mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-06 23:50:16 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject
This commit is contained in:
commit
d83bb8fb3a
@ -1,39 +1,38 @@
|
||||
在linux中4个lvcreate命令例子
|
||||
4 个 lvcreate 常用命令举例
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
逻辑卷管理(LVM)是广泛使用的技术,并拥有极其灵活磁盘管理方案。主要包含3个基础命令:
|
||||
|
||||
a. 创建物理卷使用**pvcreate**
|
||||
b. 创建卷组并给卷组增加分区**vgcreate**
|
||||
c. 创建新的逻辑卷使用**lvcreate**
|
||||
1. 创建物理卷使用**pvcreate**
|
||||
2. 创建卷组并给卷组增加分区**vgcreate**
|
||||
3. 创建新的逻辑卷使用**lvcreate**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
随后的例子着重在已经存在的卷组上使用**lvcreate**创建逻辑卷。**lvcreate**命令可以在来自自由物理扩展池的卷组分配逻辑扩展。通常,逻辑卷可以随意使用底层逻辑卷上的任意空间。修改逻辑卷将释放或重新分配在物理卷空间。这些例子已经在CentOS 5, CentOS 6, CentOS 7, RHEL 5, RHEl 6 和 RHEL 7 版本中测试通过。
|
||||
下列例子主要讲述在已经存在的卷组上使用**lvcreate**创建逻辑卷。**lvcreate**命令可以在卷组的可用物理扩展池中分配逻辑扩展。通常,逻辑卷可以随意使用底层逻辑卷上的任意空间。修改逻辑卷将释放或重新分配物理卷的空间。这些例子已经在CentOS 5, CentOS 6, CentOS 7, RHEL 5, RHEl 6 和 RHEL 7 版本中测试通过。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4个lvcreate命令例子 ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在名为vg_newlvm卷组中创建15G大小的逻辑卷:
|
||||
1. 在名为vg_newlvm的卷组中创建15G大小的逻辑卷:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# lvcreate -L 15G vg_newlvm
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# lvcreate -L 15G vg_newlvm
|
||||
|
||||
2. 在名为vg_newlvm中创建大小为2500MB的逻辑卷并命名centos7_newvol,创建块设备/dev/vg_newlvm/centos7_newvol:
|
||||
2. 在名为vg_newlvm的卷组中创建大小为2500MB的逻辑卷,并命名为centos7_newvol,这样就创建了块设备/dev/vg_newlvm/centos7_newvol:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# lvcreate -L 2500 -n centos7_newvol vg_newlvm
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# lvcreate -L 2500 -n centos7_newvol vg_newlvm
|
||||
|
||||
3.可以使用**lvcreate**命令的参数-l,能指定一些特别的逻辑卷扩展大小。也可以使用这个参数以卷组的大小百分比来扩展逻辑卷。这下列的命令创建了centos7_newvol卷组的50%大小的逻辑卷vg_newlvm:
|
||||
3. 可以使用**lvcreate**命令的参数-l来指定逻辑卷扩展的大小。也可以使用这个参数以卷组的大小百分比来扩展逻辑卷。这下列的命令创建了centos7_newvol卷组的50%大小的逻辑卷vg_newlvm:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# lvcreate -l 50%VG -n centos7_newvol vg_newlvm
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# lvcreate -l 50%VG -n centos7_newvol vg_newlvm
|
||||
|
||||
4. 使用卷组剩下的所有空间创建逻辑卷
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# lvcreate --name centos7_newvol -l 100%FREE vg_newlvm
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# lvcreate --name centos7_newvol -l 100%FREE vg_newlvm
|
||||
|
||||
更多帮助,使用**lvcreate**命令--help选项来查看:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# lvcreate --help
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
以下空号中是帮助字面翻译
|
||||
|
||||
lvcreate: Create a logical volume(创建逻辑卷)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -46,8 +45,8 @@ c. 创建新的逻辑卷使用**lvcreate**
|
||||
[-C|--contiguous {y|n}]
|
||||
[-d|--debug]
|
||||
[-h|-?|--help]
|
||||
[--ignoremonitoring](忽略监听)
|
||||
[--monitor {y|n}](监听)
|
||||
[--ignoremonitoring](忽略监控)
|
||||
[--monitor {y|n}](监控)
|
||||
[-i|--stripes Stripes [-I|--stripesize StripeSize]]
|
||||
[-k|--setactivationskip {y|n}]
|
||||
[-K|--ignoreactivationskip]
|
||||
@ -66,7 +65,7 @@ c. 创建新的逻辑卷使用**lvcreate**
|
||||
[--discards {ignore|nopassdown|passdown}]
|
||||
[--poolmetadatasize MetadataSize[bBsSkKmMgG]]]
|
||||
[--poolmetadataspare {y|n}]
|
||||
[--thinpool ThinPoolLogicalVolume{Name|Path}]精简池逻辑卷
|
||||
[--thinpool ThinPoolLogicalVolume{Name|Path}] (精简池逻辑卷)
|
||||
[-t|--test]
|
||||
[--type VolumeType](卷类型)
|
||||
[-v|--verbose]
|
||||
@ -75,18 +74,14 @@ c. 创建新的逻辑卷使用**lvcreate**
|
||||
[--version]
|
||||
VolumeGroupName [PhysicalVolumePath...]
|
||||
|
||||
lvcreate
|
||||
{ {-s|--snapshot} OriginalLogicalVolume[Path] |
|
||||
[-s|--snapshot] VolumeGroupName[Path] -V|--virtualsize VirtualSize}
|
||||
{-T|--thin} VolumeGroupName[Path][/PoolLogicalVolume]
|
||||
-V|--virtualsize VirtualSize}(
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ehowstuff.com/4-lvcreate-command-examples-on-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[skytech][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[Vic020](https://github.com/Vic020)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
性能优化:使用ramlog将日志文件转移到内存中
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ramlog 以系统守护进程的形式运行。在系统启动时它创建虚拟磁盘(ramdisk),将 /var/log 下的文件复制到虚拟磁盘中,同时把虚拟磁盘挂载为/var/log。然后所有的日志就会更新到虚拟磁盘上。而当 ramlog 重启或停止时,需要记录到硬盘上的日志就会保留在目录/var/log.hdd中。而关机的时候,(ramdisk上的)日志文件会重新保存到硬盘上,以确保日志一致性。Ramlog 2.x默认使用tmpfs文件系统,同时也可以支持ramfs和内核ramdisk。使用rsync(译注:Linux数据镜像备份工具)这个工具来同步日志。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:如果突然断电或者内核崩溃(kernel panic)时,没有保存进硬盘的日志将会丢失。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你拥有够多的可用内存,而又想把日志放进虚拟磁盘,就安装ramlog吧。它是笔记本用户、带有UPS的系统或是直接在flash中运行的系统的优良选择,可以节省日志的写入时间。
|
||||
|
||||
Ramlog的运行机制以及步骤如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Ramlog 由第一个守护进程(这取决于你所安装过的其它守护进程)启动。
|
||||
|
||||
2. 然后创建目录/var/log.hdd并将其硬链至/var/log。
|
||||
|
||||
3. 如果使用的是tmpfs(默认)或者ramfs 文件系统,将其挂载到/var/log上。
|
||||
|
||||
4. 而如果使用的是内核ramdisk,ramdisk会在/dev/ram9中创建,并将其挂载至/var/log。默认情况下ramlog会占用所有ramdisk的内存,其大小由内核参数"ramdisk_size"指定。
|
||||
|
||||
5. 接着其它的守护进程被启动,并在ramdisk中更新日志。Logrotate(译注:Linux日志轮替工具)和 ramdisk 配合的也很好。
|
||||
|
||||
6. 重启(默认一天一次)ramlog时,目录/var/log.hdd将借助rsync与/var/log保持同步。日志自动保存的频率可以通过cron(译注:Linux例行性工作调度)来控制。默认情况下,ramlog 的调度任务放置在目录/etc/cron.daily下。
|
||||
|
||||
7. 系统关机时,ramlog在最后一个守护进程关闭之前关闭。
|
||||
|
||||
8. 在ramlog关闭期间,/var/log.hdd中的文件将被同步至/var/log,接着/var/log和/var/log.hdd都被卸载,然后删除空目录/var/log.hdd。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:- 此文仅面向高级用户**
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu中安装Ramlog ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先需要用以下命令,从[这里][1]下载.deb安装包:
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://www.tremende.com/ramlog/download/ramlog_2.0.0_all.deb
|
||||
|
||||
下载ramlog\_2.0.0\_all.deb安装包完毕,使用以下命令进行安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg -i ramlog_2.0.0_all.deb
|
||||
|
||||
这一步会完成整个安装,现在你需要运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo update-rc.d ramlog start 2 2 3 4 5 . stop 99 0 1 6 .
|
||||
|
||||
现在,在更新sysklogd的初始化顺序,使之能在ramlog停止运行前正确关闭:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo update-rc.d -f sysklogd remove
|
||||
|
||||
sudo update-rc.d sysklogd start 10 2 3 4 5 . stop 90 0 1 6 .
|
||||
|
||||
然后重启系统:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo reboot
|
||||
|
||||
系统重启完毕,运行'ramlog getlogsize'来获取你当前的/var/log的空间大小。在此基础之上多分配40%的空间,确保ramdisk有足够的空间(这整个都将作为ramdisk的空间大小)。
|
||||
|
||||
编辑引导配置文件,如/etc/grub.conf,、/boot/grub/menu.lst 或/etc/lilo.conf(译注:具体哪个配置文件视不同引导加载程序而定),给你的当前内核的新增选项 'ramdisk_size=xxx' ,其中xxx是ramdisk的空间大小。
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置Ramlog ###
|
||||
|
||||
基于deb的系统中,Ramlog的配置文件位于/etc/default/ramlog,你可以在该配置文件中设置以下变量:
|
||||
|
||||
RAMDISKTYPE=0
|
||||
# 取值:
|
||||
# 0 -- tmpfs (可被交换到交换分区) -- 默认
|
||||
# 1 -- ramfs (旧内核不能设置最大空间大小,
|
||||
# 不能被交换到交换分区,和 SELinux 不兼容)
|
||||
# 2 -- 老式的内核 ramdisk
|
||||
TMPFS_RAMFS_SIZE=
|
||||
# 可以用于 tmpfs 或 ramfs 的最大内存大小
|
||||
# 这个值可以是百分比或数值(单位是 Mb),例如:
|
||||
# TMPFS_RAMFS_SIZE=40%
|
||||
# TMPFS_RAMFS_SIZE=100m
|
||||
# 该值为空表示 tmpfs/ramfs 的大小是全部内存的 50%
|
||||
# 更多选项可以参考 ‘man mount' 中的‘Mount options for tmpfs' 一节
|
||||
# (补充,在较新的内核中,ramfs 支持大小限制,
|
||||
# 虽然 man 中说没有这个挂载选项)
|
||||
# 该选项仅用于 RAMDISKTYPE=0 或 1 时
|
||||
KERNEL_RAMDISK_SIZE=MAX
|
||||
#以 kb 为单位指定的内核 ramdisk 大小,或者使用 MAX 来使用整个 ramdisk。
|
||||
#该选项仅用于 RAMDISKTYPE=2 时
|
||||
LOGGING=1
|
||||
# 0=关闭, 1=打开 。记录自身的日志到 /var/log/ramdisk
|
||||
LOGNAME=ramlog
|
||||
# 自身的日志文件名 (用于 LOGGING=1时)
|
||||
VERBOSE=1
|
||||
# 0=关闭, 1=打开 (设置为 1时,启动或停止失败时会调用 teststartstop 将细节
|
||||
# 写到日志中)
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu中卸载ramlog ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg -P ramlog
|
||||
|
||||
注意:如果ramlog卸载之前仍在运行,需要重启系统完成整个卸载工作。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/improve-system-performance-by-moving-your-log-files-to-ram-using-ramlog.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ruchi][a]
|
||||
译者:[soooogreen](https://github.com/soooogreen)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tremende.com/ramlog/download/ramlog_2.0.0_all.deb
|
||||
@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
|
||||
LinSSID - 一款Linux下的图形化Wi-Fi扫描器
|
||||
LinSSID:一款Linux下的图形化Wi-Fi扫描器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### 介绍 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如你所知,**LinSSID** 是一款可以用于寻找可用无线网络的图形化软件。它完全开源,用C++写成,使用了Linux无线工具、Qt5、Qwt6.1,它在外观和功能上与**Inssider** (MS Windows)相近。
|
||||
你可能知道,**LinSSID** 是一款可以用于寻找可用无线网络的图形化软件。它完全开源,用C++写成,使用了Linux wireless tools、Qt5、Qwt6.1,它在外观和功能上与**Inssider** (MS Windows 下的)相近。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用源码安装,如果你使用的是基于DEB的系统比如Ubuntu和LinuxMint等等,你也可以使用PPA安装。
|
||||
|
||||
你可用从[this link][1]这个链接下载并安装LinSSID。
|
||||
你可用从[这个][1]下载并安装LinSSID。
|
||||
|
||||
这里我门将使用PPA来安装并测试这个软件。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,22 +22,21 @@ LinSSID - 一款Linux下的图形化Wi-Fi扫描器
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成之后,你可以从菜单或者unity中启动。
|
||||
|
||||
你将被要求输入管理员密码。
|
||||
你需要输入管理员密码。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这就是LinSSID的界面。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在选择你想要连接无线网络的网卡,比如这里是wlan0.点击Play按钮来搜寻wi-fi网络列表。
|
||||
现在选择你想要连接无线网络的网卡,比如这里是wlan0,点击Play按钮来搜寻wi-fi网络列表。
|
||||
|
||||
几秒钟之后,LinSSID就会显示wi-fi网络了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如你在上面的截屏中所见,LinSSID显示SSID名、MAC ID、通道、隐私、加密方式、信号和协议等等信息。当然,你可以让LinSSID显示更多的选项,比如安全、带宽等等。要显示这些,进入**View**菜单并选择需要的选项。同样,它显示了不同通道中的信号随着时间信号强度的变化。最后,它可以工作在2.4Ghz和5Ghz通道上。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如你在上面的截屏中所见,LinSSID显示SSID名、MAC ID、通道、隐私、加密方式、信号和协议等等信息。当然,你可以让LinSSID显示更多的选项,比如安全设置、带宽等等。要显示这些,进入**View**菜单并选择需要的选项。同样,它显示了不同的通道中的信号随着时间信号强度的变化。最后,它可以工作在2.4Ghz和5Ghz通道上。
|
||||
|
||||
就是这样。希望这个工具对你有用。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -53,7 +52,7 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/linssid-graphical-wi-fi-scanner-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
|
||||
How to Install Telegram Messenger Application on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Telegram is an Instant Messaging (IM) application similar to whatsapp. It has a very large user base. It has a lot of features that differentiate it from other messaging application.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Telegram Messenger for Linux
|
||||
|
||||
This article aims at making you aware of telegram application followed by detailed installation instructions on Linux Box.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features of Telegram ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Implementation for mobile devices
|
||||
- Available for Desktop.
|
||||
- Application Program Interface (API) of Telegram can be Accessed by third party developers.
|
||||
- Available for Android, iphone/ipad, Windows Phone, Web-Version, PC, Mac and Linux
|
||||
- The above application provides Heavily Encrypted and self destruct messages.
|
||||
- Lets you access your message from multiple devices and platform.
|
||||
- The overall processing and message delivery is lightening fast.
|
||||
- Distributed server across the globe for security and speed.
|
||||
- Open API and Free Protocol
|
||||
- NoAds, No Subscription charge. – Free forever.
|
||||
- Powerful – No limit to media and chats
|
||||
- Several security measures that make it safe from Hackers.
|
||||
- Reply to Specific message in group. Mention @username to notify multiple users in group.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Why Telegram? ####
|
||||
|
||||
When Applications like whatsapp and other IM are providing almost same things in bag, why should someone opt for Telegram?
|
||||
|
||||
Well Availability of API to third party developer is enough to say. Moreover availability for PC which means you won’t have to struggle typing message using your mobile, but you can use your PC and that is pretty more than sufficient.
|
||||
|
||||
Also The option to connect on remote locations, Co-ordinate – Group of upto 200 Members, Sync all your devices, Send – Documents of all kind, Encrypt message, Self destruction of message, Storage of Media in Cloud, Build own tool on freely available API and what not.
|
||||
|
||||
**Testing Environment**
|
||||
|
||||
We have used Debian GNU/Linux, x86_64 architecture to test it and the overall process went very smooth for us. Here what we did stepwise.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation of Telegram Messenger in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
First go to the official Telegram site, and download Telegram source package ([tsetup.0.7.23.tar.xz][1]) for Linux system or you may use following wget command to download directly.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget https://updates.tdesktop.com/tlinux/tsetup.0.7.23.tar.xz
|
||||
|
||||
Once package has been downloaded, unpack the tarball and switch from current working directory to the extracted directory.
|
||||
|
||||
# tar -xf tsetup.0.7.23.tar.xz
|
||||
# cd Telegram/
|
||||
|
||||
Next, execute the binary file ‘Telegram’ from the command line as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
# ./Telegram
|
||||
|
||||
1. The first Impression. Click “START MESSAGING”.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Start Messaging
|
||||
|
||||
2. Enter Your phone Number. Click “NEXT”. If you have not registered for telegram before this, using the same number as entered above you will get a warning that you don’t have a telegram account yet. Click “Register Here”.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Signup for Telegram
|
||||
|
||||
3. After submitting your phone number, telegram will send you a verification code, shortly. You need to Enter it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Telegram Verification Code
|
||||
|
||||
4. Enter your First_Name, Last_name and pics and click “SIGNUP”.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Enter Account Details
|
||||
|
||||
5. After account creation, I got this interface. Everything seems at its place, even when I am new to telegram Application. The interface is really simple.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Telegram Interface
|
||||
|
||||
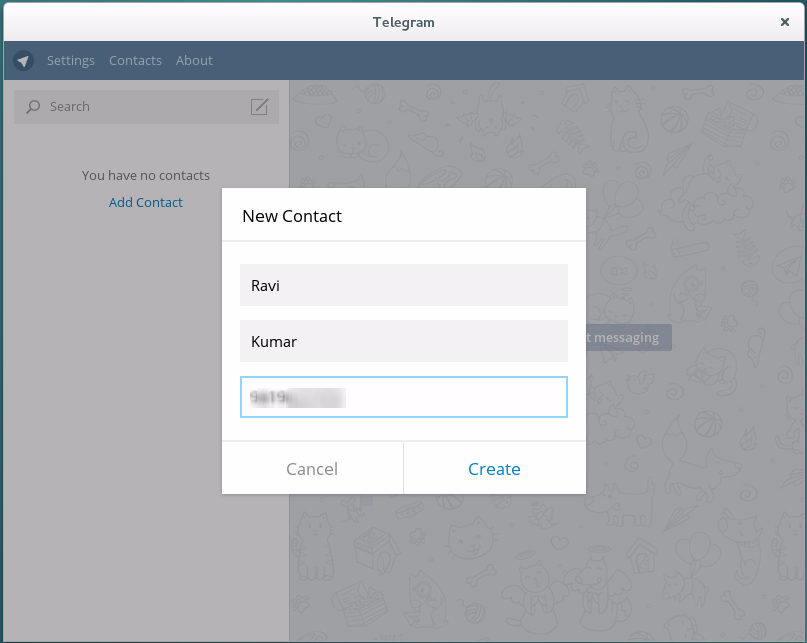
6. Click Add a contact and Enter Their first_name, last_name and Phone number. Click create when done!.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Add New Telegram Contact
|
||||
|
||||
7. If the contact you added is not on telegram already, You get a warning message and telegram will acknowledge you when your contact joins telegram.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Telegram Contact Notification
|
||||
|
||||
8. As soon as the contact joins telegram you get a message (pop-out like) that reads [YOUR_CONTACT] joined telegram.
|
||||
|
||||
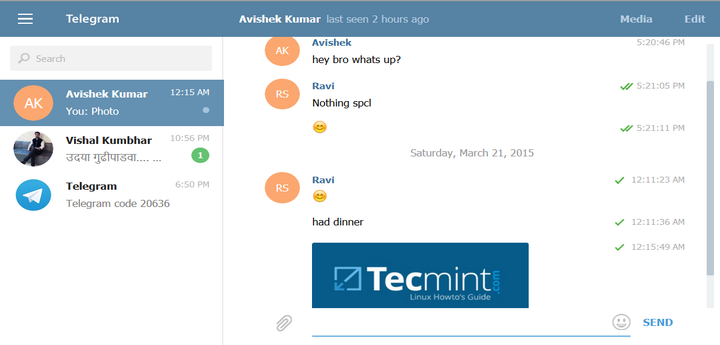
9. A formal chat window on Linux Machine. Nice experience…
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Telegram Contact Join Message
|
||||
|
||||
10. At the same time, I’ve tried messaging from my android mobile device, the interface looks similar on both.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Telegram Mobile Interface
|
||||
|
||||
11. Telegram settings page. You have a lot of options to configure.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Telegram Settings
|
||||
|
||||
12. About Telegram.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
About Telegram
|
||||
|
||||
#### Less Interesting Points ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Telegram usage protocol MTProto Mobile protocol.
|
||||
- Released Initially for iPhone in the year 2013 (August 14)..
|
||||
- People Behind this Amazing Project: Pavel and Nikolai Durov..
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I’ll be here again with another interesting article you will love to read. I take the pleasure on behalf of Tecmint to thank all our valuable readers and critics who made us stand where we are now through continuous self evolving process. Keep Connected! Keep Commenting. Share if you care for us.
|
||||
|
||||
- [https://telegram.org/][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-telegram-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:https://tdesktop.com/linux
|
||||
[2]:https://telegram.org/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
[raywang]
|
||||
Open source all over the world
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
Vic020
|
||||
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to compress JPEG images from the command line on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I have several JPEG photo images I have taken using a digital camera. I would like to optimize and compress the JPEG pictures before uploading them to Dropbox. What is the easiest way to compress JPEG images without losing their quality on Linux?
|
||||
@ -97,4 +99,4 @@ via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/compress-jpeg-images-command-line-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-compress-png-files-on-linux.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
|
||||
4 Tools to Securely Delete Files from Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Any computer user with normal level skill set knows that any data removed from computer system can be recovered later with little bit of efforts. This is a good thing in the scenario when you have accidentally deleted your critical data. But in most cases, you don't want your private data to be recovered easily. Whenever we remove anything, the operating system deletes just the index of the particular data. It means that data is still there somewhere on the disk, this method is insecure, as any smart computer hacker can use any good data recovery tool to easily recover your deleted data. Linux users utilizes the well know “**rm**” command to remove data from their operating system, but “rm” command works in the conventional fashion. Data removed using this command can be recovered by special file recovery tools.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s see how we can safely and completely remove files/folders from our Linux system. The methods mentioned below remove data completely so it becomes very hard for recovery tools to find traces of the actual data and recover it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Secure-Delete ###
|
||||
|
||||
Secure-Delete is a set of tools for Linux operating system and they provide advanced techniques for permanent removal of files. Once Secure-Delete has been installed on any Linux system, it provides following four commands:
|
||||
|
||||
- srm
|
||||
- smem
|
||||
- sfill
|
||||
- sswap
|
||||
|
||||
Run following command in the terminal to install it in ubuntu:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install secure-delete
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Run following command to install it in RHEL, Fedora or Centos:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install secure-delete
|
||||
|
||||
“**srm**” command works similarly to “rm” command, but instead of just deleting the file, it first overwrites it multiple times with some random data and then removes the file permanently. The syntax for this command is pretty simply, just specify the file or directory to remove and it will take care of the task.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo srm /home/aun/Documents/xueo/1.png
|
||||
|
||||
"**sfill**" checks the specified partition/directories for space marked as free or available, and then uses its algorithm to fill it up with some random data. In this way it ensures that there are no more recoverable files/folders on the partition.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo sfill /home
|
||||
|
||||
"**sswap**" command is used to securely wipe your swap partitions. Swap partition is used to store data for running programs. First of all find out your swap partition by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
cat /proc/swaps
|
||||
|
||||
Example output of above command is show below:
|
||||
|
||||
aun@eagle:~$ cat /proc/swaps
|
||||
Filename Type Size Used Priority
|
||||
/dev/sda5 partition 2084860 71216 -1
|
||||
|
||||
From here, you can see that swap is set to which partition, and then securely clean it by running the following command. Replace the "/dev/sda5" part with your partition name.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo sswap /dev/sda5
|
||||
|
||||
“**smem**” is used to clean the contents of memory, its true that RAM contents are cleaned when system is rebooted or powered off, but some residual traces of data still remain in the memory. This command provides secure memory cleaning, simly run smem command on the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
smem
|
||||
|
||||
### Shred ###
|
||||
|
||||
"shred" command destroys files/folder’s contents in a way that it is impossible to recover. It keeps overwriting the files with randomly generated data patterns so in this way it becomes very hard to recover any data from them even if hackers or thief uses high level of data recovery tools/equipments. Shred is installed by default on all Linux distributions, if you want, you can find its installation path by running following command:
|
||||
|
||||
aun@eagle:~$ whereis shred
|
||||
|
||||
shred: /usr/bin/shred /usr/share/man/man1/shred.1.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Run following command to remove file using shred utility.
|
||||
|
||||
shred /home/aun/Documents/xueo/1.png
|
||||
|
||||
Run following command to securely remove any partition using shred ; Replace partition name with your desired partition.
|
||||
|
||||
shred /dev/sda5
|
||||
|
||||
Shred by default overwrites file with random contents 25 times. If you want it to overwrite file more than this, simply specify the desired number with "shred -n" option.
|
||||
|
||||
shred -n 100 filename
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to truncate and remove file after overwriting, use "shred -u" option
|
||||
|
||||
shred -u filename
|
||||
|
||||
### dd ###
|
||||
|
||||
This command is originally used for Disk Cloning. It is used to copy contents of one partition or disk to another. But it is also used for securely wiping out the contents of a hard disk or partitions. Run following command to overwrite your current data with random data.You don't need to install dd command, all Linux distributions include this command already.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dd if=/dev/random of=/dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
You can also overwrite the contents of hard disk or partitions by simply replacing everything with “zero”.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
### Wipe ###
|
||||
|
||||
Wipe was originally developed to securely erase files from magnetic media. This command line utility writes special patterns to the files repeatedly. It uses fsync() call and/or the O_SYNC bit to force disk access. It uses Gutmann algorithm for repeated writes. You can remove contents of single file, folder or entire hard disk with this command, but whole hard disk format using wipe command will take good amount of time. The installation and use of this utility is pretty easy.
|
||||
|
||||
Install wipe on ubuntu by running the following command on the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo aptitude install wipe
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Install Wipe in Redhat Linux, Centos or Fedora by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install wipe
|
||||
|
||||
Once the installation is complete, run following command on the terminal to get complete list of its available options:
|
||||
|
||||
man wipe
|
||||
|
||||
Remove any file or directory as:
|
||||
|
||||
wipe filename
|
||||
|
||||
Securely remove your tmp partition by running following command:
|
||||
|
||||
wipe -r /tmp
|
||||
|
||||
Use following command to remove contents of complete partition (replace partition name with your desired partition).
|
||||
|
||||
wipe /dev/sda1
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
We hope you find this article useful, the privacy of your data is critical, its important to have such secure file removal utilities installed on your system so you may be able to remove your private data without fear of being recovered easily. All of the above mentioned tools are pretty lightweight, they take minimum system resources to run, and does not affect performance of your system in anyway. Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/security/delete-files-permanatly-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aun Raza][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunrz/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,163 @@
|
||||
7 Quirky ‘ls’ Command Tricks Every Linux User Should Know
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
We have covered most of the things on ‘ls‘ command in last two articles of our Interview series. This article is the last part of the ‘ls command‘ series. If you have not gone through last two articles of this series you may visit the links below.
|
||||
|
||||
注:以下三篇都做过源文,看看翻译了没有,如果发布了可适当改链接地址
|
||||
- [15 Basic ‘ls’ Command Examples in Linux][]
|
||||
- [15 Interview Questions on Linux “ls” Command – Part 1][]
|
||||
- [10 Useful ‘ls’ Command Interview Questions – Part 2][]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
7 Quirky ls Command Tricks
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. List the contents of a directory with time using various time styles. ###
|
||||
|
||||
To list the contents of a directory with times using style, we need to choose any of the below two methods.
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -l –time-style=[STYLE] (Method A)
|
||||
|
||||
**Note** – The above switch (`--time` style must be run with switch `-l`, else it won’t serve the purpose).
|
||||
|
||||
# ls –full-time (Method B)
|
||||
|
||||
Replace `[STYLE]` with any of the below option.
|
||||
|
||||
full-iso
|
||||
long-iso
|
||||
iso
|
||||
locale
|
||||
+%H:%M:%S:%D
|
||||
|
||||
**Note** – In the above line H(Hour), M(Minute), S(Second), D(Date) can be used in any order.
|
||||
|
||||
Moreover you just choose those relevant and not all options. E.g., `ls -l --time-style=+%H` will show only hour.
|
||||
|
||||
`ls -l --time-style=+%H:%M:%D` will show Hour, Minute and date.
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -l --time-style=full-iso
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
ls Command Full Time Style
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -l --time-style=long-iso
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Long Time Style Listing
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -l --time-style=iso
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Time Style Listing
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -l --time-style=locale
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Locale Time Style Listing
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -l --time-style=+%H:%M:%S:%D
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Date and Time Style Listing
|
||||
|
||||
# ls --full-time
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Full Style Time Listing
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Output the contents of a directory in various formats such as separated by commas, horizontal, long, vertical, across, etc. ###
|
||||
|
||||
Contents of directory can be listed using ls command in various format as suggested below.
|
||||
|
||||
- across
|
||||
- comma
|
||||
- horizontal
|
||||
- long
|
||||
- single-column
|
||||
- verbose
|
||||
- vertical
|
||||
|
||||
# ls –-format=across
|
||||
# ls --format=comma
|
||||
# ls --format=horizontal
|
||||
# ls --format=long
|
||||
# ls --format=single-column
|
||||
# ls --format=verbose
|
||||
# ls --format=vertical
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Listing Formats of ls Command
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Use ls command to append indicators like (/=@|) in output to the contents of the directory. ###
|
||||
|
||||
The option `-p` with ‘ls‘ command will server the purpose. It will append one of the above indicator, based upon the type of file.
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -p
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Append Indicators to Content
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Sort the contents of directory on the basis of extension, size, time and version. ###
|
||||
|
||||
We can use options like `--extension` to sort the output by extension, size by extension `--size`, time by using extension `-t` and version using extension `-v`.
|
||||
|
||||
Also we can use option `--none` which will output in general way without any sorting in actual.
|
||||
|
||||
# ls --sort=extension
|
||||
# ls --sort=size
|
||||
# ls --sort=time
|
||||
# ls --sort=version
|
||||
# ls --sort=none
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Sort Listing of Content by Options
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Print numeric UID and GID for every contents of a directory using ls command. ###
|
||||
|
||||
The above scenario can be achieved using flag -n (Numeric-uid-gid) along with ls command.
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -n
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Print Listing of Content by UID and GID
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Print the contents of a directory on standard output in more columns than specified by default. ###
|
||||
|
||||
Well ls command output the contents of a directory according to the size of the screen automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
We can however manually assign the value of screen width and control number of columns appearing. It can be done using switch ‘`--width`‘.
|
||||
|
||||
# ls --width 80
|
||||
# ls --width 100
|
||||
# ls --width 150
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
List Content Based on Window Sizes
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: You can experiment what value you should pass with width flag.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Include manual tab size at the contents of directory listed by ls command instead of default 8. ###
|
||||
|
||||
# ls --tabsize=[value]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
List Content by Table Size
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: Specify the `[Value]=` Numeric value.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. Stay tuned to Tecmint till we come up with next article. Do not forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments below. Like and share us and help us get spread.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-ls-command-tricks/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/15-basic-ls-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/ls-command-interview-questions/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/ls-interview-questions/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
|
||||
How to Host Open Source Code Repository in github
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Hi all, today we will be learning how to host Source Code of Open Source Software in the repository hosted by github.com . GitHub is a web-based Git repository hosting service, which offers all of the distributed revision control and source code management (SCM) functionality of Git as well as adding its own features. It provides a workplace to host powerful collaboration, code review, and code management for open source and private projects. Unlike Git, which is strictly a command-line tool, GitHub provides a web-based graphical interface and desktop as well as mobile integration. GitHub offers both paid plans for private repositories and free accounts, which are usually used to host open-source software projects.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It is fast and more flexible web based hosting service which is easy to use and to manage distributed revision control. Anyone can host their software's source code in github's repository for the use, contribution, sharing, issue tracking and many more by millions of people across the globe. Here are some easy and quick steps to easily host software's source code.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Creating a new Github Account ###
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, open your favorite browser and go to Github's homepage url ie [github][1]. Then, the homepage will be opened as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, after the homepage has been opened, please fill form shown to sign up for a new github account.
|
||||
|
||||
After the you entered the valid information required for sign up, you'll be redirected to the plan choosing step. We have 5 plans listed in this page. One can choose the plan according to their requirement. Here, we'll go for a free plan. So, click on Choose to the Free plan and click on Finish Sign up. If we are planning to create an organization then, we need to tick on Help me setup an organization next.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Creating a New Repository ###
|
||||
|
||||
After we have successfully signed up a new account or logged in to Github, we'll now need to create a new Repository to get started.
|
||||
|
||||
Click on **(+)** button which is located at the top right near the account id. Then Click on New Repository .
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, after clicking on add a new repository, we'll now be directed to the page where we'll need to enter the required information.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, after entering the required information about the new repository, we'll need to click on green Create repository button.
|
||||
|
||||
After it is done, we'll get to see something similar like this image.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Uploading an existing Project ###
|
||||
|
||||
If we want to share our existing project on Github, we'll surely need to push the codes to the repository we created. To do so, we'll first need to install git in our Linux machine. As I am running Ubuntu 14.04 LTS in my machine, I'll need to run **apt** manger to install it.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install git
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, as git is ready, we are now ready to upload the codes.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: To avoid errors, do not initialize the new repository with **README**, license, or gitignore files. You can add these files after your project has been pushed to GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
In Terminal, we'll need to change the current working directory to your local project then initialize the local directory as a Git repository/
|
||||
|
||||
$ git init
|
||||
|
||||
We'll then add the files in our new local repository. This stages them for the first commit.
|
||||
|
||||
$ git add .
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll need to commit the files that we've staged in our local repository.
|
||||
|
||||
$ git commit -m 'First commit'
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In Terminal, we'll add the URL for the remote repository where our local repostory will be pushed.
|
||||
|
||||
$ git remote add origin remote Repository url
|
||||
$ git remote -v
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note: Please do replace remote Repository url to the url of the remote repo.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, to push the changes in our local repository to GitHub's repo we'll need to run as below and enter the required credential for the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
$ git push origin master
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Cloning a Repo ###
|
||||
|
||||
If we want to download a code repository from github straight to our local drives with a single command then, we can simply use git clone command which will clone the current directory to the remote repository.
|
||||
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/aruntechgeek/linspeed.git
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Please change the above url to the repository you want to clone from.
|
||||
|
||||
### Updating a Change ###
|
||||
|
||||
If we made changes to our code and want to push them to our remote repository then after changing the changes, we should run the following commands inside that directory.
|
||||
|
||||
$ git add .
|
||||
$ git commit -m "Updating"
|
||||
$ git push
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Hurray! We have successfully hosted our Project Source Code in Github repository. Github is fast and more flexible web based hosting service which is easy to use and to manage distributed revision control. Millions of awesome Open Source projects are hosted in github. So, if you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below. Thank you ! Enjoy Github :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/usr-mgmt/host-open-source-code-repository-github/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:http://github.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
||||
How to Interactively Create a Docker Container
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Hi everyone, today we'll learn how we can interactively create a docker container using a docker image. Once we start a process in Docker from an Image, Docker fetches the image and its Parent Image, and repeats the process until it reaches the Base Image. Then the Union File System adds a read-write layer on top. That read-write layer, the information about its Parent Image and some other information like its unique id, networking configuration, and resource limits is called a **Container**. Containers has states as they can change from **running** to **exited** state. A container with state as **running** includes a tree of processes running on the CPU, isolated from the other processes running on the host where as **exited** is the state of the file system and its exit value is preserved. You can start, stop, and restart a container with it.
|
||||
|
||||
Docker Technology has brought a remarkable change in the field of IT enabling cloud service for sharing applications and automating workflows, enabling apps to be quickly assembled from components and eliminates the friction between development, QA, and production environments. In this article, we'll build CentOS Instance in which we'll host a website running under Apache Web Server.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is quick and easy tutorial on how we can create a container in an interactive method using an interactive shell.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Running a Docker Instance ###
|
||||
|
||||
Docker initially tries to fetch and run the required image locally and if its not found in local host the it pulls from the [Docker Public Registry Hub][1] . Here. we'll fetch and create a fedora instance in a Docker Container and attach a bash shell to the tty.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run -i -t fedora bash
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Installing Apache Web Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, after our Fedora base image with instance is ready, we'll now gonna install Apache Web Server interactively without creating a Dockerfile for it. To do so, we'll need to run the following commands in a terminal or shell.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# yum install httpd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# exit
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Saving the Image ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll gonna save the changes we made into the Fedora Instance. To do that, we'll first gonna need to know the Container ID of the Instance. To get that we'll need to run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker ps -a
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll save the changes as a new image by running the below command.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker commit c16378f943fe fedora-httpd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Here, the changes are saved using the Container ID and image name fedora-httpd. To make sure that the new image is running or not, we'll run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker images
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Adding the Contents to the new image ###
|
||||
|
||||
As we have our new Fedora Apache image running successfully, now we'll want to add the web contents which includes our website to Apache Web Server so that our website will run successfully out of the box. To do so, we'll need to create a new Dockerfile which will handle the operation from copying web contents to allowing port 80. To do so, we'll need to create a file Dockerfile using our favorite text editor as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
# nano Dockerfile
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll need to add the following lines into that file.
|
||||
|
||||
FROM fedora-httpd
|
||||
ADD mysite.tar /tmp/
|
||||
RUN mv /tmp/mysite/* /var/www/html
|
||||
EXPOSE 80
|
||||
ENTRYPOINT [ "/usr/sbin/httpd" ]
|
||||
CMD [ "-D", "FOREGROUND" ]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Here, in above Dockerfile, the web content which we have in mysite.tar will get automatically extracted to /tmp/ folder. Then, the entire site will move to the Apache Web root ie /var/www/html/ and the expose 80 will open port 80 so that the website will be available normally. Then, the entrypoint is set to /usr/sbin/httpd so that the Apache Server will execute.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Building and running a Container ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll build our Container using the Dockerfile we just created in order to add our website on it. To do so, we'll need to run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker build -rm -t mysite .
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After building our new container, we'll want to run the container using the command below.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run -d -P mysite
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, we've successfully built a Docker Container interactively. In this method, we build our containers and image directly via interactive shell commands. This method is quite easy and quick to build and deploy our images and containers. If you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below so that we can improve or update our contents. Thank you ! Enjoy :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/interactively-create-docker-container/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:https://registry.hub.docker.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
|
||||
Prips – Print IP address on a given range
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
prips is a tool that can be used to print all of the IP address on a given range. It can enhance the usability of tools that are made to work on only one host at a time.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Prips on ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
Open the terminal and run the following command
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install prips
|
||||
|
||||
### Using prips ###
|
||||
|
||||
### prips syntax ###
|
||||
|
||||
prips [-c] [-d delim] [-e exclude] [-f format] [-i incr] start end
|
||||
prips [-c] [-d delim] [-e exclude] [-f format] [-i incr] CIDR-block
|
||||
|
||||
### Available Options ###
|
||||
|
||||
The prips tool accepts the following command-line options:
|
||||
|
||||
- -c -- Print the range in CIDR notation.
|
||||
- -d delim -- Set the delimiter to the character with ASCII code delim where 0 <= delim <= 255.
|
||||
- -e -- Exclude ranges from the output.
|
||||
- -f format -- Set the format of addresses (hex, dec, or dot).
|
||||
- -i incr -- Set the increment to ‘x'.
|
||||
|
||||
### Prips Examples ###
|
||||
|
||||
Display all the addresses in a reserved subnet:
|
||||
|
||||
prips 192.168.32.0 192.168.32.255
|
||||
|
||||
The same, using CIDR notation:
|
||||
|
||||
prips 192.168.32/24
|
||||
|
||||
Display only the usable addresses in a class A reserved subnet using a space instead of a newline for a delimiter:
|
||||
|
||||
prips -d 32 10.0.0.1 10.255.255.255
|
||||
|
||||
Display every fourth address in a weird block:
|
||||
|
||||
prips -i 4 192.168.32.7 192.168.33.5
|
||||
|
||||
Determine the smallest CIDR block containing two addresses:
|
||||
|
||||
prips -c 192.168.32.5 192.168.32.11
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/prips-print-ip-address-on-a-given-range.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ruchi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
|
||||
@ -1,111 +0,0 @@
|
||||
系统性能优化支招:使用Ramlog将日志文件转移到RAM
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ramlog以系统守护进程的形式存在。它系统启动的时候创建了虚拟磁盘(ramdisk),将文件从目录/var/log复制到虚拟磁盘中,同时把虚拟磁盘挂载为/var/log。接着更新虚拟磁盘上所有的日志。硬盘上的日志会保留在目录/var/log中,直到ramlog重启或停止时被更新。而关机的时候,(ramdisk上的)日志文件会重新保存到硬盘上,以确保日志一致性。Ramlog 2.x默认使用tmpfs文件系统,同时也可以支持ramfs和内核ramdisk。使用rsync(译注:Linux数据镜像备份工具)这个工具来同步日志。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:没有保存进硬盘的日志将在断电或者内核混乱(kernel panic)的情况下丢失。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你拥有空间足够的可用内存,而又想把日志放进虚拟磁盘,就安装ramlog吧。它是笔记本用户、UPS系统或是直接在flash中运行的系统节省写周期的优良选择。
|
||||
|
||||
Ramlog的运行机制以及步骤:
|
||||
|
||||
1.Ramlog在第一个守护进程(这取决于你所安装过的其它守护进程)的基础上启动。
|
||||
|
||||
2.然后创建目录/var/log.hdd并将其硬链至/var/log。
|
||||
|
||||
3.如果使用的是tmpfs(默认)或者ramfs之一的文件系统,将其挂载到/var/log上。
|
||||
|
||||
而如果使用的是内核ramdisk,ramdisk将在/dev/ram9中创建,并将挂载至/var/log。默认情况下ramlog会占用所有ramdisk的内存,其大小由内核参数"ramdisk_size"指定。
|
||||
|
||||
5.接着其它的守护进程被启动,并在ramdisk中更新日志。Logrotate(译注:Linux日志轮替工具)也是在ramdiks之上运行。
|
||||
|
||||
6.重启(默认一天一次)ramlog时,目录/var/log.hdd将借助rsync与/var/log保持同步。日志自动保存的频率可以通过cron(译注:Linux例行性工作调度)来控制。默认情况下,ramlog文件放置在目录/etc/cron.daily下。
|
||||
|
||||
7.系统关机时,ramlog在最后一个守护进程关闭之前关闭。
|
||||
|
||||
在ramlog关闭期间,/var/log.hdd中的文件将被同步至/var/log,接着/var/log和/var/log.hdd都被卸载,然后删除空目录/var/log.hdd。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:- 此文仅面向高级用户**
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu中安装Ramlog ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先需要用以下命令,从[这里][1]下载.deb安装包:
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://www.tremende.com/ramlog/download/ramlog_2.0.0_all.deb
|
||||
|
||||
下载ramlog_2.0.0_all.deb安装包完毕,使用以下命令进行安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg -i ramlog_2.0.0_all.deb
|
||||
|
||||
这一步会完成整个安装,现在你需要运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo update-rc.d ramlog start 2 2 3 4 5 . stop 99 0 1 6 .
|
||||
|
||||
#现在,在初始状态下升级sysklogd,使之能在ramlog停止运行前正确关闭:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo update-rc.d -f sysklogd remove
|
||||
|
||||
sudo update-rc.d sysklogd start 10 2 3 4 5 . stop 90 0 1 6 .
|
||||
|
||||
然后重启系统:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo reboot
|
||||
|
||||
系统重启完毕,运行'ramlog getlogsize'获取/var/log的空间大小。在此基础之上多分配40%的空间,确保ramdisk有足够的空间(这整个都将作为ramdisk的空间大小)。
|
||||
|
||||
编辑引导配置文件,如/etc/grub.conf,、/boot/grub/menu.lst 或/etc/lilo.conf(译注:具体哪个配置文件视不同引导加载程序而定),kernel参数新增项'ramdisk_size=xxx'以更新当前内核,其中xxx是ramdisk的空间大小。
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置Ramlog ###
|
||||
|
||||
基于deb的系统中,Ramlog的配置文件位于/etc/default/ramlog,你可以在该目录下设置以下变量:
|
||||
|
||||
Variable (with default value):
|
||||
|
||||
Description:
|
||||
|
||||
RAMDISKTYPE=0
|
||||
# Values:
|
||||
# 0 -- tmpfs (can be swapped) -- default
|
||||
# 1 -- ramfs (no max size in older kernels,
|
||||
# cannot be swapped, not SELinux friendly)
|
||||
# 2 -- old kernel ramdisk
|
||||
TMPFS_RAMFS_SIZE=
|
||||
#Maximum size of memory to be used by tmpfs or ramfs.
|
||||
# The value can be percentage of total RAM or size in megabytes -- for example:
|
||||
# TMPFS_RAMFS_SIZE=40%
|
||||
# TMPFS_RAMFS_SIZE=100m
|
||||
# Empty value means default tmpfs/ramfs size which is 50% of total RAM.
|
||||
# For more options please check ‘man mount', section ‘Mount options for tmpfs'
|
||||
# (btw -- ramfs supports size limit in newer kernels
|
||||
# as well despite man says there are no mount options)
|
||||
# It has only effect if RAMDISKTYPE=0 or 1
|
||||
KERNEL_RAMDISK_SIZE=MAX
|
||||
#Kernel ramdisk size in kilobytes or MAX to use entire ramdisk.
|
||||
#It has only effect if RAMDISKTYPE=2
|
||||
LOGGING=1
|
||||
# 0=off, 1=on Logs can be found in /var/log/ramdisk
|
||||
LOGNAME=ramlog
|
||||
# name of the ramlog log file (makes sense if LOGGING=1)
|
||||
VERBOSE=1
|
||||
# 0=off, 1=on (if 1, teststartstop puts detials
|
||||
# to the logs and it is called after start or stop fails)
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu中卸载ramlog ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg -P ramlog
|
||||
|
||||
注意:如果ramlog卸载之前仍在运行,需要重启系统完成整个卸载工作。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/improve-system-performance-by-moving-your-log-files-to-ram-using-ramlog.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ruchi][a]
|
||||
译者:[soooogreen](https://github.com/soooogreen)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tremende.com/ramlog/download/ramlog_2.0.0_all.deb
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user