mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
commit
e36fd2691c
@ -1,47 +1,46 @@
|
||||
使用去重加密工具来备份
|
||||
使用这些去重加密工具来备份你的数据
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在体积和价值方面,数据都在增长。快速而可靠地备份和恢复数据正变得越来越重要。社会已经适应了技术的广泛使用,并懂得了如何依靠电脑和移动设备,但很少有人能够处理丢失重要数据的现实。在遭受数据损失的公司中,30% 的公司将在一年内损失一半市值,70% 的公司将在五年内停止交易。这更加凸显了数据的价值。
|
||||
|
||||
随着数据在体积上的增长,提高存储利用率尤为重要。In Computing(注:这里不知如何翻译),数据去重是一种特别的数据压缩技术,因为它可以消除重复数据的拷贝,所以这个技术可以提高存储利用率。
|
||||
无论是体积还是价值,数据都在不断增长。快速而可靠地备份和恢复数据正变得越来越重要。社会已经适应了技术的广泛使用,并懂得了如何依靠电脑和移动设备,但很少有人能够面对丢失重要数据的现实。在遭受数据损失的公司中,30% 的公司将在一年内损失一半市值,70% 的公司将在五年内停止交易。这更加凸显了数据的价值。
|
||||
|
||||
数据并不仅仅只有其创造者感兴趣。政府、竞争者、犯罪分子、偷窥者可能都热衷于获取你的数据。他们或许想偷取你的数据,从你那里进行敲诈,或看你正在做什么。对于保护你的数据,加密是非常必要的。
|
||||
随着数据在体积上的增长,提高存储利用率尤为重要。从计算机的角度说,数据去重是一种特别的数据压缩技术,因为它可以消除重复数据的拷贝,所以这个技术可以提高存储利用率。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,解决方法是我们需要一个去重加密备份软件。
|
||||
数据并不仅仅只有其创造者感兴趣。政府、竞争者、犯罪分子、偷窥者可能都热衷于获取你的数据。他们或许想偷取你的数据,从你那里进行敲诈,或看你正在做什么。因此,对于保护你的数据,加密是非常必要的。
|
||||
|
||||
对于所有的用户而言,做文件备份是一件非常必要的事,至今为止许多用户还没有采取足够的措施来保护他们的数据。一台电脑不论是工作在一个合作的环境中,还是供私人使用,机器的硬盘可能在没有任何警告的情况下挂掉。另外,有些数据丢失可能是人为的错误所引发的。如果没有做经常性的备份,数据也可能不可避免地失去掉,即使请了专业的数据恢复公司来帮忙。
|
||||
所以,解决方法是我们需要一个可以去重的加密备份软件。
|
||||
|
||||
对于所有的用户而言,做文件备份是一件非常必要的事,至今为止许多用户还没有采取足够的措施来保护他们的数据。一台电脑不论是工作在一个合作的环境中,还是供私人使用,机器的硬盘可能在没有任何警告的情况下挂掉。另外,有些数据丢失可能是人为的错误所引发的。如果没有做经常性的备份,数据也可能不可避免地丢失,即使请了专业的数据恢复公司来帮忙。
|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章将对 6 个去重加密备份工具进行简要的介绍。
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Attic ###
|
||||
|
||||
Attic 是一个可用于去重、加密,验证完整性的用 Python 写的压缩备份程序。Attic 的主要目标是提供一个高效且安全的方式来备份数据。Attic 使用的数据去重技术使得它适用于每日备份,因为只需存储改变的数据。
|
||||
Attic 是一个可用于去重、加密,验证完整性的压缩备份程序,它是用 Python 写的。Attic 的主要目标是提供一个高效且安全的方式来备份数据。Attic 使用的数据去重技术使得它适用于每日备份,因为只需存储改变的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
其特点有:
|
||||
|
||||
- 易用
|
||||
- 可高效利用存储空间,通过检查冗余的数据,数据块大小的去重被用来减少存储所用的空间
|
||||
- 可选的数据加密,使用 256 位的 AES 加密算法。数据的完整性和可靠性使用 HMAC-SHA256 来检查
|
||||
- 可高效利用存储空间,通过检查冗余的数据,对可变块大小的去重可以减少存储所用的空间
|
||||
- 可选的数据加密,使用 256 位的 AES 加密算法。数据的完整性和可靠性使用 HMAC-SHA256 来校验
|
||||
- 使用 SDSH 来进行离线备份
|
||||
- 备份可作为文件系统来挂载
|
||||
|
||||
网站: [attic-backup.org][1]
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Borg ###
|
||||
|
||||
Borg 是 Attic 的分支。它是一个安全的开源备份程序,被设计用来高效地存储那些新的或修改过的数据。
|
||||
Borg 是 Attic 的一个分支。它是一个安全的开源备份程序,被设计用来高效地存储那些新的或修改过的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
Borg 的主要目标是提供一个高效、安全的方式来存储数据。Borg 使用的数据去重技术使得它适用于每日备份,因为只需存储改变的数据。认证加密使得它适用于不完全可信的目标的存储。
|
||||
Borg 的主要目标是提供一个高效、安全的方式来存储数据。Borg 使用的数据去重技术使得它适用于每日备份,因为只需存储改变的数据。认证加密使得它适用于存储在不完全可信的位置。
|
||||
|
||||
Borg 由 Python 写成。Borg 于 2015 年 5 月被创造出来,为了回应让新的代码或重大的改变带入 Attic 的困难。
|
||||
Borg 由 Python 写成。Borg 于 2015 年 5 月被创造出来,是为了解决让新的代码或重大的改变带入 Attic 的困难。
|
||||
|
||||
其特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 易用
|
||||
- 可高效利用存储空间,通过检查冗余的数据,数据块大小的去重被用来减少存储所用的空间
|
||||
- 可选的数据加密,使用 256 位的 AES 加密算法。数据的完整性和可靠性使用 HMAC-SHA256 来检查
|
||||
- 可高效利用存储空间,通过检查冗余的数据,对可变块大小的去重被用来减少存储所用的空间
|
||||
- 可选的数据加密,使用 256 位的 AES 加密算法。数据的完整性和可靠性使用 HMAC-SHA256 来校验
|
||||
- 使用 SDSH 来进行离线备份
|
||||
- 备份可作为文件系统来挂载
|
||||
|
||||
@ -49,36 +48,32 @@ Borg 与 Attic 不兼容。
|
||||
|
||||
网站: [borgbackup.github.io/borgbackup][2]
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Obnam ###
|
||||
|
||||
Obnam (OBligatory NAMe) 是一个易用、安全的基于 Python 的备份程序。备份可被存储在本地硬盘或通过 SSH SFTP 协议存储到网上。若使用了备份服务器,它并不需要任何特殊的软件,只需要使用 SSH 即可。
|
||||
|
||||
Obnam 通过将数据数据分成数据块,并单独存储它们来达到去重的目的,每次通过增量备份来生成备份,每次备份的生成就像是一次新的快照,但事实上是真正的增量备份。Obnam 由 Lars Wirzenius 开发。
|
||||
Obnam 通过将数据分成数据块,并单独存储它们来达到去重的目的,每次通过增量备份来生成备份,每次备份的生成就像是一次新的快照,但事实上是真正的增量备份。Obnam 由 Lars Wirzenius 开发。
|
||||
|
||||
其特点有:
|
||||
|
||||
- 易用
|
||||
- 快照备份
|
||||
- 数据去重,跨文件,生成备份
|
||||
- 数据去重,跨文件,然后生成备份
|
||||
- 可使用 GnuPG 来加密备份
|
||||
- 向一个单独的仓库中备份多个客户端的数据
|
||||
- 备份检查点 (创建一个保存点,以每 100MB 或其他容量)
|
||||
- 包含多个选项来调整性能,包括调整 lru-size 或 upload-queue-size
|
||||
- 支持 MD5 校验和算法来识别重复的数据块
|
||||
- 支持 MD5 校验算法来识别重复的数据块
|
||||
- 通过 SFTP 将备份存储到一个服务器上
|
||||
- 同时支持 push(即在客户端上运行) 和 pull(即在服务器上运行)
|
||||
|
||||
网站: [obnam.org][3]
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Duplicity ###
|
||||
|
||||
Duplicity 持续地以 tar 文件格式备份文件和目录,并使用 GnuPG 来进行加密,同时将它们上传到远程(或本地)的文件服务器上。它可以使用 ssh/scp, 本地文件获取, rsync, ftp, 和 Amazon S3 等来传递数据。
|
||||
Duplicity 以 tar 文件格式增量备份文件和目录,并使用 GnuPG 来进行加密,同时将它们上传到远程(或本地)的文件服务器上。它可以使用 ssh/scp、本地文件获取、rsync、 ftp 和 Amazon S3 等来传递数据。
|
||||
|
||||
因为 duplicity 使用了 librsync, 增加的存档高效地利用了存储空间,且只记录自从上次备份依赖改变的那部分文件。由于该软件使用 GnuPG 来机密或对这些归档文件进行进行签名,这使得它们免于服务器的监视或修改。
|
||||
因为 duplicity 使用了 librsync, 增量存档可以高效地利用存储空间,且只记录自从上次备份依赖改变的那部分文件。由于该软件使用 GnuPG 来加密或对这些归档文件进行进行签名,这使得它们免于服务器的监视或修改。
|
||||
|
||||
当前 duplicity 支持备份删除的文件,全部的 unix 权限,目录,符号链接, fifo 等。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -101,39 +96,36 @@ duplicity 软件包还包含有 rdiffdir 工具。 Rdiffdir 是 librsync 的 rdi
|
||||
|
||||
网站: [duplicity.nongnu.org][4]
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### ZBackup ###
|
||||
|
||||
ZBackup 是一个通用的全局去重备份工具。
|
||||
|
||||
其特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 存储数据的并行 LZMA 或 LZO 压缩,在一个仓库中,你还可以混合使用 LZMA 和 LZO
|
||||
- 对存储数据并行进行 LZMA 或 LZO 压缩,在一个仓库中,你还可以混合使用 LZMA 和 LZO
|
||||
- 内置对存储数据的 AES 加密
|
||||
- 可选择地删除旧的备份数据
|
||||
- 能够删除旧的备份数据
|
||||
- 可以使用 64 位的滚动哈希算法,使得文件冲突的数量几乎为零
|
||||
- Repository consists of immutable files. No existing files are ever modified ====
|
||||
- 仓库中存储的文件是不可修改的,已备份的文件不会被修改。
|
||||
- 用 C++ 写成,只需少量的库文件依赖
|
||||
- 在生成环境中可以安全使用
|
||||
- 可以在不同仓库中进行数据交换而不必再进行压缩
|
||||
- 可以使用 64 位改进型 Rabin-Karp 滚动哈希算法
|
||||
- 使用 64 位改进型 Rabin-Karp 滚动哈希算法
|
||||
|
||||
网站: [zbackup.org][5]
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### bup ###
|
||||
|
||||
bup 是一个用 Python 写的备份程序,其名称是 "backup" 的缩写。在 git packfile 文件的基础上, bup 提供了一个高效的方式来备份一个系统,提供快速的增量备份和全局去重(在文件中或文件里,甚至包括虚拟机镜像)。
|
||||
bup 是一个用 Python 写的备份程序,其名称是 "backup" 的缩写。基于 git packfile 文件格式, bup 提供了一个高效的方式来备份一个系统,提供快速的增量备份和全局去重(在文件中或文件里,甚至包括虚拟机镜像)。
|
||||
|
||||
bup 在 LGPL 版本 2 协议下发行。
|
||||
|
||||
其特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 全局去重 (在文件中或文件里,甚至包括虚拟机镜像)
|
||||
- 全局去重 (在文件之间或文件内部,甚至包括虚拟机镜像)
|
||||
- 使用一个滚动的校验和算法(类似于 rsync) 来将大文件分为多个数据块
|
||||
- 使用来自 git 的 packfile 格式
|
||||
- 使用来自 git 的 packfile 文件格式
|
||||
- 直接写入 packfile 文件,以此提供快速的增量备份
|
||||
- 可以使用 "par2" 冗余来恢复冲突的备份
|
||||
- 可以作为一个 FUSE 文件系统来挂载你的 bup 仓库
|
||||
@ -145,7 +137,7 @@ bup 在 LGPL 版本 2 协议下发行。
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20150628060000607/BackupTools.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
|
||||
alim0x translating
|
||||
|
||||
The history of Android
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
The Honeycomb app lineup lost a ton of apps. This also shows the notification panel and the new quick settings.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
The default app icons were slashed from 32 to 25, and two of those were third-party games. Since Honeycomb was not for phones and Google wanted the default apps to all be tablet-optimized, a lot of apps didn't make the cut. We lost the Amazon MP3 store, Car Home, Facebook, Google Goggles, Messaging, News and Weather, Phone, Twitter, Google Voice, and Voice Dialer. Google was quietly building a music service that would launch soon, so the Amazon MP3 store needed to go anyway. Car Home, Messaging, and Phone made little sense on a non-phone device, Facebook and Twitter still don't have tablet Android apps, and Goggles, News and Weather, and Voice Dialer were barely supported applications that most people wouldn't miss.
|
||||
|
||||
Almost every app icon was new. Just like the switch from the G1 to the Motorola Droid, the biggest impetus for change was probably the bump in resolution. The Nexus S had an 800×480 display, and Gingerbread came with art assets to match. The Xoom used a whopping 1280×800 10-inch display, which meant nearly every piece of art had to go. But again, this time a real designer was in charge, and things were a lot more cohesive. Honeycomb marked the switch from a vertically scrolling app drawer to paginated horizontal drawer. This change made sense on a horizontal device, but on phones it was still much faster to navigate the app drawer with a flingable, vertical list.
|
||||
|
||||
The second Honeycomb screenshot shows the new notification panel. The gray and black Gingerbread design was tossed for another straight-black panel that gave off a blue glow. At the top was a block showing the time, date, connection status, battery, and a shortcut to the notification quick settings, and below that were the actual notifications. Non-permanent notifications could now be dismissed by tapping on an "X" on the right side of the notification. Honeycomb was the first version to enable controls within a notification. The first (and at the launch of Honeycomb, only) app to take advantage of this was the new Google Music app, which placed previous, play/pause, and next buttons in its notification. These new controls could be accessed from any app and made controlling music a breeze.
|
||||
|
||||
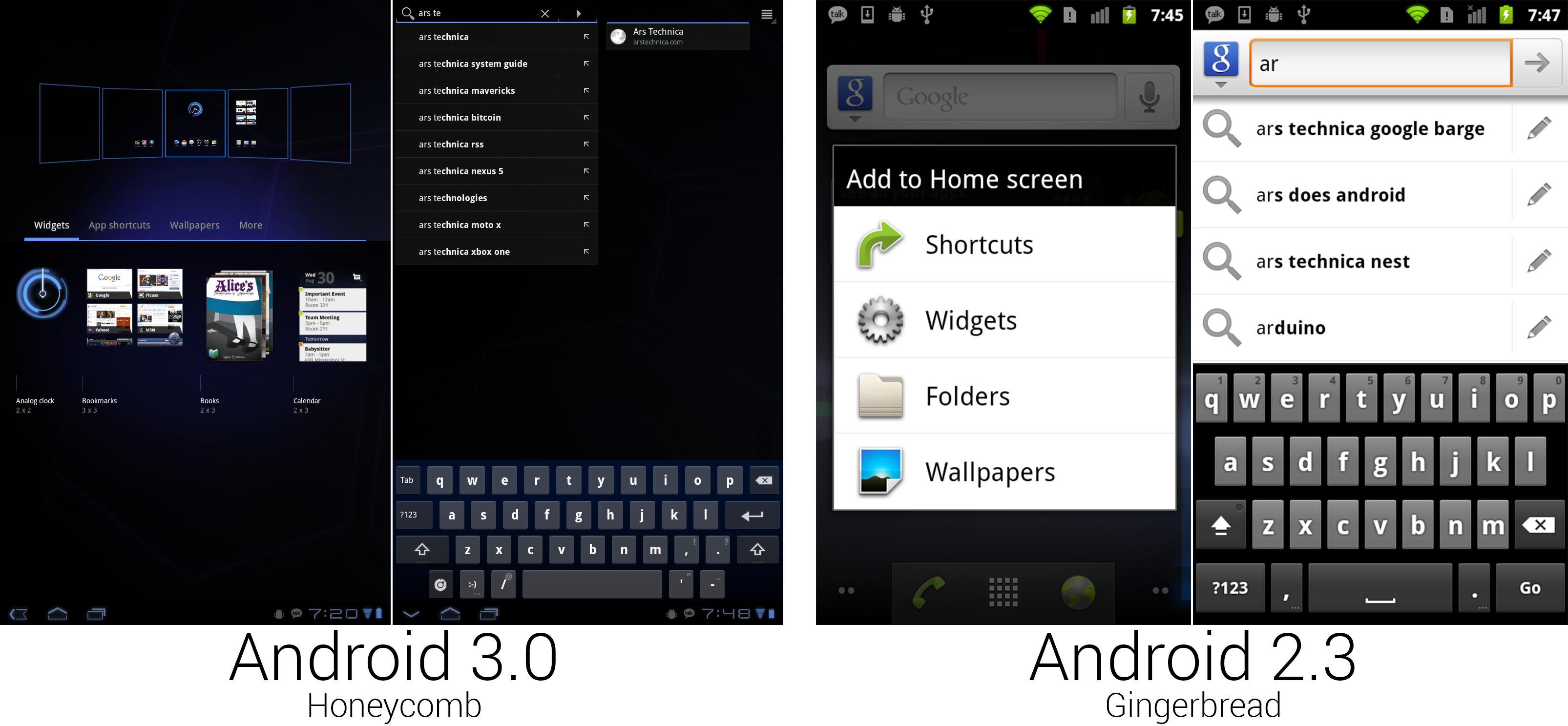
|
||||
"Add to home screen" was given a zoomed-out interface for easy organizing. The search interface split auto suggest and universal search into different panes.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
Pressing the plus button in the top right corner of the home screen or long pressing on the background would open the new home screen configuration interface. Honeycomb showed a zoomed-out view of all the home screens along the top of the screen, and it filled the bottom half of the screen with a tabbed drawer containing widgets and shortcuts. Items could be dragged out of the bottom drawer and into any of the five home screens. Gingerbread would just show a list of text, but Honeycomb showed full thumbnail previews of the widgets. This gave you a much better idea of what a widget would look like instead of an app-name-only description like "calendar."
|
||||
|
||||
The larger screen of the Motorola Xoom allowed the keyboard to take on a more PC-style layout, with keys like backspace, enter, shift, and tab put in the traditional locations. The keyboard took on a blueish tint and gained even more spacing between the keys. Google also added a dedicated smiley-face button. :-)
|
||||
|
||||
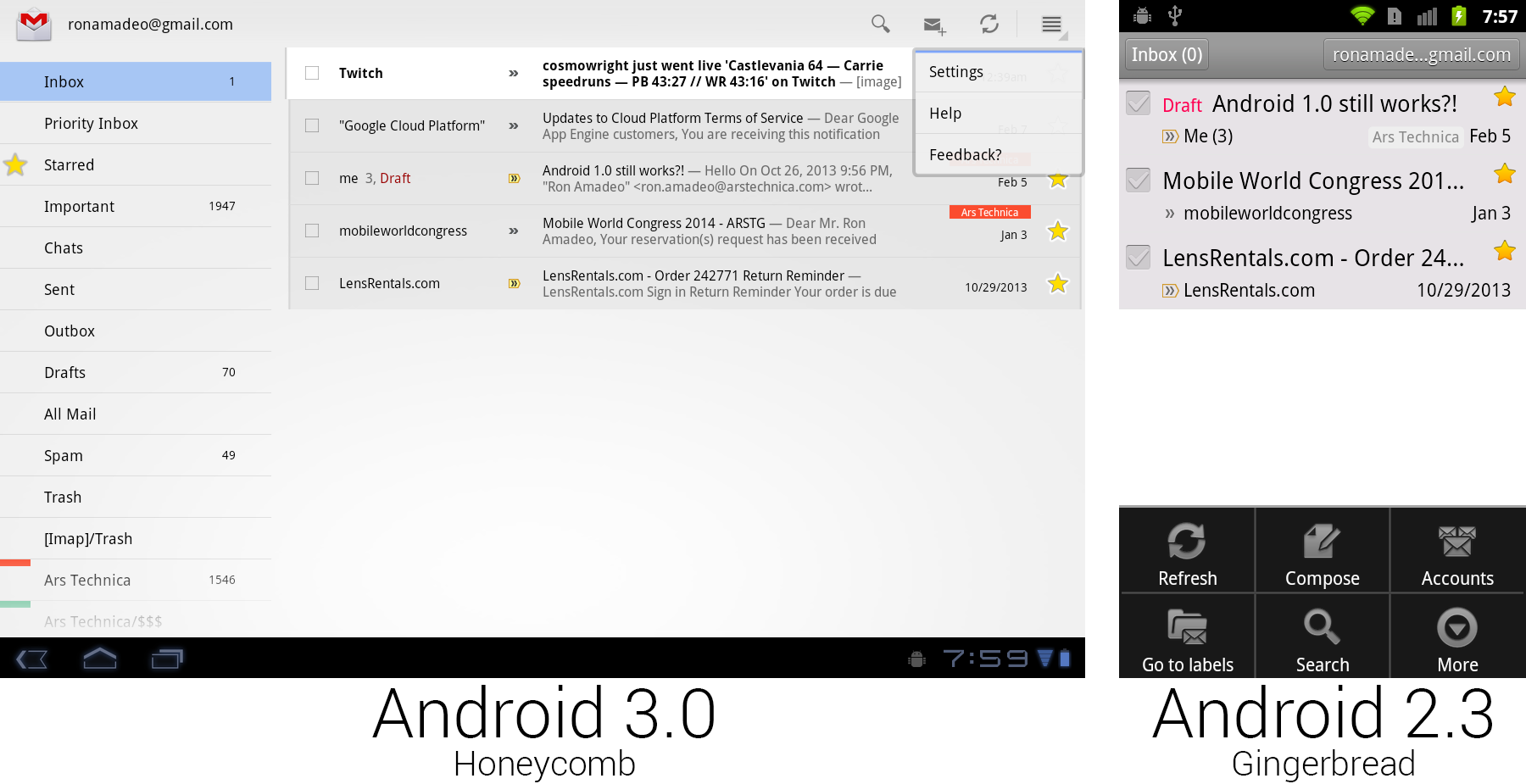
|
||||
Gmail on Honeycomb versus Gmail on Gingerbread with the menu open. Buttons were placed on the main screen for easier discovery.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
Gmail demonstrated all the new UI concepts in Honeycomb. Android 3.0 did away with hiding all the controls behind a menu button. There was now a strip of icons along the top of the screen called the Action Bar, which lifted many useful controls to the main screen where users could see them. Gmail showed buttons for search, compose, and refresh, and it put less useful controls like settings, help, and feedback in a dropdown called the "overflow" button. Tapping checkboxes or selecting text would cause the entire action bar to change to icons relating to those actions—for instance, selecting text would bring up cut, copy, and select all buttons.
|
||||
|
||||
The app icon displayed in the top left corner doubled as a navigation button called "Up." While "Back" worked similarly to a browser back button, navigating to previously visited screens, "Up" would navigate up the app hierarchy. For instance, if you were in the Android Market, pressed the "Email developer" button, and Gmail opened, "Back" would take you back to the Android Market, but "Up" would take you to the Gmail inbox. "Back" might close the current app, but "Up" never would. Apps could control the "Back" button, and they usually reprogrammed it to replicate the "Up" functionality. In practice, there was rarely a difference between the two buttons.
|
||||
|
||||
Honeycomb also introduced the "Fragments" API, which allowed developers to use a single app for tablets and phones. A "Fragment" was a single pane of a user interface. In the Gmail picture above, the left folder list was one fragment and the inbox was another fragment. Phones would show one fragment per screen, and tablets could show two side-by-side. The developer defined the look of individual fragments, and Android would decide how they should be displayed based on the current device.
|
||||
|
||||
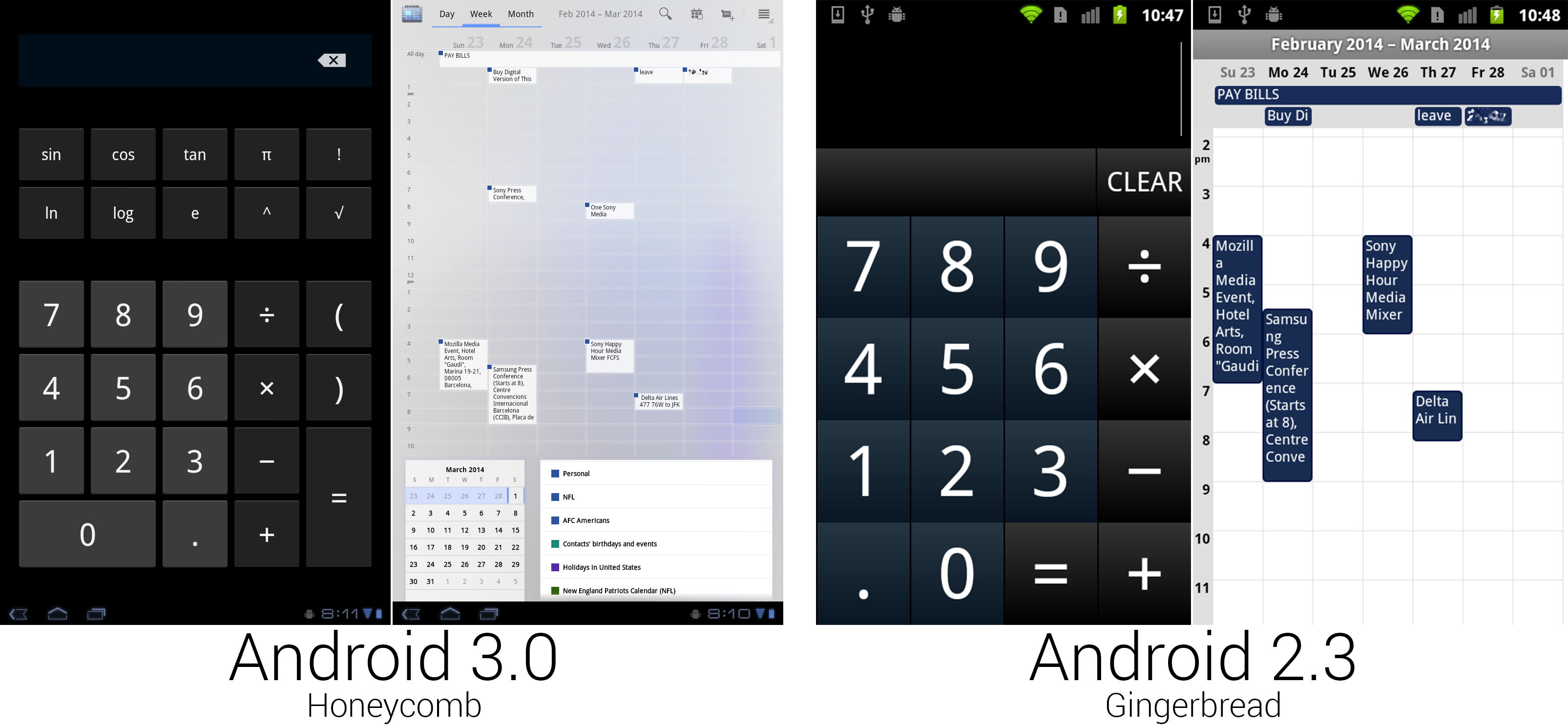
|
||||
The calculator finally used regular Android buttons, but someone spilled blue ink on the calendar.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
For the first time in Android's history, the calculator got a makeover with non-custom buttons, so it actually looked like part of the OS. The bigger screen made room for more buttons, enough that all the calculator functionality could fit on one screen. The calendar greatly benefited from the extra space, gaining much more room for appointment text and controls. The action bar at the top of the screen held buttons to switch views, along with showing the current time span and common controls. Appointment blocks switched to a white background with the calendar corner only showing in the top right corner. At the bottom (or side, in horizontal view) were boxes showing the month calendar and a list of displayed calendars.
|
||||
|
||||
The scale of the calendar could be adjusted, too. By performing a pinch zoom gesture, portrait week and day views could show between five and 19 hours of appointments on a single screen. The background of the calendar was made up of an uneven blue splotch, which didn't look particularly great and was tossed on later versions.
|
||||
|
||||
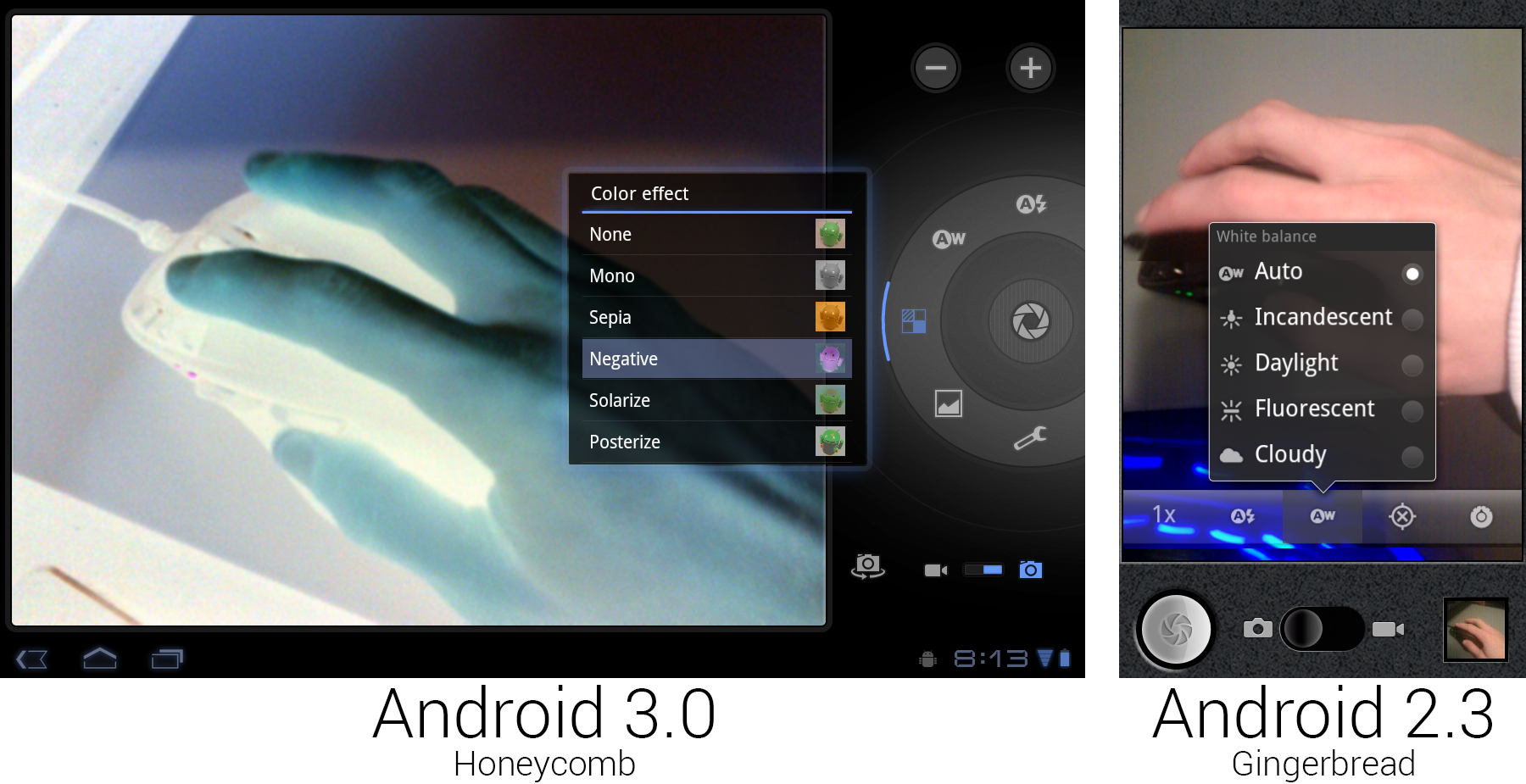
|
||||
The new camera interface, showing off the live "Negative" effect.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
The giant 10-inch Xoom tablet did have a camera, which meant that it also had a camera app. The Tron redesign finally got rid of the old faux-leather look that Google came up with in Android 1.6. The controls were laid out in a circle around the shutter button, bringing to mind the circular controls and dials on a real camera. The Cooliris-derived speech bubble popups were changed to glowing, semi-transparent black boxes. The Honeycomb screenshot shows the new "color effect" functionality, which applied a filter to the viewfinder in real time. Unlike the Gingerbread camera app, this didn't support a portrait orientation—it was limited to landscape only. Taking a portrait picture with a 10-inch tablet doesn't make much sense, but then neither does taking a landscape one.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
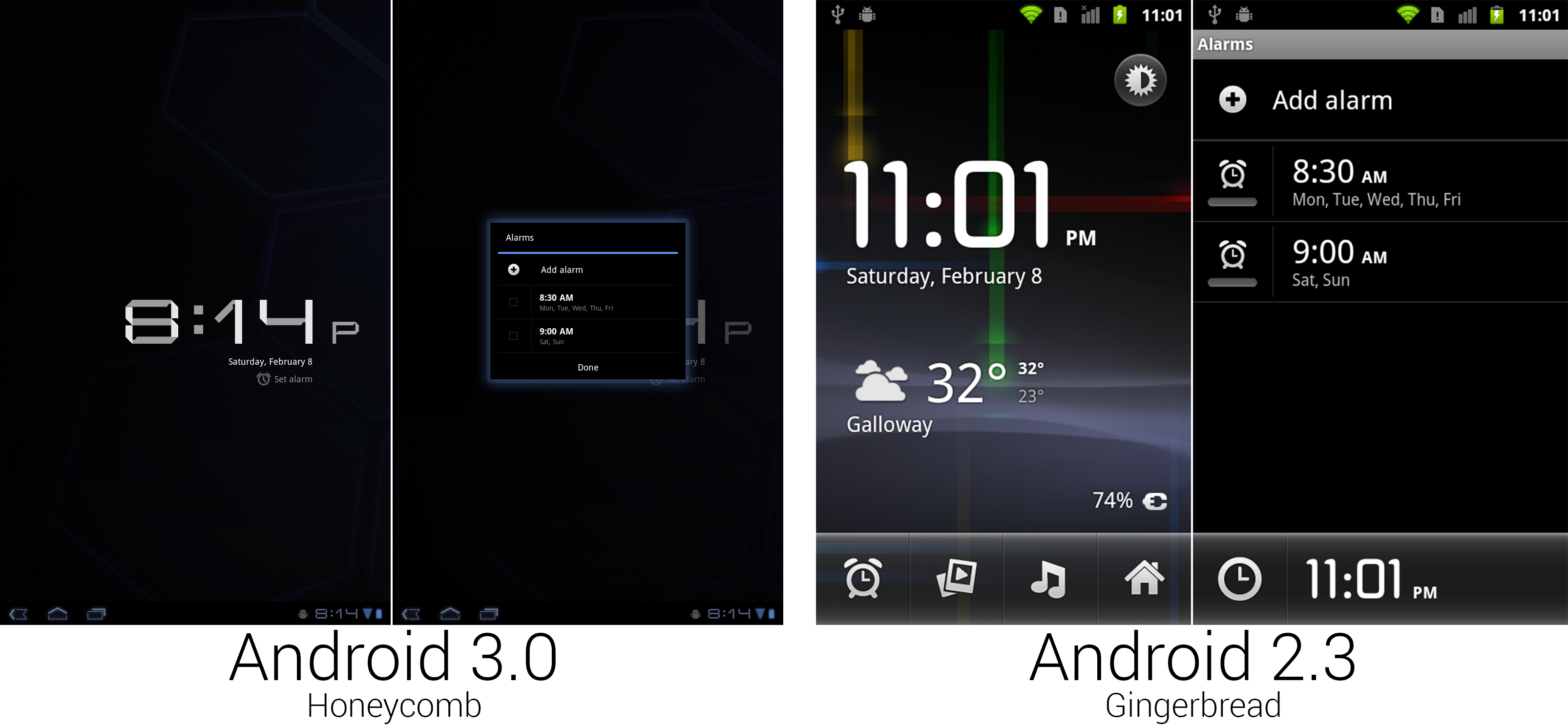
The clock app didn't get quite as much love as other areas. Google just threw it into a tiny box and called it a day.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
Tons of functionality went out the door when it came time to remake the clock app. The entire "Deskclock" concept was kicked out the door, replaced with a simple large display of the time against a plain black background. The ability to launch other apps and view the weather was gone, as was the ability of the clock app to use your wallpaper. Google sometimes gave up when it came time to design a tablet-sized interface, like here, where it just threw the alarm interface into a tiny, centered dialog box.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
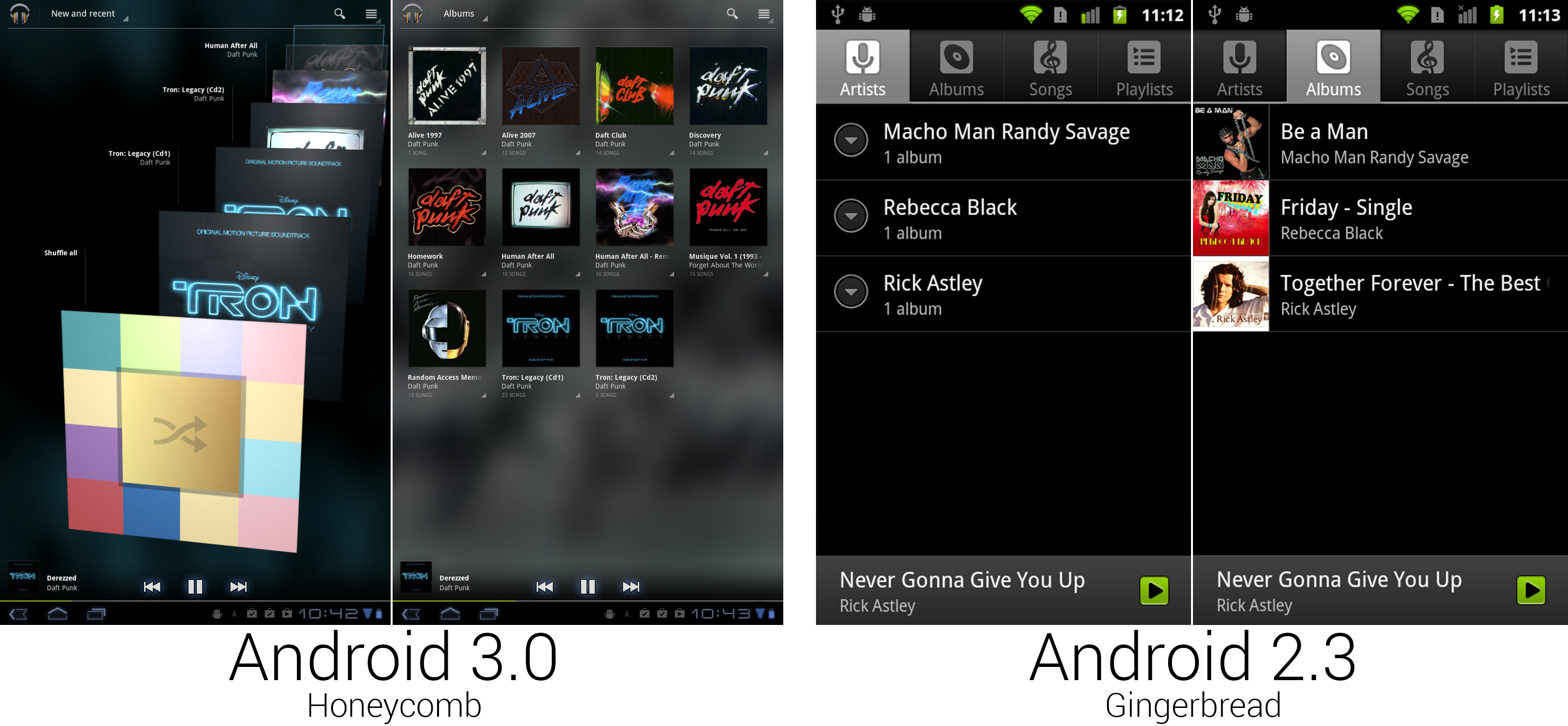
The Music app finally got the ground-up redesign it has needed forever.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
While music received a few minor additions during its life, this was really the first time since Android 0.9 that it received serious attention. The highlight of the redesign was a don't-call-it-coverflow scrolling 3D album art view, called "New and Recent." Instead of the tabs added in Android 2.1, navigation was handled by a Dropbox box in the Action Bar. While "New and Recent" had 3D scrolling album art, "Albums" used a flat grid of albums thumbnails. The other sections had totally different designs, too. "Songs" used a vertically scrolling list of text, and "Playlists," "Genres," and "Artists" used stacked album art.
|
||||
|
||||
In nearly every view, every single item had its own individual menu, usually little arrows in the bottom right corner of an item. For now, these would only show "Play" and "add to Playlist," but this version of Google Music was built for the future. Google was launching a Music service soon, and those individual menus would be needed for things like viewing other content from that artist in the Music Store and managing the cloud storage versus local storage options.
|
||||
|
||||
Just like the Cooliris Gallery in Android 2.1, Google Music would blow up one of your thumbnails and use it as a background. The bottom "Now Playing" bar now displayed the album art, playback controls, and a song progress bar.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
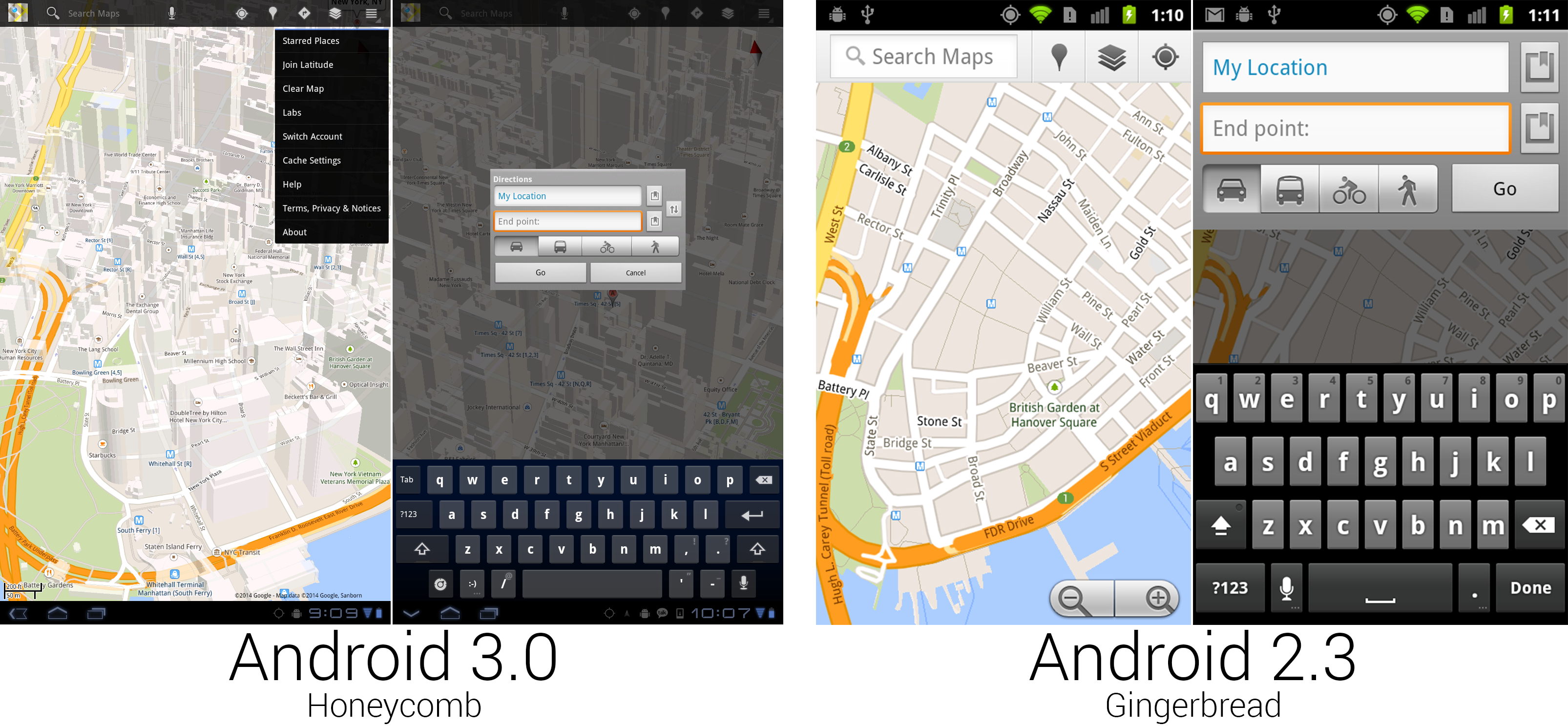
Some of the new Google Maps was really nice, and some of it was from Android 1.5.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
Google Maps received another redesign for the big screen. This one would stick around for a while and used a semi-transparent black action bar for all the controls. Search was again the primary function, given the first spot in the action bar, but this time it was an actual search bar you could type in, instead of a search bar-shaped button that launched a completely different interface. Google finally gave up on dedicating screen space to actual zoom buttons, relying on only gestures to control the map view. While the feature has since been ported to all old versions of Maps, Honeycomb was the first version to feature 3D building outlines on the map. Dragging two fingers down on the map would "tilt" the map view and show the sides of the buildings. You could freely rotate and the buildings would adjust, too.
|
||||
|
||||
Not every part of Maps was redesigned. Navigation was untouched from Gingerbread, and some core parts of the interface, like directions, were pulled straight from Android 1.6 and centered in a tiny box.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
|
||||
|
||||
[@RonAmadeo][t]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/17/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
|
||||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
alim0x translating
|
||||
|
||||
The history of Android
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
@ -80,4 +82,4 @@ via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-histor
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://techcrunch.com/2014/03/03/gartner-195m-tablets-sold-in-2013-android-grabs-top-spot-from-ipad-with-62-share/
|
||||
[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
|
||||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
|
||||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
Translating by dingdongnigetou
|
||||
|
||||
Install Plex Media Server On Ubuntu / CentOS 7.1 / Fedora 22
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In this article we will show you how easily you can setup Plex Home Media Server on major Linux distributions with their latest releases. After its successful installation of Plex you will be able to use your centralized home media playback system that streams its media to many Plex player Apps and the Plex Home will allows you to setup your environment by adding your devices and to setup a group of users that all can use Plex Together. So let’s start its installation first on Ubuntu 15.04.
|
||||
@ -188,4 +190,4 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/tools/install-plex-media-server-ubuntu-centos-7-1-fedor
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/kashifs/
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/kashifs/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
translating wi-cuckoo
|
||||
How to monitor NGINX with Datadog - Part 3
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,188 +0,0 @@
|
||||
zpl1025
|
||||
Howto Configure FTP Server with Proftpd on Fedora 22
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In this article, we'll learn about setting up an FTP server with Proftpd running Fedora 22 in our machine or server. [ProFTPD][1] is a free and open source FTP daemon software licensed under GPL. It is among most popular FTP server among machines running Linux. Its primary design aims to have an FTP server with many advanced features and provisioning users for more configuration options for easy customization. It includes a number of configuration options that are still not available with many other FTP daemons. It was initially developed by the developers as an alternative with better security and configuration to wu-ftpd server. An FTP server is a program that allows us to upload or download files and folders from a remote server where it is setup using an FTP client. Some of the features of ProFTPD daemon are as follows, you can check more features on [http://www.proftpd.org/features.html][2] .
|
||||
|
||||
- It includes a per directory ".ftpaccess" access configuration similar to Apache's ".htaccess"
|
||||
- It features multiple virtual FTP server with multiple users login and anonymous FTP services.
|
||||
- It can be run either as a stand-alone server or from inetd/xinetd.
|
||||
- Its ownership, file/folder attributes and file/folder permissions are UNIX-based.
|
||||
- It can be run as standalone mode in order to protect the system from damage that can be caused from root access.
|
||||
- The modular design of it makes it easily extensible with modules like LDAP servers, SSL/TLS encryption, RADIUS support, etc.
|
||||
- IPv6 support is also included in the ProFTPD server.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some easy to perform steps on how we can setup an FTP Server with ProFTPD in Fedora 22 operating system.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Installing ProFTPD ###
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, we'll wanna install Proftpd server in our box running Fedora 22 as its operating system. As yum package manager has been depreciated, we'll use the latest and greatest built package manager called dnf. DNF is pretty easy to use and highly user friendly package manager available in Fedora 22. We'll simply use it to install proftpd daemon server. To do so, we'll need to run the following command in a terminal or a console in sudo mode.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dnf -y install proftpd proftpd-utils
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Configuring ProFTPD ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll make changes to some configurations in the daemon. To configure the daemon, we will need to edit /etc/proftpd.conf with a text editor. The main configuration file of the ProFTPD daemon is **/etc/proftpd.conf** so, any changes made to this file will affect the FTP server. Here, are some changes we make in this initial step.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/proftpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Next, after we open the file using a text editor, we'll wanna make changes to the ServerName and ServerAdmin as hostname and email address respectively. Here's what we have made changes to those configs.
|
||||
|
||||
ServerName "ftp.linoxide.com"
|
||||
ServerAdmin arun@linoxide.com
|
||||
|
||||
After that, we'll wanna the following lines into the configuration file so that it logs access & auth into its specified log files.
|
||||
|
||||
ExtendedLog /var/log/proftpd/access.log WRITE,READ default
|
||||
ExtendedLog /var/log/proftpd/auth.log AUTH auth
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Adding FTP users ###
|
||||
|
||||
After configure the basics of the configuration file, we'll surely wanna create an FTP user which is rooted at a specific directory we want. The current users that we use to login into our machine are automatically enabled with the FTP service, we can even use it to login into the FTP server. But, in this tutorial, we'll gonna create a new user with a specified home directory to the ftp server.
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we'll create a new group named ftpgroup.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo groupadd ftpgroup
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll gonna add a new user arunftp into the group with home directory specified as /ftp-dir/
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo useradd -G ftpgroup arunftp -s /sbin/nologin -d /ftp-dir/
|
||||
|
||||
After the user has been created and added to the group, we'll wanna set a password to the user arunftp.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo passwd arunftp
|
||||
|
||||
Changing password for user arunftp.
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
Retype new password:
|
||||
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll set read and write permission of the home directory by the ftp users by executing the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo setsebool -P allow_ftpd_full_access=1
|
||||
$ sudo setsebool -P ftp_home_dir=1
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll wanna make that directory and its contents unable to get removed or renamed by any other users.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chmod -R 1777 /ftp-dir/
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Enabling TLS Support ###
|
||||
|
||||
FTP is considered less secure in comparison to the latest encryption methods used these days as anybody sniffing the network card can read the data pass through FTP. So, we'll enable TLS Encryption support in our FTP server. To do so, we'll need to a edit /etc/proftpd.conf configuration file. Before that, we'll wanna backup our existing configuration file to make sure we can revert our configuration if any unexpected happens.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo cp /etc/proftpd.conf /etc/proftpd.conf.bak
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll wanna edit the configuration file using our favorite text editor.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/proftpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll wanna add the following lines just below line we configured in step 2 .
|
||||
|
||||
TLSEngine on
|
||||
TLSRequired on
|
||||
TLSProtocol SSLv23
|
||||
TLSLog /var/log/proftpd/tls.log
|
||||
TLSRSACertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/proftpd.pem
|
||||
TLSRSACertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/proftpd.pem
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After finishing up with the configuration, we'll wanna save and exit it.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we'll need to generate the SSL certificates inside **/etc/pki/tls/certs/** directory as proftpd.pem. To do so, first we'll need to install openssl in our Fedora 22 machine.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dnf install openssl
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll gonna generate the SSL certificate by running the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/pki/tls/certs/proftpd.pem -out /etc/pki/tls/certs/proftpd.pem
|
||||
|
||||
We'll be asked with some information that will be associated into the certificate. After completing the required information, it will generate a 2048 bit RSA private key.
|
||||
|
||||
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key
|
||||
...................+++
|
||||
...................+++
|
||||
writing new private key to '/etc/pki/tls/certs/proftpd.pem'
|
||||
-----
|
||||
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
|
||||
into your certificate request.
|
||||
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
|
||||
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
|
||||
For some fields there will be a default value,
|
||||
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
|
||||
-----
|
||||
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:NP
|
||||
State or Province Name (full name) []:Narayani
|
||||
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:Bharatpur
|
||||
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:Linoxide
|
||||
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:Linux Freedom
|
||||
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:ftp.linoxide.com
|
||||
Email Address []:arun@linoxide.com
|
||||
|
||||
After that, we'll gonna change the permission of the generated certificate file in order to secure it.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chmod 600 /etc/pki/tls/certs/proftpd.pem
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Allowing FTP through Firewall ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll need to allow the ftp ports that are usually blocked by the firewall by default. So, we'll allow ports and enable access to the ftp through firewall.
|
||||
|
||||
If **TLS/SSL Encryption is enabled** run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=1024-65534/tcp
|
||||
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=1024-65534/tcp --permanent
|
||||
|
||||
If **TLS/SSL Encryption is disabled** run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=ftp
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll need to reload the firewall configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Starting and Enabling ProFTPD ###
|
||||
|
||||
After everything is set, we'll finally start our ProFTPD and give it a try. To start the proftpd ftp daemon, we'll need to run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl start proftpd.service
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll wanna enable proftpd to start on every boot.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl enable proftpd.service
|
||||
|
||||
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/proftpd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/proftpd.service.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Logging into the FTP server ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, if everything was configured and done as expected, we must be able to connect to the ftp server and login with the details we set above. Here, we'll gonna configure our FTP client, filezilla with hostname as **server's ip or url**, Protocol as **FTP**, User as **arunftp** and password as the one we set in above step 3. If you followed step 4 for enabling TLS support, then we'll need to set the Encryption type as **Require explicit FTP over TLS** but if you didn't follow step 4 and don't wanna use TLS encryption then set the Encryption type as **Plain FTP**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To setup the above configuration, we'll need goto File which is under the Menu and then click on Site Manager in which we can click on new site then configure as illustrated above.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Then, we're asked to accept the SSL certificate, that can be done by click OK. After that, we are able to upload and download required files and folders from our FTP server.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, we have successfully installed and configured our Fedora 22 box with Proftpd FTP server. Proftpd is an awesome powerful highly configurable and extensible FTP daemon. The above tutorial illustrates us how we can configure a secure FTP server with TLS encryption. It is highly recommended to configure FTP server with TLS encryption as it enables SSL certificate security to the data transfer and login. Here, we haven't configured anonymous access to the FTP cause they are usually not recommended in a protected FTP system. An FTP access makes pretty easy for people to upload and download at good efficient performance. We can even change the ports for the users for additional security. So, if you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below so that we can improve or update our contents. Thank you ! Enjoy :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/configure-ftp-proftpd-fedora-22/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.proftpd.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.proftpd.org/features.html
|
||||
@ -1,59 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by GOLinux!
|
||||
How To Fix “The Update Information Is Outdated” In Ubuntu 14.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Seeing a red triangle in top panel in Ubuntu 14.04 that displays the following error?
|
||||
|
||||
> The update information is outdated. This may be caused by network problems or by a repository that is no longer available. Please update manually by selecting ‘Show updates’ from indicator menu, and watching for any failing repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
It looks something like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Instead of red triangle, there is a pink exclamation sign because I am using one of the [best Ubuntu icon themes][1], Numix. Coming back to the error, this is a common update problem which you might see every now and then. Now you might be wondering what is causing this update error.
|
||||
|
||||
### Reason for ‘update information is outdated’ error ###
|
||||
|
||||
The reason is pretty explanatory in the error description itself. It reads “this may be caused by network problems or by a repository that is no longer available”. So, either you upgraded your system and some repository or PPA is no longer supported or you are facing some similar issue.
|
||||
|
||||
While the error is self-explanatory, the action it suggests, “Please update manually by selecting ‘Show updates’ from the indicator menu, and watching for any failing repositories.”, doesn’t work properly. If you click on Show updates, all you’ll see is that the system is already updated.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Weird isn’t it? How will we find out what is failing where and why?
|
||||
|
||||
### Fix ‘update information is outdated’ ###
|
||||
|
||||
The ‘solution’ discussed here will work for Ubuntu versions be it Ubuntu 14.04, 12.04 or 14.04. All you need to do is to open a terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T) and use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
Wait for the command to finish and look at the result. Quick tip to add here, you can [add notifications in terminal][2] so that you are notified as soon as a long command finishes execution. In the last few lines at the end of the command, see what kind of error your system is facing. Yes, you’ll see an error for sure.
|
||||
|
||||
In my case, I saw the famous [GPG error: The following could not be verified][3] error. Apparently there is some problem with [Spotify installation in Ubuntu 15.04][4].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It is very much possible that you might see a different error instead of the GPG error like me. In that case, I suggest you to go through this article which I wrote to [fix various common update errors in Ubuntu][5].
|
||||
|
||||
I know few people, specially beginners have strong aversion to command line but if you are using Linux, you simply cannot avoid terminal. Moreover, it is not that scary a thing. Give it a try, you will feel accustomed to it soon enough.
|
||||
|
||||
I hope this quick tip helped you to fix the recurring “update information is outdated” in Ubuntu. Any questions or suggestions is welcomed.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-update-information-outdated-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/notification-terminal-command-completion-ubuntu/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-gpg-error-signatures-verified-ubuntu/
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/install-spotify-ubuntu-1504/
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/fix-update-errors-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by ictlyh
|
||||
Howto Interactively Perform Tasks with Docker using Kitematic
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In this article, we'll learn about the installating Kitematic in Windows Operating System and deploying a Hello World Nginx Web Server. Kitematic is a free and open source software which is a modern designed GUI software that allows us to interactively perform tasks with docker. Kitematic has a beautiful design and pretty good interface. It is pretty fast and easy to setup our containers out of the box without needing to enter commands for it, we can deploy our apps it in just a click with its GUI inteface. Kitematic has Docker Hub Intergration which allows us to search any required image, pull and deploy our apps with it. It also has a beautiful feature to switch to CUI mode simultaneously. Currently, it includes some features like automatically map ports, visually change environment variables, configuring volumes, streamline logs and many more.
|
||||
|
||||
So. here are the easy 3 steps on how we can install Kitematic and deploy Hello World Nginx Web Server in Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Download Kitematic ###
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, we'll need to download the latest release of Kitematic available for windows operating system from the github repository ie [https://github.com/kitematic/kitematic/releases][1] . Here, we download its executable EXE file using a download manager or a web browser. After we finish downloading, we'll need to double-click the executable application file.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After double clicking the application file, we'll be asked by a security issue we'll simply click OK as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Installing Kitematic ###
|
||||
|
||||
After the executable installer has been downloaded, we'll now gonna install Kitematic in our Windows Operating System. The installer will now begin to download and install the necessary dependencies virtual box and docker to run Kitematic. If you already virtualbox installed in your system, it will upgrade it to the latest version. The installer should finish in few minutes but that depends on how fast your internet and system is. If you don't have a virtual box installed already, it may ask you for installing the virtual box network driver. It is suggested to install that as it is useful for the virtual box networking.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After the required dependencies Docker and Virtual box are installed and are running, we'll be asked to login to the Docker Hub. If we don't have an account or don't wanna login now, we can click **SKIP FOR NOW** to continue further.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you don't have an account, you can simply click on Sign Up link in the App and create an account in Docker Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
After its done, our first interface of Kitematic App will load. Here, below is how it looks. We can search for the available docker images there as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Deploying Nginx Hello World Container ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, as our Kitematic has been successfully installed, we'll now go for the deployment of containers. To run a container, we can simply search for the image in the search area. Then click on Create to deploy the container. Here in this tutorial, we'll go for deploying a small Nginx Web Server having Hello World homepage. To do so, we'll search for Hello World Nginx in the search area. Then, after we see the container information, we'll click on Create to deploy the container.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once the download of the image has been completed, it will get deployed. We can see the logs of the commands fired by the Kitematic to deploy that container. We can also see the web page preview right from the Kitematic interface. Now, we can check our Hello World page from our web browser by clicking on the preview.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If we wanna switch to command line interface and manage docker with it, there is a button called Docker CLI which will open a Powershell were we can execute docker commands.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, if we wanna configure our container and perform stuffs like changing the container name, assigning environment variables, assign ports, configure container's storage and other advanced features, we can do that from Settings tab of the container.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Finally we've successfully installed Kitematic and deployed a hello world nginx web server in Windows Operating System. It is always recommended to download and install the latest release of Kitematic as many advanced features are to be embedded. As docker works in 64 bit platform, Kitematic is also currently built for 64-bit platform of operating system. It only works on the Windows 7 and greater versions of Windows. Here, in this tutorial, we deployed an Nginx web server like wise we can deploy any docker container from its image using Kitematic with few clicks only. Kitematic is already available for Mac OS X and Windows whereas a version for Linux is still under development and will be out very soon. If you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below so that we can improve or update our contents. Thank you ! Enjoy :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/interactively-docker-kitematic/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/kitematic/kitematic/releases
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
安卓编年史
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
蜂巢的应用列表少了很多应用。上图还展示了通知中心和新的快速设置。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo 供图
|
||||
|
||||
默认的应用图标从32个减少到了25个,其中还有两个是第三方的游戏。因为蜂巢不是为手机设计的,而且谷歌希望默认应用都是为平板优化的,很多应用因此没有成为默认应用。被去掉的应用有亚马逊 MP3 商店,Car Home,Facebook,Google Goggles,信息,新闻与天气,电话,Twitter,谷歌语音,以及语音拨号。谷歌正在悄悄打造的音乐服务将于不久后面世,所以亚马逊 MP3 商店需要为它让路。Car Home,信息以及电话对一部不是手机的设备来说没有多大意义,Facebook 和 Twitter还没有平板版应用,Goggles,新闻与天气以及语音拨号几乎没什么人注意,就算移除了大多数人也不会想念它们的。
|
||||
|
||||
几乎每个应用图标都是全新设计的。就像是从 G1 切换到摩托罗拉 Droid,变化的最大动力是分辨率的提高。Nexus S 有一块800×480分辨率的显示屏,姜饼重新设计了图标等资源来适应它。Xoom 巨大的1280×800 10英寸显示屏意味着几乎所有设计都要重做。但是再说一次,这次是有真正的设计师在负责,所有东西看起来更有整体性了。蜂巢的应用列表从纵向滚动变为了横向分页式。这个变化对横屏设备有意义,而对手机来说,查找一个应用还是纵向滚动列表比较快。
|
||||
|
||||
第二张蜂巢截图展示的是新通知中心。姜饼中的灰色和黑色设计已经被抛弃了,现在是黑色面板带蓝色光晕。上面一块显示着日期时间,连接状态,电量和打开快速设置的按钮,下面是实际的通知。非持续性通知现在可以通过通知右侧的“X”来关闭。蜂巢是第一个支持通知内控制的版本。第一个(也是蜂巢发布时唯一一个)利用了此特性的应用是新的谷歌音乐,在它的通知上有上一曲,播放/暂停,下一曲按钮。这些控制可以在任何应用中访问到,这让控制音乐播放变成了一件轻而易举的事情。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
“添加到主屏幕”的缩小视图更易于组织布局。搜索界面将自动搜索建议和通用搜索分为两个面板显示。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo 供图
|
||||
|
||||
点击主屏幕右上角的加号或长按背景空白处就会打开新的主屏幕设置界面。蜂巢会在屏幕上半部分显示所有主屏的缩小视图,下半部分分页显示的是小部件和快捷方式。小部件或快捷方式可以从下半部分的抽屉中拖动到五个主屏幕中的任意一个上。姜饼只会显示一个文本列表,而蜂巢会显示小部件完整的略缩图预览。这让你更清楚一个小部件是什么样子的,而不是像原来的“日历”一样只是一个只有应用名称的描述。
|
||||
|
||||
摩托罗拉 Xoom 更大的屏幕让键盘的布局更加接近 PC 风格,退格,回车,shift 以及 tab 都在传统的位置上。键盘带有浅蓝色,并且键与键之间的空间更大了。谷歌还添加了一个专门的笑脸按钮。 :-)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
打开菜单的 Gmail 在蜂巢和姜饼上的效果。按钮布置在首屏更容易被发现。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo 供图
|
||||
|
||||
Gmail 示范了蜂巢所有的用户界面概念。安卓 3.0不再把所有控制都隐藏在菜单按钮之后。屏幕的顶部现在有一条带有图标的条带,叫做 Action Bar(操作栏),它将许多常用的控制选项提升到了主屏幕上,用户直接就能看到它们。Gmail 的操作栏显示着搜索,新邮件,刷新按钮,不常用的选项比如设置,帮助,以及反馈放在了“更多”按钮中。点击复选框或选中文本的时候时整个操作栏的图标会变成和操作相关的——举个例子,选择文本会出现复制,粘贴和全选按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
应用左上角显示的图标同时也作为称作“上一级”的导航按钮。“后退”的作用类似浏览器的后退按钮,导航到之前访问的页面,“上一级”则会导航至应用的上一层次。举例来说,如果你在安卓市场,点击“给开发者发邮件”,会打开 Gmail,“后退”会让你返回安卓市场,但是“上一级”会带你到 Gmail 的收件箱。“后退”可能会关闭当前应用,而“上一级”永远不会。应用可以控制“后退”按钮,它们往往重新定义它为“上一级”的功能。事实上,这两个按钮之间几乎没什么不同。
|
||||
|
||||
蜂巢还引入了 “Fragments” API,允许开发者开发同时适用于平板和手机的应用。一个 “Fragments”(格子) 是一个用户界面的面板。在上图的 Gmail 中,左边的文件夹列表是一个格子,收件箱是另一个格子。手机每屏显示一个格子,而平板则可以并列显示两个。开发者可以自行定义单独每个格子的外观,安卓会根据当前的设备决定如何显示它们。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
计算器使用了常规的安卓按钮,但日历看起来像是被谁打翻了蓝墨水。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo 供图
|
||||
|
||||
这是安卓历史上第一次计算器换上了没有特别定制的按钮,所以它看起来确实是系统的一部分。更大的屏幕有了更多空间容纳按钮,足够将计算器基本功能容纳在一个屏幕上。日历极大地受益于额外的显示空间,有了更多的空间显示事件文本和控制选项。顶部的操作栏有切换视图的按钮,显示当前时间跨度,以及常规按钮。事件块变成了白色背景,日历标识只在左上角显示。在底部(或横屏模式的侧边)显示的是月历和显示的日历列表。
|
||||
|
||||
日历的比例同样可以调整。通过两指缩放手势,纵向的周和日视图能够在一屏内显示五到十九小时的事件。日历的背景由不均匀的蓝色斑点组成,看起来不是特别棒,在随后的版本里就被抛弃了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
新相机界面,取景器显示的是“负片”效果。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo 供图
|
||||
|
||||
巨大的10英寸 Xoom 平板有个摄像头,这意味着它同样有个相机应用。电子风格的重新设计终于甩掉了谷歌从安卓 1.6 以来使用的仿皮革外观。控制选项以环形排布在快门键周围,让人想起真正的相机上的圆形控制转盘。Cooliris 衍生的弹出对话气泡变成了带光晕的半透明黑色选框。蜂巢的截图显示的是新的“颜色效果”功能,它能给取景器实时加上滤镜效果。不像姜饼的相机应用,它不支持竖屏模式——它被限制在横屏状态。用10英寸的平板拍摄纵向照片没多大意义,但拍摄横向照片也没多大意义。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
时钟应用相比其它地方没受到多少关照。谷歌把它扔进一个小盒子里然后就收工了。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo 供图
|
||||
|
||||
无数功能已经成形了,现在是时候来重制一下时钟了。整个“桌面时钟”概念被踢出门外,取而代之的是在纯黑背景上显示的简单又巨大的时间数字。打开其它应用查看天气的功能不见了,随之而去的还有显示你的壁纸的功能。当要设计平板尺寸的界面时,有时候谷歌就放弃了,就像这里,就只是把时钟界面扔到了一个小小的,居中的对话框里。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
音乐应用终于得到了一直以来都需要的完全重新设计。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo 供图
|
||||
|
||||
尽管音乐应用之前有得到一些小的加强,但这是自安卓 0.9 以来它第一次受到正视。重新设计的亮点是一个“别叫它封面流滚动 3D 专辑封面视图”,称作“最新和最近”。导航由操作栏的下拉框解决,取代了安卓 2.1 引入的标签页导航。尽管“最新和最近”有个 3D 滚动专辑封面,“专辑”使用的是专辑略缩图的平面方阵。另一个部分也有个完全不同的设计。“歌曲”使用了垂直滚动的文本列表,“播放列表”,“年代”和“艺术家”用的是堆砌专辑显示。
|
||||
|
||||
在几乎每个视图中,每个单独的项目有它自己单独的菜单,通常在每项的右下角有个小箭头。眼下这里只会显示“播放”和“添加到播放列表”,但这个版本的谷歌音乐是为未来搭建的。谷歌不久后就要发布音乐服务,这些独立菜单在像是在音乐商店里浏览该艺术家的其它内容,或是管理云存储和本地存储时将会是不可或缺的。
|
||||
|
||||
正如安卓 2.1 中的 Cooliris 风格的相册,谷歌音乐会将略缩图放大作为背景图片。底部的“正在播放”栏现在显示着专辑封面,播放控制,以及播放进度条。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
新谷歌地图的一些地方真的很棒,一些却是从安卓 1.5 来的。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo 供图
|
||||
|
||||
谷歌地图也为大屏幕进行了重新设计。这个设计将会持续一段时间,它对所有的控制选项用了一个半透明的黑色操作栏。搜索再次成为主要功能,占据了操作栏显要位置,但这回可是真的搜索栏,你可以在里面输入关键字,不像以前那个搜索栏形状的按钮会打开完全不同的界面。谷歌最终还是放弃了给缩放控件留屏幕空间,仅仅依靠手势来控制地图显示。尽管 3D 建筑轮廓这个特性已经被移植到了旧版本的地图中,蜂巢依然是拥有这个特性的第一个版本。双指在地图上向下拖放会“倾斜”地图的视角,展示建筑的侧面。你可以随意旋转,建筑同样会跟着进行调整。
|
||||
|
||||
并不是所有部分都进行了重新设计。导航自姜饼以来就没动过,还有些界面的核心部分,像是路线,直接从安卓 1.6 的设计拿出来,放到一个小盒子里居中放置,仅此而已。
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron是Ars Technica的评论编缉,专注于安卓系统和谷歌产品。他总是在追寻新鲜事物,还喜欢拆解事物看看它们到底是怎么运作的。
|
||||
|
||||
[@RonAmadeo][t]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/17/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
|
||||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,187 @@
|
||||
如何在 Fedora 22 上配置 Proftpd 服务器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在本文中,我们将了解如何在运行 Fedora 22 的电脑或服务器上使用 Proftpd 架设 FTP 服务器。[ProFTPD][1] 是一款免费的基于 GPL 授权开源的 FTP 服务器软件,是 Linux 上的主流 FTP 服务器。它的主要设计目标是具备许多高级功能以及能为用户提供丰富的配置选项可以轻松实现定制。它的许多配置选项在其他一些 FTP 服务器软件里仍然没有集成。最初它是被开发作为 wu-ftpd 服务器的一个更安全更容易配置的替代。FTP 服务器是这样一个软件,用户可以通过 FTP 客户端从安装了它的远端服务器上传或下载文件和目录。下面是一些 ProFTPD 服务器的主要功能,更详细的资料可以访问 [http://www.proftpd.org/features.html][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
- 每个目录都包含 ".ftpaccess" 文件用于访问控制,类似 Apache 的 ".htaccess"
|
||||
- 支持多个虚拟 FTP 服务器以及多用户登录和匿名 FTP 服务。
|
||||
- 可以作为独立进程启动服务或者通过 inetd/xinetd 启动
|
||||
- 它的文件/目录属性、属主和权限采用类 UNIX 方式。
|
||||
- 它可以独立运行,保护系统避免 root 访问可能带来的损坏。
|
||||
- 模块化的设计让它可以轻松扩展其他模块,比如 LDAP 服务器,SSL/TLS 加密,RADIUS 支持,等等。
|
||||
- ProFTPD 服务器还支持 IPv6.
|
||||
|
||||
下面是如何在运行 Fedora 22 操作系统的计算机上使用 ProFTPD 架设 FTP 服务器的一些简单步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 安装 ProFTPD ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们将在运行 Fedora 22 的机器上安装 Proftpd 软件。因为 yum 包管理器已经被抛弃了,我们将使用最新最好的包管理器 dnf。DNF 很容易使用,是 Fedora 22 上采用的非常人性化的包管理器。我们将用它来安装 proftpd 软件。这需要在终端或控制台里用 sudo 模式运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dnf -y install proftpd proftpd-utils
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 配置 ProFTPD ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们将修改软件的一些配置。要配置它,我们需要用文本编辑器编辑 /etc/proftpd.conf 文件。**/etc/proftpd.conf** 文件是 ProFTPD 软件的主要配置文件,所以,这个文件的任何改动都会影响到 FTP 服务器。在这里,是我们在初始步骤里做出的改动。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/proftpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
之后,在用文本编辑器打开这个文件后,我们会想改下 ServerName 以及 ServerAdmin,分别填入自己的域名和 email 地址。下面是我们改的。
|
||||
|
||||
ServerName "ftp.linoxide.com"
|
||||
ServerAdmin arun@linoxide.com
|
||||
|
||||
在这之后,我们将把下面的设定加到配置文件里,这样可以让服务器将访问和授权记录到相应的日志文件里。
|
||||
|
||||
ExtendedLog /var/log/proftpd/access.log WRITE,READ default
|
||||
ExtendedLog /var/log/proftpd/auth.log AUTH auth
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 添加 FTP 用户 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在设定好了基本的配置文件后,我们很自然地希望为指定目录添加 FTP 用户。目前用来登录的用户是 FTP 服务自动生成的,可以用来登录到 FTP 服务器。但是,在这篇教程里,我们将创建一个以 ftp 服务器上指定目录为主目录的新用户。
|
||||
|
||||
下面,我们将建立一个名字是 ftpgroup 的新用户组。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo groupadd ftpgroup
|
||||
|
||||
然后,我们将以目录 /ftp-dir/ 作为主目录增加一个新用户 arunftp 并加入这个组中。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo useradd -G ftpgroup arunftp -s /sbin/nologin -d /ftp-dir/
|
||||
|
||||
在创建好用户并加入用户组后,我们将为用户 arunftp 设置一个密码。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo passwd arunftp
|
||||
|
||||
Changing password for user arunftp.
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
Retype new password:
|
||||
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们将通过下面命令为这个 ftp 用户设定主目录的读写权限。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo setsebool -P allow_ftpd_full_access=1
|
||||
$ sudo setsebool -P ftp_home_dir=1
|
||||
|
||||
然后,我们会设定不允许其他用户移动或重命名这个目录以及里面的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chmod -R 1777 /ftp-dir/
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 打开 TLS 支持 ###
|
||||
|
||||
目前 FTP 所用的加密手段并不安全,任何人都可以通过监听网卡来读取 FTP 传输的数据。所以,我们将为自己的服务器打开 TLS 加密支持。这样的话,需要编辑 /etc/proftpd.conf 配置文件。在这之前,我们先备份一下当前的配置文件,可以保证在改出问题后还可以恢复。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo cp /etc/proftpd.conf /etc/proftpd.conf.bak
|
||||
|
||||
然后,我们可以用自己喜欢的文本编辑器修改配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/proftpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
然后,把下面几行附加到我们在第 2 步中所增加内容的后面。
|
||||
|
||||
TLSEngine on
|
||||
TLSRequired on
|
||||
TLSProtocol SSLv23
|
||||
TLSLog /var/log/proftpd/tls.log
|
||||
TLSRSACertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/proftpd.pem
|
||||
TLSRSACertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/proftpd.pem
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
完成上面的设定后,保存退出。
|
||||
|
||||
然后,我们需要生成 SSL 凭证 proftpd.pem 并放到 **/etc/pki/tls/certs/** 目录里。这样的话,首先需要在 Fedora 22 上安装 openssl。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dnf install openssl
|
||||
|
||||
然后,可以通过执行下面的命令生成 SSL 凭证。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/pki/tls/certs/proftpd.pem -out /etc/pki/tls/certs/proftpd.pem
|
||||
|
||||
系统会询问一些将写入凭证里的基本信息。在填完资料后,就会生成一个 2048 位的 RSA 私钥。
|
||||
|
||||
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key
|
||||
...................+++
|
||||
...................+++
|
||||
writing new private key to '/etc/pki/tls/certs/proftpd.pem'
|
||||
-----
|
||||
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
|
||||
into your certificate request.
|
||||
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
|
||||
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
|
||||
For some fields there will be a default value,
|
||||
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
|
||||
-----
|
||||
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:NP
|
||||
State or Province Name (full name) []:Narayani
|
||||
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:Bharatpur
|
||||
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:Linoxide
|
||||
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:Linux Freedom
|
||||
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:ftp.linoxide.com
|
||||
Email Address []:arun@linoxide.com
|
||||
|
||||
在这之后,我们要改变所生成凭证文件的权限以增加安全性。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chmod 600 /etc/pki/tls/certs/proftpd.pem
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 允许 FTP 通过 Firewall ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在,需要允许 ftp 端口,一般默认被防火墙阻止了。就是说,需要允许 ftp 端口能通过防火墙访问。
|
||||
|
||||
如果 **打开了 TLS/SSL 加密**,执行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=1024-65534/tcp
|
||||
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=1024-65534/tcp --permanent
|
||||
|
||||
如果 **没有打开 TLS/SSL 加密**,执行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=ftp
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
然后,重新加载防火墙设定。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 启动并激活 ProFTPD ###
|
||||
|
||||
全部设定好后,最后就是启动 ProFTPD 并试一下。可以运行下面的命令来启动 proftpd ftp 守护程序。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl start proftpd.service
|
||||
|
||||
然后,我们可以设定开机启动。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl enable proftpd.service
|
||||
|
||||
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/proftpd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/proftpd.service.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. 登录到 FTP 服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在,如果都是按照本教程设置好的,我们一定可以连接到 ftp 服务器并使用以上设置的信息登录上去。在这里,我们将配置一下 FTP 客户端 filezilla,使用 **服务器的 IP 或 URL **作为主机名,协议选择 **FTP**,用户名填入 **arunftp**,密码是在上面第 3 步中设定的密码。如果你按照第 4 步中的方式打开了 TLS 支持,还需要在加密类型中选择 **显式要求基于 TLS 的 FTP**,如果没有打开,也不想使用 TLS 加密,那么加密类型选择 **简单 FTP**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
要做上述设定,需要打开菜单里的文件,点击站点管理器,然后点击新建站点,再按上面的方式设置。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
随后系统会要求允许 SSL 凭证,点确定。之后,就可以从我们的 FTP 服务器上传下载文件和文件夹了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
最后,我们成功地在 Fedora 22 机器上安装并配置好了 Proftpd FTP 服务器。Proftpd 是一个超级强大,能高度配置和扩展的 FTP 守护软件。上面的教程展示了如何配置一个采用 TLS 加密的安全 FTP 服务器。强烈建议设置 FTP 服务器支持 TLS 加密,因为它允许使用 SSL 凭证加密数据传输和登录。本文中,我们也没有配置 FTP 的匿名访问,因为一般受保护的 FTP 系统不建议这样做。 FTP 访问让人们的上传和下载变得非常简单也更高效。我们还可以改变用户端口增加安全性。好吧,如果你有任何疑问,建议,反馈,请在下面评论区留言,这样我们就能够改善并更新文章内容。谢谢!玩的开心 :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/configure-ftp-proftpd-fedora-22/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.proftpd.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.proftpd.org/features.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 14.04中修复“update information is outdated”错误
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
看到Ubuntu 14.04的顶部面板上那个显示下面这个错误的红色三角形了吗?
|
||||
|
||||
> 更新信息过时。该错误可能是由网络问题,或者某个仓库不再可用而造成的。请通过从指示器菜单中选择‘显示更新’来手动更新,然后查看是否存在有失败的仓库。
|
||||
>
|
||||
|
||||
它看起来像这样:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这里的粉红色感叹号标记就是原来的红色三角形,因为我使用了[最佳的Ubuntu图标主题][1]之一,Numix。让我们回到该错误中,这是一个常见的更新问题,你也许时不时地会碰到它。现在,你或许想知道的是,到底是什么导致了这个更新错误的出现。
|
||||
|
||||
### 引起‘update information is outdated’错误的原因 ###
|
||||
|
||||
导致该错误的原因在其自身的错误描述中就讲得相当明白,它告诉你“这可能是由网络问题或者某个不再可用的仓库导致的”。所以,要么是你更新了系统和某些仓库,要么是PPA不再受到支持了,或者你正面对的类似问题。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然错误本身就讲得很明白,而它给出了的议操作“请通过从指示器菜单选择‘显示更新’来手动更新以查看失败的仓库”却并不能很好地解决问题。如果你点击显示更新,你所能看见的仅仅是系统已经更新。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
很奇怪,不是吗?我们怎样才能找出是什么出错了,哪里出错了,以及为什么出错呢?
|
||||
|
||||
### 修复‘update information is outdated’错误 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这里讨论的‘解决方案’可能对Ubuntu的这些版本有用:Ubuntu 14.04,12.04或14.04。你所要做的仅仅是打开终端(Ctrl+Alt+T),然后使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
等待命令结束,然后查看其结果。这里插个快速提示,你可以[在终端中添加通知][2],这样当一个耗时很长的命令结束执行时就会通知你。在该命令的最后几行中,可以看到你的系统正面临什么样的错误。是的,你肯定会看到一个错误。
|
||||
|
||||
在我这里,我看到了有名的[GPG error: The following could not be verified][3]错误。很明显,[在Ubuntu 15.04中安装声破天][4]有点问题。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
很可能你看到的不是像我一样的GPG错误,那样的话,我建议你读一读我写的这篇文章[修复Ubuntu中的各种常见更新错误][5]。
|
||||
|
||||
我知道有不少人,尤其是初学者,很是讨厌命令行,但是如果你正在使用Linux,你就无可避免会使用到终端。此外,那东西并没你想象的那么可怕。试试吧,你会很快上手的。
|
||||
|
||||
我希望这个快速提示对于你修复Ubuntu中的“update information is outdated”错误有帮助。如果你有任何问题或建议,请不吝提出,我们将无任欢迎。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-update-information-outdated-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/notification-terminal-command-completion-ubuntu/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-gpg-error-signatures-verified-ubuntu/
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/install-spotify-ubuntu-1504/
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/fix-update-errors-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
||||
如何在 Docker 中通过 Kitematic 交互式执行任务
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在本篇文章中,我们会学习如何在 Windows 操作系统上安装 Kitematic 以及部署一个 Hello World Nginx Web 服务器。Kitematic 是一个自由开源软件,它有现代化的界面设计使得允许我们在 Docker 中交互式执行任务。Kitematic 设计非常漂亮、界面也很不错。我们可以简单快速地开箱搭建我们的容器而不需要输入命令,我们可以在图形用户界面中通过简单的点击从而在容器上部署我们的应用。Kitematic 集成了 Docker Hub,允许我们搜索、拉取任何需要的镜像,并在上面部署应用。它同时也能很好地切换到命令行用户接口模式。目前,它包括了自动映射端口、可视化更改环境变量、配置卷、精简日志以及其它功能。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是在 Windows 上安装 Kitematic 并部署 Hello World Nginx Web 服务器的 3 个简单步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 下载 Kitematic ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们需要从 github 仓库 [https://github.com/kitematic/kitematic/releases][1] 中下载 Windows 操作系统可用的最新的 Kitematic 发行版。我们用下载器或者 web 浏览器下载了它的可执行 EXE 文件。下载完成后,我们需要双击可执行应用文件。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
双击应用文件之后,会问我们一个安全问题,我们只需要点击 OK 按钮,如下图所示。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 安装 Kitematic ###
|
||||
|
||||
下载好可执行安装程序之后,我们现在打算在我们的 Windows 操作系统上安装 Kitematic。安装程序现在会开始下载并安装运行 Kitematic 需要的依赖,包括 Virtual Box 和 Docker。如果已经在系统上安装了 Virtual Box,它会把它升级到最新版本。安装程序会在几分钟内完成,但取决于你网络和系统的速度。如果你还没有安装 Virtual Box,它会问你是否安装 Virtual Box 网络驱动。建议安装它,因为它有助于 Virtual Box 的网络。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
需要的依赖 Docker 和 Virtual Box 安装完成并运行后,会让我们登录到 Docker Hub。如果我们还没有账户或者还不想登录,可以点击 **SKIP FOR NOW** 继续后面的步骤。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你还没有账户,你可以在应用程序上点击注册链接并在 Docker Hub 上创建账户。
|
||||
|
||||
完成之后,就会出现 Kitematic 应用程序的第一个界面。正如下面看到的这样。我们可以搜索可用的 docker 镜像。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 部署 Nginx Hello World 容器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在,成功安装完 Kitematic 之后,我们打算部署容器。要运行一个容器,我们只需要在搜索区域中搜索镜像。然后点击 Create 按钮部署容器。在这篇教程中,我们会部署一个小的包含了 Hello World 主页的 Nginx Web 服务器。为此,我们在搜索区域中搜索 Hello World Nginx。看到了容器信息之后,我们点击 Create 来部署容器。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
镜像下载完成之后,它会自动部署。我们可以查看 Kitematic 部署容器的命令日志。我们也可以在 Kitematic 界面上预览 web 页面。现在,我们通过点击预览在 web 浏览器中查看我们的 Hello World 页面。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果我们想切换到命令行接口并用它管理 docker,这里有个称为 Docker CLI 的按钮,它会打开一个 PowerShell,在里面我们可以执行 docker 命令。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在,如果我们想配置我们的容器并执行类似更改容器名称、设置环境变量、指定端口、配置容器存储以及其它高级功能的任务,我们可以在容器设置页面做到这些。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们终于成功在 Windows 操作系统上安装了 Kitematic 并部署了一个 Hello World Ngnix 服务器。总是推荐下载安装 Kitematic 最新的发行版,因为会增加很多新的高级功能。由于 Docker 运行在 64 位平台,当前 Kitematic 也是为 64 位操作系统构建。它只能在 Windows 7 以及更高版本上运行。在这篇教程中,我们部署了一个 Nginx Web 服务器,类似地我们可以在 Kitematic 中简单的点击就能通过镜像部署任何 docker 容器。Kitematic 已经有可用的 Mac OS X 和 Windows 版本,Linux 版本也在开发中很快就会发布。如果你有任何疑问、建议或者反馈,请在下面的评论框中写下来以便我们更改地改进或更新我们的内容。非常感谢!Enjoy :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/interactively-docker-kitematic/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/kitematic/kitematic/releases
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user