mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject
This commit is contained in:
commit
dc6220204a
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
LCTT是Linux中国社区([http://linux.cn/](http://linux.cn/))的翻译组,负责从国外优秀媒体翻译Linux相关的技术、资讯、杂文等内容。
|
||||
|
||||
LCTT已经拥有四十余名活跃成员,并欢迎更多的Linux志愿者加入我们的团队。
|
||||
LCTT已经拥有近百余名活跃成员,并欢迎更多的Linux志愿者加入我们的团队。
|
||||
|
||||
LCTT的组成
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ LCTT的组成
|
||||
加入我们
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
请首先加入翻译组的QQ群,群号是:131864150,加群时请说明是志愿者。加入后记得修改您的群名片为您的github的ID。
|
||||
请首先加入翻译组的QQ群,群号是:198889102,加群时请说明是志愿者。加入后记得修改您的群名片为您的github的ID。
|
||||
|
||||
加入的成员,请先阅读[WIKI 如何开始](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject/wiki/01-如何开始)。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -89,4 +89,5 @@ LCTT的组成
|
||||
* 2013/10/12 取消对LINUX.CN注册用户的依赖,在QQ群内、文章内都采用github的注册ID。
|
||||
* 2013/10/18 正式启动man翻译计划。
|
||||
* 2013/11/10 举行第一次北京线下聚会。
|
||||
* 2014/01/02 增加了Core Translators 成员: geekpi。
|
||||
* 2014/01/02 增加了Core Translators 成员: geekpi。
|
||||
* 2014/05/04 更换了新的QQ群:198889102
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
||||
[ translating by stallonederek ]
|
||||
Linux中16个常用的查询主机硬件信息的命令
|
||||
Linux硬件信息命令大全
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### 硬件信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -88,11 +87,11 @@ lscpu命令可以用来查询处理器cpu的详细信息,只需要简单地输
|
||||
|
||||
点击下面的帖子,可以对lshw有更多的了解。
|
||||
|
||||
[Get hardware information on Linux with lshw command][1]
|
||||
[在Linux上使用lshw命令获取硬件信息][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. hwinfo - Hardware Information ###
|
||||
|
||||
hwinfo同样是一个使用非常广泛的硬件信息查询命令,类似于lshw,它同样详细或概要地报告多个部件的硬件信息,但不同的是,它有时可以给出比lshw更多的信息。
|
||||
hwinfo同样是一个使用非常广泛的硬件信息查询命令,类似于lshw,它同样可以详细或概要地报告多个部件的硬件信息,但不同的是,它有时可以给出比lshw更多的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
$ hwinfo --short
|
||||
cpu:
|
||||
@ -144,11 +143,11 @@ hwinfo同样是一个使用非常广泛的硬件信息查询命令,类似于ls
|
||||
|
||||
点击下面的链接可以查看更多关于hwinfo的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
[Check hardware information on Linux with hwinfo command][2]
|
||||
[在Linux上使用hwinfo命令获取硬件信息][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. lspci - 显示pci总线相关信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
lscpi命令可以列出pci总线上信息,以及所有连接到pci总线上的设备信息,比如vga适配器,显卡,网卡,usb端口,sata控制器等等。
|
||||
lscpi命令可以列出pci总线上信息,以及所有连接到pci总线上的设备信息,比如VGA适配器,显卡,网卡,usb端口,sata控制器等等。
|
||||
|
||||
$ lspci
|
||||
00:00.0 Host bridge: Intel Corporation 82G35 Express DRAM Controller (rev 03)
|
||||
@ -204,7 +203,7 @@ lscpi命令可以列出pci总线上信息,以及所有连接到pci总线上的
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Inxi ###
|
||||
|
||||
inxi命令是一个大的bash脚本文件,其通过从不同的信息来源和命令中获取硬件信息,最后能给出一个非常美观的,特别适合于非专业人员阅读的硬件信息报告。
|
||||
inxi命令是一个大的bash脚本文件,其通过从不同的信息来源和命令中获取硬件信息,最后能给出一个颜色高亮的,适合于非专业人员阅读的硬件信息报告。
|
||||
|
||||
$ inxi -Fx
|
||||
|
||||
@ -241,7 +240,7 @@ inxi命令是一个大的bash脚本文件,其通过从不同的信息来源和
|
||||
/dev/sda8 210G 149G 51G 75% /media/13f35f59-f023-4d98-b06f-9dfaebefd6c1
|
||||
/dev/sda5 105G 31G 75G 30% /media/4668484A68483B47
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Pydf - python版本的df ###
|
||||
### 10. pydf - python版本的df ###
|
||||
|
||||
一个增强型的python版的df命令,可以以不同的颜色显示所查询的信息,看起来比df更好看。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -394,13 +393,13 @@ hdparm命令可以获取sata设备如硬盘等设备信息。
|
||||
|
||||
每一个命令在获取信息的方式会稍微有些不同,在查询某一设备时,你也有可能要结合多个命令才能获取你想要的硬件信息。不过,这些命令都可以在大多数的linux发行版中找到,可以很容易地从默认的仓库中获取安装。
|
||||
|
||||
在桌面版系统中,这也存在一下图形界面的工具,可以方便大家记忆和使用,比如Hardinfo,I-nex就是其中非常流行的工具,他们可以提供多个硬件部件的详细信息。
|
||||
在桌面版系统中,还有一个便于使用的图形界面的工具,比如Hardinfo、I-nex就是其中非常流行的工具,他们可以提供多个硬件部件的详细信息。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.binarytides.com/linux-commands-hardware-info/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[stallonederek](https://github.com/stallonederek) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[stallonederek](https://github.com/stallonederek) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/校wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,56 +1,52 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical's Ubuntu 14.04 focuses on the long haul
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical公司的长期支持版本-Ubuntu 14.04
|
||||
Canonical公司的Ubuntu 14.04关注在长期服务上
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Ubuntu 14.04的服务器版配备Docker引擎和更好的固态硬盘支持
|
||||
|
||||
IDG新闻服务 - 因为各机构将内部开发的系统移动到了云端,Canonical公司想要他们考虑将桌面操作系统也切换了。
|
||||
来自IDG新闻服务消息:因为各机构将本地系统移动到了云端,Canonical公司希望他们同时考虑更换一下操作系统到Ubuntu上。
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical公司的Ubuntu Server产品经理Mark Baker说:“当人们移动到云端时,它往往涉及到重新设计应用程序,众多企业都想要从横向扩展和云技术中获利。”
|
||||
Canonical公司的Ubuntu Server产品经理Mark Baker说:“当人们移动到云端时,它往往涉及到重新设计应用程序,众多企业都想要获得横向扩展和云技术的便利之处。”
|
||||
|
||||
鉴于一些类似于云服务的急切因素,在未来几年内,约百分之70的CIO打算重新评估他们在IT供应商的选择,[根据Gartner的调查][1].Baker说:“我们看到这方面的证据。”
|
||||
鉴于一些类似于云服务迁移的的急迫性,[据Gartner的调查][1],在未来几年内,约百分之七十的CIO打算重新评估他们在IT供应商的选择。Baker说:“我们看到了这方面的迹象。”
|
||||
|
||||
星期四发布的Linux发行版本,服务器版Ubuntu 14.04,Canonical公司强调了在宿主环境中,机构是如何运用它来作为运行大型关键任务应用程序的基础。这个版本带有长期支持和许多云友好的软件程序,如Docker,最新版本的OpenStack。
|
||||
前不久发布的服务器版的Ubuntu 14.04中,Canonical公司强调了在宿主环境中,机构是如何运用它来作为运行大型关键任务应用程序的基础。这个版本带有长期支持和许多云方面的软件程序,如Docker,最新版本的OpenStack。
|
||||
|
||||
> Baker说:“我们现在更加意识到我们正在创造一个企业采用的平台”
|
||||
> Baker说:“我们现在更加意识到我们正在创造一个为企业所采用的平台”
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Ubuntu 14.04 是一个长期支持版本(LTS),意味着它将会有五年的补丁和支持,这使得它作为企业长期的生产应用更可行。这次它也将允许用户从Ubuntu自身的版本库系统更新软件包。
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Canonical公司每年发布两个新的Ubuntu版本,但是每两年发布一个LTS版本,其他非LTS版本只支持九个月。
|
||||
>
|
||||
>使用常规非LTS版本,九个月后,用户将不再得到bug修复,无法从Canonical那儿更新软件或操作系统。如果用户选择这样做,那他们只有约三个月来更新系统。
|
||||
>
|
||||
>使用常规的非LTS版本,九个月后,用户将不再得到bug修复,无法从Canonical那儿更新软件或操作系统。如果用户选择这样做,那他们只有约三个月来更新系统。
|
||||
>
|
||||
>长期支持来的正是时候,他将找出日益严重的基础软件安全漏洞,如OpenSSL的“心脏出血”安全漏洞[这使无数的Web应用程序容易受到攻击][2].
|
||||
>长期支持版本来的正是时候,它将解决在基础软件中发现的日益严重的安全漏洞,如OpenSSL的“心脏出血”安全漏洞[这使无数的Web应用程序容易受到攻击][2].
|
||||
|
||||
上周,微软停止支持Windows XP操作系统,可能会使数以百万计的用户[遭受攻击][3].
|
||||
上周,微软停止支持Windows XP操作系统,可能会使数以百万计的用户[面临攻击][3].
|
||||
|
||||
Baker说,使用Ubuntu服务器版操作系统的人中大约有百分之70使用LTS版本。
|
||||
Baker说,使用Ubuntu服务器版操作系统的人中大约有百分之七十使用LTS版本。
|
||||
|
||||
Baker说:“在没到合适时间的时候,机构并不想升级,五年是一段很长的时间,这给了他们找到正确迁移路径更多的选择。”
|
||||
|
||||
Baker承认,新版本是相对较轻的新包和功能,主要是由于Canonical公司为使得软件可供长期使用。
|
||||
Baker承认,新版本中相对较少的新包和功能,主要是由于Canonical公司为了使得软件可供长期使用。
|
||||
|
||||
该公司与其他硬件和软件供应商已经做了大量的互操作,如高级微设备,思科和云供应商如亚马逊,Joyent,惠普等等。
|
||||
该公司与其他硬件和软件供应商已经做了大量的沟通,如AMD,思科和云供应商如亚马逊,Joyent,惠普等等。
|
||||
|
||||
该包包括最新的OpenStack云托管软件,称为冰室[定于星期四发布][4].
|
||||
[星期四发布][4]的版本包括了称为冰室的最新的OpenStack云托管软件.
|
||||
|
||||
值得注意的是OpenStack本身只会通过接下来的下两个版本来对每个版本进行支持[一直到现在大约18个月][5].
|
||||
值得注意的是OpenStack本身只会通过接下来的下两个版本来对每个版本进行支持,[从现在开始大约18个月][5].
|
||||
|
||||
这也是Ubuntu 14.04第一次包含Docker,[一个开源的Linux应用容器引擎,支持轻量级运行完整的虚拟机][6]
|
||||
这也是Ubuntu 14.04第一次包含Docker ——[一个开源的Linux应用容器引擎,支持轻量级运行完整的虚拟机][6]
|
||||
|
||||
这也包括XFS第一版,一个最初由SGI(硅图形)公司开发的高性能的64位日志文件系统。Canonical公司的竞争对手Red Hat[计划使用XFS][7]作为小红帽Linux企业版(RHEL)的默认文件系统。
|
||||
还包括了XFS第一版,一个最初由SGI(硅图形)公司开发的高性能的64位日志文件系统。Canonical公司的竞争对手Red Hat[计划使用XFS][7]作为小红帽Linux企业版(RHEL)的默认文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
小红帽Linux企业版中同样包含Docker和OpenStack。
|
||||
|
||||
同样的,Canonical公司的Ubuntu也将更有效的支持固态硬盘(SSDs)。Ubuntu 14.04配备了Linux 3.13 内核,[一月份发布的][8]。Linux 3.13包括一个称为多队列块层的新技术,通过将作业分发到多核提高了SSD磁盘读写性能。
|
||||
同样的,Canonical公司的Ubuntu也将更有效的支持固态硬盘(SSD)。Ubuntu 14.04配备了[一月份发布的][8]Linux 3.13 内核。Linux 3.13包括一个称为多队列块层的新技术,通过将作业分发到多核提高了SSD磁盘读写性能。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.computerworld.com/s/article/9247694/Canonical_39_s_Ubuntu_14.04_focuses_on_the_long_haul?taxonomyId=122
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[tenght](https://github.com/tenght) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[tenght](https://github.com/tenght) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
|
||||
如何通过终端查询字典定义
|
||||
如何在Linux命令行下查询字典?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
大多数人在遇到他们不熟悉的单词时会查询google。或者他们有一个最喜欢的在线字典来提供答案。当你在没有网络连接的时候怎么办?或者你只有一个古老的Linux发行版且你没有GUI界面?你需要离线查找。一个好的方法在这里。
|
||||
大多数人在遇到他们不熟悉的单词时会查询google。或者他们用一个最喜欢的在线字典来提供答案。当你在没有网络连接的时候怎么办?或者你只有一个古老的Linux发行版且你没有GUI界面?你需要离线查找的话,这里有一个好的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
首先你需要本地设置dicted。**Dicted** 是一个字典数据库服务器。它允许你访问在线字典。但是等一下,这是我们希望避免的,对么?一个通过因特网的连接。这是为什么你要在本地设置。这是一个命令行客户端。
|
||||
首先你需要本地设置dictd。**dictd** 是一个字典数据库服务器。它允许你访问在线字典。但是等一下,我们不是要离线使用么?这是为什么我们要将其安装到本地的原因。它带有一个命令行客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
要在Ubuntu或者Debian上安装你要输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install dictd
|
||||
|
||||
这个很简单。现在你需要安装用的字典。安装完每个字典插件后dicted都会自动重启加载它的数据库。让我们来英语字典和英语词库(查询近义词)
|
||||
这个很简单。现在你需要安装用的字典。安装完每个字典插件后dictd都会自动重新加载它的数据库。让我们来安装英语字典和英语同义词词典。
|
||||
|
||||
输入:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,9 +27,9 @@
|
||||
dict-freedict-eng-deu - Dict package for English-German Freedict dictionary
|
||||
dict-freedict-eng-fra - Dict package for English-French Freedict dictionary
|
||||
|
||||
你成功安装完成dicted之后你可以查找定义。
|
||||
现在你已成功安装dictd了,之后你就可以查找字典了。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,让我们检查一下dicted服务是否在运行并且安装了什么数据库:
|
||||
首先,让我们检查一下dictd服务是否在运行并且安装了什么数据库:
|
||||
|
||||
$ dict -I
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,16 +42,16 @@
|
||||
gcide 203645 3859 kB 12 MB 38 MB
|
||||
moby-thesaurus 30263 528 kB 10 MB 28 MB
|
||||
|
||||
为了查询一个你需要的单词定义,你需要使用一个你已经安装的特别字典。让我们检查一下英语(gcid):
|
||||
为了查询一个单词,你可以指定要查询的字典。让我们查询一下English one字典(gcid):
|
||||
|
||||
$ dict -d gcide [word you want to look up]
|
||||
$ dict -d gcide [你要查的单词]
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不使用**-d** 参数,dicted会搜寻所有的已有数据库并返回匹配的定义。
|
||||
如果你不使用**-d** 参数,dictd会搜寻所有的安装字典并返回匹配的结果。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/look-dictionary-definitions-via-terminal/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
76
published/How to close an open DNS resolver.md
Normal file
76
published/How to close an open DNS resolver.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
如何关闭一个开放的DNS解析器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
我们在[之前的教程中][1]创建的DNS服务器是一个开放DNS解析器。开放解析器不会过滤任何来源请求,并会接受来自所有IP的查询、
|
||||
|
||||
不幸的是,开放解析器很容易成为一个攻击目标。比如,攻击者可以对开放DNS服务器发起一个拒绝服务攻击(DoS)或者更糟的分布式拒绝服务攻击(DDoS)。这些也可与IP欺骗结合,将应答包指向受害者被欺骗的IP地址。在另外的场合下称作[DNS放大攻击][2],开放的DNS服务器很容易就会成为攻击的对象。
|
||||
|
||||
根据[openresolverproject.org][3],除非有必要,运行一个开放解析器是不明智的。大多数公司要让它们的DNS服务器仅对他们的客户开放。本篇教程会只要集中于如何配置一个DNS服务器来使它停止开放解析且仅对有效的客户响应。
|
||||
|
||||
### 调整防火墙 ###
|
||||
|
||||
由于DNS运行在UDP的53端口上,系统管理可能试图仅允许来自53端口的客户端IP地址,并阻止剩余的因特网端口。虽然这可以工作,但是也会有一些问题。既然根服务器与DNS服务器的通信也用53端口,我们不得不在防火墙内也确保UDP 53端口被允许。
|
||||
|
||||
一个防火墙示例如下所示。对于生产服务器,确保你的规则匹配你的要求并遵守与公司安全制度。
|
||||
|
||||
# vim firewall-script
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## existing rules are flushed to start with a new set of rules ##
|
||||
iptables -F
|
||||
|
||||
iptables -A INPUT -s A.A.A.A/X -p udp --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
iptables -A INPUT -s B.B.B.B/Y -p udp --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
iptables -A INPUT -s C.C.C.C/Z -p udp --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
|
||||
iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 53 -j DROP
|
||||
|
||||
## making the rules persistent ##
|
||||
service iptables save
|
||||
|
||||
让脚本可执行并运行它。
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod +x firewall-script
|
||||
# ./firewall-script
|
||||
|
||||
### 阻止递归查询 ###
|
||||
|
||||
DNS查询主要可以[分为][4]递归查询和迭代查询。对于递归查询,服务器会响应客户端应答或者错误信息。如果应答不在服务器的缓存中,服务器会与根服务器通信并获得授权域名服务器。服务器会不停查询知道获得结果,或者请求超时。对于迭代查询,另一个方面讲,服务器会将客户端指向另外一个可能可以处理的服务器上,那么就会减少服务器自身的处理。
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以控制运行递归查询的IP地址。我们修改位于/etc/named.conf的配置文件并增加/修改下面的参数。
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/named.conf
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## we define ACLs to specify the source address/es ##
|
||||
acl customer-a{ A.A.A.A/X; };
|
||||
acl customer-b { B.B.B.B/Y; C.C.C.C/Z; };
|
||||
|
||||
## we call the ACLs under options directive ##
|
||||
options {
|
||||
directory "/var/named";
|
||||
allow-recursion { customer-a; customer-b; };
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
### 调整用于开放解析器的防火墙 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你必须运行一个开放解析器,建议你适当调节一下你的服务器,这样就不会被利用了。[smurfmonitor 仓库][5]提供了强大的一组可以用于开放解析器的iptables规则,比如阻止来自DNS放大攻击的域名解析请求。这个仓库会定期地更新,强烈建议DNS服务器管理员使用它。
|
||||
|
||||
总的来说,对于开放DNS解析器的攻击是很常见的,特别是对于没有适当安全防护的DNS服务器而言。这个教程延时了如何禁止一个开放DNS服务器。我们同样看到了如何使用iptables在一个开放DNS服务器上加上一层安全防护。
|
||||
|
||||
希望这对你有用。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/04/close-open-dns-resolver.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2014/04/primary-dns-server-using-centos.html
|
||||
[2]:https://www.us-cert.gov/ncas/alerts/TA13-088A
|
||||
[3]:http://openresolverproject.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc961401.aspx
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/smurfmonitor/dns-iptables-rules
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
Linux基金会发布了2014年全部活动安排
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux基金会改变了原有的活动计划模式,而是公布了一整年的所有活动安排。与此同时还发布了一部视频,可以在这里在线观看:[Linux基金会活动体验][1]。下面介绍一下今年的基金会活动重点关注方向的更多细节。
|
||||
Linux基金会改变了原有的活动计划模式,提前公布了一整年的所有活动安排。与此同时还发布了一部视频,可以在这里在线观看:[Linux基金会活动体验][1]。下面介绍一下今年的基金会活动重点关注方向的更多细节。
|
||||
|
||||
2014年活动安排,包括了北美和欧洲的LinuxCon和CloudOpen,以及Linux Foundation Collaboration Summit,Embedded Linux Conference,Android Builders Summit,和ApacheCon等等。今年北美的LinuxCon和CloudOpen会在芝加哥和Linux Kernel Summit一起合作举行。欧洲的Linux Con和CloudOpen会在德国的杜塞尔多夫举行,一起的还有Embedded Linux Conference, KVM Forum以及Linux Plumbers Conference。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -88,7 +88,7 @@ CloudOpen聚集了驱动云服务以及大数据生态环境的开源项目,
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/the-linux-foundation-delivers-complete-2014-event-schedule
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ Linux软件商店的困境
|
||||
|
||||
尽管在Linux桌面环境有很多"其他"可用的软件商店,但实际上没有哪个像Ubuntu软件中心那样支持付费应用。而我看到的唯一一个像Ubuntu软件中心那样可以在Linux桌面下发布付费应用的是Valve公司的[Steam][3]数字软件管理器,作为发行付费Linux游戏的商店而闻名。我发现Steam已经用来在其他平台[发行软件][4],所以我认为,Steam也完全可以为Linxu用户发行付费软件。
|
||||
|
||||
不像其他软件发布工具,Steam专门设计了比其他Linux替代方案更为清晰的付费处理方式。而且,Steam用一种奇妙的光线来展示游戏和软件的名字,所以,用户在浏览这些名字的时候能够选中适合自己需求的应用。
|
||||
不像其他软件发布工具,Steam专门设计了比其他Linux替代方案更为清晰的付费处理方式。而且,Steam用一种炫目的方式来展示游戏和软件的名字,所以,用户在浏览这些名字的时候能够选中适合自己需求的应用。
|
||||
|
||||
我并没有建议把Steam当作搜索开源软件的最佳替代方案,我坚决反对这种想法。我的建议是,Steam可以成为一个专门处理拥有专利的应用或游戏软件的跨发行版的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ Linux软件商店的困境
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/the-linux-software-store-conundrum-1.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 14.04服务器版提供了虚拟化、自动化、存储相关更新
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 这次发布的Ubuntu 14.04,代号Trusty Tahr(值得信赖的塔尔羊),将会给服务器版用户带来新的自动化,虚拟化和存储相关特性。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Ubuntu 14.04][1], 是由[Canonical][2]推出的基于Linux的开源操作系统最新版本,没有为PC和移动用户带来太大改动,对他们来说仅仅是较少的更新。而对服务器用户,这次最新的最重大的Ubuntu版本更新带来了更多功能,特别在自动化,云计算,以及虚拟化等方面。
|
||||
|
||||
对桌面和移动用户来说,这次即将在4月17日正式露面的Ubuntu14.04的最重大的改动是,**它带来了AppArmor安全系统的更新**。这个在桌面/移动版本中最重要的新特性,是一个运行在后台的内核强化包,那些在个人电脑,手机或者平板上使用Ubuntu的人们在Ubuntu 14.04版本中也许根本感觉不到什么大的改动。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,在服务器世界里,最新版的Ubuntu带来了更实质性的改动。特别是,**它将[Puppet][3]升级到了第3版**,Puppet是一个用来自动化IT基础设施管理的开源平台。这是个重要的更新,能够为部署大型Ubuntu服务器网络的人们带来便利(不过是在他们解决好Puppet早期版本和最新版之间的兼容性问题之后,新旧版本之间并不互相完全兼容)。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 14.04还将带来开源的**虚拟化管理程序[Xen][6]的4.4版本**。这次改动,对于旧版的Xen部署环境也需要做一些必要的调整,才可以切换到新版本上。不过,它提供了更多的新特性,而且可以协助管理Ubuntu服务器上虚拟环境的多样性,包括众多的虚拟化管理程序,[VMware][4] (VMW),[KVM][5],Xen等等。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,Ubuntu 14.04的内核基于[Linux][7] 3.13,也带来了比如更好的固态硬盘(SSD)性能等[新特性][8]。这也是很受服务器用户欢迎的,特别是那些在云和大数据领域里对性能有很高要求的用户。
|
||||
|
||||
这次的Ubuntu 14.04是一个[长期支持][9](LTS)版本,这也是服务器用户最有可能长期使用于生产环境的版本,而非LTS版本对于实际生产环境来说没有任何意义。尽管Canonical持续地集中精力于在PC和移动设备上"[统一][10]"的努力,这次Ubuntu带来的自动化,虚拟化和存储软件的更新在合适的时间点推出,有利于维持Ubuntu在服务器市场的竞争力。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/servers/041514/ubuntu-1404-server-brings-virtualization-automation-storage-updates
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/14.04/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.canonical.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://puppetlabs.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://vmware.com/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.linux-kvm.org/
|
||||
[6]:http://xen.org/
|
||||
[7]:http://kernel.org/
|
||||
[8]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/linux-kernel-updates-add-features-mobile-cloud-big-data
|
||||
[9]:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/LTS
|
||||
[10]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/can-canonical-rally-its-community-ubuntu-convergence
|
||||
@ -1,18 +1,19 @@
|
||||
Xperience UI 设计理念 —— 优雅的 Linux 桌面设计欣赏
|
||||
Xperience UI 设计理念:优雅的 Linux 桌面设计欣赏
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Xperience UI 是一个基于 Nitrux 发行板的一个界面设计的概念作品,如果其开发能够完成,它将有可能成为当今最漂亮的桌面之一。**
|
||||
|
||||
即使有些人很会折腾并使他们的桌面看起来更帅些,大多数 Linux 桌面仍可以轻易的被社区中的其他成员识别。
|
||||
即使有些人很会折腾并使他们的桌面装扮得更帅些,但是大多数 Linux 桌面仍可以轻易的被社区里面的人们认出来。
|
||||
如今折腾的人有福利了,Nitrux Xperience UI 带来了相当华丽的设计理念。
|
||||
|
||||
Nitrux 的开发者们之前最为他们的图标及一些其他设计而闻名,而如今这款桌面的界面设计质量几乎可以与现今我们能找到的任何的顶级设计相媲美。
|
||||
Nitrux 的开发者们之前因其图标及一些其他设计而闻名,而如今这款桌面的界面设计质量几乎可以与现今我们能找到的任何的顶级设计相媲美。
|
||||
|
||||
这些设计或许会让大家想起一些来自 Elementary OS 的元素,但同时她也有着非常严谨而独特的风格。
|
||||
即使这些细节很难被观察到,我们仍可以从通知区域、锁屏、或是主面板感受到设计者对其的精雕细琢。
|
||||
|
||||
这些设计理念虽然看起来很倾向于触屏设备,她仍然可以完美的融入到一个桌面系统中。
|
||||
|
||||
也许我们只能寄予期望给今后的某个 Nitrus 麾下的发行板可以采用这个设计了。
|
||||
|
||||
即使今后没人会实现这个设计(虽然我们很大把握有人会去折腾),这个设计仍然证明了 Linux 的设计也可以从头到脚都远远超出所有其他的操作系统。
|
||||
@ -49,6 +50,6 @@ Mini 启动面板 - 关机
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Xperience-UI-Concept-Could-Be-the-Most-Beautiful-Linux-Desktop-430087.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[VizV](https://github.com/vizv) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[VizV](https://github.com/vizv) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
zpl1025
|
||||
Embedded tech and use of Linux at the 2014 GPU Technology Conference
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
@ -32,4 +33,4 @@ via: http://opensource.com/life/14/4/gpu-technology-conference-2014
|
||||
[4]:http://www.nvidia.com/object/jetson-tk1-embedded-dev-kit.html
|
||||
[5]:http://steamcommunity.com/linux
|
||||
[6]:http://www.slideshare.net/CassEveritt/approaching-zero-driver-overhead
|
||||
[7]:http://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2014/03/27/researchers-win-third-annual-cuda-achievement-award-three-new-cuda-fellows-named/
|
||||
[7]:http://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2014/03/27/researchers-win-third-annual-cuda-achievement-award-three-new-cuda-fellows-named/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
zpl1025
|
||||
Ubuntu 14.04 Server Brings Virtualization, Automation, Storage Updates
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> The 14.04 release of Ubuntu Linux, code-named Trusty Tahr, will bring new automation, virtualization and storage features to Ubuntu server users.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Ubuntu 14.04][1], the newest edition of [Canonical's][2] open source Linux-based OS, will not make huge waves among PC and mobile users, for whom it brings only minor software updates. For server users, however, the latest and greatest Ubuntu release delivers more, particularly in the realms of automation, cloud computing and virtualization.
|
||||
|
||||
For desktop and mobile users, the most significant change in the upcoming release of Ubuntu 14.04, which will debut officially April 17, involves updates to the AppArmor security system. And if the biggest-ticket item on the desktop/mobile feature list is for a kernel-hardening package that runs in the background, people who use Ubuntu on their personal computers, phones and tablets aren't likely to see much change at all in Ubuntu 14.04.
|
||||
|
||||
In the server world, however, the latest Ubuntu brings more substantial change. In particular, it bumps [Puppet][3], an open source platform for automating IT infrastructure management, to version 3. That's a major update, which could come in handy for people deploying large environments of Ubuntu servers (after they sort out the incompatibilities between earlier Puppet iterations and the new version, which are not completely mutually compatibile).
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 14.04 also will feature version 4.4 of the open source [Xen][6] virtualization hypervisor. That change, too, necessitates some tweaking to bring previous Xen deployments up to speed with the new package, but it also provides additional features and helps maintain the diversity of the virtualization ecosystem on Ubuntu servers, which offer a range of hypervisors, including [VMware][4] (VMW) and [KVM][5] in addition to Xen and others.
|
||||
|
||||
On top of all of this, Ubuntu 14.04's kernel is based on [Linux][7] 3.13, which itself [brings feature updates][8] inlcuding better solid-state (SSD) disk performance. That update, too, will be welcome among server users, especially those in need of high performance in the cloud and Big Data realms.
|
||||
|
||||
Since Ubuntu 14.04 is a [long-term support][9] (LTS) release, it's one that server users, in particular, are likely to stick with for long periods within production environments, where the shorter support life spans of non-LTS releases make little sense. The updates to the automation, virtualization and storage software available on Ubuntu are therefore coming at the right moment to help keep Ubuntu competitive in the server market, even as Canonical increasingly focuses on PCs and mobile devices within the scope of its Ubuntu "[convergence][10]" efforts.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/servers/041514/ubuntu-1404-server-brings-virtualization-automation-storage-updates
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/14.04/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.canonical.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://puppetlabs.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://vmware.com/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.linux-kvm.org/
|
||||
[6]:http://xen.org/
|
||||
[7]:http://kernel.org/
|
||||
[8]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/linux-kernel-updates-add-features-mobile-cloud-big-data
|
||||
[9]:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/LTS
|
||||
[10]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/can-canonical-rally-its-community-ubuntu-convergence
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
10 Linux Platforms Meant For Embedded Systems
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux has a wide variety of uses. The platform is used by many for simple home use, while it is also the chosen platform for programmers and hackers. In addition, Linux is widely used in embedded systems and there are distributions that are tailored specifically to such systems. Here are 10 Linux platforms that can work great on embedded systems!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 1. [Ampro Embedded Linux][1] ###
|
||||
|
||||
This is a free and open source reduced footprint operating system that has been derived from Ubuntu packages.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. [BlueCat Linux from Lynx][2] ###
|
||||
|
||||
This Linux-based distribution is a part of the Lynx suite and is meant for embedded systems.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. [CacheGuard OS][3] ###
|
||||
|
||||
CacheGuard OS is an integrated Security solution based on a custom-hardened version of Linux built from scratch and specially designed to manage Web traffic.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. [Darma NAS OS][4] ###
|
||||
|
||||
This distribution has an SSL-based encrypted client server and a Java-based graphical user interface.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. [DIET-PC][5] ###
|
||||
|
||||
This is an open source thin client software kitset that allows users to build network appliances.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. [ELinOS][6] ###
|
||||
|
||||
This distribution provides a number of technologies for users working on embedded systems. It is a pretty popular Linux platform for these systems.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. [eLux][7] ###
|
||||
|
||||
This one has a pretty simple and easy-to-use interface and offers the unique situation where neither the client nor the administrator needs to have any knowledge in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. [eLux NG][8] ###
|
||||
|
||||
This one adds new models to the list of supported processors for eLux.
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. [Embedded Coyote Linux][9] ###
|
||||
|
||||
This Firewall and VPN server-based on Coyote Linux has been the platform of choice for many.
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. [Embedded Debian Project][10] ###
|
||||
|
||||
This project aims to make the Debian GNU/Linux the first choice for embedded systems.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=137612
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ampro.com/company/News/04_08_08_Ampro_Reveals_Ubuntu_Embedded_Linux.htm
|
||||
[2]:http://www.lynuxworks.com/embedded-linux/embedded-linux-virtualization.php
|
||||
[3]:http://www.cacheguard.com/cacheguard-os.html
|
||||
[4]:http://nas.darma.com/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.dietpc.org/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.sysgo.com/products/elinos-embedded-linux/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.myelux.com/index.htm?Unicon_Session=32bf53f198c94ba2ac2ce1ea45211754
|
||||
[8]:http://www.myelux.com/eluxng.htm
|
||||
[9]:http://www.myelux.com/eluxng.htm
|
||||
[10]:http://www.emdebian.org/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
||||
Open Source's Cult Of Personality Is Dying—Thankfully
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Roy Rubin, co-founder of the popular [Magento][1] open-source project, [announced this week][2] he is bowing out of the project he helped launch back in 2008.
|
||||
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
It's not the first time the leader of an open-source project has stepped away from her project, but it's remarkable by its response: Relative silence.
|
||||
|
||||
It's not because Rubin wasn't critical to Magento. He was. For six years, Rubin was the soul of Magento. But open source has grown up, and it's increasingly shedding its cult of personality. While no one wishes Linux founder Linus Torvalds gets hit by a bus, we're to the point that we, [like Linus][3], "won't care."
|
||||
|
||||
But it wasn't always this way.
|
||||
|
||||
### Worshipping The Benevolent Dictator ###
|
||||
|
||||
Successful open-source projects have long been associated with strong leaders, and for good reason. Influencing a vibrant community of individually-minded developers can be the equivalent of herding cats. While differences of opinion on the direction a particular open-source project can turn into a parting of ways (and code, called a "fork"), more often than not a "benevolent dictator for life," or project leader, will step in, exert leadership and keep the community together.
|
||||
|
||||
The term "benevolent dictator for life" (BDFL) [may have started with Guido von Rossum][4], the former Python development lead. It has since been applied to Linus Torvalds, the creator of Linux, as well as Mark Shuttleworth, Ubuntu's lead, among others. Sometimes two leaders on a project share the title, as did Adrian Holovaty and Jacob Kaplan-Moss for [Django][5].
|
||||
|
||||
At their peak, the departure of any one of these leads would have wreaked havoc on the fortunes of the project, given how closely identified the projects were with these strong leaders. Over time, however, this has changed. The Django BDFLs [moved on to other projects][6], and Django kept chugging along. Ditto Python, Lucene (Doug Cutting), JBoss (Marc Fleury) and many other projects.
|
||||
|
||||
While open source communities still rally around strong leaders, we don't seem to be as dependent on them as we once were. Open source's "cult of personality" faded, and perhaps has died altogether. But what happened?
|
||||
|
||||
### Apache And The Rise Of Community ###
|
||||
|
||||
Well, community did, for starters. I realize I'm making a somewhat subjective assertion here, but over the roughly 15 years I've been involved in open source, I've seen a gradual shift away from tightly-controlled free software projects to more loosely joined open-source communities, often with significant corporate interest.
|
||||
|
||||
While it's not clear whether the open, BSD/Apache-style licensing "chicken" came before the corporate open source interest "egg," the two together have definitely changed how open source operates.
|
||||
|
||||
This includes the need for a BDFL. For example, and while it's not a project, it's hard to imagine Free GNU without Richard Stallman. By contrast, it's pretty easy to imagine Apache Hadoop without... wait, who is in charge of Hadoop, anyway?
|
||||
|
||||
The answer? Everyone. Or [many][7], rather. It started with Doug Cutting, but it has since grown to become a community of companies and individuals (but mostly companies that employ those individuals) working together.
|
||||
|
||||
The same is true of OpenStack, which has a [host of companies involved][8]. If any particular OpenStack developer were to leave, the OpenStack show would go on. And it has thus far. The same is true of an increasing number of open-source projects.
|
||||
|
||||
### A BDFL-Free Future? ###
|
||||
|
||||
This isn't to suggest that leaders aren't needed in open source. They are. But as more open-source projects become communities of corporations, the risk of a BDFL leaving diminishes. Frankly, even if companies aren't heavily involved, projects with an Apache license may not be as dependent on a BDFL, anyway.
|
||||
|
||||
Photo of Richard Stallman [courtesy of Friprog on Flickr][9]
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://readwrite.com/2014/05/02/open-source-magento-roy-rubin-bdfl#feed=/hack&awesm=~oDgSTEdnXAjUv0
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://magento.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://magento.com/blog/magento-news/note-roy-and-mark#.U2JhPK1dVii
|
||||
[3]:http://www.serverwatch.com/server-news/if-linus-torvalds-got-hit-by-a-bus-would-linux-die.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.artima.com/weblogs/viewpost.jsp?thread=235725
|
||||
[5]:https://www.djangoproject.com/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2014/01/on-the-reign-of-benevolent-dictators-for-life-in-software/283139/
|
||||
[7]:http://hadoop.apache.org/who.html
|
||||
[8]:http://activity.openstack.org/dash/releases/
|
||||
[9]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/friprog/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
Translating by yujianxuechuan
|
||||
Raspberry Pi's Eben Upton: How We're Turning Everyone Into DIY Hackers
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Inside the mind that prototyped a $35 computer for tinkerers.
|
||||
@ -186,4 +187,4 @@ via: http://readwrite.com/2014/04/08/raspberry-pi-eben-upton-builders#awesm=~oBG
|
||||
[6]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/osde-info/8626662243
|
||||
[7]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/p8/7950485168
|
||||
[8]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/sbardella/7473604878
|
||||
[9]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/28438417@N08/8006786385/in/photolist-dcwSD8-d8PKa3-bmosVm-bmosWG-bz3YJF-e8NRQD-btyqN1-dorXrE-hTF7id-hTF7jL-hTF4mJ-hTF4jj-hTF4q1-hTF7jA-hTF7gj-gKRLrn-ftALdo-c7Qnjs-c7Qnyh-c7QmZj-c7QnY1-c7QmNY-cu8zs3-cu8BWm-cu8u5S-cu8yC3-cu8DBN-cu8wRq-cu8xNL-cu8CJj-cu8tss-cu8BcG-cu8uVL-cu8AoW-hTF7dU-hTEzCr-hTFBCp-hTFBvR-hTFBBH-hTF4hA-hTF7c1-hTEzza-hTFBM2-cdtf1b-bz7n87-gKQSJ7-gKQUko-ds8x8q-dqweVP-cVwvJq
|
||||
[9]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/28438417@N08/8006786385/in/photolist-dcwSD8-d8PKa3-bmosVm-bmosWG-bz3YJF-e8NRQD-btyqN1-dorXrE-hTF7id-hTF7jL-hTF4mJ-hTF4jj-hTF4q1-hTF7jA-hTF7gj-gKRLrn-ftALdo-c7Qnjs-c7Qnyh-c7QmZj-c7QnY1-c7QmNY-cu8zs3-cu8BWm-cu8u5S-cu8yC3-cu8DBN-cu8wRq-cu8xNL-cu8CJj-cu8tss-cu8BcG-cu8uVL-cu8AoW-hTF7dU-hTEzCr-hTFBCp-hTFBvR-hTFBBH-hTF4hA-hTF7c1-hTEzza-hTFBM2-cdtf1b-bz7n87-gKQSJ7-gKQUko-ds8x8q-dqweVP-cVwvJq
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu Fixes Security Flaw in 14.04 LTS Lock Screen
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Canonical has patched a significant security flaw in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS — one that potentially allowed attackers to gain access to a user account without needing to enter a password. **
|
||||
|
||||
The ‘[lock screen bypass][1]‘ issue, for which a fix [has now been released][2], was reported on Launchpad earlier this week.
|
||||
|
||||
In it, it describes a method through which user accounts ‘locked’ using the new Unity lock screen could be accessed without authorisation.
|
||||
|
||||
How? By right-clicking on the indicator applets until the Alt+F2 keyboard shortcut worked. From here, a would-be chancer could issue commands, open apps, access date, and even unlock the session by running the ‘**compiz –replace**‘ command.
|
||||
|
||||
A video demo of the loophole [can be viewed on YouTube][3].
|
||||
|
||||
The hack was limited to exploit by someone with local access and could not be run remotely.
|
||||
|
||||
### Other Lockscreen Issues Patched ###
|
||||
|
||||
The new lock screen, for all its glitter, has been keeping Canonical’s security team busy. The Bypass issue has not been the only flaw to have been discovered.
|
||||
|
||||
Just days before Ubuntu 14.04 LTS was due to be released, [another critical security issue][4], one which could force a computer to unlock by triggering any readily reproducible crash at the lock screen, was (as in this case, very quickly) fixed. Another shortcut-based loophole is [currently in the process of being fixed][5].
|
||||
|
||||
### Secure ###
|
||||
|
||||
With Ubuntu LTS releases favoured by many businesses, education institutions and enterprise the issues could have proven bad news. But, if anything, these issue have underline just how prompt Canonical is in responding to and fixing issues — which is hugely reassuring.
|
||||
|
||||
It also underlines just how astute the company has been in deciding to only prompt current LTS users to upgrade to 14.04 LTS as of July, when the first point release lands. This extra buffer period of three month gives the Ubuntu community and its super-hero pantheon of developers more time in which to detect and fix security issues such as these.
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re running Ubuntu 14.04 LTS remember to check for and install updates often.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/04/ubuntu-fixes-security-flaw-trusty-login-screen
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/unity/+bug/1313885
|
||||
[2]:https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/trusty/+source/unity/7.2.0+14.04.20140423-0ubuntu1.1
|
||||
[3]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d4UUB0sI5Fc
|
||||
[4]:https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/unity/+bug/1308572
|
||||
[5]:https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/trusty/+source/unity/+bug/1314247
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
How to Install Windows 8.1 and Ubuntu 14.04 LTS on the Same Computer
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Numerous Windows users are looking to also try a Linux operating system without deleting the one they are already using. They will be happy to know that this can be done quite easily and that Linux OSes are usually more friendly towards other operating systems that share the same computer.**
|
||||
|
||||
If you are a Windows user and you want to give Ubuntu a go, for example, the procedure is actually quite simple and involves very little effort from the user, who only has to pay a little attention to the procedures.
|
||||
|
||||
A normal installation of a new operating system on a PC is not complicated, not even with Linux and Ubuntu. For the most part, users only click next in the dialogs and everything is taken care of by the scripts. When you want to preserve an operating system that is also present on the same PC (it doesn't have to be a Windows one specifically), a little more work is required, but that can be handled very easily.
|
||||
|
||||
Writing an Ubuntu image from Linux is easy and it can be done with a number of applications. On Windows you will need to get Ubuntu either on a DVD or on a USB (which is preferable). In order to get Ubuntu properly copied to a USB device, you will need to download a handy little tool called [Win32 Disk Imager 0.9.5][1]. It features a simple interface and it's fully automated.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, before rebooting to get Ubuntu installed, you might want to set some free space aside that will be available for Ubuntu, but a partition will not be enough. You will need two of them, one for Ubuntu itself (10GB should suffice if you don't plan to get too many applications) and a second partition for the Swap (the pagefile equivalent for Windows), which has to be double the amount of you RAM memory. You don't need to format them, just make sure they are free. If you install Ubuntu on a second HDD, that's even better.
|
||||
|
||||
Plug the USB in and reboot. You will get a prompt to Try or Install. Choose Install and read the options you are given: Install Ubuntu Alongside Windows 8 (or whatever version you have), Replace Windows 8 with Ubuntu, or Something Else.
|
||||
|
||||
You can choose to install alongside Windows 8, but you might not like what the installer will choose for you. It's better to hit Something Else and install it manually.
|
||||
|
||||
Spot the free partition that you set aside for Ubuntu (the installer doesn't read volume names from Windows), double click on it, select EXT4 as the filesystem, and “/” as the default mount point.
|
||||
|
||||
Now select the smaller partition and choose SWAP as the filesystem. That is all. Once you hit Next, the installation will start and you will have to choose the name, password, and other such details.
|
||||
|
||||
The next time you boot you will get a simple list of operating systems that will allow you to choose whichever OS you prefer.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Install-Windows-8-1-and-Ubuntu-14-04-LTS-on-the-Same-Computer-440356.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.softpedia.com/get/CD-DVD-Tools/Data-CD-DVD-Burning/Win32-Disk-Imager.shtml
|
||||
@ -1,76 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to close an open DNS resolver
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The DNS server that we have created in the [previous tutorial][1] is an open DNS resolver. An open resolver does not filter any incoming requests, and accepts queries from any source IP address.
|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately, an open resolver can become an easy target to attackers. For example, attackers can initiate a Denial of Service (DoS) or even worse, a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack on the open DNS server. These attacks can also be combined with IP spoofing, where all the reply packets will be directed to a victim’s spoofed IP address. In another attack scenario called [DNS amplification attacks][2], an open DNS server can actively participate in the attacks.
|
||||
|
||||
According to [openresolverproject.org][3], it is not advisable to run an open resolver unless necessary. Most companies keep their DNS servers accessible to only their customers. This tutorial will focus on how to configure a DNS server so that it stops being an open resolver and responds only to valid customers.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tuning Firewall ###
|
||||
|
||||
As DNS runs on UDP port 53, system admins may attempt to allow port 53 for client IP addresses only, and block the port from the rest of the Internet. Though this will work, there are going to be some problems. Since the communication between the root servers and the DNS servers use port 53 as well, we have to make sure that the IP addresses of the root servers are also allowed on UDP port 53 in the firewall.
|
||||
|
||||
A sample firewall script is provided below. For production servers, make sure that the rules match your requirements and also comply with company security policies.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim firewall-script
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## existing rules are flushed to start with a new set of rules ##
|
||||
iptables -F
|
||||
|
||||
iptables -A INPUT -s A.A.A.A/X -p udp --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
iptables -A INPUT -s B.B.B.B/Y -p udp --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
iptables -A INPUT -s C.C.C.C/Z -p udp --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
|
||||
iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 53 -j DROP
|
||||
|
||||
## making the rules persistent ##
|
||||
service iptables save
|
||||
|
||||
Make the script executable and run it.
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod +x firewall-script
|
||||
# ./firewall-script
|
||||
|
||||
### Blocking Recursive Queries ###
|
||||
|
||||
DNS queries can be primarily [categorized][4] as recursive and iterative queries. For a recursive query, the server responds to the client with either the answer or an error message. If the answer is not available in the server cache, the server communicates with the root servers to obtain authoritative name servers. The servers keeps looking up until it gets an answer, or until the query times out. For an iterative query, on the other hand, the server simply refers the client to another server who would be able to process, thus leading to less processing on the server itself.
|
||||
|
||||
We can control the IP addresses that are allowed for recursive queries. We modify the configuration file /etc/named.conf and add/modify the following parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/named.conf
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## we define ACLs to specify the source address/es ##
|
||||
acl customer-a{ A.A.A.A/X; };
|
||||
acl customer-b { B.B.B.B/Y; C.C.C.C/Z; };
|
||||
|
||||
## we call the ACLs under options directive ##
|
||||
options {
|
||||
directory "/var/named";
|
||||
allow-recursion { customer-a; customer-b; };
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
### Tuning Firewall for Open Resolver ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you must run an open resolver, it is recommended that you tune the firewall properly so that your server cannot be exploited. [smurfmonitor repository][5] provides a powerful set of iptables rules that can be used in open resolvers, such as blocking requests for domains involved in DNS amplification attacks. The repository is updated periodically, and it is highly recommended for DNS server admins.
|
||||
|
||||
To sum up, attacks on open DNS resolvers are common, especially for DNS servers without proper security. This tutorial demonstrated how to disable an open DNS server. We have also seen how iptables can be used to add an additional layer of security to an open DNS server.
|
||||
|
||||
Hope this helps.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/04/close-open-dns-resolver.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2014/04/primary-dns-server-using-centos.html
|
||||
[2]:https://www.us-cert.gov/ncas/alerts/TA13-088A
|
||||
[3]:http://openresolverproject.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc961401.aspx
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/smurfmonitor/dns-iptables-rules
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,114 @@
|
||||
How to manage Linux containers with Docker on Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
While full hardware virtualization such as KVM, Xen or Hyper-V is great at running fully isolated instances of multiple operating systems on a physical host, it comes with various overheads in terms of performance, resource, and provisioning time. Depending on your use cases, full machine virtuailization may actually not be necessary.
|
||||
|
||||
An alternative lightweight virtualization approach is so-called [Linux Containers][1] (LXC), which provides operating system level virtualization. Without the overhead of running virtual machines, LXC allows you to run multiple instances of full Linux operating system within lightweight container sandbox. Containers can be very useful when you set up a reproducible development/test environment or deploy applications within secure sandboxes.
|
||||
|
||||
[Docker][2] is an open-source tool which was developed to facilitate the deployment of Linux containers. Docker is fast becoming a de-facto standard for container technologies, being embraced in major Linux distros such as [Ubuntu][3] and [Red Hat][4].
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I am going to demonstrate how to manage Linux containers with Docker on Ubuntu 14.04. Note that instructions may be slightly different for earlier versions of Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
At this time, the Docker package available on Ubuntu only supports 64-bit systems. To run it on 32-bit machine, you will need to [build 32-bit version of Docker from source][5].
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Docker ###
|
||||
|
||||
Installing Docker is easy with apt-get command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install docker.io
|
||||
|
||||
To allow non-root user to run Docker, add yourself to docker group. The command below will allow the current user to run Docker without root permission.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo usermod -a -G docker $USER
|
||||
|
||||
Log out and then re-login to activate group membership change.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, edit the Docker configuration file to update the location of the Docker binary.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/default/docker.io
|
||||
|
||||
> DOCKER="/usr/bin/docker.io"
|
||||
|
||||
Restart Docker service.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service docker.io restart
|
||||
|
||||
### Manage Docker Containers ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to start a new Docker container of Ubuntu operating system, first pull [Ubuntu][6] Docker image first. The command below will download Docker image over a network.
|
||||
|
||||
$ docker pull ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
You can start a Ubuntu Docker in an interactive mode as follows. The last argument "/bin/bash" is the command that will be executed inside a container once it is launched, in this case, a simple bash shell.
|
||||
|
||||
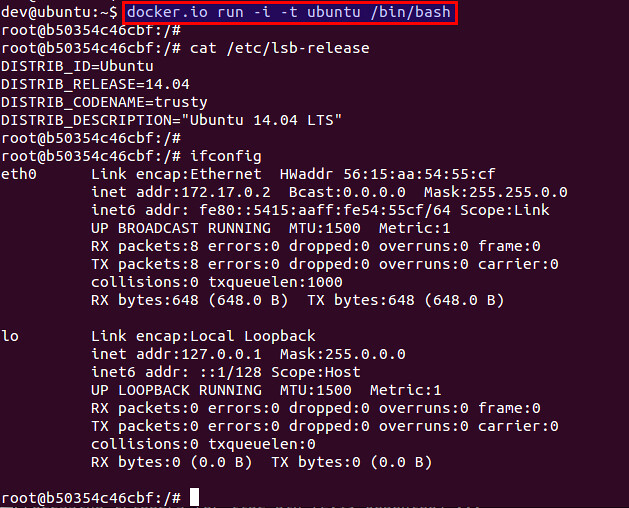
$ docker run -i -t ubuntu /bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will launch a Ubuntu container immediately (which is the beauty of containers!), and give you a shell prompt inside the container. At this point, you should be able to access a full Ubuntu operating system inside a sandboxed environment.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To exit a Docker container, type "exit" at the prompt inside the container.
|
||||
|
||||
You can launch containers in different flavors. For example, to start a Fedora container:
|
||||
|
||||
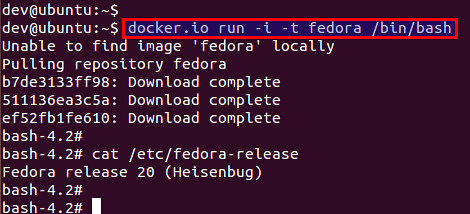
$ docker.io run -i -t fedora /bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
If a Fedora Docker image is not available locally, the command will automatically download the image first, and then launch a Docker.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to launch a container with a particular distro release, you can also do that. For example, to start a Ubuntu 13.04 Docker:
|
||||
|
||||
$ docker.io run -i -t ubuntu:13.04 /bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
### Container Networking ###
|
||||
|
||||
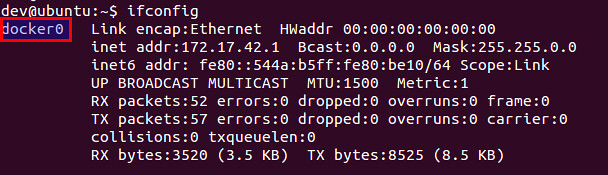
Docker uses Linux bridge to interconnect containers with each other, and to connect them to external networks. After installing Docker, you should see docker0 Linux bridge created automatically by default. Every container you create will be connected to docker0 bridge interface.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Custom Linux Bridge ####
|
||||
|
||||
If you want, you can use a custom Linux bridge to interconnect containers. For that, you can create a custom bridge and configure it as follows. You can assign a separate subnet to the bridge, and have Dockers assigned IP addresses from the subnet. I am going to use 10.0.0.0/24 as a Docker subnet.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install bridge-utils
|
||||
$ sudo brctl addbr br0
|
||||
$ sudo ifconfig br0 10.0.0.1 netmask 255.255.255.0
|
||||
|
||||
To make the custom bridge used by Docker, add "-b=br0" to DOCKER_OPTS variable in /etc/default/docker.io, and restart Docker service.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service docker.io restart
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, any new container will be connected to br0, and its IP address will automatically be assigned from 10.0.0.0/24.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Other Customizations ####
|
||||
|
||||
There are several other ways to customize the default network settings of Docker, mostly by tweaking DOCKER_OPTS variable in /etc/default/docker.io.
|
||||
|
||||
- "-dns 8.8.8.8 -dns 8.8.4.4": specify the DNS servers used by a container.
|
||||
- "-icc=false": make containers isolated from each other.
|
||||
|
||||
### Troubleshooting ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. You encounter the following error when running docker.io command.
|
||||
|
||||
> dial unix /var/run/docker.sock: no such file or directory
|
||||
|
||||
The error may be because Docker daemon is not running. Check the status of Docker daemon, and make sure to start it first.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service docker.io status
|
||||
$ sudo service docker.io start
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/manage-linux-containers-docker-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://linuxcontainers.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.docker.io/
|
||||
[3]:http://blog.docker.io/2014/04/docker-in-ubuntu-ubuntu-in-docker/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.redhat.com/about/news/press-archive/2014/4/red-hat-docker-expand-collaboration
|
||||
[5]:http://mwhiteley.com/linux-containers/2013/08/31/docker-on-i386.html
|
||||
[6]:http://xmodulo.com/go/ubuntubook
|
||||
@ -1,157 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to manage your music library from the command line on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The command line in Linux is probably one of the scariest experience for a newcomer there is. I remember spending hours back in the day trying to decode an error message in my terminal. However, it was completely worth it. If I had to pick only one reason for a newcomer to learn to deal with the command line properly today, it would probably be for the possibility to manage a music library entirely from the terminal. The software I prefer to do this is [cmus][1], short for "C* MUsic Player" as it is written entirely in C.
|
||||
|
||||
cmus is a powerful music file manager with a built-in audio player. Using its ncurses based terminal interface, you can browse your music library, and play music from playlists or queues, all from the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install cmus on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
First, you will need to set up and install cmus as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
On Ubuntu, Debian or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install cmus
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora, first [enable RPM Fusion repository][2], and then run:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install cmus
|
||||
|
||||
On CentOS, first [enable Repoforge repository][3], and then run:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install cmus
|
||||
|
||||
On Archlinux:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo pacman -S cmus
|
||||
|
||||
After installation, you can launch cmus simply by typing:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cmus
|
||||
|
||||
### Import [Music Files][4] to cmus ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing to do is to import your music files into your library. This process will immediately reveal two things: that the shortcuts are inspired by vim's, and that cmus is incredibly fast. I have successfully imported over a thousand songs in less than twenty seconds! Try that with iTunes or any graphical music library software, and you will have time to make a peanut butter sandwich before it's done.
|
||||
|
||||
To import music files on cmus, type the following vim-like command on cmus.
|
||||
|
||||
:a /path/to/your/music/folder
|
||||
|
||||
So on Xubuntu I did:
|
||||
|
||||
:a /home/adrien/Music/
|
||||
|
||||
Then all the music files in that folder appeared sorted by artist and album instantly.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Quick Start ###
|
||||
|
||||
Before starting anything, you might want to memorize the basic shortcuts to start playing your music. That is the only downside to cmus. Unless you change them, the default shortcuts are not very intuitive, and you have to learn them. In short:
|
||||
|
||||
- **x** to play or replay a track
|
||||
- **c** to pause
|
||||
- **b** to play the next track
|
||||
- **z** to play the previous track
|
||||
- **s** to activate the shuffle
|
||||
|
||||
With that, you should be ready to start!
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Usage ###
|
||||
|
||||
The interface of cmus is composed of seven tabs, that you access by hitting the appropriate number. For example, the startup screen is the "tree" tab that you can access at any time by hitting 1. This tab is pretty intuitive to use: navigate though the artist on the left panel with the up and down keys, press space to see the albums for a particular artist, use the tab key to switch to right panel with the individual songs, and finally the return key to play a song.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, the bottom banner displays the name of the artist, the album, and the title of the song currently playing, as well as the timing and the volume.
|
||||
|
||||
The second tab is similar to the first as it just displays the list of all the songs sorted by artist.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
However, the third tab is much more interesting as it displays the current playlist. To add a song from the tree view or the sorted list view to the playlist just type "y" over the selected song. Once you created the perfect playlist, save it with the command.
|
||||
|
||||
:save /path/to/playlist
|
||||
|
||||
and load it with:
|
||||
|
||||
:load /path/to/playlist
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The fourth tab displays the queue. The difference between the queue and a playlist is that once a song is played from the queue, it is then removed. To add a song to the queue, do it like adding it to the playlist, but instead use the shortcut: "e"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The fifth tab is pretty interesting too as it is a lightweight file explorer. It can be pretty useful to read a musical file somewhere on your computer without adding it to your library. The navigation is pretty standard: move with the up and down keys, and return to enter a folder or select a file.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The sixth tab is the library filters used to dynamically create a playlist. Just as it sounds, filters actually go through your library, and only display the tracks corresponding to some criteria defined. I will go through defining your own filters later on, but cmus already comes with a few ones. To try one, just use:
|
||||
|
||||
:filter [name of the filter]
|
||||
|
||||
So for example:
|
||||
|
||||
:filter classical
|
||||
|
||||
It will hide all the tracks from your library, except the ones containing "Classical" in their genre tag.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Finally, last but not least, the seventh tab is the settings. In there you can define your own shortcuts and commands. I will give an example in the next section.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Usage ###
|
||||
|
||||
As promised, now that you are more familiar with the interface, I shall give you more tips to enhance your experience.
|
||||
|
||||
To search for anything in any tab, just use the same shortcut as in vim
|
||||
|
||||
/[keyword]
|
||||
|
||||
and:
|
||||
|
||||
n
|
||||
|
||||
to look for the next occurrence of the keyword.
|
||||
|
||||
To create your own filters, use the syntax:
|
||||
|
||||
:fset [name of the new filter]=[expression]
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you can find all the old rock track with:
|
||||
|
||||
:fset oldies=genre="Rock"&date<1970
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about the expressions you can use, I invite you to dig a bit in the doc and the included filters.
|
||||
|
||||
To activate the replaygain for all the tracks, use the command:
|
||||
|
||||
:set replaygain=1
|
||||
|
||||
To change a shortcut to a different key, go to the settings tab and find the current binding expression. Say for example that I want to change the play shortcut from "x" to "w", I will then scroll until the line that says:
|
||||
|
||||
common x player-play
|
||||
|
||||
Then hit enter, and change the expression to:
|
||||
|
||||
:bind -f common w player-stop
|
||||
|
||||
To conclude, I really like cmus. There is a lot more to it than the reach of this post, so you should really read the [manual page][5] when you are ready. In short, cmus is fast, easy to learn, and respects your files. If you like the idea of managing your music library from the command line, but were not convinced by cmus, I invite you to take a shot at some alternatives like MOC and PyTone which are just as good.
|
||||
|
||||
What do you think of cmus? Do you like it or prefer a (non)GUI alternative? Let us know in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/04/manage-music-library-command-line-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://cmus.github.io/
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/06/how-to-install-rpm-fusion-on-fedora.html
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/01/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/go/mp3
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/cmus/cmus/blob/master/Doc/cmus.txt
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
[zzlyzq translating...]
|
||||
Linux findmnt Command To Find Mounted Filesystems
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The command findmnt is used to find mounted filesystems in Linux. This command will look for a particular filesystem in /etc/fstab, /etc/mtab or /proc/self/mountinfo.
|
||||
@ -108,4 +109,4 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/powerful-findmnt-command/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:ftp://ftp.kernel.org/pub/linux/utils/util-linux/
|
||||
[1]:ftp://ftp.kernel.org/pub/linux/utils/util-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,270 +0,0 @@
|
||||
翻译ing by Luoxcat
|
||||
|
||||
Linux / Unix: chroot Command Examples
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
I am a new Linux and Unix user. How do I change the root directory of a command? How do I change the root directory of a process such as web-server using a chroot command to isolate file system? How do I use a chroot to recover password or fix the damaged Linux/Unix based environment?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Each process/command on Linux and Unix-like system has current working directory called root directory of a process/command. You can change the root directory of a command using `chroot` command, which ends up changing the root directory for both current running process and its children.
|
||||
|
||||
chroot command details
|
||||
Description:Change root directory
|
||||
Category:Processes Management
|
||||
Difficulty:Advanced
|
||||
Root privileges:Yes
|
||||
|
||||
A process/command that is run in such a modified environment cannot access files outside the root directory. This modified environment is commonly known as "jailed directory" or "chroot jail". Only a privileged process and root user can use chroot command. This is useful to:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Privilege separation for unprivileged process such as Web-server or DNS server.
|
||||
1. Setting up a test environment.
|
||||
1. Run old programs or ABI in-compatibility programs without crashing application or system.
|
||||
1. System recovery.
|
||||
1. Reinstall the bootloader such as Grub or Lilo.
|
||||
1. Password recovery Reset a forgotten password and more.
|
||||
|
||||
### Purpose ###
|
||||
|
||||
> The chroot command **changes its current and root directories to the provided directory and then run command**, if supplied, or an interactive copy of the user's login shell. Please note that not every application can be chrooted.
|
||||
|
||||
### Syntax ###
|
||||
|
||||
The basic syntax is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
chroot /path/to/new/root command
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
chroot /path/to/new/root /path/to/server
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
chroot [options] /path/to/new/root /path/to/server
|
||||
|
||||
#### chroot command examples ####
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, build a mini-jail for testing purpose with bash and ls command only. First, set jail location using mkdir command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ J=$HOME/jail
|
||||
|
||||
Create directories inside $J:
|
||||
|
||||
$ mkdir -p $J
|
||||
$ mkdir -p $J/{bin,lib64,lib}
|
||||
$ cd $J
|
||||
|
||||
Copy /bin/bash and /bin/ls into $J/bin/ location using [cp command][1]:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cp -v /bin/{bash,ls} $J/bin
|
||||
|
||||
Copy required libs in $J. Use ldd command to print shared library dependencies for bash:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ldd /bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007fff8d987000)
|
||||
libtinfo.so.5 => /lib64/libtinfo.so.5 (0x00000032f7a00000)
|
||||
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x00000032f6e00000)
|
||||
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00000032f7200000)
|
||||
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00000032f6a00000)
|
||||
|
||||
Copy libs in $J correctly from the above output:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cp -v /lib64/libtinfo.so.5 /lib64/libdl.so.2 /lib64/libc.so.6 /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 $J/lib64/
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
`/lib64/libtinfo.so.5' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libtinfo.so.5'
|
||||
`/lib64/libdl.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libdl.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/libc.so.6' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libc.so.6'
|
||||
`/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2'
|
||||
|
||||
Copy required libs in $J for ls command. Use ldd command to print shared library dependencies for ls command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ldd /bin/ls
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007fff68dff000)
|
||||
libselinux.so.1 => /lib64/libselinux.so.1 (0x00000032f8a00000)
|
||||
librt.so.1 => /lib64/librt.so.1 (0x00000032f7a00000)
|
||||
libcap.so.2 => /lib64/libcap.so.2 (0x00000032fda00000)
|
||||
libacl.so.1 => /lib64/libacl.so.1 (0x00000032fbe00000)
|
||||
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00000032f7200000)
|
||||
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x00000032f6e00000)
|
||||
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00000032f6a00000)
|
||||
libpthread.so.0 => /lib64/libpthread.so.0 (0x00000032f7600000)
|
||||
libattr.so.1 => /lib64/libattr.so.1 (0x00000032f9600000)
|
||||
|
||||
You can copy libs one-by-one or try [bash shell for loop][2] as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
list="$(ldd /bin/ls | egrep -o '/lib.*\.[0-9]')"
|
||||
for i in $list; do cp -v "$i" "${J}${i}"; done
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
`/lib64/libselinux.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libselinux.so.1'
|
||||
`/lib64/librt.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/librt.so.1'
|
||||
`/lib64/libcap.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libcap.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/libacl.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libacl.so.1'
|
||||
`/lib64/libc.so.6' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libc.so.6'
|
||||
`/lib64/libdl.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libdl.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/libpthread.so.0' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libpthread.so.0'
|
||||
`/lib64/libattr.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libattr.so.1'
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, chroot into your new jail:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chroot $J /bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
Try browsing /etc or /var:
|
||||
|
||||
# ls /
|
||||
# ls /etc/
|
||||
# ls /var/
|
||||
|
||||
A chrooted bash and ls application is locked into a particular directory called $HOME/$J and unable to wander around the rest of the directory tree, and sees that directory as its "/" (root) directory. This is a tremendous boost to security if configured properly. I usually lock down the following applications using the same techniques:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Apache - Red Hat / CentOS: Chroot Apache 2 Web Server][3]
|
||||
1. [Nginx - Linux nginx: Chroot (Jail) Setup][4]
|
||||
1. [Chroot Lighttpd web server on a Linux based system][5]
|
||||
1. Chroot mail server.
|
||||
1. Chroot Bind DNS server and more.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I exit from chrooted jail? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Type exit
|
||||
|
||||
$ exit
|
||||
|
||||
Sample session from above commands:
|
||||
|
||||
[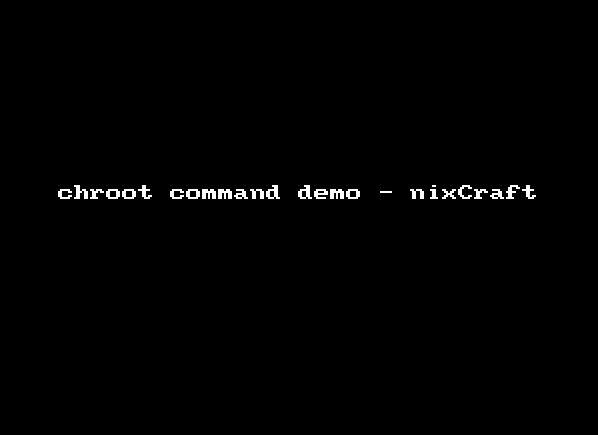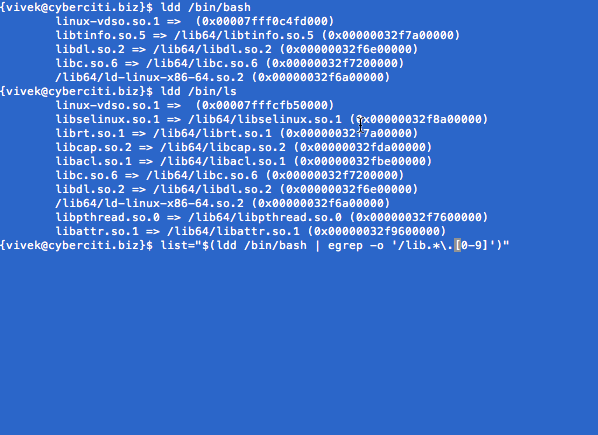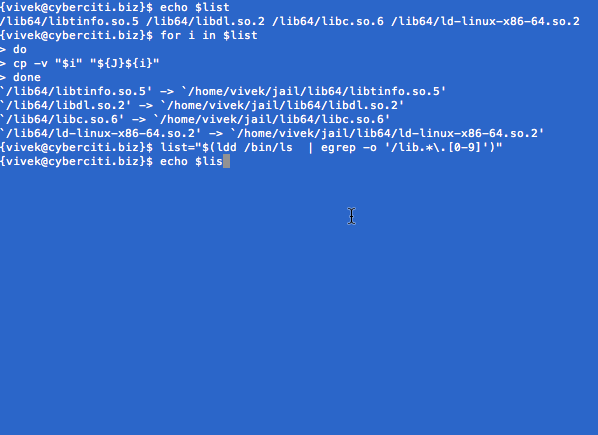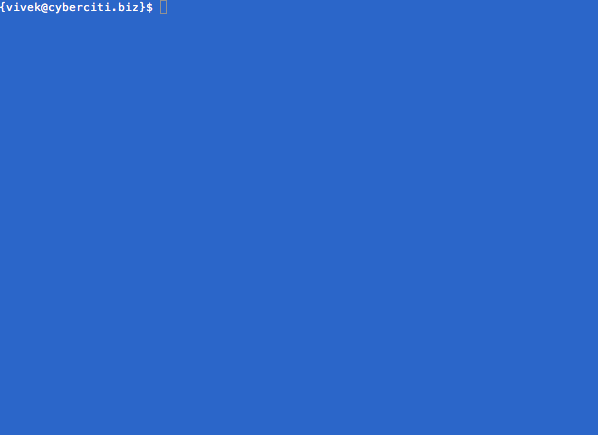][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Animated gif 01: Linux / Unix: Bash Chroot ls Command Demo
|
||||
|
||||
### Find out if service in chrooted jail or not ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can [easily find out if Postfix mail server is chrooted or not][7] using the following two commands:
|
||||
|
||||
pid=$(pidof -s master)
|
||||
ls -ld /proc/$pid/root
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs from my Linux based server:
|
||||
|
||||
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Mar 9 11:16 /proc/8613/root -> /
|
||||
|
||||
The PID 8613 pointing out to / (root) i.e. the root directory for application is not changed or chrooted. This is a quick and dirty way to find out if application is chrooted or not without opening configuration files. Here is another example from chrooted nginx server:
|
||||
|
||||
pid=$(pidof -s master)
|
||||
ls -ld /proc/$pid/root
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 nginx nginx 0 Mar 9 11:17 /proc/4233/root -> /nginxjail
|
||||
|
||||
The root directory for application is changed to /nginxjail.
|
||||
|
||||
### Rescue and fix software RAID system with chroot ###
|
||||
|
||||
I'm assuming that software RAID based Linux system is not booting. So you [booted system either using the Live CD or networked based remote rescue kernel mode][8] to fix the system. In this example, I booting RHEL based system using live Linux DVD/CD and chroot into /dev/sda1 and/or /dev/md0 to fix the problem:
|
||||
|
||||
## Recover data, at live cd prompt type the following commands. ##
|
||||
## /dev/sda1 main system partition ##
|
||||
## /dev/md0 /data partition ##
|
||||
# Set jail dir
|
||||
d=/chroot
|
||||
mkdir $d
|
||||
|
||||
# Mount sda1 and required dirs
|
||||
mount /dev/sda1 $d
|
||||
mount -o bind /dev $d/dev
|
||||
mount -o bind /sys $d/sys
|
||||
mount -o bind /dev/shm $d/dev/shm
|
||||
mount -o bind /proc $d/proc
|
||||
|
||||
# Mount software raid /dev/md0
|
||||
mount /dev/md0 $d/data
|
||||
|
||||
# Chroot to our newly created jail. This allows us to fix bootloader or grab data before everything goes to /dev/null
|
||||
chroot $d
|
||||
|
||||
# Can you see?
|
||||
ls
|
||||
df
|
||||
|
||||
# Get files to safe location
|
||||
rsync -avr /path/to/my_precious_data_dir user@safe.location.cyberciti.biz:/path/to/dest
|
||||
|
||||
# Get out of chrooted jail and reboot or format the server as per your needs ;)
|
||||
exit
|
||||
umount {dev,sys,[...],}
|
||||
reboot
|
||||
|
||||
But wait, there's more!
|
||||
|
||||
See all other chroot command related examples on nixCraft:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Ubuntu: Mount Encrypted Home Directory (~/.private) From an Ubuntu Live CD][9]
|
||||
1. [Linux Configure rssh Chroot Jail To Lock Users To Their Home Directories Only][10]
|
||||
1. [Fix a dual boot MS-Windows XP/Vista/7/Server and Linux problem][11]
|
||||
1. [Restore Debian Linux Grub boot loader][12]
|
||||
|
||||
### A note about chrooting apps on a Linux or Unix-like systems ###
|
||||
|
||||
Should you use the chroot feature all the time? In the above example, the program is fairly simple but you may end up with several different kinds of problems such as:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Missing libs in jail can result into broken jail.
|
||||
1. Complex program are difficult to chroot. I suggest you either try real [jail such as provided by FreeBSD][13] or use virtualization soultuon such as [KVM on Linux][14].
|
||||
1. App running in jail can not run any other programs, can not alter any files, and can not assume another user's identity. Loosen these restrictions, you have lessened your security, chroot or no chroot.
|
||||
|
||||
Also note that:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Do not forgot, to updated chrooted apps when you upgrade apps locally.
|
||||
1. Not every app can or should be chrooted.
|
||||
1. Any app which has to assume root privileges to operate is pointless to attempt to chroot, as root can generally escape a chroot.
|
||||
1. Chroot is not a silver bullet. Learn [how to secure and harden rest of the system too][15].
|
||||
|
||||
### chroot command options ###
|
||||
|
||||
From the [chroot(8)][16] command man page:
|
||||
|
||||
--userspec=USER:GROUP specify user and group (ID or name) to use
|
||||
--groups=G_LIST specify supplementary groups as g1,g2,..,gN
|
||||
--help display this help and exit
|
||||
--version output version information and exit
|
||||
|
||||
### See also ###
|
||||
|
||||
- [chroot(8) Linux/Unix command man page][17]
|
||||
- [Man pages chroot(2)][18]
|
||||
- [OpenBSD documentation See Apache chrooting faq for more information.][19]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/cp-copy-command-in-unix-examples/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/bash-for-loop/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/chroot-apache-under-rhel-fedora-centos-linux.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-run-nginx-in-a-chroot-jail/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-setup-lighttpd-php-mysql-chrooted-jail.html
|
||||
[6]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/?attachment_id=28148
|
||||
[7]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-chroot-service.html
|
||||
[8]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/centos-rhel-linux-mount-raid-hard-disk-from-livecd/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/ubuntu-mounting-your-encrypted-home-from-livecd/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-linux-unix-rssh-chroot-jail-setup.html
|
||||
[11]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-fix-dual-boot-windows-vista-linux.html
|
||||
[12]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/restore-debian-linux-grub-boot-loader.html
|
||||
[13]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/how-to-upgrade-freebsd-jail-vps/
|
||||
[14]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/kvm-virtualization-in-redhat-centos-scientific-linux-6/
|
||||
[15]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-security.html
|
||||
[16]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man8/chroot.8.html
|
||||
[17]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man8/chroot.8.html
|
||||
[18]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man2/chroot.2.html
|
||||
[19]:http://www.openbsd.org/faq/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
Six Steps You Need to Take to Make Ubuntu 14.04 LTS Better
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (Trusty Tahr) is a very good operating system but, like most Linux distributions out there, it's far from what users might call an optimal setup. There are numerous reasons for this fact, but we can detail a few steps that will make your Ubuntu experience increase a great deal.**
|
||||
|
||||
Even though Ubuntu is a good operating system and the latest incarnation of it, 14.04, is one of the best made so far by Canonical, most users will find that some aspects of the OS can be improved. A number of actions are actually necessary if you want a complete experience.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, right after you first start the OS, you will have to open Software & Updates and make sure that all the options in the first Ubuntu Software tab are checked. You will need these repositories activated if you want to have access to the all the important packages.
|
||||
|
||||
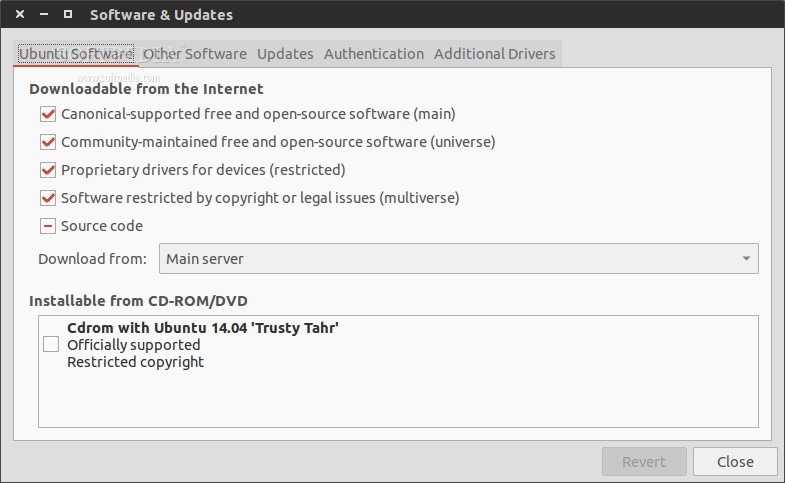
|
||||
Software & Updates repositories
|
||||
|
||||
The second thing you must do is to install the Ubuntu Restricted Extras. This features a number of important packages that can't be bundled with the operating system due to legal reasons, like Adobe's Flash and Microsoft fonts. It’s safe to download them, but the developers can't include them by default. Open a terminal and enter the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install ubuntu-restricted-extras
|
||||
|
||||
After the installation has been completed, you will also need to get rid of Empathy, the default messenger on the system. It's part of GNOME and it's actually a very limited and buggy solution. You should install Pidgin instead. Here is a list of commands that will do all this:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove empathy
|
||||
sudo apt-get install pidgin
|
||||
sudo apt-get install pidgin-plugin-pack
|
||||
|
||||
Now, if you are done with the messenger, you will need to install the drivers for the video card. If you have an Intel GPU, you don't have to do anything, but if you have an NVIDIA or AMD solution, you might want to get the proprietary drivers, which offer much better performance in games. Open Software & Updates again, click on the last tab called Additional Drivers, and select the driver you want. It will take some time, but you must be patient. Reboot.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Software & Updates drivers
|
||||
|
||||
You might also want to stop the online search that’s being performed through Unity's Dash. Open System Settings and click on Security and Privacy. In the third tab, which is called Search, you will find a button that can turn the online search off.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Stop online search in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
|
||||
|
||||
Also, you might want to customize the desktop a little. Right click on the desktop and select Change Desktop Background. You will notice a slide that is called Launcher icon size, which can be activated and the result can be seen in real time. Under the Behavior tab you will also find an option to display the menu inside the window of the application and not in the top bar of Unity.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Change the way menus are displayed
|
||||
|
||||
That's about it. Anything you do beyond this point will turn Ubuntu 14.04 LTS into your own version and it's just about cosmetics and less about features and performance.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Six-Step-You-Need-to-Take-to-Make-Ubuntu-14-04-LTS-Better-439341.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
(翻译中 by runningwater)
|
||||
Why htop Command Compete Linux top Command
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The top command in Linux is used to display a real-time view of processes that are running in the system. It provides very useful information like CPU utilization, memory consumption, and more, related to every process. But, do you know there exists another command line utility ‘htop’ that provides more information and features when compared with the traditional top command. In this article, we will discuss the ‘htop’ command with examples.
|
||||
@ -85,6 +86,6 @@ Apart from the hot keys explained till now, the htop command also provides usefu
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-htop-command/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
|
||||
检查Linux中已挂载的文件系统的findmnt命令的8个例子
|
||||
Linux 中 findmnt 命令检查已挂载的文件系统的8个实例
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### 已挂载的文件系统和设备 ###
|
||||
|
||||
linux中更常用的检查已挂载的文件系统的是mount命令,不仅用于列出已挂载的设备,而且可以在需要的时候挂载和卸载。这有一个叫做findmnt的俏皮的命令,它可以用于快速查看挂载位置和选项。
|
||||
linux 中更常用的检查已挂载的文件系统的是 mount 命令,不仅用于列出已挂载的设备,而且可以在需要的时候挂载和卸载。这有一个叫做 findmnt 的超赞命令,它可以用于快速查看挂载位置和选项。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装findmnt ###
|
||||
|
||||
findmnt命令来自util-linux软件包,默认安装在大多数像Ubuntu,Fedora,Debian发行版
|
||||
findmnt 命令来自 util-linux 软件包,默认安装在大多数发行版中,如 Ubuntu,Fedora,Debian
|
||||
|
||||
$ aptitude search util-linux
|
||||
i util-linux - Miscellaneous system utilities
|
||||
@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ findmnt命令来自util-linux软件包,默认安装在大多数像Ubuntu,Fed
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. 列出文件系统 ####
|
||||
|
||||
执行没有任何选项的findmnt将简单的在树形结构中列出所有已挂载的文件系统。
|
||||
无任何选项运行 findmnt,只会以树形结构图的方式列出所有已挂载的文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
$ findmnt
|
||||
|
||||
@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ findmnt命令来自util-linux软件包,默认安装在大多数像Ubuntu,Fed
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. df格式输出 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Findmnt可以用“-D”或“-df”选项创造一个df格式的输出报告空闲和已用磁盘空间。
|
||||
Findmnt 可以用“-D”或“-df”选项创建一个 df 格式的输出报告空闲和已用磁盘空间。
|
||||
|
||||
$ findmnt -D
|
||||
SOURCE FSTYPE SIZE USED AVAIL USE% TARGET
|
||||
@ -66,11 +66,11 @@ Findmnt可以用“-D”或“-df”选项创造一个df格式的输出报告空
|
||||
tmpfs tmpfs 1001.5M 60K 1001.5M 0% /tmp
|
||||
/dev/sda1 ext4 476.2M 107.7M 339.6M 23% /boot
|
||||
|
||||
注意以上选项直到util-linux2.20版本都不可用,碰巧的是最新版在Ubuntu13.10
|
||||
需要注意的是,以上选项 util-linux2.20 之前的版本都不可用,它正好是 Ubuntu13.10 上的最新版本
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. 从fstab读取文件系统 ####
|
||||
|
||||
使用“-s”或“-fstab”选项,findmnt将只从/etc/fstab文件和/etc/fstab.d目录读取文件系统。
|
||||
使用“-s”或“-fstab”选项,findmnt 将只从/etc/fstab文件和/etc/fstab.d目录读取文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
$ findmnt -s
|
||||
TARGET SOURCE FSTYPE OPTIONS
|
||||
@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ Findmnt可以用“-D”或“-df”选项创造一个df格式的输出报告空
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5. 通过类型过滤文件系统 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Findmnt可以打印出只基于类型的特定的文件系统,例如ext4,多个系统类型可以指定一个逗号分隔。
|
||||
Findmnt 可以打印出只基于类型的特定的文件系统,例如 ext4,多个系统类型可以指定一个逗号分隔。
|
||||
|
||||
$ findmnt -t ext4
|
||||
TARGET SOURCE FSTYPE OPTIONS
|
||||
@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ Findmnt可以打印出只基于类型的特定的文件系统,例如ext4,多
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6. 原始输出 ####
|
||||
|
||||
如果你喜欢原始风格难看的输出,那么使用“-r”或“--raw”选项。
|
||||
如果你喜欢原始风格的输出,那么使用“-r”或“--raw”选项。
|
||||
|
||||
$ findmnt --raw
|
||||
TARGET SOURCE FSTYPE OPTIONS
|
||||
@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ Findmnt可以打印出只基于类型的特定的文件系统,例如ext4,多
|
||||
/sys/fs/cgroup/systemd systemd cgroup rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,name=systemd
|
||||
/run/user/1000/gvfs gvfsd-fuse fuse.gvfsd-fuse rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,user_id=1000,group_id=1000
|
||||
|
||||
That looks very neat
|
||||
看起来非常整洁
|
||||
|
||||
#### 7. 通过源设备查找 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -137,12 +137,12 @@ That looks very neat
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个findmnt命令的简要介绍。findmnt更多的选项可以在man手册页中找到。
|
||||
这是一个 findmnt 命令的简要介绍。关于 findmnt 的更多选项可以在 man 手册页中找到。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.binarytides.com/linux-findmnt-command/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Vito](https://github.com/vito-L) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[Vito](https://github.com/vito-L) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,52 +1,57 @@
|
||||
** Linchenguang is translating this essay
|
||||
===============================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Collectl: An Advanced All-in-One Performance Monitoring Tool for Linux
|
||||
Collectl: 一个高级全能的Linux性能监控工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The most important duty of a Linux system administrator is to make sure the system he/she is administering is in a very good condition. There are many tools available for a Linux system admins that can help to monitor and display processes in a system such as top and htop, but none of these tools can compete with **collectl**.
|
||||
|
||||
对于一个Linux系统管理员来说确保自己管理的系统处于一个良好的状态是其首要责任。Linux系统管理员可以找到有很多工具来帮助自己监控和显示系统中的进程,例如 top 和 htop ,但是这些工具都不能与**collectl**相媲美。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**collectl** is a very nice feature rich command-line utility that can be used to collect performance data that describes the current system status. Unlike most of the other monitoring tools, collectl does not focus in a limited number of system metrics, instead it can gather information on many different types of system resources such as cpu, disk, memory, network, sockets, tcp, inodes, infiniband, lustre, memory, nfs, processes, quadrics, slabs and buddyinfo.
|
||||
|
||||
A very good thing about using **collectl** is that it can also play the role of utilities that are designed with only a specific purpose such as top, ps, iotop and many others. What are some features that make **colleclt** a useful tool?
|
||||
**collectl**是一款非常优秀并且有着丰富的命令行功能的实用程序,你可以用它来采集描述当前系统状态的性能数据。不同于大多数其它的系统监控工具,collectl 并非仅局限于有限的系统度量,相反,它可以收集许多不同类型的系统资源如 cpu 、disk、memory 、network 、sockets 、 tcp 、inodes 、infiniband 、 lustre 、memory、nfs、processes、quadrics、slabs和buddyinfo等。
|
||||
|
||||
After doing a lot of research I have compiled a list with some of the most important features of the collectl command-line utility for you guys.
|
||||
使用**collectl**的另一个好处就是它可以替代那些有特殊用途的工具如 top、ps、iotop 等还有其它许多这样的工具。那么**collectl**有什么特性而使其成为一个有用的工具呢?
|
||||
|
||||
### Collectl Features ###
|
||||
|
||||
- It can run interactively, as a daemon or both.
|
||||
- It can display the output in many formats.
|
||||
- It has the ability to monitor almost any subsystem.
|
||||
- It can play the role of many other utilities such as ps, top, iotop, vmstat.
|
||||
- It has the ability to record and playback the captured data.
|
||||
- It can export the data in various file formats. (this is very useful when you want to analyse the data with external tools).
|
||||
- It can run as a service to monitor remote machines or an entire server cluster.
|
||||
- It can display the data in the terminal, write to a file or a socket.
|
||||
做过研究后我总结了 collectl 的命令行功能的一些非常重要的特性。
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Install collectl in Linux ###
|
||||
### Collectl 特性 ###
|
||||
|
||||
The **collectl** utility runs on all Linux distributions, the only thing it requires to run is perl, so make sure that you have **Perl** installed in your machine before installing collectl in your machine.
|
||||
- 可以交互式地运行或作为一个守护进程,或同时二者兼备地运行。
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Debian/Ubuntu/Linux Mint ####
|
||||
- 可以以多种格式显示输出。
|
||||
|
||||
The following command can be used to install the collectl utility in Debian based machines such as Ubuntu.
|
||||
- 可以监控几乎所有的子系统。
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Debian/Ubuntu/Linux Mint ####
|
||||
- 可以替代许多工具如 ps、top、iotop、vmstat。
|
||||
|
||||
The following command can be used to install the collectl utility in Debian based machines such as Ubuntu.
|
||||
- 可以记录并回放捕获的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
- 可以将数据导出成多种数据格式。(这在你想用外部工具分析数据时非常有用)
|
||||
|
||||
- 可以作为一个服务来监控远程机或者整个服务器集群。
|
||||
|
||||
- 可以在终端显示数据,写入数据到文件或者一个套接字。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在Linux上安装collectl###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**collectl**可以在所有的Linux发行版上运行,唯一需要的就是perl语言,所以一定要确保在安装**collectl**之前你的电脑上已经安装了**Perl**。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 对于Debian/Ubuntu/Linux Mint ####
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令可以用来在以Debian为基础的设备如Ubuntu 上安装collectl。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install collectl
|
||||
|
||||
#### On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora ####
|
||||
#### 对于RHEL/CentOS/Fedora ####
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using Red Hat based distro, you can easily grab it from the repos with the yum command.
|
||||
如果你正在使用基于红帽的发行版,你可以用yum命令轻松获取它。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install collectl
|
||||
|
||||
### Some Practical Examples Of The collectl Utility ###
|
||||
### 一些关于collectl的实例 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once the installation of the collectl tool is finished, you can easily run it from the terminal, even without any option. The following command will display information on cpu, disk and network stats in a very short and human readable format.
|
||||
|
||||
安装好collectl之后,你可以轻松得在终端运行它,你甚至不需要任何选项。下面的命令将会以简短的人性化的格式显示cpu、硬盘和网络信息。
|
||||
|
||||
# collectl
|
||||
|
||||
@ -64,17 +69,20 @@ Once the installation of the collectl tool is finished, you can easily run it fr
|
||||
16 2 732 1348 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1
|
||||
22 4 993 1615 0 0 56 3 1 2 0 3
|
||||
|
||||
As you guys can see from the above output displayed in the terminal screen, it is very easy to work with the system metrics values present in the command output because it appears on a single line.
|
||||
|
||||
When the collectl utility is executed without any option it displays information about the following subsystems:
|
||||
正如上面终端上所显示的,我们很容易观察该命令输出的系统度量值,因为它只显示一整行。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
不加任何参数执行collectl会显示下面子系统的信息
|
||||
|
||||
- cpu
|
||||
- disks
|
||||
- network
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: In our case, a subsystem is every type of a system resource that can be measured.
|
||||
**提示**:在这里,一个子系统是每一种可以测量的系统资源。
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以显示除slabs以外各个子系统的统计数据,这要结合下面的**-all**选项来实现。
|
||||
|
||||
You can also display statistics for all subsystems except slabs by combining the command with the **–all** option like shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
# collectl --all
|
||||
|
||||
@ -90,10 +98,12 @@ You can also display statistics for all subsystems except slabs by combining the
|
||||
26 5 823 1238 396 428 1G 175M 1G 683M 193M 1G ssslkjjebbk 0 0 0 0 2 11 3 9 0 0 0 0 622 0 0 0 8160 240828 0 0 0 0
|
||||
15 1 753 1276 361 391 1G 175M 1G 683M 193M 1G ssslkjjebbk 0 0 40 3 1 2 0 3 0 0 0 0 623 0 0 0 8160 240829 0 0 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
But, how do you monitor the cpu usage with the help of the utility? The ‘-s‘ option should be used to controls which subsystem data is to be collected or played back.
|
||||
|
||||
For example the following command can be used to monitor the summary of the cpu usage.
|
||||
|
||||
但是,你如何用它来监控cpu的利用情况呢? ‘s’ 选项可以用来控制需要收集和回放的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
例如下面的命令可以用来对cpu使用情况进行一个总结。
|
||||
# collectl -sc
|
||||
|
||||
waiting for 1 second sample...
|
||||
@ -111,6 +121,8 @@ For example the following command can be used to monitor the summary of the cpu
|
||||
|
||||
What happens when you combine the command with “**scdn**“? The best way to learn how to use command-line tools is to practice as much as possible, so run the following command in your terminal and see what is going to happen.
|
||||
|
||||
当你将这个命令与“**scdn**”结合时会发生什么呢?学习命令行工具最好的方式就是多加练习,所以运行下面的命令看看会发生什么吧。
|
||||
|
||||
# collectl -scdn
|
||||
|
||||
waiting for 1 second sample...
|
||||
@ -128,9 +140,10 @@ What happens when you combine the command with “**scdn**“? The best way to l
|
||||
14 1 779 1383 0 0 48 6 1 1 0 1
|
||||
11 2 795 1285 0 0 0 0 2 14 1 14
|
||||
|
||||
You can easily understand that the default option is “**cdn**“, it stands for cpu, disks and network data. The result of the command is the same with the output of “**collectl -scn**“
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to collect data about the memory, use the following command.
|
||||
你可以很容易地理解默认选项中的“**cdn**”,它代表cpu、硬盘和网络数据。运行添加这个选项的collectl命令的输出和“**collectl -scn**”的输出一样。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想采集内存的数据,用下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# collectl -sm
|
||||
|
||||
@ -146,9 +159,9 @@ If you want to collect data about the memory, use the following command.
|
||||
1G 177M 1G 684M 193M 1G
|
||||
1G 177M 1G 684M 193M 1G
|
||||
|
||||
The above output is very useful when you want to get some detailed information on your memory usage, free memory and other important stuff for the performance of your system.
|
||||
上面的输出在你想要进一步了解内存使用信息,空闲的内存或者与你系统性能有关的重要资料时非常有用。
|
||||
|
||||
How about some data on tcp? Use the following command to do it.
|
||||
如果想搜集一点儿tcp的数据呢?使用下面的命令来实现吧。
|
||||
|
||||
# collectl -st
|
||||
|
||||
@ -167,7 +180,8 @@ How about some data on tcp? Use the following command to do it.
|
||||
0 0 0 0
|
||||
0 0 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
After you have gained some experience you can easily combine options to get the results you want. For example you can combine the “**t**” for tcp and “**c**” for cpu. The following command does that.
|
||||
|
||||
当你熟练到一定程度时,你就可以很轻松地得到你想要的结果了。例如你可以将关于tcp的“**t**”选项和关于cpu的“**c**”选项组合到一起。下面的命令就是如此。
|
||||
|
||||
# collectl -stc
|
||||
|
||||
@ -185,7 +199,8 @@ After you have gained some experience you can easily combine options to get the
|
||||
17 3 755 1218 0 0 0 0
|
||||
14 2 788 1321 0 0 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
It is hard for us humans to remember all the available options so I am posting the summary list of subsystems supported by the tool.
|
||||
|
||||
对于我们普通大众来说记住这些选项很困难,所以这里我整理出了这个工具支持的选项的列表。
|
||||
|
||||
- **b** – buddy info (memory fragmentation)
|
||||
- **c** – CPU
|
||||
@ -201,7 +216,7 @@ It is hard for us humans to remember all the available options so I am posting t
|
||||
- **x** – Interconnect
|
||||
- **y** – Slabs (system object caches)
|
||||
|
||||
A very important piece of data for a system administrator or a Linux user is the data collected on disk usage. The following command will help you to monitor the disk usage.
|
||||
对于一个系统管理员或者一个Linux用户来说很重要的一种数据就是硬盘的使用情况。下面的命令可以帮你监控硬盘使用情况。
|
||||
|
||||
# collectl -sd
|
||||
|
||||
@ -218,7 +233,8 @@ A very important piece of data for a system administrator or a Linux user is the
|
||||
0 0 100 7
|
||||
0 0 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use the “**-sD**” option to collect data on individual disks, but you have to know that information on total disks will not be reported.
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以使用“**-sD**”选项来采集单个硬盘的数据,但是你必须知道全部硬盘的信息不会被报告。
|
||||
|
||||
# collectl -sD
|
||||
|
||||
@ -242,6 +258,8 @@ You can also use the “**-sD**” option to collect data on individual disks, b
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use other detail subsystems to collect detailed data. The following is a list of the detail subsystems.
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以使用其它详细的子系统来采集详细的数据。下面是详细子系统的一个列表。
|
||||
|
||||
- **C** – CPU
|
||||
- **D** – Disk
|
||||
- **E** – Environmental data (fan, power, temp), via ipmitool
|
||||
@ -254,9 +272,9 @@ You can also use other detail subsystems to collect detailed data. The following
|
||||
- **Y** – Slabs (system object caches)
|
||||
- **Z** – Processes
|
||||
|
||||
There are many available options in the collectl utility, but there is not enough time and space to cover them all in only one article. However it is worth mentioning and teaching how to use the utility as **top** and **ps**.
|
||||
collectl工具中有许多选项,但是仅用一篇文章来介绍肯定是介绍不过来的。然而如何将它当作**top**和**ps**工具来使用还是值得一提的。
|
||||
|
||||
It is very easy to make collectl work as the top utility, just run the following command in your terminal and you will see the similar output the **top** tool gives you when it is executed in your Linux system.
|
||||
很容易将collectl当作top来使用,只要在Linux 系统的终端运行下面的命令你就会看到和**top**工具类似的输出。
|
||||
|
||||
# collectl --top
|
||||
|
||||
@ -287,6 +305,8 @@ It is very easy to make collectl work as the top utility, just run the following
|
||||
|
||||
And now last but not least, to use the collectl utility as the ps tool run the following command in your terminal. You will get information about processes in your system the same way as you do when you run the “**ps**” command in your terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
最后,当然不是说这不重要,我们在终端运行下面的命令就可以将collectl用作ps工具了。
|
||||
你可以得到关于你系统进程的信息,这和在终端运行“**ps**”命令是一样的。
|
||||
# collectl -c1 -sZ -i:1
|
||||
|
||||
waiting for 1 second sample...
|
||||
@ -315,13 +335,14 @@ And now last but not least, to use the collectl utility as the ps tool run the f
|
||||
21 root 20 2 0 S 0 0 0 0.00 0.00 0 00:00.00 0 0 0 0 bdi-default
|
||||
22 root 0 2 0 S 0 0 0 0.00 0.00 0 00:00.00 0 0 0 0 kintegrityd
|
||||
|
||||
I am very sure that many Linux system administrators will like this tool and will feel its power when using it to the fullest. If you like to advance your knowledge about collectl to the next level refer to its manual pages and keep practicing.
|
||||
|
||||
Just type the following command in your terminal and start reading.
|
||||
我确信许多系统管理员将会喜欢这个工具并且在充分利用它后会感受到它的强大。如果你想增进你对collectl的了解达到新的层面,你可以去参阅collectl的man手册并勤加练习。
|
||||
|
||||
在你的终端键入下面的命令开始阅读吧。
|
||||
|
||||
# man collectl
|
||||
|
||||
### Reference Links ###
|
||||
### 参考链接 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- [collectl Homepage][1]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -329,7 +350,7 @@ Just type the following command in your terminal and start reading.
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-performance-monitoring-with-collectl-tool/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[Linchenguang](https://github.com/Linchenguang) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 每日技巧- 自动备份Ubuntu 14.04到Box云存储上
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
如今你已经升级或者安装了Ubuntu 14.04, 这有另外一件事情你可能需要去做来保护你的新系统:备份!
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu内置了一个备份工具 **Déjà Dup Backup Tool**。它允许你备份你的系统并保存在本地或者通过不同的协议保存在远端服务器上。
|
||||
|
||||
还有许多其他的工具来备份你的Ubuntu计算机与文件。你可以通过[Dropbox 客户端][1]或者其他云服务来自动备份你的重要文档。你也有可能使用UbuntuOne来备份你的机器,但这不再是一个选择了。
|
||||
|
||||
另外用来备份你机器的云存储是Box。Box是一个很棒的服务,它是Dropbox的一个替代品。Box云存储的一个缺点是它没有Dropbox那样的Linux客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
它的一个好处是它有Dropbox不支持的通过WebDAV协议来备份你的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
本篇简要教程会教你如何使用Box云服务来自动备份你的Ubuntu机器。
|
||||
|
||||
在你开始之前,你首先要确保你有一个Box账号,如果没有,请先前去注册。
|
||||
|
||||
When you’re ready, open **Dash** and search for Backup. Or go to **Option (Gear) –> System Settings –> Backups**
|
||||
当你完成后,打开**Dash** 并搜索备份。或者进入**选项 (Gear) –> 系统设置 –> 备份**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
接下来,选择备份的文件夹(保存),忽略的文件夹,以及哪里保存备份。位置是我们要首先设置的。对于存储位置,我们选择**WebDAV** 。接下来输入服务器地址(如下所示), 文件夹应该是/dav/,以及你的Box用户名。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
回到概况,选择**立即备份**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你会被要求输入密码。输入后继续。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在下一屏中,你可以选择是否用密码加密备份。我建议不要这么做,因为忘记密码可能也会有危险。
|
||||
|
||||
第一次备份后,前往打开自动备份设置。接着进入计划并选择对于你最好的备份计划。
|
||||
|
||||
要打开自动备份,右上角的滑动条拖到右边。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
就是这样!你现在可以进入'保存的文件夹' 并开始加入更多需要备份的文件夹。
|
||||
|
||||
享受吧!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2014/04/daily-ubuntu-tips-automatically-backing-up-ubuntu-14-04-to-box-cloud-storage/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.liberiangeek.net/2014/04/daily-ubuntu-tips-get-dropbox-installed-in-ubuntu-14-04-trusty-tahr/
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
|
||||
Linux 中如何永久地更改 Umask 值
|
||||
如何在 Linux 中永久地更改 Umask 值
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**这篇教程教将使所有的 Linux 用户如何永久性的更改其系统的 Umask 值。特别建议全新安装的用户(为什么请见下文)**
|
||||
**这篇教程教将指导所有的 Linux 用户如何永久性地更改其系统的 Umask 值。特别建议全新安装的用户学习(想知道为什么的话,请阅读下文)**
|
||||
|
||||
Umask 是什么?解释下,UMASK 代表用户掩码或用户文件创建掩码,它用于新创建的文件和文件夹,是其默认权限基础。
|
||||
|
||||
上面的意思可以翻译成设置基于 Linux 操作系统的新建文件(包括文件夹)的默认权限的能力。为了教育的目的,下面列出了可以用来设置文件权限的一些八进制值:
|
||||
上面的意思可以解释成 任何基于 Linux 的操作系统为新建文件(包括文件夹)添加一系列默认权限的能力。出于教育目的,下面列出了一些可以用来设置文件权限的八进制值:
|
||||
|
||||
0 – 读, 写, 可执行 (rwx)
|
||||
1 – 读和写 (rw-)
|
||||
@ -17,24 +17,24 @@ Umask 是什么?解释下,UMASK 代表用户掩码或用户文件创建掩
|
||||
6 – 仅可执行 (--x)
|
||||
7 – 没有权限 (---)
|
||||
|
||||
在几乎所有的 Linux 发行版本中默认的 Umask 值是 0022(022),可以在终端模拟程序中输入 umask 命令来查看。也可以运行 “umask 八进制值” 命令(例如 umask 027)来临时改变这个值。
|
||||
|
||||
在几乎所有的 Linux 发行版本中默认 Umask 值是 0022(022),可以在终端模拟程序中输入 umask 命令来查看。也可以运行 “umask 八进制值” 命令(例如 umask 027)来临时改变这个值。
|
||||
|
||||
你也许知道,新创建的文件的默认权限设置是 0666,文件夹的是 0777。应用上面所说的 umask 值后就得到 644 和 755 权限。
|
||||
|
||||
许多人正在考虑 022 值本身的隐私问题。这就是说您所创建的文件对其他用户来说是可随意查看的,一想到这就感到不太爽。
|
||||
|
||||
言归正传,用户可以按他们所愿的修改默认的 Umask 值,当然首先要修改的值合法。要修改默认值,**请在您的 shell 配置文件中或者 /etc/profile 文件中写入一个新的 Umask 值**。
|
||||
言归正传,用户可以按他们所愿来修改默认的 Umask 值,当然首先要保证修改的值合法。要修改默认值,**请在您的 shell 配置文件中或者 /etc/profile 文件中写入一个新的 Umask 值**。
|
||||
|
||||
大功告成!从现在开始,在你的 Linux 系统上新创建的文件或文件夹都会有准确设置的权限。但请注意已经存在的文件或文件夹的权限并不会因为上面的操作而改变。
|
||||
|
||||
如果您使用的是命令行,可以在任意目录下运行 ls -lah 命令,就可以看到当前的文件权限。另外,新手也可以很容易的查看到文件权限,在基于 GNOME 桌面的环境中,通过右击文件,选择属性 -> 权限选项卡。
|
||||
如果您使用的是命令行,可以在任意目录下运行 ls -lah 命令,就可以看到当前的文件权限。另外,新手也可以很容易地查看到文件权限,在基于 GNOME 桌面的环境中,通过右击文件,选择属性 -> 权限选项卡。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在阅读这篇教程时遇到任何问题,不要犹豫,请留下评论。
|
||||
如果你在阅读这篇教程时遇到任何问题,不要犹豫,请留下您的评论。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Change-Umask-Value-Permanently-in-Linux-435026.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,157 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux的命令行中管理你的音乐库
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
linux下的命令行可能是对于新手而言最恐怖的经历了。我记得花费数天的时间来尝试解码终端中错误信息。然而,这是完全值得的。如果我如今让我说只说一个让新手学习学习命令行的原因,,那可能是完全可以在命令行中管理音乐库。我喜欢用的软件是[cmus][1],是"C* MUsic Player"(C音乐播放器)的简写,由于它完全由C写成。
|
||||
|
||||
cmus是一个强力的内置音频播放器的音乐文件管理器。使用它基于ncurses的命令行界面,你可以浏览你的音乐库,并从播放列表或队列中播放音乐,这一切都在命令行下。
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux上安装cmus ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,你需要如下设置并安装cmus。
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu, Debian 或者Linux Mint中:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install cmus
|
||||
|
||||
在Fedora上,首先[启用RPM Fusion仓库][2],接着运行:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install cmus
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS上,首先[启用Repoforge仓库][3],接着运行:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install cmus
|
||||
|
||||
在Archlinux上:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo pacman -S cmus
|
||||
|
||||
安装完之后,在命令行下如下输入就可运行cums:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cmus
|
||||
|
||||
### 导入 [音乐文件][4] 到 cmus ###
|
||||
|
||||
第一件要做的事情是导入你的音乐文件到你的库中。这个过程马上揭露了两件事情:快捷方式是受到了vim的启发,还有cmus运行的很快。我已经在20秒之内成功地导入了超过1000首歌! 在iTunes或者其他任何图形音乐库软件下试一下,你就会有足够的时间来做一份花生酱三明治。
|
||||
|
||||
要在cmus下面导入音乐,输入下面的像vim一样的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
:a /path/to/your/music/folder
|
||||
|
||||
在我的Xubuntu上,我这么做:
|
||||
|
||||
:a /home/adrien/Music/
|
||||
|
||||
接下来这个目录下所有的音乐文件会立马按照艺术家或者专辑的方式排列显示。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 快速入门 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在开始前,你可能希望记住一些基本快捷方式来开始播放你的音乐。这是cmus的唯一缺点。除非你改变它们,否则默认的快捷方式并不直观,并且你不得不学习它们。简而言之:
|
||||
|
||||
- **x** 播放或重播音乐
|
||||
- **c** 暂停
|
||||
- **b** 播放下一首音乐
|
||||
- **z** 播放前一首音乐
|
||||
- **s** 激活随机播放
|
||||
|
||||
掌握完后,你应该已经准备好开始了!
|
||||
|
||||
### 基本使用 ###
|
||||
|
||||
cmus的界面由7个标签组成,你可以按下适当的数字键来访问。比如,启动页面是一个树形标签界面,你随时可以通过按下1来访问。这个标签可以很直观地来使用:通过上下键来导航位于左侧面板的艺术家,按下空格就可以看到特定艺术家的专辑,使用tab键来切换到右侧面板来选择独立的歌曲,最后按下回车键来播放音乐。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如你所见,底部显示了艺术家的名字,专辑,和正在播放歌曲的标题,还有时间和音量。
|
||||
|
||||
第二个标签与第一个刚才显示的类似,显示了按照艺术家排列的歌曲列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
然而,第三个标签更加有趣,因为他显示了目前的播放列表。要在树形视图或者列表视图下增加一首歌曲,只要在选中的歌曲上输入'y'。一旦创建完成后,用命令行保存下来。
|
||||
|
||||
:save /path/to/playlist
|
||||
|
||||
用下面命令加载:
|
||||
|
||||
:load /path/to/playlist
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
第四个标签显示的是队列。队列与播放列表的一点不同是,一旦歌曲是按队列播放的,播放结束后就会被移出队列。要把一首歌加入队列,就像把它加到播放列表一样,但是使用快捷方式:"e"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
第五个标签也同样很有趣,因为它是一个轻量级的文件浏览器。当你在你的电脑中查找一首歌曲而不必加入到库中的时候很有用。导航方式也非常标准:用向上或者向下键,回车键用来进入文件夹或者选中一个文件。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
第六标签是一个库过滤器,用来动态创建播放列表。如它听上去的那样,过滤器会遍历你的库,并且只显示符合相关规则定义的音乐。之后我会描述定义你自己的过滤器,但是cmus已经自带了一些。要试一下,只要使用:
|
||||
|
||||
:filter [name of the filter]
|
||||
|
||||
比如:
|
||||
|
||||
:filter classical
|
||||
|
||||
除了"Classical"标签的音乐,它会隐藏你库中所有的音乐。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最后但同样重要的,第七个标签是设置。在这里,你可以定义你的快捷方式和命令。我会在下一部分给你一些例子。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 高级用法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
正如承诺那样,你现在已经更加熟悉界面了,我会给你一些贴士来增强你的体验。
|
||||
|
||||
要在标签中搜索任何东西,只要如vim那样使用相同的快捷方式
|
||||
|
||||
/[keyword]
|
||||
|
||||
还有:
|
||||
|
||||
n
|
||||
|
||||
来搜索下一处关键字。
|
||||
|
||||
要创建一个你的过滤器,使用语法:
|
||||
|
||||
:fset [name of the new filter]=[expression]
|
||||
|
||||
比如,你可以找到所有的老的摇滚音乐:
|
||||
|
||||
:fset oldies=genre="Rock"&date<1970
|
||||
|
||||
要了解更多关于你可以使用的表达式,我邀请你更多地在文档中挖掘已有的过滤器。
|
||||
|
||||
要激活重新播放所有的音乐,使用如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
:set replaygain=1
|
||||
|
||||
要改变快捷方式到不同的键上,进入设置标签并找出现有的绑定表达式。举个例子来说,我想要将播放快捷方式从"x"改到"w",我会翻到下面的行:
|
||||
|
||||
common x player-play
|
||||
|
||||
接着按下回车,并改成下面的表达式
|
||||
|
||||
:bind -f common w player-stop
|
||||
|
||||
总的来说,我真的喜欢cmus。它还有许多本篇中没有提到的技巧,因此在你准备好后,应该认真要读一下[man帮组手册][5]。简而言之,cmus是一款快速,易于学习,尊重你的文件的软件。如果你喜欢从命令行下管理音乐库的想法,但是还没对cmus深信不疑,我邀请你先试一下一些替代品,如MOC和PyTone,它们同样也很棒。
|
||||
|
||||
你认为cmus怎么样?你喜欢它么,或者作为GUI的替代品?让我在评论区知道你们的想法。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/04/manage-music-library-command-line-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://cmus.github.io/
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/06/how-to-install-rpm-fusion-on-fedora.html
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/01/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/go/mp3
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/cmus/cmus/blob/master/Doc/cmus.txt
|
||||
267
translated/tech/Linux or Unix--chroot Command Examples.md
Normal file
267
translated/tech/Linux or Unix--chroot Command Examples.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,267 @@
|
||||
Linux / Unix:chroot 命令实例讲解
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
我是刚接触 Linux 和 Unix 的新手。我该如何改变一个命令的根目录?我要怎样改变一个进程的根目录呢,比如用 chroot 命令将web服务与文件系统隔离?我要如何使用 chroot 恢复密码或修复基于 Linux/Unix的受损坏的环境?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux和类 Unix 系统下每一个进程/命令的当前工作目录称之为进程/命令的根目录。你可以使用 chroot 命令改变一个命令的根目录,这最终将会改变当前运行的进程及其子进程的根目录。
|
||||
|
||||
chroot 命令详情
|
||||
描述:更改根目录
|
||||
类型:进程管理
|
||||
难度:高级
|
||||
Root 授权:Yes
|
||||
|
||||
如果一个进程/命令运行在一个不能访问外部根目录文件的已修改环境中。这个修改环境通常被称为"监禁目录"或是"chroot jail"。只有特权进程和根用户才能使用 chroot 命令。然而这通常是很有用的:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 将特权分配给未授权的进程,例如 Web 服务或 DNS 服务。
|
||||
1. 建立测试环境。
|
||||
1. 不使程序或系统崩溃下,运行旧程序或不兼容 ABI 的程序。
|
||||
1. 系统恢复。
|
||||
1. 重新安装引导装载程序,例如 Grub 或 Lilo。
|
||||
1. 密码找回,重置一个已丢失的密码等。
|
||||
|
||||
### 用途 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> chroot 命令 **改变其当前的根目录到指定目录,然后运行命令**,如果支持的话,可以运行一个用户的登陆shell的交互式副本。请注意并不是每一个程序都可以使用 chroot 命令。
|
||||
### 语法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
基本语法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
chroot /path/to/new/root command
|
||||
|
||||
或者
|
||||
|
||||
chroot /path/to/new/root /path/to/server
|
||||
|
||||
或者
|
||||
|
||||
chroot [options] /path/to/new/root /path/to/server
|
||||
|
||||
#### chroot 命令实例 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在这个例子中,建立了一个"迷你监狱"用来测试一个只有 ls 命令的 Bash shell。首先用 mkdir 命令设定好 jail "监狱" 路径。
|
||||
|
||||
$ J=$HOME/jail
|
||||
|
||||
在 $J 内创建目录:
|
||||
|
||||
$ mkdir -p $J
|
||||
$ mkdir -p $J/{bin,lib64,lib}
|
||||
$ cd $J
|
||||
|
||||
用[cp 命令][1]将/bin/bash 和 /bin/ls 复制到 $J/bin/ 路径下:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cp -v /bin/{bash,ls} $J/bin
|
||||
|
||||
将所需库文件拷贝到$J。可以用 ldd 命令打印出 bash 所依赖的共享库。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ldd /bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
输出样例:
|
||||
|
||||
linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007fff8d987000)
|
||||
libtinfo.so.5 => /lib64/libtinfo.so.5 (0x00000032f7a00000)
|
||||
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x00000032f6e00000)
|
||||
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00000032f7200000)
|
||||
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00000032f6a00000)
|
||||
|
||||
直接拷贝上面输出中的库文件到 $J 目录:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cp -v /lib64/libtinfo.so.5 /lib64/libdl.so.2 /lib64/libc.so.6 /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 $J/lib64/
|
||||
|
||||
输出样例:
|
||||
|
||||
`/lib64/libtinfo.so.5' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libtinfo.so.5'
|
||||
`/lib64/libdl.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libdl.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/libc.so.6' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libc.so.6'
|
||||
`/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2'
|
||||
|
||||
复制 ls 命令所需的库文件到 $J 目录下。用 ldd 命令打印出 ls 命令依赖的共享库:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ldd /bin/ls
|
||||
|
||||
输出样例:
|
||||
|
||||
linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007fff68dff000)
|
||||
libselinux.so.1 => /lib64/libselinux.so.1 (0x00000032f8a00000)
|
||||
librt.so.1 => /lib64/librt.so.1 (0x00000032f7a00000)
|
||||
libcap.so.2 => /lib64/libcap.so.2 (0x00000032fda00000)
|
||||
libacl.so.1 => /lib64/libacl.so.1 (0x00000032fbe00000)
|
||||
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00000032f7200000)
|
||||
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x00000032f6e00000)
|
||||
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00000032f6a00000)
|
||||
libpthread.so.0 => /lib64/libpthread.so.0 (0x00000032f7600000)
|
||||
libattr.so.1 => /lib64/libattr.so.1 (0x00000032f9600000)
|
||||
|
||||
你可以一个个的复制库文件,为了更高效的作业,我们也可以使用[bash shell 的循环指令][2]实现:
|
||||
|
||||
list="$(ldd /bin/ls | egrep -o '/lib.*\.[0-9]')"
|
||||
for i in $list; do cp -v "$i" "${J}${i}"; done
|
||||
|
||||
输出样例:
|
||||
|
||||
`/lib64/libselinux.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libselinux.so.1'
|
||||
`/lib64/librt.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/librt.so.1'
|
||||
`/lib64/libcap.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libcap.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/libacl.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libacl.so.1'
|
||||
`/lib64/libc.so.6' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libc.so.6'
|
||||
`/lib64/libdl.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libdl.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2'
|
||||
`/lib64/libpthread.so.0' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libpthread.so.0'
|
||||
`/lib64/libattr.so.1' -> `/home/vivek/jail/lib64/libattr.so.1'
|
||||
|
||||
最后,chroot 到你的新jail:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chroot $J /bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
尝试浏览一下 /etc 或 /var:
|
||||
|
||||
# ls /
|
||||
# ls /etc/
|
||||
# ls /var/
|
||||
|
||||
改变了根目录的 bash 和 ls 程序现在被锁定在$HOME/$J这个特殊目录中,而且不能再访问外部的目录树,这个目录可以看做是它们的"/"(root)目录。如果配置正确的话,这会极大增强安全性。我通常用这种技术锁定以下的应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Apache - Red Hat / CentOS: Chroot Apache 2 Web Server][3]
|
||||
1. [Nginx - Linux nginx: Chroot (Jail) Setup][4]
|
||||
1. [Chroot Lighttpd web server on a Linux based system][5]
|
||||
1. Chroot mail server.
|
||||
1. Chroot Bind DNS server and more.
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何退出 chroot jail呢? ###
|
||||
|
||||
键入 exit 即可
|
||||
|
||||
$ exit
|
||||
|
||||
会话样例:
|
||||
|
||||
[][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Gif 动画01: Linux / Unix: Bash Chroot ls 命令演示
|
||||
|
||||
### 查找服务是否存在于 chrooted jail 内###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以用下面两个命令[轻松的找出 Postfix 邮件服务是否已经 chrooted]:
|
||||
|
||||
pid=$(pidof -s master)
|
||||
ls -ld /proc/$pid/root
|
||||
|
||||
从基本Linux服务中输出样例:
|
||||
|
||||
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Mar 9 11:16 /proc/8613/root -> /
|
||||
|
||||
PID 8613 指向了 / (root) 也就是说这个程序的根目录并没有被改变或是被 chroot。这个方法非常的快速而又直接,不需要打开配置文件。下面是从已经 chroot 的 ngnix 服务中得到的另一个例子:
|
||||
|
||||
pid=$(pidof -s master)
|
||||
ls -ld /proc/$pid/root
|
||||
|
||||
输出样例:
|
||||
|
||||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 nginx nginx 0 Mar 9 11:17 /proc/4233/root -> /nginxjail
|
||||
|
||||
程序的根目录已经改为 /nginxjail。
|
||||
|
||||
### 用 chroot 救援和修复软件RAID(磁盘阵列)系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我先假设基于软阵列的 Linux 系统无法正常启动。所以你[需要用Live CD或用网络远程进入内核应急模式][8]来修复系统。在这个例子中,我用了 Live Linux DVD/CD 启动基于 RHEL 的系统,然后再 chroot 到 /dev/sda1 和/或 /dev/md0 修复问题:
|
||||
|
||||
## 在 Live CD 的提示符下,键入以下命令来恢复数据。##
|
||||
## /dev/sda1 系统主分区##
|
||||
# 建立 jail 目录
|
||||
d=/chroot
|
||||
mkdir $d
|
||||
|
||||
# 挂载 sda1 和其他所需目录
|
||||
mount /dev/sda1 $d
|
||||
mount -o bind /dev $d/dev
|
||||
mount -o bind /sys $d/sys
|
||||
mount -o bind /dev/shm $d/dev/shm
|
||||
mount -o bind /proc $d/proc
|
||||
|
||||
# 挂载软件RAID /dev/md0
|
||||
mount /dev/md0 $d/data
|
||||
|
||||
# Chroot 到我们新建的 jail 中。这将允许我们修复引导装载系统(bootloader),或者在所有文件被/dev/null吞噬之前抓取数据。
|
||||
chroot $d
|
||||
|
||||
#你能看见吗?
|
||||
ls
|
||||
df
|
||||
|
||||
# 将文件置入安全路径
|
||||
rsync -avr /path/to/my_precious_data_dir user@safe.location.cyberciti.biz:/path/to/dest
|
||||
|
||||
# 退出 jail ,然后重启或者根据个人所需格式化服务 ;)
|
||||
exit
|
||||
umount {dev,sys,[...],}
|
||||
reboot
|
||||
|
||||
别急,还有更精彩的内容!
|
||||
|
||||
查看nixCraft下所有其他有关 chroot 命令的文章:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Ubuntu: Mount Encrypted Home Directory (~/.private) From an Ubuntu Live CD][9]
|
||||
1. [Linux Configure rssh Chroot Jail To Lock Users To Their Home Directories Only][10]
|
||||
1. [Fix a dual boot MS-Windows XP/Vista/7/Server and Linux problem][11]
|
||||
1. [Restore Debian Linux Grub boot loader][12]
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Linux 和 类Unix 系统下 chroot 应用程序的注意事项 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你应该一直用 chroot 特性吗?从上面的例子看出,这个程序是相当简单的,但是最终可能出现几种不同的问题而结束,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
1.在 jail 中缺失库文件可能直接导致 jail 崩溃。
|
||||
1.一些复杂的程序不好被 chroot。所以我建议你要么尝试[真正的jail,例如FreeBSD提供的][13],要么用虚拟化解决,比如[Linux 下的 KVM][14]。
|
||||
1.正在运行某一程序的 jail 不能再运行其他程序,不能更改任何文件,也不能"假设"另一个用户的身份。放宽这些限制,会降低你的安全性,请根据具体情况 chroot。
|
||||
|
||||
还要注意:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 当你升级本地程序时,不要忘记升级已 chroot 的程序。
|
||||
1. 并非所有程序能够或者应该被 chroot。
|
||||
1. 任何需要 root 权限操作的程序,对其 chroot 是没意义的。因为通常 root 用户都能脱离 chroot。
|
||||
1. Chroot 并不一个高招。更精的可以学习[如何保护和加强系统的各个部分][15]
|
||||
|
||||
### choort 命令选项 ###
|
||||
|
||||
取自 man 帮助页面[chroot(8)][16]:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--userspec=USER:GROUP 使用指定的 用户 和 组 (ID 或 名称)
|
||||
--groups=G_LIST 指定补充组 g1,g2,..,gN
|
||||
--help 显示帮助并退出
|
||||
--version 显示版本信息并退出
|
||||
|
||||
### 参见 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- [chroot(8) Linux/Unix 命令 man 页面][17]
|
||||
- [Man页面 chroot(2)][18]
|
||||
- [OpenBSD文档参见Apache chrooting FAQ 提取更多信息][19]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/cp-copy-command-in-unix-examples/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/bash-for-loop/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/chroot-apache-under-rhel-fedora-centos-linux.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-run-nginx-in-a-chroot-jail/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-setup-lighttpd-php-mysql-chrooted-jail.html
|
||||
[6]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/?attachment_id=28148
|
||||
[7]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-chroot-service.html
|
||||
[8]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/centos-rhel-linux-mount-raid-hard-disk-from-livecd/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/ubuntu-mounting-your-encrypted-home-from-livecd/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-linux-unix-rssh-chroot-jail-setup.html
|
||||
[11]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-fix-dual-boot-windows-vista-linux.html
|
||||
[12]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/restore-debian-linux-grub-boot-loader.html
|
||||
[13]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/how-to-upgrade-freebsd-jail-vps/
|
||||
[14]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/kvm-virtualization-in-redhat-centos-scientific-linux-6/
|
||||
[15]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-security.html
|
||||
[16]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man8/chroot.8.html
|
||||
[17]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man8/chroot.8.html
|
||||
[18]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man2/chroot.2.html
|
||||
[19]:http://www.openbsd.org/faq/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user