mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-24 02:20:09 +08:00
Merge pull request #5177 from OneNewLife/master
[Translated by OneNewLife] 20170217 How to Use Yum History to Find Out Installed or Removed Packages Info.md
This commit is contained in:
commit
dedec7fd92
@ -1,221 +0,0 @@
|
||||
OneNewLife translating
|
||||
|
||||
How to Use ‘Yum History’ to Find Out Installed or Removed Packages Info
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[YUM][1] is an interactive, rpm based, high level package manager for RHEL/CentOS systems, it enables users to install new packages, remove/erase old/unwanted packages. It can [automatically run system updates][2] and does dependency analysis, and also perform queries on the installed and/or available packages plus so much more.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, we will explain how to view history of YUM transactions in order to find out information about installed packages and those that where removed/erased from a system.
|
||||
|
||||
**Suggested Read:** [20 Linux YUM Commands for Package Management][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Below are some examples of how to use the YUM history command.
|
||||
|
||||
### View Complete YUM History
|
||||
|
||||
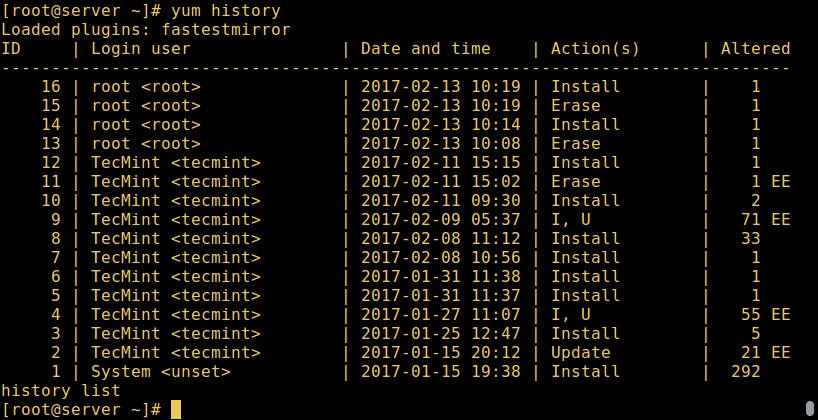
To view a full history of YUM transactions, we can run the command below which will show us the: transaction id, login user who executed the particular action, date and time when the operation happened, the actual action and additional information about any thing wrong with the operation:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][4]
|
||||
|
||||
View Yum History
|
||||
|
||||
### Use Yum to Find Package Info
|
||||
|
||||
The history sub-commands: info/list/summary can take a transaction ID or package name as an argument. Additionally, the list sub-command can take a special argument, all meaning – all transactions.
|
||||
|
||||
The previous history command is equivalent to running:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history list all
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
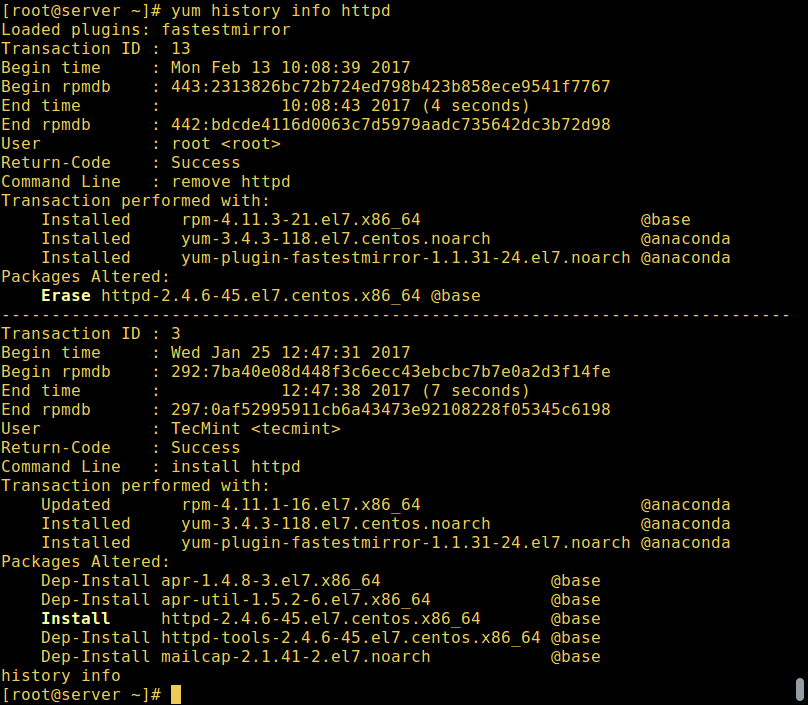
And, you can view details of transactions concerning a given package such as `httpd` web server with the `info`command as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history info httpd
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][5]
|
||||
|
||||
Yum – Find Package Info
|
||||
|
||||
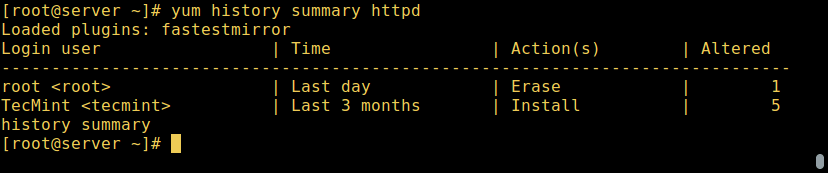
To get a summary of the transactions concerning `httpd` package, we can issue the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history summary httpd
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Yum – Find Summary of Package
|
||||
|
||||
It is also possible to use a transaction ID, the command below will display details of the transaction ID `15`.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history info 15
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][7]
|
||||
|
||||
Yum – Find Package Info Using ID
|
||||
|
||||
### Use Yum History to Find Package Transaction Info
|
||||
|
||||
There are sub-commands that print out transaction details of a specific package or group of packages. We can use `package-list` or `package_info` to view more info about `httpd` package like so:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history package-list httpd
|
||||
OR
|
||||
# yum history package-info httpd
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
Yum – Find Package Transaction Info
|
||||
|
||||
To get history about multiple packages, we can run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history package-list httpd epel-release
|
||||
OR
|
||||
# yum history packages-list httpd epel-release
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][9]
|
||||
|
||||
Yum – Find Multiple Packages Info
|
||||
|
||||
### Use Yum to Rollback Packages
|
||||
|
||||
Furthermore, there are certain history sub-commands that enable us to: undo/redo/rollback transactions.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Undo – will undo a specified transaction.
|
||||
2. redo – repeat the work of a specified transaction
|
||||
3. rollback – will undo all transactions up to the point of the specified transaction.
|
||||
|
||||
They take either a single transaction id or the keyword last and an offset from the last transaction.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, assuming we’ve done 60 transactions, “last” refers to transaction 60, and “last-4” points to transaction 56.
|
||||
|
||||
**Suggested Read:** [How to Use ‘yum-utils’ to Maintain Yum and Boost its Performance][10]
|
||||
|
||||
This is how the sub-commands above work: If we have 5 transactions: V, W, X, Y and Z, where packages where installed respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history undo 2 #will remove package W
|
||||
# yum history redo 2 #will reinstall package W
|
||||
# yum history rollback 2 #will remove packages from X, Y, and Z.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the following example, transaction 2 was a update operation, as seen below, the redo command that follows will repeat transaction 2 upgrading all the packages updated by that time:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history | grep -w "2"
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][11]
|
||||
|
||||
Yum – Find Package Transaction ID
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history redo 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][12]
|
||||
|
||||
Yum Redo Package Update
|
||||
|
||||
The redo sub-command can also take some optional arguments before we specify a transaction:
|
||||
|
||||
1. force-reinstall – reinstalls any packages that were installed in that transaction (via yum install, upgrade or downgrade).
|
||||
2. force-remove – removes any packages that were updated or downgraded.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history redo force-reinstall 16
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][13]
|
||||
|
||||
Yum – Force Install Package
|
||||
|
||||
### Find Yum History Database and Sources Info
|
||||
|
||||
These sub-commands provide us information about the history DB and additional info sources:
|
||||
|
||||
1. addon-info – will provide sources of additional information.
|
||||
2. stats – displays statistics about the current history DB.
|
||||
3. sync – enables us to alter the the rpmdb/yumdb data stored for any installed packages.
|
||||
|
||||
Consider the commands below to understand how these sub-commands practically work:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history addon-info
|
||||
# yum history stats
|
||||
# yum history sync
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To set a new history file, use the new sub-command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history new
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can find a complete information about YUM history command and several other commands in the yum man page:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# man yum
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Suggested Read:** [4 Ways to Disable/Lock Certain Package Updates Using Yum][14]
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it for now. In this guide, we explained various YUM history commands to view details of YUM transactions. Remember to offer us your thoughts concerning this guide via the comment section below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/view-yum-history-to-find-packages-info/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/auto-install-security-patches-updates-on-centos-rhel/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/View-Yum-History.png
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Yum-Find-Package-Info.png
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Yum-Find-Summary-of-Package.png
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Find-Package-Info-Using-ID.png
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Find-Package-Transaction-Info.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Find-Multiple-Package-Info.png
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-yum-package-management-with-yum-utils/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Find-Yum-Package-Transaction-ID.png
|
||||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Yum-Redo-Package-Update.png
|
||||
[13]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Yum-Force-Install-Package.png
|
||||
[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/yum-lock-disable-blacklist-certain-package-update-version/
|
||||
[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
|
||||
[17]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
|
||||
使用 Yum History 查找已安装或已删除的软件包信息
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
[YUM][1] 是 RHEL/CentOS(帽子家族)的一个基于 rpm 的交互式高级包管理器,用户可以用它来安装新的软件包、卸载或清除旧的/不需要的软件包。它可以[自动运行系统更新][2],并执行依赖分析,对已安装的或可用的软件包进行查询等等。
|
||||
|
||||
在本文中,我们将解释如何查看 `YUM` 事务的历史记录,以便于了解有关安装的软件包以及从系统中卸载/清除软件包的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
**推荐阅读:** [20 条关于 Linux 软件包管理的 YUM 命令][3]
|
||||
|
||||
以下是一些如何使用 `YUM` 历史命令的示例。
|
||||
|
||||
### 查看完整的 YUM 历史
|
||||
|
||||
要查看 `YUM` 事务完整的历史记录,我们可以运行以下命令,然后将显示:事务 ID、执行特定操作的用户、操作发生的日期和时间、实际操作以及任何错误的附加信息与操作:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history
|
||||
```
|
||||
[][4]
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 Yum 查找软件包信息
|
||||
|
||||
`history` 的子命令:info/list/summary 可以将事务 ID 或包名作为参数。此外,list 子命令可以加上特殊的参数,`all` 表示所有的事务。
|
||||
|
||||
运行以下命令查看先前的历史:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history list all
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
并且,你可以使用下面的 `info` 命令查看涉及指定软件包的事务详情,例如 `httpd`:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history info httpd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
发出以下命令可以获得包含 `httpd` 软件包的事务的摘要:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history summary httpd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][6]
|
||||
|
||||
还可以使用事务的 ID 来查找,以下命令会显示 ID 为 `15` 的事务的详情。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history info 15
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][7]
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 Yum History 查找软件包事务信息
|
||||
|
||||
有一些用于打印某个或多个软件包事务详情的子命令。我们可以使用 `package-list` 或 `package_info` 查看关于 `httpd` 的更多信息,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history package-list httpd
|
||||
或
|
||||
# yum history package-info httpd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][8]
|
||||
|
||||
要得到多个软件包的记录,我们可以运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history package-list httpd epel-release
|
||||
或
|
||||
# yum history packages-list httpd epel-release
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][9]
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 Yum 回滚软件包
|
||||
|
||||
此外,还有一些 `history` 的子命令可以让我们撤销/重做/回滚事务。
|
||||
|
||||
1. Undo - 会撤销一个指定的事务。
|
||||
2. redo - 重复一次指定的事务。
|
||||
3. rollback - 撤销指定事务之后的所有事务。
|
||||
|
||||
它们采用单个事务 id 或关键字 `last` 和从最后一个事务开始的偏移量。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,假设我们已经做了 60 个事务,`last` 是指事务 60,`last-4` 指向事务 56。
|
||||
|
||||
**推荐阅读:** [怎样使用 `yum-utils` 维持以及加速 Yum][10]
|
||||
|
||||
以上子命令是如下工作的:如果我们有 5 个事务——V,W,X,Y 和 Z,其中分别是安装各个软件包的。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history undo 2 #will remove package W
|
||||
# yum history redo 2 #will reinstall package W
|
||||
# yum history rollback 2 #will remove packages from X, Y, and Z.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在下面的示例中,事务 2 是一个更新操作,如下所示,以下 `redo` 命令将重复事务 2 直到所有软件包到更新到当前时间的最新版本:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history | grep -w "2"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][11]
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history redo 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][12]
|
||||
|
||||
`redo` 子命令同样可以在我们指定事务之前加上一些可选的参数:
|
||||
|
||||
1. force-reinstall - 重新安装所有在此事务中安装的软件包(通过 `yum install`、`upgrade` 或 `downgrade`)。
|
||||
2. force-remove - 移除所有已经更新或回滚的软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history redo force-reinstall 16
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][13]
|
||||
|
||||
### 查找 Yum History 数据库和来源信息
|
||||
|
||||
这些子命令为我们提供有关历史记录数据库和其它信息来源的信息:
|
||||
|
||||
1. addon-info - 提供更多的信息来源。
|
||||
2. stats - 显示当前历史数据库的统计信息。
|
||||
3. sync - 使我们能够更改为所有已安装软件包存储的 `rpmdb/yumdb` 数据。
|
||||
|
||||
想一下以下的命令的子命令实际上是怎样工作的:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history addon-info
|
||||
# yum history stats
|
||||
# yum history sync
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `new` 子命令设置新的历史文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum history new
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以在 yum 手册页找到关于 YUM `history` 命令和其它几个命令的完整信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# man yum
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**推荐阅读:** [4 个使用 Yum 禁用/锁定某些软件包更新的方法][14]
|
||||
|
||||
就是这么多了。在本篇指南中,我们介绍了各种 YUM `history` 命令,以查看 YUM 事务的详细信息。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 的爱好者,目前任 TecMint 的作者,志向是一名 Linux 系统管理员、web 开发者。他喜欢用电脑工作,并热衷于分享知识。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/view-yum-history-to-find-packages-info/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[OneNewLife](https://github.com/OneNewLife)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/auto-install-security-patches-updates-on-centos-rhel/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/View-Yum-History.png
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Yum-Find-Package-Info.png
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Yum-Find-Summary-of-Package.png
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Find-Package-Info-Using-ID.png
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Find-Package-Transaction-Info.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Find-Multiple-Package-Info.png
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-yum-package-management-with-yum-utils/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Find-Yum-Package-Transaction-ID.png
|
||||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Yum-Redo-Package-Update.png
|
||||
[13]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Yum-Force-Install-Package.png
|
||||
[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/yum-lock-disable-blacklist-certain-package-update-version/
|
||||
[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
|
||||
[17]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user