mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
commit
d6d3806d2e
@ -1,5 +1,6 @@
|
||||
安装Strongswan - Linux上一个基于IPsec的vpn工具
|
||||
安装 Strongswan :Linux 上一个基于 IPsec 的 VPN 工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
IPsec是一个提供网络层安全的标准。它包含认证头(AH)和安全负载封装(ESP)组件。AH提供包的完整性,ESP组件提供包的保密性。IPsec确保了在网络层的安全特性。
|
||||
|
||||
- 保密性
|
||||
@ -7,27 +8,27 @@ IPsec是一个提供网络层安全的标准。它包含认证头(AH)和安全
|
||||
- 来源不可抵赖性
|
||||
- 重放攻击防护
|
||||
|
||||
[Strongswan][1]是一个IPsec协议实现的开源代码,Strongswan代表强壮开源广域网(StrongS/WAN)。它支持IPsec的VPN两个版本的密钥自动交换(网络密钥交换(IKE)V1和V2)。
|
||||
[Strongswan][1]是一个IPsec协议的开源代码实现,Strongswan的意思是强安全广域网(StrongS/WAN)。它支持IPsec的VPN中的两个版本的密钥自动交换(网络密钥交换(IKE)V1和V2)。
|
||||
|
||||
Strongswan基本上提供了自动交换密钥共享VPN两个节点或网络,然后它使用Linux内核的IPsec(AH和ESP)实现。密钥共享使用了IKE机制的特性使用ESP编码数据。在IKE阶段,strongswan使用OpenSSL加密算法(AES,SHA等等)和其他加密类库。无论如何,ESP组成IPsec使用的安全算法,它是Linux内核实现的。Strongswan的主要特性是下面这些。
|
||||
Strongswan基本上提供了在VPN的两个节点/网关之间自动交换密钥的共享,然后它使用了Linux内核的IPsec(AH和ESP)实现。密钥共享使用了之后用于ESP数据加密的IKE 机制。在IKE阶段,strongswan使用OpenSSL的加密算法(AES,SHA等等)和其他加密类库。无论如何,IPsec中的ESP组件使用的安全算法是由Linux内核实现的。Strongswan的主要特性如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- x.509证书或基于预共享密钥认证
|
||||
- 支持IKEv1和IKEv2密钥交换协议
|
||||
- 可选内置插件和库的完整性和加密测试
|
||||
- 支持椭圆曲线DH群体和ECDSA证书
|
||||
- 可选的,对于插件和库的内置完整性和加密测试
|
||||
- 支持椭圆曲线DH群和ECDSA证书
|
||||
- 在智能卡上存储RSA私钥和证书
|
||||
|
||||
它能被使用在客户端或服务器(road warrior模式)和网关到网关的情景。
|
||||
它能被使用在客户端/服务器(road warrior模式)和网关到网关的情景。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
几乎所有的Linux发行版都支持Strongswan的二进制包。在这个教程,我们将从二进制包安装strongswan也编译strongswan合适的特性的源代码。
|
||||
几乎所有的Linux发行版都支持Strongswan的二进制包。在这个教程,我们会从二进制包安装strongswan,也会从源代码编译带有合适的特性的strongswan。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用二进制包 ###
|
||||
|
||||
可以使用以下命令安装Strongswan到Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo aptitude install strongswan
|
||||
$ sudo aptitude install strongswan
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,35 +36,35 @@ strongswan的全局配置(strongswan.conf)文件和ipsec配置(ipsec.conf/
|
||||
|
||||
### strongswan源码编译安装的依赖包 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- GMP(strongswan使用的Mathematical/Precision 库)
|
||||
- OpenSSL(加密算法在这个库里)
|
||||
- PKCS(1,7,8,11,12)(证书编码和智能卡与Strongswan集成)
|
||||
- GMP(strongswan使用的高精度数学库)
|
||||
- OpenSSL(加密算法来自这个库)
|
||||
- PKCS(1,7,8,11,12)(证书编码和智能卡集成)
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤 ####
|
||||
|
||||
**1)** 在终端使用下面命令到/usr/src/目录
|
||||
|
||||
$cd /usr/src
|
||||
$ cd /usr/src
|
||||
|
||||
**2)** 用下面命令从strongswan网站下载源代码
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo wget http://download.strongswan.org/strongswan-5.2.1.tar.gz
|
||||
$ sudo wget http://download.strongswan.org/strongswan-5.2.1.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
(strongswan-5.2.1.tar.gz 是最新版。)
|
||||
(strongswan-5.2.1.tar.gz 是当前最新版。)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**3)** 用下面命令提取下载软件,然后进入目录。
|
||||
**3)** 用下面命令提取下载的软件,然后进入目录。
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo tar –xvzf strongswan-5.2.1.tar.gz; cd strongswan-5.2.1
|
||||
$ sudo tar –xvzf strongswan-5.2.1.tar.gz; cd strongswan-5.2.1
|
||||
|
||||
**4)** 使用configure命令配置strongswan每个想要的选项。
|
||||
|
||||
./configure --prefix=/usr/local -–enable-pkcs11 -–enable-openssl
|
||||
$ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local -–enable-pkcs11 -–enable-openssl
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果GMP库没有安装,然后配置脚本将会发生下面的错误。
|
||||
如果GMP库没有安装,配置脚本将会发生下面的错误。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -71,19 +72,19 @@ strongswan的全局配置(strongswan.conf)文件和ipsec配置(ipsec.conf/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
无论如何,如果GMP已经安装而且还一致报错,然后在Ubuntu上使用下面命令创建libgmp.so库的软连到/usr/lib,/lib/,/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/路径下。
|
||||
不过,如果GMP已经安装还报上述错误的话,在Ubuntu上使用如下命令,给在路径 /usr/lib,/lib/,/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ 下的libgmp.so库创建软连接。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ln -s /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgmp.so.10.1.3 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgmp.so
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建libgmp.so软连后,再执行./configure脚本也许就找到gmp库了。无论如何,gmp头文件也许发生其他错误,像下面这样。
|
||||
创建libgmp.so软连接后,再执行./configure脚本也许就找到gmp库了。然而,如果gmp头文件发生其他错误,像下面这样。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
为解决上面的错误,使用下面命令安装libgmp-dev包
|
||||
|
||||
$sudo aptitude install libgmp-dev
|
||||
$ sudo aptitude install libgmp-dev
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -105,7 +106,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/security/install-strongswan/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[nido][a]
|
||||
译者:[wyangsun](https://github.com/wyangsun)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
|
||||
如何在树莓派 2 运行 ubuntu Snappy Core
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
物联网(Internet of Things, IoT) 时代即将来临。很快,过不了几年,我们就会问自己当初是怎么在没有物联网的情况下生存的,就像我们现在怀疑过去没有手机的年代。Canonical 就是一个物联网快速发展却还是开放市场下的竞争者。这家公司宣称自己把赌注压到了IoT 上,就像他们已经在“云”上做过的一样。在今年一月底,Canonical 启动了一个基于Ubuntu Core 的小型操作系统,名字叫做 [Ubuntu Snappy Core][1] 。
|
||||
|
||||
Snappy 代表了两种意思,它是一种用来替代 deb 的新的打包格式;也是一个用来更新系统的前端,从CoreOS、红帽子和其他系统借鉴了**原子更新**这个想法。自从树莓派 2 投入市场,Canonical 很快就发布了用于树莓派的Snappy Core 版本。而第一代树莓派因为是基于ARMv6 ,Ubuntu 的ARM 镜像是基于ARMv7 ,所以不能运行ubuntu 。不过这种状况现在改变了,Canonical 通过发布 Snappy Core 的RPI2 镜像,抓住机会证明了Snappy 就是一个用于云计算,特别是用于物联网的系统。
|
||||
|
||||
Snappy 同样可以运行在其它像Amazon EC2, Microsofts Azure, Google的 Compute Engine 这样的云端上,也可以虚拟化在 KVM、Virtuabox 和vagrant 上。Canonical Ubuntu 已经拥抱了微软、谷歌、Docker、OpenStack 这些重量级选手,同时也与一些小项目达成合作关系。除了一些创业公司,比如 Ninja Sphere、Erle Robotics,还有一些开发板生产商,比如 Odroid、Banana Pro, Udoo, PCDuino 和 Parallella 、全志,Snappy 也提供了支持。Snappy Core 同时也希望尽快运行到路由器上来帮助改进路由器生产商目前很少更新固件的策略。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,让我们看看怎么样在树莓派 2 上运行 Ubuntu Snappy Core。
|
||||
|
||||
用于树莓派2 的Snappy 镜像可以从 [Raspberry Pi 网站][2] 上下载。解压缩出来的镜像必须[写到一个至少8GB 大小的SD 卡][3]。尽管原始系统很小,但是原子升级和回滚功能会占用不小的空间。使用 Snappy 启动树莓派 2 后你就可以使用默认用户名和密码(都是ubuntu)登录系统。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
sudo 已经配置好了可以直接用,安全起见,你应该使用以下命令来修改你的用户名
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo usermod -l <new name> <old name>
|
||||
|
||||
或者也可以使用`adduser` 为你添加一个新用户。
|
||||
|
||||
因为RPI缺少硬件时钟,而 Snappy Core 镜像并不知道这一点,所以系统会有一个小 bug:处理某些命令时会报很多错。不过这个很容易解决:
|
||||
|
||||
使用这个命令来确认这个bug 是否影响:
|
||||
|
||||
$ date
|
||||
|
||||
如果输出类似 "Thu Jan 1 01:56:44 UTC 1970", 你可以这样做来改正:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo date --set="Sun Apr 04 17:43:26 UTC 2015"
|
||||
|
||||
改成你的实际时间。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在你可能打算检查一下,看看有没有可用的更新。注意通常使用的命令是不行的:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get distupgrade
|
||||
|
||||
这时系统不会让你通过,因为 Snappy 使用它自己精简过的、基于dpkg 的包管理系统。这么做的原因是 Snappy 会运行很多嵌入式程序,而同时你也会试图所有事情尽可能的简化。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们来看看最关键的部分,理解一下程序是如何与 Snappy 工作的。运行 Snappy 的SD 卡上除了 boot 分区外还有3个分区。其中的两个构成了一个重复的文件系统。这两个平行文件系统被固定挂载为只读模式,并且任何时刻只有一个是激活的。第三个分区是一个部分可写的文件系统,用来让用户存储数据。通过更新系统,标记为'system-a' 的分区会保持一个完整的文件系统,被称作核心,而另一个平行的文件系统仍然会是空的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果我们运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo snappy update
|
||||
|
||||
系统将会在'system-b' 上作为一个整体进行更新,这有点像是更新一个镜像文件。接下来你将会被告知要重启系统来激活新核心。
|
||||
|
||||
重启之后,运行下面的命令可以检查你的系统是否已经更新到最新版本,以及当前被激活的是哪个核心
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo snappy versions -a
|
||||
|
||||
经过更新-重启两步操作,你应该可以看到被激活的核心已经被改变了。
|
||||
|
||||
因为到目前为止我们还没有安装任何软件,所以可以用下面的命令更新:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo snappy update ubuntu-core
|
||||
|
||||
如果你打算仅仅更新特定的OS 版本这就够了。如果出了问题,你可以使用下面的命令回滚:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo snappy rollback ubuntu-core
|
||||
|
||||
这将会把系统状态回滚到更新之前。
|
||||
|
||||
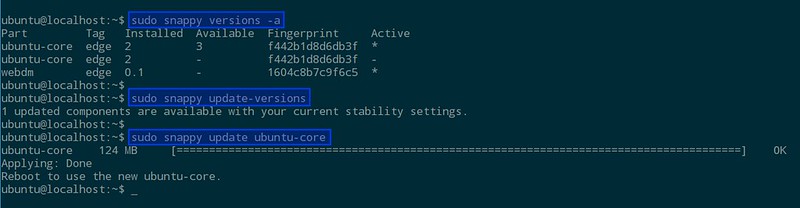
|
||||
|
||||
再来说说那些让 Snappy 变得有用的软件。这里不会讲的太多关于如何构建软件、向 Snappy 应用商店添加软件的基础知识,但是你可以通过 Freenode 上的IRC 频道 #snappy 了解更多信息,那个上面有很多人参与。你可以通过浏览器访问http://\<ip-address>:4200 来浏览应用商店,然后从商店安装软件,再在浏览器里访问 http://webdm.local 来启动程序。如何构建用于 Snappy 的软件并不难,而且也有了现成的[参考文档][4] 。你也可以很容易的把 DEB 安装包使用Snappy 格式移植到Snappy 上。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
尽管 Ubuntu Snappy Core 吸引了我们去研究新型的 Snappy 安装包格式和 Canonical 式的原子更新操作,但是因为有限的可用应用,它现在在生产环境里还不是很有用。但是既然搭建一个 Snappy 环境如此简单,这看起来是一个学点新东西的好机会。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/ubuntu-snappy-core-raspberry-pi-2.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ferdinand Thommes][a]
|
||||
译者:[Ezio](https://github.com/oska874)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/ferdinand
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ubuntu.com/things
|
||||
[2]:http://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads/
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/write-raspberry-pi-image-sd-card.html
|
||||
[4]:https://developer.ubuntu.com/en/snappy/
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@ Ubuntu 14.04中修复“update information is outdated”错误
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
看到Ubuntu 14.04的顶部面板上那个显示下面这个错误的红色三角形了吗?
|
||||
看到过Ubuntu 14.04的顶部面板上那个显示下面这个错误的红色三角形了吗?
|
||||
|
||||
> 更新信息过时。该错误可能是由网络问题,或者某个仓库不再可用而造成的。请通过从指示器菜单中选择‘显示更新’来手动更新,然后查看是否存在有失败的仓库。
|
||||
>
|
||||
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ Ubuntu 14.04中修复“update information is outdated”错误
|
||||
|
||||
### 修复‘update information is outdated’错误 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这里讨论的‘解决方案’可能对Ubuntu的这些版本有用:Ubuntu 14.04,12.04或14.04。你所要做的仅仅是打开终端(Ctrl+Alt+T),然后使用下面的命令:
|
||||
这里讨论的‘解决方案’可能对Ubuntu的这些版本有用:Ubuntu 14.04,12.04。你所要做的仅仅是打开终端(Ctrl+Alt+T),然后使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-update-information-outdated-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -56,4 +56,4 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-update-information-outdated-ubuntu/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/notification-terminal-command-completion-ubuntu/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-gpg-error-signatures-verified-ubuntu/
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/install-spotify-ubuntu-1504/
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/fix-update-errors-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
[5]:https://linux.cn/article-5603-1.html
|
||||
20
sign.md
20
sign.md
@ -1,8 +1,22 @@
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via:
|
||||
via:来源链接
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
作者:[作者名][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,
|
||||
[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:作者链接
|
||||
[1]:文内链接
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Fix No Bootable Device Found Error After Installing Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Usually, I dual boot Ubuntu and Windows but this time I decided to go for a clean Ubuntu installation i.e. eliminating Windows completely. After the clean install of Ubuntu, I ended up with a screen saying **no bootable device found** instead of the Grub screen. Clearly, the installation messed up with the UEFI boot settings.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
I am going to show you how I fixed **no bootable device found error after installing Ubuntu in Acer laptops**. It is important that I mention that I am using Acer Aspire R13 because we have to change things in firmware settings and those settings might look different from manufacturer to manufacturer and from device to device.
|
||||
|
||||
So before you go on trying the steps mentioned here, let’s first see what state my computer was in during this error:
|
||||
|
||||
- My Acer Aspire R13 came preinstalled with Windows 8.1 and with UEFI boot manager
|
||||
- Secure boot was not turned off (my laptop has just come from repair and the service guy had put the secure boot on again, I did not know until I ran up in the problem). You can read this post to know [how disable secure boot in Acer laptops][1]
|
||||
- I chose to install Ubuntu by erasing everything i.e. existing Windows 8.1, various partitions etc.
|
||||
- After installing Ubuntu, I saw no bootable device found error while booting from the hard disk. Booting from live USB worked just fine
|
||||
|
||||
In my opinion, not disabling the secure boot was the reason of this error. However, I have no data to backup my claim. It is just a hunch. Interestingly, dual booting Windows and Linux often ends up in common Grub issues like these two:
|
||||
|
||||
- [error: no such partition grub rescue][2]
|
||||
- [Minimal BASH like line editing is supported][3]
|
||||
|
||||
If you are in similar situation, you can try the fix which worked for me.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fix no bootable device found error after installing Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
Pardon me for poor quality images. My OnePlus camera seems to be not very happy with my laptop screen.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 1 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Turn the power off and boot into boot settings. I had to press Fn+F2 (to press F2 key) on Acer Aspire R13 quickly. You have to be very quick with it if you are using SSD hard disk because SSDs are very fast in booting. Depending upon your manufacturer/model, you might need to use Del or F10 or F12 keys.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2 ####
|
||||
|
||||
In the boot settings, make sure that Secure Boot is turned on. It should be under the Boot tab.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 3 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Go to Security tab and look for “Select an UEFI file as trusted for executing” and click enter.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Just for your information, what we are going to do here is to add the UEFI settings file (it was generated while Ubuntu installation) among the trusted UEFI boots in your device. If you remember, UEFI boot’s main aim is to provide security and since Secure Boot was not disabled (perhaps) the device did not intend to boot from the newly installed OS. Adding it as trusted, kind of whitelisting, will let the device boot from the Ubuntu UEFI file.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 4 ####
|
||||
|
||||
You should see your hard disk like HDD0 etc here. If you have more than one hard disk, I hope you remember where did you install Ubuntu. Press Enter here as well.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 5 ####
|
||||
|
||||
You should see <EFI> here. Press enter.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 6 ####
|
||||
|
||||
You’ll see <Ubuntu> in next screen. Don’t get impatient, you are almost there
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
You’ll see shimx64.efi, grubx64.efi and MokManager.efi file here. The important one is shimx64.efi here. Select it and click enter.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In next screen, type Yes and click enter.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 8 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Once we have added it as trused EFI file to be executed, press F10 to save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Reboot your system and this time you should be seeing the familiar Grub screen. Even if you do not see Grub screen, you should at least not be seeing “no bootable device found” screen anymore. You should be able to boot into Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
If your Grub screen was messed up after the fix but you got to login into it, you can reinstall Grub to boot into the familiar purple Grub screen of Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
I hope this tutorial helped you to fix no bootable device found error. Any questions or suggestions or a word of thanks is always welcomed.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/no-bootable-device-found-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/disable-secure-boot-in-acer/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-error-partition-grub-rescue-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/fix-minimal-bash-line-editing-supported-grub-error-linux/
|
||||
@ -1,89 +0,0 @@
|
||||
如何在树莓派2 代运行ubuntu Snappy Core
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
物联网(Internet of Things, IoT) 时代即将来临。很快,过不了几年,我们就会问自己当初是怎么在没有物联网的情况下生存的,就像我们现在怀疑过去没有手机的年代。Canonical 就是一个物联网快速发展却还是开放市场下的竞争者。这家公司宣称自己把赌注压到了IoT 上,就像他们已经在“云”上做过的一样。。在今年一月底,Canonical 启动了一个基于Ubuntu Core 的小型操作系统,名字叫做 [Ubuntu Snappy Core][1] 。
|
||||
|
||||
Snappy 是一种用来替代deb 的新的打包格式,是一个用来更新系统的前端,从CoreOS、红帽子和其他系统借鉴了**原子更新**这个想法。树莓派2 代投入市场,Canonical 很快就发布了用于树莓派的Snappy Core 版本。而第一代树莓派因为是基于ARMv6 ,Ubuntu 的ARM 镜像是基于ARMv7 ,所以不能运行ubuntu 。不过这种状况现在改变了,Canonical 通过发布用于RPI2 的镜像,抓住机会证明了Snappy 就是一个用于云计算,特别是用于物联网的系统。
|
||||
|
||||
Snappy 同样可以运行在其它像Amazon EC2, Microsofts Azure, Google的 Compute Engine 这样的云端上,也可以虚拟化在KVM、Virtuabox 和vagrant 上。Canonical Ubuntu 已经拥抱了微软、谷歌、Docker、OpenStack 这些重量级选手,同时也与一些小项目达成合作关系。除了一些创业公司,比如Ninja Sphere、Erle Robotics,还有一些开发板生产商,比如Odroid、Banana Pro, Udoo, PCDuino 和Parallella 、全志,Snappy 也提供了支持。Snappy Core 同时也希望尽快运行到路由器上来帮助改进路由器生产商目前很少更新固件的策略。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,让我们看看怎么样在树莓派2 上运行Snappy。
|
||||
|
||||
用于树莓派2 的Snappy 镜像可以从 [Raspberry Pi 网站][2] 上下载。解压缩出来的镜像必须[写到一个至少8GB 大小的SD 卡][3]。尽管原始系统很小,但是原子升级和回滚功能会占用不小的空间。使用Snappy 启动树莓派2 后你就可以使用默认用户名和密码(都是ubuntu)登录系统。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
sudo 已经配置好了可以直接用,安全起见,你应该使用以下命令来修改你的用户名
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo usermod -l <new name> <old name>
|
||||
|
||||
或者也可以使用`adduser` 为你添加一个新用户。
|
||||
|
||||
因为RPI缺少硬件时钟,而Snappy 并不知道这一点,所以系统会有一个小bug:处理某些命令时会报很多错。不过这个很容易解决:
|
||||
|
||||
使用这个命令来确认这个bug 是否影响:
|
||||
|
||||
$ date
|
||||
|
||||
如果输出是 "Thu Jan 1 01:56:44 UTC 1970", 你可以这样做来改正:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo date --set="Sun Apr 04 17:43:26 UTC 2015"
|
||||
|
||||
改成你的实际时间。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在你可能打算检查一下,看看有没有可用的更新。注意通常使用的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get distupgrade
|
||||
|
||||
不过这时系统不会让你通过,因为Snappy 使用它自己精简过的、基于dpkg 的包管理系统。这么做的原因是Snappy 会运行很多嵌入式程序,而同时你也会想着所有事情尽可能的简化。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们来看看最关键的部分,理解一下程序是如何与Snappy 工作的。运行Snappy 的SD 卡上除了boot 分区外还有3个分区。其中的两个构成了一个重复的文件系统。这两个平行文件系统被固定挂载为只读模式,并且任何时刻只有一个是激活的。第三个分区是一个部分可写的文件系统,用来让用户存储数据。通过更新系统,标记为'system-a' 的分区会保持一个完整的文件系统,被称作核心,而另一个平行文件系统仍然会是空的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果我们运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo snappy update
|
||||
|
||||
系统将会在'system-b' 上作为一个整体进行更新,这有点像是更新一个镜像文件。接下来你将会被告知要重启系统来激活新核心。
|
||||
|
||||
重启之后,运行下面的命令可以检查你的系统是否已经更新到最新版本,以及当前被激活的是那个核心
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo snappy versions -a
|
||||
|
||||
经过更新-重启两步操作,你应该可以看到被激活的核心已经被改变了。
|
||||
|
||||
因为到目前为止我们还没有安装任何软件,下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo snappy update ubuntu-core
|
||||
|
||||
将会生效,而且如果你打算仅仅更新特定的OS 版本,这也是一个办法。如果出了问题,你可以使用下面的命令回滚:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo snappy rollback ubuntu-core
|
||||
|
||||
这将会把系统状态回滚到更新之前。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
再来说说那些让Snappy 有用的软件。这里不会讲的太多关于如何构建软件、向Snappy 应用商店添加软件的基础知识,但是你可以通过Freenode 上的IRC 频道#snappy 了解更多信息,那个上面有很多人参与。你可以通过浏览器访问http://<ip-address>:4200 来浏览应用商店,然后从商店安装软件,再在浏览器里访问http://webdm.local 来启动程序。如何构建用于Snappy 的软件并不难,而且也有了现成的[参考文档][4] 。你也可以很容易的把DEB 安装包使用Snappy 格式移植到Snappy 上。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
尽管Ubuntu Snappy Core 吸引我们去研究新型的Snappy 安装包格式和Canonical 式的原子更新操作,但是因为有限的可用应用,它现在在生产环境里还不是很有用。但是既然搭建一个Snappy 环境如此简单,这看起来是一个学点新东西的好机会。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/ubuntu-snappy-core-raspberry-pi-2.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ferdinand Thommes][a]
|
||||
译者:[Ezio](https://github.com/oska874)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/ferdinand
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ubuntu.com/things
|
||||
[2]:http://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads/
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/write-raspberry-pi-image-sd-card.html
|
||||
[4]:https://developer.ubuntu.com/en/snappy/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
|
||||
修复安装完 Ubuntu 后无可引导设备错误
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
通常情况下,我启动 Ubuntu 和 Windows 双系统,但是这次我决定完全消除 Windows 纯净安装 Ubuntu。纯净安装 Ubuntu 完成后,结束时屏幕输出 **no bootable device found** 而不是进入 GRUB 界面。显然,安装搞砸了 UEFI 引导设置。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我会告诉你我是如何修复**在宏碁笔记本上安装 Ubuntu 后出现无可引导设备错误**。我声明了我使用的是宏碁灵越 R13,这很重要,因为我们需要更改固件设置,而这些设置可能因制造商和设备有所不同。
|
||||
|
||||
因此在你开始这里介绍的步骤之前,先看一下发生这个错误时我计算机的状态:
|
||||
|
||||
- 我的宏碁灵越 R13 预装了 Windows8.1 和 UEFI 引导管理器
|
||||
- 关闭了 Secure boot(我的笔记本刚维修过,维修人员又启用了它,直到出现了问题我才发现)。你可以阅读这篇博文了解[如何在宏碁笔记本中关闭 secure boot][1]
|
||||
- 我通过选择清除所有东西安装 Ubuntu,例如现有的 Windows 8.1,各种分区等。
|
||||
- 安装完 Ubuntu 之后,从硬盘启动时我看到无可引导设备错误。但能从 USB 设备正常启动
|
||||
|
||||
在我看来,没有禁用 secure boot 可能是这个错误的原因。但是,我没有数据支撑我的观点。这仅仅是预感。有趣的是,双系统启动 Windows 和 Linux 经常会出现这两个 Grub 问题:
|
||||
|
||||
- [error: no such partition grub rescue][2]
|
||||
- [Minimal BASH like line editing is supported][3]
|
||||
|
||||
如果你遇到类似的情况,你可以试试我的修复方法。
|
||||
|
||||
### 修复安装完 Ubuntu 后无可引导设备错误 ###
|
||||
|
||||
请原谅我没有丰富的图片。我的一加相机不能很好地拍摄笔记本屏幕。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第一步 ####
|
||||
|
||||
关闭电源并进入 boot 设置。我需要在宏碁灵越 R13 上快速地按 Fn+F2。如果你使用固态硬盘的话要按的非常快,因为固态硬盘启动速度很快。取决于你的制造商,你可能要用 Del 或 F10 或者 F12。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第二步 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在 boot 设置中,确保启用了 Secure Boot。它在 Boot 标签里。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第三步 ####
|
||||
|
||||
进入到 Security 标签,查找 “Select an UEFI file as trusted for executing” 并敲击回车。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
特意说明,我们这一步是要在你的设备中添加 UEFI 设置文件(安装 Ubuntu 的时候生成)到可信 UEFI 启动。如果你记得的话,UEFI 启动的主要目的是提供安全性,由于(可能)没有禁用 Secure Boot,设备不会试图从新安装的操作系统中启动。添加它到类似白名单的可信列表,会使设备从 Ubuntu UEFI 文件启动。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第四步 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在这里你可以看到你的硬盘,例如 HDD0。如果你有多块硬盘,我希望你记住你安装 Ubuntu 的那块。同样敲击回车。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 第五步 ####
|
||||
|
||||
你应该可以看到 <EFI>,敲击回车。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 第六步 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在下一个屏幕中你会看到 <Ubuntu>。耐心点,马上就好了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 第七步 ####
|
||||
|
||||
你可以看到 shimx64.efi,grubx64.efi 和 MokManager.efi 文件。重要的是 shimx64.efi。选中它并敲击回车。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在下一个屏幕中,输入 Yes 并敲击回车。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 第八步 ####
|
||||
|
||||
当我们添加它到可信 EFI 文件并执行时,按 F10 保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
重启你的系统,这时你就可以看到熟悉的 GRUB 界面了。就算你没有看到 Grub 界面,起码也再也不会看到“无可引导设备”。你应该可以进入 Ubuntu 了。
|
||||
|
||||
如果修复后搞乱了你的 Grub 界面,但你确实能登录系统,你可以重装 Grub 并进入到 Ubuntu 熟悉的紫色 Grub 界面。
|
||||
|
||||
我希望这篇指南能帮助你修复无可引导设备错误。欢迎提出任何疑问、建议或者感谢。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/no-bootable-device-found-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](http://www.mutouxiaogui.cn/blog/)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/disable-secure-boot-in-acer/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-error-partition-grub-rescue-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/fix-minimal-bash-line-editing-supported-grub-error-linux/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user