mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
translated
This commit is contained in:
parent
ba3f2d20eb
commit
dd7f97f448
@ -1,143 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
translating---geekpi
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
How to Add a New Disk Larger Than 2TB to An Existing Linux
|
|
||||||
============================================================
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Have you ever tried to do the partitioning of hard disk larger than 2TB using [fdisk utility][1] and wondered why you end up getting a warning to use GPT? Yes, you got that right. We cannot partition a hard disk larger than 2TB using fdisk tool.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In such cases, we can use parted command. The major difference lies in the partitioning formats that fdisk uses DOS partitioning table format and parted uses GPT format.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
TIP: You can use gdisk as well instead of parted tool.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In this article, we will show you to add a new disk larger than 2TB to an existing Linux server such as RHEL/CentOS or Debian/Ubuntu.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
I am using fdisk and parted utilities to do this configuration.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
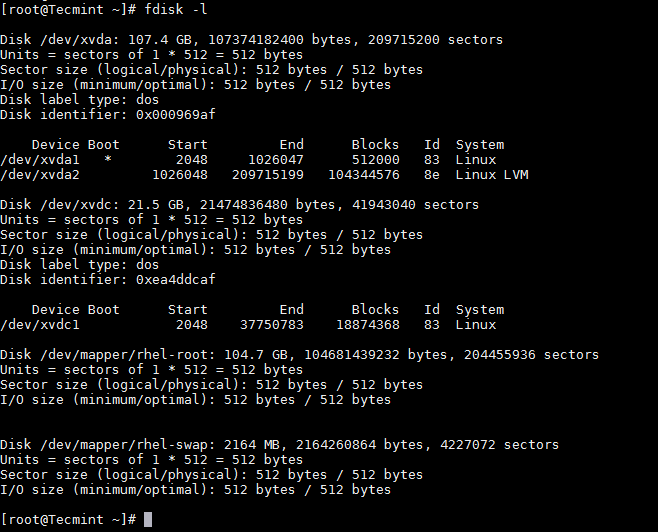
First list the current partition details using fdisk command as shown.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
# fdisk -l
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
[
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
][2]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
List Linux Partition Table
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For the purpose of this article, I am attaching a hard disk of 20GB capacity, which can be followed for disk larger than 2TB as well. Once you added a disk, verify the partition table using same fdisk command as shown.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
# fdisk -l
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
[
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
][3]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
List New Partition Table
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Tip: If you are adding a physical hard disk, you may find that partitions already created. In such cases, you can use fdsik to delete the same before using parted.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
# fdisk /dev/xvdd
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Use `d` switch for the command to delete the partition and `w` to write the changes and quit.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
][4]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Delete Linux Partition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Important: You need to be careful while deleting the partition. This will erase the data on the disk.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now its time to partition a new hard disk using parted command.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
# parted /dev/xvdd
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Set the partition table format to GPT
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
(parted) mklabel gpt
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Create the Primary partition and assign the disk capacity, here I am using 20GB (in your case it would be 2TB).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
(parted) mkpart primary 0GB 20GB
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
[
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
][5]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Create Partition using Parted
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
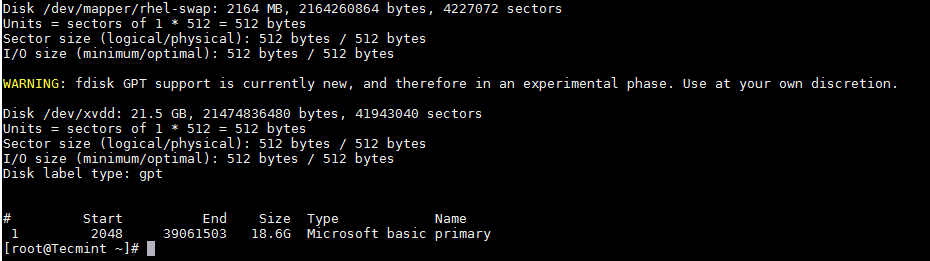
Just for curiosity, let’s see how this new partition is listed in fdisk.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
# fdisk /dev/xvdd
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
[
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
][6]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Verify Partition Details
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
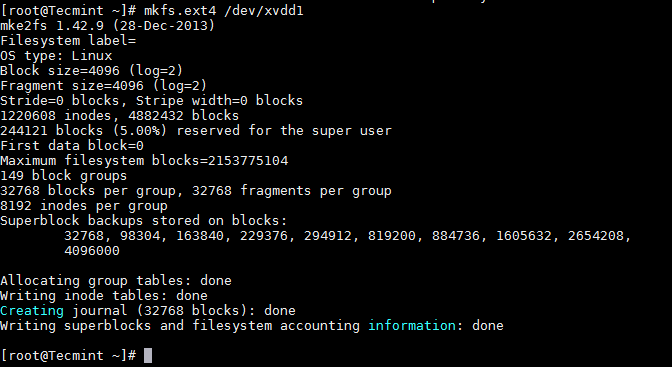
Now format and then mount the partition and add the same in /etc/fstab which controls the file systems to be mounted when the system boots.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/xvdd1
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
[
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
][7]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Format Linux Partition
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Once partition has been formatted, now it’s time mount the partition under /data1.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
# mount /dev/xvdd1 /data1
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For permanent mounting add the entry in /etc/fstab file.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
/dev/xvdd1 /data1 ext4 defaults 0 0
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Important: Kernel should support GPT in order to partition using GPT format. By default RHEL/CentOS have Kernel with GPT support, but for Debian/Ubuntu you need to recompile the kernel after changing the config.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
That’s it! In this article, we have shown you how to use the parted command. Share your comments and feedback with us.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
作者简介:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
I work on various platforms including IBM-AIX, Solaris, HP-UX, and storage technologies ONTAP and OneFS and have hands on experience on Oracle Database.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
-----------------------
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/add-disk-larger-than-2tb-to-an-existing-linux/
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
作者:[Lakshmi Dhandapani][a]
|
|
||||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
|
||||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/lakshmi/
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/fdisk-commands-to-manage-linux-disk-partitions/
|
|
||||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/List-Linux-Partition-Table.png
|
|
||||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/List-New-Partition-Table.png
|
|
||||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Delete-Linux-Partition.png
|
|
||||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Create-Partition-using-Parted.png
|
|
||||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Verify-Partition-Details.png
|
|
||||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Format-Linux-Partition.png
|
|
||||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/lakshmi/
|
|
||||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
|
|
||||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
|
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
|
|||||||
|
如何在 Linux 中添加一块大于 2TB 的新磁盘
|
||||||
|
============================================================
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
你有没有试过使用 [fdisk][1] 对大于 2TB 的硬盘进行分区,并且想知道为什么会得到需要使用 GPT 的警告? 是的,你看到的没错。我们无法使用 fdisk 对大于 2TB 的硬盘进行分区。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在这种情况下,我们可以使用 parted 命令。它的主要区别在于 fdisk 使用 DOS 分区表格式而 parted 使用 GPT 格式。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
提示:你可以使用 gdisk 来代替 parted。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在本文中,我们将介绍如何将大于 2TB 的新磁盘添加到现有的 Linux 服务器中(如 RHEL/CentOS 或 Debian/Ubuntu)中。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
我使用的是 fdisk 和 parted 来进行此配置。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
首先使用 fdisk 命令列出当前的分区详细信息,如图所示。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# fdisk -l
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
[
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
][2]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
列出 Linux 分区表
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
为了本文的目的,我加了一块 20GB 的磁盘,这也可以是大于 2TB 的磁盘。在你加完磁盘后,使用相同的 fdisk 命令验证分区表。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# fdisk -l
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
[
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
][3]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
列出新的分区表
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
提示:如果你添加了一块物理磁盘,你可能会发现分区已经创建了。此种情况下,你可以在使用 parted 之前使用 fdisk 删除它。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# fdisk /dev/xvdd
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在命令中使用 `d` 开关删除分区,使用 `w` 保存更改并退出。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
][4]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
删除 Linux 分区
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
重要:在删除分区时你需要小心点。这会擦除磁盘上的数据。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
现在是使用 parted 命令分区新的磁盘了。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# parted /dev/xvdd
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
将分区表格式化成 GPT
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
(parted) mklabel gpt
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
创建主分区并分配磁盘容量,这里我使用 20GB (在你这里可能是 2TB)。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
(parted) mkpart primary 0GB 20GB
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
[
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
][5]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
使用 parted 创建分区
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
出于好奇,让我们用 fdisk 看看新的分区。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# fdisk /dev/xvdd
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
[
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
][6]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
验证分区细节
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
现在格式化并挂载分区,并在 /etc/fstab 添加相同的信息,它控制在系统启动时挂载文件系统。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/xvdd1
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
[
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
][7]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
格式化 Linux 分区
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
一旦分区格式化之后,是时候在 /data1 下挂载分区了。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# mount /dev/xvdd1 /data1
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
要永久挂载,在 /etc/fstab 添加条目。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
/dev/xvdd1 /data1 ext4 defaults 0 0
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
重要:要使用 GPT 分区格式需要内核支持。默认上 RHEL/CentOS 的内核已经支持 GPT,但是对于 Debian/Ubuntu,你需要在修改配置之后重新编译内核。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
就是这样了!在本文中,我们向你展示了如何使用 parted 命令。与我们分享你的评论和反馈。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
作者简介:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
我在包括 IBM-AIX、Solaris、HP-UX 以及 ONTAP 和 OneFS 存储技术的不同平台上工作,并掌握 Oracle 数据库。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
-----------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
via: http://www.tecmint.com/add-disk-larger-than-2tb-to-an-existing-linux/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
作者:[Lakshmi Dhandapani][a]
|
||||||
|
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||||
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/lakshmi/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/fdisk-commands-to-manage-linux-disk-partitions/
|
||||||
|
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/List-Linux-Partition-Table.png
|
||||||
|
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/List-New-Partition-Table.png
|
||||||
|
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Delete-Linux-Partition.png
|
||||||
|
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Create-Partition-using-Parted.png
|
||||||
|
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Verify-Partition-Details.png
|
||||||
|
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Format-Linux-Partition.png
|
||||||
|
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/lakshmi/
|
||||||
|
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
|
||||||
|
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user