mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-12 01:40:10 +08:00
commit
dda7ac6479
@ -2,13 +2,13 @@ Ubuntu中跟踪多个时区的简捷方法
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**我是否要确保在我醒来时或者安排与*山姆陈*,Ohso的半个开发商,进行Skype通话时,澳大利亚一个关于Chromebook销售的推特已经售罄,我大脑同时在多个时区下工作。**
|
||||
**无论我是要在醒来时发个关于澳大利亚的 Chromebook 销售已经售罄的推特,还是要记着和Ohso的半个开发商山姆陈进行Skype通话,我大脑都需要同时工作在多个时区下。**
|
||||
|
||||
那里头有个问题,如果你认识我,你会知道我的脑容量也就那么丁点,跟金鱼差不多,里头却塞着像Windows Vista这样一个臃肿货(也就是,不是很好)。我几乎记不得昨天之前的事情,更记不得我的门和金门大桥脚之间的时间差!
|
||||
|
||||
作为臂助,我使用一些小部件和菜单项来让我保持同步。在我常规工作日的空间里,我在多个操作系统间游弋,涵盖移动系统和桌面系统,但只有一个让我最快速便捷地设置“世界时钟”。
|
||||
作为臂助,我使用一些小部件和菜单项来让我保持同步。在我常规工作日的空间里,我在多个操作系统间游弋,涵盖移动系统和桌面系统,但只有一个可以让我最快速便捷地设置“世界时钟”。
|
||||
|
||||
**而它刚好是那个名字放在门上方的东西。**
|
||||
**它的名字就是我们标题上提到的那个。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,10 +16,10 @@ Ubuntu中跟踪多个时区的简捷方法
|
||||
|
||||
Unity中默认的日期-时间指示器提供了添加并查看多个时区的支持,不需要附加组件,不需要额外的包。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 点击时钟小应用,然后uxuanze‘**时间和日期设置**’条目
|
||||
1. 点击时钟小应用,然后选择‘**时间和日期设置**’条目
|
||||
1. 在‘**时钟**’标签中,选中‘**其它位置的时间**’选框
|
||||
1. 点击‘**选择位置**’按钮
|
||||
1. 点击‘**+**’,然后输入位置名称那个
|
||||
1. 点击‘**+**’,然后输入位置名称
|
||||
|
||||
#### 其它桌面环境 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -34,13 +34,13 @@ Unity中默认的日期-时间指示器提供了添加并查看多个时区的
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon 2.4中的世界时钟日历
|
||||
*Cinnamon 2.4中的世界时钟日历*
|
||||
|
||||
**XFCE**和**LXDE**就不那么慷慨了,除了自带的“工作区”作为**多个时钟**添加到面板外,每个都需要手动配置以指定位置。两个都支持‘指示器小部件’,所以,如果你没有依赖于Unity,你可以安装/添加单独的日期/时间指示器。
|
||||
**XFCE**和**LXDE**就不那么慷慨了,除了自带的“工作区”作为**多个时钟**添加到面板外,每个都需要手动配置以指定位置。两个都支持‘指示器小部件’,所以,如果你不用Unity的话,你可以安装/添加单独的日期/时间指示器。
|
||||
|
||||
**Budgie**还刚初出茅庐,不足以胜任角落里的需求,因为Pantheon我还没试过——希望你们通过评论来让我知道得更多。
|
||||
**Budgie**还刚初出茅庐,不足以胜任这种角落里的需求,因为Pantheon我还没试过——希望你们通过评论来让我知道得更多。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Desktop Apps, Widgets & Conky Themes桌面应用、不见和Conky主题 ####
|
||||
#### 桌面应用、部件和Conky主题 ####
|
||||
|
||||
当然,面板小部件只是收纳其它国家多个时区的一种方式。如果你不满意通过面板去访问,那里还有各种各样的**桌面应用**可供使用,其中许多都可以跨版本,甚至跨平台使用。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/12/add-time-zones-world-clock-ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
|
||||
CentOS上配置rsyslog客户端用以远程记录日志
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**rsyslog**是一个开源工具,被广泛用于Linux系统以通过TCP/UDP协议转发或接收日志消息。rsyslog守护进程可以被配置称两种环境,一种是配置成日志收集服务器,rsyslog进程可以从网络中收集所有其它主机上的日志数据,这些主机已经将日志配置为发送到服务器。rsyslog的另外一个角色,就是可以配置为客户端,用来过滤和发送内部日志消息到本地文件夹(如/var/log)或一台可以路由到的远程rsyslog服务器上。
|
||||
**rsyslog**是一个开源工具,被广泛用于Linux系统以通过TCP/UDP协议转发或接收日志消息。rsyslog守护进程可以被配置成两种环境,一种是配置成日志收集服务器,rsyslog进程可以从网络中收集其它主机上的日志数据,这些主机会将日志配置为发送到另外的远程服务器。rsyslog的另外一个用法,就是可以配置为客户端,用来过滤和发送内部日志消息到本地文件夹(如/var/log)或一台可以路由到的远程rsyslog服务器上。
|
||||
|
||||
假定你的网络中已经有一台rsyslog服务器[已经起来并且处于运行中][1],本指南将为你展示如何来设置CentOS系统将其内部日志消息路由到一台远程rsyslog服务器上。这将大大改善你的系统磁盘空间的使用,尤其是你还没有一个独立的用于/var目录的大分区。
|
||||
假定你的网络中已经有一台[已经配置好并启动的][1]rsyslog服务器,本指南将为你展示如何来设置CentOS系统将其内部日志消息路由到一台远程rsyslog服务器上。这将大大改善你的系统磁盘空间的使用,尤其是当你还没有一个用于/var目录的独立的大分区。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤一: 安装Rsyslog守护进程 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,9 +35,9 @@ CentOS上配置rsyslog客户端用以远程记录日志
|
||||
|
||||
*.* @@192.168.1.25:514
|
||||
|
||||
注意,你也可以将rsyslog服务器的IP地址替换成它的DNS名称(FQDN)。
|
||||
注意,你也可以将rsyslog服务器的IP地址替换成它的主机名(FQDN)。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你只想要转发指定设备的日志消息,比如说内核设备,那么你可以在rsyslog配置文件中使用以下声明。
|
||||
如果你只想要转发服务器上的指定设备的日志消息,比如说内核设备,那么你可以在rsyslog配置文件中使用以下声明。
|
||||
|
||||
kern.* @192.168.1.25:514
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,9 +51,11 @@ CentOS上配置rsyslog客户端用以远程记录日志
|
||||
|
||||
# service rsyslog restart
|
||||
|
||||
在另外一种环境中,让我们假定你已经在机器上安装了一个名为“foobar”的应用程序,它会在/var/log下生成foobar.log日志文件。现在,你只想要将它的日志定向到rsyslog服务器,这可以通过像下面这样在rsyslog配置文件中加载imfile模块来实现。
|
||||
####非 syslog 日志的转发
|
||||
|
||||
首先,加载imfile模块,这必须只做一次。
|
||||
在另外一种环境中,让我们假定你已经在机器上安装了一个名为“foobar”的应用程序,它会在/var/log下生成foobar.log日志文件。现在,你想要将它的日志定向到rsyslog服务器,这可以通过像下面这样在rsyslog配置文件中加载imfile模块来实现。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,加载imfile模块,这只需做一次。
|
||||
|
||||
module(load="imfile" PollingInterval="5")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -73,8 +75,7 @@ CentOS上配置rsyslog客户端用以远程记录日志
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤三: 让Rsyslog进程自动启动 ###
|
||||
|
||||
To automatically start rsyslog client after every system reboot, run the following command to enable it system-wide:
|
||||
要让rsyslog客户端在每次系统重启后自动启动,请运行以下命令来在系统范围启用:
|
||||
要让rsyslog客户端在每次系统重启后自动启动,请运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
**CentOS 7:**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -86,7 +87,7 @@ To automatically start rsyslog client after every system reboot, run the followi
|
||||
|
||||
### 小结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我演示了如何将CentOS系统转变成rsyslog客户端以强制它发送日志消息到远程rsyslog服务器。这里我假定rsyslog客户端和服务器之间的连接是安全的(如,在有防火墙保护的公司网络中)。不管在任何情况下,都不要配置rsyslog客户端将日志消息通过不安全的网络转发,或者,特别是通过互联网转发,因为syslog协议是一个明文协议。要进行安全传输,可以考虑使用[TLS/SSL][2]来加密日志消息。
|
||||
在本教程中,我演示了如何将CentOS系统转变成rsyslog客户端以强制它发送日志消息到远程rsyslog服务器。这里我假定rsyslog客户端和服务器之间的连接是安全的(如,在有防火墙保护的公司网络中)。不管在任何情况下,都不要配置rsyslog客户端将日志消息通过不安全的网络转发,或者,特别是通过互联网转发,因为syslog协议是一个明文协议。要进行安全传输,可以考虑使用[TLS/SSL][2]来加密日志消息的传输。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -94,7 +95,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/configure-rsyslog-client-centos.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Caezsar M][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
答: 用 “route -n” 和 “netstat -nr” 命令,我们可以查看默认网关。除了默认的网关信息,这两个命令还可以显示当前的路由表。
|
||||
|
||||
**问:3 如何在Linux上重建初始化内存盘影响文件?**
|
||||
**问:3 如何在Linux上重建初始化内存盘镜像文件?**
|
||||
|
||||
答: 在CentOS 5.X / RHEL 5.X中,可以用mkinitrd命令来创建初始化内存盘文件,举例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,7 +30,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
**问:5 patch命令是什么?如何使用?**
|
||||
|
||||
答: 顾名思义,patch命令就是用来将修改(或补丁)写进文本文件里。Patch命令通常是接收diff的输出并把文件的旧版本转换为新版本。举个例子,Linux内核源代码由百万行代码文件构成,所以无论何时,任何代码贡献者贡献出代码,只需发送改动的部分而不是整个源代码,然后接收者用patch命令将改动写进原始的源代码里。
|
||||
答: 顾名思义,patch命令就是用来将修改(或补丁)写进文本文件里。patch命令通常是接收diff的输出并把文件的旧版本转换为新版本。举个例子,Linux内核源代码由百万行代码文件构成,所以无论何时,任何代码贡献者贡献出代码,只需发送改动的部分而不是整个源代码,然后接收者用patch命令将改动写进原始的源代码里。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个diff文件给patch使用,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -44,7 +44,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
**问:6 aspell有什么用 ?**
|
||||
|
||||
答: 顾名思义,aspell就是Linux操作系统上的一款交互式拼写检查器。aspell命令继任了更早的一个名为ispell的程序,并且作为一款嵌入式替代品 ,最重要的是它非常好用。当aspell程序主要被其它一些需要拼写检查能力的程序所使用的时候,在命令行中作为一个独立运行的工具的它也能十分有效。
|
||||
答: 顾名思义,aspell就是Linux操作系统上的一款交互式拼写检查器。aspell命令继任了更早的一个名为ispell的程序,并且作为一款免费替代品 ,最重要的是它非常好用。当aspell程序主要被其它一些需要拼写检查能力的程序所使用的时候,在命令行中作为一个独立运行的工具的它也能十分有效。
|
||||
|
||||
**问:7 如何从命令行查看域SPF记录?**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -56,7 +56,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
答: # rpm -qf /etc/fstab
|
||||
|
||||
以上命令能列出供应给“/etc/fstab”文件的包。
|
||||
以上命令能列出提供“/etc/fstab”这个文件的包。
|
||||
|
||||
**问:9 哪条命令用来查看bond0的状态?**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -64,7 +64,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
**问:10 Linux系统中的/proc文件系统有什么用?**
|
||||
|
||||
答: /proc文件系统是一个基于维护关于当前正在运行的内核状态信息的文件系统的随机存取存储器(RAM),其中包括CPU、内存、分区划分、I/O地址、直接内存访问通道和正在运行的进程。这个文件系统所代表的是各种不实际存储信息的文件,它们指向的是内存里的信息。/proc文件系统是由系统自动维护的。
|
||||
答: /proc文件系统是一个基于内存的文件系统,其维护着关于当前正在运行的内核状态信息,其中包括CPU、内存、分区划分、I/O地址、直接内存访问通道和正在运行的进程。这个文件系统所代表的并不是各种实际存储信息的文件,它们指向的是内存里的信息。/proc文件系统是由系统自动维护的。
|
||||
|
||||
**问:11 如何在/usr目录下找出大小超过10MB的文件?**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -78,21 +78,21 @@
|
||||
|
||||
答: # find /var \\! -atime -90
|
||||
|
||||
**问:14 在整个目录树下查找核心文件,如发现则删除它们且不提示确认信息。**
|
||||
**问:14 在整个目录树下查找文件“core”,如发现则无需提示直接删除它们。**
|
||||
|
||||
答: # find / -name core -exec rm {} \;
|
||||
|
||||
**问:15 strings命令有什么作用?**
|
||||
|
||||
答: strings命令用来提取和显示非文本文件的清晰内容。
|
||||
答: strings命令用来提取和显示非文本文件中的文本字符串。(LCTT 译注:当用来分析你系统上莫名其妙出现的二进制程序时,可以从中找到可疑的文件访问,对于追查入侵有用处)
|
||||
|
||||
**问:16 tee filter有什么作用 ?**
|
||||
**问:16 tee 过滤器有什么作用 ?**
|
||||
|
||||
答: tee filter用来向多个目标发送输出内容。它可以向一个文件发送一份输出的拷贝并且如果使用管道的话可以在屏幕上(或一些其它程序)输出其它内容。
|
||||
答: tee 过滤器用来向多个目标发送输出内容。如果用于管道的话,它可以将输出复制一份到一个文件,并复制另外一份到屏幕上(或一些其它程序)。
|
||||
|
||||
linuxtechi@localhost:~$ ll /etc | nl | tee /tmp/ll.out
|
||||
|
||||
在以上例子中,从ll输出的是在 /tmp/ll.out 文件中被捕获的,输出同样在屏幕上显示了出来。
|
||||
在以上例子中,从ll输出可以捕获到 /tmp/ll.out 文件中,并且同样在屏幕上显示了出来。
|
||||
|
||||
**问:17 export PS1 = ”$LOGNAME@`hostname`:\$PWD: 这条命令是在做什么?**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -108,7 +108,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
**问:20 linux中lspci命令的作用是什么?**
|
||||
|
||||
答: lspci命令用来显示你的系统上PCI总线和附加设备的信息。指定-v,-vv或-vvv来获取详细输出,加上-r参数的话,命令的输出则会更具有易读性。
|
||||
答: lspci命令用来显示你的系统上PCI总线和附加设备的信息。指定-v,-vv或-vvv来获取越来越详细的输出,加上-r参数的话,命令的输出则会更具有易读性。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -116,7 +116,7 @@ via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/20-linux-commands-interview-questions-answers/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,13 +1,11 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答 - linux如何安装WPS
|
||||
Linux有问必答 - 如何在linux上安装WPS
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**: 我听说一个好东西Kingsoft Office(译注:就是WPS),所以我想在我的Linux上试试。我怎样才能安装Kingsoft Office呢?
|
||||
|
||||
Kingsoft Office 一套办公套件,支持多个平台,包括Windows, Linux, iOS 和 Android。它包含三个组件:Writer(WPS文字)用来文字处理,Presentation(WPS演示)支持幻灯片,Spereadsheets(WPS表格)为电子表格。使用免费增值模式,其中基础版本是免费使用。比较其他的linux办公套件,如LibreOffice、 OpenOffice,最大优势在于,Kingsoft Office能最好的兼容微软的Office(译注:版权问题?了解下wps和Office的历史问题,可以得到一些结论)。因此如果你需要在windowns和linux平台间交互,Kingsoft office是一个很好的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
Kingsoft Office 是一套办公套件,支持多个平台,包括Windows, Linux, iOS 和 Android。它包含三个组件:Writer(WPS文字)用来文字处理,Presentation(WPS演示)支持幻灯片,Spereadsheets(WPS表格)是电子表格。其使用免费增值模式,其中基础版本是免费使用。比较其他的linux办公套件,如LibreOffice、 OpenOffice,其最大优势在于,Kingsoft Office能最好的兼容微软的Office(译注:版权问题?了解下wps和Office的历史问题,可以得到一些结论)。因此如果你需要在windows和linux平台间交互,Kingsoft office是一个很好的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
### CentOS, Fedora 或 RHEL中安装Kingsoft Office ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在[官方页面][1]下载RPM文件.官方RPM包只支持32位版本linux,但是你可以在64位中安装。
|
||||
|
||||
需要使用yum命令并用"localinstall"选项来本地安装这个RPM包
|
||||
@ -39,7 +37,7 @@ DEB包同样遇到一堆依赖。因此使用[gdebi][3]命令来代替dpkg来自
|
||||
|
||||
### 启动 Kingsoft Office ###
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后,你就可以在桌面管理器轻松启动Witer(WPS文字), Presentation(WPS演示), and Spreadsheets(WPS表格),如下图
|
||||
安装完成后,你就可以在桌面管理器轻松启动Witer(WPS文字), Presentation(WPS演示), and Spreadsheets(WPS表格),如下图。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Unity中:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -49,7 +47,7 @@ GNOME桌面中:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
不但如此,你也可以在命令行中启动Kingsoft Office
|
||||
不但如此,你也可以在命令行中启动Kingsoft Office。
|
||||
|
||||
启动Wirter(WPS文字),使用这个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -74,7 +72,7 @@ GNOME桌面中:
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-kingsoft-office-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Vic020/VicYu](http://www.vicyu.net)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
158
published/201501/20141203 Docker--Present and Future.md
Normal file
158
published/201501/20141203 Docker--Present and Future.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,158 @@
|
||||
Docker 的现状与未来
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker - 迄今为止发生的那些事情 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Docker 是一个专为 Linux 容器而设计的工具集,用于‘构建、交付和运行’分布式应用。它最初是 DotCloud 的一个开源项目,于2013年3月发布。这个项目越来越受欢迎,以至于 DotCloud 公司都更名为 Docker 公司(并最终[出售了原有的 PaaS 业务][1])。[Docker 1.0][2]是在2014年6月发布的,而且延续了之前每月更新一个版本的传统。
|
||||
|
||||
Docker 1.0版本的发布标志着 Docker 公司认为该平台已经充分成熟,足以用于生产环境中(由该公司与合作伙伴提供付费支持选择)。每个月发布的更新表明该项目正在迅速发展,比如增添一些新特性、解决一些他们发现的问题。该项目已经成功地分离了‘运行’和‘交付’两件事,所以来自任何版本的 Docker 镜像源都可以与其它版本共同使用(具备向前和向后兼容的特性),这为 Docker 应对快速变化提供了稳定的保障。
|
||||
|
||||
Docker 之所以能够成为最受欢迎的开源项目之一可能会被很多人看做是炒作,但是也是由其坚实的基础所决定的。Docker 的影响力已经得到整个行业许多大企业的支持,包括亚马逊, Canonical 公司, CenturyLink, 谷歌, IBM, 微软, New Relic, Pivotal, 红帽和 VMware。这使得只要有 Linux 的地方,Docker 就可以无处不在。除了这些鼎鼎有名的大公司以外,许多初创公司也在围绕着 Docker 发展,或者改变他们的发展方向来与 Docker 更好地结合起来。这些合作伙伴们(无论大或小)都将帮助推动 Docker 核心项目及其周边生态环境的快速发展。
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker 技术简要综述 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Docker 利用 Linux 的一些内核机制例如 [cGroups][3]、命名空间和 [SElinux][4] 来实现容器之间的隔离。起初 Docker 只是 [LXC][5] 容器管理器子系统的前端,但是在 0.9 版本中引入了 [libcontainer][6],这是一个原生的 go 语言库,提供了用户空间和内核之间的接口。
|
||||
|
||||
容器是基于 [AUFS][7] 这样的联合文件系统的,它允许跨多个容器共享组件,如操作系统镜像和已安装的相关库。这种文件系统的分层方法也被 [Dockerfile][8] 的 DevOps 工具所利用,这些工具能够缓存成功完成的操作。这就省下了安装操作系统和相关应用程序依赖包的时间,极大地加速测试周期。另外,在容器之间的共享库也能够减少内存的占用。
|
||||
|
||||
一个容器是从一个镜像开始运行的,它可以来自本地创建,本地缓存,或者从一个注册库(registry)下载。Docker 公司运营的 [Docker Hub 公有注册库][9],为各种操作系统、中间件和数据库提供了官方仓库存储。各个组织和个人都可以在 docker Hub 上发布的镜像的公有库,也可以注册成私有仓库。由于上传的镜像可以包含几乎任何内容,所以 Docker 提供了一种自动构建工具(以往称为“可信构建”),镜像可以从一种称之为 Dockerfile 的镜像内容清单构建而成。
|
||||
|
||||
### 容器 vs. 虚拟机 ###
|
||||
|
||||
容器会比虚拟机更高效,因为它们能够分享一个内核和分享应用程序库。相比虚拟机系统,这也将使得 Docker 使用的内存更小,即便虚拟机利用了内存超量使用的技术。部署容器时共享底层的镜像层也可以减少存储占用。IBM 的 Boden Russel 已经做了一些[基准测试][10]来说明两者之间的不同。
|
||||
|
||||
相比虚拟机系统,容器具有较低系统开销的优势,所以在容器中,应用程序的运行效率将会等效于在同样的应用程序在虚拟机中运行,甚至效果更佳。IBM 的一个研究团队已经发表了一本名为[虚拟机与 Linux 容器的性能比较]的文章[11]。
|
||||
|
||||
容器只是在隔离特性上要比虚拟机逊色。虚拟机可以利用如 Intel 的 VT-d 和 VT-x 技术的 ring-1 [硬件隔离][12]技术。这种隔离可以防止虚拟机突破和彼此交互。而容器至今还没有任何形式的硬件隔离,这使它容易受到攻击。一个称为 [Shocker][13] 的概念攻击验证表明,在 Docker 1.0 之前的版本是存在这种脆弱性的。尽管 Docker 1.0 修复了许多由 Shocker 漏洞带来的较为严重的问题,Docker 的 CTO Solomon Hykes 仍然[说][14],“当我们可以放心宣称 Docker 的开箱即用是安全的,即便是不可信的 uid0 程序(超级用户权限程序),我们将会很明确地告诉大家。”Hykes 的声明承认,其漏洞及相关的风险依旧存在,所以在容器成为受信任的工具之前将有更多的工作要做。
|
||||
|
||||
对于许多用户案例而言,在容器和虚拟机之间二者选择其一是种错误的二分法。Docker 同样可以在虚拟机中工作的很好,这让它可以用在现有的虚拟基础措施、私有云或者公有云中。同样也可以在容器里跑虚拟机,这也类似于谷歌在其云平台的使用方式。像 IaaS 服务这样普遍可用的基础设施,能够即时提供所需的虚拟机,可以预期容器与虚拟机一起使用的情景将会在数年后出现。容器管理和虚拟机技术也有可能被集成到一起提供一个两全其美的方案;这样,一个硬件信任锚微虚拟化所支撑的 libcontainer 容器,可与前端 Docker 工具链和生态系统整合,而使用提供更好隔离性的不同后端。微虚拟化(例如 Bromium 的 [vSentry][15] 和 VMware 的 [Project Fargo][16])已经用于在桌面环境中以提供基于硬件的应用程序隔离,所以类似的方法也可以用于 libcontainer,作为 Linux内核中的容器机制的替代技术。
|
||||
|
||||
### ‘容器化’ 的应用程序 ###
|
||||
|
||||
几乎所有 Linux 应用程序都可以在 Docker 容器中运行,并没有编程语言或框架的限制。唯一的实际限制是以操作系统的角度来允许容器做什么。即使如此,也可以在特权模式下运行容器,从而大大减少了限制(与之对应的是容器中的应用程序的风险增加,可能导致损坏主机操作系统)。
|
||||
|
||||
容器都是从镜像开始运行的,而镜像也可以从运行中的容器获取。本质上说,有两种方法可以将应用程序放到容器中,分别是手动构建和 Dockerfile。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 手动构建 ####
|
||||
|
||||
手动构建从启动一个基础的操作系统镜像开始,然后在交互式终端中用你所选的 Linux 提供的包管理器安装应用程序及其依赖项。Zef Hemel 在‘[使用 Linux 容器来支持便携式应用程序部署][17]’的文章中讲述了他部署的过程。一旦应用程序被安装之后,容器就可以被推送至注册库(例如Docker Hub)或者导出为一个tar文件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Dockerfile ####
|
||||
|
||||
Dockerfile 是一个用于构建 Docker 容器的脚本化系统。每一个 Dockerfile 定义了开始的基础镜像,以及一系列在容器中运行的命令或者一些被添加到容器中的文件。Dockerfile 也可以指定对外的端口和当前工作目录,以及容器启动时默认执行的命令。用 Dockerfile 构建的容器可以像手工构建的镜像一样推送或导出。Dockerfile 也可以用于 Docker Hub 的自动构建系统,即在 Docker 公司的控制下从头构建,并且该镜像的源代码是任何需要使用它的人可见的。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 单进程? ####
|
||||
|
||||
无论镜像是手动构建还是通过 Dockerfile 构建,有一个要考虑的关键因素是当容器启动时仅启动一个进程。对于一个单一用途的容器,例如运行一个应用服务器,运行一个单一的进程不是一个问题(有些关于容器应该只有一个单独的进程的争议)。对于一些容器需要启动多个进程的情况,必须先启动 [supervisor][18] 进程,才能生成其它内部所需的进程。由于容器内没有初始化系统,所以任何依赖于 systemd、upstart 或类似初始化系统的东西不修改是无法工作的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 容器和微服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
全面介绍使用微服务结构体系的原理和好处已经超出了这篇文章的范畴(在 [InfoQ eMag: Microservices][19] 有全面阐述)。然而容器是绑定和部署微服务实例的捷径。
|
||||
|
||||
大规模微服务部署的多数案例都是部署在虚拟机上,容器只是用于较小规模的部署上。容器具有共享操作系统和公用库的的内存和硬盘存储的能力,这也意味着它可以非常有效的并行部署多个版本的服务。
|
||||
|
||||
### 连接容器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
一些小的应用程序适合放在单独的容器中,但在许多案例中应用程序需要分布在多个容器中。Docker 的成功包括催生了一连串新的应用程序组合工具、编制工具及平台作为服务(PaaS)的实现。在这些努力的背后,是希望简化从一组相互连接的容器来创建应用的过程。很多工具也在扩展、容错、性能管理以及对已部署资产进行版本控制方面提供了帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 连通性 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Docker 的网络功能是相当原始的。在同一主机,容器内的服务可以互相访问,而且 Docker 也可以通过端口映射到主机操作系统,使服务可以通过网络访问。官方支持的提供连接能力的库叫做 [libchan][20],这是一个提供给 Go 语言的网络服务库,类似于[channels][21]。在 libchan 找到进入应用的方法之前,第三方应用仍然有很大空间可提供配套的网络服务。例如,[Flocker][22] 已经采取了基于代理的方法使服务实现跨主机(以及底层存储)的移植。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 合成 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Docker 本身拥有把容器连接在一起的机制,与元数据相关的依赖项可以被传递到相依赖的容器中,并用于环境变量和主机入口。如 [Fig][23] 和 [geard][24] 这样的应用合成工具可以在单一文件中展示出这种依赖关系图,这样多个容器就可以汇聚成一个连贯的系统。CenturyLink 公司的 [Panamax][25] 合成工具类似 Fig 和 geard 的底层实现方法,但新增了一些基于 web 的用户接口,并直接与 GitHub 相结合,以便于应用程序分享。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 编制 ####
|
||||
|
||||
像 [Decking][26]、New Relic 公司的 [Centurion][27] 和谷歌公司的 [Kubernetes][28] 这样的编制系统都是旨在协助容器的部署和管理其生命周期系统。也有许多 [Apache Mesos][30] (特别是 [Marathon(马拉松式)持续运行很久的框架])的案例(例如[Mesosphere][29])已经被用于配合 Docker 一起使用。通过为应用程序与底层基础架构之间(例如传递 CPU 核数和内存的需求)提供一个抽象的模型,编制工具提供了两者的解耦,简化了应用程序开发和数据中心操作。有很多各种各样的编制系统,因为许多来自内部系统的以前开发的用于大规模容器部署的工具浮现出来了;如 Kubernetes 是基于谷歌的 [Omega][32] 系统的,[Omega][32] 是用于管理遍布谷歌云环境中容器的系统。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然从某种程度上来说合成工具和编制工具的功能存在重叠,但这也是它们之间互补的一种方式。例如 Fig 可以被用于描述容器间如何实现功能交互,而 Kubernetes pods(容器组)可用于提供监控和扩展。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 平台(即服务)####
|
||||
|
||||
有一些 Docker 原生的 PaaS 服务实现,例如 [Deis][33] 和 [Flynn][34] 已经显现出 Linux 容器在开发上的的灵活性(而不是那些“自以为是”的给出一套语言和框架)。其它平台,例如 CloudFoundry、OpenShift 和 Apcera Continuum 都已经采取将 Docker 基础功能融入其现有的系统的技术路线,这样基于 Docker 镜像(或者基于 Dockerfile)的应用程序也可以与之前用支持的语言和框架的开发的应用一同部署和管理。
|
||||
|
||||
### 所有的云 ###
|
||||
|
||||
由于 Docker 能够运行在任何正常更新内核的 Linux 虚拟机中,它几乎可以用在所有提供 IaaS 服务的云上。大多数的主流云厂商已经宣布提供对 Docker 及其生态系统的支持。
|
||||
|
||||
亚马逊已经把 Docker 引入它们的 Elastic Beanstalk 系统(这是在底层 IaaS 上的一个编制系统)。谷歌使 Docker 成为了“可管理的 VM”,它提供了GAE PaaS 和GCE IaaS 之间的中转站。微软和 IBM 也都已经宣布了基于 Kubernetes 的服务,这样可以在它们的云上部署和管理多容器应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
为了给现有种类繁多的后端提供可用的一致接口,Docker 团队已经引进 [libswarm][35], 它可以集成于众多的云和资源管理系统。Libswarm 所阐明的目标之一是“通过切换服务来源避免被特定供应商套牢”。这是通过呈现一组一致的服务(与API相关联的)来完成的,该服务会通过特定的后端服务所实现。例如 Docker 服务器将支持本地 Docker 命令行工具的 Docker 远程 API 调用,这样就可以管理一组服务供应商的容器了。
|
||||
|
||||
基于 Docker 的新服务类型仍在起步阶段。总部位于伦敦的 Orchard 实验室提供了 Docker 的托管服务,但是 Docker 公司表示,收购 Orchard 后,其相关服务不会置于优先位置。Docker 公司也出售了之前 DotCloud 的PaaS 业务给 cloudControl。基于更早的容器管理系统的服务例如 [OpenVZ][36] 已经司空见惯了,所以在一定程度上 Docker 需要向主机托管商们证明其价值。
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker 及其发行版 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Docker 已经成为大多数 Linux 发行版例如 Ubuntu、Red Hat 企业版(RHEL)和 CentOS 的一个标准功能。遗憾的是这些发行版的步调和 Docker 项目并不一致,所以在发布版中找到的版本总是远远落后于最新版本。例如 Ubuntu 14.04 版本中的版本是 Docker 0.9.1,而当 Ubuntu 升级至 14.04.1 时 Docker 版本并没有随之升级(此时 Docker 已经升至 1.1.2 版本)。在发行版的软件仓库中还有一个名字空间的冲突,因为 “Docker” 也是 KDE 系统托盘的名字;所以在 Ubuntu 14.04 版本中相关安装包的名字和命令行工具都是使用“Docker.io”的名字。
|
||||
|
||||
在企业级 Linux 的世界中,情况也并没有因此而不同。CentOS 7 中的 Docker 版本是 0.11.1,这是 Docker 公司宣布准备发行 Docker 1.0 产品版本之前的开发版。Linux 发行版用户如果希望使用最新版本以保障其稳定、性能和安全,那么最好地按照 Docker 的[安装说明][37]进行,使用 Docker 公司的所提供的软件库而不是采用发行版的。
|
||||
|
||||
Docker 的到来也催生了新的 Linux 发行版,如 [CoreOS][38] 和红帽的 [Project Atomic][39],它们被设计为能运行容器的最小环境。这些发布版相比传统的发行版,带着更新的内核及 Docker 版本,对内存的使用和硬盘占用率也更低。新发行版也配备了用于大型部署的新工具,例如 [fleet][40](一个分布式初始化系统)和[etcd][41](用于元数据管理)。这些发行版也有新的自我更新机制,以便可以使用最新的内核和 Docker。这也意味着使用 Docker 的影响之一是它抛开了对发行版和相关的包管理解决方案的关注,而对 Linux 内核(及使用它的 Docker 子系统)更加关注。
|
||||
|
||||
这些新发行版也许是运行 Docker 的最好方式,但是传统的发行版和它们的包管理器对容器来说仍然是非常重要的。Docker Hub 托管的官方镜像有 Debian、Ubuntu 和 CentOS,以及一个‘半官方’的 Fedora 镜像库。RHEL 镜像在Docker Hub 中不可用,因为它是 Red Hat 直接发布的。这意味着在 Docker Hub 的自动构建机制仅仅用于那些纯开源发行版下(并愿意信任那些源于 Docker 公司团队提供的基础镜像)。
|
||||
|
||||
Docker Hub 集成了如 Git Hub 和 Bitbucket 这样源代码控制系统来自动构建包管理器,用于管理构建过程中创建的构建规范(在Dockerfile中)和生成的镜像之间的复杂关系。构建过程的不确定结果并非是 Docker 的特定问题——而与软件包管理器如何工作有关。今天构建完成的是一个版本,明天构建的可能就是更新的版本,这就是为什么软件包管理器需要升级的原因。容器抽象(较少关注容器中的内容)以及容器扩展(因为轻量级资源利用率)有可能让这种不确定性成为 Docker 的痛点。
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker 的未来 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Docker 公司对核心功能(libcontainer),跨服务管理(libswarm) 和容器间的信息传递(libchan)的发展上提出了明确的路线。与此同时,该公司已经表明愿意收购 Orchard 实验室,将其纳入自身生态系统。然而 Docker 不仅仅是 Docker 公司的,这个项目的贡献者也来自许多大牌贡献者,其中不乏像谷歌、IBM 和 Red Hat 这样的大公司。在仁慈独裁者、CTO Solomon Hykes 掌舵的形势下,为公司和项目明确了技术领导关系。在前18个月的项目中通过成果输出展现了其快速行动的能力,而且这种趋势并没有减弱的迹象。
|
||||
|
||||
许多投资者正在寻找10年前 VMware 公司的 ESX/vSphere 平台的特征矩阵,并试图找出虚拟机的普及而带动的企业预期和当前 Docker 生态系统两者的距离(和机会)。目前 Docker 生态系统正缺乏类似网络、存储和(对于容器的内容的)细粒度版本管理,这些都为初创企业和创业者提供了机会。
|
||||
|
||||
随着时间的推移,在虚拟机和容器(Docker 的“运行”部分)之间的区别将变得没那么重要了,而关注点将会转移到“构建”和“交付”方面。这些变化将会使“Docker发生什么?”变得不如“Docker将会给IT产业带来什么?”那么重要了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.infoq.com/articles/docker-future
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Chris Swan][a]
|
||||
译者:[disylee](https://github.com/disylee)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.infoq.com/author/Chris-Swan
|
||||
[1]:http://blog.dotcloud.com/dotcloud-paas-joins-cloudcontrol
|
||||
[2]:http://www.infoq.com/news/2014/06/docker_1.0
|
||||
[3]:https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/cgroups/cgroups.txt
|
||||
[4]:http://selinuxproject.org/page/Main_Page
|
||||
[5]:https://linuxcontainers.org/
|
||||
[6]:http://blog.docker.com/2014/03/docker-0-9-introducing-execution-drivers-and-libcontainer/
|
||||
[7]:http://aufs.sourceforge.net/aufs.html
|
||||
[8]:https://docs.docker.com/reference/builder/
|
||||
[9]:https://registry.hub.docker.com/
|
||||
[10]:http://bodenr.blogspot.co.uk/2014/05/kvm-and-docker-lxc-benchmarking-with.html?m=1
|
||||
[11]:http://domino.research.ibm.com/library/cyberdig.nsf/papers/0929052195DD819C85257D2300681E7B/$File/rc25482.pdf
|
||||
[12]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X86_virtualization#Hardware-assisted_virtualization
|
||||
[13]:http://stealth.openwall.net/xSports/shocker.c
|
||||
[14]:https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=7910117
|
||||
[15]:http://www.bromium.com/products/vsentry.html
|
||||
[16]:http://cto.vmware.com/vmware-docker-better-together/
|
||||
[17]:http://www.infoq.com/articles/docker-containers
|
||||
[18]:http://docs.docker.com/articles/using_supervisord/
|
||||
[19]:http://www.infoq.com/minibooks/emag-microservices
|
||||
[20]:https://github.com/docker/libchan
|
||||
[21]:https://gobyexample.com/channels
|
||||
[22]:http://www.infoq.com/news/2014/08/clusterhq-launch-flocker
|
||||
[23]:http://www.fig.sh/
|
||||
[24]:http://openshift.github.io/geard/
|
||||
[25]:http://panamax.io/
|
||||
[26]:http://decking.io/
|
||||
[27]:https://github.com/newrelic/centurion
|
||||
[28]:https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/kubernetes
|
||||
[29]:https://mesosphere.io/2013/09/26/docker-on-mesos/
|
||||
[30]:http://mesos.apache.org/
|
||||
[31]:https://github.com/mesosphere/marathon
|
||||
[32]:http://static.googleusercontent.com/media/research.google.com/en/us/pubs/archive/41684.pdf
|
||||
[33]:http://deis.io/
|
||||
[34]:https://flynn.io/
|
||||
[35]:https://github.com/docker/libswarm
|
||||
[36]:http://openvz.org/Main_Page
|
||||
[37]:https://docs.docker.com/installation/#installation
|
||||
[38]:https://coreos.com/
|
||||
[39]:http://www.projectatomic.io/
|
||||
[40]:https://github.com/coreos/fleet
|
||||
[41]:https://github.com/coreos/etcd
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux/类Unix系统中解压tar文件到不同的目录中
|
||||
如何解压 tar 文件到不同的目录中
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
我想要解压一个tar文件到一个指定的目录叫/tmp/data。我该如何在Linux或者类Unix的系统中使用tar命令解压一个tar文件到不同的目录中?
|
||||
|
||||
你不必使用cd名切换到其他的目录并解压。可以使用下面的语法解压一个文件:
|
||||
我想要解压一个tar文件到一个叫/tmp/data的指定目录。我该如何在Linux或者类Unix的系统中使用tar命令解压一个tar文件到不同的目录中?
|
||||
|
||||
你不必使用cd命令切换到其他的目录并解压。可以使用下面的语法解压一个文件:
|
||||
|
||||
### 语法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,9 +17,9 @@ GNU/tar 语法:
|
||||
|
||||
tar xf file.tar --directory /path/to/directory
|
||||
|
||||
### 示例:解压文件到另一个文件夹中 ###
|
||||
### 示例:解压文件到另一个目录中 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在本例中。我解压$HOME/etc.backup.tar到文件夹/tmp/data中。首先,你需要手动创建这个目录,输入:
|
||||
在本例中。我解压$HOME/etc.backup.tar到/tmp/data目录中。首先,需要手动创建这个目录,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir /tmp/data
|
||||
|
||||
@ -34,7 +35,7 @@ GNU/tar 语法:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Gif 01: tar命令解压文件到不同的目录
|
||||
*Gif 01: tar命令解压文件到不同的目录*
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以指定解压的文件:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -56,8 +57,8 @@ via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-extract-tar-file-to-specific-directory-o
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[nixCraft][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/about-us
|
||||
[a]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/about-us
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 14.04 中Apache从2.2迁移到2.4的问题
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
如果你将**Ubuntu**从12.04升级跨越到了14.04,那么这其中包括了一个重大的升级--**Apache**从2.2版本升级到2.4版本。**Apache**的这次升级带来了许多性能提升,**但是如果继续使用2.2的配置文件会导致很多错误**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 访问控制的改变 ###
|
||||
|
||||
从**Apache 2.4**起,所启用的授权机制比起2.2的只是针对单一数据存储的单一检查更加灵活。过去很难确定哪个 order 授权怎样被使用的,但是授权容器指令的引入解决了这些问题,现在,配置可以控制什么时候授权方法被调用,什么条件决定何时授权访问。
|
||||
|
||||
这就是为什么大多数的升级失败是由于配置错误的原因。2.2的访问控制是基于IP地址、主机名和其他角色,通过使用指令Order,来设置Allow, Deny或 Satisfy;但是2.4,这些一切都通过新的授权方式进行检查。
|
||||
|
||||
为了弄清楚这些,可以来看一些虚拟主机的例子,这些可以在/etc/apache2/sites-enabled/default 或者 /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/*你的网站名称* 中找到:
|
||||
|
||||
旧的2.2虚拟主机配置:
|
||||
|
||||
Order allow,deny
|
||||
Allow from all
|
||||
|
||||
新的2.4虚拟主机配置:
|
||||
|
||||
Require all granted
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
(LCTT 译注:Order、Allow和deny 这些将在之后的版本废弃,请尽量避免使用,Require 指令已可以提供比其更强大和灵活的功能。)
|
||||
|
||||
### .htaccess 问题 ###
|
||||
|
||||
升级后如果一些设置不工作,或者你得到重定向错误,请检查是否这些设置是放在.htaccess文件中。如果Apache 2.4没有使用 .htaccess 文件中的设置,那是因为在2.4中AllowOverride指令的默认是 none,因此忽略了.htaccess文件。你只需要做的就是修改或者添加AllowOverride All命令到你的网站配置文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
上面截图中,可以看见AllowOverride All指令。
|
||||
|
||||
### 丢失配置文件或者模块 ###
|
||||
|
||||
根据我的经验,这次升级带来的另一个问题就是在2.4中,一些旧模块和配置文件不再需要或者不被支持了。你将会收到一条“Apache不能包含相应的文件”的明确警告,你需要做的是在配置文件中移除这些导致问题的配置行。之后你可以搜索和安装相似的模块来替代。
|
||||
|
||||
### 其他需要了解的小改变 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这里还有一些其他的改变需要考虑,虽然这些通常只会发生警告,而不是错误。
|
||||
|
||||
- MaxClients重命名为MaxRequestWorkers,使之有更准确的描述。而异步MPM,如event,客户端最大连接数不等于工作线程数。旧的配置名依然支持。
|
||||
- DefaultType命令无效,使用它已经没有任何效果了。如果使用除了 none 之外的其它配置值,你会得到一个警告。需要使用其他配置设定来替代它。
|
||||
- EnableSendfile默认关闭
|
||||
- FileETag 现在默认为"MTime Size"(没有INode)
|
||||
- KeepAlive 只接受“On”或“Off”值。之前的任何不是“Off”或者“0”的值都被认为是“On”
|
||||
- 单一的 Mutex 已经替代了 Directives AcceptMutex, LockFile, RewriteLock, SSLMutex, SSLStaplingMutex 和 WatchdogMutexPath 等指令。你需要做的是估计一下这些被替代的指令在2.2中的使用情况,来决定是否删除或者使用Mutex来替代。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/apache-migration-2-2-to-2-4-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrian Dinu][a]
|
||||
译者:[Vic020/VicYu](http://vicyu.net)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/adriand/
|
||||
[1]:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答:在Linux下如何用df命令检查磁盘空间?
|
||||
在 Linux 下你所不知道的 df 命令的那些功能
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**: 我知道在Linux上我可以用df命令来查看磁盘使用空间。你能告诉我df命令的实际例子使我可以最大限度得利用它吗?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ df命令可以展示任何“mounted”文件系统的磁盘利用率。该命
|
||||
|
||||
### 用人们可读的方式展示 ###
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,df命令用1K为块来展示磁盘空间,这不容易解释。“-h”参数使df用更可读的方式打印磁盘空间(例如 100K,200M,3G)。
|
||||
默认情况下,df命令用1K为块来展示磁盘空间,这看起来不是很直观。“-h”参数使df用更可读的方式打印磁盘空间(例如 100K,200M,3G)。
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ df命令可以展示任何“mounted”文件系统的磁盘利用率。该命
|
||||
|
||||
### 展示Inode使用情况 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当你监视磁盘使用情况时,你必须注意的不仅仅是磁盘空间还有“inode”的使用情况。在Linux中,inode是用来存储特定文件的元数据的一种数据结构,在创建一个文件系统时,inode的预先定义数量将被分配。这意味着,一个文件系统可能耗尽空间不只是因为大文件用完了所有可用空间,也可能是因为很多小文件用完了所有可能的inode。用“-i”选项展示inode使用情况。
|
||||
当你监视磁盘使用情况时,你必须注意的不仅仅是磁盘空间还有“inode”的使用情况。在Linux中,inode是用来存储特定文件的元数据的一种数据结构,在创建一个文件系统时,inode的预先定义数量将被分配。这意味着,**一个文件系统可能耗尽空间不只是因为大文件用完了所有可用空间,也可能是因为很多小文件用完了所有可能的inode**。用“-i”选项展示inode使用情况。
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -i
|
||||
|
||||
@ -46,7 +46,8 @@ df命令可以展示任何“mounted”文件系统的磁盘利用率。该命
|
||||
|
||||
### 展示磁盘总利用率 ###
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下, df命令显示磁盘的单个文件系统的利用率。如果你想知道的所有文件系统的总磁盘使用量,增加“ --total ”选项。
|
||||
默认情况下, df命令显示磁盘的单个文件系统的利用率。如果你想知道的所有文件系统的总磁盘使用量,增加“ --total ”选项(见最下面的汇总行)。
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h --total
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
@ -64,7 +65,7 @@ df命令可以展示任何“mounted”文件系统的磁盘利用率。该命
|
||||
|
||||
### 展示文件系统类型 ###
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,df命令不现实文件系统类型信息。用“-T”选项来添加文件系统信息到输出中。
|
||||
默认情况下,df命令不显示文件系统类型信息。用“-T”选项来添加文件系统信息到输出中。
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -T
|
||||
|
||||
@ -92,13 +93,13 @@ df命令可以展示任何“mounted”文件系统的磁盘利用率。该命
|
||||
/dev/mapper/ubuntu-root 952893348 591583380 312882756 66% /
|
||||
/dev/sda1 233191 100025 120725 46% /boot
|
||||
|
||||
排除特定的文件系统类型,用“-x <type>”选项。同样,你可以用这个选项多次。
|
||||
排除特定的文件系统类型,用“-x <type>”选项。同样,你可以用这个选项多次来排除多种文件系统类型。
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -x tmpfs
|
||||
|
||||
### 显示一个具体的挂载点磁盘使用情况 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你用df指定一个挂载点,它将报告挂载在那个地方的文件系统的磁盘使用情况。如果你指定一个普通文件(或一个目录)而不是一个挂载点,df将现实包含这个文件(或目录)的文件系统的磁盘利用率。
|
||||
如果你用df指定一个挂载点,它将报告挂载在那个地方的文件系统的磁盘使用情况。如果你指定一个普通文件(或一个目录)而不是一个挂载点,df将显示包含这个文件(或目录)的文件系统的磁盘利用率。
|
||||
|
||||
$ df /
|
||||
|
||||
@ -116,9 +117,9 @@ df命令可以展示任何“mounted”文件系统的磁盘利用率。该命
|
||||
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
|
||||
/dev/mapper/ubuntu-root 952893348 591583528 312882608 66% /
|
||||
|
||||
### 现实虚拟文件系统的信息 ###
|
||||
### 显示虚拟文件系统的信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想显示所有已经存在的文件系统(包括虚拟文件系统)的磁盘空间信息,用“-a”选项。这里,虚拟文件系统是指没有相对应的物理设备的假的文件系统,例如,tmpfs,cgroup虚拟文件系统或FUSE文件安系统。这些虚拟文件系统大小为0,不用“-a”选项将不会被报告出来。
|
||||
如果你想显示所有已经存在的文件系统(包括虚拟文件系统)的磁盘空间信息,用“-a”选项。这里,虚拟文件系统是指没有相对应的物理设备的假文件系统,例如,tmpfs,cgroup虚拟文件系统或FUSE文件安系统。这些虚拟文件系统大小为0,不用“-a”选项将不会被报告出来。
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -a
|
||||
|
||||
@ -149,7 +150,7 @@ df命令可以展示任何“mounted”文件系统的磁盘利用率。该命
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/check-disk-space-linux-df-command.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[mtunique](https://github.com/mtunique)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答:如何检查Linux的内存使用状况
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
>**问题**:我想要监测Linux系统的内存使用状况。有哪些可用的图形界面或者命令行工具来检查当前内存使用情况?
|
||||
|
||||
当涉及到Linux系统性能优化的时候,物理内存是一个最重要的因素。自然的,Linux提供了丰富的选择来监测珍贵的内存资源的使用情况。不同的工具,在监测粒度(例如:全系统范围,每个进程,每个用户),接口方式(例如:图形用户界面,命令行,ncurses)或者运行模式(交互模式,批量处理模式)上都不尽相同。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一个可供选择的,但并不全面的图形或命令行工具列表,这些工具用来检查Linux平台中已用和可用的内存。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. /proc/meminfo ###
|
||||
|
||||
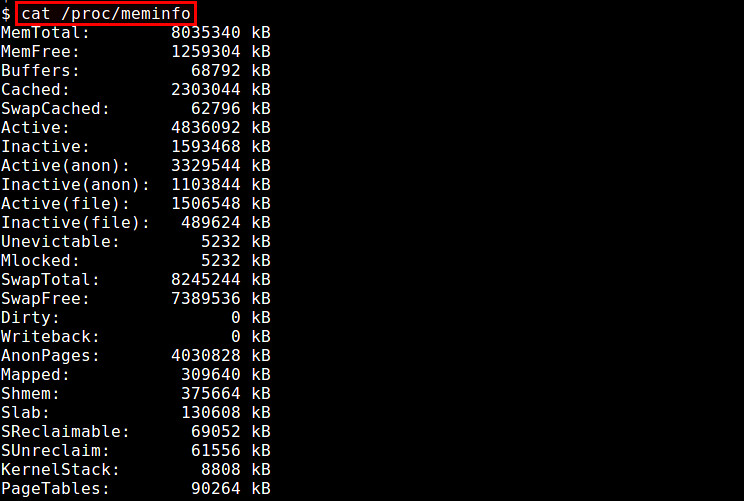
一种最简单的方法是通过“/proc/meminfo”来检查内存使用状况。这个动态更新的虚拟文件事实上是诸如free,top和ps这些与内存相关的工具的信息来源。从可用/闲置物理内存数量到等待被写入缓存的数量或者已写回磁盘的数量,只要是你想要的关于内存使用的信息,“/proc/meminfo”应有尽有。特定进程的内存信息也可以通过“/proc/\<pid>/statm”和“/proc/\<pid>/status”来获取。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cat /proc/meminfo
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. atop ###
|
||||
|
||||
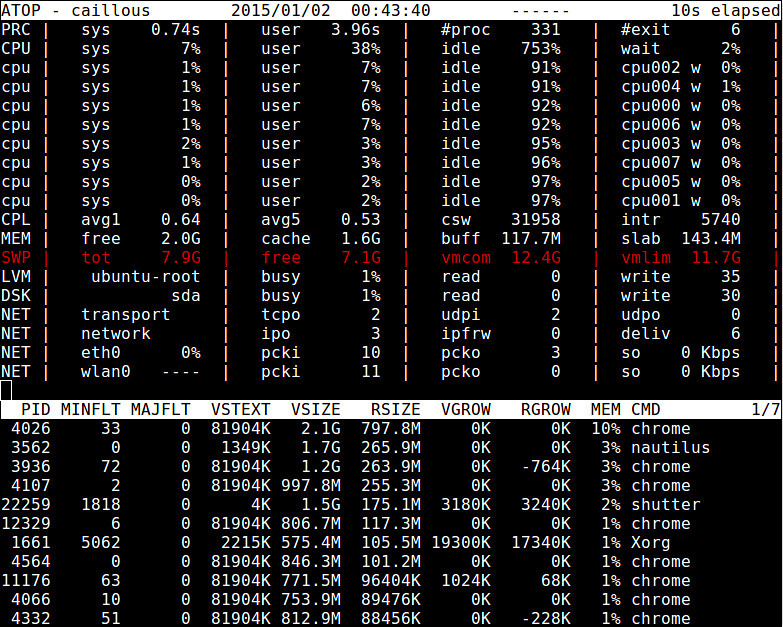
atop命令是用于终端环境的基于ncurses的交互式的系统和进程监测工具。它展示了动态更新的系统资源摘要(CPU, 内存, 网络, 输入/输出, 内核),并且用醒目的颜色把系统高负载的部分以警告信息标注出来。它同样提供了类似于top的线程(或用户)资源使用视图,因此系统管理员可以找到哪个进程或者用户导致的系统负载。内存统计报告包括了总计/闲置内存,缓存的/缓冲的内存和已提交的虚拟内存。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo atop
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. free ###
|
||||
|
||||
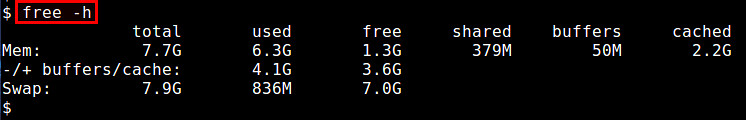
free命令是一个用来获得内存使用概况的快速简单的方法,这些信息从“/proc/meminfo”获取。它提供了一个快照,用于展示总计/闲置的物理内存和系统交换区,以及已使用/闲置的内核缓冲区。
|
||||
|
||||
$ free -h
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
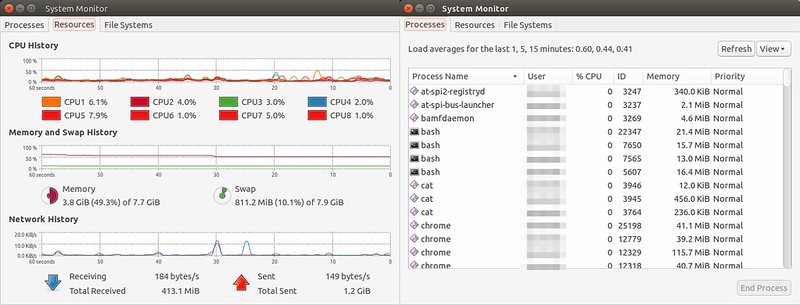
### 4. GNOME System Monitor ###
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME System Monitor 是一个图形界面应用,它展示了包括CPU,内存,交换区和网络在内的系统资源使用率的较近历史信息。它同时也可以提供一个带有CPU和内存使用情况的进程视图。
|
||||
|
||||
$ gnome-system-monitor
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. htop ###
|
||||
|
||||
htop命令是一个基于ncurses的交互式的进程视图,它实时展示了每个进程的内存使用情况。它可以报告所有运行中进程的常驻内存大小(RSS)、内存中程序的总大小、库大小、共享页面大小和脏页面大小。你可以横向或者纵向滚动进程列表进行查看。
|
||||
|
||||
$ htop
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 6. KDE System Monitor ###
|
||||
|
||||
就像GNOME桌面拥有GNOME System Monitor一样,KDE桌面也有它自己的对口应用:KDE System Monitor。这个工具的功能与GNOME版本极其相似,也就是说,它同样展示了一个关于系统资源使用情况,以及带有每个进程的CPU/内存消耗情况的实时历史记录。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ksysguard
|
||||
|
||||
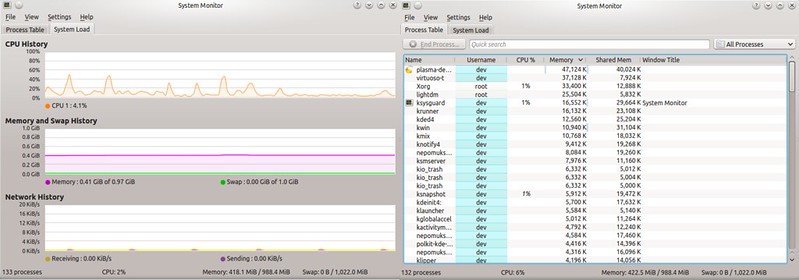
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. memstat ###
|
||||
|
||||
memstat工具对于识别正在消耗虚拟内存的可执行部分、进程和共享库非常有用。给出一个进程识别号,memstat即可识别出与之相关联的可执行部分、数据和共享库究竟使用了多少虚拟内存。
|
||||
|
||||
$ memstat -p <PID>
|
||||
|
||||
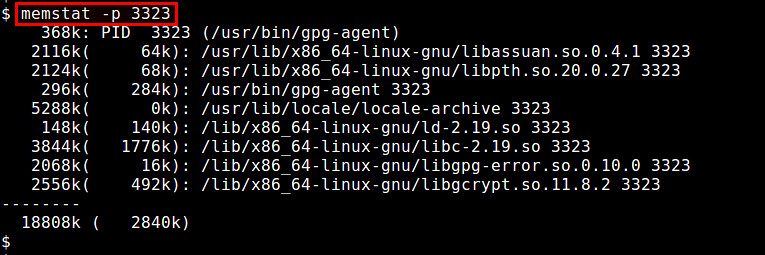
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. nmon ###
|
||||
|
||||
nmon工具是一个基于ncurses系统基准测试工具,它能够以交互方式监测CPU、内存、磁盘I/O、内核、文件系统以及网络资源。对于内存使用状况而言,它能够展示像总计/闲置内存、交换区、缓冲的/缓存的内存,虚拟内存页面换入换出的统计,所有这些都是实时的。
|
||||
|
||||
$ nmon
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 9. ps ###
|
||||
|
||||
ps命令能够实时展示每个进程的内存使用状况。内存使用报告里包括了 %MEM (物理内存使用百分比), VSZ (虚拟内存使用总量), 和 RSS (物理内存使用总量)。你可以使用“--sort”选项来对进程列表排序。例如,按照RSS降序排序:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps aux --sort -rss
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 10. smem ###
|
||||
|
||||
[smem][1]命令允许你测定不同进程和用户的物理内存使用状况,这些信息来源于“/proc”目录。它利用“按比例分配大小(PSS)”指标来精确量化Linux进程的有效内存使用情况。内存使用分析结果能够输出为柱状图或者饼图类的图形化图表。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo smem --pie name -c "pss"
|
||||
|
||||
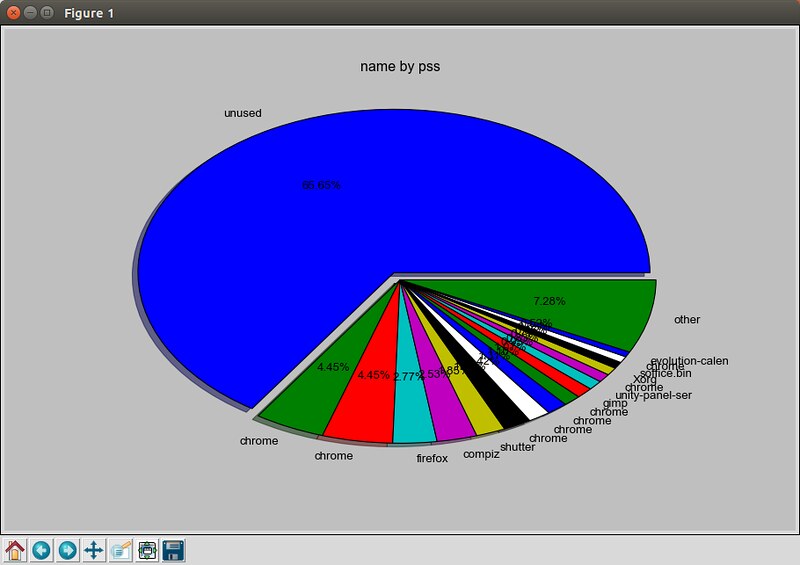
|
||||
|
||||
### 11. top ###
|
||||
|
||||
top命令提供了一个运行中进程的实时视图,以及特定进程的各种资源使用统计信息。与内存相关的信息包括 %MEM (内存使用率), VIRT (虚拟内存使用总量), SWAP (换出的虚拟内存使用量), CODE (分配给代码执行的物理内存数量), DATA (分配给非执行的数据的物理内存数量), RES (物理内存使用总量; CODE+DATA), 和 SHR (有可能与其他进程共享的内存数量)。你能够基于内存使用情况或者大小对进程列表进行排序。
|
||||
|
||||
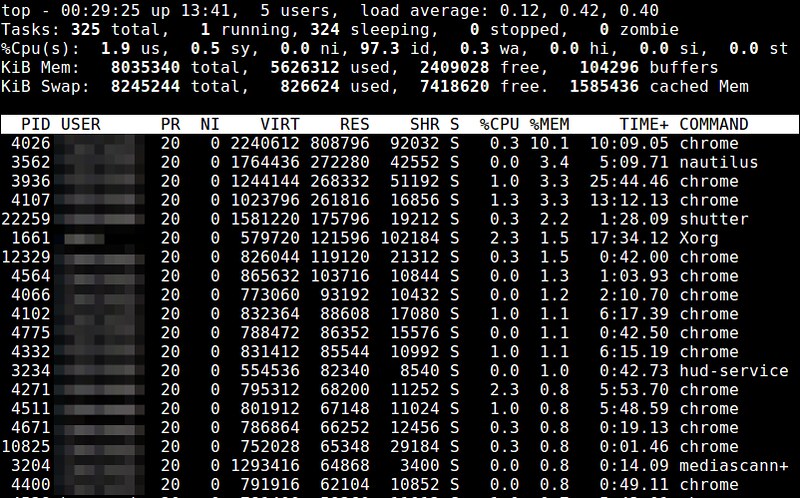
|
||||
|
||||
### 12. vmstat ###
|
||||
|
||||
vmstat命令行工具显示涵盖了CPU、内存、中断和磁盘I/O在内的各种系统活动的瞬时和平均统计数据。对于内存信息而言,命令不仅仅展示了物理内存使用情况(例如总计/已使用内存和缓冲的/缓存的内存),还同样展示了虚拟内存统计数据(例如,内存页的换入/换出,虚拟内存页的换入/换出)
|
||||
|
||||
$ vmstat -s
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/check-memory-usage-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Ping](https://github.com/mr-ping)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/visualize-memory-usage-linux.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
||||
4个最流行的Linux平台开源代码编辑器
|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
寻找**Linux平台最棒的代码编辑器**?如果你询问那些很早就玩Linux的人,他们会回答是Vi, Vim, Emacs, Nano等。但是,我今天不讨论那些。我将谈论一些新时代尖端、漂亮、时髦而且十分强大, 功能丰富的**最好的Linux平台开源代码编辑器**,它们将会提升你的编程经验。
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux平台最时髦的开源代码编辑器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我使用Ubuntu作为我的主桌面,所以我提供的安装说明是基于Ubuntu的发行版。但是这并不意味着本文列表就是**Ubuntu最好的文本编辑器**,因为本列表是适用于任何Linux发行版。而且,列表的介绍顺序并没有特定的优先级别。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Brackets ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Brackets][1]是出自[Adobe][2]的一个开源代码编辑器。它专门关注web设计者的需求,内置支持HTML, CSS和Java Script。它轻量级,但却十分强大,提供在线编辑和实时预览。而且,为了你能更好地体验Brackets,你可以使用许多可用的插件。
|
||||
|
||||
为了[在Ubuntu][3],以及其它基于Ubuntu的发行版,诸如Linux Minit上安装Brackets,你可以使用这个非官方的PPA源:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/brackets
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install brackets
|
||||
|
||||
其他的Linux发行版本,你可以通过下载源代码或相应Linux, OS X和Windows的二进制文件,进行安装。
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载Brackets源码和二进制文件][5]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Atom ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Atom][5]是为程序员准备的另一个时尚开源代码编辑器。Atom由Github开发,被誉为“21世纪可破解的文本编辑器”。Atom的界面和Sublime Text编辑器十分相似。Sublime Text是一个十分流行但闭源的文本编辑器。
|
||||
|
||||
Atom最近已经发布了 .deb 和 .rpm包,所以在Debian和基于Fedora的Linux版本上安装很简单。当然,你也可以获取它的源代码。
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载Atom .deb][6]
|
||||
- [下载Atom .rpm][7]
|
||||
- [获取Atom源代码][8]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Lime Text ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你喜欢Sublime Text,但是你对它的闭源十分反感。别担心,我们有一个[Sublime Text的开源克隆][9],叫做[Lime Text][10]。它基于Go, HTML和QT构造。说它是Sublime Text的克隆,背后原因是Sublime Text2仍有许多bug,而且Sublime Text3到目前为止仍处于测试版本。Sublime Text在开发过程中的bug是否修复,外界并不知情。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,开源爱好者们,你们可以很开心地通过下面的连接获得Lime Text的源码:
|
||||
|
||||
- [获取Lime Text源码][11]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Light Table ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
被誉为“下一代的代码编辑器”,[Light Table][12]是另一个时髦,功能丰富的开源编辑器,它更像是一个IDE,而非仅仅是一个文本编辑器。并且,有许多可以提高其性能的扩展方法。内联评价将是你会爱上它的原因。你一定要试用一下看,这样你才会体会它的实用之处。
|
||||
|
||||
- [获取Light Table的源码][13]
|
||||
|
||||
### 你的选择是什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux平台,我们不能只局限于这四种代码编辑器。这份列表仅介绍了一些时髦的,可供程序员使用的编辑器。当然,你也有许多其他的选择,比如[Notepad++的替代品Notepadqq][14]或者[SciTE][15]等等。那么,文中这四个编辑器,你最喜欢哪个呢?
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/best-modern-open-source-code-editors-for-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[su-kaiyao](https://github.com/su-kaiyao)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://brackets.io/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.adobe.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/install-brackets-ubuntu/
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/adobe/brackets/releases
|
||||
[5]:https://atom.io/
|
||||
[6]:https://atom.io/download/deb
|
||||
[7]:https://atom.io/download/rpm
|
||||
[8]:https://github.com/atom/atom/blob/master/docs/build-instructions/linux.md
|
||||
[9]:http://itsfoss.com/lime-text-open-source-alternative/
|
||||
[10]:http://limetext.org/
|
||||
[11]:https://github.com/limetext/lime
|
||||
[12]:http://lighttable.com/
|
||||
[13]:https://github.com/LightTable/LightTable
|
||||
[14]:http://itsfoss.com/notepadqq-notepad-for-linux/
|
||||
[15]:http://itsfoss.com/scite-the-notepad-for-linux/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.04即将整合Linux内核3.19分支
|
||||
----
|
||||
*Ubuntu已经开始整合一个新的内核分支*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Linux内核是一个发行版中最重要的组成部分,Ubuntu用户很想知道哪个版本将用于预计几个月后就会发布的15.04分支的稳定版中。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu和Linux内核开发周期并不同步,所以很难预测最终哪个版本将应用在Ubuntu 15.04中。目前,Ubuntu 15.04(长尾黑颚猴)使用的是Linux内核3.18,但是开发者们已经准备应用3.19分支了。
|
||||
|
||||
“我们的Vivid的内核仍然基于v3.18.2的上游稳定内核,但是我们很快将重新基于v3.18.3内核开发。我们也将把我们的非稳定版分支的基础变更到v3.19-rc5,然后上传到我们的团队PPA。”Canonical的Joseph Salisbury[说](1)。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux内核3.19仍然处于开发阶段,预计还要几个星期才会出稳定版本,但是有充足的时间将它加入到Ubuntu中并测试。但是不可能等到3.20分支了,举个例子,即使它能在4月23日前发布。
|
||||
|
||||
你现在就可以从Softpedia[下载Ubuntu 15.04](2),试用一下。这是一个每日构建版本,会包含发行版中目前已经做出的所有改善。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://linux.softpedia.com/blog/Ubuntu-15-04-to-Integrate-Linux-Kernel-3-19-Branch-Soon-471121.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文发布时间:25 Jan 2015, 20:39 GMT
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:https://lists.ubuntu.com/archives/ubuntu-devel/2015-January/038644.html
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.softpedia.com/get/Linux-Distributions/Ubuntu-Vivid-Vervet-103651.shtml
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
Android 中的 Wi-Fi 直连方式的 Bug 会导致拒绝服务
|
||||
----
|
||||
|
||||
*Google标记这个问题为低严重性,并不急着修复*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Android处理Wi-Fi直连连接的方式中的一个漏洞可以导致在搜索连接节点的时候所连接的设备重启,这个节点可能是其他手机,摄像头,游戏设备,电脑或是打印机等任何设备。
|
||||
|
||||
Wi-Fi直连技术允许无线设备之间直接建立通信,而不用加入到本地网络中。
|
||||
|
||||
###安全公司致力于协调修复这个问题
|
||||
|
||||
这个漏洞允许攻击者发送一个特定的修改过的802.11侦测响应帧给设备,从而因为WiFi监控类中的一个未处理的异常导致设备重启。
|
||||
|
||||
Core Security通过自己的CoreLabs团队发现了这个瑕疵(CVE-2014-0997),早在2014年9月就汇报给了Google。Google确认了这个问题,却把它列为低严重性,并不提供修复时间表。
|
||||
|
||||
每次Core Security联系Android安全组要求提供修复时间表的时候都会收到同样的答复。最后一次答复是1月20日,意味着这么长的时间中都没有补丁。在星期一的时候,这家安全公司公布了他们的发现。
|
||||
|
||||
这家安全公司建立了一个[概念攻击][1]来展示他们研究结果的有效性。
|
||||
|
||||
根据这个漏洞的技术细节,一些Android设备在收到一个错误的wpa_supplicant事件后可能会进入拒绝服务状态,这些事件让无线驱动和Android平台框架之间的接口有效。
|
||||
|
||||
###Google并不着急解决这个问题
|
||||
|
||||
Android安全组对于这个问题的放松态度可能是基于这个原因:这种拒绝服务状态只发生在扫描节点这一小段时间。
|
||||
|
||||
不仅如此,实际上结果也并不严重,因为它会导致设备重启。不存在数据泄漏的风险或是能引起这个问题的攻击,不会吸引攻击者。但另一方面,不管怎样都应该提供一个补丁,以减轻任何未来的潜在风险。
|
||||
|
||||
Core Security声称在Android 5.0.1及以上版本中没有测试到这个问题,他们发现的受影响的设备有Android系统4.4.4的Nexus 5和4,运行Android 4.2.2的LG D806和Samsung SM-T310,以及4.1.2版本系统的Motorola RAZR HD。
|
||||
|
||||
目前,减轻影响的方式是尽量不用Wi-Fi直连,或者升级到没有漏洞的Android版本。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Bug-In-Wi-Fi-Direct-Android-Implementation-Causes-Denial-of-Service-471299.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文发布时间:27 Jan 2015, 09:11 GMT
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ionut Ilascu][a]
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/ionut-ilascu
|
||||
[1]:http://www.coresecurity.com/advisories/android-wifi-direct-denial-service
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
|
||||
在CentOS 7中安装Jetty服务器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[Jetty][1] 是一款纯Java的HTTP **(Web) 服务器**和Java Servlet容器。 通常在更大的网络框架中,Jetty经常用于设备间的通信。但是其他Web服务器通常给人类传递文件。Jetty是一个Eclipse基金中免费开源项目。这个Web服务器用于如Apache ActiveMQ、 Alfresco、 Apache Geronimo、 Apache Maven、 Apache Spark、Google App Engine、 Eclipse、 FUSE、 Twitter的 Streaming API 和 Zimbra中。
|
||||
[Jetty][1] 是一款纯Java的HTTP **(Web) 服务器**和Java Servlet容器。 通常在更大的网络框架中,Jetty经常用于设备间的通信,而其他Web服务器通常给“人类”传递文件 :D。Jetty是一个Eclipse基金会的免费开源项目。这个Web服务器用于如Apache ActiveMQ、 Alfresco、 Apache Geronimo、 Apache Maven、 Apache Spark、Google App Engine、 Eclipse、 FUSE、 Twitter的 Streaming API 和 Zimbra中。
|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章会解释‘如何在CentOS服务器中安装Jetty服务器’。
|
||||
这篇文章会介绍‘如何在CentOS服务器中安装Jetty服务器’。
|
||||
|
||||
**首先我们要用下面的命令安装JDK:**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -58,7 +58,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
完成了!
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以在 **http://<youripaddress>:8080** 中访问了
|
||||
现在你可以在 **http://\<你的 IP 地址>:8080** 中访问了
|
||||
|
||||
就是这样。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -70,7 +70,7 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/install-jetty-web-server-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jijo][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ Developed in part by two ex-Rackspace engineers, [CoreOS][8] is a lightweight Li
|
||||
CoreOS was quickly adopted by many cloud providers, including Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services, DigitalOcean and Google Compute Engine.
|
||||
|
||||
Like CoreOS, Ubuntu Core offers an expedited process for updating components, reducing the amount of time that an administrator would need to manually manage them.
|
||||
|
||||
如同Coreos一样,Ubuntu内核提供了一个快速引擎来更新组件
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.infoworld.com/article/2860401/cloud-computing/google-cloud-offers-streamlined-ubuntu-for-docker-use.html
|
||||
@ -40,4 +40,4 @@ via: http://www.infoworld.com/article/2860401/cloud-computing/google-cloud-offer
|
||||
[5]:http://www.itworld.com/article/2695383/open-source-tools/docker-all-geared-up-for-the-enterprise.html
|
||||
[6]:http://www.itworld.com/article/2695501/cloud-computing/google-unleashes-docker-management-tools.html
|
||||
[7]:http://www.itworld.com/article/2696116/open-source-tools/coreos-linux-does-away-with-the-upgrade-cycle.html
|
||||
[8]:https://coreos.com/using-coreos/
|
||||
[8]:https://coreos.com/using-coreos/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.04 to Integrate Linux Kernel 3.19 Branch Soon
|
||||
----
|
||||
*A new kernel branch is being tracked by Ubuntu*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#The Linux kernel is one of the most important components in a distribution and Ubuntu users are interested to know what will be used in the stable edition for the 15.04 branch, which is scheduled to arrive in a couple of months.
|
||||
|
||||
The Ubuntu and the Linux kernel development cycles are not in sync and it's hard to anticipate what version will eventually land in Ubuntu 15.04. For now, Ubuntu 15.04 (Vivid Vervet) is using Linux kernel 3.18, but the developers are already looking to implement the 3.19 branch.
|
||||
|
||||
"Our Vivid kernel remains based on the v3.18.2 upstream stable kernel, but we'll be rebasing to v3.18.3 shortly. We'll also be re-basing our unstable branch to v3.19-rc5 and get that uploaded to our team PPA soon," [said](1) Canonical's Joseph Salisbury.
|
||||
|
||||
Linux kernel 3.19 is still under development and it will take a few weeks to see a stable version, but it's enough time to implement it in Ubuntu and test it properly. It won't be possible to get the 3.20 branch, for example, even if it launches before the April 23.
|
||||
|
||||
You can [download Ubuntu 15.04](2) right now from Softpedia and give it a spin. It's a daily build and it contains all the improvements made so far to the distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Data-of-20-Million-Users-Stolen-from-Dating-Website-471179.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文发布时间:25 Jan 2015, 20:39 GMT
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:https://lists.ubuntu.com/archives/ubuntu-devel/2015-January/038644.html
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.softpedia.com/get/Linux-Distributions/Ubuntu-Vivid-Vervet-103651.shtml
|
||||
@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Bug in Wi-Fi Direct Android Implementation Causes Denial of Service
|
||||
----
|
||||
*Google marks the issue as having low severity, is not in a hurry to fix it*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#A vulnerability in the way Android handles Wi-Fi Direct connections leads to rebooting the device when searching for peers to connect to, which can be anything from other phones, cameras, gaming devices, computers, or printers.
|
||||
|
||||
The Wi-Fi Direct technology allows devices capable of wireless connection to establish communication directly, without the need to join a local network.
|
||||
|
||||
##Security company insisted on proper coordination for a fix
|
||||
|
||||
The vulnerability allows an attacker to send a specially crafted 802.11 Probe Response frame to the device and crashes it due to an unhandled exception occurring on the WiFi monitoring class.
|
||||
|
||||
Core Security discovered the flaw (CVE-2014-0997) through its CoreLabs team, and reported it to Google back in September 2014. The vendor acknowledged it but classified the glitch as having low severity, with no timeline for a fix being provided.
|
||||
|
||||
The same answer was received by Core Security each time they contacted the Android security team to inform of a timeframe for rolling out a fix. The last reply of this kind was received on January 20, meaning that there is no patch for the time being. On Monday, the security company made their findings public.
|
||||
|
||||
The security company created a (proof-of-concept)[1] to demonstrate the validity of the results obtained during their research.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the technical details of the vulnerability, some Android devices can be induced a denial-of-service condition if they receive a malformed wpa_supplicant event, which makes available the interface between the wireless driver and the Android platform framework.
|
||||
|
||||
##Google is not in a hurry to eliminate the problem
|
||||
|
||||
The relaxed stance from the Android security team regarding the issue may be on account of the fact that denial-of-service condition occurs only for a short period of time, when scanning for peers.
|
||||
|
||||
More than this, the result is not severe in nature as it consists in rebooting the device. There is no risk of data exfiltration or an attack that could lead to this, which would make it unappealing to a threat actor. On the other hand, a patch should be provided regardless, in order to mitigate any potential future risks.
|
||||
|
||||
Core Security says that the issue was not detected on Android 5.0.1 and above, and among the devices affected they found Nexus 5 and 4 running version 4.4.4 of the mobile operating system, LG D806 and Samsung SM-T310 with Android 4.2.2, and Motorola RAZR HD with build 4.1.2 of the OS.
|
||||
|
||||
For the time being, mitigation consists in refraining from using Wi-Fi Direct or updating to a non-vulnerable version of Android.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Bug-In-Wi-Fi-Direct-Android-Implementation-Causes-Denial-of-Service-471299.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文发布时间:27 Jan 2015, 09:11 GMT
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ionut Ilascu][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/ionut-ilascu
|
||||
[1]:http://www.coresecurity.com/advisories/android-wifi-direct-denial-service
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
LibreOffice 4.4 Released as the Most Beautiful LibreOffice Ever
|
||||
----
|
||||
*The developer has made a lot of UI improvements*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The Document Foundation has just announced that a new major update has been released for LibreOffice and it brings important UI improvements, enough for them to call this the most beautiful version ever.
|
||||
|
||||
The Document Foundation doesn't usually make the UI the main focus of an update, but now the developers are saying that this is the most beautiful release made so far and that says a lot. Fortunately, this version is not just about interface fixes and there are plenty of other major improvements that should really provide a very good reason to get LibreOffice 4.4.
|
||||
|
||||
LibreOffice has been gaining quite a lot of fans and users, and the past couple of years have been very successful. The office suite is implemented by default in most of the important Linux distributions out there and it was adopted by numerous administrations and companies across the world. LibreOffice is proving to be a difficult adversary for Microsoft's Office and each new version makes it even better.
|
||||
LibreOffice 4.4 brings a lot of new features
|
||||
|
||||
If we move aside all the improvements made to the interface, we're still left with a ton of fixes and changes. The Document Foundation takes its job very seriously and all upgrades really improve the users' experience tremendously.
|
||||
|
||||
"LibreOffice 4.4 has got a lot of UX and design love, and in my opinion is the most beautiful ever. We have completed the dialog conversion, redesigned menu bars, context menus, toolbars, status bars and rulers to make them much more useful. The Sifr monochrome icon theme is extended and now the default on OS X. We also developed a new Color Selector, improved the Sidebar to integrate more smoothly with menus, and reworked many user interface details to follow today’s UX trends," [says Jan "Kendy" Holesovsky](1), a member of the Membership Committee and the leader of the design team.
|
||||
|
||||
Some of the other improvements include much better support for OOXML file formats, the source code has been "groomed" and cleaned after a Coverity Scan analysis, digital signatures for exported PDF files, improved import filters for Microsoft Visio, Microsoft Publisher and AbiWord files, and Microsoft Works spreadsheets, and much more.
|
||||
|
||||
For now, the PPA doesn't have the latest version, but that should change soon. For the time being, you can download the [LibreOffice 4.4](2) source packages from Softpedia, if you want to compile them yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://news.softpedia.com/news/LibreOffice-4-4-Releases-As-the-Most-Beautiful-LibreOffice-Ever-471575.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文发布时间:29 Jan 2015, 14:16 GMT
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://blog.documentfoundation.org/2015/01/29/libreoffice-4-4-the-most-beautiful-libreoffice-ever/
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.softpedia.com/get/Office/Office-Suites/LibreOffice-60713.shtml
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
OpenJDK 7 Vulnerabilities Closed in Ubuntu 14.04 and Ubuntu 14.10
|
||||
----
|
||||
*Users have been advised to upgrade as soon as possible*
|
||||
|
||||
##Canonical published details about a new OpenJDK 7 version has been pushed to the Ubuntu 14.04 LTS and Ubuntu 14.10 repositories. This update fixes a number of problems and various vulnerabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
The Ubuntu maintainers have upgraded the OpenJDK packages in the repositories and numerous fixes have been implemented. This is an important update and it covers a few libraries.
|
||||
|
||||
"Several vulnerabilities were discovered in the OpenJDK JRE related to information disclosure, data integrity and availability. An attacker could
|
||||
exploit these to cause a denial of service or expose sensitive data over the network,” reads the security notice.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, "a vulnerability was discovered in the OpenJDK JRE related to information disclosure and integrity. An attacker could exploit this to
|
||||
expose sensitive data over the network."
|
||||
|
||||
These are just a couple of the vulnerabilities identified and corrected by the developer and implemented by the maintainers/., and for a more detailed description of the problems, you can see Canonical's security notification. Users have been advised to upgrade their systems as soon as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
The flaws can be fixed if you upgrade your system to the latest openjdk-7-related packages specific to each distribution. To apply the patch, users will have to run the Update Manager application. In general, a standard system update will make all the necessary changes. All Java-related applications will have to be restarted.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://linux.softpedia.com/blog/OpenJDK-7-Vulnerabilities-Closed-in-Ubuntu-14-04-and-Ubuntu-14-10-471605.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文发布时间:29 Jan 2015, 16:53 GMT
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
WordPress Can Be Used to Leverage Critical Ghost Flaw in Linux
|
||||
-----
|
||||
*Users are advised to apply available patches immediately*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**The vulnerability revealed this week by security researchers at Qualys, who dubbed it [Ghost](1), could be taken advantage of through WordPress or other PHP applications to compromise web servers.**
|
||||
|
||||
The glitch is a buffer overflow that can be triggered by an attacker to gain command execution privileges on a Linux machine. It is present in the glibc’s “__nss_hostname_digits_dots()” function that can be used by the “gethostbyname()” function.
|
||||
|
||||
##PHP applications can be used to exploit the glitch
|
||||
|
||||
Marc-Alexandre Montpas at Sucuri says that the problem is significant because these functions are used in plenty of software and server-level mechanism.
|
||||
|
||||
“An example of where this could be a big issue is within WordPress itself: it uses a function named wp_http_validate_url() to validate every pingback’s post URL,” which is carried out through the “gethostbyname()” function wrapper used by PHP applications, he writes in a blog post on Wednesday.
|
||||
|
||||
An attacker could use this method to introduce a malicious URL designed to trigger the vulnerability on the server side and thus obtain access to the machine.
|
||||
|
||||
In fact, security researchers at Trustwave created [proof-of-concept](2) code that would cause the buffer overflow using the pingback feature in WordPress.
|
||||
|
||||
##Multiple Linux distributions are affected
|
||||
|
||||
Ghost is present in glibc versions up to 2.17, which was made available in May 21, 2013. The latest version of glibc is 2.20, available since September 2014.
|
||||
|
||||
However, at that time it was not promoted as a security fix and was not included in many Linux distributions, those offering long-term support (LTS) in particular.
|
||||
|
||||
Among the impacted operating systems are Debian 7 (wheezy), Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and 7, CentOS 6 and 7, Ubuntu 12.04. Luckily, Linux vendors have started to distribute updates with the fix that mitigates the risk. Users are advised to waste no time downloading and applying them.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to demonstrate the flaw, Qualys has created an exploit that allowed them remote code execution through the Exim email server. The security company said that it would not release the exploit until the glitch reached its half-life, meaning that the number of the affected systems has been reduced by 50%.
|
||||
|
||||
Vulnerable application in Linux are clockdiff, ping and arping (under certain conditions), procmail, pppd, and Exim mail server.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://news.softpedia.com/news/WordPress-Can-Be-Used-to-Leverage-Critical-Ghost-Flaw-in-Linux-471730.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文发布时间:30 Jan 2015, 17:36 GMT
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ionut Ilascu][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/ionut-ilascu
|
||||
[1]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Linux-Systems-Affected-by-14-year-old-Vulnerability-in-Core-Component-471428.shtml
|
||||
[2]:http://blog.spiderlabs.com/2015/01/ghost-gethostbyname-heap-overflow-in-glibc-cve-2015-0235.html
|
||||
38
sources/news/20150202 The Pirate Bay Is Now Back Online.md
Normal file
38
sources/news/20150202 The Pirate Bay Is Now Back Online.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
The Pirate Bay Is Now Back Online
|
||||
------
|
||||
*The website was closed for about seven weeks*
|
||||

|
||||
##After being [raided](1) by the police almost two months ago, (in)famous torrent website The Pirate Bay is now back online. Those who thought the website will never return will be either disappointed or happy given that The Pirate Bay seems to live once again.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to celebrate its coming back, The Pirate Bay admins have posted a Phoenix bird on the front page, which signifies the fact that the website can't be killed only damaged.
|
||||
|
||||
About two weeks after The Pirate Bay was raided the domain miraculously came back to life. Soon after a countdown appeared on the temporary homepage of The Pirate Bay indicating that the website is almost ready for a comeback.
|
||||
|
||||
The countdown hinted to February 1, as the possible date for The Pirate Bay's comeback, but it looks like those who manage the website manage to pull it out one day earlier.
|
||||
|
||||
Beginning today, those who have accounts on The Pirate Bay can start downloading the torrents they want. Other than the Phoenix on the front page there are no other messages that might point to the resurrection The Pirate Bay except for the fact that it's now operational.
|
||||
|
||||
Admins of the website said a few weeks ago they will find ways to manage and optimize The Pirate Bay, so that there will be minimal chances for the website to be closed once again. Let's see how it lasts this time.
|
||||
|
||||
##Another version of The Pirate Bay may be launched soon
|
||||
|
||||
In related news, one of the members of the original staff was dissatisfied with the decisions made by the majority regarding some of the changes made in the way admins interact with the website.
|
||||
|
||||
He told [Torrentfreak](2) earlier this week that he, along with a few others, will open his version of The Pirate Bay, which they claim will be the "real" one.
|
||||
|
||||
------
|
||||
via:http://news.softpedia.com/news/The-Pirate-Bay-Is-Now-Back-Online-471802.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文发布时间:31 Jan 2015, 22:49 GMT
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Cosmin Vasile][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/cosmin-vasile
|
||||
[1]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/The-Pirate-Bay-Is-Down-December-9-2014-466987.shtml
|
||||
[2]:http://torrentfreak.com/pirate-bay-back-online-150131/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
|
||||
Debian Forked over systemd: Birth of Devuan GNU/Linux Distribution
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Debian GNU/Linux distribution is one of the oldest Linux distribution that is currently in working state. init used to be the default central management and configuration platform for Linux operating system before systemd emerged. Systemd from the date of its release has been very much controversial.
|
||||
|
||||
Sooner or later it has replaced init on most of the Linux distribution. Debian remained no exception and Debian 8 codename JESSIE will be having systemd by default. The Debian adaptation of systemd in replacement of init caused polarization. This led to forking of Debian and hence Devuan GNU/Linux distribution born.
|
||||
|
||||
Devuan project started with the primary goal to put back nit and remove controversial systemd. A lot of Linux Distribution are based on Debian or a derivative of Debian and one does not simply fork Debian. Debian will always attract developers.
|
||||
|
||||
### What Devuan is all About? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Devuan in Italian (pronounced Devone in English) suggests “Don’t panic and keep forking Debian”, for Init-Freedom lovers. Developers see Devuan as the beginning of a process which aims at base distribution and is able to protect the freedom of developers and community.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Debian Forked over systemd: Birth of Devuan Linux
|
||||
|
||||
Devuan project priority includes – interoperability, diversity and backward compatibility. It will derive its own installer and repos from Debian and modify where ever required. If everything works smooth by the mid of 2015 users can switch to Devuan from Debian 7 and start using devuan repos.
|
||||
|
||||
The process of switching will fairly remain as simple as upgrading a Debian installation. The project will be as minimal as possible and completely in accordance of UNIX philosophy – “Doing one thing and doing it well”. The targeted users of Devuan will be System Admins, Developers and users having experience of Debian.
|
||||
|
||||
The project started by italian developers has raised a fund of 4.5k€ (EUR) in the year 2014. They have moved distro infrastructure from GitHub to GitLab, progress on Loginkit (systemd Logind replaced), discussing Logo and other important aspects useful in long run.
|
||||
|
||||
A few of the Logos are in discussion now are shown in the picture.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Devuan Logo Proposals
|
||||
|
||||
Have a look at them here at: [http://without-systemd.org/wiki/index.php/Category:Logo][1]
|
||||
|
||||
The unrest over systemd that gave birth to Devuan is good or bad? Lets have a look.
|
||||
|
||||
### Is Devuan fork a good thing? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Well! difficult to answer that forking such a huge distro is really going to be of any good. A (group of) developer(s) who initially were working with Debian got unsatisfied with systemd and forked it.
|
||||
|
||||
Now the actual number of developers working on Debian/Systemd decreased which is going to affect the productivity of both the projects. Now the same number of developers are working on two different projects.
|
||||
|
||||
What you think would be the fate of Devuan as well as Debian project? Won’t it hinder the progress of either distro and Linux in the long run?
|
||||
|
||||
Please give your [comments][2] about Devuan project.
|
||||
|
||||
注:如果可以在发布文章的时候发布一个调查,就把下面这段发成一个调查,如果不行,就直接嵌入js代码
|
||||
|
||||
<script type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8" src="http://static.polldaddy.com/p/8629256.js"></script>
|
||||
|
||||
Do you think systemd for Debian is
|
||||
|
||||
Good
|
||||
Bad
|
||||
Don't Know
|
||||
Don't Care
|
||||
Other:
|
||||
|
||||
VoteView ResultsPolldaddy.com
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Do you really feel that Debian with systemd will have a bad fate as depicted below**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Strip SystmeD
|
||||
|
||||
Time to wait for Devuan 1.0 and lets see what it could contain.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
All the major Linux Distributions Like Fedora, RedHat, openSUSE, SUSE Enterprise, Arch, Megia have already switched to Systemd, Ubuntu and Debian are in the way to replace init with systemd. Only Gentoo and Slack till date have shown no interest in systemd but who knows someday even Gentoo and slack too started moving in the same direction.
|
||||
|
||||
The reputation of Debian as a Linux Distro is something very few have reached the mark. It is blessed by some hundreds of developers and millions of users. The actual question is what percentage of users and developers were not comfortable with systemd. If the percentage is really high then what led debian to switch to systemd. Had it moved against the wishes of its users and developers. If this is the case the chance of success of devuan is pretty fair. Well how many developers put long hours of code punching for the project.
|
||||
|
||||
Hope the fate of this project will not be something like those distros which once was started with high degree of passion and enthusiasm and later the developers got uninterested.
|
||||
|
||||
Post Script : Linus Torvalds do not mind systemd that much.
|
||||
|
||||
**If you need Devuan, then join and support it now!**
|
||||
|
||||
Development : [https://git.devuan.org][3]
|
||||
Donations : [https://devuan.org/donate.html][4]
|
||||
Discussions : [https://mailinglists.dyne.org/cgi-bin/mailman/listinfo/dng][5]
|
||||
Devuan Developers : onelove@devuan.org
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/debian-forked-over-systemd-birth-of-devuan-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://without-systemd.org/wiki/index.php/Category:Logo
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/debian-forked-over-systemd-birth-of-devuan-linux/#comments
|
||||
[3]:https://git.devuan.org/
|
||||
[4]:https://devuan.org/donate.html
|
||||
[5]:https://mailinglists.dyne.org/cgi-bin/mailman/listinfo/dng
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
BQ and Canonical Officially Launch Aquaris E4.5 Ubuntu Edition, the First Ubuntu Phone
|
||||
------
|
||||
*Everything you need to know about Aquaris E4.5*
|
||||
|
||||
##BQ and Canonical have officially announced the new Aquaris E4.5 Ubuntu Edition and the fact that the phone will be available in the coming weeks through a series of flash sales.
|
||||
|
||||
Information about the imminent launch of BQ Ubuntu phone has been around for some time and now it the two companies seem to have decided to make it official. This is the first device powered by Ubuntu Touch and a lot of people will be paying very close attention to what is happening in the mobile world.
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Touch is the latest operating system from Canonical and it's a brand new experience that aims to be very different from what users can find right now on the market, and that includes systems like Jola or Firefox OS. The OS has been in the works for more than two years and it's a system designed to work on all kind of devices, across the hardware spectrum.
|
||||
|
||||
##Who is BQ and why has Canonical chosen them?
|
||||
|
||||
When Mark Shuttleworth announced the two partners for the launch of Ubuntu Touch, BQ and Meizu, most of the people watching asked the same question. Who? BQ is not a very big company, but it's a young company and it has already started to penetrate the European market with some interesting devices. In many ways, they are doing the same thing companies like Meizu or Xiaomi are trying and succeeded in China: to offer devices that are interesting and different from what everyone else is doing.
|
||||
|
||||
Many Ubuntu fans have questioned Canonical’s decision of choosing small companies and not big ones, but they are trying to do the same thing as the just-mentioned hardware makers. They want to offer an operating system radically different from what everyone else is doing. It's easy to understand why the goals of Canonical and BQ are actually one and the same.
|
||||
|
||||
##What is Ubuntu Touch?
|
||||
|
||||
The new operating system developed by Canonical embraces the fact that people are now swiping a lot more than they are tapping. Smartphones are no longer something new and everyone can understand how to swipe and get things done on a phone. Ubuntu devs have taken this to a whole new level. The operating system has no buttons, with the exception of the regular power and volume buttons. Everything is done with swiped gestures, from all sides of the screen.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, Ubuntu Touch brings a new concept to the market, that of scopes. There is no longer a home screen, just scopes defined by the user to expand the experience. For example, you can have a Music scope that aggregates all your music sources on a single screen. It's a different way of looking at your smartphone, but this is built for people who crave a new experience. Don't worry, regular apps still exist, but they are differently integrated.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
"As any kind of content can be presented via Scopes - they provide developers an easy path for their creations to be integral to the device experience. It is simple to create new Scopes via an easy to use UI toolkit with much lower development and maintenance costs than traditional apps. Canonical and BQ have worked with a host of partners to ensure that there is a wealth of interesting, relevant and dynamic content available at launch, with more content partners to follow," said Cristian Parrino, VP Mobile at Canonical.
|
||||
|
||||
##BQ’s Aquaris E4.5 Ubuntu Edition hardware specs
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, it's important to know that Aquaris E4.5 Ubuntu Edition is a dual-sim phone and it comes unlocked so that everyone can use it with their network. It boasts a MediaTek Quad-Core Cortex A7 processor running at up to 1.3 GHz, a 4.5-inch screen, 1GB RAM, rear camera with high-quality BSI sensors, Largan lens, and autofocus with dual flash(8MP), and front camera with 5MP.
|
||||
|
||||
It's also worth mentioning that several operators in Europe, including 3 Sweden, amena.com, giffgaff, and Portugal Telecom have decided to provide SIM bundles at purchase. The price is €169.90 ($191).
|
||||
|
||||
So, are you ready to buy the Aquaris E4.5 Ubuntu Edition?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/BQ-and-Canonical-Officially-Launch-Aquaris-E4-5-Ubuntu-Edition-472397.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
|
||||
What is a good EPUB reader on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
If the habit on reading books on electronic tablets is still on its way, reading books on a computer is even rarer. It is hard enough to focus on the classics of the 16th century literature, so who needs the Facebook chat pop up sound in the background in addition? But if for some reasons you wish to open an electronic book in your computer, chances are that you will need specific software. Indeed, most editors agreed with using the EPUB format for electronic books (for "Electronic PUBlication"). Hopefully, Linux is not deprived of good programs capable of dealing with such format. In short, here is a non-exhaustive list of good EPUB readers on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Calibre ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Let's dive in with maybe the biggest name of that list: [Calibre][1]. More than just an ebook reader, Calibre is a fully packaged e-library. It supports a plethora of formats (almost every I can think of), integrates a reader, a manager, a meta-data editor which can download covers from the Internet, an EPUB editor, a news reader, and a search engine to download additional books. To top it all, the interface is slick and has nothing to envy to other professional software. The only potential downside is that if you are looking for an EPUB reader, and are not interested in the whole library manager aspect, the program is too heavy for your needs.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. FBReader ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[FBReader][2] is also a library manager, but in a lighter way than Calibre. The interface is more sober, and is clearly cut in two: (1) the library aspect where you can add files, edit the meta-data, or download new books, and (2) the reader aspect. If you like simplicity, you might enjoy this program. I personally appreciate its straightforward tag and series system for classifying books.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Cool Reader ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For all of you who are just looking for a way to visualize the content of an EPUB file, I recommend [Cool Reader][5]. In the spirit of Linux applications which do only one thing and do it well, Cool Reader is optimized to just open an EPUB file, and navigate through it via handy shortcuts. And since it is based on Qt, it also follows Qt's mentality by giving a ton of settings to mess around with.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Okular ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Since we were talking about Qt applications, one of KDE's main document viewer, [Okular][3], also has the capacity to view EPUB files, once an EPUB library has been installed on the system. However, this is probably not a very good option if you are not a KDE user.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. pPub ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[pPub][4] is an old project that you can still find on Github. Its latest change seems to have been made two years ago. However, pPub is one of those programs that really deserve a second life. Written in Python and based on GTK3 and WebKit, pPub is lightweight and intuitive. The interface probably needs a little updating and is beyond sober, but the core is very good. It even supports JavaScript. So please, someone kick that up again.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. epub ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If all you need is a quick and easy way to check the content of an EPUB file, without caring about any fancy GUI, maybe an EPUB reader with command line interface might just do. [epub][6] is a minimalistic EPUB reader written in Python, which allows you to read an EPUB file in a terminal environment. You can switch between chapter/TOC views, up/down a page, and nothing more. This is as simple as any EPUB reader can possibly get.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Sigil ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Finally, last of the list is not actually an EPUB reader, but more of a standalone editor. [Sigil][7] is able to extract the content of an EPUB file, and break it down for what it really is: xhtml text, images, styles, and sometimes audio. The interface is a lot more complex than the one for a basic reader, but remains clear and well thought, on par with the features it provides. I particularly appreciate the tab system. If you are familiar with editing web pages, you will be in know territory here.
|
||||
|
||||
To conclude, there are a lot of open source EPUB readers out there. Some do nothing more, while others go way beyond that. As usual, I recommend using the one that makes the most sense for you to use. If you know more good EPUB readers on Linux that you like, please let us know in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/good-epub-reader-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrien Brochard][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/adrien
|
||||
[1]:http://calibre-ebook.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://fbreader.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://okular.kde.org/
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/sakisds/pPub
|
||||
[5]:http://crengine.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[6]:https://github.com/rupa/epub
|
||||
[7]:https://github.com/user-none/Sigil
|
||||
@ -1,111 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Best GNOME Shell Themes For Ubuntu 14.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Themes are the best way to customize your Linux desktop. If you [install GNOME on Ubuntu 14.04][1] or 14.10, you might want to change the default theme and give it a different look. To help you in this task, I have compiled here a **list of best GNOME shell themes for Ubuntu** or any other Linux OS that has GNOME shell installed on it. But before we see the list, let’s first see how to change install new themes in GNOME Shell.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install themes in GNOME Shell ###
|
||||
|
||||
To install new themes in GNOME with Ubuntu, you can use Gnome Tweak Tool which is available in software repository in Ubuntu. Open a terminal and use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gnome-tweak-tool
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can use themes by putting them in ~/.themes directory. I have written a detailed tutorial on [how to install and use themes in GNOME Shell][2], in case you need it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Best GNOME Shell themes ###
|
||||
|
||||
The themes listed here are tested on GNOME Shell 3.10.4 but it should work for all version of GNOME 3 and higher. For the sake of mentioning, the themes are not in any kind of priority order. Let’s have a look at the best GNOME themes:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Numix ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
No list can be completed without the mention of [Numix themes][3]. These themes got so popular that it encouraged [Numix team to work on a new Linux OS, Ozon][4]. Considering their design work with Numix theme, it won’t be exaggeration to call it one of the [most beautiful Linux OS][5] releasing in near future.
|
||||
|
||||
To install Numix theme in Ubuntu based distributions, use the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:numix/ppa
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install numix-icon-theme-circle
|
||||
|
||||
#### Elegance Colors ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Another beautiful theme from Satyajit Sahoo, who is also a member of Numix team. [Elegance Colors][6] has its own PPA so that you can easily install it:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:satyajit-happy/themes
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gnome-shell-theme-elegance-colors
|
||||
|
||||
#### Moka ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Moka][7] is another mesmerizing theme that is always included in the list of beautiful themes. Designed by the same developer who gave us Unity Tweak Tool, Moka is a must try:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:moka/stable
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install moka-gnome-shell-theme
|
||||
|
||||
#### Viva ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Based on Gnome’s default Adwaita theme, Viva is a nice theme with shades of black and oranges. You can download Viva from the link below.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Viva GNOME Shell Theme][8]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ciliora-Prima ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Previously known as Zukitwo Dark, Ciliora-Prima has square icons theme. Theme is available in three versions that are slightly different from each other. You can download it from the link below.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Ciliora-Prima GNOME Shell Theme][9]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Faience ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Faience has been a popular theme for quite some time and rightly so. You can install Faience using the PPA below for GNOME 3.10 and higher.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:tiheum/equinox
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install faience-theme
|
||||
|
||||
#### Paper [Incomplete] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ever since Google talked about Material Design, people have been going gaga over it. Paper GTK theme, by Sam Hewitt (of Moka Project), is inspired by Google Material design and currently under development. Which means you will not have the best experience with Paper at the moment. But if your a bit experimental, like me, you can definitely give it a try.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:snwh/pulp
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install paper-gtk-theme
|
||||
|
||||
That concludes my list. If you are trying to give a different look to your Ubuntu, you should also try the list of [best icon themes for Ubuntu 14.04][10].
|
||||
|
||||
How do you find this list of **best GNOME Shell themes**? Which one is your favorite among the one listed here? And if it’s not listed here, do let us know which theme you think is the best GNOME Shell theme.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/gnome-shell-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-install-gnome-in-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/install-switch-themes-gnome-shell/
|
||||
[3]:https://numixproject.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/numix-linux-distribution/
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/new-beautiful-linux-2015/
|
||||
[6]:http://satya164.deviantart.com/art/Gnome-Shell-Elegance-Colors-305966388
|
||||
[7]:http://mokaproject.com/
|
||||
[8]:https://github.com/vivaeltopo/gnome-shell-theme-viva
|
||||
[9]:http://zagortenay333.deviantart.com/art/Ciliora-Prima-Shell-451947568
|
||||
[10]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
|
||||
su-kaiyao translating
|
||||
|
||||
4 Best Modern Open Source Code Editors For Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Looking for **best programming editors in Linux**? If you ask the old school Linux users, their answer would be Vi, Vim, Emacs, Nano etc. But I am not talking about them. I am going to talk about new age, cutting edge, great looking, sleek and yet powerful, feature rich **best open source code editors for Linux** that would enhance your programming experience.
|
||||
|
||||
### Best modern Open Source editors for Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
I use Ubuntu as my main desktop and hence I have provided installation instructions for Ubuntu based distributions. But this doesn’t make this list as **best text editors for Ubuntu** because the list is apt for any Linux distribution. Just to add, the list is not in any particular priority order.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Brackets ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Brackets][1] is an open source code editor from [Adobe][2]. Brackets focuses exclusively on the needs of web designers with built in support for HTML, CSS and Java Script. It’s light weight and yet powerful. It provides you with inline editing and live preview. There are plenty of plugins available to further enhance your experience with Brackets.
|
||||
|
||||
To [install Brackets in Ubuntu][3] and Ubuntu based distributions such as Linux Mint, you can use this unofficial PPA:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/brackets
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install brackets
|
||||
|
||||
For other Linux distributions, you can get the source code as well as binaries for Linux, OS X and Windows on its website.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Brackets Source Code and Binaries][5]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Atom ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Atom][5] is another modern and sleek looking open source editor for programmers. Atom is developed by Github and promoted as a “hackable text editor for the 21st century”. The looks of Atom resembles a lot like Sublime Text editor, a hugely popular but closed source text editors among programmers.
|
||||
|
||||
Atom has recently released .deb and .rpm packages so that one can easily install Atom in Debian and Fedora based Linux distributions. Of course, its source code is available as well.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Atom .deb][6]
|
||||
- [Download Atom .rpm][7]
|
||||
- [Get Atom source code][8]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Lime Text ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
So you like Sublime Text editor but you are not comfortable with the fact that it is not open source. No worries. We have an [open source clone of Sublime Text][9], called [Lime Text][10]. It is built on Go, HTML and QT. The reason behind cloning of Sublime Text is that there are numerous bugs in Sublime Text 2 and Sublime Text 3 is in beta since forever. There are no transparency in its development, on whether the bugs are being fixed or not.
|
||||
|
||||
So open source lovers, rejoice and get the source code of Lime Text from the link below:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Get Lime Text Source Code][11]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Light Table ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Flaunted as “the next generation code editor”, [Light Table][12] is another modern looking, feature rich open source editor which is more of an IDE than a mere text editor. There are numerous extensions available to enhance its capabilities. Inline evaluation is what you would love in it. You have to use it to believe how useful Light Table actually is.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Get Light Table Source Code][13]
|
||||
|
||||
### What’s your pick? ###
|
||||
|
||||
No, we are not limited to just four code editors in Linux. The list was about modern editors for programmers. Of course you have plenty of other options such as [Notepad++ alternative Notepadqq][14] or [SciTE][15] and many more. So, among these four, which one is your favorite code editor for Linux?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/best-modern-open-source-code-editors-for-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://brackets.io/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.adobe.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/install-brackets-ubuntu/
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/adobe/brackets/releases
|
||||
[5]:https://atom.io/
|
||||
[6]:https://atom.io/download/deb
|
||||
[7]:https://atom.io/download/rpm
|
||||
[8]:https://github.com/atom/atom/blob/master/docs/build-instructions/linux.md
|
||||
[9]:http://itsfoss.com/lime-text-open-source-alternative/
|
||||
[10]:http://limetext.org/
|
||||
[11]:https://github.com/limetext/lime
|
||||
[12]:http://lighttable.com/
|
||||
[13]:https://github.com/LightTable/LightTable
|
||||
[14]:http://itsfoss.com/notepadqq-notepad-for-linux/
|
||||
[15]:http://itsfoss.com/scite-the-notepad-for-linux/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
Translating by H-mudcup
|
||||
|
||||
Meet Vivaldi — A New Web Browser Built for Power Users
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,4 +59,4 @@ via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/01/vivaldi-web-browser-linux-download-power
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:https://vivaldi.com/#Download
|
||||
[1]:https://vivaldi.com/#Download
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,82 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[Translating by Stevearzh]
|
||||
Why Mac users don’t switch to Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux and Mac users share at least one common thing: they prefer not to use Windows. But after that the two groups part company and tend to go their separate ways. But why don’t more Mac users switch to Linux? Is there something that prevents Mac users from making the jump?
|
||||
|
||||
[Datamation took a look at these questions][1] and tried to answer them. Datamation’s conclusion was that it’s really about the applications and workflow, not the operating system:
|
||||
|
||||
> …there are some instances where replacing existing applications with new options isn’t terribly practical – both in workflow and in overall functionality. This is an area where, sadly, Apple has excelled in. So while it’s hardly “impossible” to get around these issues, they are definitely a large enough challenge that it will give the typical Mac enthusiast pause.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> But outside of Web developers, honestly, I don’t see Mac users “en masse,” seeking to disrupt their workflows for the mere idea of avoiding the upgrade to OS X Yosemite. Granted, having seen Yosemite up close – Mac users who are considered power users will absolutely find this change-up to be hideous. However, despite poor OS X UI changes, the core workflow for existing Mac users will remain largely unchanged and unchallenged.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> No, I believe Linux adoption will continue to be sporadic and random. Ever-growing, but not something that is easily measured or accurately calculated.
|
||||
|
||||
I agree to a certain extent with Datamation’s take on the importance of applications and workflows, both things are important and matter in the choice of a desktop operating system. But I think there’s something more going on with Mac users than just that. I believe that there’s a different mentality that exists between Linux and Mac users, and I think that’s the real reason why many Mac users don’t switch to Linux.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### It’s all about control for Linux users ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux users tend to want control over their computing experience, they want to be able to change things to make them the way that they want them. One simply cannot do that in the same way with OS X or any other Apple products. With Apple you get what they give you for the most part.
|
||||
|
||||
For Mac (and iOS) users this is fine, they seem mostly content to stay within Apple’s walled garden and live according to whatever standards and options Apple gives them. But this is totally unacceptable to most Linux users. People who move to Linux usually come from Windows, and it’s there that they develop their loathing for someone else trying to define or control their computing experiences.
|
||||
|
||||
And once someone like that has tasted the freedom that Linux offers, it’s almost impossible for them to want to go back to living under the thumb of Apple, Microsoft or anyone else. You’d have to pry Linux from their cold, dead fingers before they’d accept the computing experience created for them Apple or Microsoft.
|
||||
|
||||
But you won’t find that same determination to have control among most Mac users. For them it’s mostly about getting the most out of whatever Apple has done with OS X in its latest update. They tend to adjust fairly quickly to new versions of OS X and even when unhappy with Apple’s changes they seem content to continue living within Apple’s walled garden.
|
||||
|
||||
So the need for control is a huge difference between Mac and Linux users. I don’t see it as a problem though since it just reflects the reality of two very different attitudes toward using computers.
|
||||
|
||||
### Mac users need Apple’s support mechanisms ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux users are also different in the sense that they don’t mind getting their hands dirty by getting “under the hood” of their computers. Along with control comes the personal responsibility of making sure that their Linux systems work well and efficiently, and digging into the operating system is something that many Linux users have no problem doing.
|
||||
|
||||
When a Linux user needs to fix something, chances are they will attempt to do so immediately themselves. If that doesn’t work then they’ll seek additional information online from other Linux users and work through the problem until it has been resolved.
|
||||
|
||||
But Mac users are most likely not going to do that to the same extent. That is probably one of the reasons why Apple stores are so popular and why so many Mac users opt to buy Apple Care when they get a new Mac. A Mac user can simply take his or her computer to the Apple store and ask someone to fix it for them. There they can belly up to the Genius Bar and have their computer looked at by someone Apple has paid to fix it.
|
||||
|
||||
Most Linux users would blanche at the thought of doing such a thing. Who wants some guy you don’t even know to lay hands on your computer and start trying to fix it for you? Some Linux users would shudder at the very idea of such a thing happening.
|
||||
|
||||
So it would be hard for a Mac user to switch to Linux and suddenly be bereft of the support from Apple that he or she was used to getting in the past. Some Mac users might feel very vulnerable and uncertain if they were cut off from the Apple mothership in terms of support.
|
||||
|
||||
### Mac users love Apple’s hardware ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Datamation article focused on software, but I believe that hardware also matters to Mac users. Most Apple customers tend to love Apple’s hardware. When they buy a Mac, they aren’t just buying it for OS X. They are also buying Apple’s industrial design expertise and that can be an important differentiator for Mac users. Mac users are willing to pay more because they perceive that the overall value they are getting from Apple for a Mac is worth it.
|
||||
|
||||
Linux users, on the other hand, seem less concerned by such things. I think they tend to focus more on cost and less on the looks or design of their computer hardware. For them it’s probably about getting the most value from the hardware at the lowest cost. They aren’t in love with the way their computer hardware looks in the same way that some Mac users probably are, and so they don’t make buying decisions based on it.
|
||||
|
||||
I think both points of view on hardware are equally valid. It ultimately gets down to the needs of the individual user and what matters to them when they choose to buy or, in the case of some Linux users, build their computer. Value is the key for both groups, and each has its own perceptions of what constitutes real value in a computer.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course it is [possible to run Linux on a Mac][2], directly or indirectly via virtual machine. So a user that really liked Apple’s hardware does have the option of keeping their Mac but installing Linux on it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Too many Linux distros to choose from? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Another reason that might make it hard for a Mac user to move to Linux is the sheer number of distributions to choose from in the world of Linux. While most Linux users probably welcome the huge diversity of distros available, it could also be very confusing for a Mac user who hasn’t learned to navigate those choices.
|
||||
|
||||
Over time I think a Mac user would learn and adjust by figuring out which distribution worked best for him or her. But in the short term it might be a very daunting hurdle to overcome after being used to OS X for a long period of time. I don’t think it’s insurmountable, but it’s definitely something that is worth mentioning here.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course we do have helpful resources like [DistroWatch][3] and even my own [Desktop Linux Reviews][4] blog that can help people find the right Linux distribution. Plus there are many articles available about “the best Linux distro” and that sort of thing that Mac users can use as resources when trying to figure out the distribution they want to use.
|
||||
|
||||
But one of the reasons why Apple customers buy Macs is the simplicity and all-in-one solution that they offer in terms of the hardware and software being unified by Apple. So I am not sure how many Mac users would really want to spend the time trying to find the right Linux distribution. It might be something that puts them off really considering the switch to Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### Mac users are apples and Linux users are oranges ###
|
||||
|
||||
I see nothing wrong with Mac and Linux users going their separate ways. I think we’re just talking about two very different groups of people, and it’s a good thing that both groups can find and use the operating system and software that they prefer. Let Mac users enjoy OS X and let Linux users enjoy Linux, and hopefully both groups will be happy and content with their computers.
|
||||
|
||||
Every once in a while a Mac user might stray over to Linux or vice versa, but for the most part I think the two groups live in different worlds and mostly prefer to stay separate and apart from one another. I generally don’t compare the two because when you get right down to it, it’s really just a case of apples and oranges.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://jimlynch.com/linux-articles/why-mac-users-dont-switch-to-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jim Lynch][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://jimlynch.com/author/Jim/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.datamation.com/open-source/why-linux-isnt-winning-over-mac-users-1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.howtogeek.com/187410/how-to-install-and-dual-boot-linux-on-a-mac/
|
||||
[3]:http://distrowatch.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://desktoplinuxreviews.com/
|
||||
@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
|
||||
KayGuoWhu translating
|
||||
If a 32-bit integer overflows, can we use a 40-bit structure instead of a 64-bit long one?
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
#Q:
|
||||
|
||||
If, say, a 32-bit integer is overflowing, instead of upgrading int to long, can we make use of some 40-bit type if we need a range only within 240, so that we save 24 (64-40) bits for every integer?
|
||||
|
||||
If so, how?
|
||||
|
||||
I have to deal with billions and space is a bigger constraint.
|
||||
|
||||
#A:
|
||||
|
||||
##Yes, but...
|
||||
|
||||
It is certainly possible, but it is usually nonsensical (for any program that doesn't use billions of these numbers):
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
#include <stdint.h> // don't want to rely on something like long long
|
||||
struct bad_idea
|
||||
{
|
||||
uint64_t var : 40;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here, var will indeed have a width of 40 bits at the expense of much less efficient code generated (it turns out that "much" is very much wrong -- the measured overhead is a mere 1-2%, see timings below), and usually to no avail. Unless you have need for another 24-bit value (or an 8 and 16 bit value) which you wish to pack into the same structure, alignment will forfeit anything that you may gain.
|
||||
|
||||
In any case, unless you have billions of these, the effective difference in memory consumption will not be noticeable (but the extra code needed to manage the bit field will be noticeable!).
|
||||
|
||||
###Note:
|
||||
|
||||
The question has in the mean time been updated to reflect that indeed billions of numbers are needed, so this may be a viable thing to do, presumed that you take measures not to lose the gains due to structure alignment and padding, i.e. either by storing something else in the remaining 24 bits or by storing your 40-bit values in structures of 8 each or multiples thereof).
|
||||
Saving three bytes a billion times is worthwhile as it will require noticeably fewer memory pages and thus cause fewer cache and TLB misses, and above all page faults (a single page fault weighting tens of millions instructions).
|
||||
|
||||
While the above snippet does not make use of the remaining 24 bits (it merely demonstrates the "use 40 bits" part), something akin to the following will be necessary to really make the approach useful in a sense of preserving memory -- presumed that you indeed have other "useful" data to put in the holes:
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
struct using_gaps
|
||||
{
|
||||
uint64_t var : 40;
|
||||
uint64_t useful_uint16 : 16;
|
||||
uint64_t char_or_bool : 8;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Structure size and alignment will be equal to a 64 bit integer, so nothing is wasted if you make e.g. an array of a billion such structures (even without using compiler-specific extensions). If you don't have use for an 8-bit value, you could also use an 48-bit and a 16-bit value (giving a bigger overflow margin).
|
||||
Alternatively you could, at the expense of usability, put 8 40-bit values into a structure (least common multiple of 40 and 64 being 320 = 8*40). Of course then your code which accesses elements in the array of structures will become much more complicated (though one could probably implement an operator[] that restores the linear array functionality and hides the structure complexity).
|
||||
|
||||
Update:
|
||||
Wrote a quick test suite, just to see what overhead the bitfields (and operator overloading with bitfield refs) would have. Posted code (due to length) at gcc.godbolt.org, test output from my Win7-64 machine is:
|
||||
|
||||
```TXT
|
||||
Running test for array size = 1048576
|
||||
what alloc seq(w) seq(r) rand(w) rand(r) free
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
uint32_t 0 2 1 35 35 1
|
||||
uint64_t 0 3 3 35 35 1
|
||||
bad40_t 0 5 3 35 35 1
|
||||
packed40_t 0 7 4 48 49 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Running test for array size = 16777216
|
||||
what alloc seq(w) seq(r) rand(w) rand(r) free
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
uint32_t 0 38 14 560 555 8
|
||||
uint64_t 0 81 22 565 554 17
|
||||
bad40_t 0 85 25 565 561 16
|
||||
packed40_t 0 151 75 765 774 16
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Running test for array size = 134217728
|
||||
what alloc seq(w) seq(r) rand(w) rand(r) free
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
uint32_t 0 312 100 4480 4441 65
|
||||
uint64_t 0 648 172 4482 4490 130
|
||||
bad40_t 0 682 193 4573 4492 130
|
||||
packed40_t 0 1164 552 6181 6176 130
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
What one can see is that the extra overhead of bitfields is neglegible, but the operator overloading with bitfield reference as a convenience thing is rather drastic (about 3x increase) when accessing data linearly in a cache-friendly manner. On the other hand, on random access it barely even matters.
|
||||
|
||||
These timings suggest that simply using 64-bit integers would be better since they are still faster overall than bitfields (despite touching more memory), but of course they do not take into account the cost of page faults with much bigger datasets. It might look very different once you run out of physical RAM (I didn't test that).
|
||||
|
||||
------
|
||||
|
||||
via:[stackoverflow](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/27705409/if-a-32-bit-integer-overflows-can-we-use-a-40-bit-structure-instead-of-a-64-bit/27705562#27705562)
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Damon][a][Michael Kohne][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://stackoverflow.com/users/572743/damon
|
||||
[b]:http://stackoverflow.com/users/5801/michael-kohne
|
||||
@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How are C data types “supported directly by most computers”?
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
#Q:
|
||||
|
||||
I am reading K&R's *The C Programming Language*” and came across this statement [Introduction, p. 3]:
|
||||
|
||||
>Because the data types and control structures provided by C are supported directly by most computers, the run-time library required to implement self-contained programs is tiny.
|
||||
|
||||
What does the bolded statement mean? Is there an example of a data type or a control structure that isn't supported directly by a computer?
|
||||
|
||||
#A:
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, there are data types not directly supported.
|
||||
|
||||
On many embedded systems, there is no hardware floating point unit. So, when you write code like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
float x = 1.0f, y = 2.0f;
|
||||
return x + y;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It gets translated into something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
unsigned x = 0x3f800000, y = 0x40000000;
|
||||
return _float_add(x, y);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then the compiler or standard library has to supply an implementation of `_float_add()`, which takes up memory on your embedded system. If you're counting bytes on a really tiny system, this can add up.
|
||||
|
||||
Another common example is 64-bit integers (`long long` in the C standard since 1999), which are not directly supported by 32-bit systems. Old SPARC systems didn't support integer multiplication, so multiplication had to be supplied by the runtime. There are other examples.
|
||||
|
||||
##Other languages
|
||||
|
||||
By comparison, other languages have more complicated primitives.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, a Lisp symbol requires a lot of runtime support, just like tables in Lua, strings in Python, arrays in Fortran, et cetera. The equivalent types in C are usually either not part of the standard library at all (no standard symbols or tables) or they are much simpler and don't require much runtime support (arrays in C are basically just pointers, nul-terminated strings are almost as simple).
|
||||
|
||||
##Control structures
|
||||
|
||||
A notable control structure missing from C is exception handling. Nonlocal exit is limited to `setjmp()` and `longjmp()`, which just save and restore certain parts of processor state. By comparison, the C++ runtime has to walk the stack and call destructors and exception handlers.
|
||||
|
||||
----
|
||||
via:[stackoverflow](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/27977522/how-are-c-data-types-supported-directly-by-most-computers/27977605#27977605)
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dietrich Epp][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://stackoverflow.com/users/82294/dietrich-epp
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
translating by KayGuoWhu
|
||||
Why does C++ promote an int to a float when a float cannot represent all int values?
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
7 communities driving open source development
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Not so long ago, the open source model was the rebellious kid on the block, viewed with suspicion by established industry players. Today, open initiatives and foundations are flourishing with long lists of vendor committers who see the model as a key to innovation.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Open Development of Tech Drives Innovation ###
|
||||
|
||||
Over the past two decades, open development of technology has come to be seen as a key to driving innovation. Even companies that once saw open source as a threat have come around — Microsoft, for example, is now active in a number of open source initiatives. To date, most open development has focused on software. But even that is changing as communities have begun to coalesce around open hardware initiatives. Here are seven organizations that are successfully promoting and developing open technologies, both hardware and software.
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenPOWER Foundation ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The [OpenPOWER Foundation][2] was founded by IBM, Google, Mellanox, Tyan and NVIDIA in 2013 to drive open collaboration hardware development in the same spirit as the open source software development which has found fertile ground in the past two decades.
|
||||
|
||||
IBM seeded the foundation by opening up its Power-based hardware and software technologies, offering licenses to use Power IP in independent hardware products. More than 70 members now work together to create custom open servers, components and software for Linux-based data centers.
|
||||
|
||||
In April, OpenPOWER unveiled a technology roadmap based on new POWER8 process-based servers capable of analyzing data 50 times faster than the latest x86-based systems. In July, IBM and Google released a firmware stack. October saw the availability of NVIDIA GPU accelerated POWER8 systems and the first OpenPOWER reference server from Tyan.
|
||||
|
||||
### The Linux Foundation ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Founded in 2000, [The Linux Foundation][2] is now the host for the largest open source, collaborative development effort in history, with more than 180 corporate members and many individual and student members. It sponsors the work of key Linux developers and promotes, protects and advances the Linux operating system and collaborative software development.
|
||||
|
||||
Some of its most successful collaborative projects include Code Aurora Forum (a consortium of companies with projects serving the mobile wireless industry), MeeGo (a project to build a Linux kernel-based operating system for mobile devices and IVI) and the Open Virtualization Alliance (which fosters the adoption of free and open source software virtualization solutions).
|
||||
|
||||
### Open Virtualization Alliance ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The [Open Virtualization Alliance (OVA)][3] exists to foster the adoption of free and open source software virtualization solutions like Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) through use cases and support for the development of interoperable common interfaces and APIs. KVM turns the Linux kernel into a hypervisor.
|
||||
|
||||
Today, KVM is the most commonly used hypervisor with OpenStack.
|
||||
|
||||
### The OpenStack Foundation ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Originally launched as an Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) product by NASA and Rackspace hosting in 2010, the [OpenStack Foundation][4] has become the home for one of the biggest open source projects around. It boasts more than 200 member companies, including AT&T, AMD, Avaya, Canonical, Cisco, Dell and HP.
|
||||
|
||||
Organized around a six-month release cycle, the foundation's OpenStack projects are developed to control pools of processing, storage and networking resources through a data center — all managed or provisioned through a Web-based dashboard, command-line tools or a RESTful API. So far, the collaborative development supported by the foundation has resulted in the creation of OpenStack components including OpenStack Compute (a cloud computing fabric controller that is the main part of an IaaS system), OpenStack Networking (a system for managing networks and IP addresses) and OpenStack Object Storage (a scalable redundant storage system).
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenDaylight ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Another collaborative project to come out of the Linux Foundation, [OpenDaylight][5] is a joint initiative of industry vendors, like Dell, HP, Oracle and Avaya founded in April 2013. Its mandate is the creation of a community-led, open, industry-supported framework consisting of code and blueprints for Software-Defined Networking (SDN). The idea is to provide a fully functional SDN platform that can be deployed directly, without requiring other components, though vendors can offer add-ons and enhancements.
|
||||
|
||||
### Apache Software Foundation ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The [Apache Software Foundation (ASF)][7] is home to nearly 150 top level projects ranging from open source enterprise automation software to a whole ecosystem of distributed computing projects related to Apache Hadoop. These projects deliver enterprise-grade, freely available software products, while the Apache License is intended to make it easy for users, whether commercial or individual, to deploy Apache products.
|
||||
|
||||
ASF was incorporated in 1999 as a membership-based, not-for-profit corporation with meritocracy at its heart — to become a member you must first be actively contributing to one or more of the foundation's collaborative projects.
|
||||
|
||||
### Open Compute Project ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
An outgrowth of Facebook's redesign of its Oregon data center, the [Open Compute Project (OCP)][7] aims to develop open hardware solutions for data centers. The OCP is an initiative made up of cheap, vanity-free servers, modular I/O storage for Open Rack (a rack standard designed for data centers to integrate the rack into the data center infrastructure) and a relatively "green" data center design.
|
||||
|
||||
OCP board members include representatives from Facebook, Intel, Goldman Sachs, Rackspace and Microsoft.
|
||||
|
||||
OCP recently announced two options for licensing: an Apache 2.0-like license that allows for derivative works and a more prescriptive license that encourages changes to be rolled back into the original software.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.networkworld.com/article/2866074/opensource-subnet/7-communities-driving-open-source-development.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Thor Olavsrud][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.networkworld.com/author/Thor-Olavsrud/
|
||||
[1]:http://openpowerfoundation.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[3]:https://openvirtualizationalliance.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.openstack.org/foundation/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.opendaylight.org/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.apache.org/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.opencompute.org/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
|
||||
9 Best IDEs and Code Editors for JavaScript Users
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Web designing and developing is one of the trending sectors in the recent times, where more and more peoples started to search for their career opportunities. But, Getting the right opportunity as a web developer or graphic designer is not just a piece of cake for everyone, It certainly requires a strong mind presence as well as right skills to find the find the right job. There are a lot of websites available today which can help you to get the right job description according to your knowledge. But still if you want to achieve something in this sector you must have some excellent skills like working with different platforms, IDEs and various other tools too.
|
||||
|
||||
Talking about the different platforms and IDEs used for various languages for different purposes, gone is the time when we learn just one IDE and get the optimum solutions for our web design projects easily. Today we are living in the modern lifestyle where competition is getting more and more tough on every single day. Same is the case with the IDEs, IDE is basically a powerful client application for creating and deploying applications. Today we are going to share some best javascript IDE for web designers and developers.
|
||||
|
||||
Please visit this list of best code editors for javascript user and share your thought with us.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1) [Spket][1] ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Spket IDE** is powerful toolkit for JavaScript and XML development. The powerful editor for JavaScript, XUL/XBL and Yahoo! Widget development. The JavaScript editor provides features like code completion, syntax highlighting and content outline that helps developers productively create efficient JavaScript code.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2) [Ixedit][2] ###
|
||||
|
||||
IxEdit is a JavaScript-based interaction design tool for the web. With IxEdit, designers can practice DOM-scripting without coding to change, add, move, or transform elements dynamically on your web pages.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3) [Komodo Edit][3] ###
|
||||
|
||||
Komode is free and powerful code editor for Javascript and other programming languages.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4) [EpicEditor][4] ###
|
||||
|
||||
EpicEditor is an embeddable JavaScript Markdown editor with split fullscreen editing, live previewing, automatic draft saving, offline support, and more. For developers, it offers a robust API, can be easily themed, and allows you to swap out the bundled Markdown parser with anything you throw at it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 5) [codepress][5] ###
|
||||
|
||||
CodePress is web-based source code editor with syntax highlighting written in JavaScript that colors text in real time while it’s being typed in the browser.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 6) [ACe][6] ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ace is an embeddable code editor written in JavaScript. It matches the features and performance of native editors such as Sublime, Vim and TextMate. It can be easily embedded in any web page and JavaScript application.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 7) [scripted][7] ###
|
||||
|
||||
Scripted is a fast and lightweight code editor with an initial focus on JavaScript editing. Scripted is a browser based editor and the editor itself is served from a locally running Node.js server instance.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 8) [Netbeans][8] ###
|
||||
|
||||
This is another more impressive and useful code editors for javascript and other programming languages.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 9) [Webstorm][9] ###
|
||||
|
||||
This is the smartest ID for javascript. WebStorm is a lightweight yet powerful IDE, perfectly equipped for complex client-side development and server-side development with Node.js.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://devzum.com/2015/01/31/9-best-ides-and-code-editors-for-javascript-users/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[vikas][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://devzum.com/author/vikas/
|
||||
[1]:http://spket.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.ixedit.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://komodoide.com/komodo-edit/
|
||||
[4]:http://oscargodson.github.io/EpicEditor/
|
||||
[5]:http://codepress.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[6]:http://ace.c9.io/#nav=about
|
||||
[7]:https://github.com/scripted-editor/scripted
|
||||
[8]:https://netbeans.org/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.jetbrains.com/webstorm/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
GHOST: Another Security Bug Hits Linux, But is it That Bad?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> GHOST, a newly announced security vulnerability that affects Linux servers and other systems that use the open source glibc library, is not as dangerous to data privacy as the Shellshock or Heartbleed bugs.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Heartbleed is not even a year behind us, and the open source world has been hit with another major security vulnerability in the form of [GHOST][1], which involves holes in the Linux glibc library. This time, though, the actual danger may not live up to the hype.
|
||||
|
||||
The GHOST vulnerability, which was announced last week by security researchers at [Qualys][2], resides in the gethostbyname*() functions of the glibc library. glibc is one of the core building blocks of most Linux systems, and gethostbyname*(), which resolves domain names into IP addresses, is widely used in open source applications.
|
||||
|
||||
Attackers can exploit the GHOST security hole to create a buffer overflow, making it possible to execute any kind of code they want and do all sorts of nasty things.
|
||||
|
||||
All of the above suggests that GHOST is bad news indeed. Fortunately for the open source community, however, the actual risk appears small. As TrendMicro [points out][3], the bug that makes the exploit possible has been fixed in glibc since May 2013, meaning that any Linux servers or PCs running more recent versions of the software are safe from attack.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, gethostbyname*() has been superseded by newer glibc functions that can better handle modern networking environments. Those include ones that use the IPv6 protocol, which gethostbyname*() doesn't support. As a result, newer applications often don't use the gethostbyname*() functions, and are not at risk.
|
||||
|
||||
And perhaps most importantly, there's currently no known way of executing GHOST attacks through the Web. That greatly reduces opportunities for using this vulnerability to steal the data of unsuspecting users or otherwise wreak havoc.
|
||||
|
||||
All in all, then, GHOST doesn't seem like a vulnerability that will prove as serious as Heartbleed or Shellshock, two other recent security problems that affected widely used open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/020415/ghost-another-security-bug-hits-linux-it-bad
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Christopher Tozzi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://thevarguy.com/author/christopher-tozzi
|
||||
[1]:https://community.qualys.com/blogs/laws-of-vulnerabilities/2015/01/27/the-ghost-vulnerability
|
||||
[2]:http://qualys.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://blog.trendmicro.com/trendlabs-security-intelligence/not-so-spooky-linux-ghost-vulnerability/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
LinuxQuestions Survey Results Surface Top Open Source Projects
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Many people in the Linux community look forward to the always highly detailed and reliable results of the annual surveys from LinuxQuestions.org. As [Susan covered in detail in this post][1], this year's [results][2], focused on what readers at the site deem to be the best open source projects, are now available. Most of the people at LinuxQuestions are expert-level users who are on the site to answer questions from newer Linux users.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the summary results that Susan provided in her post, below you'll find a graphical snapshot of what the experts took note of on the open source front.
|
||||
|
||||
You can get a very nice graphical summary of the findings from the LinuxQuestions survey [here][3]. Here is a snapshot of the site's determination of the best Linux distributions, where Mint and Slackware fare quite well:
|
||||
|
||||
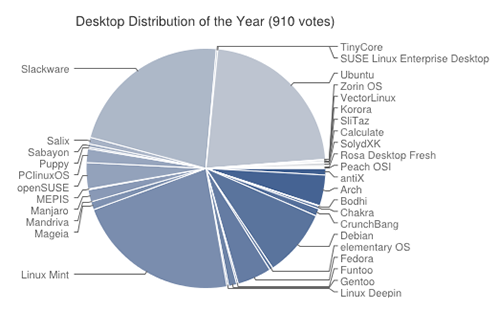
|
||||
|
||||
And below is a snapshot of the site's determination of the best cloud projects. Notably, the LinuxQuestions crowd gives very high praise to ownCloud. Definiitely check into the full results of the survey at the site, see [Susan's summary][4] of winners, and check out all the good graphics [here][5].
|
||||
|
||||
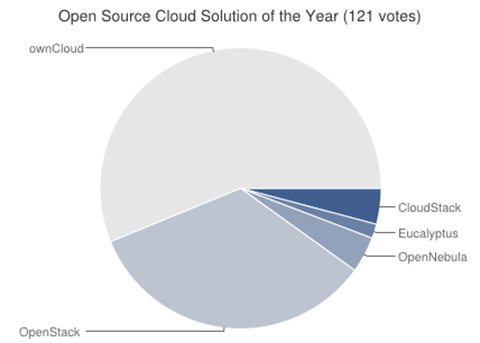
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/linuxquestions-survey-results-surface-top-open-source-projects
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sam Dean][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ostatic.com/member/samdean
|
||||
[1]:http://ostatic.com/blog/lq-members-choice-award-winners-announced
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/linux-news-59/2014-linuxquestions-org-members-choice-award-winners-4175532948/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/2014mca.php
|
||||
[4]:http://ostatic.com/blog/lq-members-choice-award-winners-announced
|
||||
[5]:http://www.linuxquestions.org/questions/2014mca.php
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
alim0x translating
|
||||
|
||||
The history of Android
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Voice Actions—a supercomputer in your pocket ###
|
||||
@ -79,4 +81,4 @@ via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-histor
|
||||
[5]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/12/google-robots-former-android-chief-will-lead-google-robotics-division/
|
||||
[6]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/12/lg-g-flex-review-form-over-even-basic-function/
|
||||
[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
|
||||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
|
||||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,223 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to create a software RAID-1 array with mdadm on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) is a storage technology that combines multiple hard disks into a single logical unit to provide fault-tolerance and/or improve disk I/O performance. Depending on how data is stored in an array of disks (e.g., with striping, mirroring, parity, or any combination thereof), different RAID levels are defined (e.g., RAID-0, RAID-1, RAID-5, etc). RAID can be implemented either in software or with a hardware RAID card. On modern Linux, basic software RAID functionality is available by default.
|
||||
|
||||
In this post, we'll discuss the software setup of a RAID-1 array (also known as a "mirroring" array), where identical data is written to the two devices that form the array. While it is possible to implement RAID-1 with partitions on a single physical hard drive (as with other RAID levels), it won't be of much use if that single hard drive fails. In fact, that's why most RAID levels normally use multiple physical drives to provide redundancy. In the event of any single drive failure, the virtual RAID block device should continue functioning without issues, and allow us to replace the faulty drive without significant production downtime and, more importantly, with no data loss. However, it does not replace the need to save periodic system backups in external storage.
|
||||
|
||||
Since the actual storage capacity (size) of a RAID-1 array is the size of the smallest drive, normally (if not always) you will find two identical physical drives in RAID-1 setup.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing mdadm on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
The tool that we are going to use to create, assemble, manage, and monitor our software RAID-1 is called mdadm (short for **m**ultiple **d**isks **adm**in). On Linux distros such as Fedora, CentOS, RHEL or Arch Linux, mdadm is available by default. On Debian-based distros, mdadm can be installed with aptitude or apt-get.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Fedora, CentOS or RHEL ####
|
||||
|
||||
As mdadm comes pre-installed, all you have to do is to start RAID monitoring service, and configure it to auto-start upon boot:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start mdmonitor
|
||||
# systemctl enable mdmonitor
|
||||
|
||||
For CentOS/RHEL 6, use these commands instead:
|
||||
|
||||
# service mdmonitor start
|
||||
# chkconfig mdmonitor on
|
||||
|
||||
#### Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint ####
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian and its derivatives, mdadm can be installed with **aptitude or apt-get**:
|
||||
|
||||
# aptitude install mdadm
|
||||
|
||||
On Ubuntu, you will be asked to configure postfix MTA for sending out email notifications (as part of RAID monitoring). You can skip it for now.
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, the installation will start with the following explanatory message to help us decide whether or not we are going to install the root filesystem on a RAID array. What we need to enter on the next screen will depend on this decision. Read it carefully:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Since we will not use our RAID-1 for the root filesystem, we will leave the answer blank:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
When asked whether we want to start (reassemble) our array automatically during each boot, choose "Yes". Note that we will need to add an entry to the /etc/fstab file later in order for the array to be properly mounted during the boot process as well.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Partitioning Hard Drives ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now it's time to prepare the physical devices that will be used in our array. For this setup, I have plugged in two 8 GB USB drives that have been identified as /dev/sdb and /dev/sdc from dmesg output:
|
||||
|
||||
# dmesg | less
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[ 60.014863] sd 3:0:0:0: [sdb] 15826944 512-byte logical blocks: (8.10 GB/7.54 GiB)
|
||||
[ 75.066466] sd 4:0:0:0: [sdc] 15826944 512-byte logical blocks: (8.10 GB/7.54 GiB)
|
||||
|
||||
We will use fdisk to create a primary partition on each disk that will occupy its entire size. The following steps show how to perform this task on /dev/sdb, and assume that this drive hasn't been partitioned yet (otherwise, we can delete the existing partition(s) to start off with a clean disk):
|
||||
|
||||
# fdisk /dev/sdb
|
||||
|
||||
Press 'p' to print the current partition table:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
(if one or more partitions are found, they can be deleted with 'd' option. Then 'w' option is used to apply the changes).
|
||||
|
||||
Since no partitions are found, we will create a new primary partition ['n'] as a primary partition ['p'], assign the partition number = ['1'] to it, and then indicate its size. You can press Enter key to accept the proposed default values, or enter a value of your choosing, as shown in the image below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now repeat the same process for /dev/sdc.
|
||||
|
||||
If we have two drives of different sizes, say 750 GB and 1 TB for example, we should create a primary partition of 750 GB on each of them, and use the remaining space on the bigger drive for another purpose, independent of the RAID array.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a RAID-1 Array ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once you are done with creating the primary partition on each drive, use the following command to create a RAID-1 array:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm -Cv /dev/md0 -l1 -n2 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1
|
||||
|
||||
Where:
|
||||
|
||||
- **-Cv**: creates an array and produce verbose output.
|
||||
- **/dev/md0**: is the name of the array.
|
||||
- **-l1** (l as in "level"): indicates that this will be a RAID-1 array.
|
||||
- **-n2**: indicates that we will add two partitions to the array, namely /dev/sdb1 and /dev/sdc1.
|
||||
|
||||
The above command is equivalent to:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --create --verbose /dev/md0 --level=1 --raid-devices=2 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1
|
||||
|
||||
If alternatively you want to add a spare device in order to replace a faulty disk in the future, you can add '--spare-devices=1 /dev/sdd1' to the above command.
|
||||
|
||||
Answer "y" when prompted if you want to continue creating an array, then press Enter:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can check the progress with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# cat /proc/mdstat
|
||||
|
||||
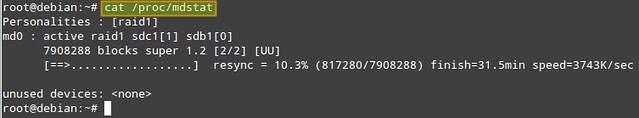
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to obtain more information about a RAID array (both while it's being assembled and after the process is finished) is:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --query /dev/md0
|
||||
# mdadm --detail /dev/md0 (or mdadm -D /dev/md0)
|
||||
|
||||
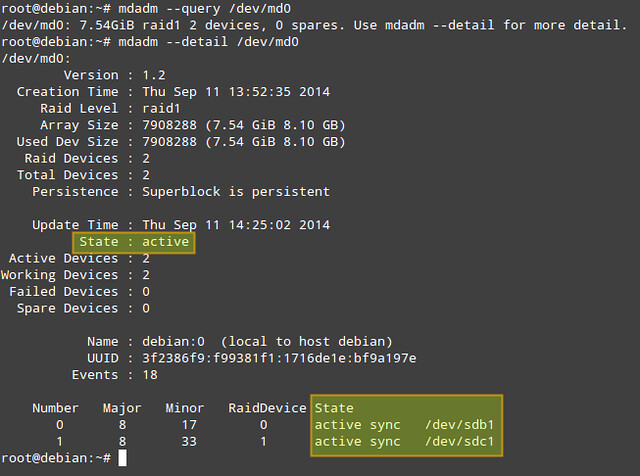
|
||||
|
||||
Of the information provided by 'mdadm -D', perhaps the most useful is that which shows the state of the array. The active state means that there is currently I/O activity happening. Other possible states are clean (all I/O activity has been completed), degraded (one of the devices is faulty or missing), resyncing (the system is recovering from an unclean shutdown such as a power outage), or recovering (a new drive has been added to the array, and data is being copied from the other drive onto it), to name the most common states.
|
||||
|
||||
### Formatting and Mounting a RAID Array ###
|
||||
|
||||
The next step is formatting (with ext4 in this example) the array:
|
||||
|
||||
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/md0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now let's mount the array, and verify that it was mounted correctly:
|
||||
|
||||
# mount /dev/md0 /mnt
|
||||
# mount
|
||||
|
||||
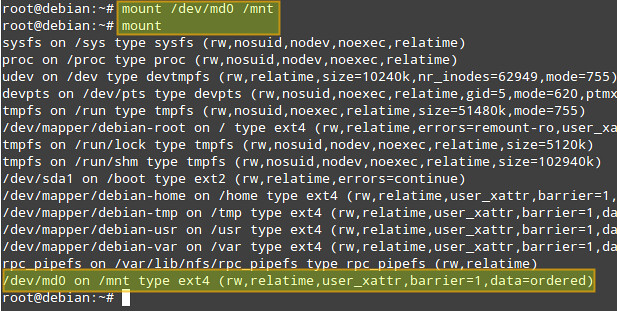
|
||||
|
||||
### Monitor a RAID Array ###
|
||||
|
||||
The mdadm tool comes with RAID monitoring capability built in. When mdadm is set to run as a daemon (which is the case with our RAID setup), it periodically polls existing RAID arrays, and reports on any detected events via email notification or syslog logging. Optionally, it can also be configured to invoke contingency commands (e.g., retrying or removing a disk) upon detecting any critical errors.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, mdadm scans all existing partitions and MD arrays, and logs any detected event to /var/log/syslog. Alternatively, you can specify devices and RAID arrays to scan in mdadm.conf located in /etc/mdadm/mdadm.conf (Debian-based) or /etc/mdadm.conf (Red Hat-based), in the following format. If mdadm.conf does not exist, create one.
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE /dev/sd[bcde]1 /dev/sd[ab]1
|
||||
|
||||
ARRAY /dev/md0 devices=/dev/sdb1,/dev/sdc1
|
||||
ARRAY /dev/md1 devices=/dev/sdd1,/dev/sde1
|
||||
.....
|
||||
|
||||
# optional email address to notify events
|
||||
MAILADDR your@email.com
|
||||
|
||||
After modifying mdadm configuration, restart mdadm daemon:
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
# service mdadm restart
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora, CentOS/RHEL 7:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart mdmonitor
|
||||
|
||||
On CentOS/RHEL 6:
|
||||
|
||||
# service mdmonitor restart
|
||||
|
||||
### Auto-mount a RAID Array ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now we will add an entry in the /etc/fstab to mount the array in /mnt automatically during boot (you can specify any other mount point):
|
||||
|
||||
# echo "/dev/md0 /mnt ext4 defaults 0 2" << /etc/fstab
|
||||
|
||||
To verify that mount works okay, we now unmount the array, restart mdadm, and remount. We can see that /dev/md0 has been mounted as per the entry we just added to /etc/fstab:
|
||||
|
||||
# umount /mnt
|
||||
# service mdadm restart (on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint)
|
||||
or systemctl restart mdmonitor (on Fedora, CentOS/RHEL7)
|
||||
or service mdmonitor restart (on CentOS/RHEL6)
|
||||
# mount -a
|
||||
|
||||
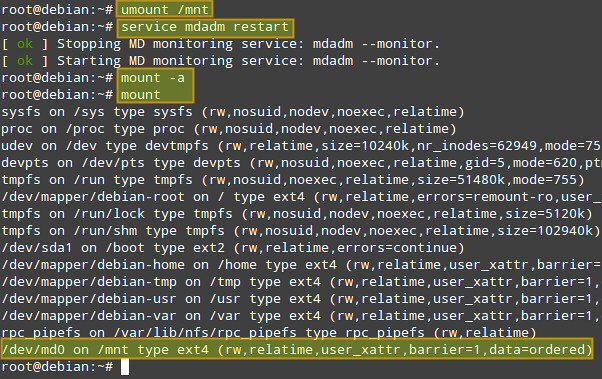
|
||||
|
||||
Now we are ready to access the RAID array via /mnt mount point. To test the array, we'll copy the /etc/passwd file (any other file will do) into /mnt:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, we need to tell the mdadm daemon to automatically start the RAID array during boot by setting the AUTOSTART variable to true in the /etc/default/mdadm file:
|
||||
|
||||
AUTOSTART=true
|
||||
|
||||
### Simulating Drive Failures ###
|
||||
|
||||
We will simulate a faulty drive and remove it with the following commands. Note that in a real life scenario, it is not necessary to mark a device as faulty first, as it will already be in that state in case of a failure.
|
||||
|
||||
First, unmount the array:
|
||||
|
||||
# umount /mnt
|
||||
|
||||
Now, notice how the output of 'mdadm -D /dev/md0' indicates the changes after performing each command below.
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm /dev/md0 --fail /dev/sdb1 #Marks /dev/sdb1 as faulty
|
||||
# mdadm --remove /dev/md0 /dev/sdb1 #Removes /dev/sdb1 from the array
|
||||
|
||||
Afterwards, when you have a new drive for replacement, re-add the drive again:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm /dev/md0 --add /dev/sdb1
|
||||
|
||||
The data is then immediately started to be rebuilt onto /dev/sdb1:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that the steps detailed above apply for systems with hot-swappable disks. If you do not have such technology, you will also have to stop a current array, and shutdown your system first in order to replace the part:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --stop /dev/md0
|
||||
# shutdown -h now
|
||||
|
||||
Then add the new drive and re-assemble the array:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm /dev/md0 --add /dev/sdb1
|
||||
# mdadm --assemble /dev/md0 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1
|
||||
|
||||
Hope this helps.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/09/create-software-raid1-array-mdadm-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/gabriel
|
||||
@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Test drive Linux with nothing but a flash drive
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
Image by : Opensource.com
|
||||
|
||||
Maybe you’ve heard about Linux and are intrigued by it. So intrigued that you want to give it a try. But you might not know where to begin.
|
||||
|
||||
You’ve probably done a bit of research online and have run across terms like dual booting and virtualization. Those terms might mean nothing to you, and you’re definitely not ready to sacrifice the operating system that you’re currently using to give Linux a try. So what can you do?
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a USB flash drive lying around, you can test drive Linux by creating a live USB. It’s a USB flash drive that contains an operating system that can start from the flash drive. It doesn’t take much technical ability to create one. Let’s take a look at how to do that and how to run Linux using a live USB.
|
||||
|
||||
### What you’ll need ###
|
||||
|
||||
Aside from a desktop or laptop computer, you’ll need:
|
||||
|
||||
- A blank USB flash drive—preferably one that has a capacity of 4 GB or more.
|
||||
- An [ISO image][1] (an archive of the contents of a hard disk) of the Linux distribution that you want to try. More about this in a moment.
|
||||
- An application called [Unetbootin][2], an open source tool, cross platform tool that creates a live USB. You don’t need to be running Linux to use it. In the instructions that below, I’m running Unetbootin on a MacBook.
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting to work ###
|
||||
|
||||
Plug your flash drive into a USB port on your computer and then fire up Unetbootin. You’ll be asked for the password that you use to log into your computer.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Remember the ISO image that was mentioned a few moments ago? There are two ways you can get one: either by downloading it from the website of the Linux distribution that you want to try, or by having Unetbootin download it for you. To do that latter, click **Select Distribution** at the top of the window, choose the distribution that you want to download, and then click **Select Version** to select the version of the distribution that you want to try.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Or, you can download the distribution yourself. Usually, the Linux distributions that I want to try aren’t in the list. If you go the second route, click **Disk image** and then click the button to search for the .iso file that you downloaded.
|
||||
|
||||
Notice the **Space used to preserve files across reboots (Ubuntu only)** option? If you’re testing Ubuntu or one of its derivatives (like Lubuntu or Xubuntu), you can set aside a few megabytes of space on your flash drive to save files like web browser bookmarks or documents that you create. When you load Ubuntu from the flash drive again, you can reuse those files.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once the ISO image is loaded, click **OK**. It takes anywhere from a couple of minutes to 10 minutes for Unetbootin to create the live USB.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Testing out the live USB ###
|
||||
|
||||
This is the point where you have to embrace your inner geek a bit. Not too much, but you will be taking a peek into the innards of your computer by going into the [BIOS][3]. Your computer’s BIOS starts various bits of hardware and controls where the computer’s operating system starts, or boots, from.
|
||||
|
||||
The BIOS usually looks for the operating system in this order (or something like it): hard drive, then CD-ROM or DVD drive, and then an external drive. You’ll want to change that order so that the external drive (in this case, your live USB) is the one that the BIOS checks first.
|
||||
|
||||
To do that, restart your computer with the flash drive plugged into a USB port. When you see the message **Press F2 to enter setup**, do just that. On some computers, the key might be F10.
|
||||
|
||||
In the BIOS, use the right arrow key on your keyboard to navigate to the **Boot** menu. You’ll see a list of drives on your computer. Use the down arrow key on your keyboard to navigate to the item labeled **USB HDD** and then press **F6** to move that item to the top of the list.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you’ve done that, press **F10** to save the changes. You’ll be kicked out of the BIOS and your computer will start up. After a short amount of time, you’ll be presented with a menu listing the options for starting the Linux distribution you’re trying out. Select **Run without installing** (or the menu item closest to it).
|
||||
|
||||
Once the desktop loads, you can connect to a wireless or wired network, browse the web, and give the pre-installed software a whirl. You can also check to see if, for example, your printer or scanner works with the Linux distribution you’re testing. If you really, really want to you can also fiddle at the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
### What to expect ###
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on the Linux distribution you’re testing and the speed of the flash drive you’re using, the operating system might take longer to load and it might run a bit slower than it would if it was installed on your hard drive.
|
||||
|
||||
As well, you’ll only have the basic software that the Linux distribution packs out of the box. You generally get a web browser, a word processor, a text editor, a media player, an image viewer, and a set of utilities. That should be enough to give you a feel for what it’s like to use Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
If you decide that you like using Linux, you can install it from the flash drive by double clicking on the installer.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/life/14/10/test-drive-linux-nothing-flash-drive
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Scott Nesbitt][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://opensource.com/users/scottnesbitt
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_image
|
||||
[2]:http://unetbootin.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[3]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BIOS
|
||||
@ -1,91 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How To Use Emoji Anywhere With Twitter's Open Source Library
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Embed them in webpages and other projects via GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Emoji, tiny characters from Japan that convey emotions through images, have already conquered the world of cellphone text messaging.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, you can post them everywhere else in the virtual world, too. Twitter has just [open-sourced][1] its emoji library so you can use them for your own websites, apps, and projects.
|
||||
|
||||
This will require a little bit of heavy lifting. Unicode has recognized and even standardized the emoji alphabet, but emoji still [aren’t fully compliant with all Web browsers][2], meaning they'll show up as “tofu,” or blank boxes, most of the time. When Twitter wanted to make emoji available, the social network teamed up with a company called [Icon Factory][3] to render browser imitations of the text message symbols. As a result, Twitter says there’s been lots of demand for access to its emoji.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, you can clone Twitter’s entire library on [GitHub][4] to use in your development projects. Here’s how to do that, and how to make emoji easier to use after you do.
|
||||
|
||||
### Obtain Unicode Support For Emoji ###
|
||||
|
||||
Unicode is an international encoding standard that assigns a string of characters to any symbol, letter, or digit people want to use online. In other words, it’s the missing link between how you read text on a computer, and how the computer reads text. For example, while you are looking at an empty space between these words, the computer sees “&mbsp.”
|
||||
|
||||
Unicode even has its own [primitive emoji][5] that can be read in the browser without any effort on your part. For example while you see a ♥, your computer is decoding the string “2665.”
|
||||
|
||||
To use Twitter’s emoji library in most cases, you simply need to add a script inside the <head> section of your HTML page:
|
||||
|
||||
<script src="//twemoji.maxcdn.com/twemoji.min.js"></script>
|
||||
|
||||
This grants your project access to the JavaScript library that contains the hundreds of emoji that work on Twitter. However, creating a document with simply this script isn’t going to make emoji appear on your site. You also need to actually insert some emoji!
|
||||
|
||||
In the <body> section, paste a few of the emoji strings you can find in Twitter’s [preview.html source code][6]. I used 🎹 and 🏁 without really knowing how they'd appear in the browser window. Yeah, you’ll have to just paste and guess. You can already see the problem we're going to fix in section two.
|
||||
|
||||
However, through some trial and error, you can turn a raw HTML file that looks like this—
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
—into a webpage that looks something like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Convert Emoji Into Readable Language ###
|
||||
|
||||
Twitter’s solution is all well and good for making a site or app emoji compliant. But if you want to be able to easily insert your favorite emoji at will via HTML, you’re going to need an easier solution than memorizing all those Unicode strings.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s where programmer Elle Kasai’s [Twemoji Awesome][7] styles come in.
|
||||
|
||||
By adding Elle’s open-source stylesheet to any webpage, you can use English words to understand which emoji you’re inserting. So if you want a heart emoji to show up, you can simply type this :
|
||||
|
||||
<i class="twa twa-heart"></i>
|
||||
|
||||
In order to do this, let’s download Elle’s project with the “Download ZIP” button on GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, let’s make a new folder on the desktop. Inside this folder, we’ll put emoji.html—the raw HTML file I showed you before, and also Elle’s [twemoji-awesome.css][8].
|
||||
|
||||
We’ll need the HTML file to acknowledge the CSS file, so in the <head> section of the html page you’ll want to add a link from the css file:
|
||||
|
||||
<link rel="stylesheet" href="twemoji-awesome.css">
|
||||
|
||||
Once you put this in, you can delete Twitter's script from before. Elle's styles each link to the Unicode string for the relevant emoji, so you no longer have to.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, go down to the body section and add a few emoji. I used <i class="twa twa-sparkling-heart"></i>, <i class="twa twa-exclamation"></i>, <i class="twa twa-lg twa-sparkles"></i> and <i class="twa twa-beer"></i>.
|
||||
|
||||
You'll end up with something like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Save and view your creation in the browser:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ta-da! Not only have you gotten a basic webpage to support emoji in the browser, you’ve also made it easy to do. Feel free to check out this tutorial on [my GitHub][9] for actual files you can clone instead of screenshots.
|
||||
|
||||
Lead image via [Get Emoji][10]; screenshots by Lauren Orsini
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://readwrite.com/2014/11/12/how-to-use-emoji-in-the-browser-window
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Lauren Orsini][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://readwrite.com/author/lauren-orsini
|
||||
[1]:https://blog.twitter.com/2014/open-sourcing-twitter-emoji-for-everyone
|
||||
[2]:http://www.unicode.org/reports/tr51/full-emoji-list.html
|
||||
[3]:https://twitter.com/iconfactory
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/twitter/twemoji
|
||||
[5]:http://www.unicode.org/reports/tr51/full-emoji-list.html
|
||||
[6]:https://github.com/twitter/twemoji/blob/gh-pages/preview.html
|
||||
[7]:http://ellekasai.github.io/twemoji-awesome/
|
||||
[8]:https://github.com/ellekasai/twemoji-awesome/blob/gh-pages/twemoji-awesome.css
|
||||
[9]:https://github.com/laurenorsini/Emoji-Everywhere
|
||||
[10]:http://getemoji.com/
|
||||
@ -1,98 +0,0 @@
|
||||
dupeGuru – Find And Remove Duplicate Files Instantly From Hard Drive
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Introduction ###
|
||||
|
||||
Disk full is one of the big trouble for us. No matter how we’re careful, sometimes we might copy the same file to multiple locations, or download the same file twice unknowingly. Therefore, sooner or later we will end up with disk full error message, which is worst when we really need some space to store important data. If you believe your system has multiple duplicate files, then **dupeGuru** might help you.
|
||||
|
||||
dupeGuru team have also developed applications called **dupeGuru Music Edition** to remove duplicate music files, and **dupeGuru Picture Edition** to remove duplicate pictures.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. dupeGuru (Standard Edition) ###
|
||||
|
||||
For those who don’t know about [dupeGuru][1], It is a free, open source, cross-platform application that can used to find and remove the duplicate files in your system. It will run under Linux, Windows, and Mac OS X platforms. It uses a quick fuzzy matching algorithm to find the duplicate files in minutes. Also, you can tweak dupeGuru to find exactly what kind of duplicate files you want to, and eliminate what kind of files from deletion. It supports English, French, German, Chinese (Simplified), Czech, Italian, Armenian, Russian, Ukrainian, Brazilian, and Vietnamese.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install dupeGuru On Ubuntu 14.10/14.04/13.10/13.04/12.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
dupeGuru developers have created a Ubuntu PPA to ease the installation. To install dupeGuru, enter the following commands one by one in your Terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:hsoft/ppa
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install dupeguru-se
|
||||
|
||||
#### Usage ####
|
||||
|
||||
Usage is very simple. Launch dupeGuru either from Unity Dash or Menu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Click + button on the bottom, and add the folder you want to scan. Click Scan button to start finding the duplicate files.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If the selected folder contains any duplicate files, it will display them. As you in the below screen shot, I have a duplicate file in the Downloads directory.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, you can decide what to do. You can either delete the duplicate file, or rename it, or copy/move it to another location. To do that select the duplicate files, or check the box that says “**Dupes only**” on the Menu bar. If you selected the Dupes only option, the duplicates files will only visible. So you can select and delete them easily. Click on the **Actions** drop-down box. Finally, select the action you want to perform. Here, I just want to delete the duplicate file, so I selected the option: **Send marked to Recycle bin**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Then, click **Proceed** to delete the duplicate files.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. dupeGuru Music Edition ###
|
||||
|
||||
[dupeGuru Music Edition][2] or dupeGuru ME in short, is just like dupeGuru. It does everything dupeGuru does, but it has more information columns (such as bitrate, duration, tags, etc..) and more scan types (filename with fields, tags and audio content). Like dupeGuru, dupeGuru ME also runs on Linux, Windows, and Mac OS X.
|
||||
|
||||
It supports variety of formats such as MP3, WMA, AAC (iTunes format), OGG, FLAC, loss-less AAC and loss-less WMA etc,
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install dupeGuru ME On Ubuntu 14.10/14.04/13.10/13.04/12.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we don’t have to add any PPA, because already the added in the previous steps. So, enter the following command to install from your Terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install dupeguru-me
|
||||
|
||||
#### Usage ####
|
||||
|
||||
Launch it either from Unity dash or Menu. The usage, interface, and look of dupeGuru ME is similar to normal dupeGuru. Add the folder you to scan and select the action you want to perform. The duplicate music files will be deleted.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. dupeGuru Picture Edition ###
|
||||
|
||||
[dupeGuru Picture Edition][3], or duepGuru PE in short, is a tool to find duplicate pictures on your computer. It is as like as dupeGuru, but is specialized for duplicate pictures matching. dupeGuru PE runs on Linux, Windows, and Mac OS X.
|
||||
|
||||
dupeGuru PE supports JPG, PNG, TIFF, GIF and BMP formats. All these formats can be compared together. The Mac OS X version of dupeGuru PE also supports PSD and RAW (CR2 and NEF) formats.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install dupeGuru PE On Ubuntu 14.10/14.04/13.10/13.04/12.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
As we have already added the PPA, We don’t need to add PPA for dupeGuru either. Just, run the following command to install it.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install dupeguru-pe
|
||||
|
||||
#### Usage ####
|
||||
|
||||
It’s also look like dupeGuru, and dupeGuru ME in terms of usage, interface, and look.I wonder why the developer have created there separate versions for each category. It would be better, a single application has all of the above three features combined.
|
||||
|
||||
Launch it, add the folder you want to scan, and select the action you want to perform. That’s it. you duplicated files will be gone.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you can’t remove them in case of any security problems, note down the location of the files, and manually delete them either from Terminal or File manager.
|
||||
|
||||
Cheers!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/dupeguru-find-remove-duplicate-files-instantly-hard-drive/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.hardcoded.net/dupeguru/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.hardcoded.net/dupeguru_me/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.hardcoded.net/dupeguru_pe/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
Translating by FSSlc
|
||||
|
||||
Undelete Files on Linux Systems
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Often times, a computer user will delete a needed file accidentally and not have an easy way to regain or recreate the file. Thankfully, files can be undeleted. When a user deletes a file, it is not gone, only hidden for some time. Here is how it all works. On a filesystem, the system has what is called a file allocation list. This list keeps track of what files are where on the storage unit (hard-drive, MicroSD card, flash-drive, etc.). When a file is deleted, the filesystem will perform one of two tasks on the allocation table. The file's entry on the file allocation table marked as "free space" or the file's entry on the list is erased and then the space is marked as free. Now, if a file needs to be placed on the storage unit, the operating system will put the file in the space marked as empty. After the new file is written to the "empty space", the deleted file is now gone forever. When a deleted file is to be recovered, the user must not manipulate any files because if the "empty space" is used, then the file can never be retrieved.
|
||||
@ -115,4 +117,4 @@ via: http://www.linux.org/threads/undelete-files-on-linux-systems.4316/
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linux.org/members/devyncjohnson.4843/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cgsecurity.org/wiki/TestDisk
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cgsecurity.org/wiki/TestDisk
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,206 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by shipsw
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Auditd - Tool for Security Auditing on Linux Server
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
First of all , we wish all our readers **Happy & Prosperous New YEAR 2015** from our Linoxide team. So lets start this new year explaining about Auditd tool.
|
||||
|
||||
Security is one of the main factor that we need to consider. We must maintain it because we don't want someone steal our data. Security includes many things. Audit, is one of it.
|
||||
|
||||
On Linux system, we know that we have a tool named **auditd**. This tool is by default exist in most of Linux operating system. What is auditd tool and how to use it? We will cover it below.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is auditd? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Auditd or audit daemon, is a userspace component to the Linux Auditing System. It’s responsible for writing audit records to the disk.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Installing auditd ###
|
||||
|
||||
On Ubuntu based system , we can use [wajig][1] tool or **apt-get tool** to install auditd.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Just follow the instruction to get it done. Once it finish it will install some tools related to auditd tool. Here are the tools :
|
||||
|
||||
- **auditctl ;** is a tool to control the behaviour of the daemon on the fly, adding rules, etc
|
||||
- **/etc/audit/audit.rules ;** is the file that contains audit rules
|
||||
- **aureport ;** is tool to generate and view the audit report
|
||||
- **ausearch ;** is a tool to search various events
|
||||
- **auditspd ;** is a tool which can be used to relay event notifications to other applications instead of writing them to disk in the audit log
|
||||
- **autrace ;** is a command that can be used to trace a process
|
||||
- **/etc/audit/auditd.conf ;** is the configuration file of auditd tool
|
||||
- When the first time we install **auditd**, there will be no rules available yet.
|
||||
|
||||
We can check it using this command :
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo auditctl -l
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To add rules on auditd, let’s continue to the section below.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to use it ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Audit files and directories access ####
|
||||
|
||||
One of the basic need for us to use an audit tool are, how can we know if someone change a file(s) or directories? Using auditd tool, we can do with those commands (please remember, we will need root privileges to configure auditd tool):
|
||||
|
||||
**Audit files**
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo auditctl -w /etc/passwd -p rwxa
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**With :**
|
||||
|
||||
- **-w path ;** this parameter will insert a watch for the file system object at path. On the example above, auditd will wacth /etc/passwd file
|
||||
- **-p ; **this parameter describes the permission access type that a file system watch will trigger on
|
||||
- **rwxa ;** are the attributes which bind to -p parameter above. r is read, w is write, x is execute and a is attribute
|
||||
|
||||
#### Audit directories ####
|
||||
|
||||
To audit directories, we will use a similar command. Let’s take a look at the command below :
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo auditctl -w /production/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The above command will watch any access to the **/production folder**.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, if we run **auditctl -l** command again, we will see that new rules are added.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now let’s see the audit log says.
|
||||
|
||||
### Viewing the audit log ###
|
||||
|
||||
After rules are added, now we can see how auditd in action. To view audit log, we can use **ausearch** tool.
|
||||
|
||||
We already add rule to watch /etc/passwd file. Now we will try to use **ausearch** tool to view the audit log.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ausearch -f /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
- **-f** parameter told ausearch to investigate /etc/passwd file
|
||||
- The result is shown below :
|
||||
> **time**->Mon Dec 22 09:39:16 2014
|
||||
> type=PATH msg=audit(1419215956.471:194): item=0 **name="/etc/passwd"** inode=142512 dev=08:01 mode=0100644 ouid=0 ogid=0 rdev=00:00 nametype=NORMAL
|
||||
> type=CWD msg=audit(1419215956.471:194): **cwd="/home/pungki"**
|
||||
> type=SYSCALL msg=audit(1419215956.471:194): arch=40000003 **syscall=5** success=yes exit=3 a0=b779694b a1=80000 a2=1b6 a3=b8776aa8 items=1 ppid=2090 pid=2231 **auid=4294967295 uid=1000 gid=1000** euid=0 suid=0 fsuid=0 egid=1000 sgid=1000 fsgid=1000 tty=pts0 ses=4294967295 **comm="sudo" exe="/usr/bin/sudo"** key=(null)
|
||||
|
||||
Now let’s we understand the result.
|
||||
|
||||
- **time ;** is when the audit is done
|
||||
- **name ;** is the object name to be audited
|
||||
- **cwd ;** is the current directory
|
||||
- **syscall ;** is related syscall
|
||||
- **auid ;** is the audit user ID
|
||||
- **uid and gid ;** are User ID and Group ID of the user who access the file
|
||||
- **comm ;** is the command that the user is used to access the file
|
||||
- **exe ;** is the location of the command of comm parameter above
|
||||
- The above audit log is the original file.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we are going to add a new user, to see how the auditd record the activity to /etc/passwd file.
|
||||
|
||||
> **time->**Mon Dec 22 11:25:23 2014
|
||||
> type=PATH msg=audit(1419222323.628:510): item=1 **name="/etc/passwd.lock"** inode=143992 dev=08:01 mode=0100600 ouid=0 ogid=0 rdev=00:00 nametype=DELETE
|
||||
> type=PATH msg=audit(1419222323.628:510): item=0 **name="/etc/"** inode=131073 dev=08:01 mode=040755 ouid=0 ogid=0 rdev=00:00 nametype=PARENT
|
||||
> type=CWD msg=audit(1419222323.628:510): **cwd="/root"**
|
||||
> type=SYSCALL msg=audit(1419222323.628:510): arch=40000003 **syscall=10** success=yes exit=0 a0=bfc0ceec a1=0 a2=bfc0ceec a3=897764c items=2 ppid=2978 pid=2994 **auid=4294967295 uid=0 gid=0** euid=0 suid=0 fsuid=0 egid=0 sgid=0 fsgid=0 tty=pts0 ses=4294967295 **comm="chfn" exe="/usr/bin/chfn"** key=(null)
|
||||
|
||||
As we can see above, that on that particular time, **/etc/passwd was accessed** by user root (uid = 0 and gid = 0) **from** directory /root (cwd = /root). The /etc/passwd file was accessed using **chfn** command which located in **/usr/bin/chfn**
|
||||
|
||||
If we type **man chfn** on the console, we will see more detail about what is chfn.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now we take a look at another example.
|
||||
|
||||
We already told auditd to watch directory /production/ . That is a new directory. So when we try to use ausearch tool at the first time, it found nothing.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, root account try to list the /production directory using ls command. The second time we use ausearch tool, it will show us some information.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> **time->**Mon Dec 22 14:18:28 2014
|
||||
> type=PATH msg=audit(1419232708.344:527): item=0 **name="/production/"** inode=797104 dev=08:01 mode=040755 ouid=0 ogid=0 rdev=00:00 nametype=NORMAL
|
||||
> type=CWD msg=audit(1419232708.344:527): cwd="/root"
|
||||
> type=SYSCALL msg=audit(1419232708.344:527): arch=40000003 syscall=295 success=yes exit=3 a0=ffffff9c a1=95761e8 a2=98800 a3=0 items=1 ppid=3033 pid=3444 **auid=4294967295 uid=0 gid=0** euid=0 suid=0 fsuid=0 egid=0 sgid=0 fsgid=0 tty=pts0 ses=4294967295 **comm="ls" exe="/bin/ls"** key=(null)
|
||||
|
||||
Similar with the previous one, we can determine that **/production folder was looked** by root account (uid=0 gid=0) **using ls command** (comm = ls) and the ls command is **located in /bin/ls folder**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Viewing the audit reports ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once we put the audit rules, it will run automatically. And after a period of time, we want to see how auditd can help us to track them.
|
||||
|
||||
Auditd comes with another tool called **aureport**. As we can guess from its name, **aureport** is a tool that produces summary reports of the audit system log.
|
||||
|
||||
We already told auditd to track /etc/passwd before. And a moment after the auditd parameter is developed, the audit.log file is created.
|
||||
|
||||
To generate the report of audit, we can use aureport tool. Without any parameters, aureport will generate a summary report of audit activity.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo aureport
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As we can see, there are some information available which cover most important area.
|
||||
|
||||
On the picture above we see there are **3 times failed authentication**. Using aureport, we can drill down to that information.
|
||||
|
||||
We can use this command to look deeper on failed authentication :
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo aureport -au
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As we can see on the picture above, there are two users which at the particular time are failed to authenticated
|
||||
|
||||
If we want to see all events related to account modification, we can use -m parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo aureport -m
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Auditd configuration file ###
|
||||
|
||||
Previously we already added :
|
||||
|
||||
- $ sudo auditctl -w /etc/passwd -p rwxa
|
||||
- $ sudo auditctl -w /production/
|
||||
- Now, if we sure the rules are OK, we can add it into
|
||||
|
||||
**/etc/audit/audit.rules** to make them permanently.Here’s how to put them into the /etc/audit/audit.rules fileSample of audit rule file
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Then don’t forget to restart auditd daemon.**
|
||||
|
||||
# /etc/init.d/auditd restart
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
# service auditd restart
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Auditd is one of the audit tool that available on Linux system. You can explore more detail about auditd and its related tools by reading its manual page. For example, just type **man auditd** to see more detail about auditd. Or type **man ausearch** to see more detail about ausearch tool.
|
||||
|
||||
**Please be careful before creating rules**. It will increase your log file size significantly if too much information to record.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/how-tos/auditd-tool-security-auditing/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Pungki Arianto][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/pungki/
|
||||
[1]:http://linoxide.com/tools/wajig-package-management-debian/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
[bazz2222222]
|
||||
How to Configure Chroot Environment in Ubuntu 14.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
There are many instances when you may wish to isolate certain applications, user, or environments within a Linux system. Different operating systems have different methods of achieving isolation, and in Linux, a classic way is through a `chroot` environment.
|
||||
@ -143,4 +144,4 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/configure-chroot-environment-ubuntu-14-04
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+archivemirrors
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+archivemirrors
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user