diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 02fc5a8227..26ea32fd81 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -49,93 +49,125 @@ LCTT的组成
* 2014/10/08 提升bazz2为Core Translators成员。
* 2014/11/04 提升zpl1025为Core Translators成员。
* 2014/12/25 提升runningwater为Core Translators成员。
+* 2015/04/19 发起 LFS-BOOK-7.7-systemd 项目。
活跃成员
-------------------------------
-目前活跃成员有:
-- CORE [wxy](https://github.com/wxy),
-- CORE [carolinewuyan](https://github.com/carolinewuyan),
-- CORE [DeadFire](https://github.com/DeadFire),
-- CORE [geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi),
-- CORE [GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux),
-- CORE [reinoir](https://github.com/reinoir),
-- CORE [bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2),
-- CORE [zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025),
-- Senior [tinyeyeser](https://github.com/tinyeyeser),
-- Senior [vito-L](https://github.com/vito-L),
-- Senior [jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng),
-- Senior [willqian](https://github.com/willqian),
-- Senior [vizv](https://github.com/vizv),
-- [runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater),
-- [luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat),
-- [Vic020](https://github.com/Vic020),
-- [KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu),
-- [alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x),
-- [ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ),
-- [2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007),
-- [flsf](https://github.com/flsf),
-- [blueabysm](https://github.com/blueabysm),
-- [barney-ro](https://github.com/barney-ro),
-- [su-kaiyao](https://github.com/su-kaiyao),
-- [crowner](https://github.com/crowner),
-- [Linchenguang](https://github.com/Linchenguang),
-- [Linux-pdz](https://github.com/Linux-pdz),
-- [linuhap](https://github.com/linuhap),
-- [yechunxiao19](https://github.com/yechunxiao19),
-- [woodboow](https://github.com/woodboow),
-- [SPccman](https://github.com/SPccman),
-- [disylee](https://github.com/disylee),
-- [cvsher](https://github.com/cvsher),
-- [ThomazL](https://github.com/ThomazL),
-- [Stevearzh](https://github.com/Stevearzh),
-- [felixonmars](https://github.com/felixonmars),
-- [scusjs](https://github.com/scusjs),
-- [johnhoow](https://github.com/johnhoow),
-- [hyaocuk](https://github.com/hyaocuk),
-- [MikeCoder](https://github.com/MikeCoder),
-- [theo-l](https://github.com/theo-l),
-- [wangjiezhe](https://github.com/wangjiezhe),
-- [jiajia9linuxer](https://github.com/jiajia9linuxer),
-- [NearTan](https://github.com/NearTan),
-- [l3b2w1](https://github.com/l3b2w1),
-- [shipsw](https://github.com/shipsw),
-- [boredivan](https://github.com/boredivan),
-- [Love-xuan](https://github.com/Love-xuan),
-- [JonathanKang](https://github.com/JonathanKang),
-- [luoyutiantang](https://github.com/luoyutiantang),
-- [owen-carter](https://github.com/owen-carter),
-- [icybreaker](https://github.com/icybreaker),
-- [tenght](https://github.com/tenght),
-- [rogetfan](https://github.com/rogetfan),
-- [liuaiping](https://github.com/liuaiping),
-- [nd0104](https://github.com/nd0104),
-- [szrlee](https://github.com/szrlee),
-- [lfzark](https://github.com/lfzark),
-- [ggaaooppeenngg](https://github.com/ggaaooppeenngg),
-- [CNprober](https://github.com/CNprober),
-- [coloka](https://github.com/coloka),
-- [213edu](https://github.com/213edu),
-- [guodongxiaren](https://github.com/guodongxiaren),
-- [Tanete](https://github.com/Tanete),
-- [zzlyzq](https://github.com/zzlyzq),
-- [yujianxuechuan](https://github.com/yujianxuechuan),
-- [ailurus1991](https://github.com/ailurus1991),
-- [FineFan](https://github.com/FineFan),
-- [shaohaolin](https://github.com/shaohaolin),
-- [tomatoKiller](https://github.com/tomatoKiller),
-- [CHINAANSHE](https://github.com/CHINAANSHE),
-- [stduolc](https://github.com/stduolc),
-- [Maclauring](https://github.com/Maclauring),
-- [Hao-Ding](https://github.com/Hao-Ding),
-- [zsJacky](https://github.com/zsJacky),
-- [small-Wood](https://github.com/small-Wood),
-- [cereuz](https://github.com/cereuz),
-- [lijhg](https://github.com/lijhg),
-- [fbigun](https://github.com/fbigun),
+目前 TP 活跃成员有:
+- CORE @wxy,
+- CORE @carolinewuyan,
+- CORE @DeadFire,
+- CORE @geekpi,
+- CORE @GOLinux,
+- CORE @reinoir,
+- CORE @bazz2,
+- CORE @zpl1025,
+- Senior @tinyeyeser,
+- Senior @vito-L,
+- Senior @jasminepeng,
+- Senior @willqian,
+- Senior @vizv,
+- @ZTinoZ,
+- @Vic020,
+- @runningwater,
+- @KayGuoWhu,
+- @luoxcat,
+- @alim0x,
+- @2q1w2007,
+- @theo-l,
+- @ictlyh,
+- @FSSlc,
+- @su-kaiyao,
+- @blueabysm,
+- @flsf,
+- @martin2011qi,
+- @SPccman,
+- @wi-cuckoo,
+- @Linchenguang,
+- @linuhap,
+- @crowner,
+- @Linux-pdz,
+- @H-mudcup,
+- @yechunxiao19,
+- @woodboow,
+- @Stevearzh,
+- @disylee,
+- @cvsher,
+- @wwy-hust,
+- @johnhoow,
+- @felixonmars,
+- @TxmszLou,
+- @shipsw,
+- @scusjs,
+- @wangjiezhe,
+- @hyaocuk,
+- @MikeCoder,
+- @ZhouJ-sh,
+- @boredivan,
+- @goreliu,
+- @l3b2w1,
+- @JonathanKang,
+- @NearTan,
+- @jiajia9linuxer,
+- @Love-xuan,
+- @coloka,
+- @owen-carter,
+- @luoyutiantang,
+- @JeffDing,
+- @icybreaker,
+- @tenght,
+- @liuaiping,
+- @mtunique,
+- @rogetfan,
+- @nd0104,
+- @mr-ping,
+- @szrlee,
+- @lfzark,
+- @CNprober,
+- @DongShuaike,
+- @ggaaooppeenngg,
+- @haimingfg,
+- @213edu,
+- @Tanete,
+- @guodongxiaren,
+- @zzlyzq,
+- @FineFan,
+- @yujianxuechuan,
+- @Medusar,
+- @shaohaolin,
+- @ailurus1991,
+- @liaoishere,
+- @CHINAANSHE,
+- @stduolc,
+- @yupmoon,
+- @tomatoKiller,
+- @zhangboyue,
+- @kingname,
+- @KevinSJ,
+- @zsJacky,
+- @willqian,
+- @Hao-Ding,
+- @JygjHappy,
+- @Maclauring,
+- @small-Wood,
+- @cereuz,
+- @fbigun,
+- @lijhg,
+- @soooogreen,
-(更新于2014/12/02,以Github contributors列表排名)
+LFS 项目活跃成员有:
+
+- @ictlyh
+- @dongfengweixiao
+- @wxy
+- @H-mudcup
+- @zpl1025
+- @KevinSJ
+- @Yuking-net
+
+(更新于2015/05/31,以Github contributors列表排名)
谢谢大家的支持!
diff --git a/published/20150225 Install Google's Material Design Inspired GTK And Icon Theme Paper in Linux.md b/published/20150225 Install Google's Material Design Inspired GTK And Icon Theme Paper in Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a4ca97ed5a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20150225 Install Google's Material Design Inspired GTK And Icon Theme Paper in Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+在 Linux 下体验谷歌 Material风格的GTK和图标主题Paper
+================================================================================
+
+
+[Paper][1]是一款即将与广大朋友们见面的一个图形工具包和图标主题,它的设计灵感来自于谷歌的设计语言[Material风格][2]。Paper由Sam Hewitt发起,Sam是[Moka项目][3]的一员,Moka总会设计出[让人满意的Ubuntu主题][4]。对于Paper,我敢说只要它一经推出,它必将是[最好的GTK主题开发包][5]之一。
+
+对的,你没有听错,Paper主题还在开发阶段。因此我建议,如果你想在你的Ubuntu或者它的衍生版本上安装Paper,最好抱着试一试的实验心态。因为你多多少少会发现一些破损的图标,但这并不影响整体体验非常棒!
+
+### 通过PPA在Ubuntu及其衍生版本上安装Paper主题 ###
+
+Sam为Ubuntu和它的衍生版本设置了一个专用的PPA(Presonal Package Archives,个人软件包档案)。我推荐你通过PPA安装而不是下载Paper主题,因为你将会定期更新主题。这个PPA可供使用的系统有Ubuntu 15.04, Ubuntu 14.10, Ubuntu 14.04, Elementary OS Freya, Elementary OS Luna, Linux Mint 17, Linux Mint 16 和其它的Ubuntu衍生版本。
+
+打开终端,输入下列命令:
+
+ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:snwh/pulp
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install paper-gtk-theme paper-icon-theme
+
+### 下载Paper GTK和图标主题 ###
+
+
+如果你不想用PPA,你可以手动下载主题和图标。但是就像刚才所说,这样你就无法自动更新。
+
+- [下载Paper图标主题][6]
+- [下载Paper的GTK主题][7]
+
+#### 把它们用起来吧 ####
+
+我希望你知道怎么在你的Ubuntu中安装或者更改主题。如果你不知道,下面几个教程将帮助你安装一个新的主题。
+
+- [如何在标准Ubuntu中更改主题][8]
+- [如何在GNOME Shell中更改主题][9]
+- [如何在Ubuntu Mint中更改主题][10]
+- [如何在Elementary OS Freya中更改主题][11]
+
+#### 就是这样! ####
+
+因为我用过[Elementary OS Freya][12]一段时间,这里有一些看起来像Elementary OS Freya的Paper主题和图标的截图。我使用了一张Material Design风格的墙纸,这样可以更好的匹配主题和图标。
+
+
+
+
+
+How do you find this Material design inspired theme? If you did use it, do share the screenshot of your desktop with rest of us here.
+
+你觉得这个Material风格的主题怎么样?如果你使用它的话,在评论里和我们分享你的桌面截图吧!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://itsfoss.com/install-paper-theme-linux/
+
+作者:[Abhishek][a]
+译者:[sevenot](https://github.com/sevenot)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
+[1]:http://snwh.org/paper/
+[2]:http://www.google.fr/design/spec/material-design/introduction.html
+[3]:http://mokaproject.com/moka-icon-theme/
+[4]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
+[5]:http://itsfoss.com/gnome-shell-themes-ubuntu-1404/
+[6]:https://github.com/snwh/paper-icon-theme
+[7]:https://github.com/snwh/paper-gtk-theme
+[8]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-install-themes-in-ubuntu-13-10/
+[9]:http://itsfoss.com/install-switch-themes-gnome-shell/
+[10]:http://itsfoss.com/install-icon-linux-mint/
+[11]:http://itsfoss.com/install-themes-icons-elementary-os-freya/
+[12]:http://itsfoss.com/tag/elementary-os-freya/
diff --git a/published/201504/20150417 How to Install Linux Kernel 4.0 from Elrepo or Source on Ubuntu or CentOs.md b/published/201504/20150417 How to Install Linux Kernel 4.0 from Elrepo or Source on Ubuntu or CentOs.md
index 1921514d8e..a725043f67 100644
--- a/published/201504/20150417 How to Install Linux Kernel 4.0 from Elrepo or Source on Ubuntu or CentOs.md
+++ b/published/201504/20150417 How to Install Linux Kernel 4.0 from Elrepo or Source on Ubuntu or CentOs.md
@@ -10,12 +10,14 @@
#### 在 64位 Ubuntu 15.04 ####
+ $ wget http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v4.0-vivid/linux-image-4.0.0-040000-generic_4.0.0-040000.201504121935_amd64.deb
$ wget http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v4.0-vivid/linux-headers-4.0.0-040000-generic_4.0.0-040000.201504121935_amd64.deb
$ sudo dpkg -i linux-headers-4.0.0*.deb linux-image-4.0.0*.deb
#### 在 32位 Ubuntu 15.04 ####
+ $ wget http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v4.0-vivid/linux-image-4.0.0-040000-generic_4.0.0-040000.201504121935_i386.deb
$ wget http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v4.0-vivid/linux-headers-4.0.0-040000-generic_4.0.0-040000.201504121935_i386.deb
$ sudo dpkg -i linux-headers-4.0.0*.deb linux-image-4.0.0*.deb
diff --git a/published/201505/20140804 Group Test--Linux Text Editors.md b/published/201505/20140804 Group Test--Linux Text Editors.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..66b271bcf4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20140804 Group Test--Linux Text Editors.md
@@ -0,0 +1,320 @@
+五款 Linux 文本编辑器测评
+================================================================================
+
+> Mayank Sharma 测试了5款不仅仅是能处理文字的超强文本编辑器。
+
+如果你使用Linux已经有很长一段时间,你知道,不管是编辑一款app的配置文件,还是修改shell脚本,或者编写/查看代码,类似LibreOffice的工具并不适合。尽管字面上看起来都是一样,但是你并不需要一个文字处理器来完成这些任务;你需要的是一个文本编辑器。
+
+在这个测评中,我们将着眼于5款更能胜任繁重文本工作的轻量级的文本编辑器。他们支持语法高亮,像拼写检查一样轻松处理代码缩进。你可以像你复制/粘贴文本那样容易地使用它们记录宏以及管理代码片段。
+
+得益于它们的插件,使得它们足以抗衡其它的以文本为中心的应用程序,一些简单的文本编辑器甚至超出了它们的设计目标。它们能胜任一个源代码编辑器的任务,甚至就是一个集成开发环境。
+
+Emacs和Vim是两款最流行和强大的纯文本编辑器。但是,由于一些原因,我们在这个测评中并没有包括它们。首先,如果你使用它们中的任何一个,那么恭喜你:你不需要更换了。其次,它们都有陡峭的学习曲线,尤其是那些熟悉了桌面环境的用户:他们很更愿意投入其他有图形界面的文本编辑器。
+
+### 目录: ###
+
+#### Gedit ####
+
+- URL:http://projects.gnome.org/gedit/
+- 版本: 3.10
+- 许可证: GPL
+- Gnome的默认文本编辑器准备好挑战了吗?
+
+#### Kate ####
+
+- URL: www.kate-editor.org
+- 版本: 3.11
+- 许可证: LGPL/GPL
+- Kate会挑战命运吗?
+
+#### Sublime Text ####
+
+- URL: www.sublimetext.com
+- 版本: 2.0.2
+- 许可证: Proprietary
+- 在自由的土地上的带有黄金般的心脏的专利软件。
+
+#### UltraEdit ####
+
+- URL: www.ultraedit.com
+- 版本: 4.1.0.4
+- 许可证: Proprietary
+- 足够证明它的价值了吗?
+
+#### jEdit ####
+
+- URL: www.jedit.org
+- 版本: 5.1.0
+- 许可证: GPL
+- 基于Java的编辑器是否会毁掉其他编辑器的世界?
+
+
+### 关键标准 ###
+
+除了Gedit和jEdit以外的所有工具,都是通过其推荐的安装方法安装在Fedora和Ubuntu上。前者已经兼容默认的Gnome桌面,后者仍然固执地反对安装在Fedora上。由于这些是相对简单的应用程序,他们没有复杂的依赖,唯一例外的是jEdit,它要求要有Oracle Java。
+
+得益于Gnome和KDE持续的努力,所有编辑器无论在哪个桌面上的外观看起来很好,功能也很正常。这不仅是作为评价的标准,也意味着你不再受制于你的桌面环境兼容的工具。
+
+除了它们独特的功能,我们也对所有候选者测试了常规的文本编辑功能。然而,它们并没有被设计为模仿现代字处理器的所有功能,我们也不以此评判。
+
+
+### 编程语言支持 ###
+
+UltraEdit 能进行语法高亮、代码折叠以及拥有项目管理的能力。也有一个罗列源文件中所有函数的功能列表,但并不适用于我们测试的任何代码文件。UltraEdit也支持HTML5,有一个能添加常用HTML标记的HTML工具栏。
+
+即使Gnome的默认文本编辑器Gedit,也有几个面向编码的功能特性,例如括号匹配、自动缩进以及为包括C, C++, Java, HTML, XML, Python, Perl, 以及许多其它编程语言进行语法高亮。
+
+如果你需要更多的编程辅助功能,看一下Sublime和Kate。
+
+Sublime支持多种编程语言并且能为(那些流行的)C#, D, Dylan, Erlang, Groovy, Haskell, Lisp, Lua, MATLAB, OCaml, R, 甚至 SQL 进行语法高亮。如果这还不够,你可以下载插件以支持更多的语言。另外,它的语法高亮功能提供了多个可定制选项。这个应用程序也会进行括号匹配,确保代码段都正确,Sublime的自动补全功能也支持用户创建的变量。就像Komodo IDE,Sublime也可以显示一个全部源代码的滚动预览图,这对于长代码文件导航和在文件中的不同部分跳转很方便。Sublime最好的功能之一就是能在编辑器内部运行特定语言,例如C++, Python, Ruby等的代码,当然假设在你的电脑上安装有编译器以及其它系统工具。省时间而且不用再开终端.
+
+你也可以用插件在Kate中开启构建系统功能。另外,你可以为GDB调试器添加一个简单的前端。Kate能和Git,Subversion以及Mercurial版本控制系统一起工作,也提供了一些项目管理的功能。除了能为超过180种语言进行语法高亮,它支持所有的这些辅助功能,例如括号匹配,自动补全和自动缩进。它也支持代码折叠,甚至在一个程序中折叠函数。
+
+唯一的遗憾的是jEdit,它声称自己是一个程序员的文本编辑器,但它缺少其他的基本功能,例如代码折叠,它甚至不能提示或者补全函数.
+
+**评分:**
+
+- Gedit:3/5
+- Kate:5/5
+- Sublime:5/5
+- UltraEdit:3/5
+- jEdit:1/5
+
+
+### 键盘控制 ###
+
+高级文本编辑器的用户希望能完全通过键盘控制和操作,一些应用程序甚至支持用户自定义快捷方式的键盘绑定。
+
+你可以轻松的使用Gedit的扩展键盘快捷键。可以在编辑文件时通过工具的快捷键调用工具,例如对一个文档进行拼写检查。你可以看到应用程序内部的一系列默认快捷键,但并没有图形化的方式去自定义它们。相似的,在Sublime中自定义键盘绑定,你需要修改它的XML的键盘映射文件。Sublime由于缺少定义键盘快捷键的图形化界面而饱受批评,但长期使用的用户支持当前的基于文件的机制:这给了他们更多的控制能力。
+
+UltraEdit为它"一切都可自定义"的座右铭感到自豪,这也包括键盘快捷键。你可以自定义菜单导航的热键,以及定义你自己的访问大量功能的组合键映射。
+
+除了完全可自定义的键盘快捷键以外,jEdit也有为Emacs预定义的键映射。Kate在这方面尤其令人映像深刻。它有简单可访问的自定义键绑定窗口。你可以更改默认的键,或者定义替代的键。另外,Kate也有一个能使用户使用Vi键操作Kate的Vi模式。
+
+**评分:**
+
+- Gedit:2/5
+- Kate:5/5
+- Sublime:3/5
+- UltraEdit:4/5
+- jEdit:5/5
+
+### 片段和宏 ###
+
+宏通过自动化重复的步骤帮助你降低花费在编辑和组织数据上的时间,而代码片段通过创建可重用的源代码块为程序员扩展类似的功能。这两者都能节省你的时间。
+
+标准的Gedit安装没有这两种功能中的任何一种,但是你可以通过独立的插件启用这些功能。片段插件随Gedit一起发布,但在Gedit内启用宏插件,则需要你手动下载和安装(被称为gedit-macropy,托管在GitHub上)。
+
+Kate也同样通过插件的形式启用片段功能。一旦加入,插件也增加了PHP,Bash和Java的片段库。你可以在侧边栏中显示片段列表以便于访问。可以通过右击片段或者快捷键组合方式编辑它的内容。然而,令人惊讶的是,它不支持宏-尽管用户从2002年就不断要求!
+
+jEdit也有一个启用片段的插件。它还可以从用户行为中记录宏或者你也可以用BeanShell 脚本语言(BeanShell支持像Perl和JavaScript那样将脚本对象封装为简单的方法)中写宏。jEdit也有一个可以从jEdit的网站中下载多种宏的插件。
+
+Sublime有创建片段和宏的内建功能,也有为大多数编程语言经常使用的函数多种片段。
+
+在UltraEdit中片段被称为智能模板,就像Sublime中一样,你可以根据正在编辑的源代码文件类型插入片段。要完成宏记录功能,UltraEdit还有集成了一个基于JavaScript的脚本语言引擎来完成自动任务。你也可以从该编辑器的网站中下载用户提交的宏和脚本。
+
+**评分:**
+
+- Gedit:3/5
+- Kate:1/5
+- Sublime:5/5
+- UltraEdit:5/5
+- jEdit:5/5
+
+
+### 易用性 ###
+
+不像那些简陋的文本编辑器,这些文本编辑器在这方面可以适应从文档写作者到程序员的各种用户的需要。与精简应用程序相反,他们的开发者在寻找添加更多功能的途径。
+
+尽管第一眼看上去这次测评中的大部分应用有一个很相似的布局,经过仔细的检查,你会发现一些可用性的差异。我们通过用户界面的合理使用来介绍它们的功能和特性,而不是铺天盖地地告诉读者。
+
+#### Gedit: 4/5 ####
+
+Gedit的外观很普通,它有一个带有很少的菜单和按钮的简单界面。这是一把双刃剑,因为有些用户可能不会发现它真正的潜能。
+
+Gedit可以在选项卡中打开多个文件,这些选项卡可以重排和在多个 Gedit窗口之间移动。用户可以选择通过插件来启用侧边栏来浏览文件或者在底部面板显示工具输出内容。这个应用程序会检测到被其它应用程序更改的文件并可以重新加载该文件。
+
+为了适配Gnome,在应用程序的最新版本中做了大量的 UI 修改。然而修改还还不稳定,尽管包括了所有的功能,但是菜单交互的一些插件还需要升级。
+
+
+
+*在功能与界面之间取得了良好的平衡,Gedit将其大部分功能隐藏在背后。*
+
+#### Kate: 5/5 ####
+
+尽管用户界面的主要部分和Gedit相似,Kate可以在两边显示选项卡并且它的菜单更加丰富。该应用程序平易近人,吸引用户来挖掘它的其它功能。
+
+Kate可以在KDE的KIO支持的所有协议上透明地打开和保存文件,包括通过HTTP, FTP, SSH, SMB 和 WebDAV。你可以用这个应用同时处理多个文件。但不同于大部分应用程序传统的水平选项卡选择栏,Kate在屏幕的两个方向都有选项卡。左侧的侧边栏显示打开的文件列表。需要同时查看一个文件不同部分的程序员也会感激它可以水平或者竖直分隔界面的能力。
+
+
+
+*Kate能搭建为功能丰富的集成开发环境。*
+
+#### Sublime: 5/5 ####
+
+Sublime支持你在不同方式同时查看多达四个文件。当你在集中精力编程时,它也有一个只显示文件和菜单的全屏无扰模式。
+
+这个编辑器还在右边有个缩略地图,这在长文件中导航非常有用。应用程序为多种编程语言提供多种常用函数的片段,这使得它对于开发者非常有用。另一个精巧的功能是,无论你使用都是文本文档或者代码,都可以任意选择和替换。
+
+
+
+*如果你不喜欢Sublime的Charcoal外观,你可以选择它包含的其它22种主题。*
+
+#### UltraEdit: 3/5 ####
+
+UltraEdit在界面的顶部和底部加载了多种工具栏。加上切换文档的选项卡、两边的面板,以及分隔区域,使得只剩下一点空间给编辑窗口。
+
+使用HTML的网络开发者有很多唾手可得的帮助。你可以通过FTP和SFTP访问远程文件。高级功能,例如记录一个宏以及比较文件,也简单易用。
+
+使用应用程序的偏好设置窗口,你可以调整应用程序的多个方面,包括颜色主题和类似语法高亮的其它功能。
+
+
+
+*UltraEdit的用户界面是高度可配置的 — 你可以像改变其它许多方面那样简单的自定义工具栏和菜单的布局。*
+
+#### jEdit: 3/5 ####
+
+在可用性方面,首先一个不好就是jEdit不能在基于RPM的发行版上安装。导航编辑器需要一些时间来适应,因为它的菜单和其它流行的应用程序顺序不同,而且有些普通桌面用户不熟悉的名字。但是,该应用程序有详细的内部帮助,这有利于缓解学习曲线。
+
+jEdit会高亮你所在的当前行,并使你能以多种查看方式分隔窗口。你可以简单地从应用程序中安装和管理插件,除了使用完整的宏,jEdit也支持你快速记录一个临时的宏。
+
+
+
+*由于它的Java基础,jEdit在任何桌面环境中都不能给人宾至如归的感觉*
+
+### 可用性和支持 ###
+
+在Gedit和Kate之间有很多相似性。两个应用程序都得益于他们各自的父项目,Gnome和KDE,捆绑在各种主流的发行版中。另外两个项目都是跨平台的,有Windows和Mac OS X版本以及原生的Linux版本。
+
+Gedit托管在Gnome的网站上,并有一个简单的用户指南、关于多种插件的信息,以及包括邮件列表和IRC通道在内的常用联系方式。你也可以在其它基于Gnome的发行版,例如Ubuntu中找到使用信息。相似地,Kate得益于KDE的资源,并包括详细的用户信息以及邮件列表和IRC通道。你也可以从应用程序中获取相应的离线用户指南。
+
+除了Linux,UltraEdit在Windows和Mac OS X中也可用,虽然在应用程序中并没有包括,但在启动时也有详细的用户指南。为了辅助用户的使用,UltraEdit保存了一个常见问题的数据库,一系列关于多种特定功能的详细介绍,用户还可以在论坛版块彼此帮助。另外,付费用户也可以通过邮件从开发者中获取支持。
+
+Sublime支持一样多的平台,但是你需要单独为每种平台购买许可证。开发者通过博客让用户了解正在进行的开发,并积极参加它的论坛。这个项目支持设施的亮点是提供免费的详细教程和视频课程。Sublime非常漂亮。
+
+由于jEdit是用java编写的,所以它在多种平台中都可用。在它的网站上你可以找到一个详细的用户指南以及一些插件帮助文档的链接。然而,这里没有能使用户和其他用户或者开发者交流的途径。
+
+**评分:**
+
+- Gedit:4/5
+- Kate:4/5
+- Sublime:5/5
+- UltraEdit:3/5
+- jEdit:2/5
+
+### 附加组件和插件 ###
+
+不同的用户有不同的需求,一个简单的轻量级应用程序只能做到这么多。这就是为什么需要插件的原因。应用程序依赖于这些小部件来扩展它们的功能集并让更多的用户使用。
+
+UltraEdit是一个例外。它没有第三方插件,但开发者将例如HtmlTidy这样的第三方工具集成到了UltraEdit。
+
+Gedit附带了好多已安装的插件,你可以下载更多的更多gedit插件包。基于和Gedit版本的兼容性,项目网站也有到多个第三方插件的链接。
+
+三个对程序员非常有用的插件是:Code Comment、在底部面板增加一个终端的Terminal Plugin以及Session Saver。当你用多个文件开发项目的时候Session Saver相当有用。你可以在选项卡中打开文件,保存会话,你可以用一键恢复,就可以按照你保存时的选项卡顺序打开所有的文件。
+
+类似的,你可以通过用内部的插件管理器增加插件来扩展Kate。除了令人映像深刻的项目插件,一些开发者使用的插件包括嵌入式终端,它能编译和调试代码,以及对数据库执行SQL查询。
+
+Sublime的插件是用Python写的,文本编辑器包括了一个类似于apt-get,能使用户查找,安装,升级和移除插件包的名为Package Control的工具。通过插件,你可以在Sublime中使用Git版本控制,以及美化JavaScript代码的JSLint工具。Sublime Linter能指出你代码中的错误,是编码人员必备的插件。
+
+jEdit拥有最令人印象深刻的插件设施。该应用有超过200个插件,可以在它们自己的专用网站中浏览。网站通过不同的类型列出了插件,例如文件管理,版本控制,文本等。你可以在每个类型下找到很多的插件。
+
+一些最好的插件是Android插件,它们提供了和Android项目协同工作的工具;你可以使用TomcatSwitch插件创建和控制外部Jakarta Tomcat服务器进程;以及类似于Vi功能的Vimulator插件。你可以通过使用jEdit的插件管理器安装这些插件。
+
+**评分:**
+
+- Gedit:3/5
+- Kate:4/5
+- Sublime:4/5
+- UltraEdit:1/5
+- jEdit:5/5
+
+### 纯文本编辑 ###
+
+尽管它们强大的额外功能甚至可能会取代几种完全成熟的应用程序,有时候可能只需要使用这些庞大的文本编辑器读、写或者编辑简单的纯文本。虽然你可以使用它们中的任何一个输入文本,我们通过普通文本编辑的方便性评价它们。
+
+Gnome的默认文本编辑器Gedit,支持取消和重做机制以及搜索和替换。它可以对多种语言进行拼写检查,并能通过使用Gnome GVFS库访问和编辑远程文件。
+
+你也可以使用Kate进行拼写检查,它也可以让你对任何高亮文本进行Google搜索。它还有一个能可视化告知用户文件中更改过但没有保存的行的行修改系统。另外,它通过允许用户在文件中使用书签简化长文档的导航。
+
+Sublime有很多可选择的编辑命令,例如缩进文本和格式化段落。它的自动保存功能帮助防止用户丢失他们的更改。高级用户还会喜欢基于正则表达式的递归查找和替换功能,以及选择多个不连续的文本块并执行统一操作。
+
+UltraEdit也允许用户在查找和替换功能中使用正则表达式,并能通过FTP编辑远程文件。
+
+JEdit一个独特的功能是它支持被称为寄存器的不限数目的剪切板。你可以复制文本片段到这些寄存器中,在编辑会话过程中都可用。
+
+**评分:**
+
+- Gedit:4/5
+- Kate:5/5
+- Sublime:5/5
+- UltraEdit:4/5
+- jEdit:4/5
+
+### 我们的评比 ###
+
+在这里的所有编辑器都足以替换你已有的文本编辑器,来编辑文本和调整配置文件。事实上,没准它们会组合起来作为你的集成开发环境。这些应用程序都有各种各样功能,它们的开发者不会考虑剥离功能,而是增加越来越多的功能。
+
+jEdit排在这次测试的最后面。因为它不仅坚持使用专有的Oracle Java运行时环境,不能在你的Fedora机器上安装,而且开发者并不积极和用户交互。
+
+UltraEdit做的稍微好一点。这个商业专用工具专注于网络开发者,不为非开发者的高级用户提供任何功能,使得它不值得推荐为免费软件的替代品。
+
+排在第三的是Gedit。作为Gnome的默认编辑器,它没有任何内在的问题,但尽管有很多积极的方面,它还是略微被Sublime和Kate超越。开诚布公地说,Kate是比Gedit更通用的编辑器,甚至考虑到他们的插件系统,评分也优于Gnome的默认编辑器。
+
+Sublime和Kate都相当好。他们在我们的大多数测试中表现同样出色。Kate由于不支持宏而落后于Sublime,但键盘友好和能简单定义自定义键绑定又使Kate找回优势。
+
+Kate成功的原因可以归结为它通过最小化学习曲线提供了最大化的功能。尽管使用它吧,不仅作为简单文本编辑器使用,或者容易使用语法高亮编辑配置文件,甚至得益于其项目管理能力能使用它协作一个复杂的编程项目。
+
+我们不是选择Kate去替换一个类似“[XX,在这里插入你最喜欢的专业工具]”的全面的集成开发环境。但是它是一个专业工具理想的、全面的、以及完美的垫脚石。
+
+Kate为能快速响应你的需要而设计,它的界面并不会使你茫然,并且和那些过于复杂的应用一样的有用。
+
+### 1st Kate ###
+
+- Licence LGPL/GPL Version 3.11
+- www.kate-editor.org
+- 拥有超能力,态度温和的文本编辑器。
+- Kate是KDE项目中最有用的应用程序之一。
+
+### 2nd Sublime Text ###
+
+- Licence 专利 Version 2.0.2
+- www.sublimetext.com
+- 值得你每分钱的专业文本编辑器 - 简单易用,功能全面而且看起来很棒。
+
+### 3rd Gedit ###
+
+- Licence GPL Version 3.10
+- http://projects.gnome.org/gedit
+- 在Gnome中就用它吧。这是一个奇妙的文本编辑器,确实令人钦佩的工作,但这里的竞争实在太大了。
+
+### 4th UltraEdit ###
+
+- Licence Proprietary Version 4.1.0.4
+- www.ultraedit.com
+- 关注于为网络开发者提供各种便利,而不为普通用户提供任何特殊功能。
+
+### 5th jEdit ###
+
+- Licence GPL Version 5.1.0
+- www.jedit.org
+- 缺乏支持,不支持Fedora,缺乏好看的界面,jEdit被贬低到最后。
+
+### 你也许希望尝试… ###
+
+随你发行版发布的默认文本编辑器也能帮助你一些高级任务。例如KDE的KWrite和Raspbian的Nano。得益于KDE的katepart组件,KWrite继承了一些Kate的功能,得益于在树莓派上的可用性,Nano也开始重现风头。
+
+如果你希望跟随Linux大师的脚步,你总是可以尝试高大上的文本编辑器Emacs和Vim。想尝试Vim强大的用户首先可以考虑gVim,它通过图形界面展现了Vim的强大。
+
+除了jEdit和Kate,这里还有其他模仿Emacs和Vim之类的旧式高级编辑器的编辑器,比如JED 编辑器和Joe's Own Editor,这两者都有Emacs的模拟模式。另一方面,如果你在寻找轻量级的代码编辑器,可以看看Bluefish和Geany。他们的存在是为了填补文本编辑器和全面集成的开发平台之间的空隙。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxvoice.com/text-editors/
+
+作者:[Ben Everard][a]
+译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
+校对:[royaso](https://github.com/royaso),[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.linuxvoice.com/author/ben_everard/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150108 Interface (NICs) Bonding in Linux using nmcli.md b/published/201505/20150108 Interface (NICs) Bonding in Linux using nmcli.md
similarity index 82%
rename from translated/tech/20150108 Interface (NICs) Bonding in Linux using nmcli.md
rename to published/201505/20150108 Interface (NICs) Bonding in Linux using nmcli.md
index 0b5bf2cd8e..fa8297599b 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150108 Interface (NICs) Bonding in Linux using nmcli.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150108 Interface (NICs) Bonding in Linux using nmcli.md
@@ -1,15 +1,15 @@
-在 Linux 中用 nmcli 命令绑定网卡(NICs)
+在 Linux 中用 nmcli 命令绑定多块网卡
================================================================================
-今天,我们来学习一下在 CentOS 7.x 中如何用 nmcli(Network Manager Command Line Interface:网络管理命令行接口) 进行网卡(NICs 译者注:Netword Interface Card,网卡或网络适配器)绑定(译者注:bond 是指把多个物理网卡绑定成一个逻辑上的网卡,这样多个网卡可以使用同一个 IP 从而可以避免单点故障)。
+今天,我们来学习一下在 CentOS 7.x 中如何用 nmcli(Network Manager Command Line Interface:网络管理命令行接口)进行网卡绑定。
-网卡绑定是将 **网卡** 逻辑地连接到一起从而允许故障转移或者提高吞吐率的方法。提高服务器网络可用性的一个方式是使用多个网卡。Linux 绑定驱动提供了一个将多个网卡聚合到一个逻辑绑定接口的方法。这是个并不影响 linux 内核中旧绑定驱动的新的实现;它提供了另一种实现方法。
+网卡(接口)绑定是将多块 **网卡** 逻辑地连接到一起从而允许故障转移或者提高吞吐率的方法。提高服务器网络可用性的一个方式是使用多个网卡。Linux 绑定驱动程序提供了一种将多个网卡聚合到一个逻辑的绑定接口的方法。这是个新的实现绑定的方法,并不影响 linux 内核中旧绑定驱动。
**网卡绑定为我们提供了两个主要的好处:**
1. **高带宽**
1. **冗余/弹性**
-现在让我们在 CentOS 7 上配置网卡绑定吧。我们需要决定选取哪些接口配置成一个组接口。
+现在让我们在 CentOS 7 上配置网卡绑定吧。我们需要决定选取哪些接口配置成一个组接口(Team interface)。
运行 **ip link** 命令查看系统中可用的接口。
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@
### 2. 添加从设备 ###
-现在让我们天际从设备到主设备 team0。这是添加从设备的语法。
+现在让我们添加从设备到主设备 team0。这是添加从设备的语法:
# nmcli con add type team-slave con-name CNAME ifname INAME master TEAM
@@ -89,7 +89,7 @@

-现在让我们和激活的端口断开连接并再次检查状态来确认主动备份配置是否像希望的那样工作。
+现在让我们把激活的端口断开连接并再次检查状态来确认主动备份配置是否像希望的那样工作。
# nmcli dev dis eno33554960
@@ -129,7 +129,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/interface-nics-bonding-linux/
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150112 What are useful command-line network monitors on Linux.md b/published/201505/20150112 What are useful command-line network monitors on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..25d7910ec7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150112 What are useful command-line network monitors on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
+又一波你可能不知道的 Linux 命令行网络监控工具
+===============================================================================
+
+对任何规模的业务来说,网络监控工具都是一个重要的功能。网络监控的目标可能千差万别。比如,监控活动的目标可以是保证长期的网络服务、安全保护、对性能进行排查、网络使用统计等。由于它的目标不同,网络监控器使用很多不同的方式来完成任务。比如对包层面的嗅探,对数据流层面的统计数据,向网络中注入探测的流量,分析服务器日志等。
+
+尽管有许多专用的网络监控系统可以365天24小时监控,但您依旧可以在特定的情况下使用命令行式的网络监控器,某些命令行式的网络监控器在某方面很有用。如果您是系统管理员,那您就应该有亲身使用一些知名的命令行式网络监控器的经历。这里有一份**Linux上流行且实用的网络监控器**列表。
+
+### 包层面的嗅探器 ###
+
+在这个类别下,监控工具在链路上捕捉独立的包,分析它们的内容,展示解码后的内容或者包层面的统计数据。这些工具在最底层对网络进行监控、管理,同样的也能进行最细粒度的监控,其代价是影响网络I/O和分析的过程。
+
+1. **dhcpdump**:一个命令行式的DHCP流量嗅探工具,捕捉DHCP的请求/回复流量,并以用户友好的方式显示解码的DHCP协议消息。这是一款排查DHCP相关故障的实用工具。
+
+2. **[dsniff][1]**:一个基于命令行的嗅探、伪造和劫持的工具合集,被设计用于网络审查和渗透测试。它可以嗅探多种信息,比如密码、NSF流量(LCTT 译注:此处疑为 NFS 流量)、email消息、网络地址等。
+
+3. **[httpry][2]**:一个HTTP报文嗅探器,用于捕获、解码HTTP请求和回复报文,并以用户友好的方式显示这些信息。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-4148-1.html)。 )
+
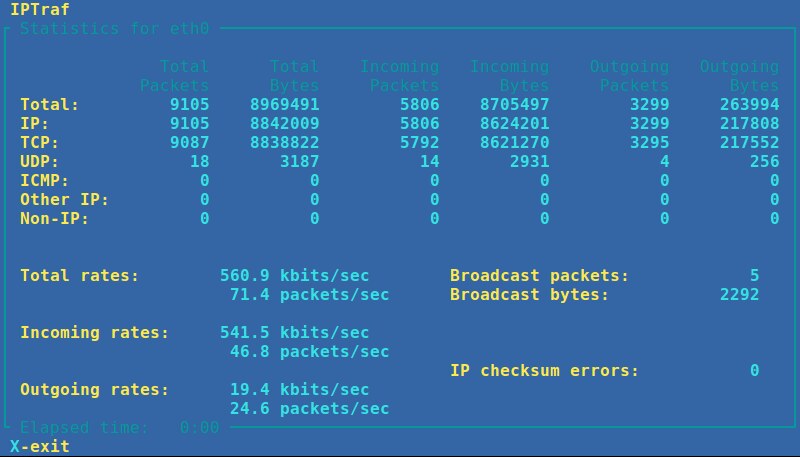
+4. **IPTraf**:基于命令行的网络统计数据查看器。它实时显示包层面、连接层面、接口层面、协议层面的报文/字节数。抓包过程由协议过滤器控制,且操作过程全部是菜单驱动的。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-5430-1.html)。)
+
+ 
+
+5. **[mysql-sniffer][3]**:一个用于抓取、解码MySQL请求相关的数据包的工具。它以可读的方式显示最频繁或全部的请求。
+
+6. **[ngrep][4]**:在网络报文中执行grep。它能实时抓取报文,并用正则表达式或十六进制表达式的方式匹配(过滤)报文。它是一个可以对异常流量进行检测、存储或者对实时流中特定模式报文进行抓取的实用工具。
+
+7. **[p0f][5]**:一个被动的基于包嗅探的指纹采集工具,可以可靠地识别操作系统、NAT或者代理设置、网络链路类型以及许多其它与活动的TCP连接相关的属性。
+
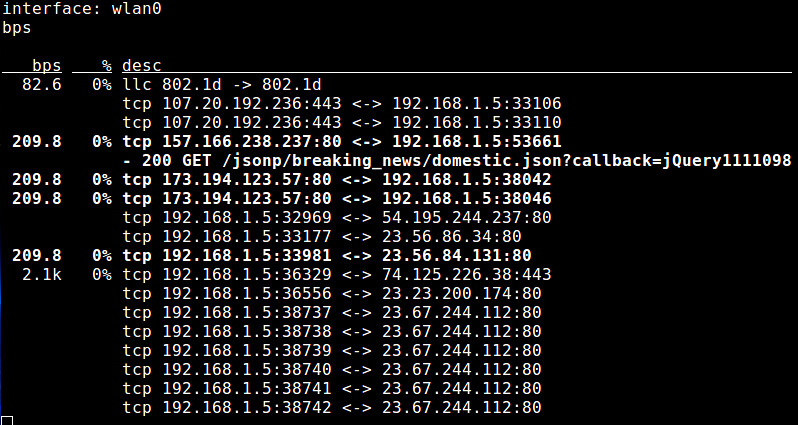
+8. **pktstat**:一个命令行式的工具,通过实时分析报文,显示连接带宽使用情况以及相关的协议(例如,HTTP GET/POST、FTP、X11)等描述信息。
+
+ 
+
+9. **Snort**:一个入侵检测和预防工具,通过规则驱动的协议分析和内容匹配,来检测/预防活跃流量中各种各样的后门、僵尸网络、网络钓鱼、间谍软件攻击。
+
+10. **tcpdump**:一个命令行的嗅探工具,可以基于过滤表达式抓取网络中的报文,分析报文,并且在包层面输出报文内容以便于包层面的分析。他在许多网络相关的错误排查、网络程序debug、或[安全][6]监测方面应用广泛。
+
+11. **tshark**:一个与Wireshark窗口程序一起使用的命令行式的嗅探工具。它能捕捉、解码网络上的实时报文,并能以用户友好的方式显示其内容。
+
+### 流/进程/接口层面的监控 ###
+
+在这个分类中,网络监控器通过把流量按照流、相关进程或接口分类,收集每个流、每个进程、每个接口的统计数据。其信息的来源可以是libpcap抓包库或者sysfs内核虚拟文件系统。这些工具的监控成本很低,但是缺乏包层面的检视能力。
+
+12. **bmon**:一个基于命令行的带宽监测工具,可以显示各种接口相关的信息,不但包括接收/发送的总量/平均值统计数据,而且拥有历史带宽使用视图。
+
+ 
+
+13. **[iftop][7]**:一个带宽使用监测工具,可以实时显示某个网络连接的带宽使用情况。它对所有带宽使用情况排序并通过ncurses的接口来进行可视化。他可以方便的监控哪个连接消耗了最多的带宽。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-1843-1.html)。)
+
+14. **nethogs**:一个基于ncurses显示的进程监控工具,提供进程相关的实时的上行/下行带宽使用信息。它对检测占用大量带宽的进程很有用。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-2808-1.html)。)
+
+15. **netstat**:一个显示许多TCP/UDP的网络堆栈的统计信息的工具。诸如打开的TCP/UDP连接书、网络接口发送/接收、路由表、协议/套接字的统计信息和属性。当您诊断与网络堆栈相关的性能、资源使用时它很有用。
+
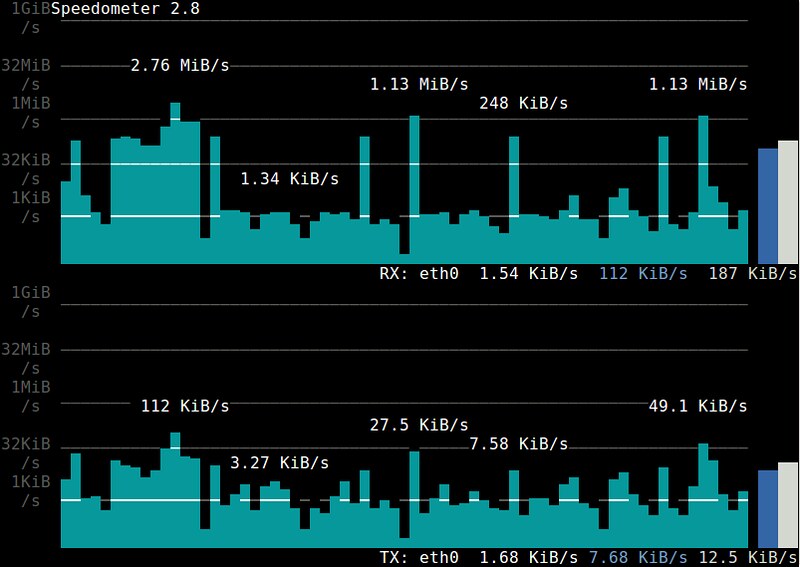
+16. **[speedometer][8]**:一个可视化某个接口发送/接收的带宽使用的历史趋势,并且基于ncurses的条状图进行显示的终端工具。
+
+ 
+
+17. **[sysdig][9]**:一个可以通过统一的界面对各个Linux子系统进行系统级综合性调试的工具。它的网络监控模块可以监控在线或离线、许多进程/主机相关的网络统计数据,例如带宽、连接/请求数等。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-4341-1.html)。)
+
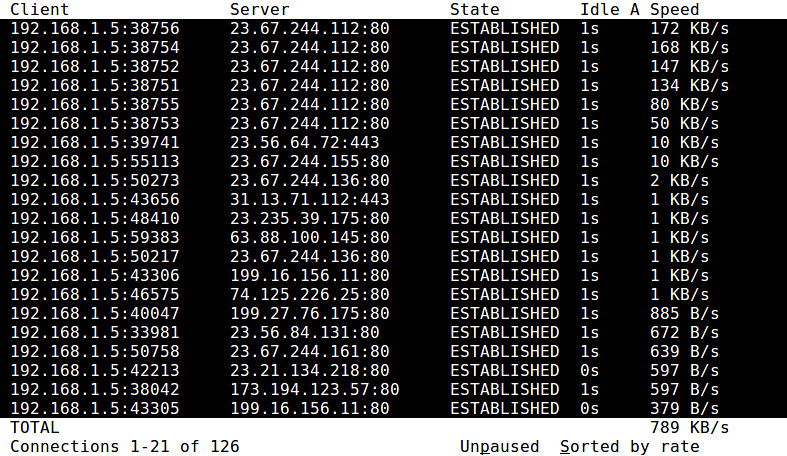
+18. **tcptrack**:一个TCP连接监控工具,可以显示活动的TCP连接,包括源/目的IP地址/端口、TCP状态、带宽使用等。
+
+ 
+
+19. **vnStat**:一个存储并显示每个接口的历史接收/发送带宽视图(例如,当前、每日、每月)的流量监控器。作为一个后台守护进程,它收集并存储统计数据,包括接口带宽使用率和传输字节总数。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-5256-1.html)。)
+
+### 主动网络监控器 ###
+
+不同于前面提到的被动的监听工具,这个类别的工具们在监听时会主动的“注入”探测内容到网络中,并且会收集相应的反应。监听目标包括路由路径、可供使用的带宽、丢包率、延时、抖动(jitter)、系统设置或者缺陷等。
+
+20. **[dnsyo][10]**:一个DNS检测工具,能够管理跨越多达1500个不同网络的开放解析器的DNS查询。它在您检查DNS传播或排查DNS设置的时候很有用。
+
+21. **[iperf][11]**:一个TCP/UDP带宽测量工具,能够测量两个端点间最大可用带宽。它通过在两个主机间单向或双向的输出TCP/UDP探测流量来测量可用的带宽。它在监测网络容量、调谐网络协议栈参数时很有用。一个叫做[netperf][12]的变种拥有更多的功能及更好的统计数据。
+
+22. **[netcat][13]/socat**:通用的网络调试工具,可以对TCP/UDP套接字进行读、写或监听。它通常和其他的程序或脚本结合起来在后端对网络传输或端口进行监听。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-1171-1.html)。)
+
+23. **nmap**:一个命令行的端口扫描和网络发现工具。它依赖于若干基于TCP/UDP的扫描技术来查找开放的端口、活动的主机或者在本地网络存在的操作系统。它在你审查本地主机漏洞或者建立维护所用的主机映射时很有用。[zmap][14]是一个类似的替代品,是一个用于互联网范围的扫描工具。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-2561-1.html)。)
+
+24. ping:一个常用的网络测试工具。通过交换ICMP的echo和reply报文来实现其功能。它在测量路由的RTT、丢包率以及检测远端系统防火墙规则时很有用。ping的变种有更漂亮的界面(例如,[noping][15])、多协议支持(例如,[hping][16])或者并行探测能力(例如,[fping][17])。(LCTT 译注:[延伸阅读](https://linux.cn/article-2303-1.html)。)
+
+ 
+
+25. **[sprobe][18]**:一个启发式推断本地主机和任意远端IP地址之间的网络带宽瓶颈的命令行工具。它使用TCP三次握手机制来评估带宽的瓶颈。它在检测大范围网络性能和路由相关的问题时很有用。
+
+26. **traceroute**:一个能发现从本地到远端主机的第三层路由/转发路径的网络发现工具。它发送限制了TTL的探测报文,收集中间路由的ICMP反馈信息。它在排查低速网络连接或者路由相关的问题时很有用。traceroute的变种有更好的RTT统计功能(例如,[mtr][19])。
+
+### 应用日志解析器 ###
+
+在这个类别下的网络监测器把特定的服务器应用程序作为目标(例如,web服务器或者数据库服务器)。由服务器程序产生或消耗的网络流量通过它的日志被分析和监测。不像前面提到的网络层的监控器,这个类别的工具能够在应用层面分析和监控网络流量。
+
+27. **[GoAccess][20]**:一个针对Apache和Nginx服务器流量的交互式查看器。基于对获取到的日志的分析,它能展示包括日访问量、最多请求、客户端操作系统、客户端位置、客户端浏览器等在内的多个实时的统计信息,并以滚动方式显示。
+
+ 
+
+28. **[mtop][21]**:一个面向MySQL/MariaDB服务器的命令行监控器,它可以将成本最大的查询和当前数据库服务器负载以可视化的方式显示出来。它在您优化MySQL服务器性能、调谐服务器参数时很有用。
+
+ 
+
+29. **[ngxtop][22]**:一个面向Nginx和Apache服务器的流量监测工具,能够以类似top指令的方式可视化的显示Web服务器的流量。它解析web服务器的查询日志文件并收集某个目的地或请求的流量统计信息。
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+在这篇文章中,我展示了许多命令行式监测工具,从最底层的包层面的监控器到最高层应用程序层面的网络监控器。了解那个工具的作用是一回事,选择哪个工具使用又是另外一回事。单一的一个工具不能作为您每天使用的通用的解决方案。一个好的系统管理员应该能决定哪个工具更适合当前的环境。希望这个列表对此有所帮助。
+
+欢迎您通过回复来改进这个列表的内容!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/useful-command-line-network-monitors-linux.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
+[1]:http://www.monkey.org/~dugsong/dsniff/
+[2]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-http-traffic-command-line-linux.html
+[3]:https://github.com/zorkian/mysql-sniffer
+[4]:http://ngrep.sourceforge.net/
+[5]:http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/p0f3/
+[6]:http://xmodulo.com/recommend/firewallbook
+[7]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-install-iftop-on-linux.html
+[8]:https://excess.org/speedometer/
+[9]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-troubleshoot-linux-server-sysdig.html
+[10]:http://xmodulo.com/check-dns-propagation-linux.html
+[11]:https://iperf.fr/
+[12]:http://www.netperf.org/netperf/
+[13]:http://xmodulo.com/useful-netcat-examples-linux.html
+[14]:https://zmap.io/
+[15]:http://noping.cc/
+[16]:http://www.hping.org/
+[17]:http://fping.org/
+[18]:http://sprobe.cs.washington.edu/
+[19]:http://xmodulo.com/better-alternatives-basic-command-line-utilities.html#mtr_link
+[20]:http://goaccess.io/
+[21]:http://mtop.sourceforge.net/
+[22]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-nginx-web-server-command-line-real-time.html
diff --git a/published/201505/20150119 Unity Greeter Badges Brings Missing Session Icons to Ubuntu Login Screen.md b/published/201505/20150119 Unity Greeter Badges Brings Missing Session Icons to Ubuntu Login Screen.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fe25f3f6dc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150119 Unity Greeter Badges Brings Missing Session Icons to Ubuntu Login Screen.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+‘Unity Greeter Badges’:将丢失的会话图标带回Ubuntu登录屏幕
+================================================================================
+
+
+新出现在**Ubuntu 15.04中的一个软件包解决了我对Unity 欢迎屏的微词:像Cinnamon这样的其它Linux桌面会话没有徽章图标。**
+
+我知道这有点吹毛求疵了;这只是对大多数人而言几乎毫无影响的视觉瑕疵罢了。但是这种不一致性时时刻刻缠绕着我,让我不胜其烦,因为Ubuntu的一些会话带有徽章图标,包括Unity、GNOME和KDE。而剩下的其它桌面环境,包括它自己的一些旁系产品,像Xubuntu,只会在会话切换列表和主用户界面显示了一个不能再简单的白点。
+
+这些点点们造成的这种不一致性刺激着我的神经,即使它只是稍纵即逝,但这种刺激不仅仅来自设计,也来自可用性方面。标牌式的标志符号对于让我们知道我们即将登陆到哪个会话很有帮助。
+
+例如,你能告诉我们这个是个什么会话呢?
+
+
+
+Budgie? 也许是 MATE? 也能是 Cinnamon……我必须点开它才能知道。
+
+没有必要这样做啊。构建Unity Greeter,就是为了让桌面环境开发者能够部署徽章到欢迎屏幕中(有些确实这样做了)。但在许多情况下,像MATE,它的包来自上游的Debian,想要移植一个“Ubuntu专用的补丁包”不太可取,也不太可能。
+
+### 一个解决方案出炉了 ###
+
+一位有经验的Debian维护者[Doug Torrance][1]有了修复该可用性瑕疵的解决方案。与其依赖桌面制造者自己来添加品牌式徽章到他们的包中,与其给Ubuntu增加维护它的责任重担,Torrance还不如自己创建了一个独立的‘unity-greeter-badges’包来收容它们。
+
+承担起了直接提供会话标志的假定责任后,该包确保能同时迎合新旧窗口管理器、会话和桌面。
+
+在30个左右的桌面环境列表中,它为以下桌面捆绑了新的会话徽章:
+
+- Xubuntu
+- Cinnamon
+- MATE
+- Cairo-Dock
+- Xmonad
+- Awesome
+- OpenBox
+- Pantheon
+
+最重要的是,‘**Unity-Greeter-Badges**’已经被Ubuntu 15.04收录进去。这就意味着Torrance的包将可以直接安装,不需要PPA,也不需要下载。没有像Unity Greeter一样成为核心包的一部分,它可以以更高效和更及时的方式更新新的图标。
+
+如果你真运行着Ubuntu 15.04,在不久的将来,你就可以从软件中心获取并安装该包了。
+
+不想等到15.04?Torrance已经为Ubuntu 14.04和Ubuntu 14.10用户做了个.deb安装器。
+
+- [下载用于Ubuntu 14.04的unity-greeter-badges][2]
+- [下载用于Ubuntu 14.10的unity-greeter-badges][3]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/01/unity-greeter-badges-brings-missing-session-icons-ubuntu-login-screen
+
+作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
+[1]:https://launchpad.net/~profzoom
+[2]:https://launchpad.net/~profzoom/+archive/ubuntu/misc/+files/unity-greeter-badges_0.1-0ubuntu1%7E201412111501%7Eubuntu14.04.1_all.deb
+[3]:https://launchpad.net/~profzoom/+archive/ubuntu/misc/+files/unity-greeter-badges_0.1-0ubuntu1%7E201412111501%7Eubuntu14.10.1_all.deb
diff --git a/published/201505/20150123 How to make a file immutable on Linux.md b/published/201505/20150123 How to make a file immutable on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..493b0096be
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150123 How to make a file immutable on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+如何在Linux下创建一个不可变更的文件
+================================================================================
+
+假如你想对Linux中的一些重要文件做写保护,这样它们就不能被删除或者被篡改成之前的版本或者其他东西,或者在其他情况下,你可能想避免某些配置文件被软件自动修改。使用`chown`和`chmod`命令修改文件的归属关系或者权限位是处理这种情况的一个解决方法,但这并不完美,因为这样无法避免有root权限的操作。这时`chattr`就派上用场了。
+
+`chattr`是一个可以设置或取消文件的标志位的Linux命令,它和标准的文件权限(读、写、执行)是分离的。与此相关的另一个命令是`lsattr`,它可以显示文件的哪些标志位被设置上了。最初只有EXT文件系统(EXT2/3/4)支持`chattr`和`lsattr`所管理的标志位,但现在很多其他的原生的Linux文件系统都支持了,比如XFS、Btrfs、ReiserFS等等。
+
+在这个教程中,我会示范如果使用`chattr`来让Linux中的文件不可变更。
+
+`chattr`和`lsattr`命令是e2fsprogs包的一部分,它在所有现代Linux发行版都预装了。
+
+下面是`chattr`的基本语法。
+
+ $ chattr [-RVf] [操作符][标志位] 文件...
+
+其中操作符可以是“+”(把选定的标志位添加到标志位列表)、“-”(从标志位列表中移除选定的标志位)、或者“=”(强制使用选定的标志位)。
+
+下面是一些可用的标志位。
+
+- **a**: 只能以追加模式打开。
+- **A**: 不能更新atime(文件访问时间)。
+- **c**: 当被写入磁盘时被自动压缩。
+- **C**: 关掉“写时复制”。
+- **i**: 不可变更。
+- **s**: 通过自动归零来安全删除。(LCTT 译注:一般情况文件被删后内容不会被修改,改标志位会使得文件被删后原有内容被“0”取代)
+
+### “不可变更”标志位 ###
+
+为了让一个文件不可变更,你需要按照如下方法为这个文件添加“不可变更”标志位。例如,对/etc/passwd文件做写保护:
+
+ $ sudo chattr +i /etc/passwd
+
+注意设置或取消一个文件的“不可变更”标志位是需要root用户权限的。现在检查该文件“不可变更”标志位是否被添加上了。
+
+ $ lsattr /etc/passwd
+
+一旦文件被设置为不可变更,任何用户都将无法修改该文件。即使是root用户也不可以修改、删除、覆盖、移动或者重命名这个文件。如果你想再次修改这个文件,需要先把“不可变更”标志位取消了。
+
+用如下命令取消“不可变更”标志位:
+
+ $ sudo chattr -i /etc/passwd
+
+
+
+如果你想让一个目录(比如/etc)连同它下边的所有内容不可变更,使用“-R”选项:
+
+ $ sudo chattr -R +i /etc
+
+### “只可追加”标志位 ###
+
+另一个有用的的标志位是“只可追加”,它只允许文件内容被追加的方式修改。你不能覆盖或者删除一个设置了“只可追加”标志位的文件。这个标志位在你想避免日志文件被意外清理掉的情况很有用。
+
+和“不可变更”标志位类似,你可以使用如下命令让文件变成“只可追加”模式:
+
+ $ sudo chattr +a /var/log/syslog
+
+注意当你复制一个“不可变更”或者“只可追加”的文件到其他地方后,新文件不会保留这些标志位!
+
+### 结论 ###
+
+在这个教程中,我展示了如何使用`chattr`和`lsattr`命令来管理额外的文件标志位,来避免文件被篡改(意外或者其他情况)的方法。注意你不能将`chattr`作为一个安全措施,因为“不可变更”标志位可以很容易被取消掉。解决这个问题的一个可能的方式是限制`chattr`命令自身的可用性,或者去掉CAP_LINUX_IMMUTABLE内核权能标志。关于`chattr`以及可用的标志位的更多细节,请参考它的man手册。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/make-file-immutable-linux.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[goreliu](https://github.com/goreliu)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
diff --git a/translated/talk/20150124 Why does C++ promote an int to a float when a float cannot represent all int values.md b/published/201505/20150124 Why does C++ promote an int to a float when a float cannot represent all int values.md
similarity index 93%
rename from translated/talk/20150124 Why does C++ promote an int to a float when a float cannot represent all int values.md
rename to published/201505/20150124 Why does C++ promote an int to a float when a float cannot represent all int values.md
index e9dd6e997c..8d0d835ad5 100644
--- a/translated/talk/20150124 Why does C++ promote an int to a float when a float cannot represent all int values.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150124 Why does C++ promote an int to a float when a float cannot represent all int values.md
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
既然float不能表示所有的int,那为什么在类型转换时C++将int转换成float?
----------
+=============
-#问题:
+###问题:
代码如下:
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ if (i == f) // 执行某段代码
编译器会将i转换成float类型,然后比较这两个float的大小,但是float能够表示所有的int吗?为什么没有将int和float转换成double类型进行比较呢?
-#回答:
+###回答:
在整型数的演变中,当`int`变成`unsigned`时,会丢掉负数部分(有趣的是,这样的话,`0u < -1`就是对的了)。
@@ -32,11 +32,11 @@ if((double) i < (double) f)
顺便提一下,在这个问题中有趣的是,`unsigned`的优先级高于`int`,所以把`int`和`unsigned`进行比较时,最终进行的是unsigned类型的比较(开头提到的`0u < -1`就是这个道理)。我猜测这可能是在早些时候(计算机发展初期),当时的人们认为`unsigned`比`int`在所表示的数值范围上受到的限制更小:现在还不需要符号位,所以可以使用额外的位来表示更大的数值范围。如果你觉得`int`可能会溢出,那么就使用unsigned好了——在使用16位表示的ints时这个担心会更明显。
----
-via:[stackoverflow](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/28010565/why-does-c-promote-an-int-to-a-float-when-a-float-cannot-represent-all-int-val/28011249#28011249)
+via: [stackoverflow](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/28010565/why-does-c-promote-an-int-to-a-float-when-a-float-cannot-represent-all-int-val/28011249#28011249)
作者:[wintermute][a]
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150126 iptraf--A TCP or UDP Network Monitoring Utility.md b/published/201505/20150126 iptraf--A TCP or UDP Network Monitoring Utility.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1fa38d9079
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150126 iptraf--A TCP or UDP Network Monitoring Utility.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+iptraf:一个实用的TCP/UDP网络监控工具
+================================================================================
+
+[iptraf][1]是一个基于ncurses的IP局域网监控器,用来生成包括TCP信息、UDP计数、ICMP和OSPF信息、以太网负载信息、节点状态信息、IP校验和错误等等统计数据。
+
+它基于ncurses的用户界面可以使用户免于记忆繁琐的命令行开关。
+
+### 特征 ###
+
+- IP流量监控器,用来显示你的网络中的IP流量变化信息。包括TCP标识信息、包以及字节计数,ICMP细节,OSPF包类型。
+- 简单的和详细的接口统计数据,包括IP、TCP、UDP、ICMP、非IP以及其他的IP包计数、IP校验和错误,接口活动、包大小计数。
+- TCP和UDP服务监控器,能够显示常见的TCP和UDP应用端口上发送的和接收的包的数量。
+- 局域网数据统计模块,能够发现在线的主机,并显示其上的数据活动统计信息。
+- TCP、UDP、及其他协议的显示过滤器,允许你只查看感兴趣的流量。
+- 日志功能。
+- 支持以太网、FDDI、ISDN、SLIP、PPP以及本地回环接口类型。
+- 利用Linux内核内置的原始套接字接口,允许它(指iptraf)能够用于各种支持的网卡上
+- 全屏,菜单式驱动的操作。
+
+###安装方法###
+
+**Ubuntu以及其衍生版本**
+
+ sudo apt-get install iptraf
+
+**Arch Linux以及其衍生版本**
+
+ sudo pacman -S iptra
+
+**Fedora以及其衍生版本**
+
+ sudo yum install iptraf
+
+### 用法 ###
+
+如果不加任何命令行选项地运行**iptraf**命令,程序将进入一种交互模式,通过主菜单可以访问多种功能。
+
+
+
+简易的上手导航菜单。
+
+
+
+选择要监控的接口。
+
+
+
+接口**ppp0**处的流量。
+
+
+
+试试吧!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/iptraf-tcpudp-network-monitoring-utility/
+
+作者:[Enock Seth Nyamador][a]
+译者:[DongShuaike](https://github.com/DongShuaike)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/seth/
+[1]:http://iptraf.seul.org/about.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150128 Docker-2 Setting up a private Docker registry.md b/published/201505/20150128 Docker-2 Setting up a private Docker registry.md
similarity index 55%
rename from translated/tech/20150128 Docker-2 Setting up a private Docker registry.md
rename to published/201505/20150128 Docker-2 Setting up a private Docker registry.md
index 6d73b53326..d1c81e1679 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150128 Docker-2 Setting up a private Docker registry.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150128 Docker-2 Setting up a private Docker registry.md
@@ -2,58 +2,58 @@
================================================================================

-[TL;DR]这是系列的第二篇文章,这系列讲述了我的公司如何把基础服务从PaaS迁移到Docker上
+[TL;DR] 这是系列的第二篇文章,这系列讲述了我的公司如何把基础服务从PaaS迁移到Docker上
-- [First part][1]: 第一篇文章里我谈到了接触Docker之前的经历;
-- [Third pard][2]: 第三篇文章里我展示如何使创建images的过程自动化以及如何用Docker部署一个Rails应用。
+- [第一篇文章][1]: 我谈到了接触Docker之前的经历;
+- [第三篇文章][2]: 我展示如何使创建镜像的过程自动化以及如何用Docker部署一个Rails应用。
----------
-为什么需要搭建一个私有的registry呢?嗯,Docker Hub(一个Docker公共仓库)只允许你拥有一个免费的私有版本库(repo)。其他的公司提供类似服务,但是价格可不便宜。另外,如果你需要部署一个基于Docker的应用产品,恐怕你不希望这些images在开放的Docker Hub被公开吧!
+为什么需要搭建一个私有的registry呢?嗯,对于新手来说,Docker Hub(一个Docker公共仓库)只允许你拥有一个免费的私有版本库(repo)。其他的公司也开始提供类似服务,但是价格可不便宜。另外,如果你需要用Docker部署一个用于生产环境的应用,恐怕你不希望将这些镜像放在公开的Docker Hub上吧!
-这篇文章提供了一个非常务实的方法来处理搭建私有Docke registry时出现的各种错综复杂的情况。我们将会使用一个运行于DigitalOcean(之后简称为DO)的非常小巧的512MB实例。并且我会假定你已经了解了Docker的基本概念,因为我必须集中精力在复杂的事情上!
+这篇文章提供了一个非常务实的方法来处理搭建私有Docker registry时出现的各种错综复杂的情况。我们将会使用一个运行于DigitalOcean(之后简称为DO)的非常小巧的512MB VPS 实例。并且我会假定你已经了解了Docker的基本概念,因为我必须集中精力在复杂的事情上!
###本地搭建###
首先你需要安装**boot2docker**以及docker CLI。如果你已经搭建好了基本的Docker环境,你可以直接跳过这一步。
-从终端运行以下命令[1][3]:
+从终端运行以下命令(我假设你使用OS X,使用 HomeBrew 来安装相关软件,你可以根据你的环境使用不同的包管理软件来安装):
+
brew install boot2docker docker
-如果一切顺利[2][4],你现在将能够启动VM,在VM当中输入下列命令:
+如果一切顺利(想要了解搭建docker环境的完整指南,请参阅 [http://boot2docker.io/][10]) ,你现在就能够通过如下命令启动一个 Docker 运行于其中的虚拟机:
+
boot2docker up
-Follow the instructions, copy and paste the export commands that boot2docker will print in the terminal. If you now run `docker ps` you should be greeted by the following line
-按照说明,复制粘贴book2docker打印在终端的export命令(这块翻译不太好)。现在运行`docker ps`命令,终端将有以下显示。
+按照屏幕显示的说明,复制粘贴book2docker在终端输出的命令。如果你现在运行`docker ps`命令,终端将有以下显示。
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
-好了,Docker已经准备就绪。我们回过头去搭建registry。
+好了,Docker已经准备就绪,这就够了,我们回过头去搭建registry。
###创建服务器###
-登录进你的DO账号,选择一个提前安装好Docker的映像文件,创建一个新的Drople。[^n]
+登录进你的DO账号,选择一个预安装了Docker的镜像文件,创建一个新的Drople。(本文写成时选择的是 Image > Applications > Docker 1.4.1 on 14.04)

-
你将会以邮件的方式收到一个根用户凭证。登录进去,然后运行`docker ps`命令来查看系统状态。
### 搭建AWS S3 ###
-我们现在将使用Amazo Simple Storage Service(S3)作为我们registry/repository的存储层。我们讲需要创建一个桶(bucket)以及用户凭证(user credentials)来允许我们的docker容器访问它。
+我们现在将使用Amazo Simple Storage Service(S3)作为我们registry/repository的存储层。我们将需要创建一个桶(bucket)以及用户凭证(user credentials)来允许我们的docker容器访问它。
-登录到我们的AWS账号(如果没有,就申请一个[http://aws.amazon.com/][5]),在控制台选择S3(Simpole Storage Service)
+登录到我们的AWS账号(如果没有,就申请一个[http://aws.amazon.com/][5]),在控制台选择S3(Simpole Storage Service)。

-点击 **Create Bucket**,为你的桶输入一个名字(把它写下来,我们一会需要用到它),然后点击**Create**。
+点击 **Create Bucket**,为你的桶输入一个名字(把它记下来,我们一会需要用到它),然后点击**Create**。

-OK!我们已经搭建好存储部分了。
+OK!我们已经搭建好存储部分了。
-### 安装AWS访问凭证###
+### 设置AWS访问凭证###
我们现在将要创建一个新的用户。退回到AWS控制台然后选择IAM(Identity & Access Management)。
@@ -65,9 +65,9 @@ OK!我们已经搭建好存储部分了。

-输入你的用户名(例如 docker-registry)然后点击Create。写下(或者下载csv文件)你的Access Key以及Secret Access Key。回到你的用户列表然后选择你刚刚创建的用户。
+输入一个用户名(例如 docker-registry)然后点击Create。写下(或者下载csv文件)你的Access Key以及Secret Access Key。回到你的用户列表然后选择你刚刚创建的用户。
-在Permission section下面,点击Attach User Policy。之后,选择Custom Policy。
+在Permission section下面,点击Attach User Policy。之后在下一屏,选择Custom Policy。

@@ -90,11 +90,11 @@ custom policy的内容如下:
]
}
-这个配置将允许用户(也就是regitstry)来对桶上的内容进行操作(读/写)(确保使用你之前创建AWS S3时使用的桶名)。总结起来:当你想把你的Docker映像从你的本机推送到仓库中时,服务器将能够将他们上传到S3。
+这个配置将允许用户(也就是regitstry)来对桶上的内容进行操作(读/写)(确保使用你之前创建AWS S3时使用的桶名)。总结一下:当你想把你的Docker镜像从你的本机推送到仓库中时,服务器就会将他们上传到S3。
### 安装registry ###
-现在回过头来看我们的DO服务器,SSH登录其上。我们将要使用[^n]一个官方Docker registry映像。[6]
+现在回过头来看我们的DO服务器,SSH登录其上。我们将要[使用][11]一个[官方Docker registry镜像][6]。
输入如下命令,开启registry。
@@ -110,25 +110,25 @@ custom policy的内容如下:
-d \
registry
-Docker将会从Docker Hub上拉取所需的文件系统层(fs layers)并启动守护容器(daemonised container)。
+Docker将会从Docker Hub上拉取所需的文件系统分层(fs layers)并启动守护容器(daemonised container)。
### 测试registry ###
如果上述操作奏效,你可以通过ping命令,或者查找它的内容来测试registry(虽然这个时候容器还是空的)。
-我们的registry非常基础,而且没有提供任何“验明正身”的方式。因为添加身份验证可不是一件轻松事(至少我认为没有一种部署方法是简单的,像是为了证明你努力过似的),我觉得 查询/拉取/推送 仓库内容的最简单方法就是通过SSH的未加密连接(通过HTTP)。
+我们的registry非常基础,而且没有提供任何“验明正身”的方式。因为添加身份验证可不是一件轻松事(至少我认为没有一种部署方法是简单的,像是为了证明你努力过似的),我觉得“查询/拉取/推送”仓库内容的最简单方法就是通过SSH通道的未加密连接(通过HTTP)。
打开SSH通道的操作非常简单:
ssh -N -L 5000:localhost:5000 root@your_registry.com
-这条命令建立了一条从registry服务器(前面执行`docker run`命令的时候我们见过它)的5000号端口到本机的5000号端口之间的连接。
+这条命令建立了一条从registry服务器(前面执行`docker run`命令的时候我们见过它)的5000号端口到本机的5000号端口之间的 SSH 管道连接。
-如果你现在登录[http://localhost:5000/v1/_ping][7],将会看到下面这个非常简短的回复。
+如果你现在用浏览器访问 [http://localhost:5000/v1/_ping][7],将会看到下面这个非常简短的回复。
{}
-这个意味着registry工作正常。你还可以通过登录[http://localhost:5000/v1/search][8]来查看registry内容,内容相似:
+这个意味着registry工作正常。你还可以通过登录 [http://localhost:5000/v1/search][8] 来查看registry内容,内容相似:
{
"num_results": 2,
@@ -145,40 +145,38 @@ Docker将会从Docker Hub上拉取所需的文件系统层(fs layers)并启动
]
}
-### 创建一个映像 ###
+### 创建一个镜像 ###
-我们现在创建一个非常简答的Docker映像,来检验我们新弄好的registry。在我们的本机上,用如下内容创建一个Dockerfile:[^n]
+我们现在创建一个非常简单的Docker镜像,来检验我们新弄好的registry。在我们的本机上,用如下内容创建一个Dockerfile(这里只有一点代码,在下一篇文章里我将会展示给你如何将一个Rails应用绑定进Docker容器中。):
-
- # Base image with ruby 2.2.0
+ # ruby 2.2.0 的基础镜像
FROM ruby:2.2.0
MAINTAINER Michelangelo Chasseur <michelangelo.chasseur@touchwa.re>
-……创建:
+并创建它:
docker build -t localhost:5000/username/repo-name .
-`localhost:5000`非常重要:Docker映像名的最前面一个部分将告知`docker push`命令我们将要把我们的image推送到哪里。在我们这个例子当中,因为我们要通过SSH管道连接远端私有registry,`localhost:5000`精确地表示了对我们的registry的一个引用。
+`localhost:5000`这个部分非常重要:Docker镜像名的最前面一个部分将告知`docker push`命令我们将要把我们的镜像推送到哪里。在我们这个例子当中,因为我们要通过SSH管道连接远程的私有registry,`localhost:5000`精确地指向了我们的registry。
-如果一切顺利,当命令执行完成返回后,你可以输入`docker images`命令来列出新近创建的映像。执行它看看会出现什么现象?
+如果一切顺利,当命令执行完成返回后,你可以输入`docker images`命令来列出新近创建的镜像。执行它看看会出现什么现象?
### 推送到仓库 ###
-接下来是更好玩的部分。实现我所描述的东西着实花了我一点时间,所以如果你第一次读的话就耐心一点吧,跟着我一起操作。我知道接下来的东西会非常复杂(如果你不自动化进程就一定会这样),但是我保证到最后你一定都能明白。在下一篇文章里我将会使用到一大波shell脚本和Rake任务,通过它们实现自动化并且用简单的命令实现部署Rails应用。
+接下来是更好玩的部分。实现我所描述的东西着实花了我一点时间,所以如果你第一次读的话就耐心一点吧,跟着我一起操作。我知道接下来的东西会非常复杂(如果你不自动化这个过程就一定会这样),但是我保证到最后你一定都能明白。在下一篇文章里我将会使用到一大波shell脚本和Rake任务,通过它们实现自动化并且用简单的命令实现部署Rails应用。
-你运行的docker命令都是实际上都是在boot2docker虚拟机上运行的。所以当你执行像`docker push some_repo`这样的命令时,是boot2docker虚拟机在与registry交互,而不是我们自己的机器。
+你在终端上运行的docker命令实际上都是使用boot2docker虚拟机来运行容器及各种东西。所以当你执行像`docker push some_repo`这样的命令时,是boot2docker虚拟机在与registry交互,而不是我们自己的机器。
-接下来是一个非常重要的点:为了将Docker映像推送到远端的私有仓库,SSH管道需要在boot2docker虚拟机上配置好。
+接下来是一个非常重要的点:为了将Docker镜像推送到远端的私有仓库,SSH管道需要在boot2docker虚拟机上配置好,而不是在你的本地机器上配置。
-由许多种方法实现它。我给你展示最简短的一种(可能不是最容易理解的,但是能够帮助你实现自动化)
+有许多种方法实现它。我给你展示最简短的一种(可能不是最容易理解的,但是能够帮助你实现自动化)
-First of all though we need to sort one last thing with SSH.
-(不太会翻译)
+在这之前,我们需要对 SSH 做最后一点工作。
-### Setting up SSH ###
+### 设置 SSH ###
-我们添加boot2docker SSH key到远端服务器已知的hosts里面。我们可以使用ssh-copy-id工具,通过下面的命令就可以安装上它了:
+让我们把boot2docker 的 SSH key添加到远端服务器的“已知主机”里面。我们可以使用ssh-copy-id工具完成,通过下面的命令就可以安装上它了:
brew install ssh-copy-id
@@ -188,7 +186,7 @@ First of all though we need to sort one last thing with SSH.
用你ssh key的真实路径代替`/Users/username/.ssh/id_boot2docker`。
-这样做能够让我们面密码登录SSH。
+这样做能够让我们免密码登录SSH。
现在我们来测试以下:
@@ -196,26 +194,23 @@ First of all though we need to sort one last thing with SSH.
分开阐述:
-- `boot2docker ssh`允许你以参数的形式传递给boot2docker虚拟机一条执行命令;
+- `boot2docker ssh`允许你以参数的形式传递给boot2docker虚拟机一条执行的命令;
- 最后面那个`&`表明这条命令将在后台执行;
- `ssh -o 'StrictHostKeyChecking no' -i /Users/michelangelo/.ssh/id_boot2docker -N -L 5000:localhost:5000 root@registry.touchwa.re &`是boot2docker虚拟机实际运行的命令;
- -`-o 'StrictHostKeyChecking no'`——不提示安全问题;
+ - `-o 'StrictHostKeyChecking no'`——不提示安全问题;
- `-i /Users/michelangelo/.ssh/id_boot2docker`指出虚拟机使用哪个SSH key来进行身份验证。(注意这里的key应该是你前面添加到远程仓库的那个)
- - 最后我们将打开一条端口5000到本地端口5000的SSH通道。
+ - 最后我们将打开一条端口5000映射到localhost:5000的SSH通道。
### 从其他服务器上拉取 ###
-你现在将可以通过下面的简单命令将你的映像推送到远端仓库:
+你现在将可以通过下面的简单命令将你的镜像推送到远端仓库:
docker push localhost:5000/username/repo_name
-在下一篇文章[9]中,我们将会了解到如何自动化处理这些事务,并且真正地容器化一个Rails应用。请继续收听!
+在下一篇[文章][9]中,我们将会了解到如何自动化处理这些事务,并且真正地容器化一个Rails应用。请继续收听!
+
如有错误,请不吝指出。祝你Docker之路顺利!
-1. 我假设你使用OS X。
-2. 想要了解搭建docker环境的完整之南,请参阅[http://boot2docker.io/][10]。
-3. 本文写成时选择的是 Image > Applications > Docker 1.4.1 on 14.04。
-4. [https://github.com/docker/docker-registry/][11]
-5. 这是一个存根,在下一篇文章里我将会展示给你如何将一个Rails应用绑定进Docker容器中。
+
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -223,12 +218,12 @@ via: http://cocoahunter.com/2015/01/23/docker-2/
作者:[Michelangelo Chasseur][a]
译者:[DongShuaike](https://github.com/DongShuaike)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
[a]:http://cocoahunter.com/author/michelangelo/
-[1]:http://cocoahunter.com/2015/01/23/docker-1/
+[1]:https://linux.cn/article-5339-1.html
[2]:http://cocoahunter.com/2015/01/23/docker-3/
[3]:http://cocoahunter.com/2015/01/23/docker-2/#fn:1
[4]:http://cocoahunter.com/2015/01/23/docker-2/#fn:2
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150128 Docker-3 Automated Docker-based Rails deployments.md b/published/201505/20150128 Docker-3 Automated Docker-based Rails deployments.md
similarity index 68%
rename from translated/tech/20150128 Docker-3 Automated Docker-based Rails deployments.md
rename to published/201505/20150128 Docker-3 Automated Docker-based Rails deployments.md
index cd3917dfcf..be256ff1da 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150128 Docker-3 Automated Docker-based Rails deployments.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150128 Docker-3 Automated Docker-based Rails deployments.md
@@ -1,12 +1,14 @@
-
自动化部署基于Docker的Rails应用
================================================================================

[TL;DR] 这是系列文章的第三篇,讲述了我的公司是如何将基础设施从PaaS移植到Docker上的。
+
- [第一部分][1]:谈论了我接触Docker之前的经历;
- [第二部分][2]:一步步搭建一个安全而又私有的registry。
+
----------
+
在系列文章的最后一篇里,我们将用一个实例来学习如何自动化整个部署过程。
### 基本的Rails应用程序###
@@ -18,99 +20,97 @@
$ rvm use 2.2.0
$ rails new && cd docker-test
-创建一个基础控制器:
+创建一个基本的控制器:
$ rails g controller welcome index
-……然后编辑 `routes.rb` ,以便让工程的根指向我们新创建的welcome#index方法:(这句话理解不太理解)
+……,然后编辑 `routes.rb` ,以便让该项目的根指向我们新创建的welcome#index方法:
root 'welcome#index'
-在终端运行 `rails s` ,然后打开浏览器,登录[http://localhost:3000][3],你会进入到索引界面当中。我们不准备给应用加上多么神奇的东西,这只是一个基础实例,用来验证当我们将要创建并部署容器的时候,一切运行正常。
+在终端运行 `rails s` ,然后打开浏览器,登录[http://localhost:3000][3],你会进入到索引界面当中。我们不准备给应用加上多么神奇的东西,这只是一个基础的实例,当我们将要创建并部署容器的时候,用它来验证一切是否运行正常。
### 安装webserver ###
我们打算使用Unicorn当做我们的webserver。在Gemfile中添加 `gem 'unicorn'`和 `gem 'foreman'`然后将它bundle起来(运行 `bundle install`命令)。
-在Rails应用启动的伺候,需要配置Unicorn,所以我们将一个**unicorn.rb**文件放在**config**目录下。[这里有一个Unicorn配置文件的例子][4]你可以直接复制粘贴Gist的内容。
+启动Rails应用时,需要先配置好Unicorn,所以我们将一个**unicorn.rb**文件放在**config**目录下。[这里有一个Unicorn配置文件的例子][4],你可以直接复制粘贴Gist的内容。
-Let's also add a Procfile with the following content inside the root of the project so that we will be able to start the app with foreman:
-接下来,在工程的根目录下添加一个Procfile,以便可以使用foreman启动应用,内容为下:
+接下来,在项目的根目录下添加一个Procfile,以便可以使用foreman启动应用,内容为下:
web: bundle exec unicorn -p $PORT -c ./config/unicorn.rb
现在运行**foreman start**命令启动应用,一切都将正常运行,并且你将能够在[http://localhost:5000][5]上看到一个正在运行的应用。
-### 创建一个Docker映像 ###
+### 构建一个Docker镜像 ###
-现在我们创建一个映像来运行我们的应用。在Rails工程的跟目录下,创建一个名为**Dockerfile**的文件,然后粘贴进以下内容:
+现在我们构建一个镜像来运行我们的应用。在这个Rails项目的根目录下,创建一个名为**Dockerfile**的文件,然后粘贴进以下内容:
- # Base image with ruby 2.2.0
+ # 基于镜像 ruby 2.2.0
FROM ruby:2.2.0
- # Install required libraries and dependencies
+ # 安装所需的库和依赖
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -qy nodejs postgresql-client sqlite3 --no-install-recommends && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
- # Set Rails version
+ # 设置 Rails 版本
ENV RAILS_VERSION 4.1.1
- # Install Rails
+ # 安装 Rails
RUN gem install rails --version "$RAILS_VERSION"
- # Create directory from where the code will run
+ # 创建代码所运行的目录
RUN mkdir -p /usr/src/app
WORKDIR /usr/src/app
- # Make webserver reachable to the outside world
+ # 使 webserver 可以在容器外面访问
EXPOSE 3000
- # Set ENV variables
+ # 设置环境变量
ENV PORT=3000
- # Start the web app
+ # 启动 web 应用
CMD ["foreman","start"]
- # Install the necessary gems
+ # 安装所需的 gems
ADD Gemfile /usr/src/app/Gemfile
ADD Gemfile.lock /usr/src/app/Gemfile.lock
RUN bundle install --without development test
- # Add rails project (from same dir as Dockerfile) to project directory
+ # 将 rails 项目(和 Dockerfile 同一个目录)添加到项目目录
ADD ./ /usr/src/app
- # Run rake tasks
+ # 运行 rake 任务
RUN RAILS_ENV=production rake db:create db:migrate
-使用提供的Dockerfile,执行下列命令创建一个映像[1][7]:
+使用上述Dockerfile,执行下列命令创建一个镜像(确保**boot2docker**已经启动并在运行当中):
$ docker build -t localhost:5000/your_username/docker-test .
-然后,如果一切正常,长日志输出的最后一行应该类似于:
+然后,如果一切正常,长长的日志输出的最后一行应该类似于:
Successfully built 82e48769506c
$ docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED VIRTUAL SIZE
localhost:5000/your_username/docker-test latest 82e48769506c About a minute ago 884.2 MB
-来运行容器吧!
+让我们运行一下容器试试!
$ docker run -d -p 3000:3000 --name docker-test localhost:5000/your_username/docker-test
-You should be able to reach your Rails app running inside the Docker container at port 3000 of your boot2docker VM[2][8] (in my case [http://192.168.59.103:3000][6]).
-通过你的boot2docker虚拟机[2][8]的3000号端口(我的是[http://192.168.59.103:3000][6]),你可以观察你的Rails应用。
+通过你的boot2docker虚拟机的3000号端口(我的是[http://192.168.59.103:3000][6]),你可以观察你的Rails应用。(如果不清楚你的boot2docker虚拟地址,输入` $ boot2docker ip`命令查看。)
### 使用shell脚本进行自动化部署 ###
-前面的文章(指文章1和文章2)已经告诉了你如何将新创建的映像推送到私有registry中,并将其部署在服务器上,所以我们跳过这一部分直接开始自动化进程。
+前面的文章(指文章1和文章2)已经告诉了你如何将新创建的镜像推送到私有registry中,并将其部署在服务器上,所以我们跳过这一部分直接开始自动化进程。
我们将要定义3个shell脚本,然后最后使用rake将它们捆绑在一起。
### 清除 ###
-每当我们创建映像的时候,
+每当我们创建镜像的时候,
- 停止并重启boot2docker;
-- 去除Docker孤儿映像(那些没有标签,并且不再被容器所使用的映像们)。
+- 去除Docker孤儿镜像(那些没有标签,并且不再被容器所使用的镜像们)。
在你的工程根目录下的**clean.sh**文件中输入下列命令。
@@ -132,22 +132,22 @@ You should be able to reach your Rails app running inside the Docker container a
$ chmod +x clean.sh
-### 创建 ###
+### 构建 ###
-创建的过程基本上和之前我们所做的(docker build)内容相似。在工程的根目录下创建一个**build.sh**脚本,填写如下内容:
+构建的过程基本上和之前我们所做的(docker build)内容相似。在工程的根目录下创建一个**build.sh**脚本,填写如下内容:
docker build -t localhost:5000/your_username/docker-test .
-给脚本执行权限。
+记得给脚本执行权限。
### 部署 ###
最后,创建一个**deploy.sh**脚本,在里面填进如下内容:
- # Open SSH connection from boot2docker to private registry
+ # 打开 boot2docker 到私有注册库的 SSH 连接
boot2docker ssh "ssh -o 'StrictHostKeyChecking no' -i /Users/username/.ssh/id_boot2docker -N -L 5000:localhost:5000 root@your-registry.com &" &
- # Wait to make sure the SSH tunnel is open before pushing...
+ # 在推送前先确认该 SSH 通道是开放的。
echo Waiting 5 seconds before pushing image.
echo 5...
@@ -165,7 +165,7 @@ You should be able to reach your Rails app running inside the Docker container a
echo Starting push!
docker push localhost:5000/username/docker-test
-如果你不理解这其中的含义,请先仔细阅读这部分[part 2][9]。
+如果你不理解这其中的含义,请先仔细阅读这部分[第二部分][2]。
给脚本加上执行权限。
@@ -179,10 +179,9 @@ You should be able to reach your Rails app running inside the Docker container a
这一点都不费工夫,可是事实上开发者比你想象的要懒得多!那么咱们就索性再懒一点!
-我们最后再把工作好好整理一番,我们现在要将三个脚本捆绑在一起,通过rake。
-
-为了更简单一点,你可以在工程根目录下已经存在的Rakefile中添加几行代码,打开Rakefile文件——pun intended——把下列内容粘贴进去。
+我们最后再把工作好好整理一番,我们现在要将三个脚本通过rake捆绑在一起。
+为了更简单一点,你可以在工程根目录下已经存在的Rakefile中添加几行代码,打开Rakefile文件,把下列内容粘贴进去。
namespace :docker do
desc "Remove docker container"
@@ -221,34 +220,27 @@ Deploy独立于build,build独立于clean。所以每次我们输入命令运
$ rake docker:deploy
-接下来就是见证奇迹的时刻了。一旦映像文件被上传(第一次可能花费较长的时间),你就可以ssh登录产品服务器,并且(通过SSH管道)把docker映像拉取到服务器并运行了。多么简单!
+接下来就是见证奇迹的时刻了。一旦镜像文件被上传(第一次可能花费较长的时间),你就可以ssh登录产品服务器,并且(通过SSH管道)把docker镜像拉取到服务器并运行了。多么简单!
也许你需要一段时间来习惯,但是一旦成功,它几乎与用Heroku部署一样简单。
备注:像往常一样,请让我了解到你的意见。我不敢保证这种方法是最好,最快,或者最安全的Docker开发的方法,但是这东西对我们确实奏效。
-- 确保**boot2docker**已经启动并在运行当中。
-- 如果你不了解你的boot2docker虚拟地址,输入` $ boot2docker ip`命令查看。
-- 点击[here][10],教你怎样搭建私有的registry。
-
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
via: http://cocoahunter.com/2015/01/23/docker-3/
作者:[Michelangelo Chasseur][a]
译者:[DongShuaike](https://github.com/DongShuaike)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
[a]:http://cocoahunter.com/author/michelangelo/
-[1]:http://cocoahunter.com/docker-1
-[2]:http://cocoahunter.com/2015/01/23/docker-2/
+[1]:https://linux.cn/article-5339-1.html
+[2]:https://linux.cn/article-5379-1.html
[3]:http://localhost:3000/
[4]:https://gist.github.com/chasseurmic/0dad4d692ff499761b20
[5]:http://localhost:5000/
[6]:http://192.168.59.103:3000/
-[7]:http://cocoahunter.com/2015/01/23/docker-3/#fn:1
-[8]:http://cocoahunter.com/2015/01/23/docker-3/#fn:2
-[9]:http://cocoahunter.com/2015/01/23/docker-2/
-[10]:http://cocoahunter.com/2015/01/23/docker-2/
+
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150205 Inxi--Find System And Hardware Information On Linux.md b/published/201505/20150205 Inxi--Find System And Hardware Information On Linux.md
similarity index 63%
rename from sources/tech/20150205 Inxi--Find System And Hardware Information On Linux.md
rename to published/201505/20150205 Inxi--Find System And Hardware Information On Linux.md
index efdc243fc6..abbfc030cf 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20150205 Inxi--Find System And Hardware Information On Linux.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150205 Inxi--Find System And Hardware Information On Linux.md
@@ -1,171 +1,172 @@
-Inxi: Find System And Hardware Information On Linux
-================================================================================
-We already have shown different [applications][1] and ways to find the system and hardware information on Linux. In that series, today we will see how to find such details using **inxi**. It can be used for forum technical support, as a debugging tool, to quickly ascertain user system configuration and hardware.
-
-**Inxi** is a command line tool that can be used to find the complete system and hardware details such as;
-
-- Hardware,
-- CPU,
-- Drivers,
-- Xorg,
-- Desktop,
-- Kernel,
-- GCC version,
-- Processes,
-- RAM usage,
-- and other useful information.
-
-### Installation ###
-
-Inxi is available in the default repositories of most modern GNU/Linux operating systems. So, we can simply install it by running the following commands.
-
-**On Debian based system:**
-
- sudo apt-get install inxi
-
-**On Fedora:**
-
- sudo yum install inxi
-
-**On RHEL based systems:**
-
-Install EPEL repository:
-
- sudo yum install epel-release
-
-Then, install inxi using command:
-
- sudo yum install inxi
-
-### Usage ###
-
-To find the quick view of the system information, run the following command from Terminal.
-
- inxi
-
-**Sample output:**
-
- CPU~Dual core Intel Core i3-2350M CPU (-HT-MCP-) clocked at Min:800.000Mhz Max:1200.000Mhz Kernel~3.13.0-45-generic x86_64 Up~6:41 Mem~1537.7/3861.3MB HDD~500.1GB(52.5% used) Procs~183 Client~Shell inxi~1.9.17
-
-Ofcourse, we can retrieve a particular hardware details. For example to retrieve the **Audio/Sound hardware details**, run the following command:
-
- inxi -A
-
-**Sample output:**
-
- Audio: Card: Intel 6 Series/C200 Series Family High Definition Audio Controller driver: snd_hda_intel
- Sound: Advanced Linux Sound Architecture ver: k3.13.0-45-generic
-
-Cool, isn’t it?
-
-Likewise, you can retrieve the details of **Graphic card** information.
-
- inxi -G
-
-**Sample output:**
-
- Graphics: Card: Intel 2nd Generation Core Processor Family Integrated Graphics Controller
- X.Org: 1.15.1 drivers: intel (unloaded: fbdev,vesa) Resolution: 1366x768@60.0hz
- GLX Renderer: Mesa DRI Intel Sandybridge Mobile GLX Version: 3.0 Mesa 10.3.0
-
-What about harddisk information? That’s also possible. To view the full **harddisk** information, run the following command.
-
- inxi -D
-
-**Sample Output:**
-
- Drives: HDD Total Size: 500.1GB (52.5% used) 1: id: /dev/sda model: ST9601325BD size: 500.1GB
-
-To display the Bios and Motherboard details:
-
- inxi -M
-
-**Sample output:**
-
- Machine: System: Dell (portable) product: Inspiron N5050
- Mobo: Dell model: 01HXXJ version: A05 Bios: Dell version: A05 date: 08/03/2012
-
-Not only hardware details, it can also displays the **list of available repositories** in our system.
-
- inxi -r
-
-**Sample output:**
-
- Repos: Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list
- deb http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty main restricted
- deb-src http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty main restricted
- deb http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty-updates main restricted
- deb-src http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty-updates main restricted
- deb http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty universe
- .
- .
- Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/intellinuxgraphics.list
- deb https://download.01.org/gfx/ubuntu/14.04/main trusty main #Intel Graphics drivers
- Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/linrunner-tlp-trusty.list
- Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/wseverin-ppa-trusty.list
- deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/wseverin/ppa/ubuntu trusty main
-
-Inxi will also display the Weather details of your location. Surprised? Yes, It should.
-
- inxi -W Erode,Tamilnadu
-
-Here **Erode** is the District and **Tamilnadu** is a state in India.
-
-Sample output:
-
- Weather: Conditions: 79 F (26 C) - Clear Time: February 4, 6:00 PM IST
-
-### Viewing Complete Hardware details ###
-
-Tired of finding each hardware details? Well, you can list all details at once using command:
-
- inxi -F
-
-**Sample output:**
-
- System: Host: sk Kernel: 3.13.0-45-generic x86_64 (64 bit) Desktop: LXDE (Openbox 3.5.2) Distro: Ubuntu 14.04 trusty
- Machine: System: Dell (portable) product: Inspiron N5050
- Mobo: Dell model: 01HXXJ version: A05 Bios: Dell version: A05 date: 08/03/2012
- CPU: Dual core Intel Core i3-2350M CPU (-HT-MCP-) cache: 3072 KB flags: (lm nx sse sse2 sse3 sse4_1 sse4_2 ssse3 vmx)
- Clock Speeds: 1: 800.00 MHz 2: 1000.00 MHz 3: 800.00 MHz 4: 800.00 MHz
- Graphics: Card: Intel 2nd Generation Core Processor Family Integrated Graphics Controller
- X.Org: 1.15.1 drivers: intel (unloaded: fbdev,vesa) Resolution: 1366x768@60.0hz
- GLX Renderer: Mesa DRI Intel Sandybridge Mobile GLX Version: 3.0 Mesa 10.3.0
- Audio: Card: Intel 6 Series/C200 Series Family High Definition Audio Controller driver: snd_hda_intel
- Sound: Advanced Linux Sound Architecture ver: k3.13.0-45-generic
- Network: Card-1: Qualcomm Atheros AR9285 Wireless Network Adapter (PCI-Express) driver: ath9k
- IF: wlan0 state: up mac:
- Card-2: Realtek RTL8101E/RTL8102E PCI Express Fast Ethernet controller driver: r8169
- IF: eth0 state: down mac:
- Drives: HDD Total Size: 500.1GB (52.5% used) 1: id: /dev/sda model: ST9500325AS size: 500.1GB
- Partition: ID: / size: 455G used: 245G (57%) fs: ext4 ID: /boot size: 236M used: 159M (72%) fs: ext2
- ID: swap-1 size: 4.19GB used: 0.00GB (0%) fs: swap
- RAID: No RAID devices detected - /proc/mdstat and md_mod kernel raid module present
- Sensors: System Temperatures: cpu: 64.5C mobo: N/A
- Fan Speeds (in rpm): cpu: N/A
- Info: Processes: 186 Uptime: 6:52 Memory: 1547.2/3861.3MB Client: Shell (bash) inxi: 1.9.17
-
-As you see in the above, inxi displays the complete hardware details.
-
-For more details, refer the man pages.
-
- man inxi
-
-### Conclusion ###
-
-Are you searching for a simple tool which displays your complete system and hardware details? Then, don’t look anywhere, inxi will give you what actually want. And, it is light weight tool available in your default repositories. What else you want more? Give it a try, you won’t be disappointed.
-
-Cheers!
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.unixmen.com/inxi-find-system-hardware-information-linux/
-
-作者:[SK][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
-[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/screenfetch-bash-screenshot-information-tool/
\ No newline at end of file
+Inxi:获取Linux的系统和硬件信息
+================================================================================
+
+我们已经展示了一些不同的[应用程序][1]和方法来获取Linux的系统和硬件信息。在这一系列里,我们将看到如何使用**inxi**来获取这些详情信息。在论坛技术支持中,它可以作为调试工具,迅速确定用户的系统配置和硬件信息。
+
+**Inxi**是一个可以获取完整的系统和硬件详情信息的命令行工具,内容包括:
+
+- 硬件
+- CPU
+- 磁盘驱动器
+- Xorg
+- 桌面环境
+- 内核
+- GCC版本
+- 进程
+- 内存占用
+- 和其他有用的信息
+
+### 安装方法 ###
+
+Inxi在多数现代GNU/Linux操作系统的默认软件仓库中。所以我们可以简单地运行下列命令安装。
+
+**在基于Debian的发行版:**
+
+ sudo apt-get install inxi
+
+**在Fedora:**
+
+ sudo yum install inxi
+
+**在基于RHEL的发行版:**
+
+安装EPEL软件仓库:
+
+ sudo yum install epel-release
+
+然后使用如下命令安装inxi:
+
+ sudo yum install inxi
+
+### 使用方法 ###
+
+在终端运行如下命令可以获取系统的概况信息。
+
+ inxi
+
+**示例输出:**
+
+ CPU~Dual core Intel Core i3-2350M CPU (-HT-MCP-) clocked at Min:800.000Mhz Max:1200.000Mhz Kernel~3.13.0-45-generic x86_64 Up~6:41 Mem~1537.7/3861.3MB HDD~500.1GB(52.5% used) Procs~183 Client~Shell inxi~1.9.17
+
+当然,我们可以获取一个特定硬件的详情信息。比如获取**声音/音频硬件详情信息**,可以运行如下命令:
+
+ inxi -A
+
+**示例输出:**
+
+ Audio: Card: Intel 6 Series/C200 Series Family High Definition Audio Controller driver: snd_hda_intel
+ Sound: Advanced Linux Sound Architecture ver: k3.13.0-45-generic
+
+很酷是吧?
+
+同样的,你可以获取**显卡**的详情信息。
+
+ inxi -G
+
+**示例输出:**
+
+ Graphics: Card: Intel 2nd Generation Core Processor Family Integrated Graphics Controller
+ X.Org: 1.15.1 drivers: intel (unloaded: fbdev,vesa) Resolution: 1366x768@60.0hz
+ GLX Renderer: Mesa DRI Intel Sandybridge Mobile GLX Version: 3.0 Mesa 10.3.0
+
+硬盘信息呢?也是可以的。运行如下命令来获取完整的**硬盘**信息。
+
+ inxi -D
+
+**示例输出:**
+
+ Drives: HDD Total Size: 500.1GB (52.5% used) 1: id: /dev/sda model: ST9601325BD size: 500.1GB
+
+显示Bios和主板详情信息:
+
+ inxi -M
+
+**示例输出:**
+
+ Machine: System: Dell (portable) product: Inspiron N5050
+ Mobo: Dell model: 01HXXJ version: A05 Bios: Dell version: A05 date: 08/03/2012
+
+不仅是硬性详情信息,它也可以显示我们系统中的**可用软件仓库列表**。
+
+ inxi -r
+
+**示例输出:**
+
+ Repos: Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list
+ deb http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty main restricted
+ deb-src http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty main restricted
+ deb http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty-updates main restricted
+ deb-src http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty-updates main restricted
+ deb http://ubuntu.excellmedia.net/archive/ trusty universe
+ .
+ .
+ Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/intellinuxgraphics.list
+ deb https://download.01.org/gfx/ubuntu/14.04/main trusty main #Intel Graphics drivers
+ Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/linrunner-tlp-trusty.list
+ Active apt sources in file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/wseverin-ppa-trusty.list
+ deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/wseverin/ppa/ubuntu trusty main
+
+Inxi还可以显示你所在位置的天气信息。感到意外吗?是的,它可以。
+
+ inxi -W Erode,Tamilnadu
+
+这里**Erode**是地区,**Tamilnadu**是印度的一个邦。
+
+示例输出:
+
+ Weather: Conditions: 79 F (26 C) - Clear Time: February 4, 6:00 PM IST
+
+### 查看完整的硬件详情信息 ###
+
+厌倦了逐一获取每种硬件的信息?你可以使用如下命令将所有信息一次列出:
+
+ inxi -F
+
+**示例输出:**
+
+ System: Host: sk Kernel: 3.13.0-45-generic x86_64 (64 bit) Desktop: LXDE (Openbox 3.5.2) Distro: Ubuntu 14.04 trusty
+ Machine: System: Dell (portable) product: Inspiron N5050
+ Mobo: Dell model: 01HXXJ version: A05 Bios: Dell version: A05 date: 08/03/2012
+ CPU: Dual core Intel Core i3-2350M CPU (-HT-MCP-) cache: 3072 KB flags: (lm nx sse sse2 sse3 sse4_1 sse4_2 ssse3 vmx)
+ Clock Speeds: 1: 800.00 MHz 2: 1000.00 MHz 3: 800.00 MHz 4: 800.00 MHz
+ Graphics: Card: Intel 2nd Generation Core Processor Family Integrated Graphics Controller
+ X.Org: 1.15.1 drivers: intel (unloaded: fbdev,vesa) Resolution: 1366x768@60.0hz
+ GLX Renderer: Mesa DRI Intel Sandybridge Mobile GLX Version: 3.0 Mesa 10.3.0
+ Audio: Card: Intel 6 Series/C200 Series Family High Definition Audio Controller driver: snd_hda_intel
+ Sound: Advanced Linux Sound Architecture ver: k3.13.0-45-generic
+ Network: Card-1: Qualcomm Atheros AR9285 Wireless Network Adapter (PCI-Express) driver: ath9k
+ IF: wlan0 state: up mac:
+ Card-2: Realtek RTL8101E/RTL8102E PCI Express Fast Ethernet controller driver: r8169
+ IF: eth0 state: down mac:
+ Drives: HDD Total Size: 500.1GB (52.5% used) 1: id: /dev/sda model: ST9500325AS size: 500.1GB
+ Partition: ID: / size: 455G used: 245G (57%) fs: ext4 ID: /boot size: 236M used: 159M (72%) fs: ext2
+ ID: swap-1 size: 4.19GB used: 0.00GB (0%) fs: swap
+ RAID: No RAID devices detected - /proc/mdstat and md_mod kernel raid module present
+ Sensors: System Temperatures: cpu: 64.5C mobo: N/A
+ Fan Speeds (in rpm): cpu: N/A
+ Info: Processes: 186 Uptime: 6:52 Memory: 1547.2/3861.3MB Client: Shell (bash) inxi: 1.9.17
+
+就像上面你看到的那样,inxi显示出了完整的硬件详情信息。
+
+更多的细节可以参考man手册。
+
+ man inxi
+
+### 结论 ###
+
+你在寻找一个可以显示完整的系统和硬件详情信息的简单工具吗?那么不用再找了,inxi会提供你所需要的。并且,它还是在你系统默认的软件仓库中的轻量级工具。你还想要更多东西吗?试一试它,你不会失望。
+
+欢呼吧!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/inxi-find-system-hardware-information-linux/
+
+作者:[SK][a]
+译者:[goreliu](https://github.com/goreliu)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
+[1]:https://linux.cn/article-1947-1.html
diff --git a/published/201505/20150205 zBackup--A versatile deduplicating backup tool.md b/published/201505/20150205 zBackup--A versatile deduplicating backup tool.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c0d9e85128
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150205 zBackup--A versatile deduplicating backup tool.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+zBackup:一个多功能的去重备份工具
+================================================================================
+zbackup是一个基于rsync思想的全局去重数据备份工具。给它传入一个大的tar文件后,它会仅存储一次该文件的重复部分,然后对结果进行压缩,并根据参数确定是否对其加密。传入另一个tar文件后,它会从之前的已备份文件中复用重复数据。只有新的改动会被保存,并且只要文件差异不是很大,需要的存储空间非常少。无论何时,之前的已备份文件都可以被完整地读出来。
+
+### zBackup特性 ###
+
+- 使用并行的LZMA或者LZO压缩算法压缩已备份数据
+- 使用内置的AES加密算法加密已备份数据
+- 可以删除旧的已备份数据
+- 使用一个64位滚动哈希,保持软碰撞数量为0
+- 备份库由不可更改的文件组成,只有库中不存在的文件才能修改
+- 使用C++语言编写,并且只有适量的依赖库
+- 可以在生产环境安全使用
+- 可以在不同备份库中交换数据而无需重新压缩
+
+### 在ubuntu中安装zBackup ###
+
+打开终端并运行如下命令:
+
+ sudo apt-get install zbackup
+
+### 使用zBackup ###
+
+`zbackup init`命令会初始化一个备份库,用来存放待备份的数据。
+
+ zbackup init [--non-encrypted] [--password-file ~/.my_backup_password ] /my/backup/repo
+
+`zbackup backup`命令备份一个由`tar c`命令创建的tar文件到刚才使用`zbackup init`初始化的备份库。(LCTT 译注:实际使用时类似这样,tar c files | zbackup ...)
+
+ zbackup [--password-file ~/.my_backup_password ] [--threads number_of_threads ] backup /my/backup/repo/backups/backup-`date ‘+%Y-%m-%d'`
+
+`zbackup restore`命令从备份库中恢复一个已备份文件到tar文件中。
+
+ zbackup [--password-file ~/.my_backup_password ] [--cache-size cache_size_in_mb ] restore /my/backup/repo/backups/backup-`date ‘+%Y-%m-%d'` > /my/precious/backup-restored.tar
+
+### 可用选项 ###
+
+- -non-encrypted -- 不加密备份库。
+- --password-file ~/.my_backup_password -- 使用位于~/.my_backup_password的口令文件来加密备份库和待备份文件,以及解密已备份文件。
+- --threads number_of_threads -- 限制并行LZMA压缩的线程数为 number_of_threads。建议在32位的系统平台使用。
+- --cache-size cache_size_in_mb -- 使用cache_size_in_mb中的缓存大小来加速恢复文件的过程。
+
+### 上述命令中 zBackup 相关文件 ###
+
+- ~/.my_backup_password 用来加密备份库和待备份文件,以及解密已备份文件。更多细节见zbackup。
+- /my/backup/repo 存放备份库的目录。
+- /my/precious/restored-tar 用来恢复已备份文件的tar文件。
+- /my/backup/repo/backups/backup-`date ‘+%Y-%m-%d'` 指定的之前已备份文件的文件名。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/zbackup-a-versatile-deduplicating-backup-tool.html
+
+作者:[ruchi][a]
+译者:[goreliu](https://github.com/goreliu)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150211 25 Tips for Intermediate Git Users.md b/published/201505/20150211 25 Tips for Intermediate Git Users.md
similarity index 82%
rename from translated/tech/20150211 25 Tips for Intermediate Git Users.md
rename to published/201505/20150211 25 Tips for Intermediate Git Users.md
index a1c1dd8328..205c83aaef 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150211 25 Tips for Intermediate Git Users.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150211 25 Tips for Intermediate Git Users.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
-25个给git熟手的技巧
+25个 Git 进阶技巧
================================================================================
-我已经使用git差不多18个月了,觉得自己对它应该已经非常了解。然后来自GitHub的[Scott Chacon][1]过来给LVS做培训,[LVS是一个赌博软件供应商和开发商][2](从2013年开始的合同),而我在第一天里就学到了很多。
+我已经使用git差不多18个月了,觉得自己对它应该已经非常了解。然后来自GitHub的[Scott Chacon][1]过来给LVS做培训([LVS是一个赌博软件供应商和开发商][2],从2013年开始的合同),而我在第一天里就学到了很多。
作为一个对git感觉良好的人,我觉得分享从社区里掌握的一些有价值的信息,也许能帮某人解决问题而不用做太深入研究。
@@ -15,21 +15,21 @@
#### 2. Git是基于指针的 ####
-保存在git里的一切都是文件。当你创建一个提交的时候,会建立一个包含你的提交信息和相关数据(名字,邮件地址,日期/时间,前一个提交,等等)的文件,并把它链接到一个文件树中。文件树中包含了对象或其他树的列表。对象或容器是和本次提交相关的实际内容(也是一个文件,你想了解的话,尽管文件名并没有包含在对象里,而是在树中)。所有这些文件都使用对象的SHA-1哈希值作为文件名。
+保存在git里的一切都是文件。当你创建一个提交的时候,会建立一个包含你的提交信息和相关数据(名字,邮件地址,日期/时间,前一个提交,等等)的文件,并把它链接到一个树文件中。这个树文件中包含了对象或其他树的列表。这里的提到的对象(或二进制大对象)是和本次提交相关的实际内容(它也是一个文件,另外,尽管文件名并没有包含在对象里,但是存储在树中)。所有这些文件都使用对象的SHA-1哈希值作为文件名。
-用这种方式,分支和标签就是简单的文件(基本上是这样),包含指向实际提交的SHA-1哈希值。使用这些索引会带来优秀的灵活性和速度,比如创建一个新分支就只要简单地创建一个包含分支名字和所分出的那个提交的SHA-1索引的文件。当然,你不需要自己做这些,而只要使用Git命令行工具(或者GUI),但是实际上就是这么简单。
+用这种方式,分支和标签就是简单的文件(基本上是这样),包含指向该提交的SHA-1哈希值。使用这些索引会带来优秀的灵活性和速度,比如创建一个新分支就是简单地用分支名字和所分出的那个提交的SHA-1索引来创建一个文件。当然,你不需要自己做这些,而只要使用Git命令行工具(或者GUI),但是实际上就是这么简单。
-你也许听说过叫HEAD的索引。这只是简单的一个文件,包含了你当前指向的那个提交的SHA-1索引值。如果你正在解决一次合并冲突然后看到了HEAD,这并不是一个特别的分支或分值上一个必须的特殊点,只是标明你当前所在位置。
+你也许听说过叫HEAD的索引。这只是简单的一个文件,包含了你当前指向的那个提交的SHA-1索引值。如果你正在解决一次合并冲突然后看到了HEAD,这并不是一个特别的分支或分支上的一个必需的特殊位置,只是标明你当前所在位置。
-所有的分支指针都保存在.git/refs/heads里,HEAD在.git/HEAD里,而标签保存在.git/refs/tags里 - 自己可以放心地进去看看。
+所有的分支指针都保存在.git/refs/heads里,HEAD在.git/HEAD里,而标签保存在.git/refs/tags里 - 自己可以随便进去看看。
-#### 3. 两个父节点 - 当然! ####
+#### 3. 两个爸爸(父节点) - 你没看错! ####
-在历史中查看一个合并提交的信息时,你将看到有两个父节点(相对于一般工作上的常规提交的情况)。第一个父节点是你所在的分支,第二个是你合并过来的分支。
+在历史中查看一个合并提交的信息时,你将看到有两个父节点(不同于工作副本上的常规提交的情况)。第一个父节点是你所在的分支,第二个是你合并过来的分支。
#### 4. 合并冲突 ####
-目前我相信你碰到过合并冲突并且解决过。通常是编辑一下文件,去掉<<<<,====,>>>>标志,保留需要留下的代码。有时能够看到这两个修改之前的代码会很不错,比如,在这两个分支上有冲突的改动之前。下面是一种方式:
+目前我相信你碰到过合并冲突并且解决过。通常是编辑一下文件,去掉<<<<,====,>>>>标志,保留需要留下的代码。有时能够看到这两个修改之前的代码会很不错,比如,在这两个现在冲突的分支之前的改动。下面是一种方式:
$ git diff --merge
diff --cc dummy.rb
@@ -45,14 +45,14 @@
end
end
-如果是二进制文件,比较差异就没那么简单了...通常你要做的就是测试这个二进制文件的两个版本来决定保留哪个(或者在二进制文件编辑器里手工复制冲突部分)。从一个特定分支获取文件拷贝(比如说你在合并master和feature123):
+如果是二进制文件,比较差异就没那么简单了...通常你要做的就是测试这个二进制文件的两个版本来决定保留哪个(或者在二进制文件编辑器里手工复制冲突部分)。从一个特定分支获取文件拷贝(比如说你在合并master和feature123两个分支):
$ git checkout master flash/foo.fla # 或者...
$ git checkout feature132 flash/foo.fla
$ # 然后...
$ git add flash/foo.fla
-另一种方式是通过git输出文件 - 你可以输出到另外的文件名,然后再重命名正确的文件(当你决定了要用哪个)为正常的文件名:
+另一种方式是通过git输出文件 - 你可以输出到另外的文件名,然后当你决定了要用哪个后,再将选定的正确文件复制为正常的文件名:
$ git show master:flash/foo.fla > master-foo.fla
$ git show feature132:flash/foo.fla > feature132-foo.fla
@@ -71,7 +71,7 @@
#### 5. 远端服务器 ####
-git的一个超强大的功能就是可以有不止一个远端服务器(实际上你一直都在一个本地仓库上工作)。你并不是一定都要有写权限,你可以有多个可以读取的服务器(用来合并他们的工作)然后写入其他仓库。添加一个新的远端服务器很简单:
+git的一个超强大的功能就是可以有不止一个远端服务器(实际上你一直都在一个本地仓库上工作)。你并不是一定都要有这些服务器的写权限,你可以有多个可以读取的服务器(用来合并他们的工作)然后写入到另外一个仓库。添加一个新的远端服务器很简单:
$ git remote add john git@github.com:johnsomeone/someproject.git
@@ -87,10 +87,10 @@ git的一个超强大的功能就是可以有不止一个远端服务器(实
$ git diff master..john/master
-你也可以查看不在远端分支的HEAD的改动:
+你也可以查看没有在远端分支上的HEAD的改动:
$ git log remote/branch..
- # 注意:..后面没有结束的refspec
+ # 注意:..后面没有结束的特定引用
#### 6. 标签 ####
@@ -99,7 +99,7 @@ git的一个超强大的功能就是可以有不止一个远端服务器(实
建立这两种类型的标签都很简单(只有一个命令行开关的差异)
$ git tag to-be-tested
- $ git tag -a v1.1.0 # 会提示输入标签信息
+ $ git tag -a v1.1.0 # 会提示输入标签的信息
#### 7. 建立分支 ####
@@ -108,7 +108,7 @@ git的一个超强大的功能就是可以有不止一个远端服务器(实
$ git branch feature132
$ git checkout feature132
-当然,如果你确定自己要新建分支并直接切换过去,可以用一个命令实现:
+当然,如果你确定自己直接切换到新建的分支,可以用一个命令实现:
$ git checkout -b feature132
@@ -117,20 +117,20 @@ git的一个超强大的功能就是可以有不止一个远端服务器(实
$ git checkout -b twitter-experiment feature132
$ git branch -d feature132
-更新:你也可以(像Brian Palmer在原博客文章的评论里提出的)只用“git branch”的-m开关在一个命令里实现(像Mike提出的,如果你只有一个分支参数,就会重命名当前分支):
+更新:你也可以(像Brian Palmer在原博客文章的评论里提出的)只用“git branch”的-m开关在一个命令里实现(像Mike提出的,如果你只指定了一个分支参数,就会重命名当前分支):
$ git branch -m twitter-experiment
$ git branch -m feature132 twitter-experiment
#### 8. 合并分支 ####
-在将来什么时候,你希望合并改动。有两种方式:
+也许在将来的某个时候,你希望将改动合并。有两种方式:
$ git checkout master
$ git merge feature83 # 或者...
$ git rebase feature83
-merge和rebase之间的差别是merge会尝试处理改动并建立一个新的混合了两者的提交。rebase会尝试把你从一个分支最后一次分离后的所有改动,一个个加到该分支的HEAD上。不过,在已经将分支推到远端服务器后不要再rebase了 - 这回引起冲突/问题。
+merge和rebase之间的差别是merge会尝试处理改动并建立一个新的混合了两者的提交。rebase会尝试把你从一个分支最后一次分离后的所有改动,一个个加到该分支的HEAD上。不过,在已经将分支推到远端服务器后不要再rebase了 - 这会引起冲突/问题。
如果你不确定在哪些分支上还有独有的工作 - 所以你也不知道哪些分支需要合并而哪些可以删除,git branch有两个开关可以帮你:
@@ -147,7 +147,7 @@ merge和rebase之间的差别是merge会尝试处理改动并建立一个新的
$ git push origin twitter-experiment:refs/heads/twitter-experiment
# origin是我们服务器的名字,而twitter-experiment是分支名字
-更新:感谢Erlend在原博客文章上的评论 - 这个实际上和`git push origin twitter-experiment`效果一样,不过使用完整的语法,你可以在两者之间使用不同的分知名(这样本地分支可以是`add-ssl-support`而远端是`issue-1723`)。
+更新:感谢Erlend在原博客文章上的评论 - 这个实际上和`git push origin twitter-experiment`效果一样,不过使用完整的语法,你可以在两者之间使用不同的分支名(这样本地分支可以是`add-ssl-support`而远端是`issue-1723`)。
如果你想在远端服务器上删除一个分支(注意分支名前面的冒号):
@@ -210,7 +210,7 @@ git会基于当前的提交信息自动创建评论。如果你更希望有自
这会让你进入一个基于菜单的交互式提示。你可以使用命令中的数字或高亮的字母(如果你在终端里打开了高亮的话)来进入相应的模式。然后就只是输入你希望操作的文件的数字了(你可以使用这样的格式,1或者1-4或2,4,7)。
-如果你想进入补丁模式(交互式模式下的‘p’或‘5’),你也可以直接进入:
+如果你想进入补丁模式(交互式模式下按‘p’或‘5’),你也可以直接进入:
$ git add -p
diff --git a/dummy.rb b/dummy.rb
@@ -226,11 +226,11 @@ git会基于当前的提交信息自动创建评论。如果你更希望有自
end
Stage this hunk [y,n,q,a,d,/,e,?]?
-你可以看到下方会有一些选项供选择用来添加该文件的这个改动,该文件的所有改动,等等。使用‘?’命令可以详细解释这些选项。
+你可以看到下方会有一些选项供选择用来添加该文件的这个改动、该文件的所有改动,等等。使用‘?’命令可以详细解释这些选项。
#### 12. 从文件系统里保存/取回改动 ####
-有些项目(比如git项目本身)在git文件系统中直接保存额外文件而并没有将它们加入到版本控制中。
+有些项目(比如Git项目本身)在git文件系统中直接保存额外文件而并没有将它们加入到版本控制中。
让我们从在git中存储一个随机文件开始:
@@ -251,7 +251,7 @@ git会基于当前的提交信息自动创建评论。如果你更希望有自
#### 13. 查看日志 ####
-如果不用‘git log’来查看最近的提交你git用不了多久。不过,有一些技巧来更好地应用。比如,你可以使用下面的命令来查看每次提交的具体改动:
+长时间使用 Git 的话,不会没用过‘git log’来查看最近的提交。不过,有一些技巧来更好地应用。比如,你可以使用下面的命令来查看每次提交的具体改动:
$ git log -p
@@ -268,7 +268,7 @@ git会基于当前的提交信息自动创建评论。如果你更希望有自
#### 14. 搜索日志 ####
-如果你想找特定作者可以这样做:
+如果你想找特定提交者可以这样做:
$ git log --author=Andy
@@ -278,7 +278,7 @@ git会基于当前的提交信息自动创建评论。如果你更希望有自
$ git log --grep="Something in the message"
-也有一个更强大的叫做pickaxe的命令用来查找删除或添加某个特定内容的提交(比如,该文件第一次出现或被删除)。这可以告诉你什么时候增加了一行(但这一行里的某个字符后面被改动过就不行了):
+也有一个更强大的叫做pickaxe的命令用来查找包含了删除或添加的某个特定内容的提交(比如,该内容第一次出现或被删除)。这可以告诉你什么时候增加了一行(但这一行里的某个字符后面被改动过就不行了):
$ git log -S "TODO: Check for admin status"
@@ -294,7 +294,7 @@ git会基于当前的提交信息自动创建评论。如果你更希望有自
$ git log --since=2.months.ago --until=1.day.ago
-默认情况下会用OR来组合查询,但你可以轻易地改为AND(如果你有超过一条的标准)
+默认情况下会用OR来组合查询,但你可以轻易地改为AND(如果你有超过一条的查询标准)
$ git log --since=2.months.ago --until=1.day.ago --author=andy -S "something" --all-match
@@ -310,7 +310,7 @@ git会基于当前的提交信息自动创建评论。如果你更希望有自
$ git show feature132@{yesterday} # 时间相关
$ git show feature132@{2.hours.ago} # 时间相关
-注意和之前部分有些不同,末尾的插入符号意思是该提交的父节点 - 开始位置的插入符号意思是不在这个分支。
+注意和之前部分有些不同,末尾的^的意思是该提交的父节点 - 开始位置的^的意思是不在这个分支。
#### 16. 选择范围 ####
@@ -321,7 +321,7 @@ git会基于当前的提交信息自动创建评论。如果你更希望有自
你也可以省略[new],将使用当前的HEAD。
-### Rewinding Time & Fixing Mistakes ###
+### 时光回溯和后悔药 ###
#### 17. 重置改动 ####
@@ -329,7 +329,7 @@ git会基于当前的提交信息自动创建评论。如果你更希望有自
$ git reset HEAD lib/foo.rb
-通常会使用‘unstage’的别名,因为看上去有些不直观。
+通常会使用‘unstage’的别名,因为上面的看上去有些不直观。
$ git config --global alias.unstage "reset HEAD"
$ git unstage lib/foo.rb
@@ -369,11 +369,11 @@ git会基于当前的提交信息自动创建评论。如果你更希望有自
#### 19. 交互式切换基础 ####
-这是一个我之前看过展示却没真正理解过的很赞的功能,现在很简单。假如说你提交了3次但是你希望更改顺序或编辑(或者合并):
+这是一个我之前看过展示却没真正理解过的很赞的功能,现在觉得它就很简单了。假如说你提交了3次但是你希望更改顺序或编辑(或者合并):
$ git rebase -i master~3
-然后会启动你的编辑器并带有一些指令。你所要做的就是修改这些指令来选择/插入/编辑(或者删除)提交和保存/退出。然后在编辑完后你可以用`git rebase --continue`命令来让每一条指令生效。
+然后这会启动你的编辑器并带有一些指令。你所要做的就是修改这些指令来选择/插入/编辑(或者删除)提交和保存/退出。然后在编辑完后你可以用`git rebase --continue`命令来让每一条指令生效。
如果你有修改,将会切换到你提交时所处的状态,之后你需要使用命令git commit --amend来编辑。
@@ -446,7 +446,7 @@ git会基于当前的提交信息自动创建评论。如果你更希望有自
$ git branch experimental SHA1_OF_HASH
-如果你访问过的话,你通常可以用git reflog来找到SHA1哈希值。
+如果你最近访问过的话,你通常可以用git reflog来找到SHA1哈希值。
另一种方式是使用`git fsck —lost-found`。其中一个dangling的提交就是丢失的HEAD(它只是已删除分支的HEAD,而HEAD^被引用为当前的HEAD所以它并不处于dangling状态)
@@ -460,7 +460,7 @@ via: https://www.andyjeffries.co.uk/25-tips-for-intermediate-git-users/
作者:[Andy Jeffries][a]
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150211 Install Linux-Dash (Web Based Monitoring tool) on Ubntu 14.10.md b/published/201505/20150211 Install Linux-Dash (Web Based Monitoring tool) on Ubntu 14.10.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..97641f0298
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150211 Install Linux-Dash (Web Based Monitoring tool) on Ubntu 14.10.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+在Ubuntu 14.10上安装基于Web的监控工具:Linux-Dash
+================================================================================
+
+Linux-Dash是一个用于GNU/Linux机器的,低开销的监控仪表盘。您可以安装试试!Linux Dash的界面提供了您的服务器的所有关键信息的详细视图,可监测的信息包括RAM、磁盘使用率、网络、安装的软件、用户、运行的进程等。所有的信息都被分成几类,您可以通过主页工具栏中的按钮跳到任何一类中。Linux Dash并不是最先进的监测工具,但它十分适合寻找灵活、轻量级、容易部署的应用的用户。
+
+### Linux-Dash的功能 ###
+
+- 使用一个基于Web的漂亮的仪表盘界面来监控服务器信息
+- 实时的按照你的要求监控RAM、负载、运行时间、磁盘配置、用户和许多其他系统状态
+- 支持基于Apache2/niginx + PHP的服务器
+- 通过点击和拖动来重排列控件
+- 支持多种类型的linux服务器
+
+### 当前控件列表 ###
+
+- 通用信息
+- 平均负载
+- RAM
+- 磁盘使用量
+- 用户
+- 软件
+- IP
+- 网络速率
+- 在线状态
+- 处理器
+- 日志
+
+### 在Ubuntu server 14.10上安装Linux-Dash ###
+
+首先您需要确认您安装了[Ubuntu LAMP server 14.10][1],接下来您需要安装下面的包:
+
+ sudo apt-get install php5-json unzip
+
+安装这个模块后,需要在apache2中启用该模块,所以您需要使用下面的命令重启apache2服务器:
+
+ sudo service apache2 restart
+
+现在您需要下载linux-dash的安装包并安装它:
+
+ wget https://github.com/afaqurk/linux-dash/archive/master.zip
+
+ unzip master.zip
+
+ sudo mv linux-dash-master/ /var/www/html/linux-dash-master/
+
+接下来您需要使用下面的命令来改变权限:
+
+ sudo chmod 755 /var/www/html/linux-dash-master/
+
+现在您便可以访问http://serverip/linux-dash-master/了。您应该会看到类似下面的输出:
+
+
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/install-linux-dash-web-based-monitoring-tool-on-ubntu-14-10.html
+
+作者:[ruchi][a]
+译者:[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
+[1]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/step-by-step-ubuntu-14-10-utopic-unicorn-lamp-server-setup.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150225 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to disable IPv6 on Linux.md b/published/201505/20150225 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to disable IPv6 on Linux.md
similarity index 69%
rename from translated/tech/20150225 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to disable IPv6 on Linux.md
rename to published/201505/20150225 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to disable IPv6 on Linux.md
index 30ad533adc..17c6ccefaa 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150225 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to disable IPv6 on Linux.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150225 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to disable IPv6 on Linux.md
@@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
-Linux有问必答时间--如何在Linux下禁用IPv6
+Linux有问必答:如何在Linux下禁用IPv6
================================================================================
-> **问题**:我发现我的一个应用程序在尝试通过IPv6建立连接,但是由于我们本地网络不允许分配IPv6的流量,IPv6连接会超时,应用程序的连接会退回到IPv4,这样就会造成不必要的延迟。由于我目前对IPv6没有任何需求,所以我想在我的Linux主机上禁用IPv6。有什么比较合适的方法呢?
+> **问题**:我发现我的一个应用程序在尝试通过IPv6建立连接,但是由于我们本地网络不允许分配IPv6的流量,IPv6连接会超时,应用程序的连接会回退到IPv4,这样就会造成不必要的延迟。由于我目前对IPv6没有任何需求,所以我想在我的Linux主机上禁用IPv6。有什么比较合适的方法呢?
-IPv6被认为是IPv4——互联网上的传统32位地址空间的替代产品,它为了解决现有IPv4地址空间即将耗尽的问题。然而,由于IPv4已经被每台主机或设备连接到了互联网上,所以想在一夜之间将它们全部切换到IPv6几乎是不可能的。许多IPv4到IPv6的转换机制(例如:双协议栈、网络隧道、代理) 已经被提出来用来促进IPv6能被采用,并且很多应用也正在进行重写,就像我们所说的,来增加对IPv6的支持。有一件事情能确定,就是在可预见的未来里IPv4和IPv6势必将共存。
+IPv6被认为是IPv4——互联网上的传统32位地址空间——的替代产品,它用来解决现有IPv4地址空间即将耗尽的问题。然而,由于已经有大量主机、设备用IPv4连接到了互联网上,所以想在一夜之间将它们全部切换到IPv6几乎是不可能的。许多IPv4到IPv6的转换机制(例如:双协议栈、网络隧道、代理) 已经被提出来用来促进IPv6能被采用,并且很多应用也正在进行重写,如我们所提倡的,来增加对IPv6的支持。有一件事情可以确定,就是在可预见的未来里IPv4和IPv6势必将共存。
-理想情况下,[向IPv6过渡的进程][1]不应该被最终的用户所看见,但是IPv4/IPv6混合环境有时会让你碰到各种源于IPv4和IPv6之间不经意间的相互作用的问题。举个例子,你会碰到应用程序超时的问题比如apt-get或ssh尝试通过IPv6连接失败、DNS服务器意外清空了IPv6的AAAA记录、或者你支持IPv6的设备不兼容你的互联网服务提供商遗留下的IPv4网络等等等等。
+理想情况下,[向IPv6过渡的进程][1]不应该被最终的用户所看见,但是IPv4/IPv6混合环境有时会让你碰到各种源于IPv4和IPv6之间不经意间的相互碰撞的问题。举个例子,你会碰到应用程序超时的问题,比如apt-get或ssh尝试通过IPv6连接失败、DNS服务器意外清空了IPv6的AAAA记录、或者你支持IPv6的设备不兼容你的互联网服务提供商遗留下的IPv4网络,等等等等。
-当然这不意味着你应该盲目地在你的Linux机器上禁用IPv6。鉴于IPv6许诺的种种好处,作为社会的一份子我们最终还是要充分拥抱它的,但是作为给最终用户进行故障排除过程的一部分,如果IPv6确实是罪魁祸首那你可以尝试去关闭它。
+当然这不意味着你应该盲目地在你的Linux机器上禁用IPv6。鉴于IPv6许诺的种种好处,作为社会的一份子我们最终还是要充分拥抱它的,但是作为给最终用户进行故障排除过程的一部分,如果IPv6确实是罪魁祸首,那你可以尝试去关闭它。
-这里有一些让你在Linux中部分或全部禁用IPv6的小技巧(例如:为一个已经确定的网络接口)。这些小贴士应该适用于所有主流的Linux发行版包括Ubuntu、Debian、Linux Mint、CentOS、Fedora、RHEL以及Arch Linux。
+这里有一些让你在Linux中部分(例如:对于某个特定的网络接口)或全部禁用IPv6的小技巧。这些小贴士应该适用于所有主流的Linux发行版包括Ubuntu、Debian、Linux Mint、CentOS、Fedora、RHEL以及Arch Linux。
### 查看IPv6在Linux中是否被启用 ###
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ IPv6被认为是IPv4——互联网上的传统32位地址空间的替代产品
### 临时禁用IPv6 ###
-如果你想要在你的Linux系统上临时关闭IPv6,你可以用 /proc 文件系统。"临时",意思是我们所做的禁用IPv6的更改在系统重启后将不被保存。IPv6会在你的Linux机器重启后再次被启用。
+如果你想要在你的Linux系统上临时关闭IPv6,你可以用 /proc 文件系统。"临时"的意思是我们所做的禁用IPv6的更改在系统重启后将不被保存。IPv6会在你的Linux机器重启后再次被启用。
要将一个特定的网络接口禁用IPv6,使用以下命令:
@@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ IPv6被认为是IPv4——互联网上的传统32位地址空间的替代产品
#### 方法一 ####
-第一种方法是请求以上提到的 /proc 对 /etc/sysctl.conf 文件进行修改。
+第一种方法是通过 /etc/sysctl.conf 文件对 /proc 进行永久修改。
换句话说,就是用文本编辑器打开 /etc/sysctl.conf 然后添加以下内容:
@@ -69,7 +69,7 @@ IPv6被认为是IPv4——互联网上的传统32位地址空间的替代产品
#### 方法二 ####
-另一个永久禁用IPv6的方法是在开机的时候执行一个必要的内核参数。
+另一个永久禁用IPv6的方法是在开机的时候传递一个必要的内核参数。
用文本编辑器打开 /etc/default/grub 并给GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX变量添加"ipv6.disable=1"。
@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ IPv6被认为是IPv4——互联网上的传统32位地址空间的替代产品
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="xxxxx ipv6.disable=1"
-上面的"xxxxx"代表任意存在着的内核参数,在它后面添加"ipv6.disable=1"。
+上面的"xxxxx"代表任何已有的内核参数,在它后面添加"ipv6.disable=1"。

@@ -97,7 +97,7 @@ Fedora、CentOS/RHEL系统:
### 禁用IPv6之后的其它可选步骤 ###
-这里有一些可选步骤在你禁用IPv6后需要考虑,这是因为当你在内核里禁用IPv6后,其它程序仍然会尝试使用IPv6。在大多数情况下,例如应用程序的运转状态不太会遭到破坏,但是出于效率或安全方面的原因,你要为他们禁用IPv6。
+这里有一些在你禁用IPv6后需要考虑的可选步骤,这是因为当你在内核里禁用IPv6后,其它程序也许仍然会尝试使用IPv6。在大多数情况下,应用程序的这种行为不太会影响到什么,但是出于效率或安全方面的原因,你可以为他们禁用IPv6。
#### /etc/hosts ####
@@ -124,7 +124,7 @@ Fedora、CentOS/RHEL系统:
默认情况下,OpenSSH服务(sshd)会去尝试捆绑IPv4和IPv6的地址。
-要强制sshd只捆绑IPv4地址,用文本编辑器打开 /etc/ssh/sshd_config 并添加以下脚本行。inet只适用于IPv4,而inet6是适用于IPv6的。
+要强制sshd只捆绑IPv4地址,用文本编辑器打开 /etc/ssh/sshd_config 并添加以下行。inet只适用于IPv4,而inet6是适用于IPv6的。
$ sudo vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
@@ -140,7 +140,7 @@ via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/disable-ipv6-linux.html
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150227 Bringing a Bunch of Best Known Linux Network Tools.md b/published/201505/20150227 Bringing a Bunch of Best Known Linux Network Tools.md
similarity index 65%
rename from translated/tech/20150227 Bringing a Bunch of Best Known Linux Network Tools.md
rename to published/201505/20150227 Bringing a Bunch of Best Known Linux Network Tools.md
index 112147414a..892ba048d0 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150227 Bringing a Bunch of Best Known Linux Network Tools.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150227 Bringing a Bunch of Best Known Linux Network Tools.md
@@ -1,18 +1,18 @@
-领略一些最著名的 Linux 网络工具
+一大波你可能不知道的 Linux 网络工具
================================================================================
-在你的系统上使用命令行工具来监控你的网络是非常实用的,并且对于 Linux 用户来说,有着许许多多现成的工具可以使用,如 nethogs, ntopng, nload, iftop, iptraf, bmon, slurm, tcptrack, cbm, netwatch, collectl, trafshow, cacti, etherape, ipband, jnettop, netspeed 以及 speedometer。
+如果要在你的系统上监控网络,那么使用命令行工具是非常实用的,并且对于 Linux 用户来说,有着许许多多现成的工具可以使用,如: nethogs, ntopng, nload, iftop, iptraf, bmon, slurm, tcptrack, cbm, netwatch, collectl, trafshow, cacti, etherape, ipband, jnettop, netspeed 以及 speedometer。
鉴于世上有着许多的 Linux 专家和开发者,显然还存在其他的网络监控工具,但在这篇教程中,我不打算将它们所有包括在内。
-上面列出的工具都有着自己的独特之处,但归根结底,它们都做着监控网络流量的工作,且并不是只有一种方法来完成这件事。例如 nethogs 可以被用来展示每个进程的带宽使用情况,以防你想知道究竟是哪个应用在消耗了你的整个网络资源; iftop 可以被用来展示每个套接字连接的带宽使用情况,而 像 nload 这类的工具可以帮助你得到有关整个带宽的信息。
+上面列出的工具都有着自己的独特之处,但归根结底,它们都做着监控网络流量的工作,只是通过各种不同的方法。例如 nethogs 可以被用来展示每个进程的带宽使用情况,以防你想知道究竟是哪个应用在消耗了你的整个网络资源; iftop 可以被用来展示每个套接字连接的带宽使用情况,而像 nload 这类的工具可以帮助你得到有关整个带宽的信息。
### 1) nethogs ###
-nethogs 是一个免费的工具,当要查找哪个 PID (注:即 process identifier,进程 ID) 给你的网络流量带来了麻烦时,它是非常方便的。它按每个进程来组织带宽,而不是像大多数的工具那样按照每个协议或每个子网来划分流量。它功能丰富,同时支持 IPv4 和 IPv6,并且我认为,若你想在你的 Linux 主机上确定哪个程序正消耗着你的全部带宽,它是来做这件事的最佳的程序。
+nethogs 是一个免费的工具,当要查找哪个 PID (注:即 process identifier,进程 ID) 给你的网络流量带来了麻烦时,它是非常方便的。它按每个进程来分组带宽,而不是像大多数的工具那样按照每个协议或每个子网来划分流量。它功能丰富,同时支持 IPv4 和 IPv6,并且我认为,若你想在你的 Linux 主机上确定哪个程序正消耗着你的全部带宽,它是来做这件事的最佳的程序。
-一个 Linux 用户可以使用 **nethogs** 来显示每个进程的 TCP 下载和上传速率,使用命令 **nethogs eth0** 来监控一个特定的设备,上面的 eth0 是那个你想获取信息的设备的名称,你还可以得到有关正在被传输的数据的传输速率的信息。
+一个 Linux 用户可以使用 **nethogs** 来显示每个进程的 TCP 下载和上传速率,可以使用命令 **nethogs eth0** 来监控一个指定的设备,上面的 eth0 是那个你想获取信息的设备的名称,你还可以得到有关正在传输的数据的传输速率信息。
-对我而言, nethogs 是非常容易使用的,或许是因为我非常喜欢它以至于我总是在我的 Ubuntu 12.04 LTS 机器中使用它来监控我的网络带宽。
+对我而言, nethogs 是非常容易使用的,或许是因为我非常喜欢它,以至于我总是在我的 Ubuntu 12.04 LTS 机器中使用它来监控我的网络带宽。
例如要想使用混杂模式来嗅探,可以像下面展示的命令那样使用选项 -p:
@@ -20,6 +20,8 @@ nethogs 是一个免费的工具,当要查找哪个 PID (注:即 process ide
假如你想更多地了解 nethogs 并深入探索它,那么请毫不犹豫地阅读我们做的关于这个网络带宽监控工具的整个教程。
+(LCTT 译注:关于 nethogs 的更多信息可以参考:https://linux.cn/article-2808-1.html )
+
### 2) nload ###
nload 是一个控制台应用,可以被用来实时地监控网络流量和带宽使用情况,它还通过提供两个简单易懂的图表来对流量进行可视化。这个绝妙的网络监控工具还可以在监控过程中切换被监控的设备,而这可以通过按左右箭头来完成。
@@ -28,19 +30,21 @@ nload 是一个控制台应用,可以被用来实时地监控网络流量和
正如你在上面的截图中所看到的那样,由 nload 提供的图表是非常容易理解的。nload 提供了有用的信息,也展示了诸如被传输数据的总量和最小/最大网络速率等信息。
-而更酷的是你可以在下面的命令的帮助下运行 nload 这个工具,这个命令是非常的短小且易记的:
+而更酷的是你只需要直接运行 nload 这个工具就行,这个命令是非常的短小且易记的:
nload
我很确信的是:我们关于如何使用 nload 的详细教程将帮助到新的 Linux 用户,甚至可以帮助那些正寻找关于 nload 信息的老手。
+(LCTT 译注:关于 nload 的更新信息可以参考:https://linux.cn/article-5114-1.html )
+
### 3) slurm ###
-slurm 是另一个 Linux 网络负载监控工具,它以一个不错的 ASCII 图来显示结果,它还支持许多键值用以交互,例如 **c** 用来切换到经典模式, **s** 切换到分图模式, **r** 用来重绘屏幕, **L** 用来启用 TX/RX(注:TX,发送流量;RX,接收流量) LED,**m** 用来在经典分图模式和大图模式之间进行切换, **q** 退出 slurm。
+slurm 是另一个 Linux 网络负载监控工具,它以一个不错的 ASCII 图来显示结果,它还支持许多按键用以交互,例如 **c** 用来切换到经典模式, **s** 切换到分图模式, **r** 用来重绘屏幕, **L** 用来启用 TX/RX 灯(注:TX,发送流量;RX,接收流量) ,**m** 用来在经典分图模式和大图模式之间进行切换, **q** 退出 slurm。

-在网络负载监控工具 slurm 中,还有许多其它的键值可用,你可以很容易地使用下面的命令在 man 手册中学习它们。
+在网络负载监控工具 slurm 中,还有许多其它的按键可用,你可以很容易地使用下面的命令在 man 手册中学习它们。
man slurm
@@ -48,11 +52,11 @@ slurm 在 Ubuntu 和 Debian 的官方软件仓库中可以找到,所以使用
sudo apt-get install slurm
-我们已经在一个教程中对 slurm 的使用做了介绍,所以请访问相关网页( 注:应该指的是[这篇文章](http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/monitor-network-load-slurm-tool/) ),并不要忘记和其它使用 Linux 的朋友分享这些知识。
+我们已经在一个[教程](http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/monitor-network-load-slurm-tool/)中对 slurm 的使用做了介绍,不要忘记和其它使用 Linux 的朋友分享这些知识。
### 4) iftop ###
-当你想在一个接口上按照主机来展示带宽使用情况时,iftop 是一个非常有用的工具。根据 man 手册,**iftop** 在一个已命名的接口或在它可以找到的第一个接口(假如没有任何特殊情况,它就像一个外部的接口)上监听网络流量,并且展示出一个表格来显示当前一对主机间的带宽使用情况。
+当你想显示连接到网卡上的各个主机的带宽使用情况时,iftop 是一个非常有用的工具。根据 man 手册,**iftop** 在一个指定的接口或在它可以找到的第一个接口(假如没有任何特殊情况,它应该是一个对外的接口)上监听网络流量,并且展示出一个表格来显示当前的一对主机间的带宽使用情况。
通过在虚拟终端中使用下面的命令,Ubuntu 和 Debian 用户可以在他们的机器中轻易地安装 iftop:
@@ -61,6 +65,8 @@ slurm 在 Ubuntu 和 Debian 的官方软件仓库中可以找到,所以使用
在你的机器上,可以使用下面的命令通过 yum 来安装 iftop:
yum -y install iftop
+
+(LCTT 译注:关于 nload 的更多信息请参考:https://linux.cn/article-1843-1.html )
### 5) collectl ###
@@ -69,7 +75,7 @@ collectl 可以被用来收集描述当前系统状态的数据,并且它支
- 记录模式
- 回放模式
-**记录模式** 允许从一个正在运行的系统中读取数据,然后将这些数据要么显示在终端中,要么写入一个或多个文件或套接字中。
+**记录模式** 允许从一个正在运行的系统中读取数据,然后将这些数据要么显示在终端中,要么写入一个或多个文件或一个套接字中。
**回放模式**
@@ -79,13 +85,15 @@ Ubuntu 和 Debian 用户可以在他们的机器上使用他们默认的包管
sudo apt-get install collectl
-还可以使用下面的命令来安装 collectl, 因为对于这些发行版本(注:这里指的是用 yum 作为包管理器的发行版本),在它们官方的软件仓库中也含有 collectl:
+还可以使用下面的命令来安装 collectl, 因为对于这些发行版本(注:这里指的是用 yum 作为包管理器的发行版本),在它们官方的软件仓库中也含有 collectl:
yum install collectl
+
+(LCTT 译注:关于 collectl 的更多信息请参考: https://linux.cn/article-3154-1.html )
### 6) Netstat ###
-Netstat 是一个用来监控**传入和传出的网络数据包统计数据**和接口统计数据的命令行工具。它为传输控制协议 TCP (包括上传和下行),路由表,及一系列的网络接口(网络接口控制器或者软件定义的网络接口) 和网络协议统计数据展示网络连接情况。
+Netstat 是一个用来监控**传入和传出的网络数据包统计数据**的接口统计数据命令行工具。它会显示 TCP 连接 (包括上传和下行),路由表,及一系列的网络接口(网卡或者SDN接口)和网络协议统计数据。
Ubuntu 和 Debian 用户可以在他们的机器上使用默认的包管理器来安装 netstat。Netsta 软件被包括在 net-tools 软件包中,并可以在 shell 或虚拟终端中运行下面的命令来安装它:
@@ -107,6 +115,8 @@ CentOS, Fedora, RHEL 用户可以在他们的机器上使用默认的包管理

+(LCTT 译注:关于 netstat 的更多信息请参考:https://linux.cn/article-2434-1.html )
+
### 7) Netload ###
netload 命令只展示一个关于当前网络荷载和自从程序运行之后传输数据总的字节数目的简要报告,它没有更多的功能。它是 netdiag 软件的一部分。
@@ -115,9 +125,9 @@ netload 命令只展示一个关于当前网络荷载和自从程序运行之后
# yum install netdiag
-Netload 在默认仓库中作为 netdiag 的一部分可以被找到,我们可以轻易地使用下面的命令来利用 **apt** 包管理器安装 **netdiag**:
+Netload 是默认仓库中 netdiag 的一部分,我们可以轻易地使用下面的命令来利用 **apt** 包管理器安装 **netdiag**:
- $ sudo apt-get install netdiag (注:这里原文为 sudo install netdiag,应该加上 apt-get)
+ $ sudo apt-get install netdiag
为了运行 netload,我们需要确保选择了一个正在工作的网络接口的名称,如 eth0, eh1, wlan0, mon0等,然后在 shell 或虚拟终端中运行下面的命令:
@@ -127,21 +137,23 @@ Netload 在默认仓库中作为 netdiag 的一部分可以被找到,我们可
### 8) Nagios ###
-Nagios 是一个领先且功能强大的开源监控系统,它使得网络或系统管理员在服务器相关的问题影响到服务器的主要事务之前,鉴定并解决这些问题。 有了 Nagios 系统,管理员便可以在一个单一的窗口中监控远程的 Linux 、Windows 系统、交换机、路由器和打印机等。它显示出重要的警告并指示出在你的网络或服务器中是否出现某些故障,这间接地帮助你在问题发生之前,着手执行补救行动。
+Nagios 是一个领先且功能强大的开源监控系统,它使得网络或系统管理员可以在服务器的各种问题影响到服务器的主要事务之前,发现并解决这些问题。 有了 Nagios 系统,管理员便可以在一个单一的窗口中监控远程的 Linux 、Windows 系统、交换机、路由器和打印机等。它会显示出重要的警告并指出在你的网络或服务器中是否出现某些故障,这可以间接地帮助你在问题发生前就着手执行补救行动。
Nagios 有一个 web 界面,其中有一个图形化的活动监视器。通过浏览网页 http://localhost/nagios/ 或 http://localhost/nagios3/ 便可以登录到这个 web 界面。假如你在远程的机器上进行操作,请使用你的 IP 地址来替换 localhost,然后键入用户名和密码,我们便会看到如下图所展示的信息:

+(LCTT 译注:关于 Nagios 的更多信息请参考:https://linux.cn/article-2436-1.html )
+
### 9) EtherApe ###
-EtherApe 是一个针对 Unix 的图形化网络监控工具,它仿照了 etherman 软件。它具有链路层,IP 和 TCP 模式并支持 Ethernet, FDDI, Token Ring, ISDN, PPP, SLIP 及 WLAN 设备等接口,再加上支持一些封装的格式。主机和链接随着流量大小和被着色的协议名称展示而变化。它可以过滤要展示的流量,并可从一个文件或运行的网络中读取数据报。
+EtherApe 是一个针对 Unix 的图形化网络监控工具,它仿照了 etherman 软件。它支持链路层、IP 和 TCP 等模式,并支持以太网, FDDI, 令牌环, ISDN, PPP, SLIP 及 WLAN 设备等接口,以及一些封装格式。主机和连接随着流量和协议而改变其尺寸和颜色。它可以过滤要展示的流量,并可从一个文件或运行的网络中读取数据包。
在 CentOS、Fedora、RHEL 等 Linux 发行版本中安装 etherape 是一件容易的事,因为在它们的官方软件仓库中就可以找到 etherape。我们可以像下面展示的命令那样使用 yum 包管理器来安装它:
yum install etherape
-我们可以使用下面的命令在 Ubuntu、Debian 及它们的衍生发行版本中使用 **apt** 包管理器来安装 EtherApe :
+我们也可以使用下面的命令在 Ubuntu、Debian 及它们的衍生发行版本中使用 **apt** 包管理器来安装 EtherApe :
sudo apt-get install etherape
@@ -149,13 +161,13 @@ EtherApe 是一个针对 Unix 的图形化网络监控工具,它仿照了 ethe
sudo etherape
-然后, **etherape** 的 **图形用户界面** 便会被执行。接着,在菜单上面的 **捕捉** 选项下,我们可以选择 **模式**(IP,链路层,TCP) 和 **接口**。一切设定完毕后,我们需要点击 **开始** 按钮。接着我们便会看到类似下面截图的东西:
+然后, **etherape** 的 **图形用户界面** 便会被执行。接着,在菜单上面的 **捕捉** 选项下,我们可以选择 **模式**(IP,链路层,TCP) 和 **接口**。一切设定完毕后,我们需要点击 **开始** 按钮。接着我们便会看到类似下面截图的东西:

### 10) tcpflow ###
-tcpflow 是一个命令行工具,它可以捕捉作为 TCP 连接(流)的一部分的传输数据,并以一种方便协议分析或除错的方式来存储数据。它重建了实际的数据流并将每个流存储在不同的文件中,以备日后的分析。它理解 TCP 序列号并可以正确地重建数据流,不管是在重发或乱序发送状态下。
+tcpflow 是一个命令行工具,它可以捕捉 TCP 连接(流)的部分传输数据,并以一种方便协议分析或除错的方式来存储数据。它重构了实际的数据流并将每个流存储在不同的文件中,以备日后的分析。它能识别 TCP 序列号并可以正确地重构数据流,不管是在重发还是乱序发送状态下。
通过 **apt** 包管理器在 Ubuntu 、Debian 系统中安装 tcpflow 是很容易的,因为默认情况下在官方软件仓库中可以找到它。
@@ -175,7 +187,7 @@ tcpflow 是一个命令行工具,它可以捕捉作为 TCP 连接(流)的一
# yum install --nogpgcheck http://pkgs.repoforge.org/tcpflow/tcpflow-0.21-1.2.el6.rf.i686.rpm
-我们可以使用 tcpflow 来捕捉全部或部分 tcp 流量并以一种简单的方式把它们写到一个可读文件中。下面的命令执行着我们想要做的事情,但我们需要在一个空目录中运行下面的命令,因为它将创建诸如 x.x.x.x.y-a.a.a.a.z 格式的文件,做完这些之后,只需按 Ctrl-C 便可停止这个命令。
+我们可以使用 tcpflow 来捕捉全部或部分 tcp 流量,并以一种简单的方式把它们写到一个可读的文件中。下面的命令就可以完成这个事情,但我们需要在一个空目录中运行下面的命令,因为它将创建诸如 x.x.x.x.y-a.a.a.a.z 格式的文件,运行之后,只需按 Ctrl-C 便可停止这个命令。
$ sudo tcpflow -i eth0 port 8000
@@ -183,49 +195,51 @@ tcpflow 是一个命令行工具,它可以捕捉作为 TCP 连接(流)的一
### 11) IPTraf ###
-[IPTraf][2] 是一个针对 Linux 平台的基于控制台的网络统计应用。它生成一系列的图形,如 TCP 连接包和字节的数目、接口信息和活动指示器、 TCP/UDP 流量故障以及 LAN 状态包和字节的数目。
+[IPTraf][2] 是一个针对 Linux 平台的基于控制台的网络统计应用。它生成一系列的图形,如 TCP 连接的包/字节计数、接口信息和活动指示器、 TCP/UDP 流量故障以及局域网内设备的包/字节计数。
在默认的软件仓库中可以找到 IPTraf,所以我们可以使用下面的命令通过 **apt** 包管理器轻松地安装 IPTraf:
$ sudo apt-get install iptraf
-在默认的软件仓库中可以找到 IPTraf,所以我们可以使用下面的命令通过 **yum** 包管理器轻松地安装 IPTraf:
+我们可以使用下面的命令通过 **yum** 包管理器轻松地安装 IPTraf:
# yum install iptraf
-我们需要以管理员权限来运行 IPTraf(注:这里原文写错为 TPTraf),并带有一个可用的网络接口名。这里,我们的网络接口名为 wlan2,所以我们使用 wlan2 来作为接口的名称:
+我们需要以管理员权限来运行 IPTraf,并带有一个有效的网络接口名。这里,我们的网络接口名为 wlan2,所以我们使用 wlan2 来作为参数:
- $ sudo iptraf wlan2 (注:这里原文为 sudo iptraf,应该加上 wlan2)
+ $ sudo iptraf wlan2

-开始一般的网络接口统计,键入:
+开始通常的网络接口统计,键入:
# iptraf -g
-为了在一个名为 eth0 的接口设备上看详细的统计信息,使用:
+查看接口 eth0 的详细统计信息,使用:
- # iptraf -d wlan2 (注:这里的 wlan2 和 上面的 eth0 不一致,下面的几句也是这种情况,请相应地改正)
+ # iptraf -d eth0
-为了看一个名为 eth0 的接口的 TCP 和 UDP 监控,使用:
+查看接口 eth0 的 TCP 和 UDP 监控信息,使用:
- # iptraf -z wlan2
+ # iptraf -z eth0
-为了展示在一个名为 eth0 的接口上的包的大小和数目,使用:
+查看接口 eth0 的包的大小和数目,使用:
- # iptraf -z wlan2
+ # iptraf -z eth0
-注意:请将上面的 wlan2 替换为你的接口名称。你可以通过运行`ip link show`命令来检查你的接口。
+注意:请将上面的 eth0 替换为你的接口名称。你可以通过运行`ip link show`命令来检查你的接口。
+
+(LCTT 译注:关于 iptraf 的更多详细信息请参考:https://linux.cn/article-5430-1.html )
### 12) Speedometer ###
-Speedometer 是一个小巧且简单的工具,它只绘出一幅包含有通过某个给定端口的上行、下行流量的好看的图。
+Speedometer 是一个小巧且简单的工具,它只用来绘出一幅包含有通过某个给定端口的上行、下行流量的好看的图。
在默认的软件仓库中可以找到 Speedometer ,所以我们可以使用下面的命令通过 **yum** 包管理器轻松地安装 Speedometer:
# yum install speedometer
-在默认的软件仓库中可以找到 Speedometer ,所以我们可以使用下面的命令通过 **apt** 包管理器轻松地安装 Speedometer:
+我们可以使用下面的命令通过 **apt** 包管理器轻松地安装 Speedometer:
$ sudo apt-get install speedometer
@@ -239,15 +253,15 @@ Speedometer 可以简单地通过在 shell 或虚拟终端中执行下面的命
### 13) Netwatch ###
-Netwatch 是 netdiag 工具集里的一部分,并且它也显示出当前主机和其他远程主机的连接情况,以及在每个连接中数据传输的速率。
+Netwatch 是 netdiag 工具集里的一部分,它也显示当前主机和其他远程主机的连接情况,以及在每个连接中数据传输的速率。
我们可以使用 yum 在 fedora 中安装 Netwatch,因为它在 fedora 的默认软件仓库中。但若你运行着 CentOS 或 RHEL , 我们需要安装 [rpmforge 软件仓库][3]。
# yum install netwatch
-Netwatch 作为 netdiag 的一部分可以在默认的软件仓库中找到,所以我们可以轻松地使用下面的命令来利用 **apt** 包管理器安装 **netdiag**:
+Netwatch 是 netdiag 的一部分,可以在默认的软件仓库中找到,所以我们可以轻松地使用下面的命令来利用 **apt** 包管理器安装 **netdiag**:
- $ sudo apt-get install netdiag(注:这里应该加上 apt-get
+ $ sudo apt-get install netdiag
为了运行 netwatch, 我们需要在虚拟终端或 shell 中执行下面的命令:
@@ -259,15 +273,15 @@ Netwatch 作为 netdiag 的一部分可以在默认的软件仓库中找到,
### 14) Trafshow ###
-Trafshow 同 netwatch 和 pktstat(注:这里原文中多了一个 trafshow)一样,可以报告当前激活的连接里使用的协议和每个连接中数据传输的速率。它可以使用 pcap 类型的滤波器来筛选出特定的连接。
+Trafshow 同 netwatch 和 pktstat 一样,可以报告当前活动的连接里使用的协议和每个连接中数据传输的速率。它可以使用 pcap 类型的过滤器来筛选出特定的连接。
-我们可以使用 yum 在 fedora 中安装 trafshow(注:这里原文为 Netwatch,应该为 trafshow),因为它在 fedora 的默认软件仓库中。但若你正运行着 CentOS 或 RHEL , 我们需要安装 [rpmforge 软件仓库][4]。
+我们可以使用 yum 在 fedora 中安装 trafshow ,因为它在 fedora 的默认软件仓库中。但若你正运行着 CentOS 或 RHEL , 我们需要安装 [rpmforge 软件仓库][4]。
# yum install trafshow
Trafshow 在默认仓库中可以找到,所以我们可以轻松地使用下面的命令来利用 **apt** 包管理器安装它:
- $ sudo apt-get install trafshow(注:原文少了 apt-get)
+ $ sudo apt-get install trafshow
为了使用 trafshow 来执行监控任务,我们需要在虚拟终端或 shell 中执行下面的命令:
@@ -275,7 +289,7 @@ Trafshow 在默认仓库中可以找到,所以我们可以轻松地使用下

-为了特别地监控 tcp 连接,如下面一样添加上 tcp 参数:
+为了专门监控 tcp 连接,如下面一样添加上 tcp 参数:
$ sudo trafshow -i wlan2 tcp
@@ -285,7 +299,7 @@ Trafshow 在默认仓库中可以找到,所以我们可以轻松地使用下
### 15) Vnstat ###
-与大多数的其他工具相比,Vnstat 有一点不同。实际上它运行一个后台服务或守护进程,并时刻记录着传输数据的大小。另外,它可以被用来生成一个带有网络使用历史记录的报告。
+与大多数的其他工具相比,Vnstat 有一点不同。实际上它运行着一个后台服务或守护进程,并时刻记录着传输数据的大小。另外,它可以被用来生成一个网络使用历史记录的报告。
我们需要开启 EPEL 软件仓库,然后运行 **yum** 包管理器来安装 vnstat。
@@ -301,7 +315,7 @@ Vnstat 在默认软件仓库中可以找到,所以我们可以使用下面的

-为了实时地监控带宽使用情况,使用 ‘-l’ 选项(实时模式)。然后它将以一种非常精确的方式来展示被上行和下行数据所使用的带宽总量,但不会显示任何有关主机连接或进程的内部细节。
+为了实时地监控带宽使用情况,使用 ‘-l’ 选项(live 模式)。然后它将以一种非常精确的方式来展示上行和下行数据所使用的带宽总量,但不会显示任何有关主机连接或进程的内部细节。
$ vnstat -l
@@ -313,7 +327,7 @@ Vnstat 在默认软件仓库中可以找到,所以我们可以使用下面的
### 16) tcptrack ###
-[tcptrack][5] 可以展示 TCP 连接的状态,它在一个给定的网络端口上进行监听。tcptrack 监控它们的状态并展示出一个经过排列且不断更新的有关来源/目标地址、带宽使用情况等信息的列表,这与 **top** 命令的输出非常类似 。
+[tcptrack][5] 可以展示 TCP 连接的状态,它在一个给定的网络端口上进行监听。tcptrack 监控它们的状态并展示出排序且不断更新的列表,包括来源/目标地址、带宽使用情况等信息,这与 **top** 命令的输出非常类似 。
鉴于 tcptrack 在软件仓库中,我们可以轻松地在 Debian、Ubuntu 系统中从软件仓库使用 **apt** 包管理器来安装 tcptrack。为此,我们需要在 shell 或虚拟终端中执行下面的命令:
@@ -329,7 +343,7 @@ Vnstat 在默认软件仓库中可以找到,所以我们可以使用下面的
注:这里我们下载了 rpmforge-release 的当前最新版本,即 0.5.3-1,你总是可以从 rpmforge 软件仓库中下载其最新版本,并请在上面的命令中替换为你下载的版本。
-**tcptrack** 需要以 root 权限或超级用户身份来运行。执行 tcptrack 时,我们需要带上那个我们想监视的网络接口 TCP 连接状况的接口名称。这里我们的接口名称为 wlan2,所以如下面这样使用:
+**tcptrack** 需要以 root 权限或超级用户身份来运行。执行 tcptrack 时,我们需要带上要监视的网络接口 TCP 连接状况的接口名称。这里我们的接口名称为 wlan2,所以如下面这样使用:
sudo tcptrack -i wlan2
@@ -345,7 +359,7 @@ Vnstat 在默认软件仓库中可以找到,所以我们可以使用下面的
### 17) CBM ###
-CBM 或 Color Bandwidth Meter 可以展示出当前所有网络设备的流量使用情况。这个程序是如此的简单,以至于应该可以从它的名称中看出其功能。CBM 的源代码和新版本可以在 [http://www.isotton.com/utils/cbm/][7] 上找到。
+CBM ( Color Bandwidth Meter) 可以展示出当前所有网络设备的流量使用情况。这个程序是如此的简单,以至于都可以从它的名称中看出其功能。CBM 的源代码和新版本可以在 [http://www.isotton.com/utils/cbm/][7] 上找到。
鉴于 CBM 已经包含在软件仓库中,我们可以简单地使用 **apt** 包管理器从 Debian、Ubuntu 的软件仓库中安装 CBM。为此,我们需要在一个 shell 窗口或虚拟终端中运行下面的命令:
@@ -359,7 +373,7 @@ CBM 或 Color Bandwidth Meter 可以展示出当前所有网络设备的流量
### 18) bmon ###
-[Bmon][8] 或 Bandwidth Monitoring ,是一个用于调试和实时监控带宽的工具。这个工具能够检索各种输入模块的统计数据。它提供了多种输出方式,包括一个基于 curses 库的界面,轻量级的HTML输出,以及 ASCII 输出格式。
+[Bmon][8] ( Bandwidth Monitoring) ,是一个用于调试和实时监控带宽的工具。这个工具能够检索各种输入模块的统计数据。它提供了多种输出方式,包括一个基于 curses 库的界面,轻量级的HTML输出,以及 ASCII 输出格式。
bmon 可以在软件仓库中找到,所以我们可以通过使用 apt 包管理器来在 Debian、Ubuntu 中安装它。为此,我们需要在一个 shell 窗口或虚拟终端中运行下面的命令:
@@ -373,7 +387,7 @@ bmon 可以在软件仓库中找到,所以我们可以通过使用 apt 包管
### 19) tcpdump ###
-[TCPDump][9] 是一个用于网络监控和数据获取的工具。它可以为我们节省很多的时间,并可用来调试网络或服务器 的相关问题。它打印出在某个网络接口上与布尔表达式匹配的数据包所包含的内容的一个描述。
+[TCPDump][9] 是一个用于网络监控和数据获取的工具。它可以为我们节省很多的时间,并可用来调试网络或服务器的相关问题。它可以打印出在某个网络接口上与布尔表达式相匹配的数据包所包含的内容的一个描述。
tcpdump 可以在 Debian、Ubuntu 的默认软件仓库中找到,我们可以简单地以 sudo 权限使用 apt 包管理器来安装它。为此,我们需要在一个 shell 窗口或虚拟终端中运行下面的命令:
@@ -389,7 +403,6 @@ tcpdump 需要以 root 权限或超级用户来运行,我们需要带上我们

-
假如你只想监视一个特定的端口,则可以运行下面的命令。下面是一个针对 80 端口(网络服务器)的例子:
$ sudo tcpdump -i wlan2 'port 80'
@@ -419,14 +432,15 @@ tcpdump 需要以 root 权限或超级用户来运行,我们需要带上我们
### 结论 ###
-在第一部分中(注:我认为原文多了 first 这个单词,总之是前后文的内容有些不连贯),我们介绍了一些在 Linux 下的网络负载监控工具,这对于系统管理员甚至是新手来说,都是很有帮助的。在这篇文章中介绍的每一个工具都有其特点,不同的选项等,但最终它们都可以帮助你来监控你的网络流量。
+在这篇文章中,我们介绍了一些在 Linux 下的网络负载监控工具,这对于系统管理员甚至是新手来说,都是很有帮助的。在这篇文章中介绍的每一个工具都具有其特点,不同的选项等,但最终它们都可以帮助你来监控你的网络流量。
+
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
via: http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/network-monitoring-tools-linux/
作者:[Bobbin Zachariah][a]
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150227 Enjoy Android Apps on Ubuntu using ARChon Runtime.md b/published/201505/20150227 Enjoy Android Apps on Ubuntu using ARChon Runtime.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4776f5c10d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150227 Enjoy Android Apps on Ubuntu using ARChon Runtime.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+使用 ARChon 运行时环境在 Ubuntu 上运行 Android 应用
+================================================================================
+
+在此之前,我们尝试过在多款安卓应用模拟器工具上运行安卓应用,比如Genymotion、VirtualBox和Android SDK等。但是,有了这套全新的Chrome安卓运行环境,就可以在Chrome浏览器中运行安卓应用了。所以,下面是一些步骤来指导你如何使用ARChon运行时环境在Ubuntu上安装安卓应用。
+
+谷歌已经公布了[首批支持原生运行在Chrome OS的安卓应用][1],而这个全新的“**安卓运行时环境**”扩展程序使其成为可能。如今,一位名为Vlad Filippov的开发者已经找到了一种把安卓应用移植到桌面端Chrome浏览器的方法。他把chromeos-apk脚本和ARChon安卓运行环境扩展程序两者紧密结合在一起,使得安卓应用可以运行在Windows、Max和Linux系统的桌面端Chrome浏览器中。
+
+应用借助这种运行环境时的性能并不是很好。同样,由于它是官方运行环境的非官方二次开发包,而且运行在Google的Chrome OS之外,因此一些如摄像头和喇叭等系统内置设备可能需要通过打补丁获得或者根本不支持。
+
+### 安装Chrome ###
+
+首先,需要在机器上安装Chrome,版本要求是Chrome 37或者更高。可以从[Chrome浏览器的下载页面][2]下载。
+
+如果打算安装开发通道版本,按照如下操作。
+
+使用这个命令为Google Chrome添加软件源列表:
+
+ $ wget -q -O - https://dl-ssl.google.com/linux/linux_signing_key.pub | sudo apt-key add -
+ $ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb/ stable main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list'
+
+
+
+添加完软件源列表后,使用下列命令更新本地的软件库索引。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+
+现在,就可以安装非稳定版的google chrome,即开发版:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install google-chrome-unstable
+
+
+
+### 安装Archon运行时环境 ###
+
+接下来,需要下载定制版的运行环境安装包,因为官方版本不被Google或Vlad Filippov创建的Chromium安卓运行环境认可。它在很多方面有别于官方版本,主要区别是它可以用于Google浏览器的各个桌面端。下面是需要下载的运行环境安装包,请根据所安装的Ubuntu系统位数选择下列的一种。
+
+**32位** Ubntu发行版:
+
+- [下载 32 位版 Ubuntu 上的 Archron][3]
+
+**64位** Ubntu发行版:
+
+- [下载 64 位版 Ubuntu 上的 Archron][4]
+
+下载好运行环境安装包后,从.zip文件中解压,并将解压得到的目录移动到Home目录。操作命令如下:
+
+ $ wget https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/releases/download/v3.0.0/ARChon-v1.1-x86_32.zip
+
+
+
+ $ unzip ARChon-v1.1-x86_32.zip ~/
+
+接下来是安装运行时环境,首先打开Google Chrome浏览器,在地址栏键入**chrome://extensions**。然后,选中“**开发者模式**”。最后,点击“**载入未打包扩展程序**”,选择刚才放置在**~/Home**下面的文件夹。
+
+### 安装 ChromeOS-APK ###
+
+如果要用到上面提到的那些应用,那么手动转换这些APK无需复杂的操作——只需要安装“[chromeos-apk][5]”命令行JavaScript工具。可以在Node Package Modules(npm)管理器中安装它。为了安装npm和chromeos-apk,在shell或终端中运行下面命令:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install npm nodejs nodejs-legacy
+
+如果**操作系统是64位**,需要安装下面这个库,命令如下:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install lib32stdc++6
+
+然后,运行这条命令来安装最新的chromeos-apk:
+
+ $ npm install -g chromeos-apk@latest
+
+
+
+取决于系统配置,可能需要以sudo权限运行后一条命令。
+
+现在,我们将找一个应用程序的APK来在Google浏览器上试一试,但务必牢记**并非所有的安卓应用都可以**,有一些可能不稳定或者缺少某些特性。大部分安装即用的通讯类应用都不适用这个环境。
+
+### 转换APK ###
+
+将**安卓APK放到~/Home**下,然后在**终端**执行下列命令进行转换:
+
+ $ chromeos-apk myapp.apk --archon
+
+如果想以全屏模式运行应用,请替换成这条命令:
+
+ $ chromeos-apk myapp.apk --archon --tablet
+
+注意:请将myapp.apk替换成待转换的安卓APK应用的文件名。
+
+为了方便,也可以使用[Twerk][6]来进行转换,这样可以跳过这一步。
+
+### 运行安卓Apk ###
+
+最后,打开chrome浏览器,然后进入chrome://extensions页面,勾选开发者模式。点击“载入未打包扩展程序”按钮,选择上面脚本刚创建的文件夹。
+
+至此,就可以打开Chrome应用启动器运行安卓应用了。
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+万岁!我们已经成功在Chrome浏览器中安装好安卓Apk应用程序了。这篇文章是关于一款由Vlad Filippov开发的、名为Archon的、时下流行的Chrome安卓运行环境。这个运行环境使用户在Chrome浏览器中运行转换过的Apk文件。目前它还不支持通讯类应用,诸如Whatsapp。因此,如果你有任何问题、建议和反馈,请在下面的评论框中写出来。非常感谢!去拥抱Archon吧!:-)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/android-apps-ubuntu-archon-runtime/
+
+作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
+译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
+[1]:http://chrome.blogspot.com/2014/09/first-set-of-android-apps-coming-to.html
+[2]:https://www.google.com/chrome/browser
+[3]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/releases/download/v3.0.0/ARChon-v1.1-x86_32.zip
+[4]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/releases/download/v3.0.0/ARChon-v1.1-x86_64.zip
+[5]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/blob/master/README.md
+[6]:https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/twerk/jhdnjmjhmfihbfjdgmnappnoaehnhiaf
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150227 How To Fix--Failed to fetch cdrom apt-get update cannot be used to add new CD-ROMs.md b/published/201505/20150227 How To Fix--Failed to fetch cdrom apt-get update cannot be used to add new CD-ROMs.md
similarity index 96%
rename from translated/tech/20150227 How To Fix--Failed to fetch cdrom apt-get update cannot be used to add new CD-ROMs.md
rename to published/201505/20150227 How To Fix--Failed to fetch cdrom apt-get update cannot be used to add new CD-ROMs.md
index 77c4c05d63..e6ced67ef0 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150227 How To Fix--Failed to fetch cdrom apt-get update cannot be used to add new CD-ROMs.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150227 How To Fix--Failed to fetch cdrom apt-get update cannot be used to add new CD-ROMs.md
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-如何修复:apt-get update无法添加新的CD-ROM
+如何修复 apt-get update 无法添加新的 CD-ROM 的错误
================================================================================

@@ -63,8 +63,8 @@
via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-failed-fetch-cdrom-aptget-update-add-cdroms/
作者:[Abhishek][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150227 How to Install Lightweight Budgie v8 Desktop in Ubuntu 14.04.md b/published/201505/20150227 How to Install Lightweight Budgie v8 Desktop in Ubuntu 14.04.md
similarity index 72%
rename from translated/tech/20150227 How to Install Lightweight Budgie v8 Desktop in Ubuntu 14.04.md
rename to published/201505/20150227 How to Install Lightweight Budgie v8 Desktop in Ubuntu 14.04.md
index 10bb779e71..ccaff360e5 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150227 How to Install Lightweight Budgie v8 Desktop in Ubuntu 14.04.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150227 How to Install Lightweight Budgie v8 Desktop in Ubuntu 14.04.md
@@ -53,11 +53,11 @@ Budgie是为Linux发行版定制的旗舰桌面,也是一个定制工程。为

-**注意点**
+**注意**
-这是一个活跃的开发版本,一些主要的特点可能还不是特别的完善,如:网络管理器,为数不多的控制组件,无通知系统斌并且无法将app锁定到任务栏。
+这是一个活跃的开发版本,一些主要的功能可能还不是特别的完善,如:没有网络管理器,没有音量控制组件(可以使用键盘控制),无通知系统并且无法将app锁定到任务栏。
-作为工作区你能够禁用滚动栏,通过设置一个默认的主题并且通过下面的命令退出当前的会话
+有一个临时解决方案可以禁用叠加滚动栏:设置另外一个默认主题,然后从终端退出当前会话:
$ gnome-session-quit
@@ -65,7 +65,7 @@ Budgie是为Linux发行版定制的旗舰桌面,也是一个定制工程。为
### 登录Budgie会话 ###
-安装完成之后,我们能在登录时选择机进入budgie桌面。
+安装完成之后,我们能在登录时选择进入budgie桌面。

@@ -79,8 +79,7 @@ Budgie是为Linux发行版定制的旗舰桌面,也是一个定制工程。为
### 结论 ###
-Hurray! We have successfully installed our Lightweight Budgie Desktop Environment in our Ubuntu 14.04 LTS "Trusty" box. As we know, Budgie Desktop is still underdevelopment which makes it a lot of stuffs missing. Though it’s based on Gnome’s GTK3, it’s not a fork. The desktop is written completely from scratch, and the design is elegant and well thought out. If you have any questions, comments, feedback please do write on the comment box below and let us know what stuffs needs to be added or improved. Thank You! Enjoy Budgie Desktop 0.8 :-)
-Budgie桌面当前正在开发过程中,因此有目前有很多功能的缺失。虽然它是基于Gnome,但不是完全的复制。Budgie是完全从零开始实现,它的设计是优雅的并且正在不断的完善。
+嗨,现在我们已经成功的在 Ubuntu 14.04 LTS 上安装了轻量级 Budgie 桌面环境。Budgie桌面当前正在开发过程中,因此有目前有很多功能的缺失。虽然它是基于Gnome 的 GTK3,但不是完全的复制。Budgie是完全从零开始实现,它的设计是优雅的并且正在不断的完善。如果你有任何问题、评论,请在下面的评论框发表。愿你喜欢 Budgie 桌面 0.8 。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -88,7 +87,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/install-lightweight-budgie-v8-desktop-ubu
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
译者:[johnhoow](https://github.com/johnhoow)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150302 How to Limit the Network Bandwidth Used by Applications in a Linux System with Trickle.md b/published/201505/20150302 How to Limit the Network Bandwidth Used by Applications in a Linux System with Trickle.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ee64fab44a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150302 How to Limit the Network Bandwidth Used by Applications in a Linux System with Trickle.md
@@ -0,0 +1,300 @@
+指南:使用Trickle限制应用程序带宽占用
+================================================================================
+
+有没有遇到过系统中的某个应用程序独占了你所有的网络带宽的情形?如果你有过这样的遭遇,那么你就会感受到Trickle这种带宽调整应用的价值。不管你是一个系统管理员还只是普通Linux用户,都需要学习如何控制应用程序的上下行速度,来确保你的网络带宽不会被某个程序霸占。
+
+
+
+*在 Linux 上安装 Trickle 带宽限制*
+
+### 什么是 Trickle? ###
+
+Trickle是一个网络带宽调整工具,可以让我们管理应用程序的网络上下行速度,使得可以避免其中的某个应用程序霸占了全部或大部分可用的带宽。换句话说,Trickle可以让你基于单个应用程序来控制网络流量速率,而不是仅仅针对与单个用户——这是在客户端网络环境中经典的带宽调整情况。
+
+### Trickle 是如何工作的?###
+
+另外,trickle 可以帮助我们基于应用来定义优先级,所以当对整个系统进行了全局限制设定,高优先级的应用依然会自动地获取更多的带宽。为了实现这个目标,trickle 对 TCP 连接上的套接字的数据发送、接收设置流量限制。我们必须注意到,除了影响传输速率之外,在这个过程中,trickle任何时候都不会以任何方式来改变其中的数据。
+
+### Trickle不能做什么? ###
+
+这么说吧,唯一的限制就是,trickle不支持静态链接的应用程序或者具有SUID或SGID位设置的二进制程序,因为它使用动态链接的方式将其载入到需要调整的进程和其关联的网络套接字之间。 Trickle此时会在这两种软件组件之间扮演代理的角色。
+
+由于trickle并不需要超级用户的权限来运行,所以用户可以设置他们自己的流量限制。可能这并不是你想要的,我们会探索如何使用全局设定来限制系统中的所有用户的流量限制。也即是说,此时系统中的每个用户具有管理各自的流量速率,但是无论如何,都会受到系统管理员给他们设置的总体限制。
+
+在这篇文章中,我们会描述如何通过trickle在linux平台上管理应用程序使用的网络带宽。为了生成所需的流量,在此会在客户端(CentOS 7 server – dev1: 192.168.0.17)上使用 ncftpput 和 ncftpget, 在服务器(Debian Wheezy 7.5 – dev2: 192.168.0.15)上使用vsftpd 来进行演示。 相同的指令也可以在RedHat,Fedora和Ubuntu等系统使用。
+
+#### 前提条件 ####
+
+1. 对于 RHEL/CentOS 7/6, [开启EPEL仓库][1]。这些用于企业版 Linux 的额外软件包是一个由Fedora项目维护的高质量、开源的软件仓库,而且百分之百与其衍生产品相兼容,如企业版本Linux和CentOS。 在这个仓库中trickle和ncftp两者都是可用的。
+
+2. 按照如下方式安装ncftp:
+
+ # yum update && sudo yum install ncftp [基于 RedHat 的系统]
+ # aptitude update && aptitude install ncftp [基于 Debian 的系统]
+
+3. 在单独的服务器上设置一个FTP服务器。需要注意的是,尽管FTP天生就不安全,但是仍然被广泛应用在安全性无关紧要的文件上传下载中。 在这篇文章中我们使用它来演示trickle的优点,同时它也会在客户端的标准输出流中显示传输速率。我们将是否在其它时间使用它放在一边讨论。
+
+ # yum update && yum install vsftpd [基于 RedHat 的系统]
+ # aptitude update && aptitude install vsftpd [基于 Debian 的系统]
+
+ 现在,在FTP服务器上按照以下方式编辑 /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf 文件。
+
+ anonymous_enable=NO
+ local_enable=YES
+ chroot_local_user=YES
+ allow_writeable_chroot=YES
+
+ 在此之后,确保在你的当前会话中启动了vsftpd,并在之后的启动中让其自动启动。
+
+ # systemctl start vsftpd [基于 systemd 的系统]
+ # systemctl enable vsftpd
+ # service vsftpd start [基于 init 的系统]
+ # chkconfig vsftpd on
+
+4. 如果你选择在一个使用 SSH 密钥进行远程访问的 CentOS/RHEL 7中搭建FTP服务器,你需要一个密码受保护的用户账户,它能访问**root目录之外**的某个目录,并有能在其中上传和下载文件的权限。
+
+ 你可以通过在你的浏览器中输入以下的URL来浏览你的家目录。一个登录窗口会弹出来提示你输入FTP服务器中的有效的用户名和密码。
+
+ ftp://192.168.0.15
+
+ 如果验证成功,你就会看到你的家目录中的内容。该教程的稍后部分中,你将可以刷新页面来显示在你之前上传过的文件。
+
+ 
+
+ *FTP 目录树*
+
+### 如何在Linux中安装 trickle ###
+
+1. 通过yum或aptitude来安装trickle.
+
+ 为了确保能够成功安装,最好在安装工具之前,保证当前的安装包是最新的版本。
+
+
+ # yum -y update && yum install trickle [基于 RedHat 的系统]
+ # aptitude -y update && aptitude install trickle [基于 Debian 的系统]
+
+2. 确认trickle是否对特定的二进制包有用。
+
+ 之前我们解释过,trickle只对使用动态或共享的库的二进制包有用。为了确认我们是否可以对某个特定的应用使用trickle,我们可以使用著名的ldd(列出动态依赖)工具。 特别地,我们会查看任何给定程序的动态依赖中其当前使用的glibc,因为其准确地定义了通过套接字通讯所使用的系统调用。
+
+ 对一个给定的二进制包执行以下命令来查看是否能对其使用trickle进行带宽调整:
+
+ # ldd $(which [binary]) | grep libc.so
+
+ 例如,
+
+ # ldd $(which ncftp) | grep libc.so
+
+ 其输出是:
+
+ # libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007efff2e6c000)
+
+ 输出中的括号中的字符可能在不同的系统平台有所不同,甚至相同的命令在不同的时候运行也会不同,因为其代表包加载到物理内存中的地址。
+
+ 如果上面的命令没有返回任何的结果,就说明这个二进制包没有使用libc包,因此trickle对其不能起到带宽调整的作用。
+
+### 学习如何使用Trickle###
+
+最基本的用法就是使用其独立模式,通过这种方式,trickle用来显式地定义给定应用程序的上传下载速率。如前所述,为了简单,我们会使用相同的应用来进行上传下载测试。
+
+#### 在独立模式下运行trickle####
+
+我们会比较在有无trickle的情况下的上传下载速率, ‘-d’选项指示下载速率(KB/s单位),而'-u'选项指示相同单位的上传速率。另外我们会使用到‘-s’选项来指定trickle应该以独立模式运行。
+
+以独立模式运行trickle的基本语法如下:
+
+ # trickle -s -d [下载速率,KB/s] -u [上传速率,KB/s]
+
+为了能够让你自己运行以下样例,确保你在自己的客户端安装了trickle和ncftp(我的是192.168.0.17)。
+
+**样例1:在有无trickle的情况下上传一个2.8 MB的PDF文件。**
+
+我们使用一个自由发布的[LInux基础知识PDF文件][2]来进行下面的测试。
+
+你可以首先使用下面的命令将这个文件下载到你当前的工作目录中:
+
+ # wget http://linux-training.be/files/books/LinuxFun.pdf
+
+下面是在没有trickle的情况下将一个文件上传到我们的FTP服务器的语法:
+
+ # ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /remote_directory local-filename
+
+其中的 /remote_directory 是相对于该用户的家目录的上传路径,而local-filename是一个你当前工作目录中的文件。
+
+特别的是,在没有trickle的情形下,我们可以得到上传峰值速率52.02MB/s(请注意,这个不是真正的平均上传速率,而是峰值开始的瞬时值),而且这个文件几乎在瞬间就完成了上传。
+
+ # ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir LinuxFun.pdf
+
+输出:
+
+ LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 52.02 MB/s
+
+在使用trickle的情况下,我们会限制上传速率在5KB/s。在第二次上传文件之前,我们需要在目标目录中删除这个文件,否则ncftp就会通知我们在目标目录中已经存在了与上传文件相同的文件,从而不会执行文件的传输:
+
+ # rm /absolute/path/to/destination/directory/LinuxFun.pdf
+
+然后:
+
+ # trickle -s -u 5 ncftpput -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 /testdir LinuxFun.pdf
+
+输出:
+
+ LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 4.94 kB/s
+
+在上面的样例中,我们看到平均的上传速率下降到了5KB/s。
+
+**样例2:在有无trickle的情况下下载相同的2.8MB的PDF文件**
+
+首先,记得从原来的源目录中删除这个PDF:
+
+ # rm /absolute/path/to/source/directory/LinuxFun.pdf
+
+请注意,下面的样例中将远程的文件下载到客户端机器的当前目录下,这是由FTP服务器的IP地址后面的“.”决定的。
+
+没有trickle的情况下:
+
+ # ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/LinuxFun.pdf
+
+输出:
+
+ LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 260.53 MB/s
+
+在有trickle的情况下,限制下载速率在20KB/s:
+
+ # trickle -s -d 30 ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/LinuxFun.pdf
+
+输出:
+
+ LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 17.76 kB/s
+
+### 在监督[非托管]模式下运行Trickle ###
+
+trickle也可以按照/etc/trickled.conf文件中定义的一系列参数运行在非托管模式下。 这个文件定义了守护线程 trickled的行为以及如何管理trickle。
+
+另外,如果你想要全局设置被所有的应用程序使用的话,我们就会需要使用trickle命令。 这个命令运行守护进程,并允许我们通过trickle定义所有应用程序共享的上传下载限制,不需要我们每次来进行指定。
+
+例如,运行:
+
+ # trickled -d 50 -u 10
+
+会导致任何通过trickle运行的应用程序的上传下载速率分别限制在30kb/s和10kb/s。
+
+请注意,你可以在任何时间都能确认守护线程trickled是否正在运行以及其运行参数:
+
+ # ps -ef | grep trickled | grep -v grep
+
+输出:
+
+ root 16475 1 0 Dec24 ? 00:00:04 trickled -d 50 -u 10
+
+**样例3:在使用/不使用trickle的情形下上传一个 19MB 的mp4文件到我们的FTP服务器。**
+
+在这个样例中,我们会使用“He is the gift”的自由分发视频,可以通过这个[链接][3]下载。
+
+我们将会在开始时通过以下的命令将这个文件下载到你的当前工作目录中:
+
+ # wget http://media2.ldscdn.org/assets/missionary/our-people-2014/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
+
+首先,我们会使用之前列出的命令来开启守护进程trickled:
+
+ # trickled -d 30 -u 10
+
+在不使用trickle时:
+
+ # ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
+
+输出:
+
+ 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 36.31 MB/s
+
+在使用trickle时:
+
+ # trickle ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
+
+输出:
+
+ 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 9.51 kB/s
+
+我们可以看到上面的输出,上传的速率下降到了约 10KB/s。
+
+** 样例4:在使用/不使用trickle的情形下下载这个相同的视频 **
+
+与样例2一样,我们会将该文件下载到当前工作目录中。
+
+在没有trickle时:
+
+ # ncftpget -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 . /testdir/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
+
+输出:
+
+ 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 108.34 MB/s
+
+有trickle的时:
+
+ # trickle ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
+
+输出:
+
+ 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 29.28 kB/s
+
+上面的结果与我们之前设置的下载限速相对应(30KB/s)。
+
+**注意:** 一旦守护进程开启之后,就没有必要使用trickle来为每个应用程序来单独设置限制。
+
+如前所述,人们可以进一步地通过trickled.conf来客制化trickle的带宽速率调整,该文件的一个典型的分段有以下部分组成:
+
+ [service]
+ Priority = <value>
+ Time-Smoothing = <value>
+ Length-Smoothing = <value>
+
+其中,
+
+- [service] 用来指示我们想要对其进行带宽使用调整的应用程序名称
+- Priority 用来让我们为某个服务制定一个相对于其他服务高的优先级,这样就不允许守护进程管理中的一个单独的应用程序来占用所有的带宽。越小的数字代表更高的优先级。
+- Time-Smoothing [以秒计]: 定义了trickled让各个应用程序传输或接收数据的时间间隔。小的间隔值(0.1-1秒)对于交互式应用程序是理想的,因为这样会具有一个更加平滑的会话体验,而一个相对较大的时间间隔值(1-10秒)对于需要批量传输应用程序就会显得更好。如果没有指定该值,默认是5秒。
+- Length-smoothing [KB 单位]: 该想法与Time-Smoothing如出一辙,但是是基于I/O操作而言。如果没有指定值,会使用默认的10KB。
+
+上述平滑值(Time-Smoothing、 Length-smoothing)的改变会被翻译为将指定的服务的使用一个间隔值而不是一个固定值。不幸的是,没有一个特定的公式来计算间隔值的上下限,主要依赖于特定的应用场景。
+
+下面是一个在CentOS 7 客户端中的trickled.conf 样例文件(192.168.0.17):
+
+ [ssh]
+ Priority = 1
+ Time-Smoothing = 0.1
+ Length-Smoothing = 2
+
+ [ftp]
+ Priority = 2
+ Time-Smoothing = 1
+ Length-Smoothing = 3
+
+使用该设置,trickled会为SSH赋予比FTP较高的传输优先级。值得注意的是,一个交互进程,例如SSH,使用了一个较小的时间间隔值,然而一个处理批量数据传输的服务如FTP,则使用一个较大的时间间隔来控制之前的样例中的上传下载速率,尽管不是百分百的由trickled指定的值,但是也已经非常接近了。
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+在该文章中,我们探索了使用trickle在基于Fedora发行版和Debian衍生版平台上来限制应用程序的带宽使用。也包含了其他的可能用法,但是不对以下情形进行限制:
+
+- 限制系统工具的下载速度,例如[wget][4],或 BT客户端.
+- 限制你的系统的包管理工具[`yum`][5]更新的速度 (如果是基于Debian系统的话,其包管理工具为[`aptitude`][6])。
+- 如果你的服务器是在一个代理或防火墙后面(或者其本身即是代理或防火墙的话),你可以使用trickle来同时设定下载和上传速率,或者客户端或外部通讯的速率。
+
+欢迎提问或留言。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/manage-and-limit-downloadupload-bandwidth-with-trickle-in-linux/
+
+作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
+译者:[theo-l](https://github.com/theo-l)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
+[1]:https://linux.cn/article-2324-1.html
+[2]:http://linux-training.be/files/books/LinuxFun.pdf
+[3]:http://media2.ldscdn.org/assets/missionary/our-people-2014/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
+[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-wget-command-examples-in-linux/
+[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
+[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/dpkg-command-examples/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150302 How to Manage KVM Virtual Environment using Commandline Tools in Linux.md b/published/201505/20150302 How to Manage KVM Virtual Environment using Commandline Tools in Linux.md
similarity index 93%
rename from translated/tech/20150302 How to Manage KVM Virtual Environment using Commandline Tools in Linux.md
rename to published/201505/20150302 How to Manage KVM Virtual Environment using Commandline Tools in Linux.md
index 3ece220dd5..7c133f90af 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150302 How to Manage KVM Virtual Environment using Commandline Tools in Linux.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150302 How to Manage KVM Virtual Environment using Commandline Tools in Linux.md
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@

-Linux系统的KVM管理
+*Linux系统的KVM管理*
在这篇文章里没有什么新的概念,我们只是用命令行工具重复之前所做过的事情,也没有什么前提条件,都是相同的过程,之前的文章我们都讨论过。
@@ -31,35 +31,40 @@ Virsh命令行工具是一款管理virsh客户域的用户界面。virsh程序
# virsh pool-define-as Spool1 dir - - - - "/mnt/personal-data/SPool1/"

-创建新存储池
+
+*创建新存储池*
**2. 查看环境中我们所有的存储池,用以下命令。**
# virsh pool-list --all

-列出所有存储池
+
+*列出所有存储池*
**3. 现在我们来构造存储池了,用以下命令来构造我们刚才定义的存储池。**
# virsh pool-build Spool1

-构造存储池
-**4. 用virsh带pool-start的命令来激活并启动我们刚才创建并构造完成的存储池。**
+*构造存储池*
+
+**4. 用带pool-start参数的virsh命令来激活并启动我们刚才创建并构造完成的存储池。**
# virsh pool-start Spool1

-激活存储池
+
+*激活存储池*
**5. 查看环境中存储池的状态,用以下命令。**
# virsh pool-list --all

-查看存储池状态
+
+*查看存储池状态*
你会发现Spool1的状态变成了已激活。
@@ -68,14 +73,16 @@ Virsh命令行工具是一款管理virsh客户域的用户界面。virsh程序
# virsh pool-autostart Spool1

-配置KVM存储池
+
+*配置KVM存储池*
**7. 最后来看看我们新的存储池的信息吧。**
# virsh pool-info Spool1

-查看KVM存储池信息
+
+*查看KVM存储池信息*
恭喜你,Spool1已经准备好待命,接下来我们试着创建存储卷来使用它。
@@ -90,12 +97,14 @@ Virsh命令行工具是一款管理virsh客户域的用户界面。virsh程序
# qemu-img create -f raw /mnt/personal-data/SPool1/SVol1.img 10G

-创建存储卷
+
+*创建存储卷*
**9. 通过使用带info的qemu-img命令,你可以获取到你的新磁盘映像的一些信息。**

-查看存储卷信息
+
+*查看存储卷信息*
**警告**: 不要用qemu-img命令来修改被运行中的虚拟机或任何其它进程所正在使用的映像,那样映像会被破坏。
@@ -120,15 +129,18 @@ Virsh命令行工具是一款管理virsh客户域的用户界面。virsh程序
# virt-install --name=rhel7 --disk path=/mnt/personal-data/SPool1/SVol1.img --graphics spice --vcpu=1 --ram=1024 --location=/run/media/dos/9e6f605a-f502-4e98-826e-e6376caea288/rhel-server-7.0-x86_64-dvd.iso --network bridge=virbr0

-创建新的虚拟机
+
+*创建新的虚拟机*
**11. 你会看到弹出一个virt-vierwer窗口,像是在通过它在与虚拟机通信。**

-虚拟机启动程式
+
+*虚拟机启动程式*

-虚拟机安装过程
+
+*虚拟机安装过程*
### 结论 ###
@@ -143,7 +155,7 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/kvm-management-tools-to-manage-virtual-machines/
作者:[Mohammad Dosoukey][a]
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150304 Linux Basics--How To Fix 'E-- var cache apt archives subprocess new pre-removal script returned error exit status 1' In Ubuntu.md b/published/201505/20150304 Linux Basics--How To Fix 'E-- var cache apt archives subprocess new pre-removal script returned error exit status 1' In Ubuntu.md
similarity index 71%
rename from translated/tech/20150304 Linux Basics--How To Fix 'E-- var cache apt archives subprocess new pre-removal script returned error exit status 1' In Ubuntu.md
rename to published/201505/20150304 Linux Basics--How To Fix 'E-- var cache apt archives subprocess new pre-removal script returned error exit status 1' In Ubuntu.md
index b086684614..09cb220cd2 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150304 Linux Basics--How To Fix 'E-- var cache apt archives subprocess new pre-removal script returned error exit status 1' In Ubuntu.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150304 Linux Basics--How To Fix 'E-- var cache apt archives subprocess new pre-removal script returned error exit status 1' In Ubuntu.md
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-Linux 基础:如何修复Ubuntu上“E: /var/cache/apt/archives/ subprocess new pre-removal script returned error exit status 1 ”的错误
+如何修复 Ubuntu 上“...script returned error exit status 1”的错误
================================================================================

@@ -6,11 +6,11 @@ Linux 基础:如何修复Ubuntu上“E: /var/cache/apt/archives/ subprocess ne
> E: /var/cache/apt/archives/ subprocess new pre-removal script returned error exit status 1
-
+
### 解决: ###
-我google了以下并找到了方法。下面是我解决的方法。
+我google了一下并找到了方法。下面是我解决的方法。
sudo apt-get clean
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade
@@ -33,11 +33,11 @@ Linux 基础:如何修复Ubuntu上“E: /var/cache/apt/archives/ subprocess ne
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-via: https://www.unixmen.com/linux-basics-how-to-fix-e-varcacheaptarchives-subprocess-new-pre-removal-script-returned-error-exit-status-1-in-ubuntu/
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/linux-basics-how-to-fix-e-varcacheaptarchives-subprocess-new-pre-removal-script-returned-error-exit-status-1-in-ubuntu/
作者:[SK][a]
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150304 Monitoring Your Network And Servers With Observium.md b/published/201505/20150304 Monitoring Your Network And Servers With Observium.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..14fc41b746
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150304 Monitoring Your Network And Servers With Observium.md
@@ -0,0 +1,174 @@
+使用Observium来监控你的网络和服务器
+================================================================================
+### 简介###
+
+在监控你的服务器、交换机或者设备时遇到过问题吗?**Observium** 可以满足你的需求。这是一个免费的监控系统,它可以帮助你远程监控你的服务器。它是一个由PHP编写的基于自动发现 SNMP 的网络监控平台,支持非常广泛的网络硬件和操作系统,包括 Cisco、Windows、Linux、HP、NetApp 等等。在此我会给出在 Ubuntu 12.04 上一步步地设置一个 **Observium** 服务器的介绍。
+
+
+
+目前有两种不同的 **observium** 版本。
+
+- Observium 社区版本是一个在 QPL 开源许可证下的免费工具,这个版本是对于较小部署的最好解决方案。该版本每6个月进行一次安全性更新。
+- 第2个版本是 Observium 专业版,该版本采用基于 SVN 的发布机制。 会得到每日安全性更新。 该工具适用于服务提供商和企业级部署。
+
+更多信息可以通过其[官网][1]获得。
+
+### 系统需求###
+
+要安装 **Observium**, 需要具有一个最新安装的服务器。**Observium** 是在 Ubuntu LTS 和 Debian 系统上进行开发的,所以推荐在 Ubuntu 或 Debian 上安装 **Observium**,因为可能在别的平台上会有一些小问题。
+
+该文章会引导你在 Ubuntu 12.04 上安装 **Observium**。对于小型的 **Observium** 安装,建议使用 256MB 内存和双核处理器的配置。
+
+### 安装需求 ###
+
+在安装 **Observuim** 之前,你需要确认安装所有的依赖关系包。
+
+首先,使用下面的命令更新你的服务器:
+
+ sudo apt-get update
+
+然后你需要安装下列运行 Observuim 所需的全部软件包。
+
+Observium 需要使用下面所列出的软件才能正确的运行:
+
+- LAMP 服务器
+- fping
+- Net-SNMP 5.4+
+- RRDtool 1.3+
+- Graphviz
+
+对于可选特性的要求:
+
+- Ipmitool - 仅在当你想要获取服务器上的 IPMI(Intelligent Platform Management Interface 智能平台管理接口)基板控制器时。
+- Libvirt-bin - 仅在当你想要使用 libvirt 进行远程 VM 主机监控时。
+
+ sudo apt-get install libapache2-mod-php5 php5-cli php5-mysql php5-gd php5-mcrypt php5-json php-pear snmp fping mysql-server mysql-client python-mysqldb rrdtool subversion whois mtr-tiny ipmitool graphviz imagemagick libvirt ipmitool
+
+### 为 Observium 创建 MySQL 数据库及其用户。
+
+现在你需要登录到 MySQL 中并为 **Observium** 创建数据库:
+
+ mysql -u root -p
+
+在用户验证成功之后,你需要按照下面的命令创建该数据库。
+
+ CREATE DATABASE observium;
+
+数据库名为 **Observium**,稍后你会需要这个信息。
+
+现在你需要创建数据库管理员用户。
+
+ CREATE USER observiumadmin@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'observiumpassword';
+
+接下来,你需要给该管理员用户相应的权限来管理创建的数据库。
+
+ GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON observium.* TO observiumadmin@localhost;
+
+你需要将权限信息写回到磁盘中来激活新的 MySQL 用户:
+
+ FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
+ exit
+
+### 下载并安装 Observium###
+
+现在我们的系统已经准备好了, 可以开始Observium的安装了。
+
+第一步,创建 Observium 将要使用的文件目录:
+
+ mkdir -p /opt/observium && cd /opt
+
+按本教程的目的,我们将会使用 Observium 的社区/开源版本。使用下面的命令下载并解压:
+
+ wget http://www.observium.org/observium-community-latest.tar.gz
+ tar zxvf observium-community-latest.tar.gz
+
+现在进入到 Observium 目录。
+
+ cd observium
+
+将默认的配置文件 '**config.php.default**' 复制到 '**config.php**',并将数据库配置选项填充到配置文件中:
+
+ cp config.php.default config.php
+ nano config.php
+
+----------
+
+ / Database config
+ $config['db_host'] = 'localhost';
+ $config['db_user'] = 'observiumadmin';
+ $config['db_pass'] = 'observiumpassword';
+ $config['db_name'] = 'observium';
+
+现在为 MySQL 数据库设置默认的数据库模式:
+
+ php includes/update/update.php
+
+现在你需要创建一个文件目录来存储 rrd 文件,并修改其权限以便让 apache 能将写入到文件中。
+
+ mkdir rrd
+ chown apache:apache rrd
+
+为了在出现问题时排错,你需要创建日志文件。
+
+ mkdir -p /var/log/observium
+ chown apache:apache /var/log/observium
+
+现在你需要为 Observium 创建虚拟主机配置。
+
+ <VirtualHost *:80>
+ DocumentRoot /opt/observium/html/
+ ServerName observium.domain.com
+ CustomLog /var/log/observium/access_log combined
+ ErrorLog /var/log/observium/error_log
+ <Directory "/opt/observium/html/">
+ AllowOverride All
+ Options FollowSymLinks MultiViews
+ </Directory>
+ </VirtualHost>
+
+下一步你需要让你的 Apache 服务器的 rewrite (重写)功能生效。
+
+为了让 'mod_rewrite' 生效,输入以下命令:
+
+ sudo a2enmod rewrite
+
+该模块在下一次 Apache 服务重启之后就会生效。
+
+ sudo service apache2 restart
+
+###配置 Observium###
+
+在登入 Web 界面之前,你需要为 Observium 创建一个管理员账户(级别10)。
+
+ # cd /opt/observium
+ # ./adduser.php admin adminpassword 10
+ User admin added successfully.
+
+下一步为发现和探寻任务设置一个 cron 任务,创建一个新的文件 ‘**/etc/cron.d/observium**’ 并在其中添加以下的内容。
+
+ 33 */6 * * * root /opt/observium/discovery.php -h all >> /dev/null 2>&1
+ */5 * * * * root /opt/observium/discovery.php -h new >> /dev/null 2>&1
+ */5 * * * * root /opt/observium/poller-wrapper.py 1 >> /dev/null 2>&1
+
+重载 cron 进程来增加新的任务。
+
+ # /etc/init.d/cron reload
+
+好啦,你已经完成了 Observium 服务器的安装拉! 使用你的浏览器登录到 **http://\<Server IP>**,然后上路吧。
+
+
+
+尽情享受吧!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/monitoring-network-servers-observium/
+
+作者:[anismaj][a]
+译者:[theo-l](http://github.com/theo-l)
+校对:[wxy](http://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](http://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/anis/
+[1]:http://www.observium.org/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150304 Share Folders On Local Network Between Ubuntu And Windows.md b/published/201505/20150304 Share Folders On Local Network Between Ubuntu And Windows.md
similarity index 81%
rename from translated/tech/20150304 Share Folders On Local Network Between Ubuntu And Windows.md
rename to published/201505/20150304 Share Folders On Local Network Between Ubuntu And Windows.md
index 972486fbf0..a2e5e59286 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150304 Share Folders On Local Network Between Ubuntu And Windows.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150304 Share Folders On Local Network Between Ubuntu And Windows.md
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
-局域网中实现Ubuntu和Windows共享文件夹
+如何在局域网中将Ubuntu文件夹共享给Windows
================================================================================

本文全面详细地向你描述了**在Ubuntu中如何实现局域网内的文件夹共享**。
-你的家中是不是有多台电脑?当你需要从一台Ubuntu电脑向另一台电脑传输数据时,是不是必须用到U盘或SD卡?你是否也觉得这个方法很烦人?我想肯定是。本文的目的就是使你在局域网内快速方便地传输文件、文档和其它较大的数据,来节省你的宝贵时间。只需一次设置,然后轻点鼠标,你就可以自由地**在Ubuntu和Windows之间共享文件**,当然这对其它Linux系统同样使用。不要担心这很容易操作,不会花费太多时间。
+你的家中是不是有多台电脑?当你需要从一台Ubuntu电脑向另一台电脑传输数据时,是不是必须用到U盘或SD卡?你是否也觉得这个方法很烦人?我想肯定是。本文的目的就是使你在局域网内快速方便地传输文件、文档和其它较大的数据,以节省你的宝贵时间。只需一次设置,然后轻点鼠标,你就可以自由地**在Ubuntu和Windows之间共享文件**,当然这对其它Linux系统同样使用。不要担心,这很容易操作,不会花费太多时间。
除此之外,尽管本文是在Ubuntu上进行实践,但这个教程在其它Linux系统上同样有用。
@@ -21,11 +21,11 @@
#### 步骤一:####
-为了在Ubuntu上实现局域网共享文件夹,右键点击打算共享的文件夹,并选择“Local Network Share”:
+为了在Ubuntu上实现局域网共享文件夹,右键点击打算共享的文件夹,并选择“Local Network Share(本地网络共享)”:

-**可能有用的故障方案**:如果在右键菜单中看不到“Local Network Share”的选项,那就新建一个终端,使用下面的命令去安装nautlius-share:
+**可能有用的故障解决方案**:如果在右键菜单中看不到“Local Network Share”的选项,那就新建一个终端,使用下面的命令去安装nautlius-share插件:
sudo apt-get install nautilus-share
@@ -35,17 +35,17 @@
#### 步骤二:####
-一旦点击“Local Network Share”,就会出现共享文件夹的选项。只需选中“Share this folder”这一项:
+一旦点击“Local Network Share”,就会出现共享文件夹的选项。只需选中“Share this folder(共享该文件夹)”这一项:

-可能的故障方案:如果提示共享服务还未安装,就像下图所示,那就点击安装服务,按照提示操作。
+**可能的故障解决方案**:如果提示共享服务还未安装,就像下图所示,那就点击安装服务,按照提示操作。

#### 步骤三:####
-一旦选中“Share this folder”的选项,就会看到按钮“Create Share”变成可用了。你也可以允许其他用户在共享文件夹中编辑文件。选项“Guest access”也是如此。
+当选中“Share this folder”的选项,就会看到按钮“Create Share(创建共享)”变得可以点击了。你也可以“Allow others to create and delete fies in this folder(允许其他用户在共享文件夹中编辑文件)”。选项“Guest access(允许访客访问)”也是如此。

@@ -55,13 +55,13 @@
### 2. 在Ubuntu上使用密码保护实现局域网共享文件夹###
-为了达到目的,首先需要配置Samba服务器。事实上,在这篇教程的前一部分我们已经用到了Samba,只是我们没有刻意强调。在介绍如何在Ubuntu上搭建Samba服务器实现局域网共享的方法之前,先快速预览一下[Samba][1]到底是什么。
+为了达到这个目的,首先需要配置Samba服务器。事实上,在这篇教程的前一部分我们已经用到了Samba,只是我们没有刻意强调。在介绍如何在Ubuntu上搭建Samba服务器实现局域网共享的方法之前,先快速预览一下[Samba][1]到底是什么。
#### Samba是什么? ####
Samba是一个允许用户通过网络共享文件、文档和打印机的软件包,无论是在Linux、Windows,还是Mac上。它适用于所有的主流平台,可以在所有支持系统上流畅运行。下面是维基百科的介绍:
-> Samba是一款重新实现SMB/CIFS网络协议的自由软件,最初由安德鲁·垂鸠开发。在第三版中,Smaba不仅支持通过不同的Windows客户端访问及分享SMB的文件夹及打印机,还可以集成到Windows Server域名,作为主要域名控制站(PDC)或者域名成员。它也可以作为Active Directory域名的一部分。
+> Samba是一款重新实现SMB/CIFS网络协议的自由软件,最初由安德鲁·垂鸠开发。在第三版中,Smaba不仅支持通过不同的Windows客户端访问及分享SMB的文件夹及打印机,还可以集成到Windows Server域,作为主域控制器(PDC)或者域成员。它也可以作为活动目录域的一部分。
#### 在Ubuntu上安装Samba服务器 ####
@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ Samba是一个允许用户通过网络共享文件、文档和打印机的软件
#### 在Ubuntu上配置Samba服务器 ####
-从dash打开Samba配置工具:
+从dash中打开Samba配置工具:

@@ -86,7 +86,7 @@ Samba是一个允许用户通过网络共享文件、文档和打印机的软件
在Server Setting中可以看到两个选项卡,‘Basic’和‘Security’。在Basic选项卡下的选项含义如下:
- 工作组 - 用户要连接的电脑所在工作组的名字。比如,如果你想连接到一台Windows电脑,你就要输入Windows电脑的工作组名字。在Windows的Samba服务器设置中,已经默认设置好统一的工作组名字。但如果你有不同的工作组名字,就在这个字段中输入自定义的工作组名字。(在Windows 7中获取工作组名字,右击计算机图标,进到属性,就能看到Windows工作组名字。)
-- 描述 - 其他用户看到的你的电脑名字。不要使用空格或计算机不支持(望更正!)的字符。
+- 描述 - 其他用户看到的你的电脑名字。不要使用空格或不适用于网络的字符。

@@ -101,14 +101,14 @@ Samba是一个允许用户通过网络共享文件、文档和打印机的软件
现在我们需要为网络共享文件创建一个系统用户。下面是非常简单的步骤:
- 在Systems Settings下点击**User Accounts**。
-- 点击**unlock**使其可用,以及+(**plus**)图标。
-- 点击+(plus)图标,创建一个新的系统用户。
+- 点击**unlock**使其可用,以及+(**加号**)图标。
+- 点击+(加号)图标,创建一个新的系统用户。

如上图所示,需要输入‘Full name’。当你输入‘Full name’时,Username会自动填充为Full name。因为创建这个用户是为了共享文件,所以还要指定Account Type为‘**Standard**’。
-完成上述步骤,点击添加,你就创建好一个系统用户。这个用户还没有被激活,所以需要为其设置密码来激活。确保Users accounts界面已经解锁。点击Account disabled。输入一个新密码,然后确认密码,点击Change。
+完成上述步骤,点击添加,你就创建好一个系统用户。这个用户还没有被激活,所以需要为其设置密码来激活。确保Users accounts界面已经解锁。点击尚不可用的账户,输入一个新密码,然后确认密码,点击Change。

@@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ Samba是一个允许用户通过网络共享文件、文档和打印机的软件
#### 通过网络共享文件夹或文件 ####
-在图形用户界面下通过Samba共享文件是很简单的。点击Plus图标,会看到如图所示的对话框:
+在图形用户界面下通过Samba共享文件是很简单的。点击加号图标,会看到如图所示的对话框:

@@ -157,9 +157,8 @@ Samba是一个允许用户通过网络共享文件、文档和打印机的软件
全部搞定!我们也可以使用终端进行网络文件共享,但这样没有本文介绍的方法这么容易。如果你确实想知道命令行操作,我会再写一篇关于在Linux上使用命令行实现网络文件共享的文章。
-所以,你是怎么找到这篇教程的呢?我希望看了这篇教程你可以**很容易地在Ubuntu和Windows之间共享文件**。如果你有任何问题或建议,请再评论里说出来。
+所以,你是怎么找到这篇教程的呢?我希望看了这篇教程你可以**很容易地在Ubuntu和Windows之间共享文件**。如果你有任何问题或建议,请在评论里说出来。
-这篇教程是在Kalc的请求下写出的。如果你也想,你可以[请求你自己的教程][2]。我们很乐意帮助你和面临同样问题的读者解决问题。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -167,7 +166,7 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/share-folders-local-network-ubuntu-windows/
作者:[Mohd Sohail][a]
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150306 How to Setup lftp--A Simple Command line FTP Program.md b/published/201505/20150306 How to Setup lftp--A Simple Command line FTP Program.md
similarity index 85%
rename from translated/tech/20150306 How to Setup lftp--A Simple Command line FTP Program.md
rename to published/201505/20150306 How to Setup lftp--A Simple Command line FTP Program.md
index df90008704..6f7d3b047f 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150306 How to Setup lftp--A Simple Command line FTP Program.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150306 How to Setup lftp--A Simple Command line FTP Program.md
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-如何设置lftp - 一个简易的命令行FTP程序
+LFTP : 一个功能强大的命令行FTP程序
================================================================================
-大家好,这篇文章是介绍Lftp以及如何在Linux操作系统下安装的。[Lftp][1]是一个基于命令行的文件传输软件也被称为FTP客户端,由Alexander Lukyanov开发并以GNU GPL协议许可发行。除了FTP,它还支持FTPS,HTTP,HTTPS,HFTP,FISH,以及SFTP。这个程序还支持FXP,允许数据绕过客户端直接在两个FTP服务器之间传输。
+大家好,这篇文章是介绍Lftp以及如何在Linux操作系统下安装的。[Lftp][1]是一个基于命令行的文件传输软件(也被称为FTP客户端),由Alexander Lukyanov开发并以GNU GPL协议许可发行。除了FTP协议外,它还支持FTPS,HTTP,HTTPS,HFTP,FISH,以及SFTP等协议。这个程序还支持FXP,允许数据绕过客户端直接在两个FTP服务器之间传输。
-他有很多很棒的高级功能,比如完整目录树递归镜像以及断点续传下载。传输任务可以安排在稍后的时间段执行,可以限制带宽,可以创建传输列表,还支持类似Unix shell的任务控制。客户端还可以在交互式或自动脚本里使用。
+它有很多很棒的高级功能,比如递归镜像整个目录树以及断点续传下载。传输任务可以安排在稍后的时间段计划执行,可以限制带宽,可以创建传输列表,还支持类似Unix shell的任务控制。客户端还可以在交互式或自动脚本里使用。
### 安装Lftp ###
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ OpenSuse系统里的包管理软件Zypper可以用来安装lftp。下面是在Op
要登录到ftp服务器或sftp服务器,我们首先需要知道所要求的认证信息,比如用户名,密码,端口。
-之后,我们想通过lftp来登录。
+之后,我们可以通过lftp来登录。
$ lftp ftp://linoxide@localhost
@@ -56,9 +56,9 @@ OpenSuse系统里的包管理软件Zypper可以用来安装lftp。下面是在Op

-### 浏览 ###
+### 导航 ###
-我们可以用**ls**命令来列出文件和目录,用**cd**命令打开目录。
+我们可以用**ls**命令来列出文件和目录,用**cd**命令进入到目录。

@@ -158,7 +158,7 @@ OpenSuse系统里的包管理软件Zypper可以用来安装lftp。下面是在Op
### 总结 ###
-哇!我们已经成功地安装了lftp并学会了使用它的一些基础的主要方式。lftp是一个非常棒的命令行ftp客户端,它支持许多额外的功能以及很酷的特性。它比其他普通ftp客户端多了很多东西。好吧,你要是有任何问题,建议,反馈,请在下面的评论区里留言。谢谢!享用lftp吧 :-)
+哇!我们已经成功地安装了lftp并学会了它的一些基础的主要使用方式。lftp是一个非常棒的命令行ftp客户端,它支持许多额外的功能以及很酷的特性。它比其他普通ftp客户端多了很多东西。好吧,你要是有任何问题,建议,反馈,请在下面的评论区里留言。谢谢!享用lftp吧 :-)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -166,7 +166,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/setup-lftp-command-line-ftp/
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150309 List Of Free Windows SSH Client Tools To Connect To Your Linux Server .md b/published/201505/20150309 List Of Free Windows SSH Client Tools To Connect To Your Linux Server .md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d75ecbb555
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150309 List Of Free Windows SSH Client Tools To Connect To Your Linux Server .md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+Windows 下的免费 SSH 客户端工具
+================================================================================
+
+如果你的操作系统是 Windows,而你想要连接 Linux 服务器相互传送文件,那么你需要一个简称 SSH 的 Secure Shell 软件。实际上,SSH 是一个网络协议,它允许你通过网络连接到 Linux 和 Unix 服务器。SSH 使用公钥加密来认证远程的计算机。你可以有多种途径使用 SSH,无论是自动连接,还是使用密码认证登录。
+
+本篇文章介绍了几种可以连接 Linux 服务器 SSH 客户端。
+
+让我们开始。
+
+### Putty ###
+
+**Putty** 是最有名的 SSH 和 telnet 客户端,最初由 Simon Tatham 为 Windows 平台开发。Putty 是一款开源软件,有可用的源代码,和一群志愿者的开发和支持。
+
+
+
+Putty 非常易于安装和使用,通常大部分的配置选项你都不需要修改。你只需要输入少量基本的参数,就可以开始很简单地建立连接会话。[点此下载][1] Putty。
+
+### Bitvise SSH Client ###
+
+**Bitvise SSH** 是一款支持 SSH 和 SFTP 的 Windows 客户端。由 Bitvise 开发和提供专业支持。这款 SSH 客户端性能强悍,易于安装、便于使用。Bitvise SSH 客户端拥有功能丰富的图形界面,通过一个有自动重连功能的内置代理进行动态端口转发。
+
+
+
+Bitvise SSH 客户端对**个人用户使用是免费的**,同时对于在组织内部的个人商业使用也一样。你可以[在这里下载 Bitvise SSH 客户端][2]。
+
+### MobaXterm ###
+
+**MobaXterm** 是你的**远程计算的终极工具箱**。在一个 Windows 应用里,它为程序员、网管、IT 管理员及其它用户提供了精心裁剪的一揽子功能,让他们的远程操作变得简约时尚。
+
+
+
+MobaXterm 提供了所有重要的**远程网络工具** (如SSH、 X11、 RDP、 VNC、 FTP、 MOSH 等等),以及 Windows 桌面上的 **Unix 命令**(bash、 ls、 cat、sed、 grep、 awk、 rsync等等),而这些都是由一个开箱即用的**单一的便携程序**所提供。MobaXterm 对**个人使用免费**,你可以[在这里][3]下载 MobaXterm。
+
+### DameWare SSH ###
+
+我认为 **DameWare SSH** 是最好的免费SSH客户端。
+
+
+
+这个免费工具是一个终端模拟器,可以让你从一个易用的控制台建立多个 telnet 和 SSH 连接。
+
+-用一个带标签的控制台界面管理多个会话
+-将常用的会话保存在 Windows 文件系统中
+-使用多套保存的证书来轻松登录不同的设备
+-使用 telnet、SSH1 和 SSH2 协议连接计算机和设备
+
+你可以从[这个链接][4]下载 **DameWare SSH**。
+
+### SmarTTY ###
+
+SmarTTY 是一款免费的多标签 SSH 客户端,支持使用 SCP 命令随时复制文件和目录。
+
+
+
+大多数 SSH 服务器每个连接支持最多10个子会话.SmarTTY 在这方面做得很好:没有烦人的多个窗口,不需要重新登录,仅仅打开一个新的标签页就可以开始了!
+
+### Cygwin ###
+
+Cygwin 是一款 GNU 和开源工具的大杂烩,提供的功能近似于一个 Windows 平台下的 Linux。
+
+
+
+**Cygwin** 包括了一个称为模拟库的 Unix 系统:cygwin.dll,集成了大量的 GNU 和其它的免费软件,以大量的可选包方式组织而成。在这些安装包中,有高质量的编译器和其他软件开发工具、一个X11服务器、一套完整的X11开发套件、GNU emacs 编辑器、Tex 和 LaTeX、openSSH(客户端和服务器),除此之外还有很多,包括在微软 Windows 下需要编译和使用 PhysioToolkit 软件的每一样东西。
+
+读完我们的文章后,不知你中意哪一款 SSH 客户端?你可以留下你的评论,描述你喜欢的系统和选择的原因。当然,如果有另外的 SSH 客户端没有被本文列举出来,你可以帮助我们补充。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/list-free-windows-ssh-client-tools-connect-linux-server/
+
+作者:[anismaj][a]
+译者:[wi-cuckoo](http://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
+校对:[wxy](http://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](http://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/anis/
+[1]:http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html
+[2]:http://www.bitvise.com/download-area
+[3]:http://mobaxterm.mobatek.net/download.html
+[4]:http://www.dameware.com/downloads/registration.aspx?productType=ssh&AppID=17471&CampaignID=70150000000PcNM
+[5]:http://cygwin.com/packages/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150310 [Fixed] Keyboard And Mouse Freeze After Suspend In Ubuntu 14.04 [Quick Tip].md b/published/201505/20150310 [Fixed] Keyboard And Mouse Freeze After Suspend In Ubuntu 14.04 [Quick Tip].md
similarity index 69%
rename from translated/tech/20150310 [Fixed] Keyboard And Mouse Freeze After Suspend In Ubuntu 14.04 [Quick Tip].md
rename to published/201505/20150310 [Fixed] Keyboard And Mouse Freeze After Suspend In Ubuntu 14.04 [Quick Tip].md
index 0e766f4f66..320ca3da60 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150310 [Fixed] Keyboard And Mouse Freeze After Suspend In Ubuntu 14.04 [Quick Tip].md
+++ b/published/201505/20150310 [Fixed] Keyboard And Mouse Freeze After Suspend In Ubuntu 14.04 [Quick Tip].md
@@ -1,5 +1,6 @@
-[已解决] Ubuntu 14.04从待机中唤醒后鼠标键盘出现僵死情况 [快速小贴士]
-================================================================================
+修复 Ubuntu 14.04 从待机中唤醒后鼠标键盘出现僵死情况
+=========
+
### 问题: ###
当Ubuntu14.04或14.10从睡眠和待机状态恢复时,鼠标和键盘出现僵死,不能点击也不能输入。解决这种情况是唯一方法就是按关机键强关系统,这不仅非常不便且令人恼火。因为在Ubuntu的默认情况中合上笔记本等同于切换到睡眠模式。
@@ -12,15 +13,15 @@
sudo apt-get install --reinstall xserver-xorg-input-all
-这则贴士源自一个自由开源读者Dev的提问。快试试这篇贴士,看看是否对你也有效。在一个类似的问题中,你可以[修复Ubuntu登录后无Unity界面、侧边栏和Dash的问题][1]
+这则贴士源自一个我们的读者Dev的提问。快试试这篇贴士,看看是否对你也有效。在一个类似的问题中,你可以[修复Ubuntu登录后无Unity界面、侧边栏和Dash的问题][1]。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
via: http://itsfoss.com/keyboard-mouse-freeze-suspend/
作者:[Abhishek][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[martin2011qi](https://github.com/martin2011qi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150316 5 Interesting Command Line Tips and Tricks in Linux--Part 1.md b/published/201505/20150316 5 Interesting Command Line Tips and Tricks in Linux--Part 1.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9344d8c482
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150316 5 Interesting Command Line Tips and Tricks in Linux--Part 1.md
@@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
+5个有趣的Linux命令行技巧
+================================================================================
+你有将Linux物尽其用吗?对很多Linux用户来说,有很多看起来是技巧的有用特性。有些时候你会需要这些技巧。本文会帮助你更好得使用一些命令,发挥其更强大的功能。
+
+
+
+*图1:5个命令行技巧*
+
+我们开始一个新的系列,在这里我们还会写一些技巧,并且用尽量小的篇幅写清楚。
+
+### 1. 我们可以使用[`history`命令][1]来查看曾经运行过的命令。 ###
+
+这里是一个`history`命令的示例输出。
+
+ # history
+
+
+
+*图2:history命令例子*
+
+从`history`命令输出看,很明显,命令的执行时间没有被打出来。有解决方法吗?有的!运行如下命令:
+
+ # HISTTIMEFORMAT="%d/%m/%y %T "
+ # history
+
+如果你想让这个修改永久生效,添加如下的一行内容到`~/.bashrc`文件中:
+
+ export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%d/%m/%y %T "
+
+然后,在终端中运行:
+
+ # source ~/.bashrc
+
+命令和选项的解释:
+
+- history – 查看运行过的命令
+- HISTIMEFORMAT – 设置时间格式的环境变量
+- %d – 天
+- %m – 月
+- %y – 年
+- %T – 时间戳
+- source – 简而言之就是将文件内容发送给shell来执行
+- .bashrc – BASH以交互方式启动时运行的脚本文件
+
+
+
+*图3:`history`命令输出的日志*
+
+### 2. 如何测试磁盘写入速度?###
+
+一行`dd`命令脚本就可以实现。
+
+ # dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/output.img bs=8k count=256k conv=fdatasync; rm -rf /tmp/output.img
+
+
+
+*图4:`dd`命令例子*
+
+命令和选项的解释:
+
+- dd – 转换和复制文件
+- if=/dev/zero – 指定输入文件,默认为stdin(标准输入)
+- of=/tmp/output.img – 指定输出文件,默认为stdout(标准输出)
+- bs – 一次读和写的块大小,最大可以以MB为单位
+- count – 复制次数
+- conv – 使用逗号分隔的策略来转换文件(LCTT 译注:比如将大写字母转换成小写,echo AA | dd conv=lcase)
+- rm – 删除文件和目录
+- -rf – (-r) 递归地删除目录和其中的内容,(-f)强行删除而不输出确认信息
+
+### 3. 你如何获取吃掉你磁盘空间的最大的6个文件?###
+
+一个使用[`du`命令][2]的简单单行脚本即可实现,`du`命令主要用于获取文件的空间使用情况。
+
+ # du -hsx * | sort -rh | head -6
+
+
+
+*图5:获取磁盘空间使用情况的方法*
+
+命令和选项的解释:
+
+- du – 估计文件的空间使用情况
+- -hsx – (-h)更易读的格式,(-s)汇总输出,(-x)跳过其他文件系统的文件
+- sort – 对文本文件按行排序
+- -rf – (-r)将比较的结果逆序输出,(-f)忽略大小写
+- head – 输出文件的头几行
+
+### 4. 获取一个文件的详细状态信息###
+
+可以使用`stat`命令
+
+ # stat filename_ext (例如:stat abc.pdf)
+
+
+
+*图6:获取文件的详细信息*
+
+### 5. 显示帮助 ###
+
+最后一个技巧是为那些入门者准备的,如果你是有经验的用户,可能不需要它,除非你想从中寻找乐趣。入门者可能有Linux命令行恐惧症,下面的命令会随机显示一个man手册页。对入门者来说,好处是总会学到新的东西,而且不会厌倦。
+
+ # man $(ls /bin | shuf | head -1)
+
+
+
+*图7:查看随机的man手册页*
+
+命令和选项的解释:
+
+- man – Linux man手册
+- ls – 列出文件
+- /bin – 系统可执行文件的路径
+- shuf – 把输入内容按行随机打乱并输出
+- head – 输出文件的头几行
+
+这就是所有的内容了。如果你知道任何类似的技巧,可以分享给我们,我们会用你的语言在网站上发表出来。
+
+不要忘记在下边评论框中留下有价值的反馈。保持联系。可以点赞或者将本文分享来帮助我们更好地传播内容。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/5-linux-command-line-tricks/
+
+作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
+译者:[goreliu](https://github.com/goreliu)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
+[1]:https://linux.cn/article-1143-1.html
+[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/check-linux-disk-usage-of-files-and-directories/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150316 How to access Gmail from the command line on Linux with Alpine.md b/published/201505/20150316 How to access Gmail from the command line on Linux with Alpine.md
similarity index 55%
rename from translated/tech/20150316 How to access Gmail from the command line on Linux with Alpine.md
rename to published/201505/20150316 How to access Gmail from the command line on Linux with Alpine.md
index ce347ad4e6..0d78b2fd34 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150316 How to access Gmail from the command line on Linux with Alpine.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150316 How to access Gmail from the command line on Linux with Alpine.md
@@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
-如何在 Linux 中使用 Alpine 在命令行里获取 Gmail
+如何在 Linux 中使用 Alpine 在命令行里访问 Gmail
================================================================================
-假如你是一个命令行爱好者,我很确信你将张开双臂欢迎任何可以使你使用这个强大的工作环境来执行哪怕一项日常任务的工具,例如从 [安排日程][1] 、 [管理财务][2] 到 获取 [Facebook][3] 、[Twitter][4]等任务。
-在这个帖子中,我将为你展示 Linux 命令行的另一个漂亮干练的使用案例:**获取 Google 的 Gmail 服务**,为此,我们将使用 Alpine,一个基于 ncurses 的多功能命令行邮件客户端(不要和 Alpine Linux 搞混淆)。我们将在 Alphine 中配置 Gmail 的 IMAP 和 SMTP 设定来通过 Google 的邮件服务器在终端环境中收取和发送邮件。在这个教程的最后,你将意识到只需几步就可以在 Alpine 中使用其他的邮件服务。
+假如你是一个命令行爱好者,我很确信你会使用这个强大的工作环境来执行哪怕是一项日常任务的工具,并为之欢呼,例如从 [安排日程][1] 、 [管理财务][2] 到 获取 [Facebook][3] 、[Twitter][4]等任务。(LCTT 译注:阅读本文的另一个前提是,假如你还能访问 Gmail 或者知道 Gmail 是什么的话。)
-诚然,已有许多卓越的基于 GUI 的邮件客户端存在,例如 Thunderbird, Evolution 或者甚至是 Web 界面,那么为什么还有人对使用命令行的邮件客户端来收取 Gmail 这样的事感兴趣呢?答案很简单。假如你需要快速地处理好事情并想避免使用不必要系统资源;或者你正工作在一个最小化安装(注:这里我感觉自己翻译有误)的服务器上,而它没有安装 X 服务(注:这里也需要更改);又或者是 X 服务在你的桌面上崩溃了,而你需要在解决这个问题之前急切地发送一些邮件。在上述所有的情况下, Alpine 都可以派上用场并在任何时间满足你的需求。
+在这个帖子中,我将为你展示 Linux 命令行的另一个漂亮干练的使用案例:**访问 Google 的 Gmail 服务**,为此,我们将使用 Alpine,一个基于 ncurses 的多功能命令行邮件客户端(不要和 Alpine Linux 搞混淆)。我们将在 Alphine 中配置 Gmail 的 IMAP 和 SMTP 设定,通过 Google 的邮件服务器在终端环境中收取和发送邮件。在这个教程的最后,你将发现只需几步就可以在 Alpine 中使用其他的邮件服务。
-除了简单的编辑,发送和接收文本类的邮件信息等功能外, Alpine 还可以进行加密,解密和对邮件信息进行数字签名,以及与 TLS(注:Transport Layer Security) 无缝集成。
+诚然,已有许多卓越的基于 GUI 的邮件客户端存在,例如 Thunderbird, Evolution 或者甚至是 Web 界面,那么为什么还有人对使用命令行的邮件客户端来收取 Gmail 这样的事感兴趣呢?答案很简单。假如你需要快速地处理好事情并想避免浪费不必要系统资源;或者你正工作在一个精简安装无操作台的服务器上,它没有安装用于图形显示的 X 服务;又或者是 X 服务在你的桌面上崩溃了,而你需要在解决这个问题之前急切地发送一些邮件。在上述所有的情况下, Alpine 都可以派上用场并在任何时间满足你的需求。
+
+除了简单的编辑,发送和接收文本类的邮件信息等功能外, Alpine 还可以进行加密,解密和对邮件信息进行数字签名,以及与 TLS(注:Transport Layer Security,传输层加密)无缝集成。
### 在 Linux 上安装 Alpine ###
@@ -22,16 +23,13 @@
# alpine
-在你第一次启用 Alpine 时,它将在当前用户的家目录下创建一个邮件文件夹(`~/mail`),并显现出主界面,正如下面的截屏所显示的那样:
-
-注:youtube视频,发布的时候做个链接吧(注:这里我不知道该如何操作,不过我已经下载了该视频,如有需要,可以发送)
-<iframe width="615" height="346" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/kuKiv3uze4U?feature=oembed"></iframe>
+在你第一次启用 Alpine 时,它将在当前用户的家目录下创建一个邮件文件夹(`~/mail`),并显现出主界面,正如下面的视频所显示的那样:YOUTUBU 视频 - http://www.youtube.com/kuKiv3uze4U 。
它的用户界面有下列几个模块:

-请随意地浏览,操作来熟悉 Alpine。你总是可以在任何时候通过敲 'Q' 来回到命令提示符界面。请注意,所有的字符界面下方都有与操作相关的帮助。
+请随意地浏览、操作来熟悉 Alpine。你总是可以在任何时候通过敲 'Q' 来回到命令提示符界面。请注意,所有的字符界面下方都有与操作相关的帮助。
在进一步深入之前,我们将为 Alpine 创建一个默认的配置文件。为此,请关闭 Alpine,然后在命令行中执行下面的命令:
@@ -39,9 +37,9 @@
### 配置 Alpine 来使用 Gmail 账号 ###
-一旦你安装了 Alpine 并至少花费了几分钟的时间来熟悉它的界面和菜单,下面便是实际配置它来使用一个已有的 Gmail 账户的时候了。
+当你安装了 Alpine 并至少花费了几分钟的时间来熟悉它的界面和菜单,下面便是实际配置它来使用一个已有的 Gmail 账户的时候了。
-在 Alpine 中执行下面的步骤之前,记得要通过你的 Web 邮件界面,在你的 Gmail 设定里启用 IMAP 协议。一旦在你的 Gmail 账户中 IMAP 被启用,执行下面的步骤来在 Alpine 中启用阅读 Gmail 信息的功能。
+在 Alpine 中执行下面的步骤之前,记得首先要通过你的 Web 邮件界面,在你的 Gmail 设定里启用 IMAP 协议。一旦在你的 Gmail 账户中启用了 IMAP ,执行下面的步骤来在 Alpine 中启用阅读 Gmail 信息的功能。
首先,启动 Alpine。
@@ -51,12 +49,12 @@
按 'A' 来新建一个文件夹并填写必要的信息:
-- **昵称**: 填写任何你想写的名字;
-- **服务器**: imap.gmail.com/ssl/user=yourgmailusername@gmail.com
+- **Nickname**: 填写任何你想写的名字;
+- **Server**: imap.gmail.com/ssl/user=yourgmailusername@gmail.com
你可以将 `Path` 和 `View` 留白不填。
-然后按 `Ctrl+X` 并在有提示时输入你的 Gmail 密码:
+然后按 `Ctrl+X` 并在提示时输入你的 Gmail 密码:

@@ -64,7 +62,7 @@
-为了验证,你可以比较在 Alpine 中显示的 "Gmail Sent" 信箱和在 Web 界面下的信箱:
+要验证的话,你可以比较在 Alpine 中显示的 "Gmail Sent" 信箱和在 Web 界面下的信箱:
@@ -73,7 +71,7 @@
# The approximate number of seconds between checks for new mail
mail-check-interval=10
-最后,我们需要配置一个 SMTP 服务器来通过 Alpine 发送邮件信息。回到先前解释过的 Alpine 的设置界面,然后按 'C' 来设定一个 Google 的 SMTP 服务器地址,你需要像下面这样编辑 `SMTP Server`(为了发送) 这一行内容:
+最后,我们需要配置一个 SMTP 服务器来通过 Alpine 发送邮件。回到先前解释过的 Alpine 的设置界面,然后按 'C' 来设定一个 Google 的 SMTP 服务器地址,你需要像下面这样编辑 `SMTP Server`(用于发送邮件)这一行内容:
smtp.gmail.com:587/tls/user=yourgmailusername@gmail.com
@@ -81,7 +79,7 @@
### 总结 ###
-在这个帖子里,我们讨论了在终端环境中如何通过一个名为 Alpha 的轻量且强大的命令行邮件客户端来获取 Gmail。 Alpine 是一个发布在 Apache Software License 2.0 协议下的自由软件,该协议与 GPL 协议相兼容。 Alpine 引以自豪的是:它不仅对新手友好,同时还做到了让那些经验丰富的系统管理员认为它是强大的。我希望在你阅读完这篇文章后,你能意识到我最后一个论断是多么的正确。
+在这个帖子里,我们讨论了在终端环境中如何通过一个名为 Alpine 的轻量且强大的命令行邮件客户端来访问 Gmail。 Alpine 是一个发布在 Apache Software License 2.0 协议下的自由软件,该协议与 GPL 协议相兼容。 Alpine 引以自豪的是:它不仅对新手友好,同时还做到了让那些经验丰富的系统管理员认为它是强大的。我希望在你阅读完这篇文章后,你能意识到我最后一个论断是多么的正确。
非常欢迎使用下面的输入框来留下你的评论或问题。我期待着你们的反馈!
@@ -91,7 +89,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/gmail-command-line-linux-alpine.html
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
@@ -100,4 +98,4 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/gmail-command-line-linux-alpine.html
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/manage-personal-expenses-command-line.html
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/access-facebook-command-line-linux.html
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/access-twitter-command-line-linux.html
-[5]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
+[5]:https://linux.cn/article-2324-1.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150316 Install Mate desktop in FreeBSD 10.1.md b/published/201505/20150316 Install Mate desktop in FreeBSD 10.1.md
similarity index 97%
rename from translated/tech/20150316 Install Mate desktop in FreeBSD 10.1.md
rename to published/201505/20150316 Install Mate desktop in FreeBSD 10.1.md
index 76d05da5ab..ed4aa9d18b 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150316 Install Mate desktop in FreeBSD 10.1.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150316 Install Mate desktop in FreeBSD 10.1.md
@@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/install-mate-desktop-freebsd-10-1/
作者:[M.el Khamlichi][a]
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150316 Systemd Boot Process a Close Look in Linux.md b/published/201505/20150316 Systemd Boot Process a Close Look in Linux.md
similarity index 75%
rename from translated/tech/20150316 Systemd Boot Process a Close Look in Linux.md
rename to published/201505/20150316 Systemd Boot Process a Close Look in Linux.md
index a2c2ea28be..747e946925 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150316 Systemd Boot Process a Close Look in Linux.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150316 Systemd Boot Process a Close Look in Linux.md
@@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
走进Linux之systemd启动过程
================================================================================
-Linux系统的启动方式有点复杂,而且总是有需要优化的地方。传统的Linux系统启动过程主要由著名的init进程(也被称为SysV init启动系统)处理,而基于init的启动系统也被确认会有效率不足的问题,systemd是Linux系统机器的另一种启动方式,宣称弥补了以[传统Linux SysV init][2]为基础的系统的缺点。在这里我们将着重讨论systemd的特性和争议,但是为了更好地理解它,也会看一下通过传统的以SysV init为基础的系统的Linux启动过程是什么样的。友情提醒一下systemd仍然处在测试阶段,而未来发布的Linux操作系统也正准备用systemd启动管理程序替代当前的启动过程。
+
+Linux系统的启动方式有点复杂,而且总是有需要优化的地方。传统的Linux系统启动过程主要由著名的init进程(也被称为SysV init启动系统)处理,而基于init的启动系统被认为有效率不足的问题,systemd是Linux系统机器的另一种启动方式,宣称弥补了以[传统Linux SysV init][2]为基础的系统的缺点。在这里我们将着重讨论systemd的特性和争议,但是为了更好地理解它,也会看一下通过传统的以SysV init为基础的系统的Linux启动过程是什么样的。友情提醒一下,systemd仍然处在测试阶段,而未来发布的Linux操作系统也正准备用systemd启动管理程序替代当前的启动过程(LCTT 译注:截止到本文发表,主流的Linux发行版已经有很多采用了 systemd)。
### 理解Linux启动过程 ###
-在我们打开Linux电脑的电源后第一个启动的进程就是init。分配给init进程的PID是1。它是系统其他所有进程的父进程。当一台Linux电脑启动后,处理器会先在系统存储中查找BIOS,之后BIOS会测试系统资源然后找到第一个引导设备,通常设置为硬盘,然后会查找硬盘的主引导记录(MBR),然后加载到内存中并把控制权交给它,以后的启动过程就由MBR控制。
+在我们打开Linux电脑的电源后第一个启动的进程就是init。分配给init进程的PID是1。它是系统其他所有进程的父进程。当一台Linux电脑启动后,处理器会先在系统存储中查找BIOS,之后BIOS会检测系统资源然后找到第一个引导设备,通常为硬盘,然后会查找硬盘的主引导记录(MBR),然后加载到内存中并把控制权交给它,以后的启动过程就由MBR控制。
-主引导记录会初始化引导程序(Linux上有两个著名的引导程序,GRUB和LILO,80%的Linux系统在用GRUB引导程序),这个时候GRUB或LILO会加载内核模块。内核会马上查找/sbin下的init进程并执行它。从这里开始init成为了Linux系统的父进程。init读取的第一个文件是/etc/inittab,通过它init会确定我们Linux操作系统的运行级别。它会从文件/etc/fstab里查找分区表信息然后做相应的挂载。然后init会启动/etc/init.d里指定的默认启动级别的所有服务/脚本。所有服务在这里通过init一个一个被初始化。在这个过程里,init每次只启动一个服务,所有服务/守护进程都在后台执行并由init来管理。
+主引导记录会初始化引导程序(Linux上有两个著名的引导程序,GRUB和LILO,80%的Linux系统在用GRUB引导程序),这个时候GRUB或LILO会加载内核模块。内核会马上查找/sbin下的“init”程序并执行它。从这里开始init成为了Linux系统的父进程。init读取的第一个文件是/etc/inittab,通过它init会确定我们Linux操作系统的运行级别。它会从文件/etc/fstab里查找分区表信息然后做相应的挂载。然后init会启动/etc/init.d里指定的默认启动级别的所有服务/脚本。所有服务在这里通过init一个一个被初始化。在这个过程里,init每次只启动一个服务,所有服务/守护进程都在后台执行并由init来管理。
关机过程差不多是相反的过程,首先init停止所有服务,最后阶段会卸载文件系统。
@@ -14,9 +15,9 @@ Linux系统的启动方式有点复杂,而且总是有需要优化的地方。
### 理解Systemd ###
-开发Systemd的主要目的就是减少系统引导时间和计算开销。Systemd(系统管理守护进程),最开始以GNU GPL协议授权开发,现在已转为使用GNU LGPL协议,它是如今讨论最热烈的引导和服务管理程序。如果你的Linux系统配置为使用Systemd引导程序,那么代替传统的SysV init,启动过程将交给systemd处理。Systemd的一个核心功能是它同时支持SysV init的后开机启动脚本。
+开发Systemd的主要目的就是减少系统引导时间和计算开销。Systemd(系统管理守护进程),最开始以GNU GPL协议授权开发,现在已转为使用GNU LGPL协议,它是如今讨论最热烈的引导和服务管理程序。如果你的Linux系统配置为使用Systemd引导程序,它取替传统的SysV init,启动过程将交给systemd处理。Systemd的一个核心功能是它同时支持SysV init的后开机启动脚本。
-Systemd引入了并行启动的概念,它会为每个需要启动的守护进程建立一个管道套接字,这些套接字对于使用它们的进程来说是抽象的,这样它们可以允许不同守护进程之间进行交互。Systemd会创建新进程并为每个进程分配一个控制组。处于不同控制组的进程之间可以通过内核来互相通信。[systemd处理开机启动进程][2]的方式非常漂亮,和传统基于init的系统比起来优化了太多。让我们看下Systemd的一些核心功能。
+Systemd引入了并行启动的概念,它会为每个需要启动的守护进程建立一个套接字,这些套接字对于使用它们的进程来说是抽象的,这样它们可以允许不同守护进程之间进行交互。Systemd会创建新进程并为每个进程分配一个控制组(cgroup)。处于不同控制组的进程之间可以通过内核来互相通信。[systemd处理开机启动进程][2]的方式非常漂亮,和传统基于init的系统比起来优化了太多。让我们看下Systemd的一些核心功能。
- 和init比起来引导过程简化了很多
- Systemd支持并发引导过程从而可以更快启动
@@ -81,7 +82,9 @@ Systemd提供了工具用于识别和定位引导相关的问题或性能影响
234ms httpd.service
191ms vmms.service
-**systemd-analyze verify** 显示在所有系统单元中是否有语法错误。**systemd-analyze plot** 可以用来把整个引导过程写入一个SVG格式文件里。整个引导过程非常长不方便阅读,所以通过这个命令我们可以把输出写入一个文件,之后再查看和分析。下面这个命令就是做这个。
+**systemd-analyze verify** 显示在所有系统单元中是否有语法错误。
+
+**systemd-analyze plot** 可以用来把整个引导过程写入一个SVG格式文件里。整个引导过程非常长不方便阅读,所以通过这个命令我们可以把输出写入一个文件,之后再查看和分析。下面这个命令就是做这个。
systemd-analyze plot > boot.svg
@@ -89,9 +92,9 @@ Systemd提供了工具用于识别和定位引导相关的问题或性能影响
Systemd并没有幸运地获得所有人的青睐,一些专家和管理员对于它的工作方式和开发有不同意见。根据对于Systemd的批评,它不是“类Unix”方式因为它试着替换一些系统服务。一些专家也不喜欢使用二进制配置文件的想法。据说编辑systemd配置非常困难而且没有一个可用的图形工具。
-### 在Ubuntu 14.04和12.04上测试Systemd ###
+### 如何在Ubuntu 14.04和12.04上测试Systemd ###
-本来,Ubuntu决定从Ubuntu 16.04 LTS开始使用Systemd来替换当前的引导过程。Ubuntu 16.04预计在2016年4月发布,但是考虑到Systemd的流行和需求,即将发布的**Ubuntu 15.04**将采用它作为默认引导程序。好消息是Ubuntu 14.04 Trusty Tahr和Ubuntu 12.04 Precise Pangolin的用户可以在他们的机器上测试Systemd。测试过程并不复杂,你所要做的只是把相关的PPA包含到系统中,更新仓库并升级系统。
+本来,Ubuntu决定从Ubuntu 16.04 LTS开始使用Systemd来替换当前的引导过程。Ubuntu 16.04预计在2016年4月发布,但是考虑到Systemd的流行和需求,刚刚发布的**Ubuntu 15.04**采用它作为默认引导程序。另外,Ubuntu 14.04 Trusty Tahr和Ubuntu 12.04 Precise Pangolin的用户可以在他们的机器上测试Systemd。测试过程并不复杂,你所要做的只是把相关的PPA包含到系统中,更新仓库并升级系统。
**声明**:请注意它仍然处于Ubuntu的测试和开发阶段。升级测试包可能会带来一些未知错误,最坏的情况下有可能损坏你的系统配置。请确保在尝试升级前已经备份好重要数据。
@@ -127,7 +130,7 @@ Systemd并没有幸运地获得所有人的青睐,一些专家和管理员对

-就这样,你的Ubuntu系统已经不在使用传统的引导程序了,改为使用Systemd管理器。重启你的机器然后查看systemd引导过程吧。
+就这样,你的Ubuntu系统已经不再使用传统的引导程序了,改为使用Systemd管理器。重启你的机器然后查看systemd引导过程吧。

@@ -141,7 +144,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/systemd-boot-process/
作者:[Aun Raza][a]
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150318 11 Linux Terminal Commands That Will Rock Your World.md b/published/201505/20150318 11 Linux Terminal Commands That Will Rock Your World.md
similarity index 60%
rename from translated/tech/20150318 11 Linux Terminal Commands That Will Rock Your World.md
rename to published/201505/20150318 11 Linux Terminal Commands That Will Rock Your World.md
index fce6ed5c80..0160abb0c2 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150318 11 Linux Terminal Commands That Will Rock Your World.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150318 11 Linux Terminal Commands That Will Rock Your World.md
@@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
-11个Linux终端命令,让你的世界摇滚起来
+11个让你吃惊的 Linux 终端命令
================================================================================
-我已经用了十年的Linux了,通过今天这篇文章我将向大家展示一系列的,我希望一开始就有人教导而不是曾在我成长道路上绊住我的Linux命令、工具和花招。
-
-
-Linux的快捷键。
+我已经用了十年的Linux了,通过今天这篇文章我将向大家展示一系列的命令、工具和技巧,我希望一开始就有人告诉我这些,而不是曾在我成长道路上绊住我。
### 1. 命令行日常系快捷键 ###
+
+
+*Linux的快捷键。*
+
如下的快捷方式非常有用,能够极大的提升你的工作效率:
- CTRL + U - 剪切光标前的内容
@@ -16,11 +17,11 @@ Linux的快捷键。
- CTRL + A - 移动光标到行首
- ALT + F - 跳向下一个空格
- ALT + B - 跳回上一个空格
-- ALT + Backspace - 删除前一个字
-- CTRL + W - 剪切光标后一个字
+- ALT + Backspace - 删除前一个单词
+- CTRL + W - 剪切光标后一个单词
- Shift + Insert - 向终端内粘贴文本
-那么为了让上诉内容更易理解来看下面的这行命令。
+那么为了让上述内容更易理解来看下面的这行命令。
sudo apt-get intall programname
@@ -28,7 +29,7 @@ Linux的快捷键。
想象现在光标正在行末,我们有很多的方法将她退回单词install并替换它。
-我可以按两次ALT+B这样光标就会在如下的位置(这里用^代替光标的位置)。
+我可以按两次ALT+B这样光标就会在如下的位置(这里用^指代光标的位置)。
sudo apt-get^intall programname
@@ -36,32 +37,36 @@ Linux的快捷键。
如果你想将浏览器中的文本复制到终端,可以使用快捷键"shift + insert"。
-
### 2. SUDO !! ###
-这个命令如果你还不知道我觉得你应该好好感谢我,因为如果你不知道那每次你在输入长串命令后看到“permission denied”后一定会痛恼不堪。
+
+
+*sudo !!*
+
+如果你还不知道这个命令,我觉得你应该好好感谢我,因为如果你不知道的话,那每次你在输入长串命令后看到“permission denied”后一定会痛恼不堪。
- sudo !!
-如何使用sudo !!?很简单。试想你刚输入了如下命令:
+如何使用sudo !!?很简单。试想你刚输入了如下命令:
apt-get install ranger
-一定会出现"Permission denied"除非你的登录了足够高权限的账户。
+一定会出现“Permission denied”,除非你已经登录了足够高权限的账户。
-sudo !!就会用sudo的形式运行上一条命令。所以上一条命令可以看成是这样:
+sudo !! 就会用 sudo 的形式运行上一条命令。所以上一条命令就变成了这样:
sudo apt-get install ranger
-如果你不知道什么是sudo[戳这里][1]。
-
-
-暂停终端运行的应用程序。
+如果你不知道什么是sudo,[戳这里][1]。
### 3. 暂停并在后台运行命令 ###
-我曾经写过一篇如何在终端后台运行命令的指南。
+
+
+*暂停终端运行的应用程序。*
+
+我曾经写过一篇[如何在终端后台运行命令的指南][13]。
- CTRL + Z - 暂停应用程序
- fg - 重新将程序唤到前台
@@ -74,41 +79,42 @@ sudo !!就会用sudo的形式运行上一条命令。所以上一条命令可以
文件编辑到一半你意识到你需要马上在终端输入些命令,但是nano在前台运行让你不能输入。
-你可能觉得唯一的方法就是保存文件,推出nano,运行命令以后在重新打开nano。
+你可能觉得唯一的方法就是保存文件,退出 nano,运行命令以后在重新打开nano。
-其实你只要按CTRL + Z前台的命令就会暂停,画面就切回到命令行了。然后你就能运行你想要运行命令,等命令运行完后在终端窗口输入“fg”就可以回到先前暂停的任务。
+其实你只要按CTRL + Z,前台的命令就会暂停,画面就切回到命令行了。然后你就能运行你想要运行命令,等命令运行完后在终端窗口输入“fg”就可以回到先前暂停的任务。
有一个尝试非常有趣就是用nano打开文件,输入一些东西然后暂停会话。再用nano打开另一个文件,输入一些什么后再暂停会话。如果你输入“fg”你将回到第二个用nano打开的文件。只有退出nano再输入“fg”,你才会回到第一个用nano打开的文件。
-
-nohup.
-
### 4. 使用nohup在登出SSH会话后仍运行命令 ###
-如果你用ssh登录别的机器时,[nohup命令]真的非常有用。
+
+
+*nohup*
+
+如果你用ssh登录别的机器时,[nohup命令][2]真的非常有用。
那么怎么使用nohup呢?
想象一下你使用ssh远程登录到另一台电脑上,你运行了一条非常耗时的命令然后退出了ssh会话,不过命令仍在执行。而nohup可以将这一场景变成现实。
-举个例子以测试为目的我用[树莓派][3]来下载发行版。
+举个例子,因为测试的需要,我用我的[树莓派][3]来下载发行版。我绝对不会给我的树莓派外接显示器、键盘或鼠标。
-我绝对不会给我的树莓派外接显示器、键盘或鼠标。
-
-一般我总是用[SSH] [4]从笔记本电脑连接到树莓派。如果我在不用nohup的情况下使用树莓派下载大型文件,那我就必须等待到下载完成后才能登出ssh会话关掉笔记本。如果是这样那我为什么要使用树莓派下文件呢?
+一般我总是用[SSH][4]从笔记本电脑连接到树莓派。如果我在不用nohup的情况下使用树莓派下载大型文件,那我就必须等待到下载完成后,才能登出ssh会话关掉笔记本。可如果是这样,那我为什么要使用树莓派下文件呢?
使用nohup的方法也很简单,只需如下例中在nohup后输入要执行的命令即可:
nohup wget http://mirror.is.co.za/mirrors/linuxmint.com/iso//stable/17.1/linuxmint-17.1-cinnamon-64bit.iso &
-
-At管理任务日程
### 5. ‘在’特定的时间运行Linux命令 ###
+
+
+*At管理任务日程*
+
‘nohup’命令在你用SSH连接到服务器,并在上面保持执行SSH登出前任务的时候十分有用。
-想一下如果你需要在特定的时间执行同一个命令,这种情况该怎么办呢?
+想一下如果你需要在特定的时间执行相同的命令,这种情况该怎么办呢?
命令‘at’就能妥善解决这一情况。以下是‘at’使用示例。
@@ -116,78 +122,80 @@ At管理任务日程
at> cowsay 'hello'
at> CTRL + D
-上面的命令能在周五下午10时38分运行程序[cowsay] [5]。
+上面的命令能在周五下午10时38分运行程序[cowsay][5]。
-使用的语法就是‘at’后追加日期时间。
+使用的语法就是‘at’后追加日期时间。当at>提示符出现后就可以输入你想在那个时间运行的命令了。
-当at>提示符出现后就可以输入你想在那个时间运行的命令了。
+CTRL + D 返回终端。
-CTRL + D返回终端。
+还有许多日期和时间的格式,都需要你好好翻一翻‘at’的man手册来找到更多的使用方式。
-还有许多日期和时间的格式都是值得的你好好翻一翻‘at’的man手册来找到更多的使用方式。
-
-
### 6. Man手册 ###
-Man手册会为你列出命令和参数的使用大纲,教你如何使用她们。
+
-Man手册看起开沉闷呆板。(我思忖她们也不是被设计来娱乐我们的)。
+*彩色man 手册*
-不过这不代表你不能做些什么来使她们变得性感点。
+Man手册会为你列出命令和参数的使用大纲,教你如何使用她们。Man手册看起来沉闷呆板。(我思忖她们也不是被设计来娱乐我们的)。
+
+不过这不代表你不能做些什么来使她们变得漂亮些。
export PAGER=most
-你需要 ‘most’;她会使你的你的man手册的色彩更加绚丽。
+你需要安装 ‘most’;她会使你的你的man手册的色彩更加绚丽。
-你可以用一下命令给man手册设定指定的行长:
+你可以用以下命令给man手册设定指定的行长:
export MANWIDTH=80
-最后,如果你有浏览器,你可以使用-H在默认浏览器中打开任意的man页。
+最后,如果你有一个可用的浏览器,你可以使用-H在默认浏览器中打开任意的man页。
man -H <command>
-注意啦,以上的命令只有在你将默认的浏览器已经设置到环境变量$BROWSER中了之后才效果哟。
+注意啦,以上的命令只有在你将默认的浏览器设置到环境变量$BROWSER中了之后才效果哟。
-
-使用htop查看进程。
### 7. 使用htop查看和管理进程 ###
-你用哪个命令找出电脑上正在运行的进程的呢?我敢打赌是‘[ps][6]’并在其后加不同的参数来得到你所想要的不同输出。
+
+
+*使用htop查看进程。*
+
+你用哪个命令找出电脑上正在运行的进程的呢?我敢打赌是‘[ps][6]’并在其后加不同的参数来得到你所想要的不同输出。
安装‘[htop][7]’吧!绝对让你相见恨晚。
-htop在终端中将进程以列表的方式呈现,有点类似于Windows中的任务管理器。
-
-你可以使用功能键的组合来切换排列的方式和展示出来的项。你也可以在htop中直接杀死进程。
+htop在终端中将进程以列表的方式呈现,有点类似于Windows中的任务管理器。你可以使用功能键的组合来切换排列的方式和展示出来的项。你也可以在htop中直接杀死进程。
在终端中简单的输入htop即可运行。
htop
-
-命令行文件管理 - Ranger.
-
### 8. 使用ranger浏览文件系统 ###
-如果说htop是命令行进程控制的好帮手那么[ranger][8]就是命令行浏览文件系统的好帮手。
+
+
+*命令行文件管理 - Ranger*
+
+如果说htop是命令行进程控制的好帮手,那么[ranger][8]就是命令行浏览文件系统的好帮手。
你在用之前可能需要先安装,不过一旦安装了以后就可以在命令行输入以下命令启动她:
ranger
-在命令行窗口中ranger和一些别的文件管理器很像,但是她是左右结构的比起上下的来意味着你按左方向键你将前进到上一个文件夹结构而右方向键则会切换到下一个。
+在命令行窗口中ranger和一些别的文件管理器很像,但是相比上下结构布局,她是左右结构的,这意味着你按左方向键你将前进到上一个文件夹,而右方向键则会切换到下一个。
在使用前ranger的man手册还是值得一读的,这样你就可以用快捷键操作ranger了。
-
-Linux取消关机。
### 9. 取消关机 ###
-无论是在命令行还是图形用户界面[关机][9]后发现自己不是真的想要关机。
+
+
+*Linux取消关机。*
+
+无论是在命令行还是图形用户界面[关机][9]后,才发现自己不是真的想要关机。
shutdown -c
@@ -197,11 +205,13 @@ Linux取消关机。
- [pkill][10] shutdown
-
-使用XKill杀死挂起进程。
### 10. 杀死挂起进程的简单方法 ###
+
+
+*使用XKill杀死挂起进程。*
+
想象一下,你正在运行的应用程序不明原因的僵死了。
你可以使用‘ps -ef’来找到该进程后杀掉或者使用‘htop’。
@@ -214,18 +224,20 @@ Linux取消关机。
那如果整个系统挂掉了怎么办呢?
-按住键盘上的‘alt’和‘sysrq’同时输入:
+按住键盘上的‘alt’和‘sysrq’不放,然后慢慢输入以下键:
- [REISUB][12]
这样不按电源键你的计算机也能重启了。
-
-youtube-dl.
### 11. 下载Youtube视频 ###
-一般来说我们大多数人都喜欢看Youtube的视频,也会通过钟爱的播放器播放Youtube的流。
+
+
+*youtube-dl.*
+
+一般来说我们大多数人都喜欢看Youtube的视频,也会通过钟爱的播放器播放Youtube的流媒体。
如果你需要离线一段时间(比如:从苏格兰南部坐飞机到英格兰南部旅游的这段时间)那么你可能希望下载一些视频到存储设备中,到闲暇时观看。
@@ -235,7 +247,7 @@ youtube-dl.
youtube-dl url-to-video
-你能在Youtubu视频页面点击分享链接得到视频的url。只要简单的复制链接在粘帖到命令行就行了(要用shift + insert快捷键哟)。
+你可以在Youtubu视频页面点击分享链接得到视频的url。只要简单的复制链接在粘帖到命令行就行了(要用shift + insert快捷键哟)。
### 总结 ###
@@ -246,8 +258,8 @@ youtube-dl.
via: http://linux.about.com/od/commands/tp/11-Linux-Terminal-Commands-That-Will-Rock-Your-World.htm
作者:[Gary Newell][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[martin2011qi](https://github.com/martin2011qi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
@@ -264,3 +276,4 @@ via: http://linux.about.com/od/commands/tp/11-Linux-Terminal-Commands-That-Will-
[10]:http://linux.about.com/library/cmd/blcmdl1_pkill.htm
[11]:http://linux.about.com/od/funnymanpages/a/funman_xkill.htm
[12]:http://blog.kember.net/articles/reisub-the-gentle-linux-restart/
+[13]:http://linux.about.com/od/commands/fl/How-To-Run-Linux-Programs-From-The-Terminal-In-Background-Mode.htm
diff --git a/published/201505/20150318 How to share a directory with Samba on Fedora or CentOS.md b/published/201505/20150318 How to share a directory with Samba on Fedora or CentOS.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e8e48ba76d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150318 How to share a directory with Samba on Fedora or CentOS.md
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
+如何在Fedora或CentOS上使用Samba共享文件夹
+================================================================================
+如今,无论在家里或者是办公场所,不同的电脑之间共享文件夹已不是什么新鲜事了。在这种趋势下,现代操作系统通过网络文件系统的方式使得电脑间数据的交换变得简单而透明。如果您工作的环境中既有微软的Windows又有Linux,那么,一个共享文件及目录的方式便是通过一个跨平台网络文件共享协议:SMB/CIFS。Windows原生的支持SMB/CIFS,Linux也通过开源的软件Samba实现了SMB/CIFS协议。
+
+在这篇文章中,我们将展示**如何使用Samba共享文件夹**。我们使用的Linux平台是**Fedora或CentOS**。这篇文章分为四部分。首先,我们在Fedora/CentOS环境下安装Sambe。接着,我们讨论如何调整SELinux和防火墙配置以允许Samba的文件共享。最后我们介绍如何使用Samba来共享文件夹。
+
+### 步骤1:在Fedora和CentOS上安装Samba ###
+
+首先,安装Samba以及进行一些基本的配置。
+
+检验Samba是否已经安装在您的系统中:
+
+ $ rpm -q samba samba-common samba-client
+
+如果上面的命令没有任何输出,这意味着Samba并未安装。这时,应使用下面的命令来安装Samba。
+
+ $ sudo yum install samba samba-common samba-client
+
+接下来,创建一个用于在网络中共享的本地文件夹。这个文件夹应该以Samba共享的方式导出到远程的用户。在这个指南中,我们会在顶层文件夹'/'中创建这个文件夹,因此,请确保您有相应的权限。
+
+ $ sudo mkdir /shared
+
+如果您想在您的home文件夹内创建共享文件夹(例如,~/shared),您必须激活SELinux中Samba的home文件夹共享选项,具体将在后面提到。
+
+在创建/shared文件夹后,设置文件夹权限以保证其余用户可以访问它。
+
+ $ sudo chmod o+rw /shared
+
+如果您不想其他用户对该文件夹拥有写权限,您需要移除命令中的'w'选项。
+
+ $ sudo chmod o+r /shared
+
+接下来,创建一个空文件来测试。这个文件可以被用来验证Samba的共享已经被挂载。
+
+ $ sudo touch /shared/file1
+
+### 步骤2:为Samba配置SELinux ###
+
+接下来,我们需要再次配置SELinux。在Fedora和CentOS发行版中SELinux是默认开启的。SELinux仅在正确的安全配置下才允许Samba读取和修改文件或文件夹。(例如,加上'samba_share_t'属性标签)。
+
+下面的命令为文件的配置添加必要的标签:
+
+ $ sudo semanage fcontext -a -t samba_share_t "<directory>(/.*)?"
+
+将<directory>替换为我们之前为Samba共享创建的本地文件夹(例如,/shared):
+
+ $ sudo semanage fcontext -a -t samba_share_t "/shared(/.*)?"
+
+我们必须执行restorecon命令来激活修改的标签,命令如下:
+
+ $ sudo restorecon -R -v /shared
+
+
+
+为了通过Samba共享在我们home文件夹内的文件夹,我们必须在SELinux中开启共享home文件夹的选项,该选项默认被关闭。下面的命令能达到该效果。如果您并未共享您的home文件夹,那么您可以跳过该步骤。
+
+ $ sudo setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs 1
+
+### 步骤3:为Samba配置防火墙 ###
+
+下面的命令用来打开防火墙中Samba共享所需的TCP/UDP端口。
+
+如果您在使用firewalld(例如,在Fedora和CentOS7下),接下来的命令将会永久的修改Samba相关的防火墙规则。
+
+ $ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=samba
+
+如果您在防火墙中使用iptables(例如,CentOS6或者更早的版本),可以使用下面的命令来打开Samba必要的向外的端口。
+
+ $ sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
+
+----------
+
+ -A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 445 -j ACCEPT
+ -A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -m state --state NEW -m udp -p udp --dport 445 -j ACCEPT
+ -A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -m state --state NEW -m udp -p udp --dport 137 -j ACCEPT
+ -A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -m state --state NEW -m udp -p udp --dport 138 -j ACCEPT
+ -A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 139 -j ACCEPT
+
+然后重启iptables服务:
+
+ $ sudo service iptables restart
+
+### 步骤4:更改Samba配置 ###
+
+后面的步骤用来配置Samba以将本地文件夹导出为Samba共享文件夹。
+
+使用文件编辑器打开Samba配置文件,并将下面的行添加到文件的末尾。
+
+ $ sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
+
+----------
+
+ [myshare]
+ comment=my shared files
+ path=/shared
+ public=yes
+ writeable=yes
+
+上面在括号内的文本(例如,"myshare")是Samba共享的资源的名字,它被用来从远程主机存取Samba共享。
+
+创建Samba用户帐户,这是挂载和导出Samba文件系统所必须的。我们可以使用smbpasswd工具来创建一个Samba用户。注意,Samba用户帐户必须是已有的Linux用户。如果您尝试使用smbpasswd添加一个不存在的用户,它会返回一个错误的消息。
+
+如果您不想使用任何已存在的Linux用户作为Samba用户,您可以在您的系统中创建一个新的用户。为安全起见,设置新用户的登录脚本为/sbin/nologin,并且不创建该用户的home文件夹。
+
+在这个例子中,我们创建了一个名叫"sambaguest"的用户,如下:
+
+ $ sudo useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin sambaguest
+ $ sudo passwd sambaguest
+
+
+
+在创建一个新用户后,使用smbpasswd命令添加Samba用户。当这个命令询问一个密码时,您可以键入一个与其用户密码不同的密码。
+
+ $ sudo smbpasswd -a sambaguest
+
+激活Samba服务,并检测Samba服务是否在运行。
+
+ $ sudo systemctl enable smb.service
+ $ sudo systemctl start smb.service
+ $ sudo systemctl is-active smb
+
+
+
+使用下面的命令来查看Samba中共享的文件夹列表。
+
+ $ smbclient -U sambaguest -L localhost
+
+
+
+接下来是在Thunar文件管理器中访问Samba共享文件夹以及对file1进行拷贝复制的截图。注意,Samba的共享内容可以通过在Thunar中通过 `smb://<samba-server-IP-address>/myshare` 这个地址来访问。
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/share-directory-samba-fedora-centos.html
+
+作者:[Kristophorus Hadiono][a]
+译者:[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/kristophorus
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150320 Locate Stolen laptops and Smart phones Using Prey Tool in Ubuntu.md b/published/201505/20150320 Locate Stolen laptops and Smart phones Using Prey Tool in Ubuntu.md
similarity index 84%
rename from translated/tech/20150320 Locate Stolen laptops and Smart phones Using Prey Tool in Ubuntu.md
rename to published/201505/20150320 Locate Stolen laptops and Smart phones Using Prey Tool in Ubuntu.md
index 2d9a5e4485..168032e2a4 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150320 Locate Stolen laptops and Smart phones Using Prey Tool in Ubuntu.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150320 Locate Stolen laptops and Smart phones Using Prey Tool in Ubuntu.md
@@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
-Ubuntu中,使用Prey定位被盗的笔记本与手机
+使用Prey定位被盗的Ubuntu笔记本与智能电话
===============================================================================
-Prey是一款跨平台的开源工具,可以帮助你找回被盗的笔记本,台式机,平板和智能手机。它已经获得了广泛的流行,声称帮助召回了成百上千台丢失的笔记本和智能手机。Prey的使用特别简单,首先安装在你的笔记本或者手机上,当你的设备不见了,用你的账号登入Prey网站,并且标记你的设备为“丢失”。只要小偷将设备接入网络,Prey就会马上发送设备的地理位置给你。如果你的笔记本有摄像头,它还会拍下小偷。
+Prey是一款跨平台的开源工具,可以帮助你找回被盗的笔记本,台式机,平板和智能手机。它已经获得了广泛的流行,声称帮助找回了成百上千台丢失的笔记本和智能手机。Prey的使用特别简单,首先安装在你的笔记本或者手机上,当你的设备不见了,用你的账号登入Prey网站,并且标记你的设备为“丢失”。只要小偷将设备接入网络,Prey就会马上发送设备的地理位置给你。如果你的笔记本有摄像头,它还会拍下该死的贼。
-Prey占用很小的系统资源;你不会对你的设备运行有任何影响。你也可以配合其他你已经在设备上安装的防盗软件使用。Prey采用安全加密的通道,在你的设备与Prey服务器之间进行数据传输。
+Prey占用很小的系统资源;你不会对你的设备运行有任何影响。你也可以配合其他你已经在设备上安装的防盗软件使用。Prey在你的设备与Prey服务器之间采用安全加密的通道进行数据传输。
### 在Ubuntu上安装并配置Prey ###
-让我们来看看如何在Ubuntu上安装和配置Prey,需要提醒的是,在配置过程中,我们必须到Prey官网进行账号注册。一旦完成上述工作,Prey将会开始监视的设备了。免费的账号最多可以监视三个设备,如果你需要添加更多的设备,你就需要购买合适的的套餐了。
+让我们来看看如何在Ubuntu上安装和配置Prey,需要提醒的是,在配置过程中,我们必须到Prey官网进行账号注册。一旦完成上述工作,Prey将会开始监视你的设备了。免费的账号最多可以监视三个设备,如果你需要添加更多的设备,你就需要购买合适的的套餐了。
-想象一下Prey多么流行与被广泛使用,它现在已经被添加到了官方的软件库中了。这意味着你不要往软件包管理器添加任何PPA。很简单地,登录你的终端,运行以下的命令来安装它:
+可以想象Prey多么流行与被广泛使用,它现在已经被添加到了官方的软件库中了。这意味着你不要往软件包管理器添加任何PPA。很简单,登录你的终端,运行以下的命令来安装它:
sudo apt-get install prey
@@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ Prey有一个明显的不足。它需要你的设备接入互联网才会发送
### 结论 ###
-这是一款小巧,非常有用的安全保护应用,可以让你在一个地方追踪你所有的设备,尽管不完美,但是仍然提供了找回被盗设备的机会。它在Linux,Windows和Mac平台上无缝运行。以上就是Prey完整使用的所有细节。
+这是一款小巧,非常有用的安全保护应用,可以让你在一个地方追踪你所有的设备,尽管不完美,但是仍然提供了找回被盗设备的机会。它在Linux,Windows和Mac平台上无缝运行。以上就是[Prey][2]完整使用的所有细节。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -62,9 +62,10 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/anti-theft-application-prey-ubuntu/
作者:[Aun Raza][a]
译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunrz/
[1]:https://preyproject.com/
+[2]:https://preyproject.com/plans
diff --git a/published/201505/20150320 Sleuth Kit--Open Source Forensic Tool to Analyze Disk Images and Recover Files.md b/published/201505/20150320 Sleuth Kit--Open Source Forensic Tool to Analyze Disk Images and Recover Files.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ba4da99105
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150320 Sleuth Kit--Open Source Forensic Tool to Analyze Disk Images and Recover Files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,159 @@
+Sleuth Kit:一个用来分析磁盘映像和恢复文件的开源取证工具
+================================================================================
+SIFT 是一个由 SANS 公司提供的基于 Ubuntu 的取证发行版。它包含许多取证工具,如 Sleuth kit/Autopsy 。但 Sleuth kit/Autopsy 可以直接在 Ubuntu 或 Fedora 发行版本上直接安装,而不必下载 SIFT 的整个发行版本。
+
+Sleuth Kit/Autopsy 是一个开源的电子取证调查工具,它可以用于从磁盘映像中恢复丢失的文件,以及为了特殊事件进行磁盘映像分析。 Autopsy 工具是 sleuth kit 的一个网页接口,支持 sleuth kit 的所有功能。这个工具在 Windows 和 Linux 平台下都可获取到。
+
+### 安装 Sleuth kit ###
+
+首先,从 [sleuthkit][1] 的网站下载 Sleuth kit 软件。使用下面的命令在虚拟终端下使用 wget 命令来下载它,下图展示了这个过程。
+
+ # wget http://cznic.dl.sourceforge.net/project/sleuthkit/sleuthkit/4.1.3/sleuthkit-4.1.3.tar.gz
+
+
+
+使用下面的命令解压 sleuthkit-4.1.3.tar.gz 并进入解压后的目录:
+
+ # tar -xvzf sleuthkit-4.1.3.tar.gz
+
+
+
+在安装 sleuth kit 之前,运行下面的命令来执行所需的检查:
+
+ #./configure
+
+
+
+然后使用 Make 命令来编译 sleuth kit :
+
+ #make
+
+
+
+最后,使用下面的命令将它安装到 **/usr/local** 目录下:
+
+ #make install
+
+
+
+### 安装 Autopsy 工具 ###
+
+Sleuth kit 已经安装完毕,现在我们将为它安装 autopsy 界面。从 [sleuthkit 的 autopsy 页面][2]下载 Autopsy 软件。使用下面的命令在虚拟终端下使用 wget 命令来下载它,下图展示了这个过程。
+
+ # wget http://kaz.dl.sourceforge.net/project/autopsy/autopsy/2.24/autopsy-2.24.tar.gz
+
+
+
+使用下面的命令解压 autopsy-2.24.tar.gz 并进入解压后的目录:
+
+ # tar -xvzf autopsy-2.24.tar.gz
+
+
+
+autopsy 的配置脚本将询问 NSRL (National Software Reference Library) 和 **Evidence_Locker** 文件夹的路径。
+
+当弹窗问及 NSRL 时,输入 "n",并在 **/usr/local** 目录下创建名为 Evidence_Locker 的文件夹。Autopsy 将在 Evidence_Locker 文件夹下存储配置文件,审计记录和输出文件。
+
+ #mkdir /usr/local/Evidence_Locker
+
+ #cd autopsy-2.24
+
+ #./configure
+
+
+
+在安装过程中添加完 Evidence_Locker 的安装路径后, autopsy 在那里存储配置文件并展现如下的信息来运行 autopsy 程序。
+
+
+
+在虚拟终端中键入 **./autopsy** 命令来启动 Sleuth kit 工具的图形界面:
+
+
+
+在浏览器中键入下面的地址来访问 autopsy 的界面:
+
+ http://localhost:9999/autopsy
+
+下图展现了 autopsy 插件的主页面:
+
+
+
+在 autopsy 工具中,点击 **新案例** 按钮来开始进行分析。键入案例名称,此次调查的描述和检查人的姓名,下图有具体的展示:
+
+
+
+在接下来的网页中,将展示在上一个的网页中键入的详细信息。接着点击 **增加主机** 按钮来添加有关要分析的机器的详细信息。
+
+
+
+在下一个网页中键入主机名,相关的描述和要分析的机器的时区设置。
+
+
+
+添加主机后,点击 **增加映像** 按钮来为取证分析添加映像文件。
+
+
+
+在接下来的网页中点击 **增加映像文件** 按钮。它将打开一个新的网页,来询问映像文件的路径和选择映像的类型以及导入的方法。
+
+
+
+正如下图中展示的那样,我们已经键入了 Linux 映像文件的路径。在我们这个例子中,映像文件类型是磁盘分区。
+
+
+
+点击“下一步”按钮并在下一页中选择 **计算散列值** 的选项,这在下图中有展示。它也将检测所给映像的文件系统类型。
+
+
+
+下面的图片展示了静态分析之前映像文件的 MD5 散列值。
+
+
+
+在下一个网页中, autopsy 展现了有关映像文件的如下信息:
+
+- 映像的挂载点
+- 映像的名称
+- 所给映像的文件系统类型
+
+点击 **详情** 按钮来获取更多有关所给映像文件的信息。它还提供了从映像文件的卷中导出未分配的片段和字符串的数据信息,这在下图中有展现。
+
+
+
+在下图中那样,点击 **分析** 按钮来开始分析所给映像。它将开启另一个页面,其中包含了映像分析的多个选项。
+
+
+
+在映像分析过程中,Autopsy 提供了如下的功能:
+
+- 文件分析
+- 关键字搜索
+- 文件类型
+- 映像详情
+- 数据单元
+
+下图展示的是在给定的 Linux 分区映像上进行文件分析:
+
+
+
+它将从所给映像中提取所有的文件和文件夹。在下图中也展示了已被删除的文件的提取:
+
+
+
+### 结论 ###
+
+希望这篇文章能够给那些进入磁盘映像静态分析领域的新手提供帮助。Autopsy 是 sleuth kit 的网页界面,提供了在 Windows 和 Linux 磁盘映像中进行诸如字符串提取,恢复被删文件,时间线分析,网络浏览历史,关键字搜索和邮件分析等功能。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/autopsy-sleuth-kit-installation-ubuntu/
+
+作者:[nido][a]
+译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/naveeda/
+[1]:http://www.sleuthkit.org/sleuthkit/download.php
+[2]:http://www.sleuthkit.org/autopsy/download.php
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150323 How to enable ssh login without entering password.md b/published/201505/20150323 How to enable ssh login without entering password.md
similarity index 89%
rename from translated/tech/20150323 How to enable ssh login without entering password.md
rename to published/201505/20150323 How to enable ssh login without entering password.md
index 4f9a4c317d..8202bc62cd 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150323 How to enable ssh login without entering password.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150323 How to enable ssh login without entering password.md
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@
$ cat .ssh/id_rsa.pub | ssh aliceB@hostB 'cat >> .ssh/authorized_keys'
-自此以后,从aliceA@hostA上ssh到aliceB@hostB上再也不需要输入密码。
+自此以后,从aliceA@hostA上ssh到aliceB@hostB上再也不需要输入密码。(LCTT 译注:上述的创建目录并复制的操作也可以通过一个 ssh-copy-id 命令一步完成:`ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub aliceB@hostB`)
### 疑难解答 ###
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/how-to-enable-ssh-login-without.html
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150323 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to compress JPEG images from the command line on Linux.md b/published/201505/20150323 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to compress JPEG images from the command line on Linux.md
similarity index 75%
rename from translated/tech/20150323 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to compress JPEG images from the command line on Linux.md
rename to published/201505/20150323 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to compress JPEG images from the command line on Linux.md
index 6d72a9f5d9..6d08d4d7f6 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150323 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to compress JPEG images from the command line on Linux.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150323 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to compress JPEG images from the command line on Linux.md
@@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
-Linux有问必答--如何使用命令行压缩JPEG图像
+Linux有问必答:如何在命令行下压缩JPEG图像
================================================================================
> **问题**: 我有许多数码照相机拍出来的照片。我想在上传到Dropbox之前,优化和压缩下JPEG图片。有没有什么简单的方法压缩JPEG图片并不损耗他们的质量?
如今拍照设备(如智能手机、数码相机)拍出来的图片分辨率越来越大。甚至3630万像素的Nikon D800已经冲入市场,并且这个趋势根本停不下来。如今的拍照设备不断地提高着照片分辨率,使得我们不得不压缩后,再上传到有储存限制、带宽限制的云。
-事实上,这里有一个非常简单的方法压缩JPEG图像。一个叫“jpegoptim”命令行工具可以帮助你“无损”美化JPEG图像,所以你可以压缩JPEG图片而不至于牺牲他们的质量。万一你的存储空间和带宽预算真的很少,jpegoptim也支持“有损耗”压缩来调整图像大小。
+事实上,这里有一个非常简单的方法压缩JPEG图像。一个叫“jpegoptim”命令行工具可以帮助你“无损”美化JPEG图像,让你可以压缩JPEG图片而不至于牺牲他们的质量。万一你的存储空间和带宽预算真的很少,jpegoptim也支持“有损”压缩来调整图像大小。
-如果要压缩PNG图像,参考[this guideline][1]例子。
+如果要压缩PNG图像,参考[这个指南][1]的例子。
### 安装jpegoptim ###
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ CentOS/RHEL安装,先开启[EPEL库][2],然后运行下列命令:
注意,原始图像会被压缩后图像覆盖。
-如果jpegoptim不能无损美化图像,将不会覆盖
+如果jpegoptim不能无损美化图像,将不会覆盖它:
$ jpegoptim -v photo.jpg
@@ -46,21 +46,21 @@ CentOS/RHEL安装,先开启[EPEL库][2],然后运行下列命令:
$ jpegoptim -d ./compressed photo.jpg
-这样,压缩的图片将会保存在./compressed目录(已同样的输入文件名)
+这样,压缩的图片将会保存在./compressed目录(以同样的输入文件名)
如果你想要保护文件的创建修改时间,使用"-p"参数。这样压缩后的图片会得到与原始图片相同的日期时间。
$ jpegoptim -d ./compressed -p photo.jpg
-如果你只是想获得无损压缩率,使用"-n"参数来模拟压缩,然后它会打印压缩率。
+如果你只是想看看无损压缩率而不是真的想压缩它们,使用"-n"参数来模拟压缩,然后它会显示出压缩率。
$ jpegoptim -n photo.jpg
### 有损压缩JPG图像 ###
-万一你真的需要要保存在云空间上,你可以使用有损压缩JPG图片。
+万一你真的需要要保存在云空间上,你还可以使用有损压缩JPG图片。
-这种情况下,使用"-m<质量>"选项,质量数范围0到100。(0是最好质量,100是最坏质量)
+这种情况下,使用"-m<质量>"选项,质量数范围0到100。(0是最好质量,100是最差质量)
例如,用50%质量压缩图片:
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ CentOS/RHEL安装,先开启[EPEL库][2],然后运行下列命令:
### 一次压缩多张JPEG图像 ###
-最常见的情况是需要压缩一个目录下的多张JPEG图像文件。为了应付这种情况,你可以使用接下里的脚本。
+最常见的情况是需要压缩一个目录下的多张JPEG图像文件。为了应付这种情况,你可以使用接下来的脚本。
#!/bin/sh
@@ -90,11 +90,11 @@ CentOS/RHEL安装,先开启[EPEL库][2],然后运行下列命令:
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/compress-jpeg-images-command-line-linux.html
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
-译者:[VicYu/Vic020](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[VicYu/Vic020](https://github.com/Vic020)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-compress-png-files-on-linux.html
-[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
+[2]:https://linux.cn/article-2324-1.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150323 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install and access CentOS remote desktop on VPS.md b/published/201505/20150323 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install and access CentOS remote desktop on VPS.md
similarity index 82%
rename from translated/tech/20150323 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install and access CentOS remote desktop on VPS.md
rename to published/201505/20150323 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install and access CentOS remote desktop on VPS.md
index 3108d1ed32..7c3db8a320 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150323 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install and access CentOS remote desktop on VPS.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150323 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install and access CentOS remote desktop on VPS.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
-Linux有问必答-- 如何在VPS上安装和访问CentOS远程桌面
+Linux有问必答:如何在VPS上安装和访问CentOS 7远程桌面
================================================================================
-> **提问**: 我想在VPS中安装CentOS桌面,并可以直接从我家远程访问GUI桌面。有什么建议可以在VPS上设置和访问CentOS远程桌面?
+> **提问**: 我想在VPS中安装CentOS桌面,并可以直接从我家远程访问GUI桌面。在VPS上设置和访问CentOS远程桌面有什么建议吗?
如何远程办公或者远程弹性化工作制在技术领域正变得越来越流行。这个趋势背后的一个技术就是远程桌面。你的桌面环境在云中,你可以在任何你去的地方,或者在家或者工作场所访问你的远程桌面。
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ Linux有问必答-- 如何在VPS上安装和访问CentOS远程桌面
### 第一步: 安装CentOS桌面 ###
-如果现在的CentOS版本是没有桌面的最小版本,你需要先在VPS上安装桌面(比如GNOME)。比如,DigitalOcean的镜像就是最小版本,它需要如下安装[桌面GUI][2]
+如果你现在安装的CentOS版本是没有桌面的最小版本,你需要先在VPS上安装桌面(比如GNOME)。比如,DigitalOcean的镜像就是最小版本,它需要如下安装[桌面GUI][2]
# yum groupinstall "GNOME Desktop"
@@ -36,15 +36,15 @@ CentOS依靠systemd来管理和配置系统服务。所以我们将使用systemd
# systemctl status vncserver@:.service
# systemctl is-enabled vncserver@.service
-默认上,刚安装的VNC服务并没有激活(禁用)。
+默认的,刚安装的VNC服务并没有激活(禁用)。
-现在服务一份通用的VNC服务文件来位用户xmodulo创建一个VNC服务配置。
+现在复制一份通用的VNC服务文件来为用户xmodulo创建一个VNC服务配置。
# cp /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@.service /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@:1.service
-用本文编辑器来打开配置文件,用实际的用户名(比如:xmodulo)来替换[Service]下面的<USER>。同样。在ExecStart后面追加 "-geometry <resolution>" 参数。最后,要修改下面两行加粗字体的两行。
+用本文编辑器来打开配置文件,用实际的用户名(比如:xmodulo)来替换[Service]下面的<USER>。同样。在ExecStart后面追加 "-geometry <resolution>" 参数。最后,要修改下面“ExecStart”和“PIDFile”两行。
# vi /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@:1.service
@@ -85,7 +85,7 @@ CentOS依靠systemd来管理和配置系统服务。所以我们将使用systemd
### 第三步:通过SSH连接到远程桌面 ###
-设计上,VNC使用的远程帧缓存(RFB)并不是一种安全的协议。那么在VNC客户端上直接连接到VNC服务器上并不是一个好主意。任何敏感信息比如密码都可以在VNC流量中被轻易地泄露。因此,我强烈建议使用SSH隧道来[加密你的VNC流量][3]。
+从设计上说,VNC使用的远程帧缓存(RFB)并不是一种安全的协议,那么在VNC客户端上直接连接到VNC服务器上并不是一个好主意。任何敏感信息比如密码都可以在VNC流量中被轻易地泄露。因此,我强烈建议使用SSH隧道来[加密你的VNC流量][3]。
在你要运行VNC客户端的本机上,使用下面的命令来创建一个连接到远程VPS的SSH通道。当被要输入SSH密码时,输入用户的密码。
@@ -99,7 +99,7 @@ CentOS依靠systemd来管理和配置系统服务。所以我们将使用systemd
-你将被要求输入VNC密码。当你输入VNC密码时,你就可以安全地连接到CentOS的远程桌面了.
+你将被要求输入VNC密码。当你输入VNC密码时,你就可以安全地连接到CentOS的远程桌面了。
@@ -111,7 +111,7 @@ via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/centos-remote-desktop-vps.html
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150323 Square 2.0 Icon Pack Is Twice More Beautiful.md b/published/201505/20150323 Square 2.0 Icon Pack Is Twice More Beautiful.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cd8c8556a0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150323 Square 2.0 Icon Pack Is Twice More Beautiful.md
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+更漂亮的 Square 2.0图标包
+================================================================================
+
+
+优雅、现代的[Square图标主题][1]最近更新到了2.0版,它比以前更漂亮了。Square图标包与其他主要的桌面环境如**Unity、 GNOME、KDE、 MATE等等**兼容。这意味着你可以在所有的流行Linux发行版如Ubuntu、Fedora、Linux Mint、elementary OS等等中使用它。 这个图标包估计包含超过了15000个图标。
+
+### 在Linux中安装Square 2.0图标包 ###
+
+有两种不同的Square图标,暗色和亮色。基于你的喜好,你可以选择二者之一。出于体验的目的,我建议你两个主题包都下载。
+
+你可以用下面的链接下载图标包。文件存储在Google Drive,因此如果你没有看见像[SourceForge][2]这样标准的下载网站时不要怀疑。
+
+- [Square Dark Icons][3]
+- [Square Light Icons][4]
+
+要使用图标主题,解压下载的文件到~/.icons文件夹下。如果它不存在,就创建它。当这些文件放好后,基于你的桌面环境,使用一个工具来改变图标主题。我以前写了一些关于这个主题的教程。如果你需要额外的帮助,那么欢迎指出来:
+
+- [如何在Ubuntu Unity中改变主题][5]
+- [如何在GNOME Shell中改变主题][6]
+- [如何在Linux Mint中改变主题][7]
+- [如何在Elementary OS Freya中改变主题][8]
+
+### 试一下 ###
+
+这是我用Square图标在Ubuntu 14.04中的效果。我背景使用的是[Ubuntu 15.04 默认壁纸][9]。
+
+
+
+Square主题中几个图标的样子:
+
+
+
+你觉得怎么样?你认为它是[Ubuntu 14.04中最佳的图标主题][10]之一么?你会分享它并期待更多关于自定义Linux桌面的文章么?
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://itsfoss.com/square-2-0-icon-pack-linux/
+
+作者:[Abhishek][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
+[1]:http://gnome-look.org/content/show.php/Square?content=163513
+[2]:http://sourceforge.net/
+[3]:http://gnome-look.org/content/download.php?content=163513&id=1&tan=62806435
+[4]:http://gnome-look.org/content/download.php?content=163513&id=2&tan=19789941
+[5]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-install-themes-in-ubuntu-13-10/
+[6]:http://itsfoss.com/install-switch-themes-gnome-shell/
+[7]:http://itsfoss.com/install-icon-linux-mint/
+[8]:http://itsfoss.com/install-themes-icons-elementary-os-freya/
+[9]:http://itsfoss.com/default-wallpapers-ubuntu-1504/
+[10]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150324 4 Tools to Securely Delete Files from Linux.md b/published/201505/20150324 4 Tools to Securely Delete Files from Linux.md
similarity index 58%
rename from translated/tech/20150324 4 Tools to Securely Delete Files from Linux.md
rename to published/201505/20150324 4 Tools to Securely Delete Files from Linux.md
index bbf0dcb3bf..5926279c9e 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150324 4 Tools to Securely Delete Files from Linux.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150324 4 Tools to Securely Delete Files from Linux.md
@@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
-# Linux 下四种安全删除文件的工具 #
+Linux 下四种安全删除文件的工具
+===============
-任何一个普通水平的计算机用户都知道,从计算机系统中删除的任意数据都可以稍候通过一些努力恢复出来。当你不小心删除了你的重要数据,这是一个不错的方案。但是大多数情况,你不希望你的隐私数据被轻易地恢复。不论何时,我们删除任意的文件,操作系统删除的仅仅是特定数据的索引。这就意味着,数据仍然保存在磁盘的某块地方,这种方法是不安全的,任何一个聪明的计算机黑客可以使用任意不错的数据恢复工具来恢复你删除的数据。Linux 用户利用我们都知晓的 "rm" 命令来从他们的操作系统中删除数据,但是 "rm" 命令在约定俗成的场景下工作。从这个命令删除的数据也可以使用特殊的文件恢复工具恢复。
+任何一个普通水平的计算机用户都知道,从计算机系统中删除的任意数据都可以稍后通过一些努力恢复出来。当你不小心删除了你的重要数据时,这是一个不错的方案。但是大多数情况,你不希望你的隐私数据被轻易地恢复。不论何时,我们删除的任意文件,操作系统删除的仅仅是对特定数据的索引。这就意味着,数据仍然保存在磁盘的某块地方,这种方法是不安全的,任何一个聪明的计算机黑客可以使用各种不错的数据恢复工具来恢复你删除的数据。Linux 用户利用我们都知晓的 "rm" 命令来从他们的操作系统中删除数据,但是 "rm" 命令也是像上面说的那样删除文件。从这个命令删除的数据也可以使用特殊的文件恢复工具恢复。
-让我们看看怎样安全并且完整地从你地 Linux 系统中删除文件或者文件夹。以下提到的工具可以完全地删除数据,因此那些恢复工具很难找到真实数据的痕迹然后恢复它。
+让我们看看怎样安全并完整地从你的 Linux 系统中删除文件或者文件夹。以下提到的工具可以完全地删除数据,因此那些恢复工具很难找到真实数据的痕迹然后恢复它。
### Secure-Delete ###
-Secure-Delete 是一组为 Linux 操作系统而生的工具集合,他们为永久删除文件提供高级的技术支持。一旦 Secure-Delete 安装在任意的 Linux 系统,它会提供如下的四个命令:
+Secure-Delete 是一组为 Linux 操作系统而生的工具集合,他们为永久删除文件提供了先进的技术支持。一旦 Secure-Delete 安装在各种 Linux 系统上,就提供了如下的四个命令:
- srm
- smem
@@ -45,13 +46,13 @@ Secure-Delete 是一组为 Linux 操作系统而生的工具集合,他们为
sudo sswap /dev/sda5
-“**smem**” 用来清理在内存中的内容,它保证当系统重启或者关机时随机存取存储器(RAM)中的内容被清理,但是残余的数据痕迹仍然保存在内存。这个命令提供安全的内存清理,简单地在终端中运行 smem 命令。
+“**smem**” 用来清理在内存中的内容,虽然当系统重启或者关机时会清理随机存取存储器(RAM)中的内容,但是内存中仍然会保留一些数据的残留痕迹。这个命令提供安全的内存清理,简单地在终端中运行 smem 命令即可。
smem
### Shred ###
-"shred" 命令销毁文件或者文件夹的内容,在某种程度上,不可能恢复。它使用随机生成的数据模式来持续重写文件,因此很难恢复任意的被销毁的数据,即使是那些黑客或者窃贼使用高水平的数据恢复工具或者设备。Shred 在 Linux 发行版中时默认安装的,如果你想,你可以运行如下命令来找到它的安装目录:
+"shred" 命令以一种不可恢复的方式来销毁文件或者文件夹的内容。它使用随机生成的数据模式来持续覆写文件,因此很难恢复任意的被销毁的数据,即使是那些黑客或者窃贼使用高水平的数据恢复工具或者设备。Shred 默认安装在所有 Linux 发行版中,如果你想,你可以运行如下命令来找到它的安装目录:
aun@eagle:~$ whereis shred
@@ -75,17 +76,17 @@ Shred 默认情况下使用随机内容重写数据 25 次。如果你想它重
### dd ###
-这个命令起初是用于磁盘克隆的。它用于一个分区或者一个磁盘复制到另一个分区或者磁盘。但是它还用于安全地清除硬盘或者分区的内容。运行如下命令使用随机数据来重写你的当前数据。你不需要安装 dd 命令,所有的 Linux 分发版都已经包含了此命令。
+这个命令起初是用于磁盘克隆的。它用于将一个分区或者一个磁盘复制到另一个分区或者磁盘。但是它还可用于安全地清除硬盘或者分区的内容。运行如下命令使用随机数据来重写你的当前数据。你不需要安装 dd 命令,所有的 Linux 分发版都已经包含了此命令。
sudo dd if=/dev/random of=/dev/sda
-你也可以重写磁盘或者分区中的内容,只需要简单地将所有替换为 “zero”。
+你也可以覆写磁盘或者分区中的内容,只需要简单地将所有替换为 “zero”。
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda
### Wipe ###
-Wipe 起初开发的目的是从磁媒体中安全地擦除文件。这个命令行工具使用特殊的模式来重复地写文件。它使用 fsync() 调用和或 O_SYNC 位来强制访问磁盘,并且使用 Gutmann 算法来重复地写。你可以使用此命令删除单个文件,文件夹或者整个磁盘的内容,但是使用 wipe 命令来删除整个磁盘的模式会耗费大量的时间。另外,安装和使用这个工具相当容易。
+Wipe 起初开发的目的是从磁性介质中安全地擦除文件。这个命令行工具使用特殊的模式来重复地写文件。它使用 fsync() 调用和/或 O_SYNC 位来强制访问磁盘,并且使用 Gutmann 算法来重复地写。你可以使用此命令删除单个文件、文件夹或者整个磁盘的内容,但是使用 wipe 命令来删除整个磁盘的模式会耗费大量的时间。另外,安装和使用这个工具相当容易。
在 ubuntu 的终端中运行如下命令来安装 wipe。
@@ -123,7 +124,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/security/delete-files-permanatly-linux/
作者:[Aun Raza][a]
译者:[dbarobin](https://github.com/dbarobin)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150324 7 Quirky' ls' Command Tricks Every Linux User Should Know.md b/published/201505/20150324 7 Quirky' ls' Command Tricks Every Linux User Should Know.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b41338034f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150324 7 Quirky' ls' Command Tricks Every Linux User Should Know.md
@@ -0,0 +1,163 @@
+Linux用户应知应会的7个‘ls’命令的独特技巧
+================================================================================
+
+在前面我们系列报道的两篇文章中,我们已经涵盖了关于‘ls’命令的绝大多数内容。本文时‘ls命令’系列的最后一部分。如果你还没有读过该系列的其它两篇文章,你可以访问下面的链接。
+
+- [Linux中的15个基本‘ls’命令示例][1]
+- [15 个‘ls’命令的面试问题(一)][2]
+- [10 个‘ls’命令面试的问题(二)][3]
+
+
+
+*7个ls命令独特技巧*
+
+### 1. 以各种时间格式附带时间戳列出目录中的内容 ###
+
+要以时间格式列出目录内容,我们需要选择以下两种方法中的任何一种。
+
+ # ls -l –time-style=[STYLE] (方法 A)
+
+**注意** - 上面的开关`--time`的格式必须和`-l`开关同时使用,否则达不到目的。
+
+ # ls -full-time (方法 B)
+
+可以用以下任何一个选项替换`[STYLE]`。
+
+ full-iso
+ long-iso
+ iso
+ locale
+ +%H:%M:%S:%D
+
+**注意** - 在上面行中,H(时),M(分),S(秒),D(日)的顺序可以任意调整。此外,你只需选择那些相关的选项,而不是所有选项。例如,`ls -l --time-style=+%H`将只显示小时。`ls -l --time-style=+%H:%M:%D`将显示小时、分钟和日。
+
+ # ls -l --time-style=full-iso
+
+
+
+*ls命令的完整 ISO时间格式*
+
+ # ls -l --time-style=long-iso
+
+
+
+*长时间格式列表*
+
+ # ls -l --time-style=iso
+
+
+
+*时间格式列表*
+
+ # ls -l --time-style=locale
+
+
+
+*本地时间格式列表*
+
+ # ls -l --time-style=+%H:%M:%S:%D
+
+
+
+*日期和时间格式列表*
+
+ # ls --full-time
+
+
+
+*完整格式时间列表*
+
+### 2. 以多种格式列出目录内容,如以逗号分隔、水平格式、长格式、垂直格式、交叉格式等列出。 ###
+
+目录内容可以用以下建议的ls命令各种格式列出:
+
+ # ls --format=across # 交叉
+ # ls --format=comma # 逗号
+ # ls --format=horizontal # 水平
+ # ls --format=long # 长格式
+ # ls --format=single-column # 单栏
+ # ls --format=verbose # 详情
+ # ls --format=vertical # 垂直
+
+
+
+*ls命令的列出格式*
+
+### 3. 使用ls命令为目录内容输出结果添加像(/=@|)这样的指示符。 ###
+
+带有`-p`选项的ls命令将实现该目的。它会根据文件类型添加上面这些指示符其中之一。
+
+ # ls -p
+
+
+
+*添加指示符到内容*
+
+### 4. 根据扩展名、大小、时间和版本对目录内容排序。 ###
+
+我们可以使用`--extension`选项来按照扩展名对输出结果排序,`--size`扩展选项按照大小排序,`-t`扩展选项按照时间排序,`-v`扩展选项对版本排序。
+
+我们也可以使用`--none`选项,它会以常规方式输出结果而不会进行排序。
+
+ # ls --sort=extension
+ # ls --sort=size
+ # ls --sort=time
+ # ls --sort=version
+ # ls --sort=none
+
+
+
+*通过选项对内容排序列出*
+
+### 5. 使用ls命令打印目录中各个项的数字UID和GID。 ###
+
+上面的环境可以通过使用带有-n标识的ls命令来实现。
+
+ # ls -n
+
+
+
+*通过UID和GID对打印内容列表*
+
+### 6. 标准输出结果中打印目录内容中比默认指定的更多栏目。 ###
+
+好吧,ls命令根据屏幕大小自动输出目录内容。
+
+然而,我们可以手动分配屏幕宽度的值和出现的栏目的控制数。这可以通过使用‘`--width`’开关实现。
+
+ # ls --width 80
+ # ls --width 100
+ # ls --width 150
+
+
+
+*根据窗口大小列出内容*
+
+**注意**: 你可以试验你可以给width标识传递什么值。
+
+### 7. 通过ls命令为列出的目录内容手动指定的制表符大小而不是默认的8。 ###
+
+ # ls --tabsize=[value]
+
+
+
+*按表尺寸列出内容*
+
+**注意**: 指定`[Value]`的数值。
+
+到目前为止,都讲完了。保持连线,我们会推出下一篇文章。别忘了在下面的评论中为我们提供有价值的反馈。为我们点赞并分享,帮我们推广。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-ls-command-tricks/
+
+作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
+[1]:https://linux.cn/article-5109-1.html
+[2]:https://linux.cn/article-5349-1.html
+[3]:https://linux.cn/article-5350-1.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150324 How to Host Open Source Code Repository in github.md b/published/201505/20150324 How to Host Open Source Code Repository in github.md
similarity index 62%
rename from translated/tech/20150324 How to Host Open Source Code Repository in github.md
rename to published/201505/20150324 How to Host Open Source Code Repository in github.md
index d382f9cd64..8b9f40d3b1 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150324 How to Host Open Source Code Repository in github.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150324 How to Host Open Source Code Repository in github.md
@@ -1,10 +1,11 @@
-怎样在Github上做开源代码库的主人
+怎样在Github上托管开源代码库
================================================================================
-大家好,今天我们要学习一下怎样管理github.com库中的开源软件源代码。GitHub是一个基于web的Git库托管服务,提供分布式修改控制和Git的源代码管理(SCM)功能并加入了自身的特点。它给开源和私有项目提供了一个互相协作的工作区、代码预览和代码管理功能。不像Git,一个完完全全的命令行工具,GitHub提供了一个基于web的图形化界面和桌面,也整合了手机。GitHub同时提供了私有库付费计划和免费账号,都是用来管理开源软件项目的。
+
+大家好,今天我们要学习一下怎样在github.com提供的仓库中托管开源软件源代码。GitHub是一个基于web的Git仓库托管服务,提供基于 git 的分布式版本控制和源代码管理(SCM)功能,并加入了自身的特点。它给开源项目和私有项目提供了一个互相协作的工作区、代码预览和代码管理功能。不像Git是一个完完全全的命令行工具,GitHub提供了一个基于web的图形化界面和桌面,也整合了手机操作。GitHub同时提供了私有库付费计划和通常用来管理开源软件项目的免费账号。

-这是一种快速灵活,基于web的托管服务,它使用方便,管理分布式修改控制系统也是相当容易,任何人都能为了将它们使用、贡献、共享、问题跟踪和更多的全球各地数以百万计的人在github的库里管理他们的软件源代码。这里有一些简单快速地管理软件源代码的方法。
+这是一种快速灵活,基于web的托管服务,它使用方便,管理分布式版本控制系统也是相当容易,任何人都能将他们的软件源代码托管到 github,让全球各地数以百万计的人可以使用它、参与贡献、共享它、进行问题跟踪以及更多的用途。这里有一些简单快速地托管软件源代码的方法。
### 1. 创建一个新的Github账号 ###
@@ -20,7 +21,7 @@
### 2. 创建一个新的库 ###
-成功注册新账号或登录上Github之后,我们需要创建一个新的库来开始我们的正题。
+成功注册新账号或登录上Github之后,我们需要创建一个新的库来开始我们的征程。
点击位于顶部靠右账号id旁边的**(+)**按钮,然后点击“New Repository”。
@@ -46,13 +47,13 @@
现在git已经准备就绪,我们要上传代码了。
-**注意**:为了避免错误,不要用**README**文件、许可证或gitignore文件来初始化新库,你可以在项目推送到Github上之后再添加它们。
+**注意**:为了避免错误,不要在初始化的新库中包含**README**、license或gitignore等文件,你可以在项目推送到Github上之后再添加它们。
-在终端上,我们需要把当前工作目录更改为你的本地项目,然后将本地目录初始化为Git库。
+在终端上,我们需要切换当前工作目录为你的本地项目的目录,然后将其初始化为Git库。
$ git init
-接着我们在我们的新的本地库里添加的文件来作为我们的首次提交内容。
+接着我们添加新的本地库里中的文件,作为我们的首次提交内容。
$ git add .
@@ -62,16 +63,16 @@

-在终端上,我们要给远程库添加URL地址,用于以后我们能提交我们本地的库。
+在终端上,添加远程库的URL地址,以便我们的本地库推送到远程。
- $ git remote add origin remote Repository url
+ $ git remote add origin 远程库的URL
$ git remote -v

-注意:请确保将远程库的URL替换成了自己的远程库的URL。
+注意:请确保将上述“远程库的URL”替换成了你自己的远程库的URL。
-现在,要将我们的本地库提交至GitHub版本库中,我们需要运行一下命令并且输入所需的用户名和密码。
+现在,要将我们的本地库的改变推送至GitHub的版本库中,我们需要运行以下命令,并且输入所需的用户名和密码。
$ git push origin master
@@ -87,9 +88,9 @@
请把以上这条URL地址更改成你想要克隆的地址。
-### 更新改动 ###
+### 推送改动 ###
-如果我们对我们的代码做了更改并想把它们提交至我们的远程库中,我们应该在该目录下运行以下命令。
+如果我们对我们的代码做了更改并想把它们推送至我们的远程库中,我们应该在该目录下运行以下命令。
$ git add .
$ git commit -m "Updating"
@@ -97,7 +98,7 @@
### 结论 ###
-啊哈!我们已经成功地管理我们在Github库中的项目源代码了。快速灵活的Github基于web的托管服务,分布式修改控制系统使用起来方便容易。数百万个非常棒的开源项目驻扎在github上。所以,如果你有任何问题、建议或反馈,请在评论中告诉我们。谢谢大家!好好享受吧 :-)
+啊哈!我们已经成功地将我们的项目源代码托管到Github的库中了。Github是快速灵活的基于web的托管服务,分布式版本控制系统使用起来方便容易。数百万个非常棒的开源项目驻扎在github上。所以,如果你有任何问题、建议或反馈,请在评论中告诉我们。谢谢大家!好好享受吧 :-)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -105,7 +106,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/usr-mgmt/host-open-source-code-repository-github/
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150324 How to Interactively Create a Docker Container.md b/published/201505/20150324 How to Interactively Create a Docker Container.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8fb5f6fa39
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150324 How to Interactively Create a Docker Container.md
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
+如何交互式地创建一个Docker容器
+===============================================================================
+
+大家好,今天我们来学习如何使用一个docker镜像交互式地创建一个Docker容器。当我们从镜像中启动一个Docker进程,Docker就会获取该镜像及其父镜像,并重复这个过程,直到到达基础镜像。然后联合文件系统(UFS)会在其顶层添加一个读写层。读写层被称之为容器,它包含了一些关于父镜像信息及一些其他的信息,如唯一ID,网络配置和资源限制等。容器是有状态的,其状态可以从 **运行态** 切换到 **退出态**。一个处于 **运行态**的容器包含了在CPU上面运行的进程树,于其它在该主机上运行的进程相隔离,而**退出态**是指文件系统的状态,并保留了其退出值。你可以使用它来启动,停止和重启一个容器。
+
+Docker技术为IT界带来了巨大的改变,它使得云服务可以用来共享应用和工作流程自动化,使得应用可以用组件快速组合,消除了开发、品质保证、产品环境间的摩擦。在这篇文章中,我们将会建立CentOS环境,然后用Apache网络服务器提供一个网站服务。
+
+这是一个快速且容易的教程,讨论我们怎样使用交互的shell,以交互的方式来创建一个容器。
+
+### 1. 运行一个Docker实例 ###
+
+Docker首先会尝试从本地取得并运行所需的镜像,如果在本地主机上没有发现,它就会从[Docker公共注册中心][1]拉取。这里,我们将会拉取镜像并在 Docker 容器中创建一个fedora实例,并连接到它的 tty 上的bash shell。
+
+ # docker run -i -t fedora bash
+
+
+
+### 2.安装Apache网络服务器 ###
+
+现在,在我们的Fedora基本镜像实例准备好后,我们将会开始交互式地安装Apache网络服务器,而不是为它创建Dockerfile。为了做到这点,我们需要在终端或者shell运行以下命令。
+
+ # yum update
+
+
+
+ # yum install httpd
+
+
+
+ # exit
+
+### 3.保存镜像 ###
+
+现在,我们要去保存在Fedora实例里做的修改。要做到这个,我们首先需要知道实例的容器ID。而为了得到ID,我们又需要运行以下命令(LCTT 译注:在容器外执行该命令)。
+
+ # docker ps -a
+
+
+
+然后,我们会保存这些改变为一个新的镜像,请运行以下命令。
+
+ # docker commit c16378f943fe fedora-httpd
+
+
+
+这里,修改已经通过使用容器ID保存起来了,镜像名字叫fedora-httpd。为了确认新的镜像是否在运行,我们将运行以下命令。
+
+ # docker images
+
+
+
+### 4. 添加内容到新的镜像 ###
+
+我们自己新的Fedora Apache镜像正成功的运行,现在我们想添加一些我们网站的网页内容到Apache网络服务器,使得网站能够开箱即用。为做到这点,我们需要创建一个新的Dockerfile,它会处理从复制网页内容到启用80端口的所有操作。要达到这样的目的,我们需要使用我们最喜欢的文本编辑器创建Dockerfile文件,像下面演示的一样。
+
+ # nano Dockerfile
+
+现在,我们需要添加以下的命令行到文件中。
+
+ FROM fedora-httpd
+ ADD mysite.tar /tmp/
+ RUN mv /tmp/mysite/* /var/www/html
+ EXPOSE 80
+ ENTRYPOINT [ "/usr/sbin/httpd" ]
+ CMD [ "-D", "FOREGROUND" ]
+
+
+
+这里,上述的Dockerfile中,放在mysite.tar里的网页内容会自动解压到/tmp/文件夹里。然后,整个站点会被移动到Apache的网页根目录/var/www/html/,命令expose 80会打开80端口,这样网站就能正常访问了。其次,入口点放在了/usr/sbin/https里面,保证Apache服务器能够执行。
+
+### 5. 构建并运行一个容器 ###
+
+现在,我们要用刚刚创建的Dockerfile创建我们的容器,以便将我们的网站添加到上面。为做到这,我们需要运行以下命令。
+
+ # docker build -rm -t mysite .
+
+
+
+建立好我们的新容器后,我们需要要用下面的命令来运行容器。
+
+ # docker run -d -P mysite
+
+
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+最后,我们已经成功的以交互式的方式建立了一个Docker容器。在本节方法中,我们是直接通过交互的shell命令建立我们的容器和镜像。在建立与配置镜像与容器时,这种方法十分简单且快速。如果你有任何问题,建议和反馈,请在下方的评论框里写下来,以便我们可以提升或者更新我们的文章。谢谢!祝生活快乐 :-)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/interactively-create-docker-container/
+
+作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
+译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
+[1]:https://registry.hub.docker.com/
diff --git a/published/201505/20150326 How to set up server monitoring system with Monit.md b/published/201505/20150326 How to set up server monitoring system with Monit.md
new file mode 100755
index 0000000000..6886e83ef2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150326 How to set up server monitoring system with Monit.md
@@ -0,0 +1,250 @@
+如何使用Monit部署服务器监控系统
+================================================================================
+很多Linux系统管理员依赖一个集中式的远程监控系统(比如[Nagios][1]或者[Cacti][2])来检查他们网络基础设备的健康状况。虽然集中式监控让管理员的生活更简单了,然而处理很多机器和服务时,专用的监控中心显然成为了一个单点故障,如果监控中心挂了或者因为什么原因(比如硬件或者网络故障)不可访问了,你就会失去整个网络基础设备情况的任何信息。
+
+一个给你的监控系统增加冗余度的方法是安装独立的监控软件(作为后备),至少在网络中的关键/核心服务器上。这样在集中式监控系统挂掉的情况,你还有能力通过后备的监控方式来获取核心服务器的运行状况。
+
+### Monit是什么? ###
+
+[Monit][3]是一个跨平台的用来监控Unix/linux系统(比如Linux、BSD、OSX、Solaris)的工具。Monit特别易于安装,而且非常轻量级(只有500KB大小),并且不依赖任何第三方程序、插件或者库。然而,Monit可以胜任全面监控、进程状态监控、文件系统变动监控、邮件通知和对核心服务的自定义动作等场景。易于安装、轻量级的实现以及强大的功能,让Monit成为一个理想的后备监控工具。
+
+我已经在一些机器使用Monit几年了,而且我对它的可靠性非常满意。甚至作为全面的监控系统,对任何Linux系统管理员来说Monit也是非常有用和强大的。在这篇教程中,我会展示如何在一个本地服务器部署Monit(作为后备监控系统)来监控常见的服务。在部署过程中,我只会展示我们用到的部分。
+
+### 在Linux安装Monit ###
+
+Monit已经被包含在多数Linux发行版的软件仓库中了。
+
+Debian、Ubuntu或者Linux Mint:
+
+ $ sudo aptitude install monit
+
+Fedora或者CentOS/RHEL:
+
+在CentOS/RHEL中,你必须首先启用[EPEL][4]或者[Repoforge][5]软件仓库.
+
+ # yum install monit
+
+Monit自带一个文档完善的配置文件,其中包含了很多例子。主配置文件在/etc/monit.conf(Fedora/CentOS/RHEL 中),或者/etc/monit/monitrc(Debian/Ubuntu/Mint 中)。Monit配置文件有两部分:“Global”(全局)和“Services”(服务)。
+
+### Global Configuration: Web Status Page (全局配置:Web状态页面) ###
+
+Monit可以使用邮件服务来发送通知,也可以使用HTTP/HTTPS页面来展示。我们先使用如下配置的web状态页面吧:
+
+- Monit监听1966端口。
+- 对web状态页面的访问是通过SSL加密的。
+- 使用monituser/romania作为用户名/口令登录。
+- 只允许通过localhost、myhost.mydomain.ro和在局域网内部(192.168.0.0/16)访问。
+- Monit使用pem格式的SSL证书。
+
+之后的步骤,我会使用一个基于Red Hat的系统。在基于Debian的系统中的步骤也是类似的。
+
+首先,在/var/cert生成一个自签名的证书(monit.pem):
+
+ # mkdir /var/certs
+ # cd /etc/pki/tls/certs
+ # ./make-dummy-cert monit.pem
+ # cp monit.pem /var/certs
+ # chmod 0400 /var/certs/monit.pem
+
+现在将下列代码片段放到Monit的主配置文件中。你可以创建一个空配置文件,或者基于自带的配置文件修改。
+
+ set httpd port 1966 and
+ SSL ENABLE
+ PEMFILE /var/certs/monit.pem
+ allow monituser:romania
+ allow localhost
+ allow 192.168.0.0/16
+ allow myhost.mydomain.ro
+
+### Global Configuration: Email Notification (全局配置:邮件通知) ###
+
+然后,我们来设置Monit的邮件通知。我们至少需要一个可用的[SMTP服务器][6]来让Monit发送邮件。这样就可以(按照你的实际情况修改):
+
+- 邮件服务器的机器名:smtp.monit.ro
+- Monit使用的发件人:monit@monit.ro
+- 邮件的收件人:guletz@monit.ro
+- 邮件服务器使用的SMTP端口:587(默认是25)
+
+有了以上信息,邮件通知就可以这样配置:
+
+ set mailserver smtp.monit.ro port 587
+ set mail-format {
+ from: monit@monit.ro
+ subject: $SERVICE $EVENT at $DATE on $HOST
+ message: Monit $ACTION $SERVICE $EVENT at $DATE on $HOST : $DESCRIPTION.
+
+ Yours sincerely,
+ Monit
+
+ }
+
+ set alert guletz@monit.ro
+
+就像你看到的,Monit会提供几个内部变量(`$DATE`、`$EVENT`、`$HOST`等),你可以按照你的需求自定义邮件内容。如果你想要从Monit所在机器发送邮件,就需要一个已经安装的与sendmail兼容的程序(如postfix或者ssmtp)。
+
+### Global Configuration: Monit Daemon (全局配置:Monit守护进程)###
+
+接下来就该配置Monit守护进程了。可以将其设置成这样:
+
+- 在120秒后进行第一次检测。
+- 每3分钟检测一次服务。
+- 使用syslog来记录日志。
+
+如下代码段可以满足上述需求。
+
+ set daemon 120
+ with start delay 240
+ set logfile syslog facility log_daemon
+
+我们必须定义“idfile”,Monit守护进程的一个独一无二的ID文件;以及“eventqueue”,当monit的邮件因为SMTP或者网络故障发不出去,邮件会暂存在这里;以及确保/var/monit路径是存在的。然后使用下边的配置就可以了。
+
+ set idfile /var/monit/id
+ set eventqueue
+ basedir /var/monit
+
+### 测试全局配置 ###
+
+现在“Global”部分就完成了。Monit配置文件看起来像这样:
+
+ # Global Section
+
+ # status webpage and acl's
+ set httpd port 1966 and
+ SSL ENABLE
+ PEMFILE /var/certs/monit.pem
+ allow monituser:romania
+ allow localhost
+ allow 192.168.0.0/16
+ allow myhost.mydomain.ro
+
+ # mail-server
+ set mailserver smtp.monit.ro port 587
+ # email-format
+ set mail-format {
+ from: monit@monit.ro
+ subject: $SERVICE $EVENT at $DATE on $HOST
+ message: Monit $ACTION $SERVICE $EVENT at $DATE on $HOST : $DESCRIPTION.
+
+ Yours sincerely,
+ Monit
+
+ }
+
+ set alert guletz@monit.ro
+
+ # delay checks
+ set daemon 120
+ with start delay 240
+ set logfile syslog facility log_daemon
+
+ # idfile and mail queue path
+ set idfile /var/monit/id
+ set eventqueue
+ basedir /var/monit
+
+现在是时候验证我们的工作了,你可以通过运行如下命令来验证存在的配置文件(/etc/monit.conf):
+
+ # monit -t
+
+ Control file syntax OK
+
+如果monit提示任何错误,请再检查下配置文件。幸运的是,错误/警告信息是可以帮助你发现问题的,比如:
+
+ monit: Cannot stat the SSL server PEM file '/var/certs/monit.pem' -- No such file or directory
+ /etc/monit/monitrc:10: Warning: hostname did not resolve 'smtp.monit.ro'
+
+一旦你确认配置文件没问题了,可以启动monit守护进程,然后等2到3分钟:
+
+ # service monit start
+
+如果你使用的是systemd,运行:
+
+ # systemctl start monit
+
+现在打开一个浏览器窗口,然后访问`https://<monit_host>:1966`。将`<monit_host>`替换成Monit所在机器的机器名或者IP地址。
+
+如果你使用的是自签名的SSL证书,你会在浏览器中看到一个警告信息。继续访问即可。
+
+
+
+你完成登录后,就会看到这个页面。
+
+
+
+在这个教程的其余部分,我们演示监控一个本地服务器和常见服务的方法。你会在[官方wiki页面][7]看到很多有用的例子。其中的多数是可以直接复制粘贴的!
+
+### Service Configuration: CPU/Memory Monitoring (服务配置:CPU、内存监控) ###
+
+我们先来监控本地服务器的CPU、内存占用。复制如下代码段到配置文件中。
+
+ check system localhost
+ if loadavg (1min) > 10 then alert
+ if loadavg (5min) > 6 then alert
+ if memory usage > 75% then alert
+ if cpu usage (user) > 70% then alert
+ if cpu usage (system) > 60% then alert
+ if cpu usage (wait) > 75% then alert
+
+你可以很容易理解上边的配置。最上边的check是指每个监控周期(全局配置里设置的120秒)都对本机进行下面的操作。如果满足了任何条件,monit守护进程就会使用邮件发送一条报警。
+
+如果某个监控项不需要每个周期都检查,可以使用如下格式,它会每240秒检查一次平均负载。
+
+ if loadavg (1min) > 10 for 2 cycles then alert
+
+### Service Configuration: SSH Service Monitoring (服务配置:SSH服务监控) ###
+
+先检查我们的sshd是否安装在/usr/sbin/sshd:
+
+ check file sshd_bin with path /usr/sbin/sshd
+
+我们还想检查sshd的启动脚本是否存在:
+
+ check file sshd_init with path /etc/init.d/sshd
+
+最后,我们还想检查sshd守护进程是否存活,并且在监听22端口:
+
+ check process sshd with pidfile /var/run/sshd.pid
+ start program "/etc/init.d/sshd start"
+ stop program "/etc/init.d/sshd stop"
+ if failed port 22 protocol ssh then restart
+ if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
+
+我们可以这样解释上述配置:我们检查是否存在名为sshd的进程,并且有一个保存其pid的文件存在(/var/run/sshd.pid)。如果任何一个不存在,我们就使用启动脚本重启sshd。我们检查是否有进程在监听22端口,并且使用的是SSH协议。如果没有,我们还是重启sshd。如果在最近的5个监控周期(5x120秒)至少重启5次了,sshd就被认为是不能用的,我们就不再检查了。
+
+
+
+### Service Configuration: SMTP Service Monitoring (服务配置:SMTP服务监控) ###
+
+现在我们来设置一个检查远程SMTP服务器(如192.168.111.102)的监控。假定SMTP服务器运行着SMTP、IMAP、SSH服务。
+
+ check host MAIL with address 192.168.111.102
+ if failed icmp type echo within 10 cycles then alert
+ if failed port 25 protocol smtp then alert
+ else if recovered then exec "/scripts/mail-script"
+ if failed port 22 protocol ssh then alert
+ if failed port 143 protocol imap then alert
+
+我们检查远程主机是否响应ICMP协议。如果我们在10个周期内没有收到ICMP回应,就发送一条报警。如果监测到25端口上的SMTP协议是异常的,就发送一条报警。如果在一次监测失败后又监测成功了,就运行一个脚本(/scripts/mail-script)。如果检查22端口上的SSH或者143端口上的IMAP协议不正常,同样发送报警。
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+在这个教程,我演示了如何在本地服务器设置Monit,当然这只是Monit功能的冰山一角。你可以花些时间阅读Monit的man手册(写得很好)。Monit可以为任何Linux系统管理员做很多事情,并且具有非常优美和易于理解的语法。如果你将一个集中式的远程监控系统和Monit一同使用,你会得到一个更可靠的监控系统。你感觉Monit怎么样?
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/server-monitoring-system-monit.html
+
+作者:[Iulian Murgulet][a]
+译者:[goreliu](https://github.com/goreliu)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/iulian
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-common-services-nagios.html
+[2]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-linux-servers-snmp-cacti.html
+[3]:http://mmonit.com/monit/
+[4]:https://linux.cn/article-2324-1.html
+[5]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
+[6]:http://xmodulo.com/mail-server-ubuntu-debian.html
+[7]:http://mmonit.com/wiki/Monit/ConfigurationExamples
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/201505/20150330 2 Ways to Create Your Own Docker Base Image.md b/published/201505/20150330 2 Ways to Create Your Own Docker Base Image.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4c0030b191
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150330 2 Ways to Create Your Own Docker Base Image.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+两种方式创建你自己的 Docker 基本映像
+================================================================================
+
+欢迎大家,今天我们学习一下 docker 基本映像以及如何构建我们自己的 docker 基本映像。[Docker][1] 是一个开源项目,提供了一个可以打包、装载和运行任何应用的轻量级容器的开放平台。它没有语言支持、框架和打包系统的限制,从小型的家用电脑到高端服务器,在何时何地都可以运行。这使它们可以不依赖于特定软件栈和供应商,像一块块积木一样部署和扩展网络应用、数据库和后端服务。
+
+Docker 映像是不可更改的只读层。Docker 使用 **Union File System** 在只读文件系统上增加可读写的文件系统,但所有更改都发生在最顶层的可写层,而其下的只读映像上的原始文件仍然不会改变。由于映像不会改变,也就没有状态。基本映像是没有父类的那些映像。Docker 基本映像主要的好处是它允许我们有一个独立运行的 Linux 操作系统。
+
+下面是我们如何可以创建自定义的基本映像的方式。
+
+### 1. 使用 Tar 创建 Docker 基本映像 ###
+
+我们可以使用 tar 构建我们自己的基本映像,我们从一个运行中的 Linux 发行版开始,将其打包为基本映像。这过程可能会有些不同,它取决于我们打算构建的发行版。在 Debian 发行版中,已经预带了 debootstrap。在开始下面的步骤之前,我们需要安装 debootstrap。debootstrap 用来获取构建基本系统需要的包。这里,我们构建基于 Ubuntu 14.04 "Trusty" 的映像。要完成这些,我们需要在终端或者 shell 中运行以下命令。
+
+ $ sudo debootstrap trusty trusty > /dev/null
+ $ sudo tar -C trusty -c . | sudo docker import - trusty
+
+
+
+上面的命令为当前文件夹创建了一个 tar 文件并输出到标准输出中,"docker import - trusty" 通过管道从标准输入中获取这个 tar 文件并根据它创建一个名为 trusty 的基本映像。然后,如下所示,我们将运行映像内部的一条测试命令。
+
+ $ docker run trusty cat /etc/lsb-release
+
+[Docker GitHub Repo][2] 中有一些允许我们快速构建基本映像的事例脚本.
+
+### 2. 使用Scratch构建基本映像 ###
+
+在 Docker registry 中,有一个被称为 Scratch 的使用空 tar 文件构建的特殊库:
+
+ $ tar cv --files-from /dev/null | docker import - scratch
+
+
+
+我们可以使用这个映像构建新的小容器:
+
+ FROM scratch
+ ADD script.sh /usr/local/bin/run.sh
+ CMD ["/usr/local/bin/run.sh"]
+
+上面的 Dockerfile 文件来自一个很小的映像。这里,它首先从一个完全空的文件系统开始,然后它复制新建的 /usr/local/bin/run.sh 为 script.sh ,然后运行脚本 /usr/local/bin/run.sh。
+
+### 结尾 ###
+
+这这个教程中,我们学习了如何构建一个开箱即用的自定义 Docker 基本映像。构建一个 docker 基本映像是一个很简单的任务,因为这里有很多已经可用的包和脚本。如果我们想要在里面安装想要的东西,构建 docker 基本映像非常有用。如果有任何疑问,建议或者反馈,请在下面的评论框中写下来。非常感谢!享受吧 :-)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/2-ways-create-docker-base-image/
+
+作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
+译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
+[1]:https://www.docker.com/
+[2]:https://github.com/docker/docker/blob/master/contrib/mkimage-busybox.sh
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150330 How to secure SSH login with one-time passwords on Linux.md b/published/201505/20150330 How to secure SSH login with one-time passwords on Linux.md
similarity index 73%
rename from translated/tech/20150330 How to secure SSH login with one-time passwords on Linux.md
rename to published/201505/20150330 How to secure SSH login with one-time passwords on Linux.md
index f3668f14f0..443f8cab25 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150330 How to secure SSH login with one-time passwords on Linux.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150330 How to secure SSH login with one-time passwords on Linux.md
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
-使用 SSH 和一次性密码安全登录 Linux
+使用一次性密码本通过 SSH 安全登录 Linux
================================================================================
-有人说,安全不是一个产品,而是一个过程(LCTT 注:安全公司 McAfee 认为,安全风险管理是一个方法论,而不是安全产品的堆叠)。虽然 SSH 协议被设计成使用加密技术来确保安全,但如果使用不当,别人还是能够破坏你的系统:比如弱密码、密钥泄露、使用的 SSH 客户端过时等,都能引发安全问题。
+有人说,安全不是一个产品,而是一个过程(LCTT 注:安全公司 McAfee 认为,安全风险管理是一个方法论,而不是安全产品的堆叠)。虽然 SSH 协议被设计成使用加密技术来确保安全,但如果使用不当,别人还是能够破坏你的系统:比如弱密码、密钥泄露、使用过时的 SSH 客户端等,都能引发安全问题。
-在考虑 SSH 认证方案时,大家普遍认为[公钥认证][1]比密码认证更安全。然而,公钥认证技术并不是为公共环境设置的,如果你在一台公用电脑上使用公钥认证登录 SSH 服务器,你的服务器已经毫无安全可言了,公用的电脑可能会记录你的公钥,或从你的内存中读取公钥。如果你不信任本地电脑,那你最好还是使用其他方式登录服务器。现在就是“一次性密码”派上用场的时候了,就像名字所示,一次性密码只能被使用一次。这种一次性密码非常合适在不安全的环境下发挥作用,就算它被窃取,也无法再次使用。
+在考虑 SSH 认证方案时,大家普遍认为[公钥认证][1]比密码认证更安全。然而,公钥认证技术并不是为公共环境设置的,如果你在一台公用电脑上使用公钥认证登录 SSH 服务器,你的服务器已经毫无安全可言了,公用的电脑可能会记录你的公钥,或从你的内存中读取公钥。如果你不信任本地电脑,那你最好还是使用其他方式登录服务器。现在就是“一次性密码(OTP)”派上用场的时候了,就像名字所示,一次性密码只能被使用一次。这种一次性密码非常合适在不安全的环境下发挥作用,就算它被窃取,也无法再次使用。
-有个一次性密码方案叫[谷歌认证][2],但在本文中,我要介绍的是另一种 SSH 登录方案:[OTPW][3],它是个一次性密码登录的软件包。不像谷歌认证,OTPW 不需要依赖任何第三方库。
+有个生成一次性密码的方法是通过[谷歌认证器][2],但在本文中,我要介绍的是另一种 SSH 登录方案:[OTPW][3],它是个一次性密码登录的软件包。不像谷歌认证,OTPW 不需要依赖任何第三方库。
### OTPW 是什么 ###
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ OTPW 由一次性密码生成器和 PAM 认证规则组成。在 OTPW 中一次
$ git clone https://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~mgk25/git/otpw
$ cd otpw
-打开 Makefile 文件,编辑以“PAMLIB=”开头的那行配置:
+打开 Makefile 文件,编辑以“PAMLIB=”开头的那行配置:
64 位系统:
@@ -49,12 +49,12 @@ OTPW 由一次性密码生成器和 PAM 认证规则组成。在 OTPW 中一次
PAMLIB=/usr/lib/security
-编译安装。需要注意的是安装过程会把 SSH 服务重启一下,所以如果你是使用 SSH 连接到服务器,做好被断开连接的准备吧。
+编译安装。需要注意的是安装过程会自动重启 SSH 服务一下,所以如果你是使用 SSH 连接到服务器,做好被断开连接的准备吧(LCTT 译注:也许不会被断开连接,即便被断开连接,请使用原来的方式重新连接即可,现在还没有换成一次性口令方式。)。
$ make
$ sudo make install
-现在你需要更新 SELinux 策略,因为 /usr/sbin/sshd 会往你的 home 目录写数据,而 SELinux 默认是不允许这么做的。如果你使用了 SELinux 服务(LCTT 注:使用 getenforce 命令查看结果,如果是 enforcing,就是打开了 SELinux 服务),如果没有使用 SELinux 服务,请跳过这一步。
+现在你需要更新 SELinux 策略,因为 /usr/sbin/sshd 会往你的 home 目录写数据,而 SELinux 默认是不允许这么做的。如果没有使用 SELinux 服务(LCTT 注:使用 getenforce 命令查看结果,如果是 enforcing,就是打开了 SELinux 服务),请跳过这一步。
$ sudo grep sshd /var/log/audit/audit.log | audit2allow -M mypol
$ sudo semodule -i mypol.pp
@@ -90,6 +90,8 @@ Debian, Ubuntu 或 Linux Mint 发行版:
Fedora 或 CentOS/RHEL 7 发行版:
$ sudo systemctl restart sshd
+
+(LCTT 译注:虽然这里重启了 sshd 服务,但是你当前的 ssh 连接应该不受影响,只是在你完成下述步骤之前,无法按照原有方式建立新的连接了。因此,保险起见,要么多开一个 ssh 连接,避免误退出当前连接;要么将重启 sshd 服务器步骤放到步骤3完成之后。)
#### 步骤3:使用 OTPW 产生一次性密码 ####
@@ -102,7 +104,7 @@ Fedora 或 CentOS/RHEL 7 发行版:
这个命令会让你输入密码前缀,当你以后登录的时候,你需要同时输入这个前缀以及一次性密码。密码前缀是另外一层保护,就算你的一次性密码表被泄漏,别人也无法通过暴力破解你的 SSH 密码。
-设置好密码前缀后,这个命令会产生 280 个一次性密码,并将它们保存在一个文本文件中(如 temporary_password.txt)。每个密码(默认是 8 个字符)由一个 3 位十进制数索引。你需要将这个密码表打印出来,并随身携带。
+设置好密码前缀后,这个命令会产生 280 个一次性密码(LCTT 译注:保存到 ~/.otpw 下),并将它们导出到一个文本文件中(如 temporary_password.txt)。每个密码(默认是 8 个字符)由一个 3 位十进制数索引。你需要将这个密码表打印出来,并随身携带。
@@ -160,7 +162,7 @@ Fedora 或 CentOS/RHEL 7 发行版:
### 总结 ###
-在这个教程中,我介绍了如何使用 OTPW 工具来设置一次性登录密码。你也许意识到了在这种两个因子的认证方式中,打印一张密码表让人感觉好 low,但是这种方式是最简单的,并且不用依赖任何第三方软件。无论你用哪种方式创建一次性密码,在你需要在一个不被信任的环境登录 SSH 服务器的时候,它们都很有用。你可以就这个主题来分享你的经验和观点。
+在这个教程中,我介绍了如何使用 OTPW 工具来设置一次性登录密码。你也许意识到了在这种双因子的认证方式中,打印一张密码表让人感觉好 low,但是这种方式是最简单的,并且不用依赖任何第三方软件。无论你用哪种方式创建一次性密码,在你需要在一个不可信任的环境登录 SSH 服务器的时候,它们都很有用。你可以就这个主题来分享你的经验和观点。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -168,11 +170,11 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/secure-ssh-login-one-time-passwords-linux.html
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
-[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-force-ssh-login-via-public-key-authentication.html
-[2]:http://xmodulo.com/two-factor-authentication-ssh-login-linux.html
+[1]:https://linux.cn/article-5444-1.html
+[2]:https://linux.cn/article-2642-1.html
[3]:http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~mgk25/otpw.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150330 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to upgrade Docker on Ubuntu.md b/published/201505/20150330 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to upgrade Docker on Ubuntu.md
similarity index 87%
rename from translated/tech/20150330 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to upgrade Docker on Ubuntu.md
rename to published/201505/20150330 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to upgrade Docker on Ubuntu.md
index 8d993c1c47..ad9ed38d09 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150330 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to upgrade Docker on Ubuntu.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150330 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to upgrade Docker on Ubuntu.md
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-Linux有问必答-- 如何在Ubuntu中升级Docker
+Linux有问必答:如何在Ubuntu中升级Docker
================================================================================
> **提问**: 我使用了Ubuntu的标准仓库安装了Docker。然而,默认安装的Docker不能满足我另外一个依赖Docker程序的版本需要。我该如何在Ubuntu中升级到Docker的最新版本?
-Docker第一次在2013年发布,它快速地演变成了一个针对分布式程序的开发平台。为了满足工业期望,Docker正在紧密地开发并持续地带来新特性的升级。这样Ubuntu发行版中的Docker版本可能很快就会过时。比如,, Ubuntu 14.10 Utopic 中的Docker版本是1.2.0, 然而最新的Docker版本是1.5.0。
+Docker第一次在2013年发布,它快速地演变成了一个针对分布式程序的开发平台。为了满足工业期望,Docker正在紧密地开发并持续地带来新特性的升级。这样Ubuntu发行版中的Docker版本可能很快就会过时。比如, Ubuntu 14.10 Utopic 中的Docker版本是1.2.0, 然而最新的Docker版本是1.6.0。

@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/upgrade-docker-ubuntu.html
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150331 Conky--The Ultimate X Based System Monitor Application.md b/published/201505/20150331 Conky--The Ultimate X Based System Monitor Application.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fb90f58168
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150331 Conky--The Ultimate X Based System Monitor Application.md
@@ -0,0 +1,151 @@
+Conky - 终极的 X 视窗系统监视器应用
+================================================================================
+Conky 是一个用 ‘C’ 语言写就的系统监视器,并在 GNU GPL 和 BSD 许可协议下发布,在 Linux 和 BSD 操作系统中都可以获取到它。这个应用是基于 X 视窗系统的,原本由 [Torsmo][1] 分支而来。
+
+#### 特点 ####
+
+- 简洁的用户界面;
+- 高度可配置;
+- 它既可使用内置的部件(超过 300 多个) 也可使用外部脚本,来在桌面或其自有容器中展示系统的状态;
+- 低资源消耗;
+- 它可显示范围广泛的系统参数,包括但不限于 CPU,内存,swap 分区 ,温度,进程,磁盘使用情况,网络状态,电池电量,邮件收发,系统消息,音乐播放器的控制,天气信息,最新新闻,升级信息等等;
+- 在许多操作系统中如 CrunchBang Linux 和 Pinguy OS 被默认安装;
+
+#### 关于 Conky 的少有人知的事实 ####
+
+- conky 这个名称来自于一个加拿大电视节目;
+- 它已被移植到 Nokia N900 上;
+- 官方已经不再维护它了;
+
+### 在 Linux 中 Conky 的安装和使用 ###
+
+在我们安装 conky 之前,我们需要使用下面的命令来安装诸如 `lm-sensors`, `curl` 和 `hddtemp` 之类的软件包:
+
+ # apt-get install lm-sensors curl hddtemp
+
+然后是检测传感器:
+
+ # sensors-detect
+
+**注**: 在被系统提示时,回答 ‘Yes’ 。
+
+检测所有探测到的传感器:
+
+ # sensors
+
+#### 样例输出 ####
+
+ acpitz-virtual-0
+ Adapter: Virtual device
+ temp1: +49.5°C (crit = +99.0°C)
+
+ coretemp-isa-0000
+ Adapter: ISA adapter
+ Physical id 0: +49.0°C (high = +100.0°C, crit = +100.0°C)
+ Core 0: +49.0°C (high = +100.0°C, crit = +100.0°C)
+ Core 1: +49.0°C (high = +100.0°C, crit = +100.0°C)
+
+Conky 既可以从软件仓库中安装,也可从源代码编译得到:
+
+ # yum install conky [在 RedHat 系的系统上]
+ # apt-get install conky-all [在 Debian 系的系统上]
+
+**注**: 在 Fedora/CentOS 上安装 conky 之前,你必须启用 [EPEL 软件仓库][2]。
+
+在安装完 conky 之后,只需输入如下命令来开启它:
+
+ $ conky &
+
+
+
+*正在运行的 Conky 监视器*
+
+这使得 conky 以一个弹窗的形式运行,并使用位于 `/etc/conky/conky.conf` 的 conky 基本配置文件。
+
+你可能想将 conky 集成到桌面上,并不想让它每次以弹窗的形式出现,下面就是你需要做的:
+
+将配置文件 `/etc/conky/conky.conf` 复制到你的家目录中,并将它重命名为 `.conkyrc`,开头的点号 (.) 是为了确保这个配置文件是隐藏的。
+
+ $ cp /etc/conky/conky.conf /home/$USER/.conkyrc
+
+现在重启 conky 来应用新的更改:
+
+ $ killall -SIGUSR1 conky
+
+
+
+*Conky 监视器窗口*
+
+你可能想编辑位于你的家目录的 conky 的配置文件,这个配置文件的内容是非常容易理解的。
+
+下面是 conky 配置文件的一个样例:
+
+
+
+*Conky 的配置*
+
+从上面的窗口中,你可以更改颜色,边框,大小,缩放比例,背景,对齐方式及几个其他属性。通过为不同的 conky 窗口设定不同的对齐方式,我们可以同时运行几个 conky 脚本。
+
+**让 conky 使用其它脚本而不是默认配置,以及如何找到这些脚本?**
+
+你可以编写你自己的 conky 脚本或使用来自于互联网的脚本;我们并不建议你使用从互联网中找到的具有潜在危险的任何脚本,除非你清楚你正在做什么。然而,有一些著名的主题和网页包含可信赖的 conky 脚本,例如下面所提及的:
+
+- [http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=281865][3]
+- [http://conky.sourceforge.net/screenshots.html][4]
+
+在上面的 URL 地址中,你将发现其中每个截图都有一个超链接,它们将指向到脚本文件。
+
+#### 测试 Conky 脚本 ####
+
+这里我将在我的 Debian Jessie 系统中运行一个由第三方写的 conky 脚本,以此来进行测试:
+
+ $ wget https://github.com/alexbel/conky/archive/master.zip
+ $ unzip master.zip
+
+切换当前工作目录到刚才解压的目录:
+
+ $ cd conky-master
+
+将 `secrets.yml.example` 重命名为 `secrets.yml`:
+
+ $ mv secrets.yml.example secrets.yml
+
+在你需要运行这个(ruby)脚本之前安装 Ruby:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install ruby
+ $ ruby starter.rb
+
+
+
+*华丽的 conky 外观*
+
+**注**: 可以修改这个脚本以展示你当前的天气,温度等;
+
+假如你想让 conky 开机自启,请在开机启动应用设置(startup Applications) 中添加如下的几行命令:
+
+ conky --pause 10
+ save and exit.
+
+最后,如此轻量级且吸引眼球的实用 GUI 软件包不再处于活跃状态且官方不再进行维护了。最新的稳定发布版本为 conky 1.9.0, 于 2012 年 5 月 3 号发布。在 Ubuntu 论坛上,一个有关用户分享 conky 配置的主题已经超过了 2000 多页。(这个论坛主题的链接为: [http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=281865/][5])
+
+- [Conky 主页][6]
+
+这就是全部内容了。保持联系,保持评论。请在下面的评论框里分享你的想法和配置。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-conky-in-ubuntu-debian-fedora/
+
+作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
+译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
+[1]:http://torsmo.sourceforge.net/
+[2]:https://linux.cn/article-2324-1.html
+[3]:http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=281865
+[4]:http://conky.sourceforge.net/screenshots.html
+[5]:http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=281865/
+[6]:http://conky.sourceforge.net/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150331 How to Generate or Encrypt or Decrypt Random Passwords in Linux.md b/published/201505/20150331 How to Generate or Encrypt or Decrypt Random Passwords in Linux.md
similarity index 70%
rename from translated/tech/20150331 How to Generate or Encrypt or Decrypt Random Passwords in Linux.md
rename to published/201505/20150331 How to Generate or Encrypt or Decrypt Random Passwords in Linux.md
index dcb675d782..b4023b5162 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150331 How to Generate or Encrypt or Decrypt Random Passwords in Linux.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150331 How to Generate or Encrypt or Decrypt Random Passwords in Linux.md
@@ -2,42 +2,45 @@
================================================================================
我们一直积极地提供有关 Linux 技巧的系列文章,如果你错过了这个系列的最新文章,你或许可以去访问下面的链接。
-注:此篇文章做过原文
-- [Linux 中 5 个有趣的命令行技巧][1] (注:这篇文章还没有被翻译,在 20150316 选的题)
+- [Linux 中 5 个有趣的命令行技巧][1]
在这篇文章中,我们将分享一些有趣 Linux 技巧,内容是有关如何产生随机密码以及加密或解密这些经过加盐或没有加盐处理的密码。
安全是数字时代中的一个主要话题。在电脑,email,云端,手机,文档和其他的场合中,我们都会使用到密码。众所周知,选择密码的基本原则是 “易记,难猜”。考虑过使用基于机器自动生成的密码吗?相信我,Linux 非常擅长这方面的工作。
-**1. 使用命令 `pwgen` 来生成一个长度为 10 个字符的唯一的随机密码。假如你还没有安装 pwgen,请使用 Apt 或 YUM 等包管理器来安装它。**
+**1. 使用命令 `pwgen` 来生成一个长度为 10 个字符的独特的随机密码。假如你还没有安装 pwgen,请使用 Apt 或 YUM 等包管理器来安装它。**
$ pwgen 10 1
-
-生成一个唯一的随机密码
+
+
+*生成一个独特的随机密码*
一口气生成若干组长度为 50 个字符的唯一的随机密码!
$ pwgen 50

-生成多组随机密码
-**2. 你还可以使用 `makepasswd` 来每次生成一个给定长度的唯一的随机密码。在你把玩 makepasswd 命令之前,请确保你已经安装了它。如若没有安装它,试试使用 Apt 或 YUM 包管理器来安装 `makepasswd`这个软件包。**
+*生成多组随机密码*
+
+**2. 你还可以使用 `makepasswd` 来每次生成一个给定长度的独特的随机密码。在你把玩 makepasswd 命令之前,请确保你已经安装了它。如若没有安装它,试试使用 Apt 或 YUM 包管理器来安装 `makepasswd`这个软件包。**
生成一个长度为 10 个字符的随机密码。该命令产生的密码的长度默认为 10。
$ makepasswd
-
-使用 makepasswd 生成唯一的密码
+
+
+*使用 makepasswd 生成独特的密码*
生成一个长度为 50 个字符的随机密码。
$ makepasswd --char 50
-生成长度为 50 的密码
+
+*生成长度为 50 的密码*
生成 7 个长度为 20 个字符的随机密码。
@@ -47,9 +50,7 @@
**3. 使用带“盐”的 Crypt(注:这里应该指的是一个函数,可以参考[这里](http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man3/crypt.3.html) ) 来加密一个密码。提供手动或自动添加 “盐”。**
-对于那些不清楚 **盐** 的意义的人,
-
-这里的 “盐” 指的是一个随机数据,它作为密码生成函数的一个额外的输入, 目的是保护密码免受词典攻击。
+对于那些不清楚 **盐** 的意义的人,这里的 “盐” 指的是一个随机数据,它作为密码生成函数的一个额外的输入, 目的是保护密码免受词典攻击。
在执行下面的操作前,请确保你已经安装了 `mkpasswd`。
@@ -58,46 +59,51 @@
$ mkpasswd tecmint
-使用 Crypt 来加密密码
+
+*使用 Crypt 来加密密码*
现在让我们来手动定义 “盐” 的值。每次它将产生相同的结果。请注意你可以输入任何你想输入的值来作为 “盐” 的值。
$ mkpasswd tecmint -s tt
-带“盐”加密密码
+
+*带“盐”加密密码*
另外, mkpasswd 还是交互式的,假如你在命令中没有提供密码,它将主动询问你来输入密码。
-**4. 使用 aes-256-cbc 加密算法并使用密码(如 “tecmint”) 并带“盐” 加密一个字符串(如 “Tecmint-is-a-Linux-Community”)。**
+**4. 使用 aes-256-cbc 加密算法并使用带“盐”的密码(如 “tecmint”) 加密一个字符串(如 “Tecmint-is-a-Linux-Community”)。**
# echo Tecmint-is-a-Linux-Community | openssl enc -aes-256-cbc -a -salt -pass pass:tecmint
-在 Linux 中加密一个字符串
-在上面例子中, [echo 命令][2](注:此篇原文也做过,这里是链接 http://linux.cn/article-3948-1.html) 的输出通过管道传递给了 openssl 命令,使得该输出被 Cipher(enc) 所加密,这个过程中使用了 aes-256-cbc 加密算法,并附带了密码 (tecmint) 和 “盐” 。
+*在 Linux 中加密一个字符串*
+
+在上面例子中, [echo 命令][2]的输出通过管道传递给了 openssl 命令,使得该输出通过加密编码方式(enc:Encoding with Cipher ) 所加密,这个过程中使用了 aes-256-cbc 加密算法,并附带了密码 (tecmint) 和 “盐” 。
**5. 使用 openssl 命令的 -aes-256-cbc 解密选项来解密上面的字符串。**
# echo U2FsdGVkX18Zgoc+dfAdpIK58JbcEYFdJBPMINU91DKPeVVrU2k9oXWsgpvpdO/Z | openssl enc -aes-256-cbc -a -d -salt -pass pass:tecmint

-在 Linux 中解密字符串
-现在就是这些内容了。假如你知道任何这类的技巧,请将你的技巧发送到 admin@tecmint.com 邮箱中,你的技巧将会以你的名义来发表,同时我们也将在我们将来的文章中把它包含进去。
+*在 Linux 中解密字符串*
+
+现在就是这些内容了。
保持联系,保持连接,敬请关注。不要忘了在下面的评论中提供给我们您有价值的反馈。
+
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
via: http://www.tecmint.com/generate-encrypt-decrypt-random-passwords-in-linux/
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
-[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/5-linux-command-line-tricks/
-[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/
\ No newline at end of file
+[1]:https://linux.cn/article-5485-1.html
+[2]:http://linux.cn/article-3948-1.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150331 Its Now Worth Try Installing PHP 7.0 on CentOS 7.x or Fedora 21.md b/published/201505/20150331 Its Now Worth Try Installing PHP 7.0 on CentOS 7.x or Fedora 21.md
similarity index 77%
rename from translated/tech/20150331 Its Now Worth Try Installing PHP 7.0 on CentOS 7.x or Fedora 21.md
rename to published/201505/20150331 Its Now Worth Try Installing PHP 7.0 on CentOS 7.x or Fedora 21.md
index bc27aec4ec..2d059a4930 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150331 Its Now Worth Try Installing PHP 7.0 on CentOS 7.x or Fedora 21.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150331 Its Now Worth Try Installing PHP 7.0 on CentOS 7.x or Fedora 21.md
@@ -1,29 +1,30 @@
-现在值得去尝试一下在CentOS 7.x或Fedora 21上面安装PHP 7.0
+在CentOS 7.x / Fedora 21 上面体验 PHP 7.0
===============================================================================
-PHP是一种为我们熟知的通用的,服务器网页脚本语言。超大量的在线网站都是用PHP编写的。PHP过去一直在更新,丰富功能,易于使用,而且很好组织的脚本语言。目前PHP的开发团队正筹备下一个PHP版本的发行,名字是PHP 7。现在的PHP版本为PHP 5.6,可能你清楚PHP 6已经流产了,PHP 7的支持者们不希望下一个重要的版本被其他分支混淆,即过去已经停止很久的PHP 6。所以决定下一个PHP主要的发行版本叫PHP 7,而不是PHP 6。PHP 7.0预计在今年十一月份发行。
-在下一个主要的PHP发行版里有一些不错的功能。
+PHP是一种为我们熟知的通用服务器网页脚本语言。非常多的在线网站都是用PHP编写的。PHP这些年来一直在持续进化,丰富其功能,变得易于使用,更好地组织的脚本语言。目前PHP的开发团队正筹备下一个PHP版本的发行,名字是PHP 7。现在的PHP版本为PHP 5.6,可能你清楚PHP 6已经流产了,PHP 7的支持者们不希望下一个重要的版本被其他分支混淆,即过去已经停止很久的PHP 6。所以决定下一个PHP主要的发行版本叫PHP 7,而不是PHP 6。PHP 7.0预计在今年十一月份发行。
-- 为了提升执行效率与记忆痕迹,PHPNG功能被添加到新的发行版中。
-- JIT引擎被收入来动态编译Zend操作码为自然机器码,以此来达到更快的处理性能。这项功能允许随后的程序调用同一份代码,这样会运行快很多。
+在下一代主要PHP版本里有一些不错的功能:
+
+- 为了改善执行效率与内存占用,新的版本添加了PHPNG功能。
+- 引入了JIT引擎来动态编译Zend操作码为自然机器码,以此来达到更快的处理性能。这项功能允许随后的程序调用同一份代码,这样会运行快很多。
- AST(抽象语法树)是最新添加的功能,它可以增强支持PHP的扩展性和用户应用。
-- 异步编程功能会添加支持并行任务,在同样的需求下。
--新的版本会支持独立多线程网页服务,这样可以使用一个单独的存储块处理很多并发的请求。
+- 添加异步编程功能以支持同一个请求中的并行任务。
+- 新的版本会支持独立的多线程网页服务器,这样可以使用一个单独的存储池处理很多并发的请求。
-### 在CcentOS/Fedora上安装PHP 7 ###
+### 在CentOS/Fedora上安装PHP 7 ###
-让我们来看看怎样在CentOS 7和Fedora 21安装PHP7。为了安装PHP7,我们首先需要克隆php-src 仓库。当克隆工作完成,我们会配置和编译它。进行下一步之前,我们要确保已经在LInux系统下安装了如下的东西,否则PHP编译会返回错误,然后流产。
+让我们来看看怎样在CentOS 7和Fedora 21安装PHP7。为了安装PHP7,我们首先需要克隆php-src 仓库。当克隆工作完成,我们再配置和编译它。进行下一步之前,我们要确保已经在LInux系统下安装了如下的组件,否则PHP编译会返回错误中止。
- Git
- autoconf
- gcc
- bison
-所有上面提到的要求可以使用Yum软件包管理器安装。用连续的一个命令应该这样:
+所有上面提到的要求可以使用Yum软件包管理器安装。以下一条命令即可完成:
yum install git autoconf gcc bison
-准备好开始安装PHP7了吗?让我们先创建一个PHP7目录,作为你的工作目录。
+准备好开始安装PHP7了吗?让我们先创建一个PHP7目录,作为你的当前工作目录。
mkdir php7
@@ -143,7 +144,7 @@ PHP是一种为我们熟知的通用的,服务器网页脚本语言。超大
--with-mysqli=/usr/bin/mysql_config
-这会花去不少的时间,一旦完成,你应该会看到如下面的输出:
+这会花去不少的时间,当完成后你应该会看到如下面的输出:
creating libtool
@@ -206,9 +207,9 @@ PHP是一种为我们熟知的通用的,服务器网页脚本语言。超大
运行下面的命令,完成编译过程。
- manke
+ make
-“make”命令过后的样例输出如下所示:
+“make”命令的样例输出如下所示:
Generating phar.php
@@ -294,7 +295,7 @@ PHP是一种为我们熟知的通用的,服务器网页脚本语言。超大
cd sapi/cli
-在这里验证PHP的版本。
+验证一下PHP的版本。
[root@localhost cli]# ./php -v
@@ -306,7 +307,7 @@ PHP是一种为我们熟知的通用的,服务器网页脚本语言。超大
### 总结 ###
-PHP 7也被[添加到了remi仓库][1],即将到来的版本主要关注执行效率的提升,新的特性致力于使PHP较好满足现代编程的需求和趋势。PHP 7.0将会有许多新的特性,丢弃一些老版本的东西。在接下来的日子里,我们希望看到新特性和弃用功能的具体情况。尽情享受吧!
+PHP 7也[添加到了remi仓库][1],这个即将到来的版本主要关注执行效率的提升,它的新特性致力于使PHP较好满足现代编程的需求和趋势。PHP 7.0将会有许多新的特性、丢弃一些老版本的东西。在接下来的日子里,我们希望看到新特性和弃用功能的具体情况。希望你喜欢!
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -314,7 +315,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-php-7-centos-7-fedora-21/
作者:[Aun Raza][a]
译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150331 Linux Email App Geary Updated--How To Install It In Ubuntu.md b/published/201505/20150331 Linux Email App Geary Updated--How To Install It In Ubuntu.md
similarity index 78%
rename from translated/tech/20150331 Linux Email App Geary Updated--How To Install It In Ubuntu.md
rename to published/201505/20150331 Linux Email App Geary Updated--How To Install It In Ubuntu.md
index c5920123c6..da976c42d0 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150331 Linux Email App Geary Updated--How To Install It In Ubuntu.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150331 Linux Email App Geary Updated--How To Install It In Ubuntu.md
@@ -1,20 +1,21 @@
-Linux Email应用 Geary 更新了 — 如何在Ubuntu上安装
+Linux Email应用 Geary 更新了
================================================================================
**Geary,Linux上流行的桌面email客户端,更新到版本0.10了 — 并且有了很多新的功能。**

-elementary OS上运行的旧版本的Geary
-Geary 0.10有一些可惜的用户界面改进以及额外的UI选项,包括:
+*elementary OS上运行的旧版本的Geary*
-- 新增: 可以对归档,删除以及移动做'Undo'操作
+Geary 0.10有一些不错的用户界面改进以及额外的UI功能,包括:
+
+- 新增: 可以撤销归档、删除以及移动等操作
- 新增: 在2列或者2列布局之间切换
- 新的 “split header bar” — 改进邮件列表,发件人布局
- 新的快捷键 — 使用j/k切换到上/下一封邮件
-根据Yorba介绍,这次更新还提出了一个 **全新的全文检索算法** ,用来改进Geary的搜索体验。
+根据Yorba介绍,这次更新还引入了一个**全新的全文检索算法** ,用来改进Geary的搜索体验。
-这个更新应该能平息一下对应用搜索能力的抱怨,那些经常觉得Geary返回的搜索结果仅仅是包装软件自身"看起来和查询语句毫不相关"的观点。
+这个更新应该能平息一下对该应用的搜索能力的抱怨:Geary返回的搜索结果就如同软件自己所宣称的“看起来和查询语句毫不相关”。
> ‘Yorba 建议所有这个软件客户端的用户升级到这个版本’
@@ -36,7 +37,7 @@ Yorba的最新版本可以从GNOME的Git账户下载可编译的源代码。但
Ubuntu用户想知道如何在 **14.04,14.10** 以及 **15.04**(那些更新爱好者) 上安装Geary 0.10。
-官方的Youba PPA包括了 **Geary最新版本** 以及Shotwell(照片管理器)和[California][2](日历应用)。请注意添加这个PPA会使你电脑上任何已经安装的这些应用更新到最近的版本。
+官方的Youba PPA包括了 **Geary 最新版本** 以及Shotwell(照片管理器)和[California][2](日历应用)。请注意添加这个PPA会使你电脑上任何已经安装的这些应用更新到最近的版本。
Capiche? Coolio.
@@ -52,7 +53,7 @@ Capiche? Coolio.
完成后,打开你的桌面环境应用启动面板并查找‘Geary’图标。点击它,添加你的账户并查看[通过信息高速公路下载了什么][3],开始使用简单的图形界面吧。
-**别忘记:你可以通过电子邮件告诉我们你想看的新闻,应用建议,以及任何你想我们包括的东西,直接点击joey@oho.io**
+**别忘记:你可以通过电子邮件告诉我们你想看的新闻,应用建议,以及任何你想我们包括的东西。**
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -60,7 +61,7 @@ via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/03/install-geary-ubuntu-linux-email-update
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150407 5 Linux Command Line Based Tools for Downloading Files and Browsing Websites.md b/published/201505/20150407 5 Linux Command Line Based Tools for Downloading Files and Browsing Websites.md
similarity index 72%
rename from translated/tech/20150407 5 Linux Command Line Based Tools for Downloading Files and Browsing Websites.md
rename to published/201505/20150407 5 Linux Command Line Based Tools for Downloading Files and Browsing Websites.md
index 631c1992c6..4e6f6f83d0 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150407 5 Linux Command Line Based Tools for Downloading Files and Browsing Websites.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150407 5 Linux Command Line Based Tools for Downloading Files and Browsing Websites.md
@@ -1,9 +1,11 @@
-5个基于Linux命令行的文件下载和网站浏览工具
+5 个基于Linux命令行的文件下载和网站浏览工具
================================================================================
-GNU/Linux最冒险迷人的部分,Linux命令行,是非常强大的工具。命令行本身功能多样,多种内建或者第三方的命令行应用使得Linux变得更加健壮和强大。Linux Shell支持多种不同类型的网络应用,无论是BT下载软件,专用下载器或者互联网冲浪。
+
+Linux命令行是GNU/Linux中最神奇迷人的部分,它是非常强大的工具。命令行本身功能多样,多种内建或者第三方的命令行应用使得Linux变得更加健壮和强大。Linux Shell支持多种不同类型的网络应用,无论是BT下载软件,专用下载器或者互联网冲浪。

-5个命令行互联网工具
+
+*5个命令行互联网工具*
这里我们介绍了5个很好的命令行互联网工具,它们非常有用,也很容易上手。
@@ -24,7 +26,8 @@ rTorrent是基于文本,用C++编写,追求高性能的Torrent客户端。
# rtorrent

-rTorrent命令行工具
+
+*rTorrent命令行工具*
#### rTorrent的功能 ####
@@ -34,18 +37,18 @@ rTorrent命令行工具
- CTRL+ s – 开始下载
- CTRL+ d – 停止运行中的下载或者移除已完成的下载
- CTRL+ k – 停止并关闭运行中的下载
-- CTRL+ r – 在上传/下载torrent之前进行Hash检查
-- CTRL+ q – 执行两次这个命令,rTorrent会直接退出而不发送停止信号
+- CTRL+ r – 在上传/下载种子之前进行Hash检查
+- CTRL+ q – 执行两次这个命令,rTorrent会直接退出而不发送“停止”信号
- Left Arrow Key – 跳到上一屏幕
- Right Arrow Key – 跳到下一屏幕
### 2. Wget ###
-Wget是GNU项目的一部分,名字由World Wide Web (WWW)衍生而来。Wget是用来递归下载,离线查看本地服务器HTML文件一个很好的工具,它可用于Windows, Max,以及Linux等大部分平台。Wget能通过HTTP,HTTPS和FTP下载文件。另外,能镜像整个网站,支持代理浏览以及暂停/回复下载使得它更为有用。
+Wget是GNU项目的一部分,名字由World Wide Web (WWW)衍生而来。Wget是用来递归下载、离线查看本地服务器HTML文件一个很好的工具,它可用于Windows, Mac,以及Linux等大部分平台。Wget能通过HTTP,HTTPS和FTP下载文件。另外,能镜像整个网站,支持代理浏览以及暂停/回复下载使得它更为有用。
#### 安装Wget ####
-由于是GNE项目的一部分,Wget在大部分标准Linux发行版中都绑定发布,不再需要独立下载安装。如果默认没有安装,你也可以使用apt或者yum安装。
+由于是GNU项目的一部分,Wget捆绑在大部分标准Linux发行版中,不再需要独立下载安装。如果默认没有安装,你也可以使用apt或者yum安装。
# apt-get install wget (基于 APT 的系统)
@@ -70,13 +73,14 @@ Wget是GNU项目的一部分,名字由World Wide Web (WWW)衍生而来。Wget
Wget是一个很棒的工具,它允许在资源有限的机器上自定义或者过滤下载。这是镜像一个网站(Yahoo.com)的wget下载截图。

-Wget 命令行文件下载
-要获取更多wget下载的例子,可以阅读我们的文章[10个Wget下载命令例子][1]。
+*Wget 命令行文件下载*
+
+要获取更多wget下载的例子,可以阅读我们的文章[Wget下载命令例子][1]。
### 3. cURL ###
-cURL是在多种协议上传输数据的命令行工具。cURL是支持FTP, HTTP, FTPS, TFTP, TELNET, IMAP, POP3等协议的客户端应用。和其它相对比,在支持LDAP,POP3方面,cURL是和wget不同的简单下载器。cURL也很好的支持代理下载,暂停下载以及恢复下载。
+cURL是在多种协议上传输数据的命令行工具。cURL是支持FTP, HTTP, FTPS, TFTP, TELNET, IMAP, POP3等协议的客户端应用。cURL是一个不同于wget 的简单下载器,和其它的相比,它支持LDAP,POP3。cURL也很好的支持代理下载,暂停下载以及恢复下载。
#### 安装cURL ####
@@ -93,14 +97,16 @@ cURL的基本使用方法
# curl www.tecmint.com

-Curl 下载数据
+
+*Curl 下载*

-Curl 下载
+
+*Curl 下载*
### 4. w3m ###
-W3m是GPL协议下发布的基于文本的web浏览器。W3m支持表格,帧,颜色,SSL连接以及内联图像。W3m由于快速浏览而出名。
+W3m是GPL协议下发布的基于文本的web浏览器。W3m支持表格,帧,颜色,SSL连接以及内联图像。W3m以快速浏览而出名。
#### 安装w3m ####
@@ -117,11 +123,12 @@ W3m在大部分Linux发行版中也是默认可用的。如果不可用的话可
# w3m www.tecmint.com

-基于文本的web浏览器w3m
+
+*基于文本的web浏览器w3m*
### 5. Elinks ###
-Elinks是基于文本,给基于Unix和基于Unix的系统使用的免费web浏览器。Elinks支持 HTTP,HTTP Cookies以及支持浏览Pery和Ruby脚本。也很好的支持基于标签的浏览。最棒的是它支持鼠标,颜色显示以及支持一系列的协议,例如HTTP, FTP, SMB, Ipv4 和 Ipv6。
+Elinks是基于文本的免费浏览器,用于Unix及基于Unix的系统。Elinks支持 HTTP,HTTP Cookies以及支持浏览Perl和Ruby脚本(LCTT 译注:应该是指 CGI)。也很好的支持选项卡浏览。最棒的是它支持鼠标、彩色以及支持一系列的协议,例如HTTP, FTP, SMB, Ipv4 和 Ipv6。
#### 安装Elinks ####
@@ -138,7 +145,8 @@ Elinks的基本使用方法
# elinks www.tecmint.com

-Elinks命令行浏览互联网
+
+*Elinks命令行浏览互联网*
就是这些了。有你们喜欢读的有趣的文章,我会再次来到这里。到那时尽请关注并保持和Tecmint的联系,别忘了在评论部分给我们你的宝贵的反馈。
@@ -148,9 +156,9 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-command-line-tools-for-downloading-files/
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
-[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-wget-command-examples-in-linux/
\ No newline at end of file
+[1]:https://linux.cn/article-4129-1.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/share/20150407 Ambient Noise Player for Ubuntu Plays Relaxing Sounds to Keep You Creative.md b/published/201505/20150407 Ambient Noise Player for Ubuntu Plays Relaxing Sounds to Keep You Creative.md
similarity index 67%
rename from translated/share/20150407 Ambient Noise Player for Ubuntu Plays Relaxing Sounds to Keep You Creative.md
rename to published/201505/20150407 Ambient Noise Player for Ubuntu Plays Relaxing Sounds to Keep You Creative.md
index f468b24754..c636b01820 100644
--- a/translated/share/20150407 Ambient Noise Player for Ubuntu Plays Relaxing Sounds to Keep You Creative.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150407 Ambient Noise Player for Ubuntu Plays Relaxing Sounds to Keep You Creative.md
@@ -1,9 +1,8 @@
-Translated by H-mudcup
-
-适用于Ubuntu的环境音播放器播放让人放松的声音保持你的创造力
+环境音播放器:让人放松的声音,保持你的创造力
================================================================================

-对于某些人来说雨声是个令人安心的声音
+
+*对于某些人来说雨声是个令人安心的声音*
**如果我想变得非常有效率,我不能听‘正常’的音乐。它会使我分心,我会开始跟着唱或者让我想起另一首歌,结局就是我在自己的音乐库里到处戳并且……反正,你懂的。**
@@ -23,11 +22,11 @@ Translated by H-mudcup
Google Play和苹果应用商店充满了环境音和白噪声的应用。现在,在Ubuntu里有同样的应用了。
-‘[Ambient Noise][1]‘ ‘[环境音][1]’——人如其名——是一个专门被设计成播放这种声音的音频播放器。他甚至可以同Ubuntu声音菜单整合到一起,给你‘选择,点击即放松’的体验。
+‘[Ambient Noise (环境音)][1] ’——人如其名,这是一个专门被设计成播放这种声音的音频播放器。他甚至可以同Ubuntu声音菜单整合到一起,给你‘选择,点击即放松’的体验。
-这个应用(又被称为‘ANoise播放器’,由Marcos Costales制作)带有**8个高品质声道**。
+这个应用(又被称为‘ANoise播放器’,由Marcos Costales制作)带有**8个高品质音频**。
-这8个预设声道涵盖了多种环境,从下雨时有节奏的声音,到夜晚大自然静谧的旋律,还有下午熙熙攘攘的咖啡店的嗡嗡声。
+这8个预设音频涵盖了多种环境,从下雨时有节奏的声音,到夜晚大自然静谧的旋律,还有下午熙熙攘攘的咖啡店的嗡嗡声。
### 在Ubuntu上安装ANoise播放器 ###
@@ -39,9 +38,9 @@ Google Play和苹果应用商店充满了环境音和白噪声的应用。现在
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install anoise
-安装好以后只需从Unity Dash(或DE里等价的地方)里打开它,通过声音菜单选择你喜欢的环境音然后……放松吧!这个应用甚至记得你上次用的环境音。
+安装好以后只需从Unity Dash(或桌面环境里类同的地方)里打开它,通过声音菜单选择你喜欢的环境音然后……放松吧!这个应用甚至记得你上次用的环境音。
-Even so, give it a try out and see if it suits your needs. I would say let me know what you think, but I will be too focused to hear — and so might you!即便如此,你还是要试一试看它是否能满足你的需要。我要说的是让我直到你是怎么想的,但是我将会专心致志到听不到你的声音——你可能也会这样!
+即便如此,你还是要试一试看它是否能满足你的需要。我要说的是让我知道你是怎么想的,但是我将会专心致志到听不到你的声音——你可能也会这样!
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -49,7 +48,7 @@ via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/ambient-noise-player-app-for-ubuntu-linu
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
译者:[H-mudcup](https://github.com/H-mudcup)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150407 How To Install CentOS Web Panel In CentOS.md b/published/201505/20150407 How To Install CentOS Web Panel In CentOS.md
similarity index 61%
rename from translated/tech/20150407 How To Install CentOS Web Panel In CentOS.md
rename to published/201505/20150407 How To Install CentOS Web Panel In CentOS.md
index b3d5e2588f..fe038b4406 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150407 How To Install CentOS Web Panel In CentOS.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150407 How To Install CentOS Web Panel In CentOS.md
@@ -1,62 +1,61 @@
-如何在CentOS上面安装CentOS网页面板
+如何在CentOS上面安装“CentOS网页面板”
===========================================================================

### 关于CentOS网页面板 ###
-目前有很多免费的或者付费的控制面板。今天,我们来讨论[CentOS网页面板(CWP)][1],这是特别为基于如CentOS,RHEL,科研用Linux系统等发行版的RPM设计的。**CWP** 是免费且开源的控制面板,可以被广泛用于简单地配置一个网页集群环境。不同于其他的控制面板,CWP是自动用高速缓存来配置LAMP的栈区。
+目前有很多免费的或者付费的控制面板。今天,我们来讨论[CentOS网页面板(CWP)][1],这是特别为基于RPM 的发行版,如CentOS,RHEL,Scientific Linux等设计的。**CWP** 是免费且开源的控制面板,可以被广泛用于简单地配置一个网页托管环境。不同于其他的控制面板,CWP能自动部署LAMP的软件栈及Varnish 缓存服务器。
### 特性 ###
-CWP有很多的特性和免费的服务。如我前面提到的一样,CWP自动在你的服务器上安装全套LAMP服务(apache,php,phpmyadmin,webmail,mailserver等等)。
+CWP有很多的特性和免费的服务。如我前面提到的一样,CWP会在你的服务器上自动安装全套的LAMP服务(apache,php,phpmyadmin,webmail,mailserver等等)。
### CWP安装过程中会安装和配置的软件列表 ###
-- Apache Web Server
+- Apache 网页服务器
- PHP 5.4
- MySQL + phpMyAdmin
- Postfix + Dovecot + roundcube webmail
-- CSF Firewall
-- File System Lock (no more website hacking, all your files are locked from changes)
-- Backups; AutoFixer for server configuration
+- CSF 防火墙
+- File System Lock (不需要修改网站,你的所有文件都会被锁定修改)
+- Backups; AutoFixer ,用于服务器配置
### 第三方应用: ###
-
- CloudLinux + CageFS + PHP Selector
-- Softaculous – Script Installer (Free and Premium)
+- Softaculous – 脚本安装器 (免费版和白金版)
#### 网页服务器: ####
-- Varnish Cache server
-- Compiles Apache from source
-- Apache reCompiler + Additional modules
-- Apache server status, configuration
-- Edit apache vhosts, vhosts templates, include configuration
-- Rebuild all apache Virtual hosts
+- Varnish 缓存服务器
+- 从代码编译 Apache
+- Apache 重新编译+附加模块
+- Apache 服务器状态,配置
+- 编辑 Apache 虚拟主机、虚拟主机模版,包括配置
+- 重建所有 Apache 虚拟主机
- suPHP & suExec
-- Mod Security + OWASP rules
-- Tomcat 8 server management
-- DoS protection
-- Perl cgi script support
+- Mod Security + OWASP 规则
+- Tomcat 8 服务器管理
+- DoS 防护
+- Perl cgi 脚本支持
#### PHP: ####
-- PHP 切换器 (在PHP版本如: 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5之间切换)
-- PHP选择器选择每个用户或者每个文件的PHP版本(PHP 4.4, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5, 5.6)
-- 简单的php编辑软件
+- PHP 切换器 (在PHP版本如: 5.2、 5.3、 5.4、 5.5之间切换)
+- PHP选择器,选择每个用户或者每个文件的PHP版本(PHP 4.4、 5.2、 5.3、 5.4、5.5、 5.6)
+- 简单的php编辑器
- 在用户面板下简单的php.ini生成器
- PHP 插件
-- PHP.ini editor & PHP info & List modules
+- PHP.ini 编辑器 & PHP 信息 和列出模块
- 每个帐号一个php.ini
-- FFMPEG,用于视频流网站
+- FFMPEG,用于视频流网站
- CloudLinux + PHP 选择器
#### 用户管理 ####
-- 添加,列举,编辑和移除用户
+- 添加、列出、编辑和移除用户
- 用户监管
-- Shell接入管理
+- Shell访问管理
- 用户限制管理
- 限制进程
- 限制访问文件
@@ -67,85 +66,85 @@ CWP有很多的特性和免费的服务。如我前面提到的一样,CWP自
#### DNS: ####
- FreeDNS
-- 添加,编辑,列举和移除DNS区块
+- 添加、编辑、列出和移除DNS区块
- 编辑域名服务的IP
- DNS区块模板编辑器
- 新的易用DNS区块管理器 (用ajax)
-- 新的DNS区块列表,带有额外的修复信息 (同时检测 rDNS, 域名服务….)
+- 新的DNS区块列表,带有额外的google解析信息 (同时检测 rDNS, 域名服务…)
#### Email: ####
- Postfix & dovecot
-- MailBoxes, Alias
+- 邮箱、别名
- Roundcube webmail
-- Postfix Mail queue
-- rDNS Checker Module
+- Postfix 邮件队列
+- rDNS 检查器模块
- 垃圾邮件拦截
- SPF & DKIM集成
-- Re-Build Postfix/Dovecot Mail server with AntiVirus, AntiSpam Protection
-- Email Auto Responder
+- 重构带有反病毒、反垃圾邮件防护的 Postfix/Dovecot 的邮件服务器
+- Email 自动应答器
#### 系统: ####
- CPU核心和时钟信息
- 内存使用信息
- 详细的磁盘状态
-- 软件信息如内核版本,正常运行时间等等.
+- 软件信息如内核版本、正常运行时间等等.
- 服务器状态
-- 检查配置管理
+- ChkConfig管理
- 网络端口使用
- 网络配置
-- SSHD配置
+- sshd 配置
- 自动修复(检查重要的配置并尝试自动修复问题)
#### 监控: ####
-- 监控服务 eg. top, apache stats, mysql etc.
-- 在面板内使用Java SSH Terminal/Console
-- 服务器配置 (eg. Apache, PHP, MySQL etc)
+- 监控服务,例如 top、 apache 状态、 mysql 等
+- 在面板内使用Java SSH 终端/控制台
+- 服务器配置 (例如 Apache、 PHP、 MySQL 等)
- 在屏幕/后台运行命令行
#### 安全: ####
- CSF防火墙
-- SSL产生器
+- SSL生成器
- SSL证书管理
- CloudLinux + CageFS
#### SQL: ####
- MySQL 数据库管理
-- 添加本地或者远程接入用户
+- 添加本地或者远程访问的用户
- 实时监控MySQL进程列表
- 创建,移除数据库
- 为每个数据库添加额外的用户
- MySQL服务器配置
-- PhpMyAdmin(这个不知道要不要译过来)
+- PhpMyAdmin
- PostgreSQL, phpPgAdmin支持
#### 额外功能: ####
-- 语言通话3 管理
-- 网络电台管理
+- TeamSpeak 3 管理器
+- Shoutcast 管理器
- 自动更新
-- 备份管理
-- 文件管理
+- 备份管理器
+- 文件管理器
- 每个域名的虚拟FTP用户
-- 控制面板帐号移植 (恢复文件,数据库和数据库用户)
-- 还有更多.
+- cPanel帐号迁移 (恢复文件,数据库和数据库用户)
+- 还有更多
### 在CentOS 6上安装CentOS网页面板 ###
-写这篇教程的时候,CWP仅仅支持最高CentOS 6.x版本。在CentOS 7和更高的版本中是行不通的。
+写这篇教程的时候,CWP仅仅支持最高CentOS 6.x版本。在CentOS 7和更高的版本中是不支持的。
#### 前期准备: ####
-**安装CWP之前,里必须知道以下的信息:**
+**安装CWP之前,你必须知道以下的信息:**
-- CWP 仅支持静态IP地址。它并不支持动态的,固定的,或者内部的IP地址。
-- CWP 并没有卸载程序。当你安装CWP后,里必须重新安装服务器来移除它。
-- 之安装CWP在一个新装的还没做任何配置改变的操作系统上。
-- 对与32位操作系统至少需要512MB RAM。
+- CWP 仅支持静态IP地址。它并不支持动态的,或者内部的IP地址。
+- CWP 并没有卸载程序。当你安装CWP后,你必须重新安装服务器来移除它。
+- 只能在一个新装的还没做任何配置改变的操作系统上安装CWP。
+- 对于32位操作系统至少需要512MB RAM。
- 64位系统需要1024MB RAM。
- 要求至少20GB的硬盘空间。
@@ -175,7 +174,7 @@ CWP有很多的特性和免费的服务。如我前面提到的一样,CWP自
如果上面的URL出现错误,用下面的链接代替。
- wget http://dll.centos-webpanle.com/files/cwp-latest
+ wget http://dl1.centos-webpanle.com/files/cwp-latest
然后,用命令开始安装CWP:
@@ -189,8 +188,7 @@ CWP有很多的特性和免费的服务。如我前面提到的一样,CWP自
安装过程会持续到30分钟或者更多,取决于你的网速。
-最后,你会看到如下安装完成的信息。
-记下一些详细信息,如mysql超级用户密码和CWP的登录URLs。你随后会需要。然后,按下回车Enter重启系统。
+最后,你会看到如下安装完成的信息。记下一些详细信息,如mysql超级用户密码和CWP的登录URL,你随后会需要它们。然后,按下回车Enter重启系统。

@@ -200,7 +198,7 @@ CWP有很多的特性和免费的服务。如我前面提到的一样,CWP自
#### 调整防火墙/路由: ####
-CWP的默认网络控制接口是**2030(http)**和**2031(https)**。你应该通过防火墙/路由允许使用这两个端口,以便远程接入CWP网络控制台。
+CWP的默认网页控制界面的端口是**2030(http)**和**2031(https)**。你应该通过防火墙/路由允许使用这两个端口,以便远程接入CWP网络控制台。
编辑iptables文件:
@@ -242,43 +240,42 @@ CWP的默认网络控制接口是**2030(http)**和**2031(https)**。你
接下来,我们得做一些事,比如:
-1.建立域名服务
-1.建立ip共享(必须是你的公共IP地址)
-1.建立至少一个集合包(或者编辑默认的包)
-1.建立root电子邮件,等等。
+1. 设置域名服务器
+1. 设置 ip 共享(必须是你的公共IP地址)
+1. 设置至少一个托管包(或者编辑默认的包)
+1. 设置 root 电子邮件,等等。
-#### 建立域名服务: ####
+#### 设置域名服务器: ####
-为建立域名服务,找到**DNS Functions -> Edit nameservers IPs**。
+为建立域名服务器,找到**DNS Functions -> Edit nameservers IPs**。

设置你的域名服务器,点击保存按钮。
-

-#### 建立共享IP和Root邮箱ID: ####
+#### 建立共享IP和Root邮件地址: ####
-在你的主机上管理网站,这是非常重要的一步。为了建立共享IP,进入**CWP Setting -> Edit settings**。
+在你的主机上托管网站,这是非常重要的一步。为了建立共享IP,进入**CWP Setting -> Edit settings**。

-输入你的静态IP和邮箱ID,然后点击保存设置按钮。
+输入你的静态IP和邮件地址,然后点击保存设置按钮。

现在,CWP可以进行网站维护了。
-#### 建立主机包 ####
+#### 建立托管包 ####
-一个主机包什么都没有,除了一个网站托管计划,包括允许访问的磁盘空间,带宽,但没有FTP帐号,邮箱IDs和数据库等等。你可以建立任意数量的网站托管计划,只要你喜欢。
+一个托管包就是一个网站托管计划,包括允许访问的磁盘空间,带宽,但没有FTP帐号,邮箱地址和数据库等等。你可以建立任意数量的网站托管计划,只要你喜欢。
-添加一个包,从CWP的控制台进入**Packages — Add a Package**
+要添加一个包,从CWP的控制台进入**Packages — Add a Package**

-输入包的名字,允许访问的磁盘配额/RAM数量,FTP/Email帐号,数据库和子域名等等。点击保持设置按钮,建立一个网站托管计划。
+输入包的名字,允许访问的磁盘配额/RAM数量,FTP/Email帐号,数据库和子域名等等。点击保存设置按钮,建立一个网站托管计划。

@@ -290,7 +287,7 @@ CWP的默认网络控制接口是**2030(http)**和**2031(https)**。你
而添加一个用户,请进入**User Account -> New Account**。
-输入域名(ex.unixmen.com),用户名,密码和邮箱id等等。最后,点击**Create**。
+输入域名(ex.unixmen.com),用户名,密码和邮箱地址等等。最后,点击**Create**。

@@ -312,12 +309,11 @@ CWP的默认网络控制接口是**2030(http)**和**2031(https)**。你
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
via: http://www.unixmen.com/how-to-install-centos-web-panel-in-centos/
作者:[SK][a]
译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150407 How to secure BGP sessions using authentication on Quagga.md b/published/201505/20150407 How to secure BGP sessions using authentication on Quagga.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9881d73c40
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150407 How to secure BGP sessions using authentication on Quagga.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+Quagga上使用验证加固BGP会话安全
+================================================================================
+BGP协议运行于TCP之上,因而,它也继承了TCP连接的所有漏洞。例如,在一个BGP会话内,攻击者可以冒充一个合法的BGP邻居,然后说服另一端的BGP路由器共享路由信息给攻击者。在攻击者通告并向邻居路由注入伪造的路由时,就会发生这个问题。毫无戒备的邻居路由器就会开始向攻击者发送通信实况,实际上这些信息并没有去向任何地方,仅仅只是被丢弃了。回到2008年,YouTube实际上也[受害于][1]这样的BGP路由中毒,并遭受了长达一个小时的视频服务大量中断。一个更加糟糕的情况是,如果攻击者是个足够懂行的人,他们可以伪装成一台透明路由器,然后嗅探经过的通信以获取敏感数据。你可以想象,这会造成深远的影响。
+
+要保护活跃的BGP会话不受攻击,许多服务提供商在BGP会话中使用[MD5校验和及预共享密钥][2]。在受保护的BGP会话中,一台发送包的BGP路由器通过使用预共享的密钥生成MD5散列值、部分IP和TCP头以及有效载荷。然后,MD5散列作为一个TCP选项字段存储。在收到包后,接受路由器用同样的方法使用预共享密钥生成它的MD5版本。它会将它的MD5散列和接收到的某个包的值进行对比,以决定是否接受该包。对于一个攻击者而言,几乎不可能猜测到校验和或其密钥。对于BGP路由器而言,它们能在使用包的内容前确保每个包的合法性。
+
+在本教程中,我们将为大家演示如何使用MD5校验和以及预共享密钥来加固两个邻居间的BGP会话的安全。
+
+### 准备 ###
+
+加固BGP会话安全是相当简单而直截了当的,我们会使用以下路由器。
+
+<table id="content">
+<tbody><tr>
+<td><b>路由器名称</b></td>
+<td><b>AS 号</b></td>
+<td><b>IP地址</b></td>
+</tr>
+<tr>
+<td>router-A</td>
+<td>100</td>
+<td>10.10.12.1/30</td>
+</tr>
+<tr>
+<td>router-B</td>
+<td>200</td>
+<td>10.10.12.2/30</td>
+</tr>
+</tbody></table>
+
+常用的Linux内核原生支持IPv4和IPv6的TCP MD5选项。因此,如果你从全新的[Linux机器][3]构建了一台Quagga路由器,TCP的MD5功能会自动启用。剩下来的事情,仅仅是配置Quagga以使用它的功能。但是,如果你使用的是FreeBSD机器或者为Quagga构建了一个自定义内核,请确保内核开启了TCP的MD5支持(如,Linux中的CONFIG_TCP_MD5SIG选项)。
+
+### 配置Router-A验证功能 ###
+
+我们将使用Quagga的CLI Shell来配置路由器,我们将使用的唯一的一个新命令是‘password’。
+
+ [root@router-a ~]# vtysh
+ router-a# conf t
+ router-a(config)# router bgp 100
+ router-a(config-router)# network 192.168.100.0/24
+ router-a(config-router)# neighbor 10.10.12.2 remote-as 200
+ router-a(config-router)# neighbor 10.10.12.2 password xmodulo
+
+本例中使用的预共享密钥是‘xmodulo’。很明显,在生产环境中,你需要选择一个更健壮的密钥。
+
+**注意**: 在Quagga中,‘service password-encryption’命令被用做加密配置文件中所有明文密码(如,登录密码)。然而,当我使用该命令时,我注意到BGP配置中的预共享密钥仍然是明文的。我不确定这是否是Quagga的限制,还是版本自身的问题。
+
+### 配置Router-B验证功能 ###
+
+我们将以类似的方式配置router-B。
+
+ [root@router-b ~]# vtysh
+ router-b# conf t
+ router-b(config)# router bgp 200
+ router-b(config-router)# network 192.168.200.0/24
+ router-b(config-router)# neighbor 10.10.12.1 remote-as 100
+ router-b(config-router)# neighbor 10.10.12.1 password xmodulo
+
+### 验证BGP会话 ###
+
+如果一切配置正确,那么BGP会话就应该起来了,两台路由器应该能交换路由表。这时候,TCP会话中的所有流出包都会携带一个MD5摘要的包内容和一个密钥,而摘要信息会被另一端自动验证。
+
+我们可以像平时一样通过查看BGP的概要来验证活跃的BGP会话。MD5校验和的验证在Quagga内部是透明的,因此,你在BGP级别是无法看到的。
+
+
+
+如果你想要测试BGP验证,你可以配置一个邻居路由,设置其密码为空,或者故意使用错误的预共享密钥,然后查看发生了什么。你也可以使用包嗅探器,像tcpdump或者Wireshark等,来分析通过BGP会话的包。例如,带有“-M <secret>”选项的tcpdump将验证TCP选项字段的MD5摘要。
+
+###小结###
+
+在本教程中,我们演示了怎样简单地加固两台路由间的BGP会话安全。相对于其它协议而言,配置过程非常简明。强烈推荐你加固BGP会话安全,尤其是当你用另一个AS配置BGP会话的时候。预共享密钥也应该安全地保存。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/bgp-authentication-quagga.html
+
+作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
+[1]:http://research.dyn.com/2008/02/pakistan-hijacks-youtube-1/
+[2]:http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2385
+[3]:https://linux.cn/article-4232-1.html
diff --git a/published/201505/20150409 4 Tools Send Email with Subject, Body and Attachment in Linux.md b/published/201505/20150409 4 Tools Send Email with Subject, Body and Attachment in Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..00003eaa19
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150409 4 Tools Send Email with Subject, Body and Attachment in Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,261 @@
+4个可以发送完整电子邮件的命令行工具
+================================================================================
+今天的文章里我们会讲到一些使用Linux命令行工具来发送带附件的电子邮件的方法。它有很多用处,比如在应用程序所在服务器上,使用电子邮件发送一个文件过来,或者你可以在脚本中使用这些命令来做一些自动化操作。在本文的例子中,我们会使用foo.tar.gz文件作为附件。
+
+有不同的命令行工具可以发送邮件,这里我分享几个多数用户会使用的工具,如`mailx`、`mutt`和`swaks`。
+
+我们即将呈现的这些工具都是非常有名的,并且存在于多数Linux发行版默认的软件仓库中,你可以使用如下命令安装:
+
+在 **Debian / Ubuntu** 系统
+
+ apt-get install mutt
+ apt-get install swaks
+ apt-get install mailx
+ apt-get install sharutils
+
+在基于Red Hat的系统,如 **CentOS** 或者 **Fedora**
+
+ yum install mutt
+ yum install swaks
+ yum install mailx
+ yum install sharutils
+
+### 1) 使用 mail / mailx ###
+
+`mailx`工具在多数Linux发行版中是默认的邮件程序,现在已经支持发送附件了。如果它不在你的系统中,你可以使用上边的命令安装。有一点需要注意,老版本的mailx可能不支持发送附件,运行如下命令查看是否支持。
+
+ $ man mail
+
+第一行看起来是这样的:
+
+ mailx [-BDdEFintv~] [-s subject] [-a attachment ] [-c cc-addr] [-b bcc-addr] [-r from-addr] [-h hops] [-A account] [-S variable[=value]] to-addr . . .
+
+如果你看到它支持`-a`的选项(-a 文件名,将文件作为附件添加到邮件)和`-s`选项(-s 主题,指定邮件的主题),那就是支持的。可以使用如下的几个例子发送邮件。
+
+**a) 简单的邮件**
+
+运行`mail`命令,然后`mailx`会等待你输入邮件内容。你可以按回车来换行。当输入完成后,按Ctrl + D,`mailx`会显示EOT表示结束。
+
+然后`mailx`会自动将邮件发送给收件人。
+
+ $ mail user@example.com
+
+ HI,
+ Good Morning
+ How are you
+ EOT
+
+**b) 发送有主题的邮件**
+
+ $ echo "Email text" | mail -s "Test Subject" user@example.com
+
+`-s`的用处是指定邮件的主题。
+
+**c) 从文件中读取邮件内容并发送**
+
+ $ mail -s "message send from file" user@example.com < /path/to/file
+
+**d) 将从管道获取到的`echo`命令输出作为邮件内容发送**
+
+ $ echo "This is message body" | mail -s "This is Subject" user@example.com
+
+**e) 发送带附件的邮件**
+
+ $ echo “Body with attachment "| mail -a foo.tar.gz -s "attached file" user@example.com
+
+`-a`选项用于指定附件。
+
+### 2) mutt ###
+
+Mutt是类Unix系统上的一个文本界面邮件客户端。它有20多年的历史,在Linux历史中也是一个很重要的部分,它是最早支持进程打分和多线程处理的客户端程序之一。按照如下的例子来发送邮件。
+
+**a) 带有主题,从文件中读取邮件的正文,并发送**
+
+ $ mutt -s "Testing from mutt" user@example.com < /tmp/message.txt
+
+**b) 通过管道获取`echo`命令输出作为邮件内容发送**
+
+ $ echo "This is the body" | mutt -s "Testing mutt" user@example.com
+
+**c) 发送带附件的邮件**
+
+ $ echo "This is the body" | mutt -s "Testing mutt" user@example.com -a /tmp/foo.tar.gz
+
+**d) 发送带有多个附件的邮件**
+
+ $ echo "This is the body" | mutt -s "Testing" user@example.com -a foo.tar.gz –a bar.tar.gz
+
+### 3) swaks ###
+
+Swaks(Swiss Army Knife,瑞士军刀)是SMTP服务上的瑞士军刀,它是一个功能强大、灵活、可编程、面向事务的SMTP测试工具,由John Jetmore开发和维护。你可以使用如下语法发送带附件的邮件:
+
+ $ swaks -t "foo@bar.com" --header "Subject: Subject" --body "Email Text" --attach foo.tar.gz
+
+关于Swaks一个重要的地方是,它会为你显示整个邮件发送过程,所以如果你想调试邮件发送过程,它是一个非常有用的工具。
+
+它会给你提供了邮件发送过程的所有细节,包括邮件接收服务器的功能支持、两个服务器之间的每一步交互。
+
+### 4) uuencode ###
+
+邮件传输系统最初是被设计来传送7位编码(类似ASCII)的内容的。这就意味这它是用来发送文本内容,而不能发会使用8位的二进制内容(如程序文件或者图片)。`uuencode`(“UNIX to UNIX encoding”,UNIX之间使用的编码方式)程序用来解决这个限制。使用`uuencode`,发送端将二进制格式的转换成文本格式来传输,接收端再转换回去。
+
+我们可以简单地使用`uuencode`和`mailx`或者`mutt`配合,来发送二进制内容,类似这样:
+
+ $ uuencode example.jpeg example.jpeg | mail user@example.com
+
+### Shell脚本:解释如何发送邮件 ###
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+
+ FROM=""
+ SUBJECT=""
+ ATTACHMENTS=""
+ TO=""
+ BODY=""
+
+ # 检查文件名对应的文件是否存在
+ function check_files()
+ {
+ output_files=""
+ for file in $1
+ do
+ if [ -s $file ]
+ then
+ output_files="${output_files}${file} "
+ fi
+ done
+ echo $output_files
+ }
+
+ echo "*********************"
+ echo "E-mail sending script."
+ echo "*********************"
+ echo
+
+ # 读取用户输入的邮件地址
+ while [ 1 ]
+ do
+ if [ ! $FROM ]
+ then
+ echo -n -e "Enter the e-mail address you wish to send mail from:\n[Enter] "
+ else
+ echo -n -e "The address you provided is not valid:\n[Enter] "
+ fi
+
+ read FROM
+ echo $FROM | grep -E '^.+@.+$' > /dev/null
+ if [ $? -eq 0 ]
+ then
+ break
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo
+
+ # 读取用户输入的收件人地址
+ while [ 1 ]
+ do
+ if [ ! $TO ]
+ then
+ echo -n -e "Enter the e-mail address you wish to send mail to:\n[Enter] "
+ else
+ echo -n -e "The address you provided is not valid:\n[Enter] "
+ fi
+
+ read TO
+ echo $TO | grep -E '^.+@.+$' > /dev/null
+ if [ $? -eq 0 ]
+ then
+ break
+ fi
+ done
+
+ echo
+
+ # 读取用户输入的邮件主题
+ echo -n -e "Enter e-mail subject:\n[Enter] "
+ read SUBJECT
+
+ echo
+
+ if [ "$SUBJECT" == "" ]
+ then
+ echo "Proceeding without the subject..."
+ fi
+
+ # 读取作为附件的文件名
+ echo -e "Provide the list of attachments. Separate names by space.
+ If there are spaces in file name, quote file name with \"."
+ read att
+
+ echo
+
+ # 确保文件名指向真实文件
+ attachments=$(check_files "$att")
+ echo "Attachments: $attachments"
+
+ for attachment in $attachments
+ do
+ ATTACHMENTS="$ATTACHMENTS-a $attachment "
+ done
+
+ echo
+
+ # 读取完整的邮件正文
+ echo "Enter message. To mark the end of message type ;; in new line."
+ read line
+
+ while [ "$line" != ";;" ]
+ do
+ BODY="$BODY$line\n"
+ read line
+ done
+
+ SENDMAILCMD="mutt -e \"set from=$FROM\" -s \"$SUBJECT\" \
+ $ATTACHMENTS -- \"$TO\" <<< \"$BODY\""
+ echo $SENDMAILCMD
+
+ mutt -e "set from=$FROM" -s "$SUBJECT" $ATTACHMENTS -- $TO <<< $BODY
+
+** 脚本输出 **
+
+ $ bash send_mail.sh
+ *********************
+ E-mail sending script.
+ *********************
+
+ Enter the e-mail address you wish to send mail from:
+ [Enter] test@gmail.com
+
+ Enter the e-mail address you wish to send mail to:
+ [Enter] test@gmail.com
+
+ Enter e-mail subject:
+ [Enter] Message subject
+
+ Provide the list of attachments. Separate names by space.
+ If there are spaces in file name, quote file name with ".
+ send_mail.sh
+
+ Attachments: send_mail.sh
+
+ Enter message. To mark the end of message type ;; in new line.
+ This is a message
+ text
+ ;;
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+有很多方法可以使用命令行/Shell脚本来发送邮件,这里我们只分享了其中4个类Unix系统可用的工具。希望你喜欢我们的文章,并且提供您的宝贵意见,让我们知道您想了解哪些新工具。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-shell-script/send-email-subject-body-attachment-linux/
+
+作者:[Bobbin Zachariah][a]
+译者:[goreliu](https://github.com/goreliu)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/bobbin/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/201505/20150409 Install Inkscape - Open Source Vector Graphic Editor.md b/published/201505/20150409 Install Inkscape - Open Source Vector Graphic Editor.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c6361e780b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150409 Install Inkscape - Open Source Vector Graphic Editor.md
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+Inkscape - 开源适量图形编辑器
+================================================================================
+Inkscape是一款开源矢量图形编辑工具,并不同于Xara X、Corel Draw和Adobe Illustrator等竞争对手,它使用的是可缩放矢量图形(SVG)图形格式。SVG是一个广泛部署、免版税使用的图形格式,由W3C SVG工作组开发和维护。这是一个跨平台工具,完美运行于Linux、Windows和Mac OS上。
+
+Inkscape始于2003年,起初它的bug跟踪系统托管于Sourceforge上,但是后来迁移到了Launchpad上。当前它最新的一个稳定版本是0.91,它不断地在发展和修改中。我们将在本文里了解一下它的突出特点和安装过程。
+
+### 显著特性 ###
+
+让我们直接来了解这款应用程序的显著特性。
+
+#### 创建对象 ####
+
+- 用铅笔工具来画出不同颜色、大小和形状的手绘线,用贝塞尔曲线(笔式)工具来画出直线和曲线,通过书法工具来应用到手写的书法笔画上等等
+- 用文本工具来创建、选择、编辑和格式化文本。在纯文本框、在路径上或在形状里操作文本
+- 方便绘制各种形状,像矩形、椭圆形、圆形、弧线、多边形、星形和螺旋形等等并调整其大小、旋转并修改(圆角化)它们
+- 用简单地命令创建并嵌入位图
+
+#### 对象处理 ####
+
+- 通过交互式操作和调整参量来扭曲、移动、测量、旋转目标
+- 可以对 Z 轴进行提升或降低操作。
+- 通过对象组合和取消组合可以创建一个虚拟层用来编辑或处理
+- 图层采用层次结构树的结构,并且能锁定或以各式各样的处理方式来重新布置
+- 分布与对齐指令
+
+#### 填充与边框 ####
+
+- 可以复制/粘贴不同风格
+- 取色工具
+- 用RGB, HSL, CMS, CMYK和色盘这四种不同的方式选色
+- 渐变层编辑器能创建和管理多停点渐变层
+- 使用图像或其它选择区作为花纹填充
+- 用一些预定义点状花纹进行笔触填充
+- 通过路径标示器标示开始、对折和结束点
+
+#### 路径上的操作 ####
+
+- 节点编辑:移动节点和贝塞尔曲线控制点,节点的对齐和分布等等
+- 布尔运算(是或否)
+- 运用可变的路径起迄点可简化路径
+- 路径插入和增设连同动态和链接偏移对象
+- 通过路径追踪把位图图像转换成路径(彩色或单色路径)
+
+#### 文本处理 ####
+
+- 所有安装好的框线字体都能用,甚至可以从右至左对齐对象
+- 格式化文本、调整字母间距、行间距或列间距
+- 路径上和形状上的文本中的文本、路径或形状都可以被编辑和修改
+
+#### 渲染 ####
+
+- Inkscape完全支持抗锯齿显示,这是一种通过柔化边界上的像素从而减少或消除凹凸锯齿的技术。
+- 支持alpha透明显示和PNG格式图片的导出
+
+### 在Ubuntu 14.04和14.10上安装Inkscape ###
+
+为了在Ubuntu上安装Inkscape,我们首先需要 [添加它的稳定版Personal Package Archive][1] (PPA) 至Advanced Package Tool (APT) 库中。打开终端并运行一下命令来添加它的PPA:
+
+ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:inkscape.dev/stable
+
+
+
+PPA添加到APT库中后,我们要用以下命令进行更新:
+
+ sudo apt-get update
+
+
+
+更新好库之后,我们准备用以下命令来完成安装:
+
+ sudo apt-get install inkscape
+
+
+
+恭喜,现在Inkscape已经被安装好了,我们可以充分利用它的丰富功能特点来编辑制作图像了。
+
+
+
+### 结论 ###
+
+Inkscape是一款特点鲜明的图形编辑工具,它给予用户充分发挥自己艺术能力的权利。它还是一款自由安装和自定义的开源应用,并且支持各种文件类型,包括JPEG, PNG, GIF和PDF及更多。访问它的 [官方网站][2] 来获取更多新闻和应用更新。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/tools/install-inkscape-open-source-vector-graphic-editor/
+
+作者:[Aun Raza][a]
+译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunrz/
+[1]:https://launchpad.net/~inkscape.dev/+archive/ubuntu/stable
+[2]:https://inkscape.org/en/
diff --git a/published/201505/20150410 This tool can alert you about evil twin access points in the area.md b/published/201505/20150410 This tool can alert you about evil twin access points in the area.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a43aa8206f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150410 This tool can alert you about evil twin access points in the area.md
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+EvilAP_Defender:可以警示和攻击 WIFI 热点陷阱的工具
+===============================================================================
+
+**开发人员称,EvilAP_Defender甚至可以攻击流氓Wi-Fi接入点**
+
+这是一个新的开源工具,可以定期扫描一个区域,以防出现恶意 Wi-Fi 接入点,同时如果发现情况会提醒网络管理员。
+
+这个工具叫做 EvilAP_Defender,是为监测攻击者所配置的恶意接入点而专门设计的,这些接入点冒用合法的名字诱导用户连接上。
+
+这类接入点被称做假面猎手(evil twin),使得黑客们可以从所接入的设备上监听互联网信息流。这可以被用来窃取证书、钓鱼网站等等。
+
+大多数用户设置他们的计算机和设备可以自动连接一些无线网络,比如家里的或者工作地方的网络。通常,当面对两个同名的无线网络时,即SSID相同,有时候甚至连MAC地址(BSSID)也相同,这时候大多数设备会自动连接信号较强的一个。
+
+这使得假面猎手攻击容易实现,因为SSID和BSSID都可以伪造。
+
+[EvilAP_Defender][1]是一个叫Mohamed Idris的人用Python语言编写,公布在GitHub上面。它可以使用一个计算机的无线网卡来发现流氓接入点,这些坏蛋们复制了一个真实接入点的SSID,BSSID,甚至是其他的参数如通道,密码,隐私协议和认证信息等等。
+
+该工具首先以学习模式运行,以便发现合法的接入点[AP],并且将其加入白名单。然后可以切换到正常模式,开始扫描未认证的接入点。
+
+如果一个恶意[AP]被发现了,该工具会用电子邮件提醒网络管理员,但是开发者也打算在未来加入短信提醒功能。
+
+该工具还有一个保护模式,在这种模式下,应用会发起一个denial-of-service [DoS]攻击反抗恶意接入点,为管理员采取防卫措施赢得一些时间。
+
+“DoS 将仅仅针对有着相同SSID的而BSSID(AP的MAC地址)不同或者不同信道的流氓 AP,”Idris在这款工具的文档中说道。“这是为了避免攻击到你的正常网络。”
+
+尽管如此,用户应该切记在许多国家,攻击别人的接入点很多时候都是非法的,甚至是一个看起来像是攻击者操控的恶意接入点。
+
+要能够运行这款工具,需要Aircrack-ng无线网套装,一个支持Aircrack-ng的无线网卡,MySQL和Python运行环境。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.infoworld.com/article/2905725/security0/this-tool-can-alert-you-about-evil-twin-access-points-in-the-area.html
+
+作者:[Lucian Constantin][a]
+译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.infoworld.com/author/Lucian-Constantin/
+[1]:https://github.com/moha99sa/EvilAP_Defender/blob/master/README.TXT
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150410 What is a good alternative to wget or curl on Linux.md b/published/201505/20150410 What is a good alternative to wget or curl on Linux.md
similarity index 71%
rename from translated/tech/20150410 What is a good alternative to wget or curl on Linux.md
rename to published/201505/20150410 What is a good alternative to wget or curl on Linux.md
index caa4010661..3af223b631 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150410 What is a good alternative to wget or curl on Linux.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150410 What is a good alternative to wget or curl on Linux.md
@@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
-Linux 上 wget 或 curl 的更佳替代品
+用腻了 wget 或 curl,有什么更好的替代品吗?
================================================================================
-如果你经常需要通过终端以非交互模式访问网络服务器(例如,从网络上下载文件,或者是测试 RESTful 网络服务接口),可能你会选择的工具是 wget 或 curl。通过大量的命令行选项,这两种工具都可以处理很多非交互网络访问的情况(比如[这里][1],[这里][2],还有[这里][3])。然而,即使像这些一样的强大的工具,也只是与你对如何使用它们的了解程度等同。除非你很精通那些又多又笨(原文是 nitty and gritty)的语法细节,这些工具对于你来说只不过是简单的网络下载器。
-就像宣传的那样,“为人类着想的类 curl 工具”,[HTTPie][4] 设计用来增强 wget 和 curl 的可用性。它的主要目标是使通过命令行与网络服务器进行交互的过程变得尽可能的人性化。为此,HTTPie 支持具有表现力,但又很简单很直观的语法。它以彩色模式显示响应,并且还有一些不错的优点,比如对 JSON 的良好支持,和持久性会话用以作业流程化。
+如果你经常需要通过终端以非交互模式访问网络服务器(例如,从网络上下载文件,或者是测试 RESTful 网络服务接口),可能你会选择的工具是 wget 或 curl。通过大量的命令行选项,这两种工具都可以处理很多非交互网络访问的情况(比如[这里][1]、[这里][2],还有[这里][3])。然而,即使像这些一样的强大的工具,你也只能发挥你所了解的那些选项的功能。除非你很精通那些繁冗的语法细节,这些工具对于你来说只不过是简单的网络下载器而已。
-我知道很多人对把像 wget 和 curl 这样的无处不在的可用的完美工具换成完全没听说过的软件心存怀疑。这种观点是好的,特别是如果你是一个系统管理员、要处理很多不同的硬件的话。然而,对于开发者和终端用户来说,重要的是效率。如果我发现了一个工具的用户友好替代,我没有看到任何问题如果你采用易于使用的版本来节省你宝贵的时间。没有必要对替换掉的工具保持信仰忠诚。毕竟,对于 Linux 来说,最好的事情是可以选择。
+就像其宣传的那样,“给人用 curl 类工具”,[HTTPie][4] 设计用来增强 wget 和 curl 的可用性。它的主要目标是使通过命令行与网络服务器进行交互的过程变得尽可能的人性化。为此,HTTPie 支持具有表现力、但又很简单很直观的语法。它以彩色模式显示响应,并且还有一些不错的优点,比如对 JSON 的良好支持,和持久性会话用以作业流程化。
-在这篇文章中,让我们来回顾并展示一下我所说的 HTTPie,一个用户友好的 wget 和 curl 的替代。
+我知道很多人对把像 wget 和 curl 这样的无处不在的、可用的、完美的工具换成完全没听说过的软件心存疑虑。这种观点是好的,特别是如果你是一个系统管理员、要处理很多不同的硬件的话。然而,对于开发者和终端用户来说,重要的是效率。如果我发现了一个工具的用户更佳替代品,那么我认为采用易于使用的版本来节省宝贵的时间是毫无疑问的。没有必要对替换掉的工具保持信仰忠诚。毕竟,对于 Linux 来说,最好的事情就是可以选择。
+
+在这篇文章中,让我们来了解并展示一下我所说的 HTTPie,一个用户友好的 wget 和 curl 的替代。
@@ -40,10 +41,9 @@ HTTPie 是用 Python 写的,所以你可以在几乎所有地方(Linux,Mac
你可以使用 <header:value> 的格式来定制头部。例如,我们发送一个 HTTP GET 请求到 www.test.com ,使用定制用户代理(user-agent)和来源(referer),还有定制头部(比如 MyParam)。
-
$ http www.test.com User-Agent:Xmodulo/1.0 Referer:http://xmodulo.com MyParam:Foo
-注意到当使用 HTTP GET 方法时,你无需指定任何 HTTP 方法。
+注意到当使用 HTTP GET 方法时,就无需明确指定 HTTP 方法。
这个 HTTP 请求看起来如下:
@@ -121,7 +121,7 @@ HTTPie 的另外一个用户友好特性是输入重定向,你可以使用缓
### 结束语 ###
-在这篇文章中,我介绍了 HTTPie,一个 wget 和 curl 的可能替代工具。除了这里展示的几个简单的例子,你可以在[官方网站][7]上找到 HTTPie 的很多有趣的应用。再次重复一遍,一款强大的工具也只相当于你对它的了解程度。从个人而言,我更热衷于 HTTPie,因为我在寻找一种更简洁的测试复杂网络接口的方法。
+在这篇文章中,我介绍了 HTTPie,一个 wget 和 curl 的可能替代工具。除了这里展示的几个简单的例子,你可以在其[官方网站][7]上找到 HTTPie 的很多有趣的应用。再次重复一遍,一款再强大的工具也取决于你对它的了解程度。从个人而言,我更倾向于 HTTPie,因为我在寻找一种更简洁的测试复杂网络接口的方法。
你怎么看?
@@ -131,15 +131,15 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/wget-curl-alternative-linux.html
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
译者:[wangjiezhe](https://github.com/wangjiezhe)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-download-multiple-files-with-wget.html
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-use-custom-http-headers-with-wget.html
-[3]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/custom-http-header-curl.html
+[3]:https://linux.cn/article-4957-1.html
[4]:https://github.com/jakubroztocil/httpie
-[5]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
+[5]:https://linux.cn/article-2324-1.html
[6]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-pip-linux.html
[7]:https://github.com/jakubroztocil/httpie
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150413 A Walk Through Some Important Docker Commands.md b/published/201505/20150413 A Walk Through Some Important Docker Commands.md
similarity index 56%
rename from translated/tech/20150413 A Walk Through Some Important Docker Commands.md
rename to published/201505/20150413 A Walk Through Some Important Docker Commands.md
index 6e350c6d1c..d58dda2d54 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150413 A Walk Through Some Important Docker Commands.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150413 A Walk Through Some Important Docker Commands.md
@@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
-一些重要Docker命令的简单介绍
+一些重要 Docker 命令的简单介绍
================================================================================
-大家好,今天我们来学习一些在你使用Docker之前需要了解的重要的 Docker 命令。Docker 是一个提供开发平台去打包,装载和运行任何应用的轻量级容器开源项目。它没有语言支持,框架和打包系统的限制,能从一个小的家庭电脑到高端服务器,在任何地方任何时间运行。这使得它们成为不依赖于一个特定的栈或供应商,部署和扩展web应用,数据库和后端服务很好的构建块。
+大家好,今天我们来学习一些在你使用 Docker 之前需要了解的重要的 Docker 命令。[Docker][1] 是一个开源项目,提供了一个可以打包、装载和运行任何应用的轻量级容器的开放平台。它没有语言支持、框架和打包系统的限制,从小型的家用电脑到高端服务器,在何时何地都可以运行。这使它们可以不依赖于特定软件栈和供应商,像一块块积木一样部署和扩展网络应用、数据库和后端服务。
Docker 命令简单易学,也很容易实现或实践。这是一些你运行 Docker 并充分利用它需要知道的简单 Docker 命令。
-### 1. 拉取一个 Docker 镜像 ###
+### 1. 拉取 Docker 镜像 ###
-由于容器是由 Docker 镜像构建的,首先我们需要拉取一个 docker 镜像来开始。我们可以从 Docker 注册 Hub 获取需要的 docker 镜像。在我们使用 pull 命令拉取任何镜像之前,由于pull命令被标识为恶意命令,我们需要保护我们的系统。为了保护我们的系统不受这个问题影响,我们需要添加 **127.0.0.1 index.docker.io** 到 /etc/hosts 条目。我们可以通过使用喜欢的文本编辑器完成。
+由于容器是由 Docker 镜像构建的,首先我们需要拉取一个 docker 镜像来开始。我们可以从 Docker Registry Hub 获取所需的 docker 镜像。在我们使用 pull 命令拉取任何镜像之前,为了避免 pull 命令的一些恶意风险,我们需要保护我们的系统。为了保护我们的系统不受这个风险影响,我们需要添加 **127.0.0.1 index.docker.io** 到 /etc/hosts 条目。我们可以通过使用喜欢的文本编辑器完成。
# nano /etc/hosts
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ Docker 命令简单易学,也很容易实现或实践。这是一些你运行

-要拉取一个 docker 进行,我们需要运行下面的命令。
+要拉取一个 docker 镜像,我们需要运行下面的命令。
# docker pull registry.hub.docker.com/busybox
@@ -28,9 +28,9 @@ Docker 命令简单易学,也很容易实现或实践。这是一些你运行

-### 2. 运行一个 Docker 容器 ###
+### 2. 运行 Docker 容器 ###
-现在,成功地拉取要求或需要的 Docker 镜像之后,我们当然想运行这个 Docker 镜像。我们可以用 docker run 命令在镜像上运行一个 docker 容器。在 Docker 镜像之上运行一个 docker 容易时我们有很多选项和标记。我们使用 -t 和 -i 标记运行一个 docker 镜像并进入容器,如下面所示。
+现在,成功地拉取要求的或所需的 Docker 镜像之后,我们当然想运行这个 Docker 镜像。我们可以用 docker run 命令在镜像上运行一个 docker 容器。在 Docker 镜像上运行一个 docker 容器时我们有很多选项和标记。我们使用 -t 和 -i 选项来运行一个 docker 镜像并进入容器,如下面所示。
# docker run -it busybox
@@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ Docker 命令简单易学,也很容易实现或实践。这是一些你运行

-### 3. 查看容器 ###
+### 3. 检查容器运行 ###
不论容器是否运行,查看日志文件都很简单。我们可以使用下面的命令去检查是否有 docker 容器在实时运行。
@@ -62,17 +62,17 @@ Docker 命令简单易学,也很容易实现或实践。这是一些你运行

-### 4. 检查 Docker 容器 ###
+### 4. 查看容器信息 ###
-我们可以使用 inspect 命令检查一个 Docker 容器的每条信息。
+我们可以使用 inspect 命令查看一个 Docker 容器的各种信息。
# docker inspect <container id>

-### 5. 杀死或删除命令 ###
+### 5. 杀死或删除 ###
-我们可以使用 docker id 杀死或者停止进程或 docker 容器,如下所示。
+我们可以使用容器 id 杀死或者停止 docker 容器(进程),如下所示。
# docker stop <container id>
@@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ Docker 命令简单易学,也很容易实现或实践。这是一些你运行
### 结论 ###
-这些都是学习充分实现和利用 Docker 很基本的 docker 命令。有了这些命令,Docker 变得很简单,提供给端用户一个简单的计算平台。根据上面的教程,任何人学习 Docker 命令都非常简单。如果你有任何问题,建议,反馈,请写到下面的评论框中以便我们改进和更新内容。多谢!享受吧 :-)
+这些都是充分学习和使用 Docker 很基本的 docker 命令。有了这些命令,Docker 变得很简单,可以提供给最终用户一个易用的计算平台。根据上面的教程,任何人学习 Docker 命令都非常简单。如果你有任何问题,建议,反馈,请写到下面的评论框中以便我们改进和更新内容。多谢! 希望你喜欢 :-)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -98,8 +98,9 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/important-docker-commands/
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
\ No newline at end of file
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
+[1]:https://www.docker.com/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150413 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change PATH environment variable on Linux.md b/published/201505/20150413 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change PATH environment variable on Linux.md
similarity index 90%
rename from translated/tech/20150413 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change PATH environment variable on Linux.md
rename to published/201505/20150413 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change PATH environment variable on Linux.md
index 5cc7a17bd2..321ce4b2d3 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150413 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change PATH environment variable on Linux.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150413 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change PATH environment variable on Linux.md
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-Linux有问必答--如何在Linux中修改环境变量PATH
+Linux有问必答:如何在Linux中修改环境变量PATH
================================================================================
> **提问**: 当我试着运行一个程序时,它提示“command not found”。 但这个程序就在/usr/local/bin下。我该如何添加/usr/local/bin到我的PATH变量下,这样我就可以不用指定路径来运行这个命令了。
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ Linux有问必答--如何在Linux中修改环境变量PATH
/usr/lib64/qt-3.3/bin:/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin:/home/xmodulo/bin:/usr/local/bin
-更新的PATH会在当前的PATH一直有效。然而,更改将在新的会话中失效。
+更新后的PATH会在当前的会话一直有效。然而,更改将在新的会话中失效。
如果你想要永久更改PATH变量,用编辑器打开~/.bashrc (或者 ~/.bash_profile),接着在最后添加下面这行。
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ Linux有问必答--如何在Linux中修改环境变量PATH
接着运行下面这行永久激活更改:
- $ source ~/.bashrc (or source ~/.bash_profile)
+ $ source ~/.bashrc (或者 source ~/.bash_profile)
### 改变系统级的环境变量 ###
@@ -66,7 +66,7 @@ via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/change-path-environment-variable-linux.html
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150413 [Solved] Ubuntu Does Not Remember Brightness Settings.md b/published/201505/20150413 [Solved] Ubuntu Does Not Remember Brightness Settings.md
similarity index 94%
rename from translated/tech/20150413 [Solved] Ubuntu Does Not Remember Brightness Settings.md
rename to published/201505/20150413 [Solved] Ubuntu Does Not Remember Brightness Settings.md
index 5cd7abadaa..d0248ff2c2 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150413 [Solved] Ubuntu Does Not Remember Brightness Settings.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150413 [Solved] Ubuntu Does Not Remember Brightness Settings.md
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-[已解决] Ubuntu下不能记住亮度设置问题
+如何解决 Ubuntu 下不能记住亮度设置的问题
================================================================================

@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-mint-brightness-settings/
作者:[Abhishek][a]
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150415 Strong SSL Security on nginx.md b/published/201505/20150415 Strong SSL Security on nginx.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..094c50bd37
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150415 Strong SSL Security on nginx.md
@@ -0,0 +1,290 @@
+增强 nginx 的 SSL 安全性
+================================================================================
+[][1]
+
+本文向你介绍如何在 nginx 服务器上设置健壮的 SSL 安全机制。我们通过禁用 SSL 压缩来降低 CRIME 攻击威胁;禁用协议上存在安全缺陷的 SSLv3 及更低版本,并设置更健壮的加密套件(cipher suite)来尽可能启用前向安全性(Forward Secrecy);此外,我们还启用了 HSTS 和 HPKP。这样我们就拥有了一个健壮而可经受考验的 SSL 配置,并可以在 Qually Labs 的 SSL 测试中得到 A 级评分。
+
+如果不求甚解的话,可以从 [https://cipherli.st][2] 上找到 nginx 、Apache 和 Lighttpd 的安全设置,复制粘帖即可。
+
+本教程在 Digital Ocean 的 VPS 上测试通过。如果你喜欢这篇教程,想要支持作者的站点的话,购买 Digital Ocean 的 VPS 时请使用如下链接:[https://www.digitalocean.com/?refcode=7435ae6b8212][3] 。
+
+本教程可以通过[发布于 2014/1/21 的][4] SSL 实验室测试的严格要求(我之前就通过了测试,如果你按照本文操作就可以得到一个 A+ 评分)。
+
+- [本教程也可用于 Apache ][5]
+- [本教程也可用于 Lighttpd ][6]
+- [本教程也可用于 FreeBSD, NetBSD 和 OpenBSD 上的 nginx ,放在 BSD Now 播客上][7]: [http://www.bsdnow.tv/tutorials/nginx][8]
+
+你可以从下列链接中找到这方面的进一步内容:
+
+- [野兽攻击(BEAST)][9]
+- [罪恶攻击(CRIME)][10]
+- [怪物攻击(FREAK )][11]
+- [心血漏洞(Heartbleed)][12]
+- [完备的前向安全性(Perfect Forward Secrecy)][13]
+- [RC4 和 BEAST 的处理][14]
+
+我们需要编辑 nginx 的配置,在 Ubuntu/Debian 上是 `/etc/nginx/sited-enabled/yoursite.com`,在 RHEL/CentOS 上是 `/etc/nginx/conf.d/nginx.conf`。
+
+本文中,我们需要编辑443端口(SSL)的 `server` 配置中的部分。在文末你可以看到完整的配置例子。
+
+*在编辑之前切记备份一下配置文件!*
+
+### 野兽攻击(BEAST)和 RC4 ###
+
+简单的说,野兽攻击(BEAST)就是通过篡改一个加密算法的 CBC(密码块链)的模式,从而可以对部分编码流量悄悄解码。更多信息参照上面的链接。
+
+针对野兽攻击(BEAST),较新的浏览器已经启用了客户端缓解方案。推荐方案是禁用 TLS 1.0 的所有加密算法,仅允许 RC4 算法。然而,[针对 RC4 算法的攻击也越来越多](http://www.isg.rhul.ac.uk/tls/) ,很多已经从理论上逐步发展为实际可行的攻击方式。此外,有理由相信 NSA 已经实现了他们所谓的“大突破”——攻破 RC4 。
+
+禁用 RC4 会有几个后果。其一,当用户使用老旧的浏览器时,比如 Windows XP 上的 IE 会用 3DES 来替代 RC4。3DES 要比 RC4 更安全,但是它的计算成本更高,你的服务器就需要为这些用户付出更多的处理成本。其二,RC4 算法能减轻 野兽攻击(BEAST)的危害,如果禁用 RC4 会导致 TLS 1.0 用户会换到更容易受攻击的 AES-CBC 算法上(通常服务器端的对野兽攻击(BEAST)的“修复方法”是让 RC4 优先于其它算法)。我认为 RC4 的风险要高于野兽攻击(BEAST)的风险。事实上,有了客户端缓解方案(Chrome 和 Firefox 提供了缓解方案),野兽攻击(BEAST)就不是什么大问题了。而 RC4 的风险却在增长:随着时间推移,对加密算法的破解会越来越多。
+
+### 怪物攻击(FREAK) ###
+
+怪物攻击(FREAK)是一种中间人攻击,它是由来自 [INRIA、微软研究院和 IMDEA][15] 的密码学家们所发现的。怪物攻击(FREAK)的缩写来自“Factoring RSA-EXPORT Keys(RSA 出口密钥因子分解)”
+
+这个漏洞可上溯到上世纪九十年代,当时美国政府禁止出口加密软件,除非其使用编码密钥长度不超过512位的出口加密套件。
+
+这造成了一些现在的 TLS 客户端存在一个缺陷,这些客户端包括: 苹果的 SecureTransport 、OpenSSL。这个缺陷会导致它们会接受出口降级 RSA 密钥,即便客户端并没有要求使用出口降级 RSA 密钥。这个缺陷带来的影响很讨厌:在客户端存在缺陷,且服务器支持出口降级 RSA 密钥时,会发生中间人攻击,从而导致连接的强度降低。
+
+攻击分为两个组成部分:首先是服务器必须接受“出口降级 RSA 密钥”。
+
+中间人攻击可以按如下流程:
+
+- 在客户端的 Hello 消息中,要求标准的 RSA 加密套件。
+- 中间人攻击者修改该消息为‘export RSA’(输出级 RSA 密钥)。
+- 服务器回应一个512位的输出级 RSA 密钥,并以其长期密钥签名。
+- 由于 OpenSSL/SecureTransport 的缺陷,客户端会接受这个弱密钥。
+- 攻击者根据 RSA 模数分解因子来恢复相应的 RSA 解密密钥。
+- 当客户端编码‘pre-master secret’(预主密码)给服务器时,攻击者现在就可以解码它并恢复 TLS 的‘master secret’(主密码)。
+- 从这里开始,攻击者就能看到了传输的明文并注入任何东西了。
+
+本文所提供的加密套件不启用输出降级加密,请确认你的 OpenSSL 是最新的,也强烈建议你将客户端也升级到新的版本。
+
+### 心血漏洞(Heartbleed) ###
+
+心血漏洞(Heartbleed) 是一个于2014年4月公布的 OpenSSL 加密库的漏洞,它是一个被广泛使用的传输层安全(TLS)协议的实现。无论是服务器端还是客户端在 TLS 中使用了有缺陷的 OpenSSL,都可以被利用该缺陷。由于它是因 DTLS 心跳扩展(RFC 6520)中的输入验证不正确(缺少了边界检查)而导致的,所以该漏洞根据“心跳”而命名。这个漏洞是一种缓存区超读漏洞,它可以读取到本不应该读取的数据。
+
+哪个版本的 OpenSSL 受到心血漏洞(Heartbleed)的影响?
+
+各版本情况如下:
+
+- OpenSSL 1.0.1 直到 1.0.1f (包括)**存在**该缺陷
+- OpenSSL 1.0.1g **没有**该缺陷
+- OpenSSL 1.0.0 分支**没有**该缺陷
+- OpenSSL 0.9.8 分支**没有**该缺陷
+
+这个缺陷是2011年12月引入到 OpenSSL 中的,并随着 2012年3月14日 OpenSSL 发布的 1.0.1 而泛滥。2014年4月7日发布的 OpenSSL 1.0.1g 修复了该漏洞。
+
+升级你的 OpenSSL 就可以避免该缺陷。
+
+### SSL 压缩(罪恶攻击 CRIME) ###
+
+罪恶攻击(CRIME)使用 SSL 压缩来完成它的魔法,SSL 压缩在下述版本是默认关闭的: nginx 1.1.6及更高/1.0.9及更高(如果使用了 OpenSSL 1.0.0及更高), nginx 1.3.2及更高/1.2.2及更高(如果使用较旧版本的 OpenSSL)。
+
+如果你使用一个早期版本的 nginx 或 OpenSSL,而且你的发行版没有向后移植该选项,那么你需要重新编译没有一个 ZLIB 支持的 OpenSSL。这会禁止 OpenSSL 使用 DEFLATE 压缩方式。如果你禁用了这个,你仍然可以使用常规的 HTML DEFLATE 压缩。
+
+### SSLv2 和 SSLv3 ###
+
+SSLv2 是不安全的,所以我们需要禁用它。我们也禁用 SSLv3,因为 TLS 1.0 在遭受到降级攻击时,会允许攻击者强制连接使用 SSLv3,从而禁用了前向安全性(forward secrecy)。
+
+如下编辑配置文件:
+
+ ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
+
+### 卷毛狗攻击(POODLE)和 TLS-FALLBACK-SCSV ###
+
+SSLv3 会受到[卷毛狗漏洞(POODLE)][16]的攻击。这是禁用 SSLv3 的主要原因之一。
+
+Google 提出了一个名为 [TLS\_FALLBACK\_SCSV][17] 的SSL/TLS 扩展,它用于防止强制 SSL 降级。如果你升级 到下述的 OpenSSL 版本会自动启用它。
+
+- OpenSSL 1.0.1 带有 TLS\_FALLBACK\_SCSV 1.0.1j 及更高。
+- OpenSSL 1.0.0 带有 TLS\_FALLBACK\_SCSV 1.0.0o 及更高。
+- OpenSSL 0.9.8 带有 TLS\_FALLBACK\_SCSV 0.9.8zc 及更高。
+
+[更多信息请参照 NGINX 文档][18]。
+
+### 加密套件(cipher suite) ###
+
+前向安全性(Forward Secrecy)用于在长期密钥被破解时确保会话密钥的完整性。PFS(完备的前向安全性)是指强制在每个/每次会话中推导新的密钥。
+
+这就是说,泄露的私钥并不能用来解密(之前)记录下来的 SSL 通讯。
+
+提供PFS(完备的前向安全性)功能的是那些使用了一种 Diffie-Hellman 密钥交换的短暂形式的加密套件。它们的缺点是系统开销较大,不过可以使用椭圆曲线的变体来改进。
+
+以下两个加密套件是我推荐的,之后[Mozilla 基金会][19]也推荐了。
+
+推荐的加密套件:
+
+ ssl_ciphers 'AES128+EECDH:AES128+EDH';
+
+向后兼容的推荐的加密套件(IE6/WinXP):
+
+ ssl_ciphers "ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-DES-CBC3-SHA:EDH-RSA-DES-CBC3-SHA:AES256-GCM-SHA384:AES128-GCM-SHA256:AES256-SHA256:AES128-SHA256:AES256-SHA:AES128-SHA:DES-CBC3-SHA:HIGH:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!DES:!MD5:!PSK:!RC4";
+
+如果你的 OpenSSL 版本比较旧,不可用的加密算法会自动丢弃。应该一直使用上述的完整套件,让 OpenSSL 选择一个它所支持的。
+
+加密套件的顺序是非常重要的,因为其决定了优先选择哪个算法。上述优先推荐的算法中提供了PFS(完备的前向安全性)。
+
+较旧版本的 OpenSSL 也许不能支持这个算法的完整列表,AES-GCM 和一些 ECDHE 算法是相当新的,在 Ubuntu 和 RHEL 中所带的绝大多数 OpenSSL 版本中不支持。
+
+#### 优先顺序的逻辑 ####
+
+- ECDHE+AESGCM 加密是首选的。它们是 TLS 1.2 加密算法,现在还没有广泛支持。当前还没有对它们的已知攻击。
+- PFS 加密套件好一些,首选 ECDHE,然后是 DHE。
+- AES 128 要好于 AES 256。有一个关于 AES256 带来的安全提升程度是否值回成本的[讨论][20],结果是显而易见的。目前,AES128 要更值一些,因为它提供了不错的安全水准,确实很快,而且看起来对时序攻击更有抵抗力。
+- 在向后兼容的加密套件里面,AES 要优于 3DES。在 TLS 1.1及其以上,减轻了针对 AES 的野兽攻击(BEAST)的威胁,而在 TLS 1.0上则难以实现该攻击。在非向后兼容的加密套件里面,不支持 3DES。
+- RC4 整个不支持了。3DES 用于向后兼容。参看 [#RC4\_weaknesses][21] 中的讨论。
+
+#### 强制丢弃的算法 ####
+
+- aNULL 包含了非验证的 Diffie-Hellman 密钥交换,这会受到中间人(MITM)攻击
+- eNULL 包含了无加密的算法(明文)
+- EXPORT 是老旧的弱加密算法,是被美国法律标示为可出口的
+- RC4 包含的加密算法使用了已弃用的 ARCFOUR 算法
+- DES 包含的加密算法使用了弃用的数据加密标准(DES)
+- SSLv2 包含了定义在旧版本 SSL 标准中的所有算法,现已弃用
+- MD5 包含了使用已弃用的 MD5 作为哈希算法的所有算法
+
+### 更多设置 ###
+
+确保你也添加了如下行:
+
+ ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
+ ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m;
+
+在一个 SSLv3 或 TLSv1 握手过程中选择一个加密算法时,一般使用客户端的首选算法。如果设置了上述配置,则会替代地使用服务器端的首选算法。
+
+- [关于 ssl\_prefer\_server\_ciphers 的更多信息][22]
+- [关于 ssl\_ciphers 的更多信息][23]
+
+### 前向安全性和 Diffie Hellman Ephemeral (DHE)参数 ###
+
+前向安全性(Forward Secrecy)的概念很简单:客户端和服务器协商一个永不重用的密钥,并在会话结束时销毁它。服务器上的 RSA 私钥用于客户端和服务器之间的 Diffie-Hellman 密钥交换签名。从 Diffie-Hellman 握手中获取的预主密钥会用于之后的编码。因为预主密钥是特定于客户端和服务器之间建立的某个连接,并且只用在一个限定的时间内,所以称作短暂模式(Ephemeral)。
+
+使用了前向安全性,如果一个攻击者取得了一个服务器的私钥,他是不能解码之前的通讯信息的。这个私钥仅用于 Diffie Hellman 握手签名,并不会泄露预主密钥。Diffie Hellman 算法会确保预主密钥绝不会离开客户端和服务器,而且不能被中间人攻击所拦截。
+
+所有版本的 nginx(如1.4.4)都依赖于 OpenSSL 给 Diffie-Hellman (DH)的输入参数。不幸的是,这意味着 Diffie-Hellman Ephemeral(DHE)将使用 OpenSSL 的默认设置,包括一个用于密钥交换的1024位密钥。因为我们正在使用2048位证书,DHE 客户端就会使用一个要比非 DHE 客户端更弱的密钥交换。
+
+我们需要生成一个更强壮的 DHE 参数:
+
+ cd /etc/ssl/certs
+ openssl dhparam -out dhparam.pem 4096
+
+然后告诉 nginx 将其用作 DHE 密钥交换:
+
+ ssl_dhparam /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem;
+
+### OCSP 装订(Stapling) ###
+
+当连接到一个服务器时,客户端应该使用证书吊销列表(CRL)或在线证书状态协议(OCSP)记录来校验服务器证书的有效性。CRL 的问题是它已经增长的太大了,永远也下载不完了。
+
+OCSP 更轻量级一些,因为我们每次只请求一条记录。但是副作用是当连接到一个服务器时必须对第三方 OCSP 响应器发起 OCSP 请求,这就增加了延迟和带来了潜在隐患。事实上,CA 所运营的 OCSP 响应器非常不可靠,浏览器如果不能及时收到答复,就会静默失败。攻击者通过 DoS 攻击一个 OCSP 响应器可以禁用其校验功能,这样就降低了安全性。
+
+解决方法是允许服务器在 TLS 握手中发送缓存的 OCSP 记录,以绕开 OCSP 响应器。这个机制节省了客户端和 OCSP 响应器之间的通讯,称作 OCSP 装订。
+
+客户端会在它的 CLIENT HELLO 中告知其支持 status\_request TLS 扩展,服务器仅在客户端请求它的时候才发送缓存的 OCSP 响应。
+
+大多数服务器最多会缓存 OCSP 响应48小时。服务器会按照常规的间隔连接到 CA 的 OCSP 响应器来获取刷新的 OCSP 记录。OCSP 响应器的位置可以从签名的证书中的授权信息访问(Authority Information Access)字段中获得。
+
+- [阅读我的教程:在 NGINX 中启用 OCSP 装订][24]
+
+### HTTP 严格传输安全(HSTS) ###
+
+如有可能,你应该启用 [HTTP 严格传输安全(HSTS)][25],它会引导浏览器和你的站点之间的通讯仅通过 HTTPS。
+
+- [阅读我关于 HSTS 的文章,了解如何配置它][26]
+
+### HTTP 公钥固定扩展(HPKP) ###
+
+你也应该启用 [HTTP 公钥固定扩展(HPKP)][27]。
+
+公钥固定的意思是一个证书链必须包括一个白名单中的公钥。它确保仅有白名单中的 CA 才能够为某个域名签署证书,而不是你的浏览器中存储的任何 CA。
+
+我已经写了一篇[关于 HPKP 的背景理论及在 Apache、Lighttpd 和 NGINX 中配置例子的文章][28]。
+
+### 配置范例 ###
+
+ server {
+
+ listen [::]:443 default_server;
+
+ ssl on;
+ ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/cert/raymii_org.pem;
+ ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/cert/ca-bundle.pem;
+
+ ssl_ciphers 'AES128+EECDH:AES128+EDH:!aNULL';
+
+ ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
+ ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m;
+
+ ssl_stapling on;
+ ssl_stapling_verify on;
+ resolver 8.8.4.4 8.8.8.8 valid=300s;
+ resolver_timeout 10s;
+
+ ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
+ ssl_dhparam /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem;
+
+ add_header Strict-Transport-Security max-age=63072000;
+ add_header X-Frame-Options DENY;
+ add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
+
+ root /var/www/;
+ index index.html index.htm;
+ server_name raymii.org;
+
+ }
+
+### 结尾 ###
+
+如果你使用了上述配置,你需要重启 nginx:
+
+ # 首先检查配置文件是否正确
+ /etc/init.d/nginx configtest
+ # 然后重启
+ /etc/init.d/nginx restart
+
+现在使用 [SSL Labs 测试][29]来看看你是否能得到一个漂亮的“A”。当然了,你也得到了一个安全的、强壮的、经得起考验的 SSL 配置!
+
+- [参考 Mozilla 关于这方面的内容][30]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/Strong_SSL_Security_On_nginx.html
+
+作者:[Remy van Elst][a]
+译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://raymii.org/
+[1]:https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=raymii.org
+[2]:https://cipherli.st/
+[3]:https://www.digitalocean.com/?refcode=7435ae6b8212
+[4]:http://blog.ivanristic.com/2014/01/ssl-labs-stricter-security-requirements-for-2014.html
+[5]:https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/Strong_SSL_Security_On_Apache2.html
+[6]:https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/Pass_the_SSL_Labs_Test_on_Lighttpd_%28Mitigate_the_CRIME_and_BEAST_attack_-_Disable_SSLv2_-_Enable_PFS%29.html
+[7]:http://www.bsdnow.tv/episodes/2014_08_20-engineering_nginx
+[8]:http://www.bsdnow.tv/tutorials/nginx
+[9]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_Security#BEAST_attack
+[10]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CRIME_%28security_exploit%29
+[11]:http://blog.cryptographyengineering.com/2015/03/attack-of-week-freak-or-factoring-nsa.html
+[12]:http://heartbleed.com/
+[13]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perfect_forward_secrecy
+[14]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_Security#Dealing_with_RC4_and_BEAST
+[15]:https://www.smacktls.com/
+[16]:https://raymii.org/s/articles/Check_servers_for_the_Poodle_bug.html
+[17]:https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-tls-downgrade-scsv-00
+[18]:http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpSslModule#ssl_protocols
+[19]:https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Server_Side_TLS
+[20]:http://www.mail-archive.com/dev-tech-crypto@lists.mozilla.org/msg11247.html
+[21]:https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Server_Side_TLS#RC4_weaknesses
+[22]:http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpSslModule#ssl_prefer_server_ciphers
+[23]:http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpSslModule#ssl_ciphers
+[24]:https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/OCSP_Stapling_on_nginx.html
+[25]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTTP_Strict_Transport_Security
+[26]:https://linux.cn/article-5266-1.html
+[27]:https://wiki.mozilla.org/SecurityEngineering/Public_Key_Pinning
+[28]:https://linux.cn/article-5282-1.html
+[29]:https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/
+[30]:https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Server_Side_TLS
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/[translated]20150417 14 Useful Examples of Linux 'sort' Command--Part 1.md b/published/201505/20150417 14 Useful Examples of Linux 'sort' Command--Part 1.md
similarity index 63%
rename from translated/tech/[translated]20150417 14 Useful Examples of Linux 'sort' Command--Part 1.md
rename to published/201505/20150417 14 Useful Examples of Linux 'sort' Command--Part 1.md
index 9653302530..c483c4035f 100644
--- a/translated/tech/[translated]20150417 14 Useful Examples of Linux 'sort' Command--Part 1.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150417 14 Useful Examples of Linux 'sort' Command--Part 1.md
@@ -1,24 +1,24 @@
-Linux ‘sort’命令的14个有用的范例 -- 第一部分
+Linux 的 ‘sort’命令的14个有用的范例(一)
=============================================================
Sort是用于对单个或多个文本文件内容进行排序的Linux程序。Sort命令以空格作为字段分隔符,将一行分割为多个关键字对文件进行排序。需要注意的是除非你将输出重定向到文件中,否则Sort命令并不对文件内容进行实际的排序(即文件内容没有修改),只是将文件内容按有序输出。
本文的目标是通过14个实际的范例让你更深刻的理解如何在Linux中使用sort命令。
-###1. 首先我们将会创建一个用于执行‘sort’命令的文本文件(tecmint.txt)。工作路径是‘/home/$USER/Desktop/tecmint’。###
+1、 首先我们将会创建一个用于执行‘sort’命令的文本文件(tecmint.txt)。工作路径是‘/home/$USER/Desktop/tecmint’。
-下面命令中的‘-e’选项将‘/’和‘/n’解析成一个新行
+下面命令中的‘-e’选项将启用‘\\’转义,将‘\n’解析成换行
$ echo -e "computer\nmouse\nLAPTOP\ndata\nRedHat\nlaptop\ndebian\nlaptop" > tecmint.txt
-###2. 在开始学习‘sort’命令前,我们先看看文件的内容及其显示方式。###
+2、 在开始学习‘sort’命令前,我们先看看文件的内容及其显示方式。
$ cat tecmint.txt
-###3. 现在,使用如下命令对文件内容进行排序。###
+3、 现在,使用如下命令对文件内容进行排序。
$ sort tecmint.txt
@@ -26,30 +26,30 @@ Sort是用于对单个或多个文本文件内容进行排序的Linux程序。So
**注意**:上面的命令并不对文件内容进行实际的排序,仅仅是将其内容按有序方式输出。
-###4. 对文件‘tecmint.txt’文件内容排序,并将排序后的内容输出到名为sorted.txt的文件中,然后使用[cat][1]命令查看验证sorted.txt文件的内容。###
+4、 对文件‘tecmint.txt’文件内容排序,并将排序后的内容输出到名为sorted.txt的文件中,然后使用[cat][1]命令查看验证sorted.txt文件的内容。
$ sort tecmint.txt > sorted.txt
$ cat sorted.txt
-###5. 现在使用‘-r’参数对‘tecmint.txt’文件内容进行逆序排序,并将输出内容重定向到‘reversesorted.txt’文件中,并使用cat命令查看文件的内容。###
+5、 现在使用‘-r’参数对‘tecmint.txt’文件内容进行逆序排序,并将输出内容重定向到‘reversesorted.txt’文件中,并使用cat命令查看文件的内容。
$ sort -r tecmint.txt > reversesorted.txt
$ cat reversesorted.txt
-###6. 创建一个新文件(lsl.txt),文件内容为在home目录下执行‘ls -l’命令的输出。###
+6、 创建一个新文件(lsl.txt),文件内容为在home目录下执行‘ls -l’命令的输出。
$ ls -l /home/$USER > /home/$USER/Desktop/tecmint/lsl.txt
$ cat lsl.txt
-我们将会看到对其他基础字段进行排序的例子,而不是对默认的初始字符进行排序。
+我们将会看到对其他字段进行排序的例子,而不是对默认的开始字符进行排序。
-###7. 基于第二列(符号连接的数量)对文件‘lsl.txt’进行排序。###
+7、 基于第二列(符号连接的数量)对文件‘lsl.txt’进行排序。
$ sort -nk2 lsl.txt
@@ -57,19 +57,19 @@ Sort是用于对单个或多个文本文件内容进行排序的Linux程序。So

-###8. 基于第9列(文件和目录的名称,非数值)对文件‘lsl.txt’进行排序。###
+8、 基于第9列(文件和目录的名称,非数值)对文件‘lsl.txt’进行排序。
$ sort -k9 lsl.txt
-###9. sort命令并非仅能对文件进行排序,我们还可以通过管道将命令的输出内容重定向到sort命令中。###
+9、 sort命令并非仅能对文件进行排序,我们还可以通过管道将命令的输出内容重定向到sort命令中。
$ ls -l /home/$USER | sort -nk5
-###10. 对文件tecmint.txt进行排序,并删除重复的行。然后检查重复的行是否已经删除了。###
+10、 对文件tecmint.txt进行排序,并删除重复的行。然后检查重复的行是否已经删除了。
$ cat tecmint.txt
$ sort -u tecmint.txt
@@ -78,23 +78,23 @@ Sort是用于对单个或多个文本文件内容进行排序的Linux程序。So
目前我们发现的排序规则:
- 除非指定了‘-r’参数,否则排序的优先级按下面规则排序
+除非指定了‘-r’参数,否则排序的优先级按下面规则排序
+
- 以数字开头的行优先级最高
- 以小写字母开头的行优先级次之
- 待排序内容按字典序进行排序
- - 默认情况下,‘sort’命令将带排序内容的每行关键字当作一个字符串进行字典序排序(数字优先级最高,参看规则 - 1)
+ - 默认情况下,‘sort’命令将带排序内容的每行关键字当作一个字符串进行字典序排序(数字优先级最高,参看规则 1)
-
-###11. 创建文件‘lsla.txt’,其内容用‘ls -la’命令的输出内容填充。###
+11、 在当前位置创建第三个文件‘lsla.txt’,其内容用‘ls -lA’命令的输出内容填充。
$ ls -lA /home/$USER > /home/$USER/Desktop/tecmint/lsla.txt
$ cat lsla.txt
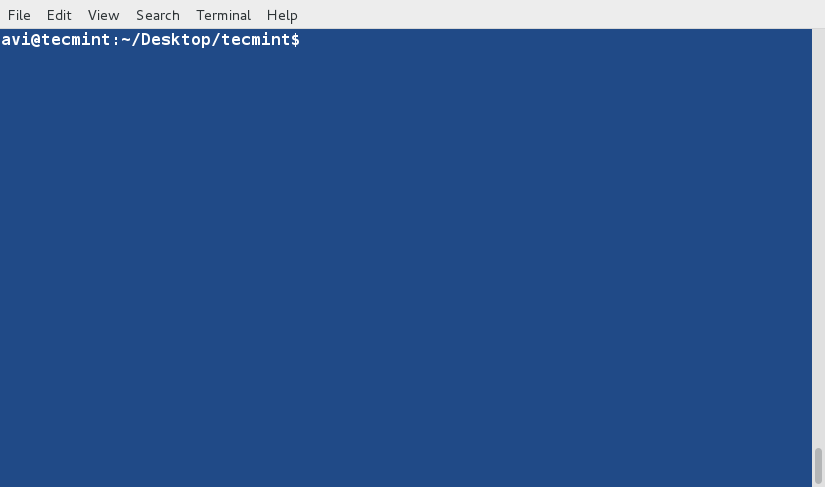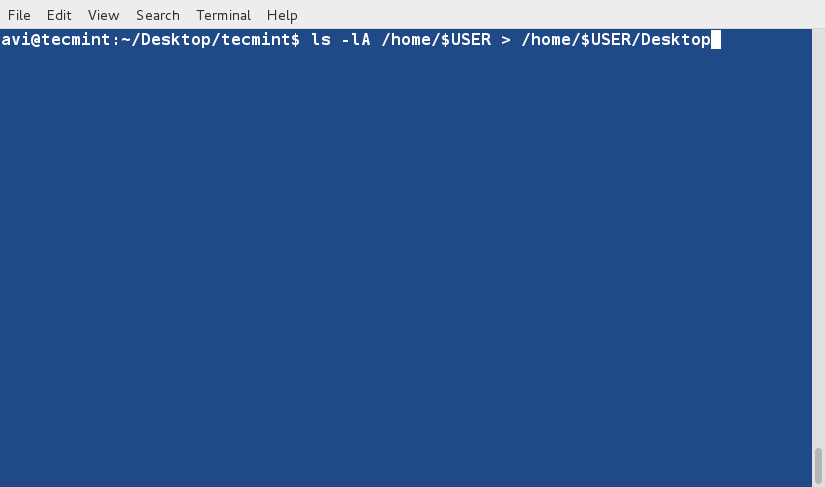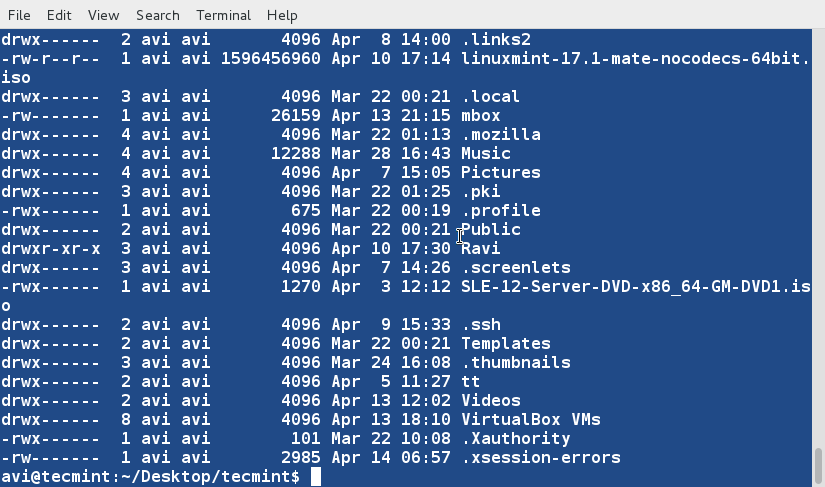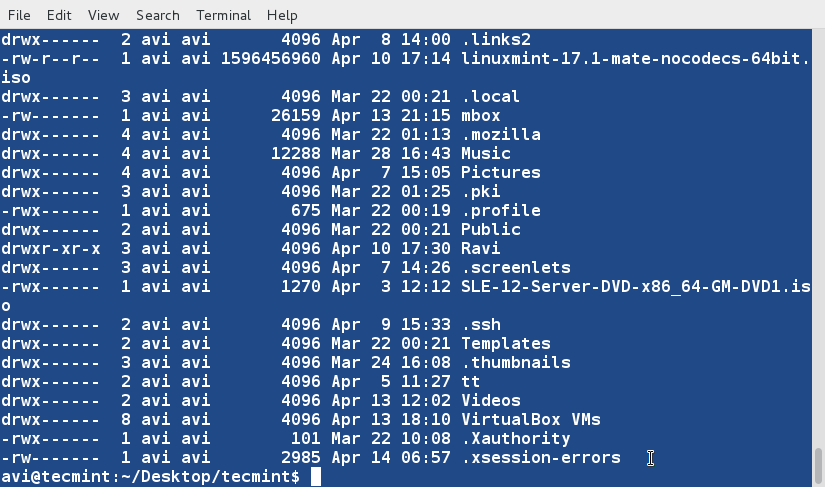
-了解ls命令的读者都知道‘ls -la’=‘ls -l’ + 隐藏文件。因此这两个文件的大部分内容都是相同的。
+了解ls命令的读者都知道‘ls -lA’ 等于 ‘ls -l’ + 隐藏文件,所以这两个文件的大部分内容都是相同的。
-###12. 对上面两个文件内容进行排序输出。###
+12、 对上面两个文件内容进行排序输出。
$ sort lsl.txt lsla.txt
@@ -102,7 +102,7 @@ Sort是用于对单个或多个文本文件内容进行排序的Linux程序。So
注意文件和目录的重复
-###13. 现在我们看看怎样对两个文件进行排序、合并,并且删除重复行。###
+13、 现在我们看看怎样对两个文件进行排序、合并,并且删除重复行。
$ sort -u lsl.txt lsla.txt
@@ -110,13 +110,13 @@ Sort是用于对单个或多个文本文件内容进行排序的Linux程序。So
此时,我们注意到重复的行已经被删除了,我们可以将输出内容重定向到文件中。
-###14. 我们同样可以基于多列对文件内容进行排序。基于第2,5(数值)和9(非数值)列对‘ls -l’命令的输出进行排序。###
+14、 我们同样可以基于多列对文件内容进行排序。基于第2,5(数值)和9(非数值)列对‘ls -l’命令的输出进行排序。
$ ls -l /home/$USER | sort -t "," -nk2,5 -k9
-先到此为止了,在接下来的文章中我们将会学习到‘sort’命令更多的详细例子。届时敬请关注Tecmint。保持分享精神。若喜欢本文,敬请将本文分享给你的朋友。
+先到此为止了,在接下来的文章中我们将会学习到‘sort’命令更多的详细例子。届时敬请关注我们。保持分享精神。若喜欢本文,敬请将本文分享给你的朋友。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -124,7 +124,7 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/sort-command-linux/
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
译者:[cvsher](https://github.com/cvsher)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150417 How to Configure MariaDB Replication on CentOS Linux.md b/published/201505/20150417 How to Configure MariaDB Replication on CentOS Linux.md
similarity index 82%
rename from translated/tech/20150417 How to Configure MariaDB Replication on CentOS Linux.md
rename to published/201505/20150417 How to Configure MariaDB Replication on CentOS Linux.md
index ca27084edf..702d3d7521 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150417 How to Configure MariaDB Replication on CentOS Linux.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150417 How to Configure MariaDB Replication on CentOS Linux.md
@@ -1,22 +1,26 @@
-如何在 CentOS Linux 中配置 MariADB 复制
+如何在 CentOS Linux 中配置 MariaDB 复制
================================================================================
-这是一个创建数据库重复版本的过程。复制过程不仅仅是复制一个数据库,同时也包括从主节点到一个从节点的更改同步。但这并不意味着从数据库就是和主数据库完全相同的副本,因为复制可以配置为只有表或者行或者列的一个模式将被复制,例如,局部复制。复制保证了特定的配置对象在不同的数据库之间保持同步。
+这是一个创建数据库重复版本的过程。复制过程不仅仅是复制一个数据库,同时也包括从主节点到一个从节点的更改同步。但这并不意味着从数据库就是和主数据库完全相同的副本,因为复制可以配置为只复制表结构、行或者列,这叫做局部复制。复制保证了特定的配置对象在不同的数据库之间保持一致。
### Mariadb 复制概念 ###
-**备份** :复制可以用来进行数据库备份。例如,你有主->从复制。如果主节点丢失(比如hdd损坏),你可以从从节点中恢复你的数据库。
+**备份** :复制可以用来进行数据库备份。例如,当你做了主->从复制。如果主节点数据丢失(比如硬盘损坏),你可以从从节点中恢复你的数据库。
-**扩展** :你可以使用主->从复制作为扩展的解决方案。例如,如果你有一些大的数据库以及SQL查询,使用复制你可以将这些查询单独分到每个复制节点。写SQL应该只在主节点进行,而只读查询可以在从节点上进行。
+**扩展** :你可以使用主->从复制作为扩展解决方案。例如,如果你有一些大的数据库以及SQL查询,使用复制你可以将这些查询分离到每个复制节点。写入操作的SQL应该只在主节点进行,而只读查询可以在从节点上进行。
-**传播解决方案** :你可以用复制来进行分发。例如,你可以将不同的销售数据分发到不同的数据库。
+**分发解决方案** :你可以用复制来进行分发。例如,你可以将不同的销售数据分发到不同的数据库。
-**故障解决方案** : 假如你有主节点->从节点1->从节点2->从节点3的复制。你可以为主节点写脚本监控,如果主节点出故障了,脚本可以快速的将从节点1作为新的主节点,有主节点->从节点1->从节点2,你的应用可以继续工作而不会停机。
+**故障解决方案** : 假如你建立有主节点->从节点1->从节点2->从节点3的复制结构。你可以为主节点写脚本监控,如果主节点出故障了,脚本可以快速的将从节点1切换为新的主节点,这样复制结构变成了主节点->从节点1->从节点2,你的应用可以继续工作而不会停机。
### 复制的简单图解示范 ###

-开始之前,你应该知道什么是**二进制日志文件**以及 Ibdata1。二进制日志文件中包括关于数据库,数据和结构的所有更改的记录,以及每条语句的执行时间。二进制日志文件包括设置日志文件和一个索引。这意味着主要的SQL语句,例如CREATE, ALTER, INSERT, UPDATE 和 DELETE 会放到这个日志文件中,而例如SELECT语句就不会被记录。这些信息可以被记录到普通的query.log文件。简单的说 **Ibdata1** 是一个包括所有表和所有数据库信息的文件。
+开始之前,你应该知道什么是**二进制日志文件**以及 Ibdata1。
+
+二进制日志文件中包括关于数据库,数据和结构的所有更改的记录,以及每条语句的执行了多长时间。二进制日志文件包括一系列日志文件和一个索引文件。这意味着主要的SQL语句,例如CREATE, ALTER, INSERT, UPDATE 和 DELETE 会放到这个日志文件中;而例如SELECT这样的语句就不会被记录,它们可以被记录到普通的query.log文件中。
+
+而 **Ibdata1** 简单的说据是一个包括所有表和所有数据库信息的文件。
### 主服务器配置 ###
@@ -39,7 +43,7 @@
sudo systemctl start mariadb.service
sudo systemctl enable mariadb.service
-输出:
+输出如下:
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mariadb.service'
@@ -51,7 +55,7 @@
sudo systemctl is-active mariadb.service
-输出:
+输出如下:
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl status mariadb.service
mariadb.service - MariaDB database server
@@ -65,11 +69,11 @@
mysql> flush privileges;
mysql> exit
-SOME_ROOT_PASSWORD - 你的 root 密码。 例如我用"q"作为密码,然后尝试登陆:
+这里 SOME_ROOT_PASSWORD 是你的 root 密码。 例如我用"q"作为密码,然后尝试登录:
sudo mysql -u root -pSOME_ROOT_PASSWORD
-输出:
+输出如下:
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 5
@@ -89,7 +93,7 @@ SOME_ROOT_PASSWORD - 你的 root 密码。 例如我用"q"作为密码,然后
test_repl - 将要被复制的模式的名字
-输出:
+输出:如下
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
@@ -105,7 +109,7 @@ SOME_ROOT_PASSWORD - 你的 root 密码。 例如我用"q"作为密码,然后
City varchar(255)
);
-输出:
+输出如下:
mysql> MariaDB [test_repl]> CREATE TABLE Persons (
-> PersonID int,
@@ -124,7 +128,7 @@ SOME_ROOT_PASSWORD - 你的 root 密码。 例如我用"q"作为密码,然后
mysql> INSERT INTO Persons VALUES (4, "LastName4", "FirstName4", "Address4", "City4");
mysql> INSERT INTO Persons VALUES (5, "LastName5", "FirstName5", "Address5", "City5");
-输出:
+输出如下:
Query OK, 5 row affected (0.00 sec)
@@ -132,7 +136,7 @@ SOME_ROOT_PASSWORD - 你的 root 密码。 例如我用"q"作为密码,然后
mysql> select * from Persons;
-输出:
+输出如下:
+----------+-----------+------------+----------+-------+
| PersonID | LastName | FirstName | Address | City |
@@ -145,9 +149,9 @@ SOME_ROOT_PASSWORD - 你的 root 密码。 例如我用"q"作为密码,然后
| 5 | LastName5 | FirstName5 | Address5 | City5 |
+----------+-----------+------------+----------+-------+
-### 配置 MariaDB 重复 ###
+### 配置 MariaDB 复制 ###
-你需要在主结点服务器上编辑 my.cnf文件来启用二进制日志以及设置服务器id。我会使用vi文本编辑器,但你可以使用任何你喜欢的,例如nano,joe。
+你需要在主节点服务器上编辑 my.cnf文件来启用二进制日志以及设置服务器id。我会使用vi文本编辑器,但你可以使用任何你喜欢的,例如nano,joe。
sudo vi /etc/my.cnf
@@ -159,7 +163,7 @@ SOME_ROOT_PASSWORD - 你的 root 密码。 例如我用"q"作为密码,然后
binlog-format=row
server_id=1
-输出:
+输出如下:

@@ -173,7 +177,7 @@ sudo mysql -u root -pq test_repl
mysql> SHOW MASTER STATUS;
-输出:
+输出如下:
+--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+
| File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB |
@@ -183,12 +187,12 @@ mysql> SHOW MASTER STATUS;
**记住** : "File" 和 "Position" 的值。在从节点中你需要使用这些值
-创建用来重复的用户
+创建用来复制的用户
mysql> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO replication_user IDENTIFIED BY 'bigs3cret' WITH GRANT OPTION;
mysql> flush privileges;
-输出:
+输出如下:
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
@@ -197,7 +201,7 @@ mysql> SHOW MASTER STATUS;
mysql> select * from mysql.user WHERE user="replication_user"\G;
-输出:
+输出如下:
mysql> select * from mysql.user WHERE user="replication_user"\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
@@ -220,11 +224,11 @@ mysql> SHOW MASTER STATUS;
### 从节点配置 ###
-所有这些命令需要在从节点中进行
+所有这些命令需要在从节点中进行。
-假设我们已经更新/升级了包括有最新的MariaDB服务器的 CentOS 7.x,而且你可以用root账号登陆到MariaDBs服务器(这在这篇文章的第一部分已经介绍过)
+假设我们已经更新/升级了包括有最新的MariaDB服务器的 CentOS 7.x,而且你可以用root账号登陆到MariaDB服务器(这在这篇文章的第一部分已经介绍过)
-登陆到Maria 数据库控制台并创建数据库
+登录到Maria 数据库控制台并创建数据库
mysql -u root -pSOME_ROOT_PASSWORD;
mysql> create database test_repl;
@@ -264,7 +268,7 @@ full-dump.sql - 你在测试服务器中创建的DB Dump。
mysql> slave start;
-输出:
+输出如下:
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
@@ -272,7 +276,7 @@ full-dump.sql - 你在测试服务器中创建的DB Dump。
mysql> show slave status\G;
-输出:
+输出如下:
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Slave_IO_State: Waiting for master to send event
@@ -352,7 +356,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/how-tos/configure-mariadb-replication-centos-linux/
作者:[Bobbin Zachariah][a]
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150417 sshuttle--A transparent proxy-based VPN using ssh.md b/published/201505/20150417 sshuttle--A transparent proxy-based VPN using ssh.md
similarity index 76%
rename from translated/tech/20150417 sshuttle--A transparent proxy-based VPN using ssh.md
rename to published/201505/20150417 sshuttle--A transparent proxy-based VPN using ssh.md
index 297f411840..953fd343b8 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150417 sshuttle--A transparent proxy-based VPN using ssh.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150417 sshuttle--A transparent proxy-based VPN using ssh.md
@@ -1,9 +1,8 @@
-sshuttle - 一个使用ssh的基于VPN的透明代理
+sshuttle:一个使用ssh的基于VPN的透明代理
================================================================================
-sshuttle允许你通过ssh创建一条从你电脑连接到任何远程服务器的VPN连接,只要你的服务器支持python2.3 或则更高的版本, 你必须有本机的root权限,但是你可以在服务端有普通账户即可。
-
-你可以在一台机器上同时运行多次sshuttle来连接到不同的服务器上,这样你就可以一次使用多个VPN, sshuttle可以转发你子网所有流量到VPN中。
+sshuttle 允许你通过 ssh 创建一条从你电脑连接到任何远程服务器的 VPN 连接,只要你的服务器支持 python2.3 或则更高的版本。你必须有本机的 root 权限,但是你可以在服务端有普通账户即可。
+你可以在一台机器上同时运行多次 sshuttle 来连接到不同的服务器上,这样你就可以同时使用多个 VPN, sshuttle可以转发你子网中所有流量到VPN中。
### 在Ubuntu中安装sshuttle ###
@@ -17,7 +16,7 @@ sshuttle允许你通过ssh创建一条从你电脑连接到任何远程服务器
sshuttle [options...] [-r [username@]sshserver[:port]] [subnets]
-#### Option 细节 ####
+#### 选项细节 ####
-r, —remote=[username@]sshserver[:port]
@@ -29,9 +28,9 @@ sshuttle允许你通过ssh创建一条从你电脑连接到任何远程服务器
sudo sshuttle -r username@sshserver 0.0.0.0/0 -vv
-当开始后,sshuttle会创建一个ssh会话到通过-r指定的服务器。如果-r被忽略了,它会在本地运行客户端和服务端,这个有时会在测试时有用。
+当开始后,sshuttle会创建一个ssh会话到由-r指定的服务器。如果-r被丢了,它会在本地运行客户端和服务端,这个有时会在测试时有用。
-连接到远程服务器后,sshuttle会上传它的(python)源码到远程服务器并执行。那么,你就不需要在远程服务器上安装sshuttle,并且客户端和服务器端间不会存在sshuttle版本冲突。
+连接到远程服务器后,sshuttle会上传它的(python)源码到远程服务器并执行。所以,你就不需要在远程服务器上安装sshuttle,并且客户端和服务器端间不会存在sshuttle版本冲突。
#### 手册中的更多例子 ####
@@ -86,7 +85,7 @@ via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/sshuttle-a-transparent-proxy-based-vpn-using-ssh.
作者:[ruchi][a]
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150420 7 Interesting Linux 'sort' Command Examples--Part 2.md b/published/201505/20150420 7 Interesting Linux 'sort' Command Examples--Part 2.md
similarity index 62%
rename from translated/tech/20150420 7 Interesting Linux 'sort' Command Examples--Part 2.md
rename to published/201505/20150420 7 Interesting Linux 'sort' Command Examples--Part 2.md
index 4602424a3a..476274b495 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20150420 7 Interesting Linux 'sort' Command Examples--Part 2.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150420 7 Interesting Linux 'sort' Command Examples--Part 2.md
@@ -1,11 +1,10 @@
-
-Linux 'sort'命令的七个有趣实例-第二部分
+Linux 的 'sort'命令的七个有趣实例(二)
================================================================================
-在上一篇文章里,我们已经探讨了关于sort命令的多个例子,如果你错过了这篇文章,可以点击下面的链接进行阅读。今天的这篇文章作为上一篇文章的继续,将讨论关于sort命令的剩余用法,与上一篇一起作为Linux ‘sort’命令的完整指南。
-注:前两天做过这个原文
-- [14 ‘sort’ Command Examples in Linux][1]
--
+在[上一篇文章][1]里,我们已经探讨了关于sort命令的多个例子,如果你错过了这篇文章,可以点击下面的链接进行阅读。今天的这篇文章作为上一篇文章的继续,将讨论关于sort命令的剩余用法,与上一篇一起作为Linux ‘sort’命令的完整指南。
+
+- [Linux 的 ‘sort’命令的14个有用的范例(一)][1]
+
在我们继续深入之前,先创建一个文本文档‘month.txt’,并且将上一次给出的数据填进去。
$ echo -e "mar\ndec\noct\nsep\nfeb\naug" > month.txt
@@ -13,7 +12,7 @@ Linux 'sort'命令的七个有趣实例-第二部分

-### 15. 通过使用’M‘选项,对’month.txt‘文件按照月份顺序进行排序。###
+15、 通过使用’M‘选项,对’month.txt‘文件按照月份顺序进行排序。
$ sort -M month.txt
@@ -21,14 +20,14 @@ Linux 'sort'命令的七个有趣实例-第二部分

-### 16. 把数据整理成方便人们阅读的形式,比如1K、2M、3G、2T,这里面的K、G、M、T代表千、兆、吉、梯。
-(译者注:好像这个选项并不是所有Linu版本都有,而且也没有实现按KMGT显示。)
+16、 把数据整理成方便人们阅读的形式,比如1K、2M、3G、2T,这里面的K、G、M、T代表千、兆、吉、梯。
+(LCTT 译注:此处命令有误,ls 命令应该增加 -h 参数,径改之)
- $ ls -l /home/$USER | sort -h -k5
+ $ ls -lh /home/$USER | sort -h -k5

-### 17. 在上一篇文章中,我们在例子4中创建了一个名为‘sorted.txt’的文件,在例子6中创建了一个‘lsl.txt’。‘sorted.txt'已经排好序了而’lsl.txt‘还没有。让我们使用sort命令来检查两个文件是否已经排好序。###
+17、 在上一篇文章中,我们在例子4中创建了一个名为‘sorted.txt’的文件,在例子6中创建了一个‘lsl.txt’。‘sorted.txt'已经排好序了而’lsl.txt‘还没有。让我们使用sort命令来检查两个文件是否已经排好序。
$ sort -c sorted.txt
@@ -40,14 +39,14 @@ Linux 'sort'命令的七个有趣实例-第二部分

-Reports Disorder. Conflict..
报告无序。存在矛盾……
-### 18. 如果文字之间的分隔符是空格,sort命令自动地将横向空格后的东西当做一个新文字单元,如果分隔符不是空格呢?###
+18、 如果文字之间的分隔符是空格,sort命令自动地将空格后的东西当做一个新文字单元,如果分隔符不是空格呢?
考虑这样一个文本文件,里面的内容可以由除了空格之外的任何符号分隔,比如‘|’,‘\’,‘+’,‘.’等……
创建一个分隔符为+的文本文件。使用‘cat‘命令查看文件内容。
+
$ echo -e "21+linux+server+production\n11+debian+RedHat+CentOS\n131+Apache+Mysql+PHP\n7+Shell Scripting+python+perl\n111+postfix+exim+sendmail" > delimiter.txt
----------
@@ -66,9 +65,9 @@ Reports Disorder. Conflict..

-如果分隔符是Tab,你需要在’+‘的位置上用$’\t’代替,如上例所示。
+如果分隔符是制表符,你需要在’+‘的位置上用$’\t’代替,如上例所示。
-### 19. 对主用户目录下使用‘ls -l’命令得到的结果基于第五列——‘数据的大小’进行一个乱序排列。
+19、 对主用户目录下使用‘ls -l’命令得到的结果基于第五列(‘文件大小’)进行一个乱序排列。
$ ls -l /home/avi/ | sort -k5 -R
@@ -76,28 +75,30 @@ Reports Disorder. Conflict..
每一次你运行上面的脚本,你得到结果可能都不一样,因为结果是随机生成的。
- 正如我在上一篇文章中提到的规则2所说——相比于大写字母,sort命令更喜欢以小写字母开始的行。看一下上一篇文章的例3,字符串‘laptop’在‘LAPTOP’前出现。
+正如我在上一篇文章中提到的规则2所说——sort命令会将以小写字母开始的行排在大写字母开始的行前面。看一下上一篇文章的例3,字符串‘laptop’在‘LAPTOP’前出现。
-### 20. 如何覆盖默认的排序优先权?在这之前我们需要先将环境变量LC_ALL的值设置为C。在命令行提示栏中运行下面的代码。###
+20、 如何覆盖默认的排序优先权?在这之前我们需要先将环境变量LC_ALL的值设置为C。在命令行提示栏中运行下面的代码。
$ export LC_ALL=C
-然后以重写默认优先权的方式对‘tecmint.txt’文件重新排序。
+然后以非默认优先权的方式对‘tecmint.txt’文件重新排序。
$ sort tecmint.txt

-重写排序优先权
-不要忘记与example 3中得到的输出结果做比较,并且你可以使用‘-f’选项,又叫‘-ignore-case’来获取非常有序的输出。
+*覆盖排序优先权*
+
+不要忘记与example 3中得到的输出结果做比较,并且你可以使用‘-f’,又叫‘-ignore-case’(忽略大小写)的选项来获取更有序的输出。
$ sort -f tecmint.txt

-### 21. 给两个输入文件进行‘sort‘,然后一口气把它们连接起来怎么样?###
+21、 给两个输入文件进行‘sort‘,然后把它们连接成一行!
我们创建两个文本文档’file1.txt‘以及’file2.txt‘,并用数据填充,如下所示,并用’cat‘命令查看文件的内容。
+
$ echo -e “5 Reliable\n2 Fast\n3 Secure\n1 open-source\n4 customizable” > file1.txt
$ cat file1.txt
@@ -117,7 +118,7 @@ Reports Disorder. Conflict..

-我所要讲的全部内容就在这里了,希望与各位保持联系,也希望各位经常来Tecmint逛逛。有反馈就在下面评论吧。
+我所要讲的全部内容就在这里了,希望与各位保持联系,也希望各位经常来逛逛。有反馈就在下面评论吧。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -125,7 +126,7 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-sort-command-examples/
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
译者:[DongShuaike](https://github.com/DongShuaike)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/share/20150423 uperTuxKart 0.9 Released--The Best Racing Game on Linux Just Got Even Better.md b/published/201505/20150423 uperTuxKart 0.9 Released--The Best Racing Game on Linux Just Got Even Better.md
similarity index 84%
rename from translated/share/20150423 uperTuxKart 0.9 Released--The Best Racing Game on Linux Just Got Even Better.md
rename to published/201505/20150423 uperTuxKart 0.9 Released--The Best Racing Game on Linux Just Got Even Better.md
index 931f51ce92..70355325b6 100644
--- a/translated/share/20150423 uperTuxKart 0.9 Released--The Best Racing Game on Linux Just Got Even Better.md
+++ b/published/201505/20150423 uperTuxKart 0.9 Released--The Best Racing Game on Linux Just Got Even Better.md
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
-
-SuperTuxKart 0.9 已发行 —— Linux 中最好的竞速类游戏变得更好了
+SuperTuxKart 0.9 已发行 —— Linux 中最好的竞速类游戏越来越棒了!
================================================================================
**热门竞速类游戏 SuperTuxKart 的新版本已经[打包发行][1]登陆下载服务器**

-Super Tux Kart 0.9 发行海报
+
+*Super Tux Kart 0.9 发行海报*
SuperTuxKart 0.9 相较前一版本做了巨大的升级,内部运行着刚出炉的新引擎(有个炫酷的名字叫‘Antarctica(南极洲)’),目的是要呈现更加炫酷的图形环境,从阴影到场景的纵深,外加卡丁车更好的物理效果。
@@ -14,14 +14,11 @@ SuperTuxKart 0.9 相较前一版本做了巨大的升级,内部运行着刚出
SuperTuxKart 0.9 中与图像的改善同样吸引人眼球的是一对**全新赛道**,新的卡丁车,新的在线账户可以记录和分享**全新推出的成就系统**里赢得的徽章,以及大量的改装和涂装的微调。
-点击播放下面的官方发行视频,看看基于调色器的 STK 0.9 所散发的光辉吧。
-
-注:youtube 视频
-<iframe width="750" height="422" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/0FEwDH7XU9Q?feature=oembed"></iframe>
+点击播放下面的官方发行视频,看看基于调色器的 STK 0.9 所散发的光辉吧。(youtube 视频:https://www.youtube.com/0FEwDH7XU9Q )
Ubuntu 用户可以从项目网站上下载新发行版已编译的二进制文件。
-- [Download SuperTuxKart 0.9][2]
+- [下载 SuperTuxKart 0.9][2]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -29,7 +26,7 @@ via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/supertuxkart-0-9-released
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
译者:[H-mudcup](https://github.com/H-mudcup)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150429 Docker 1.6 Released--How to Upgrade on Fedora or CentOS.md b/published/201505/20150429 Docker 1.6 Released--How to Upgrade on Fedora or CentOS.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6b6141211f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150429 Docker 1.6 Released--How to Upgrade on Fedora or CentOS.md
@@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
+如何在Fedora / CentOS上面升级Docker 1.6
+=============================================================================
+Docker,一个流行的将软件打包的开源容器平台,已经有了新的1.6版,增加了许多新的特性。该版本主要更新了Docker Registry、Engine、 Swarm、 Compose 和 Machine等方面。这次发布旨在提升性能、改善开发者和系统管理员的体验。让我们来快速看看有哪些新特性吧。
+
+**Docker Registry (2.0)**是一项推送Docker镜像用于存储和分享的服务,因为面临加载下的体验问题而经历了架构的改变。它仍然向后兼容。Docker Registry的编写语言现在从Python改为Google的Go语言了,以提升性能。与Docker Engine 1.6结合后,拉取镜像的能力更快了。早先的镜像是队列式输送的,而现在是并行的啦。
+
+**Docker Engine (1.6)**相比之前的版本有很大的提高。目前支持容器与镜像的标签。通过标签,你可以附加用户自定义的元数据到镜像和容器上,而镜像和容器反过来可以被其他工具使用。标签对正在运行的应用是不可见的,可以用来加速搜索容器和镜像。
+
+Windows版本的Docker客户端可以连接到远程的运行在linux上的Docker Engine。
+
+Docker目前支持日志驱动API,这允许我们发送容器日志给系统如Syslog,或者第三方。这将会使得系统管理员受益。
+
+**Swarm (0.2)**是一个Docker集群工具,可以将一个Docker主机池转换为一个虚拟主机。在新特性里,容器甚至被放在了可用的节点上。通过添加更多的Docker命令,努力支持完整的Docker API。将来,使用第三方驱动来集群会成为可能。
+
+**Compose (1.2)** 是一个Docker里定义和运行复杂应用的工具, 也得到了升级。在新版本里,可以创建多个子文件,而不是用一个没有结构的文件描述一个多容器应用。
+
+通过**Machine (0.2)**,我们可以很容易地在本地计算机、云和数据中心上搭建Docker主机。新的发布版本为开发者提供了一个相对干净地驱动界面来编写驱动。Machine集中控制供给,而不是每个独立的驱动。增加了新的命令,可以用来生成主机的TLS证书,以提高安全性。
+
+### 在Fedora / CentOS 上的升级指导 ###
+
+在这一部分里,我们将会学习如何在Fedora和CentOS上升级已有的docker到最新版本。请注意,目前的Docker仅运行在64位的架构上,Fedora和CentOS都源于RedHat,命令的使用是差不多相同的,除了在Fedora20和CentOS6.5里Docker包被叫做“docker-io”。
+
+如果你系统之前没有安装Docker,使用下面命令安装:
+
+ "yum install docker-io" – on Fedora20 / CentOS6.5
+
+ "yum install docker" - on Fedora21 / CentOS7
+
+在升级之前,备份一下docker镜像和容器卷是个不错的主意。
+
+参考[“将文件系统打成 tar 包”][1]与[“卷备份、恢复或迁移”][2],获取更多信息。
+
+目前,测试系统安装了Docker1.5。样例输出显示是来自一个Fedora20的系统。
+
+验证当前系统安装的Docker版本
+
+ [root@TestNode1 ~]#sudo docker -v
+
+ Docker version 1.5.0, build a8a31ef/1.5.0
+
+如果Docker正在运行,先停掉。
+
+ [root@TestNode1 ~]# sudo systemctl stop docker
+
+使用yum update升级到最新版,但是写这篇文章的时候,仓库并不是最新版本(1.6),因此你需要使用二进制的升级方法。
+
+ [root@TestNode1 ~]#sudo yum -y update docker-io
+
+ No packages marked for update
+
+ [root@TestNode1 ~]#sudo wget https://get.docker.com/builds/Linux/x86_64/docker-latest -O /usr/bin/docker
+
+ --2015-04-19 13:40:48-- https://get.docker.com/builds/Linux/x86_64/docker-latest
+
+ Resolving get.docker.com (get.docker.com)... 162.242.195.82
+
+ Connecting to get.docker.com (get.docker.com)|162.242.195.82|:443... connected.
+
+ HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
+
+ Length: 15443598 (15M) [binary/octet-stream]
+
+ Saving to: /usr/bin/docker
+
+ 100%[======================================>] 15,443,598 8.72MB/s in 1.7s
+
+ 2015-04-19 13:40:50 (8.72 MB/s) - /usr/bin/docker saved
+
+检查更新后的版本
+
+ [root@TestNode1 ~]#sudo docker -v
+
+ Docker version 1.6.0, build 4749651
+
+重启docker服务
+
+ [root@TestNode1 ~]# sudo systemctl start docker
+
+确认Docker在运行
+
+ [root@TestNode1 ~]# docker images
+
+ REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED VIRTUAL SIZE
+
+ fedora latest 834629358fe2 3 months ago 241.3 MB
+
+ [root@TestNode1 ~]# docker run fedora /bin/echo Hello World
+
+ Hello World
+
+CentOS安装时需要**注意**,在CentOS上安装完Docker后,当你试图启动Docker服务的时候,你可能会得到错误的信息,如下所示:
+
+ docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine
+
+ Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; disabled)
+
+ Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since Mon 2015-04-20 03:24:24 EDT; 6h ago
+
+ Docs: http://docs.docker.com
+
+ Process: 21069 ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker -d $OPTIONS $DOCKER_STORAGE_OPTIONS $DOCKER_NETWORK_OPTIONS $ADD_REGISTRY $BLOCK_REGISTRY $INSECURE_REGISTRY (code=exited, status=127)
+
+ Main PID: 21069 (code=exited, status=127)
+
+ Apr 20 03:24:24 centos7 systemd[1]: Starting Docker Application Container E.....
+
+ Apr 20 03:24:24 centos7 docker[21069]: time="2015-04-20T03:24:24-04:00" lev...)"
+
+ Apr 20 03:24:24 centos7 docker[21069]: time="2015-04-20T03:24:24-04:00" lev...)"
+
+ Apr 20 03:24:24 centos7 docker[21069]: /usr/bin/docker: relocation error: /...ce
+
+ Apr 20 03:24:24 centos7 systemd[1]: docker.service: main process exited, co.../a
+
+ Apr 20 03:24:24 centos7 systemd[1]: Failed to start Docker Application Cont...e.
+
+ Apr 20 03:24:24 centos7 systemd[1]: Unit docker.service entered failed state.
+
+这是一个已知的bug([https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1207839][3]),需要将设备映射升级到最新。
+
+ [root@centos7 ~]# rpm -qa device-mapper
+
+ device-mapper-1.02.84-14.el7.x86_64
+
+ [root@centos7 ~]# yum update device-mapper
+
+ [root@centos7 ~]# rpm -qa device-mapper
+
+ device-mapper-1.02.93-3.el7.x86_64
+
+ [root@centos7 ~]# systemctl start docker
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+尽管docker技术出现时间不长,但很快就变得非常流行了。它使得开发者的生活变得轻松,运维团队可以快速独立地创建和部署应用。通过该公司的发布,Docker的快速更新,产品质量的提升,满足用户需求,未来对于Docker来说一片光明。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/docker-1-6-features-upgrade-fedora-centos/
+
+作者:[B N Poornima][a]
+译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/bnpoornima/
+[1]:http://docs.docker.com/reference/commandline/cli/#export
+[2]:http://docs.docker.com/userguide/dockervolumes/#backup-restore-or-migrate-data-volumes
+[3]:https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1207839
+[4]:
+[5]:
+[6]:
+[7]:
+[8]:
+[9]:
+[10]:
+[11]:
+[12]:
+[13]:
+[14]:
+[15]:
+[16]:
+[17]:
+[18]:
+[19]:
+[20]:
diff --git a/published/201505/20150429 Synfig Studio 1.0--Open Source Animation Gets Serious.md b/published/201505/20150429 Synfig Studio 1.0--Open Source Animation Gets Serious.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a216674d9b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150429 Synfig Studio 1.0--Open Source Animation Gets Serious.md
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+Synfig Studio 1.0:开源动画动真格的了
+================================================================================
+
+
+**现在可以下载 Synfig Studio 这个自由、开源的2D动画软件的全新版本了。 **
+
+在这个跨平台的软件首次发行一年之后,Synfig Studio 1.0 带着一套全新改进过的功能,实现它所承诺的“创造电影级的动画的工业级解决方案”。
+
+在众多功能之上的是一个改进过的用户界面,据项目开发者说那是个用起来‘更简单’、‘更直观’的界面。客户端添加了新的**单窗口模式**,让界面更整洁,而且**使用了最新的 GTK3 库重制**。
+
+在功能方面有几个值得注意的变化,包括新加的全功能骨骼系统。
+
+这套**关节和转轴的‘骨骼’构架**非常适合2D剪纸动画,再配上这个版本新加的复杂的变形控制系统或是 Synfig 受欢迎的‘关键帧自动插入’(即:帧到帧之间的变形)应该会变得非常有效率的。(youtube视频 https://www.youtube.com/M8zW1qCq8ng )
+
+新的无损剪切工具,摩擦力效果和对逐帧位图动画的支持,可能会有助于释放开源动画师们的创造力,更别说新加的用于同步动画的时间线和声音的声效层!
+
+### 下载 Synfig Studio 1.0 ###
+
+Synfig Studio 并不是任何人都能用的工具套件,这最新发行版的最新一批改进应该能吸引一些动画制作者试一试这个软件。
+
+如果你想看看开源动画制作软件是什么样的,你可以通过下面的链接直接从工程的 Sourceforge 页下载一个适用于 Ubuntu 的最新版本的安装器。
+
+- [下载 Synfig 1.0 (64bit) .deb 安装器][1]
+- [下载 Synfig 1.0 (32bit) .deb 安装器][2]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/synfig-studio-new-release-features
+
+作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
+译者:[H-mudcup](https://github.com/H-mudcup)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
+[1]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/synfig/files/releases/1.0/linux/synfigstudio_1.0_amd64.deb/download
+[2]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/synfig/files/releases/1.0/linux/synfigstudio_1.0_x86.deb/download
diff --git a/published/201505/20150429 web caching basics terminology http headers and caching strategies.md b/published/201505/20150429 web caching basics terminology http headers and caching strategies.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..52e4e4e01f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150429 web caching basics terminology http headers and caching strategies.md
@@ -0,0 +1,181 @@
+Web缓存基础:术语、HTTP报头和缓存策略
+=====================================================================
+
+### 简介
+
+对于您的站点的访问者来说,智能化的内容缓存是提高用户体验最有效的方式之一。缓存,或者对之前的请求的临时存储,是HTTP协议实现中最核心的内容分发策略之一。分发路径中的组件均可以缓存内容来加速后续的请求,这受控于对该内容所声明的缓存策略。
+
+在这份指南中,我们将讨论一些Web内容缓存的基本概念。这主要包括如何选择缓存策略以保证互联网范围内的缓存能够正确的处理您的内容。我们将谈一谈缓存带来的好处、副作用以及不同的策略能带来的性能和灵活性的最大结合。
+
+###什么是缓存(caching)?
+
+缓存(caching)是一个描述存储可重用资源以便加快后续请求的行为的术语。有许多不同类型的缓存,每种都有其自身的特点,应用程序缓存和内存缓存由于其对特定回复的加速,都很常用。
+
+这份指南的主要讲述的Web缓存是一种不同类型的缓存。Web缓存是HTTP协议的一个核心特性,它能最小化网络流量,并且提升用户所感知的整个系统响应速度。内容从服务器到浏览器的传输过程中,每个层面都可以找到缓存的身影。
+
+Web缓存根据特定的规则缓存相应HTTP请求的响应。对于缓存内容的后续请求便可以直接由缓存满足而不是重新发送请求到Web服务器。
+
+###好处
+
+有效的缓存技术不仅可以帮助用户,还可以帮助内容的提供者。缓存对内容分发带来的好处有:
+
+- **减少网络开销**:内容可以在从内容提供者到内容消费者网络路径之间的许多不同的地方被缓存。当内容在距离内容消费者更近的地方被缓存时,由于缓存的存在,请求将不会消耗额外的网络资源。
+- **加快响应速度**:由于并不是必须通过整个网络往返,缓存可以使内容的获得变得更快。缓存放在距用户更近的地方,例如浏览器缓存,使得内容的获取几乎是瞬时的。
+- **在同样的硬件上提高速度**:对于保存原始内容的服务器来说,更多的性能可以通过允许激进的缓存策略从硬件上压榨出来。内容拥有者们可以利用分发路径上某个强大的服务器来应对特定内容负载的冲击。
+- **网络中断时内容依旧可用**:使用某种策略,缓存可以保证在原始服务器变得不可用时,相应的内容对用户依旧可用。
+
+###术语
+
+在面对缓存时,您可能对一些经常遇到的术语可能不太熟悉。一些常见的术语如下:
+
+- **原始服务器**:原始服务器是内容的原始存放地点。如果您是Web服务器管理员,它就是您所管理的机器。它负责为任何不能从缓存中得到的内容进行回复,并且负责设置所有内容的缓存策略。
+- **缓存命中率**:一个缓存的有效性依照缓存的命中率进行度量。它是可以从缓存中得到数据的请求数与所有请求数的比率。缓存命中率高意味着有很高比例的数据可以从缓存中获得。这通常是大多数管理员想要的结果。
+- **新鲜度**:新鲜度用来描述一个缓存中的项目是否依旧适合返回给客户端。缓存中的内容只有在由缓存策略指定的新鲜期内才会被返回。
+- **过期内容**:缓存中根据缓存策略的新鲜期设置已过期的内容。过期的内容被标记为“陈旧”。通常,过期内容不能用于回复客户端的请求。必须重新从原始服务器请求新的内容或者至少验证缓存的内容是否仍然准确。
+- **校验**:缓存中的过期内容可以验证是否有效以便刷新过期时间。验证过程包括联系原始服务器以检查缓存的数据是否依旧代表了最近的版本。
+- **失效**:失效是依据过期日期从缓存中移除内容的过程。当内容在原始服务器上已被改变时就必须这样做,缓存中过期的内容会导致客户端发生问题。
+
+还有许多其他的缓存术语,不过上面的这些应该能帮助您开始。
+
+###什么能被缓存?
+
+某些特定的内容比其他内容更容易被缓存。对大多数站点来说,一些适合缓存的内容如下:
+
+- Logo和商标图像
+- 普通的不变化的图像(例如,导航图标)
+- CSS样式表
+- 普通的Javascript文件
+- 可下载的内容
+- 媒体文件
+
+这些文件更倾向于不经常改变,所以长时间的对它们进行缓存能获得好处。
+
+一些项目在缓存中必须加以注意:
+
+- HTML页面
+- 会替换改变的图像
+- 经常修改的Javascript和CSS文件
+- 需要有认证后的cookies才能访问的内容
+
+一些内容从来不应该被缓存:
+
+- 与敏感信息相关的资源(银行数据,等)
+- 用户相关且经常更改的数据
+
+除上面的通用规则外,通常您需要指定一些规则以便于更好地缓存不同种类的内容。例如,如果登录的用户都看到的是同样的网站视图,就应该在任何地方缓存这个页面。如果登录的用户会在一段时间内看到站点中用户特定的视图,您应该让用户的浏览器缓存该数据而不应让任何中介节点缓存该视图。
+
+###Web内容缓存的位置
+
+Web内容会在整个分发路径中的许多不同的位置被缓存:
+
+- **浏览器缓存**:Web浏览器自身会维护一个小型缓存。典型地,浏览器使用一种策略指示缓存最重要的内容。这可能是用户相关的内容或可能会再次请求且下载代价较高。
+- **中间缓存代理**:任何在客户端和您的基础架构之间的服务器都可以按期望缓存一些内容。这些缓存可能由ISP(网络服务提供者)或者其他独立组织提供。
+- **反向缓存**:您的服务器基础架构可以为后端的服务实现自己的缓存。如果实现了缓存,那么便可以在处理请求的位置返回相应的内容而不用每次请求都使用后端服务。
+
+上面的这些位置通常都可以根据它们自身的缓存策略和内容源的缓存策略缓存一些相应的内容。
+
+###缓存头部
+
+缓存策略依赖于两个不同的因素。所缓存的实体本身需要决定是否应该缓存可接受的内容。它可以只缓存部分可以缓存的内容,但不能缓存超过限制的内容。
+
+缓存行为主要由缓存策略决定,而缓存策略由内容拥有者设置。这些策略主要通过特定的HTTP头部来清晰地表达。
+
+经过几个不同HTTP协议的变化,出现了一些不同的针对缓存方面的头部,它们的复杂度各不相同。下面列出了那些你也许应该注意的:
+
+- **`Expires`**:尽管使用范围相当有限,但`Expires`头部是非常简洁明了的。通常它设置一个未来的时间,内容会在此时间过期。这时,任何对同样内容的请求都应该回到原始服务器处。这个头部或许仅仅最适合回退模式(fall back)。
+- **`Cache-Control`**:这是`Expires`的一个更加现代化的替换物。它已被很好的支持,且拥有更加灵活的实现。在大多数案例中,它比`Expires`更好,但同时设置两者的值也无妨。稍后我们将讨论您可以设置的`Cache-Control`的详细选项。
+- **`ETag`**:`ETag`用于缓存验证。源服务器可以在首次服务一个内容时为该内容提供一个独特的`ETag`。当一个缓存需要验证这个内容是否即将过期,他会将相应的`ETag`发送回服务器。源服务器或者告诉缓存内容是一致的,或者发送更新后的内容(带着新的`ETag`)。
+- **`Last-Modified`**:这个头部指明了相应的内容最后一次被修改的时间。它可能会作为保证内容新鲜度的验证策略的一部分被使用。
+- **`Content-Length`**:尽管并没有在缓存中明确涉及,`Content-Length`头部在设置缓存策略时很重要。某些软件如果不提前获知内容的大小以留出足够空间,则会拒绝缓存该内容。
+- **`Vary`**:缓存系统通常使用请求的主机和路径作为存储该资源的键。当判断一个请求是否是请求同样内容时,`Vary`头部可以被用来提醒缓存系统需要注意另一个附加头部。它通常被用来告诉缓存系统同样注意`Accept-Encoding`头部,以便缓存系统能够区分压缩和未压缩的内容。
+
+### Vary头部的隐语
+
+`Vary`头部提供给您存储同一个内容的不同版本的能力,代价是降低了缓存的容量。
+
+在使用`Accept-Encoding`时,设置`Vary`头部允许明确区分压缩和未压缩的内容。这在服务某些不能处理压缩数据的浏览器时很重要,它可以保证基本的可用性。`Vary`的一个典型的值是`Accept-Encoding`,它只有两到三个可选的值。
+
+一开始看上去`User-Agent`这样的头部可以用于区分移动浏览器和桌面浏览器,以便您的站点提供差异化的服务。但`User-Agent`字符串是非标准的,结果将会造成在中间缓存中保存同一内容的许多不同版本的缓存,这会导致缓存命中率的降低。`Vary`头部应该谨慎使用,尤其是您不具备在您控制的中间缓存中使请求标准化的能力(也许可以,比如您可以控制CDN的话)。
+
+###缓存控制标志怎样影响缓存
+
+上面我们提到了`Cache-Control`头部如何被用与现代缓存策略标准。能够通过这个头部设定许多不同的缓存指令,多个不同的指令通过逗号分隔。
+
+一些您可以使用的指示内容缓存策略的`Cache-Control`的选项如下:
+
+- **`no-cache`**:这个指令指示所有缓存的内容在新的请求到达时必须先重新验证,再发送给客户端。这条指令实际将内容立刻标记为过期的,但允许通过验证手段重新验证以避免重新下载整个内容。
+- **`no-store`**:这条指令指示缓存的内容不能以任何方式被缓存。它适合在回复敏感信息时设置。
+- **`public`**:它将内容标记为公有的,这意味着它能被浏览器和其他任何中间节点缓存。通常,对于使用了HTTP验证的请求,其回复被默认标记为`private`。`public`标记将会覆盖这个设置。
+- **`private`**:它将内容标记为私有的。私有数据可以被用户的浏览器缓存,但*不能*被任何中间节点缓存。它通常用于用户相关的数据。
+- **`max-age`**:这个设置指示了缓存内容的最大生存期,它在最大生存期后必须在源服务器处被验证或被重新下载。在现代浏览器中这个选项大体上取代了`Expires`头部,浏览器也将其作为决定内容的新鲜度的基础。这个选项的值以秒为单位表示,最大可以表示一年的新鲜期(31536000秒)。
+- **`s-maxage`**:这个选项非常类似于`max-age`,它指明了内容能够被缓存的时间。区别是这个选项只在中间节点的缓存中有效。结合这两个选项可以构建更加灵活的缓存策略。
+- **`must-revalidate`**:它指明了由`max-age`、`s-maxage`或`Expires`头部指明的新鲜度信息必须被严格的遵守。它避免了缓存的数据在网络中断等类似的场景中被使用。
+- **`proxy-revalidate`**:它和上面的选项有着一样的作用,但只应用于中间的代理节点。在这种情况下,用户的浏览器可以在网络中断时使用过期内容,但中间缓存内容不能用于此目的。
+- **`no-transform`**:这个选项告诉缓存在任何情况下都不能因为性能的原因修改接收到的内容。这意味着,缓存不允许压缩接收到的内容(没有从原始服务器处接收过压缩版本的该内容)并发送。
+
+这些选项能够以不同的方式结合以获得不同的缓存行为。一些互斥的值如下:
+
+- `no-cache`,`no-store`以及由其他前面未提到的选项指明的常用的缓存行为
+- `public`和`private`
+
+如果`no-store`和`no-cache`都被设置,那么`no-store`会取代`no-cache`。对于非授权的请求的回复,`public`是隐含的设置。对于授权的请求的回复,`private`选项是隐含的。他们可以通过在`Cache-Control`头部中指明相应的相反的选项以覆盖。
+
+###开发一种缓存策略
+
+在理想情况下,任何内容都可以被尽可能缓存,而您的服务器只需要偶尔的提供一些验证内容即可。但这在现实中很少发生,因此您应该尝试设置一些明智的缓存策略,以在长期缓存和站点改变的需求间达到平衡。
+
+### 常见问题
+
+在许多情况中,由于内容被产生的方式(如根据每个用户动态的产生)或者内容的特性(例如银行的敏感数据),这些内容不应该被缓存。另一些许多管理员在设置缓存时可能面对的问题是外部缓存的数据未过期,但新版本的数据已经产生。
+
+这些都是经常遇到的问题,它们会影响缓存的性能和您提供的数据的准确性。然而,我们可以通过开发提前预见这些问题的缓存策略来缓解这些问题。
+
+### 一般性建议
+
+尽管您的实际情况会指导您选择的缓存策略,但是下面的建议能帮助您获得一些合理的决定。
+
+在您担心使用哪一个特定的头部之前,有一些特定的步骤可以帮助您提高您的缓存命中率。一些建议如下:
+
+- **为图像、CSS和共享的内容建立特定的文件夹**:将内容放到特定的文件夹内使得您可以方便的从您的站点中的任何页面引用这些内容。
+- **使用同样的URL来表示同样的内容**:由于缓存使用内容请求中的主机名和路径作为键,因此应保证您的所有页面中的该内容的引用方式相同,前一个建议能让这点更加容易做到。
+- **尽可能使用CSS图像拼接**:对于像图标和导航等内容,使用CSS图像拼接能够减少渲染您页面所需要的请求往返,并且允许对拼接缓存很长一段时间。
+- **尽可能将主机脚本和外部资源本地化**:如果您使用Javascript脚本和其他外部资源,如果上游没有提供合适的缓存头部,那么您应考虑将这些内容放在您自己的服务器上。您应该注意上游的任何更新,以便更新本地的拷贝。
+- **对缓存内容收集文件摘要**:静态的内容比如CSS和Javascript文件等通常比较适合收集文件摘要。这意味着为文件名增加一个独特的标志符(通常是这个文件的哈希值)可以在文件修改后绕开缓存保证新的内容被重新获取。有很多工具可以帮助您创建文件摘要并且修改HTML文档中的引用。
+
+对于不同的文件正确地选择不同的头部这件事,下面的内容可以作为一般性的参考:
+
+- **允许所有的缓存存储一般内容**:静态内容以及非用户相关的内容应该在分发链的所有节点被缓存。这使得中间节点可以将该内容回复给多个用户。
+- **允许浏览器缓存用户相关的内容**:对于每个用户的数据,通常在用户自己的浏览器中缓存是可以被接受且有益的。缓存在用户自身的浏览器能够使得用户在接下来的浏览中能够瞬时读取,但这些内容不适合在任何中间代理节点缓存。
+- **将时间敏感的内容作为特例**:如果您的数据是时间敏感的,那么相对上面两条参考,应该将这些数据作为特例,以保证过期的数据不会在关键的情况下被使用。例如,您的站点有一个购物车,它应该立刻反应购物车里面的物品。依据内容的特点,可以在`Cache-Control`头部中使用`no-cache`或`no-store`选项。
+- **总是提供验证器**:验证器使得过期的内容可以无需重新下载而得到刷新。设置`ETag`和`Last-Modified`头部将允许缓存向原始服务器验证内容,并在内容未修改时刷新该内容新鲜度以减少负载。
+- **对于支持的内容设置长的新鲜期**:为了更加有效的利用缓存,一些作为支持性的内容应该被设置较长的新鲜期。这通常比较适合图像和CSS等由用户请求用来渲染HTML页面的内容。和文件摘要一起,设置延长的新鲜期将允许缓存长时间的存储这些资源。如果资源发生改变,修改的文件摘要将会使缓存的数据无效并触发对新的内容的下载。那时,新的支持的内容会继续被缓存。
+- **对父内容设置短的新鲜期**:为了使得前面的模式正常工作,容器类的内容应该相应的设置短的新鲜期,或者设置不全部缓存。这通常是在其他协助内容中使用的HTML页面。这个HTML页面将会被频繁的下载,使得它能快速的响应改变。支持性的内容因此可以被尽量缓存。
+
+关键之处便在于达到平衡,一方面可以尽量的进行缓存,另一方面为未来保留当改变发生时从而改变整个内容的机会。您的站点应该同时具有:
+
+- 尽量缓存的内容
+- 拥有短的新鲜期的缓存内容,可以被重新验证
+- 完全不被缓存的内容
+
+这样做的目的便是将内容尽可能的移动到第一个分类(尽量缓存)中的同时,维持可以接受的缓存命中率。
+
+结论
+----
+
+花时间确保您的站点使用了合适的缓存策略将对您的站点产生重要的影响。缓存使得您可以在保证服务同样内容的同时减少带宽的使用。您的服务器因此可以靠同样的硬件处理更多的流量。或许更重要的是,客户们能在您的网站中获得更快的体验,这会使得他们更愿意频繁的访问您的站点。尽管有效的Web缓存并不是银弹,但设置合适的缓存策略会使您以最小的代价获得可观的收获。
+
+---
+
+via: https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/web-caching-basics-terminology-http-headers-and-caching-strategies
+
+作者: [Justin Ellingwood](https://www.digitalocean.com/community/users/jellingwood)
+译者:[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+推荐:[royaso](https://github.com/royaso)
+
+
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+
+
diff --git a/published/201505/20150504 How To Install Visual Studio Code On Ubuntu.md b/published/201505/20150504 How To Install Visual Studio Code On Ubuntu.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b3bb071dc5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150504 How To Install Visual Studio Code On Ubuntu.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+在Ubuntu中安装Visual Studio Code
+================================================================================
+
+
+微软令人意外地[发布了Visual Studio Code][1],并支持主要的桌面平台,当然包括linux。如果你是一名需要在ubuntu工作的web开发人员,你可以**非常轻松的安装Visual Studio Code**。
+
+我将要使用[Ubuntu Make][2]来安装Visual Studio Code。Ubuntu Make,就是以前的Ubuntu开发者工具中心,是一个命令行工具,帮助用户快速安装各种开发工具、语言和IDE。也可以使用Ubuntu Make轻松[安装Android Studio][3] 和其他IDE,如Eclipse。本文将展示**如何在Ubuntu中使用Ubuntu Make安装Visual Studio Code**。(译注:也可以直接去微软官网下载安装包)
+
+### 安装微软Visual Studio Code ###
+
+开始之前,首先需要安装Ubuntu Make。虽然Ubuntu Make存在Ubuntu15.04官方库中,**但是需要Ubuntu Make 0.7以上版本才能安装Visual Studio**。所以,需要通过官方PPA更新到最新的Ubuntu Make。此PPA支持Ubuntu 14.04, 14.10 和 15.04。
+
+注意,**仅支持64位版本**。
+
+打开终端,使用下列命令,通过官方PPA来安装Ubuntu Make:
+
+ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ubuntu-desktop/ubuntu-make
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install ubuntu-make
+
+安装Ubuntu Make完后,接着使用下列命令安装Visual Studio Code:
+
+ umake web visual-studio-code
+
+安装过程中,将会询问安装路径,如下图:
+
+
+
+在抛出一堆要求和条件后,它会询问你是否确认安装Visual Studio Code。输入‘a’来确定:
+
+
+
+确定之后,安装程序会开始下载并安装。安装完成后,你可以发现Visual Studio Code 图标已经出现在了Unity启动器上。点击图标开始运行!下图是Ubuntu 15.04 Unity的截图:
+
+
+
+### 卸载Visual Studio Code###
+
+卸载Visual Studio Code,同样使用Ubuntu Make命令。如下:
+
+ umake web visual-studio-code --remove
+
+如果你不打算使用Ubuntu Make,也可以通过微软官方下载安装文件。
+
+- [下载Visual Studio Code Linux版][4]
+
+怎样!是不是超级简单就可以安装Visual Studio Code,这都归功于Ubuntu Make。我希望这篇文章能帮助到你。如果您有任何问题或建议,欢迎给我留言。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://itsfoss.com/install-visual-studio-code-ubuntu/
+
+作者:[Abhishek][a]
+译者:[Vic020/VicYu](http://vicyu.net)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
+[1]:https://linux.cn/article-5376-1.html
+[2]:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-make
+[3]:http://itsfoss.com/install-android-studio-ubuntu-linux/
+[4]:https://code.visualstudio.com/Download
diff --git a/published/201505/20150505 Bodhi Linux Introduces Moksha Desktop.md b/published/201505/20150505 Bodhi Linux Introduces Moksha Desktop.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dcb724e7b1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150505 Bodhi Linux Introduces Moksha Desktop.md
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+Bodhi Linux 将引入 Moksha 桌面
+================================================================================
+
+
+基于Ubuntu的轻量级Linux发行版[Bodhi Linux][1]致力于构建其自家的桌面环境,这个全新桌面环境被称之为Moksha(梵文意为‘完全自由’)。Moksha将替换其原来的[Enlightenment桌面环境][2]。
+
+### 为何用Moksha替换Englightenment? ###
+
+Bodhi Linux的Jeff Hoogland最近[表示][3]了他对新版Enlightenment的不满。直到E17,Enlightenment都十分稳定,并且能满足轻量级Linux的部署需求。而E18则到处都充满了问题,Bodhi Linux只好弃之不用了。
+
+虽然最新的[Bodhi Linux 3.0发行版][4]仍然使用了E19作为其桌面(除传统模式外,这意味着,对于旧的硬件,仍然会使用E17),Jeff对E19也十分不满。他说道:
+
+> 除了性能问题外,对于我个人而言,E19并没有给我带来与E17下相同的工作流程,因为它移除了很多E17的特性。鉴于此,我不得不将我所有的3台Bodhi计算机桌面改成E17——这3台机器都是我高端的了。这不由得让我想到,我们还有多少现存的Bodhi用户也怀着和我同样的感受,所以,我[在我们的用户论坛上开启一个与此相关的讨论][5]。
+
+### Moksha是E17桌面的延续 ###
+
+Moksha将会是Bodhi所热衷的E17桌面的延续。Jeff进一步提到:
+
+> 我们将从整合所有Bodhi修改开始。多年来我们一直都只是给源代码打补丁,并修复桌面所带有的问题。如果该工作完成,我们将开始移植一些E18和E19引入的更为有用的特性,最后,我们将引入一些我们认为会改善最终用户体验的东西。
+
+### Moksha何时发布? ###
+
+下一个Bodhi更新将会是Bodhi 3.1.0,就在今年八月。这个新版本将为所有其默认安装镜像带来Moksha。让我们拭目以待,看看Moksha是否是一个好的决定。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://itsfoss.com/bodhi-linux-introduces-moksha-desktop/
+
+作者:[Abhishek][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
+[1]:http://www.bodhilinux.com/
+[2]:https://www.enlightenment.org/
+[3]:http://www.bodhilinux.com/2015/04/28/introducing-the-moksha-desktop/
+[4]:http://itsfoss.com/bodhi-linux-3/
+[5]:http://forums.bodhilinux.com/index.php?/topic/12322-e17-vs-e19-which-are-you-using-and-why/
diff --git a/published/201505/20150506 How to Securely Store Passwords and Api Keys Using Vault.md b/published/201505/20150506 How to Securely Store Passwords and Api Keys Using Vault.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e2073d0b18
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150506 How to Securely Store Passwords and Api Keys Using Vault.md
@@ -0,0 +1,164 @@
+如何使用Vault安全的存储密码和API密钥
+=======================================================================
+Vault是用来安全的获取秘密信息的工具,它可以保存密码、API密钥、证书等信息。Vault提供了一个统一的接口来访问秘密信息,其具有健壮的访问控制机制和丰富的事件日志。
+
+对关键信息的授权访问是一个困难的问题,尤其是当有许多用户角色,并且用户请求不同的关键信息时,例如用不同权限登录数据库的登录配置,用于外部服务的API密钥,SOA通信的证书等。当保密信息由不同的平台进行管理,并使用一些自定义的配置时,情况变得更糟,因此,安全的存储、管理审计日志几乎是不可能的。但Vault为这种复杂情况提供了一个解决方案。
+
+### 突出特点 ###
+
+**数据加密**:Vault能够在不存储数据的情况下对数据进行加密、解密。开发者们便可以存储加密后的数据而无需开发自己的加密技术,Vault还允许安全团队自定义安全参数。
+
+**安全密码存储**:Vault在将秘密信息(API密钥、密码、证书)存储到持久化存储之前对数据进行加密。因此,如果有人偶尔拿到了存储的数据,这也没有任何意义,除非加密后的信息能被解密。
+
+**动态密码**:Vault可以随时为AWS、SQL数据库等类似的系统产生密码。比如,如果应用需要访问AWS S3 桶,它向Vault请求AWS密钥对,Vault将给出带有租期的所需秘密信息。一旦租用期过期,这个秘密信息就不再存储。
+
+**租赁和更新**:Vault给出的秘密信息带有租期,一旦租用期过期,它便立刻收回秘密信息,如果应用仍需要该秘密信息,则可以通过API更新租用期。
+
+**撤销**:在租用期到期之前,Vault可以撤销一个秘密信息或者一个秘密信息树。
+
+### 安装Vault ###
+
+有两种方式来安装使用Vault。
+
+**1. 预编译的Vault二进制** 能用于所有的Linux发行版,下载地址如下,下载之后,解压并将它放在系统PATH路径下,以方便调用。
+
+- [下载预编译的二进制 Vault (32-bit)][1]
+- [下载预编译的二进制 Vault (64-bit)][2]
+- [下载预编译的二进制 Vault (ARM)][3]
+
+
+
+*下载相应的预编译的Vault二进制版本。*
+
+
+
+*解压下载到本地的二进制版本。*
+
+祝贺你!您现在可以使用Vault了。
+
+
+
+**2. 从源代码编译**是另一种在系统中安装Vault的方式。在安装Vault之前需要安装GO和GIT。
+
+在 **Redhat系统中安装GO** 使用下面的指令:
+
+ sudo yum install go
+
+在 **Debin系统中安装GO** 使用下面的指令:
+
+ sudo apt-get install golang
+
+或者
+
+ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gophers/go
+
+ sudo apt-get update
+
+ sudo apt-get install golang-stable
+
+在 **Redhat系统中安装GIT** 使用下面的命令:
+
+ sudo yum install git
+
+在 **Debian系统中安装GIT** 使用下面的命令:
+
+ sudo apt-get install git
+
+一旦GO和GIT都已被安装好,我们便可以开始从源码编译安装Vault。
+
+> 将下列的Vault仓库拷贝至GOPATH
+
+ https://github.com/hashicorp/vault
+
+> 测试下面的文件是否存在,如果它不存在,那么Vault没有被克隆到合适的路径。
+
+ $GOPATH/src/github.com/hashicorp/vault/main.go
+
+> 执行下面的指令来编译Vault,并将二进制文件放到系统bin目录下。
+
+ make dev
+
+
+
+### 一份Vault入门教程 ###
+
+我们已经编制了一份Vault的官方交互式教程,并带有它在SSH上的输出信息。
+
+**概述**
+
+这份教程包括下列步骤:
+
+- 初始化并启封您的Vault
+- 在Vault中对您的请求授权
+- 读写秘密信息
+- 密封您的Vault
+
+#### **初始化您的Vault**
+
+首先,我们需要为您初始化一个Vault的工作实例。在初始化过程中,您可以配置Vault的密封行为。简单起见,现在使用一个启封密钥来初始化Vault,命令如下:
+
+ vault init -key-shares=1 -key-threshold=1
+
+您会注意到Vault在这里输出了几个密钥。不要清除您的终端,这些密钥在后面的步骤中会使用到。
+
+
+
+#### **启封您的Vault**
+
+当一个Vault服务器启动时,它是密封的状态。在这种状态下,Vault被配置为知道物理存储在哪里及如何存取它,但不知道如何对其进行解密。Vault使用加密密钥来加密数据。这个密钥由"主密钥"加密,主密钥不保存。解密主密钥需要入口密钥。在这个例子中,我们使用了一个入口密钥来解密这个主密钥。
+
+ vault unseal <key 1>
+
+
+
+####**为您的请求授权**
+
+在执行任何操作之前,连接的客户端必须是被授权的。授权的过程是检验一个人或者机器是否如其所申明的那样具有正确的身份。这个身份用在向Vault发送请求时。为简单起见,我们将使用在步骤2中生成的root令牌,这个信息可以回滚终端屏幕看到。使用一个客户端令牌进行授权:
+
+ vault auth <root token>
+
+
+
+####**读写保密信息**
+
+现在Vault已经被设置妥当,我们可以开始读写默认挂载的秘密后端里面的秘密信息了。写在Vault中的秘密信息首先被加密,然后被写入后端存储中。后端存储机制绝不会看到未加密的信息,并且也没有在Vault之外解密的需要。
+
+ vault write secret/hello value=world
+
+当然,您接下来便可以读这个保密信息了:
+
+ vault read secret/hello
+
+
+
+####**密封您的Vault**
+
+还有一个用I来密封Vault的API。它将丢掉现在的加密密钥并需要另一个启封过程来恢复它。密封仅需要一个拥有root权限的操作者。这是一种罕见的"打破玻璃过程"的典型部分。
+
+这种方式中,如果检测到一个入侵,Vault数据将会立刻被锁住,以便最小化损失。如果不能访问到主密钥碎片的话,就不能再次获取数据。
+
+ vault seal
+
+
+
+这便是入门教程的结尾。
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+Vault是一个非常有用的应用,它提供了一个可靠且安全的存储关键信息的方式。另外,它在存储前加密关键信息、审计日志维护、以租期的方式获取秘密信息,且一旦租用期过期它将立刻收回秘密信息。Vault是平台无关的,并且可以免费下载和安装。要发掘Vault的更多信息,请访问其[官方网站][4]。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/how-tos/secure-secret-store-vault/
+
+作者:[Aun Raza][a]
+译者:[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunrz/
+[1]:https://dl.bintray.com/mitchellh/vault/vault_0.1.0_linux_386.zip
+[2]:https://dl.bintray.com/mitchellh/vault/vault_0.1.0_linux_amd64.zip
+[3]:https://dl.bintray.com/mitchellh/vault/vault_0.1.0_linux_arm.zip
+[4]:https://vaultproject.io/
diff --git a/published/201505/20150506 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure a Linux bridge with Network Manager on Ubuntu.md b/published/201505/20150506 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure a Linux bridge with Network Manager on Ubuntu.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b1ff96e30b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150506 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure a Linux bridge with Network Manager on Ubuntu.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+Linux 有问必答:如何在Ubuntu上配置网桥
+===============================================================================
+> **Question**: 我需要在我的Ubuntu主机上建立一个Linux网桥,共享一个网卡给其他一些虚拟主机或在主机上创建的容器。我目前正在Ubuntu上使用网络管理器(Network Manager),所以最好>能使用网络管理器来配置一个网桥。我该怎么做?
+
+网桥是一个硬件装备,用来将两个或多个数据链路层(OSI七层模型中第二层)互联,以使得不同网段上的网络设备可以互相访问。当你想要互联一个主机里的多个虚拟机器或者以太接口时,就需要在Linux主机里有一个类似桥接的概念。这里使用的是一种软网桥。
+
+有很多的方法来配置一个Linux网桥。举个例子,在一个无外接显示/键盘的服务器环境里,你可以使用[brct][1]手动地配置一个网桥。而在桌面环境下,在网络管理器里也支持网桥设置。那就让我们测试一下如何用网络管理器配置一个网桥吧。
+
+### 要求 ###
+
+为了避免[任何问题][2],建议你的网络管理器版本为0.9.9或者更高,它用在 Ubuntu 15.04或者更新的版本。
+
+ $ apt-cache show network-manager | grep Version
+
+----------
+
+ Version: 0.9.10.0-4ubuntu15.1
+ Version: 0.9.10.0-4ubuntu15
+
+### 创建一个网桥 ###
+
+使用网络管理器创建网桥最简单的方式就是通过nm-connection-editor。这款GUI(图形用户界面)的工具允许你傻瓜式地配置一个网桥。
+
+首先,启动nm-connection-editor。
+
+ $ nm-connection-editor
+
+该编辑器的窗口会显示给你一个列表,列出目前配置好的网络连接。点击右上角的“添加”按钮,创建一个网桥。
+
+
+
+接下来,选择“Bridge”(网桥)作为连接类型。
+
+
+
+现在,开始配置网桥,包括它的名字和所桥接的连接。如果没有创建过其他网桥,那么默认的网桥接口会被命名为bridge0。
+
+回顾一下,创建网桥的目的是为了通过网桥共享你的以太网卡接口,所以你需要添加以太网卡接口到网桥。在图形界面添加一个新的“桥接的连接”可以实现上述目的。点击“Add”按钮。
+
+
+
+选择“以太网”作为连接类型。
+
+
+
+在“设备的 MAC 地址”区域,选择你想要从属于网桥的接口。本例中,假设该接口是eth0。
+
+
+
+点击“常规”标签,并且选中两个复选框,分别是“当其可用时自动连接到该网络”和“所有用户都可以连接到该网络”。
+
+
+
+切换到“IPv4 设置”标签,为网桥配置DHCP或者是静态IP地址。注意,你应该为从属的以太网卡接口eth0使用相同的IPv4设定。本例中,我们假设eth0是用过DHCP配置的。因此,此处选择“自动(DHCP)”。如果eth0被指定了一个静态IP地址,那么你也应该指定相同的IP地址给网桥。
+
+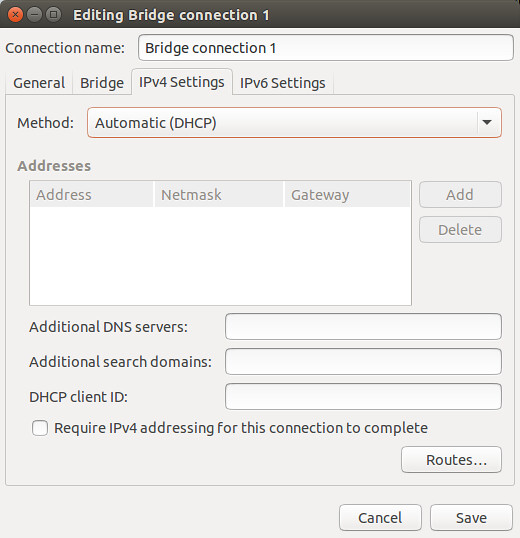
+
+最后,保存网桥的设置。
+
+现在,你会看见一个新增的网桥连接被创建在“网络连接”窗口里。因为已经从属与网桥,以前配置好的有线连接 eth0 就不再需要了,所以去删除原来的有线连接吧。
+
+
+
+这时候,网桥连接会被自动激活。从指定给eth0的IP地址被网桥接管起,你将会暂时丢失一下连接。当IP地址赋给了网桥,你将会通过网桥连接回你的以太网卡接口。你可以通过“Network”设置确认一下。
+
+
+
+同时,检查可用的接口。提醒一下,网桥接口必须已经取代了任何你的以太网卡接口拥有的IP地址。
+
+
+
+就这么多了,现在,网桥已经可以用了。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/configure-linux-bridge-network-manager-ubuntu.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-configure-linux-bridge-interface.html
+[2]:https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/network-manager/+bug/1273201
diff --git a/published/201505/20150506 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install autossh on Linux.md b/published/201505/20150506 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install autossh on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3fa2cf8a86
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150506 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install autossh on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
+Linux有问必答:如何安装autossh
+================================================================================
+> **提问**: 我打算在linux上安装autossh,我应该怎么做呢?
+
+[autossh][1] 是一款开源工具,可以帮助管理SSH会话、自动重连和停止转发流量。autossh会假定目标主机已经设定[无密码SSH登陆][2],以便autossh可以重连断开的SSH会话而不用用户操作。
+
+只要你建立[反向SSH隧道][3]或者[挂载基于SSH的远程文件夹][4],autossh迟早会派上用场。基本上只要需要维持SSH会话,autossh肯定是有用的。
+
+
+
+下面有许多linux发行版autossh的安装方法。
+
+### Debian 或 Ubuntu 系统 ###
+
+autossh已经加入基于Debian系统的基础库,所以可以很方便的安装。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install autossh
+
+### Fedora 系统 ###
+
+Fedora库同样包含autossh包,使用yum安装。
+
+ $ sudo yum install autossh
+
+### CentOS 或 RHEL 系统 ###
+
+CentOS/RHEL 6 或早期版本, 需要开启第三库[Repoforge库][5], 然后才能使用yum安装.
+
+ $ sudo yum install autossh
+
+CentOS/RHEL 7以后,autossh 已经不在Repoforge库中. 你需要从源码编译安装(例子在下面)。
+
+### Arch Linux 系统 ###
+
+ $ sudo pacman -S autossh
+
+### Debian 或 Ubuntu 系统中从源码编译安装###
+
+如果你想要使用最新版本的autossh,你可以自己编译源码安装
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install gcc make
+ $ wget http://www.harding.motd.ca/autossh/autossh-1.4e.tgz
+ $ tar -xf autossh-1.4e.tgz
+ $ cd autossh-1.4e
+ $ ./configure
+ $ make
+ $ sudo make install
+
+### CentOS, Fedora 或 RHEL 系统中从源码编译安装###
+
+在CentOS/RHEL 7以后,autossh不在是预编译包。所以你不得不从源码编译安装。
+
+ $ sudo yum install wget gcc make
+ $ wget http://www.harding.motd.ca/autossh/autossh-1.4e.tgz
+ $ tar -xf autossh-1.4e.tgz
+ $ cd autossh-1.4e
+ $ ./configure
+ $ make
+ $ sudo make install
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-autossh-linux.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[Vic020/VicYu](http://vicyu.net)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
+[1]:http://www.harding.motd.ca/autossh/
+[2]:https://linux.cn/article-5444-1.html
+[3]:http://xmodulo.com/access-linux-server-behind-nat-reverse-ssh-tunnel.html
+[4]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-mount-remote-directory-over-ssh-on-linux.html
+[5]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
diff --git a/published/201505/20150507 Command Line Tool to Monitor Linux Containers Performance.md b/published/201505/20150507 Command Line Tool to Monitor Linux Containers Performance.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..161e030c11
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150507 Command Line Tool to Monitor Linux Containers Performance.md
@@ -0,0 +1,185 @@
+监控 Linux 容器性能的命令行神器
+================================================================================
+ctop是一个新的基于命令行的工具,它可用于在容器层级监控进程。容器通过利用控制器组(cgroup)的资源管理功能,提供了操作系统层级的虚拟化环境。该工具从cgroup收集与内存、CPU、块输入输出的相关数据,以及拥有者、开机时间等元数据,并以人性化的格式呈现给用户,这样就可以快速对系统健康状况进行评估。基于所获得的数据,它可以尝试推测下层的容器技术。ctop也有助于在低内存环境中检测出谁在消耗大量的内存。
+
+### 功能 ###
+
+ctop的一些功能如下:
+
+- 收集CPU、内存和块输入输出的度量值
+- 收集与拥有者、容器技术和任务统计相关的信息
+- 通过任意栏对信息排序
+- 以树状视图显示信息
+- 折叠/展开cgroup树
+- 选择并跟踪cgroup/容器
+- 选择显示数据刷新的时间窗口
+- 暂停刷新数据
+- 检测基于systemd、Docker和LXC的容器
+- 基于Docker和LXC的容器的高级特性
+ - 打开/连接shell以进行深度诊断
+ - 停止/杀死容器类型
+
+### 安装 ###
+
+**ctop**是由Python写成的,因此,除了需要Python 2.6或其更高版本外(带有内建的光标支持),别无其它外部依赖。推荐使用Python的pip进行安装,如果还没有安装pip,请先安装,然后使用pip安装ctop。
+
+*注意:本文样例来自Ubuntu(14.10)系统*
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install python-pip
+
+使用pip安装ctop:
+
+ poornima@poornima-Lenovo:~$ sudo pip install ctop
+
+ [sudo] password for poornima:
+
+ Downloading/unpacking ctop
+
+ Downloading ctop-0.4.0.tar.gz
+
+ Running setup.py (path:/tmp/pip_build_root/ctop/setup.py) egg_info for package ctop
+
+ Installing collected packages: ctop
+
+ Running setup.py install for ctop
+
+ changing mode of build/scripts-2.7/ctop from 644 to 755
+
+ changing mode of /usr/local/bin/ctop to 755
+
+ Successfully installed ctop
+
+ Cleaning up...
+
+如果不选择使用pip安装,你也可以使用wget直接从github安装:
+
+ poornima@poornima-Lenovo:~$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yadutaf/ctop/master/cgroup_top.py -O ctop
+
+ --2015-04-29 19:32:53-- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yadutaf/ctop/master/cgroup_top.py
+
+ Resolving raw.githubusercontent.com (raw.githubusercontent.com)... 199.27.78.133
+
+ Connecting to raw.githubusercontent.com (raw.githubusercontent.com)|199.27.78.133|:443... connected.
+
+ HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 27314 (27K) [text/plain]
+
+ Saving to: ctop
+
+ 100%[======================================>] 27,314 --.-K/s in 0s
+
+ 2015-04-29 19:32:59 (61.0 MB/s) - ctop saved [27314/27314]
+
+----------
+
+ poornima@poornima-Lenovo:~$ chmod +x ctop
+
+如果cgroup-bin包没有安装,你可能会碰到一个错误消息,你可以通过安装需要的包来解决。
+
+ poornima@poornima-Lenovo:~$ ./ctop
+
+ [ERROR] Failed to locate cgroup mountpoints.
+
+ poornima@poornima-Lenovo:~$ sudo apt-get install cgroup-bin
+
+下面是ctop的输出样例:
+
+
+
+*ctop屏幕*
+
+### 用法选项 ###
+
+ ctop [--tree] [--refresh=] [--columns=] [--sort-col=] [--follow=] [--fold=, ...] ctop (-h | --help)
+
+当你进入ctop屏幕,可使用上(↑)和下(↓)箭头键在容器间导航。点击某个容器就选定了该容器,按q或Ctrl+C退出该容器。
+
+现在,让我们来看看上面列出的那一堆选项究竟是怎么用的吧。
+
+**-h / --help - 显示帮助信息**
+
+ poornima@poornima-Lenovo:~$ ctop -h
+ Usage: ctop [options]
+
+ Options:
+ -h, --help show this help message and exit
+ --tree show tree view by default
+ --refresh=REFRESH Refresh display every <seconds>
+ --follow=FOLLOW Follow cgroup path
+ --columns=COLUMNS List of optional columns to display. Always includes
+ 'name'
+ --sort-col=SORT_COL Select column to sort by initially. Can be changed
+ dynamically.
+
+
+**--tree - 显示容器的树形视图**
+
+默认情况下,会显示列表视图
+
+当你进入ctop窗口,你可以使用F5按钮在树状/列表视图间切换。
+
+**--fold=<name> - 在树形视图中折叠名为 \<name> 的 cgroup 路径**
+
+该选项需要与 --tree 选项组合使用。
+
+例子: ctop --tree --fold=/user.slice
+
+
+
+*'ctop --fold'的输出*
+
+在ctop窗口中,使用+/-键来展开或折叠子cgroup。
+
+注意:在写本文时,pip仓库中还没有最新版的ctop,还不支持命令行的‘--fold’选项
+
+**--follow= - 跟踪/高亮 cgroup 路径**
+
+例子: ctop --follow=/user.slice/user-1000.slice
+
+正如你在下面屏幕中所见到的那样,带有“/user.slice/user-1000.slice”路径的cgroup被高亮显示,这让用户易于跟踪,就算显示位置变了也一样。
+
+
+
+*'ctop --follow'的输出*
+
+你也可以使用‘f’按钮来让高亮的行跟踪选定的容器。默认情况下,跟踪是关闭的。
+
+**--refresh= - 按指定频率刷新显示,默认1秒**
+
+这对于按每用户需求来显示改变刷新率时很有用。使用‘p’按钮可以暂停刷新并选择文本。
+
+**--columns=<columns> - 限定只显示选定的列。'name' 需要是第一个字段,其后跟着其它字段。默认情况下,字段包括:owner, processes,memory, cpu-sys, cpu-user, blkio, cpu-time**
+
+例子: ctop --columns=name,owner,type,memory
+
+
+
+*'ctop --column'的输出*
+
+**-sort-col=<sort-col> - 按指定的列排序。默认使用 cpu-user 排序**
+
+例子: ctop --sort-col=blkio
+
+如果有Docker和LXC支持的额外容器,跟踪选项也是可用的:
+
+ press 'a' - 接驳到终端输出
+
+ press 'e' - 打开容器中的一个 shell
+
+ press 's' - 停止容器 (SIGTERM)
+
+ press 'k' - 杀死容器 (SIGKILL)
+
+目前 Jean-Tiare Le Bigot 还在积极开发 [ctop][1] 中,希望我们能在该工具中见到像本地 top 命令一样的特性 :-)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/how-tos/monitor-linux-containers-performance/
+
+作者:[B N Poornima][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/bnpoornima/
+[1]:https://github.com/yadutaf/ctop
diff --git a/published/201505/20150511 OpenSSL command line Root and Intermediate CA including OCSP, CRL and revocation.md b/published/201505/20150511 OpenSSL command line Root and Intermediate CA including OCSP, CRL and revocation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9bd388f67c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150511 OpenSSL command line Root and Intermediate CA including OCSP, CRL and revocation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,406 @@
+建立你自己的 CA 服务:OpenSSL 命令行 CA 操作快速指南
+================================================================================
+
+这些是关于使用 OpenSSL 生成证书授权(CA)、中间证书授权和末端证书的速记随笔,内容包括 OCSP、CRL 和 CA 颁发者信息,以及指定颁发和有效期限等。
+
+我们将建立我们自己的根 CA,我们将使用根 CA 来生成一个中间 CA 的例子,我们将使用中间 CA 来签署末端用户证书。
+
+### 根 CA ###
+
+创建根 CA 授权目录并切换到该目录:
+
+ mkdir ~/SSLCA/root/
+ cd ~/SSLCA/root/
+
+为我们的根 CA 生成一个8192位长的 SHA-256 RSA 密钥:
+
+ openssl genrsa -aes256 -out rootca.key 8192
+
+样例输出:
+
+ Generating RSA private key, 8192 bit long modulus
+ .........++
+ ....................................................................................................................++
+ e is 65537 (0x10001)
+
+如果你想要用密码保护该密钥,请添加 `-aes256` 选项。
+
+创建自签名根 CA 证书 `ca.crt`;你需要为你的根 CA 提供一个身份:
+
+ openssl req -sha256 -new -x509 -days 1826 -key rootca.key -out rootca.crt
+
+样例输出:
+
+ You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
+ into your certificate request.
+ What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
+ There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
+ For some fields there will be a default value,
+ If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
+ -----
+ Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:NL
+ State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:Zuid Holland
+ Locality Name (eg, city) []:Rotterdam
+ Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:Sparkling Network
+ Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:Sparkling CA
+ Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:Sparkling Root CA
+ Email Address []:
+
+创建一个存储 CA 序列的文件:
+
+ touch certindex
+ echo 1000 > certserial
+ echo 1000 > crlnumber
+
+放置 CA 配置文件,该文件持有 CRL 和 OCSP 末端的存根。
+
+ # vim ca.conf
+ [ ca ]
+ default_ca = myca
+
+ [ crl_ext ]
+ issuerAltName=issuer:copy
+ authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid:always
+
+ [ myca ]
+ dir = ./
+ new_certs_dir = $dir
+ unique_subject = no
+ certificate = $dir/rootca.crt
+ database = $dir/certindex
+ private_key = $dir/rootca.key
+ serial = $dir/certserial
+ default_days = 730
+ default_md = sha1
+ policy = myca_policy
+ x509_extensions = myca_extensions
+ crlnumber = $dir/crlnumber
+ default_crl_days = 730
+
+ [ myca_policy ]
+ commonName = supplied
+ stateOrProvinceName = supplied
+ countryName = optional
+ emailAddress = optional
+ organizationName = supplied
+ organizationalUnitName = optional
+
+ [ myca_extensions ]
+ basicConstraints = critical,CA:TRUE
+ keyUsage = critical,any
+ subjectKeyIdentifier = hash
+ authorityKeyIdentifier = keyid:always,issuer
+ keyUsage = digitalSignature,keyEncipherment,cRLSign,keyCertSign
+ extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth
+ crlDistributionPoints = @crl_section
+ subjectAltName = @alt_names
+ authorityInfoAccess = @ocsp_section
+
+ [ v3_ca ]
+ basicConstraints = critical,CA:TRUE,pathlen:0
+ keyUsage = critical,any
+ subjectKeyIdentifier = hash
+ authorityKeyIdentifier = keyid:always,issuer
+ keyUsage = digitalSignature,keyEncipherment,cRLSign,keyCertSign
+ extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth
+ crlDistributionPoints = @crl_section
+ subjectAltName = @alt_names
+ authorityInfoAccess = @ocsp_section
+
+ [alt_names]
+ DNS.0 = Sparkling Intermidiate CA 1
+ DNS.1 = Sparkling CA Intermidiate 1
+
+ [crl_section]
+ URI.0 = http://pki.sparklingca.com/SparklingRoot.crl
+ URI.1 = http://pki.backup.com/SparklingRoot.crl
+
+ [ocsp_section]
+ caIssuers;URI.0 = http://pki.sparklingca.com/SparklingRoot.crt
+ caIssuers;URI.1 = http://pki.backup.com/SparklingRoot.crt
+ OCSP;URI.0 = http://pki.sparklingca.com/ocsp/
+ OCSP;URI.1 = http://pki.backup.com/ocsp/
+
+如果你需要设置某个特定的证书生效/过期日期,请添加以下内容到`[myca]`:
+
+ # format: YYYYMMDDHHMMSS
+ default_enddate = 20191222035911
+ default_startdate = 20181222035911
+
+### 创建中间 CA###
+
+生成中间 CA (名为 intermediate1)的私钥:
+
+ openssl genrsa -out intermediate1.key 4096
+
+生成中间 CA 的 CSR:
+
+ openssl req -new -sha256 -key intermediate1.key -out intermediate1.csr
+
+样例输出:
+
+ You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
+ into your certificate request.
+ What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
+ There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
+ For some fields there will be a default value,
+ If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
+ -----
+ Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:NL
+ State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:Zuid Holland
+ Locality Name (eg, city) []:Rotterdam
+ Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:Sparkling Network
+ Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:Sparkling CA
+ Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:Sparkling Intermediate CA
+ Email Address []:
+
+ Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
+ to be sent with your certificate request
+ A challenge password []:
+ An optional company name []:
+
+确保中间 CA 的主体(CN)和根 CA 不同。
+
+用根 CA 签署 中间 CA 的 CSR:
+
+ openssl ca -batch -config ca.conf -notext -in intermediate1.csr -out intermediate1.crt
+
+样例输出:
+
+ Using configuration from ca.conf
+ Check that the request matches the signature
+ Signature ok
+ The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows
+ countryName :PRINTABLE:'NL'
+ stateOrProvinceName :ASN.1 12:'Zuid Holland'
+ localityName :ASN.1 12:'Rotterdam'
+ organizationName :ASN.1 12:'Sparkling Network'
+ organizationalUnitName:ASN.1 12:'Sparkling CA'
+ commonName :ASN.1 12:'Sparkling Intermediate CA'
+ Certificate is to be certified until Mar 30 15:07:43 2017 GMT (730 days)
+
+ Write out database with 1 new entries
+ Data Base Updated
+
+生成 CRL(同时采用 PEM 和 DER 格式):
+
+ openssl ca -config ca.conf -gencrl -keyfile rootca.key -cert rootca.crt -out rootca.crl.pem
+
+ openssl crl -inform PEM -in rootca.crl.pem -outform DER -out rootca.crl
+
+每次使用该 CA 签署证书后,请生成 CRL。
+
+如果你需要撤销该中间证书:
+
+ openssl ca -config ca.conf -revoke intermediate1.crt -keyfile rootca.key -cert rootca.crt
+
+### 配置中间 CA ###
+
+为该中间 CA 创建一个新文件夹,然后进入该文件夹:
+
+ mkdir ~/SSLCA/intermediate1/
+ cd ~/SSLCA/intermediate1/
+
+从根 CA 拷贝中间证书和密钥:
+
+ cp ~/SSLCA/root/intermediate1.key ./
+ cp ~/SSLCA/root/intermediate1.crt ./
+
+创建索引文件:
+
+ touch certindex
+ echo 1000 > certserial
+ echo 1000 > crlnumber
+
+创建一个新的 `ca.conf` 文件:
+
+ # vim ca.conf
+ [ ca ]
+ default_ca = myca
+
+ [ crl_ext ]
+ issuerAltName=issuer:copy
+ authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid:always
+
+ [ myca ]
+ dir = ./
+ new_certs_dir = $dir
+ unique_subject = no
+ certificate = $dir/intermediate1.crt
+ database = $dir/certindex
+ private_key = $dir/intermediate1.key
+ serial = $dir/certserial
+ default_days = 365
+ default_md = sha1
+ policy = myca_policy
+ x509_extensions = myca_extensions
+ crlnumber = $dir/crlnumber
+ default_crl_days = 365
+
+ [ myca_policy ]
+ commonName = supplied
+ stateOrProvinceName = supplied
+ countryName = optional
+ emailAddress = optional
+ organizationName = supplied
+ organizationalUnitName = optional
+
+ [ myca_extensions ]
+ basicConstraints = critical,CA:FALSE
+ keyUsage = critical,any
+ subjectKeyIdentifier = hash
+ authorityKeyIdentifier = keyid:always,issuer
+ keyUsage = digitalSignature,keyEncipherment
+ extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth
+ crlDistributionPoints = @crl_section
+ subjectAltName = @alt_names
+ authorityInfoAccess = @ocsp_section
+
+ [alt_names]
+ DNS.0 = example.com
+ DNS.1 = example.org
+
+ [crl_section]
+ URI.0 = http://pki.sparklingca.com/SparklingIntermidiate1.crl
+ URI.1 = http://pki.backup.com/SparklingIntermidiate1.crl
+
+ [ocsp_section]
+ caIssuers;URI.0 = http://pki.sparklingca.com/SparklingIntermediate1.crt
+ caIssuers;URI.1 = http://pki.backup.com/SparklingIntermediate1.crt
+ OCSP;URI.0 = http://pki.sparklingca.com/ocsp/
+ OCSP;URI.1 = http://pki.backup.com/ocsp/
+
+修改 `[alt_names]` 部分,添加你需要的主体备选名。如果你不需要主体备选名,请移除该部分包括`subjectAltName = @alt_names`的行。
+
+如果你需要设置一个指定的生效/到期日期,请添加以下内容到 `[myca]`:
+
+ # format: YYYYMMDDHHMMSS
+ default_enddate = 20191222035911
+ default_startdate = 20181222035911
+
+生成一个空白 CRL(同时以 PEM 和 DER 格式):
+
+ openssl ca -config ca.conf -gencrl -keyfile rootca.key -cert rootca.crt -out rootca.crl.pem
+
+ openssl crl -inform PEM -in rootca.crl.pem -outform DER -out rootca.crl
+
+### 生成末端用户证书 ###
+
+我们使用这个新的中间 CA 来生成一个末端用户证书,请重复以下操作来使用该 CA 为每个用户签署。
+
+ mkdir enduser-certs
+
+生成末端用户的私钥:
+
+ openssl genrsa -out enduser-certs/enduser-example.com.key 4096
+
+生成末端用户的 CSR:
+
+ openssl req -new -sha256 -key enduser-certs/enduser-example.com.key -out enduser-certs/enduser-example.com.csr
+
+样例输出:
+
+ You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
+ into your certificate request.
+ What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
+ There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
+ For some fields there will be a default value,
+ If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
+ -----
+ Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:NL
+ State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:Noord Holland
+ Locality Name (eg, city) []:Amsterdam
+ Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:Example Inc
+ Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:IT Dept
+ Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:example.com
+ Email Address []:
+
+ Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
+ to be sent with your certificate request
+ A challenge password []:
+ An optional company name []:
+
+使用中间 CA 签署末端用户的 CSR:
+
+ openssl ca -batch -config ca.conf -notext -in enduser-certs/enduser-example.com.csr -out enduser-certs/enduser-example.com.crt
+
+样例输出:
+
+ Using configuration from ca.conf
+ Check that the request matches the signature
+ Signature ok
+ The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows
+ countryName :PRINTABLE:'NL'
+ stateOrProvinceName :ASN.1 12:'Noord Holland'
+ localityName :ASN.1 12:'Amsterdam'
+ organizationName :ASN.1 12:'Example Inc'
+ organizationalUnitName:ASN.1 12:'IT Dept'
+ commonName :ASN.1 12:'example.com'
+ Certificate is to be certified until Mar 30 15:18:26 2016 GMT (365 days)
+
+ Write out database with 1 new entries
+ Data Base Updated
+
+生成 CRL(同时以 PEM 和 DER 格式):
+
+ openssl ca -config ca.conf -gencrl -keyfile intermediate1.key -cert intermediate1.crt -out intermediate1.crl.pem
+
+ openssl crl -inform PEM -in intermediate1.crl.pem -outform DER -out intermediate1.crl
+
+每次你使用该 CA 签署证书后,都需要生成 CRL。
+
+如果你需要撤销该末端用户证书:
+
+ openssl ca -config ca.conf -revoke enduser-certs/enduser-example.com.crt -keyfile intermediate1.key -cert intermediate1.crt
+
+样例输出:
+
+ Using configuration from ca.conf
+ Revoking Certificate 1000.
+ Data Base Updated
+
+通过连接根证书和中间证书来创建证书链文件。
+
+ cat ../root/rootca.crt intermediate1.crt > enduser-certs/enduser-example.com.chain
+
+发送以下文件给末端用户:
+
+ enduser-example.com.crt
+ enduser-example.com.key
+ enduser-example.com.chain
+
+你也可以让末端用户提供他们自己的 CSR,而只发送给他们这个 .crt 文件。不要把它从服务器删除,否则你就不能撤销了。
+
+### 校验证书 ###
+
+你可以对证书链使用以下命令来验证末端用户证书:
+
+ openssl verify -CAfile enduser-certs/enduser-example.com.chain enduser-certs/enduser-example.com.crt
+ enduser-certs/enduser-example.com.crt: OK
+
+你也可以针对 CRL 来验证。首先,将 PEM 格式的 CRL 和证书链相连接:
+
+ cat ../root/rootca.crt intermediate1.crt intermediate1.crl.pem > enduser-certs/enduser-example.com.crl.chain
+
+验证证书:
+
+ openssl verify -crl_check -CAfile enduser-certs/enduser-example.com.crl.chain enduser-certs/enduser-example.com.crt
+
+没有撤销时的输出:
+
+ enduser-certs/enduser-example.com.crt: OK
+
+撤销后的输出如下:
+
+ enduser-certs/enduser-example.com.crt: CN = example.com, ST = Noord Holland, C = NL, O = Example Inc, OU = IT Dept
+ error 23 at 0 depth lookup:certificate revoked
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/OpenSSL_command_line_Root_and_Intermediate_CA_including_OCSP_CRL%20and_revocation.html
+
+作者:Remy van Elst
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/20150512 Guake 0.7.0 Released--A Drop-Down Terminal for Gnome Desktops.md b/published/201505/20150512 Guake 0.7.0 Released--A Drop-Down Terminal for Gnome Desktops.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..421bc00a0b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150512 Guake 0.7.0 Released--A Drop-Down Terminal for Gnome Desktops.md
@@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
+一个用于Gnome桌面的下拉式终端: Guake 0.7.0 发布
+================================================================================
+Linux的命令行是最好、最强大的东西,它使新手着迷,并为老手和极客的提供极其强大的功能。那些在服务器和生产环境下工作的人早已认识到了这个事实。有趣的是,Linux终端是Linus Torvald在1991年写内核时实现的第一批功能之一。
+
+终端是个强大的工具,由于它没有什么可调整的部分,所以十分可靠。终端介于控制台环境和GUI环境之间。终端自身作为一个GUI程序,运行在桌面环境下。有许多终端是适用于特定的桌面环境的,其它的则是通用的。Terminator, Konsole, Gnome-Terminal, Terminology, XFCE terminal, xterm都是些常用的终端模拟器。
+
+您可以从下面的链接中获得一份使用最广泛的终端模拟器的列表。
+
+- [20 Useful Terminals for Linux][1]
+
+前几日上网时,我偶遇了名为‘Guake’的终端程序,它是用于gnome的终端模拟器。尽管这并不是我第一次听到Guake。实际上,我在大约一年前便知道了这个应用程序,但不知怎么搞的,我那时没有写写Guake,再后来我便渐渐忘掉了Guake,直到我再一次听到Guake。所以,最终,这篇文章诞生了。我将给你讲讲Guake的功能,在Debian、Ubuntu、Fedora上的安装过程以及一些测试。
+
+#### 什么是Guake? ####
+
+Guake是应用于Gnome环境的下拉式终端。主要由Python编写,使用了一些C,它以GPL2+许可证发布,适用于Linux以及类似的系统。Guake的灵感来源于电脑游戏Quake(雷神之锤)中的终端,Quake的终端能通过按下特定按键(默认为F12)从屏幕上滑下来,并在按下同样的键后滑上去。
+
+值得注意的是,Guake并不是第一个这样的应用。Yakuake(Yet Another Kuake)是一个运行于KDE的终端模拟器,Tilda是一个用GTK+写成的终端模拟器。它们的灵感都来自于雷神之锤那上下滑动的终端。
+
+#### Guake的功能 ####
+
+- 轻量级
+- 简单而优雅
+- 功能众多
+- 强大
+- 美观
+- 将终端平滑地集成于GUI中
+- 在按下预定义的键后出现/消失
+- 支持热键、标签、透明化背景,这使得它适合所有Gnome用户
+- 可配置各种方面
+- 包括许多颜色的调色板
+- 设定透明度的快捷方式
+- 通过Guake配置,可在启动时运行一个脚本
+- 可以在多个显示器上运行
+
+Guake 0.7.0最近发布,它带来了一些修正以及上面提到的一些功能。完整的版本历史和源代码包可以在[这里][2]找到。
+
+### 在Linux中安装Guake终端 ###
+
+如果您对从源码编译Guake感兴趣,您可以从上面的链接处下载Guake,并在安装前进行编译。
+
+然而Guake可以在许多的发行版中通过添加额外的仓库来安装。这里,我们将在Debian、Ubuntu、Linux Mint和Fedora下安装Guake。
+
+首先从仓库获取最新的软件包列表,并从默认的仓库安装Guake,如下所示:
+
+ ---------------- 在 Debian, Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 上 ----------------
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ apt-get install guake
+
+----------
+
+ ---------------- 在 Fedora 19 及其以后版本 ----------------
+ # yum update
+ # yum install guake
+
+安装后,可以从另一个终端中启动Guake:
+
+ $ guake
+
+在启动它后,便可以在Gnome桌面中使用F12(默认配置)来拉下、收回终端。
+
+看起来非常漂亮,尤其是透明背景。滑下来...滑上去...滑下来...滑上去...执行命令,打开另一个标签,执行命令,滑上去...滑下来...(作者已沉迷其中)
+
+
+
+*Guake实战*
+
+如果您的壁纸或活动窗口的颜色和Guake的颜色有些不搭。您可以改变您的壁纸,减少透明度或者改变Guake的颜色。
+
+下一步便是进入Guake的配置,根据每个人的需求修改设置。可以通过应用菜单或者下面的命令来运行Guake的配置。
+
+ $ guake --preferences
+
+
+
+*Guake终端配置*
+
+设置滚动
+
+
+
+*Guake滚动配置*
+
+外观设置 - 在这里您可以修改文字颜色和背景色以及透明度。
+
+
+
+*外观设置*
+
+键盘快捷键 - 在这里您可以修改Guake显示的开关快捷键。
+
+
+
+*键盘快捷键*
+
+兼容性设置 - 基本上不必设置它。
+
+
+
+*兼容性设置*
+
+### 结论 ###
+
+这个项目即不是太年轻也不是太古老,因此它已经达到了一定的成熟度,足够可靠,可以开箱即用。像我这样需要在GUI和终端间频繁切换的人来说,Guake是一个福利。我不需要管理一个多余的窗口,频繁的打开和关闭,使用tab在大量打开的应用程序中寻找终端或切换到不同的工作区来管理终端,现在我需要的只有F12。
+
+我认为对任何同时使用GUI和终端的Linux用户来说,Guake都是必须的工具。同样的,我会向任何想要在系统中结合使用GUI和终端的人推荐它,因为它既平滑又没有任何障碍。
+
+上面就是我要说的全部了。如果在安装和使用时有任何问题,请告诉我,我们会帮助您。也请您告诉我您使用Guake的经验。在下面的评论区反馈您宝贵的经验。点赞和分享以帮助我们宣传。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-guake-terminal-ubuntu-mint-fedora/
+
+作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
+译者:[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-terminal-emulators/
+[2]:https://github.com/Guake/guake/releases/tag/0.7.0
diff --git a/published/201505/20150515 New to Linux 5 Apps You Didn't Know You Were Missing.md b/published/201505/20150515 New to Linux 5 Apps You Didn't Know You Were Missing.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1d34cda0f4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150515 New to Linux 5 Apps You Didn't Know You Were Missing.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+初来乍到Linux? 你需要知道的5款好应用
+================================================================================
+
+
+当你刚刚迈入linux的世界时,你会立马动身开始使用那些知名的浏览器、云客户端、音乐播放器、邮件客户端,也许还有图形编辑器,对吗?可是,你却错过了几个非常重要的生产工具。这里将介绍给你5个应该安装的不容错过的应用。
+
+### [Synergy][1] ###
+
+Synergy 简直就是多桌面用户的福音。这是一个开源软件,它可以让你用一个鼠标和键盘跨越几台电脑、显示器和操作系统。在桌面之间切换鼠标和键盘非常简单,你只要把鼠标从一个桌面的边缘移向另一个桌面即可。
+
+
+
+当你第一次打开 Synergy,它会引导你完成设置。你的主桌面就是你将与其它桌面共享输入设备的那个。将主桌面设为服务端,将其它桌面设置为客户端。
+
+
+
+Synergy 在互连的各个桌面间维持同一张粘贴板。它也将锁屏功能融合到了一起,例如,你可以跳过锁屏一次登录到所有桌面。你可以在 **Edit 菜单的 Setting** 下调整更多的设置,比如设置密码或者将 Synergy 设置成开机自启动。
+
+(LCTT 译注:这是个[自由而开源][15]的好软件,但是如果你从它的网站下载,由于商业支持的缘故,是需要付费的;当然你可以自己[下载源代码并编译][15]。)
+
+### [BasKet Note Pads][2] ###
+
+从某种意义上来讲,用 BasKet Note Pads,就像把你的大脑刻画进计算机里一样。它把我们不经意间的想法记录下来,然后任由我们去把它们组织起来。你可以在各种任务中用到 BasKet Note Pads,比如记录笔记、制作脑图、记录代办事项、保存链接、管理你的发现、或者追踪项目数据。
+
+在 BasKet Note Pads 中,每个放到一个区域的主要的想法或项目被称作一个篮子(basket)。你可以进一步拆分,成一个或多个子篮或者兄弟篮。篮子进一步分成笔记,这些零零碎碎的笔记组成了一个项目。你可以自由组织它们,给它们打标签,和筛选它们。
+
+该应用的双面板结构的左侧以树形结构显示了你创建的所有篮子。
+
+
+
+BasKet Note Pads 第一次用起来可能有点复杂,但是如果你经常用它的话,你会觉得相当顺手。当你暂时不用它时,它会退出到系统托盘,方便你下次快速打开它。
+
+如果在 Linux 上想要一个[更简单的笔记本替代品][3]?可以试试[Springseed][4]。
+
+### [Caffeine(咖啡因)][5]###
+
+你怎样确保你的电脑不会在放一部[精彩的电影][6]中途突然休眠呢?Caffeine 会帮助你解决这个问题。当然,你并不需要为你的电脑泡一杯咖啡。你只需要安装一个轻量级的指示器 —— Caffeine。只要当前你是全屏模式,它就会禁用你的屏幕保护程序、锁屏程序,让你的电脑不会因为没有在任务中而进入睡眠模式。
+
+[点击下载][7]安装最新版本的 Caffeine。如果你想以[PPA的方式][8]安装,使用如下命令:
+
+ $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:caffeine-developers/ppa
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get install caffeine
+
+如果你的Ubuntu版本是14.10或者15.04(或者其它衍生版本),你还需要安装下面的依赖包:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install libappindicator3-1 gir1.2-appindicator3-0.1
+
+完成安装以后,将**Caffeine指示器**设置成开机自启动,这样可以使指示器显示在系统托盘里。你可以右键点击托盘图标打开应用的关联菜单,来开启或关闭Caffeine,
+
+
+
+### Easystroke ###
+
+Easystroke 是一个将[鼠标潜力][9]开发出来的应用。通过一系列的设置,用鼠标、触摸屏、手写笔的手势来完成敲击键盘、执行命令和滚动屏幕等通用操作。在 Easystroke 里能够设置的手势相当多,而且当你看到应用的界面时,你会发现应用的引导非常清晰。
+
+
+
+选择一个你喜欢的鼠标键开始设置手势。如果你喜欢,你还可以设置辅助功能键。通过Perferences>Behavior>Gesture Button 来设置。现在到**Action**选项卡里面,把你最常用的动作记录成手势吧。
+
+
+
+在 Preferences 和 Advanced 选项卡中,你可以做一些其它的调整,比如将 EasyStroke 设置成自动启动,在系统托盘中显示图标,改变滚动速度。
+
+### Guake ###
+
+我把我最喜欢的应用放在最后。Guake 是根据第一人称射击视屏游戏 [Quake][10] 模仿而来的下拉式命令行终端。不管你是否在[学习命令行终端][11],或者是有一定的基础,Guake 都可以将终端变得更加方便。你可以一键将它呼出,也可以一键将它隐藏。
+
+就像下面这张图,当打开时,Guake 的界面会覆盖在当前的屏幕上。你可以在终端中右键点击,调出 Preference 来改变 Guake 的界面,滚动方式,快捷键等等。
+
+
+
+如果[你的桌面][12]是 KDE,你可以选择一个类似的工具——[Yakuake][13].
+
+### 写下你最喜欢的Linux新发现!###
+
+还有更多[超级实用的 Linux 应用][14]等待被发现。放心,我们将一直关注,并把它们带到你们的生活中。
+
+哪一个应用是你最喜欢研究的呢?哪一个是你觉得必不可少的呢?在评论里告诉给我们吧。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/new-linux-5-apps-didnt-know-missing/
+
+作者:[Akshata][a]
+译者:[sevenot](https://github.com/sevenot)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/author/akshata/
+[1]:http://synergy-project.org/
+[2]:http://basket.kde.org/
+[3]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/try-these-3-beautiful-note-taking-apps-that-work-offline/
+[4]:http://getspringseed.com/
+[5]:https://launchpad.net/caffeine
+[6]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/popular-apps-movies-according-google/
+[7]:http://ppa.launchpad.net/caffeine-developers/ppa/ubuntu/pool/main/c/caffeine/
+[8]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/ubuntu-ppa-technology-explained/
+[9]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/4-astounding-linux-mouse-hacks/
+[10]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quake_%28video_game%29
+[11]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/4-ways-teach-terminal-commands-linux-si/
+[12]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/10-top-linux-desktop-environments-available/
+[13]:https://yakuake.kde.org/
+[14]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/linux-treasures-x-sublime-native-linux-apps-will-make-want-switch/
diff --git a/published/201505/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to block specific user agents on nginx web server.md b/published/201505/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to block specific user agents on nginx web server.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..16bc2060fb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to block specific user agents on nginx web server.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+Linux有问必答:nginx网络服务器上如何阻止特定用户代理(UA)
+================================================================================
+> **问题**: 我注意到有一些机器人经常访问我的nginx驱动的网站,并且进行一些攻击性的扫描,导致消耗掉了我的网络服务器的大量资源。我一直尝试着通过用户代理符串来阻挡这些机器人。我怎样才能在nginx网络服务器上阻挡掉特定的用户代理呢?
+
+现代互联网滋生了大量各种各样的恶意机器人和网络爬虫,比如像恶意软件机器人、垃圾邮件程序或内容刮刀,这些恶意工具一直偷偷摸摸地扫描你的网站,干些诸如检测潜在网站漏洞、收获电子邮件地址,或者只是从你的网站偷取内容。大多数机器人能够通过它们的“用户代理”签名字符串来识别。
+
+作为第一道防线,你可以尝试通过将这些机器人的用户代理字符串添加入robots.txt文件来阻止这些恶意软件机器人访问你的网站。但是,很不幸的是,该操作只针对那些“行为良好”的机器人,这些机器人被设计遵循robots.txt的规范。许多恶意软件机器人可以很容易地忽略掉robots.txt,然后随意扫描你的网站。
+
+另一个用以阻挡特定机器人的途径,就是配置你的网络服务器,通过特定的用户代理字符串拒绝要求提供内容的请求。本文就是说明如何**在nginx网络服务器上阻挡特定的用户代理**。
+
+### 在Nginx中将特定用户代理列入黑名单 ###
+
+要配置用户代理阻挡列表,请打开你的网站的nginx配置文件,找到`server`定义部分。该文件可能会放在不同的地方,这取决于你的nginx配置或Linux版本(如,`/etc/nginx/nginx.conf`,`/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/<your-site>`,`/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf`,`/etc/nginx/conf.d/<your-site>`)。
+
+ server {
+ listen 80 default_server;
+ server_name xmodulo.com;
+ root /usr/share/nginx/html;
+
+ ....
+ }
+
+在打开该配置文件并找到 `server` 部分后,添加以下 if 声明到该部分内的某个地方。
+
+ server {
+ listen 80 default_server;
+ server_name xmodulo.com;
+ root /usr/share/nginx/html;
+
+ # 大小写敏感的匹配
+ if ($http_user_agent ~ (Antivirx|Arian) {
+ return 403;
+ }
+
+ #大小写无关的匹配
+ if ($http_user_agent ~* (netcrawl|npbot|malicious)) {
+ return 403;
+ }
+
+ ....
+ }
+
+如你所想,这些 if 声明使用正则表达式匹配了任意不良用户字符串,并向匹配的对象返回403 HTTP状态码。
+`$http_user_agent`是HTTP请求中的一个包含有用户代理字符串的变量。‘~’操作符针对用户代理字符串进行大小写敏感匹配,而‘~*’操作符则进行大小写无关匹配。‘|’操作符是逻辑或,因此,你可以在 if 声明中放入众多的用户代理关键字,然后将它们全部阻挡掉。
+
+在修改配置文件后,你必须重新加载nginx以激活阻挡:
+
+ $ sudo /path/to/nginx -s reload
+
+你可以通过使用带有 “--user-agent” 选项的 wget 测试用户代理阻挡。
+
+ $ wget --user-agent "malicious bot" http://<nginx-ip-address>
+
+
+
+### 管理Nginx中的用户代理黑名单 ###
+
+目前为止,我已经展示了在nginx中如何阻挡一些用户代理的HTTP请求。如果你有许多不同类型的网络爬虫机器人要阻挡,又该怎么办呢?
+
+由于用户代理黑名单会增长得很大,所以将它们放在nginx的server部分不是个好点子。取而代之的是,你可以创建一个独立的文件,在该文件中列出所有被阻挡的用户代理。例如,让我们创建/etc/nginx/useragent.rules,并定义以下面的格式定义所有被阻挡的用户代理的图谱。
+
+ $ sudo vi /etc/nginx/useragent.rules
+
+----------
+
+ map $http_user_agent $badagent {
+ default 0;
+ ~*malicious 1;
+ ~*backdoor 1;
+ ~*netcrawler 1;
+ ~Antivirx 1;
+ ~Arian 1;
+ ~webbandit 1;
+ }
+
+与先前的配置类似,‘~*’将匹配以大小写不敏感的方式匹配关键字,而‘~’将使用大小写敏感的正则表达式匹配关键字。“default 0”行所表达的意思是,任何其它文件中未被列出的用户代理将被允许。
+
+接下来,打开你的网站的nginx配置文件,找到里面包含 http 的部分,然后添加以下行到 http 部分某个位置。
+
+ http {
+ .....
+ include /etc/nginx/useragent.rules
+ }
+
+注意,该 include 声明必须出现在 server 部分之前(这就是为什么我们将它添加到了 http 部分里)。
+
+现在,打开nginx配置定义你的服务器的部分,添加以下 if 声明:
+
+ server {
+ ....
+
+ if ($badagent) {
+ return 403;
+ }
+
+ ....
+ }
+
+最后,重新加载nginx。
+
+ $ sudo /path/to/nginx -s reload
+
+现在,任何包含有`/etc/nginx/useragent.rules`中列出的关键字的用户代理将被nginx自动禁止。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/block-specific-user-agents-nginx-web-server.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
diff --git a/published/201505/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix 'fatal error--security or pam_modules.h--No such file or directory'.md b/published/201505/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix 'fatal error--security or pam_modules.h--No such file or directory'.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6ede2366a8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix 'fatal error--security or pam_modules.h--No such file or directory'.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+如何修复 “fatal error: security/pam_modules.h: No such file or directory”
+================================================================================
+> **问题**: 我尝试在 [某某 Linux 发行版] 上编译程序,但是出现下面的编译错误:
+>
+> "pam_otpw.c:27:34: fatal error: security/pam_modules.h: No such file or directory"
+>
+> 我怎样才能修复这个错误?
+
+缺失的头文件 'security/pam_modules.h' 是 libpam 开发版的一部分,一个 PAM(Pluggable Authentication Modules:插入式验证模块)库。因此要修复这个错误,你需要安装 libpam 开发包,如下所示。
+
+对于 Debian、 Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install libpam0g-dev
+
+对与 CentOS、 Fedora 或者 RHEL:
+
+ $ sudo yum install gcc pam-devel
+
+现在验证缺失的头文件是否安装到了 /usr/include/security。
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/fatal-error-security-pam-modules.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/201505/20150521 Microsoft Open-Sources The Windows Communication Foundation.md b/published/201505/20150521 Microsoft Open-Sources The Windows Communication Foundation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bf071f9c5d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150521 Microsoft Open-Sources The Windows Communication Foundation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+微软开源了WCF框架
+================================================================================
+微软于今日(2015/5/20)宣布了针对 .NET Core 重大开源:WCF(Windows Communication Foundation)。
+
+如[MSDN][1]中的描述:“WCF是一个构建面向服务应用的框架。使用WCF,你可以从一个服务终端给另一个发送异步消息。服务终端可以是托管在IIS中连续可用的服务的一部分,也可以是托管在某个程序上的服务。服务终端可以是请求服务端数据的客户端。消息可以是一个字符或者XML,也可以是复杂的二进制流。”
+
+它的[代码放在GitHub][2],“包含了Window桌面中完整WCF框架的一部分,它支持已经可用于构建Window Store上的WCF应用的库。这些主要是基于客户端,方便移动设备和中间层服务器使用WCF进行通信。”
+
+更多的关于微软开源 WCF 的细节查看[dotNETFoundation.org blog][3]的公告。
+
+WCF听上去有点像Linux中用于进程/服务之间的进程间通讯的D-BUS。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Microsoft-Open-Source-WCF
+
+作者:[Michael Larabel][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.michaellarabel.com/
+[1]:https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms731082%28v=vs.110%29.aspx
+[2]:https://github.com/dotnet/wcf
+[3]:http://www.dotnetfoundation.org/blog/wcf-is-open-source
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/201505/20150527 Ubuntu Community Council Asks the Kubuntu Project Leader to Step Down.md b/published/201505/20150527 Ubuntu Community Council Asks the Kubuntu Project Leader to Step Down.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a47014fc9b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/20150527 Ubuntu Community Council Asks the Kubuntu Project Leader to Step Down.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+Ubuntu 社区委员会要求 Kubuntu 项目领导人下台
+================================================================================
+> 而Jonathan Riddell拒绝从Kubuntu领导人位置退出
+
+
+
+**这一切刚刚发生。一名Debian开发者以及Kubuntu委员会成员 Scott Kitterman 决定公开一些电子邮件,邮件披露了Ubuntu 社区委员会成员要求 Jonathan Riddell 从 Kubuntu 项目领导人位置退出的过程。**
+
+Jonathan Riddell 是 KDE 以及 Kubuntu 的一名开发者,多年来也是 Ubuntu 社区的一名重要成员。从 Scott Kitterman [今天曝光的社区邮件往来][1]中来看,Jonathan Riddell 被指责对 Ubuntu 以及 Kubuntu 社区的一些成员咄咄逼人和挑衅。
+
+长话短说,经过多轮邮件往来之后,Ubuntu 社区委员会的最终决定是让 Jonathan Riddell 退出他在 Ubuntu 以及Kubuntu 社区的领导人位置至少12个月,但仍可以像其他成员一样参与讨论。这个决定同时也得到了 Canonical 和Ubuntu 的创始人 Mark Shuttleworth 的支持。
+
+“很遗憾写下了讨论这个我们觉得对 Ubuntu 社区有着消极影响的问题的邮件。长期以来,Jonathan Riddell 变得越来越难以交往。Jonathan 提出了有效的问题及关注,但当收到他不赞同的答案时,他的反应就不那么让人愉快了。”在 Ubuntu 社区委员会发出的第一封认为 Jonathan Riddell 行为“不友好”的邮件中这么写道。
+
+### Jonathan Riddell拒绝从Kubuntu领导人位置退出 ###
+
+从今天 Scott Kitterman 披露邮件往来,并决定在博客上写第二篇博文来看,表明了他想从他在 Ubuntu 和 Kubuntu 的位置退出,这表明 Jonathan Riddell 可能拒绝从 Kubuntu 领导人位置退出。
+
+正如预料之中,Kubuntu 社区委员会的成员们支持 Jonathan Riddell,并且回击了 Ubuntu 社区委员会罢免 Kubuntu 项目领导人的决定。“我要感谢所有在 Kubuntu 委员会投票再次肯定我的 Kubuntu 成员。”,Jonathan Riddell 在[他的博客][2]上写道,“希望 Kubuntu 能够继续走下去,我也计划和我深爱的社区伙伴们一起为 15.10 发布而努力。”
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Ubuntu-Community-Council-Asks-the-Kubuntu-Project-Leader-to-Step-Down-482384.shtml
+
+作者:[Marius Nestor][a]
+译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/marius-nestor
+[1]:https://skitterman.wordpress.com/
+[2]:http://jriddell.org/
diff --git a/published/30 Things to Do After Minimal RHEL or CentOS 7 Installation--4.md b/published/201505/30 Things to Do After Minimal RHEL or CentOS 7 Installation--4.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/30 Things to Do After Minimal RHEL or CentOS 7 Installation--4.md
rename to published/201505/30 Things to Do After Minimal RHEL or CentOS 7 Installation--4.md
diff --git a/published/30 Things to Do After Minimal RHEL or CentOS 7 Installation--5.md b/published/201505/30 Things to Do After Minimal RHEL or CentOS 7 Installation--5.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/30 Things to Do After Minimal RHEL or CentOS 7 Installation--5.md
rename to published/201505/30 Things to Do After Minimal RHEL or CentOS 7 Installation--5.md
diff --git a/published/30 Things to Do After Minimal RHEL or CentOS 7 Installation--6.md b/published/201505/30 Things to Do After Minimal RHEL or CentOS 7 Installation--6.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/30 Things to Do After Minimal RHEL or CentOS 7 Installation--6.md
rename to published/201505/30 Things to Do After Minimal RHEL or CentOS 7 Installation--6.md
diff --git a/translated/tech/How to Manage Network using nmcli Tool in RedHat CentOS 7.x.md b/published/201505/How to Manage Network using nmcli Tool in RedHat CentOS 7.x.md
similarity index 74%
rename from translated/tech/How to Manage Network using nmcli Tool in RedHat CentOS 7.x.md
rename to published/201505/How to Manage Network using nmcli Tool in RedHat CentOS 7.x.md
index febebc89ca..bb4a3a5568 100644
--- a/translated/tech/How to Manage Network using nmcli Tool in RedHat CentOS 7.x.md
+++ b/published/201505/How to Manage Network using nmcli Tool in RedHat CentOS 7.x.md
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-在 RedHat/CentOS 7.x 中使用 cmcli 命令管理网络
+在 RedHat/CentOS 7.x 中使用 nmcli 命令管理网络
===============
[**Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7** 与 **CentOS 7**][1] 中默认的网络服务由 **NetworkManager** 提供,这是动态控制及配置网络的守护进程,它用于保持当前网络设备及连接处于工作状态,同时也支持传统的 ifcfg 类型的配置文件。
-NetworkManager 可以用于以下类型的连接:
-Ethernet,VLANS,Bridges,Bonds,Teams,Wi-Fi,mobile boradband(如移动3G)以及 IP-over-InfiniBand。针对与这些网络类型,NetworkManager 可以配置他们的网络别名,IP 地址,静态路由,DNS,VPN连接以及很多其它的特殊参数。
+
+NetworkManager 可以用于以下类型的连接:Ethernet,VLANS,Bridges,Bonds,Teams,Wi-Fi,mobile boradband(如移动3G)以及 IP-over-InfiniBand。针对与这些网络类型,NetworkManager 可以配置他们的网络别名,IP 地址,静态路由,DNS,VPN连接以及很多其它的特殊参数。
可以用命令行工具 nmcli 来控制 NetworkManager。
@@ -24,19 +24,21 @@ Ethernet,VLANS,Bridges,Bonds,Teams,Wi-Fi,mobile boradband(如移
显示所有连接。
- # nmcli connection show -a
+ # nmcli connection show -a
仅显示当前活动的连接。
# nmcli device status
-列出通过 NetworkManager 验证的设备列表及他们的状态。
+列出 NetworkManager 识别出的设备列表及他们的状态。

### 启动/停止 网络接口###
-使用 nmcli 工具启动或停止网络接口,与 ifconfig 的 up/down 是一样的。使用下列命令停止某个接口:
+使用 nmcli 工具启动或停止网络接口,与 ifconfig 的 up/down 是一样的。
+
+使用下列命令停止某个接口:
# nmcli device disconnect eno16777736
@@ -50,7 +52,7 @@ Ethernet,VLANS,Bridges,Bonds,Teams,Wi-Fi,mobile boradband(如移
# nmcli connection add type ethernet con-name NAME_OF_CONNECTION ifname interface-name ip4 IP_ADDRESS gw4 GW_ADDRESS
-根据你需要的配置更改 NAME_OF_CONNECTION,IP_ADDRESS, GW_ADDRESS参数(如果不需要网关的话可以省略最后一部分)。
+根据你需要的配置更改 NAME\_OF\_CONNECTION,IP\_ADDRESS, GW\_ADDRESS参数(如果不需要网关的话可以省略最后一部分)。
# nmcli connection add type ethernet con-name NEW ifname eno16777736 ip4 192.168.1.141 gw4 192.168.1.1
@@ -68,9 +70,11 @@ Ethernet,VLANS,Bridges,Bonds,Teams,Wi-Fi,mobile boradband(如移

+###增加一个使用 DHCP 的新连接
+
增加新的连接,使用DHCP自动分配IP地址,网关,DNS等,你要做的就是将命令行后 ip/gw 地址部分去掉就行了,DHCP会自动分配这些参数。
-例,在 eno 16777736 设备上配置一个 名为 NEW_DHCP 的 DHCP 连接
+例,在 eno 16777736 设备上配置一个 名为 NEW\_DHCP 的 DHCP 连接
# nmcli connection add type ethernet con-name NEW_DHCP ifname eno16777736
@@ -79,8 +83,8 @@ Ethernet,VLANS,Bridges,Bonds,Teams,Wi-Fi,mobile boradband(如移
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/nmcli-tool-red-hat-centos-7/
作者:[Adrian Dinu][a]
-译者:[SPccman](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[SPccman](https://github.com/SPccman)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201505/Linux grep command with 14 different examples.md b/published/201505/Linux grep command with 14 different examples.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..591a32ae43
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201505/Linux grep command with 14 different examples.md
@@ -0,0 +1,176 @@
+14 个 grep 命令的例子
+===========
+
+###概述:###
+
+所有的类linux系统都会提供一个名为**grep(global regular expression print,全局正则表达式输出)**的搜索工具。grep命令在对一个或多个文件的内容进行基于模式的搜索的情况下是非常有用的。模式可以是单个字符、多个字符、单个单词、或者是一个句子。
+
+当命令匹配到执行命令时指定的模式时,grep会将包含模式的一行输出,但是并不对原文件内容进行修改。
+
+在本文中,我们将会讨论到14个grep命令的例子。
+
+###例1 在文件中查找模式(单词)###
+
+在/etc/passwd文件中查找单词“linuxtechi”
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# grep linuxtechi /etc/passwd
+ linuxtechi:x:1000:1000:linuxtechi,,,:/home/linuxtechi:/bin/bash
+ root@Linux-world:~#
+
+###例2 在多个文件中查找模式。###
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# grep linuxtechi /etc/passwd /etc/shadow /etc/gshadow
+ /etc/passwd:linuxtechi:x:1000:1000:linuxtechi,,,:/home/linuxtechi:/bin/bash
+ /etc/shadow:linuxtechi:$6$DdgXjxlM$4flz4JRvefvKp0DG6re:16550:0:99999:7:::/etc/gshadow:adm:*::syslog,linuxtechi
+ /etc/gshadow:cdrom:*::linuxtechi
+ /etc/gshadow:sudo:*::linuxtechi
+ /etc/gshadow:dip:*::linuxtechi
+ /etc/gshadow:plugdev:*::linuxtechi
+ /etc/gshadow:lpadmin:!::linuxtechi
+ /etc/gshadow:linuxtechi:!::
+ /etc/gshadow:sambashare:!::linuxtechi
+ root@Linux-world:~#
+
+###例3 使用-l参数列出包含指定模式的文件的文件名。###
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# grep -l linuxtechi /etc/passwd /etc/shadow /etc/fstab /etc/mtab
+ /etc/passwd
+ /etc/shadow
+ root@Linux-world:~#
+
+###例4 使用-n参数,在文件中查找指定模式并显示匹配行的行号###
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# grep -n linuxtechi /etc/passwd
+ 39:linuxtechi:x:1000:1000:linuxtechi,,,:/home/linuxtechi:/bin/bash
+ root@Linux-world:~#
+
+root@Linux-world:~# grep -n root /etc/passwd /etc/shadow
+
+
+
+###例5 使用-v参数输出不包含指定模式的行###
+
+输出/etc/passwd文件中所有不含单词“linuxtechi”的行
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# grep -v linuxtechi /etc/passwd
+
+
+
+###例6 使用 ^ 符号输出所有以某指定模式开头的行###
+
+Bash脚本将 ^ 符号视作特殊字符,用于指定一行或者一个单词的开始。例如输出/etc/passes文件中所有以“root”开头的行
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# grep ^root /etc/passwd
+ root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
+ root@Linux-world:~#
+
+###例7 使用 $ 符号输出所有以指定模式结尾的行。###
+
+输出/etc/passwd文件中所有以“bash”结尾的行。
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# grep bash$ /etc/passwd
+ root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
+ linuxtechi:x:1000:1000:linuxtechi,,,:/home/linuxtechi:/bin/bash
+ root@Linux-world:~#
+
+Bash脚本将美元($)符号视作特殊字符,用于指定一行或者一个单词的结尾。
+
+###例8 使用 -r 参数递归地查找特定模式###
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# grep -r linuxtechi /etc/
+ /etc/subuid:linuxtechi:100000:65536
+ /etc/group:adm:x:4:syslog,linuxtechi
+ /etc/group:cdrom:x:24:linuxtechi
+ /etc/group:sudo:x:27:linuxtechi
+ /etc/group:dip:x:30:linuxtechi
+ /etc/group:plugdev:x:46:linuxtechi
+ /etc/group:lpadmin:x:115:linuxtechi
+ /etc/group:linuxtechi:x:1000:
+ /etc/group:sambashare:x:131:linuxtechi
+ /etc/passwd-:linuxtechi:x:1000:1000:linuxtechi,,,:/home/linuxtechi:/bin/bash
+ /etc/passwd:linuxtechi:x:1000:1000:linuxtechi,,,:/home/linuxtechi:/bin/bash
+ ............................................................................
+
+上面的命令将会递归的在/etc目录中查找“linuxtechi”单词
+
+###例9 使用 grep 查找文件中所有的空行
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# grep ^$ /etc/shadow
+ root@Linux-world:~#
+
+由于/etc/shadow文件中没有空行,所以没有任何输出
+
+###例10 使用 -i 参数查找模式###
+
+grep命令的-i参数在查找时忽略字符的大小写。
+
+我们来看一个例子,在paswd文件中查找“LinuxTechi”单词。
+
+ nextstep4it@localhost:~$ grep -i LinuxTechi /etc/passwd
+ linuxtechi:x:1001:1001::/home/linuxtechi:/bin/bash
+ nextstep4it@localhost:~$
+
+###例11 使用 -e 参数查找多个模式###
+
+例如,我想在一条grep命令中查找‘linuxtechi’和‘root’单词,使用-e参数,我们可以查找多个模式。
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# grep -e "linuxtechi" -e "root" /etc/passwd
+ root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
+ linuxtechi:x:1000:1000:linuxtechi,,,:/home/linuxtechi:/bin/bash
+ root@Linux-world:~#
+
+###例12 使用 -f 用文件指定待查找的模式###
+
+首先,在当前目录中创建一个搜索模式文件“grep_pattern”,我想文件中输入的如下内容。
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# cat grep_pattern
+ ^linuxtechi
+ root
+ false$
+ root@Linux-world:~#
+
+现在,试试使用grep_pattern文件进行搜索
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# grep -f grep_pattern /etc/passwd
+
+
+
+###例13 使用 -c 参数计算模式匹配到的数量###
+
+继续上面例子,我们在grep命令中使用-c命令计算匹配指定模式的数量
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# grep -c -f grep_pattern /etc/passwd
+ 22
+ root@Linux-world:~#
+
+###例14 输出匹配指定模式行的前或者后面N行###
+
+a)使用-B参数输出匹配行的前4行
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# grep -B 4 "games" /etc/passwd
+
+
+
+b)使用-A参数输出匹配行的后4行
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# grep -A 4 "games" /etc/passwd
+
+
+
+c)使用-C参数输出匹配行的前后各4行
+
+ root@Linux-world:~# grep -C 4 "games" /etc/passwd
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/linux-grep-command-with-14-different-examples/
+
+作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
+译者:[cvsher](https://github.com/cvsher)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/
diff --git a/published/20150521 Will Ubuntu Linux Hit 200 Million Users This Year.md b/published/20150521 Will Ubuntu Linux Hit 200 Million Users This Year.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e06a6e98bb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20150521 Will Ubuntu Linux Hit 200 Million Users This Year.md
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+Ubuntu会在今年达到2亿用户么?
+================================================================================
+距离Mark Shuttleworth表达他的目标“在4年内Ubuntu的用户达到2亿”已经过去了四年零两周。尽管Ubuntu的用户数量在过去的四年中一直在上升,但这个目标目前并未实现,并且看起来不会在今年年底实现。
+
+那是2011年5月在[UDS 布达佩斯][1],Shuttleworth表示Ubuntu将在4年内达到2亿用户。
+
+
+
+上一次我听到Ubuntu有“1千万”用户,但是并没有任何可靠的报道表明Ubuntu的用户数接近2亿。来自Valve最近的统计表明相比于Windows和OS X的用户[使用Linux的游戏用户的比重少于1%][2]。大多数基于Web计量和其他统计方式的数据倾向于表明Linux的用户总数只占很少的部分。
+
+撇开桌面版不谈,Ubuntu在过去的四年来至少在云和服务器部署方面得到了大量的占有率,并且被证明是Red Hat Enterprise的有力竞争者。Ubuntu还证明了它对基于ARM的硬件十分友好。当Mark在四年前提出他的目标时,他可能考虑到Ubuntu Phone/Touch会比目前的状况更好。可是Ubuntu Phone/Touch目前仅仅在欧洲和[中国][3]可用,并且[Ubuntu Touch软件依旧在成熟的路上][4],[仍需要大量的关键应用程序方面的工作][5]等。
+
+
+
+距离Canonical宣布[Ubuntu不久将登陆5%的PC][6]也已过去了3年。5%的目标是全球的PC装机量,但哪怕再过3年,我依旧很难相信这个目标会实现。至少在美国和欧洲,我仍难以在实体店看到Ubuntu作为预装的系统,主要的网络零售商/OEM厂商仍倾向于在特定的PC型号中提供Linux,比如Chrome OS、Android设备。
+
+另一个由开源社区提出的高傲地、落空的目标便是[GNOME将在2010年占有全球桌面市场10%的份额][7]。五年了,没有任何迹象表明他们接近了那10%的里程碑。
+
+在今天,您认为Ubuntu用户有多少呢?在未来的几年里,Ubuntu(或者Linux)的用户会有多大增长呢?通过评论来与我们分享您的想法吧。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=2015-200-Million-Goal-Retro
+
+作者:[Michael Larabel][a]
+译者:[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.michaellarabel.com/
+[1]:http://www.phoronix.com/vr.php?view=16002
+[2]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Steam-April-2015-1-Drop
+[3]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Ubuntu-MX4-In-China
+[4]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Ubuntu-Calculator-Reboot
+[5]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTgzOTM
+[6]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTA5ODM
+[7]:https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Nzg1Mw
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/share/20141013 Compact Text Editors Great for Remote Editing and Much More.md b/sources/share/20141013 Compact Text Editors Great for Remote Editing and Much More.md
index 21b0756b9a..3cdb43d879 100644
--- a/sources/share/20141013 Compact Text Editors Great for Remote Editing and Much More.md
+++ b/sources/share/20141013 Compact Text Editors Great for Remote Editing and Much More.md
@@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
-wyangsun翻译中
Compact Text Editors Great for Remote Editing and Much More
================================================================================
A text editor is software used for editing plain text files. This type of software has many different uses including modifying configuration files, writing programming language source code, jotting down thoughts, or even making a grocery list. Given that editors can be used for such a diverse range of activities, it is worth spending the time finding an editor that best suites your preferences.
diff --git a/sources/share/20150225 Install Google's Material Design Inspired GTK And Icon Theme Paper in Linux.md b/sources/share/20150225 Install Google's Material Design Inspired GTK And Icon Theme Paper in Linux.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 33aa731843..0000000000
--- a/sources/share/20150225 Install Google's Material Design Inspired GTK And Icon Theme Paper in Linux.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
-Install Google’s Material Design Inspired GTK And Icon Theme Paper in Linux
-================================================================================
-
-
-[Paper][1] is a new upcoming GTK and icon theme inspired by Google’s [Material design][2] guidelines. It is developed by Sam Hewitt, the man behind [Moka Project][3]. Moka has always been in the list of [best themes for Ubuntu][4] and looking at Paper, I can say that once it is developed completely, it will surely be listed as one of the [best GTK themes][5].
-
-Yes, you heard it right. The theme is still under development. Therefore I suggest that if you want to install Paper theme in Ubuntu or any other Linux distributions, do it only for experimentation purpose. You may see some broken icons here and there but the over all experience is nice.
-
-### Install Paper theme in Ubuntu based distributions via PPA ###
-
-Sam has a dedicated PPA for Ubuntu based distributions. I recommend that you use this PPA instead of downloading the theme because you’ll be getting the updates on the themes regularly. This PPA is available for Ubuntu 15.04, Ubuntu 14.10, Ubuntu 14.04, Elementary OS Freya, Elementary OS Luna, Linux Mint 17, Linux Mint 16 and other Linux distributions based on Ubuntu.
-
-Open a terminal and use the following commands:
-
- sudo add-apt-repository ppa:snwh/pulp
- sudo apt-get update
- sudo apt-get install paper-gtk-theme paper-icon-theme
-
-### Download Paper GTK and icon theme ###
-
-If you do not want to use the PPA, you can download the themes and icons manually. As I said previously, you won’t get the updates automatically this way.
-
-- [Download Paper icon themes][6]
-- [Download Paper GTK themes][7]
-
-#### Using Paper themes and icons ####
-
-I hope that you know how to change or install themes in your respective Linux distributions. If you are not unaware of it, below are few tutorials that could help you to install new themes:
-
-- [How to change themes in Ubuntu Unity][8]
-- [How to change themes in GNOME Shell][9]
-- [How to change themes in Linux Mint][10]
-- [How to change theme in Elementary OS Freya][11]
-
-#### Here is what Paper theme looks like ####
-
-Since I am using [Elementary OS Freya][12] these days, here are some of the screenshots of how Paper theme and icons look like in Elementary OS Freya. I have used a wallpaper with Material design look so that it blends well with the icon and themes.
-
-
-
-
-
-How do you find this Material design inspired theme? If you did use it, do share the screenshot of your desktop with rest of us here.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://itsfoss.com/install-paper-theme-linux/
-
-作者:[Abhishek][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
-[1]:http://snwh.org/paper/
-[2]:http://www.google.fr/design/spec/material-design/introduction.html
-[3]:http://mokaproject.com/moka-icon-theme/
-[4]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
-[5]:http://itsfoss.com/gnome-shell-themes-ubuntu-1404/
-[6]:https://github.com/snwh/paper-icon-theme
-[7]:https://github.com/snwh/paper-gtk-theme
-[8]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-install-themes-in-ubuntu-13-10/
-[9]:http://itsfoss.com/install-switch-themes-gnome-shell/
-[10]:http://itsfoss.com/install-icon-linux-mint/
-[11]:http://itsfoss.com/install-themes-icons-elementary-os-freya/
-[12]:http://itsfoss.com/tag/elementary-os-freya/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/share/20150323 Square 2.0 Icon Pack Is Twice More Beautiful.md b/sources/share/20150323 Square 2.0 Icon Pack Is Twice More Beautiful.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b0e5afbf8b..0000000000
--- a/sources/share/20150323 Square 2.0 Icon Pack Is Twice More Beautiful.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,56 +0,0 @@
-Square 2.0 Icon Pack Is Twice More Beautiful
-================================================================================
-
-
-Elegant, modern looking [Square icon theme][1] has recently been upgraded to version 2.0, which makes it more beautiful than ever. Square icon packs are compatible with all major desktop environments such as **Unity, GNOME, KDE, MATE** etc. Which means that you can use them for all popular Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, Fedora, Linux Mint, elementary OS etc. The vastness of this icon pack can be estimated from the fact it contains over 15,000 icons.
-
-### Install and use Square icon pack 2.0 in Linux ###
-
-There are two variants of Square icons, dark and light. Based on your preference, you can choose either of the two. For experimentation sake, I would advise you to download both variants of the icon theme.
-
-You can download the icon pack from the link below. The files are stored in Google Drive, so don’t be suspicious if you don’t see a standard website like [SourceForge][2].
-
-- [Square Dark Icons][3]
-- [Square Light Icons][4]
-
-To use the icon theme, extract the downloaded files in ~/.icons directory. If this doesn’t exist, create it. Once you have the files in the right place, based on your desktop environment, use a tool to change the icon theme. I have written some small tutorials in the past on this topic. Feel free to refer to them if you need further help:
-
-- [How to change themes in Ubuntu Unity][5]
-- [How to change themes in GNOME Shell][6]
-- [How to change themes in Linux Mint][7]
-- [How to change theme in Elementary OS Freya][8]
-
-### Give it a try ###
-
-Here is what my Ubuntu 14.04 looks like with Square icons. I am using [Ubuntu 15.04 default wallpaper][9] in the background.
-
-
-
-A quick look at several icons in the Square theme:
-
-
-
-How do you find it? Do you think it can be considered as one of the [best icon themes for Ubuntu 14.04][10]? Do share your thoughts and stay tuned for more articles on customizing your Linux desktop.
-
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://itsfoss.com/square-2-0-icon-pack-linux/
-
-作者:[Abhishek][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
-[1]:http://gnome-look.org/content/show.php/Square?content=163513
-[2]:http://sourceforge.net/
-[3]:http://gnome-look.org/content/download.php?content=163513&id=1&tan=62806435
-[4]:http://gnome-look.org/content/download.php?content=163513&id=2&tan=19789941
-[5]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-install-themes-in-ubuntu-13-10/
-[6]:http://itsfoss.com/install-switch-themes-gnome-shell/
-[7]:http://itsfoss.com/install-icon-linux-mint/
-[8]:http://itsfoss.com/install-themes-icons-elementary-os-freya/
-[9]:http://itsfoss.com/default-wallpapers-ubuntu-1504/
-[10]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/share/20150407 10 Truly Amusing Easter Eggs in Linux.md b/sources/share/20150407 10 Truly Amusing Easter Eggs in Linux.md
index 413d50d6d6..3ab7f47b79 100644
--- a/sources/share/20150407 10 Truly Amusing Easter Eggs in Linux.md
+++ b/sources/share/20150407 10 Truly Amusing Easter Eggs in Linux.md
@@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
-KevinSJ translating
10 Truly Amusing Easter Eggs in Linux
================================================================================

diff --git a/sources/share/20150429 Synfig Studio 1.0--Open Source Animation Gets Serious.md b/sources/share/20150429 Synfig Studio 1.0--Open Source Animation Gets Serious.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 70f76b418c..0000000000
--- a/sources/share/20150429 Synfig Studio 1.0--Open Source Animation Gets Serious.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
-Synfig Studio 1.0 — Open Source Animation Gets Serious
-================================================================================
-
-
-**A brand new version of the free, open-source 2D animation software Synfig Studio is now available to download. **
-
-The first release of the cross-platform software in well over a year, Synfig Studio 1.0 builds on its claim of offering “industrial-strength solution for creating film-quality animation” with a suite of new and improved features.
-
-Among them is an improved user interface that the project developers say is ‘easier’ and ‘more intuitive’ to use. The client adds a new **single-window mode** for tidy working and has been **reworked to use the latest GTK3 libraries**.
-
-On the features front there are several notable changes, including the addition of a fully-featured bone system.
-
-This **joint-and-pivot ‘skeleton’ framework** is well suited to 2D cut-out animation and should prove super efficient when coupled with the complex deformations new to this release, or used with Synfig’s popular ‘automatic interpolated keyframes’ (read: frame-to-frame morphing).
-
-注:youtube视频
-<iframe width="750" height="422" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/M8zW1qCq8ng?feature=oembed"></iframe>
-
-New non-destructive cutout tools, friction effects and initial support for full frame-by-frame bitmap animation, may help unlock the creativity of open-source animators, as might the addition of a sound layer for syncing the animation timeline with a soundtrack!
-
-### Download Synfig Studio 1.0 ###
-
-Synfig Studio is not a tool suited for everyone, though the latest batch of improvements in this latest release should help persuade some animators to give the free animation software a try.
-
-If you want to find out what open-source animation software is like for yourself, you can grab an installer for Ubuntu for the latest release direct from the project’s Sourceforge page using the links below.
-
-- [Download Synfig 1.0 (64bit) .deb Installer][1]
-- [Download Synfig 1.0 (32bit) .deb Installer][2]
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/synfig-studio-new-release-features
-
-作者:[oey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
-[1]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/synfig/files/releases/1.0/linux/synfigstudio_1.0_amd64.deb/download
-[2]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/synfig/files/releases/1.0/linux/synfigstudio_1.0_x86.deb/download
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/share/20150429 What are good command line HTTP clients.md b/sources/share/20150429 What are good command line HTTP clients.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d809be1a06..0000000000
--- a/sources/share/20150429 What are good command line HTTP clients.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,110 +0,0 @@
-What are good command line HTTP clients?
-================================================================================
-The whole is greater than the sum of its parts is a very famous quote from Aristotle, a Greek philosopher and scientist. This quote is particularly pertinent to Linux. In my view, one of Linux's biggest strengths is its synergy. The usefulness of Linux doesn't derive only from the huge raft of open source (command line) utilities. Instead, it's the synergy generated by using them together, sometimes in conjunction with larger applications.
-
-The Unix philosophy spawned a "software tools" movement which focused on developing concise, basic, clear, modular and extensible code that can be used for other projects. This philosophy remains an important element for many Linux projects.
-
-Good open source developers writing utilities seek to make sure the utility does its job as well as possible, and work well with other utilities. The goal is that users have a handful of tools, each of which seeks to excel at one thing. Some utilities work well independently.
-
-This article looks at 3 open source command line HTTP clients. These clients let you download files off the internet from a command line. But they can also be used for many more interesting purposes such as testing, debugging and interacting with HTTP servers and web applications. Working with HTTP from the command-line is a worthwhile skill for HTTP architects and API designers. If you need to play around with an API, HTTPie and cURL will be invaluable.
-
-----------
-
-
-
-
-
-HTTPie (pronounced aych-tee-tee-pie) is an open source command line HTTP client. It is a a command line interface, cURL-like tool for humans.
-
-The goal of this software is to make CLI interaction with web services as human-friendly as possible. It provides a simple http command that allows for sending arbitrary HTTP requests using a simple and natural syntax, and displays colorized output. HTTPie can be used for testing, debugging, and generally interacting with HTTP servers.
-
-#### Features include: ####
-
-- Expressive and intuitive syntax
-- Formatted and colorized terminal output
-- Built-in JSON support
-- Forms and file uploads
-- HTTPS, proxies, and authentication
-- Arbitrary request data
-- Custom headers
-- Persistent sessions
-- Wget-like downloads
-- Python 2.6, 2.7 and 3.x support
-- Linux, Mac OS X and Windows support
-- Plugins
-- Documentation
-- Test coverage
-
-- Website: [httpie.org][1]
-- Developer: Jakub Roztočil
-- License: Open Source
-- Version Number: 0.9.2
-
-----------
-
-
-
-
-
-cURL is an open source command line tool for transferring data with URL syntax, supporting DICT, FILE, FTP, FTPS, GOPHER, HTTP, HTTPS, IMAP, IMAPS, LDAP, LDAPS, POP3, POP3S, RTMP, RTSP, SCP, SFTP, SMTP, SMTPS, TELNET and TFTP.
-
-curl supports SSL certificates, HTTP POST, HTTP PUT, FTP uploading, HTTP form based upload, proxies, cookies, user+password authentication (Basic, Digest, NTLM, Negotiate, kerberos...), file transfer resume, proxy tunneling and a busload of other useful tricks.
-
-#### Features include: ####
-
-- Config file support
-- Multiple URLs in a single command line
-- Range "globbing" support: [0-13], {one,two,three}
-- Multiple file upload on a single command line
-- Custom maximum transfer rate
-- Redirectable stderr
-- Metalink support
-
-- Website: [curl.haxx.se][2]
-- Developer: Daniel Stenberg
-- License: MIT/X derivate license
-- Version Number: 7.42.0
-
-----------
-
-
-
-
-
-Wget is open source software that retrieves content from web servers. Its name is derived from World Wide Web and get. It supports HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP protocols, as well as retrieval through HTTP proxies.
-
-Wget can follow links in HTML pages and create local versions of remote web sites, fully recreating the directory structure of the original site. This is known as "recursive downloading."
-
-Wget has been designed for robustness over slow or unstable network connections.
-
-Features include:
-
-- Resume aborted downloads, using REST and RANGE
-- Use filename wild cards and recursively mirror directories
-- NLS-based message files for many different languages
-- Optionally converts absolute links in downloaded documents to relative, so that downloaded documents may link to each other locally
-- Runs on most UNIX-like operating systems as well as Microsoft Windows
-- Supports HTTP proxies
-- Supports HTTP cookies
-- Supports persistent HTTP connections
-- Unattended / background operation
-- Uses local file timestamps to determine whether documents need to be re-downloaded when mirroring
-
-- Website: [www.gnu.org/software/wget/][3]
-- Developer: Hrvoje Niksic, Gordon Matzigkeit, Junio Hamano, Dan Harkless, and many others
-- License: GNU GPL v3
-- Version Number: 1.16.3
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20150425174537249/HTTPclients.html
-
-作者:Frazer Kline
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://httpie.org/
-[2]:http://curl.haxx.se/
-[3]:https://www.gnu.org/software/wget/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/share/20150527 3 Open Source Python Shells.md b/sources/share/20150527 3 Open Source Python Shells.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c510096670
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/share/20150527 3 Open Source Python Shells.md
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
+3 Open Source Python Shells
+================================================================================
+Python is a high-level, general-purpose, structured, powerful, open source programming language that is used for a wide variety of programming tasks. It features a fully dynamic type system and automatic memory management, similar to that of Scheme, Ruby, Perl, and Tcl, avoiding many of the complexities and overheads of compiled languages. The language was created by Guido van Rossum in 1991, and continues to grow in popularity.
+
+Python is a very useful and popular computer language. One of the benefits of using an interpreted language such as Python is exploratory programming with its interactive shell. You can try out code without having to write a script. But there are limitations with the Python shell. Fortunately, there are some excellent alternative Python shells that extend on the basic shell. They each offer an excellent interactive Python experience.
+
+----------
+
+### bpython ###
+
+
+
+bpython is a fancy interface to the Python interpreter for Linux, BSD, OS X and Windows.
+
+The idea is to provide the user with all the features in-line, much like modern IDEs, but in a simple, lightweight package that can be run in a terminal window.
+
+bpython doesn't seek to create anything new or groundbreaking. Instead, it brings together a few neat ideas and focuses on practicality and usefulness.
+
+Features include:
+
+- In-line syntax highlighting - uses Pygments for lexing the code as you type, and colours appropriately
+- Readline-like autocomplete with suggestions displayed as you type
+- Expected parameter list for any Python function - seeks to display a list of parameters for any function you call
+- "Rewind" function to pop the last line of code from memory and re-evaluate
+- Send the code you've entered off to a pastebin
+- Save the code you've entered to a file
+- Auto-indentation
+- Python 3 support
+
+- Website: [www.bpython-interpreter.org][1]
+- Developer: Bob Farrell and contributors
+- License: MIT License
+- Version Number: 0.14.1
+
+----------
+
+### IPython ###
+
+
+
+IPython is an enhanced interactive Python shell. It provides a rich toolkit to help you make the most out of using Python interactively.
+
+IPython can be used as a replacement for the standard Python shell, or it can be used as a complete working environment for scientific computing (like Matlab or Mathematica) when paired with the standard Python scientific and numerical tools. It supports dynamic object introspections, numbered input/output prompts, a macro system, session logging, session restoring, complete system shell access, verbose and colored traceback reports, auto-parentheses, auto-quoting, and is embeddable in other Python programs.
+
+Features include:
+
+- Powerful interactive shells (terminal and Qt-based)
+- A browser-based notebook with support for code, rich text, mathematical expressions, inline plots and other rich media
+- Support for interactive data visualization and use of GUI toolkits
+- Flexible, embeddable interpreters to load into your own projects
+- Easy to use, high performance tools for parallel computing
+
+- Website: [ipython.org][2]
+- Developer: The IPython Development Team
+- License: BSD
+- Version Number: 3.1
+
+----------
+
+### DreamPie ###
+
+
+
+DreamPie is a Python shell which is designed to be reliable and fun.
+
+DreamPie can use just about any Python interpreter (Jython, IronPython, PyPy).
+
+Features include:
+
+- New concept for an interactive shell: the window is divided into the history box, which lets you view previous commands and their output, and the code box, where you write your code. This allows you to edit any amount of code, just like in your favorite editor, and execute it when it's ready. You can also copy code from anywhere, edit it and run it instantly
+- The Copy code only command will copy the code you want to keep, so you can save it in a file. The code is already formatted nicely with a four-space indentation
+- Automatic completion of attributes and file names
+- Automatically displays function arguments and documentation
+- Keeps your recent results in the result history, for later use
+- Can automatically fold long outputs, so you can concentrate on what's important
+- Save the history of the session as an HTML file, for future reference. You can then load the history file into DreamPie, and quickly redo previous commands
+- Automatically adds parentheses and optionally quotes when you press space after functions and methods. For example, type execfile fn and get execfile("fn")
+- Supports interactive plotting with matplotlib
+- Xupport for Python 2.5, Python 2.6, Python 3.1, Jython 2.5, IronPython 2.6, and PyPy
+- Extremely fast and responsive.
+
+- Website: [www.dreampie.org][3]
+- Developer: Noam Yorav-Raphael
+- License: GNU GPL v3
+- Version Number: 1.2.1
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20150523032756576/PythonShells.html
+
+作者:Frazer Kline
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.bpython-interpreter.org/
+[2]:http://ipython.org/
+[3]:http://www.dreampie.org/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/share/20150527 Animated Wallpaper Adds Live Backgrounds To Linux Distros.md b/sources/share/20150527 Animated Wallpaper Adds Live Backgrounds To Linux Distros.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..92eff36326
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/share/20150527 Animated Wallpaper Adds Live Backgrounds To Linux Distros.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+Animated Wallpaper Adds Live Backgrounds To Linux Distros
+================================================================================
+**We know a lot of you love having a stylish Ubuntu desktop to show off.**
+
+
+
+Live Wallpaper
+
+And as Linux makes it so easy to create a stunning workspace with a minimal effort, that’s understandable!
+
+Today, we’re highlighting — [re-highlighting][2] for those of you with long memories — a free, open-source tool that can add extra bling your OS screenshots and screencasts.
+
+It’s called **Live Wallpaper** and (as you can probably guess) it will replace the standard static desktop background with an animated alternative powered by OpenGL.
+
+And the best bit: it can be installed in Ubuntu very easily.
+
+### Animated Wallpaper Themes ###
+
+
+
+Live Wallpaper is not the only app of this type, but it is one of the the best.
+
+It comes with a number of different themes out of the box.
+
+These range from the subtle (‘noise’) to frenetic (‘nexus’), and caters to everything in between. There’s even the obligatory clock wallpaper inspired by the welcome screen of the Ubuntu Phone:
+
+- Circles — Clock inspired by Ubuntu Phone with ‘evolving circle’ aura
+- Galaxy — Spinning galaxy that can be resized/repositioned
+- Gradient Clock — A polar clock overlaid on basic gradient
+- Nexus — Brightly colored particles fire across screen
+- Noise — A bokeh design similar to the iOS dynamic wallpaper
+- Photoslide — Grid of photos from folder (default ~/Photos) animate in/out
+
+Live Wallpaper is **fully open-source** so there’s nothing to stop imaginative artists with the know-how (and patience) from creating some slick themes of their own.
+
+### Settings & Features ###
+
+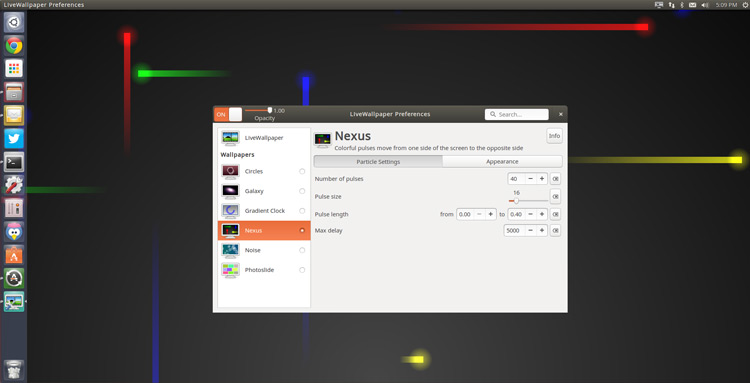
+
+Each theme can be configured or customised in some way, though certain themes have more options than others.
+
+For example, in Nexus (pictured above) you can change the number and colour of the the pulse particles, their size, and their frequency.
+
+The preferences app also provides a set of **general options** that will apply to all themes. These include:
+
+- Setting live wallpaper to run on log-in
+- Setting a custom background that the animation sits on
+- Adjusting the FPS (including option to show FPS on screen)
+- Specifying the multi-monitor behaviour
+
+With so many options available it should be easy to create a background set up that suits you.
+
+### Drawbacks ###
+
+#### No Desktop Icons ####
+
+You can’t add, open or edit files or folders on the desktop while Live Wallpaper is ‘On’.
+
+The Preferences app does list an option that will, supposedly, let you do this. It may work on really older releases but in our testing, on Ubuntu 14.10, it does nothing.
+
+One workaround that seems to work for some users of the app on Ubuntu is setting a .png image as the custom background. It doesn’t have to be a transparent .png, simply a .png.
+
+#### Resource Usage ####
+
+Animated wallpapers use more system resources than standard background images.
+
+We’re not talking about 50% load at all times —at least not with this app in our testing— but those on low-power devices and laptops will want to use apps like this cautiously. Use a [system monitoring tool][2] to keep an eye on CPU and GPU load.
+
+#### Quitting the app ####
+
+The biggest “bug” for me is the absolute lack of “quit” option.
+
+Sure, the animated wallpaper can be turned off from the Indicator Applet and the Preferences tool but quitting the app entirely, quitting the indicator applet? Nope. To do that I have to use the ‘pkill livewallpaper’ command in the Terminal.
+
+### How to Install Live Wallpaper in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS + ###
+
+
+
+To install Live Wallpaper in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS and above you will first need to add the official PPA for the app to your Software Sources.
+
+The quickest way to do this is using the Terminal:
+
+ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:fyrmir/livewallpaper-daily
+
+ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install livewallpaper
+
+You should also install the indicator applet, which lets you quickly and easily turn on/off the animated wallpaper and switch theme from the menu area, and the GUI settings tool so that you can configure each theme based on your tastes.
+
+ sudo apt-get install livewallpaper-config livewallpaper-indicator
+
+When everything has installed you will be able to launch the app and its preferences tool from the Unity Dash.
+
+
+
+Annoyingly, the Indicator Applet won’t automatically open after you install it. It does add itself to the start up list, so a quick log out > log in will get it to show.
+
+### Summary ###
+
+If you fancy breathing life into a dull desktop, give it a spin — and let us know what you think of it and what animated wallpapers you’d love to see added!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/05/animated-wallpaper-adds-live-backgrounds-to-linux-distros
+
+作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
+[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2012/11/live-wallpaper-for-ubuntu
+[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2011/11/5-system-monitoring-tools-for-ubuntu
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140818 Upstream and Downstream--why packaging takes time.md b/sources/talk/20140818 Upstream and Downstream--why packaging takes time.md
deleted file mode 100644
index fc1c708b14..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/20140818 Upstream and Downstream--why packaging takes time.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
-Upstream and Downstream: why packaging takes time
-================================================================================
-Here in the KDE office in Barcelona some people spend their time on purely upstream KDE projects and some of us are primarily interested in making distros work which mean our users can get all the stuff we make. I've been asked why we don't just automate the packaging and go and do more productive things. One view of making on a distro like Kubuntu is that its just a way to package up the hard work done by others to take all the credit. I don't deny that, but there's quite a lot to the packaging of all that hard work, for a start there's a lot of it these days.
-
-"KDE" used to be released once every nine months or less frequently. But yesterday I released the [first bugfix update to Plasma][1], to make that happen I spent some time on Thursday with David making the [first update to Frameworks 5][2]. But Plasma 5 is still a work in progress for us distros, let's not forget about [KDE SC 4.13.3][3] which Philip has done his usual spectacular job of updating in the 14.04 LTS archive or [KDE SC 4.14 betas][4] which Scarlett has been packaging for utopic and backporting to 14.04 LTS. KDE SC used to be 20 tars, now it's 169 and over 50 langauge packs.
-
-### Patches ###
-
-If we were packaging it without any automation as used to be done it would take an age but of course we do automate the repetative tasks, the [KDE SC 4.13.97 status][5] page shows all the packages and highlights obvious problems. But with 169 tars even running the automated script takes a while, then you have to fix any patches that no longer apply. We have [policies][6] to disuade having patches, any patches should be upstream in KDE or on their way upstream, but sometimes it's unavoidable that we have some to maintain which often need small changes for each upstream release.
-
-### Symbols ###
-
-Much of what we package are libraries and if one small bit changes in the library, any applications which use that library will crash. This is ABI and the rules for [binary compatibility][7] in C++ are nuts. Not infrequently someone in KDE will alter a library ABI without realising. So we maintain symbol files to list all the symbols, these can often feel like more trouble than they're worth because they need updated when a new version of GCC produces different symbols or when symbols disappear and on investigation they turn out to be marked private and nobody will be using them anyway, but if you miss a change and apps start crashing as nearly happened in KDE PIM last week then people get grumpy.
-
-### Copyright ###
-
-Debian, and so Ubuntu, documents the copyright licence of every files in every package. This is a very slow and tedious job but it's important that it's done both upstream and downstream because it you don't people won't want to use your software in a commercial setting and at worst you could end up in court. So I maintain the [licensing policy][8] and not infrequently have to fix bits which are incorrectly or unclearly licenced and answer questions such as today I was reviewing whether a kcm in frameworks had to be LGPL licenced for Eike. We write a copyright file for every package and again this can feel like more trouble than its worth, there's no easy way to automate it but by some readings of the licence texts it's necessary to comply with them and it's just good practice. It also means that if someone starts making claims like requiring licencing for already distributed binary packages I'm in an informed position to correct such nonsense.
-
-### Descriptions ###
-
-When we were packaging KDE Frameworks from scratch we had to find a descirption of each Framework. Despite policies for metadata some were quite underdescribed so we had to go and search for a sensible descirption for them. Infact not infrequently we'll need to use a new library which doesn't even have a sensible paragraph describing what it does. We need to be able to make a package show something of a human face.
-
-### Multiarch ###
-
-A recent addition to the world of .deb packaging is [MultiArch][9] which allows i386 packages to be installed on amd64 computers as well as some even more obscure combinations (powerpc on ppcel64 anyone?). This lets you run Skype on your amd64 computer without messy cludges like the ia32-libs package. However it needs quite a lot of attention from packagers of libraries marking which packages are multiarch, which depend on other multiarch or arch independent packages and even after packaging KDE Frameworks I'm not entirely comfortable with doing it.
-
-### Splitting up Packages ###
-
-We spend lots of time splitting up packages. When say Calligra gets released it's all in one big tar but you don't want all of it on your system because you just want to write a letter in Calligra Words and Krita has lots of image and other data files which take up lots of space you don't care for. So for each new release we have to work out which of the installed files go into which .deb package. It takes time and even worse occationally we can get it wrong but if you don't want heaps of stuff on your computer you don't need then it needs to be done. It's also needed for library upgrades, if there's a new version of libfoo and not all the programs have been ported to it then you can install libfoo1 and libfoo2 on the same system without problems. That's not possible with distros which don't split up packages.
-
-One messy side effect of this is that when a file moves from one .deb to another .deb made by the same sources, maybe Debian chose to split it another way and we want to follow them, then it needs a Breaks/Replaces/Conflicts added. This is a pretty messy part of .deb packaging, you need to specify which version it Breaks/Replaces/Conflicts and depending on the type of move you need to specify some combination of these three fields but even experienced packages seem to be unclear on which. And then if a backport (with files in original places) is released which has a newer version than the version you specify in the Breaks/Replaces/Conflicts it just refuses to install and stops half way through installing until a new upload is made which updates the Breaks/Replaces/Conflicts version in the packaging. I'd be interested in how this is solved in the RPM world.
-
-### Debian Merges ###
-
-Ubuntu is forked from Debian and to piggy back on their work (and add our own bugs while taking the credit) we merge in Debian's packaging at the start of each cycle. This is fiddly work involving going through the diff (and for patches that's often a diff of a diff) and changelog to work out why each alternation was made. Then we merge them together, it takes time and it's error prone but it's what allows Ubuntu to be one of the most up to date distros around even while much of the work gone into maintaining universe packages not part of some flavour has slowed down.
-
-### Stable Release Updates ###
-
-You have Kubuntu 14.04 LTS but you want more? You want bugfixes too? Oh but you want them without the possibility of regressions? Ubuntu has quite strict definition of what's allowed in after an Ubuntu release is made, this is because once upon a time someone uploaded a fix for X which had the side effect of breaking X on half the installs out there. So for any updates to get into the archive they can only be for certain packages with a track record of making bug fix releases without sneaking in new features or breaking bits. They need to be tested, have some time passed to allow for wider testing, be tested again using the versions compiled in Launchpad and then released. KDE makes bugfix releases of KDE SC every month and we update them in the latest stable and LTS releases as [4.13.3 was this week][10]. But it's not a process you can rush and will take a couple of weeks usually. That 4.13.3 update was even later then usual because we were busy with Plasma 5 and whatnot. And it's not perfect, a bug in Baloo did get through with 4.13.2. But it would be even worse if we did rush it.
-
-### Backports ###
-
-Ah but you want new features too? We don't allow in new features into the normal updates because they will have more chance of having regressions. That's why we make backports, either in the kubuntu-ppa/backports archive or in the ubuntu backports archive. This involves running the package through another automation script to change whever needs changed for the backport then compiling it all, testing it and releasing it. Maintaining and running that backport script is quite faffy so sending your thanks is always appreciated.
-
-We have an allowance to upload new bugfix (micro releases) of KDE SC to the ubuntu archive because KDE SC has a good track record of fixing things and not breaking them. When we come to wanting to update Plasma we'll need to argue for another allowance. One controvertial issue in KDE Frameworks is that there's no bugfix releases, only monthly releases with new features. These are unlikely to get into the Ubuntu archive, we can try to argue the case that with automated tests and other processes the quality is high enough, but it'll be a hard sell.
-
-### Crack of the Day ###
-
-Project Neon provides packages of daily builds of parts of KDE from Git. And there's weekly ISOs that are made from this too. These guys rock. The packages are monolithic and install in /opt to be able to live alongside your normal KDE software.
-
-### Co-installability ###
-
-You should be able to run KDELibs 4 software on a Plasma 5 desktop. I spent quite a bit of time ensuring this is possible by having no overlapping files in kdelibs/kde-runtime and kde frameworks and some parts of Plasma. This wasn't done primarily for Kubuntu, many of the files could have been split out into .deb packages that could be shared between KDELibs 4 and Plasma 5, but other disros which just installs packages in a monolithic style benefitted. Some projects like Baloo didn't ensure they were co-installable, fine for Kubuntu as we can separate the libraries that need to be coinstalled from the binaries, but other distros won't be so happy.
-
-### Automated Testing ###
-
-Increasingly KDE software comes with its own test suite. Test suites are something that has been late coming to free software (and maybe software in general) but now it's here we can have higher confidence that the software is bug free. We run these test suites as part of the package compilation process and not infrequently find that the test suite doesn't run, I've been told that it's not expected for packagers to use it in the past. And of course tests fail.
-
-### Obscure Architectures ###
-
-In Ubuntu we have some obscure architectures. 64-bit Arm is likely to be a useful platform in the years to come. I'm not sure why we care about 64-bit powerpc, I can only assume someone has paid Canonical to care about it. Not infrequently we find software compiles fine on normal PCs but breaks on these obscure platforms and we need to debug why they is. This can be a slow process on ARM which takes an age to do anything, or very slow where I don't even have access to a machine to test on, but it's all part of being part of a distro with many use-cases.
-
-### Future Changes ###
-
-At Kubuntu we've never shared infrstructure with Debian despite having 99% the same packaging. This is because Ubuntu to an extent defines itself as being the technical awesomeness of Debian with smoother processes. But for some time Debian has used git while we've used the slower bzr (it was an early plan to make Ubuntu take over the world of distributed revision control with Bzr but then Git came along and turned out to be much faster even if harder to get your head around) and they've also moved to team maintainership so at last we're planning [shared repositories][11]. That'll mean many changes in our scripts but should remove much of the headache of merges each cycle.
-
-There's also a proposal to [move our packaging to daily builds][12] so we won't have to spend a lot of time updating packaging at every release. I'm skeptical if the hassle of the infrastructure for this plus fixing packaging problems as they occur each day will be less work than doing it for each release but it's worth a try.
-
-### ISO Testing ###
-
-Every 6 months we make an Ubuntu release (which includes all the flavours of which Ubuntu [Unity] is the flagship and Kubuntu is the most handsome) and there's alphas and betas before that which all need to be tested to ensure they actually install and run. Some of the pain of this has reduced since we've done away with the alternative (text debian-installer) images but we're nowhere near where Ubuntu [Unity] or OpenSUSE is with OpenQA where there are automated installs running all the time in various setups and some magic detects problems. I'd love to have this set up.
-
-I'd welcome comments on how any workflow here can be improved or how it compares to other distributions. It takes time but in Kubuntu we have a good track record of contributing fixes upstream and we all are part of KDE as well as Kubuntu. As well as the tasks I list above about checking copyright or co-installability I do Plasma releases currently, I just saw Harald do a Phonon release and Scott's just applied for a KDE account for fixes to PyKDE. And as ever we welcome more people to join us, we're in #kubuntu-devel where free hugs can be found, and we're having a whole day of Kubuntu love at Akademy.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://blogs.kde.org/2014/08/13/upstream-and-downstream-why-packaging-takes-time
-
-作者:[Jonathan Riddell][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://blogs.kde.org/users/jriddell
-[1]:https://dot.kde.org/2014/08/12/first-bugfix-update-plasma-5
-[2]:https://dot.kde.org/2014/08/07/kde-frameworks-5.1
-[3]:http://www.kubuntu.org/news/kde-sc-4.13.3
-[4]:https://dot.kde.org/2014/07/18/kde-ships-july-updates-and-second-beta-applications-and-platform-414
-[5]:http://qa.kubuntu.co.uk/ninjas-status/build_status_4.13.97_utopic.html
-[6]:https://community.kde.org/Kubuntu/Policies
-[7]:https://techbase.kde.org/Policies/Binary_Compatibility_Issues_With_C++
-[8]:https://techbase.kde.org/Policies/Licensing_Policy
-[9]:https://help.ubuntu.com/community/MultiArch
-[10]:http://www.kubuntu.org/news/kde-sc-4.13.3
-[11]:http://lists.alioth.debian.org/pipermail/pkg-kde-talk/2014-August/001934.html
-[12]:https://lists.ubuntu.com/archives/kubuntu-devel/2014-August/008651.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20150205 GHOST--Another Security Bug Hits Linux, But is it That Bad.md b/sources/talk/20150205 GHOST--Another Security Bug Hits Linux, But is it That Bad.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 90923c1aae..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/20150205 GHOST--Another Security Bug Hits Linux, But is it That Bad.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
-GHOST: Another Security Bug Hits Linux, But is it That Bad?
-================================================================================
-> GHOST, a newly announced security vulnerability that affects Linux servers and other systems that use the open source glibc library, is not as dangerous to data privacy as the Shellshock or Heartbleed bugs.
-
-
-
-Heartbleed is not even a year behind us, and the open source world has been hit with another major security vulnerability in the form of [GHOST][1], which involves holes in the Linux glibc library. This time, though, the actual danger may not live up to the hype.
-
-The GHOST vulnerability, which was announced last week by security researchers at [Qualys][2], resides in the gethostbyname*() functions of the glibc library. glibc is one of the core building blocks of most Linux systems, and gethostbyname*(), which resolves domain names into IP addresses, is widely used in open source applications.
-
-Attackers can exploit the GHOST security hole to create a buffer overflow, making it possible to execute any kind of code they want and do all sorts of nasty things.
-
-All of the above suggests that GHOST is bad news indeed. Fortunately for the open source community, however, the actual risk appears small. As TrendMicro [points out][3], the bug that makes the exploit possible has been fixed in glibc since May 2013, meaning that any Linux servers or PCs running more recent versions of the software are safe from attack.
-
-In addition, gethostbyname*() has been superseded by newer glibc functions that can better handle modern networking environments. Those include ones that use the IPv6 protocol, which gethostbyname*() doesn't support. As a result, newer applications often don't use the gethostbyname*() functions, and are not at risk.
-
-And perhaps most importantly, there's currently no known way of executing GHOST attacks through the Web. That greatly reduces opportunities for using this vulnerability to steal the data of unsuspecting users or otherwise wreak havoc.
-
-All in all, then, GHOST doesn't seem like a vulnerability that will prove as serious as Heartbleed or Shellshock, two other recent security problems that affected widely used open source software.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/020415/ghost-another-security-bug-hits-linux-it-bad
-
-作者:[Christopher Tozzi][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://thevarguy.com/author/christopher-tozzi
-[1]:https://community.qualys.com/blogs/laws-of-vulnerabilities/2015/01/27/the-ghost-vulnerability
-[2]:http://qualys.com/
-[3]:http://blog.trendmicro.com/trendlabs-security-intelligence/not-so-spooky-linux-ghost-vulnerability/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20150310 FAQ--BSD.md b/sources/talk/20150310 FAQ--BSD.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 80f77ef656..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/20150310 FAQ--BSD.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
-FAQ: BSD
-================================================================================
-
-
-### Had history been slightly different, you’d be reading FreeBSD Voice today… ###
-
-#### So what’s the deal with this Birsa Seva Dal then? Isn’t it a political group in India? ####
-
-Very funny – you looked up the “BSD” disambiguation page on Wikipedia just to make that joke, didn’t you? Here we’re talking about the Berkeley Software Distribution, a family of operating systems that are much more widely used than you might think.
-
-#### Sorry, I couldn’t help myself. OK, so what’s the deal with these OSes? ####
-
-There are three main BSD operating systems in use today. They are based on Unix, they are open source, they tend to be used in server roles, but can also make good desktops and workstations as well. They run KDE, Firefox, LibreOffice, Apache, MySQL and pretty much any open source application you can name. They’re reliable, secure and support a lot of different hardware.
-
-#### Congratulations – you’ve just described GNU/Linux… ####
-
-True. Linux has all of the things I’ve just mentioned, and that’s why a lot of people never investigate BSD. In day-to-day usage, there isn’t a lot of difference between the BSD family and Linux, largely because they all have Unix underpinnings, and also because they share a lot of software. You could be logged into a remote machine, hacking some Python code in Vim, and checking your email in Mutt, and you wouldn’t know you were running BSD. Or you could be using an internet terminal in a cafe somewhere and not know it’s BSD.
-
-The biggest differences are in the development model and licence, and to understand this, we need to step back in time. The B in BSD refers to the University of California, Berkeley, which was a hotbed of open source Unix development back in the 1980s. As the 90s came, x86-based PCs were becoming popular and many people were interested in having a Unix-like OS on their home computers. A project called 386BSD was released in 1992 to provide just that.
-
-#### And where were all the Linux distributions at this time? ####
-
-Good question! You might know that one year before, Linus Torvalds had announced his kernel, which, when paired with the GNU project, formed a complete open source operating system. Linus had been following GNU’s own kernel (Hurd) and 386BSD, and said that had either of them been ready for daily use, he probably wouldn’t have created Linux. So the first few years of the 90s were tremendously lively for open source operating systems, and nobody was really sure which ones would succeed.
-
-Then it got messy for BSD. AT&T, the original developer of Unix, was trying to monetise its work on the operating system and claimed that BSD infringed its intellectual property rights. This culminated in a lawsuit in 1992 which severely held back BSD development. In the end, various chunks of the BSD source code had to be rewritten – while all this time, GNU/Linux was gaining features, stability and popularity.
-
-BSD was arguably in a more mature state than GNU/Linux in the early 1990s, and without these legal complications it could have become the standard on x86 PCs. We could all be using it today instead of Linux.
-
-#### But you said earlier that BSD is still widely used, so things improved after that? ####
-
-Yes. 386BSD development stagnated, but two teams of developers working over the internet created separate successor projects. FreeBSD became the most widely used flavour of BSD, and is now the closest to Linux as a desktop and server operating system, while NetBSD focused on portability (today it runs on over 50 platforms, all built from the same codebase). The third flavour, OpenBSD, forked off from NetBSD just a few years after NetBSD started due to a developer spat, and today it’s well known for its concentration on security. Over the years, OpenBSD has created many programs that have become standard on Linux, such as OpenSSH – and now we have LibreSSL too.
-
-#### So these three flavours of BSD are like Linux distributions? ####
-
-Yes and no. Each BSD has a separate codebase and separate development teams, although there is a lot of code-flow between them (especially for hardware drivers). But they are standalone operating systems with their own features, pros and cons.
-
-We mentioned that the development model of the BSDs is one feature that really distinguishes them from GNU/Linux. There’s nobody in charge of GNU/Linux as a whole: some teams are working on the GNU components, some are working on the kernel, some on boot scripts, some on manual pages, some on libraries, and so forth. The development model is often called “wild west”, with a lack of central authority, and distributions do all the hard work of fitting everything together.
-
-The BSDs, in contrast, are developed as complete projects from centralised source code trees. The kernel, the libraries, the system utilities and the manual pages are all stored and worked on in the same place. Many BSD fans argue that this gives the operating systems more coherency and stability, and from our years of dabbling with BSD we can attest that the manual pages are largely superb.
-
-
-
-#### Don’t the BSDs use anything from GNU/Linux? ####
-
-Yes, especially GCC. The GNU Compiler Collection has been the de-facto standard compiler on free Unix systems for decades, although FreeBSD has recently moved to LLVM/Clang. It’s important to note that the BSDs also use other open source projects that aren’t specifically GNU or Linux, such as the X Window System (XFree86 and X.org), Perl and so forth. And thanks to standards such as POSIX, most programs that run on Linux can be recompiled to run on the various BSD flavours.
-
-So, you could replace the L in a LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL and PHP) stack with FreeBSD, and get pretty much the same environment, with a different set of features (eg variations in filesystem and driver support). And there are some mega, super, huge users of FreeBSD, such as Netflix, which serve up ridiculous amounts of data every day. While FreeBSD makes a good desktop OS, its strengths really lie in the server room, with exceptional reliability and network performance.
-
-OpenBSD tends to be used in smaller web serving, file hosting, firewall and gateway roles where security is imperative. NetBSD is the least popular of the main BSD flavours – it can run on almost anything though, including old Amigas and Acorn boxes, and sometimes finds itself inside closed-source network devices.
-
-#### Hang on – how can someone close the source code? That ain’t kosher in Linux! ####
-
-Correct, and here we come to the other major difference with GNU/Linux. The licence for the BSD flavours (called, funnily enough, the BSD Licence) is very different to the GPL that we know. For starters, it’s much shorter. The BSD Licence essentially says: do what you want with this code, but give the original developers credit for writing it, and don’t try to sue them if it blows up your computer.
-
-So there’s nothing in the licence that forces the code to stay open, unlike with the GPL, which requires that users of the code also make their modifications freely available. This crucial difference has sparked countless flame wars over the years, with BSD fans saying that their licence is more free (because it’s less restrictive), while GNU/GPL fans say that their licence is actually more free (because it preserves freedom down the road).
-
-#### Blimey. Anyway, now that you’ve piqued my interest, where can I try out all these lovely BSD flavours? ####
-
-You can probably guess the websites – [www.openbsd.org][1], [www.freebsd.org][2] and [www.netbsd.org][3] – where you can download ISO images, boot them in VirtualBox, and play around. If you’ve been using Linux for a while, you won’t find any of them too difficult, although you’re expected to know your way around the command line. If you’re looking for something more newbie-friendly, PC-BSD
-
-([www.pcbsd.org][4]) is a customised version of FreeBSD focused on the desktop, with a fancy graphical installer and super-simple management of software. Have fun exploring!
-
-
-
-
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.linuxvoice.com/faq-bsd-2/
-
-作者:[Mike Saunders][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://www.linuxvoice.com/author/mike/
-[1]:http://www.openbsd.org/
-[2]:http://www.freebsd.org/
-[3]:http://www.netbsd.org/
-[4]:http://www.pcbsd.org/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20150520 Is Linux Better than OS X GNU Open Source and Apple in History.md b/sources/talk/20150520 Is Linux Better than OS X GNU Open Source and Apple in History.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9abc2f721f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20150520 Is Linux Better than OS X GNU Open Source and Apple in History.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+translating wi-cuckoo
+Is Linux Better than OS X? GNU, Open Source and Apple in History
+================================================================================
+> Tensions between the free software/open source community and Apple date back to the 1980s, Linux's founder called the core of Mac OS X "a piece of crap" and other anecdotes from software history.
+
+
+
+Open source fans have long had a rocky relationship with Microsoft. Everyone knows that. But, in many ways, the tension between Apple and supporters of free or open source software is even starker—even if it receives much less attention in the press.
+
+To be sure, not all open source advocates have an aversion to Apple. Anecdotally, I've seen plenty of Linux hackers sporting iPhones and iPads. In fact, some Linux users like Apple's OS X so much that they've [created a number of Linux distributions][1] designed to look just like it. (So has the [North Korean government][2], incidentally.)
+
+But relations between the Cult of Mac and the Cult of Tux—that is, the Linux community (not to mention the other, smaller segments of the free and open source software world)—have not always been completely peaceable. And that's by no means a new phenomenon, as I'm discovering as I research the history of Linux and the Free Software Foundation.
+
+### GNU vs. Apple ###
+
+The ill will dates to at least the late 1980s. By June 1988, [GNU][3], the project launched by Richard Stallman to build a completely free Unix-like operating system whose source code would be freely shared, was [strongly criticizing][4] Apple's lawsuit against [Hewlett-Packard][5] (HPQ) and [Microsoft][6] (MSFT) over what Apple claimed was improper copying of the "look and feel" of the Macintosh operating system. If Apple prevailed, GNU warned, the company "will use this new power over the public to put an end to free software that could substitute for commercial software."
+
+At the time, GNU fought against the lawsuit (which meant, ironically, that GNU was supporting Microsoft, though those were different times) by distributing "[Keep Your Lawyers Off My Computer" buttons][7]. It also urged GNU supporters to boycott Apple, warning that, even if Macintoshes seemed like good computers, Apple's success in the lawsuit could provide the company with a monopoly in the market that would greatly increase the price of computers.
+
+Apple eventually [lost the lawsuit][8], but not until 1994, after which GNU [dropped its Apple boycott][9]. In the interim, GNU remained critical of the company. In the early 1990s, even after it began promoting GNU software programs for use on other personal computing platforms, including MS-DOS PCs, [GNU affirmed][10] that, until Apple ceased pursuing a "monopoly" over computers with user interfaces similar to those of the Macintosh, "we will not provide any support for Apple machines." (It's therefore ironic that a fair amount of the software that made it into OS X, the Unix-like operating system that Apple introduced later in the 1990s, came from GNU. But that's another story.)
+
+### Torvalds on Jobs ###
+
+Despite his more laissez-faire attitude toward most issues, Linus Torvalds, the creator of the Linux kernel, was no less charitable in his attitudes toward Apple than Stallman and GNU had been. In his 2001 book "Just for Fun: The Story of an Accidental Revolutionary," Torvalds described meeting with Steve Jobs circa 1997, at the latter's invitation, to discuss Mac OS X, which Apple was then developing but had not yet released publicly.
+
+"Basically, Jobs started off by trying to tell me that on the desktop there were just two players, Microsoft and Apple, and that he thought that the best thing I could do for Linux was to get in bed with Apple and try to get the open source people behind Mac OS X," Torvalds wrote.
+
+This courting apparently turned Torvalds off quite a bit. One point of disagreement centered on Torvalds's technical disdain for Mach, the kernel on which Apple was then building its new OS X operating system, which Torvalds called "a piece of crap. It contains all the design mistakes you can make, and managed to even make up a few of its own."
+
+But more off-putting, apparently, was the way Jobs was approaching open source in developing OS X (which had many open source programs at its core): "He sort of played down the flaw in the setup: Who cares if the basic operating system, the real low-core stuff, is open source if you then have the Mac layer on top, which is not open source?"
+
+All in all, Torvalds concluded, Jobs "didn't use very many arguments. He just basically took it for granted that I would be interested" in collaborating with Apple. "He was clueless, unable to imagine that there could be entire segments of the human race who weren't the least bit concerned about increasing the Mac's market share. I think he was truly surprised at how little I cared about how big a market the Mac had—or how big a market Microsoft has."
+
+Torvalds doesn't speak for all Linux users, of course. And his views on OS X and Apple may have softened since 2001. But the fact that, in the early 2000s, the Linux community's leading figure exhibited so much disdain for Apple and the hubris of its chief says something significant about how deeply seated tensions between the Apple world and the open source/free software world are.
+
+Both of these historical tidbits offer insight into the great debate regarding the actual value of Apple's products—whether the company thrives on the quality of the hardware and software it creates, or merely benefits from exceptional marketing acumen that allows it to sell products for much more than their non-Apple functional equivalents are worth. But I'll stay out of that debate, for now.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/051815/linux-better-os-x-gnu-open-source-and-apple-
+
+作者:[Christopher Tozzi][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://thevarguy.com/author/christopher-tozzi
+[1]:https://www.linux.com/news/software/applications/773516-the-mac-ifying-of-the-linux-desktop/
+[2]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/010615/north-koreas-red-star-linux-os-made-apples-image
+[3]:http://gnu.org/
+[4]:https://www.gnu.org/bulletins/bull5.html
+[5]:http://www.hp.com/
+[6]:http://www.microsoft.com/
+[7]:http://www.duntemann.com/AppleSnakeButton.jpg
+[8]:http://www.freibrun.com/articles/articl12.htm
+[9]:https://www.gnu.org/bulletins/bull18.html#SEC6
+[10]:https://www.gnu.org/bulletins/bull12.html
diff --git a/sources/tech/2015-04-29 web caching basics terminology http headers and caching strategies.md b/sources/tech/2015-04-29 web caching basics terminology http headers and caching strategies.md
deleted file mode 100644
index df0eb8b723..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/2015-04-29 web caching basics terminology http headers and caching strategies.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,444 +0,0 @@
-Web Caching Basics: Terminology, HTTP Headers, and Caching Strategies
-=====================================================================
-
-### Introduction
-
-Intelligent content caching is one of the most effective ways to improve
-the experience for your site's visitors. Caching, or temporarily storing
-content from previous requests, is part of the core content delivery
-strategy implemented within the HTTP protocol. Components throughout the
-delivery path can all cache items to speed up subsequent requests,
-subject to the caching policies declared for the content.
-
-In this guide, we will discuss some of the basic concepts of web content
-caching. This will mainly cover how to select caching policies to ensure
-that caches throughout the internet can correctly process your content.
-We will talk about the benefits that caching affords, the side effects
-to be aware of, and the different strategies to employ to provide the
-best mixture of performance and flexibility.
-
-What Is Caching?
-----------------
-
-Caching is the term for storing reusable responses in order to make
-subsequent requests faster. There are many different types of caching
-available, each of which has its own characteristics. Application caches
-and memory caches are both popular for their ability to speed up certain
-responses.
-
-Web caching, the focus of this guide, is a different type of cache. Web
-caching is a core design feature of the HTTP protocol meant to minimize
-network traffic while improving the perceived responsiveness of the
-system as a whole. Caches are found at every level of a content's
-journey from the original server to the browser.
-
-Web caching works by caching the HTTP responses for requests according
-to certain rules. Subsequent requests for cached content can then be
-fulfilled from a cache closer to the user instead of sending the request
-all the way back to the web server.
-
-Benefits
---------
-
-Effective caching aids both content consumers and content providers.
-Some of the benefits that caching brings to content delivery are:
-
-- **Decreased network costs**: Content can be cached at various points
- in the network path between the content consumer and content origin.
- When the content is cached closer to the consumer, requests will not
- cause much additional network activity beyond the cache.
-- **Improved responsiveness**: Caching enables content to be retrieved
- faster because an entire network round trip is not necessary. Caches
- maintained close to the user, like the browser cache, can make this
- retrieval nearly instantaneous.
-- **Increased performance on the same hardware**: For the server where
- the content originated, more performance can be squeezed from the
- same hardware by allowing aggressive caching. The content owner can
- leverage the powerful servers along the delivery path to take the
- brunt of certain content loads.
-- **Availability of content during network interruptions**: With
- certain policies, caching can be used to serve content to end users
- even when it may be unavailable for short periods of time from the
- origin servers.
-
-Terminology
------------
-
-When dealing with caching, there are a few terms that you are likely to
-come across that might be unfamiliar. Some of the more common ones are
-below:
-
-- **Origin server**: The origin server is the original location of the
- content. If you are acting as the web server administrator, this is
- the machine that you control. It is responsible for serving any
- content that could not be retrieved from a cache along the request
- route and for setting the caching policy for all content.
-- **Cache hit ratio**: A cache's effectiveness is measured in terms of
- its cache hit ratio or hit rate. This is a ratio of the requests
- able to be retrieved from a cache to the total requests made. A high
- cache hit ratio means that a high percentage of the content was able
- to be retrieved from the cache. This is usually the desired outcome
- for most administrators.
-- **Freshness**: Freshness is a term used to describe whether an item
- within a cache is still considered a candidate to serve to a client.
- Content in a cache will only be used to respond if it is within the
- freshness time frame specified by the caching policy.
-- **Stale content**: Items in the cache expire according to the cache
- freshness settings in the caching policy. Expired content is
- "stale". In general, expired content cannot be used to respond to
- client requests. The origin server must be re-contacted to retrieve
- the new content or at least verify that the cached content is still
- accurate.
-- **Validation**: Stale items in the cache can be validated in order
- to refresh their expiration time. Validation involves checking in
- with the origin server to see if the cached content still represents
- the most recent version of item.
-- **Invalidation**: Invalidation is the process of removing content
- from the cache before its specified expiration date. This is
- necessary if the item has been changed on the origin server and
- having an outdated item in cache would cause significant issues for
- the client.
-
-There are plenty of other caching terms, but the ones above should help
-you get started.
-
-What Can be Cached?
--------------------
-
-Certain content lends itself more readily to caching than others. Some
-very cache-friendly content for most sites are:
-
-- Logos and brand images
-- Non-rotating images in general (navigation icons, for example)
-- Style sheets
-- General Javascript files
-- Downloadable Content
-- Media Files
-
-These tend to change infrequently, so they can benefit from being cached
-for longer periods of time.
-
-Some items that you have to be careful in caching are:
-
-- HTML pages
-- Rotating images
-- Frequently modified Javascript and CSS
-- Content requested with authentication cookies
-
-Some items that should almost never be cached are:
-
-- Assets related to sensitive data (banking info, etc.)
-- Content that is user-specific and frequently changed
-
-In addition to the above general rules, it's possible to specify
-policies that allow you to cache different types of content
-appropriately. For instance, if authenticated users all see the same
-view of your site, it may be possible to cache that view anywhere. If
-authenticated users see a user-sensitive view of the site that will be
-valid for some time, you may tell the user's browser to cache, but tell
-any intermediary caches not to store the view.
-
-Locations Where Web Content Is Cached
--------------------------------------
-
-Content can be cached at many different points throughout the delivery
-chain:
-
-- **Browser cache**: Web browsers themselves maintain a small cache.
- Typically, the browser sets a policy that dictates the most
- important items to cache. This may be user-specific content or
- content deemed expensive to download and likely to be requested
- again.
-- **Intermediary caching proxies**: Any server in between the client
- and your infrastructure can cache certain content as desired. These
- caches may be maintained by ISPs or other independent parties.
-- **Reverse Cache**: Your server infrastructure can implement its own
- cache for backend services. This way, content can be served from the
- point-of-contact instead of hitting backend servers on each request.
-
-Each of these locations can and often do cache items according to their
-own caching policies and the policies set at the content origin.
-
-Caching Headers
----------------
-
-Caching policy is dependent upon two different factors. The caching
-entity itself gets to decide whether or not to cache acceptable content.
-It can decide to cache less than it is allowed to cache, but never more.
-
-The majority of caching behavior is determined by the caching policy,
-which is set by the content owner. These policies are mainly articulated
-through the use of specific HTTP headers.
-
-Through various iterations of the HTTP protocol, a few different
-cache-focused headers have arisen with varying levels of sophistication.
-The ones you probably still need to pay attention to are below:
-
-- **`Expires`**: The `Expires` header is very straight-forward,
- although fairly limited in scope. Basically, it sets a time in the
- future when the content will expire. At this point, any requests for
- the same content will have to go back to the origin server. This
- header is probably best used only as a fall back.
-- **`Cache-Control`**: This is the more modern replacement for the
- `Expires` header. It is well supported and implements a much more
- flexible design. In almost all cases, this is preferable to
- `Expires`, but it may not hurt to set both values. We will discuss
- the specifics of the options you can set with `Cache-Control` a bit
- later.
-- **`Etag`**: The `Etag` header is used with cache validation. The
- origin can provide a unique `Etag` for an item when it initially
- serves the content. When a cache needs to validate the content it
- has on-hand upon expiration, it can send back the `Etag` it has for
- the content. The origin will either tell the cache that the content
- is the same, or send the updated content (with the new `Etag`).
-- **`Last-Modified`**: This header specifies the last time that the
- item was modified. This may be used as part of the validation
- strategy to ensure fresh content.
-- **`Content-Length`**: While not specifically involved in caching,
- the `Content-Length` header is important to set when defining
- caching policies. Certain software will refuse to cache content if
- it does not know in advanced the size of the content it will need to
- reserve space for.
-- **`Vary`**: A cache typically uses the requested host and the path
- to the resource as the key with which to store the cache item. The
- `Vary` header can be used to tell caches to pay attention to an
- additional header when deciding whether a request is for the same
- item. This is most commonly used to tell caches to key by the
- `Accept-Encoding` header as well, so that the cache will know to
- differentiate between compressed and uncompressed content.
-
-### An Aside about the Vary Header
-
-The `Vary` header provides you with the ability to store different
-versions of the same content at the expense of diluting the entries in
-the cache.
-
-In the case of `Accept-Encoding`, setting the `Vary` header allows for a
-critical distinction to take place between compressed and uncompressed
-content. This is needed to correctly serve these items to browsers that
-cannot handle compressed content and is necessary in order to provide
-basic usability. One characteristic that tells you that
-`Accept-Encoding` may be a good candidate for `Vary` is that it only has
-two or three possible values.
-
-Items like `User-Agent` might at first glance seem to be a good way to
-differentiate between mobile and desktop browsers to serve different
-versions of your site. However, since `User-Agent` strings are
-non-standard, the result will likely be many versions of the same
-content on intermediary caches, with a very low cache hit ratio. The
-`Vary` header should be used sparingly, especially if you do not have
-the ability to normalize the requests in intermediate caches that you
-control (which may be possible, for instance, if you leverage a content
-delivery network).
-
-How Cache-Control Flags Impact Caching
---------------------------------------
-
-Above, we mentioned how the `Cache-Control` header is used for modern
-cache policy specification. A number of different policy instructions
-can be set using this header, with multiple instructions being separated
-by commas.
-
-Some of the `Cache-Control` options you can use to dictate your
-content's caching policy are:
-
-- **`no-cache`**: This instruction specifies that any cached content
- must be re-validated on each request before being served to a
- client. This, in effect, marks the content as stale immediately, but
- allows it to use revalidation techniques to avoid re-downloading the
- entire item again.
-- **`no-store`**: This instruction indicates that the content cannot
- be cached in any way. This is appropriate to set if the response
- represents sensitive data.
-- **`public`**: This marks the content as public, which means that it
- can be cached by the browser and any intermediate caches. For
- requests that utilized HTTP authentication, responses are marked
- `private` by default. This header overrides that setting.
-- **`private`**: This marks the content as `private`. Private content
- may be stored by the user's browser, but must *not* be cached by any
- intermediate parties. This is often used for user-specific data.
-- **`max-age`**: This setting configures the maximum age that the
- content may be cached before it must revalidate or re-download the
- content from the origin server. In essence, this replaces the
- `Expires` header for modern browsing and is the basis for
- determining a piece of content's freshness. This option takes its
- value in seconds with a maximum valid freshness time of one year
- (31536000 seconds).
-- **`s-maxage`**: This is very similar to the `max-age` setting, in
- that it indicates the amount of time that the content can be cached.
- The difference is that this option is applied only to intermediary
- caches. Combining this with the above allows for more flexible
- policy construction.
-- **`must-revalidate`**: This indicates that the freshness information
- indicated by `max-age`, `s-maxage` or the `Expires` header must be
- obeyed strictly. Stale content cannot be served under any
- circumstance. This prevents cached content from being used in case
- of network interruptions and similar scenarios.
-- **`proxy-revalidate`**: This operates the same as the above setting,
- but only applies to intermediary proxies. In this case, the user's
- browser can potentially be used to serve stale content in the event
- of a network interruption, but intermediate caches cannot be used
- for this purpose.
-- **`no-transform`**: This option tells caches that they are not
- allowed to modify the received content for performance reasons under
- any circumstances. This means, for instance, that the cache is not
- able to send compressed versions of content it did not receive from
- the origin server compressed and is not allowed.
-
-These can be combined in different ways to achieve various caching
-behavior. Some mutually exclusive values are:
-
-- `no-cache`, `no-store`, and the regular caching behavior indicated
- by absence of either
-- `public` and `private`
-
-The `no-store` option supersedes the `no-cache` if both are present. For
-responses to unauthenticated requests, `public` is implied. For
-responses to authenticated requests, `private` is implied. These can be
-overridden by including the opposite option in the `Cache-Control`
-header.
-
-Developing a Caching Strategy
------------------------------
-
-In a perfect world, everything could be cached aggressively and your
-servers would only be contacted to validate content occasionally. This
-doesn't often happen in practice though, so you should try to set some
-sane caching policies that aim to balance between implementing long-term
-caching and responding to the demands of a changing site.
-
-### Common Issues
-
-There are many situations where caching cannot or should not be
-implemented due to how the content is produced (dynamically generated
-per user) or the nature of the content (sensitive banking information,
-for example). Another problem that many administrators face when setting
-up caching is the situation where older versions of your content are out
-in the wild, not yet stale, even though new versions have been
-published.
-
-These are both frequently encountered issues that can have serious
-impacts on cache performance and the accuracy of content you are
-serving. However, we can mitigate these issues by developing caching
-policies that anticipate these problems.
-
-### General Recommendations
-
-While your situation will dictate the caching strategy you use, the
-following recommendations can help guide you towards some reasonable
-decisions.
-
-There are certain steps that you can take to increase your cache hit
-ratio before worrying about the specific headers you use. Some ideas
-are:
-
-- **Establish specific directories for images, css, and shared
- content**: Placing content into dedicated directories will allow you
- to easily refer to them from any page on your site.
-- **Use the same URL to refer to the same items**: Since caches key
- off of both the host and the path to the content requested, ensure
- that you refer to your content in the same way on all of your pages.
- The previous recommendation makes this significantly easier.
-- **Use CSS image sprites where possible**: CSS image sprites for
- items like icons and navigation decrease the number of round trips
- needed to render your site and allow your site to cache that single
- sprite for a long time.
-- **Host scripts and external resources locally where possible**: If
- you utilize javascript scripts and other external resources,
- consider hosting those resources on your own servers if the correct
- headers are not being provided upstream. Note that you will have to
- be aware of any updates made to the resource upstream so that you
- can update your local copy.
-- **Fingerprint cache items**: For static content like CSS and
- Javascript files, it may be appropriate to fingerprint each item.
- This means adding a unique identifier to the filename (often a hash
- of the file) so that if the resource is modified, the new resource
- name can be requested, causing the requests to correctly bypass the
- cache. There are a variety of tools that can assist in creating
- fingerprints and modifying the references to them within HTML
- documents.
-
-In terms of selecting the correct headers for different items, the
-following can serve as a general reference:
-
-- **Allow all caches to store generic assets**: Static content and
- content that is not user-specific can and should be cached at all
- points in the delivery chain. This will allow intermediary caches to
- respond with the content for multiple users.
-- **Allow browsers to cache user-specific assets**: For per-user
- content, it is often acceptable and useful to allow caching within
- the user's browser. While this content would not be appropriate to
- cache on any intermediary caching proxies, caching in the browser
- will allow for instant retrieval for users during subsequent visits.
-- **Make exceptions for essential time-sensitive content**: If you
- have content that is time-sensitive, make an exception to the above
- rules so that the out-dated content is not served in critical
- situations. For instance, if your site has a shopping cart, it
- should reflect the items in the cart immediately. Depending on the
- nature of the content, the `no-cache` or `no-store` options can be
- set in the `Cache-Control` header to achieve this.
-- **Always provide validators**: Validators allow stale content to be
- refreshed without having to download the entire resource again.
- Setting the `Etag` and the `Last-Modified` headers allow caches to
- validate their content and re-serve it if it has not been modified
- at the origin, further reducing load.
-- **Set long freshness times for supporting content**: In order to
- leverage caching effectively, elements that are requested as
- supporting content to fulfill a request should often have a long
- freshness setting. This is generally appropriate for items like
- images and CSS that are pulled in to render the HTML page requested
- by the user. Setting extended freshness times, combined with
- fingerprinting, allows caches to store these resources for long
- periods of time. If the assets change, the modified fingerprint will
- invalidate the cached item and will trigger a download of the new
- content. Until then, the supporting items can be cached far into the
- future.
-- **Set short freshness times for parent content**: In order to make
- the above scheme work, the containing item must have relatively
- short freshness times or may not be cached at all. This is typically
- the HTML page that calls in the other assisting content. The HTML
- itself will be downloaded frequently, allowing it to respond to
- changes rapidly. The supporting content can then be cached
- aggressively.
-
-The key is to strike a balance that favors aggressive caching where
-possible while leaving opportunities to invalidate entries in the future
-when changes are made. Your site will likely have a combination of:
-
-- Aggressively cached items
-- Cached items with a short freshness time and the ability to
- re-validate
-- Items that should not be cached at all
-
-The goal is to move content into the first categories when possible
-while maintaining an acceptable level of accuracy.
-
-Conclusion
-----------
-
-Taking the time to ensure that your site has proper caching policies in
-place can have a significant impact on your site. Caching allows you to
-cut down on the bandwidth costs associated with serving the same content
-repeatedly. Your server will also be able to handle a greater amount of
-traffic with the same hardware. Perhaps most importantly, clients will
-have a faster experience on your site, which may lead them to return
-more frequently. While effective web caching is not a silver bullet,
-setting up appropriate caching policies can give you measurable gains
-with minimal work.
-
-
----
-
-作者: [Justin Ellingwood](https://www.digitalocean.com/community/users/jellingwood)
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-推荐:[royaso](https://github.com/royaso)
-
-via: https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/web-caching-basics-terminology-http-headers-and-caching-strategies
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150112 What are useful command-line network monitors on Linux.md b/sources/tech/20150112 What are useful command-line network monitors on Linux.md
deleted file mode 100644
index f17e45cbf4..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150112 What are useful command-line network monitors on Linux.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,135 +0,0 @@
-What are useful command-line network monitors on Linux
-================================================================================
-Network monitoring is a critical IT function for businesses of all sizes. The goal of network monitoring can vary. For example, the monitoring activity can be part of long-term network provisioning, security protection, performance troubleshooting, network usage accounting, and so on. Depending on its goal, network monitoring is done in many different ways, such as performing packet-level sniffing, collecting flow-level statistics, actively injecting probes into the network, parsing server logs, etc.
-
-While there are many dedicated network monitoring systems capable of 24/7/365 monitoring, you can also leverage command-line network monitors in certain situations, where a dedicated monitor is an overkill. If you are a system admin, you are expected to have hands-on experience with some of well known CLI network monitors. Here is a list of **popular and useful command-line network monitors on Linux**.
-
-### Packet-Level Sniffing ###
-
-In this category, monitoring tools capture individual packets on the wire, dissect their content, and display decoded packet content or packet-level statistics. These tools conduct network monitoring from the lowest level, and as such, can possibly do the most fine-grained monitoring at the cost of network I/O and analysis efforts.
-
-1. **dhcpdump**: a comman-line DHCP traffic sniffer capturing DHCP request/response traffic, and displays dissected DHCP protocol messages in a human-friendly format. It is useful when you are troubleshooting DHCP related issues.
-
-2. **[dsniff][1]**: a collection of command-line based sniffing, spoofing and hijacking tools designed for network auditing and penetration testing. They can sniff various information such as passwords, NSF traffic, email messages, website URLs, and so on.
-
-3. **[httpry][2]**: an HTTP packet sniffer which captures and decode HTTP requests and response packets, and display them in a human-readable format.
-
-4. **IPTraf**: a console-based network statistics viewer. It displays packet-level, connection-level, interface-level, protocol-level packet/byte counters in real-time. Packet capturing can be controlled by protocol filters, and its operation is full menu-driven.
-
-
-
-5. **[mysql-sniffer][3]**: a packet sniffer which captures and decodes packets associated with MySQL queries. It displays the most frequent or all queries in a human-readable format.
-
-6. **[ngrep][4]**: grep over network packets. It can capture live packets, and match (filtered) packets against regular expressions or hexadecimal expressions. It is useful for detecting and storing any anomalous traffic, or for sniffing particular patterns of information from live traffic.
-
-7. **[p0f][5]**: a passive fingerprinting tool which, based on packet sniffing, reliably identifies operating systems, NAT or proxy settings, network link types and various other properites associated with an active TCP connection.
-
-8. **pktstat**: a command-line tool which analyzes live packets to display connection-level bandwidth usages as well as descriptive information of protocols involved (e.g., HTTP GET/POST, FTP, X11).
-
-
-
-9. **Snort**: an intrusion detection and prevention tool which can detect/prevent a variety of backdoor, botnets, phishing, spyware attacks from live traffic based on rule-driven protocol analysis and content matching.
-
-10. **tcpdump**: a command-line packet sniffer which is capable of capturing nework packets on the wire based on filter expressions, dissect the packets, and dump the packet content for packet-level analysis. It is widely used for any kinds of networking related troubleshooting, network application debugging, or [security][6] monitoring.
-
-11. **tshark**: a command-line packet sniffing tool that comes with Wireshark GUI program. It can capture and decode live packets on the wire, and show decoded packet content in a human-friendly fashion.
-
-### Flow-/Process-/Interface-Level Monitoring ###
-
-In this category, network monitoring is done by classifying network traffic into flows, associated processes or interfaces, and collecting per-flow, per-process or per-interface statistics. Source of information can be libpcap packet capture library or sysfs kernel virtual filesystem. Monitoring overhead of these tools is low, but packet-level inspection capabilities are missing.
-
-12. **bmon**: a console-based bandwidth monitoring tool which shows various per-interface information, including not-only aggregate/average RX/TX statistics, but also a historical view of bandwidth usage.
-
-
-
-13. **[iftop][7]**: a bandwidth usage monitoring tool that can shows bandwidth usage for individual network connections in real time. It comes with ncurses-based interface to visualize bandwidth usage of all connections in a sorted order. It is useful for monitoring which connections are consuming the most bandwidth.
-
-14. **nethogs**: a process monitoring tool which offers a real-time view of upload/download bandwidth usage of individual processes or programs in an ncurses-based interface. This is useful for detecting bandwidth hogging processes.
-
-15. **netstat**: a command-line tool that shows various statistics and properties of the networking stack, such as open TCP/UDP connections, network interface RX/TX statistics, routing tables, protocol/socket statistics. It is useful when you diagnose performance and resource usage related problems of the networking stack.
-
-16. **[speedometer][8]**: a console-based traffic monitor which visualizes the historical trend of an interface's RX/TX bandwidth usage with ncurses-drawn bar charts.
-
-
-
-17. **[sysdig][9]**: a comprehensive system-level debugging tool with a unified interface for investigating different Linux subsystems. Its network monitoring module is capable of monitoring, either online or offline, various per-process/per-host networking statistics such as bandwidth usage, number of connections/requests, etc.
-
-18. **tcptrack**: a TCP connection monitoring tool which displays information of active TCP connections, including source/destination IP addresses/ports, TCP state, and bandwidth usage.
-
-
-
-19. **vnStat**: a command-line traffic monitor which maintains a historical view of RX/TX bandwidh usage (e.g., current, daily, monthly) on a per-interface basis. Running as a background daemon, it collects and stores interface statistics on bandwidth rate and total bytes transferred.
-
-### Active Network Monitoring ###
-
-Unlike passive monitoring tools presented so far, tools in this category perform network monitoring by actively "injecting" probes into the network and collecting corresponding responses. Monitoring targets include routing path, available bandwidth, loss rates, delay, jitter, system settings or vulnerabilities, and so on.
-
-20. **[dnsyo][10]**: a DNS monitoring tool which can conduct DNS lookup from open resolvers scattered across more than 1,500 different networks. It is useful when you check DNS propagation or troubleshoot DNS configuration.
-
-21. **[iperf][11]**: a TCP/UDP bandwidth measurement utility which can measure maximum available bandwidth between two end points. It measures available bandwidth by having two hosts pump out TCP/UDP probe traffic between them either unidirectionally or bi-directionally. It is useful when you test the network capacity, or tune the parameters of network stack. A variant called [netperf][12] exists with more features and better statistics.
-
-22. **[netcat][13]/socat**: versatile network debugging tools capable of reading from, writing to, or listen on TCP/UDP sockets. They are often used alongside with other programs or scripts for backend network transfer or port listening.
-
-23. **nmap**: a command-line port scanning and network discovery utility. It relies on a number of TCP/UDP based scanning techniques to detect open ports, live hosts, or existing operating systems on the local network. It is useful when you audit local hosts for vulnerabilities or build a host map for maintenance purpose. [zmap][14] is an alernative scanning tool with Internet-wide scanning capability.
-
-24. ping: a network testing tool which works by exchaning ICMP echo and reply packets with a remote host. It is useful when you measure round-trip-time (RTT) delay and loss rate of a routing path, as well as test the status or firewall rules of a remote system. Variations of ping exist with fancier interface (e.g., [noping][15]), multi-protocol support (e.g., [hping][16]) or parallel probing capability (e.g., [fping][17]).
-
-
-
-25. **[sprobe][18]**: a command-line tool that heuristically infers the bottleneck bandwidth between a local host and any arbitrary remote IP address. It uses TCP three-way handshake tricks to estimate the bottleneck bandwidth. It is useful when troubleshooting wide-area network performance and routing related problems.
-
-26. **traceroute**: a network discovery tool which reveals a layer-3 routing/forwarding path from a local host to a remote host. It works by sending TTL-limited probe packets and collecting ICMP responses from intermediate routers. It is useful when troubleshooting slow network connections or routing related problems. Variations of traceroute exist with better RTT statistics (e.g., [mtr][19]).
-
-### Application Log Parsing ###
-
-In this category, network monitoring is targeted at a specific server application (e.g., web server or database server). Network traffic generated or consumed by a server application is monitored by analyzing its log file. Unlike network-level monitors presented in earlier categories, tools in this category can analyze and monitor network traffic from application-level.
-
-27. **[GoAccess][20]**: a console-based interactive viewer for Apache and Nginx web server traffic. Based on access log analysis, it presents a real-time statistics of a number of metrics including daily visits, top requests, client operating systems, client locations, client browsers, in a scrollable view.
-
-
-
-28. **[mtop][21]**: a command-line MySQL/MariaDB server moniter which visualizes the most expensive queries and current database server load. It is useful when you optimize MySQL server performance and tune server configurations.
-
-
-
-29. **[ngxtop][22]**: a traffic monitoring tool for Nginx and Apache web server, which visualizes web server traffic in a top-like interface. It works by parsing a web server's access log file and collecting traffic statistics for individual destinations or requests.
-
-### Conclusion ###
-
-In this article, I presented a wide variety of command-line network monitoring tools, ranging from the lowest packet-level monitors to the highest application-level network monitors. Knowing which tool does what is one thing, and choosing which tool to use is another, as any single tool cannot be a universal solution for your every need. A good system admin should be able to decide which tool is right for the circumstance at hand. Hopefully the list helps with that.
-
-You are always welcome to improve the list with your comment!
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://xmodulo.com/useful-command-line-network-monitors-linux.html
-
-作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
-[1]:http://www.monkey.org/~dugsong/dsniff/
-[2]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-http-traffic-command-line-linux.html
-[3]:https://github.com/zorkian/mysql-sniffer
-[4]:http://ngrep.sourceforge.net/
-[5]:http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/p0f3/
-[6]:http://xmodulo.com/recommend/firewallbook
-[7]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-install-iftop-on-linux.html
-[8]:https://excess.org/speedometer/
-[9]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-troubleshoot-linux-server-sysdig.html
-[10]:http://xmodulo.com/check-dns-propagation-linux.html
-[11]:https://iperf.fr/
-[12]:http://www.netperf.org/netperf/
-[13]:http://xmodulo.com/useful-netcat-examples-linux.html
-[14]:https://zmap.io/
-[15]:http://noping.cc/
-[16]:http://www.hping.org/
-[17]:http://fping.org/
-[18]:http://sprobe.cs.washington.edu/
-[19]:http://xmodulo.com/better-alternatives-basic-command-line-utilities.html#mtr_link
-[20]:http://goaccess.io/
-[21]:http://mtop.sourceforge.net/
-[22]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-nginx-web-server-command-line-real-time.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150119 Unity Greeter Badges Brings Missing Session Icons to Ubuntu Login Screen.md b/sources/tech/20150119 Unity Greeter Badges Brings Missing Session Icons to Ubuntu Login Screen.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 1aac09e11a..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150119 Unity Greeter Badges Brings Missing Session Icons to Ubuntu Login Screen.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,58 +0,0 @@
-‘Unity Greeter Badges’ Brings Missing Session Icons to Ubuntu Login Screen
-================================================================================
-
-
-**A new package available in Ubuntu 15.04 solves a petty gripe I have with the Unity Greeter: the lack of branded icons for alternative desktop sessions like Cinnamon.**
-
-I know it’s a minor quibble; it’s a visual paper cut with minimal impact for most. But the inconsistency niggles me because Ubuntu ships with icons for a number of sessions, including Unity, GNOME and KDE. Other DEs, including some of its own flavors like Xubuntu, default to showing a plain white dot in the session switcher list and the main user pod.
-
-The inconsistency these dots create jars, even if it is only for a fleeting moment, not just in design. It’s in usability too. Branded glyphs are helpful in letting us know what session we’re about to log in to.
-
-For instance, can you tell what session this is?
-
-
-
-Budgie? Maybe MATE? Could be Cinnamon…I’d have to click on it and check first.
-
-It doesn’t have to be this way. The Unity Greeter is built such that the developers of desktop environments can ship badges that appear in the Greeter (and some do). But in many cases, like MATE whose packages are imported from upstream Debian, the inclination to carry an “Ubuntu-specific patch” is either not desirable or not possible.
-
-### A Solution Is Badged ###
-
-Experienced Debian maintainer [Doug Torrance][1] has a solution to fix this usability paper cut. Rather than rely on desktop makers themselves to add branded badges to their packages, and rather than burden Ubuntu with the responsibility of maintaining it, Torrance has created a separate ‘unity-greeter-badges’ package to house them.
-
-In assuming responsibility for providing the session glyphs directly, this package ensure that new and old window managers, session and desktops alike are catered for.
-
-Among the 30 or so desktop environments it bundles new session badges for are:
-
-- Xubuntu
-- Cinnamon
-- MATE
-- Cairo-Dock
-- Xmonad
-- Awesome
-- OpenBox
-- Pantheon
-
-The best part is that ‘**Unity-Greeter-Badges**’ has been accepted into Ubuntu 15.04. That means Torrance’s package will be available to install directly, no PPAs or downloads needed. In not being part of a core package like the Unity Greeter it can be updated with newer icons in a more efficient and timely manner.
-
-If you’re running Ubuntu 15.04 you will find the package available to install from the Software Center in the coming days.
-
-Don’t want to wait until 15.04? Torrance has made .deb installers for Ubuntu 14.04 LTS and Ubuntu 14.10 users.
-
-- [Download unity-greeter-badges for Ubuntu 14.04][2]
-- [Download unity-greeter-badges for Ubuntu 14.10][3]
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/01/unity-greeter-badges-brings-missing-session-icons-ubuntu-login-screen
-
-作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
-[1]:https://launchpad.net/~profzoom
-[2]:https://launchpad.net/~profzoom/+archive/ubuntu/misc/+files/unity-greeter-badges_0.1-0ubuntu1%7E201412111501%7Eubuntu14.04.1_all.deb
-[3]:https://launchpad.net/~profzoom/+archive/ubuntu/misc/+files/unity-greeter-badges_0.1-0ubuntu1%7E201412111501%7Eubuntu14.10.1_all.deb
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150123 How to make a file immutable on Linux.md b/sources/tech/20150123 How to make a file immutable on Linux.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 622cc4e5b3..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150123 How to make a file immutable on Linux.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,72 +0,0 @@
-How to make a file immutable on Linux
-================================================================================
-Suppose you want to write-protect some important files on Linux, so that they cannot be deleted or tampered with by accident or otherwise. In other cases, you may want to prevent certain configuration files from being overwritten automatically by software. While changing their ownership or permission bits on the files by using chown or chmod is one way to deal with this situation, this is not a perfect solution as it cannot prevent any action done with root privilege. That is when chattr comes in handy.
-
-chattr is a Linux command which allows one to set or unset attributes on a file, which are separate from the standard (read, write, execute) file permission. A related command is lsattr which shows which attributes are set on a file. While file attributes managed by chattr and lsattr are originally supported by EXT file systems (EXT2/3/4) only, this feature is now available on many other native Linux file systems such as XFS, Btrfs, ReiserFS, etc.
-
-In this tutorial, I am going to demonstrate how to use chattr to make files immutable on Linux.
-
-chattr and lsattr commands are a part of e2fsprogs package which comes pre-installed on all modern Linux distributions.
-
-Basic syntax of chattr is as follows.
-
- $ chattr [-RVf] [operator][attribute(s)] files...
-
-The operator can be '+' (which adds selected attributes to attribute list), '-' (which removes selected attributes from attribute list), or '=' (which forces selected attributes only).
-
-Some of available attributes are the following.
-
-- **a**: can be opened in append mode only.
-- **A**: do not update atime (file access time).
-- **c**: automatically compressed when written to disk.
-- **C**: turn off copy-on-write.
-- **i**: set immutable.
-- **s**: securely deleted with automatic zeroing.
-
-### Immutable Attribute ###
-
-To make a file immutable, you can add "immutable" attribute to the file as follows. For example, to write-protect /etc/passwd file:
-
- $ sudo chattr +i /etc/passwd
-
-Note that you must use root privilege to set or unset "immutable" attribute on a file. Now verify that "immutable" attribute is added to the file successfully.
-
- $ lsattr /etc/passwd
-
-Once the file is set immutable, this file is impervious to change for any user. Even the root cannot modify, remove, overwrite, move or rename the file. You will need to unset the immutable attribute before you can tamper with the file again.
-
-To unset the immutable attribute, use the following command:
-
- $ sudo chattr -i /etc/passwd
-
-
-
-If you want to make a whole directory (e.g., /etc) including all its content immutable at once recursively, use "-R" option:
-
- $ sudo chattr -R +i /etc
-
-### Append Only Attribute ###
-
-Another useful attribute is "append-only" attribute which forces a file to grow only. You cannot overwrite or delete a file with "append-only" attribute set. This attribute can be useful when you want to prevent a log file from being cleared by accident.
-
-Similar to immutable attribute, you can turn a file into "append-only" mode by:
-
- $ sudo chattr +a /var/log/syslog
-
-Note that when you copy an immutable or append-only file to another file, those attributes will not be preserved on the newly created file.
-
-### Conclusion ###
-
-In this tutorial, I showed how to use chattr and lsattr commands to manage additional file attributes to prevent (accidental or otherwise) file tampering. Beware that you cannot rely on chattr as a security measure as one can easily undo immutability. One possible way to address this limitation is to restrict the availability of chattr command itself, or drop kernel capability CAP_LINUX_IMMUTABLE. For more details on chattr and available attributes, refer to its man page.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://xmodulo.com/make-file-immutable-linux.html
-
-作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150126 Installing Cisco Packet tracer in Linux.md b/sources/tech/20150126 Installing Cisco Packet tracer in Linux.md
index edac7a7490..c55a04c12c 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20150126 Installing Cisco Packet tracer in Linux.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20150126 Installing Cisco Packet tracer in Linux.md
@@ -194,4 +194,4 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/installing-cisco-packet-tracer-linux/
[1]:https://www.netacad.com/
[2]:https://www.dropbox.com/s/5evz8gyqqvq3o3v/Cisco%20Packet%20Tracer%206.1.1%20Linux.tar.gz?dl=0
[3]:http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jre8-downloads-2133155.html
-[4]:https://www.netacad.com/
\ No newline at end of file
+[4]:https://www.netacad.com/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150205 zBackup--A versatile deduplicating backup tool.md b/sources/tech/20150205 zBackup--A versatile deduplicating backup tool.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 62eee8521c..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150205 zBackup--A versatile deduplicating backup tool.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
-zBackup – A versatile deduplicating backup tool
-================================================================================
-zbackup is a globally-deduplicating backup tool, based on the ideas found in rsync. Feed a large .tar into it, and it will store duplicate regions of it only once, then compress and optionally encrypt the result. Feed another .tar file, and it will also re-use any data found in any previous backups. This way only new changes are stored, and as long as the files are not very different, the amount of storage required is very low. Any of the backup files stored previously can be read back in full at any time.
-
-### zBackup Features ###
-
-Parallel LZMA or LZO compression of the stored data
-Built-in AES encryption of the stored data
-Possibility to delete old backup data
-Use of a 64-bit rolling hash, keeping the amount of soft collisions to zero
-Repository consists of immutable files. No existing files are ever modified
-Written in C++ only with only modest library dependencies
-Safe to use in production
-Possibility to exchange data between repos without recompression
-
-### Install zBackup in ubuntu ###
-
-Open the terminal and run the following command
-
- sudo apt-get install zbackup
-
-### Using zBackup ###
-
-zbackup init initializes a backup repository for the backup files to be stored.
-
- zbackup init [--non-encrypted] [--password-file ~/.my_backup_password ] /my/backup/repo
-
-zbackup backup backups a tar file generated by tar c to the repository initialized using zbackup init
-
- zbackup [--password-file ~/.my_backup_password ] [--threads number_of_threads ] backup /my/backup/repo/backups/backup-`date ‘+%Y-%m-%d'`
-
-zbackup restore restores the backup file to a tar file.
-
- zbackup [--password-file ~/.my_backup_password [--cache-size cache_size_in_mb restore /my/backup/repo/backups/backup-`date ‘+%Y-%m-%d'` > /my/precious/backup-restored.tar
-
-### Available Options ###
-
-- -non-encrypted -- Do not encrypt the backup repository.
-- --password-file ~/.my_backup_password -- Use the password file specified at ~/.my_backup_password to encrypt the repository and backup file, or to decrypt the backup file.
-- --threads number_of_threads -- Limit the partial LZMA compression to number_of_threads needed. Recommended for 32-bit architectures.
-- --cache-size cache_size_in_mb -- Use the cache size provided by cache_size_in_mb to speed up the restoration process.
-
-### zBackup files ###
-
-~/.my_backup_password Used to encrypt the repository and backup file, or to decrypt the backup file. See zbackup for further details.
-
-/my/backup/repo The directory used to hold the backup repository.
-
-/my/precious/restored-tar The tar used for restoring the backup.
-
-/my/backup/repo/backups/backup-`date ‘+%Y-%m-%d'` Specifies the backup file.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/zbackup-a-versatile-deduplicating-backup-tool.html
-
-作者:[ruchi][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150211 Install Linux-Dash (Web Based Monitoring tool) on Ubntu 14.10.md b/sources/tech/20150211 Install Linux-Dash (Web Based Monitoring tool) on Ubntu 14.10.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6817a75b03..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150211 Install Linux-Dash (Web Based Monitoring tool) on Ubntu 14.10.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,71 +0,0 @@
-Install Linux-Dash (Web Based Monitoring tool) on Ubntu 14.10
-================================================================================
-
-A low-overhead monitoring web dashboard for a GNU/Linux machine. Simply drop-in the app and go!.Linux Dash's interface provides a detailed overview of all vital aspects of your server, including RAM and disk usage, network, installed software, users, and running processes. All information is organized into sections, and you can jump to a specific section using the buttons in the main toolbar. Linux Dash is not the most advanced monitoring tool out there, but it might be a good fit for users looking for a slick, lightweight, and easy to deploy application.
-
-### Linux-Dash Features ###
-
-A beautiful web-based dashboard for monitoring server info
-
-Live, on-demand monitoring of RAM, Load, Uptime, Disk Allocation, Users and many more system stats
-
-Drop-in install for servers with Apache2/nginx + PHP
-
-Click and drag to re-arrange widgets
-
-Support for wide range of linux server flavors
-
-### List of Current Widgets ###
-
-- General info
-- Load Average
-- RAM
-- Disk Usage
-- Users
-- Software
-- IP
-- Internet Speed
-- Online
-- Processes
-- Logs
-
-### Install Linux-dash on ubuntu server 14.10 ###
-
-First you need to make sure you have [Ubuntu LAMP server 14.10][1] installed and Now you have to install the following package
-
- sudo apt-get install php5-json unzip
-
-After the installation this module will enable for apache2 so you need to restart the apache2 server using the following command
-
- sudo service apache2 restart
-
-Now you need to download the linux-dash package and install
-
- wget https://github.com/afaqurk/linux-dash/archive/master.zip
-
- unzip master.zip
-
- sudo mv linux-dash-master/ /var/www/html/linux-dash-master/
-
-Now you need to change the permissions using the following command
-
- sudo chmod 755 /var/www/html/linux-dash-master/
-
-Now you need to go to http://serverip/linux-dash-master/ you should see similar to the following output
-
-
-
-
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/install-linux-dash-web-based-monitoring-tool-on-ubntu-14-10.html
-
-作者:[ruchi][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
-[1]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/step-by-step-ubuntu-14-10-utopic-unicorn-lamp-server-setup.html
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150227 Enjoy Android Apps on Ubuntu using ARChon Runtime.md b/sources/tech/20150227 Enjoy Android Apps on Ubuntu using ARChon Runtime.md
deleted file mode 100644
index f85b2cf725..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150227 Enjoy Android Apps on Ubuntu using ARChon Runtime.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,114 +0,0 @@
-Enjoy Android Apps on Ubuntu using ARChon Runtime
-================================================================================
-Before, we gave try to many android app emulating tools like Genymotion, Virtualbox, Android SDK, etc to try to run android apps on it. But, with this new Chrome Android Runtime, we are able to run Android Apps on our Chrome Browser. So, here are the steps we'll need to follow to install Android Apps on Ubuntu using ARChon Runtime.
-
-Google had [announced the first set of Android apps is ready to run natively on Chrome OS][1], a feature made possible using a new ‘**Android Runtime**’ extension. Now, a developer named Vlad Filippov has figured out a way to bring Android Apps to Chrome on the desktop. His chromeos-apk script and ARChon Android Runtime extension work hand-in-hand to bring Android apps to Chrome browser on the Windows, Mac and Linux desktop.
-
-Performance of this apps through the runtime is not pretty good. Similarly, as its both an unofficial repackaging of the official runtime and running outside of Google's Chrome OS, system integration like webcam, speakers, etc. may be patchy or non-existent.
-
-### Installing Chrome ###
-
-First of all, we'll need Chrome installed in our machine, Chrome version 37 or higher is required. We can download them from the [download page of Chrome Browser][2].
-
-If you wanna install a Dev Channel version you'll need to follow below procedure.
-
-We'll need to add repository source list for Google Chrome which can be done my using the following command.
-
- $ wget -q -O - https://dl-ssl.google.com/linux/linux_signing_key.pub | sudo apt-key add -
- $ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb/ stable main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list'
-
-
-
-After adding the repository source list, we'll need to update the local repository index by the command below.
-
- $ sudo apt-get update
-
-Now, we'll gonna install google chrome unstable which is dev version.
-
- $ sudo apt-get install google-chrome-unstable
-
-
-
-### Installing Archon Runtime ###
-
-Next we'll need to download the custom-made ergo officially not endorsed by Google or Chromium Android Runtime created by Vlad Filippov. This differs from the official version in a number of ways, the chief being it can be used on desktop versions of the browser. Here below is the runtime we need to download, please select anyone of the following according to your bit of Ubuntu installed.
-
-For **32-bit** Ubuntu Distributions:
-
-- [Download Archron for 32-bit Ubuntu][3]
-
-For **64-bit** Ubuntu Distributions:
-
-- [Download Archron for 64-bit Ubuntu][4]
-
-Once the runtime has fully downloaded you will need to extract the contents from the .zip files and move the resulting directory to Home. Here is the gist commands for this steps to download and extract the contents.
-
- $ wget https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/releases/download/v3.0.0/ARChon-v1.1-x86_32.zip
-
-
-
- $ unzip ARChon-v1.1-x86_32.zip ~/
-
-Now to install the runtime, we'll gonna Open our latest Google Chrome and goto the url **chrome://extensions/** then, we'll need to check ‘**Enable developer mode**’. Finally, we'll gonna click on the ‘**load unpacked extension**’ button and select the folder which was placed into **~/Home**.
-
-### Installing ChromeOS-APK ###
-
-To convert APKs manually is something you really don’t need to do any more if you use one of the apps mentioned above — you will need to install the ‘[chromeos-apk][5]’ command line JavaScript utility. This is available to install through the Node Packaged Modules (npm) manager. To install nmp and chromeos-apk, we'll need to run the following command in a shell or terminal.
-
- $ sudo apt-get install npm nodejs nodejs-legacy
-
-**If you are running 64 bit OS**, you should grab the following library, to do so run the below commands in a shell or terminal.
-
- $ sudo apt-get install lib32stdc++6
-
-Now run the command to install the the latest chromeos-apk is:
-
- $ npm install -g chromeos-apk@latest
-
-
-
-Depending on your system configuration you may need to need to run this latter command as sudo.
-
-Now, we'll gonna for Google to find an APK of an app to give it a try, bearing in mind **not all Android apps will work**, and those that do may be unstable or lack features. Most of the messenger out of the box are not working.
-
-### Converting APK ###
-
-Place your **Android APK in ~/Home**, then return to **Terminal** to convert it using the following command:
-
- $ chromeos-apk myapp.apk --archon
-
-If you want the app in fullscreen mode then run the following instead:
-
- $ chromeos-apk myapp.apk --archon --tablet
-
-Note: Please replace myapp.apk to the Android APK app filename you want to convert.
-
-For our ease, we can also use [Twerk][6] for the conversion process if we want to skip this step.
-
-### Running Android Apk ###
-
-Finally, we'll need to open our chrome browser and then goto chrome://extensions page and enable developer mode then tap the ‘load unpacked extension’ button and select the folder the script above created.
-
-Now, we can Open the Chrome App Launcher to run it.
-
-### Conclusion ###
-
-Hurray! We have successfully installed Android Apk App in our favorite desktop browser ie Chrome Browser. This article is all about the popular Chrome Android Runtime called Archon created by Vlad Filippov. This runtime allows us to run converted Apk files in our Chrome browser. It has not yet supported messaging apps like Whatsapp, etc. So, if you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below. Thank you ! Enjoy Archon :-)
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/android-apps-ubuntu-archon-runtime/
-
-作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
-[1]:http://chrome.blogspot.com/2014/09/first-set-of-android-apps-coming-to.html
-[2]:https://www.google.com/chrome/browser
-[3]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/releases/download/v3.0.0/ARChon-v1.1-x86_32.zip
-[4]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/releases/download/v3.0.0/ARChon-v1.1-x86_64.zip
-[5]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/blob/master/README.md
-[6]:https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/twerk/jhdnjmjhmfihbfjdgmnappnoaehnhiaf
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150316 5 Interesting Command Line Tips and Tricks in Linux--Part 1.md b/sources/tech/20150316 5 Interesting Command Line Tips and Tricks in Linux--Part 1.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 352fa2816c..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150316 5 Interesting Command Line Tips and Tricks in Linux--Part 1.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,115 +0,0 @@
-5 Interesting Command Line Tips and Tricks in Linux – Part 1
-================================================================================
-Are you making most out of the Linux? There are lots of helpful features which appears to be Tips and Tricks for many of Linux Users. Sometimes Tips and Tricks become the need. It helps you get productive with the same set of commands yet with enhanced functionality.
-
-
-5 Command Line Tips and Tricks
-
-Here we are starting a new series, where we will be writing some tips and tricks and will try to yield as more as we can in small time.
-
-### 1. To audit the commands we’d run in past, we use [history command][1]. Here is a sample output of history command. ###
-
- # history
-
-
-history command example
-
-Obvious from output, the history command do not output the time stamp with the log of last executed commands. Any solution for this? Yeah! Run the below command.
-
- # HISTTIMEFORMAT="%d/%m/%y %T "
- # history
-
-If you want to permanently append this change, add the below line to `~/.bashrc`.
-
- export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%d/%m/%y %T "
-
-and then, from terminal run,
-
- # source ~/.bashrc
-
-Explanation of commands and switches.
-
-- history – GNU History Library
-- HISTIMEFORMAT – Environmental Variable
-- %d – Day
-- %m – Month
-- %y – Year
-- %T – Time Stamp
-- source – in short send the contents of file to shell
-- .bashrc – is a shell script that BASH runs whenever it is started interactively.
-
-
-history Command Logs
-
-### 2. The next gem in the list is – how to check disk write speed? Well one liner dd command script serves the purpose. ###
-
- # dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/output.img bs=8k count=256k conv=fdatasync; rm -rf /tmp/output.img
-
-
-dd Command Example
-
-Explanation of commands and switches.
-
-- dd – Convert and Copy a file
-- if=/dev/zero – Read the file and not stdin
-- of=/tmp/output.img – Write to file and not stdout
-- bs – Read and Write maximum upto M bytes, at one time
-- count – Copy N input block
-- conv – Convert the file as per comma separated symbol list.
-- rm – Removes files and folder
-- -rf – (-r) removes directories and contents recursively and (-f) Force the removal without prompt.
-
-### 3. How will you check the top six files that are eating out your space? A simple one liner script made from [du command][2], which is primarily used as file space usages. ###
-
- # du -hsx * | sort -rh | head -6
-
-
-Check Disk Space Usage
-
-Explanation of commands and switches.
-
-- du – Estimate file space usages
-- -hsx – (-h) Human Readable Format, (-s) Summaries Output, (-x) One File Format, skip directories on other file format.
-- sort – Sort text file lines
-- -rf – (-r) Reverse the result of comparison, (-f) Ignore case
-- head – output first n lines of file.
-
-### 4. The next step involves statistics in terminal of a file of every kind. We can output the statistics related to a file with the help of stat (output file/fileSystem status) command. ###
-
- # stat filename_ext (viz., stat abc.pdf)
-
-
-Check File Statistics
-
-### 5. The next and last but not the least, this one line script is for those, who are newbies. If you are an experienced user you probably don’t need it, unless you want some fun out of it. Well newbies are Linux-command-line phobic and the below one liner will generate random man pages. The benefit is as a newbie you always get something to learn and never get bored. ###
-
- # man $(ls /bin | shuf | head -1)
-
-
-Generate Random Man Pages
-
-Explanation of commands and switches.
-
-- man – Linux Man pages
-- ls – Linux Listing Commands
-- /bin – System Binary file Location
-- shuf – Generate Random Permutation
-- head – Output first n line of file.
-
-That’s all for now. If you know any such tips and tricks you may share with us and we will post the same in your words on our reputed Tecmint.com website.
-
-If you want to share any tips and tricks that you cannot make into article you may share it at tecmint[dot]com[at]gmail[dot]com and we will include it in our article. Don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments below. Keep connected. Like and share us and help us get spread.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.tecmint.com/5-linux-command-line-tricks/
-
-作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
-[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/history-command-examples/
-[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/check-linux-disk-usage-of-files-and-directories/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150316 How to Test Your Internet Speed Bidirectionally from Command Line Using 'Speedtest-CLI' Tool.md b/sources/tech/20150316 How to Test Your Internet Speed Bidirectionally from Command Line Using 'Speedtest-CLI' Tool.md
index a2e5ebc1d8..a0c77c21f9 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20150316 How to Test Your Internet Speed Bidirectionally from Command Line Using 'Speedtest-CLI' Tool.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20150316 How to Test Your Internet Speed Bidirectionally from Command Line Using 'Speedtest-CLI' Tool.md
@@ -129,4 +129,4 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/check-internet-speed-from-command-line-in-linux/
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
-[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/speedtest-mini-server-to-test-bandwidth-speed/
\ No newline at end of file
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/speedtest-mini-server-to-test-bandwidth-speed/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150318 How to Manage and Use LVM (Logical Volume Management) in Ubuntu.md b/sources/tech/20150318 How to Manage and Use LVM (Logical Volume Management) in Ubuntu.md
index d062a85336..ecfb639d54 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20150318 How to Manage and Use LVM (Logical Volume Management) in Ubuntu.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20150318 How to Manage and Use LVM (Logical Volume Management) in Ubuntu.md
@@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
-translating by runningwater
How to Manage and Use LVM (Logical Volume Management) in Ubuntu
================================================================================

diff --git a/sources/tech/20150318 How to Use LVM on Ubuntu for Easy Partition Resizing and Snapshots.md b/sources/tech/20150318 How to Use LVM on Ubuntu for Easy Partition Resizing and Snapshots.md
index 7554abd392..883c5e3203 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20150318 How to Use LVM on Ubuntu for Easy Partition Resizing and Snapshots.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20150318 How to Use LVM on Ubuntu for Easy Partition Resizing and Snapshots.md
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
+
How to Use LVM on Ubuntu for Easy Partition Resizing and Snapshots
================================================================================

diff --git a/sources/tech/20150318 How to share a directory with Samba on Fedora or CentOS.md b/sources/tech/20150318 How to share a directory with Samba on Fedora or CentOS.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 0c01862bff..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150318 How to share a directory with Samba on Fedora or CentOS.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,144 +0,0 @@
-How to share a directory with Samba on Fedora or CentOS
-================================================================================
-Nowadays sharing data across different computers is not something new at home or many work places. Riding on this trend, modern operating systems make it easy to share and exchange data transparently across computers via network file systems. If your work environment involves a mix of Microsoft Windows and Linux computers, one way to share files and folders among them is via SMB/CIFS, a cross-platform network file sharing protocol. Windows Microsoft natively supports SMB/CIFS, while Linux offers free software implementation of SMB/CIFS network protocol in Samba.
-
-In this article, we will demonstrate **how to share a directory using Samba**. The Linux platform we will use is **Fedora or CentOS**. This article is dividied into four parts. First, we will install Samba under Fedora/CentOS environment. Next, we discuss how to adjust SELinux and firewall configurations to allow file sharing with Samba. Finally, we cover how to enable Samba to share a directory.
-
-### Step One: Install Samba on Fedora or CentOS ###
-
-First thing first. Let's install Samba and configure basic settings.
-
-Check whether Samba application is already installed on your system by running:
-
- $ rpm -q samba samba-common samba-client
-
-If the above command doesn't show anything at all, it means that Samba is not installed. In that case, install Samba using the command below.
-
- $ sudo yum install samba samba-common samba-client
-
-Next, creates a local directory which will share data over network. This directory will be exported to remote users as a Samba share. In this tutorial, we will create this directory in the top-level directory '/', so make sure that you have the privileges to do it.
-
- $ sudo mkdir /shared
-
-If you want to create a shared directory inside your home directory (e.g., ~/shared), you must activate Samba home directory sharing in the SELinux options, which will be described below in more detail.
-
-After creating /shared directory, set the privileges of the directory so other users can access it.
-
- $ sudo chmod o+rw /shared
-
-If you don't want other users to be able to have write to the directory, just remove the 'w' option in chmod command as follows.
-
- $ sudo chmod o+r /shared
-
-Next, create one empty file as a test. This file will be used to verify that he Samba share is mounted properly.
-
- $ sudo touch /shared/file1
-
-### Step Two: Configure SELinux for Samba ###
-
-Next, we need to re-configure SELinux which is enabled by default in Fedora and CentOS distributions. SELinux allows Samba to read and modify files or directories only when they have the right security context (e.g., labeled with the 'samba_share_t' attribute).
-
-The following command adds the necessary label to file-context configuration:
-
- $ sudo semanage fcontext -a -t samba_share_t "<directory>(/.*)?"
-
-Replace the <directory> with the local directory we created earlier for Samba share (e.g., /shared):
-
- $ sudo semanage fcontext -a -t samba_share_t "/shared(/.*)?"
-
-To activate the label change, we then must run the restorecon command like below.
-
- $ sudo restorecon -R -v /shared
-
-
-
-To share a directory inside our home directory via Samba, we must enable sharing home directory option in SELinux because it is disabled by default. The following command achieves the desired effect. Skip this step if you are not sharing your home directory.
-
- $ sudo setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs 1
-
-### Step Three: Configure Firewall for Samba ###
-
-The next step is to open necessary TCP/UDP ports in the firewall settings for Samba to operate.
-
-If you are using firewalld (e.g., on Fedora or CentOS 7), the following command will take care of permanent firewall rule change for Samba service.
-
- $ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=samba
-
-If you are using iptables for your firewall (e.g., CentOS 6 or earlier), use the following commands to open up necessary Samba ports to the world.
-
- $ sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
-
-----------
-
- -A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 445 -j ACCEPT
- -A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -m state --state NEW -m udp -p udp --dport 445 -j ACCEPT
- -A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -m state --state NEW -m udp -p udp --dport 137 -j ACCEPT
- -A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -m state --state NEW -m udp -p udp --dport 138 -j ACCEPT
- -A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 139 -j ACCEPT
-
-Then restart iptables service:
-
- $ sudo service iptables restart
-
-### Step Four: Change Samba Configuration ###
-
-The last step is to configure Samba to export a created local directory as a Samba-share.
-
-Open the Samba configuration file with a text editor, and add the following lines at the bottom of the file.
-
- $ sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
-
-----------
-
- [myshare]
- comment=my shared files
- path=/shared
- public=yes
- writeable=yes
-
-In the above the text inside a pair of brackets (e.g., "myshare") is the name of the Samba-shared resource, which will be used to access the Samba share from a remote host.
-
-Create a Samba user account which is required to mount and export the Samba file system. To create a Samba user, use the smbpasswd tool. Note that the Samba user account must be the same as any existing Linux user. If you try to add a non-existing user with smbpasswd, it will give an error message.
-
-If you don't want to use any existing Linux user as a Samba user, you can create a new dedicated user in your system. For safety, set the new user's login shell to /sbin/nologin, and do not create its home directory.
-
-In this example, we are creating a new user named "sambaguest" as follows.
-
- $ sudo useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin sambaguest
- $ sudo passwd sambaguest
-
-
-
-After creating a new user, add the user as a Samba user using smbpasswd command. When this command asks a password, you can type a different password than the user's password.
-
- $ sudo smbpasswd -a sambaguest
-
-4. Activate the Samba service, and check whether the Samba service is running or not.
-
- $ sudo systemctl enable smb.service
- $ sudo systemctl start smb.service
- $ sudo systemctl is-active smb
-
-
-
-To see the list of shared directories in Samba, type the following command.
-
- $ smbclient -U sambaguest -L localhost
-
-
-
-The following is a screenshot of accessing the Samba-shared directory on Thunar file manager, and doing copy-paste of file1. Note that the Samba share is accessible via "smb://<samba-server-IP-address>/myshare" address on Thunar.
-
-
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://xmodulo.com/share-directory-samba-fedora-centos.html
-
-作者:[Kristophorus Hadiono][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/kristophorus
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150320 Sleuth Kit--Open Source Forensic Tool to Analyze Disk Images and Recover Files.md b/sources/tech/20150320 Sleuth Kit--Open Source Forensic Tool to Analyze Disk Images and Recover Files.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 2f138a9e3d..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150320 Sleuth Kit--Open Source Forensic Tool to Analyze Disk Images and Recover Files.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,159 +0,0 @@
-Sleuth Kit - Open Source Forensic Tool to Analyze Disk Images and Recover Files
-================================================================================
-SIFT is a Ubuntu based forensics distribution provided by SANS Inc. It consist of many forensics tools such as Sleuth kit / Autopsy etc . However, Sleuth kit/Autopsy tools can be installed on Ubuntu/Fedora distribution instead of downloading complete distribution of SIFT.
-
-Sleuth Kit /Autopsy is open source digital forensics investigation tool which is used for recovering the lost files from disk image and analysis of images for incident response. Autopsy tool is a web interface of sleuth kit which supports all features of sleuth kit. This tool is available for both Windows and Linux Platforms.
-
-### Install Sleuth kit ###
-
-First of all, download Sleuth kit software from [sleuthkit][1] website. Use wget command to download it in terminal which is shown in the figure.
-
- # wget http://cznic.dl.sourceforge.net/project/sleuthkit/sleuthkit/4.1.3/sleuthkit-4.1.3.tar.gz
-
-
-
-Extract the sleuthkit-4.1.3.tar.gz using following command and go inside the extracted directory
-
- # tar -xvzf sleuthkit-4.1.3.tar.gz
-
-
-
-Run following command which perform the requirement check before sleuth kit installation
-
- #./configure
-
-
-
-Make command compile the sleuth kit code.
-
- #make
-
-
-
-Finally following command install it under **/usr/local** path.
-
- #make install
-
-
-
-### Install Autopsy Tool ###
-
-Sleuth kit installation is complete and now we will install autopsy interface. Download Autopsy software from [sleuthkit's autopsy page][2] . Use wget command to download it in terminal which is shown in the figure.
-
- # wget http://kaz.dl.sourceforge.net/project/autopsy/autopsy/2.24/autopsy-2.24.tar.gz
-
-
-
-Extract the autopsy-2.24.tar.gz using following command and go inside the extracted directory
-
- # tar -xvzf autopsy-2.24.tar.gz
-
-
-
-Configuration script of autopsy asks for NSRL (National Software Reference Library) and path of **Evidence_Locker** folder.
-
-Enter "n" for NSRL prompt and create Evidence_Locker folder under **/usr/local** directory. Autopsy stores the configuration files, audit logs and output under Evidence_Locker folder.
-
- #mkdir /usr/local/Evidence_Locker
-
- #cd autopsy-2.24
-
- #./configure
-
-
-
-After adding Evidence_Locker path in installation process , autopsy stores configuration files in it and shows a following message to run the autopsy program.
-
-
-
-Type **./autopsy** command in terminal to start the graphical interface of Sleuth kit tool.
-
-
-
-Type following address in the web browser to access the interface of autopsy .
-
- http://localhost:9999/autopsy
-
-Main web page of autopsy plugin is shown int the following figure.
-
-
-
-Click on the **New Case** button to start analysis in autopsy tool. Enter the case name, description about the investigation and name of agent which is shown in the following figure.
-
-
-
-Following web page will appear after entering the details in the above page. Click on **Add Host** button to add details for the analyst machine.
-
-
-
-Enter host name, description and time zone setting of analyst machine on the next page.
-
-
-
-Click on the **Add Image** button to add image file for forensics analysis.
-
-
-
-Click on the **Add Image File** button on the following web page. It opens new web page which require Path of image file and select type & importing method.
-
-
-
-As shown in the following figure, we have entered path of Linux image file. In our case, image file is partition of disk.
-
-
-
-Click on the next button and select **Calculate hash** option in the next page which is shown in the following figure. It also detect the file system type of the given image.
-
-
-
-Following window shows the MD5 hash of the image file before static analysis .
-
-
-
-On the next web page, autopsy shows following information about the image file.
-
-- mount point for the image
-- name of image
-- file system type of given image
-
-Click on the **details** button to get more information about the given image file. It also offer extraction of unallocated fragments and strings from the volume of image file which is shown in the following figure.
-
-
-
-Click on **Analyze** button which is shown in the below figure to start analysis on given image . It opens another page which shows the multiple options for image analysis.
-
-
-
-Autopsy offer following features during image analysis process.
-
-- File Analysis
-- Keyword Search
-- File Type
-- Image Details
-- Data Unit
-
-File Analysis on given image of Linux partition is shown in the following figure.
-
-
-
-It extracts all files and folders from the given image . Extraction of deleted files are shown int he figure.
-
-
-
-### Conclusion ###
-
-Hopefully this article will be useful for the beginner in static forensics analysis of disk image. Autopsy is web interface for sleuth kit which provides features such as extraction of strings , recovery of deleted files, timeline analysis, extraction of web surfing history, keyword search and email analysis on windows and linux disk images.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/autopsy-sleuth-kit-installation-ubuntu/
-
-作者:[nido][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/naveeda/
-[1]:http://www.sleuthkit.org/sleuthkit/download.php
-[2]:http://www.sleuthkit.org/autopsy/download.php
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150323 How to set up networking between Docker containers.md b/sources/tech/20150323 How to set up networking between Docker containers.md
deleted file mode 100644
index dca3457c4e..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150323 How to set up networking between Docker containers.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,161 +0,0 @@
-[bazz222]
-How to set up networking between Docker containers
-================================================================================
-As you may be aware, Docker container technology has emerged as a viable lightweight alternative to full-blown virtualization. There are a growing number of use cases of Docker that the industry adopted in different contexts, for example, enabling rapid build environment, simplifying configuration of your infrastructure, isolating applications in multi-tenant environment, and so on. While you can certainly deploy an application sandbox in a standalone Docker container, many real-world use cases of Docker in production environments may involve deploying a complex multi-tier application in an ensemble of multiple containers, where each container plays a specific role (e.g., load balancer, LAMP stack, database, UI).
-
-There comes the problem of **Docker container networking**: How can we interconnect different Docker containers spawned potentially across different hosts when we do not know beforehand on which host each container will be created?
-
-One pretty neat open-source solution for this is [weave][1]. This tool makes interconnecting multiple Docker containers pretty much hassle-free. When I say this, I really mean it.
-
-In this tutorial, I am going to demonstrate **how to set up Docker networking across different hosts using weave**.
-
-### How Weave Works ###
-
-
-
-Let's first see how weave works. Weave creates a network of "peers", where each peer is a virtual router container called "weave router" residing on a distinct host. The weave routers on different hosts maintain TCP connections among themselves to exchange topology information. They also establish UDP connections among themselves to carry inter-container traffic. A weave router on each host is then connected via a bridge to all other Docker containers created on the host. When two containers on different hosts want to exchange traffic, a weave router on each host captures their traffic via a bridge, encapsulates the traffic with UDP, and forwards it to the other router over a UDP connection.
-
-Each weave router maintains up-to-date weave router topology information, as well as container's MAC address information (similar to switch's MAC learning), so that it can make forwarding decision on container traffic. Weave is able to route traffic between containers created on hosts which are not directly reachable, as long as two hosts are interconnected via an intermediate weave router on weave topology. Optionally, weave routers can be set to encrypt both TCP control data and UDP data traffic based on public key cryptography.
-
-### Prerequisite ###
-
-Before using weave on Linux, of course you need to set up Docker environment on each host where you want to run [Docker][2] containers. Check out [these][3] [tutorials][4] on how to create Docker containers on Ubuntu or CentOS/Fedora.
-
-Once Docker environment is set up, install weave on Linux as follows.
-
- $ wget https://github.com/zettio/weave/releases/download/latest_release/weave
- $ chmod a+x weave
- $ sudo cp weave /usr/local/bin
-
-Make sure that /usr/local/bin is include in your PATH variable by appending the following in /etc/profile.
-
- export PATH="$PATH:/usr/local/bin"
-
-Repeat weave installation on every host where Docker containers will be deployed.
-
-Weave uses TCP/UDP 6783 port. If you are using firewall, make sure that these port numbers are not blocked by the firewall.
-
-### Launch Weave Router on Each Host ###
-
-When you want to interconnect Docker containers across multiple hosts, the first step is to launch a weave router on every host.
-
-On the first host, run the following command, which will create and start a weave router container.
-
- $ sudo weave launch
-
-The first time you run this command, it will take a couple of minutes to download a weave image before launching a router container. On successful launch, it will print the ID of a launched weave router.
-
-To check the status of the router, use this command:
-
- $ sudo weave status
-
-
-
-Since this is the first weave router launched, there will be only one peer in the peer list.
-
-You can also verify the launch of a weave router by using docker command.
-
- $ docker ps
-
-
-
-On the second host, run the following command, where we specify the IP address of the first host as a peer to join.
-
- $ sudo weave launch <first-host-IP-address>
-
-When you check the status of the router, you will see two peers: the current host and the first host.
-
-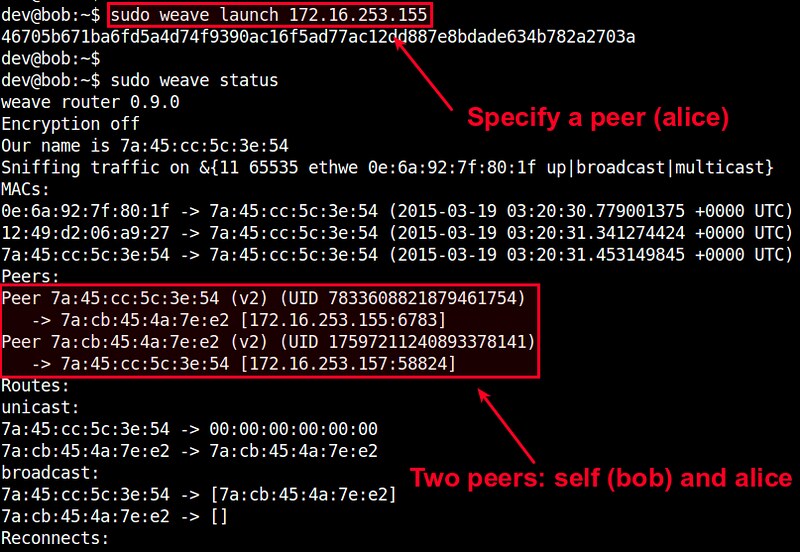
-
-As you launch more routers on subsequent hosts, the peer list will grow accordingly. When launching a router, just make sure that you specify any previously launched peer's IP address.
-
-At this point, you should have a weave network up and running, which consists of multiple weave routers across different hosts.
-
-### Interconnect Docker Containers across Multiple Hosts ###
-
-Now it is time to launch Docker containers on different hosts, and interconnect them on a virtual network.
-
-Let's say we want to create a private network 10.0.0.0/24, to interconnect two Docker containers. We will assign random IP addressses from this subnet to the containers.
-
-When you create a Docker container to deploy on a weave network, you need to use weave command, not docker command. Internally, the weave command uses docker command to create a container, and then sets up Docker networking on it.
-
-Here is how to create a Ubuntu container on hostA, and attach the container to 10.0.0.0/24 subnet with an IP addresss 10.0.0.1.
-
- hostA:~$ sudo weave run 10.0.0.1/24 -t -i ubuntu
-
-On successful run, it will print the ID of a created container. You can use this ID to attach to the running container and access its console as follows.
-
- hostA:~$ docker attach <container-id>
-
-Move to hostB, and let's create another container. Attach it to the same subnet (10.0.0.0/24) with a different IP address 10.0.0.2.
-
- hostB:~$ sudo weave run 10.0.0.2/24 -t -i ubuntu
-
-Let's attach to the second container's console as well:
-
- hostB:~$ docker attach <container-id>
-
-At this point, those two containers should be able to ping each other via the other's IP address. Verify that from each container's console.
-
-
-
-If you check the interfaces of each container, you will see an interface named "ethwe" which is assigned an IP address (e.g., 10.0.0.1 and 10.0.0.2) you specified.
-
-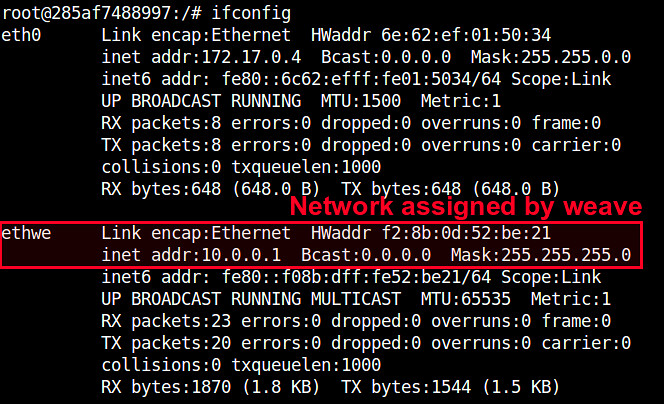
-
-### Other Advanced Usages of Weave ###
-
-Weave offers a number of pretty neat features. Let me briefly cover a few here.
-
-#### Application Isolation ####
-
-Using weave, you can create multiple virtual networks and dedicate each network to a distinct application. For example, create 10.0.0.0/24 for one group of containers, and 10.10.0.0/24 for another group of containers, and so on. Weave automatically takes care of provisioning these networks, and isolating container traffic on each network. Going further, you can flexibly detach a container from one network, and attach it to another network without restarting containers. For example:
-
-First launch a container on 10.0.0.0/24:
-
- $ sudo weave run 10.0.0.2/24 -t -i ubuntu
-
-Detach the container from 10.0.0.0/24:
-
- $ sudo weave detach 10.0.0.2/24 <container-id>
-
-Re-attach the container to another network 10.10.0.0/24:
-
- $ sudo weave attach 10.10.0.2/24 <container-id>
-
-
-
-Now this container should be able to communicate with other containers on 10.10.0.0/24. This is a pretty useful feature when network information is not available at the time you create a container.
-
-#### Integrate Weave Networks with Host Network ####
-
-Sometimes you may need to allow containers on a virtual weave network to access physical host network. Conversely, hosts may want to access containers on a weave network. To support this requirement, weave allows weave networks to be integrated with host network.
-
-For example, on hostA where a container is running on network 10.0.0.0/24, run the following command.
-
- hostA:~$ sudo weave expose 10.0.0.100/24
-
-This will assign IP address 10.0.0.100 to hostA, so that hostA itself is also connected to 10.0.0.0/24 network. Obviously, you need to choose an IP address which is not used by any other containers on the network.
-
-At this point, hostA should be able to access any containers on 10.0.0.0/24, whether or not the containers are residing on hostA. Pretty neat!
-
-### Conclusion ###
-
-As you can see, weave is a pretty useful Docker networking tool. This tutorial only covers a glimpse of [its powerful features][5]. If you are more ambitious, you can try its multi-hop routing, which can be pretty useful in multi-cloud environment, dynamic re-routing, which is a neat fault-tolerance feature, or even its distributed DNS service which allows you to name containers on weave networks. If you decide to use this gem in your environment, feel free to share your use case!
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://xmodulo.com/networking-between-docker-containers.html
-
-作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
-[1]:https://github.com/zettio/weave
-[2]:http://xmodulo.com/recommend/dockerbook
-[3]:http://xmodulo.com/manage-linux-containers-docker-ubuntu.html
-[4]:http://xmodulo.com/docker-containers-centos-fedora.html
-[5]:http://zettio.github.io/weave/features.html
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150324 7 Quirky' ls' Command Tricks Every Linux User Should Know.md b/sources/tech/20150324 7 Quirky' ls' Command Tricks Every Linux User Should Know.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9878cc8cee..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150324 7 Quirky' ls' Command Tricks Every Linux User Should Know.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,163 +0,0 @@
-7 Quirky ‘ls’ Command Tricks Every Linux User Should Know
-================================================================================
-We have covered most of the things on ‘ls‘ command in last two articles of our Interview series. This article is the last part of the ‘ls command‘ series. If you have not gone through last two articles of this series you may visit the links below.
-
-注:以下三篇都做过源文,看看翻译了没有,如果发布了可适当改链接地址
-- [15 Basic ‘ls’ Command Examples in Linux][]
-- [15 Interview Questions on Linux “ls” Command – Part 1][]
-- [10 Useful ‘ls’ Command Interview Questions – Part 2][]
-
-
-7 Quirky ls Command Tricks
-
-### 1. List the contents of a directory with time using various time styles. ###
-
-To list the contents of a directory with times using style, we need to choose any of the below two methods.
-
- # ls -l –time-style=[STYLE] (Method A)
-
-**Note** – The above switch (`--time` style must be run with switch `-l`, else it won’t serve the purpose).
-
- # ls –full-time (Method B)
-
-Replace `[STYLE]` with any of the below option.
-
- full-iso
- long-iso
- iso
- locale
- +%H:%M:%S:%D
-
-**Note** – In the above line H(Hour), M(Minute), S(Second), D(Date) can be used in any order.
-
-Moreover you just choose those relevant and not all options. E.g., `ls -l --time-style=+%H` will show only hour.
-
-`ls -l --time-style=+%H:%M:%D` will show Hour, Minute and date.
-
- # ls -l --time-style=full-iso
-
-
-ls Command Full Time Style
-
- # ls -l --time-style=long-iso
-
-
-Long Time Style Listing
-
- # ls -l --time-style=iso
-
-
-Time Style Listing
-
- # ls -l --time-style=locale
-
-
-Locale Time Style Listing
-
- # ls -l --time-style=+%H:%M:%S:%D
-
-
-Date and Time Style Listing
-
- # ls --full-time
-
-
-
-Full Style Time Listing
-
-### 2. Output the contents of a directory in various formats such as separated by commas, horizontal, long, vertical, across, etc. ###
-
-Contents of directory can be listed using ls command in various format as suggested below.
-
-- across
-- comma
-- horizontal
-- long
-- single-column
-- verbose
-- vertical
-
- # ls –-format=across
- # ls --format=comma
- # ls --format=horizontal
- # ls --format=long
- # ls --format=single-column
- # ls --format=verbose
- # ls --format=vertical
-
-
-Listing Formats of ls Command
-
-### 3. Use ls command to append indicators like (/=@|) in output to the contents of the directory. ###
-
-The option `-p` with ‘ls‘ command will server the purpose. It will append one of the above indicator, based upon the type of file.
-
- # ls -p
-
-
-Append Indicators to Content
-
-### 4. Sort the contents of directory on the basis of extension, size, time and version. ###
-
-We can use options like `--extension` to sort the output by extension, size by extension `--size`, time by using extension `-t` and version using extension `-v`.
-
-Also we can use option `--none` which will output in general way without any sorting in actual.
-
- # ls --sort=extension
- # ls --sort=size
- # ls --sort=time
- # ls --sort=version
- # ls --sort=none
-
-
-Sort Listing of Content by Options
-
-### 5. Print numeric UID and GID for every contents of a directory using ls command. ###
-
-The above scenario can be achieved using flag -n (Numeric-uid-gid) along with ls command.
-
- # ls -n
-
-
-Print Listing of Content by UID and GID
-
-### 6. Print the contents of a directory on standard output in more columns than specified by default. ###
-
-Well ls command output the contents of a directory according to the size of the screen automatically.
-
-We can however manually assign the value of screen width and control number of columns appearing. It can be done using switch ‘`--width`‘.
-
- # ls --width 80
- # ls --width 100
- # ls --width 150
-
-
-List Content Based on Window Sizes
-
-**Note**: You can experiment what value you should pass with width flag.
-
-### 7. Include manual tab size at the contents of directory listed by ls command instead of default 8. ###
-
- # ls --tabsize=[value]
-
-
-List Content by Table Size
-
-**Note**: Specify the `[Value]=` Numeric value.
-
-That’s all for now. Stay tuned to Tecmint till we come up with next article. Do not forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments below. Like and share us and help us get spread.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-ls-command-tricks/
-
-作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
-[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/15-basic-ls-command-examples-in-linux/
-[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/ls-command-interview-questions/
-[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/ls-interview-questions/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150326 How to set up server monitoring system with Monit.md b/sources/tech/20150326 How to set up server monitoring system with Monit.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c8f9efaecd..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150326 How to set up server monitoring system with Monit.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,252 +0,0 @@
-How to set up server monitoring system with Monit
-================================================================================
-Many Linux admins rely on a centralized remote monitoring system (e.g., [Nagios][1] or [Cacti][2]) to check the health of their network infrastructure. While centralized monitoring makes an admin's life easy when dealing with many hosts and devices, a dedicated monitoring box obviously becomes a single point of failure; if the monitoring box goes down or becomes unreachable for whatever reason (e.g., bad hardware or network outage), you will lose visibility on your entire infrastructure.
-
-One way to add redundancy to your monitoring system is to install standalone monitoring software (as a fallback) at least on any critical/core servers on your network. In case a centralized monitor is down, you will still be able to maintain visibility on your core servers from their backup monitor.
-
-### What is Monit? ###
-
-[Monit][3] is a cross-platform open-source tool for monitoring Unix/Linux systems (e.g., Linux, BSD, OSX, Solaris). Monit is extremely easy to install and reasonably lightweight (with only 500KB in size), and does not require any third-party programs, plugins or libraries. Yet, Monit lends itself to full-blown monitoring, capable of process status monitoring, filesystem change monitoring, email notification, customizable actions for core services, and so on. The combination of ease of setup, lightweight implementation and powerful features makes Monit an ideal candidate for a backup monitoring tool.
-
-I have been using Monit for several years on multiple hosts, and I am very pleased how reliable it has been. Even as a full-blown monitoring system, Monit is very useful and powerful for any Linux admin. In this tutorial, let me demonstrate how to set up Monit on a local server (as a backup monitor) to monitor common services. With this setup, I will only scrach the surface of what Monit can do for us.
-
-### Installation of Monit on Linux ###
-
-Most Linux distributions already include Monit in their repositories.
-
-Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
-
- $ sudo aptitude install monit
-
-Fedora or CentOS/RHEL:
-
-On CentOS/RHEL, you must enable either [EPEL][4] or [Repoforge][5] repository first.
-
- # yum install monit
-
-Monit comes with a very well documented configuration file with a lots of examples. The main configuration file is located in /etc/monit.conf in Fedora/CentOS/RHEL, or /etc/monit/monitrc in Debian/Ubuntu/Mint. Monit configuration has two parts: "Global" and "Services" sections.
-
-Gl### ###obal Configuration: Web Status Page
-
-Monit can use several mail servers for notifications, and/or an HTTP/HTTPS status page. Let's start with the web status page with the following requirements.
-
-- Monit listens on port 1966.
-- Access to the web status page is encrypted with SSL.
-- Login requires monituser/romania as user/password.
-- Login is permitted from localhost, myhost.mydomain.ro, and internal LAN (192.168.0.0/16) only.
-- Monit stores an SSL certificate in a pem format.
-
-For subsequent steps, I will use a Red Hat based system. Similar steps will be applicable on a Debian based system.
-
-First, generate and store a self-signed certificate (monit.pem) in /var/cert.
-
- # mkdir /var/certs
- # cd /etc/pki/tls/certs
- # ./make-dummy-cert monit.pem
- # cp monit.pem /var/certs
- # chmod 0400 /var/certs/monit.pem
-
-Now put the following snippet in the Monit's main configuration file. You can start with an empty configuration file or make a copy of the original file.
-
- set httpd port 1966 and
- SSL ENABLE
- PEMFILE /var/certs/monit.pem
- allow monituser:romania
- allow localhost
- allow 192.168.0.0/16
- allow myhost.mydomain.ro
-
-### Global Configuration: Email Notification ###
-
-Next, let's set up email notification in Monit. We need at least one active [SMTP server][6] which can send mails from the Monit host. Something like the following will do (adjust it for your case):
-
-- Mail server hostname: smtp.monit.ro
-- Sender email address used by monit (from): monit@monit.ro
-- Who will receive mail from monit daemon: guletz@monit.ro
-- SMTP port used by mail server: 587 (default is 25)
-
-With the above information, email notification would be configured like this:
-
- set mailserver smtp.monit.ro port 587
- set mail-format {
- from: monit@monit.ro
- subject: $SERVICE $EVENT at $DATE on $HOST
- message: Monit $ACTION $SERVICE $EVENT at $DATE on $HOST : $DESCRIPTION.
-
- Yours sincerely,
- Monit
-
- }
-
- set alert guletz@monit.ro
-
-As you can see, Monit offers several built-in variables ($DATE, $EVENT, $HOST, etc.), and you can customize your email message for your needs. If you want to send mails from the Monit host itself, you need a sendmail-compatible program (e.g., postfix or ssmtp) already installed.
-
-### Global Configuration: Monit Daemon ###
-
-The next part is setting up monit daemon. We will set it up as follows.
-
-- Performs the first check after 120 seconds.
-- Checks services once every 3 minutes.
-- Use syslog for logging.
-
-Place the following snippet to achieve the above setting.
-
- set daemon 120
- with start delay 240
- set logfile syslog facility log_daemon
-
-We must also define "idfile", a unique ID used by monit demon, and "eventqueue", a path where mails sent by monit but undelivered due to SMTP/network errors. Verifiy that path (/var/monit) already exists. The following configuration will do.
-
- set idfile /var/monit/id
- set eventqueue
- basedir /var/monit
-
-### Test Global Configuration ###
-
-Now the "Global" section is finished. The Monit configuration file will look like this:
-
- # Global Section
-
- # status webpage and acl's
- set httpd port 1966 and
- SSL ENABLE
- PEMFILE /var/certs/monit.pem
- allow monituser:romania
- allow localhost
- allow 192.168.0.0/16
- allow myhost.mydomain.ro
-
- # mail-server
- set mailserver smtp.monit.ro port 587
- # email-format
- set mail-format {
- from: monit@monit.ro
- subject: $SERVICE $EVENT at $DATE on $HOST
- message: Monit $ACTION $SERVICE $EVENT at $DATE on $HOST : $DESCRIPTION.
-
- Yours sincerely,
- Monit
-
- }
-
- set alert guletz@monit.ro
-
- # delay checks
- set daemon 120
- with start delay 240
- set logfile syslog facility log_daemon
-
- # idfile and mail queue path
- set idfile /var/monit/id
- set eventqueue
- basedir /var/monit
-
-Now it is time to check what we have done. You can test an existing configuration file (/etc/monit.conf) by running:
-
- # monit -t
-
-----------
-
- Control file syntax OK
-
-If Monit complains about any error, please review the configuration file again. Fortunately, error/warnings messages are informative. For example:
-
- monit: Cannot stat the SSL server PEM file '/var/certs/monit.pem' -- No such file or directory
- /etc/monit/monitrc:10: Warning: hostname did not resolve 'smtp.monit.ro'
-
-Once you verify the syntax of configuration, start monit daemon, and wait 2 to 3 minutes:
-
- # service monit start
-
-If you are using systemd, run:
-
- # systemctl start monit
-
-Now open a browser window, and go to https://<monit_host>:1966. Replace &<monit_host> with your Monit hostname or IP address.
-
-Note that if you have a self-signed SSL certificate, you will see a warning message in your browser.
-
-
-
-After you have completed login, you must see the following page.
-
-
-
-In the rest of the tutorial, let me show how we can monitor a local server and common services. You will see a lot of useful examples on the [official wiki page][7]. Most of them are copy-and-pastable!
-
-### Service Configuration: CPU/Memory Monitoring ###
-
-Let start with monitoring a local server's CPU/memory usage. Copy the following snippet in the configuration file.
-
- check system localhost
- if loadavg (1min) > 10 then alert
- if loadavg (5min) > 6 then alert
- if memory usage > 75% then alert
- if cpu usage (user) > 70% then alert
- if cpu usage (system) > 60% then alert
- if cpu usage (wait) > 75% then alert
-
-You can easily interpret the above configuration. The above checks are performed on local host for every monitoring cycle (which is set to 120 seconds in the Global section). If any condition is met, monit daemon will send an alert with an email.
-
-If certain properties do not need to be monitored for every cycle, you can use the following format. For example, this will monitor average load every other cycle (i.e., every 240 seconds).
-
- if loadavg (1min) > 10 for 2 cycles then alert
-
-### Service Configuration: SSH Service Monitoring ###
-
-Let's check if we have sshd binary installed in /usr/sbin/sshd:
-
- check file sshd_bin with path /usr/sbin/sshd
-
-We also want to check if the init script for sshd exist:
-
- check file sshd_init with path /etc/init.d/sshd
-
-Finally, we want to check if sshd daemon is up an running, and listens on port 22:
-
- check process sshd with pidfile /var/run/sshd.pid
- start program "/etc/init.d/sshd start"
- stop program "/etc/init.d/sshd stop"
- if failed port 22 protocol ssh then restart
- if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
-
-More specifically, we can interpret the above configuration as follows. We check if a process named sshd and a pidfile (/var/run/sshd.pid) exist. If either one does not exist, we restart sshd demon using init script. We check if a process listening on port 22 can speak SSH protocol. If not, we restart sshd daemon. If there are at least 5 restarts within the last 5 monitoring cycles (i.e., 5x120 seconds), sshd daemon is declared non-functional, and we do not try to check again.
-
-
-
-### Service Configuration: SMTP Service Monitoring ###
-
-Now let's set up a check on a remote SMTP mail server (e.g., 192.168.111.102). Let's assume that the SMTP server is running SMTP, IMAP and SSH on its LAN interface.
-
- check host MAIL with address 192.168.111.102
- if failed icmp type echo within 10 cycles then alert
- if failed port 25 protocol smtp then alert
- else if recovered then exec "/scripts/mail-script"
- if failed port 22 protocol ssh then alert
- if failed port 143 protocol imap then alert
-
-We check if the remote host responds to ICMP. If we haven't received ICMP response within 10 cycles, we send out an alert. If testing for SMTP protocol on port 25 fails, we send out an alert. If testing succeeds again after a failed test, we run a script (/scripts/mail-script). If testing for SSH and IMAP protocols fail on port 22 and 143, respectively, we send out an alert.
-
-### Conclusion ###
-
-In this tutorial, I demonstrate how to set up Monit on a local server. What I showed here is just the tip of the iceberg, as far as Monit's capabilities are concerned. Take your time and read the man page about Monit (a very good one). Monit can do a lot for any Linux admin with a very nice and easy to understand syntax. If you put together a centralized remote monitor and Monit to work for you, you will have a more reliable monitoring system. What is your thought on Monit?
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://xmodulo.com/server-monitoring-system-monit.html
-
-作者:[Iulian Murgulet][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/iulian
-[1]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-common-services-nagios.html
-[2]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-linux-servers-snmp-cacti.html
-[3]:http://mmonit.com/monit/
-[4]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
-[5]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
-[6]:http://xmodulo.com/mail-server-ubuntu-debian.html
-[7]:http://mmonit.com/wiki/Monit/ConfigurationExamples
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150330 How to Serve Git Repositories Using Gitblit Tool in Linux.md b/sources/tech/20150330 How to Serve Git Repositories Using Gitblit Tool in Linux.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 806a462675..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150330 How to Serve Git Repositories Using Gitblit Tool in Linux.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,101 +0,0 @@
-How to Serve Git Repositories Using Gitblit Tool in Linux
-================================================================================
-Hi friends, today we'll be learning how to install Gitblit in your Linux Server or PC. So, lets check out what is a Git, its features and steps to install Gitblit. [Git is a distributed revision control system][1] with an emphasis on speed, data integrity, and support for distributed, non-linear workflows. It was initially designed and developed by Linus Torvalds for Linux kernel under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 development in 2005, and has since become the most widely adopted version control system for software development.
-
-[Gitblit is a free and open source][2] built on a pure Java stack designed to handle everything from small to very large projects with speed and efficiency for serving Git repositories. It is easy to learn and has a tiny footprint with lightning fast performance. It outclasses SCM tools like Subversion, CVS, Perforce, and ClearCase with features like cheap local branching, convenient staging areas, and multiple workflows.
-
-#### Features of Gitblit ####
-
-- It can be used as a dumb repository viewer with no administrative controls or user accounts.
-- It can be used as a complete Git stack for cloning, pushing, and repository access control.
-- It can be used without any other Git tooling (including actual Git) or it can cooperate with your established tools.
-
-### 1. Creating Gitblit install directory ###
-
-First of all we'll gonna to create a directory in our server in which we'll be installing our latest gitblit in.
-
- $ sudo mkdir -p /opt/gitblit
-
- $ cd /opt/gitblit
-
-
-
-### 2. Downloading and Extracting ###
-
-Now, we will want to download the latest gitblit from the official site. Here, the current version of gitblit we are gonna install is 1.6.2 . So, please change it as the version you are gonna install in your system.
-
- $ sudo wget http://dl.bintray.com/gitblit/releases/gitblit-1.6.2.tar.gz
-
-
-
-Now, we'll be extracting our downloaded tarball package to our current folder ie /opt/gitblit/
-
- $ sudo tar -zxvf gitblit-1.6.2.tar.gz
-
-
-
-### 3. Configuring and Running ###
-
-Now, we'll configure our Gitblit configuration. If you want to customize the behavior of Gitblit server, you can do it by modifying `gitblit/data/gitblit.properties` . Now, after you are done configuring the configuration. We finally wanna run our gitblit. We have two options on running gitblit, first is that we run it manually by the command below:
-
- $ sudo java -jar gitblit.jar --baseFolder data
-
-And next is to add and use gitblit as service. Here are the steps that we'll need to follow to use gitblit as service in linux.
-
-So, As I am running Ubuntu, the command below will be sudo cp service-ubuntu.sh /etc/init.d/gitblit so please change the file name service-ubuntu.sh to the distribution you are currently running.
-
- $ sudo ./install-service-ubuntu.sh
-
- $ sudo service gitblit start
-
-
-
-Open your browser to http://localhost:8080 or https://localhost:8443 or replace "localhost" with the ip-address of the machine depending on your system configuration. Enter the default administrator credentials: admin / admin and click the Login button.
-
-
-
-Now, we'll wanna add a new user. First you'll need to login to the admin with default administrator credentials: username = **admin** and password = **admin** .
-
-Then, Goto user icon > users > (+) new user. And create a new user like as shown in the figure below.
-
-
-
-Now, we'll create a new repo out of the box. Go to repositories > (+) new repository . Then, add new repository as shown below.
-
-
-
-#### Create a new repository on the command-line ####
-
- touch README.md
- git init
- git add README.md
- git commit -m "first commit"
- git remote add origin ssh://arunlinoxide@localhost:29418/linoxide.com.git
- git push -u origin master
-
-Please replace the username arunlinoxide with the user you add.
-
-#### Push an existing repository from the command-line ####
-
- git remote add origin ssh://arunlinoxide@localhost:29418/linoxide.com.git
- git push -u origin master
-
-**Note**: It is highly recommended to everyone to change the password of username "admin" as it comes by default.
-
-### Conclusion ###
-
-Hurray, we finally installed our latest Gitblit in our Linux Computer. We can now enjoy such a beautiful version controlling system for our projects whether its small or large, no matter. With Gitblit, version controlling has been too easy. It is easy to learn and has a tiny footprint with lightning fast performance. So, if you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/serve-git-repositories-gitblit/
-
-作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
-[1]:http://git-scm.com/
-[2]:http://gitblit.com/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150331 Conky--The Ultimate X Based System Monitor Application.md b/sources/tech/20150331 Conky--The Ultimate X Based System Monitor Application.md
deleted file mode 100644
index fdb2648a36..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150331 Conky--The Ultimate X Based System Monitor Application.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,147 +0,0 @@
-Conky – The Ultimate X Based System Monitor Application
-================================================================================
-Conky is a system monitor application written in ‘C’ Programming Language and released under GNU General Public License and BSD License. It is available for Linux and BSD Operating System. The application is X (GUI) based that was originally forked from [Torsmo][1].
-
-#### Features ####
-
-- Simple User Interface
-- Higher Degree of configuration
-- It can show System stats using built-in objects (300+) as well as external scripts either on the desktop or in it’s own container.
-- Low on Resource Utilization
-- Shows system stats for a wide range of system variables which includes but not restricted to CPU, memory, swap, Temperature, Processes, Disk, Network, Battery, email, System messages, Music player, weather, breaking news, updates and blah..blah..blah
-- Available in Default installation of OS like CrunchBang Linux and Pinguy OS.
-
-#### Lesser Known Facts about Conky ####
-
-- The Name conky was derived from a Canadian Television Show.
-- It has already been ported to Nokia N900.
-- It is no more maintained officially.
-
-### Conky Installation and Usage in Linux ###
-
-Before we install conky, we need to install packages like lm-sensors, curl and hddtemp using following command.
-
- # apt-get install lm-sensors curl hddtemp
-
-Time to detect-sensors.
-
- # sensors-detect
-
-**Note**: Answer ‘Yes‘ when prompted!
-
-Check all the detected sensors.
-
- # sensors
-
-#### Sample Output ####
-
- acpitz-virtual-0
- Adapter: Virtual device
- temp1: +49.5°C (crit = +99.0°C)
-
- coretemp-isa-0000
- Adapter: ISA adapter
- Physical id 0: +49.0°C (high = +100.0°C, crit = +100.0°C)
- Core 0: +49.0°C (high = +100.0°C, crit = +100.0°C)
- Core 1: +49.0°C (high = +100.0°C, crit = +100.0°C)
-
-Conky can be installed from repo as well as, can be compiled from source.
-
- # yum install conky [On RedHat systems]
- # apt-get install conky-all [On Debian systems]
-
-**Note**: Before you install conky on Fedora/CentOS, you must have enabled [EPEL repository][2].
-
-After conky has been installed, just issue following command to start it.
-
- $ conky &
-
-
-Conky Monitor in Action
-
-It will run conky in a popup like window. It uses the basic conky configuration file located at /etc/conky/conky.conf.
-
-You may need to integrate conky with the desktop and won’t like a popup like window every-time. Here is what you need to do
-
-Copy the configuration file /etc/conky/conky.conf to your home directory and rename it as ‘`.conkyrc`‘. The dot (.) at the beginning ensures that the configuration file is hidden.
-
- $ cp /etc/conky/conky.conf /home/$USER/.conkyrc
-
-Now restart conky to take new changes.
-
- $ killall -SIGUSR1 conky
-
-
-Conky Monitor Window
-
-You may edit the conky configuration file located in your home dircetory. The configuration file is very easy to understand.
-
-Here is a sample configuration of conky.
-
-
-Conky Configuration
-
-From the above window you can modify color, borders, size, scale, background, alignment and several other properties. By setting different alignments to different conky window, we can run more than one conky script at a time.
-
-**Using script other than the default for conky and where to find it?**
-
-You may write your own conky script or use one that is available over Internet. We don’t suggest you to use any script you find on the web which can be potentially dangerous unless you know what you are doing. However a few famous threads and pages have conky script that you can trust as mentioned below.
-
-- [http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=281865][3]
-- [http://conky.sourceforge.net/screenshots.html][4]
-
-At the above url, you will find every screenshot has a hyperlink, which will redirects to script file.
-
-#### Testing Conky Script ####
-
-Here I will be running a third party written conky-script on my Debian Jessie Machine, to test.
-
- $ wget https://github.com/alexbel/conky/archive/master.zip
- $ unzip master.zip
-
-Change current working directory to just extracted directory.
-
- $ cd conky-master
-
-Rename the secrets.yml.example to secrets.yml.
-
- $ mv secrets.yml.example secrets.yml
-
-Install Ruby before you could run this (ruby) script.
-
- $ sudo apt-get install ruby
- $ ruby starter.rb
-
-
-Conky Fancy Look
-
-**Note**: This script can be modified to show your current weather, temperature, etc.
-
-If you want to start conky at boot, add the below one liner to startup Applications.
-
- conky --pause 10
- save and exit.
-
-And Finally…such a lightweight and useful GUI eye candy like package is not in active stage and is not maintained officially anymore. The last stable release was conky 1.9.0 released on May 03, 2012. A thread on Ubuntu forum has gone over 2k pages of users sharing configuration. (link to forum : [http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=281865/][5])
-
-- [Conky Homepage][6]
-
-That’s all for now. Keep connected. Keep commenting. Share your thoughts and configuration in comments below.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-conky-in-ubuntu-debian-fedora/
-
-作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
-[1]:http://torsmo.sourceforge.net/
-[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-enable-epel-repository-for-rhel-centos-6-5/
-[3]:http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=281865
-[4]:http://conky.sourceforge.net/screenshots.html
-[5]:http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=281865/
-[6]:http://conky.sourceforge.net/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150331 How to set up remote desktop on Linux VPS using x2go.md b/sources/tech/20150331 How to set up remote desktop on Linux VPS using x2go.md
index 8b3eed8330..d89c91832e 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20150331 How to set up remote desktop on Linux VPS using x2go.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20150331 How to set up remote desktop on Linux VPS using x2go.md
@@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
-translating by createyuan
-
How to set up remote desktop on Linux VPS using x2go
================================================================================
As everything is moved to the cloud, virtualized remote desktop becomes increasingly popular in the industry as a way to enhance employee's productivity. Especially for those who need to roam constantly across multiple locations and devices, remote desktop allows them to stay connected seamlessly to their work environment. Remote desktop is attractive for employers as well, achieving increased agility and flexibility in work environments, lower IT cost due to hardware consolidation, desktop security hardening, and so on.
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150407 How to secure BGP sessions using authentication on Quagga.md b/sources/tech/20150407 How to secure BGP sessions using authentication on Quagga.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 020e2277cc..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150407 How to secure BGP sessions using authentication on Quagga.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
-How to secure BGP sessions using authentication on Quagga
-================================================================================
-The BGP protocol runs over TCP, and as such, it inherits all the vulnerabilities of a TCP connection. For example, within a BGP session, an attacker may impersonate a legitimate BGP neighbor, and convince the BGP routers on the other end to share their routing information with the attacker. The problem occurs when the attacker advertises and injects bogus routes towards neighboring routers. The unsuspecting neighboring routers may then start sending live traffic towards the attacker, which in most cases goes nowhere and simply gets dropped. Back in 2008, YouTube actually [fell victim][1] to such BGP route poisoning, and suffered major outage on their video service for more than an hour. In a far worse case, if the attacker is savvy enough, they can falsely act as a transparent transit router and sniff the transit traffic for any sensitive data. As you can imagine, this can have far reaching consequences.
-
-To protect active BGP sessions against such attacks, many service providers leverage [MD5 checksum and a pre-shared key][2] for their BGP sessions. In a protected BGP session, a BGP router which sends a packet generates an MD5 hash value by using a pre-shared key, portions of the IP and TCP headers and the payload. The MD5 hash is then stored as a TCP option field. Upon receipt of the packet, a receiving router uses the same method to generate its version of the MD5 hash using a pre-shared key. It compares the hash with the one of the received packet to decide whether to accept the packet. For an attacker, it is almost impossible to guess the checksum or the key. For BGP routers, they can be assured that each packet is validated before its content is consumed.
-
-In this tutorial, we will see how we can secure a BGP session between two neighbors using MD5 checksum and a pre-shared key.
-
-### Preparation ###
-
-Securing a BGP session is fairly straightforward. We will use the following routers.
-
-注:表格
-<table id="content">
-<tbody><tr>
-<td><b>Router name</b></td>
-<td><b>AS</b></td>
-<td><b>IP address</b></td>
-</tr>
-<tr>
-<td>router-A</td>
-<td>100</td>
-<td>10.10.12.1/30</td>
-</tr>
-<tr>
-<td>router-B</td>
-<td>200</td>
-<td>10.10.12.2/30</td>
-</tr>
-</tbody></table>
-
-The stock Linux kernel supports TCP MD5 option natively for IPv4 and IPv6. Thus if you built Quagga router from a brand new [Linux box][3], TCP MD5 capability will be automatically available for Quagga. It'll be just a matter of configuring Quagga to take advantage of the capability. But if you are using a FreeBSD box or built a custom kernel for Quagga, make sure that you enable TCP MD5 support on the kernel (e.g., CONFIG_TCP_MD5SIG kernel option in Linux).
-
-### Configuring Router-A for Authentication ###
-
-We will use the CLI shell of Quagga to configure the routers. The only new command that we will use is 'password'.
-
- [root@router-a ~]# vtysh
- router-a# conf t
- router-a(config)# router bgp 100
- router-a(config-router)# network 192.168.100.0/24
- router-a(config-router)# neighbor 10.10.12.2 remote-as 200
- router-a(config-router)# neighbor 10.10.12.2 password xmodulo
-
-The pre-shared key in this example is 'xmodulo'. Obviously, in a production environment you need to select a strong key.
-
-**Note**: in Quagga, the 'service password-encryption’ command is supposed to encrypt all plain-text passwords (e.g., login password) in its configuration file. However, when I use this command, I notice that the pre-shared key in BGP configuration still remains in clear text. I am not sure whether it's a limitation of Quagga, or whether it's a version issue.
-
-### Configuring Router-B for Authentication ###
-
-We will configure router-B in a similar fashion.
-
- [root@router-b ~]# vtysh
- router-b# conf t
- router-b(config)# router bgp 200
- router-b(config-router)# network 192.168.200.0/24
- router-b(config-router)# neighbor 10.10.12.1 remote-as 100
- router-b(config-router)# neighbor 10.10.12.1 password xmodulo
-
-### Verifying a BGP session ###
-
-If everything has been configured correctly, the BGP session should be up, and both routers should be exchanging routes. At this point, every outgoing packet in a TCP session carries a MD5 digest of the packet contents and a secret key, and the digest is automatically validated by the other end point.
-
-We can verify the active BGP session by viewing BGP summary as usual. MD5 checksum verification occurs transparently within Quagga, so you don't see it at the BGP level.
-
-
-
-If you want to test BGP authentication, you can configure one neighbor without a password or deliberately use a wrong pre-shared key and see what happens. You can also use a packet sniffer like tcpdump or Wireshark to analyze the packets that go through the BGP session. For example, tcpdump with "-M <secret>" option will validate the MD5 digests found in TCP option field.
-
-To sum up, in this tutorial we demonstrate how we can easily secure the BGP session between two routers. The process is very straightforward compared to other protocols. It is always recommended to secure your BGP session, especially if you are setting up the BGP session with another AS. The pre-shared key should also be kept safe.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://xmodulo.com/bgp-authentication-quagga.html
-
-作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
-[1]:http://research.dyn.com/2008/02/pakistan-hijacks-youtube-1/
-[2]:http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2385
-[3]:http://xmodulo.com/centos-bgp-router-quagga.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150409 4 Tools Send Email with Subject, Body and Attachment in Linux.md b/sources/tech/20150409 4 Tools Send Email with Subject, Body and Attachment in Linux.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 77936b6a67..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150409 4 Tools Send Email with Subject, Body and Attachment in Linux.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,261 +0,0 @@
-4 Tools Send Email with Subject, Body and Attachment in Linux
-================================================================================
-In today's article we will cover a few ways you can use to send emails with attachments from the command line interface on Linux. It can have quite a few uses, for example to send an archive with an application from an application server to email or you can use the commands in scripts to automate some process. For our examples,we will use the file foo.tar.gz as our attachment.
-
-There are various ways to send emails from command line using different mail clients but here I am sharing few mail client utility used by most users like mailx, mutt and swaks.
-
-All the tools we will present to you are very popular and present in the repositories of most Linux distributions, you can install them using the following commands:
-
-For **Debian / Ubuntu** systems
-
- apt-get install mutt
- apt-get install swaks
- apt-get install mailx
- apt-get install sharutils
-
-For Red Hat based systems like **CentOS** or **Fedora**
-
- yum install mutt
- yum install swaks
- yum install mailx
- yum install sharutils
-
-### 1) Using mail / mailx ###
-
-The mailx utility found as the default mailer application in most Linux distributions now includes the support to attach file. If it is not available you can easily install using the following commands please take note that this may not be supported in older versions, to check this you can use the command:
-
- $ man mail
-
-And the first line should look like this:
-
-mailx [-BDdEFintv~] [-s subject] [-a attachment ] [-c cc-addr] [-b bcc-addr] [-r from-addr] [-h hops] [-A account] [-S variable[=value]] to-addr . . .
-
-As you can see it supports the -a attribute to add a file to the email and -s attribute to subject to the email. Use few of below examples to send mails.
-
-**a) Simple Mail**
-
-Run the mail command, and then mailx would wait for you to enter the message of the email. You can hit enter for new lines. When done typing the message, press Ctrl+D and mailx would display EOT.
-
-After than mailx automatically delivers the email to the destination.
-
- $ mail user@example.com
-
- HI,
- Good Morning
- How are you
- EOT
-
-**b) To send email with subject**
-
- $ echo "Email text" | mail -s "Test Subject" user@example.com
-
--s is used for defining subject for email.
-
-**c) To send message from a file**
-
- $ mail -s "message send from file" user@example.com < /path/to/file
-
-**d) To send message piped using the echo command**
-
- $ echo "This is message body" | mail -s "This is Subject" user@example.com
-
-**e) To send email with attachment**
-
- $ echo “Body with attachment "| mail -a foo.tar.gz -s "attached file" user@example.com
-
--a is used for attachments
-
-### 2) mutt ###
-
-Mutt is a text-based email client for Unix-like systems. It was developed over 20 years ago and it's an important part of Linux history, one of the first clients to support scoring and threading capabilities. Use few of below examples to send email.
-
-**a) Send email with subject & body message from a file**
-
- $ mutt -s "Testing from mutt" user@example.com < /tmp/message.txt
-
-**b) To send body message piped using the echo command**
-
- $ echo "This is the body" | mutt -s "Testing mutt" user@example.com
-
-**c) To send email with attachment**
-
- $ echo "This is the body" | mutt -s "Testing mutt" user@example.com -a /tmp/foo.tar.gz
-
-**d) To send email with multiple attachments**
-
- $ echo "This is the body" | mutt -s "Testing" user@example.com -a foo.tar.gz –a bar.tar.gz
-
-### 3) swaks ###
-
-Swaks stands for Swiss Army Knife for SMTP and it is a featureful, flexible, scriptable, transaction-oriented SMTP test tool written and maintained by John Jetmore. You can use the following syntax to send an email with attachment:
-
- $ swaks -t "foo@bar.com" --header "Subject: Subject" --body "Email Text" --attach foo.tar.gz
-
-The important thing about Swaks is that it will also debug the full mail transaction for you, so it is a very useful tool if you also wish to debug the mail sending process:
-
-As you can see it gives you full details about the sending process including what capabilities the receiving mail server supports, each step of the transaction between the 2 servers.
-
-### 4) uuencode ###
-
-Email transport systems were originally designed to transmit characters with a seven-bit encoding -- like ASCII. This meant they could send messages with plain text but not "binary" text, such as program files or image files that used all of an eight-bit byte. The program is used to solve this limitation is “uuencode”( "UNIX to UNIX encoding") which encode the mail from binary format to text format that is safe to transmit & program is used to decode the data is called “uudecode”
-
-We can easily send binary text such as a program files or image files using uuencode with mailx or mutt email client is shown by following example:
-
- $ uuencode example.jpeg example.jpeg | mail user@example.com
-
-### Shell Script : Explain how to send email ###
-
- #!/bin/bash
-
- FROM=""
- SUBJECT=""
- ATTACHMENTS=""
- TO=""
- BODY=""
-
- # Function to check if entered file names are really files
- function check_files()
- {
- output_files=""
- for file in $1
- do
- if [ -s $file ]
- then
- output_files="${output_files}${file} "
- fi
- done
- echo $output_files
- }
-
- echo "*********************"
- echo "E-mail sending script."
- echo "*********************"
- echo
-
- # Getting the From address from user
- while [ 1 ]
- do
- if [ ! $FROM ]
- then
- echo -n -e "Enter the e-mail address you wish to send mail from:\n[Enter] "
- else
- echo -n -e "The address you provided is not valid:\n[Enter] "
- fi
-
- read FROM
- echo $FROM | grep -E '^.+@.+$' > /dev/null
- if [ $? -eq 0 ]
- then
- break
- fi
- done
-
- echo
-
- # Getting the To address from user
- while [ 1 ]
- do
- if [ ! $TO ]
- then
- echo -n -e "Enter the e-mail address you wish to send mail to:\n[Enter] "
- else
- echo -n -e "The address you provided is not valid:\n[Enter] "
- fi
-
- read TO
- echo $TO | grep -E '^.+@.+$' > /dev/null
- if [ $? -eq 0 ]
- then
- break
- fi
- done
-
- echo
-
- # Getting the Subject from user
- echo -n -e "Enter e-mail subject:\n[Enter] "
- read SUBJECT
-
- echo
-
- if [ "$SUBJECT" == "" ]
- then
- echo "Proceeding without the subject..."
- fi
-
- # Getting the file names to attach
- echo -e "Provide the list of attachments. Separate names by space.
- If there are spaces in file name, quote file name with \"."
- read att
-
- echo
-
- # Making sure file names are poiting to real files
- attachments=$(check_files "$att")
- echo "Attachments: $attachments"
-
- for attachment in $attachments
- do
- ATTACHMENTS="$ATTACHMENTS-a $attachment "
- done
-
- echo
-
- # Composing body of the message
- echo "Enter message. To mark the end of message type ;; in new line."
- read line
-
- while [ "$line" != ";;" ]
- do
- BODY="$BODY$line\n"
- read line
- done
-
- SENDMAILCMD="mutt -e \"set from=$FROM\" -s \"$SUBJECT\" \
- $ATTACHMENTS -- \"$TO\" <<< \"$BODY\""
- echo $SENDMAILCMD
-
- mutt -e "set from=$FROM" -s "$SUBJECT" $ATTACHMENTS -- $TO <<< $BODY
-
-**Script Output**
-
- $ bash send_mail.sh
- *********************
- E-mail sending script.
- *********************
-
- Enter the e-mail address you wish to send mail from:
- [Enter] test@gmail.com
-
- Enter the e-mail address you wish to send mail to:
- [Enter] test@gmail.com
-
- Enter e-mail subject:
- [Enter] Message subject
-
- Provide the list of attachments. Separate names by space.
- If there are spaces in file name, quote file name with ".
- send_mail.sh
-
- Attachments: send_mail.sh
-
- Enter message. To mark the end of message type ;; in new line.
- This is a message
- text
- ;;
-
-### Conclusion ###
-
-There are many ways of send emails from command line / shell script but here we have shared 4 tools available for unix / linux based distros. Hope you enjoyed reading our article and please provide your valuable comments and also let us know if you know about any new tools.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://linoxide.com/linux-shell-script/send-email-subject-body-attachment-linux/
-
-作者:[Bobbin Zachariah][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/bobbin/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150409 Install Inkscape - Open Source Vector Graphic Editor.md b/sources/tech/20150409 Install Inkscape - Open Source Vector Graphic Editor.md
deleted file mode 100644
index fcbe4ee240..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150409 Install Inkscape - Open Source Vector Graphic Editor.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
-Translating by ZTinoZ
-Install Inkscape - Open Source Vector Graphic Editor
-================================================================================
-Inkscape is an open source vector graphic editing tool which uses Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) and that makes it different from its competitors like Xara X, Corel Draw and Adobe Illustrator etc. SVG is a widely-deployed royalty-free graphics format developed and maintained by the W3C SVG Working Group. It is a cross platform tool which runs fine on Linux, Windows and Mac OS.
-
-Inkscape development was started in 2003, Inkscape's bug tracking system was hosted on Sourceforge initially but it was migrated to Launchpad afterwards. Its current latest stable version is 0.91. It is under continuous development and bug fixes and we will be reviewing its prominent features and installing process in the article.
-
-### Salient Features ###
-
-Lets review the outstanding features of this application categorically.
-
-#### Creating Objects ####
-
-- Drawing different colored sized and shaped freehand lines through pencil tool, straight lines and curves through Bezier (pen) tool, applying freehand calligraphic strokes through calligraphic tool etc
-- Creating, selecting, editing and formatting text through text tool. Manipulating text in plain text boxes, on paths or in shapes
-- Helps draw various shapes like rectangles, ellipses, circles, arcs, polygons, stars, spirals etc and then resize, rotate and modify (turn sharp edges round) them
-- Create and embed bitmaps with simple commands
-
-#### Object manipulation ####
-
-- Skewing, moving, scaling, rotating objects through interactive manipulations and pacifying the numeric values
-- Performing raising and lowering Z-order operations
-- Grouping and ungrouping objects to create a virtual scope for editing or manipulation
-- Layers form a hierarchal tree and can be locked or rearranged for various manipulations
-- Distribution and alignment commands
-
-#### Fill and Stroke ####
-
-- Copy/paste styles
-- Pick Color tool
-- Selecting colors on a continuous plot based on vectors of RGB, HSL, CMS, CMYK and color wheel
-- Gradient editor helps creating and managing multi-stop gradients
-- Define an image or selection and use it to pattern fill
-- Dashed Strokes can be used with few predefined dashed patterns
-- Beginning, middle and ending marks through path markers
-
-#### Operation on Paths ####
-
-- Node Editing: Moving nodes and Bezier handles, node alignment and distribution etc
-- Boolean operations like yes or no conditions
-- Simplifying paths with variable levels or thresholds
-- Path insetting and outsetting along with link and offset objects
-- Converting bitmap images into paths (color and monochrome paths) through path tracing
-
-#### Text manipulation ####
-
-- All installed outlined fonts can be used even for right to left align objects
-- Formatting text, letter spacing, line spacing or kerning
-- Text on path and on shapes where both text and path or shapes can be edited or modified
-
-#### Rendering ####
-
-- Inkscape fully support anti-aliased display which is a technique that reduces or eliminates aliasing by shading the pixels along the border.
-- Support for alpha transparency display and PNG export
-
-### Install Inkscape on Ubuntu 14.04 and 14.10 ###
-
-In order to install Inkscape on Ubuntu, we will need to first [add its stable Personal Package Archive][1] (PPA) to Advanced Package Tool (APT) repository. Launch the terminal and run following command to add its PPA.
-
- sudo add-apt-repository ppa:inkscape.dev/stable
-
-
-
-Once the PPA has been added to the APT repository we need to update it using following command.
-
- sudo apt-get update
-
-
-
-After updating the repository we are ready to install inkscape which is accomplished using the following command.
-
- sudo apt-get install inkscape
-
-
-
-Congratulation, Inkscape has been installed now and all set for image editing and making full use of feature rich application.
-
-
-
-### Conclusion ###
-
-Inkscape is a feature rich graphic editing tool which empowers its user with state of the art capabilities. It is an open source application which is freely available for installation and customizations and supports wide range of file formats including but not limited to JPEG, PNG, GIF and PDF. Visit its [official website][2] for more news and updates regarding this application.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://linoxide.com/tools/install-inkscape-open-source-vector-graphic-editor/
-
-作者:[Aun Raza][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunrz/
-[1]:https://launchpad.net/~inkscape.dev/+archive/ubuntu/stable
-[2]:https://inkscape.org/en/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150410 7 Command Line Tools for Browsing Websites and Downloading Files in Linux.md b/sources/tech/20150410 7 Command Line Tools for Browsing Websites and Downloading Files in Linux.md
index f736d8bae1..d291f34511 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20150410 7 Command Line Tools for Browsing Websites and Downloading Files in Linux.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20150410 7 Command Line Tools for Browsing Websites and Downloading Files in Linux.md
@@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
-wangjiezhe translating...
7 Command Line Tools for Browsing Websites and Downloading Files in Linux
================================================================================
In the last article, we have covered few useful tools like ‘rTorrent‘, ‘wget‘, ‘cURL‘, ‘w3m‘, and ‘Elinks‘. We got lots of response to cover few other tools of same genre, if you’ve missed the first part you can go through it..
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150413 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure PCI-passthrough on virt-manager.md b/sources/tech/20150413 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure PCI-passthrough on virt-manager.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 4703e96d38..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150413 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure PCI-passthrough on virt-manager.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,57 +0,0 @@
-Vic020
-
-Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure PCI-passthrough on virt-manager
-================================================================================
-> **Question**: I would like to dedicate a physical network interface card to one of my guest VMs created by KVM. For that, I am trying to enable PCI passthrough of the NIC for the VM. How can I add a PCI device to a guest VM with PCI passthrough on virt-manager?
-
-Modern hypervisors enable efficient resource sharing among multiple guest operating systems by virtualizing and emulating hardware resources. However, such virtualized resource sharing may not always be desirable, or even should be avoided when VM performance is a great concern, or when a VM requires full DMA control of a hardware device. One technique used in this case is so-called "PCI passthrough," where a guest VM is granted an exclusive access to a PCI device (e.g., network/sound/video card). Essentially, PCI passthrough bypasses the virtualization layer, and directly exposes a PCI device to a VM. No other VM can access the PCI device.
-
-### Requirement for Enabling PCI Passthrough ###
-
-If you want to enable PCI passthrough for an HVM guest (e.g., a fully-virtualized VM created by KVM), your system (both CPU and motherboard) must meet the following requirement. If your VM is paravirtualized (created by Xen), you can skip this step.
-
-In order to enable PCI passthrough for an HVM guest VM, your system must support **VT-d** (for Intel processors) or **AMD-Vi** (for AMD processors). Intel's VT-d ("Intel Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O") is available on most high-end Nehalem processors and its successors (e.g., Westmere, Sandy Bridge, Ivy Bridge). Note that VT-d and VT-x are two independent features. A list of Intel/AMD processors with VT-d/AMD-Vi capability can be found [here][1].
-
-After you verify that your host hardware supports VT-d/AMD-Vi, you then need to do two things on your system. First, make sure that VT-d/AMD-Vi is enabled in system BIOS. Second, enable IOMMU on your kernel during booting. The IOMMU service, which is provided by VT-d,/AMD-Vi, protects host memory access by a guest VM, and is a requirement for PCI passthrough for fully-virtualized guest VMs.
-
-To enable IOMMU on the kernel for Intel processors, pass "**intel_iommu=on**" boot parameter on your Linux. Follow [this tutorial][2] to find out how to add a kernel boot parameter via GRUB.
-
-After configuring the boot parameter, reboot your host.
-
-### Add a PCI Device to a VM on Virt-Manager ###
-
-Now we are ready to enable PCI passthrough. In fact, assigning a PCI device to a guest VM is straightforward on virt-manager.
-
-Open the VM's settings on virt-manager, and click on "Add Hardware" button on the left sidebar.
-
-Choose a PCI device to assign from a PCI device list, and click on "Finish" button.
-
-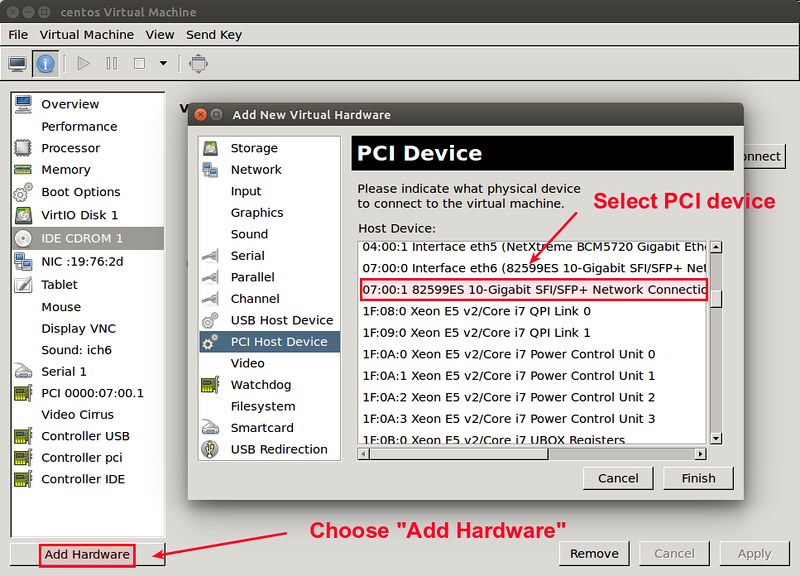
-
-Finally, power on the guest. At this point, the host PCI device should be directly visible inside the guest VM.
-
-### Troubleshooting ###
-
-If you see either of the following errors while powering on a guest VM, the error may be because VT-d (or IOMMU) is not enabled on your host.
-
- Error starting domain: unsupported configuration: host doesn't support passthrough of host PCI devices
-
-----------
-
- Error starting domain: Unable to read from monitor: Connection reset by peer
-
-Make sure that "**intel_iommu=on**" boot parameter is passed to the kernel during boot as described above.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/pci-passthrough-virt-manager.html
-
-作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
-[1]:http://wiki.xenproject.org/wiki/VTdHowTo
-[2]:http://xmodulo.com/add-kernel-boot-parameters-via-grub-linux.html
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150415 Strong SSL Security on nginx.md b/sources/tech/20150415 Strong SSL Security on nginx.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 7ee87bc0d7..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150415 Strong SSL Security on nginx.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,290 +0,0 @@
-增强 nginx 的 SSL 安全性
-================================================================================
-[][1]
-
-本文向你介绍如何在 nginx 服务器上设置高安全性的 SSL。我们通过取消 SSL 压缩降低 CRIME 攻击威胁;禁用协议上存在安全缺陷的 SSLv3 及更低版本,并设置更健壮的加密套件来尽可能启用正向保密(Forward Secrecy);我们也启用了 HSTS 和 HPKP。这样我们就拥有了一个健壮而可经受考验的 SSL 配置,并可以在 Qually Labs 的 SSL 测试中得到 A 级评分。
-
-不求甚解的话,可以从 [https://cipherli.st][2] 上找到 nginx 、Apache 和 Lighttpd 的安全设置,复制粘帖即可。
-
-本教程在 Digital Ocean 的 VPS 上测试通过。如果你喜欢这篇教程,想要支持作者的站点的话,购买 Digital Ocean 的 VPS 时请使用如下链接:[https://www.digitalocean.com/?refcode=7435ae6b8212][3] 。
-
-本教程可以通过[发布于 2014/1/21 的][4] SSL 实验室测试的严格要求(之前就通过了测试,如果你按照本文进行的话,可以得到一个 A+ 评分)。
-
-- [本教程也有对应 Apache 的][5]
-- [本教程也有对应 Lighttpd 的][6]
-- [本教程也有对应 FreeBSD, NetBSD 和 OpenBSD 上的 nginx 的,放在 BSD Now 播客][7]: [http://www.bsdnow.tv/tutorials/nginx][8]
-
-你可以从下列链接中找到这方面的进一步内容:
-
-- [BEAST 攻击][9]
-- [CRIME 攻击][10]
-- [FREAK 攻击][11]
-- [心血漏洞][12]
-- [完美正向保密][13]
-- [RC4 和 BEAST 的处理][14]
-
-我们需要编辑 nginx 的配置,在 Ubuntu/Debian 上是 `/etc/nginx/sited-enabled/yoursite.com`,在 RHEL/CentOS 上是 `/etc/nginx/conf.d/nginx.conf`
-
-本文中,我们需要编辑443端口(SSL)的 `server` 配置中的部分。在文末我们会给出完整的配置例子。
-
-*在编辑之前切记备份一下配置文件!*
-
-### The BEAST attack and RC4 ###
-
-In short, by tampering with an encryption algorithm's CBC - cipher block chaining - mode's, portions of the encrypted traffic can be secretly decrypted. More info on the above link.
-
-Recent browser versions have enabled client side mitigation for the beast attack. The recommendation was to disable all TLS 1.0 ciphers and only offer RC4. However, [RC4 has a growing list of attacks against it],(http://www.isg.rhul.ac.uk/tls/) many of which have crossed the line from theoretical to practical. Moreover, there is reason to believe that the NSA has broken RC4, their so-called "big breakthrough."
-
-Disabling RC4 has several ramifications. One, users with shitty browsers such as Internet Explorer on Windows XP will use 3DES in lieu. Triple-DES is more secure than RC4, but it is significantly more expensive. Your server will pay the cost for these users. Two, RC4 mitigates BEAST. Thus, disabling RC4 makes TLS 1.0 users susceptible to that attack, by moving them to AES-CBC (the usual server-side BEAST "fix" is to prioritize RC4 above all else). I am confident that the flaws in RC4 significantly outweigh the risks from BEAST. Indeed, with client-side mitigation (which Chrome and Firefox both provide), BEAST is a nonissue. But the risk from RC4 only grows: More cryptanalysis will surface over time.
-
-### Factoring RSA-EXPORT Keys (FREAK) ###
-
-FREAK is a man-in-the-middle (MITM) vulnerability discovered by a group of cryptographers at [INRIA, Microsoft Research and IMDEA][15]. FREAK stands for "Factoring RSA-EXPORT Keys."
-
-The vulnerability dates back to the 1990s, when the US government banned selling crypto software overseas, unless it used export cipher suites which involved encryption keys no longer than 512-bits.
-
-It turns out that some modern TLS clients - including Apple's SecureTransport and OpenSSL - have a bug in them. This bug causes them to accept RSA export-grade keys even when the client didn't ask for export-grade RSA. The impact of this bug can be quite nasty: it admits a 'man in the middle' attack whereby an active attacker can force down the quality of a connection, provided that the client is vulnerable and the server supports export RSA.
-
-There are two parts of the attack as the server must also accept "export grade RSA."
-
-The MITM attack works as follows:
-
-- In the client's Hello message, it asks for a standard 'RSA' ciphersuite.
-- The MITM attacker changes this message to ask for 'export RSA'.
-- The server responds with a 512-bit export RSA key, signed with its long-term key.
-- The client accepts this weak key due to the OpenSSL/SecureTransport bug.
-- The attacker factors the RSA modulus to recover the corresponding RSA decryption key.
-- When the client encrypts the 'pre-master secret' to the server, the attacker can now decrypt it to recover the TLS 'master secret'.
-- From here on out, the attacker sees plaintext and can inject anything it wants.
-
-The ciphersuite offered here on this page does not enable EXPORT grade ciphers. Make sure your OpenSSL is updated to the latest available version and urge your clients to also use upgraded software.
-
-### Heartbleed ###
-
-Heartbleed is a security bug disclosed in April 2014 in the OpenSSL cryptography library, which is a widely used implementation of the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol. Heartbleed may be exploited regardless of whether the party using a vulnerable OpenSSL instance for TLS is a server or a client. It results from improper input validation (due to a missing bounds check) in the implementation of the DTLS heartbeat extension (RFC6520), thus the bug's name derives from "heartbeat". The vulnerability is classified as a buffer over-read, a situation where more data can be read than should be allowed.
-
-What versions of the OpenSSL are affected by Heartbleed?
-
-Status of different versions:
-
-- OpenSSL 1.0.1 through 1.0.1f (inclusive) are vulnerable
-- OpenSSL 1.0.1g is NOT vulnerable
-- OpenSSL 1.0.0 branch is NOT vulnerable
-- OpenSSL 0.9.8 branch is NOT vulnerable
-
-The bug was introduced to OpenSSL in December 2011 and has been out in the wild since OpenSSL release 1.0.1 on 14th of March 2012. OpenSSL 1.0.1g released on 7th of April 2014 fixes the bug.
-
-By updating OpenSSL you are not vulnerable to this bug.
-
-### SSL Compression (CRIME attack) ###
-
-The CRIME attack uses SSL Compression to do its magic. SSL compression is turned off by default in nginx 1.1.6+/1.0.9+ (if OpenSSL 1.0.0+ used) and nginx 1.3.2+/1.2.2+ (if older versions of OpenSSL are used).
-
-If you are using al earlier version of nginx or OpenSSL and your distro has not backported this option then you need to recompile OpenSSL without ZLIB support. This will disable the use of OpenSSL using the DEFLATE compression method. If you do this then you can still use regular HTML DEFLATE compression.
-
-### SSLv2 and SSLv3 ###
-
-SSL v2 is insecure, so we need to disable it. We also disable SSLv3, as TLS 1.0 suffers a downgrade attack, allowing an attacker to force a connection to use SSLv3 and therefore disable forward secrecy.
-
-Again edit the config file:
-
- ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
-
-### Poodle and TLS-FALLBACK-SCSV ###
-
-SSLv3 allows exploiting of the [POODLE][16] bug. This is one more major reason to disable this.
-
-Google have proposed an extension to SSL/TLS named [TLSFALLBACKSCSV][17] that seeks to prevent forced SSL downgrades. This is automatically enabled if you upgrade OpenSSL to the following versions:
-
-- OpenSSL 1.0.1 has TLSFALLBACKSCSV in 1.0.1j and higher.
-- OpenSSL 1.0.0 has TLSFALLBACKSCSV in 1.0.0o and higher.
-- OpenSSL 0.9.8 has TLSFALLBACKSCSV in 0.9.8zc and higher.
-
-[More info on the NGINX documentation][18]
-
-### The Cipher Suite ###
-
-Forward Secrecy ensures the integrity of a session key in the event that a long-term key is compromised. PFS accomplishes this by enforcing the derivation of a new key for each and every session.
-
-This means that when the private key gets compromised it cannot be used to decrypt recorded SSL traffic.
-
-The cipher suites that provide Perfect Forward Secrecy are those that use an ephemeral form of the Diffie-Hellman key exchange. Their disadvantage is their overhead, which can be improved by using the elliptic curve variants.
-
-The following two ciphersuites are recommended by me, and the latter by [the Mozilla Foundation][19].
-
-The recommended cipher suite:
-
- ssl_ciphers 'AES128+EECDH:AES128+EDH';
-
-The recommended cipher suite for backwards compatibility (IE6/WinXP):
-
- ssl_ciphers "ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-DES-CBC3-SHA:EDH-RSA-DES-CBC3-SHA:AES256-GCM-SHA384:AES128-GCM-SHA256:AES256-SHA256:AES128-SHA256:AES256-SHA:AES128-SHA:DES-CBC3-SHA:HIGH:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!DES:!MD5:!PSK:!RC4";
-
-If your version of OpenSSL is old, unavailable ciphers will be discarded automatically. Always use the full ciphersuite above and let OpenSSL pick the ones it supports.
-
-The ordering of a ciphersuite is very important because it decides which algorithms are going to be selected in priority. The recommendation above prioritizes algorithms that provide perfect forward secrecy.
-
-Older versions of OpenSSL may not return the full list of algorithms. AES-GCM and some ECDHE are fairly recent, and not present on most versions of OpenSSL shipped with Ubuntu or RHEL.
-
-#### Prioritization logic ####
-
-- ECDHE+AESGCM ciphers are selected first. These are TLS 1.2 ciphers and not widely supported at the moment. No known attack currently target these ciphers.
-- PFS ciphersuites are preferred, with ECDHE first, then DHE.
-- AES 128 is preferred to AES 256. There has been [discussions][20] on whether AES256 extra security was worth the cost, and the result is far from obvious. At the moment, AES128 is preferred, because it provides good security, is really fast, and seems to be more resistant to timing attacks.
-- In the backward compatible ciphersuite, AES is preferred to 3DES. BEAST attacks on AES are mitigated in TLS 1.1 and above, and difficult to achieve in TLS 1.0. In the non-backward compatible ciphersuite, 3DES is not present.
-- RC4 is removed entirely. 3DES is used for backward compatibility. See discussion in [#RC4_weaknesses][21]
-
-#### Mandatory discards ####
-
-- aNULL contains non-authenticated Diffie-Hellman key exchanges, that are subject to Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attacks
-- eNULL contains null-encryption ciphers (cleartext)
-- EXPORT are legacy weak ciphers that were marked as exportable by US law
-- RC4 contains ciphers that use the deprecated ARCFOUR algorithm
-- DES contains ciphers that use the deprecated Data Encryption Standard
-- SSLv2 contains all ciphers that were defined in the old version of the SSL standard, now deprecated
-- MD5 contains all the ciphers that use the deprecated message digest 5 as the hashing algorithm
-
-### Extra settings ###
-
-Make sure you also add these lines:
-
- ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
- ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m;
-
-When choosing a cipher during an SSLv3 or TLSv1 handshake, normally the client's preference is used. If this directive is enabled, the server's preference will be used instead.
-
-- [More info on sslpreferserver_ciphers][22]
-- [More info on ssl_ciphers][23]
-
-### Forward Secrecy & Diffie Hellman Ephemeral Parameters ###
-
-The concept of forward secrecy is simple: client and server negotiate a key that never hits the wire, and is destroyed at the end of the session. The RSA private from the server is used to sign a Diffie-Hellman key exchange between the client and the server. The pre-master key obtained from the Diffie-Hellman handshake is then used for encryption. Since the pre-master key is specific to a connection between a client and a server, and used only for a limited amount of time, it is called Ephemeral.
-
-With Forward Secrecy, if an attacker gets a hold of the server's private key, it will not be able to decrypt past communications. The private key is only used to sign the DH handshake, which does not reveal the pre-master key. Diffie-Hellman ensures that the pre-master keys never leave the client and the server, and cannot be intercepted by a MITM.
-
-All versions of nginx as of 1.4.4 rely on OpenSSL for input parameters to Diffie-Hellman (DH). Unfortunately, this means that Ephemeral Diffie-Hellman (DHE) will use OpenSSL's defaults, which include a 1024-bit key for the key-exchange. Since we're using a 2048-bit certificate, DHE clients will use a weaker key-exchange than non-ephemeral DH clients.
-
-We need generate a stronger DHE parameter:
-
- cd /etc/ssl/certs
- openssl dhparam -out dhparam.pem 4096
-
-And then tell nginx to use it for DHE key-exchange:
-
- ssl_dhparam /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem;
-
-### OCSP Stapling ###
-
-When connecting to a server, clients should verify the validity of the server certificate using either a Certificate Revocation List (CRL), or an Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) record. The problem with CRL is that the lists have grown huge and takes forever to download.
-
-OCSP is much more lightweight, as only one record is retrieved at a time. But the side effect is that OCSP requests must be made to a 3rd party OCSP responder when connecting to a server, which adds latency and potential failures. In fact, the OCSP responders operated by CAs are often so unreliable that browser will fail silently if no response is received in a timely manner. This reduces security, by allowing an attacker to DoS an OCSP responder to disable the validation.
-
-The solution is to allow the server to send its cached OCSP record during the TLS handshake, therefore bypassing the OCSP responder. This mechanism saves a roundtrip between the client and the OCSP responder, and is called OCSP Stapling.
-
-The server will send a cached OCSP response only if the client requests it, by announcing support for the status_request TLS extension in its CLIENT HELLO.
-
-Most servers will cache OCSP response for up to 48 hours. At regular intervals, the server will connect to the OCSP responder of the CA to retrieve a fresh OCSP record. The location of the OCSP responder is taken from the Authority Information Access field of the signed certificate.
-
-- [View my tutorial on enabling OCSP stapling on NGINX][24]
-
-### HTTP Strict Transport Security ###
-
-When possible, you should enable [HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS)][25], which instructs browsers to communicate with your site only over HTTPS.
-
-- [View my article on HTST to see how to configure it.][26]
-
-### HTTP Public Key Pinning Extension ###
-
-You should also enable the [HTTP Public Key Pinning Extension][27].
-
-Public Key Pinning means that a certificate chain must include a whitelisted public key. It ensures only whitelisted Certificate Authorities (CA) can sign certificates for `*.example.com`, and not any CA in your browser store.
-
-I've written an article about it that has background theory and configuration examples for Apache, Lighttpd and NGINX: [https://raymii.org/s/articles/HTTPPublicKeyPinningExtension_HPKP.html][28]
-
-### Config Example ###
-
- server {
-
- listen [::]:443 default_server;
-
- ssl on;
- ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/cert/raymii_org.pem;
- ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/cert/ca-bundle.pem;
-
- ssl_ciphers 'AES128+EECDH:AES128+EDH:!aNULL';
-
- ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
- ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m;
-
- ssl_stapling on;
- ssl_stapling_verify on;
- resolver 8.8.4.4 8.8.8.8 valid=300s;
- resolver_timeout 10s;
-
- ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
- ssl_dhparam /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem;
-
- add_header Strict-Transport-Security max-age=63072000;
- add_header X-Frame-Options DENY;
- add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
-
- root /var/www/;
- index index.html index.htm;
- server_name raymii.org;
-
- }
-
-### Conclusion ###
-
-If you have applied the above config lines you need to restart nginx:
-
- # Check the config first:
- /etc/init.d/nginx configtest
- # Then restart:
- /etc/init.d/nginx restart
-
-Now use the [SSL Labs test][29] to see if you get a nice A. And, of course, have a safe, strong and future proof SSL configuration!
-
-- [Also read the Mozilla page on the subject][30]
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/Strong_SSL_Security_On_nginx.html
-
-作者:[Remy van Elst][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://raymii.org/
-[1]:https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=raymii.org
-[2]:https://cipherli.st/
-[3]:https://www.digitalocean.com/?refcode=7435ae6b8212
-[4]:http://blog.ivanristic.com/2014/01/ssl-labs-stricter-security-requirements-for-2014.html
-[5]:https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/Strong_SSL_Security_On_Apache2.html
-[6]:https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/Pass_the_SSL_Labs_Test_on_Lighttpd_%28Mitigate_the_CRIME_and_BEAST_attack_-_Disable_SSLv2_-_Enable_PFS%29.html
-[7]:http://www.bsdnow.tv/episodes/2014_08_20-engineering_nginx
-[8]:http://www.bsdnow.tv/tutorials/nginx
-[9]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_Security#BEAST_attack
-[10]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CRIME_%28security_exploit%29
-[11]:http://blog.cryptographyengineering.com/2015/03/attack-of-week-freak-or-factoring-nsa.html
-[12]:http://heartbleed.com/
-[13]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perfect_forward_secrecy
-[14]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_Security#Dealing_with_RC4_and_BEAST
-[15]:https://www.smacktls.com/
-[16]:https://raymii.org/s/articles/Check_servers_for_the_Poodle_bug.html
-[17]:https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-tls-downgrade-scsv-00
-[18]:http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpSslModule#ssl_protocols
-[19]:https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Server_Side_TLS
-[20]:http://www.mail-archive.com/dev-tech-crypto@lists.mozilla.org/msg11247.html
-[21]:https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Server_Side_TLS#RC4_weaknesses
-[22]:http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpSslModule#ssl_prefer_server_ciphers
-[23]:http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpSslModule#ssl_ciphers
-[24]:https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/OCSP_Stapling_on_nginx.html
-[25]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTTP_Strict_Transport_Security
-[26]:https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/HTTP_Strict_Transport_Security_for_Apache_NGINX_and_Lighttpd.html
-[27]:https://wiki.mozilla.org/SecurityEngineering/Public_Key_Pinning
-[28]:https://raymii.org/s/articles/HTTP_Public_Key_Pinning_Extension_HPKP.html
-[29]:https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/
-[30]:https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Server_Side_TLS
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150423 20 Awesome Docker Containers for a Desktop User.md b/sources/tech/20150423 20 Awesome Docker Containers for a Desktop User.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 060aeb755d..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150423 20 Awesome Docker Containers for a Desktop User.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,237 +0,0 @@
-20 Awesome Docker Containers for a Desktop User
-================================================================================
-Greetings to everyone, today we'll list out some awesome Desktop Apps that we can run using Docker Containers in our very own Desktop running Docker. Docker is an Open Source project that provides an open platform to pack, ship and run any application as a lightweight container. It has no boundaries of Language support, Frameworks or packaging system and can be run anywhere, anytime from a small home computers to high-end servers. It makes them great building blocks for deploying and scaling web apps, databases, and back-end services without depending on a particular stack or provider. It is basically used by the developers, Ops and Engineers as it is easy, fast and handy tool for testing or deploying their products but we can also use Docker for our Desktop usage to run a desktop apps out of the box.
-
-So here are some awesome 10 Desktop Application Docker images that we can run with Docker.
-
-### 1. Lynx ###
-
-Lynx is a all time favorite text-based web browser which is a lot familiar to most of the people running Linux. It is the oldest web browser currently in general use and development. To run Lynx, run the following command.
-
- $ docker run -it \
- --name lynx \
- jess/lynx
-
-### 2. Irssi ###
-
-Irssi is an awesome IRC Client which is based on Text Interface. To run Irssi using docker, we'll need to run the following commands in a docker installed desktop computer.
-
- docker run -it --name my-irssi -e TERM -u $(id -u):$(id -g) \
- -v $HOME/.irssi:/home/user/.irssi:ro \
- -v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro \
- irssi
-
-### 3. Chrome ###
-
-Chrome is an awesome GUI-based web browser developed by Google and is based on Open Source Project Chromium. Google Chrome is widely used, fast and secure web browser that are very much familiar to most of the people who surf internet. We can run Chrome using docker by running the following command.
-
- $ docker run -it \
- --net host \
- --cpuset 0 \
- --memory 512mb \
- -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
- -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY \
- -v $HOME/Downloads:/root/Downloads \
- -v $HOME/.config/google-chrome/:/data \
- -v /dev/snd:/dev/snd --privileged \
- --name chrome \
- jess/chrome
-
-### 4. Tor Browser ###
-
-Tor Browser is a web browser which support anonymous features. It enables us freedom to surf website or services blocked by a particular organization or ISPs. It prevents somebody watching our Internet connection from learning what we do on internet and our exact location. To run Tor Browser, run the following command.
-
- $ docker run -it \
- -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
- -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY \
- -v /dev/snd:/dev/snd --privileged \
- --name tor-browser \
- jess/tor-browser
-
-### 5. Firefox Browser ###
-
-Firefox Browser is a free and open source web browser which is developed by Mozilla Foundation. It is run by Gecko and SpiderMonkey engines. Firefox Browser has a lot of new features and is specially known for its performance and security.
-
- $ docker run -d \
- --name firefox \
- -e DISPLAY=$DISPLAY \
- -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
- kennethkl/firefox
-
-### 6. Rainbow Stream ###
-
-Rainbow Stream is a terminal based Twitter Client featuring real time tweetstream, compose, search , favorite and much more fun directly from terminal. To run Rainbow Stream, run the following command.
-
- $ docker run -it \
- -v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \
- -v $HOME/.rainbow_oauth:/root/.rainbow_oauth \
- -v $HOME/.rainbow_config.json:/root/.rainbow_config.json \
- --name rainbowstream \
- jess/rainbowstream
-
-### 7. Gparted ###
-
-Gparted is an open source software which allows us to partition disks. Now enjoy partitioning from a docker container. To run gparted, we'll need to run the following command.
-
- $ docker run -it \
- -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
- -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY \
- --device /dev/sda:/dev/sda \ # mount the device to partition
- --name gparted \
- jess/gparted
-
-### 8. GIMP Editor ###
-
-GIMP stands for Gnu Image Manipulation Program which is an awesome tool on Linux for graphics, image editing platform. It is a freely distributed piece of software for such tasks as photo retouching, image composition and image authoring.
-
- $ docker run -it \
- --rm -e DISPLAY=$DISPLAY \
- -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
- jarfil/gimp-git
-
-### 9. Thunderbird ###
-
-Thunderbird is also a free and open source email application which is developed and maintained by Mozilla Foundation. It has tons of features that an email application software should have. Thunderbird is really easy to setup and customize. To run Thunderbird in a Docker environment, run the following command.
-
- $ docker run -d \
- -e DISPLAY \
- -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:ro \
- -u docker \
- -v $HOME/docker-data/thunderbird:/home/docker/.thunderbird/ \
- yantis/thunderbird thunderbird
-
-### 10. Mutt ###
-
-Mutt is a text based email client which has bunches of cool features including color support, IMAP, POP3, SMTP support, mail storing support and much more. To run Mutt out of the box using docker, we'll need to run the following command.
-
- $ docker run -it \
- -v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \
- -e GMAIL -e GMAIL_NAME \
- -e GMAIL_PASS -e GMAIL_FROM \
- -v $HOME/.gnupg:/home/user/.gnupg \
- --name mutt \
- jess/mutt
-
-### 11. Skype ###
-
-Skype is an instant messaging, video calling software which is not open source but can be run awesome in linux. We can run Skype using Docker Containers too. To run Skype using a docker, run the following command.
-
- $ docker run -it \
- -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:ro \
- -v /dev/snd:/dev/snd --privileged \
- -e DISPLAY="unix$DISPLAY" \
- tianon/skype
-
-### 12. Cathode ###
-
-Cathode is a beautiful fully customizable terminal app with a look inspired by classic computers. We can run Cathode by running the below command.
-
- $ docker run -it \
- -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
- -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY \
- --name cathode \
- jess/1995
-
-### 13. LibreOffice ###
-
-LibreOffice is a powerful office suite which is free and open source and is maintained by The Document Foundation. It has clean interface and is a powerful tools that lets us unleash our creativity and grow our productivity. LibreOffice embeds several applications that make it the most powerful Free & Open Source Office suite on the market.
-
- $docker run \
- -v $HOME/Documents:/home/libreoffice/Documents:rw \
- -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
- -e uid=$(id -u) -e gid=$(id -g) \
- -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY --name libreoffice \
- chrisdaish/libreoffice
-
-### 14. Spotify ###
-
-Spotify gives us instant access to millions of songs from old favorites to the latest hits. To listen our favorite songs using docker, run the following command.
-
- $ docker run -it \
- -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
- -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY \
- -v /dev/snd:/dev/snd --privileged \
- --name spotify \
- jess/spotify
-
-### 15. Audacity ###
-
-Audacity is free and open source cross-platform software for recording and editing sounds. Audacity can be used for post-processing of all types of audio, including podcasts by adding effects such as normalization, trimming, and fading in and out. To run Audacity, we'll need to run the following command in a terminal or shell.
-
- $ docker run --rm \
- -u $(id -u):$(id -g) \
- -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:ro \
- -v /dev/snd:/dev/snd \
- -v "$HOME:$HOME" \
- -w "$HOME" \
- -e DISPLAY="unix$DISPLAY" \
- -e HOME \
- $(find /dev/snd/ -type c | sed 's/^/--device /') \
- knickers/audacity
-
-### 16. Eclipse ###
-
-Eclipse is an integrated development environment (IDE). It contains a base workspace and an extensible plug-in system for customizing the environment. It is mostly used to develop Java Based Applications.
-
- $ docker run -v ~/workspace/:/home/eclipse/workspace/ \
- -e DISPLAY -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:ro \
- -d leesah/eclipse
-
-### 17. VLC Media Player ###
-
-VLC is a free and open source cross-platform multimedia player and framework that plays most multimedia files as well as DVDs, Audio CDs, VCDs, and various streaming protocols. VLC Media Player is developed and maintained by VideoLAN Organization. To run VLC in docker environment, run the following command.
-
- $ docker run -v\
- $HOME/Documents:/home/vlc/Documents:rw \
- -v /dev/snd:/dev/snd --privileged \
- -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
- -e uid=$(id -u) -e gid=$(id -g) \
- -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY --name vlc \
- chrisdaish/vlc
-
-### 18. Vim Editor ###
-
-Vim is a highly configurable text-based text editor built to enable efficient text editing. It is an improved version of the vi editor distributed with most UNIX systems.
-
- $ docker run -i -t --name my-vim -v ~/:/home/dev/src haron/vim
-
-### 19. Inkscape ###
-
-Inkscape is a free and open-source vector graphics editor. It can create, edit vector graphics such as illustrations, diagrams, line arts, charts, logos and even complex paintings. Inkscape's primary vector graphics format is Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) version 1.1. It can import from or export to several other formats as well but all editing workflow must inevitably occur within the constraints of SVG format.
-
- $docker build -t rasch/inkscape --rm .
- $ docker run --rm -e DISPLAY \
- -u inkscaper
- -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
- -v $HOME/.Xauthority:/home/inkscaper/.Xauthority \
- --net=host rasch/inkscape
-
-### 20. Filezilla ###
-
-Filezilla is a free FTP solution application software. It supports FTP, SFTP, FTPS protocols. It is a powerful file management tool for client side. It is an awesome open source FTP project which is highly reliable and easy to use.
-
- $ xhost +si:localuser:$(whoami)
- $ docker run \
- -d \
- -e DISPLAY \
- -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:ro \
- -u docker \
- -v /:/host \
- -v $HOME/docker-data/filezilla:/home/docker/.config/filezilla/ \
- yantis/filezilla filezilla
-
-### Conclusion ###
-
-Running desktop application software using Docker is really an awesome experience. Docker is really an awesome platform for fast and easy development, shipping and deployment of software and packages in any place from home to office to production areas. Running desktop apps with docker is a cool way to try out the apps without really installing it into the host filesystem. So, if you have any questions, comments, feedback please do write on the comment box below and let us know what stuffs needs to be added or improved. Thank You! Enjoy with Docker :-)
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://linoxide.com/how-tos/20-docker-containers-desktop-user/
-
-作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150427 15 Things to Do After Installing Ubuntu 15.04 Desktop.md b/sources/tech/20150427 15 Things to Do After Installing Ubuntu 15.04 Desktop.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6f1114b9bb..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150427 15 Things to Do After Installing Ubuntu 15.04 Desktop.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,298 +0,0 @@
-15 Things to Do After Installing Ubuntu 15.04 Desktop
-================================================================================
-This tutorial is intended for beginners and covers some basic steps on what to do after you have installed Ubuntu 15.04 “Vivid Vervet” Desktop version on your computer in order to customize the system and install basic programs for daily usage.
-
-
-15 Things to Do After Installing Ubuntu 15.04
-
-### 1. Enable Ubuntu Extra Repositories and Update the System ###
-
-The first thing you should take care of after a fresh installation of Ubuntu is to enable Ubuntu Extra Repositories provided by official Canonical Partners and keep an up-to-date system with the last security patches and software updates.
-
-In order to accomplish this step, open from the left Launcher System Settings -> Software and Updates utility and check all Ubuntu Software and Other Software (Canonical Partners) repositories. After you finish hit the Close button and wait for the utility to Reload the cache sources tree.
-
-
-Software Updates
-
-
-Other Software (Canonical Partners)
-
-For a fast and smooth update process, open a Terminal and issue the following command in order to update the system using the new software repositories:
-
- $ sudo apt-get update
- $ sudo apt-get upgrade
-
-
-Ubuntu Upgrade
-
-### 2. Install Additional Drivers ###
-
-In order for the system to scan and install additional hardware proprietary drivers, open Software and Updates utility from System Settings, go to Additional Drivers tab and wait for the utility to scan for drivers.
-
-If some drivers matching your hardware are found, check the drivers you want to install and hit the Apply Changes button to install it. In case the proprietary drivers are not working as expected, uninstall them using the Revert button or check Do not use the device and Apply Changes.
-
-
-Install Drivers
-
-### 3. Install Synaptic and Gdebi Package Tools ###
-
-Besides Ubuntu Software Center, Synaptic is a Graphical utility for apt command line through which you can manage repositories or install, remove, search, upgrade and configure software packages. Similar way, Gdebi has the same functionality for local .deb packages. To install this two package managers on your system issue the following command on Terminal:
-
- $ sudo apt-get install synaptic gdebi
-
-
-Install Synaptic and Gdebi
-
-
-Synaptic Package Manager
-
-### 4. Change System Appearance and Behavior ###
-
-If you want to change Desktop Background or Launcher Icon Size, open System Settings –> Appearance –> Look and personalize the desktop. To move the menu to window title bar, enable workspaces and desktop icons or auto-hide the Launcher visit Behavior tab.
-
-
-System Appearances
-
-### 5. Improve System Security and Privacy ###
-
-
-System Security Enhancement
-
-
-System Security Options
-
-### 5. Disable Unneeded Startup Applications ###
-
-To improve system login speed, reveal hidden Startup Applications by issuing the below command on Terminal, open Startup Applications utility by searching it in Dash and uncheck the unneeded applications during login process.
-
- $ sudo sed -i ‘s/NoDisplay=true/NoDisplay=false/g’ /etc/xdg/autostart/*.desktop
-
-
-Disable Unwanted Applications
-
-### 6. Add Extended Multimedia Support ###
-
-By default, Ubuntu comes with a minimal support for media files. In order to play various media formats or manipulate video files, install the following multimedia applications:
-
-- VLC
-- Smplayer
-- Audacious
-- QMMP
-- Mixxx
-- XBMC
-- Handbrake
-- Openshot
-
-Use the following command line to install all with one shot:
-
- $ sudo apt-get install vlc smplayer audacious qmmp mixxx xbmc handbrake openshot
-
-
-Install Media Players
-
-
-Media Player Playlist
-
-Besides this multimedia players also install ubuntu-restricted-extras and Java support packages in order to decode and support other restricted media formats.
-
- $ sudo apt-get install ubuntu-restricted-extras openjdk-8-jdk
-
-
-Install Ubuntu Extras
-
-To enable DVD Playback and other multimedia codecs issue the following command on Terminal:
-
- $ sudo apt-get install ffmpeg gstreamer0.10-plugins-bad lame libavcodec-extra
- $ sudo /usr/share/doc/libdvdread4/install-css.sh
-
-
-Enable Video Codes
-
-### 7. Install Image Applications ###
-
-If you are a photography enthusiast and you want to handle and manipulate images on Ubuntu, probably you want to install the following imaging programs:
-
-- GIMP (alternative for Adobe Photoshop)
-- Darktable
-- Rawtherapee
-- Pinta
-- Shotwell
-- Inkscape (alternative for Adobe Illustrator)
-- Digikam
-- Cheese
-
-This applications can be installed from Ubuntu Software Center or all at once by using the following command line on Terminal:
-
- $ sudo apt-get install gimp gimp-plugin-registry gimp-data-extras darktable rawtherapee pinta shotwell inkscape
-
-
-Install Image Applications
-
-
-Rawtherapee Tool
-
-### 8. Install Media Burners ###
-
-To mount ISO images or burn a CDs or a DVD, you can choose and install from the following software:
-
-- Brasero Disk Burner
-- K3b
-- Xfburn
-- Furius ISO Mount
-
- $ sudo apt-get install brasero
- $ sudo apt-get install k3b
- $ sudo apt-get install xfburn
- $ sudo apt-get install furiusisomount
-
-
-Install Media Burners
-
-### 9. Install Archive Applications ###
-
-To handle most of archive formatted files (zip, tar.gz, zip, 7zip rar etc) install the following packages by issuing the below command:
-
- $ sudo apt-get install unace unrar zip unzip p7zip-full p7zip-rar sharutils rar uudeview mpack arj cabextract file-roller
-
-
-Install Archive Applications
-
-### 10. Install Chat Application ###
-
-If you want to talk to people all over the world, here is a list of the most popular chat applications for Linux:
-
-- Pidgin
-- Skype
-- Xchat
-- Telegram
-- aMSN
-- Viber
-
-You can install most of them from Ubuntu Software Center or by using the command line:
-
- $ sudo apt-get install pidgin
- $ sudo apt-get install skype
- $ sudo apt-get install xchat
- $ sudo apt-get install amsn
- $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:atareao/telegram -y
- $ sudo apt-get update
- $ sudo apt-get install telegram
-
-
-Install Chat Applications
-
-To install Viber application on Ubuntu visit [Viber official webpage][1], download the Debian package locally and install the viber.deb application using Gdebi package manager (left click – > Open with -> GDebi Package Installer).
-
-
-Install Viber
-
-### 11. Install Torrent Software ###
-
-The most popular torrent applications and peer-to-peer file sharing programs for Ubuntu are:
-
-- Deluge
-- Transmission
-- Qbittorrent
-- LinuxDC++
-
-To install your favorite peer-to-peer file sharing application on Ubuntu issue the following command on Terminal.
-
- $ sudo apt-get install deluge
- $ sudo apt-get install transmission
- $ sudo apt-get install qbittorrent
- $ sudo apt-get install linuxdcpp
-
-
-Install Torrent
-
-### 12. Install Windows Emulator -Wine and Gaming Support – Steam ###
-
-Wine emulator allows you to install and run Windows applications on Linux. On the other hand, Steam is a popular gaming platform for Linux based systems developed by Valve. To install both of them on your machine issue the following command on Terminal or use Ubuntu Software Center.
-
- $ sudo apt-get install steam wine winetricks
-
-
-Install Wine
-
-### 13. Install Cairo-Dock and Enable Desktop Visual Effects ###
-
-Cairo-Dock is a beautiful and flexible launcher bar for Linux desktops similar to the Mac OS X dock. To install it on Ubuntu, run the following command on Terminal.
-
- $ sudo apt-get install cairo-dock cairo-dock-plug-ins
-
-
-Install Cairo Dock
-
-
-Add Cairo Dock at Startup
-
-To enable a set of Desktop Effects, such as Cube effect, install Compiz package with the following command:
-
- $ sudo apt-get install compiz compizconfig-settings-manager compiz-plugins-extra
-
-To activate the Desktop Cube effect, search for ccsm on Dash, open CompizConfig Settings Manager, go to General Options – > Desktop Size and set Horizontal Virtual Size value to 4 and Vertical Virtual Size to 1. Then go back and check Desktop Cube (Disable Desktop Wall) and Rotate Cube boxes (Resolve Conflicts ->Disable Switch to Viewport 1) and press Ctrl+Alt+Left Mouse Click to view the cube effect.
-
-
-Enable Compiz
-
-
-Compiz Settings
-
-
-Compiz Settings Addons
-
-
-Desktop Window Rotating
-
-### 14. Add Extra Browser Support ###
-
-Ubuntu 15.04 comes by default with Mozilla Firefox Web Browser. To install other browsers such as Google Chrome or Opera, visit their official web pages, download the provided .deb packages and install them on your system using the Gdebi Package Installer.
-
-
-Enable Browser Support
-
-
-Opera Browser Support
-
-To install Chromium Open Source browser issue the following command on Terminal.
-
- $ sudo apt-get install chromium-browser
-
-### 15. Install Tweak Tools ###
-
-Want extra applications for customizing Ubuntu? Then install Unity Tweak Tool and Gnome Tweak Tool by issuing the following commands on Terminal.
-
- $ sudo apt-get install unity-tweak-tool gnome-tweak-tool
-
-
-Install Tweak Tool
-
-
-Tweak Tool Settings
-
-Another interesting tweak tool is represented by the Ubuntu Tweak package which can be obtained and installed by visiting the webpage: [http://ubuntu-tweak.com/][2].
-
-
-Tweak Tool: System Information
-
-After you have installed all this bunch of software, you might want to clean your system in order to free some space on the hard drive, by issuing the following commands:
-
- $ sudo apt-get -y autoremove
- $ sudo apt-get -y autoclean
- $ sudo apt-get -y clean
-
-This are just a few tweaks and programs that an average user might install and use on Ubuntu 15.04 Desktop for daily basic utilization. For more advanced programs, features and utilities use Ubuntu Software Center or consult Ubuntu Wiki webpage.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.tecmint.com/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-15-04-desktop/
-
-作者:[Matei Cezar][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
-[1]:http://www.viber.com/en/products/linux
-[2]:http://ubuntu-tweak.com/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150429 Docker 1.6 Released--How to Upgrade on Fedora or CentOS.md b/sources/tech/20150429 Docker 1.6 Released--How to Upgrade on Fedora or CentOS.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c3b1a737ce..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150429 Docker 1.6 Released--How to Upgrade on Fedora or CentOS.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,168 +0,0 @@
-translating wi-cuckoo
-Docker 1.6 Released - How to Upgrade on Fedora / CentOS
-================================================================================
-Docker, a popular open source container platform for packaging applications, has a new release 1.6 with lot of new features in it. This version has updates to Docker Registry, Engine, Swarm, Compose and Machine. The release aims at improvements in performance, developer and system administrator experiences. Let us take a quick look at the new features available.
-
-**Docker Registry (2.0)** which is a service for pushing Docker images for storing and sharing, has undergone architectural changes as it was facing performance issues when under load. It is still backward compatible. The language in which Docker Registry is written is now changed from Python to Google's Go to improve performance. In combination with Docker Engine 1.6, it is capable of pulling the images faster. Earlier the images were delivered sequentially, but now in parallel.
-
-**Docker Engine (1.6)** is greatly improved from its previous version. It supports containers and image labels. With labels you can attach user-defined metadata to images and containers which in turn can be used by other tools. Labels will not be visible to the running applications and can be used to speed up the searching of containers and images.
-
-There is a Windows version of the Docker client which can connect to a remote Docker engine that runs Linux.
-
-Docker now supports logging driver API that allows us to send container logs to systems like Syslog or to a third-party. It is going to be benefitting the system administrators.
-
-**Swarm (0.2)** is a clustering tool for Docker which turns a pool of Docker hosts into one virtual host. In the new feature, containers are evenly placed on the available nodes. Effort is made towards supporting the complete Docker API by adding more Docker commands. In the future, it will be possible to use third-party drivers for clustering.
-
-**Compose (1.2)** which is a tool for defining and running complex applications in Docker has also got an upgrade. In the new version, one can create multiple sub-files instead of one flat file to describe a multi-container application.
-
-With **Machine (0.2)**, we can easily create Docker hosts on local computers, clouds and data centers. The new release provides a cleaner driver interface to write drivers for providers. Provisioning is handled centrally by Machine instead of each individual driver. New command added to regenerate host's TLS certificates which increases security.
-
-### Upgrade instructions on Fedora / CentOS ###
-
-In this section, let us learn how to upgrade the existing docker version to the latest on Fedora and CentOS. Please note that currently Docker runs only on 64-bit architecture. As both Fedora and CentOS are from RedHat, commands used are pretty much identical except that the Docker package in Fedora20 and CentOS6.5 is called “docker-io”.
-
-If you do not already have Docker installed on the system, install it using:
-
- "yum install docker-io" – on Fedora20 / CentOS6.5
-
- "yum install docker" - on Fedora21 / CentOS7
-
-Before upgrading, it is good to have a backup of the docker images and container volumes.
-
-Refer [filesystem to a tar archive][1] and [volumes backups, restores or migrations options][2] for more details.
-
-Currently the test system has Docker version 1.5 installed. Output shown in the examples are from a Fedora 20 system.
-
-Verify the current version of Docker installed on the system
-
- [root@TestNode1 ~]#sudo docker -v
-
- Docker version 1.5.0, build a8a31ef/1.5.0
-
-If the Docker service is running, first stop it.
-
- [root@TestNode1 ~]# sudo systemctl stop docker
-
-Upgrade to the latest version using yum update. But at the time of writing this article, the repositories were not yet updated with the latest version(1.6). Hence you need to use the binary method of upgradation.
-
- [root@TestNode1 ~]#sudo yum -y update docker-io
-
- No packages marked for update
-
- [root@TestNode1 ~]#sudo wget https://get.docker.com/builds/Linux/x86_64/docker-latest -O /usr/bin/docker
-
- --2015-04-19 13:40:48-- https://get.docker.com/builds/Linux/x86_64/docker-latest
-
- Resolving get.docker.com (get.docker.com)... 162.242.195.82
-
- Connecting to get.docker.com (get.docker.com)|162.242.195.82|:443... connected.
-
- HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
-
- Length: 15443598 (15M) [binary/octet-stream]
-
- Saving to: /usr/bin/docker
-
- 100%[======================================>] 15,443,598 8.72MB/s in 1.7s
-
- 2015-04-19 13:40:50 (8.72 MB/s) - /usr/bin/docker saved
-
-Check the updated version
-
- [root@TestNode1 ~]#sudo docker -v
-
- Docker version 1.6.0, build 4749651
-
-Restart the docker service
-
- [root@TestNode1 ~]# sudo systemctl start docker
-
-Verify that Docker is working
-
- [root@TestNode1 ~]# docker images
-
- REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED VIRTUAL SIZE
-
- fedora latest 834629358fe2 3 months ago 241.3 MB
-
- [root@TestNode1 ~]# docker run fedora /bin/echo Hello World
-
- Hello World
-
-**Note** on CentOS installation , after installing Docker on CentOS, you might get error messages like the following while trying to start the Docker service
-
- docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine
-
- Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; disabled)
-
- Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since Mon 2015-04-20 03:24:24 EDT; 6h ago
-
- Docs: http://docs.docker.com
-
- Process: 21069 ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker -d $OPTIONS $DOCKER_STORAGE_OPTIONS $DOCKER_NETWORK_OPTIONS $ADD_REGISTRY $BLOCK_REGISTRY $INSECURE_REGISTRY (code=exited, status=127)
-
- Main PID: 21069 (code=exited, status=127)
-
- Apr 20 03:24:24 centos7 systemd[1]: Starting Docker Application Container E.....
-
- Apr 20 03:24:24 centos7 docker[21069]: time="2015-04-20T03:24:24-04:00" lev...)"
-
- Apr 20 03:24:24 centos7 docker[21069]: time="2015-04-20T03:24:24-04:00" lev...)"
-
- Apr 20 03:24:24 centos7 docker[21069]: /usr/bin/docker: relocation error: /...ce
-
- Apr 20 03:24:24 centos7 systemd[1]: docker.service: main process exited, co.../a
-
- Apr 20 03:24:24 centos7 systemd[1]: Failed to start Docker Application Cont...e.
-
- Apr 20 03:24:24 centos7 systemd[1]: Unit docker.service entered failed state.
-
-This is a known bug ( [https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1207839][3] ) and needs an upgrade of the device mapper to the latest level.
-
- [root@centos7 ~]# rpm -qa device-mapper
-
- device-mapper-1.02.84-14.el7.x86_64
-
- [root@centos7 ~]# yum update device-mapper
-
- [root@centos7 ~]# rpm -qa device-mapper
-
- device-mapper-1.02.93-3.el7.x86_64
-
- [root@centos7 ~]# systemctl start docker
-
-### Summary ###
-
-Though the docker technology is quite recent one, it is quickly gaining popularity. It has made life easy for developers and ops teams to quickly create and deploy applications respectively. With the company releasing quick updates to Docker in order to improve the product and address customer requirements, the future is definitely bright for Docker.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/docker-1-6-features-upgrade-fedora-centos/
-
-作者:[B N Poornima][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/bnpoornima/
-[1]:http://docs.docker.com/reference/commandline/cli/#export
-[2]:http://docs.docker.com/userguide/dockervolumes/#backup-restore-or-migrate-data-volumes
-[3]:https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1207839
-[4]:
-[5]:
-[6]:
-[7]:
-[8]:
-[9]:
-[10]:
-[11]:
-[12]:
-[13]:
-[14]:
-[15]:
-[16]:
-[17]:
-[18]:
-[19]:
-[20]:
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150429 KDE Plasma 5.3 Released, Here' s How To Upgrade in Kubuntu 15.04.md b/sources/tech/20150429 KDE Plasma 5.3 Released, Here' s How To Upgrade in Kubuntu 15.04.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 43b2adc3dd..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20150429 KDE Plasma 5.3 Released, Here' s How To Upgrade in Kubuntu 15.04.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,86 +0,0 @@
-KDE Plasma 5.3 Released, Here’s How To Upgrade in Kubuntu 15.04
-================================================================================
-**KDE [has announced][1] the stable release of Plasma 5.3, which comes charged with a slate of new power management features. **
-
-Having impressed and excited [with an earlier beta release in April][2], the latest update to the new stable update to the Plasma 5 desktop environments is now considered stable and ready for download.
-
-Plasma 5.3 continues to refine and finesse the new-look KDE desktop. It sees plenty of feature additions for desktop users to enjoy and **almost 400 bug fixes** packed in it should also improvements the performance and overall stability, too.
-
-### What’s New in Plasma 5.3 ###
-
-
-Better Bluetooth Management in Plasma 5.3
-
-While we touched on the majority of the **new features** [in Plasma 5.3 in an earlier article][3] many are worth reiterating.
-
-**Enhanced power management** features and configuration options, including a **new battery applet, energy usage monitor** and **animated changes in screen brightness**, will help KDE last longer on portable devices.
-
-Closing a laptop when an external monitor is connected no longer triggers ‘suspend’. This new behaviour is called ‘**cinema mode**‘ and comes enabled by default, but can be disabled using an option in power management settings.
-
-**Bluetooth functionality is improved**, with a brand new panel applet making connecting and configuring paired bluetooth devices like smartphones, keyboards and speakers easier than ever.
-
-Similarly, **trackpad configuration in KDE is easier** with Plasma 5.3 thanks to a new set-up and settings module.
-
-
-Trackpad, Touchpad. Tomato, Tomayto.
-
-For Plasma widget fans there is a new **Press and Hold** gesture. When enabled this hides the settings handle that appears when on mouseover. Instead making it only appear when long-clicking on widget.
-
-On the topic of widget-y things, several **old Plasmoid favourites are reintroduced** with this release, including a useful system monitor, handy hard-drive stats and a comic reader.
-
-### Learning More & Trying It Out ###
-
-
-
-A full list of everything — and I mean everything — that is new and improved in Plasma 5.3 is listed [in the official change log][4].
-
-Live images that let you try Plasma 5.3 on a Kubuntu base **without affecting your own system** are available from the KDE community:
-
-- [Download KDE Plasma Live Images][5]
-
-If you need super stable system you can use these live images to try the features but stick with the version of KDE that comes with your distribution on your main computer.
-
-However, if you’re happy to experiment — read: can handle any package conflicts or system issues resulting from attempting to upgrade your desktop environment — you can.
-
-### Install Plasma 5.3 in Kubuntu 15.04 ###
-
-
-
-To **install Plasma 5.3 in Kubuntu 15.04** you need to add the KDE Backports PPA, run the Software Updater tool and install any available updates.
-
-The Kubuntu backports PPA may/will also upgrade other parts of the KDE Platform other than Plasma that are installed on your system including KDE applications, frameworks and Kubuntu specific configuration files.
-
-Using the command line is by far the fastest way to upgrade to Plasma 5.3 in Kubuntu:
-
- sudo add-apt-repository ppa:kubuntu-ppa/backports
-
- sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
-
-After the upgrade process has completed, and assuming everything went well, you should reboot your computer.
-
-If you’re using an alternative desktop environment, like LXDE, Unity or GNOME, you will need to install the Kubuntu desktop package (you’ll find it in the Ubuntu Software Centre) after running both of the commands above.
-
-To downgrade to the stock version of Plasma in 15.04 you can use the PPA-Purge tool:
-
- sudo apt-get install ppa-purge
-
- sudo ppa-purge ppa:kubuntu-ppa/backports
-
-Let us know how your upgrade/testing goes in the comments below and don’t forget to mention the features you hope to see added to the Plasma 5 desktop next.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/kde-plasma-5-3-released-heres-how-to-upgrade-in-kubuntu-15-04
-
-作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
-[1]:https://www.kde.org/announcements/plasma-5.3.0.php
-[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/beta-plasma-5-3-features
-[3]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/beta-plasma-5-3-features
-[4]:https://www.kde.org/announcements/plasma-5.2.2-5.3.0-changelog.php
-[5]:https://community.kde.org/Plasma/Live_Images
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150504 How to access a Linux server behind NAT via reverse SSH tunnel.md b/sources/tech/20150504 How to access a Linux server behind NAT via reverse SSH tunnel.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b67f5aee26
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20150504 How to access a Linux server behind NAT via reverse SSH tunnel.md
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+How to access a Linux server behind NAT via reverse SSH tunnel
+================================================================================
+You are running a Linux server at home, which is behind a NAT router or restrictive firewall. Now you want to SSH to the home server while you are away from home. How would you set that up? SSH port forwarding will certainly be an option. However, port forwarding can become tricky if you are dealing with multiple nested NAT environment. Besides, it can be interfered with under various ISP-specific conditions, such as restrictive ISP firewalls which block forwarded ports, or carrier-grade NAT which shares IPv4 addresses among users.
+
+### What is Reverse SSH Tunneling? ###
+
+One alternative to SSH port forwarding is **reverse SSH tunneling**. The concept of reverse SSH tunneling is simple. For this, you will need another host (so-called "relay host") outside your restrictive home network, which you can connect to via SSH from where you are. You could set up a relay host using a [VPS instance][1] with a public IP address. What you do then is to set up a persistent SSH tunnel from the server in your home network to the public relay host. With that, you can connect "back" to the home server from the relay host (which is why it's called a "reverse" tunnel). As long as the relay host is reachable to you, you can connect to your home server wherever you are, or however restrictive your NAT or firewall is in your home network.
+
+
+
+### Set up a Reverse SSH Tunnel on Linux ###
+
+Let's see how we can create and use a reverse SSH tunnel. We assume the following. We will be setting up a reverse SSH tunnel from homeserver to relayserver, so that we can SSH to homeserver via relayserver from another computer called clientcomputer. The public IP address of **relayserver** is 1.1.1.1.
+
+On homeserver, open an SSH connection to relayserver as follows.
+
+ homeserver~$ ssh -fN -R 10022:localhost:22 relayserver_user@1.1.1.1
+
+Here the port 10022 is any arbitrary port number you can choose. Just make sure that this port is not used by other programs on relayserver.
+
+The "-R 10022:localhost:22" option defines a reverse tunnel. It forwards traffic on port 10022 of relayserver to port 22 of homeserver.
+
+With "-fN" option, SSH will go right into the background once you successfully authenticate with an SSH server. This option is useful when you do not want to execute any command on a remote SSH server, and just want to forward ports, like in our case.
+
+After running the above command, you will be right back to the command prompt of homeserver.
+
+Log in to relayserver, and verify that 127.0.0.1:10022 is bound to sshd. If so, that means a reverse tunnel is set up correctly.
+
+ relayserver~$ sudo netstat -nap | grep 10022
+
+----------
+
+ tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:10022 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 8493/sshd
+
+Now from any other computer (e.g., clientcomputer), log in to relayserver. Then access homeserver as follows.
+
+ relayserver~$ ssh -p 10022 homeserver_user@localhost
+
+One thing to take note is that the SSH login/password you type for localhost should be for homeserver, not for relayserver, since you are logging in to homeserver via the tunnel's local endpoint. So do not type login/password for relayserver. After successful login, you will be on homeserver.
+
+### Connect Directly to a NATed Server via a Reverse SSH Tunnel ###
+
+While the above method allows you to reach **homeserver** behind NAT, you need to log in twice: first to **relayserver**, and then to **homeserver**. This is because the end point of an SSH tunnel on relayserver is binding to loopback address (127.0.0.1).
+
+But in fact, there is a way to reach NATed homeserver directly with a single login to relayserver. For this, you will need to let sshd on relayserver forward a port not only from loopback address, but also from an external host. This is achieved by specifying **GatewayPorts** option in sshd running on relayserver.
+
+Open /etc/ssh/sshd_conf of **relayserver** and add the following line.
+
+ relayserver~$ vi /etc/ssh/sshd_conf
+
+----------
+
+ GatewayPorts clientspecified
+
+Restart sshd.
+
+Debian-based system:
+
+ relayserver~$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh restart
+
+Red Hat-based system:
+
+ relayserver~$ sudo systemctl restart sshd
+
+Now let's initiate a reverse SSH tunnel from homeserver as follows.
+homeserver~$ ssh -fN -R 1.1.1.1:10022:localhost:22 relayserver_user@1.1.1.1
+
+Log in to relayserver and confirm with netstat command that a reverse SSH tunnel is established successfully.
+
+ relayserver~$ sudo netstat -nap | grep 10022
+
+----------
+
+ tcp 0 0 1.1.1.1:10022 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1538/sshd: dev
+
+Unlike a previous case, the end point of a tunnel is now at 1.1.1.1:10022 (relayserver's public IP address), not 127.0.0.1:10022. This means that the end point of the tunnel is reachable from an external host.
+
+Now from any other computer (e.g., clientcomputer), type the following command to gain access to NATed homeserver.
+
+ clientcomputer~$ ssh -p 10022 homeserver_user@1.1.1.1
+
+In the above command, while 1.1.1.1 is the public IP address of relayserver, homeserver_user must be the user account associated with homeserver. This is because the real host you are logging in to is homeserver, not relayserver. The latter simply relays your SSH traffic to homeserver.
+
+### Set up a Persistent Reverse SSH Tunnel on Linux ###
+
+Now that you understand how to create a reverse SSH tunnel, let's make the tunnel "persistent", so that the tunnel is up and running all the time (regardless of temporary network congestion, SSH timeout, relay host rebooting, etc.). After all, if the tunnel is not always up, you won't be able to connect to your home server reliably.
+
+For a persistent tunnel, I am going to use a tool called autossh. As the name implies, this program allows you to automatically restart an SSH session should it breaks for any reason. So it is useful to keep a reverse SSH tunnel active.
+
+As the first step, let's set up [passwordless SSH login][2] from homeserver to relayserver. That way, autossh can restart a broken reverse SSH tunnel without user's involvement.
+
+Next, [install autossh][3] on homeserver where a tunnel is initiated.
+
+From homeserver, run autossh with the following arguments to create a persistent SSH tunnel destined to relayserver.
+
+ homeserver~$ autossh -M 10900 -fN -o "PubkeyAuthentication=yes" -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=false" -o "PasswordAuthentication=no" -o "ServerAliveInterval 60" -o "ServerAliveCountMax 3" -R 1.1.1.1:10022:localhost:22 relayserver_user@1.1.1.1
+
+The "-M 10900" option specifies a monitoring port on relayserver which will be used to exchange test data to monitor an SSH session. This port should not be used by any program on relayserver.
+
+The "-fN" option is passed to ssh command, which will let the SSH tunnel run in the background.
+
+The "-o XXXX" options tell ssh to:
+
+- Use key authentication, not password authentication.
+- Automatically accept (unknown) SSH host keys.
+- Exchange keep-alive messages every 60 seconds.
+- Send up to 3 keep-alive messages without receiving any response back.
+
+The rest of reverse SSH tunneling related options remain the same as before.
+
+If you want an SSH tunnel to be automatically up upon boot, you can add the above autossh command in /etc/rc.local.
+
+### Conclusion ###
+
+In this post, I talked about how you can use a reverse SSH tunnel to access a Linux server behind a restrictive firewall or NAT gateway from outside world. While I demonstrated its use case for a home network, you must be careful when applying it for corporate networks. Such a tunnel can be considered as a breach of a corporate policy, as it circumvents corporate firewalls and can expose corporate networks to outside attacks. There is a great chance it can be misused or abused. So always remember its implication before setting it up.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/access-linux-server-behind-nat-reverse-ssh-tunnel.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/go/digitalocean
+[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-enable-ssh-login-without.html
+[3]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-autossh-linux.html
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150515 How to Install Percona Server on CentOS 7.md b/sources/tech/20150515 How to Install Percona Server on CentOS 7.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..03affe787e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20150515 How to Install Percona Server on CentOS 7.md
@@ -0,0 +1,188 @@
+How to Install Percona Server on CentOS 7
+================================================================================
+In this article we are going to learn about percona server, an opensource drop-in replacement for MySQL and also for MariaDB. The InnoDB database engine make it very attractive and a good alternative if you need performance, reliability and a cost efficient solution
+
+In the following sections I am going to cover the installation of the percona server on the CentOS 7, I will also cover the steps needed to make backup of your current data, configuration and how to restore your backup.
+
+### Table of contents ###
+
+1. What is and why use percona
+1. Backup your databases
+1. Remove previous SQL server
+1. Installing Percona binaries
+1. Configuring Percona
+1. Securing your environment
+1. Restore your backup
+
+### 1. What is and why use Percona ###
+
+Percona is an opensource alternative to the MySQL and MariaDB databases, it's a fork of the MySQL with many improvements and unique features that makes it more reliable, powerful and faster than MySQL, and yet is fully compatible with it, you can even use replication between Oracle's MySQL and Percona.
+
+#### Features exclusive to Percona ####
+
+- Partitioned Adaptive Hash Search
+- Fast Checksum Algorithm
+- Buffer Pool Pre-Load
+- Support for FlashCache
+
+#### MySQL Enterprise and Percona specific features ####
+
+- Import Tables From Different Servers
+- PAM authentication
+- Audit Log
+- Threadpool
+
+Now that you are pretty excited to see all these good things together, we are going show you how to install and do basic configuration of Percona Server.
+
+### 2. Backup your databases ###
+
+The following, command creates a mydatabases.sql file with the SQL commands to recreate/restore salesdb and employeedb databases, replace the databases names to reflect your setup, skip if this is a brand new setup
+
+ mysqldump -u root -p --databases employeedb salesdb > mydatabases.sql
+
+Copy the current configuration file, you can also skip this in fresh setups
+
+ cp my.cnf my.cnf.bkp
+
+### 3. Remove your previous SQL Server ###
+
+Stop the MySQL/MariaDB if it's running.
+
+ systemctl stop mysql.service
+
+Uninstall MariaDB and MySQL
+
+ yum remove MariaDB-server MariaDB-client MariaDB-shared mysql mysql-server
+
+Move / Rename the MariaDB files in **/var/lib/mysql**, it's a safer and faster than just removing, it's like a 2nd level instant backup. :)
+
+ mv /var/lib/mysql /var/lib/mysql_mariadb
+
+### 4. Installing Percona binaries ###
+
+You can choose from a number of options on how to install Percona, in a CentOS system it's generally a better idea to use yum or RPM, so these are the way that are covered by this article, compiling and install from sources are not covered by this article.
+
+Installing from Yum repository:
+
+First you need to set the Percona's Yum repository with this:
+
+ yum install http://www.percona.com/downloads/percona-release/redhat/0.1-3/percona-release-0.1-3.noarch.rpm
+
+And then install Percona with:
+
+ yum install Percona-Server-client-56 Percona-Server-server-56
+
+The above command installs Percona server and clients, shared libraries, possibly Perl and perl modules such as DBI::MySQL, if that are not already installed, and also other dependencies as needed.
+
+Installing from RPM package:
+
+We can download all rpm packages with the help of wget:
+
+ wget -r -l 1 -nd -A rpm -R "*devel*,*debuginfo*" \ http://www.percona.com/downloads/Percona-Server-5.5/Percona-Server-5.5.42-37.1/binary/redhat/7/x86_64/
+
+And with rpm utility, you install all the packages once:
+
+ rpm -ivh Percona-Server-server-55-5.5.42-rel37.1.el7.x86_64.rpm \ Percona-Server-client-55-5.5.42-rel37.1.el7.x86_64.rpm \ Percona-Server-shared-55-5.5.42-rel37.1.el7.x86_64.rpm
+
+Note the backslash '\' on the end of the sentences on the above commands, if you install individual packages, remember that to met dependencies, the shared package must be installed before client and client before server.
+
+### 5. Configuring Percona Server ###
+
+#### Restoring previous configuration ####
+
+As we are moving from MariaDB, you can just restore the backup of my.cnf file that you made in earlier steps.
+
+ cp /etc/my.cnf.bkp /etc/my.cnf
+
+#### Creating a new my.cnf ####
+
+If you need a new configuration file that fit your needs or if you don't have made a copy of my.cnf, you can use this wizard, it will generate for you, through simple steps.
+
+Here is a sample my.cnf file that comes with Percona-Server package
+
+ # Percona Server template configuration
+
+ [mysqld]
+ #
+ # Remove leading # and set to the amount of RAM for the most important data
+ # cache in MySQL. Start at 70% of total RAM for dedicated server, else 10%.
+ # innodb_buffer_pool_size = 128M
+ #
+ # Remove leading # to turn on a very important data integrity option: logging
+ # changes to the binary log between backups.
+ # log_bin
+ #
+ # Remove leading # to set options mainly useful for reporting servers.
+ # The server defaults are faster for transactions and fast SELECTs.
+ # Adjust sizes as needed, experiment to find the optimal values.
+ # join_buffer_size = 128M
+ # sort_buffer_size = 2M
+ # read_rnd_buffer_size = 2M
+ datadir=/var/lib/mysql
+ socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
+
+ # Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security risks
+ symbolic-links=0
+
+ [mysqld_safe]
+ log-error=/var/log/mysqld.log
+ pid-file=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
+
+After making your my.cnf file fit your needs, it's time to start the service:
+
+ systemctl restart mysql.service
+
+If everything goes fine, your server is now up and ready to ready to receive SQL commands, you can try the following command to check:
+
+ mysql -u root -p -e 'SHOW VARIABLES LIKE "version_comment"'
+
+If you can't start the service, you can look for a reason in **/var/log/mysql/mysqld.log** this file is set by the **log-error** option in my.cnf's **[mysqld_safe]** session.
+
+ tail /var/log/mysql/mysqld.log
+
+You can also take a look in a file inside **/var/lib/mysql/** with name in the form of **[hostname].err** as the following example:
+
+ tail /var/lib/mysql/centos7.err
+
+If this also fail in show what is wrong, you can also try strace:
+
+ yum install strace && systemctl stop mysql.service && strace -f -f mysqld_safe
+
+The above command is extremely verbous and it's output is quite low level but can show you the reason you can't start service in most times.
+
+### 6. Securing your environment ###
+
+Ok, you now have your RDBMS ready to receive SQL queries, but it's not a good idea to put your precious data on a server without minimum security, it's better to make it safer with mysql_secure_instalation, this utility helps in removing unused default features, also set the root main password and make access restrictions for using this user.
+Just invoke it by the shell and follow instructions on the screen.
+
+ mysql_secure_install
+
+### 7. Restore your backup ###
+
+If you are coming from a previous setup, now you can restore your databases, just use mysqldump once again.
+
+ mysqldump -u root -p < mydatabases.sql
+
+Congratulations, you just installed Percona on your CentOS Linux, your server is now fully ready for use; You can now use your service as it was MySQL, and your services are fully compatible with it.
+
+### Conclusion ###
+
+There is a lot of things to configure in order to achieve better performance, but here is some straightforward options to improve your setup. When using innodb engine it's also a good idea to set the **innodb_file_per_table** option **on**, it gonna distribute table indexes in a file per table basis, it means that each table have it's own index file, it makes the overall system, more robust and easier to repair.
+
+Other option to have in mind is the **innodb_buffer_pool_size** option, InnoDB should have large enough to your datasets, and some value **between 70% and 80%** of the total available memory should be reasonable.
+
+By setting the **innodb-flush-method** to **O_DIRECT** you disable write cache, if you have **RAID**, this should be set to improved performance as this cache is already done in a lower level.
+
+If your data is not that critical and you don't need fully **ACID** compliant transactions, you can adjust to 2 the option **innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit**, this will also lead to improved performance.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/percona-server-centos-7/
+
+作者:[Carlos Alberto][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/carlosal/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150515 Install 'Tails 1.4′ Linux Operating System to Preserve Privacy and Anonymity.md b/sources/tech/20150515 Install 'Tails 1.4′ Linux Operating System to Preserve Privacy and Anonymity.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5731cd69f4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20150515 Install 'Tails 1.4′ Linux Operating System to Preserve Privacy and Anonymity.md
@@ -0,0 +1,181 @@
+FSSlc translating
+
+Install ‘Tails 1.4′ Linux Operating System to Preserve Privacy and Anonymity
+================================================================================
+In this Internet world and the world of Internet we perform most of our task online be it Ticket booking, Money transfer, Studies, Business, Entertainment, Social Networking and what not. We spend a major part of our time online daily. It has been getting hard to remain anonymous with each passing day specially when backdoors are being planted by organizations like NSA (National Security Agency) who are putting their nose in between every thing that we come across online. We have least or no privacy online. All the searches are logged upon the basis of user Internet surfing activity and machine activity.
+
+A wonderful browser from Tor project is used by millions which help us surfing the web anonymously however it is not difficult to trace your browsing habits and hence tor alone is not the guarantee of your safety online. You may like to check Tor features and installation instructions here:
+
+- [Anonymous Web Browsing using Tor][1]
+
+There is a operating system named Tails by Tor Projects. Tails (The Amnesic Incognito Live System) is a live operating system, based on Debian Linux distribution, which mainly focused on preserving privacy and anonymity on the web while browsing internet, means all it’s outgoing connection are forced to pass through the Tor and direct (non-anonymous) requests are blocked. The system is designed to run from any boot-able media be it USB stick or DVD.
+
+The latest stable release of Tails OS is 1.4 which was released on May 12, 2015. Powered by open source Monolithic Linux Kernel and built on top of Debian GNU/Linux Tails aims at Personal Computer Market and includes GNOME 3 as default user Interface.
+
+#### Features of Tails OS 1.4 ####
+
+- Tails is a free operating system, free as in beer and free as in speech.
+- Built on top of Debian/GNU Linux. The most widely used OS that is Universal.
+- Security Focused Distribution.
+- Windows 8 camouflage.
+- Need not to be installed and browse Internet anonymously using Live Tails CD/DVD.
+- Leave no trace on the computer, while tails is running.
+- Advanced cryptographic tools used to encrypt everything that concerns viz., files, emails, etc.
+- Sends and Receive traffic through tor network.
+- In true sense it provides privacy for anyone, anywhere.
+- Comes with several applications ready to be used from Live Environment.
+- All the softwares comes per-configured to connect to INTERNET only through Tor network.
+- Any application that tries to connect to Internet without Tor Network is blocked, automatically.
+- Restricts someone who is watching what sites you visit and restricts sites to learn your geographical location.
+- Connect to websites that are blocked and/or censored.
+- Designed specially not to use space used by parent OS even when there is free swap space.
+- The whole OS loads on RAM and is flushed when we reboot/shutdown. Hence no trace of running.
+- Advanced security implementation by encrypting USB disk, HTTPS ans Encrypt and sign emails and documents.
+
+#### What can you expect in Tails 1.4 ####
+
+- Tor Browser 4.5 with a security Slider.
+- Tor Upgraded to version 0.2.6.7.
+- Several Security holes fixed.
+- Many of the bug fixed and patches applied to Applications like curl, OpenJDK 7, tor Network, openldap, etc.
+
+To get a complete list of change logs you may visit [HERE][2]
+
+**Note**: It is strongly recommended to upgrade to Tails 1.4, if you’re using any older version of Tails.
+
+#### Why should I use Tails Operating System ####
+
+You need Tails because you need:
+
+- Freedom from network surveillance
+- Defend freedom, privacy and confidentiality
+- Security aka traffic analysis
+
+This tutorial will walk through the installation of Tails 1.4 OS with a short review.
+
+### Tails 1.4 Installation Guide ###
+
+1. To download the latest Tails OS 1.4, you may use wget command to download directly.
+
+ $ wget http://dl.amnesia.boum.org/tails/stable/tails-i386-1.4/tails-i386-1.4.iso
+
+Alternatively you may download Tails 1.4 Direct ISO image or use a Torrent Client to pull the iso image file for you. Here is the link to both downloads:
+
+- [tails-i386-1.4.iso][3]
+- [tails-i386-1.4.torrent][4]
+
+2. After downloading, verify ISO Integrity by matching SHA256 checksum with the SHA256SUM provided on the official website..
+
+ $ sha256sum tails-i386-1.4.iso
+
+ 339c8712768c831e59c4b1523002b83ccb98a4fe62f6a221fee3a15e779ca65d
+
+If you are interested in knowing OpenPGP, checking Tails signing key against Debian keyring and anything related to Tails cryptographic signature, you may like to point your browser [HERE][5].
+
+3. Next you need to write the image to USB stick or DVD ROM. You may like to check the article, [How to Create Live Bootable USB][6] for details on how to make a flash drive bootable and write ISO to it.
+
+4. Insert the Tails OS Bootable flash drive or DVD ROM in the disk and boot from it (select from BIOS to boot). The first screen – two options to select from ‘Live‘ and ‘Live (failsafe)‘. Select ‘Live‘ and press Enter.
+
+
+Tails Boot Menu
+
+5. Just before login. You have two options. Click ‘More Options‘ if you want to configure and set advanced options else click ‘No‘.
+
+
+Tails Welcome Screen
+
+6. After clicking Advanced option, you need to setup root password. This is important if you want to upgrade it. This root password is valid till you shutdown/reboot the machine.
+
+Also you may enable Windows Camouflage, if you want to run this OS on a public place, so that it seems as you are running Windows 8 operating system. Good option indeed! Is not it? Also you have a option to configure Network and Mac Address. Click ‘Login‘ when done!.
+
+
+Tails OS Configuration
+
+7. This is Tails GNU/Linux OS camouflaged by Windows Skin.
+
+
+Tails Windows Look
+
+8. It will start Tor Network in the background. Check the Notification on the top-right corner of the screen – Tor is Ready / You are now connected to the Internet.
+
+Also check what it contains under Internet Menu. Notice – It has Tor Browser (safe) and Unsafe Web Browser (Where incoming and outgoing data don’t pass through TOR Network) along with other applications.
+
+
+Tails Menu and Tools
+
+9. Click Tor and check your IP Address. It confirms my physical location is not shared and my privacy is intact.
+
+
+Check Privacy on Tails
+
+10. You may Invoke Tails Installer to clone & Install, Clone & Upgrade and Upgrade from ISO.
+
+
+Tails Installer Options
+
+11. The other option was to select Tor without any advanced option, just before login (Check step #5 above).
+
+
+Tails Without Advance Option
+
+12. You will get log-in to Gnome3 Desktop Environment.
+
+
+Tails Gnome Desktop
+
+13. If you click to Launch Unsafe browser in Camouflage or without Camouflage, you will be notified.
+
+
+Tails Browsing Notification
+
+If you do, this is what you get in a Browser.
+
+
+Tails Browsing Alert
+
+#### Is Tails for me? ####
+
+To get the above question answered, first answer a few question.
+
+- Do you need your privacy to be intact while you are online?
+- Do you want to remain hidden from Identity thieves?
+- Do you want somebody to put your nose in between your private chat online?
+- Do you really want to show your geographical location to anybody there?
+- Do you carry out banking transactions online?
+- Are you happy with the censorship by government and ISP?
+
+If the answer to any of the above question is ‘YES‘ you preferably need Tails. If answer to all the above question is ‘NO‘ you perhaps don’t need it.
+
+To know more about Tails? Point your browser to user Documentation : [https://tails.boum.org/doc/index.en.html][7]
+
+### Conclusion ###
+
+Tails is an OS which is must for those who work in an unsafe environment. An OS focused on security yet contains bundles of Application – Gnome Desktop, Tor, Firefox (Iceweasel), Network Manager, Pidgin, Claws mail, Liferea feed addregator, Gobby, Aircrack-ng, I2P.
+
+It also contain several tools for Encryption and Privacy Under the Hood, viz., LUKS, GNUPG, PWGen, Shamir’s Secret Sharing, Virtual Keyboard (against Hardware Keylogging), MAT, KeePassX Password Manager, etc.
+
+That’s all for now. Keep Connected to Tecmint. Share your thoughts on Tails GNU/Linux Operating System. What do you think about the future of the Project? Also test it Locally and let us know your experience.
+
+You may run it in [Virtualbox][8] as well. Remember Tails loads the whole OS in RAM hence give enough RAM to run Tails in VM.
+
+I tested in 1GB Environment and it worked without lagging. Thanks to all our readers for their Support. In making Tecmint a one place for all Linux related stuffs your co-operation is needed. Kudos!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-tails-1-4-linux-operating-system-to-preserve-privacy-and-anonymity/
+
+作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/tor-browser-for-anonymous-web-browsing/
+[2]:https://tails.boum.org/news/version_1.4/index.en.html
+[3]:http://dl.amnesia.boum.org/tails/stable/tails-i386-1.4/tails-i386-1.4.iso
+[4]:https://tails.boum.org/torrents/files/tails-i386-1.4.torrent
+[5]:https://tails.boum.org/download/index.en.html#verify
+[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-linux-from-usb-device/
+[7]:https://tails.boum.org/doc/index.en.html
+[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-virtualbox-on-redhat-centos-fedora/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150518 How to set up a Replica Set on MongoDB.md b/sources/tech/20150518 How to set up a Replica Set on MongoDB.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..07e16dafc1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20150518 How to set up a Replica Set on MongoDB.md
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
+How to set up a Replica Set on MongoDB
+================================================================================
+MongoDB has become the most famous NoSQL database on the market. MongoDB is document-oriented, and its scheme-free design makes it a really attractive solution for all kinds of web applications. One of the features that I like the most is Replica Set, where multiple copies of the same data set are maintained by a group of mongod nodes for redundancy and high availability.
+
+This tutorial describes how to configure a Replica Set on MonoDB.
+
+The most common configuration for a Replica Set involves one primary and multiple secondary nodes. The replication will then be initiated from the primary toward the secondaries. Replica Sets can not only provide database protection against unexpected hardware failure and service downtime, but also improve read throughput of database clients as they can be configured to read from different nodes.
+
+### Set up the Environment ###
+
+In this tutorial, we are going to set up a Replica Set with one primary and two secondary nodes.
+
+
+
+In order to implement this lab, we will use three virtual machines (VMs) running on VirtualBox. I am going to install Ubuntu 14.04 on the VMs, and install official packages for Mongodb.
+
+I am going to set up a necessary environment on one VM instance, and then clone it to the other two VM instances. Thus pick one VM named master, and perform the following installations.
+
+First, we need to add the MongoDB key for apt:
+
+ $ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 7F0CEB10
+
+Then we need to add the official MongoDB repository to our source.list:
+
+ $ sudo su
+ # echo "deb http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu "$(lsb_release -sc)"/mongodb-org/3.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.0.list
+
+Let's update repositories and install MongoDB.
+
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org
+
+Now let's make some changes in /etc/mongodb.conf.
+
+ auth = true
+ dbpath=/var/lib/mongodb
+ logpath=/var/log/mongodb/mongod.log
+ logappend=true
+ keyFile=/var/lib/mongodb/keyFile
+ replSet=myReplica
+
+The first line is to make sure that we are going to have authentication on our database. keyFile is to set up a keyfile that is going to be used by MongoDB to replicate between nodes. replSet sets up the name of our replica set.
+
+Now we are going to create our keyfile, so that it can be in all our instances.
+
+ $ echo -n "MyRandomStringForReplicaSet" | md5sum > keyFile
+
+This will create keyfile that contains a MD5 string, but it has some noise that we need to clean up before using it in MongoDB. Use the following command to clean it up:
+
+ $ echo -n "MyReplicaSetKey" | md5sum|grep -o "[0-9a-z]\+" > keyFile
+
+What grep command does is to print MD5 string with no spaces or other characters that we don't want.
+
+Now we are going to make the keyfile ready for use:
+
+ $ sudo cp keyFile /var/lib/mongodb
+ $ sudo chown mongodb:nogroup keyFile
+ $ sudo chmod 400 keyFile
+
+Now we have our Ubuntu VM ready to be cloned. Power it off, and clone it to the other VMs.
+
+
+
+I name the cloned VMs secondary1 and secondary2. Make sure to reinitialize the MAC address of cloned VMs and clone full disks.
+
+
+
+All three VM instances should be on the same network to communicate with each other. For this, we are going to attach all three VMs to "Internet Network".
+
+It is recommended that each VM instances be assigned a static IP address, as opposed to DHCP IP address, so that the VMs will not lose connectivity among themselves when a DHCP server assigns different IP addresses to them.
+
+Let's edit /etc/networks/interfaces of each VM as follows.
+
+On primary:
+
+ auto eth1
+ iface eth1 inet static
+ address 192.168.50.2
+ netmask 255.255.255.0
+
+On secondary1:
+
+ auto eth1
+ iface eth1 inet static
+ address 192.168.50.3
+ netmask 255.255.255.0
+
+On secondary2:
+
+ auto eth1
+ iface eth1 inet static
+ address 192.168.50.4
+ netmask 255.255.255.0
+
+Another file that needs to be set up is /etc/hosts, because we don't have DNS. We need to set the hostnames in /etc/hosts.
+
+On primary:
+
+ 127.0.0.1 localhost primary
+ 192.168.50.2 primary
+ 192.168.50.3 secondary1
+ 192.168.50.4 secondary2
+
+On secondary1:
+
+ 127.0.0.1 localhost secondary1
+ 192.168.50.2 primary
+ 192.168.50.3 secondary1
+ 192.168.50.4 secondary2
+
+On secondary2:
+
+ 127.0.0.1 localhost secondary2
+ 192.168.50.2 primary
+ 192.168.50.3 secondary1
+ 192.168.50.4 secondary2
+
+Check connectivity among themselves by using ping command:
+
+ $ ping primary
+ $ ping secondary1
+ $ ping secondary2
+
+### Set up a Replica Set ###
+
+After verifying connectivity among VMs, we can go ahead and create the admin user so that we can start working on the Replica Set.
+
+On primary node, open /etc/mongodb.conf, and comment out two lines that start with auth and replSet:
+
+ dbpath=/var/lib/mongodb
+ logpath=/var/log/mongodb/mongod.log
+ logappend=true
+ #auth = true
+ keyFile=/var/lib/mongodb/keyFile
+ #replSet=myReplica
+
+Restart mongod daemon.
+
+ $ sudo service mongod restart
+
+Create an admin user after conencting to MongoDB:
+
+ > use admin
+ > db.createUser({
+ user:"admin",
+ pwd:"
+ })
+ $ sudo service mongod restart
+
+Connect to MongoDB and use these commands to add secondary1 and secondary2 to our Replicat Set.
+
+ > use admin
+ > db.auth("admin","myreallyhardpassword")
+ > rs.initiate()
+ > rs.add ("secondary1:27017")
+ > rs.add("secondary2:27017")
+
+Now that we have our Replica Set, we can start working on our project. Consult the [official driver documentation][1] to see how to connect to a Replica Set. In case you want to query from shell, you have to connect to primary instance to insert or query the database. Secondary nodes will not let you do that. If you attempt to access the database on a secondary node, you will get this error message:
+
+ myReplica:SECONDARY>
+ myReplica:SECONDARY> show databases
+ 2015-05-10T03:09:24.131+0000 E QUERY Error: listDatabases failed:{ "note" : "from execCommand", "ok" : 0, "errmsg" : "not master" }
+ at Error ()
+ at Mongo.getDBs (src/mongo/shell/mongo.js:47:15)
+ at shellHelper.show (src/mongo/shell/utils.js:630:33)
+ at shellHelper (src/mongo/shell/utils.js:524:36)
+ at (shellhelp2):1:1 at src/mongo/shell/mongo.js:47
+
+I hope you find this tutorial useful. You can use Vagrant to automate your local environments and help you code faster.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/setup-replica-set-mongodb.html
+
+作者:[Christopher Valerio][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/valerio
+[1]:http://docs.mongodb.org/ecosystem/drivers/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150522 Analyzing Linux Logs.md b/sources/tech/20150522 Analyzing Linux Logs.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..38d5b4636e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20150522 Analyzing Linux Logs.md
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
+translating by zhangboyue
+Analyzing Linux Logs
+================================================================================
+There’s a great deal of information waiting for you within your logs, although it’s not always as easy as you’d like to extract it. In this section we will cover some examples of basic analysis you can do with your logs right away (just search what’s there). We’ll also cover more advanced analysis that may take some upfront effort to set up properly, but will save you time on the back end. Examples of advanced analysis you can do on parsed data include generating summary counts, filtering on field values, and more.
+
+We’ll show you first how to do this yourself on the command line using several different tools and then show you how a log management tool can automate much of the grunt work and make this so much more streamlined.
+
+### Searching with Grep ###
+
+Searching for text is the most basic way to find what you’re looking for. The most common tool for searching text is [grep][1]. This command line tool, available on most Linux distributions, allows you to search your logs using regular expressions. A regular expression is a pattern written in a special language that can identify matching text. The simplest pattern is to put the string you’re searching for surrounded by quotes
+
+#### Regular Expressions ####
+
+Here’s an example to find authentication logs for “user hoover” on an Ubuntu system:
+
+ $ grep "user hoover" /var/log/auth.log
+ Accepted password for hoover from 10.0.2.2 port 4792 ssh2
+ pam_unix(sshd:session): session opened for user hoover by (uid=0)
+ pam_unix(sshd:session): session closed for user hoover
+
+It can be hard to construct regular expressions that are accurate. For example, if we searched for a number like the port “4792” it could also match timestamps, URLs, and other undesired data. In the below example for Ubuntu, it matched an Apache log that we didn’t want.
+
+ $ grep "4792" /var/log/auth.log
+ Accepted password for hoover from 10.0.2.2 port 4792 ssh2
+ 74.91.21.46 - - [31/Mar/2015:19:44:32 +0000] "GET /scripts/samples/search?q=4972HTTP/1.0" 404 545 "-" "-”
+
+#### Surround Search ####
+
+Another useful tip is that you can do surround search with grep. This will show you what happened a few lines before or after a match. It can help you debug what lead up to a particular error or problem. The B flag gives you lines before, and A gives you lines after. For example, we can see that when someone failed to login as an admin, they also failed the reverse mapping which means they might not have a valid domain name. This is very suspicious!
+
+ $ grep -B 3 -A 2 'Invalid user' /var/log/auth.log
+ Apr 28 17:06:20 ip-172-31-11-241 sshd[12545]: reverse mapping checking getaddrinfo for 216-19-2-8.commspeed.net [216.19.2.8] failed - POSSIBLE BREAK-IN ATTEMPT!
+ Apr 28 17:06:20 ip-172-31-11-241 sshd[12545]: Received disconnect from 216.19.2.8: 11: Bye Bye [preauth]
+ Apr 28 17:06:20 ip-172-31-11-241 sshd[12547]: Invalid user admin from 216.19.2.8
+ Apr 28 17:06:20 ip-172-31-11-241 sshd[12547]: input_userauth_request: invalid user admin [preauth]
+ Apr 28 17:06:20 ip-172-31-11-241 sshd[12547]: Received disconnect from 216.19.2.8: 11: Bye Bye [preauth]
+
+#### Tail ####
+
+You can also pair grep with [tail][2] to get the last few lines of a file, or to follow the logs and print them in real time. This is useful if you are making interactive changes like starting a server or testing a code change.
+
+ $ tail -f /var/log/auth.log | grep 'Invalid user'
+ Apr 30 19:49:48 ip-172-31-11-241 sshd[6512]: Invalid user ubnt from 219.140.64.136
+ Apr 30 19:49:49 ip-172-31-11-241 sshd[6514]: Invalid user admin from 219.140.64.136
+
+A full introduction on grep and regular expressions is outside the scope of this guide, but [Ryan’s Tutorials][3] include more in-depth information.
+
+Log management systems have higher performance and more powerful searching abilities. They often index their data and parallelize queries so you can quickly search gigabytes or terabytes of logs in seconds. In contrast, this would take minutes or in extreme cases hours with grep. Log management systems also use query languages like [Lucene][4] which offer an easier syntax for searching on numbers, fields, and more.
+
+### Parsing with Cut, AWK, and Grok ###
+
+#### Command Line Tools ####
+
+Linux offers several command line tools for text parsing and analysis. They are great if you want to quickly parse a small amount of data but can take a long time to process large volumes of data
+
+#### Cut ####
+
+The [cut][5] command allows you to parse fields from delimited logs. Delimiters are characters like equal signs or commas that break up fields or key value pairs.
+
+Let’s say we want to parse the user from this log:
+
+ pam_unix(su:auth): authentication failure; logname=hoover uid=1000 euid=0 tty=/dev/pts/0 ruser=hoover rhost= user=root
+
+We can use the cut command like this to get the text after the eighth equal sign. This example is on an Ubuntu system:
+
+ $ grep "authentication failure" /var/log/auth.log | cut -d '=' -f 8
+ root
+ hoover
+ root
+ nagios
+ nagios
+
+#### AWK ####
+
+Alternately, you can use [awk][6], which offers more powerful features to parse out fields. It offers a scripting language so you can filter out nearly everything that’s not relevant.
+
+For example, let’s say we have the following log line on an Ubuntu system and we want to extract the username that failed to login:
+
+ Mar 24 08:28:18 ip-172-31-11-241 sshd[32701]: input_userauth_request: invalid user guest [preauth]
+
+Here’s how you can use the awk command. First, put a regular expression /sshd.*invalid user/ to match the sshd invalid user lines. Then print the ninth field using the default delimiter of space using { print $9 }. This outputs the usernames.
+
+ $ awk '/sshd.*invalid user/ { print $9 }' /var/log/auth.log
+ guest
+ admin
+ info
+ test
+ ubnt
+
+You can read more about how to use regular expressions and print fields in the [Awk User’s Guide][7].
+
+#### Log Management Systems ####
+
+Log management systems make parsing easier and enable users to quickly analyze large collections of log files. They can automatically parse standard log formats like common Linux logs or web server logs. This saves a lot of time because you don’t have to think about writing your own parsing logic when troubleshooting a system problem.
+
+Here you can see an example log message from sshd which has each of the fields remoteHost and user parsed out. This is a screenshot from Loggly, a cloud-based log management service.
+
+
+
+You can also do custom parsing for non-standard formats. A common tool to use is [Grok][8] which uses a library of common regular expressions to parse raw text into structured JSON. Here is an example configuration for Grok to parse kernel log files inside Logstash:
+
+ filter{
+ grok {
+ match => {"message" => "%{CISCOTIMESTAMP:timestamp} %{HOST:host} %{WORD:program}%{NOTSPACE} %{NOTSPACE}%{NUMBER:duration}%{NOTSPACE} %{GREEDYDATA:kernel_logs}"
+ }
+ }
+
+And here is what the parsed output looks like from Grok:
+
+
+
+### Filtering with Rsyslog and AWK ###
+
+Filtering allows you to search on a specific field value instead of doing a full text search. This makes your log analysis more accurate because it will ignore undesired matches from other parts of the log message. In order to search on a field value, you need to parse your logs first or at least have a way of searching based on the event structure.
+
+#### How to Filter on One App ####
+
+Often, you just want to see the logs from just one application. This is easy if your application always logs to a single file. It’s more complicated if you need to filter one application among many in an aggregated or centralized log. Here are several ways to do this:
+
+1. Use the rsyslog daemon to parse and filter logs. This example writes logs from the sshd application to a file named sshd-messages, then discards the event so it’s not repeated elsewhere. You can try this example by adding it to your rsyslog.conf file.
+
+ :programname, isequal, “sshd” /var/log/sshd-messages
+ &~
+
+2. Use command line tools like awk to extract the values of a particular field like the sshd username. This example is from an Ubuntu system.
+
+ $ awk '/sshd.*invalid user/ { print $9 }' /var/log/auth.log
+ guest
+ admin
+ info
+ test
+ ubnt
+
+3. Use a log management system that automatically parses your logs, then click to filter on the desired application name. Here is a screenshot showing the syslog fields in a log management service called Loggly. We are filtering on the appName “sshd” as indicated by the Venn diagram icon.
+
+
+
+#### How to Filter on Errors ####
+
+One of the most common thing people want to see in their logs is errors. Unfortunately, the default syslog configuration doesn’t output the severity of errors directly, making it difficult to filter on them.
+
+There are two ways you can solve this problem. First, you can modify your rsyslog configuration to output the severity in the log file to make it easier to read and search. In your rsyslog configuration you can add a [template][9] with pri-text such as the following:
+
+ "<%pri-text%> : %timegenerated%,%HOSTNAME%,%syslogtag%,%msg%n"
+
+This example gives you output in the following format. You can see that the severity in this message is err.
+
+ <authpriv.err> : Mar 11 18:18:00,hoover-VirtualBox,su[5026]:, pam_authenticate: Authentication failure
+
+You can use awk or grep to search for just the error messages. In this example for Ubuntu, we’re including some surrounding syntax like the . and the > which match only this field.
+
+ $ grep '.err>' /var/log/auth.log
+ <authpriv.err> : Mar 11 18:18:00,hoover-VirtualBox,su[5026]:, pam_authenticate: Authentication failure
+
+Your second option is to use a log management system. Good log management systems automatically parse syslog messages and extract the severity field. They also allow you to filter on log messages of a certain severity with a single click.
+
+Here is a screenshot from Loggly showing the syslog fields with the error severity highlighted to show we are filtering for errors:
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.loggly.com/ultimate-guide/logging/analyzing-linux-logs/
+
+作者:[Jason Skowronski][a] [Amy Echeverri][b] [ Sadequl Hussain][c]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.linkedin.com/in/jasonskowronski
+[b]:https://www.linkedin.com/in/amyecheverri
+[c]:https://www.linkedin.com/pub/sadequl-hussain/14/711/1a7
+[1]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/grep
+[2]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/tail
+[3]:http://ryanstutorials.net/linuxtutorial/grep.php
+[4]:https://lucene.apache.org/core/2_9_4/queryparsersyntax.html
+[5]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/cut
+[6]:http://linux.die.net/man/1/awk
+[7]:http://www.delorie.com/gnu/docs/gawk/gawk_26.html#IDX155
+[8]:http://logstash.net/docs/1.4.2/filters/grok
+[9]:http://www.rsyslog.com/doc/v8-stable/configuration/templates.html
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150526 20 Useful Terminal Emulators for Linux.md b/sources/tech/20150526 20 Useful Terminal Emulators for Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..436b28f79f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20150526 20 Useful Terminal Emulators for Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,301 @@
+Translating by ZTinoZ
+20 Useful Terminal Emulators for Linux
+================================================================================
+A Terminal emulator is a computer program that reproduces a video terminal within some other display structure. In other words the Terminal emulator has an ability to make a dumb machine appear like a client computer networked to the server. The terminal emulator allows an end user to access console as well as its applications such as text user interface and command line interface.
+
+
+
+20 Linux Terminal Emulators
+
+You may find huge number of terminal emulators to choose from this open source world. Some of them offers large range of features while others offers less features. To give a better understanding to the quality of software that are available, we have gathered a list of marvelous terminal emulator for Linux. Each title provides its description and feature along with screenshot of the software with relevant download link.
+
+### 1. Terminator ###
+
+Terminator is an advanced and powerful terminal emulator which supports multiple terminals windows. This emulator is fully customizable. You can change the size, colour, give different shapes to the terminal. Its very user friendly and fun to use.
+
+#### Features of Terminator ####
+
+- Customize your profiles and colour schemes, set the size to fit your needs.
+- Use plugins to get even more functionality.
+- Several key-shortcuts are available to speed up common activities.
+- Split the terminal window into several virtual terminals and re-size them as needed.
+
+
+
+Terminator Terminal
+
+- [Terminator Homepage][1]
+- [Download and Installation Instructions][2]
+
+### 2. Tilda ###
+
+Tilda is a stylish drop-down terminal based on GTK+. With the help of a single key press you can launch a new or hide Tilda window. However, you can add colors of your choice to change the look of the text and Terminal background.
+
+#### Features of Tilda ####
+
+ Interface with Highly customization option.
+ You can set the transparency level for Tilda window.
+ Excellent built-in colour schemes.
+
+
+
+Tilda Terminal
+
+- [Tilda Homepage][3]
+
+### 3. Guake ###
+
+Guake is a python based drop-down terminal created for the GNOME Desktop Environment. It is invoked by pressing a single keystroke, and can make it hidden by pressing same keystroke again. Its design was determined from FPS (First Person Shooter) games such as Quake and one of its main target is be easy to reach.
+
+Guake is very much similar to Yakuaka and Tilda, but it’s an experiment to mix the best of them into a single GTK-based program. Guake has been written in python from scratch using a little piece in C (global hotkeys stuff).
+
+
+
+Guake Terminal
+
+- [Guake Homepage][4]
+
+### 4. Yakuake ###
+
+Yakuake (Yet Another Kuake) is a KDE based drop-down terminal emulator very much similar to Guake terminal emulator in functionality. It’s design was inspired from fps consoles games such as Quake.
+
+Yakuake is basically a KDE application, which can be easily installed on KDE desktop, but if you try to install Yakuake in GNOME desktop, it will prompt you to install huge number of dependency packages.
+
+#### Yakuake Features ####
+
+- Fluently turn down from the top of your screen
+- Tabbed interface
+- Configurable dimensions and animation speed
+- Customizable
+
+
+
+Yakuake Terminal
+
+- [Yakuake Homepage][5]
+
+### 5. ROXTerm ###
+
+ROXterm is yet another lightweight terminal emulator designed to provide similar features to gnome-terminal. It was originally constructed to have lesser footprints and faster start-up time by not using the Gnome libraries and by using a independent applet to bring the configuration interface (GUI), but over the time it’s role has shifted to bringing a higher range of features for power users.
+
+However, it is more customizable than gnome-terminal and anticipated more at “power” users who make excessive use of terminals. It is easily integrated with GNOME desktop environment and provides features like drag & drop of items into terminal.
+
+
+
+Roxterm Terminal
+
+- [ROXTerm Homepage][6]
+
+### 6. Eterm ###
+
+Eterm is a lightest color terminal emulator designed as a replacement for xterm. It is developed with a Freedom of Choice ideology, leaving as much power, flexibility, and freedom as workable in the hands of the user.
+
+
+
+Eterm Terminal
+
+- [Eterm Homepage][7]
+
+### 7. Rxvt ###
+
+Rxvt stands for extended virtual terminal is a color terminal emulator application for Linux intended as an xterm replacement for power users who don’t need to have a feature such as Tektronix 4014 emulation and toolkit-style configurability.
+
+
+
+Rxvt Terminal
+
+- [Rxvt Homepage][8]
+
+### 8. Wterm ###
+
+Wterm is a another light weight color terminal emulator based on rxvt project. It includes features such as background images, transparency, reverse transparency and an considerable set or runtime options are accessible resulting in a very high customizable terminal emulator.
+
+
+
+wterm Terminal
+
+- [Wterm Homepage][9]
+
+### 9. LXTerminal ###
+
+LXTerminal is a default VTE-based terminal emulator for LXDE (Lightweight X Desktop Environment) without any unnecessary dependency. The terminal has got some nice features such as.
+LXTerminal Features
+
+- Multiple tabs support
+- Supports common commands like cp, cd, dir, mkdir, mvdir.
+- Feature to hide the menu bar for saving space
+- Change the color scheme.
+
+
+
+lxterminal Terminal
+
+- [LXTerminal Homepage][10]
+
+### 10. Konsole ###
+
+Konsole is yet another powerful KDE based free terminal emulator was originally created by Lars Doelle.
+Konsole Features
+
+- Multiple Tabbed terminals.
+- Translucent backgrounds.
+- Support for Split-view mode.
+- Directory and SSH bookmarking.
+- Customizable color schemes.
+- Customizable key bindings.
+- Notification alerts about activity in a terminal.
+- Incremental search
+- Support for Dolphin file manager
+- Export of output in plain text or HTML format.
+
+
+
+Konsole Terminal
+
+- [Konsole Homepage][11]
+
+### 11. TermKit ###
+
+TermKit is a elegant terminal that aims to construct aspects of the GUI with the command line based application using WebKit rendering engine mostly used in web browsers like Google Chrome and Chromium. TermKit is originally designed for Mac and Windows, but due to TermKit fork by Floby which you can now able to install it under Linux based distributions and experience the power of TermKit.
+
+
+
+TermKit Terminal
+
+- [TermKit Homepage][12]
+
+12. st
+
+st is a simple terminal implementation for X Window.
+
+
+
+st terminal
+
+- [st Homepage][13]
+
+### 13. Gnome-Terminal ###
+
+GNOME terminal is a built-in terminal emulator for GNOME desktop environment developed by Havoc Pennington and others. It allow users to run commands using a real Linux shell while remaining on the on the GNOME environment. GNOME Terminal emulates the xterm terminal emulator and brings a few similar features.
+
+The Gnome terminal supports multiple profiles, where users can able to create multiple profiles for his/her account and can customize configuration options such as fonts, colors, background image, behavior, etc. per account and define a name to each profile. It also supports mouse events, url detection, multiple tabs, etc.
+
+
+
+Gnome Terminal
+
+- [Gnome Terminal][14]
+
+### 14. Final Term ###
+
+Final Term is a open source stylish terminal emulator that has some exciting capabilities and handy features into one single beautiful interface. It is still under development, but provides significant features such as Semantic text menus, Smart command completion, GUI terminal controls, Omnipotent keybindings, Color support and many more. The following animated screen grab demonstrates some of their features. Please click on image to view demo.
+
+
+
+FinalTerm Terminal
+
+- [Final Term][15]
+
+### 15. Terminology ###
+
+Terminology is yet another new modern terminal emulator created for the Enlightenment desktop, but also can be used in different desktop environments. It has some awesome unique features, which do not have in any other terminal emulator.
+
+Apart features, terminology offers even more things that you wouldn’t assume from a other terminal emulators, like preview thumbnails of images, videos and documents, it also allows you to see those files directly from Terminology.
+
+You can watch a following demonstrations video created by the Terminology developer (the video quality isn’t clear, but still it’s enough to get the idea about Terminology).
+
+<iframe width="630" height="480" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="" src="//www.youtube.com/embed/ibPziLRGvkg"></iframe>
+
+- [Terminology][16]
+
+### 16. Xfce4 terminal ###
+
+Xfce terminal is a lightweight modern and easy to use terminal emulator specially designed for Xfce desktop environment. The latest release of xfce terminal has some new cool features such as search dialog, tab color changer, drop-down console like Guake or Yakuake and many more.
+
+
+
+Xfce Terminal
+
+- [Xfce4 Terminal][17]
+
+### 17. xterm ###
+
+The xterm application is a standard terminal emulator for the X Window System. It maintain DEC VT102 and Tektronix 4014 compatible terminals for applications that can’t use the window system directly.
+
+
+
+xterm Terminal
+
+- [xterm][18]
+
+### 18. LilyTerm ###
+
+The LilyTerm is a another less known open source terminal emulator based off of libvte that desire to be fast and lightweight. LilyTerm also include some key features such as:
+
+- Support for tabbing, coloring and reordering tabs
+- Ability to manage tabs through keybindings
+- Support for background transparency and saturation.
+- Support for user specific profile creation.
+- Several customization options for profiles.
+- Extensive UTF-8 support.
+
+
+
+Lilyterm Terminal
+
+- [LilyTerm][19]
+
+### 19. Sakura ###
+
+The sakura is a another less known Unix style terminal emulator developed for command line purpose as well as text-based terminal programs. Sakura is based on GTK and livte and provides not more advanced features but some customization options such as multiple tab support, custom text color, font and background images, speedy command processing and few more.
+
+
+
+Sakura Terminal
+
+- [Sakura][20]
+
+### 20. rxvt-unicode ###
+
+The rxvt-unicode (also known as urxvt) is a yet another highly customizable, lightweight and fast terminal emulator with xft and unicode support was developed by Marc Lehmann. It got some outstanding features such as support for international language via Unicode, the ability to display multiple font types and support for Perl extensions.
+
+
+
+rxvt unicode
+
+- [rxvt-unicode][21]
+
+If you know any other capable Linux terminal emulators that I’ve not included in the above list, please do share with me using our comment section.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-terminal-emulators/
+
+作者:[Ravi Saive][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/admin/
+[1]:https://launchpad.net/terminator
+[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/terminator-a-linux-terminal-emulator-to-manage-multiple-terminal-windows/
+[3]:http://tilda.sourceforge.net/tildaabout.php
+[4]:https://github.com/Guake/guake
+[5]:http://extragear.kde.org/apps/yakuake/
+[6]:http://roxterm.sourceforge.net/index.php?page=index&lang=en
+[7]:http://www.eterm.org/
+[8]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/rxvt/
+[9]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/wterm/
+[10]:http://wiki.lxde.org/en/LXTerminal
+[11]:http://konsole.kde.org/
+[12]:https://github.com/unconed/TermKit
+[13]:http://st.suckless.org/
+[14]:https://help.gnome.org/users/gnome-terminal/stable/
+[15]:http://finalterm.org/
+[16]:http://www.enlightenment.org/p.php?p=about/terminology
+[17]:http://docs.xfce.org/apps/terminal/start
+[18]:http://invisible-island.net/xterm/
+[19]:http://lilyterm.luna.com.tw/
+[20]:https://launchpad.net/sakura
+[21]:http://software.schmorp.de/pkg/rxvt-unicode
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150527 How to Create Own Online Shopping Store Using 'OpenCart' in Linux.md b/sources/tech/20150527 How to Create Own Online Shopping Store Using 'OpenCart' in Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ad673a03e0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20150527 How to Create Own Online Shopping Store Using 'OpenCart' in Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,225 @@
+How to Create Own Online Shopping Store Using “OpenCart” in Linux
+================================================================================
+In the Internet world we are doing everything using a computer. Electronic Commerce aka e-commerce is one one of them. E-Commerce is nothing new and it started in the early days of ARPANET, where ARPANET used to arrange sale between students of Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Stanford Artificial Intelligence Laboratory.
+
+These days there are some 100’s of E-Commerce site viz., Flipcart, eBay, Alibaba, Zappos, IndiaMART, Amazon, etc. Have you thought of making your own Amazon and Flipcart like web-based Application Server? If yes! This article is for you.
+
+Opencart is a free and open source E-Commerce Application written in PHP, which can be used to develop a shopping cart system similar to Amazon and Flipcart. If you want to sell your products online or want to serve your customers even when you are closed Opencart is for you. You can build a successful online store (for online merchants) using reliable and professional Opencart Application.
+
+### OpenCart Web Panel Demo ###
+
+- Store Front – [http://demo.opencart.com/][1]
+- Admin Login – [http://demo.opencart.com/admin/][2]
+
+ ------------------ Admin Login ------------------
+ Username: demo
+ Password: demo
+
+#### Features of Opencart ####
+
+Opencart is an application that meets all the requirements of an online merchant. It has all the features (see below) using which you can make your own E-Commerce Website.
+
+- It is a Free (as in beer) and Open Source (as in speech) Application released under GNU GPL License.
+- Everything is well documented, means you don’t need to Google and shout for help.
+- Free Life time support and updates.
+- Unlimited number of categories, Products and manufacturer supported.
+- Everything is Template based.
+- Multi-Language and Multi-Currency Supported. It ensures your product gets a global reach.
+- Built-in Product Review and Rating Features.
+- Downloadable Products (viz., ebook) supported.
+- Automatic Image Resizing supported.
+- Features like Multi tax Rates (as in various country), Viewing Related Products, Information Page, Shipping Weight Calculation, Availing Discount Coupons, etc are well implemented by default.
+- Built-in Backup and Restore tools.
+- Well implemented SEO.
+- Invoice Printing, Error Log and sales report are supported as well.
+
+#### System Requirements ####
+
+- Web Server (Apache HTTP Server Preferred)
+- PHP (5.2 and above).
+- Database (MySQLi Preferred but I am using MariaDB).
+
+#### Required PHP Libraries and Modules ####
+
+These extensions must be installed and enabled on your system to install Opencart properly on the web server.
+
+- Curl
+- Zip
+- Zlib
+- GD Library
+- Mcrypt
+- Mbstrings
+
+### Step 1: Installing Apache, PHP and MariaDB ###
+
+1. As I said, OpenCart requires certain technical requirements such as Apache, PHP with extensions and Database (MySQL or MariaDB) to be installed on the system, in order to run Opencart properly.
+
+Let’s install Apache, PHP and MariaDB using following Command.
+
+**Install Apache**
+
+ # apt-get install apache2 (On Debian based Systems)
+ # yum install httpd (On RedHat based Systems)
+
+**Install PHP and Extensions**
+
+ # apt-get install php5 libapache2-mod-php5 php5-curl php5-mcrypt (On Debian based Systems)
+ # yum install php php-mysql php5-curl php5-mcrypt (On RedHat based Systems)
+
+**Install MariaDB**
+
+ # apt-get install mariadb-server mariadb-client (On Debian based Systems)
+ # yum install mariadb-server mariadb (On RedHat based Systems)
+
+2. After installing all the above required things, you can start the Apache and MariaDB services using following commands.
+
+ ------------------- On Debian based Systems -------------------
+ # systemctl restart apache2.service
+ # systemctl restart mariadb.service
+
+----------
+
+ ------------------- On RedHat based Systems -------------------
+ # systemctl restart httpd.service
+ # systemctl restart mariadb.service
+
+### Step 2: Downloading and Setting OpenCart ###
+
+3. The most recent version of OpenCart (2.0.2.0) can be obtained from [OpenCart website][3] or directly from github.
+
+Alternatively, you may use following wget command to download the latest version of OpenCart directly from github repository as shown below.
+
+ # wget https://github.com/opencart/opencart/archive/master.zip
+
+4. After downloading zip file, copy to Apache Working directory (i.e. /var/www/html) and unzip the master.zip file.
+
+ # cp master.zip /var/www/html/
+ # cd /var/www/html
+ # unzip master.zip
+
+5. After extracting ‘master.zip‘ file, cd to extracted directory and move the content of upload directory to the root of the application folder (opencart-master).
+
+ # cd opencart-master
+ # mv -v upload/* ../opencart-master/
+
+6. Now you need to rename or copy OpenCart configuration files as shown below.
+
+ # cp /var/www/html/opencart-master/admin/config-dist.php /var/www/html/opencart-master/admin/config.php
+ # cp /var/www/html/opencart-master/config-dist.php /var/www/html/opencart-master/config.php
+
+7. Next, set correct Permissions to the files and folders of /var/www/html/opencart-master. You need to provide RWX permission to all the files and folders there, recursively.
+
+ # chmod 777 -R /var/www/html/opencart-master
+
+**Important**: Setting permission 777 may be dangerous, so as soon as you finish setting up everything, revert back to permission 755 recursively on the above folder.
+
+### Step 3: Creating OpenCart Database ###
+
+8. Next step is to create a database (say opencartdb) for the E-Commerce site to store data on the database. Connect to databaser server and create a database, user and grant correct privileges on the user to have full control over the database.
+
+ # mysql -u root -p
+ CREATE DATABASE opencartdb;
+ CREATE USER 'opencartuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'mypassword';
+ GRANT ALL PRIVILEDGES ON opencartdb.* TO 'opencartuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED by 'mypassword';
+
+### Step 4: OpenCart Web Installation ###
+
+9. Once everything set correctly, navigate to the web browser and type `http://<web server IP address>` to access the OpenCart web installation.
+
+Click ‘CONTINUE‘ to Agree the License Agreement.
+
+
+
+Accept OpenCart License
+
+10. The next screen is Pre-installation Server Setup Check, to see that the server has all the required modules are installed properly and have correct permission on the OpenCart files.
+
+If any red marks are highlighted on #1 or #2, that means you need to install those components properly on the server to meet web server requirements.
+
+If there are any red marks on #3 or #4, that means there is issue with your files. If everything is correctly configured you should see all green marks are visible (as seen below), you may press “Continue“.
+
+
+
+Server Requirement Check
+
+11. On the next screen enter your Database Credentials like Database Driver, Hostname, User-name, Password, database. You should not touch db_port and Prefix, until and unless you know what you are doing.
+
+Also Enter User_name, Password and Email Address for Administrative account. Note these credentials will be used for logging in to Opencart Admin Panel as root, so keep it safe. Click continue when done!
+
+
+
+OpenCart Database Details
+
+12. The next screen shows message like “Installation Complete” with the Tag Line Ready to Start Selling. Also it warns to delete the installation directory, as everything required to setup using this directory has been accomplished.
+
+
+
+OpenCart Installation Completes
+
+To Remove install directory, you may like to run the below command.
+
+ # rm -rf /var/www/html/opencart-master/install
+
+### Step 4: Access OpenCart Web and Admin ###
+
+13. Now point your browser to `http://<web server IP address>/opencart-master/` and you would see something like the below screenshot.
+
+
+
+OpenCart Product Showcase
+
+14. In order to login to Opencart Admin Panel, point your browser to http://<web server IP address>/opencart-master/admin and fill the Admin Credentials you input, while setting it up.
+
+
+
+OpenCart Admin Login
+
+15. If everything ok! You should be able to see the Admin Dashboard of Opencart.
+
+
+
+OpenCart Dashboard
+
+Here in Admin Dashboard you may set up a lots of options like categories, product, options, Manufacturers, Downloads, Review, Information, Extension Installer, Shipping, Payment options, order totals, gift voucher, Paypal, Coupons, Affiliates, marketing, mails, Design and Settings, Error logs, in-built analytics and what not.
+
+#### What after testing the tools? ####
+
+If you have already tested the Application and finds it customizable, flexible, Rock Solid, Easy to maintain and use, you may need a good hosting provider to host OpenCart application, that remains live 24X7 support. Though there are a lot of options for hosting providers we recommend Hostgator.
+
+Hostgator is a Domain Registrant and Hosting Provider that is very well known for the service and feature it provides. It Provides you with UNLIMITED Disk Space, UNLIMITED Bandwidth, Easy to install (1-click install script), 99.9% Uptime, Award winning 24x7x365 Technical Support and 45 days money back guarantee, which means if you didn’t like the product and service you get your money back within 45 days of purchasing and mind it 45 days is a long time to Test.
+
+So if you have something to sell you can do it for free (by free I mean, Think of the cost you would spend on getting a physical store and then compare it with virtual store setting-up cost. You will feel its free).
+
+**Note**: When you buy hosting (and/or Domain) from Hostgator you will get a **Flat 25% OFF**. This offer is valid only for the readers of Tecmint Site.
+
+All you have to do is to Enter Promocode “**TecMint025**” during the payment of hosting. For reference see the preview of payment screen with promo code.
+
+
+
+[Sign up for Hostgator][4] (Coupon code: TecMint025)
+
+**Note**: Also worth mentioning, that for each hosting you buy from Hostgator to host OpenCart, we will get a small amount of commission, just to keep Tecmint Live (by Paying Bandwidth and hosting charges of server).
+
+So If you buy it using the above code, you get discount and we will get a small amount. Also note that you won’t pay anything extra, infact you will be paying 25% less on total bill.
+
+### Conclusion ###
+
+OpenCart is an application that performs out-of-the box. It is easy to install and you have the option to choose best suited templates, add your products and you become an online merchant.
+
+A lots of community made extensions(free and paid) makes it rich. It is a wonderful application for those who want to setup a virtual store and remain accessible to their customer 24X7. Let me know yours experience with the application. Any suggestion and feedback is welcome as well.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/create-e-commerce-online-shopping-store-using-opencart-in-linux/
+
+作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
+[1]:http://demo.opencart.com/
+[2]:http://demo.opencart.com/admin/
+[3]:http://www.opencart.com/index.php?route=download/download/
+[4]:http://secure.hostgator.com/%7Eaffiliat/cgi-bin/affiliates/clickthru.cgi?id=tecmint
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150527 How to edit your documents collaboratively on Linux.md b/sources/tech/20150527 How to edit your documents collaboratively on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..91d2bf6441
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20150527 How to edit your documents collaboratively on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+How to edit your documents collaboratively on Linux
+================================================================================
+> "Developed many years before by some high-strung, compulsive assistant, the Bulletin was simply a Word document that lived in a shared folder both Emily and I could access. Only one of us could open it at a time and add a new message, thought, or question to the itemized list. Then we'd print out the updated version and place it on the clipboard that sat on the shelf over my desk, removing the old ones as we went." ("The Devil Wears Prada" by Lauren Weisberger)
+
+Even today such a "collaborative editing" is in use where only one person can open a shared file, make changes to it, and then inform others about what and when was modified.
+
+ONLYOFFICE is an open source online office suite integrated with different management tools for documents, emails, events, tasks and client relations.
+
+Using ONLYOFFICE office suite, a group of people can edit text, spreadsheet or presentation within a browser simultaneously. Leave comments directly in their document and interact with each other using the integrated chat. And, finally, save the document as a PDF file for further printing. As an added bonus, it gives the possibility to view the document history and restore the previous revision/version if needed.
+
+In this tutorial, I will describe how to deploy your own online office suite using [ONLYOFFICE Free Edition][1], an ONLYOFFICE self-hosted version distributed under GNU AGPL v3.
+
+### Installing ONLYOFFICE on Linux ###
+
+ONLYOFFICE installation requires the presence of mono (version 4.0.0 or later), nodejs, libstdc++6, nginx and mysql-server in your Linux system. To simplify the installation process and avoid dependency errors, I install ONLYOFFICE using Docker. In this case there is only one dependency to be installed - [Docker][2].
+
+Just to remind, Docker is an open-source project that automates the deployment of applications inside software containers. If Docker is not available on your Linux system, install it first by referring to Docker installation instructions for [Debian-based][3] or [Red-Hat based][4] systems.
+
+Note that you will need Docker 1.4.1 or later. To check the installed Docker version, use the following command.
+
+ $ docker version
+
+To try ONLYOFFICE inside a Docker container, simply execute the following commands:
+
+ $ sudo docker run -i -t -d --name onlyoffice-document-server onlyoffice/documentserver
+ $ sudo docker run -i -t -d -p 80:80 -p 443:443 --link onlyoffice-document-server:document_server onlyoffice/communityserver
+
+These commands will download the [official ONLYOFFICE Docker image][5] with all dependencies needed for its correct work.
+
+It's also possible to install [ONLYOFFICE Online Editors][6] separately on a Linux server, and easily integrate it into your website or cloud application via API provided.
+
+### Running a Self-Hosted Online Office ###
+
+To open your online office, enter localhost (http://IP-Address/) in the address bar of your browser. The Welcome page will open:
+
+
+
+Enter a password and specify the email address you will use to access your office the next time.
+
+### Editing Your Documents Online ###
+
+First, click the Documents link to open **the My Documents** folder.
+
+
+
+#### STEP 1. Select a Document to Edit ####
+
+To create a new document right there, click on the **Create** button in the upper left corner, and choose the file type from the drop-down list. To edit a file stored on your hard disk drive, upload it to **Documents** clicking the **Upload** button next to **Create** button.
+
+
+
+#### STEP 2. Share your Document ####
+
+Use the **Share** button to the right side if you are in the **My Documents** folder, or follow **File >> Document Info ... >> Change Access Rights** if you are inside your document.
+
+In the opened **Sharing Settings** window, click on the **People outside portal** link on the left, open the access to the document, and give full access to it by enabling the **Full Access** radio button.
+
+Finally, choose a way to share the link to your document, send it via email or one of the available social networks: Google+, Facebook, or Twitter.
+
+
+
+#### STEP 3. Start the Collaborative Editing ####
+
+To start co-editing the document, the invited person just needs to follow the provided link.
+
+The text passages edited by your co-editors will be automatically marked with dashed lines of different colors.
+
+
+
+As soon as one of your collaborators saves his/her changes, you will see a note appearing in the left upper corner of the top toolbar, indicating that there areupdates.
+
+
+
+To save your changes and get updates, click on the **Save** icon. All the updates will then be highlighted.
+
+
+
+#### STEP 4. Interact with your Co-editors ####
+
+To leave some comments, select a text passage with the mouse, right-click on it and, and choose the **Add comment** option from the context menu.
+
+
+
+To interact with co-editors in real time, use the integrated chat instead. All the users who currently edit the document will be listed on the **Chat** panel. To open it, click on the **Chat** icon at the left-side bar. To start a discussion, enter your message into an appropriate field on the **Chat** panel.
+
+
+
+### Useful Tips ###
+
+As final notes, here are some useful tips for you to take full advantage of ONLYOFFICE.
+
+#### Tip #1. Editing your Docs from Cloud Storage Services, Like ownCloud ####
+
+If you store your documents in other web resources like Box, Dropbox, Google Drive, OneDrive, SharePoint or ownCloud, you can easily synchronize them with the ONLYOFFICE.
+
+In the opened 'Documents' module, click one of the icons under the **Add the account** caption: Google, Box, DropBox, OneDrive, ownCloud or 'Add account', and enter the requested data.
+
+#### Tip #2. Editing Your Docs on iPad ####
+
+To add some changes to your document on the go, I use ONLYOFFICE Documents app for iPad. You can download and install it from [iTune][7], then you need to enter your ONLYOFFICE portal address, email and password to access your documents. The feature set is almost the same.
+
+To evaluate ONLYOFFICE Online Editors features, you can use the [cloud version][8] for personal use.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/edit-documents-collaboratively-linux.html
+
+作者:[Tatiana Kochedykova][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/tatiana
+[1]:http://www.onlyoffice.org/
+[2]:http://xmodulo.com/recommend/dockerbook
+[3]:http://xmodulo.com/manage-linux-containers-docker-ubuntu.html
+[4]:http://xmodulo.com/docker-containers-centos-fedora.html
+[5]:https://registry.hub.docker.com/u/onlyoffice/communityserver/
+[6]:http://onlyoffice.org/sources#document
+[7]:https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/onlyoffice-documents/id944896972
+[8]:https://personal.onlyoffice.com/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150527 Howto Manage Host Using Docker Machine in a VirtualBox.md b/sources/tech/20150527 Howto Manage Host Using Docker Machine in a VirtualBox.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ea827ec74e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20150527 Howto Manage Host Using Docker Machine in a VirtualBox.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+Howto Manage Host Using Docker Machine in a VirtualBox
+================================================================================
+Hi all, today we'll learn how to create and manage a Docker host using Docker Machine in a VirtualBox. Docker Machine is an application that helps to create Docker hosts on our computer, on cloud providers and inside our own data center. It provides easy solution for creating servers, installing Docker on them and then configuring the Docker client according the users configuration and requirements. This API works for provisioning Docker on a local machine, on a virtual machine in the data center, or on a public cloud instance. Docker Machine is supported on Windows, OSX, and Linux and is available for installation as one standalone binary. It enables us to take full advantage of ecosystem partners providing Docker-ready infrastructure, while still accessing everything through the same interface. It makes people able to deploy the docker containers in the respective platform pretty fast and in pretty easy way with just a single command.
+
+Here are some easy and simple steps that helps us to deploy docker containers using Docker Machine.
+
+### 1. Installing Docker Machine ###
+
+Docker Machine supports awesome on every Linux Operating System. First of all, we'll need to download the latest version of Docker Machine from the [Github site][1] . Here, we'll use curl to download the latest version of Docker Machine ie 0.2.0 .
+
+**For 64 Bit Operating System**
+
+ # curl -L https://github.com/docker/machine/releases/download/v0.2.0/docker-machine_linux-amd64 > /usr/local/bin/docker-machine
+
+**For 32 Bit Operating System**
+
+ # curl -L https://github.com/docker/machine/releases/download/v0.2.0/docker-machine_linux-i386 > /usr/local/bin/docker-machine
+
+After downloading the latest release of Docker Machine, we'll make the file named **docker-machine** under **/usr/local/bin/** executable using the command below.
+
+ # chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-machine
+
+After doing the above, we'll wanna ensure that we have successfully installed docker-machine. To check it, we can run the docker-machine -v which will give output of the version of docker-machine installed in our system.
+
+ # docker-machine -v
+
+
+
+To enable Docker commands on our machines, make sure to install the Docker client as well by running the command below.
+
+ # curl -L https://get.docker.com/builds/linux/x86_64/docker-latest > /usr/local/bin/docker
+ # chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker
+
+### 2. Creating VirualBox VM ###
+
+After we have successfully installed Docker Machine in our Linux running machine, we'll definitely wanna go for creating a Virtual Machine using VirtualBox. To get started, we need to run docker-machine create command followed by --driver flag with string as virtualbox as we are trying to deploy docker inside of Virtual Box running VM and the final argument is the name of the machine, here we have machine name as "linux". This command will download [boot2docker][2] iso which is a light-weighted linux distribution based on Tiny Core Linux with the Docker daemon installed and will create and start a VirtualBox VM with Docker running as mentioned above.
+
+To do so, we'll run the following command in a terminal or shell in our box.
+
+ # docker-machine create --driver virtualbox linux
+
+
+
+Now, to check whether we have successfully create a Virtualbox running Docker or not, we'll run the command **docker-machine** ls as shown below.
+
+ # docker-machine ls
+
+
+
+If the host is active, we can see * under the ACTIVE column in the output as shown above.
+
+### 3. Setting Environment Variables ###
+
+Now, we'll need to make docker talk with the machine. We can do that by running docker-machine env and then the machine name, here we have named **linux** as above.
+
+ # eval "$(docker-machine env linux)"
+ # docker ps
+
+This will set environment variables that the Docker client will read which specify the TLS settings. Note that we'll need to do this every time we reboot our machine or start a new tab. We can see what variables will be set by running the following command.
+
+ # docker-machine env linux
+
+ export DOCKER_TLS_VERIFY=1
+ export DOCKER_CERT_PATH=/Users/<your username>/.docker/machine/machines/dev
+ export DOCKER_HOST=tcp://192.168.99.100:2376
+
+### 4. Running Docker Containers ###
+
+Finally, after configuring the environment variables and Virtual Machine, we are able to run docker containers in the host running inside the Virtual Machine. To give it a test, we'll run a busybox container out of it run running **docker run busybox** command with **echo hello world** so that we can get the output of the container.
+
+ # docker run busybox echo hello world
+
+
+
+### 5. Getting Docker Host's IP ###
+
+We can get the IP Address of the running Docker Host's using the **docker-machine ip** command. We can see any exposed ports that are available on the Docker host’s IP address.
+
+ # docker-machine ip
+
+
+
+### 6. Managing the Hosts ###
+
+Now we can manage as many local VMs running Docker as we desire by running docker-machine create command again and again as mentioned in above steps
+
+If you are finished working with the running docker, we can simply run **docker-machine stop** command to stop the whole hosts which are Active and if wanna start again, we can run **docker-machine start**.
+
+ # docker-machine stop
+ # docker-machine start
+
+You can also specify a host to stop or start using the host name as an argument.
+
+ $ docker-machine stop linux
+ $ docker-machine start linux
+
+### Conclusion ###
+
+Finally, we have successfully created and managed a Docker host inside a VirtualBox using Docker Machine. Really, Docker Machine enables people fast and easy to create, deploy and manage Docker hosts in different platforms as here we are running Docker hosts using Virtualbox platform. This virtualbox driver API works for provisioning Docker on a local machine, on a virtual machine in the data center. Docker Machine ships with drivers for provisioning Docker locally with Virtualbox as well as remotely on Digital Ocean instances whereas more drivers are in the work for AWS, Azure, VMware, and other infrastructure. If you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below so that we can improve or update our contents. Thank you ! Enjoy :-)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/host-virtualbox-docker-machine/
+
+作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
+[1]:https://github.com/docker/machine/releases
+[2]:https://github.com/boot2docker/boot2docker
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150528 11 pointless but awesome Linux terminal tricks.md b/sources/tech/20150528 11 pointless but awesome Linux terminal tricks.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..74baa5fb5b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20150528 11 pointless but awesome Linux terminal tricks.md
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
+Translating by goreliu ...
+
+11 pointless but awesome Linux terminal tricks
+================================================================================
+Here are some great Linux terminal tips and tricks, each one as pointless as it is awesome.
+
+
+
+### All work and no play... ###
+
+Linux is one of the most astoundingly functional and utilitarian Operating Systems around when it comes to working from the command line. Need to perform a particular task? Odds are there is an application or script you can use to get it done. Right from the terminal. But, as they say in the good book, "All work and no play make Jack really bored or something." So here is a collection of my favorite pointless, stupid, annoying or amusing things that you can do right in your Linux Terminal.
+
+
+
+### Give the terminal an attitude ###
+
+Step 1) Type "sudo visudo".
+
+Step 2) At the bottom of the "Defaults" (near the top of the file) add, on a new line, "Defaults insults".
+
+Step 3) Save the file.
+
+"What did I just do to my computer?" you may be asking yourself. Something wonderful. Now, whenever you issue a sudo command and misstype your password, your computer will call you names. My favorite: "Listen, burrito brains, I don't have time to listen to this trash."
+
+
+
+### apt-get moo ###
+
+That screenshot you see? That's what typing "apt-get moo" (on a Debian-based system) does. That's it. Don't go looking for this to do something fancy. It won't. That, I kid you not, is it. But it's one of the most commonly known little Easter eggs on Linux. So I include it here, right near the beginning, so I won't get 5,000 emails telling me I missed it in this list.
+
+
+
+### aptitude moo ###
+
+A bit more entertaining is aptitude's take on "moo." Type "aptitude moo" (on Ubuntu and the like) and you'll be corrected about thinking "moo" would do anything. But you know better. Try the same command again, this time with an optional "-v" attribute. Don't stop there. Add v's, one at a time, until aptitude gives you what you want.
+
+
+
+### Arch: Put Pac-Man in pacman ###
+
+This is one just for the Arch-lovers out there. The de facto package manager, pacman, is pretty fantastic already. Let's make it even better.
+
+Step 1) Open "/etc/pacman.conf".
+
+Step 2) In the "# Misc options", remove the "#" from in front of "Color".
+
+Step 3) Add "ILoveCandy".
+
+Now the progress for installing new packages, in pacman, will include a little tiny Pac-Man. Which should really just be the default anyway.
+
+
+
+### Cowsay! ###
+
+Making aptitude moo is neat, I guess, but you really can't use it for much. Enter "cowsay." It does what you think. You make a cow say things. Anything you like. And it's not even limited to cows. Calvin, Beavis, and the Ghostbusters logo are all available in full ASCII art glory – type "cowsay -l" for a full list of what's available in this, Linux's most powerful tool. Remember that, like most great terminal applications, you can pipe the output from other applications straight into cowsay (ala "fortune | cowsay").
+
+
+
+### Become an 3l33t h@x0r ###
+
+Typing "nmap" isn't something one typically needs to do on a day-to-day basis. But when one does need to "whip out the nmap," one wants to look as l33t as humanly possible. Add a "-oS" to any nmap command (such as "nmap -oS - google.com"). Bam. You're now in what is officially known as "[Script Kiddie Mode][1]." Angelina Jolie and Keanu Reeves would be proud.
+
+
+
+### Getting all Discordian ddate ###
+
+If you've ever been sitting around thinking, "Hey! I want today's date to be written in an essentially useless, but whimsical, way"…try typing "ddate". Results like "Today is Setting Orange, the 72nd day of Discord in the YOLD 3181," can really spice up your server logs.
+
+Note: Technically, this is a real thing called the [Discordian Calendar][2], used (in theory) by the followers of [Discordianism][3]. Which means I probably offended somebody. Or maybe not. I'm not really sure. Either way, ddate is a handy tool in any office.
+
+
+
+### I See Colors Everywhere! ###
+
+Tired of boring old text? Looking to spruce things up and show the world your true style? lolcat. Install it. Use it. Everywhere. It takes any text input and turns it into a rainbow of wonder and enchantment. Piping text into lolcat (ala "fortune | lolcat") is sure to liven up any party.
+
+
+
+### The Steam Locomotive ###
+
+Animated ASCII art steam locomotive in your terminal. You want this. You need this. Install and run "sl". Use "sl -l" for a tiny version. Or, if you want to really spend some time on this, "sl-h". This is the full train, including passenger cars.
+
+
+
+### Reverse any text ###
+
+Pipe the output of any text into "rev" and it will reverse the text. "fortune | rev" gives you a fortune. In reverse. Which is, as odd as it may seem, not a misfortune.
+
+
+
+### The Matrix is still cool, right? ###
+
+Want your terminal to do that scrolling text, l33t, Matrix-y thing? "cmatrix" is your friend. You can even have it output different colors, which is snazzy. Learn how by typing "man cmatrix". Or, better yet, "man cmatrix | lolcat". Which, really, is the most pointless (but wonderful) thing you can do in the Linux Terminal. So that's where I leave you.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.networkworld.com/article/2926630/linux/11-pointless-but-awesome-linux-terminal-tricks.html
+
+作者:[Bryan Lunduke][a]
+译者:[goreliu](https://github.com/goreliu)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.networkworld.com/author/Bryan-Lunduke/
+[1]:http://nmap.org/book/output-formats-script-kiddie.html
+[2]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Discordian_calendar
+[3]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Discordianism
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150528 27 'DNF' Fork of Yum Commands for RPM Package Management in Linux.md b/sources/tech/20150528 27 'DNF' Fork of Yum Commands for RPM Package Management in Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2ada2ac4cd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20150528 27 'DNF' Fork of Yum Commands for RPM Package Management in Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,289 @@
+translating by wwy-hust
+
+27 ‘DNF’ (Fork of Yum) Commands for RPM Package Management in Linux
+================================================================================
+DNF aka Dandified YUM is a next generation Package Manager for RPM based Distribution. It was first introduced in Fedora 18 and it is replaced [YUM utility][1] in recent release of Fedora 22.
+
+
+
+DNF aims at improving the bottlenecks of YUM viz., Performance, Memory Usages, Dependency Resolution, Speed and lots of other factors. DNF does Package Management using RPM, libsolv and hawkey library. Though it does not come per-installed in CentOS and RHEL 7 you can yum, dnf and use it alongside the yum.
+
+You may like to read more about DNF here:
+
+- [Reasons Behind Replacing Yum with DNF][2]
+
+The latest stable release of DNF is 1.0 (at the time of writing of post) which was released on May 11, 2015. It (and all previous version of DNF) is mostly written in Python and is released under GPL v2 License.
+
+### Installation of DNF ###
+
+DNF in not available in the default repository of RHEL/CentOS 7. However Fedora 22 ships with DNF implemented officially.
+
+To install DNF on RHEL/CentOS systems, you need to first install and enable epel-release repository.
+
+ # yum install epel-release
+ OR
+ # yum install epel-release -y
+
+Though it is not ethical to use ‘-y‘ with yum as it is recommended to see what is being installed in your system. However if this does not matter you much you may use ‘-y’ with yum to install everything automatically without user’s intervention.
+
+Next, install DNS package using yum command from epel-release repository.
+
+ # yum install dnf
+
+After dnf installed successfully, it’s time to show you 27 practical usage of dnf commands with examples that will help you to manage packages in RPM based distribution easily and effectively.
+
+### 1. Check DNF Version ###
+
+Check the version of DNF installed on your System.
+
+ # dnf --version
+
+
+
+### 2. List Enabled DNF Repositories ###
+
+The option ‘repolist‘ with dnf command, will display all enabled repositories under your system.
+
+ # dnf repolist
+
+
+
+### 3. List all Enabled and Disabled DNF Repositories ###
+
+The option ‘repolist all‘ will print all the enabled/disabled repositories under your system.
+
+ # dnf repolist all
+
+
+
+### 4. List all Available and Installed Packages using DNF ###
+
+The command “dnf list” will list all the available packages from all the repositories and installed packages on your Linux system.
+
+ # dnf list
+
+
+
+### 5. List all Installed Packages using DNF ###
+
+While the “dnf list” command shows all the available/installed packages from all the repositories. However, you have the option to list only the installed packages using option “list installed” as shown below.
+
+ # dnf list installed
+
+
+
+### 6. List all Available Packages using DNF ###
+
+Similarly, the “list available” option, will list all the packages available to be installed from all the enabled repositories.
+
+ # dnf list available
+
+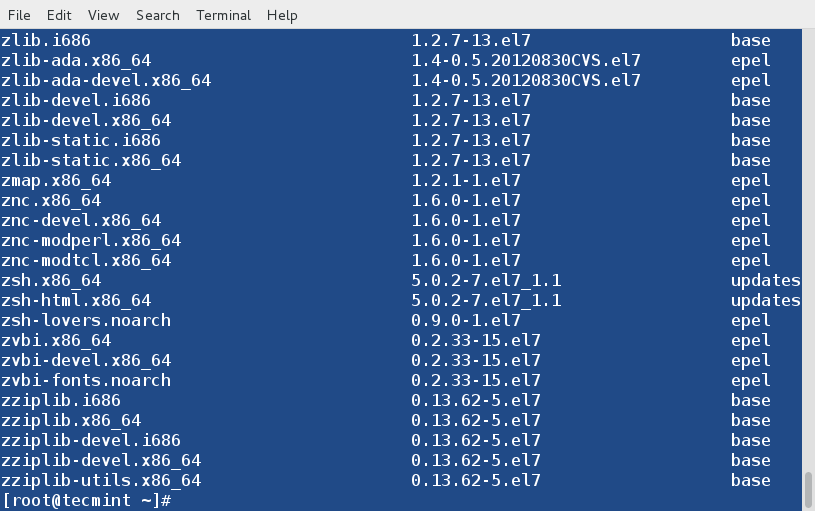
+
+### 7. Search for a Package using DNF ###
+
+If incase, you’ve no idea about the package that you want install, in such situation you may use ‘search‘ option with dnf command to search for the package that matches the word or string (say nano).
+
+ # dnf search nano
+
+
+
+### 8. See what Provides a file/sub-package? ###
+
+The dnf option “provides” find the name of the package that provides specific file/sub-package. For example, if you would like to find what provides ‘/bin/bash‘ on your system?
+
+ # dnf provides /bin/bash
+
+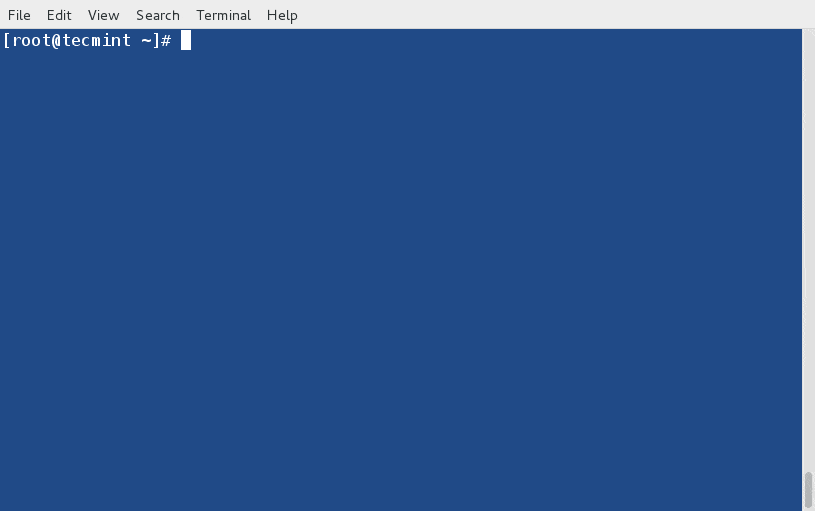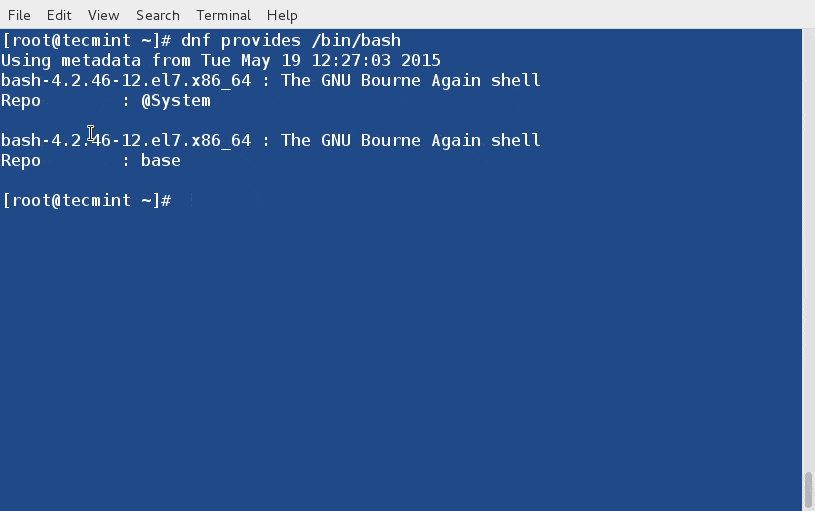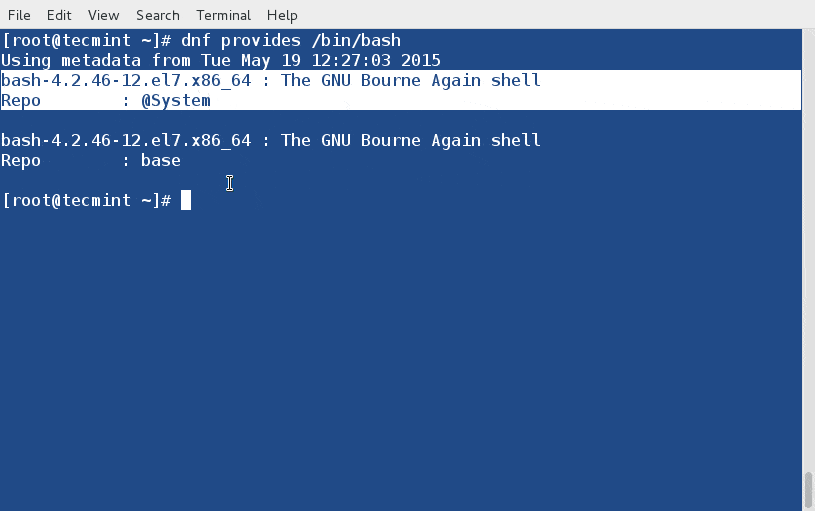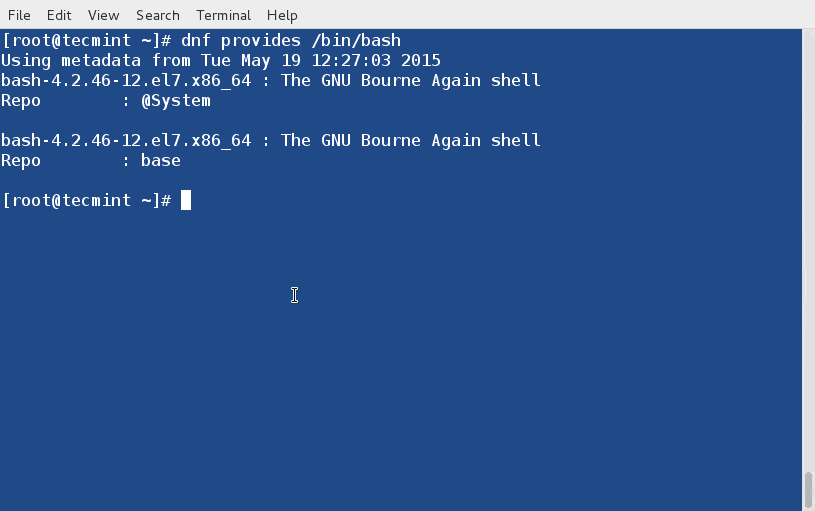
+
+### 9. Get Details of a Package using DNF ###
+
+Let’s assume you want to know the information of a package before installing it on the system, you may use “info” switch to get a detailed information about a package (say nano) as below.
+
+ # dnf info nano
+
+
+
+### 10. Install a Package with DNF ###
+
+To install a package called nano, just run the below command it will automatically resolve and install all required dependencies for package nano.
+
+ # dnf install nano
+
+
+
+### 11. Updating a Package using DNF ###
+
+You may update only a specific package (say systemd) and leave everything on the system untouched.
+
+ # dnf update systemd
+
+
+
+### 12. Check for System Updates using DNF ###
+
+Check updates for all the system packages installed into the system simply as.
+
+ # dnf check-update
+
+
+
+### 13. Update All System Packages using DNF ###
+
+You may update the whole system including all the installed packages with following commands.
+
+ # dnf update
+ OR
+ # dnf upgrade
+
+
+
+### 14. Remove/Erase a Package using DNF ###
+
+To remove or erase any unwanted package (say nano), you may use “remove” or “erase” switch with dnf command to remove it.
+
+ # dnf remove nano
+ OR
+ # dnf erase nano
+
+
+
+### 15. Remove Orphan Packages using DNF ###
+
+Those packages that were installed to satisfy dependency may be useless if not being used by other applications. To remove those orphan packages execute the below command.
+
+ # dnf autoremove
+
+
+
+### 16. Remove Cached Packages using DNF ###
+
+A lot of time we encounter out-of-date headers and unfinished transactions which results into error while executing dnf. We may clean all the cached packages and headers containing remote package information simply by executing.
+
+ # dnf clean all
+
+
+
+### 17. Get Help on Specific DNF Command ###
+
+You may get help of any specific dnf command (say clean) just by executing the below command.
+
+ # dnf help clean
+
+
+
+### 18. List all DNF Commands and Options ###
+
+To list help on all available dnf commands and option simply type.
+
+ # dnf help
+
+
+
+### 19. View History of DNF ###
+
+You may call dnf history to look at the list of already executed dnf commands. This way you can be aware of what was installed/removed with time stamp.
+
+ # dnf history
+
+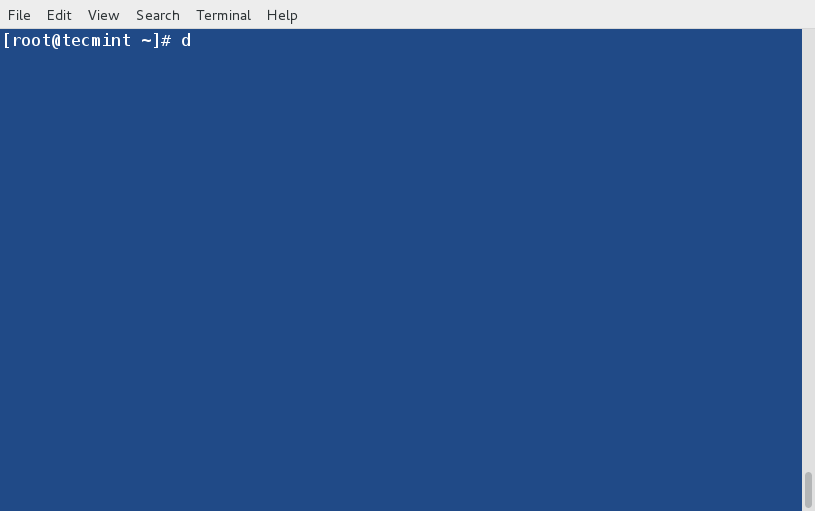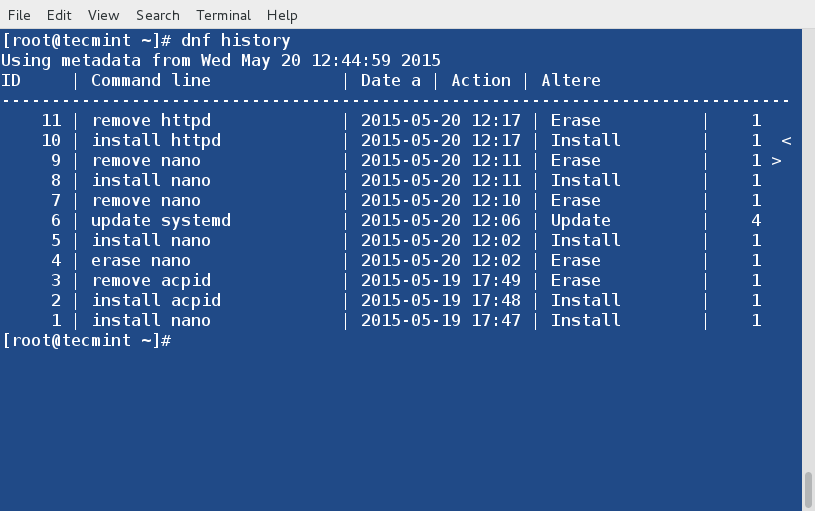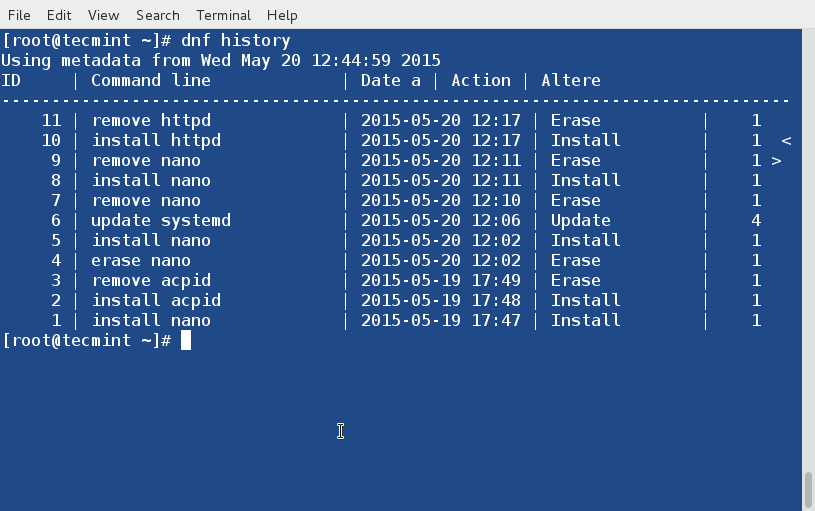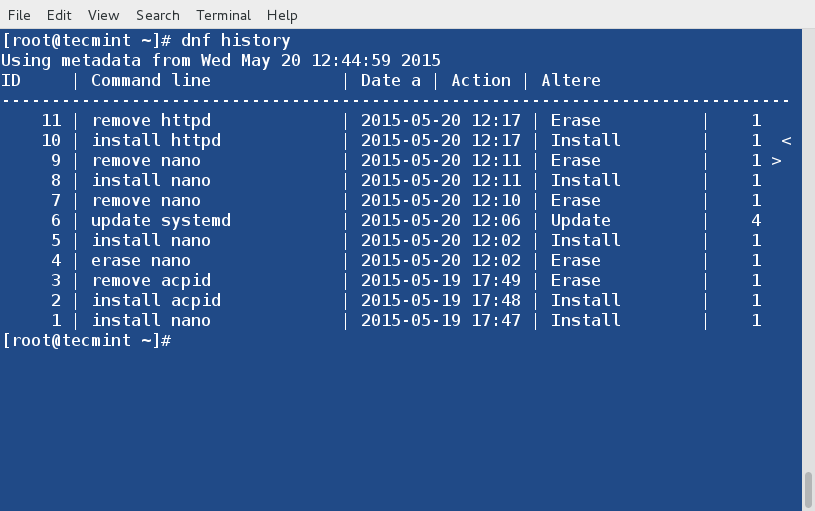
+
+### 20. List all Group Packages ###
+
+The command “dnf grouplist” will print all available or installed packages, if nothing is mentioned, it will list all known groups.
+
+ # dnf grouplist
+
+
+
+### 21. Install a Group Package using DNF ###
+
+To install a Group of packages bundled together as group package (say Educational Software) simply as.
+
+ # dnf groupinstall 'Educational Software'
+
+
+
+### 22. Update a Group Package ###
+
+Let’s update a Group Package (say Educational Software) by executing the below command.
+
+ # dnf groupupdate 'Educational Software'
+
+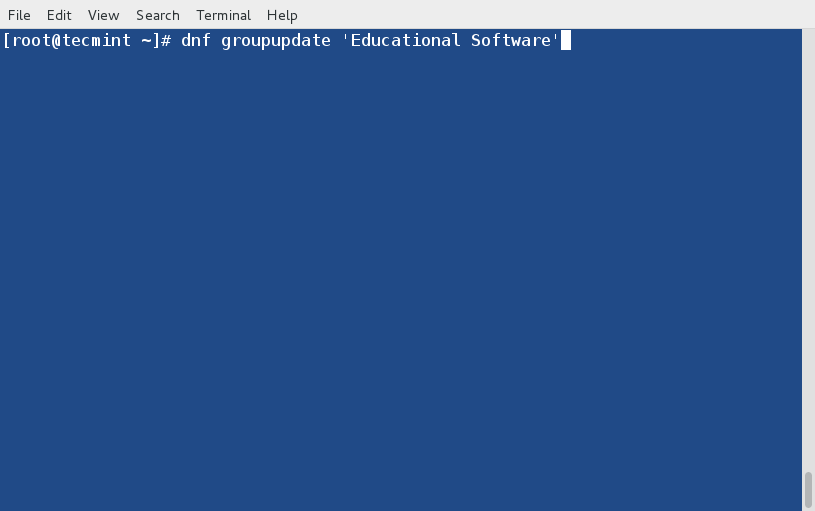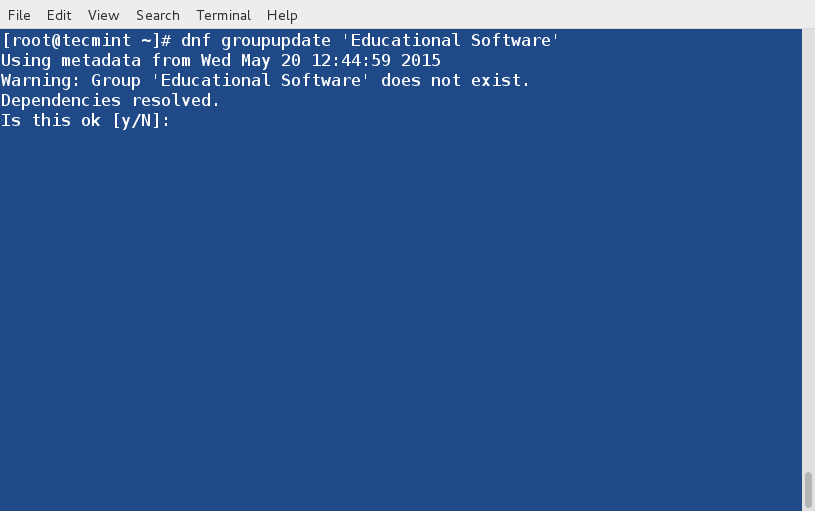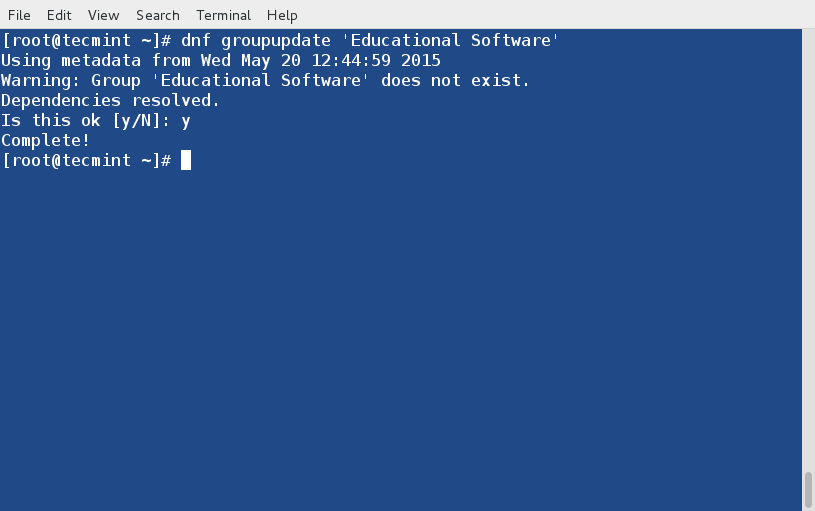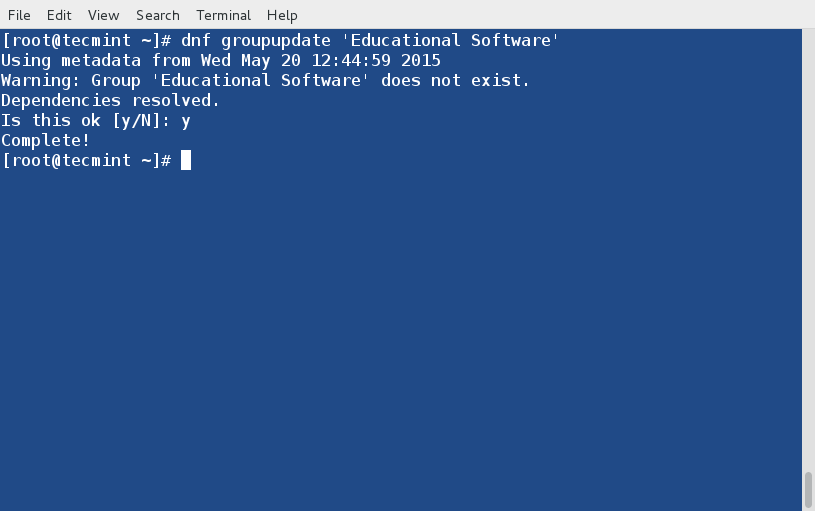
+
+### 23. Remove a Group Package ###
+
+We can remove the group Package (say Educational Software) as.
+
+ # dnf groupremove 'Educational Software'
+
+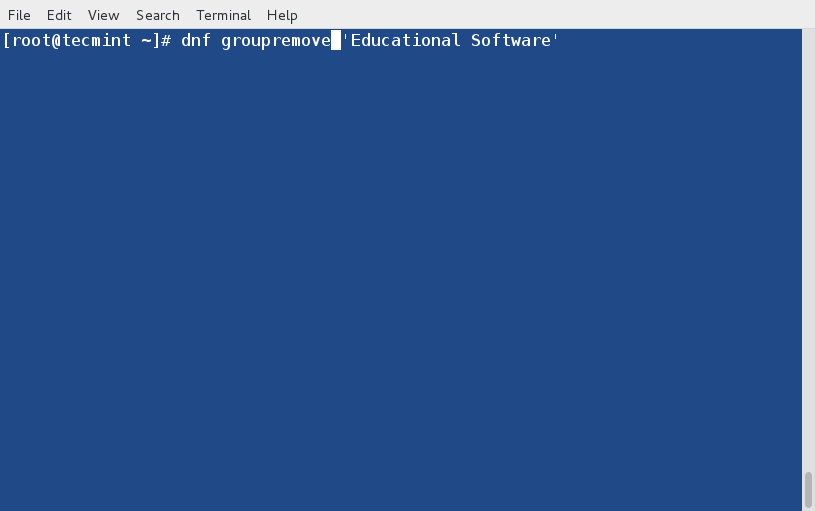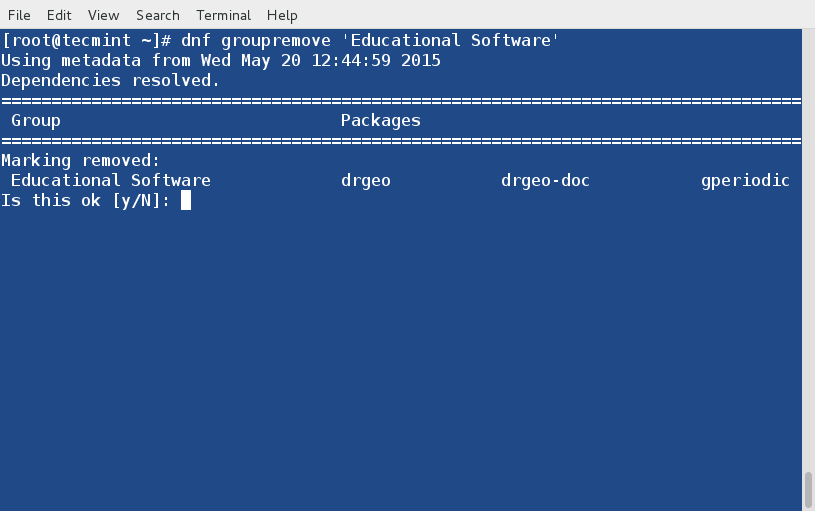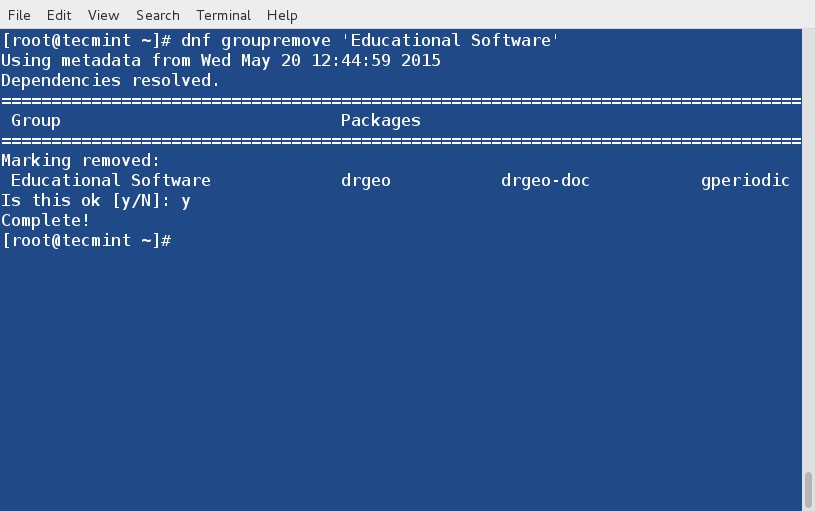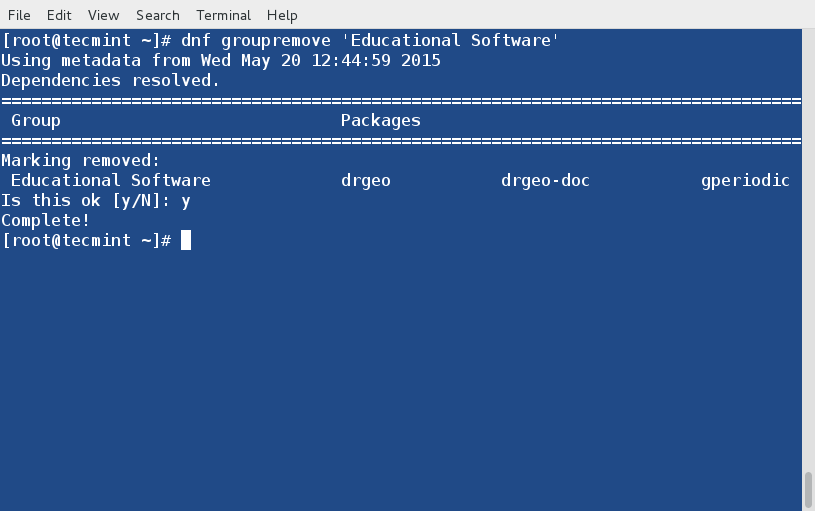
+
+### 24. Install a Package from Specific Repository ###
+
+DNF makes it possible to install any specific package (say phpmyadmin) from a repo (epel) as simply as,
+
+ # dnf --enablerepo=epel install phpmyadmin
+
+
+
+### 25. Synchronize Installed Packages to Stable Release ###
+
+The command “dnf distro-sync” will provides necessary options to synchronize all installed packages to most recent stable version available from any enabled repository. If no package is selected, all installed packages are synchronized.
+
+ # dnf distro-sync
+
+
+
+### 26. Reinstall a Package ###
+
+The command “dnf reinstall nano” will reinstall an already installed package (say nano).
+
+ # dnf reinstall nano
+
+
+
+### 27. Downgrade a Package ###
+
+The option “downgrade” will downgrades the named package (say acpid) to lower version if possible.
+
+ # dnf downgrade acpid
+
+Sample Output
+
+ Using metadata from Wed May 20 12:44:59 2015
+ No match for available package: acpid-2.0.19-5.el7.x86_64
+ Error: Nothing to do.
+
+**My observation**: DNF does not downgraded the package as it is supposed to. It has also been reported as bug.
+
+### Conclusion ###
+
+DNF is the upper state of the end of the art Package Manager YUM. It tends to do a lot of processing automatically which is not going to be praised by many experienced Linux System Administrator, as I believe. As a matter of example:
+
+- `--skip-broken` is not recognized by DNF and there is no alternative.
+- There is nothing like ‘resolvedep‘ command however you may run dnf provides.
+- There is no ‘deplist‘ command to find package dependency.
+- You exclude a repo, means the exclusion apply on all operations, unlike yum which excludes those repos only at the time of install and updates, etc.
+
+Several Linux users are not happy the way Linux Ecosystem is moving. First [Systemd removed init system][3] v and now DNF will be replacing YUM sooner in Fedora 22 and later in RHEL and CentOS.
+
+What do you think? are distributions and the whole Linux ecosystem is not valuing it’s users and moving against their will. Also it is often said in IT industry – “Why fix, If not broken?”, and neither init System V is broken nor YUM.
+
+That’s all for now. Please let me know your valuable thoughts in the comments below. Like and share us and help us get spread.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/dnf-commands-for-fedora-rpm-package-management/
+
+作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
+[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/dnf-next-generation-package-management-utility-for-linux/
+[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/systemd-replaces-init-in-linux/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150528 Things To Do After Installing Fedora 22.md b/sources/tech/20150528 Things To Do After Installing Fedora 22.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..023869a9f3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20150528 Things To Do After Installing Fedora 22.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+Translating by GOLinux!
+Things To Do After Installing Fedora 22
+================================================================================
+Fedora 22 the latest entrant in the community developed line of Red hat operating systems is released on the 26th of May 2015. A lot of speculation and anticipation has been associated with this release of the venerable fedora. Well there are some major changes that are being proposed for Fedora 22.
+
+Systemd is the new kid in the block when it comes to initialization daemons, it is poised to replace the venerable sysvinit module that has long been a part of the Linux ecosystem. Another major change that users will come across in the base python version. Its just that python in available in two different flavors the 2.x and 3.x lines. Each has its fair share of quirks and benefits. So users who might prefer the 2.x flavor might want to install their favorite python. The dandified Yum installer that has been around since Fedora 18 is all set to replace the age old YUM installer. Fedora has finally decided that it is time that DNF replace YUM.
+
+### 1) Install VLC media player ###
+
+Fedora 22 comes with a default media player viz. gnome videos (previously known as totem). If that is fine by you we can skip this step and move ahead. However if you like me prefer the most widely used VLC you can go ahead and install it from the RPMFusion repos. You can do that with :
+
+ sudo dnf install vlc -y
+
+### 2) Configure RPMFusion Repos ###
+
+As I already mentioned Fedora is very strict with its ideologies, it does not ship with any non-free components with it. The official repositories does not provide some essential software containing non-free components like multimedia codes. So it is necessary to install some 3rd party repositories which will provide us some essential software. Luckily RPMFusion repositories come to the rescue.
+
+ $ sudo dnf install --nogpgcheck http://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-22.noarch.rpm
+
+### 3) Install Multimedia Codecs ###
+
+As is said some multimedia codecs and plugins don't ship with fedora. Now who would like to miss out on their favorite shows and movies just because the codes are proprietary. Try this:
+
+ $ sudo dnf install gstreamer-plugins-bad gstreamer-plugins-bad-free-extras gstreamer-plugins-ugly gstreamer-ffmpeg gstreamer1-libav gstreamer1-plugins-bad-free-extras gstreamer1-plugins-bad-freeworld gstreamer-plugins-base-tools gstreamer1-plugins-good-extras gstreamer1-plugins-ugly gstreamer1-plugins-bad-free gstreamer1-plugins-good gstreamer1-plugins-base gstreamer1
+
+### 4) Update your system ###
+
+Fedora is a bleeding edge distribution and hence it releases updates which will fix bugs and loopholes present in your system continuously. Hence it is a good practice to keep your system up to date.
+
+ $ sudo dnf update -y
+
+### 5) Uninstall software you may not need ###
+
+Fedora comes with a set of pre-chosen packages that most users can utilize, however for more advanced users, you may recognize that you do not need all of it. It's easy enough to remove any packages you don't need using the following command - I chose to uninstall rhythmbox because I know I won't use it:
+
+ $ sudo dnf remove rhythmbox
+
+### 6) Install Adobe Flash ###
+
+We all wish Adobe Flash didn't exist anymore since it is not always know for being the most secure or resource efficient, but for awhile it's here to stay. The only way to install Adobe Flash for Fedora 22 is to install the official RPM from Adobe, as shown below.
+
+You can download the RPM [here][1]. After downloading the file, you can right click and open it like this:
+
+
+
+Right click and select "Open With Software Install"
+
+Then, simply click install on the window that pops up:
+
+
+
+Click on "Install" to complete the process of installing the custom RPM from Adobe
+
+Once the process completes, the "Install" button will change to "Remove" and the installation should have finished. If your browser is open during the process, it may ask you to close it first or restart it after the install for the changes to take effect.
+
+### 7) Spin Up a VM with Gnome Boxes ###
+
+So you just installed Fedora and you're loving it, but maybe you need Windows still for something proprietary, or maybe you just want to play with another Linux distro. In any situation, you can use Gnome Boxes, provided with Fedora 22, to easily create a VM or use a live distribution. Follow the steps below to get started using an ISO of your choice! Who knows, maybe you can even check out a [Fedora Spin][2].
+
+First open Gnome Boxes and select "New" in the top left:
+
+
+
+Click "New" to start the process of adding a new virtual machine.
+
+Next, click to open a file and choose an ISO:
+
+
+
+After choosing to select a file or ISO, select your ISO. In this case, I had a Debian ISO I installed
+
+Finally, customize the VM settings or use the defaults and click "Create." The VM will start by default and the available VMs will be available in Gnome Boxes as little thumbnails.
+
+
+
+Customize the settings to whatever you choose, or keep the defaults. Click "Create" when you are done and the VM will be ready to go.
+
+### 8) Install Google Chrome ###
+
+Firefox is included with Fedora 22, but as with most software, everyone has their browser of choice. If yours happens to be Google Chrome, you can follow the instructions above for Adobe Flash player, however, obviously use the RPM from Google for whichever version of Chrome you download. The latest version can usually be found [here][3].
+
+### 9) Add Social Media and Other Online Accounts ###
+
+Gnome has some nice built in functionality to accommodate accounts for things like Facebook, Google, and other online accounts. You can access the Online Accounts settings through the main Gnome Settings application. You can access the settings by right clicking on the desktop or by finding it in the applications. Then, simply click on Online Accounts and add the accounts of your choosing. If you add an account like Google, for example, you can use it as the default for things like sending email, calendar appointments, interacting with photos and documents, and more.
+
+### 10) Install KDE or another Desktop Environment ###
+
+Some of us just don't like Gnome, and that's okay. Run the following command in Terminal to install everything necessary to use KDE instead. The same instructions can be applied to xfce, lxde, or other desktop environments as well.
+
+ $ sudo dnf install @kde-desktop
+
+After the install finishes, log out. When you click on your username, notice the little gear wheel that indicates settings. Click it and select "Plasma." When you log in again, you will be greeted by a fresh KDE desktop.
+
+
+
+The Plasma environment after just installing it on Fedora 22
+
+### Conclusion ###
+
+That’s it you are all set to go. Use the system and try out things. If you don't find something according to your liking, linux gives you the freedom to change them. Fedora comes with the latest Gnome shell as its desktop environment, too heavy for you and don't like it. Try KDE or some light weight DE like cinnamon, xfce etc. Wish you a very happy and hassle free Fedora experience. !!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/things-do-after-installing-fedora-22/
+
+作者:[Jonathan DeMasi][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/jonathande/
+[1]:https://get.adobe.com/flashplayer/
+[2]:http://spins.fedoraproject.org/
+[3]:https://www.google.com/intl/en/chrome/browser/desktop/index.html
diff --git a/translated/share/20140804 Group Test--Linux Text Editors.md b/translated/share/20140804 Group Test--Linux Text Editors.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 1976cfca32..0000000000
--- a/translated/share/20140804 Group Test--Linux Text Editors.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,320 +0,0 @@
-组测试: Linux 文本编辑器
-================================================================================
-> Mayank Sharma 测试了5款不仅仅是能处理字的超级文本编辑器。
-
-如果你使用Linux已经有很长一段时间,你知道,不管是编辑一款app的配置文件,一起用shell脚本骇客,或者编写/查看代码,类似LobreOffice的工具并不能满足。尽管字面上看起来意思一样,你不需要一个字处理器来完成这些任务;你需要一个文本编辑器。
-
-在这个组测试中,我们将着眼于5款不仅仅是能胜任繁重文本任务的简陋的文本编辑器。他们能高亮语法,像拼写检查一样轻松处理代码缩进。你可以像你复制/粘贴文本那样容易地使用他们记录宏以及管理代码片段。
-
-得益于能向它们注入足以抗衡其它类型的以文本为中心的应用程序能力的插件,一些简单的文本编辑器甚至超过了它们的设计目标。它们能胜任一个源代码编辑器的任务,甚至是一个集成开发环境。
-
-Emacs和Vim是两款最流行和强大的纯文本编辑器。但是,由于一些原因,我们在这个组测试中并没有包括它们。首先,如果你使用它们中的任何一个,那么恭喜你:你不需要更换了。其次,它们都有陡峭的学习曲线,尤其是那些熟悉了桌面环境的用户:他们很更愿意投入其他有图形界面的文本编辑器。
-
-### 目录: ###
-
-#### Gedit ####
-
-- URL:http://projects.gnome.org/gedit/
-- 版本: 3.10
-- 许可证: GPL
-- Gnome的默认文本编辑器准备好挑战了?
-
-#### Kate ####
-
-- URL: www.kate-editor.org
-- 版本: 3.11
-- 许可证: LGPL/GPL
-- Kate会挑战命运吗?
-
-#### Sublime Text ####
-
-- URL: www.sublimetext.com
-- 版本: 2.0.2
-- 许可证: Proprietary
-- 在自由与黄金心脏土地上的私有软件。
-
-#### UltraEdit ####
-
-- URL: www.ultraedit.com
-- 版本: 4.1.0.4
-- 许可证: Proprietary
-- 它做的足够多去证明它的价值了吗?
-
-#### jEdit ####
-
-- URL: www.jedit.org
-- 版本: 5.1.0
-- 许可证: GPL
-- 基于Java的编辑器是否会扰乱其他编辑器的世界?
-
-
-在展示一个有功能的应用程序和将它们所有的东西曝光给用户之间有一个很好的平衡。Geddit隐藏了它的大部分功能。
-
-### 关键标准 ###
-
-除了Gedit和jEdit以外的所有工具,都是通过推荐的安装方法安装在Fedora和Ubuntu上。前者已经兼容默认的Gnome桌面,后者仍然固执地反对安装在Fedora上。由于这些是相对简单的应用程序,他们没有复杂的依赖,唯一例外的是jEdit,它要求要有Oracle Java。
-
-得益于Gnome和KDE持续的努力,不论他们运行的桌面环境,所有编辑器看起来很好,功能也很正常。这不仅是作为评价的标准,也意味着你不再受制于要找到和你的桌面环境兼容的工具。
-
-除了它们奇特的功能,我们也对所有候选者测试了通用文本编辑功能。然而,它们并没有被设计为模仿现代字处理器的所有功能,我们也不以此评判。
-
-
-
-Kate能搭建为功能丰富的集成开发环境。
-
-### 编程语言支持 ###
-
-UltraEdit 能进行语法高亮,代码折叠以及拥有项目管理的能力。这也有一个罗列源文件中所有函数的功能列表,但并不适用于我们任何的测试代码文件。UltraEdit也支持HTML5,有能添加常用HTML标记的HTML工具栏。
-
-即使Gnome的默认文本编辑器Gedit,也有几个面向编码的功能特性,例如括号匹配,自动缩进以及为包括C, C++, Java, HTML, XML, Python, Perl, 以及许多其它编程语言进行语法高亮。
-
-如果你需要更多的编程辅助,看一下Sublime和Kate。Sublime支持多种编程语言并且(正如流行的那些)能为C#, D, Dylan, Erlang, Groovy, Haskell, Lisp, Lua, MATLAB, OCaml, R, 甚至 SQL 进行语法高亮。如果这还不够,你可以下载插件以支持更多的语言。
-
-另外,它的语法高亮功能提供了多个可定制选项。这个应用程序也会进行括号匹配,确保代码段都正确,Sublime的自动补全功能也支持用户创建的变量。
-
-正如Komodo IDE,Sublime也可滚动浏览显示完整的代码,这对于长代码文件导航和在文件中的不同部分跳转很方便。
-
-Sublime最好的功能之一就是能在编辑器内部为特定语言,例如C++, Python, Ruby等运行代码,当然假设在你的电脑上安装有编译器以及其它系统工具。省时间而且不用再开终端.
-
-你也可以用插件在Kate中开启构建系统功能。另外,你可以为GDB调试器添加一个简单的前端。Kate能和Git,Subversion以及Mercurial版本控制系统一起工作,也提供了一些项目管理的功能。
-
-除了能为超过180中语言进行语法高亮,它支持所有的这些辅助功能,例如括号匹配,自动补全和自动缩进。它也支持代码折叠,甚至在一个程序中折叠函数。
-
-唯一的遗憾的是jEdit,它声称自己是一个程序员的文本编辑器,但它缺少其他的基本功能,例如代码折叠,它甚至不能提示或者不全函数.
-
-**评分:**
-
-- Gedit:3/5
-- Kate:5/5
-- Sublime:5/5
-- UltraEdit3/5
-- jEdit:1/5
-
-
-
-如果你不喜欢Sublime的Charcoal外观,你可以选择它包含的其它22中主题。
-
-### 键盘控制 ###
-
-高级文本编辑器用户希望能完全通过键盘控制和操作,一些应用程序甚至运行他们的用户自定义快捷方式的键盘绑定。
-
-你可以轻松的使用Gedit的扩展键盘快捷键。这里有编辑文件,为普通任务,例如对一个文档进行拼写检查,唤起工具的快捷键。你可以获取应用程序内部的一系列默认快捷键,但并没有图形化的方式去自定义它们。相似的,在Sublime中自定义键绑定,你需要修改他的XML键映射文件。Sublime由于缺少定义键盘快捷键的图形化界面而饱受批评,但长期使用的用户支持当前的基于文件的机制:这给他们更多的控制能力。
-
-UltraEdit为它"一切都可自定义"的座右铭感到自豪,这也包括键盘快捷键。你可以自定义菜单导航的热键,以及定义你自己的访问大量函数的多键键映射。
-
-除了完全可自定义的键盘快捷键以外,jEdit也有为Emacs预定义的键映射。Kate在这方面尤其令人映像深刻。它有简单可访问的自定义键绑定窗口。你可以更改默认的键,或者定义替代的键。另外,Kate也有一个能使用户使用Vi键操作Kate的Vi模式。
-
-**Verdict:**
-
-- Gedit:2/5
-- Kate:5/5
-- Sublime:3/5
-- UltraEdit:4/5
-- jEdit:5/5
-
-### 片段和宏 ###
-
-宏通过自动化重复的步骤帮助你降低花费在编辑和组织数据上的时间,而代码片段通过创建可重用的源代码块为程序员扩展类似的功能。这两者都能节省你的时间。
-
-标准的Gedit安装没有这两种功能中的任何一种,但是你可以通过独立的插件启用这些功能。片段插件随Gedit一起发布,但在Gedit内部启用宏插件之前你需要手动下载和安装(被称为gedit-macropy,托管在GitHub上)。
-
-Kate也同样通过插件的形式启用片段功能。一旦加入,插件也增加了片段的PHP,Bash和Java库。你可以在侧边栏中显示片段列表以便于访问。可以通过右击片段或者快捷键组合方式编辑它的内容。然而,令人惊讶的是,它不支持宏-尽管用户从2002年开始重复要求!
-
-jEdit也有一个启用片段的插件。但是它可以从用户行为中记录宏或者你也可以在BeanShell 脚本语言(BeanShell支持像Perl和JavaScript那样将脚本对象封锁为简单的方法)中写宏。jEdit也有一个可以从jEdit的网站中下载多种宏的插件。
-
-Sublime有创建片段和宏的内建功能,也有为大多数编程语言经常使用的函数多种片段。
-
-在UltraEdit中片段被称为智能模板,正如Sublime你可以根据正在编辑的源代码文件类型插入片段。要完成宏记录功能,UltraEdit还有一个基于JavaScript的集成脚本语言来完成自动任务。你也可以从编辑器的网站中下载用户提交的宏和脚本。
-
-**Verdict:**
-
-- Gedit:3/5
-- Kate:1/5
-- Sublime:5/5
-- UltraEdit:5/5
-- jEdit:5/5
-
-
-
-UltraEdit的用户界面是高度可配置的 — 你可以正如改变其它许多方面那样简单的自定义工具栏和菜单的布局。]
-
-### 易用性 ###
-
-不像一个准系统文本编辑器,文本编辑器的这个功能洋溢着适应大范围用户的功能 - 从文档写作者到程序员。从应用程序剥离相反,他们的开发者在寻找添加更多功能的途径。
-
-尽管第一眼看上去这次组测试中的大部分应用有一个很相似的布局,经过仔细的检查,你会发现一些可用性差异。我们通过用户界面的合理使用来介绍它们的功能和特性,而不是铺天盖地地告诉读者。
-
-### Gedit: 4/5 ###
-
-Gedit有很普通的外观。通过最小化菜单和按钮有一个简单的界面。但这也是一种双刃剑,因为有些用户可能不会发现它真正的潜能。
-
-Gedit可以通过在窗口中能重排和移动的选项卡打开多个文件。用户可以通过使用一个插件选择性地启用旁边或者底部用来显示文件浏览和工具输出的面板。这个应用程序会检测到被其它应用程序更改的文件并可以重新加载这个文件。
-
-为了适配Gnome,在应用程序的最后一个版本中考虑了大量的用户界面。然而它还并不稳定,尽管包括了所有的功能,和菜单交互的一些插件还需要升级。
-
-### Kate: 5/5 ###
-
-尽管用户界面的主要部分和Gedit的相似,Kate可以在两边显示选项卡并且它的菜单更加丰富。该应用程序平易近人,让用户可以挖掘其它功能。
-
-Kate可以在KDE的KIO支持的所有协议上透明地打开和保存文件,包括HTTP, FTP, SSH, SMB 和 WebDAV。你可以用这个应用同时处理多个文件。但不同于大部分应用程序传统的水平选项卡选择栏,Kate在屏幕的两个方向都有选项卡。左侧的侧边栏显示打开文件的索引。需要同时查看一个文件不同部分的程序员也会感激它可以水平或者竖直分隔界面的能力。
-
-### Sublime: 5/5 ###
-
-
-Sublime支持你在不同方式同时查看多达四个文件。当你在zone下,这里也有一个只显示文件和菜单的全屏模式。
-
-这个编辑器还在右边有个小地图,这在长文件中导航非常有用。应用程序为多种编程语言提供多种流行功能的片段,这使得它对于开发者非常有用。另一个精巧的功能是,无论你使用都是文本文档或者代码,都可以交换和随机选择。
-
-### UltraEdit: 3/5 ###
-
-
-UltraEdit在界面的顶部和底部加载了多种工具栏。由于有在文档中跳转的选项卡,两边的面板,以及复杂区别,使得只剩下一点空间给编辑窗口。
-
-使用HTML的网络开发者有很多唾手可得的帮助。你可以通过FTP和SFTP访问远程文件。高级功能,例如记录一个宏以及比较文件,也简单易用。
-
-使用应用程序的Preference窗口,你可以调整应用程序的多个方面,包括颜色主题和类似语法高亮的其它功能。
-
-### jEdit: 3/5 ###
-
-在可用性方面,首先一个不好就是jEdit不能在基于RPM的发行版上安装。导航编辑器需要一些时间来适应,因为它的菜单和其它流行的应用程序顺序不同,而且有些普通桌面用户不熟悉的名字。但是,该应用程序有详细的内部帮助,这有利于缓解学习曲线。
-
-jEdit高亮你所在的当前行,并使你能一多种查看方式分隔窗口。你可以简单地从应用程序中安装和管理插件,除了全宏,jEdit也支持你记录快速临时的宏。
-
-
-
-由于它的Java基础,jEdit在任何桌面环境中都不能给人宾至如归的感觉
-
-### 可用性和支持 ###
-
-在Gedit和Kate之间有很多相似性。两个应用程序都得益于他们各自的父项目,Gnome和KDE,并绑定在各种主流的发行版中。另外两个项目都是交叉平台的,有Windows和Mac OS X版本以及本来的Linux版本。
-
-Gedit托管在Gnome的网络设施上并有一个简单的用户指南,关于多种插件的信息,以及包括邮件列表和IRC通道的常用保持联系方式。你也可以在其它基于Gnome的发行版,例如Ubuntu中找到使用信息。相似地,Kate得益于KDE的资源,并包括详细的用户信息以及邮件列表和IRC通道。你也可以从应用程序中获取相应的离线用户指南。
-
-除了Linux,UltraEdit在Windows和Mac OS X中也可用,虽然在应用程序中并没有包括,但在启动时也有详细的用户指南。为了辅助用户,UltraEdit保存了一个常见问题的数据库,一系列关于多种特定功能的详细信息的有用提示,用户还可以在论坛版块彼此帮助。另外,付费用户也可以通过邮件从开发者中获取支持。
-
-Sublime支持相同数目的平台,但是你需要单独为每种平台购买许可证。开发者通过博客使用户了解正在进行的开发,并积极参加了主持论坛。这个项目支持设施的亮点是提供免费的详细教程和视频课程。Sublime非常可爱。
-
-由于是用java编写的,jEdit在多种平台中都可用。在它的网站上你可以找到一个详细的用户指南以及一些插件帮助文档的链接。然而,这里没有能使用户和其他用户或者开发者交流的途径。
-
-**判定:**
-
-- Gedit: 4/5
-- Kate: 4/5
-- Sublime: 5/5
-- UltraEdit: 3/5
-- jEdit: 2/5
-
-### 附加和插件 ###
-
-不同的用户有不同的需求,一个简单的轻量级应用程序只能做到这么多。这就是为什么需要插件的原因。应用程序依赖于这些小部件来扩展它们的功能集并让更多的用户使用。
-
-UltraEdit是一个另外。它没有第三方插件,但开发者确实支出了例如HtmlTidy的第三方工具已经安装到了UltraEdit。
-
-Gedit附带了好多已安装的插件,你可以从gedit-插件包下载更多的插件。基于和Gedit版本的兼容性,项目网站也有到多个第三方插件的链接。
-
-三个对程序员非常有用的插件是Code Comment,在底部面板增加一个终端的Terminal Plugin以及Session Saver。当你用多个文件开发项目的时候Session Saver相当有用。你可以在选项卡中打开文件,保存会话,当你用一个单击回复的时候,可以按照你保存时的选项卡顺序打开所有的文件。
-
-类似的,你可以通过用内部的插件管理器增加插件来扩展Kate。除了令人映像深刻的项目插件,一些开发者使用的插件包括嵌入式终端,能编译和调试代码,以及对数据库执行SQL查询。
-
-Sublime的插件是用Python写的,文本编辑器包括了一个类似于apt-get,能使用户查找,安装,升级和移除插件包的名为Package Control的工具。通过插件,你可以在Sublime中使用Git版本控制,以及改进JavaScript的JSLint工具。Sublime Linter能指出你代码中的错误,是编码人员必备的插件。
-
-jEdit拥有最令人映像深刻的插件设施。该应用有超过200个插件,可以在它们自己的专用网站中浏览。网站通过不同的类型列举了插件,例如文件管理,版本控制,文本等。你可以在每个类型下找到很多的插件。
-
-一些最好的插件是Android插件,它们提供了和Android项目协同工作的工具;你可以使用TomcatSwitch插件创建和控制外部Jakarta Tomcat服务器进程;以及类似于Vi功能的Vimulator插件。你可以通过使用jEdit的插件管理器安装这些插件。
-
-**评定**
-
-- Gedit: 3/5
-- Kate: 4/5
-- Sublime: 4/5
-- UltraEdit: 1/5
-- jEdit: 5/5
-
-### 纯文本编辑 ###
-
-尽管它们强大的额外功能甚至可能会取代几个流派完全成熟的应用程序,有时候可能只需要使用这些庞大的文本编辑器读写或者编辑简单的纯文本。虽然你可以使用它们中的任何一个输入文本,我们通过普通文本编辑的方便性评价它们。
-
-Gnome的默认文本编辑器Gedit,支持取消和重做机制以及搜索和替换。它可以对多种语言进行拼写检查,并能通过使用Gnome GVFS库访问和编辑远程文件。
-
-你也可以使用Kate进行拼写检查,它也可以让你对任何高亮文本进行Google搜索。它还有一个能可视化告知用户文件中更改过但没有保存的行的行修改系统。另外,它通过允许用户在文件中使用书签简化长文档的导航。
-
-Sublime有很多可选择的编辑命令,例如缩进文本和格式化段落。它的自动保存功能帮助防止用户丢失他们的更改。高级用户还会喜欢基于正则表达式的递归查找和替换功能,以及选择多个不连续的文本块并执行统一操作。
-
-UltraEdit也允许用户在查找和替换功能中使用正则表示,并能通过FTP编辑远程文件。JEdit一个独特的功能是它支持被称为寄存器的不限数目的剪切板。你可以复制文本片段到这些寄存器中,在编辑会话过程中都可用。
-
-**评定:**
-
-- Gedit: 4/5
-- Kate: 5/5
-- Sublime: 5/5
-- UltraEdit: 4/5
-- jEdit: 4/5
-
-### 我们的评比 ###
-
-在这里的所有编辑器都足以替换你已有的文本编辑器去用来编辑文本和调整配置文件。事实上,没准它们会组合起来作为你的集成开发环境。这些应用程序都有各种各样功能,它们的开发者不会考虑剥离功能,而是增加越来越多的功能。
-
-jEdit排在这次测试的最后面。因为它不仅坚持使用专有的Oracle Java运行环境,不能在你的Fedora机器上安装,而且开发者不积极的和用户交互。
-
-UltraEdit做的稍微好一点。这个商业专用工具专注于网络开发者,不为非开发者高级用户提供任何功能,使得它不值得推荐为免费软件的替代品。
-
-排在第三的是Gedit。作为Gnome的默认编辑器,它没有任何内在的错误,但尽管有很多积极的方面,它还是略微被Sublime和Kate超越。开诚布公地说,Kate是比Gedit更通用的编辑器,甚至考虑到他们的插件系统,评分也优于Gnome的默认编辑器。
-
-Sublime和Kate都相当好。他们在我们的大多数测试中表现同样出色。由于不支持宏而落后于Sublime,但键盘友好和能简单定义自定义键绑定又使Kate找回优势。
-
-Kate成功的原因可以归结为它通过最小化学习曲线提供了最大化数目的功能。尽量使用它吧,不仅作为简单文本编辑器使用,或者容易使用语法高亮编辑配置文件,甚至得益于项目管理能力能使用它协作一个复杂的编程项目。
-
-我们不是选择Kate去替换一个类似[在这里插入你最喜欢的专业工具]的全面的集成开发环境。但是它是一个专业工具理想的全面的以及完美的垫脚石。
-
-Kate为能快速响应你的需要而设计,它的界面并不会使你茫然,并且和那些过于复杂的应用一样的有用。
-
-### 1st Kate ###
-
-- Licence LGPL/GPL Version 3.11
-- www.kate-editor.org
-- 拥有超能力,最终温和的文本编辑器。
-- Kate是KDE项目中最有用的应用程序之一。
-
-### 2nd Sublime Text ###
-
-- Licence Proprietary Version 2.0.2
-- www.sublimetext.com
-- 值得你每分钱的专业文本编辑器 - 简单易用,功能全面而且看起来很棒。
-
-### 3rd Gedit ###
-
-- Licence GPL Version 3.10
-- http://projects.gnome.org/gedit
-- 从Gnome中完成。这是一个奇妙的文本编辑器,确实令人钦佩的工作,但这里的竞争实在太大了。
-
-### 4th UltraEdit ###
-
-- Licence Proprietary Version 4.1.0.4
-- www.ultraedit.com
-- 关注于为网络开发者绑定便利,而不为普通用户提供任何特殊功能。
-
-### 5th jEdit ###
-
-- Licence GPL Version 5.1.0
-- www.jedit.org
-- 缺乏支持,不支持Fedora,缺乏好看的界面,jEdit被贬低到最后。
-
-### 你也许希望尝试… ###
-
-随你发行版发布的默认文本编辑器也能帮助你一些高级任务。例如KDE的KWrite和Raspbian的Nano。得益于KDE的katepart组件,KWrite继承了一些Kate的功能,得益于在树莓派上的可用性,Nano也开始重现风头。
-
-如果你希望跟随Linux大师的脚步,你总是可以尝试崇高的文本编辑机Emacs和Vim。想尝试Vim强大的用户首先可以考虑gVim,它通过图形界面展现了Vim的强大。
-
-除了jEdit和Kate,这里还有其他模仿例如Emacs和Vim之类的老派高级编辑器的编辑器,比如JED 编辑器和Joe's Own Editor,这两者都有Emacs的模拟模式。另一方面,如果你在寻找轻量级的代码编辑器,可以看看Bluefish和Geany。他们的存在是为了填补文本编辑器和全面集成的开发平台之间的空隙。
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.linuxvoice.com/text-editors/
-
-作者:[Ben Everard][a]
-译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
-校对:[royaso](https://github.com/royaso)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://www.linuxvoice.com/author/ben_everard/
diff --git a/translated/share/20150410 This tool can alert you about evil twin access points in the area.md b/translated/share/20150410 This tool can alert you about evil twin access points in the area.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 963460501d..0000000000
--- a/translated/share/20150410 This tool can alert you about evil twin access points in the area.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
-这个工具可以提醒你一个区域内的假面猎手接入点 (注:evil twin暂无相关翻译)
-===============================================================================
-**开发人员称,EvilAP_Defender甚至可以攻击流氓Wi-Fi接入点**
-
-一个新的开源工具可以定期扫描一个区域,以防流氓Wi-Fi接入点,同时如果发现情况会提醒网络管理员。
-
-这个工具叫做EvilAP_Defender,是为监测攻击者配置的恶意接入点而专门设计的,这些接入点冒用合法的名字诱导用户连接上。
-
-这类接入点被称做假面猎手,使得黑客们从接入的设备上监听互联网信息流。这可以被用来窃取证书,破坏网站等等。
-
-大多数用户设置他们的计算机和设备可以自动连接一些无线网络,比如家里的或者工作地方的网络。尽管如此,当面对两个同名的无线网络时,即SSID相同,有时候甚至时MAC地址也相同,这时候大多数设备会自动连接信号较强的一个。
-
-这使得假面猎手的攻击容易实现,因为SSID和BSSID都可以伪造。
-
-[EvilAP_Defender][1]是一个叫Mohamed Idris的人用Python语言编写,公布在GitHub上面。它可以使用一个计算机的无线网卡来发现流氓接入点,这些接入点复制了一个真实接入点的SSID,BSSID,甚至是其他的参数如通道,密码,隐私协议和认证信息。
-
-该工具首先以学习模式运行,为了发现合法的接入点[AP],并且加入白名单。然后切换到正常模式,开始扫描未认证的接入点。
-
-如果一个恶意[AP]被发现了,该工具会用电子邮件提醒网络管理员,但是开发者也打算在未来加入短信提醒功能。
-
-该工具还有一个保护模式,在这种模式下,应用会发起一个denial-of-service [DoS]攻击反抗恶意接入点,为管理员采取防卫措施赢得一些时间。
-
-“DoS不仅针对有着相同SSID的恶意AP,也针对BSSID(AP的MAC地址)不同或者不同信道的,”Idris在这款工具的文档中说道。“这是避免攻击你的合法网络。”
-
-尽管如此,用户应该切记在许多国家,攻击别人的接入点,甚至一个可能一个攻击者操控的恶意的接入点,很多时候都是非法的。
-
-为了能够运行这款工具,需要Aircrack-ng无线网套装,一个支持Aircrack-ng的无线网卡,MySQL和Python运行环境。
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.infoworld.com/article/2905725/security0/this-tool-can-alert-you-about-evil-twin-access-points-in-the-area.html
-
-作者:[Lucian Constantin][a]
-译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://www.infoworld.com/author/Lucian-Constantin/
-[1] https://github.com/moha99sa/EvilAP_Defender/blob/master/README.TXT
diff --git a/translated/share/20150429 What are good command line HTTP clients.md b/translated/share/20150429 What are good command line HTTP clients.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fa9ef01c54
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/share/20150429 What are good command line HTTP clients.md
@@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
+什么是好的命令行HTTP客户端?
+==============================================================================
+整体大于各部分之和,这是引自希腊哲学家和科学家的亚里士多德的名言。这句话特别切中Linux。在我看来,Linux最强大的地方之一就是它的协作性。Linux的实用性并不仅仅源自大量的开源程序(命令行)。相反,其协作性来自于这些程序的综合利用,有时是结合更大型的应用。
+
+Unix哲学引发了一场“软件工具”的运动,关注开发简洁,基础,干净,模块化和扩展性好的代码,并可以运用于其他的项目。这种哲学为许多的Linux项目留下了一个重要的元素。
+
+好的开源开发者写程序为了确保该程序尽可能运行正确,同时能与其他程序很好地协作。目标就是使用者拥有一堆方便的工具,每一个力求干不止一件事。许多程序能独立工作得很好。
+
+这篇文章讨论3个开源命令行HTTP客户端。这些客户端可以让你使用命令行从互联网上下载文件。但同时,他们也可以用于许多有意思的地方,如测试,调式和与HTTP服务器或网络应用互动。对于HTTP架构师和API设计人员来说,使用命令行操作HTTP是一个值得花时间学习的技能。如果你需要来回使用API,HTTPie和cURL,这没什么价值。
+
+-------------
+
+
+
+
+
+HTTPie(发音 aych-tee-tee-pie)是一款开源命令行HTTP客户端。它是一个命令行界面,类cURL的工具。
+
+该软件的目标是使得与网络服务器的交互尽可能的人性化。其提供了一个简单的http命令,允许使用简单且自然的语句发送任意的HTTP请求,并显示不同颜色的输出。HTTPie可以用于测试,调式和与HTTP服务器的一般交互。
+
+#### 功能包括:####
+
+- 可表达,直观的语句
+- 格式化,颜色区分的终端输出
+- 内建JSON支持
+- 表单和文件上传
+- HTTPS,代理和认证
+- 任意数据请求
+- 自定义标题 (此处header不确定是否特别意义)
+- 持久会话
+- 类Wget下载
+- Python 2.6,2.7和3.x支持
+- Linux,Mac OS X 和 Windows支持
+- 支持插件
+- 帮助文档
+- 测试覆盖 (直译有点别扭)
+
+- 网站:[httpie.org][1]
+- 开发者: Jakub Roztočil
+- 证书: 开源
+- 版本号: 0.9.2
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+cURL是一个开源命令行工具,用于使用URL语句传输数据,支持DICT, FILE, FTP, FTPS, GOPHER, HTTP, HTTPS,IMAP, IMAPS, LDAP, LDAPS, POP3, POP3S, RTMP, RTSP, SCP, SFTP, SMTP, SMTPS, TELNET和TFTP。
+
+cURL支持SSL证书,HTTP POST,HTTP PUT,FTP上传,HTTP基于表单上传,代理,缓存,用户名+密码认证(Basic, Digest, NTLM, Negotiate, kerberos...),文件传输恢复, 代理通道和一些其他实用窍门的总线负载。(这里的名词我不明白其专业意思)
+
+#### 功能包括:####
+
+- 配置文件支持
+- 一个单独命令行多个URL
+- “globbing”漫游支持: [0-13],{one, two, three}
+- 一个命令上传多个文件
+- 自定义最大传输速度
+- 重定向标准错误输出
+- Metalink支持
+
+- 网站: [curl.haxx.se][2]
+- 开发者: Daniel Stenberg
+- 证书: MIT/X derivate license
+- 版本号: 7.42.0
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+Wget是一个从网络服务器获取信息的开源软件。其名字源于World Wide Web 和 get。Wget支持HTTP,HTTPS和FTP协议,同时也通过HTTP代理获取信息。
+
+Wget可以根据HTML页面的链接,创建远程网络站点的本地版本,是完全重造源站点的目录结构。这种方式被冠名“recursive downloading。”
+
+Wget已经设计可以加快低速或者不稳定的网络连接。
+
+功能包括:
+
+- 使用REST和RANGE恢复中断的下载
+- 使用文件名
+- 多语言的基于NLS的消息文件
+- 选择性地转换下载文档里地绝对链接为相对链接,使得下载文档可以本地相互链接
+- 在大多数类UNIX操作系统和微软Windows上运行
+- 支持HTTP代理
+- 支持HTTP数据缓存
+- 支持持续地HTTP连接
+- 无人照管/后台操作
+- 当远程对比时,使用本地文件时间戳来决定是否需要重新下载文档 (mirroring没想出合适的表达)
+
+- 站点: [www.gnu.org/software/wget/][3]
+- 开发者: Hrvoje Niksic, Gordon Matzigkeit, Junio Hamano, Dan Harkless, and many others
+- 证书: GNU GPL v3
+- 版本号: 1.16.3
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20150425174537249/HTTPclients.html
+
+作者:Frazer Kline
+译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://httpie.org/
+[2]:http://curl.haxx.se/
+[3]:https://www.gnu.org/software/wget/
diff --git a/translated/share/20150515 This Ubuntu App Applies Instagram Style Filters to Your Photos.md b/translated/share/20150515 This Ubuntu App Applies Instagram Style Filters to Your Photos.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ae5e6df6eb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/share/20150515 This Ubuntu App Applies Instagram Style Filters to Your Photos.md
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
+一个Ubuntu中给你的照片加Instagram风格滤镜的程序
+================================================================================
+**在Ubuntu中寻找一个给你的照片加Instagram风格的滤镜程序么?**
+
+拿起你的自拍棒跟着这个来。
+
+
+XnRetro是一个照片编辑应用
+
+### XnRetro 照片编辑器 ###
+
+**XnRetro** 是一个可以让你快速给你照片添加“类Instagram”效果的程序。
+
+你知道我说的这些效果:划痕、噪点、框架、过处理、复古和怀旧色调(因为在这个数字时代,我们必须知道无尽的自拍不能称为怀旧的自己。)
+
+无论你认为这些效果是愚蠢的艺术价值或者创作的捷径,这些滤镜非常流行切可以帮助那些平平照片添加个性。
+
+
+#### XnRetro的功能 ####
+
+**XnRetro有下面那些功能**
+
+- 20色彩滤镜
+- 15中光效果(虚化、泄露等等)
+- 28框架和边框
+- 5中插图 (带力度控制)
+- Image adjustments for contrast, gamma, saturation, etc
+- 对比度、伽马、饱和度等图像调整
+- 矩形修剪选项
+
+
+灯光效果调整
+
+你可以(理论上)编辑。jpg或者.png文件并且直接在app中等想到社交媒体上。
+
+我说“理论”上的意思是保存.jpg图像无法正常在linux版的程序上工作(你可以保存.png的图像)。相似的,大多数内置的社交链接失效或者无法导出。
+
+要使用**15中光影效果**你需要在XnRetro的‘light’文件夹下重新保存.jpg文件成.png文件。编辑‘light.xml’来匹配新的文件名,点击保存那没灯光效果就可以没有问题的加载进XnRetro了。
+
+> ‘用户友好的XnRetro很难打败-一旦你用顺之后。’
+
+**XnRetro值得安装么?**
+
+XnRetro并不是完美的。它看上去很丑、很难正确的安装并且已经纪念没有更新了。
+
+它还可以使用,输了保存.jpg文件外。同时也是那些像Gimp或者Shotwell的那些‘正规’图片调整工具的一个灵活替代品。
+
+While web apps and Chrome Apps¹ like [Pixlr Touch Up][1] and [Polarr][2] offer similar features you may be looking for a truly native solution.
+虽然web应用和Chrome Apps¹像[Pixlr Touch Up][1] 和 [Polarr][2]提供另外相似的功能,而你也许正在寻找真正原生的解决方案。
+
+对于此,用户友好带有容易使用滤镜的XnRetro很难被打败。
+
+### 下载Ubuntu下的XnRetro ###
+
+XnRetro没有可用的.deb安装包。它以二进制文件的形式发型,这意味着你需要每次双击程序来运行。它也只有32位的版本。
+
+你可以使用下面的XnRetro下载链接。下载完成后你需要解压压缩包并进入。双击里面的‘xnretro’程序。
+
+- [下载Linux版XnRetro (32位, tar.gz)][3]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/05/instagram-photo-filters-ubuntu-desktop-app
+
+作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
+[1]:http://www.omgchrome.com/?s=pixlr
+[2]:http://www.omgchrome.com/the-best-chrome-apps-of-2014/
+[3]:http://www.xnview.com/en/xnretro/#downloads
diff --git a/translated/share/20150527 How to Develop Own Custom Linux Distribution From Scratch.md b/translated/share/20150527 How to Develop Own Custom Linux Distribution From Scratch.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..059f07b195
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/share/20150527 How to Develop Own Custom Linux Distribution From Scratch.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+��δ����Լ���Linux���а�
+================================================================================
+���Ƿ�����������Լ���Linux���а棿ÿ��Linux�û�������ʹ��Linux�Ĺ����ж������һ�������Լ��ķ��а棬����һ�Ρ���Ҳ�����⣬��Ϊһ��Linux������Ҳ���ǹ�����һ���Լ���Linux���а档����һ��Linux���а汻����Linux From Scratch (LFS)��
+
+�ڿ�ʼ֮ǰ�����ܽ���һЩLFS�����ݣ����£�
+
+### 1. ��Щ��Ҫ���������Լ���Linux���а����Ӧ���˽����һ��Linux���а棨������ζ�Ŵ�ͷ��ʼ��������һ�����е�Linux���а�IJ�ͬ ###
+
+�����ֻ�����������Ļ��ʾ�����Ƶ�¼�Լ�ӵ�и��õ������ʹ�����顣������ѡ���κ�һ��Linux���а沢�Ұ�������ϲ�ý��и��Ի����á����⣬���������ù��߿���������
+
+������������б�����ļ���boot-loaders���ںˣ���ѡ��ʲô�ñ�����������Ȼ�������Լ�������һ�ж�������ô����ҪLinux From Scratch (LFS)��
+
+**ע��**�������ֻ��Ҫ����Linuxϵͳ����������飬���ָ�ϲ��ʺ��������������������һ��Linux���а棬�������˽���ô��ʼ�Լ�һЩ��������Ϣ����ô���ָ������Ϊ����д��
+
+### 2. ����һ��Linux���а棨LFS���ĺô� ###
+
+- �����˽�Linuxϵͳ���ڲ���������
+- ��������һ��������Ӧ�������ϵͳ
+- ��������ϵͳ��LFS������dz����գ���Ϊ���Ըð���/���ð���ʲôӵ�о��Ե��ƿ�
+- ��������ϵͳ��LFS���ڰ�ȫ���ϻ����
+
+### 3. ����һ��Linux���а棨LFS���Ļ��� ###
+
+����һ��Linuxϵͳ��ζ�Ž�������Ҫ�Ķ�������һ���ұ���֮������Ҫ������ġ����ĺ�ʱ�䡣��������Ҫһ�����õ�Linuxϵͳ���㹻�Ĵ��̿ռ�������Linuxϵͳ��
+
+### 4. ��Ȥ���ǣ�Gentoo/GNU Linux��ij����������ӽ���LFS��Gentoo��LFS������ȫ��Դ�����Ķ��Ƶ�Linuxϵͳ ###
+
+### 5. ��Ӧ����һ���о����Linux�û����Ա����������������൱���˽⣬�����Ǹ�shell�ű���ר�ҡ��˽�һ�ű�����ԣ�C��ã�����ʹ����������Щ������������һ�����֣�ֻҪ����һ�������ѧϰ�ߣ����Ժܿ������֪ʶ����Ҳ���Կ�ʼ������Ҫ���Dz�Ҫ��LFS�����ж�ʧ�������顣 ###
+
+����������ᶨ�����»���LFS���е�һ��ʱ������
+
+### 6. ��������Ҫһ��һ����ָ��������һ��Linux��LFS�Ǵ���Linux�Ĺٷ�ָ�ϡ����ǵĴ��վ��tradepubҲΪ���ǵĶ���������LFS��ָ�ϣ���ͬ������ѵġ� ###
+
+�����Դ��������������Linux From Scratch���鼮��
+
+[][1]
+
+����: [Linux From Scratch][1]
+
+### ���ڣ�Linux From Scratch ###
+
+�Ȿ������LFS����Ŀ��ͷ��Gerard Beekmans�����ģ���Matthew Burgess��Bruse Dubbs���༭�����˶���LFS��Ŀ�������쵼�ˡ��Ȿ�����ݺܹ㷺����338ҳ����
+
+�������ݰ���������LFS��������������Linux��LFS�������������ű���ʹLFS����������¼�����к���������֪����LFS��Ŀ�����ж�����
+
+�Ȿ�黹�����˱���һ������Ԥ��ʱ�䡣Ԥ����ʱ���Ա����һ������ʱ����Ϊ�ο������еĶ���������������ķ�ʽ���֣���������������˵��
+
+������г�ԣ��ʱ�䲢�������Թ����Լ���Linux���а����Ȥ����ô�����Բ������������������飨������أ��Ļ��ᡣ����Ҫ���ģ����������Ȿ����һ��������Linuxϵͳ���κ�Linux���а棬�㹻�Ĵ��̿ռ伴�ɣ��п�ʼ�������Լ���Linuxϵͳ��ʱ������顣
+
+���Linuxʹ�����ԣ���������Լ����ֹ���һ���Լ���Linux���а棬������ֽ���Ӧ��֪����ȫ���ˣ���������Ϣ�����Բο��������ӵ����е����ݡ�
+
+�������˽����Ķ�/ʹ���Ȿ��ľ������Ȿ�꾡��LFSָ�ϵ�ʹ���Ƿ��㹻��������Ѿ�������һ��LFS����������ǵĶ���һЩ���飬��ӭ���Ժͷ�����
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/create-custom-linux-distribution-from-scratch/
+
+���ߣ�[Avishek Kumar][a]
+���ߣ�[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
+У�ԣ�[У����ID](https://github.com/У����ID)
+
+������ [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) ԭ�����룬[Linux�й�](https://linux.cn/) �����Ƴ�
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
+[1]:http://tecmint.tradepub.com/free/w_linu01/prgm.cgi
diff --git a/translated/talk/20150310 FAQ--BSD.md b/translated/talk/20150310 FAQ--BSD.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..97bcd4f246
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/talk/20150310 FAQ--BSD.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+BSD��������
+================================================================================
+
+
+### ������ʷ���в�ͬ�������ڽ�������FreeBSD������... ###
+
+#### ��ô�����Birsa Seva Dal����ô�����أ��ѵ�����һ��ӡ�ȵ�������֯ô�� ####
+
+����Ȥ����������ά���ٿ��ϡ�BSD������������ҳ����Ϊ�˽��������Ц������ô���������������۲������������а棨Berkeley Software Distribution����һ�������������õĸ��㷺�IJ���ϵͳ���塣
+
+#### ��Ǹ���ҿ��Ʋ�ס�Լ�����ô����Щ����ϵͳ����ô�����أ� ####
+
+���죬��Ҫʹ�õ�BSD����ϵͳ�����֡����Ƕ�����Unix�����Ƕ���Դ�����Ҵ�ൣ�η������Ľ�ɫ����Ҳ�ܵ���������������վ����������KDE��Firefox��LibreOffice��Apache��MySQL����������˵�ó����ֵĿ�Դ���������Ƕ����ȶ�����ȫ��֧�����ͬ��Ӳ����
+
+#### ��ϲ�㣡��ղ�������GNU/Linux�� ####
+
+�ǵģ�Linuxӵ���Ҹղ��ᵽ�����ж�������Ҳ��Ϊʲô�ܶ��˴���������BSD�����ճ���ʹ���У�Linux��BSD��û��̫��IJ�ͬ������Ҫ����Ϊ���Ƕ���UnixΪ�����������úܶ������������Ե�¼��Զ����������Vim��дһЩPython���룬ʹ��Mutt�������email�������ܲ�δ��ʶ������ʹ��BSD���������ڿ��ȹ�����ͨ�������ն�ʹ����������֪������BSD��
+
+���������������ڿ���ģ�ͺ�����֤��Ϊ�˽���Щ��������Ҫ�ص���ȥ����BSD�У�B�����ż��������Ǵ�ѧ��������У��University of California, Berkeley������1980����������ǿ�ԴUnix�����ķ�Դ�ء�����90���������x86��PC������У������˶������ǵļ�ͥ�����а�װUnix�����ϵͳ��������Ȥ��һ������386BSD����Ŀ����ʱ�����������ṩ�����Ĺ��ܡ�
+
+#### ��ô�����е�Linux���а��Ǹ�ʱ���������أ� ####
+
+�ʵúã���Ҳ��֪��һ��ǰ��Linus Torvalds�Ѿ������������ںˣ�����GNU��Ŀ���ʱ������������Ŀ�Դ����ϵͳ��Linus��ʱ�Ѿ��ڸ���GNU���ںˣ�Hurd����386BSD������̸���������ʱ�����ں���һ�����Ա������ճ���������ܾͲ��ᴴ��Linux�ˡ����ԣ�90�����ͷ���꣬��Դ����ϵͳ����������û����֪���ĸ�ϵͳ������ʤ����
+
+��������BSD������һЩ�鷳��Unix����Ŀ�����AT&T��ͼ�����ǵĹ����л��һЩ���棬��������BSD�ַ������ǵ�֪ʶ��Ȩ������������1992���һ���Ͻ������������������BSD�Ŀ������̡��������BSDԴ��ķ�֧���뱻��д��������ʱ��GNU/Linux�Ѿ��ḻ�˹��ܣ�����ȶ��������ˡ�
+
+��90�����BSD����֤��GNU/Linux���ӳ��죬���û����Щ�����鷳���������Ѿ���Ϊ��x86 PC�ı��ˡ����죬���ǿ��ܶ���ʹ����������Linux��
+
+#### �����ᵽBSD��Ȼ���㷺��ʹ�ã�����������������ô�� ####
+
+�ǵġ�386BSD�Ŀ���ͣ���ˣ�������ֻ�����Ŷ�������ķ�ʽ���������������������ijɹ�����Ŀ��FreeBSD��Ϊ��ʹ����㷺��BSD�汾����Ŀǰ�Ǻ�Linux�����Ƶ�ϵͳ����������ͷ������汾��Ȼ��NetBSD�۽��ڿ���ֲ�ԣ����������������ڳ���50�ֲ�ͬƽ̨�ϣ�������ͬ���Ĵ���汾������һ���汾��OpenBSD������NetBSD��ʼ���þ���Ϊ�����ߵĿڽǶ���ΪNetBSD�ķ�֧�����ˣ����죬����רע�ڰ�ȫ����������������OpenBSD����������������Ƕ�����Linux�ı�������˵OpenSSH - ���ԣ�������������LibreSSL��
+
+#### ���ԣ������ְ汾��BSD��Linux���а�����ô�� ####
+
+Ҳ��Ҳ���ǣ�ÿ��BSD�汾�����Լ��Ĵ���⡢��ͬ�Ŀ����Ŷӡ��������Ǽ�������õĴ��루������Ӳ�����������������Ǹ���ӵ������ɫ���ŵ��ȱ���������IJ���ϵͳ��
+
+�����ᵽ����BSD�Ŀ���ģ��������������GNU/Linux�������Ҫ�ص㡣��GNU/Linux��û���˶���������и���һЩ�Ŷ���GNU������湤����һЩ�Ŷ��ڿ����ںˣ�һЩ�ڿ��������ű���һЩ��д�ֲᣬһЩ��д��ȵȡ������Ŀ���ģ��ͨ��������ȱ������Ȩ���ġ��������������������ɷ��а渺����ʹ���ж��������ƺϡ�
+
+��BSD���෴�����Ǵ����뻯��Դ�������п�������Ϊһ�����塣�ںˡ��⡢ϵͳ������ĵ�ҳ������һ���ط�������ͬ���ķ�ʽʹ�á�����BSD��˿���ƣ�����ص���˲���ϵͳ�����һ���Ժ��ȶ��ԡ�ͨ������Щ��ʹ��BSD�ľ������������ǿ���֤���ֲ�ҳ�Ѿ���÷dz��걸��
+
+
+
+#### �ѵ�BSDû��ʹ��GNU/Linux���κζ���ô�� ####
+
+�ǵģ�������GCC����ʮ������GNU Compiler Collection�Ѿ���Ϊ��ʵ���ϵ�Unixϵͳ������������FreeBSD����Ѿ�ת��ʹ��LLVM/Clang�ˡ�ֵ��ע�����BSD��������һЩ�����Ŀ�Դ��Ŀ�������Dz�����GNU����Linux������˵X Window System��XFree86��X.org����Perl�ȵȡ������ҿ�����POSIXһ���ı�������������Linux�ϵij��������BSD������汾�ϱ�������С�
+
+��ˣ�������LAMP��Linux��Apache��MySQL��PHP���е�L�ij�FreeBSD���������Ի�ü���ͬ���Ļ������Լ�һЩ��ͬ�����ԣ����磬���ļ�ϵͳ������֧�ַ��棩��FreeBSD�д������û�������Netflix��ÿ���ṩ�����������ݡ�����FreeBSD������һ���õ����滷���������ij������ڷ��������棬��ӵ�г���Ѱ���Ŀɿ��Ժ��������ܡ�
+
+OpenBSD���������ڰ�ȫ��ʮ�ֱ�Ҫ�ij��ϣ���С��Web�����ļ��йܡ�����ǽ�����ء�NetBSD��BSD��Ҫ���а�������е�һ�������������ڼ�������ƽ̨�ϣ��������ϵ�Amigas��Acorn boxes����ʱ�������ڱ�Դ�������豸���ҵ�������Ӱ��
+
+#### �ȵȣ���ô�����˽���Դ�����Դ�أ�����Linux���Dz����ʵ� ####
+
+�Եģ���������̸��������GNU/Linux����Ҫ��ͬ��BSD�汾������֤������Ȥ������BSD����֤���dz���ͬ��������֪��GPL������������˵��BSD���̡�BSD����֤��Ҫ�����ǣ�����ݴ��룬�����������£�����������Ŀ�����Ա������Ȩ�������������㻵��ĵ���ʱ��Ҫ������ϡ�
+
+��ˣ�������֤��û���κ�����ǿ�ƴ��뿪Դ������GPL����Ҫ��ʹ����ݴ�����û������ǵ���Ҳ��Դ����һ��Ҫ�IJ�ͬ�����˻������������ļ������ۣ�BSD�ķ�˿��˵���ǵ�����֤�������ɣ���Ϊ������ô�ϸ���GNU/GPL�ķ�˿˵���ǵ�֤��Ÿ����ɣ���Ϊ�����������������ɣ�
+
+#### ��ѽ��������ô˵�����Ѿ��������ҵ���Ȥ�����������ܳ�����Щ�ɰ���BSD�汾�أ� ####
+
+������Ѿ����Բµ���Щ��վ�� �C [www.openbsd.org][1]��[www.freebsd.org][2]��[www.netbsd.org][3]�����������������ISO������VirtualBox���������ǣ�Ȼ��ʼ��ˣ��������Ѿ�����һ��ʱ���Linux����������Ҫ�˽���Щ������ⲻ��̫�ѡ��������Ѱ��һЩ�����ָ����ѺõĶ�������������PC-BSD��PC-BSD([www.pcbsd.org][4])��һ������FreeBSD�ĸ��Ի����ư汾����רע�����棬�����۵�ͼ�λ���װ���ͳ�����������������ף�������죡
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxvoice.com/faq-bsd-2/
+
+���ߣ�[Mike Saunders][a]
+���ߣ�[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
+У�ԣ�[У����ID](https://github.com/У����ID)
+
+������ [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) ԭ�����룬[Linux�й�](http://linux.cn/) �����Ƴ�
+
+[a]:http://www.linuxvoice.com/author/mike/
+[1]:http://www.openbsd.org/
+[2]:http://www.freebsd.org/
+[3]:http://www.netbsd.org/
+[4]:http://www.pcbsd.org/
diff --git a/translated/talk/20150511 Open Source History--Why Did Linux Succeed.md b/translated/talk/20150511 Open Source History--Why Did Linux Succeed.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..85b2473719
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/talk/20150511 Open Source History--Why Did Linux Succeed.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+开源旧事:Linux为什么能成功?
+================================================================================
+> Linux,这个始于1991年由Lnius Torvalds开发的类Unix操作系统内核已经成为开源世界的中心,人们不禁追问为什么Linux成功了,而包括GNU HURD和BSD在内的那么多相似的项目却失败了?
+
+
+
+自由软件和开源世界的发展史中最令人不解的问题之一是为什么Linux取得了如此辉煌的成功,然而其它同样尝试打造自由开源、类Unix操作系统内核的项目却没能那么成功?这个问题难以回答,但我总结了一些原因,在下面与大家分享。
+
+不过,首先得明确:当我谈论Linux是一个巨大的成功时所表达的含义。我对Linux成功的定义和对其它类Unix操作系统内核不一样,后者中一些是开源的,一些不是,而且它们繁荣发展的时期是Linux诞生的时期。[GNU][1]的HURD,一个发起于[1991年5月][1]的自由但不是免费的内核,便是其中之一。其它的包括现在大部分人都没听说过的Unix,比如由加州大学伯克利分校开发出来的BSD的各种各样Unix衍生版,由微软主导的Unix系统Xenix,包括Minix在内的学术版本Unix,和在AT&T赞助下开发的最初的Unix。在更早的数十年内,它对于学术界和商业届的计算发展至关重要,但到19世纪90年代就已经几乎已经消失在人们的视野里。
+
+#### 相关阅读 ####
+
+- [Open Source History: Tracing the Origins of Hacker Culture and the Hacker Ethic][3]
+- [Unix and Personal Computers: Reinterpreting the Origins of Linux][4]
+
+因此,得说明的是,我所写的是关于内核,而不是完整的操作系统。在很大程度上,Linux内核的成功归功于GNU整个项目。GNU这个项目产生了一套至关重要的工具,包括编译器、调试器和BASH shell的实现,这些对于构建一个类Unix操作系统是必需的。但是GNU的开发者们从没开发出一个HURD内核的可行版本(尽管他们仍在[不懈努力中][5])。相反,Linux呈现出来的则是一个将GNU各个部分紧密连接在一起的内核,尽管这超出了GNU的初衷。
+
+因此,值得人们去追问为什么Linux,一个由Linus Torvalds这个芬兰的无名程序员于1991年——和HURD同一年——发起的内核,能够禁受考验并发展壮大?在当时的大环境下,很多拥有强力商业支持的、由当时炙手可热的黑客领头的类Unix内核都没能够发展起来。为了说明这个问题,我找到了一些和这个问题相关的解释。为此我研究了自由软件和开源世界的发展史,和不同解释的优缺点。
+
+### Linux采用去中心化的开发方式 ###
+
+这个观点来源于Eric S. Raymond的文章,“[大教堂与市集][6]”和其相关资料。这些资料验证了一种情形:当大量的贡献者以一种去中心化的组织结构持续不断地协同合作时,软件开发的效率最佳。Linux的开发证明了这一点,与之相反的是,比如,GNU HURD采用了一种相对更集中化的方法来管理代码开发。其结果如同Raymond所言,显然在十年的时间里都没能成功构建出一个完整的操作系统。
+
+在一定程度上,这个解释有道理,但仍有一些明显的不足。举例来说,Torvalds在指导Linux代码开发过程中毫无争议地承担起一个更加有权威的角色,他可以决定接受或拒绝代码,这一点并非Raymond和其他人所想的那样。其次,这个观点不能解释除了没能开发出一个可行的系统内核外GNU仍然成功地生产出那么多优秀的软件。如果只有去中心化的开发方式才能很好地指导开源软件世界里的项目,那么GNU所有的编程工作都应该是徒劳无功的,但事实并非如此。
+
+### Linux是实用型的,而GNU是空想型的 ###
+
+个人而言,我觉得下面这个说法是最引人注目的,即Linux之所发展得如此迅速是因为它的创建者是一个实用主义者,他起初只是想写一个内核,使其能够在他家里的电脑上运行一个裁剪过的Unix操作系统,而不是成为以改变世界为目标的自由软件的一部分,而后者正是GNU项目的一贯目标。
+
+然而,这个解释仍然有一些不能完全让人信服的地方。特别是,尽管Torvalds本人信奉实用主义的原则,但无论以前还是现在,并非所有参与到他的项目中的成员都和他一样信奉这一原则。尽管如此,Linux仍然取得了成功。
+
+而且,如果实用主义是Linux持续发展的关键,那么就要再问一遍:为什么GNU除了没能开发出一个内核外还是成功地开发出这么多有用的工具?如果拥有某一种对软件的坚定政治信仰是追求成功的项目路上的绊脚石,那么GNU早应该是一个彻头彻尾的失败者,而不会是一个开发了那么多如今依然为IT世界提供坚实基础的优秀软件包的开拓者。
+
+最后(但并不是最不重要),许多诞生于19世纪80年代末期和90年代初期的Unix变体,尤其是一些BSD分支,都是实用主义的产物。它们的开发者们致力于开发出可以自由分享而不是受到高昂商业证书限制的Unix变体,但他们对于编程或者共享代码并非完全局限于意识形态。Torvalds同样如此,因此很难说Linux和成功和其它Unix项目的失败是意识形态在作怪。
+
+### 操作系统设计 ###
+
+当谈到Linux的成功时,不可忽视的是Linux和其它Unix变体之间的诸多技术差异。Richard Stallman,GNU项目的创始人,在一封给我的电子邮件中解释了为什么HURD的开发进度频频滞后:“GNU Hurd确实不是一次实用上的成功。部分原因是它的基本设计使它像是一个研究项目。(我之所以选择这样的设计,是考虑到这是快速实现一个可用内核的捷径。)”
+
+就Torvalds独自编写出Linux的所有代码这点而言,Linux也有别于其它Unix变体。当他在1991年8月[第一次发布Linux][7]时他的一个初衷就是拥有一个属于他自己的Unix,免费共享代码。这点特性使得Linux区别于同时期的大部分Unix变体,后者一般是从AT&T Unix或伯克利的BSD中衍生出基础代码。
+
+我并不是一个计算机科学家,所以我没有资格去评判是否Lunux代码就优于其他Unix代码,以此来解释Linux的成功。虽然这并不能解释Linux和其它Unix内核在文化和人力上的不同,但这个观点对我来说解释得通,因为似乎在理解Linux成功这一点上它比代码更加重要。(译者尽力了+_+)
+
+### Linux背后的社区提供了有力支持 ###
+
+Stallman也写到Linux成功的“主要原因”是“Torvalds使Linux成为一个自由软件,所以相比Hurd有更多来自社区的支持涌入Linux的发展中。”但这对于Linux的成长轨迹并非是一个完美的解释,因为它不能说明为什么自由软件的开发者们追随了Torvalds而不是HURD或其它某个Unix。但它仍然突出了这个转变是Linux盛行的很大一部分。(译者尽力了)
+
+对于自由软件社区支持Linux的决定有一个更全面的理由可以用来解释为什么开发者们这么做。起初,Linux只是一个默默无闻的小项目,以任何标准来衡量,它比同时期其它的一些尝试创建一个更加自由的Unix,比如NET BSD和386/BSD,都要显得微不足道。同样,最初并不清楚Linux和自由软件运行目标的亲和力是怎样。创建伊始,Torvalds只是在一份防止Linux不被商业使用的证书下发布了Linux。至于后来他为了保护源代码的开放性转向使用GNU的通用公开证书则是后话了。
+
+所以,这些就是我所找到的Linux作为一个开源操作系统之所以取得成功的解释,可以肯定Linux的成就在某些方面(但比如桌面版的Linux从未成为它的支持者希望成为的样子)已经是可以衡量的成功。总之,Linux业已以其它任何类Unix操作系统都没有实现的方式成为了计算机世界的基石。也许源于BSD的苹果公司的OS X和iOS系统也很接近这一点,但它们没有在其它方面像Linux影响互联网一样扮演着如此重要的中心角色。
+
+对于为什么Linux能成为它已经成为的样子,或者为什么它在Unix世界的竞争对手们几乎全部变得默默无闻的问题你有其它的想法吗?如果有,我很乐意听到你的想法。(诚然,BSD的变体如今仍有一批追随者,而一些商用的Unix对于[Red Hat][8](RHT)为[他们的用户提供支持][9]来说也仍然十分重要。但这些Unix中没有一个能够像Linux一样几乎征服了从Web服务器到智能手机的每一个领域。)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/050415/open-source-history-why-did-linux-succeed
+
+作者:[hristopher Tozzi][a]
+译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://thevarguy.com/author/christopher-tozzi
+[1]:http://gnu.org/
+[2]:http://www.gnu.org/software/hurd/history/hurd-announce
+[3]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/042915/open-source-history-tracing-origins-hacker-culture-and-ha
+[4]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/042715/unix-and-personal-computers-reinterpreting-origins-linux
+[5]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/042015/30-years-hurd-lives-gnu-updates-open-source-
+[6]:http://www.catb.org/esr/writings/cathedral-bazaar/cathedral-bazaar/
+[7]:https://groups.google.com/forum/#!topic/comp.os.minix/dlNtH7RRrGA[1-25]
+[8]:http://www.redhat.com/
+[9]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/032614/red-hat-grants-certification-award-unix-linux-migration-a
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150302 How to Limit the Network Bandwidth Used by Applications in a Linux System with Trickle.md b/translated/tech/20150302 How to Limit the Network Bandwidth Used by Applications in a Linux System with Trickle.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b8ed29b47c..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20150302 How to Limit the Network Bandwidth Used by Applications in a Linux System with Trickle.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,314 +0,0 @@
-如何在linux上使用Trickle来限制应用程序的网络宽带使用.
-================================================================================
-有没有遇到过系统中的某个应用程序独占了你所有的网络宽带的情形?如果你有过这样的遭遇,那么你就会感受到Trickle宽带调整应用角色的价值.不管你是一个系统管理员还是仅仅Linux用户,都需要学习如何控制应用程序的上下行速度,来确保你的网络宽带不会被某个程序
-霸占.
-
-
-Install Trickle Bandwidth Limit in Linux
-
-### 什么是 Trickle? ###
-
-Trickle是一个网络宽带调整工具,可以让我们管理应用程序的网络上下行速度,使得可以避免其中的某个应用程序吃掉了全部或大部分可用的宽带.换句话说,Trickle可以让你基于单个应用程序来控制
-网络流量速率,而不是仅仅针对与单个用户--在客户端网络环境中经典的宽带调整样例,
-
-### Trickle是如何工作的?###
-
-另外,tricle可以帮助我们基于应用来定义优先级,所以当对整个系统进行了全局限制设定,高优先级的应用依然会自动地获取更多的宽带。为了实现这个目标,tricle设置通过TCP连接的套接字对数
-据发送、数据接收路径的流量限制。我们必须注意到,除了影响传输速率之外,tricle任何时候都不会以任何方式来改变其处理过程。
-
-### Trickle不能做什么? ###
-
-这么说吧,唯一的限制就是,tricle静态连接的应用或者具有SUID或SGID位设置的二进制--因为他们使用动态链接并且将其自身加载到调整过程以及其关联的网络套接字之间。 Trickle此时会在这两种软件
-组件之间扮演代理的角色。
-
-由于trickle并不会需要超级用户的权限来运行,所以用户可以设置用户独立的流量限制,可能这并不是你想要的,我们会探索如何使用全局设定来限制系统中的所有用户的流量限制。也即是说,此时系统中的每个用户具有管理
-各自的流量速率,但是无论如何,都会受到系统管理员给他们设置的边界限制。
-
-在这边文章中,我们会描述如何通过trickle在linux平台上管理应用程序使用的网络宽带。为了生成必要流量,在此会在客户端(CentOS 7 server – dev1: 192.168.0.17)上使用 ncftpput 和
- ncftpget, 在服务器(Debian Wheezy 7.5 – dev2: 192.168.0.15)上使用vsftpd 来进行演示。 相同的指令也可以在RedHat,Fedora和Ubuntu等系统使用。
-
-#### 前提条件 ####
-
-1. 对于 RHEL/CentOS 7/6, [开启EPEL仓库][1]。EPEL的Extra Packages是一个 有Fedora项目维护的高质量、开源的软件仓库,而且百分之百与其衍生产品相兼容,如
-企业版本Linux和CentOS. 在这个仓库中trickle和ncftp两者都是可用的。
-
-2. 按照如下方式安装ncftp:
-
- # yum update && sudo yum install ncftp [On RedHat based systems]
- # aptitude update && aptitude install ncftp [On Debian based systems]
-
-3. 在单独的服务器上设置一个FTP服务器。需要注意的是,尽管FTP天生就不安全,但是
-仍然被广泛应用在安全性无关紧要的文件上传下载中。 在这篇文章中我们使用它来演示
-trickle的优点,同时它也会在客户端的标准输出流中显示传输速率,我们将是否在另外
-的日期时间中使用放在一边讨论。
-
- # yum update && yum install vsftpd [On RedHat based systems]
- # aptitude update && aptitude install vsftpd [On Debian based systems]
-
-现在,在FTP服务器上按照以下方式编辑 /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf 文件。
-
- anonymous_enable=NO
- local_enable=YES
- chroot_local_user=YES
- allow_writeable_chroot=YES
-
-在此之后,确保在你的当前会话中开启了vsftpd,并在之后的启动中让其自动启动。
-
- # systemctl start vsftpd [For systemd-based systems]
- # systemctl enable vsftpd
- # service vsftpd start [For init-based systems]
- # chkconfig vsftpd on
-
-4. 如果你选在在一个CentOS/RHEL 7中为FTP服务器的远程访问配备SSH秘钥,你需要
-一个具有适合访问root目录之外的目录和文件内容上传下载权限并密码受保护的用户账户。
-
-你可以通过在你的浏览器中输入以下的URL来浏览你的Home目录。一个登陆窗口会弹出来
-提示你输入FTP服务器中的有效的用户名和密码。
-
- ftp://192.168.0.15
-
-如果验证成功,你就会看到你的home目录中的内容。该教程的稍后部分中,你将可以刷新
-页面来显示在你之前上传过的文件。
-
-
-FTP Directory Tree
-
-### 如何在Linux中安装 Tricle ###
-
-1. 通过yum或aptitude来安装tricle.
-
-为了确保能够成功安装,最好在安装工具之前,保证当前的安装包是最新的版本。
-
-
- # yum -y update && yum install trickle [On RedHat based systems]
- # aptitude -y update && aptitude install trickle [On Debian based systems]
-
-2. 确认trickle是否对特定的二进制包有用。
-
-之前我们解释过,trickle只对使用动态或共享包的二进制包有用。为了确认我们是否可以对某个特定的应用使用trickle,我们可以使用著名的ldd(
-列出动态依赖)工具。 特别地,我们会查看任何给定程序的动态依赖中检查其当前使用的glibc,因为其准确地定义了使用套接字交流中使用的系统调用。
-
-对一个给定的二进制包执行以下命令来查看是否能对其使用trickle进行宽带调整:
-
- # ldd $(which [binary]) | grep libc.so
-
-例如,
-
- # ldd $(which ncftp) | grep libc.so
-
-其输出是:
-
- # libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007efff2e6c000)
-
-输出中的括号中的字符可能在不同的系统平台中发生改变,甚至相同的命令在不同的时候运行也会,因为其代表包加载到物理内存中的地址。
-
-如果上面的命令没有返回任何的结果,就说明这个二进制包没有使用libc包,因此tricle对其不能起到宽带调整的作用。
-
-### 学习如何使用Trickle###
-
-最基本的用法就是使用其单模式,通过这种方式,trickle用来显示地定义给定应用程序的上传下载速率。如前所述,为了简单性,我们会使用相同的应用
-来进行上传下载测试。
-
-#### 在单模式下运行trickle####
-
-我们会比较在有无trickle的情况下的上传下载速率, ‘-d’选项指示下载速率(KB/s单位),而'-u'选项指示相同单位的上传速率。另外我们会使用到‘-s’
-选项来指定trickle应该以单模式运行。
-
-以单模式运行trickle的基本语法如下:
-
- # trickle -s -d [download rate in KB/s] -u [upload rate in KB/s]
-
-为了能够让你自己运行以下样例,确保你在自己的客户端安装了trickle和ncftp(我的是192.168.0.17)。
-
-**样例1:在有无trickle的情况下上传一个2.8 MB的PDF文件。**
-
-我们使用一个自由发布的LInux基础知识PDF文件来进行下面的测试[文件链接][2]。
-
-你可以首先使用下面的命令将这个文件下载到你当前的工作目录中:
- # wget http://linux-training.be/files/books/LinuxFun.pdf
-
-下面是在没有trickle的情况下将一个文件上传到我们的FTP服务器的语法:
-
- # ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /remote_directory local-filename
-
-其中的 /remote_directory 是相对于用户名的Home目录的上传路径,而local-filename是一个你当前工作目录中的文件。
-
-特别的是,在没有trickle的情形下,我们可以得到上传峰值速率52.02MB/s(请注意,这个不是真正的平均上传速率,而是峰值开始的瞬时值),而且这个文件几乎
-在瞬间就完成了上传。
-
- # ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir LinuxFun.pdf
-
-输出:
-
- LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 52.02 MB/s
-
-在使用trickle的情况下,我们会限制上传速率在5KB/s。在第二次上传文件之前,我们需要在目标目录中删除这个文件,否则ncftp就会通知我们在目标
-目录中已经存在了与上传文件相同的文件,从而不会执行文件的传输:
- # rm /absolute/path/to/destination/directory/LinuxFun.pdf
-
-然后:
-
- # trickle -s -u 5 ncftpput -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 /testdir LinuxFun.pdf
-
-输出:
-
- LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 4.94 kB/s
-
-在上面的样例中,我们看到平均的上传速率下降到了5KB/s。
-
-**样例2:在有无trickle的情况下下载相同过得2.8MB的PDF文件**
-
-首先,记得从原来的源文目录中删除这个PDF:
-
- # rm /absolute/path/to/source/directory/LinuxFun.pdf
-
-请注意,下面的样例中将远程的文件下载到客户端机器的当前目录下,这是由FTP服务器的IP地址后面的·.·决定的。
-
-没有trickle的情况下:
-
- # ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/LinuxFun.pdf
-
-输出:
-
- LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 260.53 MB/s
-
-在有trickle的情况下,限制下载速率在20KB/s:
-
- # trickle -s -d 30 ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/LinuxFun.pdf
-
-输出:
-
- LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 17.76 kB/s
-
-### 在有监督的模式下运行Trickle [未管理的]###
-
-Tricle也可以在未管理的模式下运行,通过跟随在/etc/tricled.conf文件中定义的一系列参数。 这个文件定义了守护线程 trickled的行为以及如何管理tricle。
-
-另外,如果你想要全局设置被所有的应用程序使用的话,我们就会需要使用tricle命令。 这个命令运行守护线程并允许我们通过trickle定义所有应用程序共享的上传下载限制,不需要我们每次来进行指定。
-
-例如,运行:
-
- # trickled -d 50 -u 10
-
-会导致任何通过tricle运行的应用程序的上传下载速率分别限制在30kb/s和10kb/s。
-
-请注意,你可以在任何时间都能确认守护线程tricled是否正在运行以及其运行参数:
-
- # ps -ef | grep trickled | grep -v grep
-
-输出:
-
- root 16475 1 0 Dec24 ? 00:00:04 trickled -d 50 -u 10
-
-**样例3:在是否使用tricle的情形下上传一个 19MB 的mp4文件到我们的FTP服务器。**
-
-在这个样例中,我们会使用“He is the gift”的自由分布视频,可以通过这个[链接][3]下载。
-
-我们将会在开始通过以下的命令将这个文件下载到你的当前工作目录中:
-
- # wget http://media2.ldscdn.org/assets/missionary/our-people-2014/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
-
-首先,我们会使用之前列出的命令来开启守护进程trickled:
-
- # trickled -d 30 -u 10
-
-在没有trickle时:
-
- # ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
-
-输出:
-
- 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 36.31 MB/s
-
-有trickle的时:
-
- # trickle ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
-
-输出:
-
- 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 9.51 kB/s
-
-我们可以看到上面的输出,上传的速率下降到了约 10KB/s。
-
-** 样例4:在有无trickle的情形下下载这个相同的视频 **
-
-与样例2一样,我们会将该文件下载到当前工作目录中。
-
-在没有trickle时:
-
- # ncftpget -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 . /testdir/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
-
-输出:
-
- 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 108.34 MB/s
-
-有trickle的时:
-
- # trickle ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
-
-输出:
- 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 29.28 kB/s
-
-上面的结果与我们之前设置的下载限速相对应(30KB/s)。
-
-**注意:** 一旦守护进程开启之后,没有必要使用trickle来为每个应用程序来单独设置限制。
-
-如前所述,每个人都可以进一步地通过tricled.conf来客制化tricle的宽带速率调整,该文件的一个典型的分区有以下部分组成:
-
- [service]
- Priority = <value>
- Time-Smoothing = <value>
- Length-Smoothing = <value>
-
-其中,
-
-- [service] 用来指示我们想要对其进行宽带使用调整的应用程序名称
-- Priority 用来让我们为某个服务制定一个相对于其他服务高的优先级,这样就不允许守护进程管理中的一个单独的应用程序来占用所有的宽带。越小的数字代表更高的优先级。
-- Time-Smoothing [以秒计]: 定义了trickled让各个应用程序传输或接收数据的时间间隔。小的间隔值(0.1-1秒)对于交互式应用程序是理想的,因为这样会具有一个更加平滑的会话体验,而一个相对较大
-的时间间隔值(1-10秒)对于需要批量传输应用程序就会显得更好。如果没有指定该值,默认是5秒。
-- Length-smoothing [KB 单位]: 该想法与Time-Smoothing如出一辙,但是是基于I/O操作而言。如果没有指定值,会使用默认的10KB。
-
-平滑值的改变会被翻译为将指定的服务的使用一个间隔值而不是一个固定值。不幸的是,没有一个特定的公式来计算间隔值的上下限,主要依赖于特定的应用场景。
-
-下面是一个在CentOS 7 客户端中的tricled.conf 样例文件(192.168.0.17):
-
- [ssh]
- Priority = 1
- Time-Smoothing = 0.1
- Length-Smoothing = 2
-
- [ftp]
- Priority = 2
- Time-Smoothing = 1
- Length-Smoothing = 3
-
-使用该设置,tricled会为SSH赋予比FTP较高的传输优先级。值得注意的是,一个交互进程,例如SSH,使用了一个较小的时间间隔值,然而一个处理批量数据传输的服务如FTP使用一个较大的时间
-间隔来负责之前的样例中的上传下载速率,尽管不是百分百的有trickled指定的值,但是也已经非常接近了。
-
-### 总结 ###
-在该文章中,我们探索了任何使用trickle在基于Fedora发行版和Debian衍生版平台上来限制应用程序的宽带使用.也包含了其他的可能用法,但是不对以下情形进行限制:
-
-- 限制系统下载工具的下载速度,例如[wget][4],或 BT客户端.
-
-- 限制你的系统的包管理工具`[yun][5]`更新的速度 (如果是基于Debian系统的话,其包管理工具为`[aptitude][6]`)。
-
-- 如果你的服务器是在一个代理或防火墙后面(或者其本身即是代理或防火墙的话),你可以使用trickle来同时设定下载和上传速率,或者与客户端或外部交流速率。
-
-欢迎提问或留言.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.tecmint.com/manage-and-limit-downloadupload-bandwidth-with-trickle-in-linux/
-
-作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
-译者:[theo-l](https://github.com/theo-l)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
-[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-enable-epel-repository-for-rhel-centos-6-5/
-[2]:http://linux-training.be/files/books/LinuxFun.pdf
-[3]:http://media2.ldscdn.org/assets/missionary/our-people-2014/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
-[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-wget-command-examples-in-linux/
-[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
-[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/dpkg-command-examples/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150304 Monitoring Your Network And Servers With Observium.md b/translated/tech/20150304 Monitoring Your Network And Servers With Observium.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9c78793904..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20150304 Monitoring Your Network And Servers With Observium.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,172 +0,0 @@
-
-使用Observium来监控你的网络和服务器
-================================================================================
-### 简介###
-
-在监控你的服务器,交换机或者物理机器时有过问题吗?, **Observium**可以满足你的需求.作为一个免费的监控系统,可以帮助你远程监控你的服务器.它是一个由PHP编写的基于自动发现SNMP的网络监控平台,支持非常广泛的网络硬件和操作系统,包括 Cisco,Windows,Linux,HP,NetApp等.在此我会通过在Ubuntu12.04上设置一个**Observium**服务器的同时提供相应的步骤.
-
-
-
-目前存在两种不同的**observium**版本.
-
-- Observium 社区版本是一个在QPL开源许可证下的免费工具,这个版本时对于较小部署的最好解决方案. 该版本每6个月得到一次安全性更新.
-- 第2个版本是Observium Professional, 该版本在基于SVN的发布机制下的发行版. 会得到每日安全性更新. 该工具适用于服务提供商和企业级部署.
-
-更多信息可以通过其官网获得[website of Observium][1].
-
-### 系统需求###
-
-为了安装 **Observium**, 需要具有一个最新安装的服务器。**Observium**是在Ubuntu LTS和Debian系统上进行开发的,所以推荐在Ubuntu或Debian上安装**Observium**,因为可能在别的平台上会有一些小问题。
-
-该文章会知道你如何在Ubuntu12.04上进行安装**Observium**。对于小型的**Observium**安装,推荐的基础配置要有256MB内存和双核处理器。
-
-### 安装需求 ###
-
-在安装**Observuim**之前,你需要确认安装所有的依赖关系包。
-
-首先,使用下面的命令更新的服务器:
-
- sudo apt-get update
-
-然后你需要安装运行Observuim 所需的全部包。
-
-Observium需要使用下面所列出的软件才能正确的运行:
-
-- LAMP server
-- fping
-- Net-SNMP 5.4+
-- RRDtool 1.3+
-- Graphviz
-
-对于可选特性的要求:
-
-- Ipmitool - 只有当你想要探寻IPMI(Intelligent Platform Management Interface智能平台管理接口)基板控制器。
-- Libvirt-bin - 只有当你想要使用libvirt进行远程VM主机监控时。
-
- sudo apt-get install libapache2-mod-php5 php5-cli php5-mysql php5-gd php5-mcrypt php5-json php-pear snmp fping mysql-server mysql-client python-mysqldb rrdtool subversion whois mtr-tiny ipmitool graphviz imagemagick libvirt ipmitool
-
-### 为Observium创建MySQL 数据库和用户。
-
-现在你需要登录到MySQL中并为**Observium**创建数据库:
- mysql -u root -p
-
-在用户验证成功之后,你需要按照下面的命令创建该数据库。
-
- CREATE DATABASE observium;
-
-数据库名为**Observium**,稍后你会需要这个信息。
-
-现在你需要创建数据库管理员用户。
-
- CREATE USER observiumadmin@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'observiumpassword';
-
-接下来,你需要给该管理员用户相应的权限来管理创建的数据库。
-
- GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON observium.* TO observiumadmin@localhost;
-
-你需要将权限信息写回到磁盘中来激活新的MySQL用户:
-
- FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
- exit
-
-### 下载并安装 Observium###
-
-现在我们的系统已经准备好了, 可以开始Observium的安装了。
-
-第一步,创建Observium将要使用的文件目录:
- mkdir -p /opt/observium && cd /opt
-
-为了达到本教程的目的,我们将会使用Observium的社区/开源版本。使用下面的命令下载并解压:
-
- wget http://www.observium.org/observium-community-latest.tar.gz
- tar zxvf observium-community-latest.tar.gz
-
-现在进入到Observium目录。
-
- cd observium
-
-将默认的配置文件'**config.php.default**'复制到'**config.php**',并将数据库配置选项填充到配置文件中:
-
- cp config.php.default config.php
- nano config.php
-
-----------
-
- / Database config
- $config['db_host'] = 'localhost';
- $config['db_user'] = 'observiumadmin';
- $config['db_pass'] = 'observiumpassword';
- $config['db_name'] = 'observium';
-
-现在为MySQL数据库设置默认的数据库模式:
- php includes/update/update.php
-
-现在你需要创建一个文件目录来存储rrd文件,并修改其权限以便让apache能将写入到文件中。
-
- mkdir rrd
- chown apache:apache rrd
-
-为了在出现问题时进行问题修理,你需要创建日志文件。
-
- mkdir -p /var/log/observium
- chown apache:apache /var/log/observium
-
-现在你需要为Observium创建虚拟主机配置。
-
- <VirtualHost *:80>
- DocumentRoot /opt/observium/html/
- ServerName observium.domain.com
- CustomLog /var/log/observium/access_log combined
- ErrorLog /var/log/observium/error_log
- <Directory "/opt/observium/html/">
- AllowOverride All
- Options FollowSymLinks MultiViews
- </Directory>
- </VirtualHost>
-
-下一步你需要让你的Apache服务器的rewrite(重写)功能生效。
-
-为了让'mod_rewrite'生效,输入以下命令:
-
- sudo a2enmod rewrite
-
-该模块在下一次Apache服务重启之后就会生效。
-
- sudo service apache2 restart
-
-###配置Observium###
-
-在登入网络接口之前,你需要为Observium创建一个管理员账户(级别10)。
-
- # cd /opt/observium
- # ./adduser.php admin adminpassword 10
- User admin added successfully.
-
-下一步为发现和探寻工作设置一个cron任务,创建一个新的文件‘**/etc/cron.d/observium**’ 并在其中添加以下的内容。
-
- 33 */6 * * * root /opt/observium/discovery.php -h all >> /dev/null 2>&1
- */5 * * * * root /opt/observium/discovery.php -h new >> /dev/null 2>&1
- */5 * * * * root /opt/observium/poller-wrapper.py 1 >> /dev/null 2>&1
-
-重载cron进程来获取系的人物实体。
-
- # /etc/init.d/cron reload
-
-好啦,你已经完成了Observium服务器的安装拉! 使用你的浏览器登录到**http://<Server IP>**,然后上路巴。
-
-
-
-尽情享受吧!
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://www.unixmen.com/monitoring-network-servers-observium/
-
-作者:[anismaj][a]
-译者:[theo-l](https://github.com/theo-l)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://www.unixmen.com/author/anis/
-[1]:http://www.observium.org/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150309 List Of Free Windows SSH Client Tools To Connect To Your Linux Server .md b/translated/tech/20150309 List Of Free Windows SSH Client Tools To Connect To Your Linux Server .md
deleted file mode 100644
index ccb4bc2fec..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20150309 List Of Free Windows SSH Client Tools To Connect To Your Linux Server .md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
-在windows下,连接你的Linux服务器的ssh免费客户端工具列举\
-================================================================================
-你的操作系统是Windows,而你想要连接Linux服务器相互传送文件.于是你需要一个Secure Shell,简称SSH.实际上,SSH是一个网络协议,允许你通过网络连接到Linux和Unix服务器.SSH使用公钥加密来认证远程的计算机.你可以有多种途径使用SSH,要么自动地连接,或者使用密码认证登录.
-
-本篇文章讲述了几种SSH客户端,供选择使用来连接你的Linux服务器.
-
-我们开始.
-
-### Putty ###
-
-**Putty**是最有名的SSH和telnet客户端,最初由Simon Tatham为Windows平台开发.Putty是一款开源软件,有可用的源代码,和一群志愿者的发展和支持.
-
-
-
-Putty非常易于安装和使用,通常你不需要改大部分的配置选项.你只需要输入少量基本的参赛,就可以开始最简单的对话连接[here][1].
-
-### Bitvise SSH Client ###
-
-**Bitvise SSH **是一款支持SSH和SFTP的Windows客户端.由Bitvise专业地提供支持和发展.这款SSH客户端性能强悍,易于安装和使用.Bitvise SSH客户端功能丰富,拥有图形界面,通过一个有自动重连能力的内置代理允许用户动态端口运行.
-
-
-
-Bitvise SSH客户端对个人用户使用**是**免费的,同时对于在组织内部的单独商业使用也一样.你可以[在这里下载Bitvise SSH客户端][2]
-
-### MobaXterm ###
-
-**M偶吧Xterm**是你的**终极工具箱,解决远程计算**.在单一的Windows应用里,它提供了许多裁剪过的的功能,针对程序员,网络管理者,IT管理员和相当一部分需要在更简单界面(此处原文为in a more simple fashion,有点费解)远程作业的用户.
-
-
-
-MobaXterm提供了所有重要的**远程网络工具** (如SSH, X11, RDP, VNC, FTP, MOSH 等等),和**Unix 命令**(bash, ls, cat, sed, grep, awk, rsync等等)适用于Windows桌面,在一个**单独便于携带的可执行文件里**,其工作独立于工具箱.MobaXterm对**个人使用免费**.你可以下载MobaXterm[在这里][3].
-
-### DameWare SSH ###
-
-我认为**DameWare SSH**是最好的免费SSH客户端.
-
-
-
-这个免费工具是一个终端模拟器,可以让你实现从一个易用控制台的多种telnet和SSH连接.
-
--用一个带标签的控制台界面管理多方会话
--在Windows文件系统中保存喜欢的会话
--获取多个保存的证书集合,用于轻松登录不同的设备
--使用telnet,SSH1和SSH2协议连接计算机和设备
-
-你可以从[这个链接][4]下载 **DameWare SSH**
-
-### SmarTTY ###
-
-SmarTTY是一款免费的多标签SSH客户端,支持使用SCP命令及时复制文件和目录
-
-
-
-大多数SSH服务器每次连接支持最多10个子会话.SmarTTY在这方面做得很好:没有烦人的多个窗口,不需要重新登录,仅仅打开一个新的标签页就可以开始了!
-
-### Cygwin ###
-
-Cygwin是一款GNU和开源工具的大杂烩,提供的功能近似一个Windows平台下的Linux.
-
-
-
-**Cygwin**包括了一个Unix系统,集模拟库,cygwin.dll,GNU大量集合和其他被归类了的大量可选免费应用软件包.在这些安装包中,有高质量的编译器和其他软件开发工具,一个X11服务器,一套完整的X11开发套件,GNU emacs编辑器,Tex和LaTeX,openSSH(客户端和服务器),除此之外还有很多,包括在微软Windows下需要编译和使用PhysioToolkit软件的每一样东西.
-
-读完我们的文章后,不知你中意哪一款SSH客户端?你可以留下你的评论,描述你喜欢的系统和选择的原因.当然,如果有另外的SSH客户端没有被本文列举出来,你可以帮助我们补充.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://www.unixmen.com/list-free-windows-ssh-client-tools-connect-linux-server/
-
-作者:[anismaj][a]
-译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://www.unixmen.com/author/anis/
-[1]:http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html
-[2]:http://www.bitvise.com/download-area
-[3]:http://mobaxterm.mobatek.net/download.html
-[4]:http://www.dameware.com/downloads/registration.aspx?productType=ssh&AppID=17471&CampaignID=70150000000PcNM
-[5]:http://cygwin.com/packages/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150323 How to set up networking between Docker containers.md b/translated/tech/20150323 How to set up networking between Docker containers.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3481dd8faa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150323 How to set up networking between Docker containers.md
@@ -0,0 +1,160 @@
+如何在 Docker 容器之间设置网络
+================================================================================
+你也许已经知道了,Docker 容器技术是现有的成熟虚拟化技术的一个替代方案。它被企业应用在越来越多的领域中,比如快速部署环境、简化基础设施的配置流程、多客户环境间的互相隔离等等。当你开始在真实的生产环境使用 Docker 容器去部署应用沙箱时,你可能需要用到多个容器部署一套复杂的多层应用系统,其中每个容器负责一个特定的功能(例如负载均衡、LAMP 栈、数据库、UI 等)。
+
+那么问题来了:有多台宿主机,我们事先不知道会在哪台宿主机上创建容器,如果保证在这些宿主机上创建的容器们可以互相联网?
+
+联网技术哪家强?开源方案找 [weave][1]。这个工具可以为你省下不少烦恼。听我的准没错,谁用谁知道。
+
+于是本教程的主题就变成了“**如何使用 weave 在不同主机上的 Docker 容器之间设置网络**”。
+
+### Weave 是如何工作的 ###
+
+
+
+让我们先来看看 weave 怎么工作:先创建一个由多个 peer 组成的对等网络,每个 peer 是一个虚拟路由器容器,叫做“weave 路由器”,它们分布在不同的宿主机上。这个对等网络的每个 peer 之间会维持一个 TCP 链接,用于互相交换拓扑信息,它们也会建立 UDP 链接用于容器间通信。一个 weave 路由器通过桥接技术连接到其他本宿主机上的其他容器。当处于不同宿主机上的两个容器想要通信,一台宿主机上的 weave 路由器通过网桥截获数据包,使用 UDP 协议封装后发给另一台宿主机上的 weave 路由器。
+
+每个 weave 路由器会刷新整个对等网络的拓扑信息,像容器的 MAC 地址(就像交换机的 MAC 地址学习一样获取其他容器的 MAC 地址),因此它可以决定数据包的下一跳是往哪个容器的。weave 能让两个处于不同宿主机的容器进行通信,只要这两台宿主机在 weave 拓扑结构内连到同一个 weave 路由器。另外,weave 路由器还能使用公钥加密技术将 TCP 和 UDP 数据包进行加密。
+
+### 准备工作 ###
+
+在使用 weave 之前,你需要在所有宿主机上安装 Docker[2] 环境,参考[这些][3][教程][4],在 Ubuntu 或 CentOS/Fedora 发行版中安装 Docker。
+
+Docker 环境部署完成后,使用下面的命令安装 weave:
+
+ $ wget https://github.com/zettio/weave/releases/download/latest_release/weave
+ $ chmod a+x weave
+ $ sudo cp weave /usr/local/bin
+
+注意你的 PATH 环境变量要包含 /usr/local/bin 这个路径,请在 /etc/profile 文件中加入一行(LCTT 注:要使环境变量生效,你需要执行这个命令: src /etc/profile):
+
+ export PATH="$PATH:/usr/local/bin"
+
+在每台宿主机上重复上面的操作。
+
+Weave 在 TCP 和 UDP 上都使用 6783 端口,如果你的系统开启了防火墙,请确保这两个端口不会被防火墙挡住。
+
+### 在每台宿主机上开启 Weave 路由器 ###
+
+当你想要让处于在不同宿主机上的容器能够互相通信,第一步要做的就是在每台宿主机上开启 weave 路由器。
+
+第一台宿主机,运行下面的命令,就会创建并开启一个 weave 路由器容器(LCTT 注:前面说过了,weave 路由器也是一个容器):
+
+ $ sudo weave launch
+
+第一次运行这个命令的时候,它会下载一个 weave 镜像,这会花一些时间。下载完成后就会自动运行这个镜像。成功启动后,终端会打印这个 weave 路由器的 ID 号。
+
+下面的命令用于查看路由器状态:
+
+ $ sudo weave status
+
+
+
+第一个 weave 路由器就绪了,目前为止整个 peer 对等网络中只有一个 peer 成员。
+
+你也可以使用 doceker 的命令来查看 weave 路由器的状态:
+
+ $ docker ps
+
+
+
+第二台宿主机部署步骤稍微有点不同,我们需要为这台宿主机的 weave 路由器指定第一台宿主机的 IP 地址,命令如下:
+
+ $ sudo weave launch <first-host-IP-address>
+
+当你查看路由器状态,你会看到两个 peer 成员:当前宿主机和第一个宿主机。
+
+
+
+当你开启更多路由器,这个 peer 成员列表会更长。当你新开一个路由器时,要指定前一个宿主机的 IP 地址,请注意不是第一个宿主机的 IP 地址。
+
+现在你已经有了一个 weave 网络了,它由位于不同宿主机的 weave 路由器组成。
+
+### 把不同宿主机上的容器互联起来 ###
+
+接下来要做的就是在不同宿主机上开启 Docker 容器,并使用虚拟网络将它们互联起来。
+
+假设我们创建一个私有网络 10.0.0.0/24 来互联 Docker 容器,并为这些容器随机分配 IP 地址。
+
+如果你想新建一个能加入 weave 网络的容器,你就需要使用 weave 命令来创建,而不是 docker 命令。原因是 weave 命令内部会调用 docker 命令来新建容器然后为它设置网络。
+
+下面的命令是在宿主机 hostA 上建立一个 Ubuntu 容器,然后将它放到 10.0.0.0/24 网络中,分配的 IP 地址为 10.0.0.1:
+
+ hostA:~$ sudo weave run 10.0.0.1/24 -t -i ubuntu
+
+成功运行后,终端会打印出容器的 ID 号。你可以使用这个 ID 来访问这个容器:
+
+ hostA:~$ docker attach <container-id>
+
+在宿主机 hostB 上,也创建一个 Ubuntu 容器,IP 地址为 10.0.0.2:
+
+ hostB:~$ sudo weave run 10.0.0.2/24 -t -i ubuntu
+
+访问下这个容器的控制台:
+
+ hostB:~$ docker attach <container-id>
+
+这两个容器能够互相 ping 通,你可以通过容器的控制台检查一下。
+
+
+
+如果你检查一下每个容器的网络配置,你会发现有一块名为“ethwe”的网卡,你分配给容器的 IP 地址出现在它们那里(比如这里分别是 10.0.0.1 和 10.0.0.2)。
+
+
+
+### Weave 的其他高级用法 ###
+
+weave 提供了一些非常巧妙的特性,我在这里作下简单的介绍。
+
+#### 应用分离 ####
+
+使用 weave,你可以创建多个虚拟网络,并为每个网络设置不同的应用。比如你可以为一群容器创建 10.0.0.0/24 网络,为另一群容器创建 10.10.0.0/24 网络,weave 会自动帮你维护这些网络,并将这两个网络互相隔离。另外,你可以灵活地将一个容器从一个网络移到另一个网络而不需要重启容器。举个例子:
+
+首先开启一个容器,运行在 10.0.0.0/24 网络上:
+
+ $ sudo weave run 10.0.0.2/24 -t -i ubuntu
+
+然后让它脱离这个网络:
+
+ $ sudo weave detach 10.0.0.2/24 <container-id>
+
+最后将它加入到 10.10.0.0/24 网络中:
+
+ $ sudo weave attach 10.10.0.2/24 <container-id>
+
+
+
+现在这个容器可以与 10.10.0.0/24 网络上的其它容器进行通信了。当你要把容器加入一个网络,而这个网络暂时不可用时,上面的步骤就很有帮助了。
+
+#### 将 weave 网络与宿主机网络整合起来 ####
+
+有时候你想让虚拟网络中的容器能访问物理主机的网络。或者相反,宿主机需要访问容器。为满足这个功能,weave 允许虚拟网络与宿主机网络整合。
+
+举个例子,在宿主机 hostA 上一个容器运行在 10.0.0.0/24 中,运行使用下面的命令:
+
+ hostA:~$ sudo weave expose 10.0.0.100/24
+
+这个命令把 IP 地址 10.0.0.100 分配给宿主机 hostA,这样一来 hostA 也连到了 10.0.0.0/24 网络上了。很明显,你在为宿主机选择 IP 地址的时候,需要选一个没有被其他容器使用的地址。
+
+现在 hostA 就可以访问 10.0.0.0/24 上的所有容器了,不管这些容器是否位于 hostA 上。好巧妙的设定啊,32 个赞!
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+如你所见,weave 是一个很有用的 docker 网络配置工具。这个教程只是[它强悍功能][5]的冰山一角。如果你想进一步玩玩,你可以试试它的以下功能:多跳路由功能,这个在 multi-cloud 环境(LCTT 注:多云,企业使用多个不同的云服务提供商的产品,比如 IaaS 和 SaaS,来承载不同的业务)下还是很有用的;动态重路由功能是一个很巧妙的容错技术;或者它的分布式 DNS 服务,它允许你为你的容器命名。如果你决定使用这个好东西,欢迎分享你的使用心得。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/networking-between-docker-containers.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
+[1]:https://github.com/zettio/weave
+[2]:http://xmodulo.com/recommend/dockerbook
+[3]:http://xmodulo.com/manage-linux-containers-docker-ubuntu.html
+[4]:http://xmodulo.com/docker-containers-centos-fedora.html
+[5]:http://zettio.github.io/weave/features.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150324 How to Interactively Create a Docker Container.md b/translated/tech/20150324 How to Interactively Create a Docker Container.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9661e8d3f2..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20150324 How to Interactively Create a Docker Container.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,99 +0,0 @@
-如何交互式地创建一个Docker容器
-===============================================================================
-大家好,今天我们来学习如何使用一个docker镜像交互式地创建一个Docker容器。一旦我们从镜像中启动一个Docker进程,Docker就会在父镜像与子镜像间来回搬运,重复工作,直到到达子镜像。然后联合文件系统会在顶层添加一个读写层。读写层又叫一个 **Container** 包含一些信息,关于它的父镜像和一些其他的信息,如单独的ID,网络配置和资源限制。容器已经声明,他们可以从 **running** 切换到 **exited** 状态。一个处于 **running** 状态的容器包含了很多分支在CPU上面运行,独立于其他在主机上运行的进程,而主机上 **exited** 是文件系统的状态,它的退出变量值是保留的。你可以使用读写层来启动,停止和重启一个容器。
-
-Docker技术为IT界带来了巨大的改变,它使得云服务可以用来共享应用和工作流程自动化,使得应用可以从组件快速组合,消除了开发与品质保证和产品环境间的摩擦。在这篇文章中,我们将会建立CentOS环境,然后维护一个网站,在Apache网络服务器下运行。
-
-这是快速且容易的教程,讨论我们怎样使用一个交互的shell,以一个交互的方式来创建一个容器。
-
-### 1. 运行一个Docker实例 ###
-
-Docker一开始尝试从本地取得和运行所需的镜像,如果在本地主机上没有发现,它就会从[Docker公共注册中心][1]拉取。这里,我们将会在一个DOcker容器里取得并创建一个fedora实例,附加一个bash shell到tty
-
- # docker run -i -t fedora bash
-
-
-
-### 2.安装Apache网络服务器 ###
-
-现在,在我们的Fedora基本镜像准备好后,我们将会开始交互式地安装Apache网络服务器,而不必为它创建Dockerfile。为了做到这点,我们需要在终端或者shell运行以下命令。
-
- # yum update
-
-
-
- # yum install httpd
-
-
-
- # exit
-
-### 3.Saving the Image ###
-
-现在,我们要去保存在Fedora实例里做的修改。要做到这个,我们首先需要知道实例的容器ID。而为了得到ID,我们又需要运行以下命令。
-
- # docker ps -a
-
-
-
-然后,我们会保存这些改变为一个新的镜像,请运行以下命令。
-
- # docker commit c16378f943fe fedora-httpd
-
-
-
-这里,修改已经通过使用容器ID保存起来了,镜像名字叫fedora-httpd。为了确认新的镜像时候在运行,我们将运行以下命令
-
- # docker images
-
-
-
-### 4. 添加内容到新的镜像 ###
-
-我们自己新的Fedora Apache镜像正成功的运行,现在我们想添加一些网页内容到Apache网络服务器,包括我们的网站,使得网站能够脱离盒子正确运行。为做到这点,我们需要创建一个新的Dockerfile,它会处理从复制网页内容到使用80端口的所有操作。而为做到这,我们又需要使用我们最喜欢的文本编辑器创建Dockerfile文件,像下面演示的一样。
-
- # nano Dockerfile
-
-现在,我们需要添加以下的命令行到文件中。
-
- FROM fedora-httpd
- ADD mysite.tar /tmp/
- RUN mv /tmp/mysite/* /var/www/html
- EXPOSE 80
- ENTRYPOINT [ "/usr/sbin/httpd" ]
- CMD [ "-D", "FOREGROUND" ]
-
-
-
-这里,运行Dockerfile,mysite.tar里的网页内容会自动解压到/temp/文件夹里。然后,整个文件会被转移到Apache网页根目录/var/www/html/,命令expose 80会打开80端口,这样网站就能正常访问。其次,入口点放在了/usr/sbin/https里面,保证Apache服务器能够执行。
-
-### 5. 建立并运行一个容器 ###
-
-现在,为了添加我们网站在上面,我们要用刚刚创建的Dockerfile创建我们的容器,为做到这,我们需要运行以下命令。
-
- # docker build -rm -t mysite .
-
-
-
-我们建立自己的容器后,我们想要用下面的命令来运行容器。
-
- # docker run -d -P mysite
-
-
-
-### 总结 ###
-
-最后,我们已经成功的以交互式的方式建立了一个Docker容器。在本节方法中,我们是直接通过交互的shell命令建立我们的容器和镜像。这种方法十分简单且快速,在建立与配置镜像与容器方面。如果你有任何问题,建议和反馈,请在下方的评论框里写下来,以便我们可以提升或者更新我们的文章。谢谢!祝生活快乐 :-)
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/interactively-create-docker-container/
-
-作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
-译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
-[1]:https://registry.hub.docker.com/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150330 2 Ways to Create Your Own Docker Base Image.md b/translated/tech/20150330 2 Ways to Create Your Own Docker Base Image.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 63188ebc5b..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20150330 2 Ways to Create Your Own Docker Base Image.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,57 +0,0 @@
-创建你自己的Docker基本映像的2中方式
-================================================================================
-欢迎大家,今天我们学习一下docker基本映像以及如何构建我们自己的docker基本映像。[Docker][1]是一个开源项目,为打包,装载和运行任何应用提供开发平台的轻量级容器。它没有语言支持,框架和打包系统的限制,从小型的家用电脑到高端的服务器,在何时何地都可以运行。这使它们成为不依赖于特定栈和供应商,很好的部署和扩展网络应用,数据库和后端服务的构建块。
-
-Docker映像是不可更改的只读层。Docker使用**Union File System**在只读文件系统上增加读写文件系统。但所有更改都发生在最顶层的可写层,最底部,在只读映像上的原始文件仍然不会改变。由于映像不会改变,也就没有状态。基本映像是没有父类的那些映像。Docker基本映像主要的好处是它允许我们有一个独立允许的Linux操作系统。
-
-下面是我们如何可以创建自定义基本映像的方式。
-
-### 1. 使用Tar创建Docker基本映像 ###
-
-我们可以使用tar构建我们自己的基本映像,我们从将要打包为基本映像的运行中的Linux发行版开始构建。这过程可以会有些不同,它取决于我们打算构建的发行版。在Linux的发行版Debian中,已经预装了debootstrap。在开始下面的步骤之前,我们需要安装debootstrap。debootstrap用来获取构建基本系统需要的包。这里,我们构建基于Ubuntu 14.04 "Trusty" 的映像。做这些,我们需要在终端或者shell中运行以下命令。
-
- $ sudo debootstrap trusty trusty > /dev/null
- $ sudo tar -C trusty -c . | sudo docker import - trusty
-
-
-
-上面的命令为当前文件夹创建了一个tar文件并输出到STDOUT中,"docker import - trusty"从STDIN中获取这个tar文件并根据它创建一个名为trusty的基本映像。然后,如下所示,我们将运行映像内部的一条测试命令。
-
- $ docker run trusty cat /etc/lsb-release
-
-[Docker GitHub Repo][2] 中有一些允许我们快速构建基本映像的事例脚本.
-
-### 2. 使用Scratch构建基本映像 ###
-
-在Docker的注册表中,有一个被称为Scratch的使用空tar文件构建的特殊库:
-
- $ tar cv --files-from /dev/null | docker import - scratch
-
-
-
-
-我们可以使用这个映像构建新的小容器:
-
-FROM scratch
-ADD script.sh /usr/local/bin/run.sh
-CMD ["/usr/local/bin/run.sh"]
-
-上面的Docker文件来自一个很小的映像。这里,它首先从一个完全空的文件系统开始,然后它复制新建的/usr/local/bin/run.sh为script.sh,然后运行脚本/usr/local/bin/run.sh。
-
-### 结尾 ###
-
-这这个教程中,我们学习了如果构建一个自定义的Docker基本映像。构建一个docker基本映像是一个很简单的任务,因为这里有很多已经可用的包和脚本。如果我们想要在里面安装想要的东西,构建docker基本映像非常有用。如果有任何疑问,建议或者反馈,请在下面的评论框中写下来。非常感谢!享受吧 :-)
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/2-ways-create-docker-base-image/
-
-作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
-译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
-[1]:https://www.docker.com/
-[2]:https://github.com/docker/docker/blob/master/contrib/mkimage-busybox.sh
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150330 How to Serve Git Repositories Using Gitblit Tool in Linux.md b/translated/tech/20150330 How to Serve Git Repositories Using Gitblit Tool in Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..45c09f3475
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150330 How to Serve Git Repositories Using Gitblit Tool in Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+如何在Linux下使用Gitblit工具创建Git仓库服务
+================================================================================
+嗨!朋友,今天我们将学习如何在你的Linux服务器或者PC上安装Gitblit工具。首先,我们看看什么是Git,它的功能以及安装Gitblit的步骤。[Git是分布式版本控制系统][1],它强调速度、数据一致性,并且支持分布式、非线性工作流。它最初由Linus Torvalds在2005年为Linux内核设计和开发,使用GPL2证书,并因此成为软件开发中使用最广泛的版本控制系统。
+
+[Gitblit是完全开源的软件][2],它基于纯粹的Java堆栈,被设计以在Git仓库速度和效率方面胜任从小型到极大型的项目。它很容易学习和上手,并有着闪电般的性能。它在廉价的本地分支、便于staging、多工作流等方面远胜过一些SCM(版本控制)工具,比如Subversion、CVS、Perforce和ClearCase。
+
+#### Gitblit的功能 ####
+
+- 它可以做为一个无声的仓库视图,没有管理控制以及用户账户。
+- 它可以做为完整的Git堆栈,拥有clone, pushing和仓库存取控制。
+- 它能独立于其他Git工具使用(包括实际的Git),它能和您已创建的工具合作。
+
+### 1.创建Gitblit安装目录 ###
+
+首先我们将在我们的服务器上建立一个目录,我们将在该目录下安装最新的Gitblit。
+
+ $ sudo mkdir -p /opt/gitblit
+
+ $ cd /opt/gitblit
+
+
+
+### 2. 下载并解压 ###
+
+现在,我们将从Gitblit官方站点下载最新版的Gitblit。这里我们将安装1.6.2版本。所以,请在安装时根据具体的版本对命令进行修改。
+
+ $ sudo wget http://dl.bintray.com/gitblit/releases/gitblit-1.6.2.tar.gz
+
+
+
+接下来,我们将解压下载到的tarball压缩包至之前创建的目录 /opt/gitblit/
+
+ $ sudo tar -zxvf gitblit-1.6.2.tar.gz
+
+
+
+### 3.配置并运行 ###
+
+现在,我们将对Gitblit进行配置。如果你想要定制Gitblit的行为,你可以修改`gitblit/data/gitblit.properties`。在完成配置后,我们将运行安装好的gitblit。有两种方式来运行gitblit,第一种是通过下面的命令手动运行:
+
+ $ sudo java -jar gitblit.jar --baseFolder data
+
+另一种是将gitblit添加为服务。下面是在linux下将gitblit添加为服务的步骤。
+
+由于我在使用Ubuntu,下面的命令将是 sudo cp service-ubuntu.sh /etc/init.d/gitblit。所以请根据你的发行版修改文件名service-ubuntu.sh为相应的你运行的发行版。
+
+ $ sudo ./install-service-ubuntu.sh
+
+ $ sudo service gitblit start
+
+
+
+在你的浏览器中打开http://localhost:8080或https://localhost:8443,也可以将localhost根据本地配置替换为IP地址。输入默认的管理员凭证:admin/admin并点击login按钮。
+
+
+
+现在,我们将添加一个新的用户。首先,你需要以admin用户登录,username = **admin**,password = **admin**。
+
+然后,点击 user icon > users > (+) new user 来创建一个新用户,如下图所示。
+
+
+
+现在,我们将创建一个开箱可用的仓库。点击 repositories > (+) new repository。然后,如下图所示添加新的仓库。
+
+
+
+#### 使用命令行创建一个新的仓库 ####
+
+ touch README.md
+ git init
+ git add README.md
+ git commit -m "first commit"
+ git remote add origin ssh://arunlinoxide@localhost:29418/linoxide.com.git
+ git push -u origin master
+
+请将用户名arunlinoxide替换为你添加的用户名。
+
+#### 在命令行中push一个已存在的仓库 ####
+
+ git remote add origin ssh://arunlinoxide@localhost:29418/linoxide.com.git
+ git push -u origin master
+
+**注意**:强烈建议所有人修改用户名“admin”的密码。
+
+### 结论 ###
+
+欢呼吧!我们已经在Linux电脑中安装好了最新版本的Gitblit。接下来我们便可以在我们的大小工程中享受这样一个优美的版本控制系统。有了Gitblit,版本控制便再容易不过了。它有易于学习、轻量级、高性能的特点。因此,如果你有任何的问题、建议和反馈,请在留言处留言。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/serve-git-repositories-gitblit/
+
+作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
+译者:[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
+[1]:http://git-scm.com/
+[2]:http://gitblit.com/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20150331 How to Install WordPress with Nginx in a Docker Container.md b/translated/tech/20150331 How to Install WordPress with Nginx in a Docker Container.md
similarity index 57%
rename from sources/tech/20150331 How to Install WordPress with Nginx in a Docker Container.md
rename to translated/tech/20150331 How to Install WordPress with Nginx in a Docker Container.md
index 9f74c672f4..849dd4a853 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20150331 How to Install WordPress with Nginx in a Docker Container.md
+++ b/translated/tech/20150331 How to Install WordPress with Nginx in a Docker Container.md
@@ -1,26 +1,26 @@
-How to Install WordPress with Nginx in a Docker Container
+如何在 Docker 容器里的 Nginx 中安装 WordPress
================================================================================
-Hi all, today we'll learn how to install WordPress running Nginx Web Server in a Docker Container. WordPress is an awesome free and open source Content Management System running thousands of websites throughout the globe. [Docker][1] is an Open Source project that provides an open platform to pack, ship and run any application as a lightweight container. It has no boundaries of Language support, Frameworks or packaging system and can be run anywhere, anytime from a small home computers to high-end servers. It makes them great building blocks for deploying and scaling web apps, databases, and back-end services without depending on a particular stack or provider.
+大家好,今天我们来学习一下如何在 Docker 容器上运行的 Nginx Web 服务器中安装 WordPress。WordPress 是一个很好的免费开源的内容管理系统,全球成千上万的网站都在使用它。[Docker][1] 是一个提供开放平台来打包,分发和运行任何应用的开源轻量级容器项目。它没有语言支持,框架或打包系统的限制,可以在从小的家用电脑到高端服务器的任何地方任何时间运行。这让它们成为可以用于部署和扩展网络应用,数据库和后端服务而不必依赖于特定的栈或者提供商的很好的构建块。
-Today, we'll deploy a docker container with the latest WordPress package with necessary prerequisites ie Nginx Web Server, PHP5, MariaDB Server, etc. Here are some short and sweet steps to successfully install a WordPress running Nginx in a Docker Container.
+今天,我们会在 docker 容器上部署最新的 WordPress 软件包,包括需要的前提条件,例如 Nginx Web 服务器、PHP5、MariaDB 服务器等。下面是在运行在 Docker 容器上成功安装 WordPress 的简单步骤。
-### 1. Installing Docker ###
+### 1. 安装 Docker ###
-Before we really start, we'll need to make sure that we have Docker installed in our Linux machine. Here, we are running CentOS 7 as host so, we'll be running yum manager to install docker using the below command.
+在我们真正开始之前,我们需要确保在我们的 Linux 机器上已经安装了 Docker。我们使用的主机是 CentOS 7,因此我们用下面的命令使用 yum 管理器安装 docker。
# yum install docker
-
+
# systemctl restart docker.service
-### 2. Creating WordPress Dockerfile ###
+### 2. 创建 WordPress Docker 文件 ###
-We'll need to create a Dockerfile which will automate the installation of the wordpress and its necessary pre-requisites. This Dockerfile will be used to build the image of WordPress installation we created. This WordPress Dockerfile fetches a CentOS 7 image from the Docker Registry Hub and updates the system with the latest available packages. It then installs the necessary softwares like Nginx Web Server, PHP, MariaDB, Open SSH Server and more which are essential for the Docker Container to work. It then executes a script which will initialize the installation of WordPress out of the box.
+我们需要创建用于自动安装 wordpress 以及前提条件的 docker 文件。这个 docker 文件将用于构建 WordPress 的安装镜像。这个 WordPress docker 文件会从 Docker 库中心获取 CentOS 7 镜像并用最新的可用更新升级系统。然后它会安装必要的软件,例如 Nginx Web 服务器、PHP、MariaDB、Open SSH 服务器以及其它保证 Docker 容器正常运行不可缺少的组件。最后它会执行一个初始化 WordPress 安装的脚本。
# nano Dockerfile
-Then, we'll need to add the following lines of configuration inside that Dockerfile.
+然后,我们需要将下面的配置行添加到 Docker 文件中。
FROM centos:centos7
MAINTAINER The CentOS Project <cloud-ops@centos.org>
@@ -48,15 +48,15 @@ Then, we'll need to add the following lines of configuration inside that Dockerf
CMD ["/bin/bash", "/start.sh"]
-
+
-### 3. Creating Start script ###
+### 3. 创建启动 script ###
-After we create our Dockerfile, we'll need to create a script named start.sh which will run and configure our WordPress installation. It will create and configure database, passwords for wordpress. To create it, we'll need to open start.sh with our favorite text editor.
+我们创建了 docker 文件之后,我们需要创建用于运行和配置 WordPress 安装的脚本,名称为 start.sh。它会为 WordPress 创建并配置数据库和密码。用我们喜欢的文本编辑器打开 start.sh。
# nano start.sh
-After opening start.sh, we'll need to add the following lines of configuration into it.
+打开 start.sh 之后,我们要添加下面的配置行到文件中。
#!/bin/bash
@@ -67,7 +67,7 @@ After opening start.sh, we'll need to add the following lines of configuration i
}
__create_user() {
- # Create a user to SSH into as.
+ # 创建用于 SSH 登录的用户
SSH_USERPASS=`pwgen -c -n -1 8`
useradd -G wheel user
echo user:$SSH_USERPASS | chpasswd
@@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ After opening start.sh, we'll need to add the following lines of configuration i
}
__mysql_config() {
- # Hack to get MySQL up and running... I need to look into it more.
+ # 启用并运行 MySQL
yum -y erase mariadb mariadb-server
rm -rf /var/lib/mysql/ /etc/my.cnf
yum -y install mariadb mariadb-server
@@ -86,18 +86,18 @@ After opening start.sh, we'll need to add the following lines of configuration i
}
__handle_passwords() {
- # Here we generate random passwords (thank you pwgen!). The first two are for mysql users, the last batch for random keys in wp-config.php
+ # 在这里我们生成随机密码(感谢 pwgen)。前面两个用于 mysql 用户,最后一个用于 wp-config.php 的随机密钥。
WORDPRESS_DB="wordpress"
MYSQL_PASSWORD=`pwgen -c -n -1 12`
WORDPRESS_PASSWORD=`pwgen -c -n -1 12`
- # This is so the passwords show up in logs.
+ # 这是在日志中显示的密码。
echo mysql root password: $MYSQL_PASSWORD
echo wordpress password: $WORDPRESS_PASSWORD
echo $MYSQL_PASSWORD > /mysql-root-pw.txt
echo $WORDPRESS_PASSWORD > /wordpress-db-pw.txt
- # There used to be a huge ugly line of sed and cat and pipe and stuff below,
- # but thanks to @djfiander's thing at https://gist.github.com/djfiander/6141138
- # there isn't now.
+ # 这里原来是一个包括 sed、cat、pipe 和 stuff 的很长的行,但多亏了
+ # @djfiander 的 https://gist.github.com/djfiander/6141138
+ # 现在没有了
sed -e "s/database_name_here/$WORDPRESS_DB/
s/username_here/$WORDPRESS_DB/
s/password_here/$WORDPRESS_PASSWORD/
@@ -116,7 +116,7 @@ After opening start.sh, we'll need to add the following lines of configuration i
}
__start_mysql() {
- # systemctl start mysqld.service
+ # systemctl 启动 mysqld 服务
mysqladmin -u root password $MYSQL_PASSWORD
mysql -uroot -p$MYSQL_PASSWORD -e "CREATE DATABASE wordpress; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON wordpress.* TO 'wordpress'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '$WORDPRESS_PASSWORD'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;"
killall mysqld
@@ -127,7 +127,7 @@ After opening start.sh, we'll need to add the following lines of configuration i
supervisord -n
}
- # Call all functions
+ # 调用所有函数
__check
__create_user
__mysql_config
@@ -136,17 +136,17 @@ After opening start.sh, we'll need to add the following lines of configuration i
__start_mysql
__run_supervisor
-
+
-After adding the above configuration, we'll need to save it and then exit.
+增加完上面的配置之后,保存并关闭文件。
-### 4. Creating Configuration files ###
+### 4. 创建配置文件 ###
-Now, we'll need to create configuration file for Nginx Web Server named nginx-site.conf .
+现在,我们需要创建 Nginx Web 服务器的配置文件,命名为 nginx-site.conf。
# nano nginx-site.conf
-Then, we'll add the following configuration to the config file.
+然后,增加下面的配置信息到配置文件。
user nginx;
worker_processes 1;
@@ -230,13 +230,13 @@ Then, we'll add the following configuration to the config file.
}
}
-
+
-Now, we'll create supervisord.conf file and add the following lines as shown below.
+现在,创建 supervisor.conf 文件并添加下面的行。
# nano supervisord.conf
-Then, add the following lines.
+然后,添加以下行。
[unix_http_server]
file=/tmp/supervisor.sock ; (the path to the socket file)
@@ -286,60 +286,60 @@ Then, add the following lines.
events = PROCESS_LOG
result_handler = supervisor_stdout:event_handler
-
+
-After adding, we'll save and exit the file.
+添加完后,保存并关闭文件。
-### 5. Building WordPress Container ###
+### 5. 构建 WordPress 容器 ###
-Now, after done with creating configurations and scripts, we'll now finally use the Dockerfile to build our desired container with the latest WordPress CMS installed and configured according to the configuration. To do so, we'll run the following command in that directory.
+现在,完成了创建配置文件和脚本之后,我们终于要使用 docker 文件来创建安装最新的 WordPress CMS(译者注:Content Management System,内容管理系统)所需要的容器,并根据配置文件进行配置。做到这点,我们需要在对应的目录中运行以下命令。
# docker build --rm -t wordpress:centos7 .
-
+
-### 6. Running WordPress Container ###
+### 6. 运行 WordPress 容器 ###
-Now, to run our newly built container and open port 80 and 22 for Nginx Web Server and SSH access respectively, we'll run the following command.
+现在,执行以下命令运行新构建的容器,并为 Nginx Web 服务器和 SSH 访问打开88 和 22号相应端口 。
# CID=$(docker run -d -p 80:80 wordpress:centos7)
-
+
-To check the process and commands executed inside the container, we'll run the following command.
+运行以下命令检查进程以及容器内部执行的命令。
# echo "$(docker logs $CID )"
-TO check if the port mapping is correct or not, run the following command.
+运行以下命令检查端口映射是否正确。
# docker ps
-
+
-### 7. Web Interface ###
+### 7. Web 界面 ###
-Finally if everything went accordingly, we'll be welcomed with WordPress when pointing the browser to http://ip-address/ or http://mywebsite.com/ .
+最后如果一切正常的话,当我们用浏览器打开 http://ip-address/ 或者 http://mywebsite.com/ 的时候会看到 WordPress 的欢迎界面。
-
+
-Now, we'll go step wise through the web interface and setup wordpress configuration, username and password for the WordPress Panel.
+现在,我们将通过 Web 界面为 WordPress 面板设置 WordPress 的配置、用户名和密码。
-
+
-Then, use the username and password entered above into the WordPress Login page.
+然后,用上面用户名和密码输入到 WordPress 登录界面。
-
+
-### Conclusion ###
+### 总结 ###
-We successfully built and run WordPress CMS under LEMP Stack running in CentOS 7 Operating System as the docker OS. Running WordPress inside a container makes a lot safe and secure to the host system from the security perspective. This article enables one to completely configure WordPress to run under Docker Container with Nginx Web Server. If you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below so that we can improve or update our contents. Thank you ! Enjoy :-)
+我们已经成功地在以 CentOS 7 作为 docker OS 的 LEMP 栈上构建并运行了 WordPress CMS。从安全层面来说,在容器中运行 WordPress 对于宿主系统更加安全可靠。这篇文章介绍了在 Docker 容器中运行的 Nginx Web 服务器上使用 WordPress 的完整配置。如果你有任何问题、建议、反馈,请在下面的评论框中写下来,让我们可以改进和更新我们的内容。非常感谢!Enjoy :-)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-wordpress-nginx-docker-container/
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150413 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure PCI-passthrough on virt-manager.md b/translated/tech/20150413 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure PCI-passthrough on virt-manager.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0344095bc2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150413 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure PCI-passthrough on virt-manager.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+Linux有问必答:如何在虚拟机上配置PCI-passthrough
+================================================================================
+> **提问**:我想要设置一块物理网卡到用KVM创建的虚拟机上。我打算开启网卡的PCI passthrough给这台虚拟机。请问,我如何才能增加一个PCI设备通过PCI直通到虚拟机上?
+
+如今的hypervisor能够高效地在多个虚拟操作系统分享和模拟硬件资源。然而,虚拟资源分享,虚拟机的性能,或者是虚拟机需要硬件DMA的完全控制,不是总能使人满意。一项名叫“PCI passthrough”的技术可以用在一个虚拟机需要独享PCI设备时(例如:network/sound/video card)。本质上,PCI passthrough越过了虚拟层,直接扩展PCI设备到虚拟机。但是其他虚拟机不能同时共享。
+
+
+### 开启“PCI Passthrough”的准备 ###
+
+如果你想要为一台HVM实例开启PCI passthrough(例如,一台KVM创建的full虚拟机),你的母系统(包括CPU和主板)必须满足以下条件。但是如果你的虚拟机是para-V(由Xen创建),你可以挑过这步。
+
+为了开启PCI passthrough,系统需要支持**VT-d** (Intel处理器)或者**AMD-Vi** (AMD处理器)。Intel的VT-D(“英特尔虚拟化技术支持直接I/ O”)是适用于最高端的Nehalem处理器和它的后继者(例如,Westmere、Sandy Bridge的,Ivy Bridge)。注意:VT-d和VT-x是两个独立功能。intel/AMD处理器支持VT-D/AMD-VI功能的列表可以[点击这里][1]。
+
+完成验证你的设备支持VT-d/AMD-Vi后,还有两件事情需要做。首先,确保VT-d/AMD-Vi已经在BIOS中开启。然后,在内核启动过程中开启IOMMU。IOMMU服务,是VT-d,/AMD-Vi提供,可以保护虚拟机访问的主机内存,同时它也是full虚拟机支持PCI passthrough的前提。
+
+Intel处理器中,内核开启IOMMU通过在启动参数中修改“**intel_iommu=on**”。参看[这篇教程][2]获得如何通过GRUB修改内核启动参数。
+
+配置完成启动参数后,重启电脑。
+
+### 添加PCI设备到虚拟机 ###
+
+我们已经完成了开启PCI Passthrough的准备。事实上,只需通过虚拟机管理就可以给虚拟机分配一个PCI设备。
+
+打开虚拟机设置,在左边工具栏点击‘增加硬件’按钮。
+
+选择从PCI设备表一个PCI设备来分配,点击“完成”按钮
+
+
+
+最后,开启实例。目前为止,主机的PCI设备已经可以由虚拟机直接访问了。
+
+### 常见问题 ###
+
+在虚拟机启动时,如果你看见下列任何一个错误,这个错误有可能由于母机VT-d (或 IOMMU)未开启导致。
+
+ Error starting domain: unsupported configuration: host doesn't support passthrough of host PCI devices
+
+----------
+
+ Error starting domain: Unable to read from monitor: Connection reset by peer
+
+请确保"**intel_iommu=on**"启动参数已经按上文叙述开启。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/pci-passthrough-virt-manager.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[Vic020/VicYu](http://vicyu.net)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
+[1]:http://wiki.xenproject.org/wiki/VTdHowTo
+[2]:http://xmodulo.com/add-kernel-boot-parameters-via-grub-linux.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150423 20 Awesome Docker Containers for a Desktop User.md b/translated/tech/20150423 20 Awesome Docker Containers for a Desktop User.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..055c1eb9b5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150423 20 Awesome Docker Containers for a Desktop User.md
@@ -0,0 +1,236 @@
+20个为桌面用户准备的令人惊叹的Docker容器
+================================================================================
+大家好,今天我们会列出一些很棒的运行在Docker容器中的桌面软件,我们可以在自己的桌面系统中运行它们。Docker是一个开源的项目,它提供可以将应用程序作为一个轻量级容器来打包、传送和运行的开放平台。它没有语言支持、框架或打包系统的限制,可以运行在任何地方,从小型的家用电脑到高端的服务器。它可以使部署和扩展web应用程序、数据库和后端服务像搭积木一样容易,而不依赖特定技术栈或提供商。它主要是由开发、运维工程师使用的,因为它简单、快速和方便,可以用来测试和辅助开发他们产品,但是我们也可以在桌面环境使用Docker,这样一些桌面程序可以开箱即用。
+
+下边是20个非常棒的桌面软件docker镜像,我们可以使用Docker来运行。
+
+### 1. Lynx ###
+
+Lynx是一个一直以来最受欢迎的文本界面网页浏览器,它对多数Linux用户来说都很熟悉。它应该是现在还在日常和开发环境中被使用的最古老的网页浏览器了。可以使用如下命令运行Lync。
+
+ $ docker run -it \
+ --name lynx \
+ jess/lynx
+
+### 2. Irssi ###
+
+Irssi是一个非常棒的文本界面IRC客户端。可以使用如下命令运行Irssi。
+
+ docker run -it --name my-irssi -e TERM -u $(id -u):$(id -g) \
+ -v $HOME/.irssi:/home/user/.irssi:ro \
+ -v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro \
+ irssi
+
+### 3. Chrome ###
+
+Chrome是一个令人惊叹的图形界面网页浏览器,由Google开发,它基于开源的Chromium项目。Google Chrome是一个被广泛使用的、快速安全的网页浏览器,经常上网的人会非常熟悉它。我们可以使用如下命令在Docker中运行Chrome。
+
+ $ docker run -it \
+ --net host \
+ --cpuset 0 \
+ --memory 512mb \
+ -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
+ -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY \
+ -v $HOME/Downloads:/root/Downloads \
+ -v $HOME/.config/google-chrome/:/data \
+ -v /dev/snd:/dev/snd --privileged \
+ --name chrome \
+ jess/chrome
+
+### 4. Tor浏览器 ###
+
+Tor浏览器是一个支持匿名访问的网页浏览器。它让我们可以自由地在网络世界遨游,或者浏览被特定组织或者网络服务提供商封锁的网站。它会阻止有人通过监视我们的网络连接来窃取我们在网络上的一举一动以及我们的确切位置。运行如下命令运行Tor浏览器。
+
+ $ docker run -it \
+ -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
+ -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY \
+ -v /dev/snd:/dev/snd --privileged \
+ --name tor-browser \
+ jess/tor-browser
+
+### 5. Firefox浏览器 ###
+
+Firefox浏览器是一个自由并且开源的网页浏览器,它由Mozilla基金会开发。它使用Gecko和SpiderMonkey引擎。Firefox浏览器有很多新特性,并且它以性能和安全性著称。
+
+ $ docker run -d \
+ --name firefox \
+ -e DISPLAY=$DISPLAY \
+ -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
+ kennethkl/firefox
+
+### 6. Rainbow Stream ###
+
+Rainbow Stream是一个文本界面的Twitter客户端,有实时显示tweetstream、搜索、喜欢和更多其他特性,可以直接在终端使用。使用如下命令运行Rainbow Stream。
+
+ $ docker run -it \
+ -v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \
+ -v $HOME/.rainbow_oauth:/root/.rainbow_oauth \
+ -v $HOME/.rainbow_config.json:/root/.rainbow_config.json \
+ --name rainbowstream \
+ jess/rainbowstream
+
+### 7. Gparted ###
+
+Gparted是一个用来给磁盘分区的开源软件。现在可以在Docker容器里享受分区的乐趣。可以使用如下命令运行gparted。
+
+ $ docker run -it \
+ -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
+ -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY \
+ --device /dev/sda:/dev/sda \ # mount the device to partition
+ --name gparted \
+ jess/gparted
+
+### 8. GIMP图片编辑器 ###
+
+GIMP(Gnu Image Manipulation Program)是一个令人惊叹的Linux图片编辑软件。它是一个可以自由分发的可以处理照片修正、图像合成和图像创作等任务的工具。
+
+ $ docker run -it \
+ --rm -e DISPLAY=$DISPLAY \
+ -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
+ jarfil/gimp-git
+
+### 9. Thunderbird ###
+
+Thunderbird是一个自由并且开源的电子邮件软件,它由Mozilla基金会开发和维护。它有众多一个电子邮件软件应该具有的功能。Thunderbird非常易于安装和定制。使用如下命令在Docker中运行Thunderbird。
+
+ $ docker run -d \
+ -e DISPLAY \
+ -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:ro \
+ -u docker \
+ -v $HOME/docker-data/thunderbird:/home/docker/.thunderbird/ \
+ yantis/thunderbird thunderbird
+
+### 10. Mutt ###
+
+Mutt是一个文本界面的电子邮件客户端,有很多很酷的功能,如颜色支持,IMAP、POP3、SMTP支持,邮件存储支持等。 使用如下命令运行Mutt。
+
+ $ docker run -it \
+ -v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \
+ -e GMAIL -e GMAIL_NAME \
+ -e GMAIL_PASS -e GMAIL_FROM \
+ -v $HOME/.gnupg:/home/user/.gnupg \
+ --name mutt \
+ jess/mutt
+
+### 11. Skype ###
+
+Skype是一个支持文字、语音和视频的即时通讯软件,它不是开源的,但在Linux下可以很棒地运行。我们同样可以在Docker中运行Skype,使用如下命令。
+
+ $ docker run -it \
+ -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:ro \
+ -v /dev/snd:/dev/snd --privileged \
+ -e DISPLAY="unix$DISPLAY" \
+ tianon/skype
+
+### 12. Cathode ###
+
+Cathode是一个漂亮并且高度可定制的终端模拟器,灵感来自经典的计算机。使用如下命令运行Cathode。
+
+ $ docker run -it \
+ -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
+ -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY \
+ --name cathode \
+ jess/1995
+
+### 13. LibreOffice ###
+
+LibreOffice是一个功能强大的办公套件,它是自由和开源的,现在由The Document基金会维护。它有干净的界面和强大的功能,让我们释放创造力和提升生产力。LibreOffice将数个应用程序集成在一起,是市面上最强大的自由并且开源的办公套件。
+ $docker run \
+ -v $HOME/Documents:/home/libreoffice/Documents:rw \
+ -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
+ -e uid=$(id -u) -e gid=$(id -g) \
+ -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY --name libreoffice \
+ chrisdaish/libreoffice
+
+### 14. Spotify ###
+
+Spotify可以即时访问数百万的歌曲,从经典老歌到最新单曲。可以使用如下命令在Docker中听我们最喜欢的歌曲。
+
+ $ docker run -it \
+ -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
+ -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY \
+ -v /dev/snd:/dev/snd --privileged \
+ --name spotify \
+ jess/spotify
+
+### 15. Audacity ###
+
+Audacity是一个自由并且开源的跨平台软件,用来录制和编辑音频。Audacity可以用来做所有类型音频(例如podcast)的后期处理,如归一化、调整、淡入淡出。使用如下命令来运行Audacity。
+
+ $ docker run --rm \
+ -u $(id -u):$(id -g) \
+ -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:ro \
+ -v /dev/snd:/dev/snd \
+ -v "$HOME:$HOME" \
+ -w "$HOME" \
+ -e DISPLAY="unix$DISPLAY" \
+ -e HOME \
+ $(find /dev/snd/ -type c | sed 's/^/--device /') \
+ knickers/audacity
+
+### 16. Eclipse ###
+
+Eclipse是一个集成开发环境。它包含基本的工作区和用来定制环境的可扩展插件系统。它在Java开发者中很流行。
+
+ $ docker run -v ~/workspace/:/home/eclipse/workspace/ \
+ -e DISPLAY -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:ro \
+ -d leesah/eclipse
+
+### 17. VLC媒体播放器 ###
+
+VLC是一个自由并且开源的跨平台多媒体播放器,可以播放本地文件、DVD、CD、VCD和各种流媒体。VLC由VideoLAN组织开发和维护。使用如下命令运行VLC。
+
+ $ docker run -v\
+ $HOME/Documents:/home/vlc/Documents:rw \
+ -v /dev/snd:/dev/snd --privileged \
+ -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
+ -e uid=$(id -u) -e gid=$(id -g) \
+ -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY --name vlc \
+ chrisdaish/vlc
+
+### 18. Vim编辑器 ###
+
+Vim是一个高度可配置的文本界面文字编辑器,为高效的文本编辑而生。它是预装在多数UNIX系统中的vi编辑器的改进版本。
+
+ $ docker run -i -t --name my-vim -v ~/:/home/dev/src haron/vim
+
+### 19. Inkscape ###
+
+Inkscape是一个自由并且开源的矢量图形编辑器。它可以创建、编辑矢量图形,如插图、图示、线条艺术、图表、徽标以及更复杂的绘画。Inkscape使用的主要矢量图形格式是SVG 1.1版本。它也可以导入和导出一些其他的格式,但实际编辑使用的还是SVG格式。
+
+ $docker build -t rasch/inkscape --rm .
+ $ docker run --rm -e DISPLAY \
+ -u inkscaper
+ -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
+ -v $HOME/.Xauthority:/home/inkscaper/.Xauthority \
+ --net=host rasch/inkscape
+
+### 20. Filezilla ###
+
+Filezilla是一个自由的FTP解决方案,支持FTP、SFTP、FTPS协议。它的客户端是一个功能强大的文件管理工具。它是一个很棒的高度可靠和易用的开源FTP解决方案。
+
+ $ xhost +si:localuser:$(whoami)
+ $ docker run \
+ -d \
+ -e DISPLAY \
+ -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:ro \
+ -u docker \
+ -v /:/host \
+ -v $HOME/docker-data/filezilla:/home/docker/.config/filezilla/ \
+ yantis/filezilla filezilla
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+使用Docker运行桌面软件真的是很棒的体验。Docker是一个快速、简单的开发平台,适合从家里、办公室到生产环境里传送和开发软件的场景。使用Docker运行桌面软件是试用而不将其安装到自己实体机文件系统中的很酷的方法。如果你有任何问题、评论或者反馈,清写在下方的评论框中,让我们知道哪些是需要增加或者改进的。谢谢!享受Docker吧 :-)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/how-tos/20-docker-containers-desktop-user/
+
+作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
+译者:[goreliu](https://github.com/goreliu)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150427 15 Things to Do After Installing Ubuntu 15.04 Desktop.md b/translated/tech/20150427 15 Things to Do After Installing Ubuntu 15.04 Desktop.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e806e8e436
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150427 15 Things to Do After Installing Ubuntu 15.04 Desktop.md
@@ -0,0 +1,298 @@
+安装完Ubuntu 15.04桌面后要做的15件事
+================================================================================
+本教程适用于新手和在自己的电脑上安装好Ubuntu 15.04 “Vivid Vervet” 桌面之后为了自定义自己的系统并安装一些基本程序作为日常使用的已经做了一些准备的人。
+
+
+安装完Ubuntu 15.04桌面后要做的15件事
+
+### 1. 启用Ubuntu额外软件库并更新系统 ###
+
+在刚装好Ubuntu之后你应该要关心的第一件事是启用官方合作伙伴提供的Ubuntu额外软件库并且通过最近一次的安全补丁和软件更新来保持系统是最新状态。
+
+要完成这一步,依次从左边菜单中打开System Settings -> Software and Updates工具并检查所有Ubuntu软件和其他软件库(官方合作伙伴所提供),点击关闭按钮并等待重新加载缓存源树。
+
+
+Software Updates
+
+
+Other Software (Canonical Partners)
+
+经过一系列快速平滑的更新过程之后,打开终端并输入以下命令来让系统使用新软件库:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get upgrade
+
+
+Ubuntu Upgrade
+
+### 2. 安装额外驱动 ###
+
+为了能让系统扫描并安装额外的硬件专有驱动,我们依然从System Settings打开Software and Updates工具,选择Additional Drivers标签并等待该工具扫描驱动。
+
+如果有驱动匹配到了你的硬件,查看你想要安装的驱动并点击Apply按钮来安装它,以防专有驱动没有如期工作,用Revert按钮就能卸载它们或勾选Do not use the device后点击Apply按钮。
+
+
+Install Drivers
+
+### 3. 安装Synaptic和Gdebi工具 ###
+
+除了Ubuntu Software Center,Synaptic是一个apt图形化工具,通过它你能管理、安装、卸载、搜索和升级软件库并配置软件包。同样的,Gdebi在功能上也有相同的地方。在终端上输入以下命令来安装这两个包:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install synaptic gdebi
+
+
+Install Synaptic and Gdebi
+
+
+Synaptic Package Manager
+
+### 4. 更改系统外观和运行状态 ###
+
+如果你想要更改桌面背景或图标大小,依次打开System Settings –> Appearance –> Look并对桌面进行个性化设置,把菜单移动到窗口标题栏,在Behavior标签中启动workspaces和desktop icons或开关auto-hide the Launcher。
+
+
+System Appearances
+
+### 5. 提升系统安全性和隐私性 ###
+
+
+System Security Enhancement
+
+
+System Security Options
+
+### 6. 禁用不需要开机自启动的应用程序 ###
+
+要提高登录系统的速度,通过输入以下命令来显示被隐藏的开机启动应用程序,在Dash中搜索它就能打开Startup Applications工具并反选不需要再登录系统的过程中启动的程序。
+
+ $ sudo sed -i ‘s/NoDisplay=true/NoDisplay=false/g’ /etc/xdg/autostart/*.desktop
+
+
+Disable Unwanted Applications
+
+### 7. 添加扩展多媒体支持 ###
+
+默认情况下,Ubuntu对多媒体文件支持不是很好。为了能播放各种不同的多媒体格式或解析视频文件,可以安装以下多媒体应用程序:
+
+- VLC
+- Smplayer
+- Audacious
+- QMMP
+- Mixxx
+- XBMC
+- Handbrake
+- Openshot
+
+用以下命令来一次性安装所有的这些应用程序:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install vlc smplayer audacious qmmp mixxx xbmc handbrake openshot
+
+
+Install Media Players
+
+
+Media Player Playlist
+
+除了多媒体播放器,安装ubuntu-restricted-extras和Java支持包也可以解码并支持其它受约束的多媒体格式。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install ubuntu-restricted-extras openjdk-8-jdk
+
+
+Install Ubuntu Extras
+
+在终端上输入以下命令来启用DVD Playback和其它多媒体解码器:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install ffmpeg gstreamer0.10-plugins-bad lame libavcodec-extra
+ $ sudo /usr/share/doc/libdvdread4/install-css.sh
+
+
+Enable Video Codes
+
+### 8. 安装图像处理应用程序 ###
+
+如果你是一个摄影爱好者,想在Ubuntu上处理调整图像,或许需要安装一下图像处理程序:
+
+- GIMP (alternative for Adobe Photoshop)
+- Darktable
+- Rawtherapee
+- Pinta
+- Shotwell
+- Inkscape (alternative for Adobe Illustrator)
+- Digikam
+- Cheese
+
+这些应用程序能从Ubuntu Software Center中安装或者立刻在终端上使用以下命令:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install gimp gimp-plugin-registry gimp-data-extras darktable rawtherapee pinta shotwell inkscape
+
+
+Install Image Applications
+
+
+Rawtherapee Tool
+
+### 9. 安装媒体烧录软件 ###
+
+如果要挂载ISO镜像或烧录一张CD或DVD,你可以选择并安装以下软件中的一款:
+
+- Brasero Disk Burner
+- K3b
+- Xfburn
+- Furius ISO Mount
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install brasero
+ $ sudo apt-get install k3b
+ $ sudo apt-get install xfburn
+ $ sudo apt-get install furiusisomount
+
+
+Install Media Burners
+
+### 10. 安装压缩应用程序 ###
+
+如果要处理大多数归档格式的文件(zip, tar.gz, zip, 7zip rar等等),输入以下命令来安装这些包:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install unace unrar zip unzip p7zip-full p7zip-rar sharutils rar uudeview mpack arj cabextract file-roller
+
+
+Install Archive Applications
+
+### 11. 安装聊天应用程序 ###
+
+如果你想要和世界各地的人们聊天,这里有一份最流行的Linux聊天应用程序列表:
+
+- Pidgin
+- Skype
+- Xchat
+- Telegram
+- aMSN
+- Viber
+
+你可以从Ubuntu Software Center中安装它们或使用以下命令:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install pidgin
+ $ sudo apt-get install skype
+ $ sudo apt-get install xchat
+ $ sudo apt-get install amsn
+ $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:atareao/telegram -y
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get install telegram
+
+
+Install Chat Applications
+
+想要在Ubuntu上安装Viber可以访问[Viber官方网站][1]下载Debian安装包到本地并用Gdebi包管理工具来安装viber.deb应用程序(右击 –> 打开 -> GDebi Package Installer).
+
+
+Install Viber
+
+### 12. 安装种子软件 ###
+
+在Ubuntu最流行的种子应用程序和P2P文件共享程序是:
+
+- Deluge
+- Transmission
+- Qbittorrent
+- LinuxDC++
+
+想要在Ubuntu上安装你最喜欢的P2P文件共享应用程序,可以在终端上输入以下命令:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install deluge
+ $ sudo apt-get install transmission
+ $ sudo apt-get install qbittorrent
+ $ sudo apt-get install linuxdcpp
+
+
+Install Torrent
+
+### 13. 安装Windows仿真器-Wine和游戏支持平台-Steam ###
+
+Wine仿真器允许你在Linux上安装并运行Window应用程序。在另一方面,Steam是一款Valve开发的流行于Linux系统的游戏平台。想要在你的机器上安装它们,可以输入以下命令或使用Ubuntu Software Center。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install steam wine winetricks
+
+
+Install Wine
+
+### 14. 安装Cairo-Dock并启用桌面视觉效果 ###
+
+Cairo-Dock是一款漂亮且灵巧的用于Linux桌面上的启动条,类似于Mac OS X dock。想要在Ubuntu上安装它,可以在终端上运行以下命令:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install cairo-dock cairo-dock-plug-ins
+
+
+Install Cairo Dock
+
+
+Add Cairo Dock at Startup
+
+想要启用某一套桌面效果,例如Cube效果,可以使用以下命令来安装Compiz包:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install compiz compizconfig-settings-manager compiz-plugins-extra
+
+想要激活桌面Cube效果,在Dash上查找ccsm,打开CompizConfig Settings Manager,找到General Options – > Desktop Size并设置Horizontal Virtual Size的值为4,Vertical Virtual Size的值为1。然后返回检查Desktop Cube框(禁用Desktop Wall)和Rotate Cube框(解决冲突 -> 禁止切换视图1)并Ctrl+Alt+鼠标左击来查看cube效果。
+
+
+Enable Compiz
+
+
+Compiz Settings
+
+
+Compiz Settings Addons
+
+
+Desktop Window Rotating
+
+### 15. 添加额外浏览器支持 ###
+
+Ubuntu 15.04默认浏览器是Mozilla Firefox。想要安装其它浏览器比如Google Chrome或Opera,可以访问它们的官方网站,下载所提供的.deb包并用Gdebi Package Installer在你的系统上安装它们。
+
+
+Enable Browser Support
+
+
+Opera Browser Support
+
+想要安装Chromium开源浏览器请在终端上输入以下命令:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install chromium-browser
+
+### 16. 安装Tweak工具 ###
+
+想要用额外的应用程序来自定义Ubuntu吗?在终端上输入以下命令来安装Unity Tweak工具和Gnome Tweak工具:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install unity-tweak-tool gnome-tweak-tool
+
+
+Install Tweak Tool
+
+
+Tweak Tool Settings
+
+另一个有趣的tweak工具主要是Ubuntu Tweak包,可以通过访问官方网站来获取并安装: [http://ubuntu-tweak.com/][2].
+
+
+Tweak Tool: System Information
+
+在你安装好这一连串软件之后,你或许想要清理一下你的系统来释放一点硬盘上的空间,输入以下命令即可:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get -y autoremove
+ $ sudo apt-get -y autoclean
+ $ sudo apt-get -y clean
+
+这只是tweaks工具中的其中一些和普通用户日常生活中可能会在Ubuntu 15.04桌面上安装使用的程序。想要了解更多高级的程序,特性和功能,请使用Ubuntu Software Center或查阅Ubuntu Wiki主页。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-15-04-desktop/
+
+作者:[Matei Cezar][a]
+译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
+[1]:http://www.viber.com/en/products/linux
+[2]:http://ubuntu-tweak.com/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150429 KDE Plasma 5.3 Released, Here' s How To Upgrade in Kubuntu 15.04.md b/translated/tech/20150429 KDE Plasma 5.3 Released, Here' s How To Upgrade in Kubuntu 15.04.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1e2a36a0a7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150429 KDE Plasma 5.3 Released, Here' s How To Upgrade in Kubuntu 15.04.md
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
+
+KDE Plasma 5.3已发布,Kubuntu 15.04升级攻略
+================================================================================
+**KDE[已经宣布][1]Plasma 5.3的稳定版已经准备就绪,它包含了一个新的电源管理方面的稳定特性。**
+
+[先前四月份的beta版][2]已经让我们印象深刻,甚至跃跃欲试了,Plasma 5桌面环境的稳定版更新的最新更新已经稳定,并且可以下载了。
+
+Plasma 5.3继续改善和细化了全新的KDE桌面,它添加了大量的特性供桌面用户体验。同时也修复了**多达400个错误**,这对性能和稳定性方面也进行了大量改善。
+
+### Plasma 5.3中的新东西 ###
+
+
+Plasma 5.3中更好的蓝牙管理
+
+而[在早期关于Plasma 5.3的文章][3]中,我们触及了大量**新特性**,这其中很多都值得反复说道说道。
+
+**加强的电源管理**特性和配置选项,包括**新的电源小程序、能源使用监控**和**动态屏幕亮度变化**,将有助于让KDE在移动设备上加强续航能力。
+
+在连接了外部监视器的时候合上笔记本盖子时,不会再触发‘挂起’操作。这个新的行为被称之为‘**影院模式**’,并且默认开启。但是,可以通功过电源管理设置中的相关选项禁用。
+
+**蓝牙功能被改善**,带来了一个全新的面板小程序,使得在连接到并配置配对的蓝牙设备,如只能手机、键盘和扬声器时,比以往更为便捷。
+
+同样,对于Plasma 5.3,**KDE中的轨迹板配置更为方便**,这多亏了新的安装和设置模块。
+
+轨迹板、触控板。Tomato, Tomayto。
+
+对于Plasma小部件狂热者,带来了一个**按住并锁定**手势。当启用该功能,会隐藏移动鼠标时出现的设置处理。取而代之的是,它只会在长点击小部件时发生该行为。
+
+谈到widget-y这类事情时,该发布版中**再次引入了几个旧的Plasmoid最受欢迎的东西**,包括一个有用的系统监视器、便利的硬盘驱动器统计和一个漫画阅读器。
+
+### 了解更多&尝试 ###
+
+
+
+一张全部内容的完整列表——我说全部内容——是指Plasma 5.3中[在官方修改日志中][4]列出的新的和改进的内容。
+
+你可以从KDE社区获取Live镜像,试用Kubuntu上的Plasma 5.3,**而不会影响到你自己的系统**:
+
+- [下载KDE Plasma Live镜像][5]
+
+如果你需要超级稳定的系统,你可以使用这些镜像来尝试新特性,但是你可以继续使用你的主要计算机上与你的版本对应的KDE版本。
+
+但是,如果你对实验版满意——请阅:能够处理任何包冲突,或者由尝试升级桌面环境而导致的系统问题——那么你可以安装。
+
+### 安装Plasma 5.3到Kubuntu 15.04 ###
+
+
+
+要**安装Plasma 5.3到Kubuntu 15.04**中,你需要添加KDE 移植PPA,运行软件更新器工具并安装任何可用的更新。
+
+Kubuntu移植PPA可能也会升级除了安装在你系统上的Plasma外的其它KDE平台组件,包括KDE应用程序、框架和Kubuntu特定配置文件。
+
+目前为止,使用命令行来升级Kubuntu中的到Plasma 5.3是最快速的方法:
+
+ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:kubuntu-ppa/backports
+
+ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
+
+在升级过程完成后,如果一切顺利,你应该重启计算机。
+
+如果你正在使用一个备用桌面环境,比如LXDE、Unity或者GNOME,则你需要在运行完上面的两个命令后安装Kubuntu桌面包(你可以在Ubuntu软件中心找到)。
+To downgrade to the stock version of Plasma in 15.04 you can use the PPA-Purge tool:
+
+ sudo apt-get install ppa-purge
+
+ sudo ppa-purge ppa:kubuntu-ppa/backports
+
+请在下面的评论中留言,让我们知道你怎么升级/测试过程是怎样的,别忘了告诉我们你在下一个Plasma 5桌面中要看到的特性。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/kde-plasma-5-3-released-heres-how-to-upgrade-in-kubuntu-15-04
+
+作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
+[1]:https://www.kde.org/announcements/plasma-5.3.0.php
+[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/beta-plasma-5-3-features
+[3]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/04/beta-plasma-5-3-features
+[4]:https://www.kde.org/announcements/plasma-5.2.2-5.3.0-changelog.php
+[5]:https://community.kde.org/Plasma/Live_Images
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150504 How to Install and Configure 'PowerDNS' (with MariaDB) and 'PowerAdmin' in RHEL or CentOS 7.md b/translated/tech/20150504 How to Install and Configure 'PowerDNS' (with MariaDB) and 'PowerAdmin' in RHEL or CentOS 7.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0f7bc3d62f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150504 How to Install and Configure 'PowerDNS' (with MariaDB) and 'PowerAdmin' in RHEL or CentOS 7.md
@@ -0,0 +1,422 @@
+RHEL/CentOS 7中安装并配置‘PowerDNS’(与MariaDB搭配)和‘PowerAdmin’
+================================================================================
+PowerDNS是一个运行在许多Linux/Unix衍生版上的DNS服务器,它可以使用不同的后端进行配置,包括BIND类型的区域文件、相关的数据库,或者负载均衡/失效转移算法。它也可以被配置成一台DNS递归器,作为服务器上的一个独立进程运行。
+
+PowerDNS授权服务器的最新版本是3.4.4,但是当前EPEL仓库中可以获得的版本是3.4.3。我推荐安装EPEL仓库中提供的那一个,因为该版本已经在CentOS和Fedora中测试过。那样,你也可以在今后很容易地更新PowerDNS。
+
+本文倾向于向你演示如何安装并配置以MariaDB作为后端的PowerDNS和
+出于本文的写作目的,我将使用以下服务器:
+
+ 主机名: centos7.localhost
+ IP地址: 192.168.0.102
+
+### 步骤 1: 安装带有MariaDB后端的PowerDNS ###
+
+#### 1. 首先,你需要为你的系统启用EPEL仓库,只需使用: ####
+
+ # yum install epel-release.noarch
+
+
+启用Epel仓库
+
+#### 2. 下一步是安装MariaDB服务器。运行以下命令即可达成: ####
+
+ # yum -y install mariadb-server mariadb
+
+
+安装MariaDB服务器
+
+#### 3. 接下来,我们将配置并启用MySQL,并设置开机启动: ####
+
+ # systemctl enable mariadb.service
+ # systemctl start mariadb.service
+
+
+启用MariaDB开机启动
+
+#### 4. 由于MySQL服务正在运行,我们将为MariaDB设置密码进行安全加固,运行以下命令: ####
+
+ # mysql_secure_installation
+
+#### 按照指示做 ####
+
+ /bin/mysql_secure_installation: line 379: find_mysql_client: command not found
+
+ NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
+ SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
+
+ In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
+ password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
+ you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
+ so you should just press enter here.
+
+ Enter current password for root (enter for none): Press ENTER
+ OK, successfully used password, moving on...
+
+ Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
+ root user without the proper authorisation.
+
+ Set root password? [Y/n] y
+ New password: ← Set New Password
+ Re-enter new password: ← Repeat Above Password
+ Password updated successfully!
+ Reloading privilege tables..
+ ... Success!
+
+
+ By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
+ to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
+ them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
+ go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
+ production environment.
+
+ Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y ← Choose “y” to disable that user
+ ... Success!
+
+ Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
+ ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
+
+ Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] n ← Choose “n” for no
+ ... skipping.
+
+ By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
+ access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
+ before moving into a production environment.
+
+ Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y ← Choose “y” for yes
+ - Dropping test database...
+ ... Success!
+ - Removing privileges on test database...
+ ... Success!
+
+ Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
+ will take effect immediately.
+
+ Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y ← Choose “y” for yes
+ ... Success!
+
+ Cleaning up...
+
+ All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
+ installation should now be secure.
+
+ Thanks for using MariaDB!
+
+#### 5. MariaDB配置成功后,我们可以继续去安装PowerDNS。运行以下命令即可轻易完成: ####
+
+ # yum -y install pdns pdns-backend-mysql
+
+
+安装带有MariaDB后端的PowerDNS
+
+#### 6. PowerDNS的配置文件位于`/etc/pdns/pdns`,在编辑之前,我们将为PowerDNS服务配置一个MySQL数据库。首先,我们将连接到MySQL服务器并创建一个名为powerdns的数据库: ####
+
+ # mysql -u root -p
+ MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE powerdns;
+
+
+创建PowerDNS数据库
+
+#### 7. 接下来,我们将创建一个名为powerdns的数据库用户: ####
+
+ MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON powerdns.* TO 'powerdns'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY ‘tecmint123’;
+ MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON powerdns.* TO 'powerdns'@'centos7.localdomain' IDENTIFIED BY 'tecmint123';
+ MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
+
+
+创建PowerDNS用户
+
+**注意**: 请将“tecmint123”替换为你想要设置的实际密码。
+
+#### 8. 我们继续创建PowerDNS要使用的数据库表。像堆积木一样执行以下这些: ####
+
+ MariaDB [(none)]> USE powerdns;
+ MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE TABLE domains (
+ id INT auto_increment,
+ name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
+ master VARCHAR(128) DEFAULT NULL,
+ last_check INT DEFAULT NULL,
+ type VARCHAR(6) NOT NULL,
+ notified_serial INT DEFAULT NULL,
+ account VARCHAR(40) DEFAULT NULL,
+ primary key (id)
+ );
+
+
+创建用于PowerDNS的表域
+
+ MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE UNIQUE INDEX name_index ON domains(name);
+ MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE TABLE records (
+ id INT auto_increment,
+ domain_id INT DEFAULT NULL,
+ name VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
+ type VARCHAR(6) DEFAULT NULL,
+ content VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
+ ttl INT DEFAULT NULL,
+ prio INT DEFAULT NULL,
+ change_date INT DEFAULT NULL,
+ primary key(id)
+ );
+
+
+创建用于PowerDNS的索引域
+
+ MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE INDEX rec_name_index ON records(name);
+ MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE INDEX nametype_index ON records(name,type);
+ MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE INDEX domain_id ON records(domain_id);
+
+
+创建索引记录
+
+ MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE TABLE supermasters (
+ ip VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL,
+ nameserver VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
+ account VARCHAR(40) DEFAULT NULL
+ );
+
+
+创建表的超主
+
+你现在可以输入以下命令退出MySQL控制台:
+
+ MariaDB [(none)]> quit;
+
+#### 9. 最后,我们可以继续以MySQL作为后台的方式配置PowerDNS。请打开PowerDNS的配置文件: ####
+
+ # vim /etc/pdns/pdns.conf
+
+在该文件中查找像下面这样的行:
+
+ #################################
+ # launch Which backends to launch and order to query them in
+ #
+ # launch=
+
+在这后面放置以下代码:
+
+ launch=gmysql
+ gmysql-host=localhost
+ gmysql-user=powerdns
+ gmysql-password=user-pass
+ gmysql-dbname=powerdns
+
+修改“user-pass”为你先前设置的实际密码,配置如下:
+
+
+配置PowerDNS
+
+保存修改并退出。
+
+#### 10. 现在,我们将启动并添加PowerDNS到系统开机启动列表: ####
+
+ # systemctl enable pdns.service
+ # systemctl start pdns.service
+
+
+启用并启动PowerDNS
+
+到这一步,你的PowerDNS服务器已经起来并运行了。要获取更多关于PowerDNS的信息,你可以参考手册[http://downloads.powerdns.com/documentation/html/index.html][1]
+
+### 步骤 2: 安装PowerAdmin来管理PowerDNS ###
+
+#### 11. 现在,我们将安装PowerAdmin——一个友好的网页接口PowerDNS服务器管理器。由于它是用PHP写的,我们将需要安装PHP和一台网络服务器(Apache): ####
+
+ # yum install httpd php php-devel php-gd php-imap php-ldap php-mysql php-odbc php-pear php-xml php-xmlrpc php-mbstring php-mcrypt php-mhash gettext
+
+
+安装Apache PHP
+
+PowerAdmin也需要两个PEAR包:
+
+ # yum -y install php-pear-DB php-pear-MDB2-Driver-mysql
+
+
+安装Pear
+
+你也可以参考一下文章了解CentOS 7中安装LAMP堆栈的完整指南:
+
+- [CentOS 7中安装LAMP][2]
+
+安装完成后,我们将需要启动并设置Apache开机启动:
+
+ # systemctl enable httpd.service
+ # systemctl start httpd.service
+
+
+启用Apache开机启动
+
+#### 12. 由于已经满足PowerAdmin的所有系统要求,我们可以继续下载软件包。因为Apache默认的网页目录位于/var/www/html/,我们将下载软件包到这里。 ####
+
+ # cd /var/www/html/
+ # wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/poweradmin/poweradmin-2.1.7.tgz
+ # tar xfv poweradmin-2.1.7.tgz
+
+
+下载PowerAdmin
+
+#### 13. 现在,我们可以启动PowerAdmin的网页安装器了,只需打开: ####
+
+ http://192.168.0.102/poweradmin-2.1.7/install/
+
+这会进入安装过程的第一步:
+
+
+选择安装语言
+
+上面的页面会要求你为PowerAdmin选择语言,请选择你想要使用的那一个,然后点击“进入步骤 2”按钮。
+
+#### 14. 安装器需要PowerDNS数据库: ####
+
+
+PowerDNS数据库
+
+#### 15. 因为我们已经创建了一个,所以我们可以继续进入下一步。你会被要求提供先前配置的数据库详情,你也需要为Poweradmin设置管理员密码: ####
+
+
+输入PowerDNS数据库配置
+
+#### 16. 输入这些信息后,进入步骤 4。你将创建为Poweradmin创建一个受限用户。这里你需要输入的字段是: ####
+
+- 用户名 - PowerAdmin用户名。
+- 密码 – 上述用户的密码。
+- 注册人 - 当创建SOA记录而你没有制定注册人时,该值会被使用。
+- 辅助域名服务器 – 该值在创建新的DNS区域时会被用于作为主域名服务器。
+
+
+PowerDNS配置设置
+
+#### 17. 在下一步中,Poweradmin会要求你在数据库表中创建新的受限数据库用户,它会提供你需要在MySQL控制台输入的代码: ####
+
+
+创建新的数据库用户
+
+#### 18. 现在打开终端并运行: ####
+
+ # mysql -u root -p
+
+提供你的密码并执行由Poweradmin提供的代码:
+
+ MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
+ ON powerdns.*
+ TO 'powermarin'@'localhost'
+ IDENTIFIED BY '123qweasd';
+
+
+为用户授予Mysql权限
+
+#### 19. 现在,回到浏览器中并继续下一步。安装器将尝试创建配置文件到/var/www/html/poweradmin-2.1.7/inc。 ####
+
+文件名是config.inc.php。为防止该脚本没有写权限,你可以手动复制这些内容到上述文件中:
+
+
+配置PowerDNS设置
+
+#### 20. 现在,进入最后页面,该页面会告知你安装已经完成以及如何访问安装好的Poweradmin: ####
+
+
+PowerDNS安装完成
+
+你可以通过运行以下命令来启用其他动态DNS提供商的URL:
+
+ # cp install/htaccess.dist .htaccess
+
+出于该目的,你将需要在Apache的配置中启用mod_rewrite。
+
+#### 21. 现在,需要移除从Poweradmin的根目录中移除“install”文件夹,这一点很重要。使用以下命令: ####
+
+ # rm -fr /var/www/html/poweradmin/install/
+
+在此之后,你可以通过以下方式访问PowerAdmin:
+
+ http://192.168.0.102/poweradmin-2.1.7/
+
+
+PowerDNS登录
+
+在登录后,你应该会看到Poweradmin的主页:
+
+
+PowerDNS仪表盘
+
+到这里,安装已经完成了,你也可以开始管理你的DNS区域了。
+
+### 步骤 3: PowerDNS中添加、编辑和删除DNS区域 ###
+
+#### 22. 要添加新的主区域,只需点击“添加主区域”: ####
+
+
+添加主区域
+
+在下一页中,你需要填写一些东西:
+
+- 域 – 你要添加区域的域。
+- 所有者 – 设置DNS区域的所有者。
+- 模板 – DNS模板 – 留空。
+- DNSSEC – Donany名称系统安全扩展(可选——检查你是否需要)。
+
+点击“添加区域”按钮来添加DNS区域。
+
+
+主DNS区域
+
+现在,你可以点击“首页”链接回到Poweradmin的首页。要查看所有现存的DNS区域,只需转到“列出区域”:
+
+
+检查区域列表
+
+你现在应该看到一个可用DNS区域列表:
+
+
+检查DNS区域列表
+
+#### 23. 要编辑现存DNS区域或者添加新的记录,点击编辑图标: ####
+
+
+编辑DNS区域
+
+在接下来的页面,你会看到你选择的DNS区域的条目:
+
+
+主DNS区域条目
+
+#### 24. 在此处添加新的DNS区域,你需要设置以下信息: ####
+
+- 名称 – 条目名称。只需添加域/子域的第一部分,Poweradmin会添加剩下的。
+- 类型 – 选择记录类型。
+- 优先级 – 记录优先级。
+- TTL – 存活时间,以秒计算。
+
+出于本文目的,我将为子域new.example.com添加一个A记录用于解析IP地址192.168.0.102,设置存活时间为14400秒:
+
+
+添加新DNS记录
+
+最后,点击“添加记录”按钮。
+
+#### 25. 如果你想要删除DNS区域,你可以回到“列出区域”页面,然后点击你想要删除的DNS区域旁边“垃圾桶”图标: ####
+
+
+删除DNS区域
+
+Poweradmin将问你是否确定想要删除DNS区域。只需点击“是”来完成删除。
+
+如要获取更多关于怎样创建、编辑和删除区域的说明,你可以参与Poweradmin的文档:
+
+[https://github.com/poweradmin/poweradmin/wiki/Documentation][3]
+
+我希望你已经发现本文很有趣,也很有用。一如既往,如果你有问题或要发表评论,请别犹豫,在下面评论区提交你的评论吧。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-powerdns-poweradmin-mariadb-in-centos-rhel/
+
+作者:[Marin Todorov][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/marintodorov89/
+[1]:http://downloads.powerdns.com/documentation/html/index.html
+[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-lamp-in-centos-7/
+[3]:https://github.com/poweradmin/poweradmin/wiki/Documentation
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150504 Useful Commands to Create Commandline Chat Server and Remove Unwanted Packages in Linux.md b/translated/tech/20150504 Useful Commands to Create Commandline Chat Server and Remove Unwanted Packages in Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cd90e2bfb7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150504 Useful Commands to Create Commandline Chat Server and Remove Unwanted Packages in Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
+Linux中,创建聊天服务器、移除冗余软件包的实用命令
+=============================================================================
+这里,我们来看Linux命令行实用技巧的下一个部分。如果你错过了Linux Tracks之前的文章,可以从这里找到。
+
+- [5 Linux Command Line Tracks][1]
+
+本篇中,我们将会介绍6个命令行小技巧,包括使用Netcat命令创建Linux命令行聊天,从某个命令的输出中对某一列做加法,移除Debian和CentOS上多余的包,从命令行中获取本地与远程的IP地址,在终端获得彩色的输出与解码各样的颜色,最后是Linux命令行里井号标签的使用。让我们来一个一个地看一下。
+
+
+6个实用的命令行技巧
+
+### 1. 创建Linux命令行聊天服务 ###
+我们大家使用聊天服务都有很长一段时间了。对于Google Chat,Hangout,Facebook Chat,Whatsapp,Hike和其他一些应用与集成的聊天服务,我们都很熟悉了。那你知道Linux的nc命令可以使你的Linux盒子变成一个聊天服务器,而仅仅只需要一行命令吗。什么是nc命令,它又是怎么工作的呢?
+
+nc是Linux netcat命令的旧版。nc就像瑞士军刀一样,内建呢大量的功能。nc可用做调式工具,调查工具,使用TCP/UDP读写网络连接,DNS正向/反向检查。
+
+nc主要用在端口扫描,文件传输,后台和端口监听。nc可以使用任何闲置的端口和任何本地网络源地址。
+
+使用nc命令(在192.168.0.7的服务器上)创建一个命令行即时信息传输服务器。
+
+ $ nc -l -vv 11119
+
+对上述命令的解释。
+
+- -v : 表示 Verbose
+- -vv : 更多的 Verbose
+- -p : 本地端口号
+
+你可以用任何其他的本地端口号替换11119。
+
+接下来在客户端机器(IP地址:192.168.0.15),运行下面的命令初始化聊天会话(信息传输服务正在运行)。
+
+ $ nc 192.168.0.7:11119
+
+
+
+**注意**:你可以按下ctrl+c终止会话,同时nc聊天是一个一对一的服务。
+
+### 2. Linux中如何统计某一列的总值 ###
+
+如何统计在终端里,某个命令的输出中,其中一列的数值总和,
+
+‘ls -l’命令的输出。
+
+ $ ls -l
+
+
+
+注意到第二列代表软连接的数量,第五列则是文件的大小。假设我们需要汇总第五列的数值。
+
+仅仅列出第五列的内容。我们会使用‘awk’命令做到这点。‘$5’即代表第五列。
+
+ $ ls -l | awk '{print $5}'
+
+
+
+现在,通过管道连接,使用awk打印出第五列数值的总和。
+
+ $ ls -l | awk '{print $5}' | awk '{total = total + $1}END{print total}'
+
+
+
+### 在Linux里如何移除废弃包 ###
+
+废弃包是指那些作为其他包的依赖而被安装,但是当源包被移除之后就不再需要的包。
+
+假设我们安装了gtprogram,依赖是gtdependency。除非我们安装了gtdependency,否则安装不了gtprogram。
+
+当我们移除gtprogram的时候,默认并不会移除gtdependency。并且如果我们不移除gtdependency的话,它就会遗留下来成为废弃包,与其他任何包再无联系。
+
+ # yum autoremove [On RedHat Systems]
+
+
+
+ # apt-get autoremove [On Debian Systems]
+
+
+
+你应该经常移除废弃包,保持Linux机器仅仅加载一些需要的东西。
+
+### 4. 如何获得Linux服务器本地的与公网的IP地址 ###
+
+为了获得本地IP地址,运行下面的一行脚本。
+
+ $ ifconfig | grep "inet addr:" | awk '{print $2}' | grep -v '127.0.0.1' | cut -f2 -d:
+
+你必须安装了ifconfig,如果没有,使用apt或者yum工具安装需要的包。这里我们将会管道连接ifconfig的输出,并且结合grep命令找到包含“intel addr:”的字符串。
+
+我们知道对于输出本地IP地址,ifconfig命令足够用了。但是ifconfig生成了许多的输出,而我们关注的地方仅仅是本地IP地址,不是其他的。
+
+ # ifconfig | grep "inet addr:"
+
+
+
+尽管目前的输出好多了,但是我们需要过滤出本地的IP地址,不含其他东西。针对这个,我们将会使用awk打印出第二列输出,通过管道连接上述的脚本。
+
+ # ifconfig | grep “inet addr:” | awk '{print $2}'
+
+
+
+上面图片清楚的表示,我们已经很大程度上自定义了输出,当仍然不是我们想要的。本地环路地址 127.0.0.1 仍然在结果中。
+
+我们可以使用grep的-v选项,这样会打印出不匹配给定参数的其他行。每个机器都有同样的环路地址 127.0.0.1,所以使用grep -v打印出不包含127.0.0.1的行,通过管道连接前面的脚本。
+
+ # ifconfig | grep "inet addr" | awk '{print $2}' | grep -v '127.0.0.1'
+
+
+
+我们差不多得到想要的输出了,仅仅需要从开头替换掉字符串`(addr:)`。我们将会使用cut命令单独打印出第二列。一二列之间并不是用tab分割,而是`(:)`,所以我们需要使用到域分割符选项`(-d)`,通过管道连接上面的输出。
+
+ # ifconfig | grep "inet addr:" | awk '{print $2}' | grep -v '127.0.0.1' | cut -f2 -d:
+
+
+
+最后!期望的结果出来了。
+
+### 5.如何在Linux终端彩色输出 ###
+
+你可能在终端看见过彩色的输出。同时你也可能知道在终端里允许/禁用彩色输出。如果都不知道的话,里可以参考下面的步骤。
+
+在Linux中,每个用户都有`'.bashrc'`文件,被用来管理你的终端输出。打开并且编辑该文件,用你喜欢的编辑器。注意一下,这个文件是隐藏的(文件开头为点的代表隐藏文件)。
+
+ $ vi /home/$USER/.bashrc
+
+确保以下的行没有被注释掉。ie.,行开头没有#。
+
+ if [ -x /usr/bin/dircolors ]; then
+ test -r ~/.dircolors && eval "$(dircolors -b ~/.dircolors)" || eval "$(dirc$
+ alias ls='ls --color=auto'
+ #alias dir='dir --color=auto'
+ #alias vdir='vdir --color=auto'
+
+ alias grep='grep --color=auto'
+ alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
+ alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
+ fi
+
+
+
+完成后!保存并退出。为了让改动生效,需要注销账户后再次登录。
+
+现在,你会看见列出的文件和文件夹名字有着不同的颜色,根据文件类型来决定。为了解码颜色,可以运行下面的命令。
+
+ $ dircolors -p | less
+
+
+
+### 6.如何用井号标记和Linux命令和脚本 ###
+
+我们一直在Twitter,Facebook和Google Plus(可能是其他我们没有提到的地方)上使用井号标签。那些井号标签使得其他人搜索一个标签更加容易。可是很少人知道,我们可以在Linux命令行使用井号标签。
+
+我们已经知道配置文件里的`#`,在大多数的编程语言中,这个符号被用作注释行,即不被执行。
+
+运行一个命令,然后为这个命令创建一个井号标签,这样之后我们就可以找到它。假设我们有一个很长的脚本,就上面第四点被执行的命令。现在为它创建一个井号标签。我们知道ifconfig可以被sudo或者root执行,因此用root来执行。
+
+ # ifconfig | grep "inet addr:" | awk '{print $2}' | grep -v '127.0.0.1' | cut -f2 -d: #myip
+
+上述脚本被’mytag‘给标记了。现在在reverse-i-search(按下ctrl+r)搜索一下这个标签,在终端里,并输入’mytag‘。你可以从这里开始执行。
+
+
+
+你可以创建很多的井号标签,为每个命令,之后使用reverse-i-search找到它。
+
+目前就这么多了。我们一直在辛苦的工作,创造有趣的,有知识性的内容给你。你觉得我们是如何工作的呢?欢迎咨询任何问题。你可以在下面评论。保持联络!Kudox。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-commandline-chat-server-and-remove-unwanted-packages/
+
+作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
+译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/5-linux-command-line-tricks/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150505 How to Manage 'Systemd' Services and Units Using 'Systemctl' in Linux.md b/translated/tech/20150505 How to Manage 'Systemd' Services and Units Using 'Systemctl' in Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a78dc01820
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150505 How to Manage 'Systemd' Services and Units Using 'Systemctl' in Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,579 @@
+在Linux中使用‘Systemctl’管理‘Systemd’服务和单元
+================================================================================
+Systemctl是一个systemd工具,主要负责控制systemd系统和服务管理器。
+
+Systemd是一个系统管理守护进程、工具和库的集合,用于取代System V初始进程。Systemd的功能是用于集中管理和配置类UNIX系统。
+
+在Linux生态系统中,Systemd被部署到了大多数的标准Linux发行版中,只有位数不多的几个尚未部署。Systemd通常是所有其它守护进程的父进程,但并非总是如此。
+
+
+使用Systemctl管理Linux服务
+
+本文旨在阐明在运行systemd的系统上“如何控制系统和服务”。
+
+### Systemd初体验和Systemctl基础 ###
+
+#### 1. 首先检查你的系统中是否安装有systemd并确定当前安装的版本 ####
+
+ # systemd --version
+
+ systemd 215
+ +PAM +AUDIT +SELINUX +IMA +SYSVINIT +LIBCRYPTSETUP +GCRYPT +ACL +XZ -SECCOMP -APPARMOR
+
+上例中很清楚地表明,我们安装了215版本的systemd。
+
+#### 2. 检查systemd和systemctl的二进制文件和库文件的安装位置 ####
+
+ # whereis systemd
+ systemd: /usr/lib/systemd /etc/systemd /usr/share/systemd /usr/share/man/man1/systemd.1.gz
+
+
+ # whereis systemctl
+ systemctl: /usr/bin/systemctl /usr/share/man/man1/systemctl.1.gz
+
+#### 3. 检查systemd是否运行 ####
+
+ # ps -eaf | grep [s]ystemd
+
+ root 1 0 0 16:27 ? 00:00:00 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd --switched-root --system --deserialize 23
+ root 444 1 0 16:27 ? 00:00:00 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-journald
+ root 469 1 0 16:27 ? 00:00:00 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-udevd
+ root 555 1 0 16:27 ? 00:00:00 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-logind
+ dbus 556 1 0 16:27 ? 00:00:00 /bin/dbus-daemon --system --address=systemd: --nofork --nopidfile --systemd-activation
+
+**注意**:systemd是作为父进程(PID=1)运行的。在上面带(-e)参数的ps命令输出中,选择所有进程,(-
+
+a)选择除会话前导外的所有进程,并使用(-f)参数输出完整格式列表(如 -eaf)。
+
+也请注意上例中后随的方括号和样例剩余部分。方括号表达式是grep的字符类表达式的一部分。
+
+#### 4. 分析systemd启动进程 ####
+
+ # systemd-analyze
+ Startup finished in 487ms (kernel) + 2.776s (initrd) + 20.229s (userspace) = 23.493s
+
+#### 5. 分析启动时各个进程花费的时间 ####
+
+ # systemd-analyze blame
+
+ 8.565s mariadb.service
+ 7.991s webmin.service
+ 6.095s postfix.service
+ 4.311s httpd.service
+ 3.926s firewalld.service
+ 3.780s kdump.service
+ 3.238s tuned.service
+ 1.712s network.service
+ 1.394s lvm2-monitor.service
+ 1.126s systemd-logind.service
+ ....
+
+#### 6. 分析启动时的关键链 ####
+
+ # systemd-analyze critical-chain
+
+ The time after the unit is active or started is printed after the "@" character.
+ The time the unit takes to start is printed after the "+" character.
+
+ multi-user.target @20.222s
+ └─mariadb.service @11.657s +8.565s
+ └─network.target @11.168s
+ └─network.service @9.456s +1.712s
+ └─NetworkManager.service @8.858s +596ms
+ └─firewalld.service @4.931s +3.926s
+ └─basic.target @4.916s
+ └─sockets.target @4.916s
+ └─dbus.socket @4.916s
+ └─sysinit.target @4.905s
+ └─systemd-update-utmp.service @4.864s +39ms
+ └─auditd.service @4.563s +301ms
+ └─systemd-tmpfiles-setup.service @4.485s +69ms
+ └─rhel-import-state.service @4.342s +142ms
+ └─local-fs.target @4.324s
+ └─boot.mount @4.286s +31ms
+ └─systemd-fsck@dev-disk-by\x2duuid-79f594ad\x2da332\x2d4730\x2dbb5f\x2d85d19608096
+ └─dev-disk-by\x2duuid-79f594ad\x2da332\x2d4730\x2dbb5f\x2d85d196080964.device @4
+
+**重要**:Systemctl接受服务(.service),挂载点(.mount),套接口(.socket)和设备(.device)作为单元。
+
+#### 7. 列出所有可用单元 ####
+
+ # systemctl list-unit-files
+
+ UNIT FILE STATE
+ proc-sys-fs-binfmt_misc.automount static
+ dev-hugepages.mount static
+ dev-mqueue.mount static
+ proc-sys-fs-binfmt_misc.mount static
+ sys-fs-fuse-connections.mount static
+ sys-kernel-config.mount static
+ sys-kernel-debug.mount static
+ tmp.mount disabled
+ brandbot.path disabled
+ .....
+
+#### 8. 列出所有运行中单元 ####
+
+ # systemctl list-units
+
+ UNIT LOAD ACTIVE SUB DESCRIPTION
+ proc-sys-fs-binfmt_misc.automount loaded active waiting Arbitrary Executable File Formats File Syste
+ sys-devices-pc...0-1:0:0:0-block-sr0.device loaded active plugged VBOX_CD-ROM
+ sys-devices-pc...:00:03.0-net-enp0s3.device loaded active plugged PRO/1000 MT Desktop Adapter
+ sys-devices-pc...00:05.0-sound-card0.device loaded active plugged 82801AA AC'97 Audio Controller
+ sys-devices-pc...:0:0-block-sda-sda1.device loaded active plugged VBOX_HARDDISK
+ sys-devices-pc...:0:0-block-sda-sda2.device loaded active plugged LVM PV Qzyo3l-qYaL-uRUa-Cjuk-pljo-qKtX-VgBQ8
+ sys-devices-pc...0-2:0:0:0-block-sda.device loaded active plugged VBOX_HARDDISK
+ sys-devices-pl...erial8250-tty-ttyS0.device loaded active plugged /sys/devices/platform/serial8250/tty/ttyS0
+ sys-devices-pl...erial8250-tty-ttyS1.device loaded active plugged /sys/devices/platform/serial8250/tty/ttyS1
+ sys-devices-pl...erial8250-tty-ttyS2.device loaded active plugged /sys/devices/platform/serial8250/tty/ttyS2
+ sys-devices-pl...erial8250-tty-ttyS3.device loaded active plugged /sys/devices/platform/serial8250/tty/ttyS3
+ sys-devices-virtual-block-dm\x2d0.device loaded active plugged /sys/devices/virtual/block/dm-0
+ sys-devices-virtual-block-dm\x2d1.device loaded active plugged /sys/devices/virtual/block/dm-1
+ sys-module-configfs.device loaded active plugged /sys/module/configfs
+ ...
+
+#### 9. 列出所有失败单元 ####
+
+ # systemctl --failed
+
+ UNIT LOAD ACTIVE SUB DESCRIPTION
+ kdump.service loaded failed failed Crash recovery kernel arming
+
+ LOAD = Reflects whether the unit definition was properly loaded.
+ ACTIVE = The high-level unit activation state, i.e. generalization of SUB.
+ SUB = The low-level unit activation state, values depend on unit type.
+
+ 1 loaded units listed. Pass --all to see loaded but inactive units, too.
+ To show all installed unit files use 'systemctl list-unit-files'.
+
+#### 10. 检查某个单元(cron.service)是否启用 ####
+
+ # systemctl is-enabled crond.service
+
+ enabled
+
+#### 11. 检查某个单元或服务是否运行 ####
+
+ # systemctl status firewalld.service
+
+ firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
+ Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled)
+ Active: active (running) since Tue 2015-04-28 16:27:55 IST; 34min ago
+ Main PID: 549 (firewalld)
+ CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service
+ └─549 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid
+
+ Apr 28 16:27:51 tecmint systemd[1]: Starting firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon...
+ Apr 28 16:27:55 tecmint systemd[1]: Started firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon.
+
+### 使用Systemctl控制并管理服务 ###
+
+#### 12. 列出所有服务(包括启用的和禁用的) ####
+
+ # systemctl list-unit-files --type=service
+
+ UNIT FILE STATE
+ arp-ethers.service disabled
+ auditd.service enabled
+ autovt@.service disabled
+ blk-availability.service disabled
+ brandbot.service static
+ collectd.service disabled
+ console-getty.service disabled
+ console-shell.service disabled
+ cpupower.service disabled
+ crond.service enabled
+ dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service enabled
+ ....
+
+#### 13. Linux中如何启动、重启、停止、重载服务以及检查服务(httpd.service)状态 ####
+
+ # systemctl start httpd.service
+ # systemctl restart httpd.service
+ # systemctl stop httpd.service
+ # systemctl reload httpd.service
+ # systemctl status httpd.service
+
+ httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
+ Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; enabled)
+ Active: active (running) since Tue 2015-04-28 17:21:30 IST; 6s ago
+ Process: 2876 ExecStop=/bin/kill -WINCH ${MAINPID} (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
+ Main PID: 2881 (httpd)
+ Status: "Processing requests..."
+ CGroup: /system.slice/httpd.service
+ ├─2881 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
+ ├─2884 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
+ ├─2885 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
+ ├─2886 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
+ ├─2887 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
+ └─2888 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
+
+ Apr 28 17:21:30 tecmint systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server...
+ Apr 28 17:21:30 tecmint httpd[2881]: AH00558: httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully q...ssage
+ Apr 28 17:21:30 tecmint systemd[1]: Started The Apache HTTP Server.
+ Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
+
+**注意**:当我们使用systemctl的start,restart,stop和reload命令时,我们不会不会从终端获取到任何输出内容,只有status命令可以打印输出。
+
+#### 14. 如何激活服务并在启动时启用或禁用服务(系统启动时自动启动服务) ####
+
+ # systemctl is-active httpd.service
+ # systemctl enable httpd.service
+ # systemctl disable httpd.service
+
+#### 15. 如何屏蔽(让它不能启动)或显示服务(httpd.service) ####
+
+ # systemctl mask httpd.service
+ ln -s '/dev/null' '/etc/systemd/system/httpd.service'
+
+ # systemctl unmask httpd.service
+ rm '/etc/systemd/system/httpd.service'
+
+#### 16. 使用systemctl命令杀死服务 ####
+
+ # systemctl kill httpd
+ # systemctl status httpd
+
+ httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
+ Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; enabled)
+ Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since Tue 2015-04-28 18:01:42 IST; 28min ago
+ Main PID: 2881 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
+ Status: "Total requests: 0; Current requests/sec: 0; Current traffic: 0 B/sec"
+
+ Apr 28 17:37:29 tecmint systemd[1]: httpd.service: Got notification message from PID 2881, but recepti...bled.
+ Apr 28 17:37:29 tecmint systemd[1]: httpd.service: Got notification message from PID 2881, but recepti...bled.
+ Apr 28 17:37:39 tecmint systemd[1]: httpd.service: Got notification message from PID 2881, but recepti...bled.
+ Apr 28 17:37:39 tecmint systemd[1]: httpd.service: Got notification message from PID 2881, but recepti...bled.
+ Apr 28 17:37:49 tecmint systemd[1]: httpd.service: Got notification message from PID 2881, but recepti...bled.
+ Apr 28 17:37:49 tecmint systemd[1]: httpd.service: Got notification message from PID 2881, but recepti...bled.
+ Apr 28 17:37:59 tecmint systemd[1]: httpd.service: Got notification message from PID 2881, but recepti...bled.
+ Apr 28 17:37:59 tecmint systemd[1]: httpd.service: Got notification message from PID 2881, but recepti...bled.
+ Apr 28 18:01:42 tecmint systemd[1]: httpd.service: control process exited, code=exited status=226
+ Apr 28 18:01:42 tecmint systemd[1]: Unit httpd.service entered failed state.
+ Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
+
+### 使用Systemctl控制并管理挂载点 ###
+
+#### 17. 列出所有系统挂载点 ####
+
+ # systemctl list-unit-files --type=mount
+
+ UNIT FILE STATE
+ dev-hugepages.mount static
+ dev-mqueue.mount static
+ proc-sys-fs-binfmt_misc.mount static
+ sys-fs-fuse-connections.mount static
+ sys-kernel-config.mount static
+ sys-kernel-debug.mount static
+ tmp.mount disabled
+
+#### 18. 挂载、卸载、重新挂载、重载系统挂载点并检查系统中挂载点状态 ####
+
+ # systemctl start tmp.mount
+ # systemctl stop tmp.mount
+ # systemctl restart tmp.mount
+ # systemctl reload tmp.mount
+ # systemctl status tmp.mount
+
+ tmp.mount - Temporary Directory
+ Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/tmp.mount; disabled)
+ Active: active (mounted) since Tue 2015-04-28 17:46:06 IST; 2min 48s ago
+ Where: /tmp
+ What: tmpfs
+ Docs: man:hier(7)
+
+ http://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/systemd/APIFileSystems
+
+ Process: 3908 ExecMount=/bin/mount tmpfs /tmp -t tmpfs -o mode=1777,strictatime (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
+
+ Apr 28 17:46:06 tecmint systemd[1]: Mounting Temporary Directory...
+ Apr 28 17:46:06 tecmint systemd[1]: tmp.mount: Directory /tmp to mount over is not empty, mounting anyway.
+ Apr 28 17:46:06 tecmint systemd[1]: Mounted Temporary Directory.
+
+#### 19. 在启动时激活、启用或禁用挂载点(系统启动时自动挂载) ####
+
+ # systemctl is-active tmp.mount
+ # systemctl enable tmp.mount
+ # systemctl disable tmp.mount
+
+#### 20. 在Linux中屏蔽(让它不能启动)或显示挂载点 ####
+
+ # systemctl mask tmp.mount
+
+ ln -s '/dev/null' '/etc/systemd/system/tmp.mount'
+
+ # systemctl unmask tmp.mount
+
+ rm '/etc/systemd/system/tmp.mount'
+
+### 使用Systemctl控制并管理套接口 ###
+
+#### 21. 列出所有可用系统套接口 ####
+
+ # systemctl list-unit-files --type=socket
+
+ UNIT FILE STATE
+ dbus.socket static
+ dm-event.socket enabled
+ lvm2-lvmetad.socket enabled
+ rsyncd.socket disabled
+ sshd.socket disabled
+ syslog.socket static
+ systemd-initctl.socket static
+ systemd-journald.socket static
+ systemd-shutdownd.socket static
+ systemd-udevd-control.socket static
+ systemd-udevd-kernel.socket static
+
+ 11 unit files listed.
+
+#### 22. 在Linux中启动、重启、停止、重载套接口并检查其状态####
+
+ # systemctl start cups.socket
+ # systemctl restart cups.socket
+ # systemctl stop cups.socket
+ # systemctl reload cups.socket
+ # systemctl status cups.socket
+
+ cups.socket - CUPS Printing Service Sockets
+ Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/cups.socket; enabled)
+ Active: active (listening) since Tue 2015-04-28 18:10:59 IST; 8s ago
+ Listen: /var/run/cups/cups.sock (Stream)
+
+ Apr 28 18:10:59 tecmint systemd[1]: Starting CUPS Printing Service Sockets.
+ Apr 28 18:10:59 tecmint systemd[1]: Listening on CUPS Printing Service Sockets.
+
+#### 23. 在启动时激活套接口,并启用或禁用它(系统启动时自启动) ####
+
+ # systemctl is-active cups.socket
+ # systemctl enable cups.socket
+ # systemctl disable cups.socket
+
+#### 24. 屏蔽(使它不能启动)或显示套接口 ####
+
+ # systemctl mask cups.socket
+ ln -s '/dev/null' '/etc/systemd/system/cups.socket'
+
+ # systemctl unmask cups.socket
+ rm '/etc/systemd/system/cups.socket'
+
+### 服务的CPU利用率(分配额) ###
+
+#### 25. 获取当前某个服务的CPU分配额(如httpd) ####
+
+ # systemctl show -p CPUShares httpd.service
+
+ CPUShares=1024
+
+**注意**:各个服务的默认CPU分配份额=1024,你可以增加/减少某个进程的CPU分配份额。
+
+#### 26. 将某个服务(httpd.service)的CPU分配份额限制为2000 CPUShares/ ####
+
+ # systemctl set-property httpd.service CPUShares=2000
+ # systemctl show -p CPUShares httpd.service
+
+ CPUShares=2000
+
+**注意**:当你为某个服务设置CPUShares,会自动创建一个以服务名命名的目录(httpd.service),里面包含了一个名为90-CPUShares.conf的文件,该文件含有CPUShare限制信息,你可以通过以下方式查看该文件:
+
+ # vi /etc/systemd/system/httpd.service.d/90-CPUShares.conf
+
+ [Service]
+ CPUShares=2000
+
+#### 27. 检查某个服务的所有配置细节 ####
+
+ # systemctl show httpd
+
+ Id=httpd.service
+ Names=httpd.service
+ Requires=basic.target
+ Wants=system.slice
+ WantedBy=multi-user.target
+ Conflicts=shutdown.target
+ Before=shutdown.target multi-user.target
+ After=network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target systemd-journald.socket basic.target system.slice
+ Description=The Apache HTTP Server
+ LoadState=loaded
+ ActiveState=active
+ SubState=running
+ FragmentPath=/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service
+ ....
+
+#### 28. 分析某个服务(httpd)的关键链 ####
+
+ # systemd-analyze critical-chain httpd.service
+
+ The time after the unit is active or started is printed after the "@" character.
+ The time the unit takes to start is printed after the "+" character.
+
+ httpd.service +142ms
+ └─network.target @11.168s
+ └─network.service @9.456s +1.712s
+ └─NetworkManager.service @8.858s +596ms
+ └─firewalld.service @4.931s +3.926s
+ └─basic.target @4.916s
+ └─sockets.target @4.916s
+ └─dbus.socket @4.916s
+ └─sysinit.target @4.905s
+ └─systemd-update-utmp.service @4.864s +39ms
+ └─auditd.service @4.563s +301ms
+ └─systemd-tmpfiles-setup.service @4.485s +69ms
+ └─rhel-import-state.service @4.342s +142ms
+ └─local-fs.target @4.324s
+ └─boot.mount @4.286s +31ms
+ └─systemd-fsck@dev-disk-by\x2duuid-79f594ad\x2da332\x2d4730\x2dbb5f\x2d85d196080964.service @4.092s +149ms
+ └─dev-disk-by\x2duuid-79f594ad\x2da332\x2d4730\x2dbb5f\x2d85d196080964.device @4.092s
+
+#### 29. 获取某个服务(httpd)的依赖性列表 ####
+
+ # systemctl list-dependencies httpd.service
+
+ httpd.service
+ ├─system.slice
+ └─basic.target
+ ├─firewalld.service
+ ├─microcode.service
+ ├─rhel-autorelabel-mark.service
+ ├─rhel-autorelabel.service
+ ├─rhel-configure.service
+ ├─rhel-dmesg.service
+ ├─rhel-loadmodules.service
+ ├─paths.target
+ ├─slices.target
+ │ ├─-.slice
+ │ └─system.slice
+ ├─sockets.target
+ │ ├─dbus.socket
+ ....
+
+#### 30. 按等级列出控制组 ####
+
+ # systemd-cgls
+
+ ├─1 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd --switched-root --system --deserialize 23
+ ├─user.slice
+ │ └─user-0.slice
+ │ └─session-1.scope
+ │ ├─2498 sshd: root@pts/0
+ │ ├─2500 -bash
+ │ ├─4521 systemd-cgls
+ │ └─4522 systemd-cgls
+ └─system.slice
+ ├─httpd.service
+ │ ├─4440 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
+ │ ├─4442 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
+ │ ├─4443 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
+ │ ├─4444 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
+ │ ├─4445 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
+ │ └─4446 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
+ ├─polkit.service
+ │ └─721 /usr/lib/polkit-1/polkitd --no-debug
+ ....
+
+#### 31. 按CPU、内存、输入和输出列出控制组 ####
+
+ # systemd-cgtop
+
+ Path Tasks %CPU Memory Input/s Output/s
+
+ / 83 1.0 437.8M - -
+ /system.slice - 0.1 - - -
+ /system.slice/mariadb.service 2 0.1 - - -
+ /system.slice/tuned.service 1 0.0 - - -
+ /system.slice/httpd.service 6 0.0 - - -
+ /system.slice/NetworkManager.service 1 - - - -
+ /system.slice/atop.service 1 - - - -
+ /system.slice/atopacct.service 1 - - - -
+ /system.slice/auditd.service 1 - - - -
+ /system.slice/crond.service 1 - - - -
+ /system.slice/dbus.service 1 - - - -
+ /system.slice/firewalld.service 1 - - - -
+ /system.slice/lvm2-lvmetad.service 1 - - - -
+ /system.slice/polkit.service 1 - - - -
+ /system.slice/postfix.service 3 - - - -
+ /system.slice/rsyslog.service 1 - - - -
+ /system.slice/system-getty.slice/getty@tty1.service 1 - - - -
+ /system.slice/systemd-journald.service 1 - - - -
+ /system.slice/systemd-logind.service 1 - - - -
+ /system.slice/systemd-udevd.service 1 - - - -
+ /system.slice/webmin.service 1 - - - -
+ /user.slice/user-0.slice/session-1.scope 3 - - - -
+
+### 控制系统运行等级 ###
+
+#### 32. 启动系统救援模式 ####
+
+ # systemctl rescue
+
+ Broadcast message from root@tecmint on pts/0 (Wed 2015-04-29 11:31:18 IST):
+
+ The system is going down to rescue mode NOW!
+
+#### 33. 进入紧急模式 ####
+
+ # systemctl emergency
+
+ Welcome to emergency mode! After logging in, type "journalctl -xb" to view
+ system logs, "systemctl reboot" to reboot, "systemctl default" to try again
+ to boot into default mode.
+
+#### 34. 列出当前使用的运行等级 ####
+
+ # systemctl get-default
+
+ multi-user.target
+
+#### 35. 启动运行等级5,即图形模式 ####
+
+ # systemctl isolate runlevel5.target
+ OR
+ # systemctl isolate graphical.target
+
+#### 36. 启动运行等级3,即多用户模式(命令行) ####
+
+ # systemctl isolate runlevel3.target
+ OR
+ # systemctl isolate multiuser.target
+
+#### 36. 设置多用户模式或图形模式为默认运行等级 ####
+
+ # systemctl set-default runlevel3.target
+
+ # systemctl set-default runlevel5.target
+
+#### 37. 重启、停止、挂起、休眠系统或使系统进入混合睡眠 ####
+
+ # systemctl reboot
+
+ # systemctl halt
+
+ # systemctl suspend
+
+ # systemctl hibernate
+
+ # systemctl hybrid-sleep
+
+对于不知运行等级为何物的人,说明如下。
+
+- Runlevel 0 : 关闭系统
+- Runlevel 1 : 救援?维护模式
+- Runlevel 3 : 多用户,无图形系统
+- Runlevel 4 : 多用户,无图形系统
+- Runlevel 5 : 多用户,图形化系统
+- Runlevel 6 : 关闭并重启机器
+
+到此为止吧。保持连线,进行评论。别忘了在下面的评论中为我们提供一些有价值的反馈哦。喜欢我们、与我们分享,求扩散。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/manage-services-using-systemd-and-systemctl-in-linux/
+
+作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150506 First Step Guide for Learning Shell Scripting.md b/translated/tech/20150506 First Step Guide for Learning Shell Scripting.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..af71b8f4ca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150506 First Step Guide for Learning Shell Scripting.md
@@ -0,0 +1,460 @@
+Shell脚本学习初次操作指南
+================================================================================
+
+
+通常,当人们提到“shell脚本语言”时,浮现在他们脑海中是bash,ksh,sh或者其它相类似的linux/unix脚本语言。脚本语言是与计算机交流的另外一种途径。使用图形化窗口界面(不管是windows还是linux都无所谓)用户可以移动鼠标并点击各种对象,比如按钮、列表、选框等等。但这种方式在每次用户想要计算机/服务器完成相同任务时(比如说批量转换照片,或者下载新的电影、mp3等)却是十分不方便。要想让所有这些事情变得简单并且自动化,我们可以使用shell脚本。
+
+某些编程语言,像pascal、foxpro、C、java之类,在执行前需要先进行编译。它们需要合适的编译器来让我们的代码完成某个任务。
+
+而其它一些编程语言,像php、javascript、visualbasic之类,则不需要编译器,因此它们需要解释器,而我们不需要编译代码就可以运行程序。
+
+shell脚本也像解释器一样,但它通常用于调用外部已编译的程序。然后,它会捕获输出结果、退出代码并根据情况进行处理。
+
+Linux世界中最为流行的shell脚本语言之一,就是bash。而我认为(这是我自己的看法)原因在于,默认情况下bash shell可以让用户便捷地通过历史命令(先前执行过的)导航,与之相反的是,ksh则要求对.profile进行一些调整,或者记住一些“魔术”组合键来查阅历史并修正命令。
+
+好了,我想这些介绍已经足够了,剩下来哪个环境最适合你,就留给你自己去判断吧。从现在开始,我将只讲bash及其脚本。在下面的例子中,我将使用CentOS 6.6和bash-4.1.2。请确保你有相同版本,或者更高版本。
+
+### Shell脚本流 ###
+
+shell脚本语言就跟和几个人聊天类似。你只需把所有命令想象成能帮你做事的那些人,只要你用正确的方式来请求他们去做。比如说,你想要写文档。首先,你需要纸。然后,你需要把内容说给某个人听,让他帮你写。最后,你想要把它存放到某个地方。或者说,你想要造一所房子,因而你需要请合适的人来清空场地。在他们说“事情干完了”,那么另外一些工程师就可以帮你来砌墙。最后,当这些工程师们也告诉你“事情干完了”的时候,你就可以叫油漆工来给房子粉饰了。如果你让油漆工在墙砌好前就来粉饰,会发生什么呢?我想,他们会开始发牢骚了。几乎所有这些像人一样的命令都会说话,如果它们完成了工作而没有发生什么问题,那么它们就会告诉“标准输出”。如果它们不能做你叫它们做的事——它们会告诉“标准错误”。这样,最后,所有的命令都通过“标准输入”来听你的话。
+
+快速实例——当你打开linux终端并写一些文本时——你正通过“标准输入”和bash说话。那么,让我们来问问bash shell **who am i**吧。
+
+ root@localhost ~]# who am i <--- you speaking through the standard input to bash shell
+ root pts/0 2015-04-22 20:17 (192.168.1.123) <--- bash shell answering to you through the standard output
+
+现在,让我们说一些bash听不懂的问题:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# blablabla <--- 哈,你又在和标准输入说话了
+ -bash: blablabla: command not found <--- bash通过标准错误在发牢骚了
+
+“:”之前的第一个单词通常是向你发牢骚的命令。实际上,这些流中的每一个都有它们自己的索引号:
+
+- 标准输入(**stdin**) - 0
+- 标准输出(**stdout**) - 1
+- 标准错误(**stderr**) - 2
+
+如果你真的想要知道哪个输出命令说了些什么——你需要重定向(在命令后使用大于号“>”和流索引)那次发言到文件:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# blablabla 1> output.txt
+ -bash: blablabla: command not found
+
+在本例中,我们试着重定向1(**stdout**)流到名为output.txt的文件。让我们来看对该文件内容所做的事情吧,使用cat命令可以做这事:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat output.txt
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+看起来似乎是空的。好吧,现在让我们来重定向2(**stderr**)流:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# blablabla 2> error.txt
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+好吧,我们看到牢骚话没了。让我们检查一下那个文件:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat error.txt
+ -bash: blablabla: command not found
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+果然如此!我们看到,所有牢骚话都被记录到errors.txt文件里头去了。
+
+有时候,命令会同时产生**stdout**和**stderr**。要重定向它们到不同的文件,我们可以使用以下语句:
+
+ command 1>out.txt 2>err.txt
+
+要缩短一点语句,我们可以忽略“1”,因为默认情况下**stdout**会被重定向:
+
+ command >out.txt 2>err.txt
+
+好吧,让我们试试做些“坏事”。让我们用rm命令把file1和folder1给删了吧:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# rm -vf folder1 file1 > out.txt 2>err.txt
+
+现在来检查以下输出文件:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat out.txt
+ removed `file1'
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat err.txt
+ rm: cannot remove `folder1': Is a directory
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+正如我们所看到的,不同的流被分离到了不同的文件。有时候,这也不似很方便,因为我们想要查看出现错误时,在某些操作前面或后面所连续发生的事情。要实现这一目的,我们可以重定向两个流到同一个文件:
+
+ command >>out_err.txt 2>>out_err.txt
+
+注意:请注意,我使用“>>”替代了“>”。它允许我们附加到文件,而不是覆盖文件。
+
+我们可以重定向一个流到另一个:
+
+ command >out_err.txt 2>&1
+
+让我来解释一下吧。所有命令的标准输出将被重定向到out_err.txt,错误输出将被重定向到1-st流(上面已经解释过了),而该流会被重定向到同一个文件。让我们看这个实例:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# rm -fv folder2 file2 >out_err.txt 2>&1
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat out_err.txt
+ rm: cannot remove `folder2': Is a directory
+ removed `file2'
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+看着这些组合的输出,我们可以将其说明为:首先,**rm**命令试着将folder2删除,而它不会成功,因为linux要求**-r**键来允许**rm**命令删除文件夹,而第二个file2会被删除。通过为**rm**提供**-v**(详情)键,我们让rm命令告诉我们每个被删除的文件或文件夹。
+
+这些就是你需要知道的,关于重定向的几乎所有内容了。我是说几乎,因为还有一个更为重要的重定向工具,它称之为“管道”。通过使用|(管道)符号,我们通常重定向**stdout**流。
+
+比如说,我们有这样一个文本文件:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat text_file.txt
+ This line does not contain H e l l o word
+ This lilne contains Hello
+ This also containd Hello
+ This one no due to HELLO all capital
+ Hello bash world!
+
+而我们需要找到其中某些带有“Hello”的行,Linux中有个**grep**命令可以完成该工作:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# grep Hello text_file.txt
+ This lilne contains Hello
+ This also containd Hello
+ Hello bash world!
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+当我们有个文件,想要在里头搜索的时候,这用起来很不错。当如果我们需要在另一个命令的输出中查找某些东西,这又该怎么办呢?是的,当然,我们可以重定向输出到文件,然后再在文件里头查找:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# fdisk -l>fdisk.out
+ [root@localhost ~]# grep "Disk /dev" fdisk.out
+ Disk /dev/sda: 8589 MB, 8589934592 bytes
+ Disk /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root: 7205 MB, 7205814272 bytes
+ Disk /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_swap: 855 MB, 855638016 bytes
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+如果你打算grep一些双引号引起来带有空格的内容呢!
+
+注意: fdisk命令显示关于Linux操作系统磁盘驱动器的信息
+
+就像我们看到的,这种方式很不方便,因为我们不一会儿就把临时文件空间给搞乱了。要完成该任务,我们可以使用管道。它们允许我们重定向一个命令的**stdout**到另一个命令的**stdin**流:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# fdisk -l | grep "Disk /dev"
+ Disk /dev/sda: 8589 MB, 8589934592 bytes
+ Disk /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root: 7205 MB, 7205814272 bytes
+ Disk /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_swap: 855 MB, 855638016 bytes
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+如你所见,我们不需要任何临时文件就获得了相同的结果。我们把**fdisk stdout**重定向到了**grep stdin**。
+
+**注意** : 管道重定向总是从左至右的。
+
+还有几个其它重定向,但是我们将把它们放在后面讲。
+
+### 在shell中显示自定义信息 ###
+
+正如我们所知道的,通常,与shell的交流以及shell内的交流是以对话的方式进行的。因此,让我们创建一些真正的脚本吧,这些脚本也会和我们讲话。这会让你学到一些简单的命令,并对脚本的概念有一个更好的理解。
+
+假设我们是某个公司的总服务台经理,我们想要创建某个shell脚本来注册呼叫信息:电话号码、用户名以及问题的简要描述。我们打算把这些信息存储到普通文本文件data.txt中,以便今后统计。脚本它自己就是以对话的方式工作,这会让总服务台的工作人员的小日子过得轻松点。那么,首先我们需要显示问题。对于现实信息,我们可以用echo和printf命令。这两个都是用来显示信息的,但是printf更为强大,因为我们可以通过它很好地格式化输出,我们可以让它右对齐、左对齐或者为信息留出专门的空间。让我们从一个简单的例子开始吧。要创建文件,请使用你喜欢的文本编辑器(kate,nano,vi,……),然后创建名为note.sh的文件,里面写入这些命令:
+
+ echo "Phone number ?"
+
+### Script执行 ###
+
+在保存文件后,我们可以使用bash命令来运行,把我们的文件作为它的参数:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# bash note.sh
+ Phone number ?
+
+实际上,这样来执行脚本是很不方便的。如果不使用**bash**命令作为前缀来执行,会更舒服一些。要让脚本可执行,我们可以使用**chmod**命令:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# ls -la note.sh
+ -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 22 Apr 23 20:52 note.sh
+ [root@localhost ~]# chmod +x note.sh
+ [root@localhost ~]# ls -la note.sh
+ -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 22 Apr 23 20:52 note.sh
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+
+
+**注意** : ls命令显示了当前文件夹内的文件。通过添加-la键,它会显示更多文件信息。
+
+如我们所见,在**chmod**命令执行前,脚本只有读(r)和写(w)权限。在执行**chmod +x**后,它就获得了执行(x)权限。(关于权限的更多细节,我会在下一篇文章中讲述。)现在,我们只需这么来运行:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# ./note.sh
+ Phone number ?
+
+在脚本名前,我添加了./组合。.(点)在unix世界中意味着当前位置(当前文件夹),/(斜线)是文件夹分隔符。(在Windows系统中,我们使用\(反斜线)实现同样功能)所以,这整个组合的意思是说:“从当前文件夹执行note.sh脚本”。我想,如果我用完整路径来运行这个脚本的话,你会更加清楚一些:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# /root/note.sh
+ Phone number ?
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+它也能工作。
+
+如果所有linux用户都有相同的默认shell,那就万事OK。如果我们只是执行该脚本,默认的用户shell就会用于解析脚本内容并运行命令。不同的shell有着一丁点不同的语法、内部命令等等,所以,为了保证我们的脚本会使用**bash**,我们应该添加**#!/bin/bash**到文件首行。这样,默认的用户shell将调用**/bin/bash**,而只有在那时候,脚本中的命令才会被执行:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat note.sh
+ #!/bin/bash
+ echo "Phone number ?"
+
+直到现在,我们才100%确信**bash**会用来解析我们的脚本内容。让我们继续。
+
+### 读取输入 ###
+
+在现实信息后,脚本会等待用户回答。那儿有个**read**命令用来接收用户的回答:
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+ echo "Phone number ?"
+ read phone
+
+在执行后,脚本会等待用户输入,直到用户按[ENTER]键:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# ./note.sh
+ Phone number ?
+ 12345 <--- 这儿是我输入的内容
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+你输入的所有东西都会被存储到变量**phone**中,要显示变量的值,我们同样可以使用**echo**命令:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat note.sh
+ #!/bin/bash
+ echo "Phone number ?"
+ read phone
+ echo "You have entered $phone as a phone number"
+ [root@localhost ~]# ./note.sh
+ Phone number ?
+ 123456
+ You have entered 123456 as a phone number
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+在**bash** shell中,我们使用**$**(美元)符号作为变量标示,除了读入到变量和其它为数不多的时候(将在今后说明)。
+
+好了,现在我们准备添加剩下的问题了:
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+ echo "Phone number?"
+ read phone
+ echo "Name?"
+ read name
+ echo "Issue?"
+ read issue
+ [root@localhost ~]# ./note.sh
+ Phone number?
+ 123
+ Name?
+ Jim
+ Issue?
+ script is not working.
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+### 使用流重定向 ###
+
+太完美了!剩下来就是重定向所有东西到文件data.txt了。作为字段分隔符,我们将使用/(斜线)符号。
+
+**注意** : 你可以选择任何你认为是最好,但是确保文件内容不会包含这些符号在内。它会导致在文本行中产生额外字段。
+
+别忘了使用“>>”来代替“>”,因为我们想要将输出内容附加到文件末!
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# tail -2 note.sh
+ read issue
+ echo "$phone/$name/$issue">>data.txt
+ [root@localhost ~]# ./note.sh
+ Phone number?
+ 987
+ Name?
+ Jimmy
+ Issue?
+ Keybord issue.
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat data.txt
+ 987/Jimmy/Keybord issue.
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+**注意** : **tail**命令显示了文件的最后**-n**行。
+
+搞定。让我们再来运行一次看看:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# ./note.sh
+ Phone number?
+ 556
+ Name?
+ Janine
+ Issue?
+ Mouse was broken.
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat data.txt
+ 987/Jimmy/Keybord issue.
+ 556/Janine/Mouse was broken.
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+我们的文件在增长,让我们在每行前面加个日期吧,这对于今后摆弄这些统计数据时会很有用。要实现这功能,我们可以使用date命令,并指定某种格式,因为我不喜欢默认格式:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# date
+ Thu Apr 23 21:33:14 EEST 2015 <---- date命令的默认输出
+ [root@localhost ~]# date "+%Y.%m.%d %H:%M:%S"
+ 2015.04.23 21:33:18 <---- 格式化后的输出
+
+有几种方式可以读取命令输出到变脸,在这种简单的情况下,我们将使用`(反引号):
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat note.sh
+ #!/bin/bash
+ now=`date "+%Y.%m.%d %H:%M:%S"`
+ echo "Phone number?"
+ read phone
+ echo "Name?"
+ read name
+ echo "Issue?"
+ read issue
+ echo "$now/$phone/$name/$issue">>data.txt
+ [root@localhost ~]# ./note.sh
+ Phone number?
+ 123
+ Name?
+ Jim
+ Issue?
+ Script hanging.
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat data.txt
+ 2015.04.23 21:38:56/123/Jim/Script hanging.
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+嗯…… 我们的脚本看起来有点丑啊,让我们来美化一下。如果你要手动读取**read**命令,你会发现read命令也可以显示一些信息。要实现该功能,我们应该使用-p键加上信息:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat note.sh
+ #!/bin/bash
+ now=`date "+%Y.%m.%d %H:%M:%S"`
+ read -p "Phone number: " phone
+ read -p "Name: " name
+ read -p "Issue: " issue
+ echo "$now/$phone/$name/$issue">>data.txt
+
+你可以直接从控制台查找到各个命令的大量有趣的信息,只需输入:**man read, man echo, man date, man ……**
+
+同意吗?它看上去是好多了!
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# ./note.sh
+ Phone number: 321
+ Name: Susane
+ Issue: Mouse was stolen
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat data.txt
+ 2015.04.23 21:38:56/123/Jim/Script hanging.
+ 2015.04.23 21:43:50/321/Susane/Mouse was stolen
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+光标在消息的后面(不是在新的一行中),这有点意思。
+
+循环
+
+是时候来改进我们的脚本了。如果用户一整天都在接电话,如果每次都要去运行,这岂不是很麻烦?让我们让这些活动都永无止境地循环去吧:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat note.sh
+ #!/bin/bash
+ while true
+ do
+ read -p "Phone number: " phone
+ now=`date "+%Y.%m.%d %H:%M:%S"`
+ read -p "Name: " name
+ read -p "Issue: " issue
+ echo "$now/$phone/$name/$issue">>data.txt
+ done
+
+我已经交换了**read phone**和**now=`date`**行。这是因为我想要在输入电话号码后再获得时间。如果我把它放在循环**- the**的首行,变量就会在数据存储到文件中后获得时间。而这并不好,因为下一次呼叫可能在20分钟后,甚至更晚。
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# ./note.sh
+ Phone number: 123
+ Name: Jim
+ Issue: Script still not works.
+ Phone number: 777
+ Name: Daniel
+ Issue: I broke my monitor
+ Phone number: ^C
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat data.txt
+ 2015.04.23 21:38:56/123/Jim/Script hanging.
+ 2015.04.23 21:43:50/321/Susane/Mouse was stolen
+ 2015.04.23 21:47:55/123/Jim/Script still not works.
+ 2015.04.23 21:48:16/777/Daniel/I broke my monitor
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+注意: 要从无限循环中退出,你可以按[Ctrl]+[C]键。Shell会显示^表示Ctrl键。
+
+### 使用管道重定向 ###
+
+让我们添加更多功能到我们的“弗兰肯斯坦”,我想要脚本在每次呼叫后显示某个统计数据。比如说,我想要查看各个号码呼叫了我几次。对于这个,我们应该cat文件data.txt:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat data.txt
+ 2015.04.23 21:38:56/123/Jim/Script hanging.
+ 2015.04.23 21:43:50/321/Susane/Mouse was stolen
+ 2015.04.23 21:47:55/123/Jim/Script still not works.
+ 2015.04.23 21:48:16/777/Daniel/I broke my monitor
+ 2015.04.23 22:02:14/123/Jimmy/New script also not working!!!
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+现在,所有输出我们都可以重定向到**cut**命令,让**cut**来把每行切成一块一块(我们使用分隔符“/”),然后打印第二个字段:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat data.txt | cut -d"/" -f2
+ 123
+ 321
+ 123
+ 777
+ 123
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+现在,我们可以把这个输出重定向打另外一个命令**sort**:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat data.txt | cut -d"/" -f2|sort
+ 123
+ 123
+ 123
+ 321
+ 777
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+然后只留下唯一的行。要统计唯一条目,只需添加**-c**键到**uniq**命令:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# cat data.txt | cut -d"/" -f2 | sort | uniq -c
+ 3 123
+ 1 321
+ 1 777
+ [root@localhost ~]#
+
+只要把这个添加到我们的循环的最后:
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+ while true
+ do
+ read -p "Phone number: " phone
+ now=`date "+%Y.%m.%d %H:%M:%S"`
+ read -p "Name: " name
+ read -p "Issue: " issue
+ echo "$now/$phone/$name/$issue">>data.txt
+ echo "===== We got calls from ====="
+ cat data.txt | cut -d"/" -f2 | sort | uniq -c
+ echo "--------------------------------"
+ done
+
+运行:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# ./note.sh
+ Phone number: 454
+ Name: Malini
+ Issue: Windows license expired.
+ ===== We got calls from =====
+ 3 123
+ 1 321
+ 1 454
+ 1 777
+ --------------------------------
+ Phone number: ^C
+
+
+
+当前场景贯穿了几个熟知的步骤:
+
+- 显示消息
+- 获取用户输入
+- 存储值到文件
+- 处理存储的数据
+
+但是,如果用户有点责任心,他有时候需要输入数据,有时候需要统计,或者可能要在存储的数据中查找一些东西呢?对于这些事情,我们需要使用switches/cases,并知道怎样来很好地格式化输出。这对于在shell中“画”表格的时候很有用。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-shell-script/guide-start-learning-shell-scripting-scratch/
+
+作者:[Petras Liumparas][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/petrasl/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150506 How to Setup OpenERP (Odoo) on CentOS 7.x.md b/translated/tech/20150506 How to Setup OpenERP (Odoo) on CentOS 7.x.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0cd972b425
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150506 How to Setup OpenERP (Odoo) on CentOS 7.x.md
@@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
+如何在CentOS 7.x中安装OpenERP(Odoo)
+================================================================================
+各位好,这篇教程关于的是如何在CentOS 7中安装Odoo(就是我们所知的OpenERP)。你是不是在考虑为你的业务安装一个不错的ERP(企业资源规划)软件?那么OpenERP就是你寻找的最好的程序,因为它是一款为你的商务提供杰出特性的自由开源软件。
+
+[OpenERP][1]是一款自由开源的传统的OpenERP(企业资源规划),它包含了开源CRM、网站构建、电子商务、项目管理、计费账务、销售点、人力资源、市场、生产、采购管理以及其他模块用于提高效率及销售。Odoo可以作为独立程序,但是它可以无缝集成因此你可以在安装数个程序后得到一个全功能的开源ERP。
+
+因此,下面是在你的CentOS上安装OpenERP的步骤。
+
+### 1. 安装 PostgreSQL ###
+
+首先,首先我们需要更新CentOS 7的软件包来确保是最新的包,补丁和安全更新。要更新我们的系统,我们要在shell下运行下面的命令。
+
+ # yum clean all
+ # yum update
+
+现在我们要安装PostgreSQL,因为OpenERP使用PostgreSQL作为他的数据库。要安装它,我们需要运行下面的命令。
+
+ # yum install postgresql postgresql-server postgresql-libs
+
+
+
+、安装完成后,我们需要用下面的命令初始化数据库。
+
+ # postgresql-setup initdb
+
+
+
+我们接着设置PostgreSQL来使它每次开机启动。
+
+ # systemctl enable postgresql
+ # systemctl start postgresql
+
+因为我们还没有为用户“postgresql”设置密码,我们现在设置。
+
+ # su - postgres
+ $ psql
+ postgres=# \password postgres
+ postgres=# \q
+ # exit
+
+
+
+### 2. 设置Odoo仓库 ###
+
+在初始化数据库初始化完成后,我们要添加EPEL(企业版Linux的额外包)到我们的CentOS中。Odoo(或者OpenERP)依赖于Python运行时以及其他包没有包含在标准仓库中。这样我们要位企业版Linux添加额外的包仓库支持来解决Odoo所需要的依赖。要安装完成,我们需要运行下面的命令。
+
+ # yum install epel-release
+
+
+
+现在,安装EPEL后,我们现在使用yum-config-manager添加Odoo(OpenERp)的仓库。
+
+ # yum install yum-utils
+
+ # yum-config-manager --add-repo=https://nightly.odoo.com/8.0/nightly/rpm/odoo.repo
+
+
+
+### 3. 安装Odoo 8 (OpenERP) ###
+
+在CentOS 7中添加Odoo 8(OpenERP)的仓库后。我们使用下面的命令来安装Odoo 8(OpenERP)。
+
+ # yum install -y odoo
+
+上面的命令会安装odoo以及必须的依赖的包。
+
+
+
+现在我们使用下面的命令在每次启动后启动Odoo服务。
+
+ # systemctl enable odoo
+ # systemctl start odoo
+
+
+
+### 4. 防火墙允许 ###
+
+因为Odoo使用8069端口,我们需要在防火墙中允许远程访问。我们使用下面的命令来在防火墙中允许8069防火墙。
+
+ # firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8069/tcp --permanent
+ # firewall-cmd --reload
+
+
+
+**注意:默认上,只有本地的连接才允许。如果我们要允许PostgreSQL的远程访问,我们需要在pg_hba.conf添加下面图片中一行**
+
+ # nano /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf
+
+
+
+### 5. Web接口 ###
+
+我们已经在CentOS 7中安装了最新的Odoo 8(OpenERP),我们可以在浏览器中输入http://ip-address:8069来访问Odoo。 接着,我们要做的第一件事就是创建一个新的数据库和新的密码。注意,主密码默认是管理员密码。接着,我们可以在面板中输入用户名和密码。
+
+
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+Odoo 8(OpenERP)是世界上最好的开源ERP程序。我们做了一件出色的工作来安装它因为OpenERP是由许多模块组成的针对商务和公司的完整ERP程序。因此,如果你有任何问题、建议、反馈请在下面的评论栏写下。谢谢你!享受OpenERP(Odoo 8)吧 :-)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/setup-openerp-odoo-centos-7/
+
+作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
+[1]:https://www.odoo.com/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150506 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to disable entering password for default keyring to unlock on Ubuntu desktop.md b/translated/tech/20150506 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to disable entering password for default keyring to unlock on Ubuntu desktop.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2871298396
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150506 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to disable entering password for default keyring to unlock on Ubuntu desktop.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+Linux有问必答——Ubuntu桌面上如何禁用默认的密钥环解锁密码输入
+================================================================================
+>**问题**:当我启动我的Ubuntu桌面时,出现了一个弹出对话框,要求我输入密码来解锁默认的密钥环。我怎样才能禁用这个“解锁默认密钥环”弹出窗口,并自动解锁我的密钥环?
+
+密钥环被认为是用来以加密方式存储你的登录信息的本地数据库。各种桌面应用(如浏览器、电子邮件客户端)使用密钥环来安全地存储并管理你的登录凭证、机密、密码、证书或密钥。对于那些需要检索存储在密钥环中的信息的应用程序,需要解锁该密钥环。
+
+Ubuntu桌面所使用的GNOME密钥环被整合到了桌面登录中,该密钥环会在你验证进入桌面后自动解锁。但是,如果你设置了自动登录桌面或者是从休眠中唤醒,你默认的密钥环仍然可能“被锁定”的。在这种情况下,你会碰到这一提示:
+
+>“为密钥环‘默认密钥环’输入密码来解锁。某个应用想要访问密钥环‘默认密钥环’,但它被锁定了。”
+>
+
+
+如果你想要避免在每次弹出对话框出现时输入密码来解锁默认密钥环,那么你可以这样做。
+
+在做之前,请先了解禁用密码提示后可能出现的结果。通过自动解锁默认密钥环,你可以让任何使用你桌面的人无需知道你的密码而能获取你的密钥环(以及存储在密钥环中的任何信息)。
+
+### 禁用默认密钥环解锁密码 ###
+
+打开Dash,然后输入“密码”来启动“密码和密钥”应用。
+
+
+
+或者,使用seahorse命令从命令行启动图形界面。
+
+ $ seahorse
+
+在左侧面板中,右击“默认密钥环”,并选择“修改密码”。
+
+
+
+输入你的当前登录密码。
+
+
+在设置“默认”密钥环新密码的密码框中留空。
+
+
+
+在询问是否不加密存储密码对话框中点击“继续”。
+
+
+
+搞定。从今往后,那个该死的解锁密钥环提示对话框再也不会来烦你了。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/disable-entering-password-unlock-default-keyring.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150506 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install Shrew Soft IPsec VPN client on Linux.md b/translated/tech/20150506 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install Shrew Soft IPsec VPN client on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..abe1d3943d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150506 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install Shrew Soft IPsec VPN client on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
+Linux有问必答——Linux上如何安装Shrew Soft IPsec VPN
+================================================================================
+> **Question**: I need to connect to an IPSec VPN gateway. For that, I'm trying to use Shrew Soft VPN client, which is available for free. How can I install Shrew Soft VPN client on [insert your Linux distro]?
+> **问题**:我需要连接到一个IPSec VPN网关,鉴于此,我尝试使用Shrew Soft VPN客户端,它是一个免费版本。我怎样才能安装Shrew Soft VPN客户端到[插入你的Linux发行版]?
+
+市面上有许多商业VPN网关,同时附带有他们自己的专有VPN客户端软件。虽然也有许多开源的VPN服务器/客户端备选方案,但它们通常缺乏复杂的IPsec支持,比如互联网密钥交换(IKE),这是一个标准的IPsec协议,用于加固VPN密钥交换和验证安全。Shrew Soft VPN是一个免费的IPsec VPN客户端,它支持多种验证方法、密钥交换、加密以及防火墙穿越选项。
+
+下面介绍如何安装Shrew Soft VPN客户端到Linux平台。
+
+首先,从[官方站点][1]下载它的源代码。
+
+### 安装Shrew VPN客户端到Debian, Ubuntu或者Linux Mint ###
+
+Shrew Soft VPN客户端图形界面要求使用Qt 4.x。所以,作为依赖,你需要安装其开发文件。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install cmake libqt4-core libqt4-dev libqt4-gui libedit-dev libssl-dev checkinstall flex bison
+ $ wget https://www.shrew.net/download/ike/ike-2.2.1-release.tbz2
+ $ tar xvfvj ike-2.2.1-release.tbz2
+ $ cd ike
+ $ cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr -DQTGUI=YES -DETCDIR=/etc -DNATT=YES .
+ $ make
+ $ sudo make install
+ $ cd /etc/
+ $ sudo mv iked.conf.sample iked.conf
+
+### 安装Shrew VPN客户端到CentOS, Fedora或者RHEL ###
+
+与基于Debian的系统类似,在编译前你需要安装一堆依赖包,包括Qt4。
+
+ $ sudo yum install qt-devel cmake gcc-c++ openssl-devel libedit-devel flex bison
+ $ wget https://www.shrew.net/download/ike/ike-2.2.1-release.tbz2
+ $ tar xvfvj ike-2.2.1-release.tbz2
+ $ cd ike
+ $ cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr -DQTGUI=YES -DETCDIR=/etc -DNATT=YES .
+ $ make
+ $ sudo make install
+ $ cd /etc/
+ $ sudo mv iked.conf.sample iked.conf
+
+在基于Red Hat的系统中,最后一步需要用文本编辑器打开/etc/ld.so.conf文件,并添加以下行。
+
+ $ sudo vi /etc/ld.so.conf
+
+----------
+
+ include /usr/lib/
+
+重新加载运行时绑定的共享库文件,以容纳新安装的共享库:
+
+ $ sudo ldconfig
+
+### 启动Shrew VPN客户端 ###
+
+首先,启动IKE守护进程(iked)。该守护进作为VPN客户端程通过IKE协议与远程主机经由IPSec通信。
+
+ $ sudo iked
+
+
+
+现在,启动qikea,它是一个IPsec VPN客户端前端。该GUI应用允许你管理远程站点配置并初始化VPN连接。
+
+
+
+要创建一个新的VPN配置,点击“添加”按钮,然后填入VPN站点配置。创建配置后,你可以通过点击配置来初始化VPN连接。
+
+
+
+### 故障排除 ###
+
+1. 我在运行iked时碰到了如下错误。
+
+ iked: error while loading shared libraries: libss_ike.so.2.2.1: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
+
+要解决该问题,你需要更新动态链接器来容纳libss_ike库。对于此,请添加库文件的位置路径到/etc/ld.so.conf文件中,然后运行ldconfig命令。
+
+ $ sudo ldconfig
+
+验证libss_ike是否添加到了库路径:
+
+ $ ldconfig -p | grep ike
+
+----------
+
+ libss_ike.so.2.2.1 (libc6,x86-64) => /lib/libss_ike.so.2.2.1
+ libss_ike.so (libc6,x86-64) => /lib/libss_ike.so
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-shrew-soft-ipsec-vpn-client-linux.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
+[1]:https://www.shrew.net/download/ike
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150507 Install uGet Download Manager 2.0 in Debian Ubuntu Linux Mint and Fedora.md b/translated/tech/20150507 Install uGet Download Manager 2.0 in Debian Ubuntu Linux Mint and Fedora.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d5c2fc98f5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150507 Install uGet Download Manager 2.0 in Debian Ubuntu Linux Mint and Fedora.md
@@ -0,0 +1,134 @@
+在 Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint 及 Fedora 中安装 uGet 下载管理器 2.0
+================================================================================
+在经历了一段漫长的开发期后,期间发布了超过 11 个开发版本,最终 uGet 项目小组高兴地宣布 uGet 的最新稳定版本 uGet 2.0 已经可以下载使用了。最新版本包含许多吸引人的特点,例如一个新的设定对话框,改进了 aria2 插件对 BitTorrent 和 Metalink 协议的支持,同时对位于横栏中的 uGet RSS 信息提供了更好的支持,其他特点包括:
+
+- 一个新的 “检查更新” 按钮,提醒您有关新的发行版本的信息;
+- 增添新的语言支持并升级了现有的语言;
+- 增加了一个新的 “信息横栏” ,允许开发者轻松地向所有的用户提供有关 uGet 的信息;
+- 通过对文档、提交反馈和错误报告等内容的链接,增强了帮助菜单;
+- 将 uGet 下载管理器集成到了 Linux 平台下的两个主要的浏览器 Firefox 和 Google Chrome 中;
+- 改进了对 Firefox 插件 ‘FlashGot’ 的支持;
+
+### 何为 uGet ###
+
+uGet (先前名为 UrlGfe) 是一个开源,免费,且极其强大的基于 GTK 的多平台下载管理器应用程序,它用 C 语言写就,在 GPL 协议下发布。它提供了一大类的功能,如恢复先前的下载任务,支持多重下载,使用一个独立的配置来支持分类,剪贴板监视,下载队列,从 HTML 文件中导出 URL 地址,集成在 Firefox 中的 Flashgot 插件中,使用集成在 uGet 中的 aria2(一个命令行下载管理器) 来下载 torrent 和 metalink 文件。
+
+我已经在下面罗列出了 uGet 下载管理器的所有关键特点,并附带了详细的解释。
+
+#### uGet 下载管理器的关键特点 ####
+
+- 下载队列: 可以将你的下载任务放入一个队列中。当某些下载任务完成后,将会自动开始下载队列中余下的文件;
+- 恢复下载: 假如在某些情况下,你的网络中断了,不要担心,你可以从先前停止的地方继续下载或重新开始;
+- 下载分类: 支持多种分类来管理下载;
+- 剪贴板监视: 将要下载的文件类型复制到剪贴板中,便会自动弹出下载提示框以下载刚才复制的文件;
+- 批量下载: 允许你轻松地一次性下载多个文件;
+- 支持多种协议: 允许你轻松地使用 aria2 命令行插件通过 HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, BitTorrent 及 Metalink 等协议下载文件;
+- 多连接: 使用 aria2 插件,每个下载同时支持多达 20 个连接;
+- 支持 FTP 登录或匿名 FTP 登录: 同时支持使用用户名和密码来登录 FTP 或匿名 FTP ;
+- 队列下载: 新增队列下载,现在你可以对你的所有下载进行安排调度;
+- 通过 FlashGot 与 FireFox 集成: 与作为一个独立支持的 Firefox 插件的 FlashGot 集成,从而可以处理单个或大量的下载任务;
+- CLI 界面或虚拟终端支持: 提供命令行或虚拟终端选项来下载文件;
+- 自动创建目录: 假如你提供了一个先前并不存在的保存路径,uGet 将会自动创建这个目录;
+- 下载历史管理: 跟踪记录已下载和已删除的下载任务的条目,每个列表支持 9999 个条目,比当前默认支持条目数目更早的条目将会被自动删除;
+- 多语言支持: uGet 默认使用英语,但它可支持多达 23 种语言;
+- Aria2 插件: uGet 集成了 Aria2 插件,来为 aria2 提供更友好的 GUI 界面;
+
+如若你想了解更加完整的特点描述,请访问 uGet 官方的 [特点页面][1].
+
+### 在 Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint 及 Fedora 中安装 uGet ###
+
+uGet 开发者在 Linux 平台下的各种软件仓库中添加了 uGet 的最新版本,所以你可以在你使用的 Linux 发行版本下使用受支持的软件仓库来安装或升级 uGet 。
+
+当前,一些 Linux 发行版本下的 uGet 可能不是最新的,但你可以到 [uGet 下载页面][2] 去了解你所用发行版本的支持状态,在那里选择你喜爱的发行版本来了解更多的信息。
+
+#### 在 Debian 下 ####
+
+在 Debian 的测试版本 (Jessie) 和不稳定版本 (Sid) 中,你可以在一个可信赖的基础上,使用官方的软件仓库轻易地安装和升级 uGet 。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get install uget
+
+#### 在 Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 下 ####
+
+在 Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 下,你可以使用官方的 PPA `ppa:plushuang-tw/uget-stable` 安装和升级 uGet ,通过使用这个 PPA,你可以自动地与最新版本保持同步。
+
+ $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:plushuang-tw/uget-stable
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get install uget
+
+#### 在 Fedora 下 ####
+
+在 Fedora 20 – 21 下,最新版本的 uGet(2.0) 可以从官方软件仓库中获得,从这些软件仓库中安装是非常值得信赖的。
+
+ $ sudo yum install uget
+
+**注**: 在旧版本的 Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint 和 Fedora 下,用户也可以安装 uGet , 但可获取的版本为 1.10.4 。假如你期待使用升级版本(例如 2.0 版本),你需要升级你的系统并添加 uGet 的 PPA 以此来获取最新的稳定版本。
+
+### 安装 aria2 插件 ###
+
+[aria2][3] 是一个卓越的命令行下载管理应用,在 uGet 中它作为一个 aria2 插件,为 uGet 增添了更为强大的功能,如下载 toorent,metalinks 文件,支持多种协议和多来源下载等功能。
+
+默认情况下,uGet 在当今大多数的 Linux 系统中使用 `curl` 来作为后端,但 aria2 插件将 curl 替换为 aria2 来作为 uGet 的后端。
+
+aria2 是一个单独的软件包,需要独立安装。你可以在你的 Linux 发行版本下,使用受支持的软件仓库来轻易地安装 aria2 的最新版本,或根据 [下载 aria2 页面][4] 来安装它,该页面详细解释了在各个发行版本中如何安装 aria2 。
+
+#### 在 Debian, Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 下 ####
+
+利用下面的命令,使用 aria2 的个人软件仓库来安装最新版本的 aria2 :
+
+ $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:t-tujikawa/ppa
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get install aria2
+
+#### 在 Fedora 下 ####
+
+Fedora 的官方软件仓库中已经添加了 aria2 软件包,所以你可以轻易地使用下面的 yum 命令来安装它:
+
+ $ sudo yum install aria2
+
+#### 开启 uGet ####
+
+为了启动 uGet,从桌面菜单的搜索栏中键入 "uGet"。可参考如下的截图:
+
+
+开启 uGet 下载管理器
+
+
+uGet 版本: 2.0
+
+#### 在 uGet 中激活 aria2 插件 ####
+
+为了激活 aria2 插件, 从 uGet 菜单接着到 `编辑 –> 设置 –> 插件` , 从下拉菜单中选择 "aria2"。
+
+
+为 uGet 启用 Aria2 插件
+
+### uGet 2.0 截图赏析 ###
+
+
+使用 Aria2 下载文件
+
+
+使用 uGet 下载 Torrent 文件
+
+
+使用 uGet 进行批量下载
+
+针对其他 Linux 发行版本和 Windows 平台的 RPM 包和 uGet 的源文件都可以在 uGet 的[下载页面][5] 下找到。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-uget-download-manager-in-linux/
+
+作者:[Ravi Saive][a]
+译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/admin/
+[1]:http://uget.visuex.com/features
+[2]:http://ugetdm.com/downloads
+[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-aria2-a-multi-protocol-command-line-download-manager-in-rhel-centos-fedora/
+[4]:http://ugetdm.com/downloads-aria2
+[5]:http://ugetdm.com/downloads
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150511 Fix Various Update Errors In Ubuntu 14.04.md b/translated/tech/20150511 Fix Various Update Errors In Ubuntu 14.04.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3780b4f948
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150511 Fix Various Update Errors In Ubuntu 14.04.md
@@ -0,0 +1,151 @@
+修复Ubuntu 14.04中各种更新错误
+================================================================================
+
+
+在Ubuntu更新中,谁没有碰见个错误?在Ubuntu和其它基于Ubuntu的Linux发行版中,更新错误很常见,也为数不少。这些错误出现的原因多种多样,修复起来也很简单。在本文中,我们将见到Ubuntu中各种类型频繁发生的更新错误以及它们的修复方法。
+
+### 合并列表问题 ###
+
+当你在终端中运行更新命令时,你可能会碰到这个错误“[合并列表错误][1]”,就像下面这样:
+
+> E:Encountered a section with no Package: header,
+>
+> E:Problem with MergeList /var/lib/apt/lists/archive.ubuntu.com_ubuntu_dists_precise_universe_binary-i386_Packages,
+>
+> E:The package lists or status file could not be parsed or opened.’
+
+可以使用以下命令来修复该错误:
+
+ sudo rm -r /var/lib/apt/lists/*
+ sudo apt-get clean && sudo apt-get update
+
+### 下载仓库信息失败 -1 ###
+
+实际上,有两种类型的[下载仓库信息失败错误][2]。如果你的错误是这样的:
+
+> W:Failed to fetch bzip2:/var/lib/apt/lists/partial/in.archive.ubuntu.com_ubuntu_dists_oneiric_restricted_binary-i386_Packages Hash Sum mismatch,
+>
+> W:Failed to fetch bzip2:/var/lib/apt/lists/partial/in.archive.ubuntu.com_ubuntu_dists_oneiric_multiverse_binary-i386_Packages Hash Sum mismatch,
+>
+> E:Some index files failed to download. They have been ignored, or old ones used instead
+
+那么,你可以用以下命令修复:
+
+ sudo rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
+ sudo apt-get update
+
+### 下载仓库信息失败 -2 ###
+
+下载仓库信息失败的另外一种类型是由于PPA过时导致的。通常,当你运行更新管理器,并看到这样的错误时:
+
+
+
+你可以运行sudo apt-get update来查看哪个PPA更新失败,你可以把它从源列表中删除。你可以按照这个截图指南来[修复下载仓库信息失败错误][3]。
+
+### 下载包文件失败错误 ###
+
+一个类似的错误是[下载包文件失败错误][4],像这样:
+
+
+
+该错误很容易修复,只需修改软件源为主服务器即可。转到软件和更新,在那里你可以修改下载服务器为主服务器:
+
+
+
+### 部分更新错误 ###
+
+在终端中运行更新会出现[部分更新错误][5]:
+
+> Not all updates can be installed
+>
+> Run a partial upgrade, to install as many updates as possible
+
+在终端中运行以下命令来修复该错误:
+
+ sudo apt-get install -f
+
+### 加载共享库时发生错误 ###
+
+该错误更多是安装错误,而不是更新错误。如果尝试从源码安装程序,你可能会碰到这个错误:
+
+> error while loading shared libraries:
+>
+> cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
+
+该错误可以通过在终端中运行以下命令来修复:
+
+ sudo /sbin/ldconfig -v
+
+你可以在这里查找到更多详细内容[加载共享库时发生错误][6]。
+
+### 无法获取锁/var/cache/apt/archives/lock ###
+
+在另一个程序在使用APT时,会发生该错误。假定你正在Ubuntu软件中心安装某个东西,然后你又试着在终端中运行apt。
+
+> E: Could not get lock /var/cache/apt/archives/lock – open (11: Resource temporarily unavailable)
+>
+> E: Unable to lock directory /var/cache/apt/archives/
+
+通常,只要你把所有其它使用apt的程序关了,这个问题就会好的。但是,如果问题持续,可以使用以下命令:
+
+ sudo rm /var/lib/apt/lists/lock
+
+如果上面的命令不起作用,可以试试这个命令:
+
+ sudo killall apt-get
+
+关于该错误的更多信息,可以在[这里][7]找到。
+
+### GPG错误: 下列签名无法验证 ###
+
+在添加一个PPA时,可能会导致以下错误[GPG错误: 下列签名无法验证][8],这通常发生在终端中运行更新时:
+
+> W: GPG error: http://repo.mate-desktop.org saucy InRelease: The following signatures couldn’t be verified because the public key is not available: NO_PUBKEY 68980A0EA10B4DE8
+
+我们所要做的,就是获取系统中的这个公钥,从信息中获取密钥号。在上述信息中,密钥号为68980A0EA10B4DE8。该密钥可通过以下方式使用:
+
+ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys 68980A0EA10B4DE8
+
+在添加密钥后,再次运行更新就没有问题了。
+
+### BADSIG错误 ###
+
+另外一个与签名相关的Ubuntu更新错误是[BADSIG错误][9],它看起来像这样:
+
+> W: A error occurred during the signature verification. The repository is not updated and the previous index files will be used. GPG error: http://extras.ubuntu.com precise Release: The following signatures were invalid: BADSIG 16126D3A3E5C1192 Ubuntu Extras Archive Automatic Signing Key
+>
+> W: GPG error: http://ppa.launchpad.net precise Release:
+>
+> The following signatures were invalid: BADSIG 4C1CBC1B69B0E2F4 Launchpad PPA for Jonathan French W: Failed to fetch http://extras.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/precise/Release
+
+要修复该BADSIG错误,请在终端中使用以下命令:
+
+ sudo apt-get clean
+ cd /var/lib/apt
+ sudo mv lists oldlist
+ sudo mkdir -p lists/partial
+ sudo apt-get clean
+ sudo apt-get update
+
+本文汇集了你可能会碰到的**Ubuntu更新错误**,我希望这会对你处理这些错误有所帮助。你在Ubuntu中是否也碰到过其它更新错误呢?请在下面的评论中告诉我,我会试着写个快速指南。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-update-errors-ubuntu-1404/
+
+作者:[Abhishek][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
+[1]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-fix-problem-with-mergelist/
+[2]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-ubuntu-error-failed-to-download-repository-information-check-your-internet-connection/
+[3]:http://itsfoss.com/failed-to-download-repository-information-ubuntu-13-04/
+[4]:http://itsfoss.com/fix-failed-download-package-files-error-ubuntu/
+[5]:http://itsfoss.com/fix-partial-upgrade-error-elementary-os-luna-quick-tip/
+[6]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-open-shared-object-file-quick-tip/
+[7]:http://itsfoss.com/fix-ubuntu-install-error/
+[8]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-gpg-error-signatures-verified-ubuntu/
+[9]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-badsig-error-quick-tip/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150512 45 Zypper Commands to Manage 'Suse' Linux Package Management.md b/translated/tech/20150512 45 Zypper Commands to Manage 'Suse' Linux Package Management.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..efa807f2f3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150512 45 Zypper Commands to Manage 'Suse' Linux Package Management.md
@@ -0,0 +1,767 @@
+45 个用于 ‘Suse‘ Linux 包管理的 Zypper 命令
+======================================================================
+SUSE( Software and System Entwicklung,即软件和系统开发。其中‘entwicklung‘是德语,意为开发)Linux是 Novell 公司在 Linux 内核基础上发布的操作系统。SUSE Linux 有两个发行分支。其中之一名为 OpenSUSE,这是一款自由而且免费的操作系统。该系统由开源社区开发维护,支持一些最新版本的应用软件,其最新的稳定版本为 13.2。
+
+另外一个分支是SUSE Linux 企业版。该分支是一个为企业及商业化产品设计的 Linux 发行版,包含了大量的企业应用以及适用于商业产品生产环境的特性。其最新的稳定版本为 12。
+
+以下的链接包含了安装企业版 SUSE Linux 服务器的详细信息。
+
+- [如何安装企业版 SUSE Linux 12][1]
+
+Zypper 和 Yast 是 SUSE Linux 平台上的软件包管理工具,他们的底层使用了 RPM(译者注:RPM 最初指 Redhat Pacakge Manager ,现普遍解释为递归短语 RPM Package Manager 的缩写)。
+
+Yast(Yet another Setup Tool )是 OpenSUSE 以及企业版 SUSE 上用于系统管理、设置和配置的工具。
+
+Zypper 是软件包管理器ZYpp的命令行接口,可用于安装、删除SUSE Linux上的软件以及进行系统更新。ZYpp为Zypper和Yast提供底层支持。
+
+本文将介绍实际应用中常见的一些Zypper命令。这些命令用来进行安装、更新、删除等任何软件包管理器所能够胜任的工作。
+
+**重要** : 切记所有的这些指令都将在系统全局范围内产生影响,所以必须以 root 身份执行,否则命令将失败。
+
+### 获取基本的 Zypper 帮助信息 ###
+
+1. 不带任何选项的执行 zypper, 将输出该命令的全局选项以及子命令列表(译者注:全局选项,global option,控制台命令的输入分为可选参数和位置参数两大类。按照习惯,一般可选参数称为选项'option',而位置参数称为参数 'argument')。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper
+ Usage:
+ zypper [--global-options]</code></pre>
+
+2. 获取一个具体的子命令的帮助信息,比如 'in' (install),可以执行下面的命令
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper help in</code></pre>
+ 或者
+ <pre><code>%> zypper help install
+ install (in) [options] {capability | rpm_file_uri}
+
+ Install packages with specified capabilities or RPM files with specified
+ location. A capability is NAME[.ARCH][OP], where OP is one
+ of <, <=, =, >=, >.
+
+ Command options:
+ --from <alias|#|URI> Select packages from the specified repository.
+ -r, --repo <alias|#|URI> Load only the specified repository.
+ -t, --type Type of package (package, patch, pattern, product, srcpackage).
+ Default: package.
+ -n, --name Select packages by plain name, not by capability.
+ -C, --capability Select packages by capability.
+ -f, --force Install even if the item is already installed (reinstall),
+ downgraded or changes vendor or architecture.
+ --oldpackage Allow to replace a newer item with an older one.
+ Handy if you are doing a rollback. Unlike --force
+ it will not enforce a reinstall.
+ --replacefiles Install the packages even if they replace files from other,
+ already installed, packages. Default is to treat file conflicts
+ as an error. --download-as-needed disables the fileconflict check.
+ ...... </code></pre>
+
+3. 安装之前搜索一个安转包(以 gnome-desktop 为例 )
+
+ <pre><code># zypper se gnome-desktop
+
+ Retrieving repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Debug' metadata ............................................................[done]
+ Building repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Debug' cache .................................................................[done]
+ Retrieving repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Non-Oss' metadata ......................................................... [done]
+ Building repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Non-Oss' cache ...............................................................[done]
+ Retrieving repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Oss' metadata ..............................................................[done]
+ Building repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Oss' cache ...................................................................[done]
+ Retrieving repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Update' metadata ...........................................................[done]
+ Building repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Update' cache ................................................................[done]
+ Retrieving repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Update-Non-Oss' metadata ...................................................[done]
+ Building repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Update-Non-Oss' cache ........................................................[done]
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+
+ S | Name | Summary | Type
+ --+---------------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------+-----------
+ | gnome-desktop2-lang | Languages for package gnome-desktop2 | package
+ | gnome-desktop2 | The GNOME Desktop API Library | package
+ | libgnome-desktop-2-17 | The GNOME Desktop API Library | package
+ | libgnome-desktop-3-10 | The GNOME Desktop API Library | package
+ | libgnome-desktop-3-devel | The GNOME Desktop API Library -- Development Files | package
+ | libgnome-desktop-3_0-common | The GNOME Desktop API Library -- Common data files | package
+ | gnome-desktop-debugsource | Debug sources for package gnome-desktop | package
+ | gnome-desktop-sharp2-debugsource | Debug sources for package gnome-desktop-sharp2 | package
+ | gnome-desktop2-debugsource | Debug sources for package gnome-desktop2 | package
+ | libgnome-desktop-2-17-debuginfo | Debug information for package libgnome-desktop-2-17 | package
+ | libgnome-desktop-3-10-debuginfo | Debug information for package libgnome-desktop-3-10 | package
+ | libgnome-desktop-3_0-common-debuginfo | Debug information for package libgnome-desktop-3_0-common | package
+ | libgnome-desktop-2-17-debuginfo-32bit | Debug information for package libgnome-desktop-2-17 | package
+ | libgnome-desktop-3-10-debuginfo-32bit | Debug information for package libgnome-desktop-3-10 | package
+ | gnome-desktop-sharp2 | Mono bindings for libgnome-desktop | package
+ | libgnome-desktop-2-devel | The GNOME Desktop API Library -- Development Files | packag
+ | gnome-desktop-lang | Languages for package gnome-desktop | package
+ | libgnome-desktop-2-17-32bit | The GNOME Desktop API Library | package
+ | libgnome-desktop-3-10-32bit | The GNOME Desktop API Library | package
+ | gnome-desktop | The GNOME Desktop API Library | srcpackage</code></pre>
+
+4. 获取一个模式包的信息(以 lamp_server 为例)。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper info -t pattern lamp_server
+
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+
+
+ Information for pattern lamp_server:
+ ------------------------------------
+ Repository: openSUSE-13.2-Update
+ Name: lamp_server
+ Version: 20141007-5.1
+ Arch: x86_64
+ Vendor: openSUSE
+ Installed: No
+ Visible to User: Yes
+ Summary: Web and LAMP Server
+ Description:
+ Software to set up a Web server that is able to serve static, dynamic, and interactive content (like a Web shop). This includes Apache HTTP Server, the database management system MySQL,
+ and scripting languages such as PHP, Python, Ruby on Rails, or Perl.
+ Contents:
+
+ S | Name | Type | Dependency
+ --+-------------------------------+---------+-----------
+ | apache2-mod_php5 | package |
+ | php5-iconv | package |
+ i | patterns-openSUSE-base | package |
+ i | apache2-prefork | package |
+ | php5-dom | package |
+ | php5-mysql | package |
+ i | apache2 | package |
+ | apache2-example-pages | package |
+ | mariadb | package |
+ | apache2-mod_perl | package |
+ | php5-ctype | package |
+ | apache2-doc | package |
+ | yast2-http-server | package |
+ | patterns-openSUSE-lamp_server | package |</code></pre>
+
+5. 开启一个Zypper Shell 的会话。
+
+ <pre><code> %>zypper shell </code></pre>
+ 或者
+ <pre><code> %>zypper sh </code></pre>
+
+ <pre><code>zypper> help
+ Usage:
+ zypper [--global-options]</code></pre>
+
+**注意**:在 Zypper shell里面可以通过键入 ‘help‘ 获得全局选项以及子命令的列表。
+### Zypper 软件库管理 ###
+
+#### 列举已定义的软件库 ####
+
+6. 使用 'zypper repos' 或者 'zypper lr' 来列举所有已定以的软件库。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper repos</code></pre>
+ 或者
+ <pre><code>%> zypper lr
+ | Alias | Name | Enabled | Refresh
+ --+---------------------------+------------------------------------+---------+--------
+ 1 | openSUSE-13.2-0 | openSUSE-13.2-0 | Yes | No
+ 2 | repo-debug | openSUSE-13.2-Debug | Yes | Yes
+ 3 | repo-debug-update | openSUSE-13.2-Update-Debug | No | Yes
+ 4 | repo-debug-update-non-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Update-Debug-Non-Oss | No | Yes
+ 5 | repo-non-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Non-Oss | Yes | Yes
+ 6 | repo-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Oss | Yes | Yes
+ 7 | repo-source | openSUSE-13.2-Source | No | Yes
+ 8 | repo-update | openSUSE-13.2-Update | Yes | Yes
+ 9 | repo-update-non-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Update-Non-Oss | Yes | Yes</code></pre>
+
+7. 在表格里面显示 zypper URI
+
+ <pre><code># zypper lr -u
+ | Alias | Name | Enabled | Refresh | URI
+ --+---------------------------+------------------------------------+---------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------
+ 1 | openSUSE-13.2-0 | openSUSE-13.2-0 | Yes | No | cd:///?devices=/dev/disk/by-id/ata-VBOX_CD-ROM_VB2-01700376
+ 2 | repo-debug | openSUSE-13.2-Debug | Yes | Yes | http://download.opensuse.org/debug/distribution/13.2/repo/oss/
+ 3 | repo-debug-update | openSUSE-13.2-Update-Debug | No | Yes | http://download.opensuse.org/debug/update/13.2/
+ 4 | repo-debug-update-non-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Update-Debug-Non-Oss | No | Yes | http://download.opensuse.org/debug/update/13.2-non-oss/
+ 5 | repo-non-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Non-Oss | Yes | Yes | http://download.opensuse.org/distribution/13.2/repo/non-oss/
+ 6 | repo-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Oss | Yes | Yes | http://download.opensuse.org/distribution/13.2/repo/oss/
+ 7 | repo-source | openSUSE-13.2-Source | No | Yes | http://download.opensuse.org/source/distribution/13.2/repo/oss/
+ 8 | repo-update | openSUSE-13.2-Update | Yes | Yes | http://download.opensuse.org/update/13.2/
+ 9 | repo-update-non-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Update-Non-Oss | Yes | Yes | http://download.opensuse.org/update/13.2-non-oss/</code></pre>
+
+8. 根据优先级列举软件库。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper lr -P
+ | Alias | Name | Enabled | Refresh | Priority
+ --+---------------------------+------------------------------------+---------+---------+---------
+ 1 | openSUSE-13.2-0 | openSUSE-13.2-0 | Yes | No | 99
+ 2 | repo-debug | openSUSE-13.2-Debug | Yes | Yes | 99
+ 3 | repo-debug-update | openSUSE-13.2-Update-Debug | No | Yes | 99
+ 4 | repo-debug-update-non-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Update-Debug-Non-Oss | No | Yes | 99
+ 5 | repo-non-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Non-Oss | Yes | Yes | 85
+ 6 | repo-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Oss | Yes | Yes | 99
+ 7 | repo-source | openSUSE-13.2-Source | No | Yes | 99
+ 8 | repo-update | openSUSE-13.2-Update | Yes | Yes | 99
+ 9 | repo-update-non-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Update-Non-Oss | Yes | Yes | 99</code></pre>
+
+#### 刷新软件库 ####
+
+9. 使用 'zypper refresh' or 'zypper ref' 来刷新 zypper 软件库。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper refresh </code></pre>
+ 或者
+ <pre><code>%> zypper ref
+ Repository 'openSUSE-13.2-0' is up to date.
+ Repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Debug' is up to date.
+ Repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Non-Oss' is up to date.
+ Repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Oss' is up to date.
+ Repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Update' is up to date.
+ Repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Update-Non-Oss' is up to date.
+ All repositories have been refreshed. </code></pre>
+
+10. 刷新一个指定的软件库(以 'repo-non-oss' 为例 )。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper refresh repo-non-oss
+ Repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Non-Oss' is up to date.
+ Specified repositories have been refreshed. </code></pre>
+
+11. 强制更新一个软件库(以 'repo-non-oss' 为例 )。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper ref -f repo-non-oss
+ Forcing raw metadata refresh
+ Retrieving repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Non-Oss' metadata ............................................................[done]
+ Forcing building of repository cache
+ Building repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Non-Oss' cache ............................................................[done]
+ Specified repositories have been refreshed.</code></pre>
+
+#### 修改软件库 ####
+
+本文中我们使用‘zypper modifyrepo‘ 或者 ‘zypper mr‘ 来关闭或者开启 zypper 软件库。
+
+12. 在关闭一个软件库之前,我们需要知道在 zypper中,每一个软件库有一个唯一的标示数字与之关联,该数字用于打开或者关闭与之相联系的软件库。假设我们需要关闭 'repo-oss' 软件库,那么我们可以通过以下的法来获得该软件库的标志数字。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper lr
+ | Alias | Name | Enabled | Refresh
+ --+---------------------------+------------------------------------+---------+--------
+ 1 | openSUSE-13.2-0 | openSUSE-13.2-0 | Yes | No
+ 2 | repo-debug | openSUSE-13.2-Debug | Yes | Yes
+ 3 | repo-debug-update | openSUSE-13.2-Update-Debug | No | Yes
+ 4 | repo-debug-update-non-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Update-Debug-Non-Oss | No | Yes
+ 5 | repo-non-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Non-Oss | Yes | Yes
+ 6 | repo-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Oss | No | Yes
+ 7 | repo-source | openSUSE-13.2-Source | No | Yes
+ 8 | repo-update | openSUSE-13.2-Update | Yes | Yes
+ 9 | repo-update-non-oss | openSUSE-13.2-Update-Non-Oss | Yes | Yes</code></pre>
+从以上输出的列表中我们可以看到 'repo-oss' 库的标示数字是 6,因此通过以下的命令来关闭该库。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper mr -d 6
+ Repository 'repo-oss' has been successfully disabled.</code></pre>
+
+13. 如果需要再次开启软件库 ‘repo-oss‘, 接上例,与之相关联的标示数字为 6。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper mr -e 6
+ Repository 'repo-oss' has been successfully enabled.</code></pre>
+
+14. 针对某一个软件库(以 'repo-non-oss' 为例 )开启自动刷新( auto-refresh )和 rpm 缓存,并设置该软件库的优先级,比如85。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper mr -rk -p 85 repo-non-oss
+ Repository 'repo-non-oss' priority has been left unchanged (85)
+ Nothing to change for repository 'repo-non-oss'.</code></pre>
+
+15. 对所有的软件库关闭 rpm 文件缓存。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper mr -Ka
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'openSUSE-13.2-0'.
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-debug'.
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-debug-update'.
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-debug-update-non-oss'.
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-non-oss'.
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-oss'.
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-source'.
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-update'.
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-update-non-oss'.</pre></code>
+
+16. 对所有的软件库开启 rpm 文件缓存。
+ <pre><code> zypper mr -ka
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'openSUSE-13.2-0'.
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-debug'.
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-debug-update'.
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-debug-update-non-oss'.
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-non-oss'.
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-oss'.
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-source'.
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-update'.
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-update-non-oss'.</code></pre>
+
+17. 关闭远程库的rpm 文件缓存
+ <pre><code>%> zypper mr -Kt
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-debug'.
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-debug-update'.
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-debug-update-non-oss'.
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-non-oss'.
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-oss'.
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-source'.
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-update'.
+ RPM files caching has been disabled for repository 'repo-update-non-oss'.</code></pre>
+
+18. 开启远程软件库的 rpm 文件缓存。
+ <pre><code>%> zypper mr -kt
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-debug'.
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-debug-update'.
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-debug-update-non-oss'.
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-non-oss'.
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-oss'.
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-source'.
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-update'.
+ RPM files caching has been enabled for repository 'repo-update-non-oss'.</pre></code>
+
+#### 增加新的软件库 ####
+
+可以通过这两个 zypper 指令 – 'zypper addrepo' 和 'zypper ar' 来增加新的软件库。在此过程中可以使用 URL 或者软件库的别名。
+
+19. 增加一个新的软件库( 以 “http://download.opensuse.org/update/12.3/” 为例 )。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper ar http://download.opensuse.org/update/11.1/ update
+ Adding repository 'update' .............................................................................................................................................................[done]
+ Repository 'update' successfully added
+ Enabled : Yes
+ Autorefresh : No
+ GPG check : Yes
+ URI : http://download.opensuse.org/update/11.1/</code></pre>
+
+20. 更改一个软件库的名字,这将仅仅改变软件库的别名。 命令 'zypper namerepo' 或者 'zypperr nr' 可以胜任此工作。例如更改标示数字为10的软件库的名字为 'upd8',或者说将标示数字为10的软件库的别名改为 'upd8',可以使用下面的命令。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper nr 10 upd8
+ Repository 'update' renamed to 'upd8'.</code></pre>
+
+#### 删除软件库 ####
+
+21. 删除一个软件库。要从系统删除一个软件库可以使 'zypper removerepo' 或者 'zypper rr'。例如以下的命令可以删除软件库 'upd8'
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper rr upd8
+ # Removing repository 'upd8' .........................................................................................[done]
+ Repository 'upd8' has been removed.</code></pre>
+
+### 使用 zypper 进行软件包管理 ###
+
+#### 用 zypper 安装一个软件包 ####
+
+22. 在 zypper 中,我们可以通过软件包的功能名称来安装一个软件包。以 Firefox 为例,以下的命令可以用来安装该软件包。
+ <pre><code>%> zypper in MozillaFirefox
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ The following 128 NEW packages are going to be installed:
+ adwaita-icon-theme at-spi2-atk-common at-spi2-atk-gtk2 at-spi2-core cantarell-fonts cups-libs desktop-file-utils fontconfig gdk-pixbuf-query-loaders gstreamer gstreamer-fluendo-mp3
+ gstreamer-plugins-base gtk2-branding-openSUSE gtk2-data gtk2-immodule-amharic gtk2-immodule-inuktitut gtk2-immodule-thai gtk2-immodule-vietnamese gtk2-metatheme-adwaita
+ gtk2-theming-engine-adwaita gtk2-tools gtk3-data gtk3-metatheme-adwaita gtk3-tools hicolor-icon-theme hicolor-icon-theme-branding-openSUSE libasound2 libatk-1_0-0 libatk-bridge-2_0-0
+ libatspi0 libcairo2 libcairo-gobject2 libcanberra0 libcanberra-gtk0 libcanberra-gtk2-module libcanberra-gtk3-0 libcanberra-gtk3-module libcanberra-gtk-module-common libcdda_interface0
+ libcdda_paranoia0 libcolord2 libdrm2 libdrm_intel1 libdrm_nouveau2 libdrm_radeon1 libFLAC8 libfreebl3 libgbm1 libgdk_pixbuf-2_0-0 libgraphite2-3 libgstapp-1_0-0 libgstaudio-1_0-0
+ libgstpbutils-1_0-0 libgstreamer-1_0-0 libgstriff-1_0-0 libgsttag-1_0-0 libgstvideo-1_0-0 libgthread-2_0-0 libgtk-2_0-0 libgtk-3-0 libharfbuzz0 libjasper1 libjbig2 libjpeg8 libjson-c2
+ liblcms2-2 libLLVM libltdl7 libnsssharedhelper0 libogg0 liborc-0_4-0 libpackagekit-glib2-18 libpango-1_0-0 libpciaccess0 libpixman-1-0 libpulse0 libsndfile1 libsoftokn3 libspeex1
+ libsqlite3-0 libstartup-notification-1-0 libtheoradec1 libtheoraenc1 libtiff5 libvisual libvorbis0 libvorbisenc2 libvorbisfile3 libwayland-client0 libwayland-cursor0 libwayland-server0
+ libX11-xcb1 libxcb-dri2-0 libxcb-dri3-0 libxcb-glx0 libxcb-present0 libxcb-render0 libxcb-shm0 libxcb-sync1 libxcb-util1 libxcb-xfixes0 libXcomposite1 libXcursor1 libXdamage1 libXevie1
+ libXfixes3 libXft2 libXi6 libXinerama1 libxkbcommon-0_4_3 libXrandr2 libXrender1 libxshmfence1 libXtst6 libXv1 libXxf86vm1 Mesa Mesa-libEGL1 Mesa-libGL1 Mesa-libglapi0
+ metatheme-adwaita-common MozillaFirefox MozillaFirefox-branding-openSUSE mozilla-nss mozilla-nss-certs PackageKit-gstreamer-plugin pango-tools sound-theme-freedesktop
+
+ The following 10 recommended packages were automatically selected:
+ gstreamer-fluendo-mp3 gtk2-branding-openSUSE gtk2-data gtk2-immodule-amharic gtk2-immodule-inuktitut gtk2-immodule-thai gtk2-immodule-vietnamese libcanberra0 libpulse0
+ PackageKit-gstreamer-plugin
+
+ 128 new packages to install.
+ Overall download size: 77.2 MiB. Already cached: 0 B After the operation, additional 200.0 MiB will be used.
+ Continue? [y/n/? shows all options] (y): y
+ Retrieving package cantarell-fonts-0.0.16-1.1.noarch (1/128), 74.1 KiB (115.6 KiB unpacked)
+ Retrieving: cantarell-fonts-0.0.16-1.1.noarch.rpm .........................................................................................................................[done (63.4 KiB/s)]
+ Retrieving package hicolor-icon-theme-0.13-2.1.2.noarch (2/128), 40.1 KiB ( 50.5 KiB unpacked)
+ Retrieving: hicolor-icon-theme-0.13-2.1.2.noarch.rpm ...................................................................................................................................[done]
+ Retrieving package sound-theme-freedesktop-0.8-7.1.2.noarch (3/128), 372.6 KiB (460.3 KiB unpacked) </code></pre>
+
+23. 安装指定版本号的软件包,(以 gcc 5.1 为例)。
+ <pre><code> %>zypper in 'gcc<5.1'
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ The following 13 NEW packages are going to be installed:
+ cpp cpp48 gcc gcc48 libasan0 libatomic1-gcc49 libcloog-isl4 libgomp1-gcc49 libisl10 libitm1-gcc49 libmpc3 libmpfr4 libtsan0-gcc49
+
+ 13 new packages to install.
+ Overall download size: 14.5 MiB. Already cached: 0 B After the operation, additional 49.4 MiB will be used.
+ Continue? [y/n/? shows all options] (y): y </code></pre>
+
+24. 为特定的CPU架构安装软件包(以兼容 i586 的 gcc 为例)。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper in gcc.i586
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ The following 13 NEW packages are going to be installed:
+ cpp cpp48 gcc gcc48 libasan0 libatomic1-gcc49 libcloog-isl4 libgomp1-gcc49 libisl10 libitm1-gcc49 libmpc3 libmpfr4 libtsan0-gcc49
+
+ 13 new packages to install.
+ Overall download size: 14.5 MiB. Already cached: 0 B After the operation, additional 49.4 MiB will be used.
+ Continue? [y/n/? shows all options] (y): y
+ Retrieving package libasan0-4.8.3+r212056-2.2.4.x86_64 (1/13), 74.2 KiB (166.9 KiB unpacked)
+ Retrieving: libasan0-4.8.3+r212056-2.2.4.x86_64.rpm .......................................................................................................................[done (79.2 KiB/s)]
+ Retrieving package libatomic1-gcc49-4.9.0+r211729-2.1.7.x86_64 (2/13), 14.3 KiB ( 26.1 KiB unpacked)
+ Retrieving: libatomic1-gcc49-4.9.0+r211729-2.1.7.x86_64.rpm ...............................................................................................................[done (55.3 KiB/s)] </code></pre>
+
+25. 为特定的CPU架构安装指定版本号的软件包(以兼容 i586 且版本低于5.1的 gcc 为例)
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper in 'gcc.i586<5.1'
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ The following 13 NEW packages are going to be installed:
+ cpp cpp48 gcc gcc48 libasan0 libatomic1-gcc49 libcloog-isl4 libgomp1-gcc49 libisl10 libitm1-gcc49 libmpc3 libmpfr4 libtsan0-gcc49
+
+ 13 new packages to install.
+ Overall download size: 14.4 MiB. Already cached: 129.5 KiB After the operation, additional 49.4 MiB will be used.
+ Continue? [y/n/? shows all options] (y): y
+ In cache libasan0-4.8.3+r212056-2.2.4.x86_64.rpm (1/13), 74.2 KiB (166.9 KiB unpacked)
+ In cache libatomic1-gcc49-4.9.0+r211729-2.1.7.x86_64.rpm (2/13), 14.3 KiB ( 26.1 KiB unpacked)
+ In cache libgomp1-gcc49-4.9.0+r211729-2.1.7.x86_64.rpm (3/13), 41.1 KiB ( 90.7 KiB unpacked) </code></pre>
+
+26. 从指定的软件库里面安装一个软件包,例如从 amarok 中安装 libxine。
+ <pre><code>%> zypper in amarok upd:libxine1
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+ The following 202 NEW packages are going to be installed:
+ amarok bundle-lang-kde-en clamz cups-libs enscript fontconfig gdk-pixbuf-query-loaders ghostscript-fonts-std gptfdisk gstreamer gstreamer-plugins-base hicolor-icon-theme
+ hicolor-icon-theme-branding-openSUSE htdig hunspell hunspell-tools icoutils ispell ispell-american kde4-filesystem kdebase4-runtime kdebase4-runtime-branding-openSUSE kdelibs4
+ kdelibs4-branding-openSUSE kdelibs4-core kdialog libakonadi4 l
+ .....</code></pre>
+
+27. 通过指定软件包的名字安装软件包。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper in -n git
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ The following 35 NEW packages are going to be installed:
+ cvs cvsps fontconfig git git-core git-cvs git-email git-gui gitk git-svn git-web libserf-1-1 libsqlite3-0 libXft2 libXrender1 libXss1 perl-Authen-SASL perl-Clone perl-DBD-SQLite perl-DBI
+ perl-Error perl-IO-Socket-SSL perl-MLDBM perl-Net-Daemon perl-Net-SMTP-SSL perl-Net-SSLeay perl-Params-Util perl-PlRPC perl-SQL-Statement perl-Term-ReadKey subversion subversion-perl tcl
+ tk xhost
+
+ The following 13 recommended packages were automatically selected:
+ git-cvs git-email git-gui gitk git-svn git-web perl-Authen-SASL perl-Clone perl-MLDBM perl-Net-Daemon perl-Net-SMTP-SSL perl-PlRPC perl-SQL-Statement
+
+ The following package is suggested, but will not be installed:
+ git-daemon
+
+ 35 new packages to install.
+ Overall download size: 15.6 MiB. Already cached: 0 B After the operation, additional 56.7 MiB will be used.
+ Continue? [y/n/? shows all options] (y): y </code></pre>
+
+28. 通过通配符来安装软件包,例如,安装所有 php5 的软件包。
+ <pre><code>%> zypper in php5*
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ Problem: php5-5.6.1-18.1.x86_64 requires smtp_daemon, but this requirement cannot be provided
+ uninstallable providers: exim-4.83-3.1.8.x86_64[openSUSE-13.2-0]
+ postfix-2.11.0-5.2.2.x86_64[openSUSE-13.2-0]
+ sendmail-8.14.9-2.2.2.x86_64[openSUSE-13.2-0]
+ exim-4.83-3.1.8.i586[repo-oss]
+ msmtp-mta-1.4.32-2.1.3.i586[repo-oss]
+ postfix-2.11.0-5.2.2.i586[repo-oss]
+ sendmail-8.14.9-2.2.2.i586[repo-oss]
+ exim-4.83-3.1.8.x86_64[repo-oss]
+ msmtp-mta-1.4.32-2.1.3.x86_64[repo-oss]
+ postfix-2.11.0-5.2.2.x86_64[repo-oss]
+ sendmail-8.14.9-2.2.2.x86_64[repo-oss]
+ postfix-2.11.3-5.5.1.i586[repo-update]
+ postfix-2.11.3-5.5.1.x86_64[repo-update]
+ Solution 1: Following actions will be done:
+ do not install php5-5.6.1-18.1.x86_64
+ do not install php5-pear-Auth_SASL-1.0.6-7.1.3.noarch
+ do not install php5-pear-Horde_Http-2.0.1-6.1.3.noarch
+ do not install php5-pear-Horde_Image-2.0.1-6.1.3.noarch
+ do not install php5-pear-Horde_Kolab_Format-2.0.1-6.1.3.noarch
+ do not install php5-pear-Horde_Ldap-2.0.1-6.1.3.noarch
+ do not install php5-pear-Horde_Memcache-2.0.1-7.1.3.noarch
+ do not install php5-pear-Horde_Mime-2.0.2-6.1.3.noarch
+ do not install php5-pear-Horde_Oauth-2.0.0-6.1.3.noarch
+ do not install php5-pear-Horde_Pdf-2.0.1-6.1.3.noarch
+ ....</code></pre>
+
+29. 使用模式名称(模式名称是一类软件包的名字)来批量安装软件包
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper in -t pattern lamp_server
+ ading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ The following 29 NEW packages are going to be installed:
+ apache2 apache2-doc apache2-example-pages apache2-mod_perl apache2-prefork patterns-openSUSE-lamp_server perl-Data-Dump perl-Encode-Locale perl-File-Listing perl-HTML-Parser
+ perl-HTML-Tagset perl-HTTP-Cookies perl-HTTP-Daemon perl-HTTP-Date perl-HTTP-Message perl-HTTP-Negotiate perl-IO-HTML perl-IO-Socket-SSL perl-libwww-perl perl-Linux-Pid
+ perl-LWP-MediaTypes perl-LWP-Protocol-https perl-Net-HTTP perl-Net-SSLeay perl-Tie-IxHash perl-TimeDate perl-URI perl-WWW-RobotRules yast2-http-server
+
+ The following NEW pattern is going to be installed:
+ lamp_server
+
+ The following 10 recommended packages were automatically selected:
+ apache2 apache2-doc apache2-example-pages apache2-mod_perl apache2-prefork perl-Data-Dump perl-IO-Socket-SSL perl-LWP-Protocol-https perl-TimeDate yast2-http-server
+
+ 29 new packages to install.
+ Overall download size: 7.2 MiB. Already cached: 1.2 MiB After the operation, additional 34.7 MiB will be used.
+ Continue? [y/n/? shows all options] (y): </code></pre>
+
+30. 使用一行命令安转一个软件包同时卸载另一个软件包,例如在安装 nano 的同时卸载 vi
+
+ <pre><code># zypper in nano -vi
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ '-vi' not found in package names. Trying capabilities.
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ The following 2 NEW packages are going to be installed:
+ nano nano-lang
+
+ The following package is going to be REMOVED:
+ vim
+
+ The following recommended package was automatically selected:
+ nano-lang
+
+ 2 new packages to install, 1 to remove.
+ Overall download size: 550.0 KiB. Already cached: 0 B After the operation, 463.3 KiB will be freed.
+ Continue? [y/n/? shows all options] (y):
+ ...</code></pre>
+
+31. 使用 zypper 安装 rpm 软件包。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper in teamviewer*.rpm
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ The following 24 NEW packages are going to be installed:
+ alsa-oss-32bit fontconfig-32bit libasound2-32bit libexpat1-32bit libfreetype6-32bit libgcc_s1-gcc49-32bit libICE6-32bit libjpeg62-32bit libpng12-0-32bit libpng16-16-32bit libSM6-32bit
+ libuuid1-32bit libX11-6-32bit libXau6-32bit libxcb1-32bit libXdamage1-32bit libXext6-32bit libXfixes3-32bit libXinerama1-32bit libXrandr2-32bit libXrender1-32bit libXtst6-32bit
+ libz1-32bit teamviewer
+
+ The following recommended package was automatically selected:
+ alsa-oss-32bit
+
+ 24 new packages to install.
+ Overall download size: 41.2 MiB. Already cached: 0 B After the operation, additional 119.7 MiB will be used.
+ Continue? [y/n/? shows all options] (y):
+ ..</code></pre>
+
+#### 使用 zypper 卸载软件包 ####
+
+32. 命令 ‘zypper remove‘ 和 ‘zypper rm‘ 用于卸载软件包。例如卸载 apache2:
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper remove apache2 </code></pre>
+ 或者
+ <pre><code>%> zypper rm apache2
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ The following 2 packages are going to be REMOVED:
+ apache2 apache2-prefork
+
+ 2 packages to remove.
+ After the operation, 4.2 MiB will be freed.
+ Continue? [y/n/? shows all options] (y): y
+ (1/2) Removing apache2-2.4.10-19.1 ........................................................................[done]
+ (2/2) Removing apache2-prefork-2.4.10-19.1 ................................................................[done] </code></pre>
+
+#### 使用Zypper 进行软件包更新 ####
+
+33. 更新所有的软件包,可以使用 ‘zypper update‘ 或者 ‘zypper up‘。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper up </code></pre>
+ 或者
+ <pre><code>%> zypper update
+
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ Nothing to do. </code></pre>
+
+34. 更新指定的软件包,例如更新 apache2 以及 openssh。
+
+ <pre><code> zypper up apache2 openssh
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ No update candidate for 'apache2-2.4.10-19.1.x86_64'. The highest available version is already installed.
+ No update candidate for 'openssh-6.6p1-5.1.3.x86_64'. The highest available version is already installed.
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ Nothing to do.</code></pre>
+
+35. 安装一个软件库,例如 ariadb,如果该库存在则更新之。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper in mariadb
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ 'mariadb' is already installed.
+ No update candidate for 'mariadb-10.0.13-2.6.1.x86_64'. The highest available version is already installed.
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ Nothing to do.</code></pre>
+
+#### 安装源文件并且构建依赖关系 ####
+
+命令 ‘zypper source-install‘ 或者 ‘zypper si‘ 可以用于从源文件编译软件包
+
+36. 安装某一个软件包的源文件及其依赖关系,例如 mariadb。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper si mariadb
+ Reading installed packages...
+ Loading repository data...
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ The following 36 NEW packages are going to be installed:
+ autoconf automake bison cmake cpp cpp48 gcc gcc48 gcc48-c++ gcc-c++ libaio-devel libarchive13 libasan0 libatomic1-gcc49 libcloog-isl4 libedit-devel libevent-devel libgomp1-gcc49 libisl10
+ libitm1-gcc49 libltdl7 libmpc3 libmpfr4 libopenssl-devel libstdc++48-devel libtool libtsan0-gcc49 m4 make ncurses-devel pam-devel readline-devel site-config tack tcpd-devel zlib-devel
+
+ The following source package is going to be installed:
+ mariadb
+
+ 36 new packages to install, 1 source package.
+ Overall download size: 71.5 MiB. Already cached: 129.5 KiB After the operation, additional 183.9 MiB will be used.
+ Continue? [y/n/? shows all options] (y): y </code></pre>
+
+37. 仅为某一个软件包安装源文件,例如 mariadb
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper in -D mariadb
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ 'mariadb' is already installed.
+ No update candidate for 'mariadb-10.0.13-2.6.1.x86_64'. The highest available version is already installed.
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ Nothing to do. </code></pre>
+
+38. 仅为某一个软件包安装依赖关系,例如 mariadb
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper si -d mariadb
+ Reading installed packages...
+ Loading repository data...
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ The following 36 NEW packages are going to be installed:
+ autoconf automake bison cmake cpp cpp48 gcc gcc48 gcc48-c++ gcc-c++ libaio-devel libarchive13 libasan0 libatomic1-gcc49 libcloog-isl4 libedit-devel libevent-devel libgomp1-gcc49 libisl10
+ libitm1-gcc49 libltdl7 libmpc3 libmpfr4 libopenssl-devel libstdc++48-devel libtool libtsan0-gcc49 m4 make ncurses-devel pam-devel readline-devel site-config tack tcpd-devel zlib-devel
+
+ The following package is recommended, but will not be installed due to conflicts or dependency issues:
+ readline-doc
+
+ 36 new packages to install.
+ Overall download size: 33.7 MiB. Already cached: 129.5 KiB After the operation, additional 144.3 MiB will be used.
+ Continue? [y/n/? shows all options] (y): y</code></pre>
+
+#### Zypper in Scripts and Applications ####
+
+39. 安装一个软件包,并且在安装过程中跳过与用户的交互, 例如 mariadb。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper --non-interactive in mariadb
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ 'mariadb' is already installed.
+ No update candidate for 'mariadb-10.0.13-2.6.1.x86_64'. The highest available version is already installed.
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ Nothing to do.</code></pre>
+
+40. 卸载一个软件包,并且在卸载过程中跳过与用户的交互,例如 mariadb
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper --non-interactive rm mariadb
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ The following package is going to be REMOVED:
+ mariadb
+
+ 1 package to remove.
+ After the operation, 71.8 MiB will be freed.
+ Continue? [y/n/? shows all options] (y): y
+ (1/1) Removing mariadb-10.0.13-2.6.1 .............................................................................[done] </code></pre>
+
+41. 将 zypper 输出用 XML 格式打印。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper --xmlout
+ Usage:
+ zypper [--global-options] <command> [--command-options] [arguments]
+
+ Global Options
+ ....</code></pre>
+
+42. 禁止详细信息输出到屏幕。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper --quiet in mariadb
+ The following NEW package is going to be installed:
+ mariadb
+
+ 1 new package to install.
+ Overall download size: 0 B. Already cached: 7.8 MiB After the operation, additional 71.8 MiB will be used.
+ Continue? [y/n/? shows all options] (y):
+ ...</code></pre>
+
+43. 在卸载过程中禁止详细信息输出到屏幕
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper --quiet rm mariadb </code></pre>
+
+44. 自动地同意版权或者协议。
+ <pre><code>%> zypper patch --auto-agree-with-licenses
+ Loading repository data...
+ Reading installed packages...
+ Resolving package dependencies...
+
+ Nothing to do.</code></pre>
+
+#### 清除 Zypper 缓存以及查看历史信息 ####
+
+45. 以下指令可以用来清理Zypper缓存。
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper clean
+ All repositories have been cleaned up.</code></pre>
+
+如果需要一次性地清理元数据以及软件包缓存,可以通过 -all/-a 选项来达到目的
+
+ <pre><code>%> zypper clean -a
+ All repositories have been cleaned up.</code></pre>
+
+46. 查看 Zypper 的历史信息。籍由 Zypper 所有的软件包管理动作,包括安装、更新以及卸载都会在 /var/log/zypp/history中保留历史信息。可以通过 cat 来查看此文件,或者通过过滤器来筛选希望看到的信息。
+
+ <pre><code> cat /var/log/zypp/history
+ 2015-05-07 15:43:03|install|boost-license1_54_0|1.54.0-10.1.3|noarch||openSUSE-13.2-0|0523b909d2aae5239f9841316dafaf3a37b4f096|
+ 2015-05-07 15:43:03|install|branding-openSUSE|13.2-3.6.1|noarch||openSUSE-13.2-0|6609def94b1987bf3f90a9467f4f7ab8f8d98a5c|
+ 2015-05-07 15:43:03|install|bundle-lang-common-en|13.2-3.3.1|noarch||openSUSE-13.2-0|ca55694e6fdebee6ce37ac7cf3725e2aa6edc342|
+ 2015-05-07 15:43:03|install|insserv-compat|0.1-12.2.2|noarch||openSUSE-13.2-0|6160de7fbf961a279591a83a1550093a581214d9|
+ 2015-05-07 15:43:03|install|libX11-data|1.6.2-5.1.2|noarch||openSUSE-13.2-0|f1cb58364ba9016c1f93b1a383ba12463c56885a|
+ 2015-05-07 15:43:03|install|libnl-config|3.2.25-2.1.2|noarch||openSUSE-13.2-0|aab2ded312a781e93b739b418e3d32fe4e187020|
+ 2015-05-07 15:43:04|install|wireless-regdb|2014.06.13-1.2|noarch||openSUSE-13.2-0|be8cb16f3e92af12b5ceb977e37e13f03c007bd1|
+ 2015-05-07 15:43:04|install|yast2-trans-en_US|3.1.0-2.1|noarch||openSUSE-13.2-0|1865754e5e0ec3c149ac850b340bcca55a3c404d|
+ 2015-05-07 15:43:04|install|yast2-trans-stats|2.19.0-16.1.3|noarch||openSUSE-13.2-0|b107d2b3e702835885b57b04d12d25539f262d1a|
+ 2015-05-07 15:43:04|install|cracklib-dict-full|2.8.12-64.1.2|x86_64||openSUSE-13.2-0|08bd45dbba7ad44e3a4837f730be76f55ad5dcfa|
+ ......</code></pre>
+
+#### 使用 Zypper 进行SUSE系统升级 ####
+
+47. 可以使用 Zypper 命令的 'dist-upgrade' 选项来将当前的SUSE Linux升级至最新版本。
+ <pre><code># zypper dist-upgrade
+ You are about to do a distribution upgrade with all enabled repositories. Make sure these repositories are compatible before you continue. See 'man zypper' for more information about this command.
+ Building repository 'openSUSE-13.2-0' cache .....................................................................[done]
+ Retrieving repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Debug' metadata ............................................................[done]
+ Building repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Debug' cache .................................................................[done]
+ Retrieving repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Non-Oss' metadata ..........................................................[done]
+ Building repository 'openSUSE-13.2-Non-Oss' cache ...............................................................[done]</code></pre>
+
+正文至此结束。希望本文可以帮助读者尤其是新手们管理SUSE Linux系统和服务器。如果您觉得某些比较重要的命令被作者漏掉了,请在评论部分写下您的返回,作者将根据评论对文章进行更新。保持联络,保持评论,多谢支持。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+原文地址: http://www.tecmint.com/zypper-commands-to-manage-suse-linux-package-management/
+
+作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
+译者:[张博约](https://github.com/zhangboyue)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/installation-of-suse-linux-enterprise-server-12/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150512 A Shell Script to Monitor Network, Disk Usage, Uptime, Load Average and RAM Usage in Linux.md b/translated/tech/20150512 A Shell Script to Monitor Network, Disk Usage, Uptime, Load Average and RAM Usage in Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..58eb9f18ca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150512 A Shell Script to Monitor Network, Disk Usage, Uptime, Load Average and RAM Usage in Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
+Linux中用于监控网络、磁盘使用、开机时间、平均负载和内存使用率的shell脚本
+================================================================================
+系统管理员的任务真的很艰难,因为他/她必须监控服务器、用户、日志,还得创建备份,等等等等。对于大多数重复性的任务,大多数管理员都会写一个自动化脚本来日复一日重复这些任务。这里,我们已经写了一个shell脚本给大家,用来自动化完成系统管理员所要完成的常规任务,这可能在多数情况下,尤其是对于新手而言十分有用,他们能通过该脚本获取到大多数的他们想要的信息,包括系统、网络、用户、负载、内存、主机、内部IP、外部IP、开机时间等。
+
+我们已经注意并进行了格式化输出(在一定程度上哦)。此脚本不包含任何恶意内容,并且它能以普通用户帐号运行。事实上,我们也推荐你以普通用户运行该脚本,而不是root。
+
+
+监控Linux系统健康的Shell脚本
+
+你可以通过给Tecmint和脚本作者合适的积分,获得自由使用/修改/再分发下面代码的权利。我们已经试着在一定程度上自定义了输出结果,除了要求的输出内容外,其它内容都不会生成。我们也已经试着使用了那些Linux系统中通常不使用的变量,这些变量可能也是自由代码。
+
+#### 最小系统要求 ####
+
+你所需要的一切,就是一台正常运转的Linux盒子。
+
+#### 依赖性 ####
+
+对于一个标准的Linux发行版,使用此包时没有任何依赖。此外,该脚本不需要root权限来执行。但是,如果你想要安装,则必须输入一次root密码。
+
+#### 安全性 ####
+
+我们也关注到了系统安全问题,所以在安装此包时,不需要安装任何额外包,也不需要root访问权限来运行。此外,源代码是采用Apache 2.0许可证发布的,这意味着只要你保留Tecmint的版权,你可以自由地编辑、修改并再分发该代码。
+
+### 如何安装和运行脚本? ###
+
+首先,使用[wget命令][1]下载监控脚本`“tecmint_monitor.sh”`,给它赋予合适的执行权限。
+
+ # wget http://tecmint.com/wp-content/scripts/tecmint_monitor.sh
+ # chmod 755 tecmint_monitor.sh
+
+强烈建议你以普通用户身份安装该脚本,而不是root。安装过程中会询问root密码,并且在需要的时候安装必要的组件。
+
+要安装`“tecmint_monitor.sh”`脚本,只需像下面这样使用-i(安装)选项就可以了。
+
+ /tecmint_monitor.sh -i
+
+在提示你输入root密码时输入该密码。如果一切顺利,你会看到像下面这样的安装成功信息。
+
+ Password:
+ Congratulations! Script Installed, now run monitor Command
+
+安装完毕后,你可以通过在任何位置,以任何用户调用命令`‘monitor’`来运行该脚本。如果你不喜欢安装,你需要在每次运行时输入路径。
+
+ # ./Path/to/script/tecmint_monitor.sh
+
+现在,以任何用户从任何地方运行monitor命令,就是这么简单:
+
+ $ monitor
+
+
+
+你一运行命令,就会获得下面这些各种各样和系统相关的信息:
+
+- 互联网连通性
+- 操作系统类型
+- 操作系统名称
+- 操作系统版本
+- 架构
+- 内核版本
+- 主机名
+- 内部IP
+- 外部IP
+- 域名服务器
+- 已登录用户
+- 内存使用率
+- 交换分区使用率
+- 磁盘使用率
+- 平均负载
+- 系统开机时间
+
+使用-v(版本)开关来检查安装的脚本的版本。
+
+ $ monitor -v
+
+ tecmint_monitor version 0.1
+ Designed by Tecmint.com
+ Released Under Apache 2.0 License
+
+### 小结 ###
+
+该脚本在一些机器上可以开机即用,这一点我已经检查过。相信对于你而言,它也会正常工作。如果你们发现了什么毛病,可以在评论中告诉我。这个脚本还不是结束,这仅仅是个开始。从这里开始,你可以将它提升到任何等级。如果你想要编辑脚本,将它带入一个更深的层次,尽管随意去做吧,别忘了给我们合适的积分,也别忘了把你更新后的脚本拿出来和我们分享哦,这样,我们也能通过给你合适的积分来更新此文。
+
+别忘了和我们分享你的想法或者脚本,我们会在这儿帮助你。谢谢你们给予的所有挚爱。保持连线,不要走开哦。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-server-health-monitoring-script/
+
+作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-wget-command-examples-in-linux/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150512 How To Run Docker Client Inside Windows OS.md b/translated/tech/20150512 How To Run Docker Client Inside Windows OS.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f23c109149
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150512 How To Run Docker Client Inside Windows OS.md
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
+如何在 Windows 操作系统中运行 Docker 客户端
+================================================================================
+大家好,今天我们来了解一下 Windows 操作系统中的 Docker 以及在其中安装 Docker Windows 客户端的知识。Docker 引擎使用 Linux 特定内核特性,因此不能通过 Windows 内核运行,Docker 引擎创建一个小的虚拟系统运行 Linux 并利用它的资源和内核。Windows Docker 客户端用虚拟化 Docker 引擎构建,运行以及管理 盒子以外的 Docker 容器。这里有个由 Boot2Docker 团队开发的名为 Boot2Docker 的应用程序,它创建运行在基于[Linux 微内核][1]的小型 Linux 系统上的虚拟机,是特意为在 Windows 上运行 [Docker][2] 容器开发的。它完全运行在 RAM 中,需要大约 27M 内存并能在 5s(YMMV,译者注:your mileage may vary,因人而异) 内启动。因此,在用于 Windows 的 Docker 引擎被开发出来之前,我们在 Windows 机器里只能运行 Linux 容器。
+
+下面是安装 Docker 客户端并在上面运行容器的简单步骤。
+
+### 1. 下载 Boot2Docker ###
+
+在我们开始安装之前,我们需要 Boot2Docker 的可执行文件。可以从 [它的 Github][3] 下载最新版本的 Boot2Docker。在这篇指南中,我们从网站中下载版本 v1.6.1。我们从那网页中用我们喜欢的浏览器或者下载管理器下载了名为 [docker-install.exe][4] 的文件。
+
+
+
+### 2. 安装 Boot2Docker ###
+
+现在我们运行安装文件,它会安装 Window Docker 客户端、用于 Windows 的 Git(MSYS-git)、VirtualBox、Boot2Docker Linux ISO 以及 Boot2Docker 管理工具,这些对于在盒子之外运行 Docker 引擎都至关重要。
+
+
+
+### 3. 运行 Boot2Docker ###
+
+
+
+安装完成必要的组件之后,我们从桌面 Boot2Docker 快捷方式启动 Boot2Docker。它会要求你输入以后用于验证的 SSH 密钥。然后会启动一个配置好的用于管理在虚拟机中运行的 Docker 的 unix shell。
+
+
+
+为了检查是否正确配置,运行下面的 docker version 命令。
+
+ docker version
+
+
+
+### 4. 运行 Docker ###
+
+由于 **Boot2Docker Start** 自动启动了一个已经正确设置好环境变量的 shell,我们可以马上开始使用 Docker。**请注意,如果我们将 Boot2Docker 作为一个远程 Docker 守护进程,那么不要在 docker 命令之前加 sudo。**
+
+现在,让我们来试试 **hello-world** 例子镜像,它会下载 hello-world 镜像,运行并输出 "Hello from Docker" 信息。
+
+ $ docker run hello-world
+
+
+
+### 5. 使用命令提示符(CMD) 运行 Docker###
+
+现在,如果你想开始用命令提示符使用 Docker,你可以打开命令提示符(CMD.exe)。由于 Boot2Docker 要求 ssh.exe 在 PATH 中,我们需要在命令提示符中输入以下命令使得 %PATH% 环境变量中包括 Git 安装目录下的 bin 文件夹。
+
+ set PATH=%PATH%;"c:\Program Files (x86)\Git\bin"
+
+
+
+运行上面的命令之后,我们可以在命令提示符中运行 **boot2docker start** 启动 Boot2Docker 虚拟机。
+
+ boot2docker start
+
+
+
+**注意**: 如果你看到 machine does no exist 的错误信息,就运行 **boot2docker init** 命令。
+
+然后复制控制台中的命令到 cmd.exe 中为控制台窗口设置环境变量,然后我们就可以像平常一样运行 docker 容器了。
+
+### 6. 使用 PowerShell 运行 Docker ###
+
+为了能在 PowerShell 中运行 Docker,我们需要启动一个 PowerShell 窗口并添加 ssh.exe 到 PATH 变量。
+
+ $Env:Path = "${Env:Path};c:\Program Files (x86)\Git\bin"
+
+运行完上面的命令,我们还需要运行
+
+ boot2docker start
+
+
+
+这会打印用于设置环境变量连接到虚拟机内部运行的 Docker 的 PowerShell 命令。我们只需要在 PowerShell 中运行这些命令就可以和平常一样运行 docker 容器。
+
+### 7. 用 PUTTY 登录 ###
+
+Boot2Docker 在%USERPROFILE%\.ssh 目录生成和使用用于登录的公共和私有密钥,我们也需要使用这个文件夹中的私有密钥。私有密钥需要转换为 PuTTY 的格式。我们可以通过 puttygen.exe 实现。
+
+我们需要打开 puttygen.exe 并从 %USERPROFILE%\.ssh\id_boot2docker 中导入("File"->"Load" 菜单)私钥,然后点击 "Save Private Key"。然后用保存的文件通过 PuTTY 用 docker@127.0.0.1:2022 登录。
+
+### 8. Boot2Docker 选项 ###
+
+Boot2Docker 管理工具提供了一些命令,如下所示。
+
+ $ boot2docker
+
+ Usage: boot2docker.exe [<options>] {help|init|up|ssh|save|down|poweroff|reset|restart|config|status|info|ip|shellinit|delete|download|upgrade|version} [<args>]
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+通过 Docker Windows 客户端使用 Docker 很有趣。Boot2Docker 管理工具是一个能使任何 Docker 容器能像在 Linux 主机上平稳运行的很棒的应用程序。如果你更仔细的话,你会发现 boot2docker 默认用户的用户名是 docker,密码是 tcuser。最新版本的 boot2docker 设置了一个 host-only 的网络适配器提供访问容器的端口。一般来说是 192.168.59.103,但可以通过 VirtualBox 的 DHCP 实现改变。如果你有任何问题、建议、反馈,请在下面的评论框中写下来然后我们可以改进或者更新我们的内容。非常感谢!Enjoy:-)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/run-docker-client-inside-windows-os/
+
+作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
+译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
+[1]:http://tinycorelinux.net/
+[2]:https://www.docker.io/
+[3]:https://github.com/boot2docker/windows-installer/releases/latest
+[4]:https://github.com/boot2docker/windows-installer/releases/download/v1.6.1/docker-install.exe
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150512 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to view torrent file content on Linux.md b/translated/tech/20150512 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to view torrent file content on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8b5ba22907
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150512 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to view torrent file content on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+Linux有问必答——Linux上如何查看torrent文件内容
+================================================================================
+> **问题**: 我从网站上下载了一个torrent文件。Linux上有没有工具让我查看torrent文件的内容?例如,我想知道torrent里面都有什么文件。
+
+torrent文件(也就是扩展名为**.torrent**的文件)是BitTorrent元数据文件,里面存储了BitTorrent客户端用来从BitTorrent点对点网络下载共享文件的信息(如,追踪器URL、文件列表、大小、校验和、创建日期等)。在单个torrent文件里面,可以列出一个或多个文件用于共享。
+
+torrent文件内容由BEncode编码为BitTorrent数据序列化格式,因此,要查看torrent文件的内容,你需要相应的解码器。
+
+事实上,任何图形化的BitTorrent客户端(如Transmission或uTorrent)都带有BEncode解码器,所以,你可以用它们直接打开来查看torrent文件的内容。然而,如果你不想要使用BitTorrent客户端来检查torrent文件,你可以试试这个命令行torrent查看器,它叫[dumptorrent][1]。
+
+**dumptorrent**命令可以使用内建的BEncode解码器打印torrent文件的详细信息(如,文件名、大小、跟踪器URL、创建日期、信息散列等等)。
+
+### 安装DumpTorrent到Linux ###
+
+要安装dumptorrent到Linux,你可以从源代码来构建它。
+
+在Debian、Ubuntu或Linux Mint上:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install gcc make
+ $ wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/dumptorrent/dumptorrent/1.2/dumptorrent-1.2.tar.gz
+ $ tar -xvf dumptorrent-1.2.tar.gz
+ $ cd dumptorrent-1.2
+ $ make
+ $ sudo cp dumptorrent /usr/local/bin
+
+在CentOS、Fedora或RHEL上:
+
+ $ sudo yum install gcc make
+ $ wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/dumptorrent/dumptorrent/1.2/dumptorrent-1.2.tar.gz
+ $ tar -xvf dumptorrent-1.2.tar.gz
+ $ cd dumptorrent-1.2
+ $ make
+ $ sudo cp dumptorrent /usr/local/bin
+
+确保你的路径中[包含][2]了/usr/local/bin。
+
+### 查看torrent的内容 ###
+
+要检查torrent的内容,只需要运行dumptorrent,并将torrent文件作为参数执行。这会打印出torrent的概要,包括文件名、大小和跟踪器URL。
+
+ $ dumptorrent <torrent-file>
+
+
+要查看torrent的完整内容,请添加“-v”选项。它会打印更多关于torrent的详细信息,包括信息散列、片长度、创建日期、创建者,以及完整的声明列表。
+
+ $ dumptorrent -v <torrent-file>
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/view-torrent-file-content-linux.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
+[1]:http://dumptorrent.sourceforge.net/
+[2]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/change-path-environment-variable-linux.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150515 Basic Networking Commands with Docker Containers.md b/translated/tech/20150515 Basic Networking Commands with Docker Containers.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d4b90aa7f2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150515 Basic Networking Commands with Docker Containers.md
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
+关于Docker容器的基础网络命令
+================================================================================
+各位好,今天我们将学习一些Docker容器的基础命令。Docker是一个提供了开放平台来打包、发布并以一个轻量级容器运行任意程序的开放平台。它没有语言支持、框架或者打包系统的限制,可在任何时间、任何地方在小到家用电脑大到高端服务器上运行。这使得在部署和扩展网络应用、数据库和终端服务时不依赖于特定的栈或者提供商。Docker注定是用于网络的如它正应用于数据中心、ISP和越来越多的网络服务。
+
+因此,这里有一些你在管理Docker容器的时候会用到的一些命令。
+
+### 1. 找到Docker接口 ###
+
+Docker默认会创建一个名为docker0的网桥接口来连接外部的世界。docker容器运行时直接连接到网桥接口docker0。默认上,docker会分配172.17.42.1/16给docker0,它是所有运行容器ip地址的子网。得到Docker接口的ip地址非常简单。要找出docker0网桥接口和连接到网桥上的docker容器,我们可以在终端或者安装了docker的shell中运行ip命令。
+
+ # ip a
+
+
+
+### 2. 得到Docker容器的ip地址 ###
+
+如我们上面读到的,docker在主机中创建了一个叫docker0的网桥接口。如我们创建一个心的docker容器一样,它自动被默认分配了一个在子网范围内的ip地址。因此,要检测运行中的Docker容器的ip地址,我们需要进入一个正在运行的容器并用下面的命令检查ip地址。首先,我们运行一个新的容器并进入。如果你已经有一个正在运行的容器,你可以跳过这个步骤。
+
+ # docker run -it ubuntu
+
+现在,我们可以运行ip a来得到容器的ip地址了。
+
+ # ip a
+
+
+
+### 3. 映射暴露的端口 ###
+
+要映射配置在Dockerfile的暴露端口,我们只需用下面带上-P标志的命令。这会打开docker容器的随机端口并映射到Dockerfile中定义的端口。下面是使用-P来打开/映射定义的端口的例子。
+
+ # docker run -itd -P httpd
+
+
+
+上面的命令会映射Dockerfile中定义的httpd 80端口到容器的端口上。我们用下面的命令来查看正在运行的容器暴露的端口。
+
+ # docker ps
+
+并且可以用下面的curl命令来检查。
+
+ # curl http://localhost:49153
+
+
+
+### 4. 映射到特定的端口上 ###
+
+我们也可以映射暴露端口或者docker容器端口到我们指定的端口上。要实现这个,我们用-p标志来定义我们的需要。这里是我们的一个例子。
+
+ # docker run -itd -p 8080:80 httpd
+
+上面的命令会映射8080端口到80上。我们可以运行curl来检查这点。
+
+ # curl http://localhost:8080
+
+
+
+### 5. 创建自己的网桥 ###
+
+要给容器创建一个自定义的IP地址,在本篇中我们会创建一个名为bro的新网桥。要分配需要的ip地址,我们需要在运行docker的主机中运行下面的命令。
+
+ # stop docker.io
+ # ip link add br0 type bridge
+ # ip addr add 172.30.1.1/20 dev br0
+ # ip link set br0 up
+ # docker -d -b br0
+
+
+
+创建完docker网桥之后,我们要让docker的守护进程知道它。
+
+ # echo 'DOCKER_OPTS="-b=br0"' >> /etc/default/docker
+ # service docker.io start
+
+
+
+到这里,桥接后的接口将会分配给容器新的在桥接子网内的ip地址。
+
+### 6. 链接到另外一个容器上 ###
+
+我们可以用Dokcer连接一个容器到另外一个上。我们可以在不容的容器上运行不同的程序,并且相互连接或链接。链接允许容器间相互连接并安全地从一个容器上传输信息给另一个容器。要做到这个,我们可以使用--link标志。首先,我们使用--name标志来表示training/postgres镜像。
+
+ # docker run -d --name db training/postgres
+
+
+
+完成之后,我们将容器db与training/webapp链接来形成新的叫web的容器。
+
+ # docker run -d -P --name web --link db:db training/webapp python app.py
+
+
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+Docker网络很神奇也好玩,因为有我们可以对docker容器做很多事情。这里有些简单和基础的我们可以把玩docker网络命令。docker的网络是非常高级的。我们可以用它做很多事情。如果你有任何的问题、建议、反馈请在下面的评论栏写下来以便于我们我们可以提升或者更新文章的内容。谢谢! 玩得开心!:-)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/networking-commands-docker-containers/
+
+作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150518 10 Amazing and Mysterious Uses of Symbol or Operator in Linux Commands.md b/translated/tech/20150518 10 Amazing and Mysterious Uses of Symbol or Operator in Linux Commands.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4225cf9bb4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150518 10 Amazing and Mysterious Uses of Symbol or Operator in Linux Commands.md
@@ -0,0 +1,193 @@
+10����!��������Linux�������¾��˺�������÷�
+================================================================================
+`'!'`������Linux�в��������������ţ���������������ʷ�����¼��ȡ��������ĵ�ִ��֮ǰ���е�����������������Ѿ���Bash Shell�о���ȷ�еؼ�顣������û���Թ������������ڱ��Shell�����С��������ǽ�����Linux�������з���`'!'`�Ǿ��˺�������÷���
+
+### 1. ʹ�����ִ���ʷ�����б�����һ��������ִ�� ###
+
+��Ҳ��û����ʶ�������Դ���ʷ�����б���֮ǰ�Ѿ�ִ�е���������ҳ�һ�������С����ȣ�ͨ��"history"�������֮ǰ�������š�
+
+ $ history
+
+
+
+���ڣ�ֻ��Ҫʹ����ʷ�����������ʾ�ڸ�����ǰ������ֱ�����������������磬����һ����`history`����б����1551�����
+
+ $ !1551
+
+
+
+���������Ϊ1551����������������[top����][1]���������ˡ�����ͨ��ID����ִ��֮ǰ������ķ�ʽ�����ã�����������Щ����ܳ�������¡���ֻ��Ҫʹ��**![history������������]**����Ե�������
+
+### 2. ����֮ǰ�ĵ����ڶ��������߸������ ###
+
+����������һ�ַ�ʽ������֮ǰִ�е����ͨ��ʹ��-1�����������-2���������ڶ������-7�����������߸�����ȡ�
+
+����ʹ��history���������ִ�й���������б���history�����ִ�к��б�Ҫ����Ϊ������ͨ������ȷ��û��`rm command > file`�������ᵼ��Σ�յ����������ִ�е������������ڰ˸�����ʮ�����
+
+ $ history
+ $ !-6
+ $ !-8
+ $ !-10
+
+
+ͨ�������������֮ǰִ�е�����
+
+### 3. ����������ݲ������Է���������µ����� ###
+
+����Ҫ��ʾ`/home/$USER/Binary/firefox`�ļ��е����ݣ������ִ�У�
+
+ $ ls /home/$USER/Binary/firefox
+
+������������ʶ����Ӧ��ִ��'ls -l'���鿴�ĸ��ļ��ǿ�ִ���ļ��������Ӧ������������������ô�������Ҳ���Ҫ���ҽ���Ҫ���µ������д������IJ��������ƣ�
+
+ $ ls -l !$
+
+����`!$`�������ִ�е�����IJ������ݵ�����µ������С�
+
+
+����һ������IJ������ݸ�������
+
+### 4. ���ʹ��!���������������IJ��� ###
+
+����˵�������洴����һ���ı��ļ�file1.txt��
+
+ $ touch /home/avi/Desktop/1.txt
+
+Ȼ����cp������ʹ�þ���·������������`/home/avi/Downloads`��
+
+ $ cp /home/avi/Desktop/1.txt /home/avi/downloads
+
+���ڣ����Ǹ�cp�������������������һ����`/home/avi/Desktop/1.txt`���ڶ�����`/home/avi/Downloads`�������Ƿֱ������ǣ�ʹ��`echo [arguments]`����ӡ������ͬ�IJ�����
+
+ $ echo "1st Argument is : !^"
+ $ echo "2nd Argument is : !cp:2"
+
+ע���һ����������ʹ��`"!^"`���д�ӡ��������������ͨ��`"![������]:[�������]"`��ӡ��
+
+������������У���һ��������`cp`���ڶ�������Ҳ��Ҫ����ӡ�������`"!cp:2"`������κ��������xyz����ʱ��5��������������Ҫ��õ��ĸ�������������ʹ��`"!xyz:4"`�����еIJ���������ͨ��`"!*"`����á�
+
+
+�������������IJ���
+
+### 5. �Թؼ���Ϊ����ִ���ϸ������� ###
+
+���ǿ����Թؼ���Ϊ����ִ���ϴ�ִ�е�������Դ���������������⣺
+
+ $ ls /home > /dev/null [����1]
+ $ ls -l /home/avi/Desktop > /dev/null [����2]
+ $ ls -la /home/avi/Downloads > /dev/null [����3]
+ $ ls -lA /usr/bin > /dev/null [����4]
+
+��������ʹ����ͬ�������ls�������в�ͬ�Ŀ��غͲ�ͬ�IJ����ļ��С����ң����ǻ���������ݵ�`/dev/null`�����Dz�δ�������������ն����ɺܸɾ���
+
+�����Թؼ���Ϊ����ִ���ϸ������
+
+ $ ! ls [����1]
+ $ ! ls -l [����2]
+ $ ! ls -la [����3]
+ $ ! ls -lA [����4]
+
+���������������淢��������ʹ�ùؼ���`ls`��ִ�������Ѿ�ִ�й������
+
+
+�Թؼ���Ϊ����ִ������
+
+### 6. !!������������ ###
+
+������ʹ��`(!!)`����/�����ϸ����е������������һЩ��/�����������ϸ�������Ҹ���չʾһЩʵ���龳��
+
+������������һ�нű�������ҵ�˽��IP�������ִ���ˣ�
+
+ $ ip addr show | grep inet | grep -v 'inet6'| grep -v '127.0.0.1' | awk '{print $2}' | cut -f1 -d/
+
+���ţ���ͻȻ��������Ҫ������ű�������ض���һ��ip.txt���ļ�����ˣ��Ҹ���ô���أ��Ҹ�����������������ض���һ���ļ�ô��һ���Ľ��������ʹ�����ϵ�����������`'> ip.txt'`��������ض����ļ���
+
+ $ ip addr show | grep inet | grep -v 'inet6'| grep -v '127.0.0.1' | awk '{print $2}' | cut -f1 -d/ > ip.txt
+
+�������л������"���ϵ�����"�����ڣ��������������������������������һ�нű���
+
+ $ ifconfig | grep "inet addr:" | awk '{print $2}' | grep -v '127.0.0.1' | cut -f2 -d:
+
+һ��������������ű���Bash��ʾ���㷵���˴�����Ϣ`"bash: ifconfig: command not found"`��ԭ���Ѳ£��������˱�Ӧ��rootȨ�����е����
+
+���ԣ���ô����أ����Ǻ�����root�û���¼�����ٴμ�����������������ϵ�����Ҳ�������ˡ���ˣ�������Ҫ����`"!!"`��ȥ�����ţ�������Ϊ�Ǹ��û������ϸ����
+
+ $ su -c "!!" root
+
+����su�������л���root�û��ģ�`-c`������ij�û������ض����������Ҫ�IJ�����`!!`���������滻Ϊ�ϴ����е�����Եģ�����Ҫ�ṩroot���롣
+
+
+!!������������
+
+��ͨ����������龰��ʹ��`!!`��
+
+1.��������ͨ�û�������apt-get����ͨ���յ���ʾ˵��û��Ȩ����ִ�С�
+
+ $ apt-get upgrade && apt-get dist-upgrade
+
+�ðɣ��д������ģ�ʹ��������������ɹ���ִ��...
+
+ $ su -c !!
+
+ͬ���������ڣ�
+
+ $ service apache2 start
+ ��
+ $ /etc/init.d/apache2 start
+ ��
+ $ systemctl start apache2
+
+��ͨ�û�������Ȩִ����Щ�������������У�
+
+ $ su -c 'service apache2 start'
+ ��
+ $ su -c '/etc/init.d/apache2 start'
+ ��
+ $ su -c 'systemctl start apache2'
+
+### 7.����һ��Ӱ�����г���![FILE_NAME]���ļ����� ###
+
+`!`�����ǣ��������Գ���`'!'`����ļ������е��ļ�/��չִ�����
+
+A.���ļ����Ƴ������ļ���2.txt���⡣
+
+ $ rm !(2.txt)
+
+B.���ļ����Ƴ����е��ļ����ͣ�pdf���ͳ��⡣
+
+ $ rm !(*.pdf)
+
+### 8.���ij���ļ��У�����/home/avi/Tecmint���Ƿ���ڣ�����ӡ ###
+
+�������ʹ��`'! -d'`����֤�ļ����Ƿ���ڣ����ļ��в�����ʱ����ʹ��������AND������`(&&)`���д�ӡ�����ļ��д���ʱ����ʹ��OR������`(||)`���д�ӡ��
+
+���ϣ���`[ ! -d /home/avi/Tecmint ]`�����Ϊ0ʱ������ִ��AND������������ݣ���������ִ��OR����`(||)`��������ݡ�
+
+ $ [ ! -d /home/avi/Tecmint ] && printf '\nno such /home/avi/Tecmint directory exist\n' || printf '\n/home/avi/Tecmint directory exist\n'
+
+### 9.���ij�ļ����Ƿ���ڣ�������������˳������� ###
+
+���������������������ﵱ�������ļ��в�����ʱ����������˳���
+
+ $ [ ! -d /home/avi/Tecmint ] && exit
+
+### 10.�������home�ļ����ڲ�����һ���ļ��У��ȷ�˵test�������� ###
+
+���ǽű������е�һ�����õ�ʵ�֣����������ļ��в�����ʱ������һ����
+
+ [ ! -d /home/avi/Tecmint ] && mkdir /home/avi/Tecmint
+
+�����ȫ���ˡ������֪����ż����������ֵ���˽��`'!'`ʹ�÷����������ڷ����ĵط��������Ὠ�顣������ϵ��
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/mysterious-uses-of-symbol-or-operator-in-linux-commands/
+
+���ߣ�[Avishek Kumar][a]
+���ߣ�[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
+У�ԣ�[У����ID](https://github.com/У����ID)
+
+������ [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) ԭ�����룬[Linux�й�](https://linux.cn/) �����Ƴ�
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/12-top-command-examples-in-linux/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150518 70 Expected Shell Scripting Interview Questions and Answers.md b/translated/tech/20150518 70 Expected Shell Scripting Interview Questions and Answers.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b5ccd63e0a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150518 70 Expected Shell Scripting Interview Questions and Answers.md
@@ -0,0 +1,399 @@
+70 个可能的 Shell 脚本面试问题及解答
+================================================================================
+我们为你的面试准备选择了 70 个可能的 shell 脚面问题及解答。了解脚本或至少知道基础知识对系统管理员来说至关重要,它也有助于你在工作环境中自动完成很多任务。在过去的几年里,我们注意到所有的 linux 工作职位都要求脚本技能。
+
+### 1) 如何向脚本传递参数 ? ###
+
+./script argument
+
+**例子** : 显示文件名称脚本
+
+./show.sh file1.txt
+
+ cat show.sh
+ #!/bin/bash
+ cat $1
+
+### 2) 如何在脚本中使用参数 ? ###
+
+第一个参数: $1,
+第二个参数 : $2
+
+例子 : 脚本会复制文件(arg1) 到目标地址(arg2)
+
+./copy.sh file1.txt /tmp/
+
+ cat copy.sh
+ #!/bin/bash
+ cp $1 $2
+
+### 3) 如何计算传递进来的参数 ? ###
+
+$#
+
+### 4) 如何在脚本中获取脚本名称 ? ###
+
+$0
+
+### 5) 如何检查之前的命令是否运行成功 ? ###
+
+$?
+
+### 6) 如何获取文件的最后一行 ? ###
+
+tail -1
+
+### 7) 如何获取文件的第一行 ? ###
+
+head -1
+
+### 8) 如何获取一个文件每一行的第三个元素 ? ###
+
+awk '{print $3}'
+
+### 9) 假如第一个等于 FIND,如何获取文件中每行的第二个元素 ###
+
+awk '{ if ($1 == "FIND") print $2}'
+
+### 10) 如何调试 bash 脚本 ###
+
+Add -xv to #!/bin/bash
+
+例子
+
+#!/bin/bash –xv
+
+### 11) 举例如何写一个函数 ? ###
+
+function example {
+echo "Hello world!"
+}
+
+### 12) 如何向 string 添加 string ? ###
+
+V1="Hello"
+V2="World"
+V3=$V1+$V2
+echo $V3
+
+Output
+
+Hello+World
+
+### 13) 如何进行两个整数相加 ? ###
+
+V1=1
+V2=2
+V3=$V1+$V2
+echo $V3
+
+Output
+3
+
+### 14) 如何检查文件系统中是否存在某个文件 ? ###
+
+if [ -f /var/log/messages ]
+then
+echo "File exists"
+fi
+
+### 15) 写出 shell 脚本中所有循环语法 ? ###
+
+#### for loop : ####
+
+for i in $( ls ); do
+echo item: $i
+done
+
+#### while loop : ####
+
+#!/bin/bash
+COUNTER=0
+while [ $COUNTER -lt 10 ]; do
+echo The counter is $COUNTER
+let COUNTER=COUNTER+1
+done
+
+#### untill oop : ####
+
+#!/bin/bash
+COUNTER=20
+until [ $COUNTER -lt 10 ]; do
+echo COUNTER $COUNTER
+let COUNTER-=1
+done
+
+### 16) 每个脚本开始的 #!/bin/sh 或 #!/bin/bash 表示什么意思 ? ###
+
+这一行说明要使用的 shell。#!/bin/bash 表示脚本使用 /bin/bash。对于 python 脚本,就是 #!/usr/bin/python
+
+### 17) 如何获取文本文件的第 10 行 ? ###
+
+head -10 file|tail -1
+
+### 18) bash 脚本文件的第一个符号是什么 ###
+
+#
+
+### 19) 命令:[ -z "" ] && echo 0 || echo 1 的输出是什么 ###
+
+0
+
+### 20) 命令 “export” 有什么用 ? ###
+
+使变量在子 shell 中公有
+
+### 21) 如何在后台运行脚本 ? ###
+
+在脚本后面添加 “&”
+
+### 22) "chmod 500 script" 做什么 ? ###
+
+使脚本所有者拥有可执行权限
+
+### 23) ">" 做什么 ? ###
+
+重定向输出流到文件或另一个流。
+
+### 24) & 和 && 有什么区别 ###
+
+& - 希望脚本在后台运行的时候使用它
+&& - 当第一个脚本成功完成才执行命令/脚本的时候使用它
+
+### 25) 什么时候要在 [ condition ] 之前使用 “if” ? ###
+
+当条件满足时需要运行多条命令的时候。
+
+### 26) 命令: name=John && echo 'My name is $name' 的输出是什么 ###
+
+My name is $name
+
+### 27) bash shell 脚本中哪个符号用于注释 ? ###
+
+#
+
+### 28) 命令: echo ${new:-variable} 的输出是什么 ###
+
+variable
+
+### 29) ' 和 " 引号有什么区别 ? ###
+
+' - 当我们不希望把变量转换为值的时候使用它。
+" - 会计算所有变量的值并用值代替。
+
+### 30) 如何在脚本文件中重定向标准输入输出流到 log.txt 文件 ? ###
+
+在脚本文件中添加 "exec >log.txt 2>&1" 命令
+
+### 31) 如何只用 echo 命令获取 string 变量的一部分 ? ###
+
+echo ${variable:x:y}
+x - 起始位置
+y - 长度
+例子:
+variable="My name is Petras, and I am developer."
+echo ${variable:11:6} # 会显示 Petras
+
+### 32) 如果给定字符串 variable="User:123:321:/home/dir" 如何只用 echo 命令获取 home_dir ? ###
+
+echo ${variable#*:*:*:}
+或
+echo ${variable##*:}
+
+### 33) 如何从上面的字符串中获取 “User” ? ###
+
+echo ${variable%:*:*:*}
+或
+echo ${variable%%:*}
+
+### 34) 如何使用 awk 列出 UID 小于 100 的用户 ? ###
+
+awk -F: '$3<100' /etc/passwd
+
+### 35) 写程序为用户计算主组数目并显示次数和组名 ###
+
+cat /etc/passwd|cut -d: -f4|sort|uniq -c|while read c g
+do
+{ echo $c; grep :$g: /etc/group|cut -d: -f1;}|xargs -n 2
+done
+
+### 36) 如何在 bash shell 中更改标注域分隔符为 ":" ? ###
+
+IFS=":"
+
+### 37) 如何获取变量长度 ? ###
+
+${#variable}
+
+### 38) 如何打印变量的最后 5 个字符 ? ###
+
+echo ${variable: -5}
+
+### 39) ${variable:-10} 和 ${variable: -10} 有什么区别? ###
+
+${variable:-10} - 如果之前没有给 variable 赋值则输出 10
+${variable: -10} - 输出 variable 的最后 10 个字符
+
+### 40) 如何只用 echo 命令替换字符串的一部分 ? ###
+
+echo ${variable//pattern/replacement}
+
+### 41) 哪个命令将命令替换为大写 ? ###
+
+tr '[:lower:]' '[:upper:]'
+
+### 42) 如何计算本地用户数目 ? ###
+
+wc -l /etc/passwd|cut -d" " -f1
+或者
+cat /etc/passwd|wc -l
+
+### 43) 不用 wc 命令如何计算字符串中的单词数目 ? ###
+
+set ${string}
+echo $#
+
+### 44) "export $variable" 或 "export variable" 哪个正确 ? ###
+
+export variable
+
+### 45) 如何列出第二个字母是 a 或 b 的文件 ? ###
+
+ls -d ?[ab]*
+
+### 46) 如何将整数 a 加到 b 并赋值给 c ? ###
+
+c=$((a+b))
+或
+c=`expr $a + $b`
+或
+c=`echo "$a+$b"|bc`
+
+### 47) 如何去除字符串中的所有空格 ? ###
+
+echo $string|tr -d " "
+
+### 48) 重写命令输出变量转换为复数的句子: item="car"; echo "I like $item" ? ###
+
+item="car"; echo "I like ${item}s"
+
+### 49) 写出输出数字 0 到 100 中 3 的倍数(0 3 6 9 …)的命令 ? ###
+
+for i in {0..100..3}; do echo $i; done
+或
+for (( i=0; i<=100; i=i+3 )); do echo "Welcome $i times"; done
+
+### 50) 如何打印传递给脚本的所有参数 ? ###
+
+echo $*
+或
+echo $@
+
+### 51) [ $a == $b ] 和 [ $a -eq $b ] 有什么区别 ###
+
+[ $a == $b ] - 用于字符串比较
+[ $a -eq $b ] - 用于数字比较
+
+### 52) = 和 == 有什么区别 ###
+
+= - 用于为变量复制
+== - 用于字符串比较
+
+### 53) 写出测试 $a 是否大于 12 的命令 ? ###
+
+[ $a -gt 12 ]
+
+### 54) 写出测试 $b 是否小于等于 12 的命令 ? ###
+
+[ $b -le 12 ]
+
+### 55) 如何检查字符串是否以字母 "abc" 开头 ? ###
+
+[[ $string == abc* ]]
+
+### 56) [[ $string == abc* ]] 和 [[ $string == "abc*" ]] 有什么区别 ###
+
+[[ $string == abc* ]] - 检查字符串是否以字母 abc 开头
+[[ $string == "abc* " ]] - 检查字符串是否完全等于 abc*
+
+### 57) 如何列出以 ab 或 xy 开头的用户名 ? ###
+
+egrep "^ab|^xy" /etc/passwd|cut -d: -f1
+
+### 58) bash 中 $! 表示什么意思 ? ###
+
+后台最近命令的 PID
+
+### 59) $? 表示什么意思 ? ###
+
+前台最近命令的结束状态
+
+### 60) 如何输出当前 shell 的 PID ? ###
+
+echo $$
+
+### 61) 如何获取传递给脚本的参数数目 ? ###
+
+echo $#
+
+### 62) $* 和 $@ 有什么区别 ###
+
+$* - 以一个字符串形式输出所有传递到脚本的参数
+$@ - 以 $IFS 为分隔符列出所有传递到脚本中的参数
+
+### 63) 如何在 bash 中定义数组 ? ###
+
+array=("Hi" "my" "name" "is")
+
+### 64) 如何打印数组的第一个元素 ? ###
+
+echo ${array[0]}
+
+### 65) 如何打印数组的所有元素 ? ###
+
+echo ${array[@]}
+
+### 66) 如何输出所有数组索引 ? ###
+
+echo ${!array[@]}
+
+### 67) 如何移除数组中索引为 2 的元素 ? ###
+
+unset array[2]
+
+### 68) 如何在数组中添加 id 为 333 的元素 ? ###
+
+array[333]="New_element"
+
+### 69) shell 脚本如何获取输入的值 ? ###
+
+a) 通过参数
+
+./script param1 param2
+
+b) 通过 read 命令
+
+read -p "Destination backup Server : " desthost
+
+### 70) 在脚本中如何使用 "expect" ? ###
+
+/usr/bin/expect << EOD
+spawn rsync -ar ${line} ${desthost}:${destpath}
+expect "*?assword:*"
+send "${password}\r"
+expect eof
+EOD
+
+好运 !! 如果你有任何疑问或者问题需要解答都可以在下面的评论框中写下来。让我们知道这对你的面试有所帮助:-)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-shell-script/shell-scripting-interview-questions-answers/
+
+作者:[Petras Liumparas][a]
+译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/petrasl/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix '404 Not Found' error with 'apt-get update' on old Ubuntu.md b/translated/tech/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix '404 Not Found' error with 'apt-get update' on old Ubuntu.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9880f7953f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix '404 Not Found' error with 'apt-get update' on old Ubuntu.md
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+Linux有问必答——在旧的Ubuntu上如何修复“apt-get update”的“404 Not Found”错误
+================================================================================
+> **问题**: 我的PC上安装了旧版的Ubuntu 13.04(急切的浣熊)。当我在上面运行“sudo apt-get update”时,它丢给了我一大堆“404 Not Found”错误,结果是我不能使用apt-get或aptitude来安装或更新任何软件包了。由于该错误的原因,我甚至不能将它升级到更新的版本。我怎样才能修复这个问题啊?
+>
+
+
+每个Ubuntu版本都有生命结束周期(EOL)时间;常规的Ubuntu发行版提供18个月的支持,而LTS(长期支持)版本则长达3年(服务器版本)和5年(桌面版本)。当某个Ubuntu版本达到生命结束周期时,其仓库就不能再访问了,你也不能再从Canonical获取任何维护更新和安全补丁。在撰写本文时,Ubuntu 13.04(急切的浣熊)已经达到了它的生命结束周期。
+
+如果你所使用的Ubuntu系统已经被结束生命周期,你就会从apt-get或aptitude得到以下404错误,因为它的仓库已经被遗弃了。
+
+ W: Failed to fetch http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/raring-backports/multiverse/binary-i386/Packages 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.91.13 80]
+
+ W: Failed to fetch http://extras.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/raring/main/binary-amd64/Packages 404 Not Found
+
+ W: Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/raring-security/universe/binary-i386/Packages 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.88.149 80]
+
+ E: Some index files failed to download. They have been ignored, or old ones used instead
+
+对于那些还在使用旧版本Ubuntu的用户,Canonical维护了一个old-releases.ubuntu.com的网站,这里包含了结束生命周期的仓库归档。因此,当Canonical对你安装的Ubuntu版本结束支持时,你需要将仓库切换到old-releases.ubuntu.com(除非你在结束生命周期之前想要升级)。
+
+这里,通过切换到旧版本仓库提供了一个快速修复“404 Not Found”错误的便捷方式。
+
+首先,使用旧版本仓库替换main/security仓库,就像下面这样。
+
+ $ sudo sed -i -r 's/([a-z]{2}\.)?archive.ubuntu.com/old-releases.ubuntu.com/g' /etc/apt/sources.list
+ $ sudo sed -i -r 's/security.ubuntu.com/old-releases.ubuntu.com/g' /etc/apt/sources.list
+
+然后,使用文本编辑器打开/etc/apt/sources.list,并查找extras.ubuntu.com。该仓库也不再支持Ubuntu 13.04了,所以你需要使用“#”号将extras.ubuntu.com注释掉。
+
+ #deb http://extras.ubuntu.com/ubuntu raring main
+ #deb-src http://extras.ubuntu.com/ubuntu raring main
+
+现在,你应该可以在旧版不受支持的Ubuntu上安装或更新软件包了。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/404-not-found-error-apt-get-update-ubuntu.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix 'Encountered a section with no Package--header' error on Raspbian.md b/translated/tech/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix 'Encountered a section with no Package--header' error on Raspbian.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..54e0f393d1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix 'Encountered a section with no Package--header' error on Raspbian.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+Linux 有问必答--如何修复 Raspbian 上的 “Encountered a section with no Package: header” 错误
+================================================================================
+> **问题**: 我在 Raspberry Pi 上安装新版的 Rasbian。但当我使用 sudo apt-get update 命令更新 APT 软件包索引的时候,它抛出下面的错误:
+
+ E: Encountered a section with no Package: header
+ E: Problem with MergeList /var/lib/dpkg/status
+ E: The package lists or status file could not be parsed or opened.
+
+> 之后我不能在 Raspbian 上安装任何软件包。我怎样才能解决这个错误?
+
+
+
+错误说 "Problem with MergeList /var/lib/dpkg/status" 表示由于某些原因状态文件损坏了,因此无法解释。这个状态文件包括了已经安装的 deb 软件包的信息,因此需要小心备份。
+
+在这种情况下,由于这是新安装的 Raspbian,你可以安全地删除状态文件,然后用下面的命令重新生成。
+
+ $ sudo rm /var/lib/dpkg/status
+ $ sudo touch /var/lib/dpkg/status
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/encountered-section-with-no-package-header-error.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to view threads of a process on Linux.md b/translated/tech/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to view threads of a process on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a91a2b3ed3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to view threads of a process on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+Linux有问必答——Linux上如何查看某个进程的线程
+================================================================================
+> **问题**: 我的程序创建并在它里头执行了多个线程,我怎样才能在该程序创建线程后监控其中单个线程?我想要看到带有它们名称的单个线程详细情况(如,CPU/内存使用率)。
+
+线程是现代操作系统上进行并行执行的一个流行的编程方面的抽象概念。当一个程序内有多个线程被叉分出用以执行多个流时,这些线程就会在它们之间共享特定的资源(如,内存地址空间、打开的文件),以使叉分开销最小化,并避免大量花销IPC(进程间通信)频道。这些功能让线程在并发执行时成为一个高效的机制。
+
+在Linux中,程序中创建的线程(也称为轻量级进程,LWP)会具有和程序的PID相同的“线程组ID”。然后,各个线程会获得其自身的线程ID(TID)。对于Linux内核调度器而言,线程不过是恰好共享特定资源的标准的进程。经典的命令行工具,如ps或top,都可以用来显示线程级别的信息,默认情况下它们会显示进程级别的信息。
+
+这里提供了**在Linux上显示某个进程的线程**的几种方式。
+
+### 方法一:PS ###
+
+在ps命令中,“-T”选项可以开启线程查看。下面的命令列出了由进程号为<pid>的进程创建的所有线程。
+
+ $ ps -T -p <pid>
+
+
+
+“SID”栏表示线程ID,而“CMD”栏则显示了线程名称。
+
+### 方法二: Top ###
+
+top命令可以实时显示各个线程情况。要在top输出中开启线程查看,请调用top命令的“-H”选项,该选项会列出所有Linux线程。在top运行时,你也可以通过按“H”键将线程查看模式切换为开或关。
+
+ $ top -H
+
+
+
+要让top输出某个特定进程<pid>并检查该进程内运行的线程状况:
+
+ $ top -H -p <pid>
+
+
+
+### 方法三: Htop ###
+
+一个对用户更加友好的方式是,通过htop查看单个进程的线程,它是一个基于ncurses的交互进程查看器。该程序允许你在树状视图中监控单个独立线程。
+
+要在htop中启用线程查看,请开启htop,然后按<F2>来进入htop的设置菜单。选择“设置”栏下面的“显示选项”,然后开启“树状视图”和“显示自定义线程名”选项。按<F10>退出设置。
+
+
+
+现在,你就会看到下面这样单个进程的线程视图。
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/view-threads-process-linux.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--What is the Apache error log location on Linux.md b/translated/tech/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--What is the Apache error log location on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c43ac481e7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150518 Linux FAQs with Answers--What is the Apache error log location on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+Linux有问必答——Linux上Apache错误日志的位置在哪里?
+================================================================================
+> **问题**: 我尝试着解决我 Linux 系统上的 Apache 网络服务器的错误,Apache的错误日志文件放在[你的 Linux 版本]的哪个位置呢?
+
+错误日志和访问日志文件为系统管理员提供了有用的信息,比如,为网络服务器排障,[保护][1]系统不受各种各样的恶意活动侵犯,或者只是进行[各种各样的][2][分析][3]以监控 HTTP 服务器。根据你网络服务器配置的不同,其错误/访问日志可能放在你系统中不同位置。
+
+本文可以帮助你**找到Linux上的Apache错误日志**。
+
+
+
+### Debian,Ubuntu或Linux Mint上的Apache错误日志位置 ###
+
+#### 默认的错误日志 ####
+
+在基于Debian的Linux上,系统范围的Apache错误日志默认位置是**/var/log/apache2/error.log**。默认位置可以通过编辑Apache的配置文件进行修改。
+
+#### 自定义的错误日志 ####
+
+要找到自定义的错误日志位置,请用文本编辑器打开 /etc/apache2/apache2.conf,然后查找以 ErrorLog 开头的行,该行指定了自定义的 Apache 错误日志文件的位置。例如,在未经修改的 Apache 配置文件中可以找到以下行:
+
+ ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
+
+在本例中,该位置使用 APACHE_LOG_DIR 环境变量进行配置,该变量在 /etc/apache2/envvars 中已被定义。
+
+ export APACHE_LOG_DIR=/var/log/apache2$SUFFIX
+
+在实际情况中, ErrorLog 可能会指向你 Linux 系统中任意路径。
+
+#### 使用虚拟主机自定义的错误日志 ####
+
+如果在 Apache 网络服务器中使用了虚拟主机, ErrorLog 指令可能会在虚拟主机容器内指定,在这种情况下,上面所说的系统范围的错误日志位置将被忽略。
+
+启用了虚拟主机后,各个虚拟主机可以定义其自身的自定义错误日志位置。要找出某个特定虚拟主机的错误日志位置,你可以打开 /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/<your-site>.conf,然后查找 ErrorLog 指令,该指令会显示站点指定的错误日志文件。
+
+### CentOS,Fedora或RHEL上的Apache错误日志位置 ###
+
+#### 默认的错误日志 ####
+
+在基于 Red Hat 的Linux中,系统范围的 Apache 错误日志文件默认被放置在**/var/log/httpd/error_log**。该默认位置可以通过修改 Apache 配置文件进行自定义。
+
+#### 自定义的错误日志 ####
+
+要找出 Apache 错误日志的自定义位置,请用文本编辑器打开 /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf,然后查找 ServerRoot,该参数显示了 Apache 服务器目录树的顶层,日志文件和配置都位于该目录树中。例如:
+
+ ServerRoot "/etc/httpd"
+
+现在,查找 ErrorLog 开头的行,该行指出了 Apache 网络服务器将错误日志写到了哪里去。注意,指定的位置是 ServerRoot 值的相对位置。例如:
+
+ ErrorLog "log/error_log"
+
+结合上面的两个指令,可以获得完整的错误日志路径,默认情况下该路径就是 /etc/httpd/logs/error_log。在全新安装的Apache中,这是一个到 /var/log/httpd/error_log 的符号链接。
+
+在实际情况中, ErrorLog 可能指向你 Linux 系统中的任意位置。
+
+#### 使用虚拟主机自定义的错误日志 ####
+
+如果你启用了虚拟主机,你可以通过检查 /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf(或其它任何定义了虚拟主机的文件)来找到各个虚拟主机的错误日志位置。在独立的虚拟主机部分查找 ErrorLog。如,在下面的虚拟主机部分,错误日志的位置是 /var/www/xmodulo.com/logs/error_log。
+
+ <VirtualHost *:80>
+ ServerAdmin webmaster@xmodulo.com
+ DocumentRoot /var/www/xmodulo.com/public_html
+ ServerName www.xmodulo.com
+ ServerAlias xmodulo.com
+ ErrorLog /var/www/xmodulo.com/logs/error_log
+ CustomLog /var/www/xmodulo.com/logs/access_log
+ <VirtualHost>
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/apache-error-log-location-linux.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/configure-fail2ban-apache-http-server.html
+[2]:http://xmodulo.com/interactive-apache-web-server-log-analyzer-linux.html
+[3]:http://xmodulo.com/sql-queries-apache-log-files-linux.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150520 How to Use Docker Machine with a Cloud Provider.md b/translated/tech/20150520 How to Use Docker Machine with a Cloud Provider.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..acf052d493
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150520 How to Use Docker Machine with a Cloud Provider.md
@@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
+如何在云服务提供商的机器使用Docker Machine
+================================================================================
+大家好,今天我们来学习如何使用Docker Machine在各种云服务提供商的平台部署Docker。Docker Machine是一个可以帮助我们在自己的电脑、云服务提供商的机器以及我们数据中心的机器上创建Docker机器的应用程序。它为创建服务器、在服务器中安装Docker、根据用户需求配置Docker客户端提供了简单的解决方案。驱动API对本地机器、数据中心的虚拟机或者公用云机器都适用。Docker Machine支持Windows、OSX和Linux,并且提供一个独立的二进制文件,可以直接使用。它让我们可以充分利用支持Docker的基础设施的生态环境合作伙伴,并且使用相同的接口进行访问。它让人们可以使用一个命令来简单而迅速地在不同的云平台部署Docker容器。
+
+
+### 1. 安装Docker Machine ###
+
+Docker Machine可以很好地支持每一种Linux发行版。首先,我们需要从Github网站下载最新版本的。这里我们使用curl来下载目前最新0.2.0版本的Docker Machine。
+
+在64位操作系统运行:
+
+ # curl -L https://github.com/docker/machine/releases/download/v0.2.0/docker-machine_linux-amd64 > /usr/local/bin/docker-machine
+
+在32位操作系统运行:
+
+ # curl -L https://github.com/docker/machine/releases/download/v0.2.0/docker-machine_linux-i386 > /usr/local/bin/docker-machine
+
+下载最新版本的Docker Machine并将docker-machine文件放到了/usr/local/bin/后,添加执行权限:
+
+ # chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-machine
+
+完成如上操作后,我们需要确认已经成功安装docker-machine了。可以运行如下命令检查,它会输出系统中docker-machine的版本:
+
+ # docker-machine -v
+
+
+
+另外机器上需要有docker命令,可以使用如下命令安装:
+
+ # curl -L https://get.docker.com/builds/linux/x86_64/docker-latest > /usr/local/bin/docker
+ # chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker
+
+### 2. 创建机器 ###
+
+在自己的Linux机器上安装好了Docker Machine之后,我们想要将一个docker虚拟机部署到云服务器上。Docker Machine支持几个流行的云平台,如igital Ocean、Amazon Web Services(AWS)、Microsoft Azure、Google Cloud Computing等等,所以我们可以在不同的平台使用相同的接口来部署Docker。本文中我们会使用digitalocean驱动在Digital Ocean的服务器上部署Docker,--driver选项指定digitalocean驱动,--digitalocean-access-token选项指定[Digital Ocean Control Panel][1]提供的API Token,命令最后的是我们创建的Docker虚拟机的机器名。运行如下命令:
+
+ # docker-machine create --driver digitalocean --digitalocean-access-token <API-Token> linux-dev
+
+ # eval "$(docker-machine env linux-dev)"
+
+
+
+**注意**: 这里linux-dev是我们将要创建的机器的名称。`<API-Token>`是一个安全key,可以在Digtal Ocean Control Panel生成。要找到这个key,我们只需要登录到我们的Digital Ocean Control Panel,然后点击API,再点击Generate New Token,填写一个名称,选上Read和Write。然后我们就会得到一串十六进制的key,那就是`<API-Token>`,简单地替换到上边的命令中即可。
+
+运行如上命令后,我们可以在Digital Ocean Droplet Panel中看到一个具有默认配置的droplet已经被创建出来了。
+
+
+
+简便起见,docker-machine会使用默认配置来部署Droplet。我们可以通过增加选项来定制我们的Droplet。这里是一些digitalocean相关的选项,我们可以使用它们来覆盖Docker Machine所使用的默认配置。
+
+ --digitalocean-image "ubuntu-14-04-x64" 是选择Droplet的镜像
+ --digitalocean-ipv6 enable 是启用IPv6网络支持
+ --digitalocean-private-networking enable 是启用专用网络
+ --digitalocean-region "nyc3" 是选择部署Droplet的区域
+ --digitalocean-size "512mb" 是选择内存大小和部署的类型
+
+如果你想在其他云服务使用docker-machine,并且想覆盖默认的配置,可以运行如下命令来获取Docker Mackine默认支持的对每种平台适用的参数。
+
+ # docker-machine create -h
+
+### 3. 选择活跃机器 ###
+
+部署Droplet后,我们想马上运行一个Docker容器,但在那之前,我们需要检查下活跃机器是否是我们需要的机器。可以运行如下命令查看。
+
+ # docker-machine ls
+
+
+
+ACTIVE一列有“*”标记的是活跃机器。
+
+现在,如果我们想将活跃机器切换到需要的机器,运行如下命令:
+
+ # docker-machine active linux-dev
+
+**注意**:这里,linux-dev是机器名,我们打算激活这个机器,并且在其中运行Docker容器。
+
+### 4. 运行一个Docker容器 ###
+
+现在,我们已经选择了活跃机器,就可以运行Docker容器了。可以测试一下,运行一个busybox容器来执行`echo hello word`命令,这样就可以得到输出:
+
+ # docker run busybox echo hello world
+
+注意:如果你试图在一个装有32位操作系统的宿主机部署Docker容器,使用SSH来运行docker是个好办法。这样你就可以简单跳过这一步,直接进入下一步。
+
+### 5. SSH到Docker机器中 ###
+
+如果我们想在机器或者Droplet上控制之前部署的Docker机器,可以使用docker-machine ssh命令来SSH到机器上:
+
+ # docker-machine ssh
+
+
+
+SSH到机器上之后,我们可以在上边运行任何Docker容器。这里我们运行一个nginx:
+
+ # docker run -itd -p 80:80 nginx
+
+操作完毕后,我们需要运行exit命令来退出Droplet或者服务器。
+
+ # exit
+
+### 5. 删除机器 ###
+
+删除在运行的机器以及它的所有镜像和容器,我们可以使用docker-machine rm命令:
+
+ # docker-machine rm linux-dev
+
+
+
+使用docker-machine ls命令检查是否成功删除了:
+
+ # docker-machine ls
+
+
+
+### 6. 在不使用驱动的情况新增一个机器 ###
+
+我们可以在不使用驱动的情况往Docker增加一台机器,只需要一个URL。它可以使用一个已有机器的别名,所以我们就不需要每次在运行docker命令时输入完整的URL了。
+
+ $ docker-machine create --url=tcp://104.131.50.36:2376 custombox
+
+### 7. 管理机器 ###
+
+如果你已经让Docker运行起来了,可以使用简单的**docker-machine stop**命令来停止所有正在运行的机器,如果需要再启动的话可以运行**docker-machine start**:
+
+ # docker-machine stop
+ # docker-machine start
+
+你也可以使用如下命令来使用机器名作为参数来将其停止或启动:
+
+ $ docker-machine stop linux-dev
+ $ docker-machine start linux-dev
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+Docker Machine是一个非常棒的工具,可以使用Docker容器快速地部署服务。文中我们使用Digital Ocean Platform作演示,但Docker Machine还支持其他平台,如Amazon Web Service、Google Cloud Computing。使用Docker Machine,快速、安全地在几种不同平台部署Docker容器变得很简单了。因为Docker Machine还是Beta版本,不建议在生产环境使用。如果你有任何问题、建议、反馈,请在下方的评论框中写下来,我们会改进或者更新我们的内容。谢谢!享受吧 :-)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/use-docker-machine-cloud-provider/
+
+作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
+译者:[goreliu](https://github.com/goreliu)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
+[1]:https://cloud.digitalocean.com/settings/applications
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150520 How to Use tmpfs on RHEL or CentOS 7.0.md b/translated/tech/20150520 How to Use tmpfs on RHEL or CentOS 7.0.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7f3e37b3fe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150520 How to Use tmpfs on RHEL or CentOS 7.0.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+如何在RHEL/CentOS 7.0中使用tmpfs
+================================================================================
+ 7中的tmpfs,这是一个将所有文件和文件夹写到虚拟内存中而不是实际写到磁盘中的虚拟文件系统。这意味中tmpfs中所有的内容都是临时的,在取消挂载、系统重启或者电源切断后内容都将会丢失。技术的角度上来说,tmpfs将搜有的内容放在内核内部缓存中并且会增大或者缩小来容纳文件并可从交换空间中交换处不需要的页。
+
+CentOS默认使用tmpfs做的事可用df -h命令的输出来看:
+
+ # df –h
+
+
+
+/dev - 含有针对所有设备的设备文件的目录
+/dev/shm – 包含共享内存分配
+/run - 用于系统日志
+/sys/fs/cgroup - 用于cgrpups, 一个针对特定进程限制、管制和审计资源利用的内核特性
+
+/tmp目录, 你可以用下面的两种方法来做到:
+
+### 使用systemctl来在/tmp中启用tmpfs ###
+
+你可以使用systemctl命令在tmp目录启用tmpfs, 首先用下面的命令来检查这个特性是否可用:
+
+ # systemctl is-enabled tmp.mount
+
+这会显示当先的状态,你可以使用下面的命令来启用它:
+
+ # systemctl enable tmp.mount
+
+
+
+这会控制/tmp目录并挂载tmpfs。
+
+### 手动挂载/tmp/文件系统 ###
+
+你可以在/etc/fstab中添加下面这行在/tmp挂载tmpfs。
+
+ tmpfs /tmp tmpfs size=512m 0 0
+
+接着运行这条命令
+
+ # mount –a
+
+
+
+这应该就会在df -h中显示tmpfs了,同样也会在你下次重启是会自动挂载。
+
+### 立即创建tmpfs ###
+
+如果由于一些原因,你写昂立即创建tmpfs,你可以使用下面的命令:
+
+ # mount -t tmpfs -o size=1G tmpfs /mnt/mytmpfs
+
+当然你可以在size选项中指定你希望的大小和希望的挂载点,只要记住是有效的目录就行了。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/file-system/use-tmpfs-rhel-centos-7-0/
+
+作者:[Adrian Dinu][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/adriand/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150520 How to compile and install wxWidgets on Ubuntu or Debian or Linux Mint.md b/translated/tech/20150520 How to compile and install wxWidgets on Ubuntu or Debian or Linux Mint.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1f733207f3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150520 How to compile and install wxWidgets on Ubuntu or Debian or Linux Mint.md
@@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
+如何在Ubuntu/Debian/Linux Mint中编译和安装wxWidgets
+================================================================================
+### wxWidgets ###
+
+wxWidgets是一个程序开发框架/库, 允许你在Windows、Mac、Linux中使用相同的代码跨平台开发。
+
+它主要用C++写成,但也可以与其他语言绑定比如Python、Perl、Ruby。
+
+本教程中我将向你展示如何在基于Debian的linux中如Ubuntu和Linux Mint中编译wxwidgets 3.0+。
+
+从源码编译wxWidgets并不困难,仅仅需要几分钟。
+
+库可以按不同的方式来编译,比如静态或者动态库。
+
+### 1. 下载 wxWidgets ###
+
+第一步你需要从[wxwidgets.org][1]下载wxWidgets源码文件。
+
+做完后,解压到目录。
+
+### 2. 设置编译环境 ###
+
+要编译wxwidgets,我们需要一些工具包括C++编译器, 在Linux上是g++。所有这些可以通过apt-get工具从仓库中安装。
+
+我们还需要wxWidgets依赖的GTK开发库。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install libgtk-3-dev build-essential checkinstall
+
+>checkinstall工具允许我们为wxwidgets创建一个安装包,这样之后就可以轻松的使用包管理器来卸载。
+
+### 3. 编译 wxWidgets ###
+
+进入到wxWidgets解压后的目录。为了保持清洁,创建一个编译用的目录。
+
+ $ mkdir gtk-build
+ $ cd gtk-build/
+
+现在运行configure和make命令。每个将花费一些时间来完成。
+
+ $ ../configure --disable-shared --enable-unicode
+ $ make
+
+"--disable-shared"选项将会编译静态库而不是动态库。
+
+make命令完成后,编译也成功了。是时候安装wxWidgets到正确的目录。
+
+更多信息请参考install.txt和readme.txt,这可在wxwidgets中的/docs/gtk/目录下找到。
+
+### 4. 安装 checkinstall ###
+
+现在我们不使用"make install"命令,我们使用checkinstall命令来创建一个wxwidgets的deb安装包。运行命令:
+
+ $ sudo checkinstall
+
+checkinstall会询问几个问题,请保证在提问后提供一个版本号,否则将会失败。
+
+完成这一切后,wxWidgets就安装好了,deb文件也会创建在相同的目录下。
+
+### 5. 追踪安装的文件 ###
+
+如果你想要检查文件安装的位置,使用dpkg命令后面跟上checkinstall提供的报名。
+
+ $ dpkg -L package_name
+ /.
+ /usr
+ /usr/local
+ /usr/local/lib
+ /usr/local/lib/libwx_baseu-3.0.a
+ /usr/local/lib/libwx_gtk3u_propgrid-3.0.a
+ /usr/local/lib/libwx_gtk3u_html-3.0.a
+ /usr/local/lib/libwxscintilla-3.0.a
+ /usr/local/lib/libwx_gtk3u_ribbon-3.0.a
+ /usr/local/lib/libwx_gtk3u_stc-3.0.a
+ /usr/local/lib/libwx_gtk3u_qa-3.0.a
+ /usr/local/lib/libwx_baseu_net-3.0.a
+ /usr/local/lib/libwxtiff-3.0.a
+
+### 6. 编译示例 ###
+
+编译wxWidgets完成后就可以马上编译示例程序了。在相同的目录下,一个新的sample目录已经创建了。
+
+进入它并运行下面的命令
+
+ $ compile samples
+ $ cd samples/
+ $ make
+
+make命令完成后,进入sampl子目录,这里就有一个可以马上运行的Demo程序了。
+
+### 7. 编译你的第一个程序 ###
+
+你完成编译demo程序后,可以写你自己的程序来编译了。这个也很简单。
+
+假设你用的是C++这样你可以使用编辑器的高亮特性。比如gedit、kate、kwrite等等。或者用全功能的IDE像Geany、Codelite、Codeblocks等等。
+
+然而你的第一个程序只需要用一个文本编辑器来快速完成。
+
+这里就是
+
+ #include <wx/wx.h>
+
+ class Simple : public wxFrame
+ {
+ public:
+ Simple(const wxString& title)
+ : wxFrame(NULL, wxID_ANY, title, wxDefaultPosition, wxSize(250, 150))
+ {
+ Centre();
+ }
+ };
+
+ class MyApp : public wxApp
+ {
+ public:
+ bool OnInit()
+ {
+ Simple *simple = new Simple(wxT("Simple"));
+ simple->Show(true);
+ return true;
+ }
+ };
+
+ wxIMPLEMENT_APP(MyApp);
+
+现在保存并用下面的命令编译。
+
+ # compile
+ $ g++ basic.cpp `wx-config --cxxflags --libs std` -o program
+
+ # run
+ $ ./program
+
+#### 和非标准的库一起编译 ####
+
+面展示的wx-config命令默认只支持标准的库。如果你使用的是Aui库,那么你需要指定额外用到的库。
+
+ $ g++ code.cpp `wx-config --cxxflags --libs std,aui` -o program
+
+更多的信息参考这里[这里][2]。
+
+### 资源 ###
+
+下载wxWidgets的源码和帮助
+[https://www.wxwidgets.org/downloads/][3]
+
+wxWidgets编译的wiki页面
+[https://wiki.wxwidgets.org/Compiling_and_getting_started][4]
+
+使用wxWidgets最新版本(3.0+)的事项
+[https://wiki.wxwidgets.org/Updating_to_the_Latest_Version_of_wxWidgets][5]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.binarytides.com/install-wxwidgets-ubuntu/
+
+作者:[Silver Moon][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://plus.google.com/117145272367995638274/posts
+[1]:https://www.wxwidgets.org/downloads/
+[2]:https://wiki.wxwidgets.org/Updating_to_the_Latest_Version_of_wxWidgets#The_wx-config_script
+[3]:https://www.wxwidgets.org/downloads/
+[4]:https://wiki.wxwidgets.org/Compiling_and_getting_started
+[5]:https://wiki.wxwidgets.org/Updating_to_the_Latest_Version_of_wxWidgets
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150520 Shell Script to Backup Files or Directories Using rsync.md b/translated/tech/20150520 Shell Script to Backup Files or Directories Using rsync.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..639e58ede9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150520 Shell Script to Backup Files or Directories Using rsync.md
@@ -0,0 +1,170 @@
+Shell脚本:使用rsync备份文件/目录
+================================================================================
+本文,我们带来了shell脚本,用来使用rsync命令将你本地Linux机器上的文件/目录备份到远程Linux服务器上。使用该脚本实施备份会是一个交互的方式,你需要提供远程备份服务器的主机名/ip地址和文件夹位置。我们保留了一个独立文件,在这个文件中你需要提供需要备份的文件/目录。我们添加了两个脚本,**第一个脚本**在每次拷贝完一个文件后询问密码(如果你启用了ssh验证密钥,那么就不会询问密码),而第二个脚本中,则只会提示一次输入密码。
+
+我们打算备份bckup.txt,dataconfig.txt,docs和orcledb。
+
+ [root@Fedora21 tmp]# ls -l
+ total 12
+ -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 May 15 10:43 bckrsync.sh
+ -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 May 15 10:44 bckup.txt
+ -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 May 15 10:46 dataconfig.txt
+ drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 May 15 10:45 docs
+ drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 May 15 10:44 oracledb
+
+该文件包含了备份文件/目录的详情
+
+ [root@Fedora21 tmp]# cat /tmp/bckup.txt
+ /tmp/oracledb
+ /tmp/dataconfig.txt
+ /tmp/docs
+ [root@Fedora21 tmp]#
+
+### 脚本 1: ###
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+
+ #We will save path to backup file in variable
+ backupf='/tmp/bckup.txt'
+
+ #Next line just prints message
+ echo "Shell Script Backup Your Files / Directories Using rsync"
+
+ #next line check if entered value is not null, and if null it will reask user to enter Destination Server
+ while [ x$desthost = "x" ]; do
+
+ #next line prints what userd should enter, and stores entered value to variable with name desthost
+ read -p "Destination backup Server : " desthost
+
+ #next line finishes while loop
+ done
+
+ #next line check if entered value is not null, and if null it will reask user to enter Destination Path
+ while [ x$destpath = "x" ]; do
+
+ #next line prints what userd should enter, and stores entered value to variable with name destpath
+ read -p "Destination Folder : " destpath
+
+ #next line finishes while loop
+ done
+
+ #Next line will start reading backup file line by line
+ for line in `cat $backupf`
+
+ #and on each line will execute next
+ do
+
+ #print message that file/dir will be copied
+ echo "Copying $line ... "
+ #copy via rsync file/dir to destination
+
+ rsync -ar "$line" "$desthost":"$destpath"
+
+ #this line just print done
+ echo "DONE"
+
+ #end of reading backup file
+ done
+
+#### 运行带有输出结果的脚本 ####
+
+ [root@Fedora21 tmp]# ./bckrsync.sh
+ Shell Script Backup Your Files / Directories Using rsync
+ Destination backup Server : 104.*.*.41
+ Destination Folder : /tmp
+ Copying /tmp/oracledb ...
+ The authenticity of host '104.*.*.41 (104.*.*.41)' can't be established.
+ ECDSA key fingerprint is 96:11:61:17:7f:fa:......
+ Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
+ Warning: Permanently added '104.*.*.41' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
+ root@104.*.*.41's password:
+ DONE
+ Copying /tmp/dataconfig.txt ...
+ root@104.*.*.41's password:
+ DONE
+ Copying /tmp/docs ...
+ root@104.*.*.41's password:
+ DONE
+ [root@Fedora21 tmp]#
+
+### 脚本 2: ###
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+
+ #We will save path to backup file in variable
+ backupf='/tmp/bckup.txt'
+
+ #Next line just prints message
+ echo "Shell Script Backup Your Files / Directories Using rsync"
+
+ #next line check if entered value is not null, and if null it will reask user to enter Destination Server
+ while [ x$desthost = "x" ]; do
+
+ #next line prints what userd should enter, and stores entered value to variable with name desthost
+ read -p "Destination backup Server : " desthost
+
+ #next line finishes while loop
+ done
+
+ #next line check if entered value is not null, and if null it will reask user to enter Destination Path
+ while [ x$destpath = "x" ]; do
+
+ #next line prints what userd should enter, and stores entered value to variable with name destpath
+ read -p "Destination Folder : " destpath
+
+ #next line finishes while loop
+ done
+
+ #next line check if entered value is not null, and if null it will reask user to enter password
+ while [ x$password = "x" ]; do
+ #next line prints what userd should enter, and stores entered value to variable with name password. #To hide password we are using -s key
+ read -sp "Password : " password
+ #next line finishes while loop
+ done
+
+ #Next line will start reading backup file line by line
+ for line in `cat $backupf`
+
+ #and on each line will execute next
+ do
+
+ #print message that file/dir will be copied
+ echo "Copying $line ... "
+ #we will use expect tool to enter password inside script
+ /usr/bin/expect << EOD
+ #next line set timeout to -1, recommended to use
+ set timeout -1
+ #copy via rsync file/dir to destination, using part of expect — spawn command
+
+ spawn rsync -ar ${line} ${desthost}:${destpath}
+ #as result of previous command we expect “password” promtp
+ expect "*?assword:*"
+ #next command enters password from script
+ send "${password}\r"
+ #next command tells that we expect end of file (everything finished on remote server)
+ expect eof
+ #end of expect pard
+ EOD
+ #this line just print done
+ echo "DONE"
+
+ #end of reading backup file
+ done
+
+#### 运行第二个带有输出结果的脚本的屏幕截图 ####
+
+
+
+希望这些脚本对你备份会有帮助!!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-shell-script/shell-script-backup-files-directories-rsync/
+
+作者:[Yevhen Duma][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/yevhend/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150521 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change system proxy settings from the command line on Ubuntu desktop.md b/translated/tech/20150521 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change system proxy settings from the command line on Ubuntu desktop.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..526de3549e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150521 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change system proxy settings from the command line on Ubuntu desktop.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+Linux 有问必答--如何在桌面版 Ubuntu 中用命令行更改系统代理设置
+================================================================================
+> **问题**: 我经常需要在桌面版 Ubuntu 中更改系统代理设置,但我不想通过繁琐的 GUI 菜单链:"系统设置" -> "网络" -> "网络代理"。在命令行中有更方便的方法更改桌面版的代理设置吗?
+
+在桌面版 Ubuntu 中,它的桌面环境设置,包括系统代理设置,都存储在 DConf 数据库,这是简单的键值对存储。如果你想通过系统设置菜单修改桌面属性,更改会持久保存在后端的 DConf 数据库。在 Ubuntu 中更改 DConf 数据库有基于图像用户界面和非图形用户界面的两种方式。系统设置或者 dconf-editor 是访问 DConf 数据库的图形方法,而 gsettings 或 dconf 就是能更改数据库的命令行工具。
+
+下面介绍如何用 gsettings 从命令行更改系统代理设置。
+
+
+
+gsetting 读写特定 Dconf 设置的基本用法如下:
+
+更改 DConf 设置:
+
+ $ gsettings set <schema> <key> <value>
+
+读取 DConf 设置:
+
+ $ gsettings get <schema> <key>
+
+### 通过命令行更改系统代理设置为手动 ###
+
+桌面版 Ubuntu 中下面的命令会更改 HTTP 代理设置为 "my.proxy.com:8000"。
+
+ $ gsettings set org.gnome.system.proxy.http host 'my.proxy.com'
+ $ gsettings set org.gnome.system.proxy.http port 8000
+ $ gsettings set org.gnome.system.proxy mode 'manual'
+
+如果你还想更改 HTTPS/FTP 代理为手动,用这些命令:
+
+ $ gsettings set org.gnome.system.proxy.https host 'my.proxy.com'
+ $ gsettings set org.gnome.system.proxy.https port 8000
+ $ gsettings set org.gnome.system.proxy.ftp host 'my.proxy.com'
+ $ gsettings set org.gnome.system.proxy.ftp port 8000
+
+更改套接字主机设置为手动:
+
+ $ gsettings set org.gnome.system.proxy.socks host 'my.proxy.com'
+ $ gsettings set org.gnome.system.proxy.socks port 8000
+
+上面的更改都只适用于当前的桌面用户。如果你想在系统范围内使用代理设置更改,在 gsettings 命令面前添加 sudo。例如:
+
+ $ sudo gsettings set org.gnome.system.proxy.http host 'my.proxy.com'
+ $ sudo gsettings set org.gnome.system.proxy.http port 8000
+ $ sudo gsettings set org.gnome.system.proxy mode 'manual'
+
+### 在命令行中更改系统代理设置为自动 ###
+
+如果你正在使用 [自动配置代理][1] (proxy auto configuration,PAC),输入以下命令更改为 PAC。
+
+ $ gsettings set org.gnome.system.proxy mode 'auto'
+ $ gsettings set org.gnome.system.proxy autoconfig-url http://my.proxy.com/autoproxy.pac
+
+### 在命令行中清除系统代理设置 ###
+
+最后,清除所有 手动/自动 代理设置,还原为无代理设置:
+
+ $ gsettings set org.gnome.system.proxy mode 'none'
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/change-system-proxy-settings-command-line-ubuntu-desktop.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-proxy-auto-config-on-ubuntu-desktop.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150521 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install Unity Tweak Tool on Ubuntu desktop.md b/translated/tech/20150521 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install Unity Tweak Tool on Ubuntu desktop.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..def6860616
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150521 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install Unity Tweak Tool on Ubuntu desktop.md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+Linux 有问必答--如何在桌面版 Ubuntu 中安装 Unity Tweak Tool
+================================================================================
+> **问题**: 我试着给刚安装的桌面版 Ubuntu 自定制桌面。我想使用 Unity Tweak Tool。我怎样才能在 Ubuntu 上安装 Unity Tweak Tool 呢?
+
+[Unity Tweak Tool][1] 是个流行的 Unity 桌面自定制工具。顾名思义,该工具只适用于 Ubuntu 的默认桌面环境(例如,基于 Unity 的 GNOME 桌面)。这个多功能的工具允许你通过非常直观和简单易用的图形用户界面自定义多种 Unity 桌面特性。它的菜单看起来类似于 Ubuntu 的官方系统设置,但它的桌面自定制能力远远超过默认的系统设置。通过使用 Unity Tweak Tool,你可以自定制外观、行为以及很多桌面组件的配置,例如工作区、窗口、图标、主题、光标、字体、滑动、热键等等。如果你是 Unity 桌面用户,Unity Tweak Tool 一定是个必不可少的应用程序。
+
+
+
+尽管 Unity Tweak Tool 是桌面版 Ubuntu 的重要工具,并没有在桌面版 Ubuntu 中预安装。为了能自定制 Unity 桌面,下面介绍一下如何在桌面版 Ubuntu 中安装 Unity Tweak Tool。
+
+### 在 Ubuntu 13.04 或更高版本中安装 Unity Tweak Tool ###
+
+从 Ubuntu 13.04 开始, Ubuntu 的基础库中就有 Unity Tweak Tool 了。因此它的安装非常简单:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install unity-tweak-tool
+
+启动 Unity Tweak Tool:
+
+ $ unity-tweak-tool
+
+如果你想使用最新版本的 Unity Tweak Tool,你可以从它的 PPA 中安装(如下所述)。
+
+### 在 Ubuntu 12.10 中安装 Unity Tweak Tool ###
+
+注意,Unity Tweak Tool 要求 Ubuntu 12.10 或更高的版本。如果你想着 Ubuntu 上安装它,你可以安装下面方法使用 PPA。当你想测试最新的开发版的时候这个 PPA 库也非常有用。
+
+ $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:freyja-dev/unity-tweak-tool-daily
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get install unity-tweak-tool
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-unity-tweak-tool-ubuntu-desktop.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
+[1]:https://launchpad.net/unity-tweak-tool
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150525 Linux ntopng--Network Monitoring Tool Installation Screenshots.md b/translated/tech/20150525 Linux ntopng--Network Monitoring Tool Installation Screenshots.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dc039ba551
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150525 Linux ntopng--Network Monitoring Tool Installation Screenshots.md
@@ -0,0 +1,189 @@
+Linux ntopng——网络监控工具的安装(附截图)
+================================================================================
+当今世界,人们的计算机都相互连接,互联互通。小到你的家庭局域网(LAN),大到最大的一个被我们称为的——互联网。当你管理一台联网的计算机时,你就是在管理最关键的组件之一。由于大多数开发出的应用程序都基于网络,网络就连接起了这些关键点。
+
+这就是为什么我们需要网络监控工具。最好的网络监控工具之一,它叫作ntop。来自[维基百科][1]的知识“ntop是一个网络探测器,它以与top显示进程般类似的方式显示网络使用率。在交互模式中,它显示了用户终端上的网络状态。在网页模式中,它作为网络服务器,创建网络状态的HTML转储文件。它支持NetFlow/sFlowemitter/collector,这是一个基于HTTP的客户端界面,用于创建ntop为中心的监控应用和RRD用于持续地存储通信数据”
+
+15年后的今天,你将见到ntopng——下一代ntop。
+
+### ntopng是什么 ###
+
+Ntopng是一个基于网页的高速通信分析器和流量收集器。Ntopng基于ntop,它运行于所有Unix平台、MacOS X和Windows。
+
+### 特性 ###
+
+从[ntopng网站][2]上,我们可以看到他们说它有众多的特性。这里列出了其中一些:
+
+- 按各种协议对网络通信排序
+- 显示网络通信和IPv4/v6激活的主机
+- 持续不断以RRD格式存储定位主机的通信数据到磁盘
+- 通过nDPI,ntop的DPI框架,发现应用协议
+- 显示各种协议间的IP通信分布
+- 分析IP通信,并根据源/目的地址进行排序
+- 显示IP通信子网的矩阵(谁在和谁通信?)
+- 报告按协议类型排序的IP协议使用率
+- 生成HTML5/AJAX网络通信数据
+
+### 安装 ###
+
+Ntop为CentOS和**基于64位**Ubuntu预编译好了包,你可以在[他们的下载页面][3]找到这些包。对于32位操作系统,你必须从源代码编译。本文在**CentOS 6.4 32位**版本上**测试过**。但是,它也可以在其它基于CentOS/RedHat的Linux版本上工作。让我们开始吧。
+
+#### 先决条件 ####
+
+#### 开发工具 ####
+
+你必须确保你安装了编译ntopng所需的所有开发工具,要安装开发工具,你可以使用yum命令:
+
+ # yum groupinstall ‘Development Tools’
+
+#### 安装TCL ####
+
+ # yum install tcl
+
+#### 安装libpcap ####
+
+ # yum install libpcap libcap-devel
+
+#### 安装Redis ####
+
+ # wget http://redis.googlecode.com/files/redis-2.6.13.tar.gz
+ # tar zxfv redis-2.6.13.tar.gz
+ # cd redis-2.6.13
+ # make 32bit
+ # make test
+ # make install
+
+### 安装ntopng ###
+
+#### 方法 1 : ####
+
+ # wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/ntop/files/ntopng/ntopng-1.1_6932.tgz/download
+ # tar zxfv ntopng-1.1_6932.tgz
+ # cd ntopng-1.1_6932
+ # ./configure
+ # make
+ # make install
+
+#### 方法 2 : ####
+
+在我的CentOS 6.4上,我使用方法 1时收到了一个错误消息,错误消息内容如下:
+
+ ./third-party/LuaJIT-2.0.2/src/libluajit.a : could not read symbols : File in wrong format
+
+所以,我**切换**到了**SVN**来安装。对于此方法,需要联网,步骤如下:
+
+ # svn co https://svn.ntop.org/svn/ntop/trunk/ntopng/
+ # ./autogen.sh
+ # ./configure
+ # make
+ # make install
+
+*由于ntopng是一个基于网页的应用,你的系统必须安装有工作良好的网络服务器*
+
+### 为ntopng创建配置文件 ###
+
+如果一切都已安装完毕,那么我们该来运行它了。默认情况下,如果我们在./configure这一步没有明确修改安装文件夹的话,redis和ntopng将安装到/usr/local/文件夹。接下来,我们需要为ntopng创建配置文件。在本文中,我们使用vi作为文本编辑器。你也可以使用你所中意的文本编辑器来创建ntopng的配置文件。
+
+ # cd /usr/local/etc
+ # mkdir ntopng
+ # cd ntopng
+ # vi ntopng.start
+
+ 放入这些行:
+ --local-network “10.0.2.0/24”
+ --interface 1
+
+ # vi ntopng.pid
+
+ 放入该行:
+ -G=/var/run/ntopng.pid
+
+保存这些文件,然后继续下一步。
+
+### 运行ntopng ###
+
+我们假定你已正确安装了网络服务器,那么下一步就是运行redis服务器。
+
+ # /usr/local/bin/redis-server
+
+
+
+然后,**运行**ntopng
+
+ # /usr/local/bin/ntopng
+
+
+
+### 测试ntopng ###
+
+现在,你可以通过访问[http://yourserver.name:3000][4]来测试ntopng应用,你将会看到ntopng登录页面。首次登录,你可以使用用户‘**admin**’和密码‘**admin**’。
+
+
+
+仪表盘相当简洁。当你登入后,你将看到关于最高流量通信者页面。
+
+
+
+如果你点击右侧顶部的**流量菜单**,ntopng将会显示活动流量的更多细节。
+
+
+
+在**主机菜单**上,你可以看到连接到流的所有主机
+
+
+
+如果你点击**主机 > 交互**,ntop将显示一个漂亮的主机间的交互信息图表。
+
+
+
+**仪表盘菜单**组成部分:
+
+#### 顶级主机(发送+接收) ####
+
+
+
+#### 顶级应用协议 ####
+
+
+
+**界面菜单**将引领你进入更多内部菜单。
+包菜单将给你显示包的分布大小。
+
+
+
+**协议菜单**将为你显示使用了多少协议及其使用百分比。
+
+
+
+
+
+你也可以通过使用**历史活跃度菜单**查看活跃度
+
+
+
+
+
+最后一项要点是,你也可以通过顶部右侧区域的**设置菜单**(齿轮图标的那一个)管理哪些用户可以访问ntopng。
+
+
+
+Ntopng为你提供了一个范围宽广的时间线,从5分钟到1年都可以。你只需要点击你想要现实的时间线。图标本身是可以点击的,你可以点击它来进行缩放。
+
+当然,ntopng能做的事比上面图片中展示的还要多得多。你也可以将定位和电子地图服务整合进来。在ntopng自己的网站上,有已付费的模块可供使用,如nprobe可以扩展ntopng可以提供给你的信息。更多关于ntopng的信息,你可以访问[ntopng网站][5]。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/ntopng-network-monitoring-tool/
+
+作者:[Pungki Arianto][a]
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/pungki/
+[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ntop
+[2]:http://www.ntop.org/products/ntop/
+[3]:http://www.nmon.net/packages/
+[4]:http://yourserver.name:3000/
+[5]:http://www.ntop.org/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150527 3 Useful Hacks Every Linux User Must Know.md b/translated/tech/20150527 3 Useful Hacks Every Linux User Must Know.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..25c1ef3e3d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150527 3 Useful Hacks Every Linux User Must Know.md
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+每个Linux用户都应该知道的3个有用技巧
+================================================================================
+Linux世界充满了乐趣,我们越深入进去,就会发现越多有趣的事物。我们会努力给你提供一些小技巧,让你和其他人有所不同,下面就是我们准备的3个小技巧。
+
+### 1. 如何在不使用Cron的情况调度Linux下的作业 ###
+在Linux下,调度一个作业/命令可以缩写为Cron。当我们需要调度一个作业时,我们会使用Cron,但你知道我们在不使用Cron的情况也可以调度一个在将来时间运行的作业吗?你可以按照如下建议操作……
+
+每5秒钟运行一个命令(date)然后将结果写入到一个文件(data.txt)。为了实现这一点,我们可以直接在命令提示符运行如下单行脚本。
+
+ $ while true; do date >> date.txt ; sleep 5 ; done &
+
+上述脚本的解释:
+
+- `while true` :让脚本进入一个条件总为真的循环中,也就是制造一个死循环,将里边的命令一遍遍地重复运行。
+- `do` :`do`是`while`语句中的关键字,它之后的命令会被执行,在它后边可以放置一个或一系列命令。
+- `date >> date.txt` :运行date命令,并将其输出写入到data.txt文件中。注意我们使用`>>`,而不是`>`。
+- `>>` :对文件(date.txt)进行追加写的操作,这样每次运行命令后,输出内容会被追加到文件中。如果使用`>`的话,则会一遍遍地覆盖之前的内容。
+- `sleep 5` :让脚本处于5秒睡眠状态,然后再运行之后的命令。注意这里的时间单位只能用秒。也就是说如果你想让命令每6分钟运行一次,你应该使用`sleep 360`。
+- `done` :`while`循环语句块结束的标记。
+- `&` :将整个进程放到后台运行。
+
+类似地,我们可以这样运行任何脚本。下边的例子是每100秒运行一个名为`script_name.sh`的脚本。
+
+另外值得一提的是上边的脚本文件必须处于当前目录中,否则需要使用完整路径(`/home/$USER/…/script_name.sh`)。实现如上功能的单行脚本如下:
+
+ $ while true; do /bin/sh script_name.sh ; sleep 100 ; done &
+
+**总结**:上述的单行脚本并不是Cron的替代品,因为Cron工具支持众多选项,更加灵活,可定制性也更高。然而如果我们想运行某些测试,比如I/O评测,上述的单行脚本也管用。
+
+还可以参考:[11 Linux Cron Job Scheduling Examples][1]
+
+### 2. 如何不使用clear命令清空终端的内容 ###
+
+你如何清空终端的内容?你可能会认为这是一个傻问题。好吧,大家都清楚可以使用`clear`命令。如果养成使用`ctrl + l`快捷键的习惯,我们会节省大量时间。
+
+`Ctrl + l`快捷键的效果和`clear`命令一样。所以下一次你就可以使用`ctrl + l`来清空终端的内容了。
+
+**总结**:因为`ctrl + l`是一个快捷键,我们不可以在脚本中使用。所以如果我们需要在脚本中清空屏幕内容,还是需要使用`clear`命令。但我能想到的所有其他情况,`ctrl + l`都更加有效。
+
+### 3. 运行一个命令,然后自动回到当前的工作目录 ###
+
+这是一个很多人可能不知道的令人吃惊的技巧。你可能想运行任何一个命令,然后再回到当前目录。你只需要将命令放在一个圆括号里。
+
+我们来看一个例子:
+
+ avi@deb:~$ (cd /home/avi/Downloads/)
+
+#### 示例输出 ####
+
+ avi@deb:~
+
+它首先会cd到Downloads目录,然后又回到了之前的家目录。也许你认为里边的命令根本没有执行,或者是出了某种错误,因为从命令提示符看不出任何变化。让我们简单修改一下这个命令:
+
+ avi@deb:~$ (cd /home/avi/Downloads/ && ls -l)
+
+#### 示例输出 ####
+
+ -rw-r----- 1 avi avi 54272 May 3 18:37 text1.txt
+ -rw-r----- 1 avi avi 54272 May 3 18:37 text2.txt
+ -rw-r----- 1 avi avi 54272 May 3 18:37 text3.txt
+ avi@deb:~$
+
+在上述命令中,它首先进入Downloads目录,然后列出文件内容,最后又回到了当前目录。并且它证明了命令成功执行了。你可以在括号中包含任何命令,执行完都会顺利返回到当前目录。
+
+这就是全部内容了,如果你知道任何类似的Linux技巧,你可以在文章下面的评论框中分享给我们,不要忘记将本文和朋友分享 :)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/useful-linux-hacks-commands/
+
+作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
+译者:[goreliu](https://github.com/goreliu)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/11-cron-scheduling-task-examples-in-linux/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150527 How To Check Laptop CPU Temperature In Ubuntu.md b/translated/tech/20150527 How To Check Laptop CPU Temperature In Ubuntu.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ace8999edb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150527 How To Check Laptop CPU Temperature In Ubuntu.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+如何在Ubuntu中检查笔记本CPU的温度
+================================================================================
+
+
+笔记本过热是最近一个常见的问题。监控硬件温度或许可以帮助你诊断笔记本为什么会过热。本篇中,我们会**了解如何在Ubuntu中检查CPU的温度**。
+
+我们将使用一个GUI工具[Psensor][1],它允许你在Linux中监控硬件温度。用Psensor你可以:
+
+- 监控cpu和主板的温度
+- 监控NVidia GPU的文档
+- 监控硬盘的温度
+- 监控风扇的速度
+- 监控CPU的利用率
+
+Psensor最新的版本同样提供了Ubuntu中的指示小程序,这样使得在Ubuntu中监控温度变得更加容易。你可以选择在面板的右上角显示温度。它还会在温度上过阈值后通知。
+
+
+### 如何在Ubuntu 15.04 和 14.04中安装Psensor ###
+
+在安装Psensor前,你需要安装和配置[lm-sensors][2],一个用于硬件监控的命令行工具。如果你想要测量磁盘温度,你还需要安装[hddtemp][3]。要安装这些工具,运行下面的这些命令:
+
+ sudo apt-get install lm-sensors hddtemp
+
+接着开始检测硬件传感器:
+
+ sudo sensors-detect
+
+要确保已经工作,运行下面的命令:
+
+ sensors
+
+它会给出下面这样的输出:
+
+ acpitz-virtual-0
+ Adapter: Virtual device
+ temp1: +43.0°C (crit = +98.0°C)
+
+ coretemp-isa-0000
+ Adapter: ISA adapter
+ Physical id 0: +44.0°C (high = +100.0°C, crit = +100.0°C)
+ Core 0: +41.0°C (high = +100.0°C, crit = +100.0°C)
+ Core 1: +40.0°C (high = +100.0°C, crit = +100.0°C)
+
+如果一切看上去没问题,使用下面的命令安装Psensor:
+
+ sudo apt-get install psensor
+
+安装完成后,在Unity Dash中运行程序。第一次运行时,你应该配置Psensor该监控什么状态。
+
+
+
+### 在面板显示温度 ###
+
+如果你想要在面板中显示温度,进入**Sensor Preferences**:
+
+
+
+在 **Application Indicator** 菜单下,选择你想要显示温度的组件并勾上 **Display sensor in the label** 选项。
+
+
+
+### 每次启动启动Psensor ###
+
+进入 **Preferences->Startup** 并选择 **Launch on session startup** 使每次启动时启动Psensor。
+
+
+
+就是这样。你所要做的就是在这里监控CPU温度。你可以时刻注意并帮助你找出使计算机过热的进程。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://itsfoss.com/check-laptop-cpu-temperature-ubuntu/
+
+作者:[Abhishek][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
+[1]:http://wpitchoune.net/blog/psensor/
+[2]:http://www.lm-sensors.org/
+[3]:https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Hddtemp
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150527 How to Kill Linux Processes or Unresponsive Applications Using 'xkill' Command.md b/translated/tech/20150527 How to Kill Linux Processes or Unresponsive Applications Using 'xkill' Command.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..20211ab6bf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150527 How to Kill Linux Processes or Unresponsive Applications Using 'xkill' Command.md
@@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
+如何使用xkill命令傻点Linux进程/未响应的程序
+================================================================================
+我们如何在Linux中杀掉一个资源/进程?很明显我们会找出资源的pid然后用kill命令。
+
+更准确一点,我们可以找到资源(这里就是terminal)的PID:
+
+ $ ps -A | grep -i terminal
+
+ 6228 ? 00:00:00 gnome-terminal
+
+上面的输出中,‘6288’就是进程(gnome-terminal)的pid, 使用下面的命令来杀掉进程。
+
+ $ kill 6228
+
+kill命令会发送一个信号给该pid的进程。
+
+另外一个方法是我们可以使用pkill命令,它可以基于进程的名字或者其他的属性来杀掉进程。同样我们要杀掉一个叫terminal的进程可以这么做:
+
+ $ pkill terminal
+
+**注意**: pkill命令后面进程名的长度不大于15个字符
+
+pkill看上去更加容易上手,因为你你不用找出进程的pid。但是如果你要对系统做更好的控制,那么没有什么可以打败'kill'。使用kill命令可以更好地审视你要杀掉的进程。
+
+我们已经有一篇覆盖了[kill、pkill和killall命令][1]间细节的指导了。
+
+对于那些运行X Server的人而言,有另外一个工具称为xkill可以将进程从X Window中杀掉而不必传递它的名字或者pid。
+
+xkill工具强制X server关闭于它客户端之间的联系,这可以让X resource关闭这个客户端。xkill是X11工具集中一个非常容易上手的杀掉无用窗口的工具。
+
+它支持的选项如在同时运行多个X Server时使用-display选项后面跟上显示号连接到指定的X server,使用-all(并不建议)杀掉所有在屏幕上的所遇顶层窗口,同时将帧(-frame)也计算在内。
+
+要得到所有的客户端你可以运行:
+
+ $ xlsclients
+
+#### 示例输出 ####
+
+ ' ' /usr/lib/libreoffice/program/soffice
+ deb gnome-shell
+ deb Docky
+ deb google-chrome-stable
+ deb soffice
+ deb gnome-settings-daemon
+ deb gnome-terminal-server
+
+如果后面没有跟上资源id,xkill会将鼠标指针变成一个特殊符号,类似于“X”。只需在你要杀掉的窗口上点击,它就会杀掉它与server端的通信,这个程序就被杀掉了。
+
+
+ $ xkill
+
+
+
+使用xkill杀掉进程
+
+需要注意的是xkill并不能保证它的通信会被成功杀掉/退出。大多数程序会在与服务端的通信被关闭后杀掉。然而仍有少部分会继续运行。
+
+需要指出的点是:
+
+- 这个工具只能在X11 server运行的时候才能使用,因为这是X11工具的一部分。
+- 不要在你杀掉一个资源而它没有完全退出时而困惑。
+- 这不是kill的替代品
+
+**我需要在linux命令行中使用xkill么**
+
+不是,你不必在命令行中运行xkill。你可以设置一个快捷键,并用它来调用xkill。
+
+下面是如何在典型的gnome3桌面中设置键盘快捷键。
+
+进入设置-> 选择键盘。点击'+'并添加一个名字和命令。点击点击新条目并按下你想要的组合键。我的是Ctrl+Alt+Shift+x。
+
+
+
+Gnome 设置
+
+
+
+添加快捷键
+
+下次你要杀掉X资源只要用组合键就行了(Ctrl+Alt+Shift+x),你看到你的鼠标变成x了。点击想要杀掉的x资源就行了。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/kill-processes-unresponsive-programs-in-ubuntu/
+
+作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-kill-a-process-in-linux/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20150527 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to mount an LVM partition on Linux.md b/translated/tech/20150527 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to mount an LVM partition on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..391769edc2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20150527 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to mount an LVM partition on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+Linux有问必答 -- 如何在Linux中挂载LVM分区
+================================================================================
+> **提问**: 我有一个USB盘包含了LVM分区。 我想要在Linux中访问这些LVM分区。我该如何在Linux中挂载LVM分区?
+
+】LVM是逻辑卷管理工具,它允许你使用逻辑卷和卷组的概念来管理磁盘空间。使用LVM相比传统分区最大的好处是弹性地位用户和程序分配空间而不用考虑每个物理磁盘的大小。
+
+在LVM中,那些创建了逻辑分区的物理存储是传统的分区(比如:/dev/sda2,/dev/sdb1)。这些分区必须被初始化位“物理卷”并被标签(如,“Linux LVM”)来使它们可以在LVM中使用。一旦分区被标记被LVM分区,你不能直接用mount命令挂载。
+
+如果你尝试挂载一个LVM分区(比如/dev/sdb2), 你会得到下面的错误。
+
+ $ mount /dev/sdb2 /mnt
+
+----------
+
+ mount: unknown filesystem type 'LVM2_member'
+
+
+
+要正确地挂载LVM分区,你必须挂载分区创建的“逻辑分区”。下面就是如何做的。
+
+=首先,用下面的命令检查可用的卷组:
+
+ $ sudo pvs
+
+----------
+
+ PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree
+ /dev/sdb2 vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0 lvm2 a-- 237.60g 0
+
+
+
+物理卷的名字和卷组的名字分别在PV和VG列的下面。本例中,只有一个创建在dev/sdb2下的组“vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0”。
+
+接下来检查卷组中存在的逻辑卷,使用lvdisplay命令:
+
+ $ sudo lvdisplay <volume-group-name>
+
+使用lvdisplay显示了可用卷的信息(如:设备名、卷名、卷大小等等)。
+
+ $ sudo lvdisplay /dev/vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0
+
+----------
+
+ --- Logical volume ---
+ LV Path /dev/vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0/lv_root
+ LV Name lv_root
+ VG Name vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0
+ LV UUID imygta-P2rv-2SMU-5ugQ-g99D-A0Cb-m31eet
+ LV Write Access read/write
+ LV Creation host, time livecd.centos, 2015-03-16 18:38:18 -0400
+ LV Status available
+ # open 0
+ LV Size 50.00 GiB
+ Current LE 12800
+ Segments 1
+ Allocation inherit
+ Read ahead sectors auto
+ - currently set to 256
+ Block device 252:0
+
+
+
+如果你想要挂载一个特定的逻辑卷,使用“LV Path”下面的设备名(如:/dev/vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0/lv_home)。
+
+ $ sudo mount /dev/vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0/lv_home /mnt
+
+你可以用mount命令不带任何参数检查挂载状态,这会显示所有已挂载的文件系统。
+
+ $ mount
+
+
+
+如果你想在每次启动时自动挂载逻辑卷,在/etc/fstab中添加下面的行,你可以指定卷的文件系统类型(如 ext4),它可以从mount命令的输出中找。
+
+ /dev/vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0/lv_home /mnt ext4 defaults 0 0
+
+现在逻辑卷会在每次启动时挂载到/mnt。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/mount-lvm-partition-linux.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
\ No newline at end of file