what if we want to monitor something other than network services for a remote host? For example, we may want to monitor the disk utilization or [CPU processor load][1] of a remote host. Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE) is a tool that can help with doing that. NRPE allows one to execute Nagios plugins installed on remote hosts, and integrate them with an [existing Nagios server][2].
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial will cover how to set up NRPE on an existing Nagios deployment. The tutorial is primarily divided into two parts:
|
||||
|
||||
- Configure remote hosts.
|
||||
- Configure a Nagios monitoring server.
|
||||
|
||||
We will then finish off by defining some custom commands that can be used with NRPE.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure Remote Hosts for NRPE ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step One: Installing NRPE Service ####
|
||||
|
||||
You need to install NRPE service on every remote host that you want to monitor using NRPE. NRPE service daemon on each remote host will then communicate with a Nagios monitoring server.
|
||||
|
||||
Necessary packages for NRPE service can easily be installed using apt-get or yum, subject to the platform. In case of CentOS, we will need to [add Repoforge repository][3] as NRPE is not available in CentOS repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
**On Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install nagios-nrpe-server
|
||||
|
||||
**On CentOS, Fedora or RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install nagios-nrpe
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Two: Preparing Configuration File ####
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration file /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg is similar for Debian-based and RedHat-based systems. The configuration file is backed up, and then updated as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## NRPE service port can be customized ##
|
||||
server_port=5666
|
||||
|
||||
## the nagios monitoring server is permitted ##
|
||||
## NOTE: There is no space after the comma ##
|
||||
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,X.X.X.X-IP_v4_of_Nagios_server
|
||||
|
||||
## The following examples use hard-coded command arguments.
|
||||
## These parameters can be modified as needed.
|
||||
|
||||
## NOTE: For CentOS 64 bit, use /usr/lib64 instead of /usr/lib ##
|
||||
|
||||
command[check_users]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_users -w 5 -c 10
|
||||
command[check_load]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_load -w 15,10,5 -c 30,25,20
|
||||
command[check_hda1]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w 20% -c 10% -p /dev/hda1
|
||||
command[check_zombie_procs]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 5 -c 10 -s Z
|
||||
command[check_total_procs]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 150 -c 200
|
||||
|
||||
Now that the configuration file is ready, NRPE service is ready to be fired up.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Three: Initiating NRPE Service ####
|
||||
|
||||
For RedHat-based systems, the NRPE service needs to be added as a startup service.
|
||||
|
||||
**On Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# service nagios-nrpe-server restart
|
||||
|
||||
**On CentOS, Fedora or RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# service nrpe restart
|
||||
# chkconfig nrpe on
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Four: Verifying NRPE Service Status ####
|
||||
|
||||
Information about NRPE daemon status can be found in the system log. For a Debian-based system, the log file will be /var/log/syslog. The log file for a RedHat-based system will be /var/log/messages. A sample log is provided below for reference.
|
||||
|
||||
nrpe[19723]: Starting up daemon
|
||||
nrpe[19723]: Listening for connections on port 5666
|
||||
nrpe[19723]: Allowing connections from: 127.0.0.1,X.X.X.X
|
||||
|
||||
In case firewall is running, TCP port 5666 should be open, which is used by NRPE daemon.
|
||||
|
||||
# netstat -tpln | grep 5666
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5666 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 19885/nrpe
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure Nagios Monitoring Server for NRPE ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first step in configuring an existing Nagios monitoring server for NRPE is to install NRPE plugin on the server.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step One: Installing NRPE Plugin ####
|
||||
|
||||
In case the Nagios server is running on a Debian-based system (Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint), a necessary package can be installed using apt-get.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install nagios-nrpe-plugin
|
||||
|
||||
After the plugin is installed, the check_nrpe command, which comes with the plugin, is modified a bit.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios-plugins/config/check_nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## the default command is overwritten ##
|
||||
define command{
|
||||
command_name check_nrpe
|
||||
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -c '$ARG1$'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
In case the Nagios server is running on a RedHat-based system (CentOS, Fedora or RHEL), you can install NRPE plugin using yum. On CentOS, [adding Repoforge repository][4] is necessary.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install nagios-plugins-nrpe
|
||||
|
||||
Now that the NRPE plugin is installed, proceed to configure a Nagios server following the rest of the steps.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Two: Defining Nagios Command for NRPE Plugin ####
|
||||
|
||||
First, we need to define a command in Nagios for using NRPE.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios/objects/commands.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## NOTE: For CentOS 64 bit, use /usr/lib64 instead of /usr/lib ##
|
||||
define command{
|
||||
command_name check_nrpe
|
||||
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -c '$ARG1$'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Three: Adding Host and Command Definition ####
|
||||
|
||||
Next, define remote host(s) and commands to execute remotely on them.
|
||||
|
||||
The following shows sample definitions of a remote host a command to execute on the host. Naturally, your configuration will be adjusted based on your requirements. The path to the file is slightly different for Debian-based and RedHat-based systems. But the content of the files are identical.
|
||||
|
||||
**On Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios3/conf.d/nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
**On CentOS, Fedora or RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios/objects/nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
define host{
|
||||
use linux-server
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
alias server-1
|
||||
address X.X.X.X-IPv4_address_of_remote_host
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
define service {
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
service_description Check Load
|
||||
check_command check_nrpe!check_load
|
||||
check_interval 1
|
||||
use generic-service
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Four: Restarting Nagios Service ####
|
||||
|
||||
Before restarting Nagios, updated configuration is verified with a dry run.
|
||||
|
||||
**On Ubuntu, Debian, or Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# nagios3 -v /etc/nagios3/nagios.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
**On CentOS, Fedora or RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# nagios -v /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
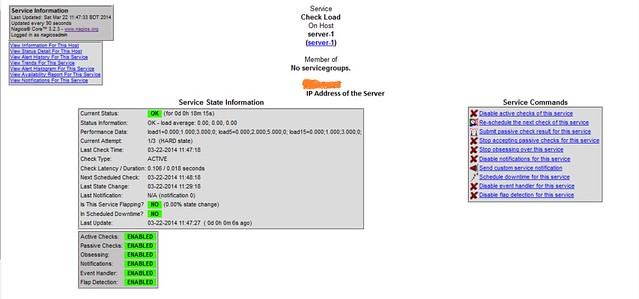
If everything goes well, Nagios service can be restarted.
|
||||
|
||||
# service nagios restart
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuring Custom Commands with NRPE ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Setup on Remote Servers ####
|
||||
|
||||
The following is a list of custom commands that can be used with NRPE. These commands are defined in the file /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg located at the remote servers.
|
||||
|
||||
## Warning status when load average exceeds 1, 2 and 1 for 1, 5, 15 minute interval, respectively.
|
||||
## Critical status when load average exceeds 3, 5 and 3 for 1, 5, 15 minute interval, respectively.
|
||||
command[check_load]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_load -w 1,2,1 -c 3,5,3
|
||||
|
||||
## Warning level 25% and critical level 10% for free space of /home.
|
||||
## Could be customized to monitor any partition (e.g. /dev/sdb1, /, /var, /home)
|
||||
command[check_disk]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w 25% -c 10% -p /home
|
||||
|
||||
## Warn if number of instances for process_ABC exceeds 10. Critical for 20 ##
|
||||
command[check_process_ABC]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 1:10 -c 1:20 -C process_ABC
|
||||
|
||||
## Critical if the number of instances for process_XYZ drops below 1 ##
|
||||
command[check_process_XYZ]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 1: -c 1: -C process_XYZ
|
||||
|
||||
#### Setup on Nagios Monitoring Server ####
|
||||
|
||||
To apply the custom commands defined above, we modify the service definition at Nagios monitoring server as follows. The service definition could go to the file where all the services are defined (e.g., /etc/nagios/objects/nrpe.cfg or /etc/nagios3/conf.d/nrpe.cfg)
|
||||
|
||||
## example 1: check process XYZ ##
|
||||
define service {
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
service_description Check Process XYZ
|
||||
check_command check_nrpe!check_process_XYZ
|
||||
check_interval 1
|
||||
use generic-service
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
## example 2: check disk state ##
|
||||
define service {
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
service_description Check Process XYZ
|
||||
check_command check_nrpe!check_disk
|
||||
check_interval 1
|
||||
use generic-service
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
To sum up, NRPE is a powerful add-on to Nagios as it provides provision for monitoring a remote server in a highly configurable fashion. Using NRPE, we can monitor server load, running processes, logged in users, disk states and other parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
Hope this helps.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/03/nagios-remote-plugin-executor-nrpe-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2012/08/how-to-measure-average-cpu-utilization.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/install-configure-nagios-linux.html
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/01/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/01/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,236 @@
|
||||
如何在 Linux 环境下配置 Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
就网络管理而言,Nagios 是最强大的工具之一。Nagios 可以监控远程主机的可访问性,以及其中正在运行的服务的状态。不过,如果我们想要监控远程主机中网络服务以外的东西呢?比方说,我们可能想要监控远程主机上的磁盘利用率或者 [CPU 处理器负载][1]。Nagios Remote Plugin Executor(NRPE)便是一个可以帮助你完成这些操作的工具。NRPE 允许你执行在远程主机上安装的 Nagios 插件,并且将它们集成到一个[已经存在的 Nagios 服务器][2]里。
|
||||
|
||||
本教程将会介绍如何在一个已经部署好的 Nagios 中配置 NRPE。本教程主要分为两部分:
|
||||
|
||||
- 配置远程主机。
|
||||
- 配置 Nagios 监控服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
之后我们会以定义一些可以被 NRPE 使用的自定义命令来结束本教程。
|
||||
|
||||
### 为 NRPE 配置远程主机 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第一步:安装 NRPE 服务 ####
|
||||
|
||||
你需要在你想要使用 NRPE 监控的每一台远程主机上安装 NRPE 服务。每一台远程主机上的 NRPE 服务守护进程将会与一台 Nagios 监控服务器进行通信。
|
||||
|
||||
取决于所在的平台, NRPE 服务所需要的软件包可以很容易地用 apt-get 或者 yum 来安装。对于 CentOS 来说,由于 NRPE 并不在 CentOS 的仓库中,我们需要[添加 Repoforge 仓库][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 Debian、Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install nagios-nrpe-server
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 CentOS、Fedora 或者 RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install nagios-nrpe
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第二步:准备配置文件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
配置文件 /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg 在基于 Debian 或者 RedHat 的系统中比较相近。让我们备份并修改配置文件:
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## NRPE 服务端口是可以自定义的 ##
|
||||
server_port=5666
|
||||
|
||||
## 允许 Nagios 监控服务器访问 ##
|
||||
## 注意:逗号后面没有空格 ##
|
||||
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,X.X.X.X-IP_v4_of_Nagios_server
|
||||
|
||||
## 下面的例子中我们硬编码了参数。
|
||||
## 这些参数可以按需修改。
|
||||
|
||||
## 注意:对于 CentOS 64 位用户,请使用 /usr/lib64 替代 /usr/lib ##
|
||||
|
||||
command[check_users]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_users -w 5 -c 10
|
||||
command[check_load]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_load -w 15,10,5 -c 30,25,20
|
||||
command[check_hda1]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w 20% -c 10% -p /dev/hda1
|
||||
command[check_zombie_procs]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 5 -c 10 -s Z
|
||||
command[check_total_procs]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 150 -c 200
|
||||
|
||||
现在配置文件已经准备好了,NRPE 服务已经可以启动了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第三步:初始化 NRPE 服务 ####
|
||||
|
||||
对于基于 RedHat 的系统,NRPE 服务需要被添加为启动服务。
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 Debian、Ubuntu、Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# service nagios-nrpe-server restart
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 CentOS、Fedora 或者 RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# service nrpe restart
|
||||
# chkconfig nrpe on
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第四步:验证 NRPE 服务状态 ####
|
||||
|
||||
NRPE 守护进程的状态信息可以在系统日志中找到。对于基于 Debian 的系统,日志文件在 /var/log/syslog,而基于 RedHat 的系统的日志文件则是 /var/log/messages。下面提供一段样例日志以供参考:
|
||||
|
||||
nrpe[19723]: Starting up daemon
|
||||
nrpe[19723]: Listening for connections on port 5666
|
||||
nrpe[19723]: Allowing connections from: 127.0.0.1,X.X.X.X
|
||||
|
||||
如果使用了防火墙,被 NRPE 守护进程使用的 TCP 端口 5666 应该被开启。
|
||||
|
||||
# netstat -tpln | grep 5666
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5666 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 19885/nrpe
|
||||
|
||||
### 为 NRPE 配置 Nagios 监控服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为 NRPE 配置已有的 Nagios 监控服务器的第一步是在服务器上安装 NRPE 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第一步:安装 NRPE 插件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
当 Nagios 服务器运行在基于 Debian 的系统(Debian、Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint)上时,需要的软件宝可以通过 apt-get 安装。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install nagios-nrpe-plugin
|
||||
|
||||
插件安装完成后,对随插件安装的 check_nrpe 命令稍作修改。
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios-plugins/config/check_nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## 默认命令会被覆盖 ##
|
||||
define command{
|
||||
command_name check_nrpe
|
||||
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -c '$ARG1$'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
如果 Nagios 服务器运行在基于 RedHat 的系统(CentOS、Fedora 或者 RHEL)上,你可以通过 yum 安装 NRPE 插件。对于 CentOS,[添加 Repoforge 仓库][4] 是必要的。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install nagios-plugins-nrpe
|
||||
|
||||
现在 NRPE 插件已经安装完成,继续下面的步骤以配置一台 Nagios 服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第二步:为 NRPE 插件定义 Nagios 命令 ####
|
||||
|
||||
我们需要首先在 Nagios 中定义一个命令来使用 NRPE。
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios/objects/commands.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## 注意:对于 CentOS 64 位用户,请使用 /usr/lib64 替代 /usr/lib ##
|
||||
define command{
|
||||
command_name check_nrpe
|
||||
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -c '$ARG1$'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第三步:添加主机与命令定义 ####
|
||||
|
||||
接下来定义远程主机以及我们将要在它们上面运行的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的例子为一台远程主机定义了一个可以在上面执行的命令。一般来说,你的配置需要按照你的需求来改变。配置文件的路径在基于 Debian 和基于 RedHat 的系统上略有不同,不过文件的内容是完全一样的。
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 Debian、Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios3/conf.d/nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 CentOS、Fedora 或者 RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios/objects/nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
define host{
|
||||
use linux-server
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
alias server-1
|
||||
address X.X.X.X-IPv4_address_of_remote_host
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
define service {
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
service_description Check Load
|
||||
check_command check_nrpe!check_load
|
||||
check_interval 1
|
||||
use generic-service
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第四步:重启 Nagios 服务 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在重启 Nagios 之前,可以通过测试来验证配置。
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 Ubuntu、Debian 或者 Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# nagios3 -v /etc/nagios3/nagios.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 CentOS、Fedora 或者 RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# nagios -v /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
如果一切正常,我们就可以重启 Nagios 服务了。
|
||||
|
||||
# service nagios restart
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 为 NRPE 配置自定义命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 远程服务器上的配置 ####
|
||||
|
||||
下面列出了一些可以用于 NRPE 的自定义命令。这些命令在远程服务器的 /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg 文件中定义。
|
||||
|
||||
## 当 1、5、15 分钟的平均负载分别超过 1、2、1 时进入警告状态
|
||||
## 当 1、5、15 分钟的平均负载分别超过 3、5、3 时进入严重警告状态
|
||||
command[check_load]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_load -w 1,2,1 -c 3,5,3
|
||||
|
||||
## 对于 /home 目录的可用空间设置了警告级别为 25%,以及严重警告级别为 10%。
|
||||
## 可以定制为监控任何分区(比如 /dev/sdb1、/、/var、/home)
|
||||
command[check_disk]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w 25% -c 10% -p /home
|
||||
|
||||
## 当 process_ABC 的实例数量超过 10 时警告,超过 20 时严重警告 ##
|
||||
command[check_process_ABC]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 1:10 -c 1:20 -C process_ABC
|
||||
|
||||
## 当 process_ABC 的实例数量跌到 1 以下时严重警告 ##
|
||||
command[check_process_XYZ]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 1: -c 1: -C process_XYZ
|
||||
|
||||
#### Nagios 监控服务器上的配置 ####
|
||||
|
||||
我们通过修改 Nagios 监控服务器里的服务定义来应用上面定义的自定义命令。服务定义可以写在所有服务被定义的地方(比如 /etc/nagios/objects/nrpe.cfg 或 /etc/nagios3/conf.d/nrpe.cfg)
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例 1:检查进程 XYZ ##
|
||||
define service {
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
service_description Check Process XYZ
|
||||
check_command check_nrpe!check_process_XYZ
|
||||
check_interval 1
|
||||
use generic-service
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例 2:检查磁盘状态 ##
|
||||
define service {
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
service_description Check Process XYZ
|
||||
check_command check_nrpe!check_disk
|
||||
check_interval 1
|
||||
use generic-service
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
总而言之,NRPE 是 Nagios 的一个强大的扩展,它提供了高度可定制的远程服务器监控方案。使用 NRPE,我们可以监控系统的负载、运行的进程、已登录的用户、磁盘状态,以及其它的指标。
|
||||
|
||||
希望这些可以帮到你。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/03/nagios-remote-plugin-executor-nrpe-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
|
||||
译者:[felixonmars](https://github.com/felixonmars)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2012/08/how-to-measure-average-cpu-utilization.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/install-configure-nagios-linux.html
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/01/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/01/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user