mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-30 02:40:11 +08:00
commit
d6d3466234
sources
share
talk
20150827 The Strangest Most Unique Linux Distros.md20151012 The Brief History Of Aix HP-UX Solaris BSD And LINUX.md
tech
translated
@ -1,125 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Open Source Alternatives to LastPass
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
LastPass is a cross-platform password management program. For Linux, it is available as a plugin for Firefox, Chrome, and Opera. LastPass Sesame is available for Ubuntu/Debian and Fedora. There is also a version of LastPass compatible with Firefox Portable for installing on a USB key. And with LastPass Pocket for Ubuntu/Debian, Fedora and openSUSE, there's good coverage. While LastPass is a highly rated service, it is proprietary software. And LastPass has recently been absorbed by LogMeIn. If you're looking for an open source alternative, this article is for you.
|
||||
|
||||
We all face information overload. Whether you conduct business online, read for your job, or just read for pleasure, the internet is a vast source of information. Retaining that information on a long-term basis can be difficult. However, it is essential to recall certain items of information immediately. Passwords are one such example.
|
||||
|
||||
As a computer user, you face the dilemma of choosing the same password or a unique password for each service or web site you use. Matters are complicated because some sites place restrictions on the selection of the password. For example, a site may insist on a minimum number of characters, capital letters, numerals, and other characters which make choosing the same password for each site to be impossible. More importantly, there are good security reasons not to duplicate passwords. This inevitably means that individuals will simply have too many passwords to remember. One solution is to keep the passwords in written form. However, this is also highly insecure.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead of trying to remember an endless array of passwords, a popular solution is to use password manager software. In fact, this type of software is an essential tool for the active internet user. It makes it easy to retrieve, manage and secure all of your passwords. Most passwords are encrypted, either by the program or the filesystem. Consequently, the user only has to remember a single password. Password managers encourage users to choose unique, non-intuitive strong passwords for each service.
|
||||
|
||||
To provide an insight into the quality of software available for Linux, I introduce 4 excellent open source alternatives to LastPass.
|
||||
|
||||
### KeePassX ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
KeePassX is a multi-platform port of KeePass, an open source and cross-platform password manager. This utility helps you to manage your passwords in a secure way. You can put all your passwords in one database, which is locked with one master key or a key-disk. This lets users only need to remember one single master password or insert the key-disk to unlock the whole database.
|
||||
|
||||
The databases are encrypted using the algorithms AES (alias Rijndael) or Twofish using a 256 bit key.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Extensive management- title for each entry for better identification:
|
||||
- Determine different expiration dates
|
||||
- Insertion of attachments
|
||||
- User-defined symbols for groups and entries
|
||||
- Fast entry duplication
|
||||
- Sorting entries in groups
|
||||
- Search function: in specific groups or in the complete database
|
||||
- Auto-Type, a feature that allows you to e.g. log in to a web page by pressing a single key combination. KeePassX does the rest of the typing for you. Auto-Type reads the title of currently active window on your screen and matches it to the configured database entries
|
||||
- Database security with access to the KeePassX database being granted either with a password, a key-file (e.g. a CD or a memory-stick) or both
|
||||
- Automatic generation of secure passwords
|
||||
- Precaution features, quality indicator for chosen passwords hiding all passwords behind asterisks
|
||||
- Encryption- either the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) or the Twofish algorithm are used, with encryption of the database in 256 bit sized increments
|
||||
- Import and export of entries. Import from PwManager (*.pwm) and KWallet (*.xml) files, Export as textfile (*.txt)
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [www.keepassx.org][1]
|
||||
- Developer: KeePassX Team
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.4.3
|
||||
|
||||
### Encryptr ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Encryptr is an open source zero-knowledge cloud-based password manager / e-wallet powered by Crypton. Crypton is a JavaScript library that allows developers to write web applications where the server knows nothing of the contents a user is storing.
|
||||
|
||||
Encryptr stores your sensitive data like passwords, credit card data, PINs, or access codes, in the cloud. However, because it was built on the zero-knowledge Crypton framework, Encryptr ensures that only the user has the ability to access or read the confidential information.
|
||||
|
||||
Being cross-platform, it allows users to securely access their confidential data from a single account from the cloud, no matter where they are.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Very secure Zero-Knowledge Crypton Framework only ever encrypts or decrypts your data locally on your device
|
||||
- Simple to use
|
||||
- Cloud based
|
||||
- Stores three types of data it stores passwords, credit card numbers and general key/value pairs
|
||||
- Optional "Notes" field to all entries
|
||||
- Filtering / searching the entry list
|
||||
- Local encrypted caching of entries to speed up load time
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [encryptr.org][2]
|
||||
- Developer: Tommy Williams
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.2.0
|
||||
|
||||
### RatticDB ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
RatticDB is an open source Django based password management service.
|
||||
|
||||
RatticDB is built to be 'Password Lifecycle Management' and not simply a 'Password Storage Engine'. RatticDB aims to help you keep track of what passwords need to be changed and when. It does not include application level encryption.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Simple ACL scheme
|
||||
- Change Queue feature that allows users to see when they need to update passwords for the applications they use
|
||||
- Ansible configurations
|
||||
-
|
||||
- Website: [rattic.org][3]
|
||||
- Developer: Daniel Hall
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.3.1
|
||||
|
||||
### Seahorse ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Seahorse is a Gnome front end for GnuPG - the Gnu Privacy Guard program. Its goal is to provide an easy to use Key Management Tool, along with an easy to use interface for encryption operations.
|
||||
|
||||
It is a tool for secure communications and data storage. Data encryption and digital signature creation can easily be performed through a GUI and Key Management operations can easily be carried out through an intuitive interface.
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, Seahorse includes a Gedit plugin, can handle files using Nautilus, an applet for managing stuff put in the clipboard and an agent for storing private passphrases, as well as a GnuPG and OpenSSH key manager.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Encrypt/decrypt/sign files and text
|
||||
- Manage your keys and keyring
|
||||
- Synchronize your keys and your keyring with key servers
|
||||
- Sign keys and publish
|
||||
- Cache your passphrase so you don't have to keep typing it
|
||||
- Backup your keys and keyring
|
||||
- Add an image in any GDK supported format as a OpenGPG photo ID
|
||||
- Create SSH keys, configure them, cache them
|
||||
- Internationalization support
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [www.gnome.org/projects/seahorse][4]
|
||||
- Developer: Jacob Perkins, Jose Carlos, Garcia Sogo, Jean Schurger, Stef Walter, Adam Schreiber
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 3.18.0
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20151108125950773/LastPassAlternatives.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.keepassx.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://encryptr.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://rattic.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.gnome.org/projects/seahorse/
|
||||
@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FSSlc Translating
|
||||
|
||||
The Strangest, Most Unique Linux Distros
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
From the most consumer focused distros like Ubuntu, Fedora, Mint or elementary OS to the more obscure, minimal and enterprise focused ones such as Slackware, Arch Linux or RHEL, I thought I've seen them all. Couldn't have been any further from the truth. Linux eco-system is very diverse. There's one for everyone. Let's discuss the weird and wacky world of niche Linux distros that represents the true diversity of open platforms.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Puppy Linux**: An operating system which is about 1/10th the size of an average DVD quality movie rip, that's Puppy Linux for you. The OS is just 100 MB in size! And it can run from RAM making it unusually fast even in older PCs. You can even remove the boot medium after the operating system has started! Can it get any better than that? System requirements are bare minimum, most hardware are automatically detected, and it comes loaded with software catering to your basic needs. [Experience Puppy Linux][1].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Suicide Linux**: Did the name scare you? Well it should. 'Any time - any time - you type any remotely incorrect command, the interpreter creatively resolves it into rm -rf / and wipes your hard drive'. Simple as that. I really want to know the ones who are confident enough to risk their production machines with [Suicide Linux][2]. **Warning: DO NOT try this on production machines!** The whole thing is available in a neat [DEB package][3] if you're interested.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
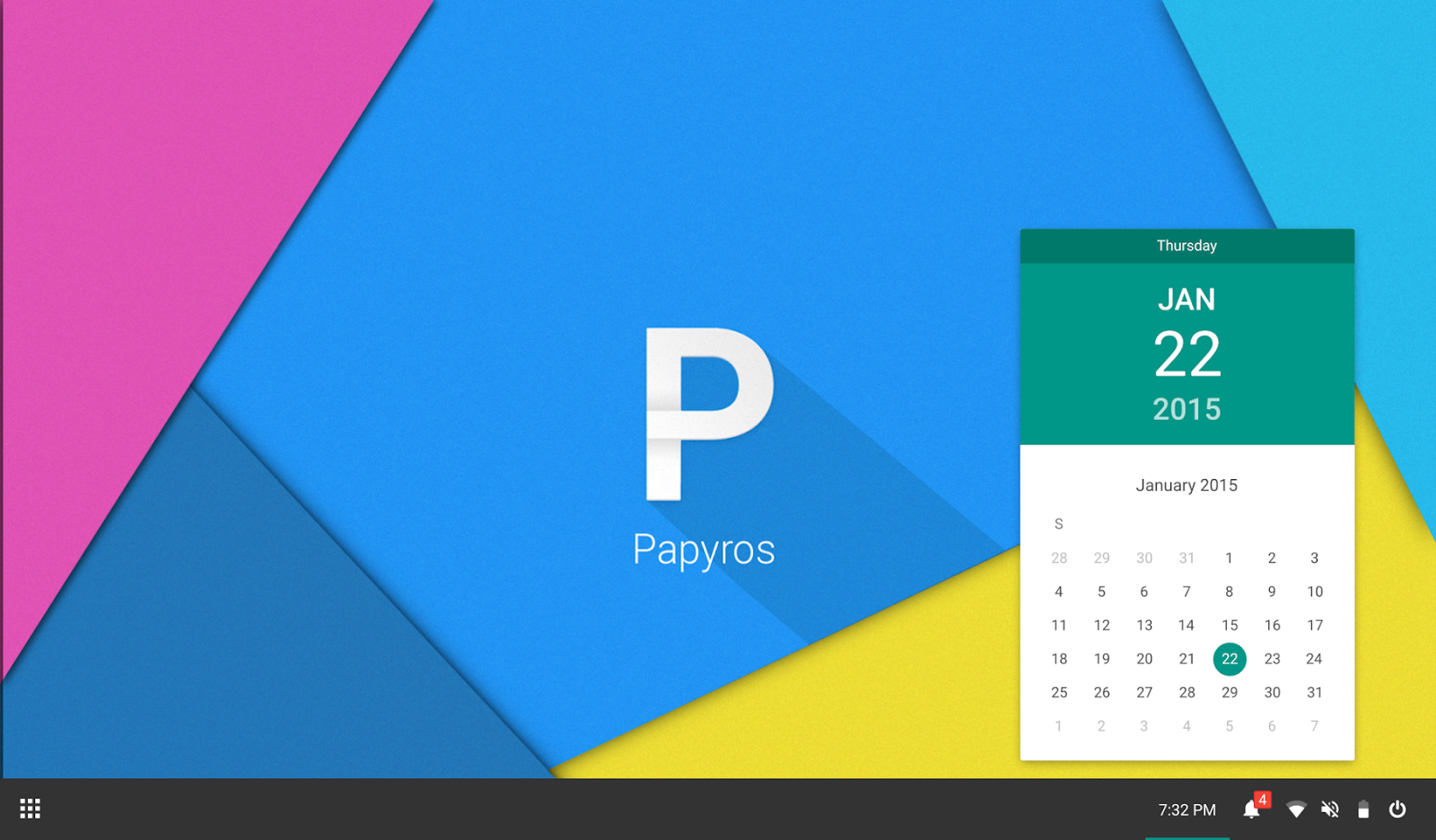
**PapyrOS**: "Strange" in a good way. PapyrOS is trying to adapt the material design language of Android into their brand new Linux distribution. Though the project is in early stages, it already looks very promising. The project page says the OS is 80% complete and one can expect the first Alpha release anytime soon. We did a small write up on [PapyrOS][4] when it was announced and by the looks of it, PapyrOS might even become a trend-setter of sorts. Follow the project on [Google+][5] and contribute via [BountySource][6] if you're interested.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
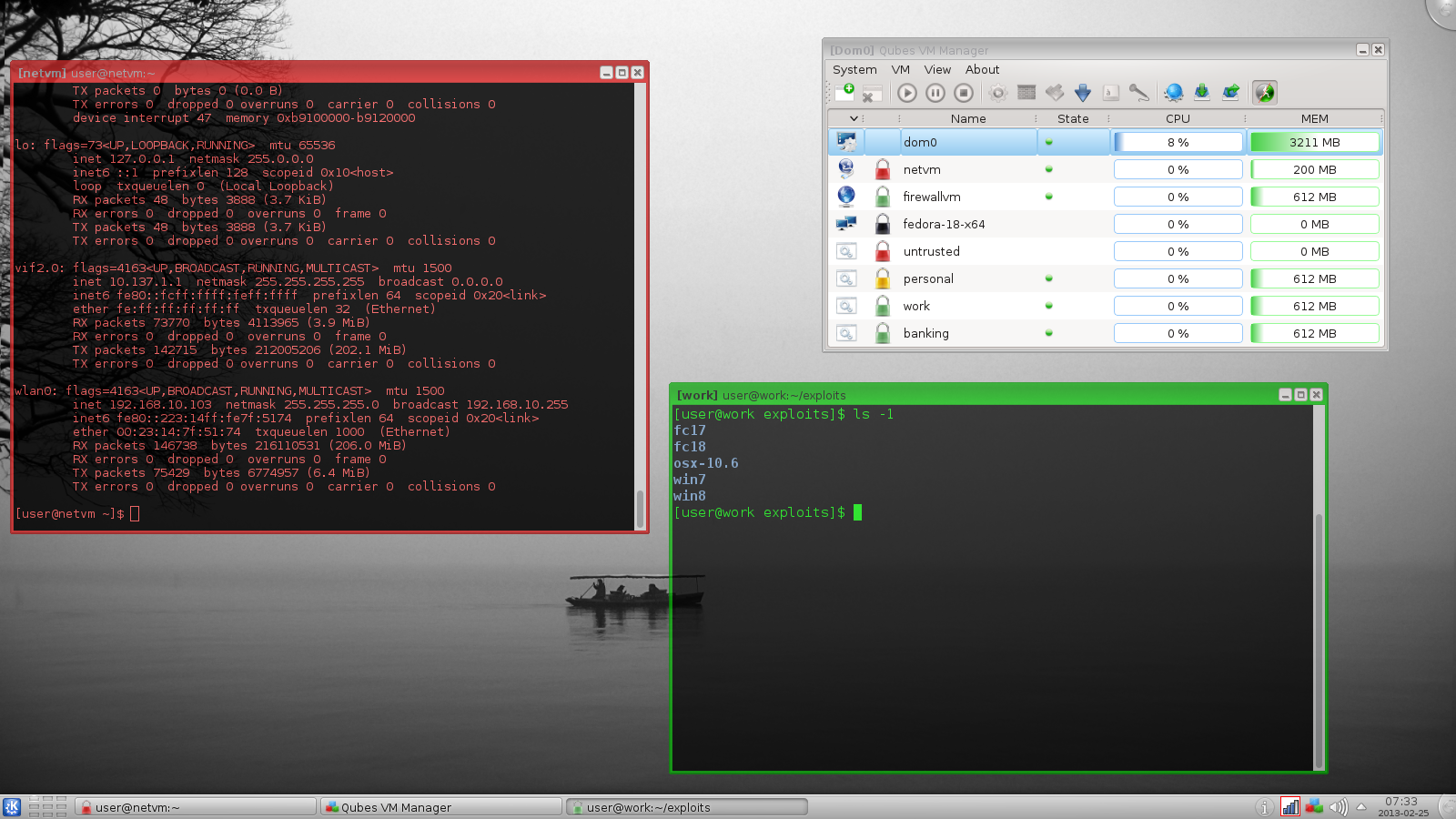
**Qubes OS**: Qubes is an open-source operating system designed to provide strong security using a Security by Compartmentalization approach. The assumption is that there can be no perfect, bug-free desktop environment. And by implementing a 'Security by Isolation' approach, [Qubes Linux][7] intends to remedy that. Qubes is based on Xen, the X Window System, and Linux, and can run most Linux applications and supports most Linux drivers. Qubes was selected as a finalist of Access Innovation Prize 2014 for Endpoint Security Solution.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu Satanic Edition**: Ubuntu SE is a Linux distribution based on Ubuntu. "It brings together the best of free software and free metal music" in one comprehensive package consisting of themes, wallpapers, and even some heavy-metal music sourced from talented new artists. Though the project doesn't look actively developed anymore, Ubuntu Satanic Edition is strange in every sense of that word. [Ubuntu SE (Slightly NSFW)][8].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
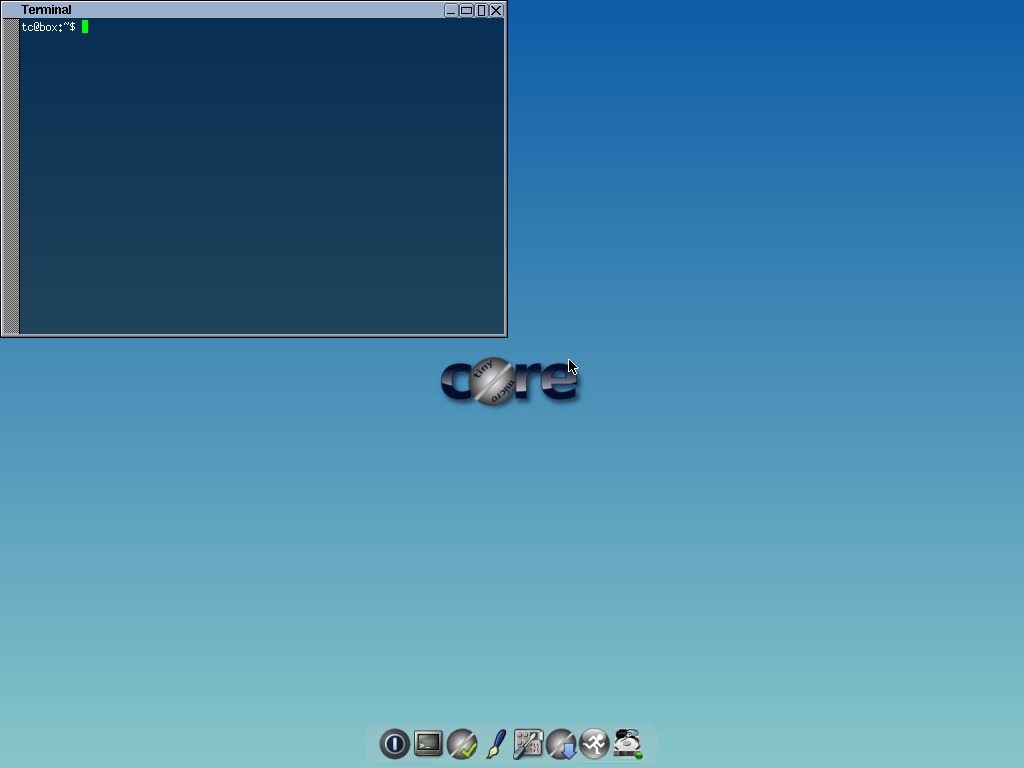
**Tiny Core Linux**: Puppy Linux not small enough? Try this. Tiny Core Linux is a 12 MB graphical Linux desktop! Yep, you read it right. One major caveat: It is not a complete desktop nor is all hardware completely supported. It represents only the core needed to boot into a very minimal X desktop typically with wired internet access. There is even a version without the GUI called Micro Core Linux which is just 9MB in size. [Tiny Core Linux][9] folks.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**NixOS**: A very experienced-user focused Linux distribution with a unique approach to package and configuration management. In other distributions, actions such as upgrades can be dangerous. Upgrading a package can cause other packages to break, upgrading an entire system is much less reliable than reinstalling from scratch. And top of all that you can't safely test what the results of a configuration change will be, there's no "Undo" so to speak. In NixOS, the entire operating system is built by the Nix package manager from a description in a purely functional build language. This means that building a new configuration cannot overwrite previous configurations. Most of the other features follow this pattern. Nix stores all packages in isolation from each other. [More about NixOS][10].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**GoboLinux**: This is another very unique Linux distro. What makes GoboLinux so different from the rest is its unique re-arrangement of the filesystem. It has its own subdirectory tree, where all of its files and programs are stored. GoboLinux does not have a package database because the filesystem is its database. In some ways, this sort of arrangement is similar to that seen in OS X. [Get GoboLinux][11].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Hannah Montana Linux**: Here is a Linux distro based on Kubuntu with a Hannah Montana themed boot screen, KDM, icon set, ksplash, plasma, color scheme, and wallpapers (I'm so sorry). [Link][12]. Project not active anymore.
|
||||
|
||||
**RLSD Linux**: An extremely minimalistic, small, lightweight and security-hardened, text-based operating system built on Linux. "It's a unique distribution that provides a selection of console applications and home-grown security features which might appeal to hackers," developers claim. [RLSD Linux][13].
|
||||
|
||||
Did we miss anything even stranger? Let us know.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.techdrivein.com/2015/08/the-strangest-most-unique-linux-distros.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Manuel Jose
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://puppylinux.org/main/Overview%20and%20Getting%20Started.htm
|
||||
[2]:http://qntm.org/suicide
|
||||
[3]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/suicide-linux/files/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.techdrivein.com/2015/02/papyros-material-design-linux-coming-soon.html
|
||||
[5]:https://plus.google.com/communities/109966288908859324845/stream/3262a3d3-0797-4344-bbe0-56c3adaacb69
|
||||
[6]:https://www.bountysource.com/teams/papyros
|
||||
[7]:https://www.qubes-os.org/
|
||||
[8]:http://ubuntusatanic.org/
|
||||
[9]:http://tinycorelinux.net/
|
||||
[10]:https://nixos.org/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.gobolinux.org/
|
||||
[12]:http://hannahmontana.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[13]:http://rlsd2.dimakrasner.com/
|
||||
@ -1,102 +0,0 @@
|
||||
zpl1025 translating
|
||||
The Brief History Of Aix, HP-UX, Solaris, BSD, And LINUX
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Always remember that when doors close on you, other doors open. [Ken Thompson][1] and [Dennis Richie][2] are a great example for such saying. They were two of the best information technology specialists in the **20th** century as they created the **UNIX** system which is considered one the most influential and inspirational software that ever written.
|
||||
|
||||
### The UNIX systems beginning at Bell Labs ###
|
||||
|
||||
**UNIX** which was originally called **UNICS** (**UN**iplexed **I**nformation and **C**omputing **S**ervice) has a great family and was never born by itself. The grandfather of UNIX was **CTSS** (**C**ompatible **T**ime **S**haring **S**ystem) and the father was the **Multics** (**MULT**iplexed **I**nformation and **C**omputing **S**ervice) project which supports interactive timesharing for mainframe computers by huge communities of users.
|
||||
|
||||
UNIX was born at **Bell Labs** in **1969** by **Ken Thompson** and later **Dennis Richie**. These two great researchers and scientists worked on a collaborative project with **General Electric** and the **Massachusetts Institute of Technology** to create an interactive timesharing system called the Multics.
|
||||
|
||||
Multics was created to combine timesharing with other technological advances, allowing the users to phone the computer from remote terminals, then edit documents, read e-mail, run calculations, and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
Over the next five years, AT&T corporate invested millions of dollars in the Multics project. They purchased mainframe computer called GE-645 and they dedicated to the effort of the top researchers at Bell Labs such as Ken Thompson, Stuart Feldman, Dennis Ritchie, M. Douglas McIlroy, Joseph F. Ossanna, and Robert Morris. The project was too ambitious, but it fell troublingly behind the schedule. And at the end, AT&T leaders decided to leave the project.
|
||||
|
||||
Bell Labs managers decided to stop any further work on operating systems which made many researchers frustrated and upset. But thanks to Thompson, Richie, and some researchers who ignored their bosses’ instructions and continued working with love on their labs, UNIX was created as one the greatest operating systems of all times.
|
||||
|
||||
UNIX started its life on a PDP-7 minicomputer which was a testing machine for Thompson’s ideas about the operating systems design and a platform for Thompsons and Richie’s game simulation that was called Space and Travel.
|
||||
|
||||
> “What we wanted to preserve was not just a good environment in which to do programming, but a system around which a fellowship could form. We knew from experience that the essence of communal computing, as supplied by remote-access, time-shared machines, is not just to type programs into a terminal instead of a keypunch, but to encourage close communication”. Dennis Richie Said.
|
||||
|
||||
UNIX was so close to be the first system under which the programmer could directly sit down at a machine and start composing programs on the fly, explore possibilities and also test while composing. All through UNIX lifetime, it has had a growing more capabilities pattern by attracting skilled volunteer effort from different programmers impatient with the other operating systems limitations.
|
||||
|
||||
UNIX has received its first funding for a PDP-11/20 in 1970, the UNIX operating system was then officially named and could run on the PDP-11/20. The first real job from UNIX was in 1971, it was to support word processing for the patent department at Bell Labs.
|
||||
|
||||
### The C revolution on UNIX systems ###
|
||||
|
||||
Dennis Richie invented a higher level programming language called “**C**” in **1972**, later he decided with Ken Thompson to rewrite the UNIX in “C” to give the system more portability options. They wrote and debugged almost 100,000 code lines that year. The migration to the “C” language resulted in highly portable software that require only a relatively small machine-dependent code to be then replaced when porting UNIX to another computing platform.
|
||||
|
||||
The UNIX was first formally presented to the outside world in 1973 on Operating Systems Principles, where Dennis Ritchie and Ken Thompson delivered a paper, then AT&T released Version 5 of the UNIX system and licensed it to the educational institutions, and then in 1975 they licensed Version 6 of UNIX to companies for the first time with a cost **$20.000**. The most widely used version of UNIX was Version 7 in 1980 where anybody could purchase a license but it was very restrictive terms in this license. The license included the source code, the machine dependents kernel which was written in PDP-11 assembly language. At all, versions of UNIX systems were determined by its user manuals editions.
|
||||
|
||||
### The AIX System ###
|
||||
|
||||
In **1983**, **Microsoft** had a plan to make a **Xenix** MS-DOS’s multiuser successor, and they created Xenix-based Altos 586 with **512 KB** RAM and **10 MB** hard drive by this year with cost $8,000. By 1984, 100,000 UNIX installations around the world for the System V Release 2. In 1986, 4.3BSD was released that included internet name server and the **AIX system** was announced by **IBM** with Installation base over 250,000. AIX is based on Unix System V, this system has BSD roots and is a hybrid of both.
|
||||
|
||||
AIX was the first operating system that introduced a **journaled file system (JFS)** and an integrated Logical Volume Manager (LVM). IBM ported AIX to its RS/6000 platform by 1989. The Version 5L was a breakthrough release that was introduced in 2001 to provide Linux affinity and logical partitioning with the Power4 servers.
|
||||
|
||||
AIX introduced virtualization by 2004 in AIX 5.3 with Advanced Power Virtualization (APV) which offered Symmetric multi-threading, micro-partitioning, and shared processor pools.
|
||||
|
||||
In 2007, IBM started to enhance its virtualization product, by coinciding with the AIX 6.1 release and the architecture of Power6. They also rebranded Advanced Power Virtualization to PowerVM.
|
||||
|
||||
The enhancements included form of workload partitioning that was called WPARs, that are similar to Solaris zones/Containers, but with much better functionality.
|
||||
|
||||
### The HP-UX System ###
|
||||
|
||||
The **Hewlett-Packard’s UNIX (HP-UX)** was based originally on System V release 3. The system initially ran exclusively on the PA-RISC HP 9000 platform. The Version 1 of HP-UX was released in 1984.
|
||||
|
||||
The Version 9, introduced SAM, its character-based graphical user interface (GUI), from which one can administrate the system. The Version 10, was introduced in 1995, and brought some changes in the layout of the system file and directory structure, which made it similar to AT&T SVR4.
|
||||
|
||||
The Version 11 was introduced in 1997. It was HP’s first release to support 64-bit addressing. But in 2000, this release was rebranded to 11i, as HP introduced operating environments and bundled groups of layered applications for specific Information Technology purposes.
|
||||
|
||||
In 2001, The Version 11.20 was introduced with support for Itanium systems. The HP-UX was the first UNIX that used ACLs (Access Control Lists) for file permissions and it was also one of the first that introduced built-in support for Logical Volume Manager.
|
||||
|
||||
Nowadays, HP-UX uses Veritas as primary file system due to partnership between Veritas and HP.
|
||||
|
||||
The HP-UX is up to release 11iv3, update 4.
|
||||
|
||||
### The Solaris System ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Sun’s UNIX version, **Solaris**, was the successor of **SunOS**, which was founded in 1992. SunOS was originally based on the BSD (Berkeley Software Distribution) flavor of UNIX but SunOS versions 5.0 and later were based on Unix System V Release 4 which was rebranded as Solaris.
|
||||
|
||||
SunOS version 1.0 was introduced with support for Sun-1 and Sun-2 systems in 1983. Version 2.0 was introduced later in 1985. In 1987, Sun and AT&T announced that they would collaborate on a project to merge System V and BSD into only one release, based on SVR4.
|
||||
|
||||
The Solaris 2.4 was first Sparc/x86 release by Sun. The last release of the SunOS was version 4.1.4 announced in November 1994. The Solaris 7 was the first 64-bit Ultra Sparc release and it added native support for file system metadata logging.
|
||||
|
||||
Solaris 9 was introduced in 2002, with support for Linux capabilities and Solaris Volume Manager. Then, Solaris 10 was introduced in 2005, and has number of innovations, such as support for its Solaris Containers, new ZFS file system, and Logical Domains.
|
||||
|
||||
The Solaris system is presently up to version 10 as the latest update was released in 2008.
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
By 1991 there were growing requirements for a free commercial alternative. Therefore **Linus Torvalds** set out to create new free operating system kernel that eventually became **Linux**. Linux started with a small number of “C” files and under a license which prohibited commercial distribution. Linux is a UNIX-like system and is different than UNIX.
|
||||
|
||||
Version 3.18 was introduced in 2015 under a GNU Public License. IBM said that more than 18 million lines of code are Open Source and available to developers.
|
||||
|
||||
The GNU Public License becomes the most widely available free software license which you can find nowadays. In accordance with the Open Source principles, this license permits individuals and organizations the freedom to distribute, run, share by copying, study, and also modify the code of the software.
|
||||
|
||||
### UNIX vs. Linux: Technical Overview ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Linux can encourage more diversity, and Linux developers come from wider range of backgrounds with different experiences and opinions.
|
||||
- Linux can run on wider range of platforms and also types of architecture than UNIX.
|
||||
- Developers of UNIX commercial editions have a specific target platform and audience in mind for their operating system.
|
||||
- **Linux is more secure than UNIX** as it is less affected by virus threats or malware attacks. Linux has had about 60-100 viruses to date, but at the same time none of them are currently spreading. On the other hand, UNIX has had 85-120 viruses but some of them are still spreading.
|
||||
- With commands of UNIX, tools and elements are rarely changed, and even some interfaces and command lines arguments still remain in later versions of UNIX.
|
||||
- Some Linux development projects get funded on a voluntary basis such as Debian. The other projects maintain a community version of commercial Linux distributions such as SUSE with openSUSE and Red Hat with Fedora.
|
||||
- Traditional UNIX is about scale up, but on the other hand Linux is about scale out.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/brief-history-aix-hp-ux-solaris-bsd-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[M.el Khamlichi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/pirat9/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/ken-thompson-unix-systems-father/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.unixmen.com/dennis-m-ritchie-father-c-programming-language/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
正在翻译:zky001
|
||||
How to Configure Tripwire IDS on Debian
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
This article is about Tripwire installation and configuration on Debian OS. It is a host based Intrusion detection system (IDS) for Linux environment. Prime function of tripwire IDS is to detect and report any unauthorized change (files and directories ) on linux system. After tripwire installation, baseline database created first, tripwire monitors and detects changes such as new file addition/creation, file modification and user who changed it etc. If the changes are legitimate, you can accept the changes to update tripwire database.
|
||||
@ -371,9 +372,9 @@ In this article, we learned installation and basic configuration of open source
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/security/configure-tripwire-ids-debian/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[nido][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
译者:[译者zky001](https://github.com/zky001)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/naveeda/
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/naveeda/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
||||
LastPass的开源替代品
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
LastPass是一个跨平台的密码管理程序。在Linux平台中,它可作为Firefox, Chrome和Opera浏览器的插件使用。LastPass Sesame支持Ubuntu/Debian与Fedora系统。此外,LastPass还有安装在Firefox Portable的便携版,可将其安装在USB设备上。再加上适用于Ubuntu/Debian, Fedora和openSUSE的LastPass Pocket, 其具有良好的跨平台覆盖性。虽然LastPass备受好评,但它是一个专有软件。此外,LastPass最近被LogMeIn收购。如果你在找一个开源的替代品,这篇文章可能会对你有所帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
我们正面临着信息大爆炸。无论你是要在线经营生意,找工作,还是只为了休闲来进行阅读,互联网都是一个广大的信息源。在这种情况下,长期保留信息是很困难的。然而,及时地获取某些特定信息非常重要。密码就是这样的一个例子。
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个电脑用户,你可能会面临在不同服务或网站使用相同或不同密码的困境。这个事情非常复杂,因为有些网站会限制你对密码的选择。比如,一个网站可能会限制密码的最小位数,大写字母,数字或者特殊字符,这使得在所有网站使用统一密码变得不可能。更重要的是,不在不同网站中使用同一密码有安全方面的原因。这样就不可避免地意味着人们经常会有很多密码要记。一个解决方案是将所有的密码写下来。然而,这种做法也极度的不安全。
|
||||
|
||||
为了解决需要记忆无穷多串密码的问题,目前比较流行的解决方案是使用密码管理软件。事实上,这类软件对于活跃的互联网用户来说极为实用。它使得你获取、管理和安全保存所有密码变得极为容易,而大多数密码都是被软件或文件系统加密过的。因此,用户只需要记住一个简单的密码就可以获取到其它所有密码。密码管理软件鼓励用户对于不同服务去采用独一无二的,非直观的强密码。
|
||||
|
||||
为了让大家更深入地了解Linux软件的质量,我将介绍4款优秀的、可替代LastPass的开源软件。
|
||||
|
||||
### KeePassX ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
KeePassX提供KeePass的多平台接口,是一款开源、跨平台的密码管理软件。这款软件可以帮助你以安全的方式保管密码。你可以将所有密码保存在一个数据库中,而这个数据库被一个主密码或密码盘来保管。
|
||||
|
||||
密码数据库使用AES(即Rijndael)或者TwoFish算法进行加密,密钥长度为256位。
|
||||
|
||||
该软件功能包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 多重管理模式 - 使每条密码更容易被识别
|
||||
- 可设置密码过期时间
|
||||
- 可插入附件
|
||||
- 可为不同分组或密码自定义标志
|
||||
- 在分组中对密码排序
|
||||
- 搜索函数:可在特定分组或整个数据库中搜索
|
||||
- Auto-Type: 这个功能允许你在登录网站时只需要按下几个键。KeePassX可以帮助你输入剩下的密码。Auto-Type通过读取当前窗口的标题,对密码数据库进行搜索来获取相应的密码
|
||||
- 数据库安全性强,用户可通过密码或一个密钥文件(可存储在CD或U盘中)访问数据库
|
||||
- 自动生成安全的密码
|
||||
- 具有预防措施,获取选中的密码并检查其安全性
|
||||
- 加密 - 用256位密钥,通过AES(高级加密标准)或TwoFish算法加密数据库
|
||||
- 密码可以导入或导出。可从PwManager文件(*.pwm)或KWallet文件(*.xml)中导入密码,可导出为文本(*.txt)格式。
|
||||
|
||||
- 软件官网:[www.keepassx.org][1]
|
||||
- 开发者:KeepassX Team
|
||||
- 软件许可证:GNU GPL V2
|
||||
- 版本号:0.4.3
|
||||
|
||||
### Encryptr ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Encryptr是一个开源的、零知晓的、基于云端的密码管理/电子钱包软件,以Crypton为基础开发。Crypton是一个Javascript库,允许开发者利用其开发应用,上传文件至服务器,而服务器无法知道用户所存储的文件内容。
|
||||
|
||||
Encryptr可将你的敏感信息,比如密码、信用卡数据、PIN码、或认证码存储在云端。然而,由于它基于零知晓的Cypton框架开发,Encryptr可保证只有用户才拥有访问或读取秘密信息的权限。
|
||||
|
||||
由于其跨平台的特性,Encryptr允许用户随时随地、安全地通过一个账户从云端获取机密信息。
|
||||
|
||||
软件特性包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 使用极安全、零知晓的Crypton框架,软件只在本地加密/解密数据
|
||||
- 易于使用
|
||||
- 基于云端
|
||||
- 可存储三种类型的数据:密码、信用卡账号以及通用的键值对
|
||||
- 可对每条密码设置“备注”项
|
||||
- 对本地密码进行缓存加密,以节省上传时间
|
||||
|
||||
- 软件官网: [encryptr.org][2]
|
||||
- 开发者: Tommy Williams
|
||||
- 软件许可证: GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- 版本号: 1.2.0
|
||||
|
||||
### RatticDB ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
RatticDB是一个开源的、基于Django的密码管理服务。
|
||||
|
||||
RatticDB被设计为一个“密码生命周期管理工具”而不是单单一个“密码存储工具”。RatticDB致力于及时提醒用户哪些密码在何时需要更改。它不提供应用层面的密码加密。
|
||||
|
||||
软件特性包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 简洁的ACL设计
|
||||
- 可改变队列功能,可让用户知晓何时需要更改某应用的密码
|
||||
- Ansible配置
|
||||
|
||||
- 软件官网: [rattic.org][3]
|
||||
- 开发者: Daniel Hall
|
||||
- 软件许可证: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本号: 1.3.1
|
||||
|
||||
### Seahorse ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Seahorse是一个于Gnome前端运行的GnuPG - GNU隐私保护软件。它的目标是提供一个易于使用密钥管理工具,一并提供一个易于使用的界面来控制加密操作。
|
||||
|
||||
Seahorse是一个工具,用来提供安全沟通和数据存储服务。数据加密和数字密钥生成操作可以轻易通过GUI来演示,密钥管理操作也可以轻易通过直观的界面来进行。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,Seahorse包含一个Gedit插件,可以使用鹦鹉螺文件管理器管理文件,一个管理剪贴板中事物的小程序,一个存储私密密码的代理,还有一个GnuPG和OpenSSH的密钥管理工具。
|
||||
|
||||
软件特性包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 对文本进行加密/解密/签名
|
||||
- 管理密钥及密钥环
|
||||
- 将密钥及密钥环于密钥服务器同步
|
||||
- 密码签名及发布
|
||||
- 将密码缓存起来,无需多次重复键入
|
||||
- 对密钥及密钥环进行备份
|
||||
- 可添加一个GDK支持格式的图片作为OpenGPG图片ID
|
||||
- 生成SSH密钥,对其进行验证及储存
|
||||
- 多语言支持
|
||||
|
||||
- 软件官网: [www.gnome.org/projects/seahorse][4]
|
||||
- 开发者: Jacob Perkins, Jose Carlos, Garcia Sogo, Jean Schurger, Stef Walter, Adam Schreiber
|
||||
- 软件许可证: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本号: 3.18.0
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20151108125950773/LastPassAlternatives.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[StdioA](https://github.com/StdioA)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.keepassx.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://encryptr.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://rattic.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.gnome.org/projects/seahorse/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
||||
那些奇特的 Linux 发行版本
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
从大多数消费者所关注的诸如 Ubuntu,Fedora,Mint 或 elementary OS 到更加晦涩、轻量级和企业级的诸如 Slackware,Arch Linux 或 RHEL,这些发行版本我都已经见识过了。除了这些,难道没有其他别的了吗?其实 Linux 的生态系统是非常多样化的,对每个人来说,总有一款适合你。下面就让我们讨论一些稀奇古怪的小众 Linux 发行版本吧,它们代表着开源平台真正的多样性。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Puppy Linux**: 它是一个仅有一个普通 DVD 光盘容纳十分之一大小的操作系统,这就是 Puppy Linux。整个操作系统仅有 100MB 大小!并且它还可以在内存中运行,这使得它运行极快,甚至是在老式的 PC 机上。 在操作系统启动后,你甚至可以移除安装介质!还有什么比这个更好的吗? 系统所需的资源极小,大多数的硬件都会被自动检测到,并且它预装了能够满足你基本需求的软件。[在这里体验 Puppy Linux 吧][1].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Suicide Linux(自杀 Linux)**: 这个名字吓到你了吗?我想应该是。 ‘任何时候 -注意是任何时候-一旦你输入不正确的命令,解释器都会创造性地将它重定向为 `rm -rf /` 命令,然后擦除你的硬盘’。它就是这么简单。我真的很想知道那些自信到将[Suicide Linux][2] 安装到生产机上的家伙。 **警告:不要在生产机上尝试这个!** 假如你感兴趣的话,现在可以通过一个简洁的[DEB 包][3]来获取到它。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**PapyrOS**: 它在好的方面上 “奇怪”。PapyrOS 正尝试着将 Android 的 material design 设计语言应用到新品牌的 Linux 发行版本上。尽管这个项目还处于早期阶段,看起来它已经很有前景。该项目的网页上说该系统已经完成了 80%,随后人们可以期待它的第一个 Alpha 发行版本。在该项目被宣告提出时,我们做了[PapyrOS][4]的小幅报道,从它的外观上看,它甚至可能会引领潮流。假如你感兴趣的话,可在[Google+][5]上关注该项目并可通过[BountySource][6]来贡献出你的力量。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Qubes OS**: Qubes 是一个开源的操作系统,通过使用安全划分的方法,被设计用来提供强大的安全性。其前提假设是不存在完美的没有 bug 的桌面环境。并通过实现一个‘安全隔离’ 的方法,[Qubes Linux][7]尝试去弥补那些 bug。Qubes 基于 Xen,X 视窗系统和 Linux,并可运行大多数的 Linux 应用,支持大多数的 Linux 驱动。Qubes 入选了 Access Innovation Prize 2014 for Endpoint Security Solution 决赛名单。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu Satanic Edition**: Ubuntu SE 是一个基于 Ubuntu 的发行版本。通过一个含有主题、壁纸甚至来源于某些天才新晋艺术家的重金属音乐的综合软件包,“它同时带来了最好的自由软件和免费的金属音乐” 。尽管这个项目看起来不再被活跃地发展了, Ubuntu Satanic Edition 甚至在其名字上都显得奇异。 [Ubuntu SE (Slightly NSFW)][8]。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Tiny Core Linux**: Puppy Linux 还不够小?试试这个吧。 Tiny Core Linux 是一个 12MB 大小的图形化 Linux 桌面!是的,你没有读错。一个主要的补充说明:它不是一个完整的桌面,也并不完全支持所有的硬件。它只含有能够启动进入一个非常小巧的 X 桌面,支持有线网络连接的核心部件。它甚至还有一个名为 Micro Core Linux 的没有 GUI 的版本,仅有 9MB 大小。[Tiny Core Linux][9]。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**NixOS**: 它是一个非常关注经验用户的 Linux 发行版本,有着独特的方式来打包和配置管理。在其他的发行版本中,诸如升级的操作可能是非常危险的。升级一个软件包可能会引起其他包无法使用,相比于从头安装一个系统,升级整个系统则显得不是那么可信。在那些你不能安全地测试由一个配置的改变所带来的结果的更改之上,它们通常没有“重来”这个选项。在 NixOS 中,整个系统由 Nix 包管理器按照一个纯功能性的构建语言的描述来构建。这意味着一个新的配置不会重写先前的配置。大多数其他的特色功能也遵循着这个模式。Nix 相互分离地存储所有的软件包。有关 NixOS 的更多内容请看[这里][10]。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**GoboLinux**: 这是另一个非常奇特的 Linux 发行版本。它与其他系统如此不同的原因是它有着独特的重管理文件系统。它有着自己独特的子目录树,其中存储着所有的文件和程序。GoboLinux 没有专门的包数据库,因为其文件系统就是它的数据库。在某些方面,这类管理有些类似于 OS X 上所看到的功能。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Hannah Montana Linux**: 它是一个基于 Kubuntu 的 Linux 发行版本,它有着 Hannah Montana 主题的开机启动界面、KDM(KDE Display Manager)、图标集、ksplash、plasma、颜色主题和壁纸(请抱歉)。[这是它的链接][12]。这个项目现在不再活跃了。
|
||||
|
||||
**RLSD Linux**: 它是一个极其精简、小巧、轻量和安全加固的,建立在 Linux 内核上的基于文本的操作系统。开发者称 “它是一个独特的发行版本,提供一系列的控制台应用和本地化的安全特性,对黑客或许有吸引力。” [RLSD Linux][13].
|
||||
|
||||
我们还错过了某些更加奇特的发行版本吗?请让我们知晓吧。
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.techdrivein.com/2015/08/the-strangest-most-unique-linux-distros.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Manuel Jose
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://puppylinux.org/main/Overview%20and%20Getting%20Started.htm
|
||||
[2]:http://qntm.org/suicide
|
||||
[3]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/suicide-linux/files/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.techdrivein.com/2015/02/papyros-material-design-linux-coming-soon.html
|
||||
[5]:https://plus.google.com/communities/109966288908859324845/stream/3262a3d3-0797-4344-bbe0-56c3adaacb69
|
||||
[6]:https://www.bountysource.com/teams/papyros
|
||||
[7]:https://www.qubes-os.org/
|
||||
[8]:http://ubuntusatanic.org/
|
||||
[9]:http://tinycorelinux.net/
|
||||
[10]:https://nixos.org/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.gobolinux.org/
|
||||
[12]:http://hannahmontana.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[13]:http://rlsd2.dimakrasner.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
Aix, HP-UX, Solaris, BSD, 和 LINUX 简史
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
有句话说,当一扇门在你面前关上的时候,另一扇门就会打开。[Ken Thompson][1] 和 [Dennis Richie][2] 两个人就是最好的例子。他们俩是 **20世纪** 最优秀的信息技术专家,因为他们创造了 **UNIX**,最具影响力和创新性的软件之一。
|
||||
|
||||
### UNIX 系统诞生于贝尔实验室 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**UNIX** 最开始的名字是 **UNICS** (**UN**iplexed **I**nformation and **C**omputing **S**ervice),它有一个大家庭,并不是从石头里蹦出来的。UNIX的祖父是 **CTSS** (**C**ompatible **T**ime **S**haring **S**ystem),它的父亲是 **Multics** (**MULT**iplexed **I**nformation and **C**omputing **S**ervice),这个系统能支持大量用户通过交互式分时使用大型机。
|
||||
|
||||
UNIX 诞生于 **1969** 年,由 **Ken Thompson** 以及后来加入的 **Dennis Richie** 共同完成。这两位优秀的研究员和科学家一起在一个**通用电子**和**麻省理工学院**的合作项目里工作,项目目标是开发一个叫 Multics 的交互式分时系统。
|
||||
|
||||
Multics 的目标是整合分时共享以及当时其他先进技术,允许用户在远程终端通过电话登录到主机,然后可以编辑文档,阅读电子邮件,运行计算器,等等。
|
||||
|
||||
在之后的五年里,AT&T 公司为 Multics 项目投入了数百万美元。他们购买了 GE-645 大型机,聚集了贝尔实验室的顶级研究人员,例如 Ken Thompson, Stuart Feldman, Dennis Ritchie, M. Douglas McIlroy, Joseph F. Ossanna, 以及 Robert Morris。但是项目目标太过激进,进度严重滞后。最后,AT&T 高层决定放弃这个项目。
|
||||
|
||||
贝尔实验室的管理层决定停止这个让许多研究人员无比纠结的操作系统上的所有遗留工作。不过要感谢 Thompson,Richie 和一些其他研究员,他们把老板的命令丢到一边,并继续在实验室里满怀热心地忘我工作,最终孵化出前无古人后无来者的 UNIX。
|
||||
|
||||
UNIX 的第一声啼哭是在一台 PDP-7 微型机上,它是 Thompson 测试自己在操作系统设计上的点子的机器,也是 Thompson 和 Richie 一起玩 Space and Travel 游戏的模拟器。
|
||||
|
||||
> “我们想要的不仅是一个优秀的编程环境,而是能围绕这个系统形成团体。按我们自己的经验,通过远程访问和分时共享主机实现的公共计算,本质上不只是用终端输入程序代替打孔机而已,而是鼓励密切沟通。”Dennis Richie 说。
|
||||
|
||||
UNIX 是第一个靠近理想的系统,在这里程序员可以坐在机器前自由摆弄程序,探索各种可能性并随手测试。在 UNIX 整个生命周期里,因为大量因为其他操作系统限制而投身过来的高手做出的无私贡献,它的功能模型一直保持上升趋势。
|
||||
|
||||
UNIX 在 1970 年因为 PDP-11/20 获得了首次资金注入,之后正式更名为 UNIX 并支持在 PDP-11/20 上运行。UNIX 带来的第一次收获是在 1971 年,贝尔实验室的专利部门配备来做文字处理。
|
||||
|
||||
### UNIX 上的 C 语言革命 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Dennis Richie 在 1972 年发明了一种叫 “**C**” 的高级编程语言,之后他和 Ken Thompson 决定用 “C” 重写 UNIX 系统,来支持更好的移植性。他们在那一年里编写和调试了差不多 100,000 行代码。在使用了 “C” 语言后,系统可移植性非常好,只需要修改一小部分机器相关的代码就可以将 UNIX 移植到其他计算机平台上。
|
||||
|
||||
UNIX 第一次公开露面是在 1973 年 Dennis Ritchie 和 Ken Thompson 在操作系统原理上发表的一篇论文,然后 AT&T 发布了 UNIX 系统第 5 版,并授权给教育机构使用,然后在 1976 年第一次以 **$20.000** 的价格授权企业使用 UNIX 第 6 版。应用最广泛的是 1980 年发布的 UNIX 第 7 版,任何人都可以购买,只是授权条款非常有限。授权内容包括源代码,以及用 PDP-11 汇编语言写的及其相关内核。各种版本 UNIX 系统完全由它的用户手册确定。
|
||||
|
||||
### AIX 系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在 **1983** 年,**Microsoft** 计划开发 **Xenix** 作为 MS-DOS 的多用户版继任者,他们在那一年花了 $8,000 搭建了一台拥有 **512 KB** 内存以及 **10 MB**硬盘并运行 Xenix 的 Altos 586。而到 1984 年为止,全世界已经安装了超过 100,000 份 UNIX System V 第二版。在 1986 年发布了包含因特网域名服务的 4.3BSD,而且 **IBM** 宣布 **AIX 系统**的安装数已经超过 250,000。AIX 基于 Unix System V 开发,这套系统拥有 BSD 风格的根文件系统,是两者的结合。
|
||||
|
||||
AIX 第一次引入了 **日志文件系统 (JFS)** 以及集成逻辑卷管理器 (LVM)。IBM 在 1989 年将 AIX 移植到自己的 RS/6000 平台。2001 年发布的 5L 版是一个突破性的版本,提供了 Linux 友好性以及支持 Power4 服务器的逻辑分区。
|
||||
|
||||
在 2004 年发布的 AIX 5.3 引入了支持 Advanced Power Virtualization (APV) 的虚拟化技术,支持对称多线程,微分区,以及可分享的处理器池。
|
||||
|
||||
在 2007 年,IBM 同时发布 AIX 6.1 和 Power6 架构,开始加强自己的虚拟化产品。他们还将 Advanced Power Virtualization 重新包装成 PowerVM。
|
||||
|
||||
这次改进包括被称为 WPARs 的负载分区形式,类似于 Solaris 的 zones/Containers,但是功能更强。
|
||||
|
||||
### HP-UX 系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**惠普 UNIX (HP-UX)** 源于 System V 第 3 版。这套系统一开始只支持 PA-RISC HP 9000 平台。HP-UX 第 1 版发布于 1984 年。
|
||||
|
||||
HP-UX 第 9 版引入了 SAM,一个基于角色的图形用户界面 (GUI),用户可以用来管理整个系统。在 1995 年发布的第 10 版,调整了系统文件分布以及目录结构,变得有点类似 AT&T SVR4。
|
||||
|
||||
第 11 版发布于 1997 年。这是 HP 第一个支持 64 位寻址的版本。不过在 2000 年重新发布成 11i,因为 HP 为特定的信息技术目的,引入了操作环境和分级应用的捆绑组。
|
||||
|
||||
在 2001 年发布的 11.20 版宣称支持 Itanium 系统。HP-UX 是第一个使用 ACLs(访问控制列表)管理文件权限的 UNIX 系统,也是首先支持内建逻辑卷管理器的系统之一。
|
||||
|
||||
如今,HP-UX 因为 HP 和 Veritas 的合作关系使用了 Veritas 作为主文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
HP-UX 目前最新的版是 11iv3, update 4。
|
||||
|
||||
### Solaris 系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Sun 的 UNIX 版本是 **Solaris**,用来接替 1992 年创建的 **SunOS**。SunOS 一开始基于 BSD(伯克利软件发行版)风格的 UNIX,但是 SunOS 5.0 版以及之后的版本都是基于重新包装成 Solaris 的 Unix System V 第 4 版。
|
||||
|
||||
SunOS 1.0 版于 1983 年发布,用于支持 Sun-1 和 Sun-2 平台。随后在 1985 年发布了 2.0 版。在 1987 年,Sun 和 AT&T 宣布合作一个项目以 SVR4 为基础将 System V 和 BSD 合并成一个版本。
|
||||
|
||||
Solaris 2.4 是 Sun 发布的第一个 Sparc/x86 版本。1994 年 11 月份发布的 SunOS 4.1.4 版是最后一个版本。Solaris 7 是首个 64 位 Ultra Sparc 版本,加入了对文件系统元数据记录的原生支持。
|
||||
|
||||
Solaris 9 发布于 2002 年,支持 Linux 特性以及 Solaris 卷管理器。之后,2005 年发布了 Solaris 10,带来许多创新,比如支持 Solaris Containers,新的 ZFS 文件系统,以及逻辑域。
|
||||
|
||||
目前 Solaris 最新的版本是 第 10 版,最后的更新发布于 2008 年。
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
到了 1991 年,用来替代商业操作系统的免费系统的需求日渐高涨。因此 **Linus Torvalds** 开始构建一个免费操作系统,最终成为 **Linux**。Linux 最开始只有一些 “C” 文件,并且使用了阻止商业发行的授权。Linux 是一个类 UNIX 系统但又不尽相同。
|
||||
|
||||
2015 年 发布了基于 GNU Public License 授权的 3.18 版。IBM 声称有超过 1800 万行开源代码开放给开发者。
|
||||
|
||||
如今 GNU Public License 是应用最广泛的免费软件授权方式。根据开源软件原则,这份授权允许个人和企业自由分发,运行,通过拷贝共享,学习,以及修改软件源码。
|
||||
|
||||
### UNIX vs. Linux: 技术概要 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Linux 鼓励多样性,Linux 的开发人员有更宽广的背景,有更多不同经验和意见。
|
||||
- Linux 比 UNIX 支持更多的平台和架构。
|
||||
- UNIX 商业版本的开发人员会为他们的操作系统考虑特定目标平台以及用户。
|
||||
- **Linux 比 UNIX 有更好的安全性**,更少受病毒或恶意软件攻击。Linux 上大约有 60-100 种病毒,但是没有任何一种还在传播。另一方面,UNIX 上大约有 85-120 种病毒,但是其中有一些还在传播中。
|
||||
- 通过 UNIX 命令,系统上的工具和元素很少改变,甚至很多接口和命令行参数在后续 UNIX 版本中一直沿用。
|
||||
- 有些 Linux 开发项目以自愿为基础进行资助,比如 Debian。其他项目会维护一个和商业 Linux 的社区版,比如 SUSE 的 openSUSE 以及红帽的 Fedora。
|
||||
- 传统 UNIX 是扩大规模,而另一方面 Linux 是扩大范围。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/brief-history-aix-hp-ux-solaris-bsd-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[M.el Khamlichi][a]
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/pirat9/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/ken-thompson-unix-systems-father/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.unixmen.com/dennis-m-ritchie-father-c-programming-language/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user