mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-30 02:40:11 +08:00
20150205-2 选题
This commit is contained in:
parent
012b1048e2
commit
e3fb947386
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
LinuxQuestions Survey Results Surface Top Open Source Projects
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Many people in the Linux community look forward to the always highly detailed and reliable results of the annual surveys from LinuxQuestions.org. As [Susan covered in detail in this post][1], this year's [results][2], focused on what readers at the site deem to be the best open source projects, are now available. Most of the people at LinuxQuestions are expert-level users who are on the site to answer questions from newer Linux users.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the summary results that Susan provided in her post, below you'll find a graphical snapshot of what the experts took note of on the open source front.
|
||||
|
||||
You can get a very nice graphical summary of the findings from the LinuxQuestions survey [here][3]. Here is a snapshot of the site's determination of the best Linux distributions, where Mint and Slackware fare quite well:
|
||||
|
||||
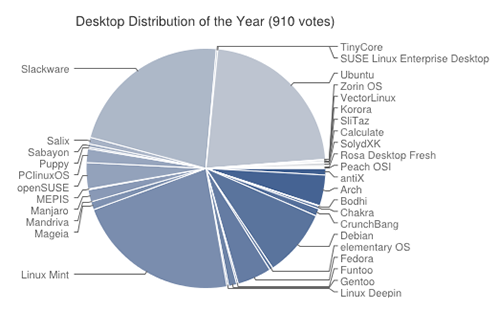
|
||||
|
||||
And below is a snapshot of the site's determination of the best cloud projects. Notably, the LinuxQuestions crowd gives very high praise to ownCloud. Definiitely check into the full results of the survey at the site, see [Susan's summary][4] of winners, and check out all the good graphics [here][5].
|
||||
|
||||
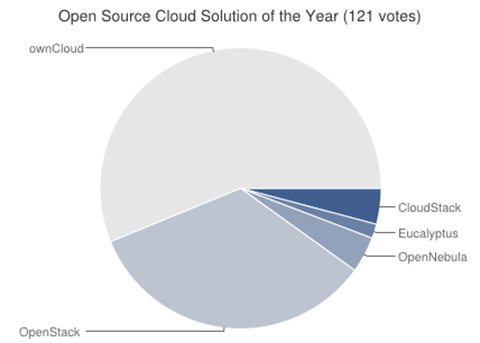
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/linuxquestions-survey-results-surface-top-open-source-projects
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sam Dean][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ostatic.com/member/samdean
|
||||
[1]:http://ostatic.com/blog/lq-members-choice-award-winners-announced
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/linux-news-59/2014-linuxquestions-org-members-choice-award-winners-4175532948/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/2014mca.php
|
||||
[4]:http://ostatic.com/blog/lq-members-choice-award-winners-announced
|
||||
[5]:http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/2014mca.php
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,377 @@
|
||||
25 Linux Shell Scripting interview Questions & Answers
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Q:1 What is Shell Script and why it is required ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: A Shell Script is a text file that contains one or more commands. As a system administrator we often need to issue number of commands to accomplish the task, we can add these all commands together in a text file (Shell Script) to complete daily routine task.
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:2 What is the default login shell and how to change default login shell for a specific user ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: In Linux like Operating system “/bin/bash” is the default login shell which is assigned while user creation. We can change default shell using the “chsh” command . Example is shown below :
|
||||
|
||||
# chsh <username> -s <new_default_shell>
|
||||
# chsh linuxtechi -s /bin/sh
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:3 What are the different type of variables used in a shell Script ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: In a shell script we can use two types of variables :
|
||||
|
||||
- System defined variables
|
||||
- User defined variables
|
||||
|
||||
System defined variables are defined or created by Operating System(Linux) itself. These variables are generally defined in Capital Letters and can be viewed by “**set**” command.
|
||||
|
||||
User defined variables are created or defined by system users and the values of variables can be viewed by using the command “`echo $<Name_of_Variable>`”
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:4 How to redirect both standard output and standard error to the same location ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: There two method to redirect std output and std error to the same location:
|
||||
|
||||
Method:1 2>&1 (# ls /usr/share/doc > out.txt 2>&1 )
|
||||
|
||||
Method:2 &> (# ls /usr/share/doc &> out.txt )
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:5 What is the Syntax of “nested if statement” in shell scripting ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans : Basic Syntax is shown below :
|
||||
|
||||
if [ Condition ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
command1
|
||||
command2
|
||||
…..
|
||||
else
|
||||
if [ condition ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
command1
|
||||
command2
|
||||
….
|
||||
else
|
||||
command1
|
||||
command2
|
||||
…..
|
||||
fi
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:6 What is the use of “$?” sign in shell script ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans:While writing a shell script , if you want to check whether previous command is executed successfully or not , then we can use “$?” with if statement to check the exit status of previous command. Basic example is shown below :
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:~# ls /usr/bin/shar
|
||||
/usr/bin/shar
|
||||
root@localhost:~# echo $?
|
||||
0
|
||||
|
||||
If exit status is 0 , then command is executed successfully
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:~# ls /usr/bin/share
|
||||
|
||||
ls: cannot access /usr/bin/share: No such file or directory
|
||||
root@localhost:~# echo $?
|
||||
2
|
||||
|
||||
If the exit status is other than 0, then we can say command is not executed successfully.
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:7 How to compare numbers in Linux shell Scripting ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: test command is used to compare numbers in if-then statement. Example is shown below :
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
x=10
|
||||
y=20
|
||||
|
||||
if [ $x -gt $y ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
echo “x is greater than y”
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo “y is greater than x”
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:8 What is the use of break command ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: The break command is a simple way to escape out of a loop in progress. We can use the break command to exit out from any loop, including while and until loops.
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:9 What is the use of continue command in shell scripting ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans The continue command is identical to break command except it causes the present iteration of the loop to exit, instead of the entire loop. Continue command is useful in some scenarios where error has occurred but we still want to execute the next commands of the loop.
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:10 Tell me the Syntax of “Case statement” in Linux shell scripting ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: The basic syntax is shown below :
|
||||
|
||||
case word in
|
||||
value1)
|
||||
command1
|
||||
command2
|
||||
…..
|
||||
last_command
|
||||
!!
|
||||
value2)
|
||||
command1
|
||||
command2
|
||||
……
|
||||
last_command
|
||||
;;
|
||||
esac
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:11 What is the basic syntax of while loop in shell scripting ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Like the for loop, the while loop repeats its block of commands a number of times. Unlike the for loop, however, the while loop iterates until its while condition is no longer true. The basic syntax is :
|
||||
|
||||
while [ test_condition ]
|
||||
do
|
||||
commands…
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:12 How to make a shell script executable ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Using the chmod command we can make a shell script executable. Example is shown below :
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod a+x myscript.sh
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:13 What is the use of “#!/bin/bash” ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: #!/bin/bash is the first of a shell script , known as shebang , where # symbol is called hash and ‘!’ is called as bang. It shows that command to be executed via /bin/bash.
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:14 What is the syntax of for loop in shell script ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Basic Syntax of for loop is given below :
|
||||
|
||||
for variables in list_of_items
|
||||
do
|
||||
command1
|
||||
command2
|
||||
….
|
||||
last_command
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:15 How to debug a shell script ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: A shell script can be debug if we execute the script with ‘-x’ option ( sh -x myscript.sh). Another way to debug a shell script is by using ‘-nv’ option ( sh -nv myscript.sh).
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:16 How compare the strings in shell script ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: test command is used to compare the text strings. The test command compares text strings by comparing each character in each string.
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:17 What are the Special Variables set by Bourne shell for command line arguments ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: The following table lists the special variables set by the Bourne shell for command line arguments .
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格部分
|
||||
<table width="659" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4">
|
||||
<colgroup>
|
||||
<col width="173">
|
||||
<col width="453"> </colgroup>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td width="173" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">Special Variables</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">Holds</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td width="173" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">$0</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">Name of the Script from the command line</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td width="173" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">$1</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">First Command-line argument</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td width="173" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">$2</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">Second Command-line argument</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td width="173" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">…..</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">…….</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td width="173" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">$9</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">Ninth Command line argument</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td width="173" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">$#</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">Number of Command line arguments</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td width="173" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">$*</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453" valign="top">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">All Command-line arguments, separated with spaces</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:18 How to test files in a shell script ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: test command is used to perform different test on the files. Basic test are listed below :
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格部分
|
||||
<table width="644" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="4">
|
||||
<colgroup>
|
||||
<col width="173">
|
||||
<col width="453"> </colgroup>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr valign="top">
|
||||
<td width="173">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">Test</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">Usage</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top">
|
||||
<td width="173">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">-d file_name</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">Returns true if the file exists and is a directory</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top">
|
||||
<td width="173">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">-e file_name</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">Returns true if the file exists</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top">
|
||||
<td width="173">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">-f file_name</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">Returns true if the file exists and is a regular file</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top">
|
||||
<td width="173">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">-r file_name</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">Returns true if the file exists and have read permissions</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top">
|
||||
<td width="173">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">-s file_name</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">Returns true if the file exists and is not empty</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top">
|
||||
<td width="173">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">-w file_name</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">Returns true if the file exists and have write permissions</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top">
|
||||
<td width="173">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">-x file_name</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="453">
|
||||
<p align="left" class="western">Returns true if the file exists and have execute permissions</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:19 How to put comments in your shell script ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Comments are the messages to yourself and for other users that describe what a script is supposed to do and how its works.To put comments in your script, start each comment line with a hash sign (#) . Example is shown below :
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
# This is a command
|
||||
echo “I am logged in as $USER”
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:20 How to get input from the terminal for shell script ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: ‘read’ command reads in data from the terminal (using keyboard). The read command takes in whatever the user types and places the text into the variable you name. Example is shown below :
|
||||
|
||||
# vi /tmp/test.sh
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
echo ‘Please enter your name’
|
||||
read name
|
||||
echo “My Name is $name”
|
||||
|
||||
# ./test.sh
|
||||
Please enter your name
|
||||
LinuxTechi
|
||||
My Name is LinuxTechi
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:21 How to unset or de-assign variables ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: ‘unset’ command is used to de-assign or unset a variable. Syntax is shown below :
|
||||
|
||||
# unset <Name_of_Variable>
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:22 How to perform arithmetic operation ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: There are two ways to perform arithmetic operations :
|
||||
|
||||
1. Using `expr` command (# expr 5 + 2 )
|
||||
2. using a dollar sign and square brackets ( `$[ operation ]` ) Example : test=$[16 + 4] ; test=$[16 + 4]
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:23 Basic Syntax of do-while statement ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: The do-while statement is similar to the while statement but performs the statements before checking the condition statement. The following is the format for the do-while statement:
|
||||
|
||||
do
|
||||
{
|
||||
statements
|
||||
} while (condition)
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:24 How to define functions in shell scripting ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: A function is simply a block of of code with a name. When we give a name to a block of code, we can then call that name in our script, and that block will be executed. Example is shown below :
|
||||
|
||||
$ diskusage () { df -h ; }
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:25 How to use bc (bash calculator) in a shell script ? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Use the below Syntax to use bc in shell script.
|
||||
|
||||
variable=`echo “options; expression” | bc`
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/linux-shell-scripting-interview-questions-answers/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
|
||||
Install Strongswan - A Tool to Setup IPsec Based VPN in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
IPsec is a standard which provides the security at network layer. It consist of authentication header (AH) and encapsulating security payload (ESP) components. AH provides the packet Integrity and confidentiality is provided by ESP component . IPsec ensures the following security features at network layer.
|
||||
|
||||
- Confidentiality
|
||||
- Integrity of packet
|
||||
- Source Non. Repudiation
|
||||
- Replay attack protection
|
||||
|
||||
[Strongswan][1] is an open source implementation of IPsec protocol and Strongswan stands for Strong Secure WAN (StrongS/WAN). It supports the both version of automatic keying exchange in IPsec VPN (Internet keying Exchange (IKE) V1 & V2).
|
||||
|
||||
Strongswan basically provides the automatic keying sharing between two nodes/gateway of the VPN and after that it uses the Linux Kernel implementation of IPsec (AH & ESP). Key shared using IKE mechanism is further used in the ESP for the encryption of data. In IKE phase, strongswan uses the encryption algorithms (AES,SHA etc) of OpenSSL and other crypto libraries. However, ESP component of IPsec uses the security algorithm which are implemented in the Linux Kernel. The main features of Strongswan are given below.
|
||||
|
||||
- 509 certificates or pre-shared keys based Authentication
|
||||
- Support of IKEv1 and IKEv2 key exchange protocols
|
||||
- Optional built-in integrity and crypto tests for plugins and libraries
|
||||
- Support of elliptic curve DH groups and ECDSA certificates
|
||||
- Storage of RSA private keys and certificates on a smartcard.
|
||||
|
||||
It can be used in the client / server (road warrior) and gateway to gateway scenarios.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Install ###
|
||||
|
||||
Almost all Linux distro’s, supports the binary package of Strongswan. In this tutorial, we will install the strongswan from binary package and also the compilation of strongswan source code with desirable features.
|
||||
|
||||
### Using binary package ###
|
||||
|
||||
Strongswan can be installed using following command on Ubuntu 14.04 LTS .
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo aptitude install strongswan
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The global configuration (strongswan.conf) file and ipsec configuration (ipsec.conf/ipsec.secrets) files of strongswan are under /etc/ directory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pre-requisite for strongswan source compilation & installation ###
|
||||
|
||||
- GMP (Mathematical/Precision Library used by strongswan)
|
||||
- OpenSSL (Crypto Algorithms from this library)
|
||||
- PKCS (1,7,8,11,12)(Certificate encoding and smart card integration with Strongswan )
|
||||
|
||||
#### Procedure ####
|
||||
|
||||
**1)** Go to /usr/src/ directory using following command in the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
$cd /usr/src
|
||||
|
||||
**2)** Download the source code from strongswan site suing following command
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo wget http://download.strongswan.org/strongswan-5.2.1.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
(strongswan-5.2.1.tar.gz is the latest version.)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**3)** Extract the downloaded software and go inside it using following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo tar –xvzf strongswan-5.2.1.tar.gz; cd strongswan-5.2.1
|
||||
|
||||
**4)** Configure the strongswan as per desired options using configure command.
|
||||
|
||||
./configure --prefix=/usr/local -–enable-pkcs11 -–enable-openssl
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If GMP library is not installed, then configure script will generate following error.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, first of all, install the GMP library using following command and then run the configure script.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
However, if GMP is already installed and still above error exists then create soft link of libgmp.so library at /usr/lib , /lib/, /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ paths in Ubuntu using following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ln -s /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgmp.so.10.1.3 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgmp.so
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After the creation of libgmp.so softlink, again run the ./configure script and it may find the gmp library. However, it may generate another error of gmp header file which is shown the following figure.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Install the libgmp-dev package using following command for the solution of above error.
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo aptitude install libgmp-dev
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After installation of development package of gmp library, again run the configure script and if it does not produce any error, then the following output will be displayed.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Type the following commands for the compilation and installation of strongswan.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo make ; sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
After the installation of strongswan , the Global configuration (strongswan.conf) and ipsec policy/secret configuration files (ipsec.conf/ipsec.secretes) are placed in **/usr/local/etc** directory.
|
||||
|
||||
Strongswan can be used as tunnel or transport mode depends on our security need. It provides well known site-2-site and road warrior VPNs. It can be use easily with Cisco,Juniper devices.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/security/install-strongswan/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[nido][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/naveeda/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.strongswan.org/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user