mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject
This commit is contained in:
commit
e002c68768
@ -1,20 +1,14 @@
|
||||
Linux cp 命令的15个示例 - 创建文件和目录的副本
|
||||
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
拷贝文件和目录是每一个操作系统的基本指令。备份行为基本上是创建文件和目录的副本。在Linux系统下,我们可以用**cp**命令来实现。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### copy 命令是什么 ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
正如我们在上文提到的,**cp**是一个用来创建文件和目录副本的命令。在这里我们提供了一些在日常操作中可能用到的cp命令的实例。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 不带任何参数下,运行cp ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这是 cp 命令最基础的使用。 拷贝名为 myfile.txt 从一个位置到另一个位置,我们可以像这样子输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cp myfile.txt /home/pungki/office
|
||||
@ -53,7 +47,7 @@ Linux cp 命令的15个示例 - 创建文件和目录的副本
|
||||
如果你收到错误信息,则目录不会被拷贝到目标文件夹。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 创建文件的硬链接,而不是拷贝它们####
|
||||
#### 4. 创建文件的硬链接,而不是拷贝它们####
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -103,7 +97,8 @@ Linux cp 命令的15个示例 - 创建文件和目录的副本
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6. 不随符号链接拷贝原文件 #####[译注:意思是只拷贝符号链接文件]
|
||||
#### 6. 不随符号链接拷贝原文件 ####
|
||||
[译注:意思是只拷贝符号链接文件]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以用 **-P** 选项来实现。当对符号链接使用 cp 命令,它会照原样拷贝它自身。来看看下面的示例。
|
||||
@ -1,17 +1,17 @@
|
||||
每日 Ubuntu 小技巧——英特尔图形安装程序 1.0.3 发布,支持 Ubuntu 13.10
|
||||
每日 Ubuntu 小技巧——Intel图形安装程序 1.0.3 发布,支持 Ubuntu 13.10
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
对于那些使用因特尔显卡台式机或者笔记本来运行 Ubuntu Linux 13.10 的用户来说,有件事可能想要完成——安装 Linux 版本的因特尔图形安装程序。
|
||||
对于那些使用Intel显卡台式机或者笔记本来运行 Ubuntu Linux 13.10 的用户来说,有件事可能想要完成——安装 Linux 版本的Intel图形安装程序。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 版本的英特尔图形安装程序允许用户方便地安装最新的英特尔图形和视频驱动程序。直到最近,仍不支持 Ubuntu 13.10。
|
||||
Linux 版本的Intel图形安装程序允许用户方便地安装最新的Intel图形和视频驱动程序。现在之前,仍不支持 Ubuntu 13.10。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想保持目前英特尔卡在你机器中的最新驱动程序,你可能需要这个安装程序。它能增强、优化并提供英特尔图形硬件最好的用户体验。
|
||||
如果你想保持目前Intel卡在你机器中的最新驱动程序,你可能需要这个安装程序。它能增强、优化并提供Intel图形硬件最好的用户体验。
|
||||
|
||||
[https://01.org/linuxgraphics/downloads/2013/intelr-graphics-installer-1.0.3-linux][1]
|
||||
访问官网:[https://01.org/linuxgraphics/downloads/2013/intelr-graphics-installer-1.0.3-linux][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 中安装英特尔图形安装程序 ###
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 中安装Intel图形安装程序 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你确定你的计算机有英特尔图形卡,而且你正在运行的版本是 Ubuntu 13.10,继续下面的学习如何安装这个包,
|
||||
如果你确定你的计算机有Intel图形卡,而且你正在运行的版本是 Ubuntu 13.10,继续下面的学习如何安装这个包,
|
||||
|
||||
有些用户安装和配置驱动程序包后曾造成系统问题,所以你应该在安装前持谨慎态度,并备份你的系统。当你完成后,执行下面的命令来下载32位版本的软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -33,11 +33,11 @@ Linux 版本的英特尔图形安装程序允许用户方便地安装最新的
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
为了让你的系统信任英特尔图形安装程序,您必须运行下面命令来添加 key 到 Ubuntu 的软件库中。
|
||||
为了让你的系统信任Intel图形安装程序,您必须运行下面命令来添加 key 到 Ubuntu 的软件库中。
|
||||
|
||||
wget --no-check-certificate https://download.01.org/gfx/RPM-GPG-KEY-ilg -O - | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
|
||||
就这么简单。如果你按照以上步骤做了,你的机器应该能正确运行英特尔驱动程序。如果不是,可能是你的显卡不兼容,或者是不支持。
|
||||
就这么简单。如果你按照以上步骤做了,你的机器应该能正确运行Intel驱动程序。如果不是,可能是你的显卡不兼容,或者是不支持。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,18 +1,18 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux上将HTML页面转化成png图片
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
将一个特定页面抓取为一张png图片的最简单的方法是使用[CutyCapt][1],这是一种在Linux下的方便地将HTML网页转化成不同向量和位图图像格式的命令行工具(比如,SVG, PDF, PS, PNG, JPEG, TIFF, GIF)。CutyCapt内部使用WebKit渲染引擎来导出网页渲染输出到图片文件中。它使用Qt构建,CutyCapt实际上是一个也可以在Windows上使用的跨平台应用。
|
||||
将一个特定页面抓取为一张png图片的最简单的方法是使用[CutyCapt][1],这是一种在Linux下的方便地将HTML网页转化成矢量图形和位图图像格式的命令行工具(比如,SVG, PDF, PS, PNG, JPEG, TIFF, GIF)。CutyCapt内部使用WebKit渲染引擎来导出网页渲染输出到图片文件中。它使用Qt构建,CutyCapt实际上是一个也可以在Windows上使用的跨平台应用。
|
||||
|
||||
在本篇教程中,我会描述如何**将一个HTML网页使用CutyCapt转化成png图片**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Linux上 CutyCapt###
|
||||
### 在Linux上安装 CutyCapt###
|
||||
|
||||
这是在特定Linux发行版上的安装命令。
|
||||
|
||||
**在Debian, Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint 安装 CutyCapt **
|
||||
####在Debian, Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint 安装 CutyCapt
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install cutycapt
|
||||
|
||||
**在Fedora上安装 CutyCapt**
|
||||
####在Fedora上安装 CutyCapt
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install subversion qt-devel qtwebkit-devel gcc-c++ make
|
||||
$ svn co svn://svn.code.sf.net/p/cutycapt/code/ cutycapt
|
||||
@ -31,7 +31,7 @@
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
$ sudo cp CutyCapt /usr/local/bin/cutycapt
|
||||
|
||||
### 在CentOS 或者 RHEL安装 CutyCapt ###
|
||||
#### 在CentOS 或者 RHEL安装 CutyCapt
|
||||
|
||||
首先在你的Linux上[启用EPEL仓库][3]。接着和在Fedora上一样使用相同的步骤编译安装。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,7 +57,6 @@
|
||||
|
||||
如果你要不含X的服务器上运行CutyCapt,你可以在服务器上安装Xvfb(轻量级“假的”X11 服务)。这样CutyCapt就不会报错了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
要在Debian, Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint 上安装Xvfb:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install xvfb
|
||||
@ -76,7 +75,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/02/convert-html-web-page-png-image-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -7,19 +7,17 @@ Linux 移动或重命名文件/目录-mv 的10个实用例子
|
||||
|
||||
mv 命令是一个与**cp**类似的命令,但是它**并非**创建文件或目录的复制品/副本。不管你在使用什么版本的Linux系统,mv 都默认安装在你的Linux系统上了。来看一下 mv 命令在日常操作中的一些例子。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.移动文件 ###
|
||||
#### 1.移动文件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
移动文件时需要注意的是文件的源地址和目标地址**必须不同**。这里有个例子。想要将**file_1.txt**文件从当前目录移动到其它目录,以**/home/pungki/**为例,语法应该如下:
|
||||
移动文件时需要注意的是文件的源地址和目标地址**必须不同**。这里有个例子,想要将**file_1.txt**文件从当前目录移动到其它目录,以**/home/pungki/**为例,语法应该如下:
|
||||
|
||||
$ mv file_1.txt /home/pungki/office
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如我们所见,当我们移动 file_txt 文件时,先前目录的 file_1.txt 就**被删除了**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.移动多个文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.移动多个文件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
如果想一次移动多个文件,我们可以将他们放在一行并用空格分开。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,24 +25,22 @@ mv 命令是一个与**cp**类似的命令,但是它**并非**创建文件或
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你的文件有规律可循的话那么你就可以利用它。比如,为了移除所有以**.txt**为扩展名的文件,我们可以用下面的命令:
|
||||
如果你的文件有规律可循的话那么你就可以使用通配符。比如,为了移除所有以**.txt**为扩展名的文件,我们可以用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ mv *.txt /home/pungki/office
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3.移动目录 ###
|
||||
#### 3.移动目录 ####
|
||||
|
||||
不同于复制命令,用 mv 命令移动目录相当直接。移动目录你可以使用不带选项的 mv 命令。看下面的截图就一目了然了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4.重命名文件或目录 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4.重命名文件或目录 ####
|
||||
|
||||
我们也用 mv 命令来重命名文件或目录。不过目标位置和源位置必须相同才可以。然后文件名必须不同。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
假定我们当前所在目录为**/home/pungki/Documents**,而我们想将**file_1.txt重命名为file_2.txt**。那么命令应该如下:
|
||||
|
||||
$ mv file_1.txt file_2.txt
|
||||
@ -55,8 +51,7 @@ mv 命令是一个与**cp**类似的命令,但是它**并非**创建文件或
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 重命名目录 ###
|
||||
#### 5. 重命名目录 ####
|
||||
|
||||
上一段的规则同样适用于目录。请看这个例子:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -64,8 +59,7 @@ mv 命令是一个与**cp**类似的命令,但是它**并非**创建文件或
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 打印移动信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6. 打印移动信息 ####
|
||||
|
||||
当你移动或重命名一大堆文件或目录时,你可能会想在不去目标位置去查看的情况下知道你自己的命令是否成功地执行了。这就要用到**-v**选项了。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -77,10 +71,9 @@ mv 命令是一个与**cp**类似的命令,但是它**并非**创建文件或
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 使用交互模式 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当你将文件移动到其它位置,而那个位置恰好有同样的文件,这时 mv 命令会覆盖掉原来的文件。对于mv的这一行为一般不会有什么提示。如果想产生一个关于覆盖文件的提示,我们可以使用**-i**选项。
|
||||
#### 7. 使用交互模式 ####
|
||||
|
||||
当你将文件移动到其它位置,而那个位置恰好有同样的文件,这时 mv 命令会覆盖掉原来的文件。对于mv的这一行为一般不会有什么提示。如果想产生一个关于覆盖文件的提示,我们可以使用**-i**选项。(译注:通常发行版会通过alias命令,将-i作为默认选项,所以会有提示。)
|
||||
|
||||
假设我们想将 file_1.txt 移动到 /home/pungki/office。同时,/home/pungki/office 目录下已经有file_1.txt文件了。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -88,32 +81,28 @@ mv 命令是一个与**cp**类似的命令,但是它**并非**创建文件或
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这个提示会让我们知道目标位置处file_1.txt的存在。如果我们按**y**键,那么那个文件将会被删除,否则不会。
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. 使用更新选项 ###
|
||||
#### 8. 使用更新选项 ####
|
||||
|
||||
-i 选项会提示我们关于覆盖文件的提示,而 -u 则只在源文件比目标文件新时才执行更新。让我们看一看下面的例子:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
假如 file_1.txt 和 file_2.txt有如下特点:
|
||||
|
||||
File_1.txt has 84 bytes file size and it last modified time is 12:00
|
||||
File_2.txt has 0 bytes file size and it last modified time is 11:59
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们想将它们移动到 /home/pungki/office 目录下。***但是目标地址**已经有file_1.txt和file_2.txt了。
|
||||
|
||||
我们用下面的命令将file_1.txt 和file_2.txt从当前目录移动到/home/pungki/office
|
||||
|
||||
$ mv -uv *.txt /home/pungki/office
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到这些文件被移动了。能移动这些文件是因为它们最近的修改时间戳比 /home/pungki/office 目录中的文件新。
|
||||
|
||||
### 9.不要覆盖任何已存在的文件 ###
|
||||
#### 9.不要覆盖任何已存在的文件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
如果**-i**选项询问我们是否要覆盖文件,那么 -n 选项将不会允许我们覆盖任何已存在的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -123,9 +112,7 @@ mv 命令是一个与**cp**类似的命令,但是它**并非**创建文件或
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. 复制时创建备份 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 10. 复制时创建备份 ####
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,移动文件将会覆盖已存在的目标文件。但是如果我们移动错了文件而目标文件已经被新的文件覆盖了,这时应该怎么办才好呢?**有没有一种方法可以恢复之前的文件呢?答案是肯定的**。我们可以用**-b**选项。该选项会在新文件覆盖旧文件时将旧文件做备份。这里我们还以第8点为例。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -135,7 +122,17 @@ mv 命令是一个与**cp**类似的命令,但是它**并非**创建文件或
|
||||
|
||||
如截图中所见,在 /home/pungki/office 目录下出现了名为**file_1.txt~ and file_2.txt~ 的文件。那个波浪符号(~)意味着**这些文件是备份文件。从它们的属性中我们可以看到,这些文件比file_1.txt和file_2.txt要旧。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ##
|
||||
#### 11. 无条件覆盖已经存在的文件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
(译注:这一节是译者补充的,原文遗漏了这个重要选项)
|
||||
|
||||
当你希望无论如何都覆盖已经存在的文件或目录时,你可以使用 -f 选项。如果同时指定了 -f 选项和 -i 或 -n 选项,则 -f 选项会覆盖它们——即不进行任何提示而覆盖,所以,在使用此参数时,知道你在做什么。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mv -f *.txt /home/pungki/office
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
移动文件和目录命令是Linux系统的基本命令。通常你可以通过**man mv** 或者 **mv --help**显示mv的手册页以了解更多详细信息。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -143,8 +140,8 @@ mv 命令是一个与**cp**类似的命令,但是它**并非**创建文件或
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/mv-command-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Linchenguang](https://github.com/Linchenguang) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[Linchenguang](https://github.com/Linchenguang) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-cp-command/
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-2687-1.html
|
||||
@ -3,19 +3,15 @@
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**越来越多的人期待着 Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (Trusty Tahr) 的发布,并希望她能在不改变用户习惯的前提下替代 Windows XP。
|
||||
因此我们将在本文尝试给大家分析下这个两个系统的优缺点**
|
||||
因此我们将在本文尝试给大家分析下这个两个系统的优缺点。**
|
||||
|
||||
很多 Windows XP 用户在微软宣布四月份后即将停止对他们的操作系统提供安全更新后作出改变。
|
||||
他们像大多数改用 Linux 的用户一样,有着大量的系统操作和兼容性方面各式各样的问题。
|
||||
而事实是这些原 XP 用户可能顾虑太多了,理由如下:
|
||||
很多 Windows XP 用户在微软宣布四月份后即将停止对他们的操作系统提供安全更新后作出改变。他们像大多数改用 Linux 的用户一样,有着大量的系统操作和兼容性方面各式各样的问题。而事实是这些原 XP 用户可能顾虑太多了,理由如下:
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在一生中哪怕就装过一次 Windows,祝贺你,因为你已经知道该如何安装 Ubuntu 这类的系统了。
|
||||
Ubuntu 为用户提供了一个很直观而且没有太多复杂选项的安装界面。
|
||||
如果你在一生中哪怕就装过一次 Windows,祝贺你,因为你已经知道该如何安装 Ubuntu 这类的系统了。Ubuntu 为用户提供了一个很直观而且没有太多复杂选项的安装界面。
|
||||
|
||||
唯一可能会使你疑惑的就是系统分区时出现的大量陌生词汇了,比如“交换空间(swap)”和“EXT4文件系统”。
|
||||
不过好消息是在 Linux 下你或许永远不需要多个分区了。
|
||||
唯一可能会使你疑惑的就是系统分区时出现的大量陌生词汇了,比如“交换空间(swap)”和“EXT4文件系统”。不过好消息是在 Linux 下你或许永远不需要多个分区了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -85,6 +81,6 @@ Linux 有所有你需要的功能,没有任何理由不去使用一个基于
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Ubuntu-14-04-LTS-vs-Windows-XP-Pros-and-Cons-430084.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[VizV](https://github.com/vizv) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[VizV](https://github.com/vizv) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,61 +0,0 @@
|
||||
crowner 吃睡睡吃
|
||||
5 Linux Distributions that Deserve more Love
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As I wrote in my previous post, [Linux is Everywhere][1] and there are hundreds if not thousands of different distributions. Some are very famous, some boasts of their 10 million user base and then there are others who live in the shadow of famous distributions. Some distributions struggle to even gain a fraction of what big distributions enjoy and a few handful of distributions die every year. But today we are here to discuss about few distributions that being awesome still don’t get the love they deserve. It doesn’t matter if the distribution is original or forked or based on some other distribution, if it does the job, is stable enough for daily use and is not getting the love it deserves, it will be on the list.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Rosa ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[ROSA Desktop][2], is a Linux distribution featuring a highly customized KDE desktop with a number of modifications designed to enhance the user-friendliness of the working environment developed by ROSA, a Russian company who also develops an “Enterprise Server” edition of ROSA which is based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux. This is one of the most customized distributions you can find on web with many in-house features like a completely redesigned login Screen, a tool named “TimeFrame” which allows you to easily monitor your activity at specified dates, heavily modified “Dolhpin” file manager, Rocket Bar, Simple Welcome, Rosa Media Player and many others.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Korora ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Korora][3] was born out of a desire to make Linux easier for new users, while still being useful for experts. Originally based on Gentoo Linux in 2005, Korora was re-born in 2010 as a Fedora Remix with tweaks and extras to make the system “just work” out of the box. Korora is a mix of Fedora + RPM Fusion + Korora packages, where Korora provides the bleeding edge and stability of a Red Hat distribution, it effortlessly works out of the box. Many people complain about Fedora of being too vanilla but Fedora is designed that way, people who love Fedora but still want something that works out of box, Korora is for you.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Chakra Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you are a KDE fan and you cannot wait for months to use the latest software then there’s a match for you made in heaven, they call it Chakra Linux which started as a Arch Linux fork but has turned into an independent distribution with its own repositories, packages, Kernel and half/rolling release cycle.
|
||||
|
||||
[Chakra Linux][4] works mostly out of the box and has all the goodness of Arch Linux. Some may argue that why not use Arch Linux and then install KDE instead of using Chakra Linux. First the install process, no matter how hard everyone try to convince you how easy it is, it is not. An OS should be easy to use and even easier to install, not the other way around.
|
||||
|
||||
Chakra Linux is one of the very few true KDE distributions available, so you can be assured that you will get the very best KDE experience while using Chakra Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Ubuntu Gnome ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu might have been the centre of controversy for past few years, especially the decision to switch to Unity but I personally kind of like Unity. On other side it has always been so buggy on my Nvidia setup and I have seen people constantly complaining about weird Unity behaviour. There were other Semi-official flavours available but none of them really felt like a true Ubuntu experience until [Ubuntu Gnome][5] arrived.
|
||||
|
||||
There is nothing much to write about this, Ubuntu Gnome is just Ubuntu with a Gnome Shell, I felt like it should make the list. Ubuntu has been the favourite distribution for a long time and because of few bad decisions Canonical made, the distribution should not suffer. I am happy to say that Ubuntu Gnome feels every bit of original Ubuntu while lacking the Canonical’s rude and forceful behaviour.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Sabayon Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Sabayon][6] Linux is a Gentoo-based distribution which follows the works-out-of-the-box philosophy and it does that without skipping a beat. It may sound a bit biased but Sabayon is one of the very few distributions that ‘actually’ works out of the box across a wide range of systems.
|
||||
|
||||
Sabayon follows a no nonsense philosophy and everything works as it is supposed to, you don’t have to mess with the terminal to get things done, you don’t have to add ‘extra’ repositories to add the most obvious functionality, everything is there in one place, by the way you can do all those things if you want to but the point is you cannot force the user, if I want to use Arch Linux without banging my head with the terminal, I should be able to do that.
|
||||
|
||||
Sabayon is a bleeding edge, fast and surprisingly stable distribution for which the credit goes to rock solid Gentoo core. It is very easy to use with your choice of DE, even easier to install, works out of the box, features a very simple and capable package manager, comes with most of the required applications and it can still be customized deep down like any other distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxfederation.com/linux-distributions-love/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linuxfederation.com/linux-everywhere/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.rosalab.com/products/desktop_fresh
|
||||
[3]:https://kororaproject.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.chakra-project.org/
|
||||
[5]:http://ubuntugnome.org/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.sabayon.org/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
乌龙茶占坑
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – HPLIP 3.14.3 Released – Upgrade In Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
HP Linux Imaging and printing (HPLIP) is an open-source package sponsored by HP to deliver full feature HP printer drivers to the Linux community.
|
||||
@ -50,4 +51,4 @@ via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2014/03/daily-ubuntu-tips-hplip-3-14-3-released
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://hplipopensource.com/hplip-web/supported_devices/index.html
|
||||
[2]:http://sourceforge.net/p/hplip/news/2014/03/hplip-3143-public-release-/
|
||||
[2]:http://sourceforge.net/p/hplip/news/2014/03/hplip-3143-public-release-/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,139 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Glances – An Advanced Real Time System Monitoring Tool for Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Earlier, we’ve written about many Linux [System Monitor Tools][1] that can be used to monitor performance of Linux systems, but we think that, most users prefer the default one that comes with every Linux distributions (**top** command).
|
||||
|
||||
The [top command][2] is real time task manager in Linux and the most frequently used system monitoring tool in **GNU/Linux** distributions to find the performance related bottlenecks in system which help us to take corrective actions. It has a nice minimalist interface, comes with few amount of reasonable options that enables us to get a better idea about overall system performance quickly.
|
||||
|
||||
However, sometimes its very tricky to find an application/process that consuming lots of system resources is a bit difficult under top. Because top command doesn’t have a ability to highlights programs that are eating too much of **CPU**, **RAM**, other resources.
|
||||
|
||||
For keeping such approach, here we are bringing a powerful system monitor program called “**Glances**” that automatically highlights programs that are utilizing highest system resources and providing maximum of information about Linux/Unix server.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is Glances? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Glances** is a cross-platform command-line curses-based system monitoring tool written in **Python** language which use the **psutil** library to grab informations from the system. With Glance, we can monitor **CPU, Load Average, Memory, Network Interfaces, Disk I/O, Processes** and **File System** spaces utilization.
|
||||
|
||||
Glances is a free tool and licensed under **GPL** to monitory **GNU/Linux** and **FreeBSD** operating systems. There are lots of interesting options available in Glances as well. One of the main features we have seen in Glances is that we can set thresholds (**careful**, **warning** and **critical**) in configuration file and informations will be shown in colors which indicates the bottleneck in the system.
|
||||
|
||||
### Glances Features ###
|
||||
|
||||
- CPU Informations (user related applications, system core programs and idle programs.
|
||||
- Total memory Information including RAM, Swap, Free memory etc.
|
||||
- The average CPU load for the past 1min, 5mins and 15 mins.
|
||||
- Network Download/Upload rates of network connections.
|
||||
- Total number of processes, active ones, sleeping processes etc.
|
||||
- Disk I/O related (read or write) speed details
|
||||
- Currently mounted devices disk usages.
|
||||
- Top processes with their CPU/Memory usages, Names and location of application.
|
||||
- Shows the current date and time at bottom.
|
||||
- Highlights processes in Red that consumes highest system resources.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example screen grab of Glances.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Installation of Glances in Linux/Unix Systems ###
|
||||
|
||||
Although it’s a very young utility, you can install “**Glances**” in **Red Hat** based systems by turning on [EPEL repository][3] and then run the following command on the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora ####
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install -y glances
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Debian/Ubuntu/Linux Mint ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-add-repository ppa:arnaud-hartmann/glances-stable
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install glances
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage of Glances ###
|
||||
|
||||
To start, issue the basic syntax on the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
# glances
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Press ‘**q**‘ or (‘**ESC**‘ or ‘**Ctrl&C**‘ also works) to quit from Glances terminal. Here, is the another screen grab taken from the **CentOS 6.5** system.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
y default, interval time is set to ’**1**‘ second. But you can define the custom interval time while running glances from the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
# glances -t 2
|
||||
|
||||
### Glances Color Codes ###
|
||||
|
||||
Meaning of Glances color code:
|
||||
|
||||
- GREEN: OK (everything is fine)
|
||||
- BLUE: CAREFUL (need attention)
|
||||
- VIOLET: WARNING (alert)
|
||||
- RED: CRITICAL (critical)
|
||||
|
||||
We can set thresholds in configuration file. By default thresholds set is (**careful=50, warning=7**0 and **critical=90**), we can customized as per our needs. The default configuration file is located at ‘**/etc/glances/glances.conf**’.
|
||||
|
||||
### Glances Options ###
|
||||
|
||||
Besides, several command line options, glances provides many more **hot keys** to find output information while glances is running. Below are the list of several hot keys.
|
||||
|
||||
- a – Sort processes automatically
|
||||
- c – Sort processes by CPU%
|
||||
- m – Sort processes by MEM%
|
||||
- p – Sort processes by name
|
||||
- i – Sort processes by I/O rate
|
||||
- d – Show/hide disk I/O stats ols
|
||||
- f – Show/hide file system statshddtemp
|
||||
- n – Show/hide network stats
|
||||
- s – Show/hide sensors stats
|
||||
- y – Show/hide hddtemp stats
|
||||
- l – Show/hide logs
|
||||
- b – Bytes or bits for network I/Oools
|
||||
- w – Delete warning logs
|
||||
- x – Delete warning and critical logs
|
||||
- x – Delete warning and critical logs
|
||||
- 1 – Global CPU or per-CPU stats
|
||||
- h – Show/hide this help screen
|
||||
- t – View network I/O as combination
|
||||
- u – View cumulative network I/O
|
||||
- q – Quit (Esc and Ctrl-C also work)
|
||||
|
||||
### Use Glances on Remote Systems ###
|
||||
|
||||
With the Glances, you can even monitor remote systems too. To use ‘**glances**‘ on remote systems, run the ‘**glances -s**‘ (-s enables server/client mode) command on the server.
|
||||
|
||||
# glances -s
|
||||
|
||||
Define the password for the Glances server
|
||||
Password:
|
||||
Password (confirm):
|
||||
Glances server is running on 0.0.0.0:61209
|
||||
|
||||
**Note** : Once, you issue ‘**glances**‘ command, it will prompt you to define the password for the Glances server. Define the password and hit enter, you see glances running on port **61209**.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, go to the remote host and execute the following command to connect to a Glances server by specifying IP address or hostname as shown below. Here ‘**172.16.27.56**‘ is my glances server IP Address.
|
||||
|
||||
# glances -c -P 172.16.27.56
|
||||
|
||||
Below are few notable points that user must know while using glances in server/client mode.
|
||||
|
||||
* In server mode, you can set the bind address -B ADDRESS and listening TCP port -p PORT.
|
||||
* In client mode, you can set the TCP port of the server -p PORT.
|
||||
* Default binding address is 0.0.0.0, but it listens on all network interfaces at port 61209.
|
||||
* In server/client mode, limits are set by the server side.
|
||||
* You can also define a password to access to the server -P password.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Glances** is a much resources friendly tool for most users. But if you’re a system administrator who’d like to quickly get overall “idea” about systems by just glancing at command line, then this tool will be must have tool for system administrators.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/glances-an-advanced-real-time-system-monitoring-tool-for-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/command-line-tools-to-monitor-linux-performance/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/12-top-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-enable-epel-repository-for-rhel-centos-6-5/
|
||||
@ -1 +0,0 @@
|
||||
这里放新闻类文章,要求时效性
|
||||
1
sources/news/README.md
Normal file
1
sources/news/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
这里放新闻类文章,要求时效性
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
Mir Display Server May Not Arrive on Desktops As Default Until 2016
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Ubuntu’s next generation display server Mir, developed by Canonical as a flexible alternative to Wayland and XServer, could be facing another delay on its way to the desktop. **
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The technology was initially positioned as a candidate for shipping by default on the desktop later this year but, [in a video address][1] to developers, Mark Shuttleworth has now intimated that Mir may not find its way on to the Ubuntu desktop until the release of Ubuntu 16.04 LTS — in 2016.
|
||||
|
||||
Responding to a question asking when users could expect to find it available on PCs, Shuttleworth replied:
|
||||
|
||||
> “I expect Mir to be the display server [to be default] as soon as it’s rock solid and we have a story we’re really proud of on it. You can run it on your desktop [now], but we don’t want to let a love of technology interfere with our mission to be great for the user. This is a great place for us to set the bar very high in terms of performance…where we have freedom to get it right, without having to worry too much about compatibility.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> By 16.04 it’ll be the default display server…That’s the kind of timeline we’re looking at.”
|
||||
|
||||
### Mir Oh Mir ###
|
||||
|
||||
It’s not immediately clear what impact, if any, such a delay would mean for Unity 8, scheduled to arrive on desktops this October.
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, it’s also not clear from his words whether the ‘by 16.04′ references a pure Mir experience or something akin to the Mir + Xmir hybrid proposed for Ubuntu 13.10. Either way a slip in timeframe is a hazard of any development process. Display servers are not easy technologies to build, particularly when designing one to span all manner of screen sizes and form factors.
|
||||
|
||||
This delay, if as assured as some news outlets are reporting it as being, won’t be the first to scupper Canonical’s plans. Ubuntu [originally intended to land a Mir Hybrid in Ubuntu 13.10][2], but technical flaws prevented that from happened. Its inclusion in the upcoming release of 14.04 LTS [was also ruled][3] out early on.
|
||||
|
||||
### Mir As It Is ###
|
||||
|
||||
As disappointing as the above may read Mir is continuing to evolve at breakneck pace. In fact, while it won’t be default, it will be possible to install a Mir session in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS, bundled with an in-progress version of the Unity 8 desktop. It’s also rocking out as the default on Ubuntu Touch for both phones and tablets.
|
||||
|
||||
But on the desktop it looks like things may take a little longer. Unlike on phones and tablets, where Ubuntu is able to make use of Android device drivers [via Hybris][4], there are currently no proprietary AMD, Intel or Nvidia desktop graphics drivers supporting Mir. Upstream support in open-source drivers remain patchy at best, with Canonical [being forced][5] to carry patches to enable functionality.
|
||||
|
||||
**The more time Canonical has to refine, iterate and improve on the technology in its desktop form, the better the end user experience of it will be.**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/03/mir-default-display-server-ubuntu-2016
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dWTVe5Mdv0Y&feature=share&t=29m19s
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/10/xmir-longer-default-supported-cards-13-10
|
||||
[3]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/11/expect-ubuntu-14-04-lts
|
||||
[4]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hybris_(software)
|
||||
[5]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/09/intel-remove-xmir-support-in-xorg-video-driver
|
||||
268
sources/tech/Linux or Unix--chroot Command Examples.md
Normal file
268
sources/tech/Linux or Unix--chroot Command Examples.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,268 @@
|
||||
Linux / Unix: chroot Command Examples
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
I am a new Linux and Unix user. How do I change the root directory of a command? How do I change the root directory of a process such as web-server using a chroot command to isolate file system? How do I use a chroot to recover password or fix the damaged Linux/Unix based environment?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Each process/command on Linux and Unix-like system has current working directory called root directory of a process/command. You can change the root directory of a command using `chroot` command, which ends up changing the root directory for both current running process and its children.
|
||||
|
||||
chroot command details
|
||||
Description:Change root directory
|
||||
Category:Processes Management
|
||||
Difficulty:Advanced
|
||||
Root privileges:Yes
|
||||
|
||||
A process/command that is run in such a modified environment cannot access files outside the root directory. This modified environment is commonly known as "jailed directory" or "chroot jail". Only a privileged process and root user can use chroot command. This is useful to:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Privilege separation for unprivileged process such as Web-server or DNS server.
|
||||
1. Setting up a test environment.
|
||||
1. Run old programs or ABI in-compatibility programs without crashing application or system.
|
||||
1. System recovery.
|
||||
1. Reinstall the bootloader such as Grub or Lilo.
|
||||
1. Password recovery Reset a forgotten password and more.
|
||||
|
||||
### Purpose ###
|
||||
|
||||
> The chroot command **changes its current and root directories to the provided directory and then run command**, if supplied, or an interactive copy of the user's login shell. Please note that not every application can be chrooted.
|
||||
|
||||
### Syntax ###
|
||||
|
||||
The basic syntax is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
chroot /path/to/new/root command
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
chroot /path/to/new/root /path/to/server
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
chroot [options] /path/to/new/root /path/to/server
|
||||
|
||||
#### chroot command examples ####
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, build a mini-jail for testing purpose with bash and ls command only. First, set jail location using mkdir command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ J=$HOME/jail
|
||||
|
||||
Create directories inside $J:
|
||||
|
||||
$ mkdir -p $J
|
||||
$ mkdir -p $J/{bin,lib64,lib}
|
||||
$ cd $J
|
||||
|
||||
Copy /bin/bash and /bin/ls into $J/bin/ location using [cp command][1]:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cp -v /bin/{bash,ls} $J/bin
|
||||
|
||||
Copy required libs in $J. Use ldd command to print shared library dependencies for bash:
|
||||
|
||||
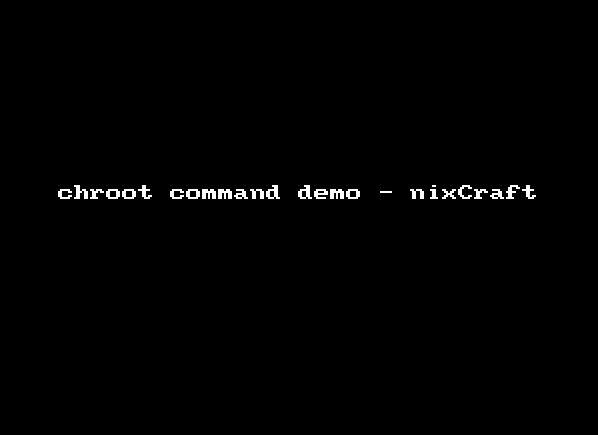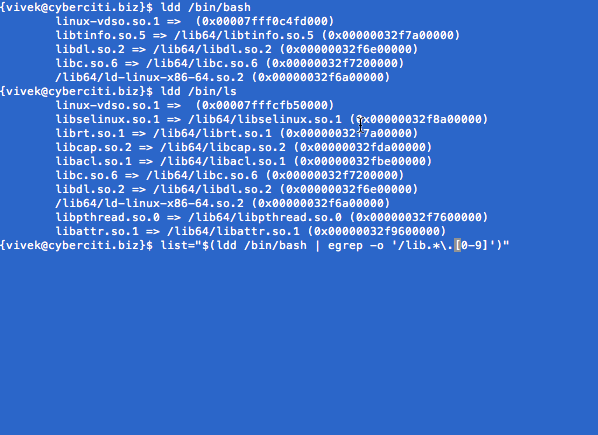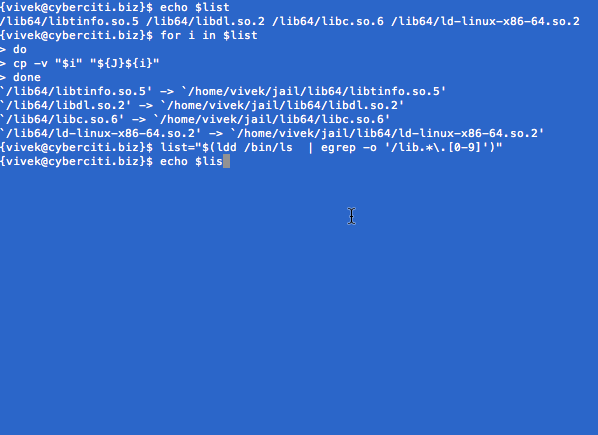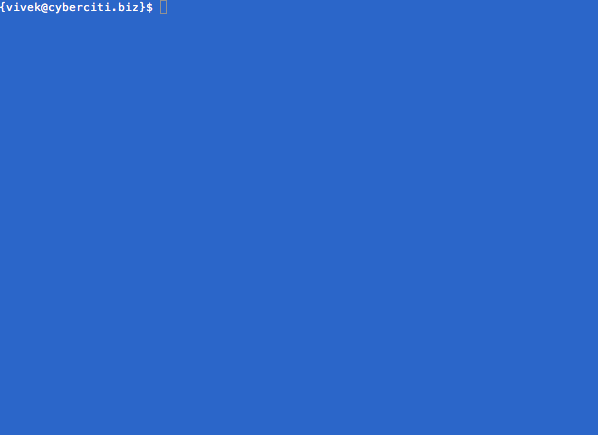
$ ldd /bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007fff8d987000)
|
||||
libtinfo.so.5 => /lib64/libtinfo.so.5 (0x00000032f7a00000)
|
||||
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x00000032f6e00000)
|
||||
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00000032f7200000)
|
||||
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00000032f6a00000)
|
||||
|
||||
Copy libs in $J correctly from the above output:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cp -v /lib64/libtinfo.so.5 /lib64/libdl.so.2 /lib64/libc.so.6 /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 $J/lib64/
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
`/lib64/libtinfo.so.5' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libtinfo.so.5'
|
||||
`/lib64/libdl.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libdl.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/libc.so.6' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libc.so.6'
|
||||
`/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2'
|
||||
|
||||
Copy required libs in $J for ls command. Use ldd command to print shared library dependencies for ls command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ldd /bin/ls
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007fff68dff000)
|
||||
libselinux.so.1 => /lib64/libselinux.so.1 (0x00000032f8a00000)
|
||||
librt.so.1 => /lib64/librt.so.1 (0x00000032f7a00000)
|
||||
libcap.so.2 => /lib64/libcap.so.2 (0x00000032fda00000)
|
||||
libacl.so.1 => /lib64/libacl.so.1 (0x00000032fbe00000)
|
||||
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00000032f7200000)
|
||||
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x00000032f6e00000)
|
||||
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00000032f6a00000)
|
||||
libpthread.so.0 => /lib64/libpthread.so.0 (0x00000032f7600000)
|
||||
libattr.so.1 => /lib64/libattr.so.1 (0x00000032f9600000)
|
||||
|
||||
You can copy libs one-by-one or try [bash shell for loop][2] as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
list="$(ldd /bin/ls | egrep -o '/lib.*\.[0-9]')"
|
||||
for i in $list; do cp -v "$i" "${J}${i}"; done
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
`/lib64/libselinux.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libselinux.so.1'
|
||||
`/lib64/librt.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/librt.so.1'
|
||||
`/lib64/libcap.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libcap.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/libacl.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libacl.so.1'
|
||||
`/lib64/libc.so.6' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libc.so.6'
|
||||
`/lib64/libdl.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libdl.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/libpthread.so.0' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libpthread.so.0'
|
||||
`/lib64/libattr.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libattr.so.1'
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, chroot into your new jail:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chroot $J /bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
Try browsing /etc or /var:
|
||||
|
||||
# ls /
|
||||
# ls /etc/
|
||||
# ls /var/
|
||||
|
||||
A chrooted bash and ls application is locked into a particular directory called $HOME/$J and unable to wander around the rest of the directory tree, and sees that directory as its "/" (root) directory. This is a tremendous boost to security if configured properly. I usually lock down the following applications using the same techniques:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Apache - Red Hat / CentOS: Chroot Apache 2 Web Server][3]
|
||||
1. [Nginx - Linux nginx: Chroot (Jail) Setup][4]
|
||||
1. [Chroot Lighttpd web server on a Linux based system][5]
|
||||
1. Chroot mail server.
|
||||
1. Chroot Bind DNS server and more.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I exit from chrooted jail? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Type exit
|
||||
|
||||
$ exit
|
||||
|
||||
Sample session from above commands:
|
||||
|
||||
[][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Animated gif 01: Linux / Unix: Bash Chroot ls Command Demo
|
||||
|
||||
### Find out if service in chrooted jail or not ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can [easily find out if Postfix mail server is chrooted or not][7] using the following two commands:
|
||||
|
||||
pid=$(pidof -s master)
|
||||
ls -ld /proc/$pid/root
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs from my Linux based server:
|
||||
|
||||
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Mar 9 11:16 /proc/8613/root -> /
|
||||
|
||||
The PID 8613 pointing out to / (root) i.e. the root directory for application is not changed or chrooted. This is a quick and dirty way to find out if application is chrooted or not without opening configuration files. Here is another example from chrooted nginx server:
|
||||
|
||||
pid=$(pidof -s master)
|
||||
ls -ld /proc/$pid/root
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 nginx nginx 0 Mar 9 11:17 /proc/4233/root -> /nginxjail
|
||||
|
||||
The root directory for application is changed to /nginxjail.
|
||||
|
||||
### Rescue and fix software RAID system with chroot ###
|
||||
|
||||
I'm assuming that software RAID based Linux system is not booting. So you [booted system either using the Live CD or networked based remote rescue kernel mode][8] to fix the system. In this example, I booting RHEL based system using live Linux DVD/CD and chroot into /dev/sda1 and/or /dev/md0 to fix the problem:
|
||||
|
||||
## Recover data, at live cd prompt type the following commands. ##
|
||||
## /dev/sda1 main system partition ##
|
||||
## /dev/md0 /data partition ##
|
||||
# Set jail dir
|
||||
d=/chroot
|
||||
mkdir $d
|
||||
|
||||
# Mount sda1 and required dirs
|
||||
mount /dev/sda1 $d
|
||||
mount -o bind /dev $d/dev
|
||||
mount -o bind /sys $d/sys
|
||||
mount -o bind /dev/shm $d/dev/shm
|
||||
mount -o bind /proc $d/proc
|
||||
|
||||
# Mount software raid /dev/md0
|
||||
mount /dev/md0 $d/data
|
||||
|
||||
# Chroot to our newly created jail. This allows us to fix bootloader or grab data before everything goes to /dev/null
|
||||
chroot $d
|
||||
|
||||
# Can you see?
|
||||
ls
|
||||
df
|
||||
|
||||
# Get files to safe location
|
||||
rsync -avr /path/to/my_precious_data_dir user@safe.location.cyberciti.biz:/path/to/dest
|
||||
|
||||
# Get out of chrooted jail and reboot or format the server as per your needs ;)
|
||||
exit
|
||||
umount {dev,sys,[...],}
|
||||
reboot
|
||||
|
||||
But wait, there's more!
|
||||
|
||||
See all other chroot command related examples on nixCraft:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Ubuntu: Mount Encrypted Home Directory (~/.private) From an Ubuntu Live CD][9]
|
||||
1. [Linux Configure rssh Chroot Jail To Lock Users To Their Home Directories Only][10]
|
||||
1. [Fix a dual boot MS-Windows XP/Vista/7/Server and Linux problem][11]
|
||||
1. [Restore Debian Linux Grub boot loader][12]
|
||||
|
||||
### A note about chrooting apps on a Linux or Unix-like systems ###
|
||||
|
||||
Should you use the chroot feature all the time? In the above example, the program is fairly simple but you may end up with several different kinds of problems such as:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Missing libs in jail can result into broken jail.
|
||||
1. Complex program are difficult to chroot. I suggest you either try real [jail such as provided by FreeBSD][13] or use virtualization soultuon such as [KVM on Linux][14].
|
||||
1. App running in jail can not run any other programs, can not alter any files, and can not assume another user's identity. Loosen these restrictions, you have lessened your security, chroot or no chroot.
|
||||
|
||||
Also note that:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Do not forgot, to updated chrooted apps when you upgrade apps locally.
|
||||
1. Not every app can or should be chrooted.
|
||||
1. Any app which has to assume root privileges to operate is pointless to attempt to chroot, as root can generally escape a chroot.
|
||||
1. Chroot is not a silver bullet. Learn [how to secure and harden rest of the system too][15].
|
||||
|
||||
### chroot command options ###
|
||||
|
||||
From the [chroot(8)][16] command man page:
|
||||
|
||||
--userspec=USER:GROUP specify user and group (ID or name) to use
|
||||
--groups=G_LIST specify supplementary groups as g1,g2,..,gN
|
||||
--help display this help and exit
|
||||
--version output version information and exit
|
||||
|
||||
### See also ###
|
||||
|
||||
- [chroot(8) Linux/Unix command man page][17]
|
||||
- [Man pages chroot(2)][18]
|
||||
- [OpenBSD documentation See Apache chrooting faq for more information.][19]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/cp-copy-command-in-unix-examples/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/bash-for-loop/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/chroot-apache-under-rhel-fedora-centos-linux.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-run-nginx-in-a-chroot-jail/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-setup-lighttpd-php-mysql-chrooted-jail.html
|
||||
[6]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/?attachment_id=28148
|
||||
[7]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-chroot-service.html
|
||||
[8]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/centos-rhel-linux-mount-raid-hard-disk-from-livecd/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/ubuntu-mounting-your-encrypted-home-from-livecd/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-linux-unix-rssh-chroot-jail-setup.html
|
||||
[11]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-fix-dual-boot-windows-vista-linux.html
|
||||
[12]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/restore-debian-linux-grub-boot-loader.html
|
||||
[13]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/how-to-upgrade-freebsd-jail-vps/
|
||||
[14]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/kvm-virtualization-in-redhat-centos-scientific-linux-6/
|
||||
[15]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-security.html
|
||||
[16]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man8/chroot.8.html
|
||||
[17]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man8/chroot.8.html
|
||||
[18]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man2/chroot.2.html
|
||||
[19]:http://www.openbsd.org/faq/
|
||||
60
translated/5 Linux Distributions that Deserve more Love.md
Normal file
60
translated/5 Linux Distributions that Deserve more Love.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
|
||||
5个需要更多关爱的Linux发行版
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
就像我以前在文章里写的, [Linux 无处不在,][1]所以即使没有数千种,也有数百种之多的发行版。有一些发行版非常有名,其中一些拥有上千万的用户基础,而有一些 却只能生活在这些光辉闪耀的发行版的阴影之中。有一些发行版在大的发行版轻松享受的业务范围的连接处挣扎求存,同时每年都有一些触手可及的发行版灭亡。但是我们今天在这里讨论几个还没有得到他们应得的关爱的发行版。不论这个发行版是原始的或分支或基于其他的发行版的,如果它工作起来对于日常使用是足够稳定的,同时没有得到应得的关爱,它将在列表中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Rosa ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[ROSA Desktop][2], 是一个拥有高度定制性的KDE桌面发行版,它有大量来自 ROSA 的改动旨在加强工作环境开发的用户友好性。ROSA是一家俄国公司,他还提供了一个基于红帽的企业版的企业服务器版ROSA给开发者。这是你在网上能找到的最具有定制性的发行版之一,它拥有大量的的家用特性像一个完全重新设计的登录窗口,一个叫做“TimeFrame”的日程管理软件,大量改动的“Dolhpin”文件管理器,Rocket Bar,Simple Welcome,Rosa Media Player和很多其他的软件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Korora ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Korora][3] 是基于让 Linux新手用起来更容易,但同时也是一个对专家很有用的愿望产生的系统。最初是2005年基于Gentoo Linux 的系统 ,korora在2010年作为一个Fedora 的混音版重新出世,它搭载 tweaks和一些额外的功能以使系统可以开箱即用。korora拥有一个融合的Fedora + RPM Fusion+ korora的包系统。其中korora提供尖端和一个红帽发行版的稳定,让它可以毫不费力的实现开箱即用。许多人抱怨Fedora太麻烦,但是 Fedora就是这样设计的啊。对于喜欢 Fedora 同时仍希望可以开箱即用的人们,korora就是为你准备的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Chakra Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你是KDE的铁杆粉丝而且你无法忍受长达几个月的等待时间才能用上最新的软件,那么你有一款天堂般的选择,他们管它叫Chakra Linux。这个发行版最初是Arch Linux的一个分支,但是现在已经是一个独立的发行版了,它拥有自己的仓库、包、内核和半/滚动发布周期。
|
||||
|
||||
[Chakra Linux][4] 工作性能很好而且拥有Arch Linux的所有优点。有些人可能争论为什么不直接用Arch Linux,然后用KDE代替 Chakra Linux。首先是安装过程,无论每个人如何证明你自己装起来多容易,事实上并非如此。一个OS应该很容易使用同时安装起来更容易,而不是别的样。
|
||||
|
||||
Chakra Linux 是很少的一个可以获得的、真正的KDE发行版,因此可以保证你可以拥有到最好的KDE体验在你使用 Chakra Linux的时候。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Ubuntu Gnome ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 可能是近些年颇受关注和争论的一个版本,尤其是转到 Unity 的决定,但是我个人对 Unity 感觉很好。另一方面,我在装 Nivida的时候它的错误是如此的多,而且我经常看到有人抱怨 Unity 糟糕的表现。还有其他的半官方的的版本可以选择但是没有一个真的很像Ubuntu的体验,直到[Ubuntu Gnome][5] 出现。
|
||||
|
||||
关于这个不需要说太多, Ubuntu Gnome 就是一个披着 Gnome Shell 外壳的 Ubuntu, (“之所以列出来是因为”)我觉得它应该在名单上。Ubuntu 曾经因为 Canonical 极少犯错误而风靡一时,这个发行版也不该太惨。我可以很高兴的告诉你,你可以从 Ubuntu Gnome 中感受到原始的 Ubuntu 的每一项优点同时避开 Canonical 的那些粗鲁的暴力措施。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Sabayon Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Sabayon][6] Linux 是一个基于 Gentoo 的发行版的、遵循开箱即用的哲学而且它做的很踏实一步都没有跳过。这听起来有点偏但 Sabayon 在大量的系统中是极少数的真正可以开箱即用的发行版 。
|
||||
|
||||
Sabayon 遵循不说废话的哲学,一切按它应该是的方式运行,你不需要关心终端是否把事情做好了,你不需要添加额外的库增加最明显的功能,一切都在一个地方,顺道说一下,如果你愿意你可以做但问题是你不能强迫用户做所有的这些事情.如果我想用Arch Linux但是不想用终端使我痛苦的撞头,我就应该能做到。
|
||||
|
||||
Sabayon 是一个尖端的,快速的和令人惊讶的稳定发行版,归功于坚实的Gentoo的核心。它用你选择的DE很容易使用,安装更方便,开箱即用,拥有一个很简单的功能和很强大的包管理器,配备所需的大部分应用程序,然后它仍然可以被深度定制,就像任何其他的分布。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxfederation.com/linux-distributions-love/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[crowner](https://github.com/crowner) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linuxfederation.com/linux-everywhere/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.rosalab.com/products/desktop_fresh
|
||||
[3]:https://kororaproject.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.chakra-project.org/
|
||||
[5]:http://ubuntugnome.org/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.sabayon.org/
|
||||
@ -1 +0,0 @@
|
||||
这里放新闻类文章,要求时效性
|
||||
1
translated/news/README.md
Normal file
1
translated/news/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
这里放新闻类文章,要求时效性
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user