mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-03 23:40:14 +08:00
commit
dd1cf6220a
@ -1,279 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating---geekpi
|
||||
|
||||
How to Install, Configure and Secure FTP Server in CentOS 7 – [Comprehensive Guide]
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a traditional and widely used standard tool for [transferring files between a server and clients][1] over a network, especially where no authentication is necessary (permits anonymous users to connect to a server). We must understand that FTP is unsecure by default, because it transmits user credentials and data without encryption.
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, we will describe the steps to install, configure and secure a FTP server (VSFTPD stands for “Very Secure FTP Daemon“) in CentOS/RHEL 7 and Fedora distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that all the commands in this guide will be run as root, in case you are not operating the server with the root account, use the [sudo command][2] to gain root privileges.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Installing FTP Server
|
||||
|
||||
1. Installing vsftpd server is straight forward, just run the following command in the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum install vsftpd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. After the installation completes, the service will be disabled at first, so we need to start it manually for the time being and enable it to start automatically from the next system boot as well:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# systemctl start vsftpd
|
||||
# systemctl enable vsftpd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Next, in order to allow access to FTP services from external systems, we have to open port 21, where the FTP daemons are listening as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=21/tcp
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=ftp
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Configuring FTP Server
|
||||
|
||||
4. Now we will move over to perform a few configurations to setup and secure our FTP server, let us start by making a backup of the original config file /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# cp /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf.orig
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, open the config file above and set the following options with these corresponding values:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
anonymous_enable=NO # disable anonymous login
|
||||
local_enable=YES # permit local logins
|
||||
write_enable=YES # enable FTP commands which change the filesystem
|
||||
local_umask=022 # value of umask for file creation for local users
|
||||
dirmessage_enable=YES # enable showing of messages when users first enter a new directory
|
||||
xferlog_enable=YES # a log file will be maintained detailing uploads and downloads
|
||||
connect_from_port_20=YES # use port 20 (ftp-data) on the server machine for PORT style connections
|
||||
xferlog_std_format=YES # keep standard log file format
|
||||
listen=NO # prevent vsftpd from running in standalone mode
|
||||
listen_ipv6=YES # vsftpd will listen on an IPv6 socket instead of an IPv4 one
|
||||
pam_service_name=vsftpd # name of the PAM service vsftpd will use
|
||||
userlist_enable=YES # enable vsftpd to load a list of usernames
|
||||
tcp_wrappers=YES # turn on tcp wrappers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Now configure FTP to allow/deny FTP access to users based on the user list file `/etc/vsftpd.userlist`.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, users listed in `userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.userlist` are denied login access with userlist_deny option set to YES, if userlist_enable=YES.
|
||||
|
||||
However, userlist_deny=NO alters the setting, meaning that only users explicitly listed in userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.userlist will be permitted to login.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
userlist_enable=YES # vsftpd will load a list of usernames, from the filename given by userlist_file
|
||||
userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.userlist # stores usernames.
|
||||
userlist_deny=NO
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That’s not all, when users login to the FTP server, they are placed in a chroot’ed jail, this is the local root directory which will act as their home directory for the FTP session only.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we will look at two possible scenarios of how to chroot FTP users to Home directories (local root) directory for FTP users, as explained below.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Now add these two following options to restrict FTP users to their Home directories.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
chroot_local_user=YES
|
||||
allow_writeable_chroot=YES
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
chroot_local_user=YES means local users will be placed in a chroot jail, their home directory after login by default settings.
|
||||
|
||||
And also by default, vsftpd does not allow the chroot jail directory to be writable for security reasons, however, we can use the option allow_writeable_chroot=YES to override this setting.
|
||||
|
||||
Save the file and close it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Securing FTP Server with SELinux
|
||||
|
||||
7. Now, let’s set the SELinux boolean below to allow FTP to read files in a user’s home directory. Note that this was initially done using the the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# setsebool -P ftp_home_dir on
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
However, the `ftp_home_dir` directive has been disabled by default as explained in this bug report: [https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1097775][3].
|
||||
|
||||
Now we will use semanage command to set SELinux rule to allow FTP to read/write user’s home directory.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# semanage boolean -m ftpd_full_access --on
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, we have to restart vsftpd to effect all the changes we made so far above:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# systemctl restart vsftpd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Testing FTP Server
|
||||
|
||||
8. Now we will test FTP server by creating a FTP user with [useradd command][4].
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# useradd -m -c “Ravi Saive, CEO” -s /bin/bash ravi
|
||||
# passwd ravi
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Afterwards, we have to add the user ravi to the file /etc/vsftpd.userlist using the [echo command][5] as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# echo "ravi" | tee -a /etc/vsftpd.userlist
|
||||
# cat /etc/vsftpd.userlist
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
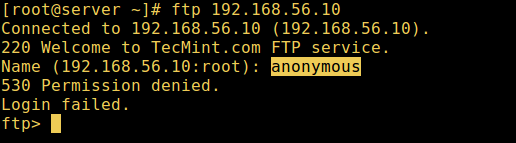
9. Now it’s time to test if our settings above are working correctly. Let’s start by testing anonymous logins, we can see from the screen shot below that anonymous logins are not permitted:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ftp 192.168.56.10
|
||||
Connected to 192.168.56.10 (192.168.56.10).
|
||||
220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service.
|
||||
Name (192.168.56.10:root) : anonymous
|
||||
530 Permission denied.
|
||||
Login failed.
|
||||
ftp>
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Test Anonymous FTP Login
|
||||
|
||||
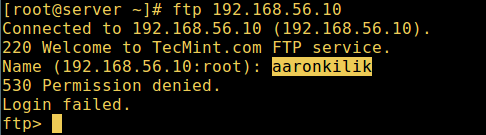
10. Let’s also test if a user not listed in the file /etc/vsftpd.userlist will be granted permission to login, which is not the case as in the screen shot below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ftp 192.168.56.10
|
||||
Connected to 192.168.56.10 (192.168.56.10).
|
||||
220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service.
|
||||
Name (192.168.56.10:root) : aaronkilik
|
||||
530 Permission denied.
|
||||
Login failed.
|
||||
ftp>
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][7]
|
||||
|
||||
FTP User Login Failed
|
||||
|
||||
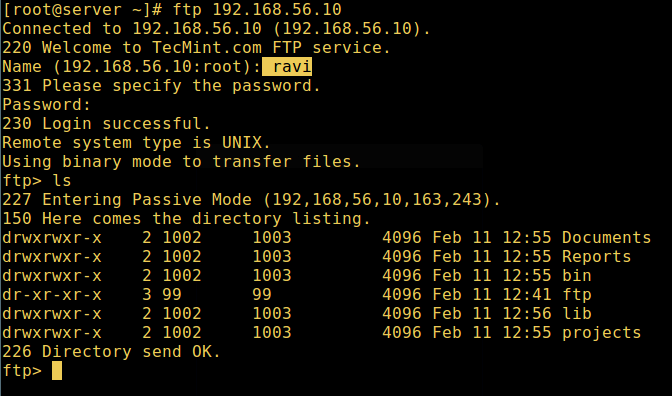
11. Now do a final check if a user listed in the file /etc/vsftpd.userlist, is actually placed in his/her home directory after login:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ftp 192.168.56.10
|
||||
Connected to 192.168.56.10 (192.168.56.10).
|
||||
220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service.
|
||||
Name (192.168.56.10:root) : ravi
|
||||
331 Please specify the password.
|
||||
Password:
|
||||
230 Login successful.
|
||||
Remote system type is UNIX.
|
||||
Using binary mode to transfer files.
|
||||
ftp> ls
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
FTP User Login Successful[
|
||||
|
||||
Warning: Using `allow_writeable_chroot=YES` has certain security implications, especially if the users have upload permission, or shell access.
|
||||
|
||||
Only activate this option if you exactly know what you are doing. It’s important to note that these security implications arenot vsftpd specific, they apply to all FTP daemons which offer to put local users in chroot jails as well.
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, we will look at a more secure way of setting a different non-writable local root directory in the next section.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 5: Configure Different FTP User Home Directories
|
||||
|
||||
12. Open the vsftpd configuration file again and start by commenting the unsecure option below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#allow_writeable_chroot=YES
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then create the alternative local root directory for the user (`ravi`, yours is probably different) and remove write permissions to all users to this directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mkdir /home/ravi/ftp
|
||||
# chown nobody:nobody /home/ravi/ftp
|
||||
# chmod a-w /home/ravi/ftp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
13. Next, create a directory under the local root where the user will store his/her files:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mkdir /home/ravi/ftp/files
|
||||
# chown ravi:ravi /home/ravi/ftp/files
|
||||
# chmod 0700 /home/ravi/ftp/files/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then add/modify the following options in the vsftpd config file with these values:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
user_sub_token=$USER # inserts the username in the local root directory
|
||||
local_root=/home/$USER/ftp # defines any users local root directory
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save the file and close it. Once again, let’s restart the service with the new settings:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# systemctl restart vsftpd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
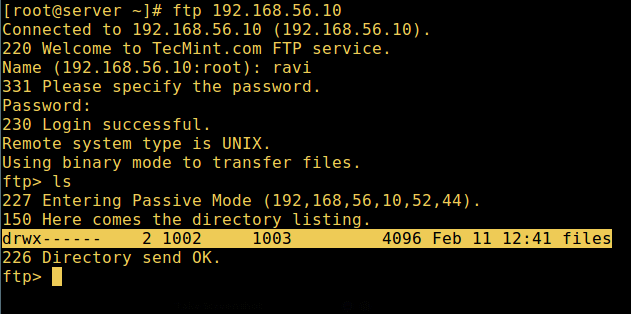
14. Now do a final test again and see that the users local root directory is the FTP directory we created in his home directory.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ftp 192.168.56.10
|
||||
Connected to 192.168.56.10 (192.168.56.10).
|
||||
220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service.
|
||||
Name (192.168.56.10:root) : ravi
|
||||
331 Please specify the password.
|
||||
Password:
|
||||
230 Login successful.
|
||||
Remote system type is UNIX.
|
||||
Using binary mode to transfer files.
|
||||
ftp> ls
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][9]
|
||||
|
||||
FTP User Home Directory Login Successful
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it! In this article, we described how to install, configure as well as secure a FTP server in CentOS 7, use the comment section below to write back to us concerning this guide/share any useful information about this topic.
|
||||
|
||||
**Suggested Read:** [Install ProFTPD Server on RHEL/CentOS 7][10]
|
||||
|
||||
In the next article, we will also show you how to [secure an FTP server using SSL/TLS][11] connections in CentOS 7, until then, stay connected to TecMint.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-ftp-server-in-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/scp-commands-examples/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/sudoers-configurations-for-setting-sudo-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1097775
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/add-users-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Test-Anonymous-FTP-Login.png
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/FTP-User-Login-Failed.png
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/FTP-User-Login.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/FTP-User-Home-Directory-Login-Successful.png
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-proftpd-in-centos-7/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/secure-vsftpd-using-ssl-tls-on-centos/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,277 @@
|
||||
如何在 CentOS 7 中安装、配置 SFTP - [全面指南]
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
FTP(文件传输协议)是一种用于通过网络[在服务器和客户端之间传输文件][1]的传统并广泛使用的标准工具,特别是在不需要身份验证的情况下(允许匿名用户连接到服务器)。我们必须明白,默认情况下 FTP 是不安全的,因为它不加密传输用户凭据和数据。
|
||||
|
||||
在本指南中,我们将介绍在 CentOS/RHEL7 和 Fedora 发行版中安装、配置和保护 FTP 服务器( VSFTPD 代表 “Very Secure FTP Daemon”)的步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,本指南中的所有命令将以 root 身份运行,以防你不使用 root 帐户操作服务器,请使用 [sudo命令][2] 获取 root 权限。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 1:安装 FTP 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
1. 安装 vsftpd 服务器很直接,只要在终端运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum install vsftpd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 安装完成后,服务会先被禁用,因此我们需要手动启动,并设置在下次启动时自动启用:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# systemctl start vsftpd
|
||||
# systemctl enable vsftpd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. 接下来,为了允许从外部系统访问 FTP 服务,我们需要打开 FTP 守护进程监听 21 端口:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=21/tcp
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=ftp
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 2: 配置 FTP 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
4. 现在,我们会进行一些配置来设置并加密我们的 FTP 服务器,让我们先备份一下原始配置文件 /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# cp /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf.orig
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,打开上面的文件,并将下面的选项设置相关的值:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
anonymous_enable=NO # disable anonymous login
|
||||
local_enable=YES # permit local logins
|
||||
write_enable=YES # enable FTP commands which change the filesystem
|
||||
local_umask=022 # value of umask for file creation for local users
|
||||
dirmessage_enable=YES # enable showing of messages when users first enter a new directory
|
||||
xferlog_enable=YES # a log file will be maintained detailing uploads and downloads
|
||||
connect_from_port_20=YES # use port 20 (ftp-data) on the server machine for PORT style connections
|
||||
xferlog_std_format=YES # keep standard log file format
|
||||
listen=NO # prevent vsftpd from running in standalone mode
|
||||
listen_ipv6=YES # vsftpd will listen on an IPv6 socket instead of an IPv4 one
|
||||
pam_service_name=vsftpd # name of the PAM service vsftpd will use
|
||||
userlist_enable=YES # enable vsftpd to load a list of usernames
|
||||
tcp_wrappers=YES # turn on tcp wrappers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. 现在基于用户列表文件 `/etc/vsftpd.userlist` 来配置 FTP 允许/拒绝用户访问。
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,如果设置了 userlist_enable=YES,当 userlist_deny 选项设置为 YES 的时候,`userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.userlist` 中的用户列表被拒绝登录。
|
||||
|
||||
然而, userlist_deny=NO 更改了设置,意味着只有在 userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.userlist 显式指定的用户才允许登录。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
userlist_enable=YES # vsftpd will load a list of usernames, from the filename given by userlist_file
|
||||
userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.userlist # stores usernames.
|
||||
userlist_deny=NO
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这并不是全部,当用户登录到 FTP 服务器时,它们会进入 chroot jail 中,这是仅作为 FTP 会话主目录的本地根目录。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,我们将介绍如何将 FTP 用户 chroot 到 FTP 用户的家目录(本地 root)中的两种可能情况,如下所述。
|
||||
|
||||
6. 接下来添加下面的选项来限制 FTP 用户到它们自己的家目录。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
chroot_local_user=YES
|
||||
allow_writeable_chroot=YES
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
chroot_local_user=YES 意味着用户可以设置 chroot jail,默认是登录后的家目录。
|
||||
|
||||
同样默认的是,出于安全原因,vsftpd 不会允许 chroot jail 目录可写,然而,我们可以添加 allow_writeable_chroot=YES 来覆盖这个设置。
|
||||
|
||||
保存并关闭文件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 用 SELinux 加密 FTP 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
7. 现在,让我们设置下面的 SELinux 布尔值来允许 FTP 能读取用户家目录下的文件。请注意,这最初是使用以下命令完成的:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# setsebool -P ftp_home_dir on
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然而,`ftp_home_dir` 指令由于这个 bug 报告:[https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1097775][3] 默认是禁用的。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们会使用 semanage 命令来设置 SELinux 规则来允许 FTP 读取/写入用户的家目录。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# semanage boolean -m ftpd_full_access --on
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这时,我们需要重启 vsftpd 来使目前的设置生效:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# systemctl restart vsftpd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 4: 测试 FTP 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
8. 现在我们会用[ useradd 命令][4]创建一个 FTP 用户来测试 FTP 服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# useradd -m -c “Ravi Saive, CEO” -s /bin/bash ravi
|
||||
# passwd ravi
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
之后,我们如下使用[ echo 命令][5]添加用户 ravi 到文件 /etc/vsftpd.userlist 中:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# echo "ravi" | tee -a /etc/vsftpd.userlist
|
||||
# cat /etc/vsftpd.userlist
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
9. 现在是时候测试我们上面的设置是否可以工作了。让我们使用匿名登录测试,我们可以从下面的截图看到匿名登录不被允许。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ftp 192.168.56.10
|
||||
Connected to 192.168.56.10 (192.168.56.10).
|
||||
220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service.
|
||||
Name (192.168.56.10:root) : anonymous
|
||||
530 Permission denied.
|
||||
Login failed.
|
||||
ftp>
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][6]
|
||||
|
||||
测试 FTP 匿名登录
|
||||
|
||||
10. 让我们也测试一下没有列在 /etc/vsftpd.userlist 中的用户是否有权限登录,这不是下面截图中的例子:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ftp 192.168.56.10
|
||||
Connected to 192.168.56.10 (192.168.56.10).
|
||||
220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service.
|
||||
Name (192.168.56.10:root) : aaronkilik
|
||||
530 Permission denied.
|
||||
Login failed.
|
||||
ftp>
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][7]
|
||||
|
||||
FTP 用户登录失败
|
||||
|
||||
11. 现在最后测试一下列在 /etc/vsftpd.userlis 中的用户是否在登录后真的进入了他/她的家目录:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ftp 192.168.56.10
|
||||
Connected to 192.168.56.10 (192.168.56.10).
|
||||
220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service.
|
||||
Name (192.168.56.10:root) : ravi
|
||||
331 Please specify the password.
|
||||
Password:
|
||||
230 Login successful.
|
||||
Remote system type is UNIX.
|
||||
Using binary mode to transfer files.
|
||||
ftp> ls
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
用户成功登录
|
||||
|
||||
警告:使用 `allow_writeable_chroot=YES' 有一定的安全隐患,特别是用户具有上传权限或 shell 访问权限时。
|
||||
|
||||
只有当你完全知道你正做什么时才激活此选项。重要的是要注意,这些安全性影响并不是 vsftpd 特定的,它们适用于所有 FTP 守护进程,它们也提供将本地用户置于 chroot jail中。
|
||||
|
||||
因此,我们将在下一节中看到一种更安全的方法来设置不同的不可写本地根目录。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 5: 配置不同的 FTP 家目录
|
||||
|
||||
12. 再次打开 vsftpd 配置文件,并将下面不安全的选项注释掉:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#allow_writeable_chroot=YES
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接着为用户(`ravi`,你的可能不同)创建另外一个替代根目录,并将所有用户对该目录的可写权限移除:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mkdir /home/ravi/ftp
|
||||
# chown nobody:nobody /home/ravi/ftp
|
||||
# chmod a-w /home/ravi/ftp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
13. 接下来,在用户存储他/她的文件的本地根目录下创建一个文件夹:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mkdir /home/ravi/ftp/files
|
||||
# chown ravi:ravi /home/ravi/ftp/files
|
||||
# chmod 0700 /home/ravi/ftp/files/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
、接着在 vsftpd 配置文件中添加/修改这些选项:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
user_sub_token=$USER # 在本地根目录下插入用户名
|
||||
local_root=/home/$USER/ftp # 定义任何用户的本地根目录
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并关闭文件。再说一次,有新的设置后,让我们重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# systemctl restart vsftpd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
14. 现在最后在测试一次查看用户本地根目录就是我们在他的家目录创建的 FTP 目录。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# ftp 192.168.56.10
|
||||
Connected to 192.168.56.10 (192.168.56.10).
|
||||
220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service.
|
||||
Name (192.168.56.10:root) : ravi
|
||||
331 Please specify the password.
|
||||
Password:
|
||||
230 Login successful.
|
||||
Remote system type is UNIX.
|
||||
Using binary mode to transfer files.
|
||||
ftp> ls
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][9]
|
||||
|
||||
FTP 用户家目录登录成功
|
||||
|
||||
就是这样了!在本文中,我们介绍了如何在 CentOS 7 中安装、配置以及加密的 FTP 服务器,使用下面的评论栏给我们回复,或者分享关于这个主题的任何有用信息。
|
||||
|
||||
**建议阅读:** [在 RHEL/CentOS 7 上安装 ProFTPD 服务器] [10]
|
||||
|
||||
在下一篇文章中,我们还将向你介绍如何在 CentOS 7 中[保护使用 SSL/TLS][11]连接的 FTP 服务器,再此之前,请继续关注 TecMint。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
Aaron Kili 是一名 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,即将从事 Linux 系统管理员和网页开发工作,他日前是 TecMint 技术网站的原创作者,非常喜欢使用电脑工作,坚信分享知识是一种美德。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-ftp-server-in-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/scp-commands-examples/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/sudoers-configurations-for-setting-sudo-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1097775
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/add-users-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Test-Anonymous-FTP-Login.png
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/FTP-User-Login-Failed.png
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/FTP-User-Login.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/FTP-User-Home-Directory-Login-Successful.png
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-proftpd-in-centos-7/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/secure-vsftpd-using-ssl-tls-on-centos/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user