mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-09 01:30:10 +08:00
Merge pull request #1973 from ZTinoZ/master
Finish the translation by ZTinoZ
This commit is contained in:
commit
db9d15e90d
@ -1,26 +1,25 @@
|
||||
Translating by ZTinoZ
|
||||
8 Tips to Solve Linux & Unix Systems Hard Disk Problmes Like Disk Full Or Can’t Write to the Disk
|
||||
磁盘写满或磁盘不可写?解决Linux和UNIX系统这些硬盘问题的8个小贴士
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Can't write to the hard disk on a Linux or Unix-like systems? Want to diagnose corrupt disk issues on a server? Want to find out why you are getting "disk full" messages on screen? Want to learn how to solve full/corrupt and failed disk issues. Try these eight tips to diagnose a Linux and Unix server hard disk drive problems.
|
||||
不能在Linux或者类UNIX系统的硬盘上写入数据?想解决服务器上磁盘损坏的问题吗?想知道你为什么总是在屏幕上看到“磁盘已满”的字眼吗?想学习处理这些问题的办法吗?试试一下这8个解决Linux及UNIX服务器硬盘问题的小贴士吧。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### #1 - Error: No space left on device ###
|
||||
### #1 - 错误: 设备上无剩余空间 ###
|
||||
|
||||
When the Disk is full on Unix-like system you get an error message on screen. In this example, I'm running [fallocate command][1] and my system run out of disk space:
|
||||
当你的类UNIX系统磁盘写满了时你会在屏幕上看到这样的信息。本例中,我运行[fallocate命令][1]然后我的系统就会提示磁盘空间已经耗尽:
|
||||
|
||||
$ fallocate -l 1G test4.img
|
||||
fallocate: test4.img: fallocate failed: No space left on device
|
||||
|
||||
The first step is to run the df command to find out information about total space and available space on a file system including partitions:
|
||||
第一步是运行df命令来查看一个有分区的文件系统的总磁盘空间和可用空间的信息:
|
||||
|
||||
$ df
|
||||
|
||||
OR try human readable output format:
|
||||
或者试试可读性比较强的输出格式:
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
部分输出内容:
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
|
||||
/dev/sda6 117G 54G 57G 49% /
|
||||
@ -34,201 +33,200 @@ Sample outputs:
|
||||
/dev/sda8 94G 579M 89G 1% /ftpusers
|
||||
/dev/sda10 4.0G 4.0G 0 100% /ftpusers/tmp
|
||||
|
||||
From the df command output it is clear that /dev/sda10 has 4.0Gb of total space of which 4.0Gb is used.
|
||||
使用df命令输出可以清楚地发现,在 /dev/sda10 分区下总共4.0Gb的空间被全部写满了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Fixing problem when the disk is full ####
|
||||
#### 修复磁盘写满的问题 ####
|
||||
|
||||
1.[Compress uncompressed log and other files][2] using gzip or bzip2 or tar command:
|
||||
1.[用gzip,bzip2或tar命令压缩未压缩的日志和其它文件][2]:
|
||||
|
||||
gzip /ftpusers/tmp/*.log
|
||||
bzip2 /ftpusers/tmp/large.file.name
|
||||
|
||||
2.Delete [unwanted files using rm command][3] on a Unix-like system:
|
||||
2.在类UNIX系统中[用rm命令删除不想要的文件][3]:
|
||||
|
||||
m -rf /ftpusers/tmp/*.bmp
|
||||
rm -rf /ftpusers/tmp/*.bmp
|
||||
|
||||
3.Move files to other [system or external hard disk using rsync command][4]:
|
||||
3.[用rsync命令移动文件至其它系统或外置硬盘][4]:
|
||||
|
||||
rsync --remove-source-files -azv /ftpusers/tmp/*.mov /mnt/usbdisk/
|
||||
rsync --remove-source-files -azv /ftpusers/tmp/*.mov server2:/path/to/dest/dir/
|
||||
|
||||
4.[Find out the largest directories or files eating disk space][5] on a Unix-like systesm:
|
||||
4.在类UNIX系统中[找出最占磁盘空间的目录或文件][5]:
|
||||
|
||||
du -a /ftpusers/tmp | sort -n -r | head -n 10
|
||||
du -cks * | sort -rn | head
|
||||
|
||||
5.[Truncate a particular file][6]. This is useful for log file:
|
||||
5.[清空指定文件][6]。这招对日志文件很有效:
|
||||
|
||||
truncate -s 0 /ftpusers/ftp.upload.log
|
||||
### bash/sh etc ##
|
||||
### bash/sh等 ##
|
||||
>/ftpusers/ftp.upload.log
|
||||
## perl ##
|
||||
perl -e'truncate "filename", LENGTH'
|
||||
|
||||
6.Find and remove large files that are open but have been deleted on Linux or Unix:
|
||||
6.在Linux和UNIX中找出并删除显示着但已经被删除的大文件:
|
||||
|
||||
## Works on Linux/Unix/OSX/BSD etc ##
|
||||
## 基于Linux/Unix/OSX/BSD等系统 ##
|
||||
lsof -nP | grep '(deleted)'
|
||||
|
||||
## Only works on Linux ##
|
||||
## 只基于Linux ##
|
||||
find /proc/*/fd -ls | grep '(deleted)'
|
||||
|
||||
To truncate it:
|
||||
清空它:
|
||||
|
||||
## works on Linux/Unix/BSD/OSX etc all ##
|
||||
## 基于Linux/Unix/OSX/BSD等所有系统 ##
|
||||
> "/path/to/the/deleted/file.name"
|
||||
## works on Linux only ##
|
||||
## 只基于Linux ##
|
||||
> "/proc/PID-HERE/fd/FD-HERE"
|
||||
|
||||
### #2 - Is the file system is in read-only mode? ###
|
||||
### #2 - 文件系统是只读模式吗? ###
|
||||
|
||||
You may end up getting an error such as follows when you try to create a file or save a file:
|
||||
当你尝试新建或保存一个文件时,你可能最终得到诸如以下的错误:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cat > file
|
||||
-bash: file: Read-only file system
|
||||
|
||||
Run mount command to find out if the file system is mounted in read-only mode:
|
||||
运行mount命令来查看被挂载的文件系统是否处于只读状态:
|
||||
|
||||
$ mount
|
||||
$ mount | grep '/ftpusers'
|
||||
|
||||
To fix this problem, simply remount the file system in read-write mode on a Linux based system:
|
||||
在基于Linux的系统中要修复这个问题,只需将这个处于只读状态的文件系统重新挂载即可:
|
||||
|
||||
# mount -o remount,rw /ftpusers/tmp
|
||||
|
||||
Another example, from my [FreeBSD 9.x server to remount / in rw mode][7]:
|
||||
另外,我是这样[用rw模式重新挂载FreeBSD 9.x服务器的根目录][7]的:
|
||||
|
||||
# mount -o rw /dev/ad0s1a /
|
||||
|
||||
### #3 - Am I running out of inodes? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes, df command reports that there is enough free space but system claims file-system is full. You need to check [for the inode][8] which identifies the file and its attributes on a file systems using the following command:
|
||||
有时候,df命令能显示出磁盘有空余的空间但是系统却声称文件系统已经写满了。此时你需要用以下命令来检查能在文件系统中识别文件及其属性的[索引节点][8]:
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -i
|
||||
$ df -i /ftpusers/
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
部分输出内容:
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem Inodes IUsed IFree IUse% Mounted on
|
||||
/dev/sda8 6250496 11568 6238928 1% /ftpusers
|
||||
|
||||
So /ftpusers has 62,50,496 total inodes but only 11,568 are used. You are free to create another 62,38,928 files on /ftpusers partition. If 100% of your inodes are used, try the following options:
|
||||
所以 /ftpusers 下有总计62,50,496KB大小的索引节点但是只有11,568KB被使用。你可以在 /ftpusers 位置下另外创建62,38,928KB大小的文件。如果你的索引节点100%被使用了,试试看以下的选项:
|
||||
|
||||
- Find unwanted files and delete or move to another server.
|
||||
- Find unwanted large files and delete or move to another server.
|
||||
- 找出不想要的文件并删除它,或者把它移动到其它服务器上。
|
||||
- 找出不想要的大文件并删除它,或者把它移动到其它服务器上。
|
||||
|
||||
### #4 - Is my hard drive is dying? ###
|
||||
### #4 - 我的硬盘驱动器宕了吗? ###
|
||||
|
||||
[I/O errors in log file (such as /var/log/messages) indicates][9] that something is wrong with the hard disk and it may be failing. You can check hard disk for errors using smartctl command, which is control and monitor utility for SMART disks under Linux and UNIX like operating systems. The syntax is:
|
||||
[日志文件中的输入/输出错误(例如 /var/log/messages)][9]说明硬盘出了一些问题并且可能已经失效,你可以用smartctl命令来查看硬盘的错误,这是一个在类UNIX系统下控制和监控硬盘状态的一个命令。语法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
smartctl -a /dev/DEVICE
|
||||
# check for /dev/sda on a Linux server
|
||||
# 在Linux服务器下检查 /dev/sda
|
||||
smartctl -a /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use "Disk Utility" to get the same information
|
||||
你也可以用"Disk Utility"这个软件来获得同样的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
[][10]
|
||||
|
||||
Fig. 01: Gnome disk utility (Applications > System Tools > Disk Utility)
|
||||
图 01: Gnome磁盘工具(Applications > System Tools > Disk Utility)
|
||||
|
||||
> **Note**: Don't expect too much from SMART tool. It may not work in some cases. Make backup on a regular basis.
|
||||
> **注意**: 不要对SMART工具期望太高,它在某些状况下无法工作,我们要定期做备份。
|
||||
|
||||
### #5 - Is my hard drive and server is too hot? ###
|
||||
|
||||
High temperatures can cause server to function poorly. So you need to maintain the proper temperature of the server and disk. High temperatures can result into server shutdown or damage to file system and disk. [Use hddtemp or smartctl utility to find out the temperature of your hard on a Linux or Unix based system][11] by reading data from S.M.A.R.T. on drives that support this feature. Only modern hard drives have a temperature sensor. hddtemp supports reading S.M.A.R.T. information from SCSI drives too. hddtemp can work as simple command line tool or as a daemon to get information from all servers:
|
||||
### #5 - 我的硬盘驱动器和服务器是不是太热了? ###
|
||||
|
||||
高温会引起服务器低效,所以你需要把服务器和磁盘维持在一个平稳适当的温度,高温甚至能导致服务器宕机或损坏文件系统和磁盘。[用hddtemp或smartctl功能,通过从支持此特点的驱动上的SMART技术来读取数据的方式,从而查出你的Linux或基于UNIX系统上的硬件温度。][11]只有现代硬驱动器有温度传感器。hddtemp功能也支持从SCSI驱动器读取SMART信息。hddtemp能作为一个简单的命令行工具或守护程序来从所有服务器中获取信息:
|
||||
hddtemp /dev/DISK
|
||||
hddtemp /dev/sg0
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
部分输出内容:
|
||||
|
||||
[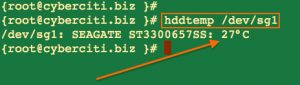][12]
|
||||
|
||||
Fig.02: hddtemp in action
|
||||
图 02: hddtemp正在运行
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the smartctl command as follows too:
|
||||
你也可以像下面显示的那样使用smartctl命令:
|
||||
|
||||
smartctl -d ata -A /dev/sda | grep -i temperature
|
||||
|
||||
#### How do I get the CPU temperature? ####
|
||||
#### 我怎么获取CPU的温度 ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can use Linux hardware monitoring tool such as [lm_sensor to get the cpu temperature on a Linux based][13] system:
|
||||
你可以使用Linux硬件监控工具例如像[用基于Linux系统的lm_sensor功能来获取CPU温度][13]:
|
||||
|
||||
sensors
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs from Debian Linux server:
|
||||
Debian服务器的部分输出内容:
|
||||
|
||||
[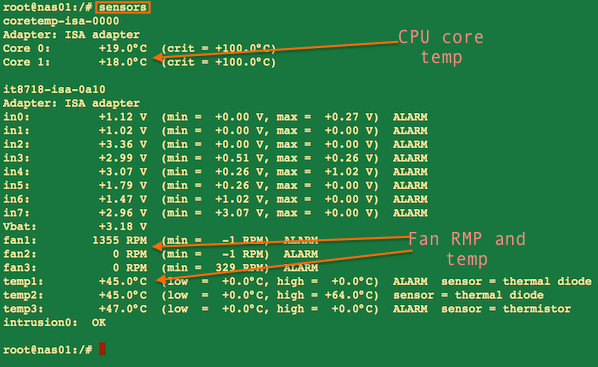][14]
|
||||
|
||||
Fig.03: sensors command providing cpu core temperature and other info on a Linux
|
||||
图 03: sensors命令提供了一台Linux计算机的CPU核心温度和其它信息
|
||||
|
||||
### #6 - Dealing with corrupted file systems ###
|
||||
### #6 - 处理损坏的文件系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
File system on server may be get corrupted due to a hard reboot or some other error such as bad blocks. You can [repair corrupted file systems with the following fsck command][15]:
|
||||
服务器上的文件系统可能会因为硬件重启或一些其它的错误比如坏区而损坏。你可以[用fsck命令来修复损坏的文件系统][15]:
|
||||
|
||||
umount /ftpusers
|
||||
fsck -y /dev/sda8
|
||||
|
||||
See [how to surviving a Linux filesystem failures][16] for more info.
|
||||
来看看[怎么应对Linux文件系统故障][16]的更多信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### #7 - Dealing with software RAID on a Linux ###
|
||||
### #7 - 处理Linux中的软阵列 ###
|
||||
|
||||
To find the current status of a Linux software raid type the following command:
|
||||
输入以下命令来查看Linux软阵列的最近状态:
|
||||
|
||||
## get detail on /dev/md0 raid ##
|
||||
## 获得 /dev/md0 上磁盘阵列的具体内容 ##
|
||||
mdadm --detail /dev/md0
|
||||
|
||||
## Find status ##
|
||||
## 查看状态 ##
|
||||
cat /proc/mdstat
|
||||
watch cat /proc/mdstat
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
部分输出内容:
|
||||
|
||||
[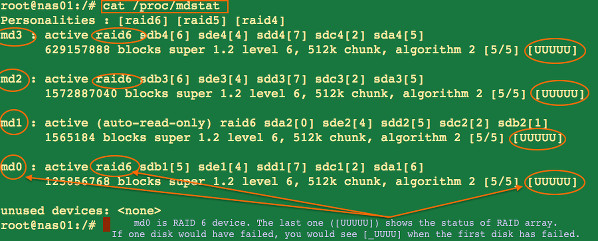][17]
|
||||
|
||||
Fig. 04: Find the status of a Linux software raid command
|
||||
图 04: 查看Linux软阵列状态命令
|
||||
|
||||
You need to replace a failed hard drive. You must u remove the correct failed drive. In this example, I'm going to replace /dev/sdb (2nd hard drive of RAID 6). It is not necessary to take the storage offline to repair the RAID on Linux. This only works if your server support hot-swappable hard disk:
|
||||
你需要把有故障的硬件驱动器更换掉,别删错了。本例中,我更换了 /dev/sdb (RAID 6中的第二个硬件驱动器)。没必要依靠离线存储文件来修复Linux上的磁盘阵列,因为这只在你的服务器支持热插拔硬盘的情况下才能工作:
|
||||
|
||||
## remove disk from an array md0 ##
|
||||
## 从一个md0阵列中删除磁盘 ##
|
||||
mdadm --manage /dev/md0 --fail /dev/sdb1
|
||||
mdadm --manage /dev/md0 --remove /dev/sdb1
|
||||
|
||||
# Do the same steps again for rest of /dev/sdbX ##
|
||||
# Power down if not hot-swappable hard disk: ##
|
||||
# 对 /dev/sdbX 的剩余部分做相同操作 ##
|
||||
# 如果不是热插拔硬盘就执行关机操作 ##
|
||||
shutdown -h now
|
||||
|
||||
## copy partition table from /dev/sda to newly replaced /dev/sdb ##
|
||||
## 从 /dev/sda 复制分区表至新的 /dev/sdb 下 ##
|
||||
sfdisk -d /dev/sda | sfdisk /dev/sdb
|
||||
fdisk -l
|
||||
|
||||
## Add it ##
|
||||
## 添加 ##
|
||||
mdadm --manage /dev/md0 --add /dev/sdb1
|
||||
# do the same steps again for rest of /dev/sdbX ##
|
||||
# 对 /dev/sdbX 的剩余部分做相同操作 ##
|
||||
|
||||
# Now md0 will sync again. See it on screen ##
|
||||
# 现在md0会再次同步,通过显示屏查看 ##
|
||||
watch cat /proc/mdstat
|
||||
|
||||
See our [tips on increasing RAID sync speed on Linux][18] for more information.
|
||||
来看看[加快Linux磁盘阵列同步速度的小贴士][18]来获取更多信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### #8 - Dealing with hardware RAID ###
|
||||
### #8 - 处理硬阵列 ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the samrtctl command or vendor specific command to find out the status of RAID and disks in your controller:
|
||||
你可以用samrtctl命令或者供应商特定的命令来查看磁盘阵列和你所管理的磁盘的状态:
|
||||
|
||||
## SCSI disk
|
||||
## SCSI磁盘
|
||||
smartctl -d scsi --all /dev/sgX
|
||||
|
||||
## Adaptec RAID array
|
||||
## Adaptec磁盘阵列
|
||||
/usr/StorMan/arcconf getconfig 1
|
||||
|
||||
## 3ware RAID Array
|
||||
## 3ware磁盘阵列
|
||||
tw_cli /c0 show
|
||||
|
||||
See your vendor specific documentation to replace a failed disk.
|
||||
对照供应商特定文档来更换你的故障磁盘。
|
||||
|
||||
### Monitoring disk health ###
|
||||
### 监控磁盘的健康状况 ###
|
||||
|
||||
See our previous tutorials:
|
||||
来看看我们先前的教程:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Monitoring hard disk health with smartd under Linux or UNIX operating systems][19]
|
||||
1. [Shell script to watch the disk space][20]
|
||||
@ -237,9 +235,9 @@ See our previous tutorials:
|
||||
1. [Perl script to monitor disk space and send an email][23]
|
||||
1. [NAS backup server disk monitoring shell script][24]
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
I hope these tips will help you troubleshoot system disk issue on a Linux/Unix based server. I also recommend implementing a good backup plan in order to have the ability to recover from disk failure, accidental file deletion, file corruption, or complete server destruction:
|
||||
我希望以上这些小贴士会帮助你改善在基于Linux/Unix服务器上的系统磁盘问题。我还建议执行一个好的备份计划从而有能力从磁盘故障、意外的文件删除操作、文件损坏和服务器完全被破坏等意外情况中恢复:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Debian / Ubuntu: Install Duplicity for encrypted backup in cloud][25]
|
||||
- [HowTo: Backup MySQL databases, web server files to a FTP server automatically][26]
|
||||
@ -252,7 +250,7 @@ I hope these tips will help you troubleshoot system disk issue on a Linux/Unix b
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/datacenter/linux-unix-bsd-osx-cannot-write-to-hard-disk/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[nixCraft][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user