mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-25 00:50:15 +08:00
commit
e1c9b11c8d
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
Syncthing: 一个跨计算机的私人的文件/文件夹安全同步工具
|
||||
Syncthing: 一个在计算机之间同步文件/文件夹的私密安全同步工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### 简介 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Syncthing** 是一个免费开源的工具,它能在你的各个网络计算机间同步文件/文件夹。它不像其它的同步工具,如**BitTorrent Sync**和**Dropbox**那样,它的同步数据是直接从一个系统中直接传输到另一个系统的,并且它是完全开源的,安全且私有的。你所有的珍贵数据都会被存储在你的系统中,这样你就能对你的文件和文件夹拥有全面的控制权,没有任何的文件或文件夹会被存储在第三方系统中。此外,你有权决定这些数据该存于何处,是否要分享到第三方,或这些数据在互联网上的传输方式。
|
||||
**Syncthing**是一个免费开源的工具,它能在你的各个网络计算机间同步文件/文件夹。它不像其它的同步工具,如**BitTorrent Sync**和**Dropbox**那样,它的同步数据是直接从一个系统中直接传输到另一个系统的,并且它是完全开源的,安全且私密的。你所有的珍贵数据都会被存储在你的系统中,这样你就能对你的文件和文件夹拥有全面的控制权,没有任何的文件或文件夹会被存储在第三方系统中。此外,你有权决定这些数据该存于何处,是否要分享到第三方,或这些数据在互联网上的传输方式。
|
||||
|
||||
所有的信息通讯都使用TLS进行加密,这样你的数据便能十分安全地逃离窥探。Syncthing有一个强大的响应式的网页管理界面(WebGUI,下同),它能够帮助用户简便地添加,删除和管理那些通过网络进行同步的文件夹。通过使用Syncthing,你可以在多个系统上一次同步多个文件夹。在安装和使用上,Syncthing是一个可移植的,简单但强大的工具。即然文件或文件夹是从一部计算机中直接传输到另一计算机中的,那么你就无需考虑向云服务供应商支付金钱来获取额外的云空间。你所需要的仅仅是非常稳定的LAN/WAN连接和你的系统中足够的硬盘空间。它支持所有的现代操作系统,包括GNU/Linux, Windows, Mac OS X, 当然还有Android。
|
||||
所有的信息通讯都使用TLS进行加密,这样你的数据便能十分安全地逃离窥探。Syncthing有一个强大的响应式的网页管理界面(WebGUI,下同),它能够帮助用户简便地添加、删除和管理那些通过网络进行同步的文件夹。通过使用Syncthing,你可以在多个系统上一次同步多个文件夹。在安装和使用上,Syncthing是一个可移植的、简单而强大的工具。即然文件或文件夹是从一部计算机中直接传输到另一计算机中的,那么你就无需考虑向云服务供应商支付金钱来获取额外的云空间。你所需要的仅仅是非常稳定的LAN/WAN连接以及在你的系统中有足够的硬盘空间。它支持所有的现代操作系统,包括GNU/Linux, Windows, Mac OS X, 当然还有Android。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ Syncthing: 一个跨计算机的私人的文件/文件夹安全同步工具
|
||||
### 系统1细节: ###
|
||||
|
||||
- **操作系统**: Ubuntu 14.04 LTS server;
|
||||
- **主机名**: server1.unixmen.local;
|
||||
- **主机名**: **server1**.unixmen.local;
|
||||
- **IP地址**: 192.168.1.150.
|
||||
- **系统用户**: sk (你可以使用你自己的系统用户)
|
||||
- **同步文件夹**: /home/Sync/ (Syncthing会默认创建)
|
||||
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ Syncthing: 一个跨计算机的私人的文件/文件夹安全同步工具
|
||||
### 系统2细节 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- **操作系统**: Ubuntu 14.10 server;
|
||||
- **主机名**: server.unixmen.local;
|
||||
- **主机名**: **server**.unixmen.local;
|
||||
- **IP地址**: 192.168.1.151.
|
||||
- **系统用户**: sk (你可以使用你自己的系统用户)
|
||||
- **同步文件夹**: /home/Sync/ (Syncthing会默认创建)
|
||||
@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ Syncthing: 一个跨计算机的私人的文件/文件夹安全同步工具
|
||||
|
||||
cd syncthing-linux-amd64-v0.10.20/
|
||||
|
||||
复制可执行文件"Syncthing"到**$PATH**:
|
||||
复制可执行文件"syncthing"到**$PATH**:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo cp syncthing /usr/local/bin/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ Syncthing: 一个跨计算机的私人的文件/文件夹安全同步工具
|
||||
|
||||
syncthing
|
||||
|
||||
当你执行上述命令后,syncthing会生成一个配置以及一些关键值(keys),并且在你的浏览器上打开一个管理界面。,
|
||||
当你执行上述命令后,syncthing会生成一个配置以及一些配置键值,并且在你的浏览器上打开一个管理界面。
|
||||
|
||||
输入示例:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -78,11 +78,11 @@ Syncthing: 一个跨计算机的私人的文件/文件夹安全同步工具
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:41:07 INFO: Device BQXVO3D-VEBIDRE-MVMMGJI-ECD2PC3-T5LT3JB-OK4Z45E-MPIDWHI-IRW3NAZ is "server1" at [dynamic]
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:41:07 INFO: Completed initial scan (rw) of folder default
|
||||
|
||||
Syncthing已经被成功地初始化了,网页管理接口也可以通过浏览器在URL: **http://localhost:8080**进行访问了。如上面输入所看到的,Syncthing在你的**home**目录中的Sync目录**下自动为你创建了一个名为**default**的文件夹。
|
||||
Syncthing已经被成功地初始化了,网页管理接口也可以通过浏览器访问URL: **http://localhost:8080**。如上面输入所看到的,Syncthing在你的**home**目录中的Sync目录**下自动为你创建了一个名为**default**的文件夹。
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,Syncthing的网页管理界面(WebGUI)只能在本地端口(localhost)中进行访问,你需要在两个系统中进行以下操作:
|
||||
默认情况下,Syncthing的网页管理界面只能在本地端口(localhost)中进行访问,要从远程进行访问,你需要在两个系统中进行以下操作:
|
||||
|
||||
首先,按下CTRL+C键来停止Syncthing初始化进程。现在你回到了终端界面。
|
||||
首先,按下CTRL+C键来终止Syncthing初始化进程。现在你回到了终端界面。
|
||||
|
||||
编辑**config.xml**文件,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -115,17 +115,18 @@ Syncthing已经被成功地初始化了,网页管理接口也可以通过浏
|
||||
现在,在你的浏览器上打开**http://ip-address:8080/**。你会看到下面的界面:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
网页管理界面分为两个窗格,在左窗格中,你应该可以看到同步的文件夹列表。如前所述,文件夹**default**在你初始化Syncthing时被自动创建。如果你想同步更多文件夹,点击**Add Folder**按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
在右窗格中,你可以看到已连接的设备数。现在这里只有一个,就是你现在正在操作的计算机。
|
||||
|
||||
### 网页管理界面(WebGUI)上设置Syncthing ###
|
||||
### 网页管理界面上设置Syncthing ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了提高安全性,让我们启用TLS,并且设置访问网页管理界面的管理员用户和密码。要做到这点,点击右上角的齿轮按钮,然后选择**Settings**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
输入管理员的帐户名/密码。我设置的是admin/Ubuntu。你可以使用一些更复杂的密码。
|
||||
输入管理员的帐户名/密码。我设置的是admin/Ubuntu。你应该使用一些更复杂的密码。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -155,7 +156,7 @@ Syncthing已经被成功地初始化了,网页管理接口也可以通过浏
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
接着会出现下面的界面。在Device区域粘贴**系统1 ID **。输入设备名称(可选)。在地址区域,你可以输入其它系统(译者注:即粘贴的ID所属的系统,此应为系统1)的IP地址,或者使用默认值。默认值为**dynamic**。最后,选择要同步的文件夹。在我们的例子中,同步文件夹为**default**。
|
||||
接着会出现下面的界面。在Device区域粘贴**系统1 ID **。输入设备名称(可选)。在地址区域,你可以输入其它系统( LCTT 译注:即粘贴的ID所属的系统,此应为系统1)的IP地址,或者使用默认值。默认值为**dynamic**。最后,选择要同步的文件夹。在我们的例子中,同步文件夹为**default**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -181,7 +182,7 @@ Syncthing已经被成功地初始化了,网页管理接口也可以通过浏
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在,在任一个系统中的“**default**”文件夹中放进任意文件或文件夹。你应该可以看到这些文件/文件夹被自动同步到其它系统。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -197,7 +198,7 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/syncthing-private-secure-tool-sync-filesfolders-comp
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[XLCYun](https://github.com/XLCYun)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,16 @@
|
||||
XBMC:自制遥控
|
||||
为 Kodi 自制遥控器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**通过运行在 Android 手机上的自制遥控器来控制你的家庭媒体播放器。**
|
||||
|
||||
**XBMC** 一款很优秀的软件,能够将几乎所有电脑变身成媒体中心。它可以播放音乐和视频,显示图片,甚至还能显示天气预报。为了在配置成家庭影院后方便使用,你可以通过手机 app 访问运行在已连接到 Wi-Fi 的 XBMC 机器上的服务来控制它。可以找到很多这种工具,几乎覆盖所有智能手机系统。
|
||||
**Kodi** 是一款很优秀的软件,能够将几乎所有电脑变身成媒体中心。它可以播放音乐和视频,显示图片,甚至还能显示天气预报。为了在配置成家庭影院后方便使用,你可以通过手机 app 访问运行在连接到 Wi-Fi 的 XBMC 机器上的服务来控制它。可以找到很多这种工具,几乎覆盖所有智能手机系统。
|
||||
|
||||
> ### Kodi ###
|
||||
> **XBMC**
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 在你阅读这篇文章的时候,**XBMC** 可能已经成为历史。因为法律原因(因为名字 **XBMC** 或 X**-Box Media Center** 里引用了不再支持的过时硬件)项目组决定使用新的名字 **Kodi**。不过,除了名字,其他的都会保持原样。或者说除开通常新版本中所期待的大量新改进。这一般不会影响到遥控软件,它应该能在已有的 **XBMC** 系统和新的 Kodi 系统上都能工作。
|
||||
> Kodi 原名叫做 XBMC,在你阅读这篇文章的时候,**XBMC** 已经成为历史。因为法律原因(因为名字 **XBMC** 或 X**-Box Media Center** 里引用了不再支持的过时硬件)项目组决定使用新的名字 **Kodi**。不过,除了名字,其他的都会保持原样。或者说除开通常新版本中所期待的大量新改进。这一般不会影响到遥控软件,它应该能在已有的 **XBMC** 系统和新的 Kodi 系统上都能工作。
|
||||
|
||||
我们目前配置了一个 **XBMC** 系统用于播放音乐,不过我们找到的所有 XBMC 遥控没一个好用的,特别是和媒体中心连接的电视没打开的时候。它们都有点太复杂了,集成了太多功能在手机的小屏幕上。我们希望能有这样的系统,从最开始就是设计成只用于访问音乐库和电台插件,所以我们决定自己实现一个。它不需要用到 XBMC 的所有功能,因为除了音乐以外的任务,我们可以简单地切换使用通用的 XBMC 遥控。我们的测试系统是一个刷了 RaspBMC 发行版的树莓派,但是我们要做的工具并不受限于树莓派或那个发行版,它应该可以匹配任何安装了相关插件的基于 Linux 的 XBMC 系统。
|
||||
我们目前已经配置好了一个用于播放音乐的 **Kodi** 系统,不过我们找到的所有 Kodi 遥控没一个好用的,特别是和媒体中心连接的电视没打开的时候。它们都有点太复杂了,集成了太多功能在手机的小屏幕上。我们希望能有这样的系统,从最开始就是设计成只用于访问音乐库和电台插件,所以我们决定自己实现一个。它不需要用到 Kodi 的所有功能,因为除了音乐以外的任务,我们可以简单地切换使用通用的 Kodi 遥控。我们的测试系统是一个刷了 RaspBMC 发行版的树莓派,但是我们要做的工具并不受限于树莓派或Kodi那个发行版,它应该可以匹配任何安装了相关插件的基于 Linux 的 Kodi 系统。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,遥控程序需要一个用户界面。大多数 XBMC 遥控程序都是独立的 app。不过对于我们要做的这个音乐控制程序,我们希望用户可以不用安装任何东西就可以使用。显然我们需要使用网页界面。XBMC 本身自带网页服务器,但是为了获得更多权限,我们还是使用了独立的网页框架。在同一台电脑上跑两个以上网页服务器没有问题,只不过它们不能使用相同的端口。
|
||||
首先,遥控程序需要一个用户界面。大多数 Kodi 遥控程序都是独立的 app。不过对于我们要做的这个音乐控制程序,我们希望用户可以不用安装任何东西就可以使用。显然我们需要使用网页界面。Kodi 本身自带网页服务器,但是为了获得更多权限,我们还是使用了独立的网页框架。在同一台电脑上跑两个以上网页服务器没有问题,只不过它们不能使用相同的端口。
|
||||
|
||||
有几个网页框架可以使用。而我们选用 Bottle 是因为它是一个简单高效的框架,而且我们也确实用不到任何高级功能。Bottle 是一个 Python 模块,所以这也将是我们编写服务器模块的语言。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ XBMC:自制遥控
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install python-bottle
|
||||
|
||||
遥控程序实际上只是连接用户和系统的中间层。Bottle 提供了和用户交互的方式,而我们将通过 JSON API 来和 **XBMC** 交互。这样可以让我们通过发送 JSON 格式消息的方式去控制媒体播放器。
|
||||
遥控程序实际上只是连接用户和系统的中间层。Bottle 提供了和用户交互的方式,而我们将通过 JSON API 来和 **Kodi** 交互。这样可以让我们通过发送 JSON 格式消息的方式去控制媒体播放器。
|
||||
|
||||
我们将用到一个叫做 xbmcjson 的简单 XBMC JASON API 封装。足够用来发送控制请求,而不需要关心实际的 JSON 格式以及和服务器通讯的无聊事。它没有包含在 PIP 包管理中,所以你得直接从 **GitHub** 安装:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,13 +35,13 @@ XBMC:自制遥控
|
||||
from xbmcjson import XBMC
|
||||
from bottle import route, run, template, redirect, static_file, request
|
||||
import os
|
||||
xbmc = XBMC(“http://192.168.0.5/jsonrpc”, “xbmc”, “xbmc”)
|
||||
@route(‘/hello/<name>’)
|
||||
xbmc = XBMC("http://192.168.0.5/jsonrpc", "xbmc", "xbmc")
|
||||
@route('/hello/<name>')
|
||||
def index(name):
|
||||
return template(‘<h1>Hello {{name}}!</h1>’, name=name)
|
||||
run(host=”0.0.0.0”, port=8000)
|
||||
return template('<h1>Hello {{name}}!</h1>', name=name)
|
||||
run(host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
|
||||
|
||||
这样程序将连接到 **XBMC**(不过实际上用不到);然后 Bottle 会开始伺服网站。在我们的代码里,它将监听主机 0.0.0.0(意味着允许所有主机连接)的端口 8000。它只设定了一个站点,就是 /hello/XXXX,这里的 XXXX 可以是任何内容。不管 XXXX 是什么都将作为参数名传递给 index()。然后再替换进去 HTML 网页模版。
|
||||
这样程序将连接到 **Kodi**(不过实际上用不到);然后 Bottle 会开始提供网站服务。在我们的代码里,它将监听主机 0.0.0.0(意味着允许所有主机连接)的端口 8000。它只设定了一个站点,就是 /hello/XXXX,这里的 XXXX 可以是任何内容。不管 XXXX 是什么都将作为参数名传递给 index()。然后再替换进去 HTML 网页模版。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以先试着把上面内容写到一个文件(我们取的名字是 remote.py),然后用下面的命令启动:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,56 +51,56 @@ XBMC:自制遥控
|
||||
|
||||
@route() 用来设定网页服务器的路径,而函数 index() 会返回该路径的数据。通常是返回由模版生成的 HTML 页面,但是并不是说只能这样(后面会看到)。
|
||||
|
||||
随后,我们将给应用添加更多页面入口,让它变成一个全功能的 XBMC 遥控,但仍将采用相同代码结构。
|
||||
随后,我们将给应用添加更多页面入口,让它变成一个全功能的 Kodi 遥控,但仍将采用相同代码结构。
|
||||
|
||||
XBMC JSON API 接口可以从和 XBMC 机器同网段的任意电脑上访问。也就是说你可以在自己的笔记本上开发,然后再布置到媒体中心上,而不需要浪费时间上传每次改动。
|
||||
XBMC JSON API 接口可以从和 Kodi 机器同网段的任意电脑上访问。也就是说你可以在自己的笔记本上开发,然后再布置到媒体中心上,而不需要浪费时间上传每次改动。
|
||||
|
||||
模版 - 比如前面例子里的那个简单模版 - 是一种结合 Python 和 HTML 来控制输出的方式。理论上,这俩能做很多很多事,但是会非常混乱。我们将只是用它们来生成正确格式的数据。不过,在开始动手之前,我们先得准备点数据。
|
||||
|
||||
> ### Paste ###
|
||||
> **Paste**
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Bottle 自带网页服务器,就是我们用来测试遥控程序的。不过,我们发现它性能有时不够好。当我们的遥控程序正式上线时,我们希望页面能更快一点显示出来。Bottle 可以和很多不同的网页服务器配合工作,而我们发现 Paste 用起来非常不错。而要使用的话,只要简单地安装(Debian 系统里的 python-paste 包),然后修改一下代码里的 run 调用:
|
||||
> Bottle 自带网页服务器,我们用它来测试遥控程序。不过,我们发现它性能有时不够好。当我们的遥控程序正式上线时,我们希望页面能更快一点显示出来。Bottle 可以和很多不同的网页服务器配合工作,而我们发现 Paste 用起来非常不错。而要使用的话,只要简单地安装(Debian 系统里的 python-paste 包),然后修改一下代码里的 run 调用:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> run(host=hostname, port=hostport, server=”paste”)
|
||||
> run(host=hostname, port=hostport, server="paste")
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 你可以在 [http://bottlepy.org/docs/dev/deployment.html][1] 找到如何使用其他服务器的相关细节。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 从 XBMC 获取数据 ####
|
||||
#### 从 Kodi 获取数据 ####
|
||||
|
||||
XBMC JSON API 分成 14 个命名空间:JSONRPC, Player, Playlist, Files, AudioLibrary, VideoLibrary, Input, Application, System, Favourites, Profiles, Settings, Textures 和 XBMC。每个都可以通过 Python 的 XBMC 对象访问(Favourites 除外,明显是个疏忽)。每个命名空间都包含许多方法用于对程序的控制。例如,Playlist.GetItems() 可以用来获取某个特定播放列表的内容。服务器会返回给我们 JSON 格式的数据,但 xbmcjson 模块会为我们转化成 Python 词典。
|
||||
|
||||
我们需要用到 XBMC 里的两个组件来控制播放:播放器和播放列表。播放器带有播放列表并在每首歌结束时从列表里取下一首。为了查看当前正在播放的内容,我们需要获取正在工作的播放器的 ID,然后根据它找到当前播放列表的 ID。这个可以通过下面的代码来实现:
|
||||
我们需要用到 Kodi 里的两个组件来控制播放:播放器和播放列表。播放器处理播放列表并在每首歌结束时从列表里取下一首。为了查看当前正在播放的内容,我们需要获取正在工作的播放器的 ID,然后根据它找到当前播放列表的 ID。这个可以通过下面的代码来实现:
|
||||
|
||||
def get_playlistid():
|
||||
player = xbmc.Player.GetActivePlayers()
|
||||
if len(player[‘result’]) > 0:
|
||||
playlist_data = xbmc.Player.GetProperties({“playerid”:0, “properties”:[“playlistid”]})
|
||||
if len(playlist_data[‘result’]) > 0 and “playlistid” in playlist_data[‘result’].keys():
|
||||
return playlist_data[‘result’][‘playlistid’]
|
||||
if len(player['result']) > 0:
|
||||
playlist_data = xbmc.Player.GetProperties({"playerid":0, "properties":["playlistid"]})
|
||||
if len(playlist_data['result']) > 0 and "playlistid" in playlist_data['result'].keys():
|
||||
return playlist_data['result']['playlistid']
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
|
||||
如果当前没有播放器在工作(就是说,返回数据的结果部分的长度是 0),或者当前播放器不带播放列表,这样的话函数会返回 -1。其他时候,它会返回当前播放列表的数字 ID。
|
||||
如果当前没有播放器在工作(就是说,返回数据的结果部分的长度是 0),或者当前播放器没有处理播放列表,这样的话函数会返回 -1。其他时候,它会返回当前播放列表的数字 ID。
|
||||
|
||||
当我们拿到当前播放列表的 ID 后,就可以获取列表的细节内容。按照我们的需求,有两个重要的地方:播放列表里包含的项,以及当前播放所处的位置(已经播放过的项并不会从播放列表移除,只是移动当前播放位置)。
|
||||
当我们拿到当前播放列表的 ID 后,就可以获取该列表的细节内容。按照我们的需求,有两个重要的地方:播放列表里包含的项,以及当前播放所处的位置(已经播放过的项并不会从播放列表移除,只是移动当前播放位置)。
|
||||
|
||||
def get_playlist():
|
||||
playlistid = get_playlistid()
|
||||
if playlistid >= 0:
|
||||
data = xbmc.Playlist.GetItems({“playlistid”:playlistid, “properties”: [“title”, “album”, “artist”, “file”]})
|
||||
position_data = xbmc.Player.GetProperties({“playerid”:0, ‘properties’:[“position”]})
|
||||
position = int(position_data[‘result’][‘position’])
|
||||
return data[‘result’][‘items’][position:], position
|
||||
data = xbmc.Playlist.GetItems({"playlistid":playlistid, "properties": ["title", "album", "artist", "file"]})
|
||||
position_data = xbmc.Player.GetProperties({"playerid":0, 'properties':["position"]})
|
||||
position = int(position_data['result']['position'])
|
||||
return data['result']['items'][position:], position
|
||||
return [], -1
|
||||
|
||||
这样可以返回以正在播放的项开始的列表(因为我们并不关心已经播放过的内容),而且也包含了位置信息用来从列表里移除项。
|
||||
这样可以返回正在播放的项开始的列表(因为我们并不关心已经播放过的内容),而且也包含了用来从列表里移除项的位置信息。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
API 文档在这里:[http://wiki.xbmc.org/?title=JSON-RPC_API/v6][2]。它列出了所有支持的函数,但是关于具体如何使用的描述有点太简单了。
|
||||
|
||||
> ### JSON ###
|
||||
> **JSON**
|
||||
>
|
||||
> JSON 是 JavaScript Object Notation 的缩写,开始设计用于 JavaScript 对象的序列化。目前仍然起到这个作用,但是它也是用来编码任意数据的一种很好用的方式。
|
||||
> JSON 是 JavaScript Object Notation 的缩写,最初设计用于 JavaScript 对象的序列化。目前仍然起到这个作用,但是它也是用来编码任意数据的一种很好用的方式。
|
||||
>
|
||||
> JSON 对象都是这样的格式:
|
||||
>
|
||||
@ -110,18 +110,18 @@ API 文档在这里:[http://wiki.xbmc.org/?title=JSON-RPC_API/v6][2]。它列
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 在字典数据结构里,值本身可以是另一个 JSON 对象,或者一个列表,所以下面的格式也是正确的:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> {“name”:“Ben”, “jobs”:[“cook”, “bottle-washer”], “appearance”: {“height”:195, “skin”:“fair”}}
|
||||
> {"name":"Ben", "jobs":["cook", "bottle-washer"], "appearance": {"height":195, "skin":"fair"}}
|
||||
>
|
||||
> JSON 通常在网络服务中用来发送和接收数据,并且大多数编程语言都能很好地支持,所以如果你熟悉 Python 的话,你应该可以使用你熟悉的编程语言调用相同的接口来轻松地控制 XBMC。
|
||||
> JSON 通常在网络服务中用来发送和接收数据,并且大多数编程语言都能很好地支持,所以如果你熟悉 Python 的话,你应该可以使用你熟悉的编程语言调用相同的接口来轻松地控制 Kodi。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 整合到一起 ####
|
||||
|
||||
把之前的功能连接到 HTML 页面很简单:
|
||||
|
||||
@route(‘/juke’)
|
||||
@route('/juke')
|
||||
def index():
|
||||
current_playlist, position = get_playlist()
|
||||
return template(‘list’, playlist=current_playlist, offset = position)
|
||||
return template('list', playlist=current_playlist, offset = position)
|
||||
|
||||
只需要抓取播放列表(调用我们之前定义的函数),然后将结果传递给负责显示的模版。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -131,57 +131,57 @@ API 文档在这里:[http://wiki.xbmc.org/?title=JSON-RPC_API/v6][2]。它列
|
||||
% if playlist is not None:
|
||||
% position = offset
|
||||
% for song in playlist:
|
||||
<strong> {{song[‘title’]}} </strong>
|
||||
% if song[‘type’] == ‘unknown’:
|
||||
<strong> {{song['title']}} </strong>
|
||||
% if song['type'] == 'unknown':
|
||||
Radio
|
||||
% else:
|
||||
{{song[‘artist’][0]}}
|
||||
{{song['artist'][0]}}
|
||||
% end
|
||||
% if position != offset:
|
||||
<a href=”/remove/{{position}}”>remove</a>
|
||||
<a href="/remove/{{position}}">remove</a>
|
||||
% else:
|
||||
<a href=”/skip/{{position}}”>skip</a>
|
||||
<a href="/skip/{{position}}">skip</a>
|
||||
% end
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
% position += 1
|
||||
% end
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到,模版大部分是用 HTML 写的,只有一小部分用来控制输出的其他代码。用两个括号括起来的变量是输出位置(像我们在第一个 ‘hello world’ 例子里看到的)。你也可以嵌入以百分号开头的 Python 代码。因为没有缩进,你需要用一个 % end 来结束当前的代码块(就像循环或 if 语句)。
|
||||
可以看到,模版大部分是用 HTML 写的,只有一小部分用来控制输出的其他代码。用两个大括号括起来的变量是输出位置(像我们在第一个 'hello world' 例子里看到的)。你也可以嵌入以百分号开头的 Python 代码。因为没有缩进,你需要用一个 `% end` 来结束当前的代码块(就像循环或 if 语句)。
|
||||
|
||||
这个模版首先检查列表是否为空,然后遍历里面的每一项。每一项会用粗体显示歌曲名字,然后是艺术家名字,然后是一个是否跳过(如果是当前正在播的歌曲)或从列表移除的链接。所有歌曲的类型都是 ‘song’,如果类型是 ‘unknown’,那就不是歌曲而是网络电台。
|
||||
这个模版首先检查列表是否为空,然后遍历里面的每一项。每一项会用粗体显示歌曲名字,然后是艺术家名字,然后是一个是否跳过(如果是当前正在播的歌曲)或从列表移除的链接。所有歌曲的类型都是 'song',如果类型是 'unknown',那就不是歌曲而是网络电台。
|
||||
|
||||
/remove/ 和 /skip/ 路径只是简单地封装了 XBMC 控制功能,在改动生效后重新加载 /juke:
|
||||
|
||||
@route(‘/skip/<position>’)
|
||||
@route('/skip/<position>')
|
||||
def index(position):
|
||||
print xbmc.Player.GoTo({‘playerid’:0, ‘to’:’next’})
|
||||
redirect(“/juke”)
|
||||
@route(‘/remove/<position>’)
|
||||
print xbmc.Player.GoTo({'playerid':0, 'to':'next'})
|
||||
redirect("/juke")
|
||||
@route('/remove/<position>')
|
||||
def index(position):
|
||||
playlistid = get_playlistid()
|
||||
if playlistid >= 0:
|
||||
xbmc.Playlist.Remove({‘playlistid’:int(playlistid), ‘position’:int(position)})
|
||||
redirect(“/juke”)
|
||||
xbmc.Playlist.Remove({'playlistid':int(playlistid), 'position':int(position)})
|
||||
redirect("/juke")
|
||||
|
||||
当然,如果不能往列表里添加歌曲的话那这个列表管理功能也不行。
|
||||
|
||||
因为一旦播放列表结束,它就消失了,所以你需要重新创建一个,这会让事情复杂一些。而且有点让人迷惑的是,播放列表是通过调用 Playlist.Clear() 方法来创建的。这个方法也还用来删除包含网络电台(类型是 unknown)的播放列表。另一个麻烦的地方是列表里的网络电台开始播放后就不会停,所以如果当前在播网络电台,也会需要清除播放列表。
|
||||
|
||||
这些页面包含了指向 /play/<songid> 的链接来播放歌曲。通过下面的代码处理:
|
||||
这些页面包含了指向 /play/\<songid> 的链接来播放歌曲。通过下面的代码处理:
|
||||
|
||||
@route(‘/play/<id>’)
|
||||
@route('/play/<id>')
|
||||
def index(id):
|
||||
playlistid = get_playlistid()
|
||||
playlist, not_needed= get_playlist()
|
||||
if playlistid < 0 or playlist[0][‘type’] == ‘unknown’:
|
||||
xbmc.Playlist.Clear({“playlistid”:0})
|
||||
xbmc.Playlist.Add({“playlistid”:0, “item”:{“songid”:int(id)}})
|
||||
xbmc.Player.open({“item”:{“playlistid”:0}})
|
||||
if playlistid < 0 or playlist[0]['type'] == 'unknown':
|
||||
xbmc.Playlist.Clear({"playlistid":0})
|
||||
xbmc.Playlist.Add({"playlistid":0, "item":{"songid":int(id)}})
|
||||
xbmc.Player.open({"item":{"playlistid":0}})
|
||||
playlistid = 0
|
||||
else:
|
||||
xbmc.Playlist.Add({“playlistid”:playlistid, “item”:{“songid”:int(id)}})
|
||||
xbmc.Playlist.Add({"playlistid":playlistid, "item":{"songid":int(id)}})
|
||||
remove_duplicates(playlistid)
|
||||
redirect(“/juke”)
|
||||
redirect("/juke")
|
||||
|
||||
最后一件事情是实现 remove_duplicates 调用。这并不是必须的 - 而且还有人并不喜欢这个 - 不过可以保证同一首歌不会多次出现在播放列表里。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -191,40 +191,40 @@ API 文档在这里:[http://wiki.xbmc.org/?title=JSON-RPC_API/v6][2]。它列
|
||||
|
||||
还需要处理一下 UI,不过功能已经有了。
|
||||
|
||||
> ### 日志 ###
|
||||
> **日志**
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 通常拿到 XBMC JSON API 并不清楚能用来做什么,而且它的文档也有点模糊。找出如何使用的一种方式是看别的遥控程序是怎么做的。如果打开日志功能,就可以在使用其他遥控程序的时候看到哪个 API 被调用了,然后就可以应用到在自己的代码里。
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 要打开日志功能,把 XBMC 媒体中心 接到显示器上,再依次进入设置 > 系统 > 调试,打开允许调试日志。在打开日志功能后,还需要登录到 XBMC 机器上(比如通过 SSH),然后就可以查看日志了。日志文件的位置应该显示在 XBMC 界面左上角。在 RaspBMC 系统里,文件位置是 /home/pi/.xbmc/temp/xbmc.log。你可以通过下面的命令实时监视哪个 API 接口被调用了:
|
||||
> 要打开日志功能,把 Kodi 媒体中心 接到显示器上,再依次进入设置 > 系统 > 调试,打开允许调试日志。在打开日志功能后,还需要登录到 Kodi 机器上(比如通过 SSH),然后就可以查看日志了。日志文件的位置应该显示在 Kodi 界面左上角。在 RaspBMC 系统里,文件位置是 /home/pi/.xbmc/temp/xbmc.log。你可以通过下面的命令实时监视哪个 API 接口被调用了:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> cd /home/pi/.xbmc/temp
|
||||
> tail -f xbmc.log | grep “JSON”
|
||||
> tail -f xbmc.log | grep "JSON"
|
||||
|
||||
#### 增加功能 ####
|
||||
|
||||
上面的代码都是用来播放 XBMC 媒体库里的歌曲的,但我们还希望能播放网络电台。每个插件都有自己的独立 URL 可以通过普通的 XBMC JSON 命令来获取信息。举个例子,要从电台插件里获取选中的电台,可以使用;
|
||||
上面的代码都是用来播放 Kodi 媒体库里的歌曲的,但我们还希望能播放网络电台。每个插件都有自己的独立 URL 可以通过普通的 XBMC JSON 命令来获取信息。举个例子,要从电台插件里获取选中的电台,可以使用;
|
||||
|
||||
@route(‘/radio/’)
|
||||
@route('/radio/')
|
||||
def index():
|
||||
my_stations = xbmc.Files.GetDirectory({“directory”:”plugin://plugin.audio.radio_de/stations/my/”, “properties”:
|
||||
[“title”,”thumbnail”,”playcount”,”artist”,”album”,”episode”,”season”,”showtitle”]})
|
||||
if ‘result’ in my_stations.keys():
|
||||
return template(‘radio’, stations=my_stations[‘result’][‘files’])
|
||||
my_stations = xbmc.Files.GetDirectory({"directory":"plugin://plugin.audio.radio_de/stations/my/", "properties":
|
||||
["title","thumbnail","playcount","artist","album","episode","season","showtitle"]})
|
||||
if 'result' in my_stations.keys():
|
||||
return template('radio', stations=my_stations['result']['files'])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return template(‘error’, error=’radio’)
|
||||
return template('error', error='radio')
|
||||
|
||||
这样可以返回一个可以和歌曲一样能添加到播放列表的文件。不过,这些文件能一直播下去,所以(之前说过)在添加其他歌曲的时候需要重新创建列表。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 共享歌曲 ####
|
||||
|
||||
除了伺服页面模版,Bottle 还支持静态文件。方便用于那些不会因为用户输入而改变的内容。可以是 CSS 文件,一张图片或是一首 MP3 歌曲。在我们的简单遥控程序里(目前)还没有任何用来美化的 CSS 或图片,不过我们增加了一个下载歌曲的途径。这个可以让媒体中心变成一个存放歌曲的 NAS 盒子。在需要传输大量数据的时候,最好还是用类似 Samba 的功能,但只是下几首歌到手机上的话使用静态文件也是很好的方式。
|
||||
除了伺服页面模版,Bottle 还支持静态文件,方便用于那些不会因为用户输入而改变的内容。可以是 CSS 文件,一张图片或是一首 MP3 歌曲。在我们的简单遥控程序里(目前)还没有任何用来美化的 CSS 或图片,不过我们增加了一个下载歌曲的途径。这个可以让媒体中心变成一个存放歌曲的 NAS 盒子。在需要传输大量数据的时候,最好还是用类似 Samba 的功能,但只是下几首歌到手机上的话使用静态文件也是很好的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
通过歌曲 ID 来下载的 Bottle 代码:
|
||||
|
||||
@route(‘/download/<id>’)
|
||||
@route('/download/<id>')
|
||||
def index(id):
|
||||
data = xbmc.AudioLibrary.GetSongDetails({“songid”:int(id), “properties”:[“file”]})
|
||||
full_filename = data[‘result’][‘songdetails’][‘file’]
|
||||
data = xbmc.AudioLibrary.GetSongDetails({"songid":int(id), "properties":["file"]})
|
||||
full_filename = data['result']['songdetails']['file']
|
||||
path, filename = os.path.split(full_filename)
|
||||
return static_file(filename, root=path, download=True)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -232,13 +232,13 @@ API 文档在这里:[http://wiki.xbmc.org/?title=JSON-RPC_API/v6][2]。它列
|
||||
|
||||
我们已经把所有的代码过了一遍,不过还需要一点工作来把它们集合到一起。可以自己去 GitHub 页面 [https://github.com/ben-ev/xbmc-remote][3] 看下。
|
||||
|
||||
> ### 设置 ###
|
||||
> **设置**
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 我们的遥控程序已经开发完成,还需要保证让它在媒体中心每次开机的时候都能启动。有几种方式,最简单的是在 /etc/rc.local 里增加一行命令来启动。我们的文件位置在 /opt/xbmc-remote/remote.py,其他文件也和它一起。然后在 /etc/rc.local 最后的 exit 0 之前增加了下面一行。
|
||||
>
|
||||
> cd /opt/xbmc-remote && python remote.py &
|
||||
|
||||
> ### GitHub ###
|
||||
> **GitHub**
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 这个项目目前还只是个架子,但是 - 我们运营杂志就意味着没有太多自由时间来编程。不过,我们启动了一个 GitHub 项目,希望能持续完善, 而如果你觉得这个项目有用的话,欢迎做出贡献。
|
||||
>
|
||||
@ -252,7 +252,7 @@ via: http://www.linuxvoice.com/xbmc-build-a-remote-control/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ben Everard][a]
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ Linux mkdir、tar 和 kill 命令的 4 个有用小技巧
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
4 个有用的 Linux 小技巧
|
||||
*4 个有用的 Linux 小技巧*
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 假设你要创建一个类似于下面很长的/复杂的目录树。实现这最有效的方法是什么呢? ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -37,9 +37,9 @@ Linux mkdir、tar 和 kill 命令的 4 个有用小技巧
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
检查目录结构
|
||||
*检查目录结构*
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以用上面的方式创建任意复制的目录树结构。注意这仅仅是一个普通的命令,但是用 ‘{}’ 来创建层级目录。需要的时候如果在 shell 脚本中使用是非常有用的。
|
||||
我们可以用上面的方式创建任意复杂的目录树结构。注意这仅仅是一个普通的命令,但是用 ‘{}’ 来创建层级目录。需要的时候如果在 shell 脚本中使用是非常有用的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 在桌面(/home/$USER/Desktop)创建一个文件(例如 test)并填入以下内容。 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ c. 解压 tar 包。
|
||||
|
||||
我们也可以采用另外一种方式。
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以在 Tar 包所在位置解压并复制/移动解压后的文件到所需的目标位置,例如:
|
||||
我们也可以在 Tar 包所在位置解压并复制/移动解压后的文件到所需的目标位置,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
$ tar -jxvf firefox-37.0.2.tar.bz2
|
||||
$ cp -R firefox/ /opt/
|
||||
@ -122,7 +122,7 @@ c. 解压 tar 包。
|
||||
|
||||
-C 选项提取文件到指定目录(这里是 /opt/)。
|
||||
|
||||
这并不是关于选项(-C)的问题,而是习惯的问题。养成使用带 -C 选项 tar 命令的习惯。这会使你的工作更加轻松。从现在开始不要再移动归档文件或复制/移动解压后的文件了,在 Downloads 文件夹保存 tar 包并解压到你想要的任何地方吧。
|
||||
这并不是关于选项(-C)的问题,**而是习惯的问题**。养成使用带 -C 选项 tar 命令的习惯。这会使你的工作更加轻松。从现在开始不要再移动归档文件或复制/移动解压后的文件了,在 Downloads 文件夹保存 tar 包并解压到你想要的任何地方吧。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 常规方式我们怎样杀掉一个进程? ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -188,7 +188,7 @@ c. 解压 tar 包。
|
||||
|
||||
它没有输出任何东西并返回到窗口意味着没有名称中包含 apache2 的进程在运行。
|
||||
|
||||
这就是我要说的所有东西。上面讨论的点肯定远远不够,但也肯定对你有所帮助。我们不仅仅是介绍教程使你学到一些新的东西,更重要的是想告诉你 ‘在同样的情况下如何变得更有效率’。在下面的评论框中告诉我们你的反馈吧。保持联系,继续评论。
|
||||
这就是我要说的所有东西。上面讨论的点肯定远远不够,但也肯定对你有所帮助。我们不仅仅是介绍教程使你学到一些新的东西,更重要的是想告诉你 ‘**在同样的情况下如何变得更有效率**’。在下面的评论框中告诉我们你的反馈吧。保持联系,继续评论。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -196,7 +196,7 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/mkdir-tar-and-kill-commands-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,24 +1,24 @@
|
||||
PHP 安全
|
||||
PHP 安全编程建议
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 简介 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为提供互联网服务,当你在开发代码的时候必须时刻保持安全意识。可能大部分 PHP 脚本都对安全问题不敏感;这很大程度上是因为有大量的无经验程序员在使用这门语言。但是,没有理由让你基于粗略估计你代码的影响性而有不一致的安全策略。当你在服务器上放任何经济相关的东西时,就有可能会有人尝试破解它。创建一个论坛程序或者任何形式的购物车,被攻击的可能性就上升到了无穷大。
|
||||
要提供互联网服务,当你在开发代码的时候必须时刻保持安全意识。可能大部分 PHP 脚本都对安全问题都不在意,这很大程度上是因为有大量的*无经验程序员*在使用这门语言。但是,没有理由让你因为对你的代码的不确定性而导致不一致的安全策略。当你在服务器上放任何涉及到钱的东西时,就有可能会有人尝试破解它。创建一个论坛程序或者任何形式的购物车,被攻击的可能性就上升到了无穷大。
|
||||
|
||||
### 背景 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了确保你的 web 内容安全,这里有一些一般的安全准则:
|
||||
为了确保你的 web 内容安全,这里有一些常规的安全准则:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 别相信表单 ####
|
||||
|
||||
攻击表单很简单。通过使用一个简单的 JavaScript 技巧,你可以限制你的表单只允许在评分域中填写 1 到 5 的数字。如果有人关闭了他们浏览器的 JavaScript 功能或者提交自定义的表单数据,你客户端的验证就失败了。
|
||||
|
||||
用户主要通过表单参数和你的脚本交互,因此他们是最大的安全风险。你应该学到什么呢?总是要验证 PHP 脚本中传递到其它任何 PHP 脚本的数据。在本文中,我们向你演示了如何分析和防范跨站点脚本(XSS)攻击,它可能劫持用户凭据(甚至更严重)。你也会看到如何防止会玷污或毁坏你数据的 MySQL 注入攻击。
|
||||
用户主要通过表单参数和你的脚本交互,因此他们是最大的安全风险。你应该学到什么呢?在 PHP 脚本中,总是要验证 传递给任何 PHP 脚本的数据。在本文中,我们向你演示了如何分析和防范跨站脚本(XSS)攻击,它可能会劫持用户凭据(甚至更严重)。你也会看到如何防止会玷污或毁坏你数据的 MySQL 注入攻击。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 别相信用户 ####
|
||||
|
||||
假设你网站获取的每一份数据都充满了有害的代码。清理每一部分,就算你相信没有人会尝试攻击你的站点。
|
||||
假定你网站获取的每一份数据都充满了有害的代码。清理每一部分,即便你相信没有人会尝试攻击你的站点。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 关闭全局变量 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -32,9 +32,9 @@ PHP 安全
|
||||
|
||||
<input name="username" type="text" size="15" maxlength="64">
|
||||
|
||||
运行 process.php 的时候,启用了注册全局变量的 PHP 会为该参数赋值为 $username 变量。这会比通过 **$\_POST['username']** 或 **$\_GET['username']** 访问它节省敲击次数。不幸的是,这也会给你留下安全问题,因为 PHP 设置该变量的值为通过 GET 或 POST 参数发送到脚本的任何值,如果你没有显示地初始化该变量并且你不希望任何人去操作它,这就会有一个大问题。
|
||||
运行 process.php 的时候,启用了注册全局变量的 PHP 会将该参数赋值到 $username 变量。这会比通过 **$\_POST['username']** 或 **$\_GET['username']** 访问它节省击键次数。不幸的是,这也会给你留下安全问题,因为 PHP 会设置该变量的值为通过 GET 或 POST 的参数发送到脚本的任何值,如果你没有显示地初始化该变量并且你不希望任何人去操作它,这就会有一个大问题。
|
||||
|
||||
看下面的脚本,假如 $authorized 变量的值为 true,它会给用户显示验证数据。正常情况下,只有当用户正确通过了假想的 authenticated\_user() 函数验证,$authorized 变量的值才会被设置为真。但是如果你启用了 **register\_globals**,任何人都可以发送一个 GET 参数,例如 authorized=1 去覆盖它:
|
||||
看下面的脚本,假如 $authorized 变量的值为 true,它会给用户显示通过验证的数据。正常情况下,只有当用户正确通过了这个假想的 authenticated\_user() 函数验证,$authorized 变量的值才会被设置为真。但是如果你启用了 **register\_globals**,任何人都可以发送一个 GET 参数,例如 authorized=1 去覆盖它:
|
||||
|
||||
<?php
|
||||
// Define $authorized = true only if user is authenticated
|
||||
@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ PHP 安全
|
||||
|
||||
这个故事的寓意是,你应该从预定义的服务器变量中获取表单数据。所有通过 post 表单传递到你 web 页面的数据都会自动保存到一个称为 **$\_POST** 的大数组中,所有的 GET 数据都保存在 **$\_GET** 大数组中。文件上传信息保存在一个称为 **$\_FILES** 的特殊数据中。另外,还有一个称为 **$\_REQUEST** 的复合变量。
|
||||
|
||||
要从一个 POST 方法表单中访问 username 域,可以使用 **$\_POST['username']**。如果 username 在 URL 中就使用 **$\_GET['username']**。如果你不确定值来自哪里,用 **$\_REQUEST['username']**。
|
||||
要从一个 POST 方法表单中访问 username 字段,可以使用 **$\_POST['username']**。如果 username 在 URL 中就使用 **$\_GET['username']**。如果你不确定值来自哪里,用 **$\_REQUEST['username']**。
|
||||
|
||||
<?php
|
||||
$post_value = $_POST['post_value'];
|
||||
@ -61,12 +61,12 @@ $\_REQUEST 是 $\_GET、$\_POST、和 $\_COOKIE 数组的结合。如果你有
|
||||
|
||||
- **register\_globals** 设置为 off
|
||||
- **safe\_mode** 设置为 off
|
||||
- **error\_reporting** 设置为 off。如果出现错误了,这会向用户浏览器发送可见的错误报告信息。对于生产服务器,使用错误日志代替。开发服务器如果在防火墙后面就可以启用错误日志。
|
||||
- **error\_reporting** 设置为 off。如果出现错误了,这会向用户浏览器发送可见的错误报告信息。对于生产服务器,使用错误日志代替。开发服务器如果在防火墙后面就可以启用错误日志。(LCTT 译注:此处据原文逻辑和常识,应该是“开发服务器如果在防火墙后面就可以启用错误报告,即 on。”)
|
||||
- 停用这些函数:system()、exec()、passthru()、shell\_exec()、proc\_open()、和 popen()。
|
||||
- **open\_basedir** 为 /tmp(以便保存会话信息)目录和 web 根目录设置值,以便脚本不能访问选定区域外的文件。
|
||||
- **expose\_php** 设置为 off。该功能会向 Apache 头添加包含版本数字的 PHP 签名。
|
||||
- **allow\_url\_fopen** 设置为 off。如果你小心在你代码中访问文件的方式-也就是你验证所有输入参数,这并不严格需要。
|
||||
- **allow\_url\_include** 设置为 off。这实在没有明智的理由任何人会想要通过 HTTP 访问包含的文件。
|
||||
- **open\_basedir** 为 /tmp(以便保存会话信息)目录和 web 根目录,以便脚本不能访问这些选定区域外的文件。
|
||||
- **expose\_php** 设置为 off。该功能会向 Apache 头添加包含版本号的 PHP 签名。
|
||||
- **allow\_url\_fopen** 设置为 off。如果你能够注意你代码中访问文件的方式-也就是你验证所有输入参数,这并不严格需要。
|
||||
- **allow\_url\_include** 设置为 off。对于任何人来说,实在没有明智的理由会想要访问通过 HTTP 包含的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
一般来说,如果你发现想要使用这些功能的代码,你就不应该相信它。尤其要小心会使用类似 system() 函数的代码-它几乎肯定有缺陷。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -74,13 +74,13 @@ $\_REQUEST 是 $\_GET、$\_POST、和 $\_COOKIE 数组的结合。如果你有
|
||||
|
||||
### SQL 注入攻击 ###
|
||||
|
||||
由于 PHP 传递到 MySQL 数据库的查询语句是按照强大的 SQL 编程语言编写的,你就有某些人通过在 web 查询参数中使用 MySQL 语句尝试 SQL 注入攻击的风险。通过在参数中插入有害的 SQL 代码片段,攻击者会尝试进入(或破坏)你的服务器。
|
||||
由于 PHP 传递到 MySQL 数据库的查询语句是用强大的 SQL 编程语言编写的,就有了某些人通过在 web 查询参数中使用 MySQL 语句尝试 SQL 注入攻击的风险。通过在参数中插入有害的 SQL 代码片段,攻击者会尝试进入(或破坏)你的服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
假如说你有一个最终会放入变量 $product 的表单参数,你使用了类似下面的 SQL 语句:
|
||||
|
||||
$sql = "select * from pinfo where product = '$product'";
|
||||
|
||||
如果参数是直接从表单中获得的,使用 PHP 自带的数据库特定转义函数,类似:
|
||||
如果参数是直接从表单中获得的,应该使用 PHP 自带的数据库特定转义函数,类似:
|
||||
|
||||
$sql = 'Select * from pinfo where product = '"'
|
||||
mysql_real_escape_string($product) . '"';
|
||||
@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ $\_REQUEST 是 $\_GET、$\_POST、和 $\_COOKIE 数组的结合。如果你有
|
||||
|
||||
39'; DROP pinfo; SELECT 'FOO
|
||||
|
||||
$sql 的结果就是:
|
||||
那么 $sql 的结果就是:
|
||||
|
||||
select product from pinfo where product = '39'; DROP pinfo; SELECT 'FOO'
|
||||
|
||||
@ -110,15 +110,15 @@ $sql 的结果就是:
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:要自动转义任何表单数据,可以启用魔术引号(Magic Quotes)。**
|
||||
|
||||
一些 MySQL 破坏可以通过限制 MySQL 用户权限避免。任何 MySQL 账户可以限制为只允许对选定的表进行特定类型的查询。例如,你可以创建只能选择行的 MySQL 用户。但是,这对于动态数据并不十分有用,另外,如果你有敏感的用户信息,可能某些人能访问一些数据,但你并不希望如此。例如,一个访问账户数据的用户可能会尝试注入访问另一个账户号码的代码,而不是为当前会话指定的号码。
|
||||
一些 MySQL 破坏可以通过限制 MySQL 用户权限避免。任何 MySQL 账户可以限制为只允许对选定的表进行特定类型的查询。例如,你可以创建只能选择行的 MySQL 用户。但是,这对于动态数据并不十分有用,另外,如果你有敏感的用户信息,可能某些人能访问其中一些数据,但你并不希望如此。例如,一个访问账户数据的用户可能会尝试注入访问另一个人的账户号码的代码,而不是为当前会话指定的号码。
|
||||
|
||||
### 防止基本的 XSS 攻击 ###
|
||||
|
||||
XSS 表示跨站点脚本。不像大部分攻击,该漏洞发生在客户端。XSS 最常见的基本形式是在用户提交的内容中放入 JavaScript 以便偷取用户 cookie 中的数据。由于大部分站点使用 cookie 和 session 验证访客,偷取的数据可用于模拟该用于-如果是一个典型的用户账户就会深受麻烦,如果是管理员账户甚至是彻底的惨败。如果你不在站点中使用 cookie 和 session ID,你的用户就不容易被攻击,但你仍然应该明白这种攻击是如何工作的。
|
||||
XSS 表示跨站脚本。不像大部分攻击,该漏洞发生在客户端。XSS 最常见的基本形式是在用户提交的内容中放入 JavaScript 以便偷取用户 cookie 中的数据。由于大部分站点使用 cookie 和 session 验证访客,偷取的数据可用于模拟该用户-如果是一个常见的用户账户就会深受麻烦,如果是管理员账户甚至是彻底的惨败。如果你不在站点中使用 cookie 和 session ID,你的用户就不容易被攻击,但你仍然应该明白这种攻击是如何工作的。
|
||||
|
||||
不像 MySQL 注入攻击,XSS 攻击很难预防。Yahoo、eBay、Apple、以及 Microsoft 都曾经受 XSS 影响。尽管攻击不包含 PHP,你可以使用 PHP 来剥离用户数据以防止攻击。为了防止 XSS 攻击,你应该限制和过滤用户提交给你站点的数据。正是因为这个原因大部分在线公告板都不允许在提交的数据中使用 HTML 标签,而是用自定义的标签格式代替,例如 **[b]** 和 **[linkto]**。
|
||||
不像 MySQL 注入攻击,XSS 攻击很难预防。Yahoo、eBay、Apple、以及 Microsoft 都曾经受 XSS 影响。尽管攻击不包含 PHP,但你可以使用 PHP 来剥离用户数据以防止攻击。为了防止 XSS 攻击,你应该限制和过滤用户提交给你站点的数据。正是因为这个原因,大部分在线公告板都不允许在提交的数据中使用 HTML 标签,而是用自定义的标签格式代替,例如 **[b]** 和 **[linkto]**。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们来看一个如何防止这类攻击的简单脚本。对于更完善的解决办法,可以使用 SafeHHTML,本文的后面部分会讨论到。
|
||||
让我们来看一个如何防止这类攻击的简单脚本。对于更完善的解决办法,可以使用 SafeHTML,本文的后面部分会讨论到。
|
||||
|
||||
function transform_HTML($string, $length = null) {
|
||||
// Helps prevent XSS attacks
|
||||
@ -137,23 +137,21 @@ XSS 表示跨站点脚本。不像大部分攻击,该漏洞发生在客户端
|
||||
return $string;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
这个函数将 HTML 特定字符转换为 HTML 字面字符。一个浏览器对任何通过这个脚本的 HTML 以无标记的文本呈现。例如,考虑下面的 HTML 字符串:
|
||||
这个函数将 HTML 特定的字符转换为 HTML 字面字符。一个浏览器对任何通过这个脚本的 HTML 以非标记的文本呈现。例如,考虑下面的 HTML 字符串:
|
||||
|
||||
<STRONG>Bold Text</STRONG>
|
||||
|
||||
一般情况下,HTML 会显示为:
|
||||
一般情况下,HTML 会显示为:**Bold Text**
|
||||
|
||||
Bold Text
|
||||
|
||||
但是,通过 **transform\_HTML()** 后,它就像初始输入一样呈现。原因是处理的字符串中标签字符串是 HTML 条目。**transform\_HTML()** 结果字符串的纯文本看起来像下面这样:
|
||||
但是,通过 **transform\_HTML()** 后,它就像原始输入一样呈现。原因是处理的字符串中的标签字符串转换为 HTML 实体。**transform\_HTML()** 的结果字符串的纯文本看起来像下面这样:
|
||||
|
||||
<STRONG>Bold Text</STRONG>
|
||||
|
||||
该函数的实质是 htmlentities() 函数调用,它会将 <、>、和 & 转换为 **<**、**>**、和 **&**。尽管这会处理大部分的普通攻击,有经验的 XSS 攻击者有另一种把戏:用十六进制或 UTF-8 编码恶意脚本,而不是采用普通的 ASCII 文本,从而希望能饶过你的过滤器。他们可以在 URL 的 GET 变量中发送代码,例如,“这是十六进制代码,你能帮我运行吗?” 一个十六进制例子看起来像这样:
|
||||
该函数的实质是 htmlentities() 函数调用,它会将 <、>、和 & 转换为 **\<**、**\>**、和 **\&**。尽管这会处理大部分的普通攻击,但有经验的 XSS 攻击者有另一种把戏:用十六进制或 UTF-8 编码恶意脚本,而不是采用普通的 ASCII 文本,从而希望能绕过你的过滤器。他们可以在 URL 的 GET 变量中发送代码,告诉浏览器,“这是十六进制代码,你能帮我运行吗?” 一个十六进制例子看起来像这样:
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="http://host/a.php?variable=%22%3e %3c%53%43%52%49%50%54%3e%44%6f%73%6f%6d%65%74%68%69%6e%67%6d%61%6c%69%63%69%6f%75%73%3c%2f%53%43%52%49%50%54%3e">
|
||||
|
||||
浏览器渲染这信息的时候,结果就是:
|
||||
浏览器渲染这个信息的时候,结果就是:
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="http://host/a.php?variable="> <SCRIPT>Dosomethingmalicious</SCRIPT>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -163,20 +161,20 @@ XSS 表示跨站点脚本。不像大部分攻击,该漏洞发生在客户端
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 SafeHTML ###
|
||||
|
||||
之前脚本的问题比较简单,它不允许任何类型的用户标记。不幸的是,这里有上百种方法能使 JavaScript 跳过用户的过滤器,从用户输入中剥离 HTML,没有方法可以防止这种情况。
|
||||
之前脚本的问题比较简单,它不允许任何类型的用户标记。不幸的是,这里有上百种方法能使 JavaScript 跳过用户的过滤器,并且要从用户输入中剥离全部 HTML,还没有方法可以防止这种情况。
|
||||
|
||||
当前,没有任何一个脚本能保证无法被破解,尽管有一些确实比大部分要好。有白名单和黑名单两种方法加固安全,白名单比较简单而且更加有效。
|
||||
|
||||
一个白名单解决方案是 PixelApes 的 SafeHTML 反跨站点脚本解析器。
|
||||
一个白名单解决方案是 PixelApes 的 SafeHTML 反跨站脚本解析器。
|
||||
|
||||
SafeHTML 能识别有效 HTML,能追踪并剥离任何危险标签。它用另一个称为 HTMLSax 的软件包进行解析。
|
||||
|
||||
按照下面步骤安装和使用 SafeHTML:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 到 [http://pixel-apes.com/safehtml/?page=safehtml][1] 下载最新版本的 SafeHTML。
|
||||
1. 把文件放到你服务器的类文件夹。该文件夹包括 SafeHTML 和 HTMLSax 起作用需要的所有东西。
|
||||
1. 在脚本中包含 SafeHTML 类文件(safehtml.php)。
|
||||
1. 创建称为 $safehtml 的新 SafeHTML 对象。
|
||||
1. 把文件放到你服务器的类文件夹。该文件夹包括 SafeHTML 和 HTMLSax 功能所需的所有东西。
|
||||
1. 在脚本中 `include` SafeHTML 类文件(safehtml.php)。
|
||||
1. 创建一个名为 $safehtml 的新 SafeHTML 对象。
|
||||
1. 用 $safehtml->parse() 方法清理你的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个完整的例子:
|
||||
@ -203,45 +201,45 @@ SafeHTML 能识别有效 HTML,能追踪并剥离任何危险标签。它用另
|
||||
|
||||
你可能犯的最大错误是假设这个类能完全避免 XSS 攻击。SafeHTML 是一个相当复杂的脚本,几乎能检查所有事情,但没有什么是能保证的。你仍然需要对你的站点做参数验证。例如,该类不能检查给定变量的长度以确保能适应数据库的字段。它也不检查缓冲溢出问题。
|
||||
|
||||
XSS 攻击者很有创造力,他们使用各种各样的方法来尝试达到他们的目标。可以阅读 RSnake 的 XSS 教程[http://ha.ckers.org/xss.html][2] 看一下这里有多少种方法尝试使代码跳过过滤器。SafeHTML 项目有很好的程序员一直在尝试阻止 XSS 攻击,但无法保证某些人不会想起一些奇怪和新奇的方法来跳过过滤器。
|
||||
XSS 攻击者很有创造力,他们使用各种各样的方法来尝试达到他们的目标。可以阅读 RSnake 的 XSS 教程[http://ha.ckers.org/xss.html][2] ,看一下这里有多少种方法尝试使代码跳过过滤器。SafeHTML 项目有很好的程序员一直在尝试阻止 XSS 攻击,但无法保证某些人不会想起一些奇怪和新奇的方法来跳过过滤器。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:XSS 攻击严重影响的一个例子 [http://namb.la/popular/tech.html][3],其中显示了如何一步一步创建会超载 MySpace 服务器的 JavaScript XSS 蠕虫。**
|
||||
**注意:XSS 攻击严重影响的一个例子 [http://namb.la/popular/tech.html][3],其中显示了如何一步一步创建一个让 MySpace 服务器过载的 JavaScript XSS 蠕虫。**
|
||||
|
||||
### 用单向哈希保护数据 ###
|
||||
|
||||
该脚本对输入的数据进行单向转换-换句话说,它能对某人的密码产生哈希签名,但不能解码获得原始密码。为什么你希望这样呢?应用程序会存储密码。一个管理员不需要知道用户的密码-事实上,只有用户知道他的/她的密码是个好主意。系统(也仅有系统)应该能识别一个正确的密码;这是 Unix 多年来的密码安全模型。单向密码安全按照下面的方式工作:
|
||||
该脚本对输入的数据进行单向转换,换句话说,它能对某人的密码产生哈希签名,但不能解码获得原始密码。为什么你希望这样呢?应用程序会存储密码。一个管理员不需要知道用户的密码,事实上,只有用户知道他/她自己的密码是个好主意。系统(也仅有系统)应该能识别一个正确的密码;这是 Unix 多年来的密码安全模型。单向密码安全按照下面的方式工作:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 当一个用户或管理员创建或更改一个账户密码时,系统对密码进行哈希并保存结果。主机系统忽视明文密码。
|
||||
1. 当一个用户或管理员创建或更改一个账户密码时,系统对密码进行哈希并保存结果。主机系统会丢弃明文密码。
|
||||
2. 当用户通过任何方式登录到系统时,再次对输入的密码进行哈希。
|
||||
3. 主机系统抛弃输入的明文密码。
|
||||
3. 主机系统丢弃输入的明文密码。
|
||||
4. 当前新哈希的密码和之前保存的哈希相比较。
|
||||
5. 如果哈希的密码相匹配,系统就会授予访问权限。
|
||||
|
||||
主机系统完成这些并不需要知道原始密码;事实上,原始值完全不相关。一个副作用是,如果某人侵入系统并盗取了密码数据库,入侵者会获得很多哈希后的密码,但无法把它们反向转换为原始密码。当然,给足够时间、计算能力,以及弱用户密码,一个攻击者还是有可能采用字典攻击找出密码。因此,别轻易让人碰你的密码数据库,如果确实有人这样做了,让每个用户更改他们的密码。
|
||||
主机系统完成这些并不需要知道原始密码;事实上,原始密码完全无所谓。一个副作用是,如果某人侵入系统并盗取了密码数据库,入侵者会获得很多哈希后的密码,但无法把它们反向转换为原始密码。当然,给足够时间、计算能力,以及弱用户密码,一个攻击者还是有可能采用字典攻击找出密码。因此,别轻易让人碰你的密码数据库,如果确实有人这样做了,让每个用户更改他们的密码。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 加密 Vs 哈希 ####
|
||||
|
||||
技术上来来说,这过程并不是加密。哈希和加密是不相同的,这有两个理由:
|
||||
技术上来来说,哈希过程并不是加密。哈希和加密是不同的,这有两个理由:
|
||||
|
||||
不像加密,数据不能被解密。
|
||||
不像加密,哈希数据不能被解密。
|
||||
|
||||
是有可能(但很不常见)两个不同的字符串会产生相同的哈希。并不能保证哈希是唯一的,因此别像数据库中的唯一键那样使用哈希。
|
||||
是有可能(但非常罕见)两个不同的字符串会产生相同的哈希。并不能保证哈希是唯一的,因此别像数据库中的唯一键那样使用哈希。
|
||||
|
||||
function hash_ish($string) {
|
||||
return md5($string);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
md5() 函数基于 RSA 数据安全公司的消息摘要算法(即 MD5)返回一个由 32 个字符组成的十六进制串。然后你可以将那个 32 位字符串插入到数据库中,和另一个 md5 字符串相比较,或者就用这 32 个字符。
|
||||
上面的 md5() 函数基于 RSA 数据安全公司的消息摘要算法(即 MD5)返回一个由 32 个字符组成的十六进制串。然后你可以将那个 32 位字符串插入到数据库中和另一个 md5 字符串相比较,或者直接用这 32 个字符。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 破解脚本 ####
|
||||
|
||||
几乎不可能解密 MD5 数据。或者说很难。但是,你仍然需要好的密码,因为根据整个字典生成哈希数据库仍然很简单。这里有在线 MD5 字典,当你输入 **06d80eb0c50b49a509b49f2424e8c805** 后会得到结果 “dog”。因此,尽管技术上 MD5 不能被解密,这里仍然有漏洞-如果某人获得了你的密码数据库,你可以肯定他们肯定会使用 MD5 字典破译。因此,当你创建基于密码的系统的时候尤其要注意密码长度(最小 6 个字符,8 个或许会更好)和包括字母和数字。并确保字典中没有这个密码。
|
||||
几乎不可能解密 MD5 数据。或者说很难。但是,你仍然需要好的密码,因为用一整个字典生成哈希数据库仍然很简单。有一些在线 MD5 字典,当你输入 **06d80eb0c50b49a509b49f2424e8c805** 后会得到结果 “dog”。因此,尽管技术上 MD5 不能被解密,这里仍然有漏洞,如果某人获得了你的密码数据库,你可以肯定他们肯定会使用 MD5 字典破译。因此,当你创建基于密码的系统的时候尤其要注意密码长度(最小 6 个字符,8 个或许会更好)和包括字母和数字。并确保这个密码不在字典中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 用 Mcrypt 加密数据 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不需要以可阅读形式查看密码,采用 MD5 就足够了。不幸的是,这里并不总是有可选项-如果你提供以加密形式存储某人的信用卡信息,你可能需要在后面的某个点进行解密。
|
||||
如果你不需要以可阅读形式查看密码,采用 MD5 就足够了。不幸的是,这里并不总是有可选项,如果你提供以加密形式存储某人的信用卡信息,你可能需要在后面的某个地方进行解密。
|
||||
|
||||
最早的一个解决方案是 Mcrypt 模块,用于允许 PHP 高速加密的附件。Mcrypt 库提供了超过 30 种计算方法用于加密,并且提供短语确保只有你(或者你的用户)可以解密数据。
|
||||
最早的一个解决方案是 Mcrypt 模块,这是一个用于允许 PHP 高速加密的插件。Mcrypt 库提供了超过 30 种用于加密的计算方法,并且提供口令确保只有你(或者你的用户)可以解密数据。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们来看看使用方法。下面的脚本包含了使用 Mcrypt 加密和解密数据的函数:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -282,21 +280,21 @@ md5() 函数基于 RSA 数据安全公司的消息摘要算法(即 MD5)返
|
||||
**mcrypt()** 函数需要几个信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- 需要加密的数据
|
||||
- 用于加密和解锁数据的短语,也称为键。
|
||||
- 用于加密和解锁数据的口令,也称为键。
|
||||
- 用于加密数据的计算方法,也就是用于加密数据的算法。该脚本使用了 **MCRYPT\_SERPENT\_256**,但你可以从很多算法中选择,包括 **MCRYPT\_TWOFISH192**、**MCRYPT\_RC2**、**MCRYPT\_DES**、和 **MCRYPT\_LOKI97**。
|
||||
- 加密数据的模式。这里有几个你可以使用的模式,包括电子密码本(Electronic Codebook) 和加密反馈(Cipher Feedback)。该脚本使用 **MCRYPT\_MODE\_CBC** 密码块链接。
|
||||
- 一个 **初始化向量**-也称为 IV,或着一个种子-用于为加密算法设置种子的额外二进制位。也就是使算法更难于破解的额外信息。
|
||||
- 键和 IV 字符串的长度,这可能随着加密和块而不同。使用 **mcrypt\_get\_key\_size()** 和 **mcrypt\_get\_block\_size()** 函数获取合适的长度;然后用 **substr()** 函数将键的值截取为合适的长度。(如果键的长度比要求的短,别担心-Mcrypt 会用 0 填充。)
|
||||
- 一个 **初始化向量**-也称为 IV 或者种子,用于为加密算法设置种子的额外二进制位。也就是使算法更难于破解的额外信息。
|
||||
- 键和 IV 字符串的长度,这可能随着加密和块而不同。使用 **mcrypt\_get\_key\_size()** 和 **mcrypt\_get\_block\_size()** 函数获取合适的长度;然后用 **substr()** 函数将键的值截取为合适的长度。(如果键的长度比要求的短,别担心,Mcrypt 会用 0 填充。)
|
||||
|
||||
如果有人窃取了你的数据和短语,他们只能一个个尝试加密算法直到找到正确的那一个。因此,在使用它之前我们通过对键使用 **md5()** 函数增加安全,就算他们获取了数据和短语,入侵者也不能获得想要的东西。
|
||||
|
||||
入侵者同时需要函数,数据和短语-如果真是如此,他们可能获得了对你服务器的完整访问,你只能大清洗了。
|
||||
入侵者同时需要函数,数据和口令,如果真是如此,他们可能获得了对你服务器的完整访问,你只能大清洗了。
|
||||
|
||||
这里还有一个数据存储格式的小问题。Mcrypt 以难懂的二进制形式返回加密后的数据,这使得当你将其存储到 MySQL 字段的时候可能出现可怕错误。因此,我们使用 **base64encode()** 和 **base64decode()** 函数转换为和 SQL 兼容的字母格式和检索行。
|
||||
这里还有一个数据存储格式的小问题。Mcrypt 以难懂的二进制形式返回加密后的数据,这使得当你将其存储到 MySQL 字段的时候可能出现可怕错误。因此,我们使用 **base64encode()** 和 **base64decode()** 函数转换为和 SQL 兼容的字母格式和可检索行。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 破解脚本 ####
|
||||
|
||||
除了实验多种加密方法,你还可以在脚本中添加一些便利。例如,不是每次都提供键和模式,而是在包含的文件中声明为全局常量。
|
||||
除了实验多种加密方法,你还可以在脚本中添加一些便利。例如,不用每次都提供键和模式,而是在包含的文件中声明为全局常量。
|
||||
|
||||
### 生成随机密码 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -331,8 +329,8 @@ md5() 函数基于 RSA 数据安全公司的消息摘要算法(即 MD5)返
|
||||
函数按照下面步骤工作:
|
||||
|
||||
- 函数确保 **$num\_chars** 是非零的正整数。
|
||||
- 函数初始化 **$accepted\_chars** 变量为密码可能包含的字符列表。该脚本使用所有小写字母和数字 0 到 9,但你可以使用你喜欢的任何字符集合。
|
||||
- 随机数生成器需要一个种子,从而获得一系列类随机值(PHP 4.2 及之后版本中并不严格要求)。
|
||||
- 函数初始化 **$accepted\_chars** 变量为密码可能包含的字符列表。该脚本使用所有小写字母和数字 0 到 9,但你可以使用你喜欢的任何字符集合。(LCTT 译注:有时候为了便于肉眼识别,你可以将其中的 0 和 O,1 和 l 之类的都去掉。)
|
||||
- 随机数生成器需要一个种子,从而获得一系列类随机值(PHP 4.2 及之后版本中并不需要,会自动播种)。
|
||||
- 函数循环 **$num\_chars** 次,每次迭代生成密码中的一个字符。
|
||||
- 对于每个新字符,脚本查看 **$accepted_chars** 的长度,选择 0 和长度之间的一个数字,然后添加 **$accepted\_chars** 中该数字为索引值的字符到 $password。
|
||||
- 循环结束后,函数返回 **$password**。
|
||||
@ -347,7 +345,7 @@ via: http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/363897/PHP-Security
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SamarRizvi][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
140
published/20150713 How to manage Vim plugins.md
Normal file
140
published/20150713 How to manage Vim plugins.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,140 @@
|
||||
如何管理 Vim 插件
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Vim是Linux上一个轻量级的通用文本编辑器。虽然它开始时的学习曲线对于一般的Linux用户来说可能很困难,但比起它的好处,这些付出完全是值得的。vim 可以通过完全可定制的插件来增加越来越多的功能。但是,由于它的功能配置比较难,你需要花一些时间去了解它的插件系统,然后才能够有效地去个性化定置Vim。幸运的是,我们已经有一些工具能够使我们在使用Vim插件时更加轻松。而我日常所使用的就是Vundle。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是Vundle ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Vundle][1]意即Vim Bundle,是一个vim插件管理器。Vundle能让你很简单地实现插件的安装、升级、搜索或者清除。它还能管理你的运行环境并且在标签方面提供帮助。在本教程中我们将展示如何安装和使用Vundle。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装Vundle ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,如果你的Linux系统上没有Git的话,先[安装Git][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
接着,创建一个目录,Vim的插件将会被下载并且安装在这个目录上。默认情况下,这个目录为~/.vim/bundle。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mkdir -p ~/.vim/bundle
|
||||
|
||||
现在,使用如下指令安装Vundle。注意Vundle本身也是一个vim插件。因此我们同样把vundle安装到之前创建的目录~/.vim/bundle下。
|
||||
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/gmarik/Vundle.vim.git ~/.vim/bundle/Vundle.vim
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置Vundle ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在配置你的.vimrc文件如下:
|
||||
|
||||
set nocompatible " 必需。
|
||||
filetype off " 必须。
|
||||
|
||||
" 在这里设置你的运行时环境的路径。
|
||||
set rtp+=~/.vim/bundle/Vundle.vim
|
||||
|
||||
" 初始化vundle
|
||||
call vundle#begin()
|
||||
|
||||
" 这一行应该永远放在开头。
|
||||
Plugin 'gmarik/Vundle.vim'
|
||||
|
||||
" 这个示范来自https://github.com/gmarik/Vundle.vim README
|
||||
Plugin 'tpope/vim-fugitive'
|
||||
|
||||
" 取自http://vim-scripts.org/vim/scripts.html的插件
|
||||
Plugin 'L9'
|
||||
|
||||
" 该Git插件没有放在GitHub上。
|
||||
Plugin 'git://git.wincent.com/command-t.git'
|
||||
|
||||
"本地计算机上的Git仓库路径 (例如,当你在开发你自己的插件时)
|
||||
Plugin 'file:///home/gmarik/path/to/plugin'
|
||||
|
||||
" vim脚本sparkup存放在这个名叫vim的仓库下的一个子目录中。
|
||||
" 将这个路径正确地设置为runtimepath。
|
||||
Plugin 'rstacruz/sparkup', {'rtp': 'vim/'}
|
||||
|
||||
" 避免与L9发生名字上的冲突
|
||||
Plugin 'user/L9', {'name': 'newL9'}
|
||||
|
||||
"所有的插件都应该在这一行之前。
|
||||
call vundle#end() " 必需。
|
||||
|
||||
容我简单解释一下上面的设置:默认情况下,Vundle将从github.com或者vim-scripts.org下载和安装vim插件。你也可以改变这个默认行为。
|
||||
|
||||
要从github安装插件:
|
||||
|
||||
Plugin 'user/plugin'
|
||||
|
||||
要从 http://vim-scripts.org/vim/scripts.html 处安装:
|
||||
|
||||
Plugin 'plugin_name'
|
||||
|
||||
要从另外一个git仓库中安装:
|
||||
|
||||
Plugin 'git://git.another_repo.com/plugin'
|
||||
|
||||
从本地文件中安装:
|
||||
|
||||
Plugin 'file:///home/user/path/to/plugin'
|
||||
|
||||
你同样可以定制其它东西,例如你的插件的运行时路径,当你自己在编写一个插件时,或者你只是想从其它目录——而不是~/.vim——中加载插件时,这样做就非常有用。
|
||||
|
||||
Plugin 'rstacruz/sparkup', {'rtp': 'another_vim_path/'}
|
||||
|
||||
如果你有同名的插件,你可以重命名你的插件,这样它们就不会发生冲突了。
|
||||
|
||||
Plugin 'user/plugin', {'name': 'newPlugin'}
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用Vum命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
一旦你用vundle设置好你的插件,你就可以通过几个vundle命令来安装、升级、搜索插件,或者清除没有用的插件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 安装一个新的插件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
`PluginInstall`命令将会安装所有列在你的.vimrc文件中的插件。你也可以通过传递一个插件名给它,来安装某个的特定插件。
|
||||
|
||||
:PluginInstall
|
||||
:PluginInstall <插件名>
|
||||
|
||||
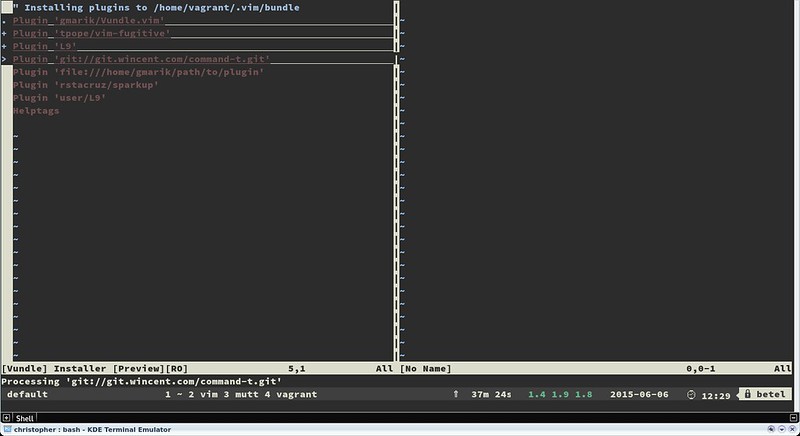
|
||||
|
||||
#### 清除没有用的插件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
如果你有任何没有用到的插件,你可以通过`PluginClean`命令来删除它。
|
||||
|
||||
:PluginClean
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 查找一个插件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想从提供的插件清单中安装一个插件,搜索功能会很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
:PluginSearch <文本>
|
||||
|
||||
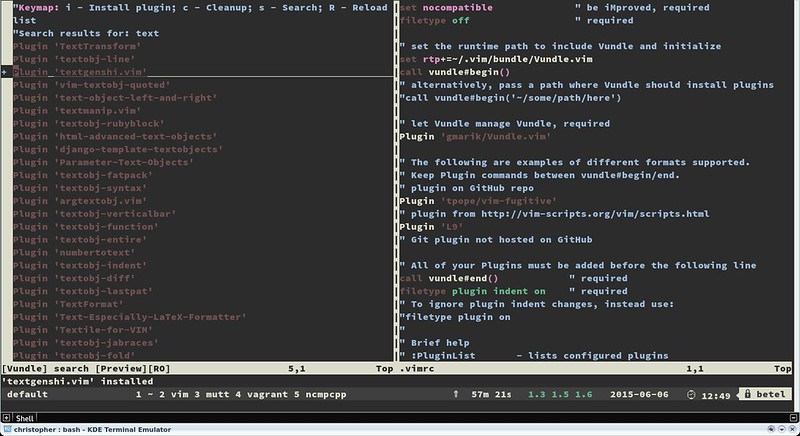
|
||||
|
||||
在搜索的时候,你可以在交互式分割窗口中安装、清除、重新搜索或者重新加载插件清单。安装后的插件不会自动加载生效,要使其加载生效,可以将它们添加进你的.vimrc文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Vim是一个妙不可言的工具。它不单单是一个能够使你的工作更加顺畅高效的默认文本编辑器,同时它还能够摇身一变,成为现存的几乎任何一门编程语言的IDE。
|
||||
|
||||
注意,有一些网站能帮你找到适合的vim插件。猛击 [http://www.vim-scripts.org][3], Github或者 [http://www.vimawesome.com][4] 获取新的脚本或插件。同时记得使用为你的插件提供的帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
和你最爱的编辑器一起嗨起来吧!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/manage-vim-plugins.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Christopher Valerio][a]
|
||||
译者:[XLCYun(袖里藏云)](https://github.com/XLCYun)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/valerio
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/VundleVim/Vundle.vim
|
||||
[2]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-git-linux.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.vim-scripts.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.vimawesome.com/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@ Ubuntu 下 CCleaner 的 4 个替代品
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
回首我使用 Windows 的那些日子,[CCleaner][1] 是我用来释放空间,删除垃圾文件和加速 Windows 的最喜爱的工具。我知道,当从 Windows 切换到 Linux 时,我并不是唯一期望 CCleaner 拥有 Linux 版本的人。假如你正在寻找 Linux 下 CCleaner 的替代品,我将在下面列举 4 个这样的应用,它们可以用来清理 Ubuntu 或基于 Ubuntu 的 Linux 发行版本。但在我们看这个清单之前,让我们考虑一下 Linux 是否需要系统清理工具这个问题。
|
||||
回首我使用 Windows 的那些日子,[CCleaner][1] 是我用来释放空间、删除垃圾文件和加速 Windows 的最喜爱的工具。我知道,当从 Windows 切换到 Linux 时,我并不是唯一期望 CCleaner 拥有 Linux 版本的人。假如你正在寻找 Linux 下 CCleaner 的替代品,我将在下面列举 4 个这样的应用,它们可以用来清理 Ubuntu 或基于 Ubuntu 的 Linux 发行版本。但在我们看这个清单之前,先让我们考虑一下 Linux 是否需要系统清理工具这个问题。
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux 需要像 CCleaner 那样的系统清理工具吗? ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,18 +12,18 @@ Ubuntu 下 CCleaner 的 4 个替代品
|
||||
|
||||
所以,概括起来,它在系统范围内清理在你的浏览器或媒体播放器中的临时文件。你或许知道 Windows 有在系统中保存垃圾文件的喜好,那 Linux 呢?它是如何处理临时文件的呢?
|
||||
|
||||
与 Windows 不同, Linux 自动地清理所有的临时文件(在 `/tmp` 中存储)。在 Linux 中没有注册表,这进一步减轻了头痛。在最坏情况下,你可能会有一些损坏的软件包,不再需要软件包以及网络浏览历史记录, cookies ,缓存等。
|
||||
与 Windows 不同, Linux 自动地清理所有的临时文件(在 `/tmp` 中存储)。在 Linux 中没有注册表,这进一步减轻了头痛。在最坏情况下,你可能会有一些损坏的不再需要的软件包,以及丢失一些网络浏览历史记录, cookies ,缓存等。
|
||||
|
||||
### 这意味着 Linux 不必需要系统清理工具了吗? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 假如你可以运行某些命令来清理偶尔使用的软件包,手动删除浏览历史记录等,那么答案是:No;
|
||||
- 假如你不想从一个地方跳到另一个地方来运行命令,并想用一个工具来删除所有可通过一次或多次点击所选择的东西,那么答案是:Yes。
|
||||
- 假如你可以运行某些命令来清理偶尔使用的软件包,手动删除浏览历史记录等,那么答案是:不需要;
|
||||
- 假如你不想不断地从一个地方跳到另一个地方来运行命令,并想用一个工具来删除所有可通过一次或多次点击所选择的东西,那么答案是:需要。
|
||||
|
||||
假如你的答案是 Yes,就让我们继续看看一些类似于 CCleaner 的工具,用它们清理你的 Ubuntu 系统。
|
||||
假如你的答案是“需要”,就让我们继续看看一些类似于 CCleaner 的工具,用它们清理你的 Ubuntu 系统。
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu 下 CCleaner 的替代品 ###
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,我使用的系统是 Ubuntu,因为下面讨论的一些工具只存在于基于 Ubuntu 的 Linux 发行版本中,而剩下的在所有的 Linux 发行版本中都可使用。
|
||||
请注意,我使用的系统是 Ubuntu,因为下面讨论的一些工具只存在于基于 Ubuntu 的 Linux 发行版本中,而另外一些在所有的 Linux 发行版本中都可使用。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. BleachBit ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -32,10 +32,10 @@ Ubuntu 下 CCleaner 的 4 个替代品
|
||||
[BleachBit][3] 是一个跨平台的应用程序,在 Windows 和 Linux 平台下都可使用。它有一个很长的支持清理的程序的列表,这样可以让你选择性的清理缓存,cookies 和日志文件。让我们快速浏览它的特点:
|
||||
|
||||
- 简洁的图形界面确认框,你可以预览或删除
|
||||
- 多平台: Linux 和 Windows
|
||||
- 支持多平台: Linux 和 Windows
|
||||
- 免费且开源
|
||||
- 粉碎文件以隐藏它们的内容并防止数据恢复
|
||||
- 重写可用的磁盘空间来隐藏先前删除的文件
|
||||
- 重写空闲的磁盘空间来隐藏先前删除的文件内容
|
||||
- 也拥有命令行界面
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,在 Ubuntu 14.04 and 15.04 中都可以获取到 BleachBit,你可以在终端中使用下面的命令来安装:
|
||||
@ -103,7 +103,7 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/ccleaner-alternatives-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,17 +1,17 @@
|
||||
|
||||
在 RHEL/CentOS 上为Web服务器设置 “XR”(Crossroads) 负载均衡器
|
||||
在 RHEL/CentOS 上为Web服务器架设 “XR”(Crossroads) 负载均衡器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Crossroads 是一个独立的服务,并且是一个开源的负载均衡和故障转移实用程序,基于Linux和TCP服务。它可用于HTTP,HTTPS,SSH,SMTP和DNS等,它也是一个多线程的工具,它只消耗一个存储空间以此来提高性能达到负载均衡的目的。
|
||||
Crossroads 是一个独立的服务,它是一个用于Linux和TCP服务的开源负载均衡和故障转移实用程序。它可用于HTTP,HTTPS,SSH,SMTP 和 DNS 等,它也是一个多线程的工具,在提供负载均衡服务时,它可以只使用一块内存空间以此来提高性能。
|
||||
|
||||
首先来看看 XR 是如何工作的。我们可以找到 XR 分派的网络客户端和服务器之间到负载均衡服务器上的请求。
|
||||
首先来看看 XR 是如何工作的。我们可以将 XR 放到网络客户端和服务器之间,它可以将客户端的请求分配到服务器上以平衡负载。
|
||||
|
||||
如果一台服务器宕机,XR 会转发客户端请求到另一个服务器,所以客户感觉不到停机时间。看看下面的图来了解什么样的情况下,我们要使用 XR 处理。
|
||||
如果一台服务器宕机,XR 会转发客户端请求到另一个服务器,所以客户感觉不到停顿。看看下面的图来了解什么样的情况下,我们要使用 XR 处理。
|
||||
|
||||
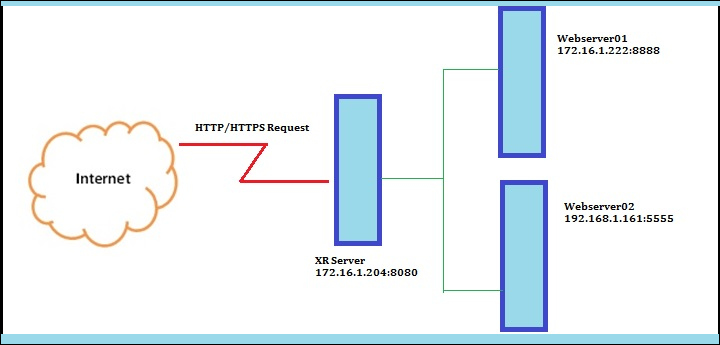
|
||||
|
||||
安装 XR Crossroads 负载均衡器
|
||||
*安装 XR Crossroads 负载均衡器*
|
||||
|
||||
有两个 Web 服务器,一个网关服务器,我们安装和设置 XR 接收客户端请求,分发到服务器之间。
|
||||
这里有两个 Web 服务器,一个网关服务器,我们将在网关服务器上安装和设置 XR 以接收客户端请求,并分发到服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
XR Crossroads 网关服务器:172.16.1.204
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,9 +25,9 @@ Crossroads 是一个独立的服务,并且是一个开源的负载均衡和故
|
||||
|
||||
### 第1步:在网关服务器上安装 XR Crossroads 负载均衡器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**1. 不幸的是,没有为 crosscroads 提供可用的 RPM 包,我们只能从源码安装。**
|
||||
**1. 不幸的是,没有为 crossroads 提供可用的 RPM 包,我们只能从源码安装。**
|
||||
|
||||
要编译 XR,你必须在系统上安装 C++ 编译器和 GNU make 组件,才能继续无差错的安装。
|
||||
要编译 XR,你必须在系统上安装 C++ 编译器和 GNU make 组件,才能避免安装错误。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install gcc gcc-c++ make
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,36 +42,35 @@ Crossroads 是一个独立的服务,并且是一个开源的负载均衡和故
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
安装 XR Crossroads 负载均衡器
|
||||
*安装 XR Crossroads 负载均衡器*
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后,二进制文件安装在 /usr/sbin 目录下,XR 的配置文件在 /etc 下名为 “xrctl.xml” 。
|
||||
|
||||
**2. 最后一个条件,你需要两个web服务器。为了方便使用,我在一台服务器中创建两个 Python SimpleHTTPServer 实例。**
|
||||
|
||||
要了解如何设置一个 python SimpleHTTPServer,请阅读我们此处的文章 [Create Two Web Servers Easily Using SimpleHTTPServer][2].
|
||||
|
||||
要了解如何设置一个 python SimpleHTTPServer,请阅读我们此处的文章 [使用 SimpleHTTPServer 轻松创建两个 web 服务器][2].
|
||||
|
||||
正如我所说的,我们要使用两个web服务器,webserver01 通过8888端口运行在172.16.1.222上,webserver02 通过5555端口运行在192.168.1.161上。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
XR WebServer 01
|
||||
*XR WebServer 01*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
XR WebServer 02
|
||||
*XR WebServer 02*
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: 配置 XR Crossroads 负载均衡器 ###
|
||||
### 第2步: 配置 XR Crossroads 负载均衡器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**3. 这个位置是最关键的。现在我们要做的就是配置`xrctl.xml` 文件并通过 XR 服务器接受来自互联网的请求分发到 web 服务器之间。**
|
||||
**3. 所需都已经就绪。现在我们要做的就是配置`xrctl.xml` 文件并通过 XR 服务器接受来自互联网的请求分发到 web 服务器上。**
|
||||
|
||||
现在打开`xrctl.xml`文件用 [vi/vim editor][3].
|
||||
现在用 [vi/vim 编辑器][3]打开`xrctl.xml`文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/xrctl.xml
|
||||
|
||||
并作如下修改。
|
||||
|
||||
<?xml version=<94>1.0<94> encoding=<94>UTF-8<94>?>
|
||||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
|
||||
<configuration>
|
||||
<system>
|
||||
<uselogger>true</uselogger>
|
||||
@ -100,9 +99,9 @@ XR WebServer 02
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
配置 XR Crossroads 负载均衡器
|
||||
*配置 XR Crossroads 负载均衡器*
|
||||
|
||||
在这里,你可以看到在 xrctl.xml 做了一个非常基本的 XR 配置。我已经定义了 XR 服务器是什么,XR 的后端服务和端口及网络接口端是什么。
|
||||
在这里,你可以看到在 xrctl.xml 中配置了一个非常基本的 XR 。我已经定义了 XR 服务器在哪里,XR 的后端服务和端口及 XR 的 web 管理界面是什么。
|
||||
|
||||
**4. 现在,你需要通过以下命令来启动该 XR 守护进程。**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -111,27 +110,27 @@ XR WebServer 02
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
启动 XR Crossroads
|
||||
*启动 XR Crossroads*
|
||||
|
||||
**5. 好的。现在是时候来检查该配置是否可以工作正常了。打开两个网页浏览器,输入 XR 服务器端口的 IP 地址,并查看输出。**
|
||||
**5. 好的。现在是时候来检查该配置是否可以工作正常了。打开两个网页浏览器,输入 XR 服务器的 IP 地址和端口,并查看输出。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
验证 Web 服务器负载均衡
|
||||
*验证 Web 服务器负载均衡*
|
||||
|
||||
太棒了。它工作正常。是时候玩玩 XR 了。
|
||||
太棒了。它工作正常。是时候玩玩 XR 了。(LCTT 译注:可以看到两个请求分别分配到了不同服务器。)
|
||||
|
||||
**6. 现在可以登录到 XR Crossroads 仪表盘,看看我们已经配置的网络接口的端口。在网络接口输入你的 XR 服务器的 IP 地址和端口你将看到在 xrctl.xml 中的配置。**
|
||||
**6. 现在可以通过我们配置的网络管理界面的端口来登录到 XR Crossroads 仪表盘。在浏览器输入你的 XR 服务器的 IP 地址和你配置在 xrctl.xml 中的管理端口。**
|
||||
|
||||
http://172.16.1.204:8010
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
XR Crossroads 仪表盘
|
||||
*XR Crossroads 仪表盘*
|
||||
|
||||
看起来很像了。它容易理解,用户界面友好,易于使用。它在右上角显示每个服务器能容纳多少个连接连同关于接收该请求的附加细节。你也可以设置每个服务器承担的负载量,最大连接数和平均负载等。。
|
||||
看起来像上面一样。它容易理解,用户界面友好,易于使用。它在右上角显示每个服务器能容纳多少个连接,以及关于接收该请求的附加细节。你也可以设置每个服务器承担的负载量,最大连接数和平均负载等。
|
||||
|
||||
最大的好处是,即使没有配置文件 xrctl.xml,你也可以做到这一点。你唯一要做的就是运行以下命令,它会做这项工作。
|
||||
最大的好处是,即使没有配置文件 xrctl.xml,你也可以做到这一点。你唯一要做的就是运行以下命令,它就会把这一切搞定。
|
||||
|
||||
# xr --verbose --server tcp:172.16.1.204:8080 --backend 172.16.1.222:8888 --backend 192.168.1.161:5555
|
||||
|
||||
@ -139,12 +138,12 @@ XR Crossroads 仪表盘
|
||||
|
||||
- -verbose 将显示命令执行后的信息。
|
||||
- -server 定义你在安装包中的 XR 服务器。
|
||||
- -backend 定义你需要平衡到 Web 服务器的流量。
|
||||
- tcp 的定义,它使用 TCP 服务。
|
||||
- -backend 定义你需要平衡分配到 Web 服务器的流量。
|
||||
- tcp 说明我们使用 TCP 服务。
|
||||
|
||||
欲了解更多详情,有关文件及 CROSSROADS 的配置,请访问他们的官方网站: [https://crossroads.e-tunity.com/][4].
|
||||
|
||||
XR Corssroads 使用许多方法来提高服务器性能,避免宕机,让你的管理任务更轻松,更简便。希望你喜欢此文章,并随时在下面发表你的评论和建议,方便与 Tecmint 保持联系。
|
||||
XR Corssroads 使用许多方法来提高服务器性能,避免宕机,让你的管理任务更轻松,更简便。希望你喜欢此文章,并随时在下面发表你的评论和建议,方便与我们保持联系。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -152,7 +151,7 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/setting-up-xr-crossroads-load-balancer-for-web-serve
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Thilina Uvindasiri][a]
|
||||
译者:[strugglingyouth](https://github.com/strugglingyouth)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by ZTinoZ
|
||||
7 command line tools for monitoring your Linux system
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Here is a selection of basic command line tools that will make your exploration and optimization in Linux easier. **
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Dive on in ###
|
||||
|
||||
One of the great things about Linux is how deeply you can dive into the system to explore how it works and to look for opportunities to fine tune performance or diagnose problems. Here is a selection of basic command line tools that will make your exploration and optimization easier. Most of these commands are already built into your Linux system, but in case they aren’t, just Google “install”, the command name, and the name of your distro and you’ll find which package needs installing (note that some commands are bundled with other commands in a package that has a different name from the one you’re looking for). If you have any other tools you use, let me know for our next Linux Tools roundup.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### How we did it ###
|
||||
|
||||
FYI: The screenshots in this collection were created on [Debian Linux 8.1][1] (“Jessie”) running in a virtual machine under [Oracle VirtualBox 4.3.28][2] under [OS X 10.10.3][3] (“Yosemite”). See my next slideshow “[How to install Debian Linux in a VirtualBox VM][4]” for a tutorial on how to build your own Debian VM.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Top command ###
|
||||
|
||||
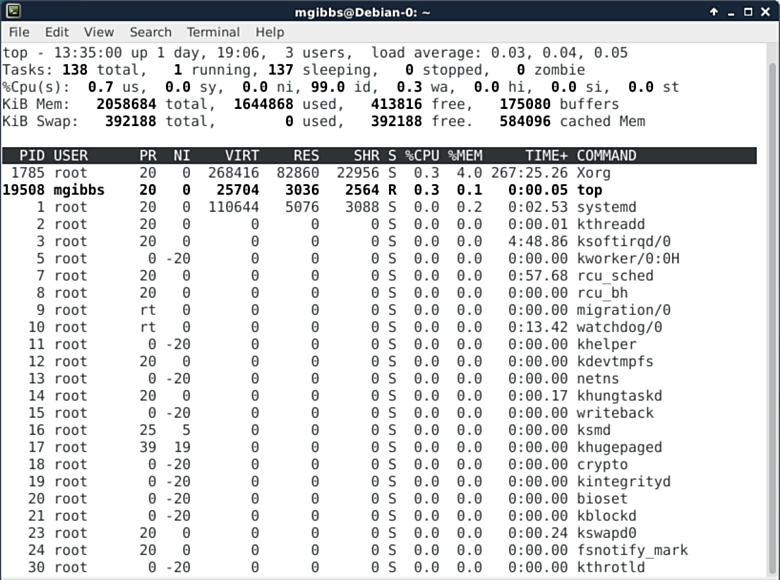
One of the simpler Linux system monitoring tools, the **top command** comes with pretty much every flavor of Linux. This is the default display, but pressing the “z” key switches the display to color. Other hot keys and command line switches control things such as the display of summary and memory information (the second through fourth lines), sorting the list according to various criteria, killing tasks, and so on (you can find the complete list at [here][5]).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
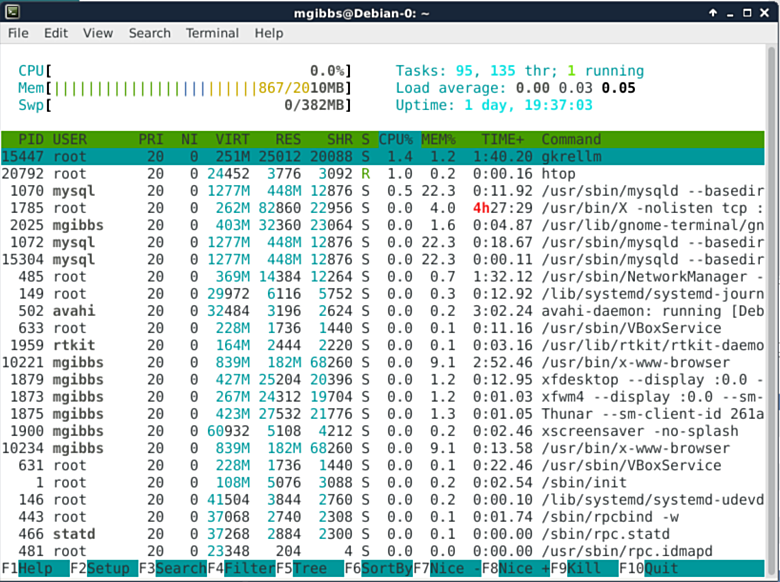
### htop ###
|
||||
|
||||
Htop is a more sophisticated alternative to top. Wikipedia: “Users often deploy htop in cases where Unix top does not provide enough information about the systems processes, for example when trying to find minor memory leaks in applications. Htop is also popularly used interactively as a system monitor. Compared to top, it provides a more convenient, cursor-controlled interface for sending signals to processes.” (For more detail go [here][6].)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
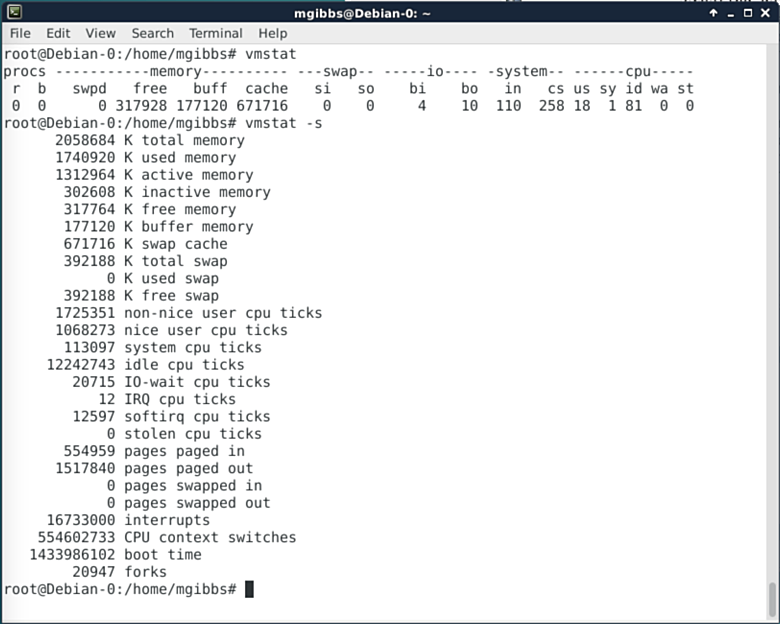
### Vmstat ###
|
||||
|
||||
Vmstat is a simpler tool for monitoring your Linux system performance statistics but that makes it highly suitable for use in shell scripts. Fire up your regex-fu and you can do some amazing things with vmstat and cron jobs. “The first report produced gives averages since the last reboot. Additional reports give information on a sampling period of length delay. The process and memory reports are instantaneous in either case” (go [here][7] for more info.).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
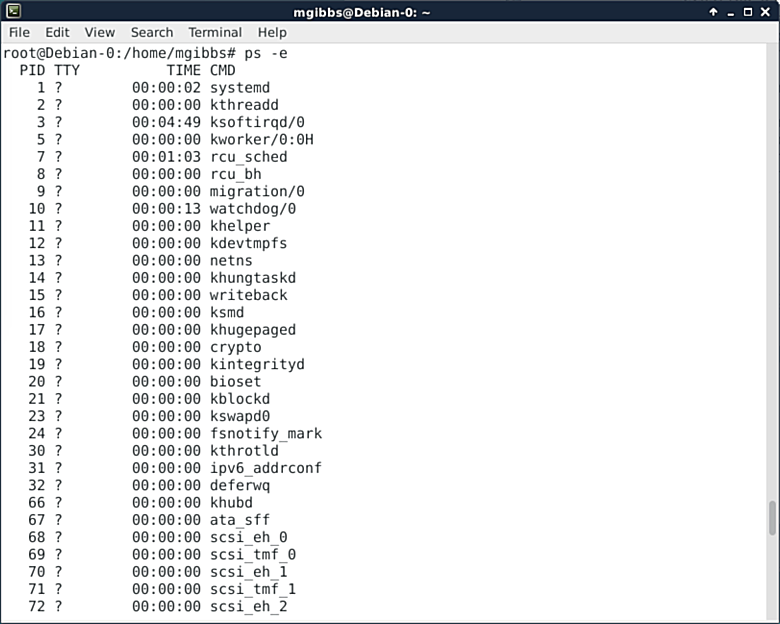
### ps ###
|
||||
|
||||
The ps command shows a list of running processes. In this case, I’ve used the “-e”switch to show everything, that is, all processes running (I’ve scrolled back to the top of the output otherwise the column names wouldn’t be visible). This command has a lot of switches that allow you to format the output as needed. Add a little of the aforementioned regex-fu and you’ve got a powerful tool. Go [here][8] for the full details.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
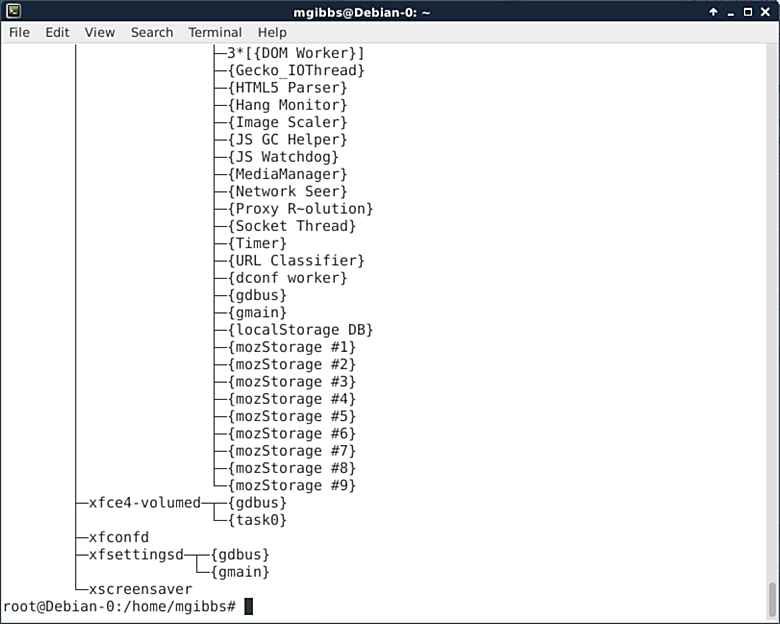
### Pstree ###
|
||||
|
||||
Pstree “shows running processes as a tree. The tree is rooted at either pid or init if pid is omitted. If a user name is specified, all process trees rooted at processes owned by that user are shown.”This is a really useful tool as the tree helps you sort out which process is dependent on which process (go [here][9]).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
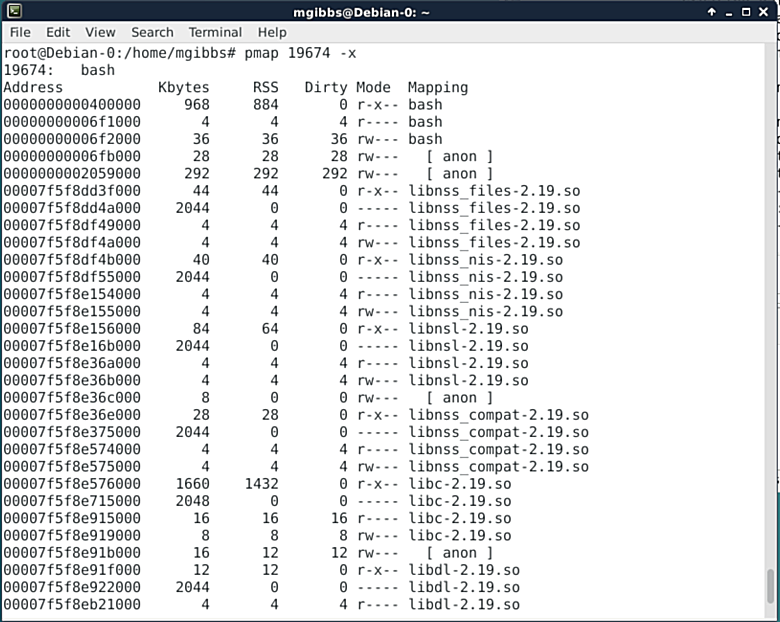
### pmap ###
|
||||
|
||||
Understanding just how an app uses memory is often crucial in debugging, and the pmap produces just such information when given a process ID (PID). The screenshot shows the medium weight output generated by using the “-x”switch. You can get pmap to produce even more detailed information using the “-X”switch but you’ll need a much wider terminal window.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
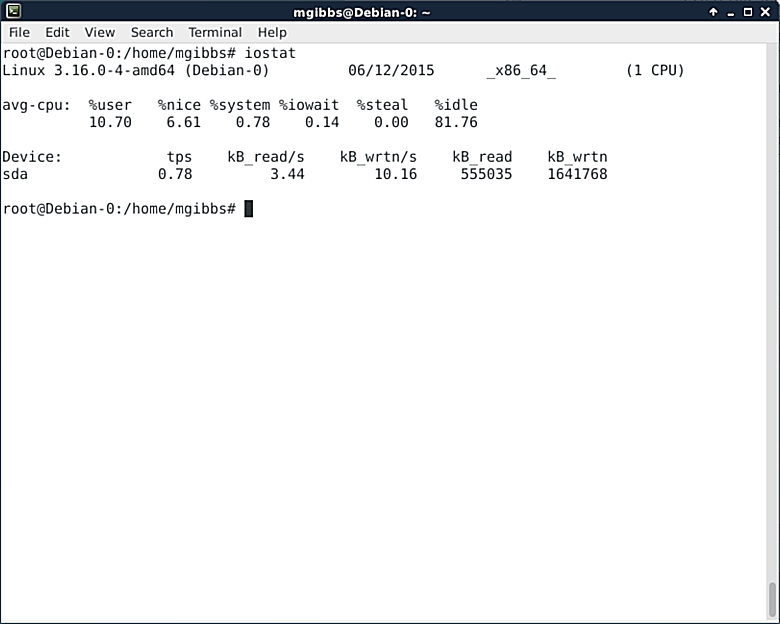
### iostat ###
|
||||
|
||||
A crucial factor in your Linux system’s performance is processor and storage usage, which are what the iostat command reports on. As with the ps command, iostat has loads of switches that allow you to select the output format you need as well as sample performance over a time period and then repeat that sampling a number of times before reporting. See [here][10].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.networkworld.com/article/2937219/linux/7-command-line-tools-for-monitoring-your-linux-system.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Mark Gibbs][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.networkworld.com/author/Mark-Gibbs/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.debian.org/releases/stable/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.virtualbox.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.apple.com/osx/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.networkworld.com/article/2937148/how-to-install-debian-linux-8-1-in-a-virtualbox-vm
|
||||
[5]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/top
|
||||
[6]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/htop
|
||||
[7]:http://linuxcommand.org/man_pages/vmstat8.html
|
||||
[8]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/ps
|
||||
[9]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/pstree
|
||||
[10]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/iostat
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
alim0x translating
|
||||
|
||||
The history of Android
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
translating...
|
||||
|
||||
How to set up IPv6 BGP peering and filtering in Quagga BGP router
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In the previous tutorials, we demonstrated how we can set up a [full-fledged BGP router][1] and configure [prefix filtering][2] with Quagga. In this tutorial, we are going to show you how we can set up IPv6 BGP peering and advertise IPv6 prefixes through BGP. We will also demonstrate how we can filter IPv6 prefixes advertised or received by using prefix-list and route-map features.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating...
|
||||
|
||||
Fix Minimal BASH like line editing is supported GRUB Error In Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The other day when I [installed Elementary OS in dual boot with Windows][1], I encountered a Grub error at the reboot time. I was presented with command line with error message:
|
||||
|
||||
**Minimal BASH like line editing is supported. For the first word, TAB lists possible command completions. anywhere else TAB lists possible device or file completions.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Indeed this is not an error specific to Elementary OS. It is a common [Grub][2] error that could occur with any Linux OS be it Ubuntu, Fedora, Linux Mint etc.
|
||||
|
||||
In this post we shall see **how to fix this “minimal BASH like line editing is supported” Grub error in Ubuntu** based Linux systems.
|
||||
|
||||
> You can read this tutorial to fix similar and more frequent issue, [error: no such partition grub rescue in Linux][3].
|
||||
|
||||
### Prerequisites ###
|
||||
|
||||
To fix this issue, you would need the followings:
|
||||
|
||||
- A live USB or disk of the same OS and same version
|
||||
- A working internet connection in the live session
|
||||
|
||||
Once you make sure that you have the prerequisites, let’s see how to fix the black screen of death for Linux (if I can call it that ;)).
|
||||
|
||||
### How to fix this “minimal BASH like line editing is supported” Grub error in Ubuntu based Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
I know that you might point out that this Grub error is not exclusive to Ubuntu or Ubuntu based Linux distributions, then why am I putting emphasis on the world Ubuntu? The reason is, here we will take an easy way out and use a tool called **Boot Repair** to fix our problem. I am not sure if this tool is available for other distributions like Fedora. Without wasting anymore time, let’s see how to solve minimal BASH like line editing is supported Grub error.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Boot in lives session ###
|
||||
|
||||
Plug in the live USB and boot in to the live session.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Install Boot Repair ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once you are in the lives session, open the terminal and use the following commands to install Boot Repair:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yannubuntu/boot-repair
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install boot-repair
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Follow this tutorial to [fix failed to fetch cdrom apt-get update cannot be used to add new CD-ROMs error][4], if you encounter it while running the above command.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Repair boot with Boot Repair ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once you installed Boot Repair, run it from the command line using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
boot-repair &
|
||||
|
||||
Actually things are pretty straight forward from here. You just need to follow the instructions provided by Boot Repair tool. First, click on **Recommended repair** option in the Boot Repair.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It will take couple of minutes for Boot Repair to analyze the problem with boot and Grub. Afterwards, it will provide you some commands to use in the command line. Copy the commands one by one in terminal. For me it showed me a screen like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It will do some processes after you enter these commands:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once the process finishes, it will provide you a URL which consists of the logs of the boot repair. If your boot issue is not fixed even now, you can go to the forum or mail to the dev team and provide them the URL as a reference. Cool, isn’t it?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After the boot repair finishes successfully, shutdown your computer, remove the USB and boot again. For me it booted successfully but added two additional lines in the Grub screen. Something which was not of importance to me as I was happy to see the system booting normally again.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Did it work for you? ###
|
||||
|
||||
So this is how I fixed **minimal BASH like line editing is supported Grub error in Elementary OS Freya**. How about you? Did it work for you? Feel free to ask a question or drop a suggestion in the comment box below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-minimal-bash-line-editing-supported-grub-error-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/guide-install-elementary-os-luna/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.gnu.org/software/grub/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-error-partition-grub-rescue-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/fix-failed-fetch-cdrom-aptget-update-add-cdroms/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
KevinSJ Translating
|
||||
How to monitor NGINX - Part 1
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
Translating by GOLinux!
|
||||
How To Fix “The Update Information Is Outdated” In Ubuntu 14.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Seeing a red triangle in top panel in Ubuntu 14.04 that displays the following error?
|
||||
|
||||
> The update information is outdated. This may be caused by network problems or by a repository that is no longer available. Please update manually by selecting ‘Show updates’ from indicator menu, and watching for any failing repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
It looks something like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Instead of red triangle, there is a pink exclamation sign because I am using one of the [best Ubuntu icon themes][1], Numix. Coming back to the error, this is a common update problem which you might see every now and then. Now you might be wondering what is causing this update error.
|
||||
|
||||
### Reason for ‘update information is outdated’ error ###
|
||||
|
||||
The reason is pretty explanatory in the error description itself. It reads “this may be caused by network problems or by a repository that is no longer available”. So, either you upgraded your system and some repository or PPA is no longer supported or you are facing some similar issue.
|
||||
|
||||
While the error is self-explanatory, the action it suggests, “Please update manually by selecting ‘Show updates’ from the indicator menu, and watching for any failing repositories.”, doesn’t work properly. If you click on Show updates, all you’ll see is that the system is already updated.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Weird isn’t it? How will we find out what is failing where and why?
|
||||
|
||||
### Fix ‘update information is outdated’ ###
|
||||
|
||||
The ‘solution’ discussed here will work for Ubuntu versions be it Ubuntu 14.04, 12.04 or 14.04. All you need to do is to open a terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T) and use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
Wait for the command to finish and look at the result. Quick tip to add here, you can [add notifications in terminal][2] so that you are notified as soon as a long command finishes execution. In the last few lines at the end of the command, see what kind of error your system is facing. Yes, you’ll see an error for sure.
|
||||
|
||||
In my case, I saw the famous [GPG error: The following could not be verified][3] error. Apparently there is some problem with [Spotify installation in Ubuntu 15.04][4].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It is very much possible that you might see a different error instead of the GPG error like me. In that case, I suggest you to go through this article which I wrote to [fix various common update errors in Ubuntu][5].
|
||||
|
||||
I know few people, specially beginners have strong aversion to command line but if you are using Linux, you simply cannot avoid terminal. Moreover, it is not that scary a thing. Give it a try, you will feel accustomed to it soon enough.
|
||||
|
||||
I hope this quick tip helped you to fix the recurring “update information is outdated” in Ubuntu. Any questions or suggestions is welcomed.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-update-information-outdated-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/notification-terminal-command-completion-ubuntu/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-gpg-error-signatures-verified-ubuntu/
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/install-spotify-ubuntu-1504/
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/fix-update-errors-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
|
||||
FSSlc translating
|
||||
|
||||
How To Manage StartUp Applications In Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ever felt the need to **control startup applications in Ubuntu**? You should, if you feel that your Ubuntu system is very slow at the boot time.
|
||||
|
||||
Every time you boot in to an operating system, a number of applications start automatically. These are called ‘startup applications’ or ‘start up programs’. Over the time, when you have plenty of application installed in your system, you’ll find that there are too many of these ‘startup applications’ which start at the boot time automatically, eats up the system resource and slows down the system. This might result in a sluggish Ubuntu experience, which I think, you don’t want at all.
|
||||
|
||||
A way to make Ubuntu faster is to control startup applications. Ubuntu provides you GUI tools that you can use to find out the startup programs, disable them entirely or delay their execution so that you won’t have each application trying to run at the same time.
|
||||
|
||||
In this post we shall see **how to control startup applications, how to run an application at startup and how to find hidden startup applications in Ubuntu**. The instructions provided here are applicable to all Ubuntu versions such as Ubuntu 12.04, Ubuntu 14.04 and Ubuntu 15.04.
|
||||
|
||||
### Manage startup applications in Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Ubuntu provides Startup Applications utility that you could use. No need of installation. Just go in Unity Dash and look for startup applications.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Click on it to start. Here is what my startup applications look like:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Remove startup applications in Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now it is up to you what you find useless. For me [Caribou][1], on screen keyboard program, is not of any use at the startup. I would prefer to remove it.
|
||||
|
||||
You can choose to either prevent it from starting up at boot time but keeping it in the startup applications list for future reactivation. Click on close to save your preference.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To remove a program from startup applications list, select it and click on Remove from the right window pane.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that, this will NOT uninstall the program. Just that the program will not start automatically at each boot. You can do it with all the programs that you don’t like.
|
||||
|
||||
### Delay the start up programs ###
|
||||
|
||||
What if you do not want to remove programs at the start up but you are worried about system performance at the boot time. What you can do is to add a delay in various programs so that not all the programs will be starting at the same time.
|
||||
|
||||
Select a program and click Edit.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This will show the command that runs this particular program.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
All you need to do is to add sleep XX; before the command. It will add a delay of XX seconds before running the actual commands to run the applications. For example if I want Variety [wallpaper management application][2] for 2 minutes, I’ll add sleep 120; before the command like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Save it and close it. You’ll see the impact at the next boot.
|
||||
|
||||
### Add a program in the startup applications ###
|
||||
|
||||
This could be tricky for beginners. You see, things are in commands at the bottom of everything in Linux. We just saw in the previous section that these startup programs are just some commands being run at each boot. If you want to add a new program in the startup, you’ll need to know the command that runs the application.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 1: How to find the command to run an application? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Go in the Unity Dash and search for Main Menu:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This contains all the program that you have installed in various categories. In old Ubuntu days, you would see similar menu for selecting and running applications.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Just look for your application under various categories and click on the Properties tab to see the command that runs this application. For example, I want to run Transmission Torrent client on start up.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This will give me the command that runs Transmission:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now I’ll use the same information to add Transmission in startup applications.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2: Adding programs in startup ####
|
||||
|
||||
Go again in Startup Applications and click on Add. This will ask you enter a name, command and description. The command is the most important of all. You can use whatever name and description you want. Use the command you got from previous step and click on Add.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
That’s it. You’ll see it in the next boot up, running automatically. This is all you can do with startup applications in Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
So, far we have discussed about applications that are visible in startup but there are many more services, daemons and programs that are not visible to Startup applications. In next section, we shall see how to see hidden startup programs in Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
### See hidden startup program in Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
To see what are the services running at startup, open a terminal and use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo sed -i 's/NoDisplay=true/NoDisplay=false/g' /etc/xdg/autostart/*.desktop
|
||||
|
||||
This is just a quick find and replace command that changes the NoDisplay=false with NoDisplay=true in all the programs that are in autostart. Once you do this, open Startup Applications again and now you shall see many more programs here:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can manage these startup applications the same way which were described earlier. I hope this tutorial helped you to control startup program in Ubuntu. Any questions or suggestions are always welcomed.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/manage-startup-applications-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.gnome.org/action/show/Projects/Caribou?action=show&redirect=Caribou
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/applications-manage-wallpapers-ubuntu/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
Translating by ictlyh
|
||||
Howto Interactively Perform Tasks with Docker using Kitematic
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In this article, we'll learn about the installating Kitematic in Windows Operating System and deploying a Hello World Nginx Web Server. Kitematic is a free and open source software which is a modern designed GUI software that allows us to interactively perform tasks with docker. Kitematic has a beautiful design and pretty good interface. It is pretty fast and easy to setup our containers out of the box without needing to enter commands for it, we can deploy our apps it in just a click with its GUI inteface. Kitematic has Docker Hub Intergration which allows us to search any required image, pull and deploy our apps with it. It also has a beautiful feature to switch to CUI mode simultaneously. Currently, it includes some features like automatically map ports, visually change environment variables, configuring volumes, streamline logs and many more.
|
||||
|
||||
So. here are the easy 3 steps on how we can install Kitematic and deploy Hello World Nginx Web Server in Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Download Kitematic ###
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, we'll need to download the latest release of Kitematic available for windows operating system from the github repository ie [https://github.com/kitematic/kitematic/releases][1] . Here, we download its executable EXE file using a download manager or a web browser. After we finish downloading, we'll need to double-click the executable application file.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After double clicking the application file, we'll be asked by a security issue we'll simply click OK as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Installing Kitematic ###
|
||||
|
||||
After the executable installer has been downloaded, we'll now gonna install Kitematic in our Windows Operating System. The installer will now begin to download and install the necessary dependencies virtual box and docker to run Kitematic. If you already virtualbox installed in your system, it will upgrade it to the latest version. The installer should finish in few minutes but that depends on how fast your internet and system is. If you don't have a virtual box installed already, it may ask you for installing the virtual box network driver. It is suggested to install that as it is useful for the virtual box networking.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After the required dependencies Docker and Virtual box are installed and are running, we'll be asked to login to the Docker Hub. If we don't have an account or don't wanna login now, we can click **SKIP FOR NOW** to continue further.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you don't have an account, you can simply click on Sign Up link in the App and create an account in Docker Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
After its done, our first interface of Kitematic App will load. Here, below is how it looks. We can search for the available docker images there as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Deploying Nginx Hello World Container ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, as our Kitematic has been successfully installed, we'll now go for the deployment of containers. To run a container, we can simply search for the image in the search area. Then click on Create to deploy the container. Here in this tutorial, we'll go for deploying a small Nginx Web Server having Hello World homepage. To do so, we'll search for Hello World Nginx in the search area. Then, after we see the container information, we'll click on Create to deploy the container.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once the download of the image has been completed, it will get deployed. We can see the logs of the commands fired by the Kitematic to deploy that container. We can also see the web page preview right from the Kitematic interface. Now, we can check our Hello World page from our web browser by clicking on the preview.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If we wanna switch to command line interface and manage docker with it, there is a button called Docker CLI which will open a Powershell were we can execute docker commands.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, if we wanna configure our container and perform stuffs like changing the container name, assigning environment variables, assign ports, configure container's storage and other advanced features, we can do that from Settings tab of the container.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Finally we've successfully installed Kitematic and deployed a hello world nginx web server in Windows Operating System. It is always recommended to download and install the latest release of Kitematic as many advanced features are to be embedded. As docker works in 64 bit platform, Kitematic is also currently built for 64-bit platform of operating system. It only works on the Windows 7 and greater versions of Windows. Here, in this tutorial, we deployed an Nginx web server like wise we can deploy any docker container from its image using Kitematic with few clicks only. Kitematic is already available for Mac OS X and Windows whereas a version for Linux is still under development and will be out very soon. If you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below so that we can improve or update our contents. Thank you ! Enjoy :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/interactively-docker-kitematic/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/kitematic/kitematic/releases
|
||||
@ -1,315 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[translating by xiqingongzi]
|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA Series: Reviewing Essential Commands & System Documentation – Part 1
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
RHCSA (Red Hat Certified System Administrator) is a certification exam from Red Hat company, which provides an open source operating system and software to the enterprise community, It also provides support, training and consulting services for the organizations.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA Exam Preparation Guide
|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA exam is the certification obtained from Red Hat Inc, after passing the exam (codename EX200). RHCSA exam is an upgrade to the RHCT (Red Hat Certified Technician) exam, and this upgrade is compulsory as the Red Hat Enterprise Linux was upgraded. The main variation between RHCT and RHCSA is that RHCT exam based on RHEL 5, whereas RHCSA certification is based on RHEL 6 and 7, the courseware of these two certifications are also vary to a certain level.
|
||||
|
||||
This Red Hat Certified System Administrator (RHCSA) is essential to perform the following core system administration tasks needed in Red Hat Enterprise Linux environments:
|
||||
|
||||
- Understand and use necessary tools for handling files, directories, command-environments line, and system-wide / packages documentation.
|
||||
- Operate running systems, even in different run levels, identify and control processes, start and stop virtual machines.
|
||||
- Set up local storage using partitions and logical volumes.
|
||||
- Create and configure local and network file systems and its attributes (permissions, encryption, and ACLs).
|
||||
- Setup, configure, and control systems, including installing, updating and removing software.
|
||||
- Manage system users and groups, along with use of a centralized LDAP directory for authentication.
|
||||
- Ensure system security, including basic firewall and SELinux configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
To view fees and register for an exam in your country, check the [RHCSA Certification page][1].
|
||||
|
||||
To view fees and register for an exam in your country, check the RHCSA Certification page.
|
||||
|
||||
In this 15-article RHCSA series, titled Preparation for the RHCSA (Red Hat Certified System Administrator) exam, we will going to cover the following topics on the latest releases of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.
|
||||
|
||||
- Part 1: Reviewing Essential Commands & System Documentation
|
||||
- Part 2: How to Perform File and Directory Management in RHEL 7
|
||||
- Part 3: How to Manage Users and Groups in RHEL 7
|
||||
- Part 4: Editing Text Files with Nano and Vim / Analyzing text with grep and regexps
|
||||
- Part 5: Process Management in RHEL 7: boot, shutdown, and everything in between
|
||||
- Part 6: Using ‘Parted’ and ‘SSM’ to Configure and Encrypt System Storage
|
||||
- Part 7: Using ACLs (Access Control Lists) and Mounting Samba / NFS Shares
|
||||
- Part 8: Securing SSH, Setting Hostname and Enabling Network Services
|
||||
- Part 9: Installing, Configuring and Securing a Web and FTP Server
|
||||
- Part 10: Yum Package Management, Automating Tasks with Cron and Monitoring System Logs
|
||||
- Part 11: Firewall Essentials and Control Network Traffic Using FirewallD and Iptables
|
||||
- Part 12: Automate RHEL 7 Installations Using ‘Kickstart’
|
||||
- Part 13: RHEL 7: What is SELinux and how it works?
|
||||
- Part 14: Use LDAP-based authentication in RHEL 7
|
||||
- Part 15: Virtualization in RHEL 7: KVM and Virtual machine management
|
||||
|
||||
In this Part 1 of the RHCSA series, we will explain how to enter and execute commands with the correct syntax in a shell prompt or terminal, and explained how to find, inspect, and use system documentation.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA: Reviewing Essential Linux Commands – Part 1
|
||||
|
||||
#### Prerequisites: ####
|
||||
|
||||
At least a slight degree of familiarity with basic Linux commands such as:
|
||||
|
||||
- [cd command][2] (change directory)
|
||||
- [ls command][3] (list directory)
|
||||
- [cp command][4] (copy files)
|
||||
- [mv command][5] (move or rename files)
|
||||
- [touch command][6] (create empty files or update the timestamp of existing ones)
|
||||
- rm command (delete files)
|
||||
- mkdir command (make directory)
|
||||
|
||||
The correct usage of some of them are anyway exemplified in this article, and you can find further information about each of them using the suggested methods in this article.
|
||||
|
||||
Though not strictly required to start, as we will be discussing general commands and methods for information search in a Linux system, you should try to install RHEL 7 as explained in the following article. It will make things easier down the road.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 7 Installation Guide][7]
|
||||
|
||||
### Interacting with the Linux Shell ###
|
||||
|
||||
If we log into a Linux box using a text-mode login screen, chances are we will be dropped directly into our default shell. On the other hand, if we login using a graphical user interface (GUI), we will have to open a shell manually by starting a terminal. Either way, we will be presented with the user prompt and we can start typing and executing commands (a command is executed by pressing the Enter key after we have typed it).
|
||||
|
||||
Commands are composed of two parts:
|
||||
|
||||
- the name of the command itself, and
|
||||
- arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Certain arguments, called options (usually preceded by a hyphen), alter the behavior of the command in a particular way while other arguments specify the objects upon which the command operates.
|
||||
|
||||
The type command can help us identify whether another certain command is built into the shell or if it is provided by a separate package. The need to make this distinction lies in the place where we will find more information about the command. For shell built-ins we need to look in the shell’s man page, whereas for other binaries we can refer to its own man page.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Check Shell built in Commands
|
||||
|
||||
In the examples above, cd and type are shell built-ins, while top and less are binaries external to the shell itself (in this case, the location of the command executable is returned by type).
|
||||
|
||||
Other well-known shell built-ins include:
|
||||
|
||||
- [echo command][8]: Displays strings of text.
|
||||
- [pwd command][9]: Prints the current working directory.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
More Built in Shell Commands
|
||||
|
||||
**exec command**
|
||||
|
||||
Runs an external program that we specify. Note that in most cases, this is better accomplished by just typing the name of the program we want to run, but the exec command has one special feature: rather than create a new process that runs alongside the shell, the new process replaces the shell, as can verified by subsequent.
|
||||
|
||||
# ps -ef | grep [original PID of the shell process]
|
||||
|
||||
When the new process terminates, the shell terminates with it. Run exec top and then hit the q key to quit top. You will notice that the shell session ends when you do, as shown in the following screencast:
|
||||
|
||||
注:youtube视频
|
||||
<iframe width="640" height="405" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="allowfullscreen" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/f02w4WT73LE"></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
**export command**
|
||||
|
||||
Exports variables to the environment of subsequently executed commands.
|
||||
|
||||
**history Command**
|
||||
|
||||
Displays the command history list with line numbers. A command in the history list can be repeated by typing the command number preceded by an exclamation sign. If we need to edit a command in history list before executing it, we can press Ctrl + r and start typing the first letters associated with the command. When we see the command completed automatically, we can edit it as per our current need:
|
||||
|
||||
注:youtube视频
|
||||
<iframe width="640" height="405" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="allowfullscreen" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/69vafdSMfU4"></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
This list of commands is kept in our home directory in a file called .bash_history. The history facility is a useful resource for reducing the amount of typing, especially when combined with command line editing. By default, bash stores the last 500 commands you have entered, but this limit can be extended by using the HISTSIZE environment variable:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux history Command
|
||||
|
||||
But this change as performed above, will not be persistent on our next boot. In order to preserve the change in the HISTSIZE variable, we need to edit the .bashrc file by hand:
|
||||
|
||||
# for setting history length see HISTSIZE and HISTFILESIZE in bash(1)
|
||||
HISTSIZE=1000
|
||||
|
||||
**Important**: Keep in mind that these changes will not take effect until we restart our shell session.
|
||||
|
||||
**alias command**
|
||||
|
||||
With no arguments or with the -p option prints the list of aliases in the form alias name=value on standard output. When arguments are provided, an alias is defined for each name whose value is given.
|
||||
|
||||
With alias, we can make up our own commands or modify existing ones by including desired options. For example, suppose we want to alias ls to ls –color=auto so that the output will display regular files, directories, symlinks, and so on, in different colors:
|
||||
|
||||
# alias ls='ls --color=auto'
|
||||
|
||||
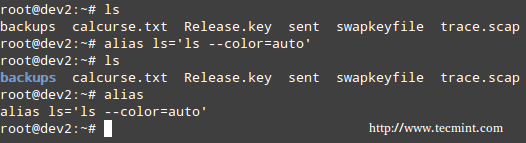
|
||||
|
||||
Linux alias Command
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: That you can assign any name to your “new command” and enclose as many commands as desired between single quotes, but in that case you need to separate them by semicolons, as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
# alias myNewCommand='cd /usr/bin; ls; cd; clear'
|
||||
|
||||
**exit command**
|
||||
|
||||
The exit and logout commands both terminate the shell. The exit command terminates any shell, but the logout command terminates only login shells—that is, those that are launched automatically when you initiate a text-mode login.
|
||||
|
||||
If we are ever in doubt as to what a program does, we can refer to its man page, which can be invoked using the man command. In addition, there are also man pages for important files (inittab, fstab, hosts, to name a few), library functions, shells, devices, and other features.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Examples: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- man uname (print system information, such as kernel name, processor, operating system type, architecture, and so on).
|
||||
- man inittab (init daemon configuration).
|
||||
|
||||
Another important source of information is provided by the info command, which is used to read info documents. These documents often provide more information than the man page. It is invoked by using the info keyword followed by a command name, such as:
|
||||
|
||||
# info ls
|
||||
# info cut
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, the /usr/share/doc directory contains several subdirectories where further documentation can be found. They either contain plain-text files or other friendly formats.
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure you make it a habit to use these three methods to look up information for commands. Pay special and careful attention to the syntax of each of them, which is explained in detail in the documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
**Converting Tabs into Spaces with expand Command**
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes text files contain tabs but programs that need to process the files don’t cope well with tabs. Or maybe we just want to convert tabs into spaces. That’s where the expand tool (provided by the GNU coreutils package) comes in handy.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, given the file NumbersList.txt, let’s run expand against it, changing tabs to one space, and display on standard output.
|
||||
|
||||
# expand --tabs=1 NumbersList.txt
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux expand Command
|
||||
|
||||
The unexpand command performs the reverse operation (converts spaces into tabs).
|
||||
|
||||
**Display the first lines of a file with head and the last lines with tail**
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the head command followed by a filename, will display the first 10 lines of the said file. This behavior can be changed using the -n option and specifying a certain number of lines.
|
||||
|
||||
# head -n3 /etc/passwd
|
||||
# tail -n3 /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux head and tail Command
|
||||
|
||||
One of the most interesting features of tail is the possibility of displaying data (last lines) as the input file grows (tail -f my.log, where my.log is the file under observation). This is particularly useful when monitoring a log to which data is being continually added.
|
||||
|
||||
Read More: [Manage Files Effectively using head and tail Commands][10]
|
||||
|
||||
**Merging Lines with paste**
|
||||
|
||||
The paste command merges files line by line, separating the lines from each file with tabs (by default), or another delimiter that can be specified (in the following example the fields in the output are separated by an equal sign).
|
||||
|
||||
# paste -d= file1 file2
|
||||
|
||||
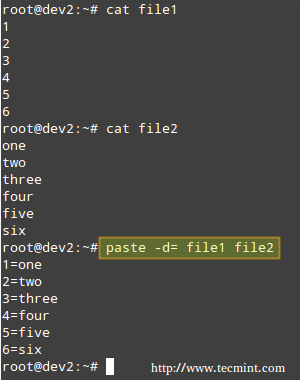
|
||||
|
||||
Merge Files in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
**Breaking a file into pieces using split command**
|
||||
|
||||
The split command is used split a file into two (or more) separate files, which are named according to a prefix of our choosing. The splitting can be defined by size, chunks, or number of lines, and the resulting files can have a numeric or alphabetic suffixes. In the following example, we will split bash.pdf into files of size 50 KB (-b 50KB), using numeric suffixes (-d):
|
||||
|
||||
# split -b 50KB -d bash.pdf bash_
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Split Files in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
You can merge the files to recreate the original file with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# cat bash_00 bash_01 bash_02 bash_03 bash_04 bash_05 > bash.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
**Translating characters with tr command**
|
||||
|
||||
The tr command can be used to translate (change) characters on a one-by-one basis or using character ranges. In the following example we will use the same file2 as previously, and we will change:
|
||||
|
||||
- lowercase o’s to uppercase,
|
||||
- and all lowercase to uppercase
|
||||
|
||||
# cat file2 | tr o O
|
||||
# cat file2 | tr [a-z] [A-Z]
|
||||
|
||||
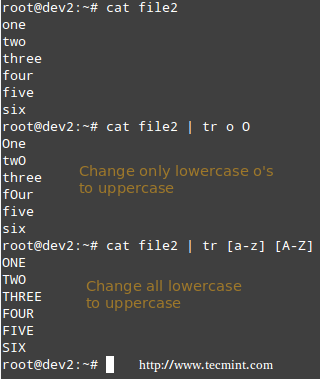
|
||||
|
||||
Translate Characters in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
**Reporting or deleting duplicate lines with uniq and sort command**
|
||||
|
||||
The uniq command allows us to report or remove duplicate lines in a file, writing to stdout by default. We must note that uniq does not detect repeated lines unless they are adjacent. Thus, uniq is commonly used along with a preceding sort (which is used to sort lines of text files).
|
||||
|
||||
By default, sort takes the first field (separated by spaces) as key field. To specify a different key field, we need to use the -k option. Please note how the output returned by sort and uniq change as we change the key field in the following example:
|
||||
|
||||
# cat file3
|
||||
# sort file3 | uniq
|
||||
# sort -k2 file3 | uniq
|
||||
# sort -k3 file3 | uniq
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Remove Duplicate Lines in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
**Extracting text with cut command**
|
||||
|
||||
The cut command extracts portions of input lines (from stdin or files) and displays the result on standard output, based on number of bytes (-b), characters (-c), or fields (-f).
|
||||
|
||||
When using cut based on fields, the default field separator is a tab, but a different separator can be specified by using the -d option.
|
||||
|
||||
# cut -d: -f1,3 /etc/passwd # Extract specific fields: 1 and 3 in this case
|
||||
# cut -d: -f2-4 /etc/passwd # Extract range of fields: 2 through 4 in this example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Extract Text From a File in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the output of the two examples above was truncated for brevity.
|
||||
|
||||
**Reformatting files with fmt command**
|
||||
|
||||
fmt is used to “clean up” files with a great amount of content or lines, or with varying degrees of indentation. The new paragraph formatting defaults to no more than 75 characters wide. You can change this with the -w (width) option, which set the line length to the specified number of characters.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, let’s see what happens when we use fmt to display the /etc/passwd file setting the width of each line to 100 characters. Once again, output has been truncated for brevity.
|
||||
|
||||
# fmt -w100 /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
File Reformatting in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
**Formatting content for printing with pr command**
|
||||
|
||||
pr paginates and displays in columns one or more files for printing. In other words, pr formats a file to make it look better when printed. For example, the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -a /etc | pr -n --columns=3 -h "Files in /etc"
|
||||
|
||||
Shows a listing of all the files found in /etc in a printer-friendly format (3 columns) with a custom header (indicated by the -h option), and numbered lines (-n).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
File Formatting in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we have discussed how to enter and execute commands with the correct syntax in a shell prompt or terminal, and explained how to find, inspect, and use system documentation. As simple as it seems, it’s a large first step in your way to becoming a RHCSA.
|
||||
|
||||
If you would like to add other commands that you use on a periodic basis and that have proven useful to fulfill your daily responsibilities, feel free to share them with the world by using the comment form below. Questions are also welcome. We look forward to hearing from you!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/rhcsa-exam-reviewing-essential-commands-system-documentation/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.redhat.com/en/services/certification/rhcsa
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/cd-command-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/ls-command-interview-questions/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/advanced-copy-command-shows-progress-bar-while-copying-files/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/rename-multiple-files-in-linux/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/8-pratical-examples-of-linux-touch-command/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/redhat-enterprise-linux-7-installation/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/pwd-command-examples/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/view-contents-of-file-in-linux/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
[translating by xiqingongzi]
|
||||
RHCSA Series: How to Perform File and Directory Management – Part 2
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In this article, RHCSA Part 2: File and directory management, we will review some essential skills that are required in the day-to-day tasks of a system administrator.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,78 +1,79 @@
|
||||
sevenot translating
|
||||
10 Top Distributions in Demand to Get Your Dream Job
|
||||
sevenot translated
|
||||
10大帮助你获得理想的职业的需求分布
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
We are coming up with a series of five articles which aims at making you aware of the top skills which will help you in getting yours dream job. In this competitive world you can not rely on one skill. You need to have balanced set of skills. There is no measure of a balanced skill set except a few conventions and statistics which changes from time-to-time.
|
||||
我们用了5篇系列文章,来让人们意识到那些可以帮助他们获得理想职业的顶级技能。在这个充满竞争的社会里,你不能仅仅依赖一项仅能,你需要在多个职业技能上都有所涉猎。我们并不能权衡这些技能,但是我们可以参考这些几乎不变的惯例和统计数据。
|
||||
|
||||
The below article and remaining to follow is the result of close study of job boards, posting and requirements of various IT Companies across the globe of last three months. The statistics keeps on changing as the demand and market changes. We will try our best to update the list when there is any major changes.
|
||||
The Five articles of this series are…
|
||||
下面的文章和紧跟其后的内容,是针对全球各大IT公司上一季度对员工技能要求的详细调查报告。统计数据真实的反映了需求和市场的变化。我们会尽力让这份报告保持时效性,特别是有明显变化的时候。这五篇系列文章是:
|
||||
|
||||
- 10 Distributions in Demand to Get Your Dream Job
|
||||
- [10 Famous IT Skills in Demand That Will Get You Hired][1]
|
||||
- 10 Programming Skills That Will Help You to Get Dream Job
|
||||
- 10 IT Networking Protocols Skills to Land Your Dream Job
|
||||
- 10 Professional Certifications in Demand That Will Get You Hired
|
||||
-10大帮助你获得理想的职业的需求分布
|
||||
-[10大帮助你获得职位的著名 IT 技能][1]
|
||||
-10大帮助你获得理想职位的项目技能
|
||||
-10大帮助你赢得理想职位的网络技能
|
||||
-10大帮助你获得理想职位的个人认证
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Windows ###
|
||||
|
||||
The operating System developed by Microsoft not only dominates the PC market but it is also the most sought OS skill from job perspective irrespective of all the odds and criticism that follows. It has shown a growth in demand which equals to 0.1% in the last quarter.
|
||||
微软研发的windows操作系统不仅在PC市场上占据龙头地位,而且从职位视角来看也是最枪手的操作系统工作,不管你是赞成还是反对。有资料显示上一季度需求增长达到0.1%.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : Windows 8.1
|
||||
最新版本 : Windows 8.1
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Red Hat Enterprise Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat Enterprise Linux is a commercial Linux Distribution developed by Red Hat Inc. It is one of the Most widely used Linux distribution specially in corporates and production. It comes at number two having a overall growth in demand which equals to 17% in the last quarter.
|
||||
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 是一个商业发行版本的企业级Linux,它由红帽公司研发。它是世界上运用最广的Linux发行版本,特别是在生产环境和协同工作方面。上一季度其整体需求上涨17%,位列第二。
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : RedHat Enterprise Linux 7.1
|
||||
最新版本 : RedHat Enterprise Linux 7.1
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Solaris ###
|
||||
|
||||
The UNIX Operating System developed by Sun Microsystems and now owned by Oracle Inc. comes at number three. It has shown a growth in demand which equals to 14% in the last quarter.
|
||||
排在第三的是 Solaris UNIX操作系统,最初由Sun Microsystems公司研发,现由Oracle公司负责继续研发。在上一季度起需求率上涨14%.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : Oracle Solaris 10 1/13
|
||||
最新版本:Oracle Solaris 10 1/13
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. AIX ###
|
||||
|
||||
Advanced Interactive eXecutive is a Proprietary Unix Operating System by IBM stands at number four. It has shown a growth in demand which equals to 11% in the last quarter.
|
||||
排在第四的是AIX,这是一款由IBM研发的专用 Unix 操作系统。在上一季度需求率上涨11%。
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : AIX 7
|
||||
最新版本 : AIX 7
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Android ###
|
||||
|
||||
One of the most widely used open source operating system designed specially for mobile, tablet computers and wearable gadgets is now owned by Google Inc. comes at number five. It has shown a growth in demand which equals to 4% in the last quarter.
|
||||
排在第5的是谷歌公司研发的安卓系统,它是一款使用非常广泛的开源操作系统,专门为手机、平板电脑、可穿戴设备设计的。在上一季度需求率上涨4%。
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : Android 5.1 aka Lollipop
|
||||
最新版本 : Android 5.1 aka Lollipop
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. CentOS ###
|
||||
|
||||
Community Enterprise Operating System is a Linux distribution derived from RedHat Enterprise Linux. It comes at sixth position in the list. Market has shown a growth in demand which is nearly 22% for CentOS, in the last quarter.
|
||||
排在第6的是 CentOS,它是从 RedHat Enterprise Linux 衍生出的一个发行版本。在上一季度需求率上涨接近22%。
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : CentOS 7
|
||||
最新版本 : CentOS 7
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Linux Operating System designed for Humans and designed by Canonicals Ltd. Ubuntu comes at position seventh. It has shown a growth in demand which equals to 11% in the last quarter.
|
||||
Latest Stable Release :
|
||||
排在第7的是Ubuntu,这是一款由Canonicals公司研发设计的Linux系统,旨在服务于个人。上一季度需求率上涨11%。
|
||||
最新版本 :
|
||||
|
||||
- Ubuntu 14.10 (9 months security and maintenance update).
|
||||
- Ubuntu 14.04.2 LTS
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Suse ###
|
||||
|
||||
Suse is a Linux operating System owned by Novell. The Linux distribution is famous for YaST configuration tool. It comes at position eight. It has shown a growth in demand which equals to 8% in the last quarter.
|
||||
排在第8的是由Novell研发的 Suse,这款发行版本的Linux操作系统因为YaST 配置工具而闻名。其上一季度需求率上涨8%。
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : 13.2
|
||||
最新版本 : 13.2
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Debian ###
|
||||
|
||||
The very famous Linux Operating System, mother of 100’s of Distro and closest to GNU comes at number nine. It has shown a decline in demand which is nearly 9% in the last quarter.
|
||||
The very famous Linux Operating System, mother of 100’s of Distro and closest to GNU comes at number nine.
|
||||
排在第9的是非常有名的 Linux 操作系统Debian,非常贴近GNU。其上一季度需求率上涨9%。
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : Debian 7.8
|
||||
最新版本: Debian 7.8
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. HP-UX ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Proprietary UNIX Operating System designed by Hewlett-Packard comes at number ten. It has shown a decline in the last quarter by 5%.
|
||||
排在第10的是Hewlett-Packard公司研发的专用 Linux 操作系统HP-UX,上一季度需求率上涨5%。
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : 11i v3 Update 13
|
||||
最新版本 : 11i v3 Update 13
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格数据--不需要翻译--开始
|
||||
<table border="0" cellspacing="0">
|
||||
@ -134,14 +135,14 @@ Latest Stable Release : 11i v3 Update 13
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
注:表格数据--不需要翻译--结束
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I’ll be coming up with the next article of this series very soon. Till then stay tuned and connected to Tecmint. Don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments below. Like and share us and help us get spread.
|
||||
以上便是全部信息,我会尽快推出下一篇系列文章,敬请关注Tecmint。不要忘了留下您宝贵的评论。如果您喜欢我们的文章并且与我们分享您的见解,这对我们的工作是一种鼓励。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/top-distributions-in-demand-to-get-your-dream-job/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[weychen](https://github.com/weychen)
|
||||
译者:[sevenot](https://github.com/sevenot)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
||||
监控你的Linux系统的7个命令行工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**这里有一些基本的命令行工具,让你能更简单地探索和操作Linux。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 深入 ###
|
||||
|
||||
关于Linux最棒的一件事之一是你能深入操作系统多深,来探索它是如何工作的并寻找机会来微调性能或诊断问题。这里有一些基本的命令行工具,让你能更简单地探索和操作Linux。大多数的这些命令是在你的Linux系统中已经内建的,但假设它们不是,就用谷歌搜索命令名和你的发行版名吧,你会找到哪些包需要安装(注意,一些命令是和其它命令捆绑起来打成一个包的,你所找的包可能写的是其它的名字)。如果你知道一些你所使用的其它工具,欢迎评论。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 我们怎么做 ###
|
||||
|
||||
须知: 本文中的截图取自[Debian Linux 8.1][1] (“Jessie”),其运行在[OS X 10.10.3][3] (“Yosemite”)操作系统下[Oracle VirtualBox 4.3.28][2]中的一台虚拟机里。想要建立你的Debian虚拟机,可以看看我的这篇教程——“[How to install Debian Linux in a VirtualBox VM][4]”。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Top ###
|
||||
|
||||
作为Linux系统监控工具中比较易用的一个,**top命令**能带我们一览Linux中的几乎每一处。以下这张图是它的默认界面,但是按“z”键可以切换不同的显示颜色。其它热键和命令则有其它的功能,例如显示概要信息和内存信息(第四行第二个),根据各种不一样的条件排序、终止进程任务等等(你可以在[这里][5]找到完整的列表)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### htop ###
|
||||
|
||||
相比top,它的替代品Htop则更为精致。维基百科是这样描述的:“用户经常会部署htop以防Unix top不能提供关于系统进程的足够信息,比如说当你在尝试发现应用程序里的一个小的内存泄露问题,Htop一般也能作为一个系统监听器来使用。相比top,它提供了一个更方便的光标控制界面来向进程发送信号。” (想了解更多细节猛戳[这里][6].)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Vmstat ###
|
||||
|
||||
Vmstat是一款监控Linux系统性能数据的简易工具,这让它在shell脚本中使用更合适。打开你的regex-fu,用vmstat和cron作业来做一些激动人心的事情吧。“产出的第一份报告给出的是上一次系统重启之后的均值,另外其一份报告给出的则是从前一个报告起间隔周期中的信息。进程和内存报告在任何情况下都是不停更新的”(猛戳[这里][7]获取更多信息)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### ps ###
|
||||
|
||||
ps命令展现的是正在运行中的进程列表。在这种情况下,我们用“-e”选项来显示每个进程,也就是所有正在运行的进程了(我把列表滚动到了头部否则列名就看不到了)。这个命令有很多选项允许你去按需格式化输出。只要使用上述一点点的regex-fu你就能得到一个强大的工具了。猛戳[这里][8]获取更多信息。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Pstree ###
|
||||
|
||||
Pstree“以树状图显示正在运行中的进程。如果pid被省略的话那树结构是以pid或init为父进程,如果用户名指定,那所有进程树都会以该用户所属的进程为父进程进行显示。”以树状图来帮你将进程之间的所属关系进行分类,这的确是个很有效的工具(戳[这里][9])。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### pmap ###
|
||||
|
||||
理解一个应用程序在调试过程中如何使用内存是至关重要的,而pmap的作用就是当给出一个进程ID(PID)时显示出相关信息。上面的截图展示的是使用“-x”选项所产生的部分输出,你也可以用pmap的“-X”选项来获取更多的细节信息但是前提是你要有个更宽的终端窗口。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### iostat ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux系统的一个至关重要的性能指标是处理器和存储的使用率,它也是iostat命令所报告的内容。如同ps命令一样,iostat有很多选项允许你选择你需要的输出格式,除此之外还有某一段时间范围内的简单性能输出并在报告之前重复抽样多次。详情戳[这里][10]。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.networkworld.com/article/2937219/linux/7-command-line-tools-for-monitoring-your-linux-system.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Mark Gibbs][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.networkworld.com/author/Mark-Gibbs/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.debian.org/releases/stable/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.virtualbox.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.apple.com/osx/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.networkworld.com/article/2937148/how-to-install-debian-linux-8-1-in-a-virtualbox-vm
|
||||
[5]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/top
|
||||
[6]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/htop
|
||||
[7]:http://linuxcommand.org/man_pages/vmstat8.html
|
||||
[8]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/ps
|
||||
[9]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/pstree
|
||||
[10]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/iostat
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
修复Linux中的提供最小化类BASH命令行编辑GRUB错误
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
这两天我[安装了Elementary OS和Windows双系统][1],在启动的时候遇到了一个Grub错误。命令行中呈现如下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
**提供最小化类BASH命令行编辑。对于第一个词,TAB键补全可以使用的命令。除此之外,TAB键补全可用的设备或文件。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
事实上这并不是Elementary OS独有的错误。这是常见的[Grub][2]错误,会在Ubuntu,Fedora,Linux Mint等Linux操作系统上发生。
|
||||
|
||||
通过这篇文章里我们可以学到基于Linux系统**如何修复Ubuntu中出现的“minimal BASH like line editing is supported” Grub错误**。
|
||||
|
||||
> 你可以参阅这篇教程来修复类似的高频问题,[错误:分区未找到Linux grub救援模式][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 先决条件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要修复这个问题,你需要达成以下的条件:
|
||||
|
||||
- 一个包含相同版本、相同OS的LiveUSB或磁盘
|
||||
- 当前会话的Internet连接正常工作
|
||||
|
||||
在确认了你拥有先决条件了之后,让我们看看如何修复Linux的死亡黑屏(如果我可以这样的称呼它的话;))。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在基于Ubuntu的Linux中修复“minimal BASH like line editing is supported” Grub错误 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我知道你一定疑问这种Grub错误并不局限于在基于Ubuntu的Linux发行版上发生,那为什么我要强调在基于Ubuntu的发行版上呢?原因是,在这里我们将采用一个简单的方法并叫作**Boot Repair**的工具来修复我们的问题。我并不确定在其他的诸如Fedora的发行版中是否有这个工具可用。不再浪费时间,我们来看如何修复minimal BASH like line editing is supported Grub错误。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 1: 引导进入lives会话 ###
|
||||
|
||||
插入live USB,引导进入live会话。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 2: 安装 Boot Repair ###
|
||||
|
||||
等你进入了lives会话后,打开终端使用以下命令来安装Boot Repair:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yannubuntu/boot-repair
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install boot-repair
|
||||
|
||||
注意:推荐这篇教程[如何修复 apt-get update 无法添加新的 CD-ROM 的错误][4],如果你在运行以上命令是遭遇同样的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 3: 使用Boot Repair修复引导 ###
|
||||
|
||||
装完Boot Repair后,在命令行运行如下命令启动:
|
||||
|
||||
boot-repair &
|
||||
|
||||
其实操作非常简单直接,你仅需按照Boot Repair工具提供的说明操作即可。首先,点击Boot Repair中的**Recommended repair**选项。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Boot Repair需要花费一些时间来分析引导和Grub中存在的问题。然后,它会提供一些可在命令行中直接运行的命令。将这些命令一个个在终端中执行。我这边屏幕上显示的是:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在输入了这些命令之后,它会执行执行一段时间:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在这一过程结束后,它会提供一个由boot repair的日志组成的网页网址。如果你的引导问题这样都没有修复,你就可以去社区或是发邮件给开发团队并提交该网址作为参考。很酷!不是吗?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在boot repair成功完成后,关闭你的电脑,移除USB并再次引导。我这就能成功的引导了,但是在Grub画面上会多出额外的两行。相比于看到系统能够再次正常引导的喜悦这些对我来说并不重要。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 对你有效吗? ###
|
||||
|
||||
这就是我修复**Elementary OS Freya中的minimal BASH like line editing is supported Grub 错误**的方法。怎么样?是否对你也有效呢?请自由的在下方的评论区提出你的问题和建议。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-minimal-bash-line-editing-supported-grub-error-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[martin2011qi](https://github.com/martin2011qi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/guide-install-elementary-os-luna/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.gnu.org/software/grub/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-error-partition-grub-rescue-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/fix-failed-fetch-cdrom-aptget-update-add-cdroms/
|
||||
@ -1,149 +0,0 @@
|
||||
|
||||
如何管理Vim插件
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Vim是Linux上一个轻量级的通用文本编辑器。虽然它开始时的学习曲线对于一般的Linux用户来说可能很困难,但比起它的好处,这些付出完全是值得的。随着功能的增长,在插件工具的应用下,Vim是完全可定制的。但是,由于它高级的功能配置,你需要花一些时间去了解它的插件系统,然后才能够有效地去个性化定置Vim。幸运的是,我们已经有一些工具能够使我们在使用Vim插件时更加轻松。而我日常所使用的就是Vundle.
|
||||
### 什么是Vundle ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Vundle][1]是一个vim插件管理器,用于支持Vim包。Vundle能让你很简单地实现插件的安装,升级,搜索或者清除。它还能管理你的运行环境并且在标签方面提供帮助。
|
||||
### 安装Vundle ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,如果你的Linux系统上没有Git的话,先[安装Git][2].
|
||||
|
||||
接着,创建一个目录,Vim的插件将会被下载并且安装在这个目录上。默认情况下,这个目录为~/.vim/bundle。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mkdir -p ~/.vim/bundle
|
||||
|
||||
现在,安装Vundle如下。注意Vundle本身也是一个vim插件。因此我们同样把vundle安装到之前创建的目录~/.vim/bundle下。
|
||||
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/gmarik/Vundle.vim.git ~/.vim/bundle/Vundle.vim
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置Vundle ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在配置你的.vimrc文件如下:
|
||||
|
||||
set nocompatible " This is required
|
||||
" 这是被要求的。(译注:中文注释为译者所加,下同。)
|
||||
filetype off " This is required
|
||||
" 这是被要求的。
|
||||
|
||||
" Here you set up the runtime path
|
||||
" 在这里设置你的运行时环境的路径。
|
||||
set rtp+=~/.vim/bundle/Vundle.vim
|
||||
|
||||
" Initialize vundle
|
||||
" 初始化vundle
|
||||
call vundle#begin()
|
||||
|
||||
" This should always be the first
|
||||
" 这一行应该永远放在前面。
|
||||
Plugin 'gmarik/Vundle.vim'
|
||||
|
||||
" This examples are from https://github.com/gmarik/Vundle.vim README
|
||||
" 这个示范来自https://github.com/gmarik/Vundle.vim README
|
||||
Plugin 'tpope/vim-fugitive'
|
||||
|
||||
" Plugin from http://vim-scripts.org/vim/scripts.html
|
||||
" 取自http://vim-scripts.org/vim/scripts.html的插件
|
||||
Plugin 'L9'
|
||||
|
||||
" Git plugin not hosted on GitHub
|
||||
" Git插件,但并不在GitHub上。
|
||||
Plugin 'git://git.wincent.com/command-t.git'
|
||||
|
||||
"git repos on your local machine (i.e. when working on your own plugin)
|
||||
"本地计算机上的Git仓库路径 (例如,当你在开发你自己的插件时)
|
||||
Plugin 'file:///home/gmarik/path/to/plugin'
|
||||
|
||||
" The sparkup vim script is in a subdirectory of this repo called vim.
|
||||
" Pass the path to set the runtimepath properly.
|
||||
" vim脚本sparkup存放在这个名叫vim的仓库下的一个子目录中。
|
||||
" 提交这个路径来正确地设置运行时路径
|
||||
Plugin 'rstacruz/sparkup', {'rtp': 'vim/'}
|
||||
|
||||
" Avoid a name conflict with L9
|
||||
" 避免与L9发生名字上的冲突
|
||||
Plugin 'user/L9', {'name': 'newL9'}
|
||||
|
||||
"Every Plugin should be before this line
|
||||
"所有的插件都应该在这一行之前。
|
||||
call vundle#end() " required 被要求的
|
||||
|
||||
容我简单解释一下上面的设置:默认情况下,Vundle将从github.com或者vim-scripts.org下载和安装vim插件。你也可以改变这个默认行为。
|
||||
|
||||
要从github安装(安装插件,译者注,下同):
|
||||
Plugin 'user/plugin'
|
||||
|
||||
要从http://vim-scripts.org/vim/scripts.html处安装:
|
||||
Plugin 'plugin_name'
|
||||
|
||||
要从另外一个git仓库中安装:
|
||||
|
||||
Plugin 'git://git.another_repo.com/plugin'
|
||||
|
||||
从本地文件中安装:
|
||||
|
||||
Plugin 'file:///home/user/path/to/plugin'
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
你同样可以定制其它东西,例如你的插件运行时路径,当你自己在编写一个插件时,或者你只是想从其它目录——而不是~/.vim——中加载插件时,这样做就非常有用。
|
||||
|
||||
Plugin 'rstacruz/sparkup', {'rtp': 'another_vim_path/'}
|
||||
|
||||
如果你有同名的插件,你可以重命名你的插件,这样它们就不会发生冲突了。
|
||||
|
||||
Plugin 'user/plugin', {'name': 'newPlugin'}
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用Vum命令 ###
|
||||
一旦你用vundle设置好你的插件,你就可以通过几个vundle命令来安装,升级,搜索插件,或者清除没有用的插件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 安装一个新的插件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
所有列在你的.vimrc文件中的插件,都会被PluginInstall命令安装。你也可以通递一个插件名给它,来安装某个的特定插件。
|
||||
:PluginInstall
|
||||
:PluginInstall <插件名>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 清除没有用的插件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
如果你有任何没有用到的插件,你可以通过PluginClean命令来删除它.
|
||||
:PluginClean
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 查找一个插件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想从提供的插件清单中安装一个插件,搜索功能会很有用
|
||||
:PluginSearch <文本>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在搜索的时候,你可以在交互式分割窗口中安装,清除,重新搜索或者重新加载插件清单.安装后的插件不会自动加载生效,要使其加载生效,可以将它们添加进你的.vimrc文件中.
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Vim是一个妙不可言的工具.它不单单是一个能够使你的工作更加顺畅高效的默认文本编辑器,同时它还能够摇身一变,成为现存的几乎任何一门编程语言的IDE.
|
||||
|
||||
注意,有一些网站能帮你找到适合的vim插件.猛击[http://www.vim-scripts.org][3], Github或者 [http://www.vimawesome.com][4] 获取新的脚本或插件.同时记得为你的插件使用帮助供应程序.
|
||||
|
||||
和你最爱的编辑器一起嗨起来吧!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/manage-vim-plugins.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Christopher Valerio][a]
|
||||
译者:[XLCYun(袖里藏云)](https://github.com/XLCYun)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/valerio
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/VundleVim/Vundle.vim
|
||||
[2]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-git-linux.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.vim-scripts.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.vimawesome.com/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,193 @@
|
||||
每个Linux人应知应会的12个有用的PHP命令行用法
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在我上一篇文章“[在Linux命令行中使用并执行PHP代码][1]”中,我同时着重讨论了直接在Linux命令行中运行PHP代码以及在Linux终端中执行PHP脚本文件。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在Linux命令行运行PHP代码——第二部分
|
||||
|
||||
本文旨在让你了解一些相当不错的Linux终端中的PHP用法特性。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们先在PHP交互shell中来对`php.ini`设置进行一些配置吧。
|
||||
|
||||
**6. 设置PHP命令行提示符**
|
||||
|
||||
要设置PHP命令行提示,你需要在Linux终端中使用下面的php -a(启用PHP交互模式)命令开启一个PHP交互shell。
|
||||
|
||||
$ php -a
|
||||
|
||||
然后,设置任何东西(比如说Hi Tecmint ::)作为PHP交互shell的命令提示符,操作如下:
|
||||
|
||||
php > #cli.prompt=Hi Tecmint ::
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
启用PHP交互Shell
|
||||
|
||||
同时,你也可以设置当前时间作为你的命令行提示符,操作如下:
|
||||
|
||||
php > #cli.prompt=`echo date('H:m:s');` >
|
||||
|
||||
22:15:43 >
|
||||
|
||||
**7. 每次输出一屏**
|
||||
|
||||
在我们上一篇文章中,我们已经在原始命令中通过管道在很多地方使用了‘less‘命令。通过该操作,我们可以在那些不能一次满屏输出的地方获得每次一屏的输出。但是,我们可以通过配置php.ini文件,设置pager的值为less以每次输出一屏,操作如下:
|
||||
|
||||
$ php -a
|
||||
php > #cli.pager=less
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
固定PHP屏幕输出
|
||||
|
||||
这样,下次当你运行一个命令(比如说条调试器`phpinfo();`)的时候,而该命令的输出内容又太过庞大而不能固定在一屏,它就会自动产生适合你当前屏幕的输出结果。
|
||||
|
||||
php > phpinfo();
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
PHP信息输出
|
||||
|
||||
**8. 建议和TAB补全**
|
||||
|
||||
PHP shell足够智能,它可以显示给你建议和进行TAB补全,你可以通过TAB键来使用该功能。如果对于你想要用TAB补全的字符串而言有多个选项,那么你需要使用两次TAB键来完成,其它情况则使用一次即可。
|
||||
|
||||
如果有超过一个的可能性,请使用两次TAB键。
|
||||
|
||||
php > ZIP [TAB] [TAB]
|
||||
|
||||
如果只有一个可能性,只要使用一次TAB键。
|
||||
|
||||
php > #cli.pager [TAB]
|
||||
|
||||
你可以一直按TAB键来获得选项,直到选项值满足要求。所有的行为都将记录到`~/.php-history`文件。
|
||||
|
||||
要检查你的PHP交互shell活动日志,你可以执行:
|
||||
|
||||
$ nano ~/.php_history | less
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
检查PHP交互Shell日志
|
||||
|
||||
**9. 你可以在PHP交互shell中使用颜色,你所需要知道的仅仅是颜色代码。**
|
||||
|
||||
使用echo来打印各种颜色的输出结果,看我信手拈来:
|
||||
|
||||
php > echo “color_code1 TEXT second_color_code”;
|
||||
|
||||
一个更能说明问题的例子是:
|
||||
|
||||
php > echo "\033[0;31m Hi Tecmint \x1B[0m";
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
在PHP Shell中启用彩色
|
||||
|
||||
到目前为止,我们已经看到,按回车键意味着执行命令,然而PHP Shell中各个命令结尾的分号是必须的。
|
||||
|
||||
**10. PHP shell中的用以打印后续组件的路径名称**
|
||||
|
||||
PHP shell中的basename函数从给出的包含有到文件或目录路径的后续组件的路径名称。
|
||||
|
||||
basename()样例#1和#2。
|
||||
|
||||
php > echo basename("/var/www/html/wp/wp-content/plugins");
|
||||
php > echo basename("www.tecmint.com/contact-us.html");
|
||||
|
||||
上述两个样例都将输出:
|
||||
|
||||
plugins
|
||||
contact-us.html
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
在PHP中打印基本名称
|
||||
|
||||
**11. 你可以使用PHP交互shell在你的桌面创建文件(比如说test1.txt),就像下面这么简单**
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch("/home/avi/Desktop/test1.txt");
|
||||
|
||||
我们已经见识了PHP交互shell在数学运算中有多优秀,这里还有更多一些例子会令你吃惊。
|
||||
|
||||
**12. 使用PHP交互shell打印比如像tecmint.com这样的字符串的长度**
|
||||
|
||||
strlen函数用于获取指定字符串的长度。
|
||||
|
||||
php > echo strlen("tecmint.com");
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
在PHP中打印字符串长度
|
||||
|
||||
**13. PHP交互shell可以对数组排序,是的,你没听错**
|
||||
|
||||
声明变量a,并将其值设置为array(7,9,2,5,10)。
|
||||
|
||||
php > $a=array(7,9,2,5,10);
|
||||
|
||||
对数组中的数字进行排序。
|
||||
|
||||
php > sort($a);
|
||||
|
||||
以排序后的顺序打印数组中的数字,同时打印序号,第一个为[0]。
|
||||
|
||||
php > print_r($a);
|
||||
Array
|
||||
(
|
||||
[0] => 2
|
||||
[1] => 5
|
||||
[2] => 7
|
||||
[3] => 9
|
||||
[4] => 10
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
在PHP中对数组排序
|
||||
|
||||
**14. 在PHP交互Shell中获取Pi的值**
|
||||
|
||||
php > echo pi();
|
||||
|
||||
3.1415926535898
|
||||
|
||||
**15. 打印某个数比如32的平方根**
|
||||
|
||||
php > echo sqrt(150);
|
||||
|
||||
12.247448713916
|
||||
|
||||
**16. 从0-10的范围内回显一个随机数**
|
||||
|
||||
php > echo rand(0, 10);
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
在PHP中获取随机数
|
||||
|
||||
**17. 获取某个指定字符串的md5sum和sha1sum,例如,让我们在PHP Shell中检查某个字符串(比如说avi)的md5sum和sha1sum,并交叉检查这些带有bash shell生成的md5sum和sha1sum的结果。**
|
||||
|
||||
php > echo md5(avi);
|
||||
3fca379b3f0e322b7b7967bfcfb948ad
|
||||
|
||||
php > echo sha1(avi);
|
||||
8f920f22884d6fea9df883843c4a8095a2e5ac6f
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo -n avi | md5sum
|
||||
3fca379b3f0e322b7b7967bfcfb948ad -
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo -n avi | sha1sum
|
||||
8f920f22884d6fea9df883843c4a8095a2e5ac6f -
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
在PHP中检查md5sum和sha1sum
|
||||
|
||||
这里只是PHP Shell中所能获取的功能和PHP Shell的交互特性的惊鸿一瞥,这些就是到现在为止我所讨论的一切。保持和tecmint的连线,在评论中为我们提供你有价值的反馈吧。为我们点赞并分享,帮助我们扩散哦。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/execute-php-codes-functions-in-linux-commandline/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/run-php-codes-from-linux-commandline/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,174 @@
|
||||
Linux命令行中使用和执行PHP代码——第一部分
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
PHP是一个开元服务器端脚本语言,最初这三个字母代表的是“Personal Home Page”,而现在则代表的是“PHP:Hypertext Preprocessor”,它是个递归首字母缩写。它是一个跨平台脚本语言,深受C、C++和Java的影响。
|
||||

|
||||
Linux命令行中运行PHP代码——第一部分
|
||||
|
||||
PHP的语法和C、Java以及带有一些PHP特性的Perl变成语言中的语法十分相似,它眼下大约正被2.6亿个网站所使用,当前最新的稳定版本是PHP版本5.6.10。
|
||||
|
||||
PHP是HTML的嵌入脚本,它便于开发人员快速写出动态生成的页面。PHP主要用于服务器端(而Javascript则用于客户端)以通过HTTP生成动态网页,然而,当你知道可以在Linux终端中不需要网页浏览器来执行PHP时,你或许会大为惊讶。
|
||||
|
||||
本文将阐述PHP脚本语言的命令行方面。
|
||||
|
||||
**1. 在安装完PHP和Apache2后,我们需要安装PHP命令行解释器。**
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install php5-cli [Debian and alike System)
|
||||
# yum install php-cli [CentOS and alike System)
|
||||
|
||||
接下来我们通常要做的是,在‘/var/www/html‘(这是 Apache2 在大多数发行版中的工作目录)这个位置创建一个内容为 ‘<?php phpinfo(); ?>‘,名为 ‘infophp.php‘ 的文件来测试(是否安装正确),执行以下命令即可。
|
||||
|
||||
# echo '<?php phpinfo(); ?>' > /var/www/html/infophp.php
|
||||
|
||||
然后,将浏览器指向http://127.0.0.1/infophp.php, 这将会在网络浏览器中打开该文件。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
检查PHP信息
|
||||
|
||||
不需要任何浏览器,在Linux终端中也可以获得相同的结果。在Linux命令行中执行‘/var/www/html/infophp.php‘,如:
|
||||
|
||||
# php -f /var/www/html/infophp.php
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
从命令行检查PHP信息
|
||||
|
||||
由于输出结果太大,我们可以通过管道将上述输出结果输送给 ‘less‘ 命令,这样就可以一次输出一屏了,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# php -f /var/www/html/infophp.php | less
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
检查所有PHP信息
|
||||
|
||||
这里,‘-f‘选项解析病执行命令后跟随的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
**2. 我们可以直接在Linux命令行使用`phpinfo()`这个十分有价值的调试工具而不需要从文件来调用,只需执行以下命令:**
|
||||
|
||||
# php -r 'phpinfo();'
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
PHP调试工具
|
||||
|
||||
这里,‘-r‘ 选项会让PHP代码在Linux终端中不带`<`和`>`标记直接执行。
|
||||
|
||||
**3. 以交互模式运行PHP并做一些数学运算。这里,‘-a‘ 选项用于以交互模式运行PHP。**
|
||||
|
||||
# php -a
|
||||
|
||||
Interactive shell
|
||||
|
||||
php > echo 2+3;
|
||||
5
|
||||
php > echo 9-6;
|
||||
3
|
||||
php > echo 5*4;
|
||||
20
|
||||
php > echo 12/3;
|
||||
4
|
||||
php > echo 12/5;
|
||||
2.4
|
||||
php > echo 2+3-1;
|
||||
4
|
||||
php > echo 2+3-1*3;
|
||||
2
|
||||
php > exit
|
||||
|
||||
输入 ‘exit‘ 或者按下 ‘ctrl+c‘ 来关闭PHP交互模式。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
启用PHP交互模式
|
||||
|
||||
**4. 你可以仅仅将PHP脚本作为shell脚本来运行。首先,创建在你当前工作目录中创建一个PHP样例脚本。**
|
||||
|
||||
# echo -e '#!/usr/bin/php\n<?php phpinfo(); ?>' > phpscript.php
|
||||
|
||||
注意,我们在该PHP脚本的第一行使用#!/usr/bin/php,就像在shell脚本中那样(/bin/bash)。第一行的#!/usr/bin/php告诉Linux命令行将该脚本文件解析到PHP解释器中。
|
||||
|
||||
其次,让该脚本可执行:
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod 755 phpscript.php
|
||||
|
||||
接着来运行它,
|
||||
|
||||
# ./phpscript.php
|
||||
|
||||
**5. 你可以完全靠自己通过交互shell来创建简单函数,这你一定会被惊到了。下面是循序渐进的指南。**
|
||||
|
||||
开启PHP交互模式。
|
||||
|
||||
# php -a
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个函授,将它命名为 addition。同时,声明两个变量 $a 和 $b。
|
||||
|
||||
php > function addition ($a, $b)
|
||||
|
||||
使用花括号来在其间为该函数定义规则。
|
||||
|
||||
php > {
|
||||
|
||||
定义规则。这里,该规则讲的是添加这两个变量。
|
||||
|
||||
php { echo $a + $b;
|
||||
|
||||
所有规则定义完毕,通过闭合花括号来封装规则。
|
||||
|
||||
php {}
|
||||
|
||||
测试函数,添加数字4和3,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
php > var_dump (addition(4,3));
|
||||
|
||||
#### 样例输出 ####
|
||||
|
||||
7NULL
|
||||
|
||||
你可以运行以下代码来执行该函数,你可以测试不同的值,你想来多少次都行。将里头的 a 和 b 替换成你自己的值。
|
||||
|
||||
php > var_dump (addition(a,b));
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
php > var_dump (addition(9,3.3));
|
||||
|
||||
#### 样例输出 ####
|
||||
|
||||
12.3NULL
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
创建PHP函数
|
||||
|
||||
你可以一直运行该函数,直至退出交互模式(ctrl+z)。同时,你也应该注意到了,上面输出结果中返回的数据类型为 NULL。这个问题可以通过要求 php 交互 shell用 return 代替 echo 返回结果来修复。
|
||||
|
||||
只需要在上面的函数的中 ‘echo‘ 声明用 ‘return‘ 来替换
|
||||
|
||||
替换
|
||||
|
||||
php { echo $a + $b;
|
||||
|
||||
为
|
||||
|
||||
php { return $a + $b;
|
||||
|
||||
剩下的东西和原理仍然一样。
|
||||
|
||||
这里是一个样例,在该样例的输出结果中返回了正确的数据类型。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
PHP函数
|
||||
|
||||
永远都记住,用户定义的函数不会从一个shell会话保留到下一个shell会话,因此,一旦你退出交互shell,它就会丢失了。
|
||||
|
||||
希望你喜欢此次会话。保持连线,你会获得更多此类文章。保持关注,保持健康。请在下面的评论中为我们提供有价值的反馈。点赞并分享,帮助我们扩散。
|
||||
|
||||
还请阅读: [12个Linux终端中有用的的PHP命令行用法——第二部分][1]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/run-php-codes-from-linux-commandline/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[vishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/execute-php-codes-functions-in-linux-commandline/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,320 @@
|
||||
[translating by xiqingongzi]
|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA系列: 复习基础命令及系统文档 – 第一部分
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
RHCSA (红帽认证系统工程师) 是由给商业公司提供开源操作系统和软件的RedHat公司举行的认证考试, 除此之外,红帽公司还为这些企业和机构提供支持、训练以及咨询服务
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA 考试准备指南
|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA 考试(考试编号 EX200)通过后可以获取由Red Hat 公司颁发的证书. RHCSA 考试是RHCT(红帽认证技师)的升级版,而且RHCSA必须在新的Red Hat Enterprise Linux(红帽企业版)下完成.RHCT和RHCSA的主要变化就是RHCT基于 RHEL5 , 而RHCSA基于RHEL6或者7, 这两个认证的等级也有所不同.
|
||||
|
||||
红帽认证管理员所会的最基础的是在红帽企业版的环境下执行如下系统管理任务:
|
||||
|
||||
- 理解并会使用命令管理文件、目录、命令行以及系统/软件包的文档
|
||||
- 使用不同的启动等级启动系统,认证和控制进程,启动或停止虚拟机
|
||||
- 使用分区和逻辑卷管理本地存储
|
||||
- 创建并且配置本地文件系统和网络文件系统,设置他们的属性(许可、加密、访问控制表)
|
||||
- 部署、配置、并且控制系统,包括安装、升级和卸载软件
|
||||
- 管理系统用户和组,独立使用集中制的LDAP目录权限控制
|
||||
- 确保系统安全,包括基础的防火墙规则和SELinux配置
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
关于你所在国家的考试注册费用参考 [RHCSA Certification page][1].
|
||||
|
||||
关于你所在国家的考试注册费用参考RHCSA 认证页面
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在这个有15章的RHCSA(红帽认证管理员)备考系列,我们将覆盖以下的关于红帽企业Linux第七版的最新的信息
|
||||
|
||||
- Part 1: 回顾必会的命令和系统文档
|
||||
- Part 2: 在RHEL7如何展示文件和管理目录
|
||||
- Part 3: 在RHEL7中如何管理用户和组
|
||||
- Part 4: 使用nano和vim管理命令/ 使用grep和正则表达式分析文本
|
||||
- Part 5: RHEL7的进程管理:启动,关机,以及其他介于二者之间的.
|
||||
- Part 6: 使用 'Parted'和'SSM'来管理和加密系统存储
|
||||
- Part 7: 使用ACLs(访问控制表)并挂载 Samba /NFS 文件分享
|
||||
- Part 8: 加固SSH,设置主机名并开启网络服务
|
||||
- Part 9: 安装、配置和加固一个Web,FTP服务器
|
||||
- Part 10: Yum 包管理方式,使用Cron进行自动任务管理以及监控系统日志
|
||||
- Part 11: 使用FirewallD和Iptables设置防火墙,控制网络流量
|
||||
- Part 12: 使用Kickstart 自动安装RHEL 7
|
||||
- Part 13: RHEL7:什么是SeLinux?他的原理是什么?
|
||||
- Part 14: 在RHEL7 中使用基于LDAP的权限控制
|
||||
- Part 15: RHEL7的虚拟化:KVM 和虚拟机管理
|
||||
|
||||
在第一章,我们讲解如何输入和运行正确的命令在终端或者Shell窗口,并且讲解如何找到、插入,以及使用系统文档
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA:回顾必会的Linux命令 - 第一部分
|
||||
|
||||
#### 前提: ####
|
||||
|
||||
至少你要熟悉如下命令
|
||||
|
||||
- [cd command][2] (改变目录)
|
||||
- [ls command][3] (列举文件)
|
||||
- [cp command][4] (复制文件)
|
||||
- [mv command][5] (移动或重命名文件)
|
||||
- [touch command][6] (创建一个新的文件或更新已存在文件的时间表)
|
||||
- rm command (删除文件)
|
||||
- mkdir command (创建目录)
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中你将会找到更多的关于如何更好的使用他们的正确用法和特殊用法.
|
||||
|
||||
虽然没有严格的要求,但是作为讨论常用的Linux命令和方法,你应该安装RHEL7 来尝试使用文章中提到的命令.这将会使你学习起来更省力.
|
||||
|
||||
- [红帽企业版Linux(RHEL)7 安装指南][7]
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用Shell进行交互 ###
|
||||
如果我们使用文本模式登陆Linux,我们就无法使用鼠标在默认的shell。另一方面,如果我们使用图形化界面登陆,我们将会通过启动一个终端来开启shell,无论那种方式,我们都会看到用户提示,并且我们可以开始输入并且执行命令(当按下Enter时,命令就会被执行)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
当我们使用文本模式登陆Linux时,
|
||||
命令是由两个部分组成的:
|
||||
|
||||
- 命令本身
|
||||
- 参数
|
||||
|
||||
某些参数,称为选项(通常使用一个连字符区分),改变了由其他参数定义的命令操作.
|
||||
|
||||
命令的类型可以帮助我们识别某一个特定的命令是由shell内建的还是由一个单独的包提供。这样的区别在于我们能够找到更多关于该信息的命令,对shell内置的命令,我们需要看shell的ManPage,如果是其他提供的,我们需要看它自己的ManPage.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
检查Shell的内建命令
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的例子中, cd 和 type 是shell内建的命令,top和 less 是由其他的二进制文件提供的(在这种情况下,type将返回命令的位置)
|
||||
其他的内建命令
|
||||
|
||||
- [echo command][8]: 展示字符串
|
||||
- [pwd command][9]: 输出当前的工作目录
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
更多内建函数
|
||||
|
||||
**exec 命令**
|
||||
|
||||
运行我们指定的外部程序。请注意,最好是只输入我们想要运行的程序的名字,不过exec命令有一个特殊的特性:使用旧的shell运行,而不是创建新的进程,可以作为子请求的验证.
|
||||
|
||||
# ps -ef | grep [shell 进程的PID]
|
||||
|
||||
当新的进程注销,Shell也随之注销,运行 exec top 然后按下 q键来退出top,你会注意到shell 会话会结束,如下面的屏幕录像展示的那样:
|
||||
|
||||
注:youtube视频
|
||||
<iframe width="640" height="405" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="allowfullscreen" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/f02w4WT73LE"></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
**export 命令**
|
||||
|
||||
输出之后执行的命令的环境的变量
|
||||
|
||||
**history 命令**
|
||||
|
||||
展示数行之前的历史命令.在感叹号前输入命令编号可以再次执行这个命令.如果我们需要编辑历史列表中的命令,我们可以按下 Ctrl + r 并输入与命令相关的第一个字符.
|
||||
当我们看到的命令自动补全,我们可以根据我们目前的需要来编辑它:
|
||||
|
||||
注:youtube视频
|
||||
<iframe width="640" height="405" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="allowfullscreen" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/69vafdSMfU4"></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
命令列表会保存在一个叫 .bash_history的文件里.history命令是一个非常有用的用于减少输入次数的工具,特别是进行命令行编辑的时候.默认情况下,bash保留最后输入的500个命令,不过可以通过修改 HISTSIZE 环境变量来增加:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux history 命令
|
||||
|
||||
但上述变化,在我们的下一次启动不会保留。为了保持HISTSIZE变量的变化,我们需要通过手工修改文件编辑:
|
||||
|
||||
# 设置history请看 HISTSIZE 和 HISTFILESIZE 在 bash(1)的文档
|
||||
HISTSIZE=1000
|
||||
|
||||
**重要**: 我们的更改不会生效,除非我们重启了系统
|
||||
|
||||
**alias 命令**
|
||||
没有参数或使用-p参数将会以 名称=值的标准形式输出alias 列表.当提供了参数时,一个alias 将被定义给给定的命令和值
|
||||
|
||||
使用alias ,我们可以创建我们自己的命令,或修改现有的命令,包括需要的参数.举个例子,假设我们想别名 ls 到 ls –color=auto ,这样就可以使用不同颜色输出文件、目录、链接
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# alias ls='ls --color=auto'
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux 别名命令
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: 你可以给你的新命令起任何的名字,并且附上足够多的使用单引号分割的参数,但是这样的情况下你要用分号区分开他们.
|
||||
|
||||
# alias myNewCommand='cd /usr/bin; ls; cd; clear'
|
||||
|
||||
**exit 命令**
|
||||
|
||||
Exit和logout命令都是退出shell.exit命令退出所有的shell,logout命令只注销登陆的shell,其他的自动以文本模式启动的shell不算.
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们对某个程序由疑问,我们可以看他的man Page,可以使用man命令调出它,额外的,还有一些重要的文件的手册页(inittab,fstab,hosts等等),库函数,shells,设备及其他功能
|
||||
|
||||
#### 举例: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- man uname (输出系统信息,如内核名称、处理器、操作系统类型、架构等).
|
||||
- man inittab (初始化守护设置).
|
||||
|
||||
另外一个重要的信息的来源就是info命令提供的,info命令常常被用来读取信息文件.这些文件往往比manpage 提供更多信息.通过info 关键词调用某个命令的信息
|
||||
|
||||
# info ls
|
||||
# info cut
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
另外,在/usr/share/doc 文件夹包含了大量的子目录,里面可以找到大量的文档.他们包含文本文件或其他友好的格式.
|
||||
确保你使用这三种方法去查找命令的信息。重点关注每个命令文档中介绍的详细的语法
|
||||
|
||||
**使用expand命令把tabs转换为空格**
|
||||
|
||||
有时候文本文档包含了tabs但是程序无法很好的处理的tabs.或者我们只是简单的希望将tabs转换成空格.这就是为什么expand (GNU核心组件提供)工具出现,
|
||||
|
||||
举个例子,给我们一个文件 NumberList.txt,让我们使用expand处理它,将tabs转换为一个空格.并且以标准形式输出.
|
||||
|
||||
# expand --tabs=1 NumbersList.txt
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux expand 命令
|
||||
|
||||
unexpand命令可以实现相反的功能(将空格转为tab)
|
||||
|
||||
**使用head输出文件首行及使用tail输出文件尾行**
|
||||
|
||||
通常情况下,head命令后跟着文件名时,将会输出该文件的前十行,我们可以通过 -n 参数来自定义具体的行数。
|
||||
|
||||
# head -n3 /etc/passwd
|
||||
# tail -n3 /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux 的 head 和 tail 命令
|
||||
|
||||
tail 最有意思的一个特性就是能够展现信息(最后一行)就像我们输入文件(tail -f my.log,一行一行的,就像我们在观察它一样。)这在我们监控一个持续增加的日志文件时非常有用
|
||||
|
||||
更多: [Manage Files Effectively using head and tail Commands][10]
|
||||
|
||||
**使用paste合并文本文件**
|
||||
paste命令一行一行的合并文件,默认会以tab来区分每一行,或者其他你自定义的分行方式.(下面的例子就是输出使用等号划分行的文件).
|
||||
# paste -d= file1 file2
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Merge Files in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
**使用split命令将文件分块**
|
||||
|
||||
split 命令常常用于把一个文件切割成两个或多个文由我们自定义的前缀命名的件文件.这些文件可以通过大小、区块、行数,生成的文件会有一个数字或字母的后缀.在下面的例子中,我们将切割bash.pdf ,每个文件50KB (-b 50KB) ,使用命名后缀 (-d):
|
||||
|
||||
# split -b 50KB -d bash.pdf bash_
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在Linux下划分文件
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用如下命令来合并这些文件,生成源文件:
|
||||
|
||||
# cat bash_00 bash_01 bash_02 bash_03 bash_04 bash_05 > bash.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
**使用tr命令改变字符**
|
||||
|
||||
tr 命令多用于变化(改变)一个一个的字符活使用字符范围.和之前一样,下面的实例我们江使用同样的文件file2,我们将实习:
|
||||
|
||||
- 小写字母 o 变成大写
|
||||
- 所有的小写字母都变成大写字母
|
||||
|
||||
# cat file2 | tr o O
|
||||
# cat file2 | tr [a-z] [A-Z]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在Linux中替换文字
|
||||
|
||||
**使用uniq和sort检查或删除重复的文字**
|
||||
|
||||
uniq命令可以帮我们查出或删除文件中的重复的行,默认会写出到stdout.我们应当注意, uniq 只能查出相邻的两个相同的单纯,所以, uniq 往往和sort 一起使用(sort一般用于对文本文件的内容进行排序)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
默认的,sort 以第一个参数(使用空格区分)为关键字.想要定义特殊的关键字,我们需要使用 -k参数,请注意如何使用sort 和uniq输出我们想要的字段,具体可以看下面的例子
|
||||
|
||||
# cat file3
|
||||
# sort file3 | uniq
|
||||
# sort -k2 file3 | uniq
|
||||
# sort -k3 file3 | uniq
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
删除文件中重复的行
|
||||
|
||||
**从文件中提取文本的命令**
|
||||
|
||||
Cut命令基于字节(-b),字符(-c),或者区块(-f)从stdin活文件中提取到的部分将会以标准的形式展现在屏幕上
|
||||
|
||||
当我们使用区块切割时,默认的分隔符是一个tab,不过你可以通过 -d 参数来自定义分隔符.
|
||||
|
||||
# cut -d: -f1,3 /etc/passwd # 这个例子提取了第一块和第三块的文本
|
||||
# cut -d: -f2-4 /etc/passwd # 这个例子提取了第一块到第三块的文本
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
从文件中提取文本
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
注意,上方的两个输出的结果是十分简洁的。
|
||||
|
||||
**使用fmt命令重新格式化文件**
|
||||
|
||||
fmt 被用于去“清理”有大量内容或行的文件,或者有很多缩进的文件.新的锻炼格式每行不会超过75个字符款,你能改变这个设定通过 -w(width 宽度)参数,它可以设置行宽为一个特定的数值
|
||||
|
||||
举个例子,让我们看看当我们用fmt显示定宽为100个字符的时候的文件/etc/passwd 时会发生什么.再来一次,输出值变得更加简洁.
|
||||
|
||||
# fmt -w100 /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux文件重新格式化
|
||||
|
||||
**使用pr命令格式化打印内容**
|
||||
|
||||
pr 分页并且在列中展示一个或多个用于打印的文件. 换句话说,使用pr格式化一个文件使他打印出来时看起来更好.举个例子,下面这个命令
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -a /etc | pr -n --columns=3 -h "Files in /etc"
|
||||
|
||||
以一个友好的排版方式(3列)输出/etc下的文件,自定义了页眉(通过 -h 选项实现),行号(-n)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux的文件格式
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中,我们已经讨论了如何在Shell或终端以正确的语法输入和执行命令,并解释如何找到,检查和使用系统文档。正如你看到的一样简单,这就是你成为RHCSA的第一大步
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想添加一些其他的你经常使用的能够有效帮你完成你的日常工作的基础命令,并为分享他们而感到自豪,请在下方留言.也欢迎提出问题.我们期待您的回复.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/rhcsa-exam-reviewing-essential-commands-system-documentation/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.redhat.com/en/services/certification/rhcsa
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/cd-command-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/ls-command-interview-questions/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/advanced-copy-command-shows-progress-bar-while-copying-files/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/rename-multiple-files-in-linux/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/8-pratical-examples-of-linux-touch-command/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/redhat-enterprise-linux-7-installation/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/pwd-command-examples/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/view-contents-of-file-in-linux/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user