+
+
+
+保存并关闭文件。
+
+#### 5. 创建虚拟主机配置文件####
+
+默认情况下,apache有一个默认的虚拟主机文件叫000-default.conf。我们将会复制**000-default.conf**文件内容到我们新的虚拟主机配置文件中。
+
+ sudo cp /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf /etc/apache2/sites-available/unixmen1.local.conf
+ sudo cp /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf /etc/apache2/sites-available/unixmen2.local.conf
+
+确保虚拟主机配置文件末尾包含.conf扩展名。
+
+现在,修改unximen1.local.conf文件以符合需求。
+
+ sudo vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/unixmen1.local.conf
+
+使相关的变化直接呈现在unixmen1站点中(译注:以“#”开头的注释行可以忽略。)。
+
+
+ # The ServerName directive sets the request scheme, hostname and port that
+ # the server uses to identify itself. This is used when creating
+ # redirection URLs. In the context of virtual hosts, the ServerName
+ # specifies what hostname must appear in the request's Host: header to
+ # match this virtual host. For the default virtual host (this file) this
+ # value is not decisive as it is used as a last resort host regardless.
+ # However, you must set it for any further virtual host explicitly.
+ #ServerName www.example.com
+
+ ServerAdmin webmaster@unixmen1.local
+ ServerName unixmen1.local
+ ServerAlias www.unixmen1.local
+ DocumentRoot /var/www/unixmen1.local/public_html
+
+ # Available loglevels: trace8, ..., trace1, debug, info, notice, warn,
+ # error, crit, alert, emerg.
+ # It is also possible to configure the loglevel for particular
+ # modules, e.g.
+ #LogLevel info ssl:warn
+
+ ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
+ CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
+
+ # For most configuration files from conf-available/, which are
+ # enabled or disabled at a global level, it is possible to
+ # include a line for only one particular virtual host. For example the
+ # following line enables the CGI configuration for this host only
+ # after it has been globally disabled with "a2disconf".
+ #Include conf-available/serve-cgi-bin.conf
+
+
+
+同理,修改第二台主机文件。
+
+ sudo vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/unixmen2.local.conf
+
+使相关的修改在unixmen2 站点呈现出来。
+
+
+ # The ServerName directive sets the request scheme, hostname and port that
+ # the server uses to identify itself. This is used when creating
+ # redirection URLs. In the context of virtual hosts, the ServerName
+ # specifies what hostname must appear in the request's Host: header to
+ # match this virtual host. For the default virtual host (this file) this
+ # value is not decisive as it is used as a last resort host regardless.
+ # However, you must set it for any further virtual host explicitly.
+ #ServerName www.example.com
+
+ ServerAdmin webmaster@unixmen2.local
+ ServerName unixmen2.local
+ ServerAlias www.unixmen2.local
+ DocumentRoot /var/www/unixmen2.local/public_html
+
+ # Available loglevels: trace8, ..., trace1, debug, info, notice, warn,
+ # error, crit, alert, emerg.
+ # It is also possible to configure the loglevel for particular
+ # modules, e.g.
+ #LogLevel info ssl:warn
+
+ ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
+ CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
+
+ # For most configuration files from conf-available/, which are
+ # enabled or disabled at a global level, it is possible to
+ # include a line for only one particular virtual host. For example the
+ # following line enables the CGI configuration for this host only
+ # after it has been globally disabled with "a2disconf".
+ #Include conf-available/serve-cgi-bin.conf
+
+
+
+修改虚拟主机文件后,禁用默认的虚拟主机配置(000.default.conf),然后启用新的虚拟主机配置,如下所示。
+
+ sudo a2dissite 000-default.conf
+ sudo a2ensite unixmen1.local.conf
+ sudo a2ensite unixmen2.local.conf
+
+最后,重启apache服务器。
+
+ sudo service apache2 restart
+
+就是这样。现在,我们成功地配置了apach虚拟主机在我们的Ubuntu服务器上
+
+###测试虚拟主机###
+
+编辑**/etc/hosts**文件,
+
+ sudo vi /etc/hosts
+
+在文件末尾添加如下所示的虚拟域名。
+
+ 192.168.1.250 unixmen1.local
+ 192.168.1.250 unixmen2.local
+
+保存并关闭文件。
+
+打开你的浏览器并访问**http://unixmen1.local** 或 **http://unixmen2.local**。你将会看到我们之前创建的示例页。
+
+**Unixmen1.local 测试页:**
+
+
+
+
+**Unixmen2.local 测试页**
+
+
+
+如果你想从你的远程系统访问这些站点,你需要在你的DNS服务器添加实际域名记录。不过,我没有真实的域名和DNS服务器,我只想通过我的本地系统测试,那么它刚好如我所愿地工作。
+
+Cheers!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/setup-virtual-hosts-apache-ubuntu-14-04-lts/
+
+译者:[disylee](https://github.com/disylee) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201406/20140607 Cup 2014 Brazil--Watch FIFA World Cup 2014 Competition in Your Linux Desktop.md b/published/201406/20140607 Cup 2014 Brazil--Watch FIFA World Cup 2014 Competition in Your Linux Desktop.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d7922c31ee
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140607 Cup 2014 Brazil--Watch FIFA World Cup 2014 Competition in Your Linux Desktop.md
@@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
+在linux桌面上观看2014年巴西世界杯比赛!
+================================================================================
+足球是世界上受众最广和观众最多的运动,现代足球起源于英国。足球运动员平均每场比赛要跑6个多英里。上届南非世界杯有近10亿的电视观众,而今年的的观赛数量预计还要增加。
+
+2014年第20界世界杯在巴西举行,时间安排为从6月12号开始持续到7月13号,共有32个国家参加这项赛事。
+
+爱足球的小伙子们,我们将要介绍一款可以提供最新的赛况以及你喜欢的球队的进球数信息的应用程序,它叫做“icup 2014 Brazil”。下面让我们介绍它的特点,用法和安装等。
+
+
+
+*iCup 2014 Brazil*
+
+### 什么是“icup 2014 Brazil” ###
+
+“icup 2014 Brazil”简单的说是一个应用程序,在linux桌面为你提供2014年世界杯的最新比赛赛况。
+
+### “icup 2014 Brazil”的特点###
+
+- 自适应的用户界面,比如自动缩放
+- 迅速查看战绩
+- 支持Facebook、twitter和Google+社交分享功能
+- 支持Retina显示输出
+- 实时跟踪比赛结果
+- 包括32个国家的国歌小工具配合露天广场效果很不错
+- 内置日历和时区工具,实时的显示当天数据,图像化展示最新的战况和得分
+- 支持代理
+
+
+### 平台和框架支持 ###
+
+这款软件可以运行在Mac、windows和linux上,特别提醒,在Linux上,它是为x86的CPU设计的,虽然它也可以在x64的平台上安装,不过我们需要做一下设置。
+
+#### 在不同平台的技术规范 ####
+
+- 实时结果,日历,数据分组,第二阶段整合,社交网络连接和多语言支持,这些支持全平台
+- Retina显示支持,这个不支持windows和linux,仅支持Mac OS
+- 详细的统计-支持linux。在windows和Mac需要捐赠才行
+- 声音小工具-支持MAC和linux,windows不确定
+
+**重要**: 上面的特点都支持,一些具体的特性除了linux外都不是免费提供的,这是为了支付服务器和带宽费用。对于linux用户来说,任何细节不需要关心,高兴的用去吧。
+
+### Linux下安装“icup 2014 Brazil” ###
+
+首先去[“icup 2014 Brazil”官方下载页面][1]下载你电脑平台的软件版本
+
+#### 32位下的安装步骤 ####
+
+ # cd Downloads/
+ # tar xvf iCup_2014_FREE-Brazil_1.1_linux.tar.bz2
+ # cd iCup\ 2014\ FREE\ -\ Brazil\ 1.1/
+ # chmod 755 iCup\ 2014\ FREE\ -\ Brazil
+
+如上文所说,这个应用程序只为X86架构设计,为了在64位架构下安装32位的软件,我们需要在系统上安装一些软件包:**GTK+2**和**libstdc++.so.6**。
+
+不只是这款软件,一大堆Linux下的软件不支持64位架构,例如**Skype**,我们也需要这样调整我们的系统来安装这些软件。
+
+#### 在64位系统下 ####
+
+安装**GTK+2**和**libstdc++so.6**,用如下apt或者yum命令
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install libgtk2.0-0 libstdc++6 [在基于Debian系统上执行这个命令]
+
+如果有报错的话,运行下面的命令来解决
+
+ $ sudo apt-get -f install
+
+----------
+
+ # yum install gtk2 libstdc++ [在基于Redhat系统上执行这个命令]
+
+需要的软件包安装完后,就可以在64位系统下安装32位的软件了,进入你的下载目录,找到“**icup 2014 Brazil**”安装包然后执行下面的命令
+
+ # cd Downloads/
+ # tar xvf iCup_2014_FREE-Brazil_1.1_linux.tar.bz2
+ # cd iCup\ 2014\ FREE\ -\ Brazil\ 1.1/
+ # chmod 755 iCup\ 2014\ FREE\ -\ Brazil
+
+然后,进入软件所在目录,双击可执行文件启动软件。下面的截屏图中看不到所有的信息,**因为本文写作时2014年世界杯现在还没开始呢,开始后我们就能看到结果了**。
+
+
+
+iCup Brazil 2014
+
+无具体信息,世界杯尚未开始。
+
+
+
+Match Detailed Information
+
+分组和队伍
+
+
+
+Groups and Teams
+
+第二阶段详细信息
+
+
+
+2nd stage Detailed Information
+
+比赛细节,尚未完整
+
+
+
+Match Summary
+
+集成语言切换和社交分享按钮
+
+
+
+Language Change
+
+Linux上捐赠是可选的,你可以贡献你的心意。
+
+
+
+Donation
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+上面的这个软件有望成为足球粉丝的一大福利,赶快在线试用吧。
+
+好了,我马上又有一个有趣的文章了。请保持关注Tecmint.com。请在评论区对我们的工作给予反馈。
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/view-fifa-world-cup-matche-results/
+
+译者:[jiajia9linuxer](https://github.com/jiajia9linuxer) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.e-link.it/icup/brazil2014/icup-brazil-2014-desktop-app.php
diff --git a/published/201406/20140607 How To Extract Images From Videos Using ffmpeg.md b/published/201406/20140607 How To Extract Images From Videos Using ffmpeg.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d86b18b2b3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140607 How To Extract Images From Videos Using ffmpeg.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+如何使用ffmpeg从视频中提取图片
+================================================================================
+
+你曾想过从一个视频文件中提取图片吗?在Linux下就可以,在这个教程中我将使用ffmpeg来从视频中获取图片。
+
+### 什么是ffmpeg?What is ffmpeg? ###
+
+ffmpeg是一个非常有用的命令行程序,它可以用来转码媒体文件。它是领先的多媒体框架FFmpeg的一部分,其有很多功能,比如解码、编码、转码、混流、分离、转化为流、过滤以及播放几乎所有的由人和机器创建的媒体文件。
+
+在这个框架中包含有各种工具,每一个用于完成特定的功能。例如,ffserver能够将多媒体文件转化为用于实时广播的流,ffprobe用于分析多媒体流,ffplay可以当作一个简易的媒体播放器,**ffmpeg**则能够转换多媒体文件格式。
+
+如果你感兴趣,以下列出的是FFmpeg框架中包含的开发者库:
+
+- libavutil是一个包含简化编程功能的库,其中包括随机数生成器,数据结构,数学代码,核心多媒体工具等更多东西。
+- libavcodec是一个包含音频/视频解码器和编码器的库。
+- libavformat是一个包含了多媒体格式的分离器和混流器的库。
+- libavdevice是一个包含输入输出设备的库,用于捕捉和渲染很多来自常用的多媒体输入/输出软件框架的数据,包括Video4Linux,Video4Linux2,VfW和ALSA。
+- libavfilter是一个包含媒体过滤器的库。
+- libswscale是一个用于执行高度优化的图像缩放和颜色空间/像素格式转换操作的库。
+- libswresample是一个用于执行高度优化的音频重采样,重新矩阵和取样格式转换操作的库。
+
+**注意**:ffmpeg和FFmpeg不是同一个东西。FFmpeg是框架,而ffmpeg是一个其中的一个功能。
+
+### 开始行动 ###
+
+如果你想跟着教程做,你需要在你的linux机中安装ffmpeg命令行功能。Ubuntu用户可以在终端运行以下命令轻松安装ffmpeg功能。
+
+ sudo apt-get install ffmpeg
+
+Fedora用户可以从源中直接安装ffmpeg。
+
+ yum install ffmpeg
+
+或者你可以编译源代码。在你使用源代码编译并安装它之前,你需要从官网上下载源代码,使用以下命令。
+
+ wget http://www.ffmpeg.org/releases/ffmpeg-2.2.3.tar.bz2
+
+用下面命令解压文档。
+
+ tar -xvjf ffmpeg-2.2.3.tar.bz2
+
+文档解压完成后进入解压后的目录运行以下命令。
+
+ ./configure
+ make
+
+编译完成后运行下面的命令安装ffmpeg。
+
+ su -c 'make install'
+
+全部的事情并没有完成,而你将要做的所有事就是在终端键入一些命令而且将能够从任何视频文件中抓取图片。
+
+在做之后的步骤前,确保你在想要提取图片的视频文件的目录下。使用cd命令切换到正确的目录。教程中我使用的视频在我的桌面上,我用以下命令将目录切换到我的桌面。
+
+ cd /home/oltjano/Desktop
+
+之后我使用以下命令从视频中提取图片。
+
+ ffmpeg -i "你是我的小呀小苹果儿.mp4" -r 1 -q:v 2 -f image2 image-3%d.jpeg
+
+**-i**选项用来获取输入文件,在这里是视频文件名**你是我的小呀小苹果儿.mp4**,-r选项设置每秒提取图片的帧数。我想要每秒提取一帧。
+
+之后有一个重要的选项是-q:v,应该留意这个选项并且我很喜欢用它,它用来设置提取到的图片质量。我总是设置值为2来从视频中获取高质量图片。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/extract-images-videos-using-ffmpeg/
+
+译者:[linuhap](https://github.com/linuhap) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201406/20140607 How To Install iCup 2014 In Linux.md b/published/201406/20140607 How To Install iCup 2014 In Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dd38b3238c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140607 How To Install iCup 2014 In Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+在Linux上用iCup追世界杯
+================================================================================
+
+
+嗨,Linux 极客们,
+
+在本文简短的叙述中,我将教您如何在Linux中安装一个非常棒的2014FIFA世界杯APP。这个应用叫iCup,支持Windows,Mac以及伟大的Linux。
+
+我看足球比赛已经有很长的时间了,所以我得在我的电脑上装个这样的应用来保持更新2014世界杯的最新情况。我可不想在我朋友们面前看起来像一无所知的笨货。iCup应用正好提供了每一场赛程、比分、球队教练组等信息。更有提供实时比赛更新,给您提供 正在进行的比赛的最新数据。
+
+### 支持以下功能: ###
+
+- 30种语言支持,完全本地化(使用语言菜单选择)
+- 独家的灵活界面可随意调整窗口大小
+- 可按日期或阶段检索比赛日历
+- 可视化分组
+- 支持自动转变比赛时间来适应本地时间和格式
+- 一键化社交网络发表比赛评论(支持Facebook,Google+和Twitter)
+- 支持代理(支持基本认证和摘要认证方法)
+
+我已经在Ubuntu12.04LTS上用过而且真的很好用!目前为止,这款软件还没有出错或者崩溃过。通过[官方网站][1]您可以下载到压缩包并且十分轻松地安装这个很棒的应用,然后您可以解压到任何您喜欢的地方。解压完成后,双击iCup 2014 FREE- Brazil运行。
+
+iCup真心好用,我希望您也能用其享受世界杯!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/install-icup-2014-linux/
+
+译者:[Vic020](http://www.vicyu.net) 校对:[213edu](http://ryanhu.me/)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.e-link.it/icup/brazil2014/icup-brazil-2014-desktop-app.php
diff --git a/published/201406/20140607 Linux--Bash Delete All Files In Directory Except Few.md b/published/201406/20140607 Linux--Bash Delete All Files In Directory Except Few.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d75e0c9ce5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140607 Linux--Bash Delete All Files In Directory Except Few.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+Linux:使用bash删除目录中的特定文件
+================================================================================
+
+
+我是一名Linux新用户。现在我需要清理一个下载目录中的文件,其实我就是想从~/Download/文件夹删去除了以下格式的文件外所以其它文件:
+
+- *.iso - 所有的iso格式的文件。
+- *.zip - 所有zip格式的文件。
+
+我如何在一个基于Linux,OS X 或者 Unix-like 系统上的bash shell中删除特定的文件呢?
+
+Bash shell 支持丰富的文件模式匹配符例如:
+
+- * - 匹配所有的文件。
+- ? - 匹配文件名中的单个字母。
+- [...] - 匹配封闭括号中的任何一个字母。
+
+### 策略 #1: 见识一下扩展的模式匹配符 ###
+
+这里你需要用系统内置的shopt命令来开启shell中的extglob选项,然后你就可以使用扩展的模式符了,这些模式匹配符如下:
+
+1. ?(模式列表) - 匹配零次或一次给定的模式。
+1. *(模式列表) - 匹配零次或多次给定的模式。
+1. +(模式列表) - 至少匹配一次给定的模式。
+1. @(模式列表) - 匹配一次给定的模式。
+1. !(模式列表) - 不匹配给定模式。
+
+一个模式列表就是一个或多个用 | 分开的模式(文件名)。
+
+首先要打开extgolb选项:
+
+ shopt -s extglob
+
+#### 在Bash中删掉除*.zip和*.iso文件以外的所有文件 ####
+
+rm 命令的语法格式为:
+
+ ## 仅保留 file1 文件 ##
+ rm !(file1)
+
+ ## 仅保留 file1 和 file2 文件##
+ rm !(file1|file2)
+
+ ## 仅保留 zip 文件 ##
+ rm !(*.zip)
+
+ ## 仅保留 zip 和 iso 文件 ##
+ rm !(*.zip|*.iso)
+
+ ## 你也可以使用完整的目录 ##
+ rm /Users/vivek/!(*.zip|*.iso|*.mp3)
+
+ ## 也可以传递参数 ##
+ rm [选项] !(*.zip|*.iso)
+ rm -v !(*.zip|*.iso)
+ rm -f !(*.zip|*.iso)
+ rm -v -i !(*.php)
+
+最后,关闭 extglob 选项方法如下:
+
+ shopt -u extglob
+
+### 策略 #2: 使用bash的 GLOBIGNORE 变量删除指定文件以外的所有文件 ###
+
+摘自 [bash(1)][1] 手册页:
+
+> 这是一个用冒号分开的模式列表,通过路径展开方式定义了要忽略的文件集合。如果一个匹配到路径展开模式的文件也匹配GLOBIGNORE中的模式,那么它会从匹配列表中移除。
+
+要删除所有文件只保留 zip 和 iso 文件,应如下设置 GLOBIGNORE:
+
+ ## 只在 BASH 中可行 ##
+ cd ~/Downloads/
+ GLOBIGNORE=*.zip:*.iso
+ rm -v *
+ unset GLOBIGNORE
+
+### 策略 #3: 用 find 命令删除所有其它文件仅保留 zip 和 iso 文件 ###
+
+
+如果你正在使用 tcsh/csh/sh/ksh 或者其它shell,你可以在Unix-like系统上试着用下面find命令的语法格式来删除文件:
+
+ find /dir/ -type f -not -name '匹配模式' -delete
+
+或者
+
+ ## 对于怪异的文件名可以使用 xargs ##
+ find /dir/ -type f -not -name '匹配模式' -print0 | xargs -0 -I {} rm {}
+ find /dir/ -type f -not -name '匹配模式' -print0 | xargs -0 -I {} rm [选项] {}
+
+
+想要删除 ~/source 目录下除 php 以外的文件,键入:
+
+ find ~/sources/ -type f -not -name '*.php' -delete
+
+或者
+
+ find ~/sources/ -type f -not -name '*.php' -print0 | xargs -0 -I {} rm -v {}
+
+只保留 *.zip 和 *.iso 文件的语法如下:
+
+ find . -type f -not \( -name '*zip' -or -name '*iso' \) -delete
+
+
+更多信息参见[bash command man page][1]和[find command man page][2]。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/linux-bash-delete-all-files-in-directory-except-few/
+
+译者:[Linchenguang](https://github.com/Linchenguang) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man1/bash.1.html
+[2]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man1/find.1.html
diff --git a/published/201406/20140607 New OpenSSL breach is no Heartbleed-but needs to be taken seriously.md b/published/201406/20140607 New OpenSSL breach is no Heartbleed-but needs to be taken seriously.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..733881d0e1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140607 New OpenSSL breach is no Heartbleed-but needs to be taken seriously.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+新的OpenSSL分支未包含Heartbleed漏洞,但需要认真看待
+================================================================================
+> 摘要:当被最新的OpenSSL安全问题困扰时,你最好解决它,虽然它并不像Heartbleed那样糟糕。
+
+这一周对于开源的Secure Socket Layer (SSL)来说真是糟糕的一周。
+
+首先,[GnuTLS低调的宣称,存在一个不大][1]但确实存在的缺陷。然后,大范围流行的OpenSSL被发现包含一个[中间人漏洞][2]。在[Heartbleed漏洞][3]惨剧后,OpenSSL要醒醒了。
+
+
+
+这个漏洞,根据谷歌高级软件工程师Adam Langley描述,已经[至少存在了15年时间][4]。可惜Core Infrastructure Initiative(CII)[提供了让更多的程序员来拯救OpenSSL的资金][5],却尚未来得及发挥作用。
+
+也就是说这个漏洞依然是和Heartbleed漏洞一样糟糕。对于一些新手,攻击者需要在系统和浏览器或其它启用了SSL的客户端之间来利用这个安全漏洞。
+
+尽管它只是可能被利用,你依然需要尽可能快的通过升级来解决这个漏洞。就像[NTT Com Security][6]的评估服务负责人Chris Camejo在邮件采访里说的,“这很糟糕,因为已经存在了这么长的时间,看起来传播范围相当广泛。”
+
+他补充到:“如果利用它,攻击者可以解密流量。从SSL的设计目的看,这是一个很严重的问题。SSL被广泛地用来在网站和邮件中保护很多的密码,信用卡卡号和其他的敏感信息。”
+
+在另外一个采访中,Red Hat的产品安全高级负责人Mark Cox详细深入地介绍了[细节][7]。Cox说,OpenSSL已修正了一些安全缺陷,但是我们需要想办法告诉人们不要因为Heartbleed而陷入恐慌。
+
+Cox解释说,Heartbleed漏洞在公布之前得到了修补,但利用此漏洞的消息在修补程序之前传开,因此在这个问题上招致了许多抱怨。最新的情况,已有七个安全问题得到了修补,但其中只有两项需要管理员和用户的关注。
+
+Cox继续说道,第一个,是数据报传输层安全 (DTLS)的bug。到目前为止,还没有已知的攻击,但是存在针对它攻击成功的潜在性。
+
+因此,虽然DTLS使用不广泛,如果您确实在使用它,它应尽快修补。
+
+Cox然后说,“这个问题的实际上是中间人攻击”。实际上,真的要有个“在中间的”人,来利用易受攻击的服务器和客户端之间的漏洞。
+
+但如果有人真的这样做到了,他们就能“绕过SSL并拿到原始数据...这是一个相当严重的问题”。
+
+但是,如同从理论上讲任何人都可以利用Heartbleed漏洞来攻击SSL服务器。攻击并利用此漏洞需要能接触到客户端和服务器之间的通信网络。例如,成功的攻击可能需要架设一个假的公开Wi-Fi接入点,才能攻击到使用这个WIFI的Android版本的Chrome网络浏览器与未安装修补程序的Web服务器之间的SSL通讯。幸运的是,谷歌[已经发布了更新的版本的浏览器][8],35.0.1916.141,以消除此问题。
+
+Cox继续说,最易受攻击的系统是未安装修补程序的Android设备使用一个假的Wi-Fi接入点。Morrell补充说因为Android用户并没有被他们的手机供应商和电信公司重视,安全漏洞更新前他们可能会受漏洞影响相当长的时间。
+
+幸运的是,如果他们用连接的服务器已经更新,他们也不会受到攻击。
+
+OpenSSL安全社区自5月初以来已经知道这个问题。社区与Red Hat、其他主要Linux和开源社团和硬件供应商,要解决这个问题,不只是简单修补bug,而且要测试修复,以便他们可以确认漏洞已经修复,大家都已经安全了,而没有引入任何新的安全问题,并可在大多数 OpenSSL服务器和客户端的组合上工作。
+
+现在,这个补丁已经有了,OpenSSL试着通过补丁解决安全缺陷,向公众表明对这些问题不必有任何不必要的恐慌。Cox补充说,主要的Linux供应商,如Red Hat和Ubuntu,已经有可用的修补程序。
+
+所有的管理员都需要给服务器下载并安装补丁,而不是放任安全漏洞。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.zdnet.com/new-openssl-breech-is-no-heartbleed-but-needs-to-be-taken-seriously-7000030273/
+
+译者:[lolipop](https://github.com/stduolc) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.zdnet.com/another-serious-gnutls-bug-exposes-linux-clients-to-server-attacks-7000030205
+[2]:http://www.zdnet.com/openssl-fixes-another-severe-vulnerability-7000030253/
+[3]:http://www.zdnet.com/heartbleed-serious-openssl-zero-day-vulnerability-revealed-7000028166
+[4]:https://www.imperialviolet.org/2014/06/05/earlyccs.html
+[5]:http://www.zdnet.com/corporations-put-their-cash-where-their-open-source-security-is-7000030023/
+[6]:http://www.nttcomsecurity.com/us/
+[7]:http://ec.libsyn.com/p/6/a/5/6a58036510bae37c/CloudEvangelistPodcast_Ep92_MarkCox.mp3?d13a76d516d9dec20c3d276ce028ed5089ab1ce3dae902ea1d06c88537d1ce596fdc&c_id=7251647)
+[8]:http://googlechromereleases.blogspot.com/2014/06/chrome-for-android-update.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/201406/20140607 Nuvola Player 2.4.0 Released -- A Online Cloud Music Player for Linux.md b/published/201406/20140607 Nuvola Player 2.4.0 Released -- A Online Cloud Music Player for Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fe32c4c48d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140607 Nuvola Player 2.4.0 Released -- A Online Cloud Music Player for Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
+Linux下的在线云音乐播放器 —— Nuvola Player 2.4.0发布
+================================================================================
+**Nuvola Player**是一个开源的播放器,可以在其web界面中运行像Amazon云播放器,Bandcamp,Deezer,8tracks,Google Play音乐,Grooveshark,Hyper Machine以及Pandora等等云音乐服务,同时它也能整合到Linux桌面中。
+
+该应用程序以插件的形式提供了大量的功能特性,像桌面通知、系统托盘、多媒体键、媒体播放器小程序、停靠栏菜单、歌词、last.fm等等。
+
+**2014年5月31日**,**Nuvola Player 2.4.0**的一个新版本发布了 —— 它带来了一些新的特性,包括两个新的服务“Logitech Media Server”和“This is My Jam ”,以及众多的bug修复。
+
+### 这个发布中有什么新东西 ###
+
+- 删除了破损的隐藏Google+按钮选项,因为Google修改代码过于频繁了。
+- 加快了服务设置的启用速度,不需要再重新加载。
+- 修复了暂停和播放/暂停动作开关。
+- 为Chrome添加了兼容问题警告桌面通知。
+- 提供了页面内导航按钮(现在用户可以在Google Play标识旁边的顶部栏中找到它)。
+- 添加了“Logitech Media Server”和“This is My Jam ”服务。
+- 包含了对鼠标后退/前进按钮的支持。
+- 修复了对GNOME锁屏通知的支持。
+
+要查看完整的特性列表,请访问官方发行[声明页面][1]
+
+## 在Debian, Ubuntu和Linux Mint中安装Nuvola Player ##
+
+官方的Nuvola Player仓库中包含了**Ubuntu 14.04, 13.10, 12.10, 12.04**以及**Linux Mint 17, 16, 15, 14.**可用的二进制包,你可以通过添加Nuvola Player仓库到你的系统中来安装二进制包‘nuvolaplayer’。
+
+### 在Ubuntu和Linux Mint上 ###
+
+打开终端并运行以下一系列命令:
+
+ $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:nuvola-player-builders/stable
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get upgrade
+ $ sudo apt-get install nuvolaplayer
+
+**注**:请不要忽略系统更新命令‘sudo apt-get upgrade’,否则你的apt-get安装Flash插件可能会失败。
+
+如果你不需要Nuvola Player支持Flash插件,你可以忽略系统升级命令,并使用以下命令来安装不带Flash支持得nuvolaplayer。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get --no-install-recommends install nuvolaplayer
+
+### 在Debian上 ###
+
+对于**Debian Wheezy**和**Debian Sid**,可以从官方仓库中获取稳定的Nuvola Player二进制包。你可以使用下面这一堆命令来安装最新的稳定版。
+
+首先,打开终端并导入公钥,然后添加仓库到‘**sources.list**‘文件,接着像下面这样进行一次系统更新来安装nuvolaplayer。
+
+#### Debian Wheezy ####
+
+ $ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys 706C220A
+ $ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://ppa.fenryxo.cz/nuvola-player/ wheezy main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list'
+ $ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb-src http://ppa.fenryxo.cz/nuvola-player/ wheezy main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list'
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get install nuvolaplayer
+
+#### Debian Sid ####
+
+ $ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys 706C220A
+ $ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://ppa.fenryxo.cz/nuvola-player/ sid main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list'
+ $ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb-src http://ppa.fenryxo.cz/nuvola-player/ sid main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list'
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get install nuvolaplayer
+
+**注**:Nuvola Player依赖于打包的Flash插件,而该插件会因为存在库文件冲突(**GTK+ 2和**GTK+ 3**)而默认不会安装。
+
+要解决该问题,我们需要启用flash**PPA**组件来安装‘**nuvolaplayer-flashplugin**‘包,命令如下。
+
+ $ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://ppa.fenryxo.cz/nuvola-player/ sid main beta flash" >> /etc/apt/sources.list'
+ $ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb-src http://ppa.fenryxo.cz/nuvola-player/ sid main beta flash" >> /etc/apt/sources.list'
+ $ apt-get update
+ $ apt-get install nuvolaplayer-flashplugin
+
+一旦完成安装,你可以在**菜单**中找到该应用并启动它。记住,想要听音乐,你必须连接到互联网。
+
+### Nuvola Player美图欣赏 ###
+
+
+选择音乐服务
+
+
+Grooveshark音乐服务
+
+
+Grooveshark播放音乐
+
+
+Nuvola Player首选项
+
+
+Google Play音乐
+
+
+Rdio音乐服务
+
+
+关于Nuvola Player
+
+对于其它Linux发行版,你可以从 Nuvola Player[启动板下载][2]页下载源码tarball。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-nuvola-player-in-linux/
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://nuvolaplayer.fenryxo.cz/releases/2.4.html
+[2]:https://launchpad.net/nuvola-player/+download
diff --git a/published/201406/20140607 Practical Interview Questions and Answers on Linux Shell Scripting.md b/published/201406/20140607 Practical Interview Questions and Answers on Linux Shell Scripting.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..460f0d01ec
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140607 Practical Interview Questions and Answers on Linux Shell Scripting.md
@@ -0,0 +1,174 @@
+实用的Linux SHELL面试问题及答案
+================================================================================
+
+随着之前有关面试的系列文章,读者的反应比较强烈,所以我决定出一篇有关Linux Shell相关的面试文章,如果对本文有什么意见或意见的话,欢迎反馈到我的邮箱里。
+
+如果想要阅读已发表在Tecmint.com的文章,可以点击链接,链接到[访谈系列] [1],在这里我们已经介绍很多题目即文章。,FTP,MySQL和Apache的,脚本,Linux命令等。
+
+
+> 实用的shell脚本面试问题
+
+这边提到的5个面试问题,延续之前的有关Linux面试问题和答案。如果你是Tecmint.com的读者,你的支持我非常感谢。
+
+### 1. 写一个shell脚本来得到当前的日期,时间,用户名和当前工作目录。 ###
+
+> **答案** : 输出用户名,当前日期和时间,以及当前工作目录的命令就是logname,date,who i am和pwd。
+
+现在,创建一个名为**`userstats.sh`**文件,将下面的代码添加到它。
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+ echo "Hello, $LOGNAME"
+ echo "Current date is `date`"
+ echo "User is `who i am`"
+ echo "Current directory `pwd`"
+
+给它添加执行权限,并且执行他。
+
+ # chmod 755 userstats.sh
+ # ./userstats.sh
+
+#### 样例输出 ####
+
+ Hello, avi
+ Current date is Sat Jun 7 13:05:29 IST 2014
+ User is avi pts/0 2014-06-07 11:59 (:0)
+ Current directory /home/avi/Desktop
+
+### 2.写一个shell脚本,进行两个数字的相加,如果没有输入参数就输出错误信息和一行使用说明###
+
+> **答案** : 下面是简单的shell脚本以及描述,如果没有命令行参数,它会抛出错误与如何使用脚本的说明。
+
+再创建一个名为**`twonumbers.sh`**文件和下面的内容添加到文件里。
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+ # The Shebang
+
+ if [ $# -ne 2 ]
+ # If two Inputs are not received from Standard Input
+
+ then
+ # then execute the below statements
+
+ echo "Usage - $0 x y"
+ # print on standard output, how-to use the script (Usage - ./1.sh x y )
+
+ echo " Where x and y are two nos for which I will print sum"
+ # print on standard output, “Where x and y are two nos for which I will print sum ”
+
+ exit 1
+ # Leave shell in Error Stage and before the task was successfully carried out.
+
+ fi
+ # End of the if Statement.
+
+ echo "Sum of $1 and $2 is `expr $1 + $2`"
+ # If the above condition was false and user Entered two numbers as a command Line Argument,
+ it will show the sum of the entered numbers.
+
+给他添加可执行权限,并且执行。
+
+ # chmod 755 two-numbers.sh
+
+**情形一**: 未输入两个数字作为命令行参数运行脚本,你将得到下面的输出。
+
+#### 样例输出 ####
+
+ # ./two-numbers.sh
+
+ Usage - ./two-numbers.sh x y
+ Where x and y are two nos for which I will print sum
+
+**情形二**: 当数字存在时,你会得到如图所示的结果。
+
+ $ ./two-numbers.sh 4 5
+
+ Sum of 4 and 5 is 9
+
+因此,上述shell脚本满足了问题的要求。
+
+### 3.你需要打印一个给定的数字的反序,如输入10572,输出27501,如果没有输入数据,应该抛出错误和使用脚本说明。在此之前,告诉我你需要在这里使用的算法。 ###
+
+#### 算法 ####
+
+1. 输入的数字为n
+2. 赋值 rev=0, sd=0 (反向和单个数字设置为0)
+3. n % 10, 将得到最左边的数字
+4. 反向数字可以用这个方法生成 rev * 10 + sd
+5. 对输入数字进行右位移操作(除以10)
+6. 如果n > 0, 进入第三步,否则进行第七步
+7. 输出rev
+
+现在,创建一个名为**`numbers.sh**`文件,并添加以下代码。
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+ if [ $# -ne 1 ]
+ then
+ echo "Usage: $0 number"
+ echo " I will find reverse of given number"
+ echo " For eg. $0 0123, I will print 3210"
+ exit 1
+ fi
+
+ n=$1
+ rev=0
+ sd=0
+
+ while [ $n -gt 0 ]
+ do
+ sd=`expr $n % 10`
+ rev=`expr $rev \* 10 + $sd`
+ n=`expr $n / 10`
+ done
+ echo "Reverse number is $rev"
+
+授予对文件的执行权限,并运行如下所示的脚本。
+
+ # chmod 755 numbers.h
+
+**情形一**: 当输入不包含命令行参数,你将得到下面的输出。
+
+#### 样例输出 ####
+
+ ./numbers.sh
+
+ Usage: ./numbers.sh number
+ I will find reverse of given number
+ For eg. ./2.sh 123, I will print 321
+
+**情形二**: 正常输入
+
+ $ ./numbers.sh 10572
+
+ Reverse number is 27501
+
+上面的脚本非常完美,输出正是我们需要的。
+
+### 4. 你应该直接用终端,而不是依靠任何shell脚本来进行实数计算。你会怎么做(比如实数7.56+2.453)? ###
+
+> **答案** : 我们需要用如下所述的特殊方式使用bc命令。将7.56+2.453作为输入通过管道进入bc中。
+
+ $ echo 7.56 + 2.453 | bc
+
+ 10.013
+
+### 5. 你需要给出圆周率的值,精度为小数点后100位,什么是最简单的方法。 ###
+
+> **答案** : 找圆周率的值最简单的方法,我们只是需要发出以下命令。
+
+ # pi 100
+
+ 3.141592653589793238462643383279502884197169399375105820974944592307816406286208998628034825342117067
+
+很明显!安装我们必须有包**`pi`**。只用一个**apt**或**yum**命令,就能获得所需的软件包,同时用最简单方法来实现这个需求。
+
+就是这样。我会很快在Tecmint.com发表另一个有趣的文章。至此敬请关注。别忘了向我们提供您在的评论和反馈。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/practical-interview-questions-on-linux-shell-scripting/
+
+译者:[MikeCoder](https://github.com/MikeCoder) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/category/interview-questions/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/201406/20140607 Steam Hits The Big 500 For Linux Games.md b/published/201406/20140607 Steam Hits The Big 500 For Linux Games.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8bf6cc7b5f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140607 Steam Hits The Big 500 For Linux Games.md
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+Steam平台Linux游戏突破500大关
+================================================================================
+
+
+这是一个很棒的里程碑不是吗?Steam上现在已经有500个(截至6月7日已有509个)兼容Linux的游戏了,对任何人而言这都着实是个巨大的数目。人们将不再一直说着“可是Linux上没有游戏”,但令人悲伤的是他们会说Linux上几乎没有AAA级的游戏大作(这确实是事实),但这会是一个循序渐进建立起游戏生态的过程。
+
+我一直在说这个(译注:指Linux游戏会增多的), 但我仍从没想过我们会有一天像这样实现它。我毫不怀疑今年晚些时候我们能够有XCOM,Civilization(文明)以及更多即将到来游戏令人惊喜的发布消息。
+
+一旦Steam Machines/SteamOS发布,如果它们获得了成功我们应该可以看到Linux平台游戏数目甚至上升得更快。
+
+所以,Steam上的支持Linux平台的游戏数目达到1000还要多久?也许是今年末,谁知道呢!
+
+我现在要去拿我的派对帽了...你也要庆祝这个里程碑吗?
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/steam-hits-the-big-500-for-linux-games.3849
+
+译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201406/20140607 Ubuntu One Formally Shuts Down.md b/published/201406/20140607 Ubuntu One Formally Shuts Down.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fcc13acc67
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140607 Ubuntu One Formally Shuts Down.md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+Ubuntu One服务正式关闭
+================================================================================
+**Ubuntu One服务现已正式关闭。在7月31日之前你还能够获取你存储的文件,否则它们将被永远删除。**
+
+Canonical在今年早些时候宣布[将会关闭这项服务][1],理由是缺乏付费用户以及和Google,Dropbox以及其它云存储服务日益增加的竞争,这是他们作出这个决定的首要原因。
+
+在尝试登录Ubuntu One控制面板的时候会显示下图所示的通知来提醒用户服务已经中止:
+
+
+
+本月早些时候Ubuntu 12.04 LTS收到了一个推送更新,提醒用户Ubuntu One不久后将会被从桌面移除,至于Ubuntu 14.04 LTS,在四月发布时就已没有预装Ubuntu One。
+
+### 获取你的数据 ###
+
+要将你的数据以**.zip**文件的形式下载下来,你只需登录,然后点击在通知下方的橙色按钮。
+
+Canonical也和云存储迁移服务商[mover.io][2]达成合作,允许用户直接从Ubuntu One向其它服务,比如Dropbox,Google Drive以及Copy导入文件。
+
+Mover,一个云存储迁移服务商,它盛誉Ubuntu One为“...一个世界级的文件同步及分享产品”,现向Ubuntu One用户免费提供数据迁移服务,尽管它需要用户创建一个账户。该公司通常只允许免费用户迁移最多2GB的数据。
+
+向了解通过mover.io将你的数据迁移到Google Drive的更多细节,请查阅下列知识库文章。
+
+- [从Ubuntu One向Google Drive迁移][3]
+
+### 关于退款 ###
+
+对于那些已经为额外存储空间以及Ubuntu One音乐服务付费的用户,Canonical告知这些用户将会在接下来7到10天内收到退款。
+
+如果你正在寻找Ubuntu One的替代服务,可以查看我们总结的[读者中使用的最流行的云服务][4]。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/06/ubuntu-one-discontinued-grab-files-now
+
+译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/04/canonical-axe-ubuntu-one-file-music-services-grab-data-now
+[2]:http://mover.io/
+[3]:http://support.mover.io/knowledgebase/articles/346927-how-to-transfer-from-ubuntu-one-to-google-drive
+[4]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/04/three-alternatives-ubuntu-one
diff --git a/published/201406/20140609 How To Know If Your System Has USB 3.0 Port In Linux [Quick Tip].md b/published/201406/20140609 How To Know If Your System Has USB 3.0 Port In Linux [Quick Tip].md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4b4e7a03e2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140609 How To Know If Your System Has USB 3.0 Port In Linux [Quick Tip].md
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+[小白技巧]如何在Linux中知道你的系统是否有USB 3.0 端口
+================================================================================
+
+近来的大多数的新计算机都有了USB 3.0接口了。但是**你怎么知道你的计算机有没有USB 3.0接口**?这篇短文中,我们会告诉如何在Linux下知道你的系统上有USB 3还是USB3接口。
+
+### 在Linux终端中检测是否有USB 3.0 端口 ###
+
+打开一个终端,并使用下面的命令:
+
+ lsusb
+
+这个命令会显示你系统下USB的总线信息。检查一下结果,如果你看到像“3.0 root hub”字样,这意味着你系统有USB 3.0。比如,在我的电脑上,它这样显示:
+
+
+
+这个技巧在所有的Linux系统上,像Ubuntu,Linux Mint,Fedora等等都有效。现在当你知道你有USB 3.0 端口之后,**如何辨别哪个口是USB 3.0,哪个是USB 2.0。
+
+### 辨别哪个口是USB 3.0 ###
+
+通常USB 3.0 口被标记为SS(“Super Speed”的缩写)。如果你的系统制造商没有标记SS或者USB 3,那么你可以检查端口的内部通常是蓝色的。
+
+
+
+我希望这个快捷提示能够帮助你知道你系统是否有USB 3.0 并可以分辨出USB 3.0 口
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://itsfoss.com/find-usb-3-port-linux/
+
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201406/20140609 Open Source LDAP Solutions.md b/published/201406/20140609 Open Source LDAP Solutions.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..29d7b636d9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140609 Open Source LDAP Solutions.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+开源LDAP解决方案
+================================================================================
+LDAP(轻量级目录访问协议)是一个用于访问目录服务的应用协议,它运行在TCP/IP堆栈的上一层,采用简单的编码方法,并提供了便捷的方式来连接到互联网目录,特别是基于X.500的目录服务,并对它们进行搜索和修改。LDAP是一个开放的、中立的,并且具有工业标准的应用协议,它采用客户端-服务器模式。
+
+该协议主要针对管理应用程序和提供对目录读/写操作的浏览器应用程序。
+
+使用LDAP服务器的主要好处在于,整个组织的信息可以合并到一个中央仓库统一管理。LDAP支持安全套接协议层(SSL)和传输层安全协议(TLS),因而敏感信息可以受到保护。LDAP服务器用于多种任务,包括但不限于这些服务:用户认证、机器认证、用户/系统分组、资源追踪、组织演示以及应用配置存储。
+
+为了提供对可用开源软件质量的深刻了解,我们列出了5个高品质的LDAP解决方案。
+
+现在,让我们浏览手头上的5个LDAP解决方案吧。每个标题,我们都提供了连接页面,里面有对其功能特性的深度分析,同时提供了相关资源和评论的链接。
+
+### LDAP解决方案 ###
+
+- [389目录服务器][1] - 企业级开源LDAP服务器
+- [OpenDJ][2] - API经济的云目录服务
+- [OpenLDAP][3] - 应用程序和开发工具的LDAP套件
+- [freeIPA][4] - 身份/策略管理
+- [ApacheDS][5] - 编写的LDAP和Kerberos服务器
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20140607022012848/LDAPSolutions.html
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://port389.org/
+[2]:http://opendj.forgerock.org/
+[3]:http://www.openldap.org/
+[4]:http://www.freeipa.org/
+[5]:http://directory.apache.org/apacheds/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/201406/20140609 OpenELEC 4.0.4 现已发布, 基于 XBMC 13.1 “Gotham”.md b/published/201406/20140609 OpenELEC 4.0.4 现已发布, 基于 XBMC 13.1 “Gotham”.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f68626be5f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140609 OpenELEC 4.0.4 现已发布, 基于 XBMC 13.1 “Gotham”.md
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+嵌入式多媒体中心 OpenELEC 4.0.4
+================================================================================
+
+![] (http://i1-news.softpedia-static.com/images/news2/OpenELEC-4-0-4-Is-Out-and-Based-on-XBMC-13-1-quot-Gotham-quot-445802-2.jpg)
+
+**OpenELEC 4.0.4已经发布,它是一个专门设计运行XBMC的嵌入式系统,一个开放源代码的娱乐媒体中心。它构建 XBMC 13.1 基础之上。**
+
+OpenELEC 开发商非常密切地跟着 XBMC 的产品开发周期,目前已经发布了他们的最新的 4.0.4 的版本。它基于 XBMC 13.1 "Gotham",并且开发者们做了一些自己的改动。
+
+“此版本包括一些bug修正、安全修复和来自于 OpenELEC 4.0.3 的改进。除了通常的错误修正和软件包更新,我们已经使用最新的补丁文件升级 XBMC 至最新的 XBMC 13.1 (final)。这个版本包含了在 XBMC 13.0 发布之后的很多已知问题的修复(其中有些我们已包括 OpenELEC 4.0.0中)。”
+
+“我们在popcornmix的帮助下发现并修复了一些和树莓派相关内核问题、 固件和 XBMC 代码中的问题,非常感谢他的帮助 !OpenELEC 4.0.4 现在是一个稳定版本,包含了OpenELEC 4.0系列的bug修正和安全漏洞修复 。”开发商的官方网站上如是写道。
+
+OpenELEC 4.0.4 界面更加美观而且更新和修复了许多问题。例如,e2fsprogs 已更新到版本 1.42.10、 bluez 已更新到版本 5.19、 fontconfig 版本更新到 2.11.1,也默认集成了 systemd 213 和修复了一些安全问题的gnutls 3.2.12,而且使用了一个新的 Linux 内核3.14.5。
+
+此外,DVB T2 已经添加了对 GeniaTech T220 / August T210 设备的支持,由于其驱动程序尚不完善而允许禁用WOL、也添加了尚不完善的"e1000e"驱动,树莓派的支持补丁已更新。
+
+如果你已经有一个旧版的 OpenELEC,你可能需要考虑升级的系统而不是从头开始安装它。如果想顺利地完成安装,至少应该是 3.2 版本。
+
+如果您尝试从旧版本操作系统的更新,您可能发现一些插件和插件都不再工作。所以最明智的办法就是,在尝试升级之前备份你的系统。
+
+以 XBMC 13.1 "Gotham" 版本为基,配有 Android 硬件解码、 许多树莓派和 Android 速度方面的改善,立体 3D 渲染,更好的触摸屏支持,改进了 UPnP 功能,很多的音频引擎的改进,更好地字幕搜索、 对开发者增加的如 Python 和 JSON RPC API等 ,FFmpeg 1.2,还有更多。
+
+查阅官方 [公告] [1] 的更改和改进的完整列表。
+
+### 下载最新的 OpenELEC 4.0.4: ###
+- [OpenELEC 4.0.4 (tar.bz2) 64-bit][2][binary] [145 MB]
+- [OpenELEC 4.0.4 (tar.bz2) 32-bit][3][binary] [142 MB]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/OpenELEC-4-0-4-Is-Out-and-Based-on-XBMC-13-1-quot-Gotham-quot-445802.shtml
+
+译者:[owen-carter](https://github.com/owen-carter) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://openelec.tv/news/22-releases/129-openelec-4-0-4-released
+[2]:http://openelec.tv/get-openelec/download/viewdownload/8/339
+[3]:http://openelec.tv/get-openelec/download/viewdownload/8/338
diff --git a/published/201406/20140610 How to set up Internet connection sharing with iptables on Linux.md b/published/201406/20140610 How to set up Internet connection sharing with iptables on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..34066c0167
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140610 How to set up Internet connection sharing with iptables on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
+怎样使用linux的iptables工具进行网络共享
+================================================================================
+
+在本教程中,我将解释多个设备怎样在linux下共享一个网络连接。目前无线路由器已经成为主流的消费品,从而解决了本文这一问题。这里假设你家中并没有一台无线路由器,不过,你却有一台已经有"猫"和有线网卡的的linux主机。"猫"是以动态公有IP地址的模式连接到互联网,主机的网卡连接到你的交换机或者集线器。其他设备(如linux或者windows的PC或者笔记本)以网桥的形式连接,并且没有连接到互联网。为了共享linux主机的互联网,你必须把主机转换成网关,以便它能实现从其他设备中传送和接受信息。
+
+### 术语字汇 ###
+
+
+- **私有IP地址**(路由不可达地址)是一个被用于本地局域网的IP地址(在互联网中不可见)。
+- **公用IP地址**(路由可达地址)是一个在互联网中可见的IP地址。
+- **IP伪装**是一项允许一系列机器通过MASQ网关连接互联网的功能。这些MASQ网关之外的机器在互联网中是不可见的。MASQ之后的机器中任何流入或流出的数据必须经过MASQ网关。
+- **网络地址转换**(NAT)是一项通过IP伪装技术可以使私有IP地址访问互联网的功能。
+
+### Hardware Requirements ###
+
+硬件要求
+
+- 一台有两个接口(一个公有IP地址和其他的私有IP地址)的linux主机,这个主机将被用作网关。
+- 一台或者多台拥有私有IP地址的linux/windows系统的PC或者笔记本。
+- 交换机/集线器(可选)。
+
+### 教程步骤 ###
+
+接下来的过程需要在linux主机(用于共享的网关)上完成。
+
+#### 1、激活IP转发 ####
+
+为了设置网络共享,你需要在linux主机上更改一个内核参数来使能IP转发功能。内核启动参数设定在/etc/sysctl.conf文件中。
+
+打开这个文件,定位到含有"# net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0"的这一行,移除#号(即取消注释),然后将其值设置为1,改好之后应该和下面的一致。
+
+ net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
+
+你还要使激活IP转发功能生效,通过执行下面的命令:
+
+ $ sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
+ $ sudo sysctl -p
+
+#### 2、NAT配置 ####
+
+另一个网络共享的重要部分是NAT配置,这可以通过使用iptables的命令,iptables包含四个防火墙的规则表:
+
+- FILTER (默认表格)
+- NAT
+- MANGLE
+- RAW
+
+这个教程中我们将仅使用两个表格:FILTER和NAT表格。
+
+首先,刷新所有活跃的防火墙的规则。
+
+ $ sudo iptables -X
+ $ sudo iptables -F
+ $ sudo iptables -t nat -X
+ $ sudo iptables -t nat -F
+
+
+在输入表格中,你需要设置转发链(FORWARD)成可接受的(ACCEPT)目的地,因此所有通过主机的数据包将会被正确的处理。
+
+ $ sudo iptables -I INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
+ $ sudo iptables -I FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
+
+
+在NAT表中,你必须为你的WAN口启用IP伪装功能,我们假设WAN口协议是ppp0。为了在ppp0接口上使能IP伪造技术,我们使用以下的命令:
+
+ $ sudo iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -o ppp0 -j MASQUERADE
+
+#### 3、配置私有IP地址 ####
+
+在linux主机上的所有配置完成后,你需要配置其他设备(linux/windows的PC或笔记本)的DNS服务器以及默认网关,让它们的数据流可以指向linux主机。注意你不需要在linux主机上设置一个DNS服务器,从其他设备发出的每一个DNS请求都会通过上游的ISP自动转发到linux主机上。
+
+如果你的其他设备上用的系统是linux,你可以通过以下命令来更改他们的默认网关和DNS服务器。假设你的网段是192.168.1.0/24的私有IP地址网段,linux主机上绑定的IP地址是192.168.1.1。
+
+ $ sudo ip route del default
+ $ sudo ip route add default via 192.168.1.1
+ $ sudo sh -c "echo 'nameserver 192.168.1.1' > /etc/resolv.conf"
+
+如果还有其他的linux设备,那么你可以重复以上命令。
+
+如果你有windows设备,你可以通过控制面板的网络连接属性来更改默认网关和DNS服务器。
+
+#### 4、完整的脚本 ####
+
+这是一个在linux主机上设置网络连接共享的一个完整的脚本。WAN口(ppp0协议)需要根据你具体的网络接口协议来替换。
+
+ $ sudo vi /usr/local/bin/ishare
+
+----------
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+
+ ## Internet connection shating script
+
+ sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
+ sysctl -p
+ iptables -X
+ iptables -F
+ iptables -t nat -X
+ iptables -t nat -F
+ iptables -I INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
+ iptables -I FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
+ iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -o ppp0 -j MASQUERADE
+
+保存以上的脚本到/usr/local/bin/ishare,然后添加可执行权限通过执行下面的命令。
+
+ $ sudo chmox +x /usr/local/bin/ishare
+
+如果你需要这个脚本开机启动,你需要在/etc/rc.local文件中执行这个脚本,并在该文件中的"exit 0"之前添加下面一行。
+
+ /usr/local/bin/ishare
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/06/internet-connection-sharing-iptables-linux.html
+
+译者:[yujianxuechuan](https://github.com/yujianxuechuan) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201406/20140610 IPFire 2.13 Core 78 Linux Firewall OS Receives OpenSSL Fixes.md b/published/201406/20140610 IPFire 2.13 Core 78 Linux Firewall OS Receives OpenSSL Fixes.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d067b72f80
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140610 IPFire 2.13 Core 78 Linux Firewall OS Receives OpenSSL Fixes.md
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+Linux防火墙发行版 IPFire 发布新版本
+================================================================================
+
+
+**ipfire.org团队的 Michael Tremer 发布了 IPFire 2.13 Core 78 的最新稳定版本, 这是一个基于Linux的防火墙发行版,本次发布已经包含了最新的OpenSSL补丁。**
+
+IPFire 是一个模块化 Linux 发行版,它可以用为防火墙、 代理服务器或 VPN 网关。IPFire 开发人员的主要关注点之一就是安全,每一步修改都确保用户的安全。
+
+开发者在其博客上说:“在负责提供SSL/TLS协议和其他加密功能的openssl库中发现了几个安全漏洞。详细的细节可以在原始的 openssl 安全建议里面找到”
+
+他们解释说所有计划为Core Update 78准备的更新被延迟提交到core Update 79。这意味着用户为其需要等更长时间。
+
+OpenSSL 的开发人员发现了另一轮的 OpenSSL 的问题,但问题很快被修复,最新Linux发行版已包含此次修复。
+
+开发者推荐 IPFire 的所有用户升级。更多的细节可以在[这里][1]发现.
+
+下载IPFire 2.13 Core 78:
+
+- [IPFire 2.15 Core 78 (ISO)][2][iso] [122 MB]
+- [IPFire 3.0 Alpha 1 (ISO)][3][iso] [76 MB]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/IPFire-2-13-Core-78-Linux-Firewall-OS-Receives-OpenSSL-Fixes-445876.shtml
+
+译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.ipfire.org/news/ipfire-2-15-core-update-78-released
+[2]:http://downloads.ipfire.org/releases/ipfire-2.x/2.15-core78/ipfire-2.15.i586-full-core78.iso
+[3]:http://www.rowie.at/ipfire/iso/ipfire-3.0-alpha1.i686.iso
diff --git a/published/201406/20140610 Open Source SDN Project OpenDaylight Adds New Members.md b/published/201406/20140610 Open Source SDN Project OpenDaylight Adds New Members.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6b322e7495
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140610 Open Source SDN Project OpenDaylight Adds New Members.md
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+开源SDN项目OpenDaylight添加新成员
+================================================================================
+[Linux基金会][1]的[OpenDaylight][2] 项目旨在促进开源的[软件定义网络][3] (SDN) 发展。 [Extreme Networks][4] (EXTR), [Flextronics][5]和[Oracle][6] (ORCL) 现在也加入了该项目。
+
+三个公司6月5日正式加入OpenDaylight,其成员数达到到39。该项目还有195位协作开发人员,以建立一个开放源码的SDN平台。
+
+新成员带来了在数据中心和云计算的设计和基础设施的专长。Extreme Networks是专业提供高性能网络解决方案的企业,而Flextronics提供系统设计、生产和物流。Oracle有广泛的业务,同时专注于各种领域的云计算和数据中心。
+
+OpenDaylight 领导人很高兴该项目的会员增多,并进一步走向创造一个以开放标准为中心和避免垄断的SDN生态系统。OpenDaylight执行主任Jacques Neela说:"更多的声音意味着更多的讨论和更好的代码,我们很高兴看到各种多样性的新成员加入来加宽探讨SDN和NFV的领域"。
+
+OpenDaylight的第一款正式软件是在2013年4月发布的,该软件在同年二月首次以Hydrogen的名字出现。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/open-source-sdn-project-opendaylight-adds-new-members
+
+译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://linuxfoundation.org/
+[2]:http://www.opendaylight.org/
+[3]:http://thevarguy.com/sdn
+[4]:http://www.extremenetworks.com/
+[5]:http://www.flextronics.com/
+[6]:http://oracle.com/
+[7]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/020514/embargo-until-feb-4-1130-am-est-opendaylight-releases-fir
diff --git a/published/201406/20140610 Top 7 Desktop Environment For Linux.md b/published/201406/20140610 Top 7 Desktop Environment For Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0047b56864
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140610 Top 7 Desktop Environment For Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+Linux 平台七大桌面环境通览
+================================================================================
+通常的 Linux 发行版都使用 KDE 或者 GNOME 作为默认的桌面环境。它们都给用户提供了一个原始的并且有吸引力的桌面,并且内置了各式各样的多媒体软件、系统程序、游戏、实用程序、网页开发工具、编程工具等等。这两个桌面致力于提供给用户一个拥有类似于 Windows 操作系统体验的尖端计算环境,而不是如何更少的占用系统资源。
+
+如果你正在使用 Ubuntu (或者其他Linux发行版) 并且厌倦了始终使用 Unity 桌面,那么你应该看看这些可以替代 Unity 的选择。我收集了 7 种桌面环境。它们都很棒。在你读完这篇文章之后,请试着使用它们吧。
+
+### [Mate][1] ###
+
+
+
+MATE 是 GNOME2 的一个分支。它提供了一个自然且吸引人的桌面环境。它是 Linux 和其它类 Unix 工作环境中的传统工作框架的代表。MATE 在保留传统的桌面体验的同时正在不断进步使用新的技术。
+
+在 Ubuntu 14.04 中,可以直接从 Ubuntu 软件中心获取 MATE 桌面。
+
+### [KDE][2] ###
+
+
+
+KDE 是另一个类似于 GNOME 一样的重量级桌面环境。它在本文章所提及的7种桌面环境中被认为是最华丽最重量级的一个。它同样是一个类似于 Windows 的桌面,在这一点上没有什么特殊的变化。不过 KDE 非常有特点,但是随之而来的是可以通过大量的设置来提升你的桌面体验。同样的,有很多关于 KDE 的话题,所以你可以很舒服的使用 KDE,并让它以你希望的方式工作。
+
+### [Cinnamon][3] ###
+
+
+
+Cinnamon 是一个基于 Gtk+ 的环境。它最初作为 GNOME Shell 的一个用户界面分支,由 Linux Mint 为其创建的。 Cinnamon 的核心设计目标是让桌面终端和触屏设备都能完美操作。无论是使用鼠标,还是使用触摸屏都可以获得同样便捷的操作。不像 KDE Plasma 工作空间,只有一种图形用户体验。当前版本—— Cinnamon 2.0 于2013年10月10日发布。
+
+### [Unity][4] ###
+
+
+
+Unity 是 GNOME 桌面环境的一个界面,由 Canonical 公司创建,用于 Ubuntu 系统中。Unity 最初现身于 Ubuntu 10.10 的上网本版本中。它起初打算充分利用上网本的屏幕空间,例如一个竖直的应用启动器和一个节省空间的多功能顶部菜单栏。Unity 不像 GNOME、KDE、 Xfce 或者 LXDE 是许多软件的合集,它是为了可用性而开发的。
+
+### [GNOME Shell][5] ###
+
+
+
+GNOME 提供了桌面核心接口例如交换窗口,启动应用程序以及显示提示。它利用先进的图形硬件来实现吸引人的、创新的界面思想,提供了愉悦简单的用户体验。GNOME Shell 定义了 GNOME 3 的客户体验。
+
+作为 GNOME 的一个重要组成部分, GNOME Shell 的稳定版本首次发布于2011年3月3日。
+
+### [Xfce][6] ###
+
+
+
+Xfce 是一个轻量级的桌面环境,围绕 GTK 框架实现。它看起来很像 Gnome 2 和 MATE,然而 Xfce 是它们的轻量级替代品。相较于 KDE 和 GNOME 3 而言,Xfce 非常轻量级,所以它对于运行轻量级的工具或者那些希望实现最大执行效率的框架使用者来说是理想的环境。它还不是可以获得的最轻量级的选择 - 请继续往下看 - 然而,Xfce 的确完成了执行效率和功能的平衡。
+
+### [LXDE][7] ###
+
+
+
+LXDE 显然是桌面环境中最轻量级的选择,至少在传统的桌面标准中是这样。这个基于 GTK 的桌面环境使用了很多轻量级的选择替代了默认的应用(例如 Abiword, Gnumeric, 而不是 LibreOffice)。它没有提供炫目的视觉震撼 ,总体感觉也不是特别的棒,没有高级的设置。但是,LXDE 仍然提供了漂亮的桌面和完整的功能。当你需要快速简洁时,它就是你的选择。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://pulpybucket.com/top-7-desktop-environment-linux/
+
+译者:[wwhio](https://github.com/wwhio) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://mate-desktop.org/
+[2]:http://kde.org/
+[3]:http://cinnamon.linuxmint.com/
+[4]:https://unity.ubuntu.com/
+[5]:http://www.gnome.org/
+[6]:http://xfce.org/
+[7]:http://lxde.org/
+
diff --git a/published/201406/20140611 HTG Explains--What' s the Difference Between Linux and BSD.md b/published/201406/20140611 HTG Explains--What' s the Difference Between Linux and BSD.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c55fb6af45
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140611 HTG Explains--What' s the Difference Between Linux and BSD.md
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+Linux 与 BSD 有什么不同?
+================================================================================
+
+
+Linux 和 BSD 都是免费的,开源的,类Unix系统。他们甚至使用很多相同的软件。他们看上去简直就像是一个操作系统,那么,它们有什么不同吗?
+
+其实,两者之间的不同,远远超出了我们下面提到的这些,尤其是在构建完整操作系统和许可授权的哲学思想上,更是相差甚远。通过这篇短文将可以简单的了解它们之间的不同。
+
+### 基础 ###
+
+[许多人所称的“Linux”实际上不是 Linux][1]。Linux 从技术上说只是 Linux 内核,典型的 Linux 发行版则包括了 Linux 内核和许多软件。这是[为什么 Linux 有时被称为 GNU/Linux][2]。事实上,许多在 Linux 上使用的软件同样也在 BSD 上使用。
+
+Linux 和 BSD 都是类 UNIX 操作系统。我们可以通过阅读[类 UNIX 操作系统历史][3]发现 Linux 和 BSD 有不同的谱系。Linux 是由 Linus Torvalds 在芬兰上大学的时候开发的。BSD 则代表“Berkeley Software Distribution,伯克利软件套件”,其源于对加州大学伯克利分校所开发的贝尔实验室UNIX的一系列修改,它最终发展成一个完整的操作系统,现在有多个不同的BSD分支。
+
+
+
+### 内核 vs. 完整操作系统 ###
+
+严格的说,Linux 是只是一个内核。制作 Linux 发行版所要做的工作就是,汇集那些创建一个完整 Linux 操作系统所需的所有软件,将它组合成一个像 Ubuntu、Mint、Debian、RedHat 或者是 Arch 这样的 [Linux 发行版][4]。有许多不同的 Linux 发行版。
+
+与此相反的是,BSD 这个名字则代表其内核和操作系统。例如,FreeBSD 提供了 FreeBSD 内核和 FreeBSD 操作系统。它是作为一个单一的项目维护的。换句话说,如果你想要安装 FreeBSD,就只有一个 FreeBSD 可供你安装。如果你想要安装 Linux,你首先需要在许多 Linux 发行版之间选择。
+
+BSD 包括一个名为 Ports 的系统,它提供了一种安装软件包的方式。Ports 系统包含了软件包的源代码,所以您的计算机如果想安装软件的话,则需要先编译他们。(如果您曾经使用过以前流行的 Gentoo,有点类似那样。)不过,软件包也可以是预安装的二进制形式,以便你不需要花时间和系统资源编译他们就能运行。
+
+
+
+### 许可证 ###
+
+许可证是典型的差异,虽然它不会对大多数人产生影响。Linux 使用 GNU 通用公共许可证,即 GPL。如果你修改了 Linux 内核,并将其分发,你就必须放出您的修改的源代码。
+
+BSD 使用 BSD 许可证。如果你修改了 BSD 内核或发行版,并且发布它,你根本不需要必须发布其源代码。你可以自由地对你的 BSD 代码做任何你想做的事情,你没有义务发布的你修改的源代码,当然你想发布也行。
+
+两者都是[开放源码][5]的,但是以不同的方式。人们有时会陷入关于哪种许可证是“更自由”的辩论。GPL 可以帮助用户以确保他们可以拥有 GPL 软件的源代码,并限制开发人员迫使他们开放代码。BSD 许可证并不能确保用户可以拥有源代码,而是给开发人员选择是否公布代码的权利,即使他们想要把它变成一个闭源项目。
+
+### BSD分支 ###
+
+以下是通常认可的三个“主流” BSD 操作系统:
+
+- [FreeBSD][6]: FreeBSD 是最受欢迎的 BSD,针对高性能和易用性。它支持英特尔和 AMD 的32位和64位处理器。
+- [NetBSD][7]: NetBSD 被设计运行在几乎任何架构上,支持更多的体系结构。在他们的主页上的格言是"理所当然,我们运行在 NetBSD 上"。
+- [OpenBSD][8]:OpenBSD 为最大化的安全性设计的 —— 这不仅仅它宣称的功能,在实践中也确实如此。它是为银行和其他重要机构的关键系统设计的。
+
+还有两个其他的重要 BSD 操作系统:
+
+- [DragonFly BSD][9]: DragonFly BSD 的设计目标是提供一个运行在多线程环境中的操作系统 —— 例如,计算机集群。
+- [Darwin / Mac OS X][10]: Mac OS X 实际上基于 Darwin 操作系统,而 Darwin 系统基于 BSD。它与其他的 BSD 有点不同,虽然底层内核和其他的软件是开源代码(BSD 代码),但操作系统的大部分是闭源的 Mac OS 代码)。苹果在 BSD 基础上开发了 Mac OS X 和 iOS,这样他们就不必写操作系统底层,就像 [谷歌在 Linux 基础上开发 android 系统][11]一样。
+
+
+
+### 你为什么会选择 BSD 而不是 Linux?###
+
+Linux 显然比 FreeBSD 更受欢迎。例如,Linux 往往会比 FreeBSD 更早提供新硬件的支持。BSD 有一个兼容包可用,使之能像大多数的其他软件一样原生的执行 Linux 二进制程序。
+
+如果您使用过 Linux, FreeBSD 不会让你感觉到太大的不同。如果把 FreeBSD 作为桌面操作系统,你也可以使用相同的 GNOME,KDE 或 Xfce [桌面环境][12],你也可以在BSD上使用 Linux 上的大多数的其他软件。有一点需要注意,FreeBSD 不会自动安装的图形化桌面,所以你要花相对于 Linux 更多的心思来照顾你的BSD。BSD 更守旧一些。
+
+FreeBSD 的可靠性和稳定性也许更适合作为服务器的操作系统。而厂商也会选择 BSD 而不是 Linux 作为其操作系统,因为这样他们就不必放出他们修改的代码。
+
+如果你是一个 PC 桌面用户,你真的不需要太过在意 BSD。你可能会喜欢 Linux,因为它具有更先进的硬件支持,更容易安装,具有现代操作系统的特点。如果你关注服务器或嵌入式的设备,你可能会更喜欢 FreeBSD。
+
+我们可能会听到一些人说他们在桌面电脑上使用 FreeBSD,你当然也可能是其中之一!但像 Ubuntu 或 Mint 一样的开源操作系统对于多数用户来说更体验良好和更先进些。
+
+图片来源: [atzerok on Flickr][13]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.howtogeek.com/190773/htg-explains-whats-the-difference-between-linux-and-bsd/
+
+译者:[MikeCoder](https://github.com/MikeCoder) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.howtogeek.com/177213/linux-isnt-just-linux-8-pieces-of-software-that-make-up-linux-systems/
+[2]:http://www.howtogeek.com/139287/the-great-debate-is-it-linux-or-gnulinux/
+[3]:http://www.howtogeek.com/182649/htg-explains-what-is-unix/
+[4]:http://www.howtogeek.com/132624/htg-explains-whats-a-linux-distro-and-how-are-they-different/
+[5]:http://www.howtogeek.com/129967/htg-explains-what-is-open-source-software-and-why-you-should-care/
+[6]:http://www.freebsd.org/
+[7]:http://www.netbsd.org/
+[8]:http://www.openbsd.org/
+[9]:http://www.dragonflybsd.org/
+[10]:http://opensource.apple.com/
+[11]:http://www.howtogeek.com/189036/android-is-based-on-linux-but-what-does-that-mean/
+[12]:http://www.howtogeek.com/163154/linux-users-have-a-choice-8-linux-desktop-environments/
+[13]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/atzerok/5378691454
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/201406/20140611 How to Prevent Other Users From Accessing Your Home Directory in Ubuntu 14.04.md b/published/201406/20140611 How to Prevent Other Users From Accessing Your Home Directory in Ubuntu 14.04.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1fc3f32824
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140611 How to Prevent Other Users From Accessing Your Home Directory in Ubuntu 14.04.md
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+[小白技巧]如何在Linux中阻止其它用户访问你的家目录
+================================================================================
+
+
+如果你和其他人共享Ubuntu机器,那么你可能要设置多个用户,希望其他用户登录到他们自己的帐号,并只能访问他们自己的家目录。但是,默认情况下,任何一个用户都可以访问任何一个家目录。
+
+当你在Ubuntu中添加一个新用户时,adduser工具为新的帐号添加了一个新的家目录。默认情况下,该目录位于根下面的/home/目录下,并以该帐号的用户名命名。例如,/home/lori。Ubuntu中创建的用户家目录具有其它人可读/执行权限,这就给系统中所有其他用户可以读另外外一些用户的家目录中的内容的权利。具体请阅读我们的[文件权限在Linux中是如何工作的][1]一文。
+
+**注**:当我们在文中提到输入什么时,输入的文字内容是在引号中的,不要输入引号,除非我们另外指定。
+
+你可以很容易地修改你的家目录的权限来保护你的私人文件。要检查你家目录的权限,输入Ctrl + Alt + T打开终端窗口,并在提示符后输入以下命令,然后按回车。使用你自己的用户名来替换下面的“用户名”。
+
+ ls -ld /home/lori
+
+**注**:该命令仅包含小写的L,而不是数字1。(LCTT译注:这是给完全小白的提示,绝大部分人可以无视这个备注了)
+
+在该行的开头,列出了该文件的权限。就像我们在[文章][1]中关于Linux权限部分讲的那样。
+
+> r表示“读”,w表示“写”,而x表示“执行”。目录权限以“d”开头,而不是“-”。你也会注意到权限值占了10个位置。你可以忽略第一个,后面是3个一组,分为3组。第一组是属主(owner)权限,第二组是属组(group)权限,最后一组是其它人(other或world)权限。
+
+因此,下面列出的家目录的属主具有读、写和执行权限,而属组和其它人具有读和执行权限。
+
+
+
+要修改这些权限,在提示符下输入以下行并回车
+
+ sudo chmod 0750 /home/lori
+
+当提示你输入密码时,请输入并回车。
+
+**注**:chmod命令使用八进制数作为一种指定权限的方式。我们讲Linux权限的[文章][1]中使用了一种不同的方法,它需要几个步骤,但是可能更易于理解。使用八进制数来指定权限,是一种更快的方法。不管使用什么方法,只要你用着舒服就好。要学习使用八进制数设置权限,请阅读此[文章][2]。
+
+
+
+按上箭头两次,再次调用“ls -ld /home/用户名”命令来检查权限。注意,其它人权限现在都是破折号(-),这就意味着其它人将无法读、写或执行你家目录中的任何东西了。
+
+然而,和你同组的用户可以读和执行你家目录中的文件和文件夹。如果你不想除你之外的任何人访问你的家目录,可以在chmod命令中输入“0700”。
+
+**注**:要获取关于Linux中用户和组管理的更多信息,请查看我们的[文章][3]
+
+要关闭终端窗口,在提示符下输入“exit”并回车。
+
+
+
+现在,当其系统中的其他用户试着要访问你的家目录时,下面的对话框就会弹出来了。
+
+
+
+甚至你也可以在创建新用户时让Ubuntu使用指定的权限。要完成此项任务,你需要编辑adduser配置文件。要编辑该文件,在提示符下输入以下命令并回车。
+
+ gksudo gedit /etc/adduser.conf
+
+我们使用gedit来编辑该文件,你也可以使用你想要的其它文本编辑器。
+
+注:gksudo命令看似和sudo命令一样,但是它是用来以root身份运行图形化程序的,而sudo命令用来以root身份运行命令行程序。
+
+
+
+在弹出对话框中的密码编辑框内输入你的密码并按回车或点击确定(OK)。
+
+
+
+在adduser.conf文件中向下滚动到DIR_MODE命令处,这里的默认值是“0755”。修改该值来反映你想要授权给各种用户类型(属主,属组,其它人)的不同权限(r,w,x),如我们先前讨论过的“0750”或“0700”。点击保存(Save)。
+
+
+
+从gedit的文件(File)菜单选择退出(Quit)来关闭gedit,你也可以点击窗口左上角的X按钮来关闭它。
+
+
+
+点击窗口左上角的X来关闭终端窗口。
+
+
+
+现在,你家目录中文件会保持私有。切记,如果有其他用户和你处于同一组中,你也许要为你的家目录权限剔除组和大众权限。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.howtogeek.com/190084/how-to-prevent-other-users-from-accessing-your-home-directory-in-ubuntu-14.04/
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.howtogeek.com/67987/htg-explains-how-do-linux-file-permissions-work/
+[2]:http://www.linux.org/threads/file-permissions-chmod.4094/
+[3]:http://www.howtogeek.com/howto/36845/the-beginners-guide-to-managing-users-and-groups-in-linux/
diff --git a/published/201406/20140612 Command Line Tuesdays--Part One.md b/published/201406/20140612 Command Line Tuesdays--Part One.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..29b9dafdc2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140612 Command Line Tuesdays--Part One.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+命令行星期二 —— 第一篇
+================================================================================
+极客们,我们又回来了!真抱歉让你们久等了,但我保证,我们又回归正轨了。我们满怀热情与大家相约,让我们激情燃烧,寻找刺激吧:)
+
+现在,整个的想法已经在之前的开场白中告诉你们了,所以现在让我们来干点正事吧。就像肖茨先生书里讲得那样,我们需要来了解一下shell是个什么东西,终端模拟器又是个什么东西,因为我们要在这里头干活。
+
+肖茨在他的书中写道,shell实际上是当我们谈论命令行时所谈论的东西。shell基本上一个程序,它将你敲击键盘的动作传递给计算机;它也是某种形式的翻译器,将你所讲的东西翻译给计算机听。在这世界上活着的shell真是五花八门,但是活得最好的要数**bash**了,它在GNU/Linux中随处可见。我们也叫它Bourne Again Shell,这是一个精巧的双关语,因为自从Bourne先生创造了它的祖先**sh**后,Brian Fox又把它重写成为一个自由的sh替代品。啊哈!GUN人和他们的幽默,真的很精明。:)
+
+
+
+接下来我所需要,是一个让我们能和shell交互的东西,它就是终端模拟器。每个Linux发行版都自带了一个,至于长什么样就得看你使用的桌面环境了,可能是KDE的**Konsole**,也可能是Gnome的**Gnome terminal**等等。肖茨先生说了,你可以挖掘出你所偏爱的一个,但是大部分时间我还是用桌面环境给我提供的那个吧。
+
+现在来发动你的终端。打开后,你会见到一行字,这行字告诉你用户名和机器的主机名,它叫作shell提示符。它告诉你它准备好了,你可以输入命令了。让我们来随便玩玩,随便输入点什么东西进去,然后敲回车看看。
+
+呵呵,还记开篇我们讲过,我们需要像学诗歌一样来学习命令吗?记得就好,随意乱来可干不了啥事。
+
+现在,按那个上箭头,你会发现命令又回来了。这是啥魔法?你键盘上的上箭头用来取出历史命令。终端会保存总计500个你输入过的命令,所以别一次又一次地重复敲它们了,你可以用上/下箭头来查找它们。左右箭头用来在指定行中移动光标,这样你就可以在文本中编辑或者插入了。另外注意,想用**ctrl+v**来粘贴文本是不行的。你可以在某个地方将它设置成快捷键,但是它常常不是那么回事。检查你的模拟器的快捷键!(在Konsole中,它位于设置 > 配置快捷键)
+
+现在,为了我们不再被‘命令找不到’抽一巴掌,让我们试试一些简单的。敲个**date**来试试。(是的,我不知道有这么个命令,这真着实让我兴奋了一把):)
+
+
+
+你又来了。当你能打开终端并输入date命令来查看日期时,为什么在时钟中看看内建日历会让你不胜其烦 :) 只是开个玩笑。就像肖茨书里写的那样,它确实是个简单的命令,更有用也更复杂的命令会在以后介绍。跟date相关的命令是cal - 它会显示当前月的日历。
+
+你也可以试试**df**,它会列出你驱动器上的空闲空间。
+
+
+
+或者试试**free**来显示空闲内存:
+
+
+
+如果你已经跟上了敲击键盘的节奏,你可以输入**exit**命令来关闭终端模拟器了,而不是去点击那个x了。
+
+嗯,本周我们就到此为止吧,免得有太多的要学的东西来占据你紧巴巴的日程了。下面来个小结(你可以把结论写下来,做个备份吧),在这一篇中,我们学习了:
+
+- 什么是shell
+- 我们需要用什么来和shell交流(终端模拟器)
+- 使用光标按钮来驾驭终端命令以及退出终端
+
+四个简单的命令:
+
+- **date** – 显示当前日期
+- **cal** – 显示当前月份的日历
+- **df** – shows the amount of free space on your hard drives
+- **free** – amount of free memory
+
+### 下周二我们将会做什么呢? ###
+
+我们会学习在文件系统中导航(bin、etc等等这所有的文件夹都是些什么东西?它们用来干什么?怎样通过终端来浏览它们)。到那时……
+
+### 你就有得乐了! ###
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://news.opensuse.org/2014/06/10/command-line-tuesdays-part-one/
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/201406/20140612 Dpkg Vulnerabilities Closed in Ubuntu 14.04.md b/published/201406/20140612 Dpkg Vulnerabilities Closed in Ubuntu 14.04.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8285809c1a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140612 Dpkg Vulnerabilities Closed in Ubuntu 14.04.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+Ubuntu 14.04中Dpkg的漏洞已被修复
+================================================================================
+
+
+**Canonical宣布存在于Ubuntu 14.04 LTS,Ubuntu 13.10,Ubuntu 12.10,Ubuntu 12.04 LTS以及Ubuntu 10.04 LTS操作系统中的dpkg漏洞已经被修复。**
+
+Canonical公司刚刚放出dpkg包的一个更新,修复了这个用于所有Ubuntu版本的重要软件中的一个问题。
+
+“我们发现这个问题出现在dpkg在解压源码包的时候,它会使dpkg不能正确地处理某些补丁。如果一位用户或一个自动化系统被欺骗而解压了特别修改过的源码包,远程攻击者就能修改目标解压路径之外的文件,导致拒绝服务攻击或潜在的获取系统权限的风险。”安全通知中这样写道。
+
+想了解这个问题的更多细节描述,你可以查看Canonical的[安全通知][1]。Canonical建议用户尽快升级自己的系统。
+
+如果你将各个发行版系统的libdpkg-perl包升级到最新版本即可修复这个漏洞。要安装这个更新,你只需运行更新管理器/软件更新器即可。
+
+一般来说,一个普通的系统更新就可以完成所有必需的改动,用户不必重启PC或笔记本来应用这个补丁。这个更新同样可以在终端中实现,只需使用 apt-get dist-upgrade 命令。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Dpkg-Vulnerabilities-Closed-in-Ubuntu-14-04-446282.shtml
+
+译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.ubuntu.com/usn/usn-2242-1/
diff --git a/published/201406/20140616 How To Install Numix Icon Theme In Fedora 20.md b/published/201406/20140616 How To Install Numix Icon Theme In Fedora 20.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e21aff39d7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140616 How To Install Numix Icon Theme In Fedora 20.md
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+Numix图标主题张冠李戴,Fedora 20劲爆酷爽
+================================================================================
+[Numix主题][1]现在已经风行了有一段时间了,我想我们大多数人都知道它。在上一篇稿子中,我们已经讨论了[在Manjaro Linux上安装Numix主题和其它社区分支][2]。
+
+今天,我们打算在Fedora 20上搞点相同的花样出来。
+
+我们首先需要安装**fedy**,这个东西将帮助我们一起来干这事。如果你现在还没在你的Fedora系统上安上Fedy,那么[追随我们前一教程的脚步来安装它][3]。
+
+### 安装Numix主题 ###
+
+打开终端,把下面的命令跑一遍吧(确定你已经安装了fedy了吧)。
+
+ sudo fedy -e numix_themes
+
+
+
+### 安装Gnome优化工具 ###
+
+ sudo yum install gnome-tweak-tool
+
+启动Gnome优化工具:
+
+
+
+现在修改外观设置下的所有设置,把他们全都指向Numix吧,就像下面的图表中那样。
+
+
+
+你已经搞定了!
+
+
+
+尽情爽吧!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/install-numix-icon-theme-fedora-20/
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://numixproject.org/
+[2]:http://www.unixmen.com/install-numix-icon-theme-manjaro-linux/
+[3]:http://www.unixmen.com/tweak-fedora-system-using-fedy/
diff --git a/published/201406/20140616 Ubuntu Desktop Next 14.10 Images Available to Download.md b/published/201406/20140616 Ubuntu Desktop Next 14.10 Images Available to Download.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3ba634f919
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140616 Ubuntu Desktop Next 14.10 Images Available to Download.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+运行Unity 8的Ubuntu镜像已可下载测试
+================================================================================
+
+
+*运行在平板上的Unity 8 *
+
+**出乎意料,默认使用Unity 8和Mir的Ubuntu 14.10 桌面版,[现已可下载了][1]**
+
+根据[上个月的讨论][2]Ubuntu 14.10镜像计划提供单独的Unity 8桌面。 提供此镜像目的是给开发者和测试人员提供一个了解从传统界面到使用两种新技术的界面的变化的手段。
+
+此镜像并不用于普通用户测试。这个版本会并将会是极不稳定而充满bug的,在十月之前还会不断有变动。所有想要一个完美的、可用的或统一的的桌面的人都会失望,因为这个Unity 8桌面版镜像现在用的是平板的UI。
+
+### 工作进行中 ###
+
+为Mir和Unity 8建立完备的窗口管理特性的工作正在进行中。同样的,在桌面显卡完全兼容Mir之前,硬件支持和用户体验之间还相距甚远,而且还不支持虚拟机。
+
+桌面Unity 8界面将开始融合平板UI,用户会提出界面与原来相差太大的问题,对此详见Ubuntu的创始人Mark Shuttleworth最近的视频的问答模块。
+
+这是个好消息,微软在桌面Windows8上强加了平板界面和为触摸屏设计的UI。结果被骂的不轻,不得不总是进行"改进"——在你吐槽后才让步,来对付投诉。
+
+### 下载Unity 8桌面版本 ###
+
+按计划标准的Ubuntu 14.10预定在10月23日发行稳定版,其继续基于 X.Org,Compiz和Unity 7。而运行在Mir的Unity8则预计在2016年4月的下一个 LTS之前成为新的的默认桌面。
+
+此版本还不具有可用性,下方链接的镜像只是为了协助开发人员测试和完善,并不能让你穿越体验到未来的Ubuntu。
+
+- [下载下一代Ubuntu14.10 (.iso)][3]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/06/unity-8-daily-build-images-go-live
+
+译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://blueprints.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+spec/client-1410-unity8-desktop-iso
+[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/05/ubuntu-unity-8-desktop-flavour-discussed
+[3]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-desktop-next/daily-live/current/
diff --git a/published/201406/20140616 Ubuntu for Phones Activated on 10,000 Devices.md b/published/201406/20140616 Ubuntu for Phones Activated on 10,000 Devices.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..518da4deb2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140616 Ubuntu for Phones Activated on 10,000 Devices.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+手机版Ubuntu在第10,000台设备上被激活
+================================================================================
+
+
+**Canonical公司日前宣布手机版Ubuntu操作系统在第10,000台设备上被激活,这是一个重要的里程碑。**
+
+手机版Ubuntu项目于2013年初公布,开发团队之后就一直在上面工作。他们花了一些时间才拿出一个可用的版本,之后在这个基础上不断地改善。
+
+这个10,000台里程碑之所以重要,是因为公司本身并没有销售任何装载这款操作系统的设备。到目前为止,只有Nexus用户(手机或平板)才可以安装它。这对于一个只提供下载的操作系统来说意义重大。
+
+“Ubuntu手机/平板用户需要在他们的设备上登录Ubuntu One账号,才可以下载或更新应用。这就让我们可以为用户提供许多从Android或iOS借鉴过来的功能,例如在新手机上或是手机重置之后自动重新安装所有应用,或是浏览商城网站(很快发布)时可以选择直接安装应用到设备上。”
+
+“这个功能的另外一个效果是,它可以让我们知道有多少唯一的Ubuntu One账号登陆过商城来下载应用,而这个数字在本周突破了10,000的记录。”科能公司的Michal Hall[说][1]。
+
+目前,用户不需要在Nexus设备上删除Android,因为可以支持双启动,而且还有好几种方式。而预装Ubuntu系统的设备将在今年晚些时候出货,希望赶在假日旺季之前,社区成员已经有非常高的热情了。
+
+Canonical公司还建立了一套Ubuntu SDK来帮助开发者为这个新操作系统开发应用,而且已经有很多从其他平台移植的原生应用了。它们还没做好,但是离正式发布还有几个月,还有大量时间来准备足够数量的原生应用,不仅仅是替代的网页应用。
+
+如果你有Nexus 4手机或是Nexus 7平板,你现在就可以在上面安装Ubuntu。细节上仍然还有些粗糙,但是你会发现你已经熟悉的设备会变得大不一样,请多花点时间,然后你会喜欢它的。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Ubuntu-for-Phones-Activated-on-10-000-Devices-446824.shtml
+
+译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://developer.ubuntu.com/2014/06/10000-users-of-ubuntu-phone/
diff --git a/published/201406/20140617 14 Apps To Boost Ubuntu.md b/published/201406/20140617 14 Apps To Boost Ubuntu.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..943eddf5d5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140617 14 Apps To Boost Ubuntu.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+14个可以提升Linux桌面体验的应用程序
+==============================
+
+转战到Ubuntu,或者是别的流行的Linux发行版,不仅仅是操作系统的操作方式的改变,更多的是你还需要一些能支持你完成工作的好的应用。
+
+在这篇文章中,我将分享一些我精选出来不可或缺的应用程序,并谈谈在我的日常工作中如何有效地使用它们。
+
+### 日常使用的应用程序 ###
+
+一般当说到Linux桌面上的应用,我总是将这些应用划分为两大类,频繁使用的和一些别的应用。下边我为大家介绍的是一些自己日常使用的应用。
+
+1) **Firefox** — 有时我也会使用用其他的浏览器,但最近[火狐浏览器][1]已经成为我可以长期信赖的朋友。可靠的、 安全的、 跨平台的,火狐浏览器完全满足了我的日常冲浪需求。
+
+除了访问书签和网页,我还依靠火狐浏览器来处理我的各种部署在局域网服务器上的工作,如 [Plex][2], [Zoneminder][3], 路由器/WEB应用防火墙, 及我的文件服务器。所有这些均可以使用火狐浏览器进行访问。
+
+2) **Parcelite**— 如果没有一个像样的剪贴板管理器我简直没法开始工作,至少对我来说,你无法找到在GNOME 下的[Parcelite][4]有什么不足。使用简单,易于访问而且它提供了很多的有用的选项。Parcelite选项应有尽有,包括了从热键设置到空格处理方式。尽管已经有很多的剪贴板管理器,但它们却很难击败 Parcelite。
+
+3) **Bittorrent Sync** — 我已经使用过了各种开源替代方案进行文件同步,但是他们在正式发布之前还需要进行进一步开发。应该说[Bittorrent Synchas][5]从来没有让我失望过。它运行和安装都很简单和方便,这多亏了新的GUI的实现,而且 Bittorrent Sync 允许我快速地从一台机器到另外一台机器传输巨大的视频文件,而无需浪费时间去将大量的文件同步到“云端”。
+
+我还发现它是与别人分享大型文件的最佳方法,在分享的同时能一直保持 IP 地址和目录的隐蔽。尽管有许多的替代品,我仍然坚定地成为了Bittorrent Sync的骨灰粉丝。
+
+4) **System Monitor** — 因为TOP实在是滚动地太快了,所以我个人更喜欢一个具有选项卡式的 GUI,因为它能够让我的眼睛更轻松些。使用 GNOME 的系统监视器,我可以很快地发现一个失控的进程,并且轻松地kill掉它而不需吹灰之力。与[TOP][7]这样的终端程序不同的是,我可以实时的以图形化的方式去查看我的 CPU、 内存和磁盘的使用情况。作为一个拥有正常视觉的人,很难找到一个比用条形图来展示我还拥有多少的空间的更好方式。当然这也同样适用于其它的实时资源使用情况的监视。
+
+5) **PulseAudioControl** — 每一天,我总是需要在多个声音设备之间来回穿梭。有时我需要将其中一个设为默认设备,然后却可能会从火狐浏览器音频完全切换到到另一个设备。因为我想控制我的尽可能多的音频,然后我就发现 [PulseAudioControl][8]是一个无价的工具。
+
+### 一些别的软件 ###
+
+在本节中,我将分享我使用,但可能并不一定是每天都使用的应用程序。许多这些应用程序都是开放源代码的,有一些不是,但是它们对我个人都非常具有价值。
+
+
+6) **Skype** — 无论是拨入[Jupiter Broadcasting][9] 收听每周共同主持的播客,或者只是简单联系一个业务,[Skype][10] 见证了互联网视频会议的发展史。测试完成无数的替代品后,我总是会发现自己还是终回到了Skype。即使有真的很棒的开源选择像[Ekiga][11] 和 [Jitsi][12],而在最后Skype总是与大家同在 —— 切换到Skype是一件很幸运的事。
+
+7)**Kdenlive** — 我使用两个不同的视频编辑器,当我要处理一个需要大量编辑的视频剪辑项目的时候,[Kdenlive][13]是我用于图片合成和编辑大型的复杂的视频的工具。我已经成功地在 Kdenlive 里边做过6个素材轨道的编辑,但同样的负载量早已经让别的视频剪辑软件崩溃了。
+
+8)**OpenShot** — 大多数情况下,我会将[OpenShot][14]作为视频剪辑任务的首选神兵利器。快速的编辑和两个素材轨道工作区让你可以流畅而操作简单。我还发现它提供了很棒的无与伦比的特效。调制标题效果和超赞的的视频转场效果使OpenShot在我自己的视频项目上成为一款超棒的视频制作软件。
+
+9)**SpiderOak** — 在使用了无数云备份服务这么多年后, [SpiderOak][15] 已经成为了我的至爱。易于安装和使用,我超喜欢它所提供的增量选项而且使用起来是如此的简单。只需一次设置,不再操心,之后SpiderOak将会挑起你的文件搬运大任。
+
+10) **Dropbox** — 许多年来,我已经与[Dropbox][16] 爱恨交织。尽管它的跨平台特性这意味着我可以从任何位置访问文件,我慢慢地发现我自己越来越少依赖这个基于云计算的备份解决方案。尽管如此,它允许我从任何 web 浏览器中访问文件,即使是从我不经常使用的计算机,这使得抛弃 Dropbox 更是难上加难。
+
+11) **Writer** — 自从我第一次在Windows的OpenOffice里面使用过它之后,我一直都在使用[Writer][17]。今天,我使用LibreOffice 所带的Writer来满足我的需求,它可以做一切一个文字处理器可以做的事情。现在,公正地说,一些专有的办公套件可能会提供附加功能在Writer中是没有的,但是99%的人需要的功能在Writer这里都有。就我个人而言,我会永远是一个LibreOffice Writer粉。
+
+12)**SimpleScreenRecorder** — 多年来,我发现自己使用 [SimpleScreenRecorder][18]远超过其他同类软件,它能很好支持多监视器模式,再加上它甚至可以捕获基于 OpenGL 的应用程序的视频。易于使用和可靠的 SimpleScreenRecorder 让我的工作更加得心应手。我把它推荐给那些只是偶尔需要,懒得使用其它屏幕捕捉软件的同学们。
+
+13)**SimpleScan** — 当我需要扫描文档的时候,我一点都不想将大把大把的时间花费在配置的臃肿的程序上。 [Simple Scan][19] 可以在这方面做得很好。智能的SANE扫描数据库,Simple Scan将与市面上的任何扫描仪或多功能一体打印机/扫描仪很好的进行协作。此外还有一点好处就是它会设置成的最佳分辨率,当然你还可以很方便手动调整任何你需要的设置。
+
+14)**Baobab**(磁盘使用分析器) — 我不断听到关于如何硬盘价格已回落。这或许没错,但现实却是我却囊中羞涩。这意味着我需要充分利用我能利用的所有硬盘空间,为了实现这个目的,我使用 [Baobab][20] 来观察我在我的硬盘上的可用空间,而且还可以直观地看到到底是哪一个目录正在蚕食我宝贵的硬盘空间。
+
+### 真正的具有生产力的软件 ###
+
+谈到我所依赖的这些软件,我们真正关心的是他们能为我们完成什么样的任务,而不是它们所拥有的光辉头衔和自身的许可证。linux不需要软件的传奇时代早已过去。多数的计算机上的工作,除了有限的几个例外,大都可以在linux桌面上轻松地如我所说的那样完成。
+
+很明显有一些对于你来说是必不可少的软件,但是也许不是我必须用的。你所倚重的软件是什么?您可在下方进行评论并与我们的读者进行分享那些优秀的软件。
+
+------
+
+via: http://www.datamation.com/applications/14-apps-to-boost-ubuntu-1.html
+
+译者:[owen-carter](https://github.com/owen-carter) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/new/
+[2]:https://plex.tv/
+[3]:http://www.zoneminder.com/
+[4]:http://parcellite.sourceforge.net/
+[5]:http://www.bittorrent.com/sync
+[6]:https://help.gnome.org/users/gnome-system-monitor/3.12/
+[7]:http://linux.about.com/od/commands/l/blcmdl1_top.htm
+[8]:http://freedesktop.org/software/pulseaudio/pavucontrol/
+[9]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jupiter_Broadcasting
+[10]:http://www.skype.com/en/download-skype/skype-for-linux/
+[11]:http://ekiga.org/
+[12]:https://jitsi.org/
+[13]:http://www.kdenlive.org/
+[14]:http://www.openshot.org/
+[15]:https://spideroak.com/
+[16]:https://www.dropbox.com/
+[17]:http://www.libreoffice.org/discover/writer/
+[18]:http://www.maartenbaert.be/simplescreenrecorder/
+[19]:https://launchpad.net/simple-scan
+[20]:http://www.marzocca.net/linux/baobab/baobab-getting-started.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/201406/20140619 Improve Battery Life with Laptop Mode Tools 1.65.md b/published/201406/20140619 Improve Battery Life with Laptop Mode Tools 1.65.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c0b86bc475
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140619 Improve Battery Life with Laptop Mode Tools 1.65.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+用笔记本模式工具1.65来延长电池续航能力
+================================================================================
+
+
+
+笔记本模式工具是一个Liunx电源管理工具包,它可以让用户以多种方式延长笔记本电池续航能力,现在它已经升级到1.65。
+
+笔记本模式工具的发布的版本曾经很少而且间隔很长,但开发者在最新的版本中做了一些很有意思的改变,虽然此次更新与以前不同。
+
+根据更新日志,grep找不到$device/uevent的错误已得到修复、 sysfs/enabled已被"ip link down"所取代、 添加了对iwlwifi的支持,运行时电源管理框架现在更健壮,并且usb-autosuspend模块已被去除。
+
+此外,当笔记本电脑恢复时,笔记本模式工具将强制以初始化模式运行,最新版本已添加英特尔 PState 驱动程序的模块,并已实现挂起/休眠接口。
+
+用户不须更改自动设置。更改自动设置可能会导致更多的问题,但通常看来他们总是会去动它。此外,要注意到每个功能究竟是做什么的,否则你可能会搞出更多问题。
+
+看官方[公告][1]来了解更多细节。
+
+现在就下载用笔记本模式工具1.65:
+
+- [http://samwel.tk/laptop_mode/packages][2]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Improve-Battery-Life-with-Laptop-Mode-Tools-1-65-447397.shtml
+
+译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://launchpad.net/laptop-mode-tools/+announcement/12779
+[2]:http://samwel.tk/laptop_mode/packages
diff --git a/published/201406/20140619 Red Hat to Acquire eNovance, Focus Together on OpenStack.md b/published/201406/20140619 Red Hat to Acquire eNovance, Focus Together on OpenStack.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..88ef29adb0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140619 Red Hat to Acquire eNovance, Focus Together on OpenStack.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+红帽携手eNovance,共进OpenStack市场
+================================================================================
+
+
+
+正在OpenStack峰会于亚特兰大举办的同时,红帽确认了数项与OpenStack相关的项目。其中一项是,红帽正与开源云计算市场的领导者eNovance进行[合作][1] 。双方将推动网络功能虚拟化(Network Functions Virtualization)及将电信功能融入OpenStack中。红帽[宣布][2]将以七千万欧元或九千五百万美金的现金和股票投资eNovance。
+
+eNovance 是OpenStack市场上重要的角色, 特别以其和电信公司的合作而为人所知。eNovance帮助服务提供商和大型私企搭建部署云基础架构,快速且成本低廉。这也将为红帽开创新的产品线。
+
+IDC 分析员 Laura DuBois 和 Ashish Nadkarni 在2014春季OpenStack 峰会上指出 “像eNovance这样的集成商将继续助力云服务提供商和企业,建立OpenStack云。OpenStack的前景开起来十分光明。"
+
+eNovance 是OpenStack十大上游贡献者之一, 也是OpenStack 基金唯一的欧洲金牌合作商。 该公司在全球有超过150家客户,包括 Alcatel-Lucent、 AXA,、 Cisco、 Cloudwatt 和 Ericsson. 在巴黎、蒙特利尔、班加罗尔、印度,都设有办公室。
+
+2013年,红帽和 eNovance 第一次展开[合作][3] ,为其共同客户提供OpenStack 部署和集成服务。该服务基于Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack 平台。 今年五月的OpenStack峰会上, 两家公司宣布了[进一步的合作][4] ,推动网络功能虚拟(NFV) 和电信在OpenStack上的创新,意在提供业界最完整、电信级的 通讯服务,基于Linux、内核级虚拟机 (KVM)和 OpenStack。
+
+eNovance的联合创始人、首席执行官Raphaël Ferreira, 在声明中说:
+
+> “和红帽一样,eNovance也认为部署和集成OpenStack已成趋势,这是企业市场上的变革力量。 我们非常高兴能成为红帽的一部分。红帽不仅仅提供一流的OpenStack发行版本,也和我们一样坚信: 最好以连续、无缝的方式部署、集成OpenStack。”
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ostatic.com/blog/red-hat-to-acquire-enovance-focus-together-on-openstack
+
+译者:[tengpeng](https://github.com/tengpeng) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.redhat.com/about/news/press-archive/2014/5/red-hat-and-enovance-to-deliver-carrier-grade-openstack
+[2]:http://www.marketwatch.com/story/red-hat-to-acquire-enovance-a-leader-in-openstack-integration-services-2014-06-18
+[3]:http://cts.businesswire.com/ct/CT?id=smartlink&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.redhat.com%2Fabout%2Fnews%2Fpress-archive%2F2013%2F11%2Fred-hat-and-enovance-partner-to-accelerate-adoption-of-red-hat-enterprise-linux-openstack-platform&esheet=50888828&newsitemid=20140618005543&lan=en-US&anchor=first+partnered+in+2013&index=1&md5=1721061ca22652d2a4413085db70361b
+[4]:http://cts.businesswire.com/ct/CT?id=smartlink&ppppppppt-pt-lopppppppppptpt-lpt-pt-locapt-pt-ptptppptppppt-ptptptppp
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/201406/20140620 Celebrating 30 Years of X.md b/published/201406/20140620 Celebrating 30 Years of X.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9466266aea
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140620 Celebrating 30 Years of X.md
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+X 窗口系统已经30岁了!
+================================================================================
+X.org基金会很自豪地宣布一个特别的日子:30年前,1984年六月19日,Bob Scheifler发布了X窗口系统。
+
+有关X窗口系统的介绍参见: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X11#Introduction][1]
+
+在这30年中,X作为UNIX桌面无处不在。在今天,数以百万计的用户使用着桌面环境如GNOME,KDE,Xfce,Unity,Enlightenment等等,而这些都使用X作为其底层技术。
+
+X的开发者们做出了巨大的突破,把X从原本为VAX VS100 CPU编写的一个程序发展成为在今天可在笔记本电脑上进行3D渲染的图形用户界面。事实上,X的出现早于图形处理单元(GPU)概念的出现,甚至是比推广这项技术公司——于1999上市的Nvidia更早。
+
+
+
+尽管X已经服务了很长时间,但是X仍将做出改进并继续陪伴我们。
+
+请不要感到惊奇, X的出现早于:
+
+- Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, Solaris, Microsoft Windows
+- POSIX, C89, C99, C++, Java
+- 互联网
+- GPL 和 FSF
+
+X是第一个主要的开源软件项目,比Free Software 和 Open Source Software更早。和我们一起庆祝吧,因为没有X,桌面就不会是今天这个样子。
+
+- X.Org 品牌总监
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://comments.gmane.org/gmane.comp.freedesktop.xorg.announce/2177
+
+译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X11#Introduction
diff --git a/published/201406/20140620 ENCRYPT DNS TRAFFIC IN LINUX WITH DNSCRYPT (VIA OPENDNS).md b/published/201406/20140620 ENCRYPT DNS TRAFFIC IN LINUX WITH DNSCRYPT (VIA OPENDNS).md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f46c2ad7de
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140620 ENCRYPT DNS TRAFFIC IN LINUX WITH DNSCRYPT (VIA OPENDNS).md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+使用DNSCrypt来加密您与OpenDNS之间的通信
+================================================================================
+**正如SSL能将HTTP通信变为加密过的HTTPS通信,DNSCrypt, 物如其名, 是一款能加密您电脑与OpenDNS之间的通信的小神器。**
+
+DNSCrypt刚问世的时候,官方公布它只是一款Mac才能用的工具,但根据最近一篇由OpenDNS发的[文章][1]表明,虽然还没有用户界面,但其实当Mac版DNSCrypt推出的时候源码已经放到了Github上了, Linux的用户也可以安装以及使用哦!
+
+### 为神马要使用 DNSCrypt? ###
+
+**DNSCrypt可以加密您电脑与OpenDNS服务器的所有通信,加密可以防止中间人攻击,信息窥觑,DNS劫持。更能防止网络供应商对某些网站的封锁。**
+
+这是世界上第一款加密DNS通信的工具,虽然TOR可以加密DNS的请求,但毕竟它们只是在出口节点加密而已。
+
+> 这款工具并不需要对域名或其工作方式做任何的改变,它只是提供了个该工具的用户与机房里的DNS服务器之间的加密方式而已。
+
+您可以在[GitHub][3]的[OpenSND DNSCrypt][2]页面阅读更多的相关信息。
+
+### 如何在Linux使用DNSCrypt ###
+
+首先下载安装[Download DNSCrypt][4], 然后在Terminal里输入这个命令:
+
+ sudo /usr/sbin/dnscrypt-proxy --daemonize
+
+
+
+然后把您的DNS服务器调成"127.0.0.1" - 在GNOME界面下的话,只要到Network Connections(网络连接)选项然后选择"Edit"并在"DNS servers"输入"127.0.0.1"就好了。如果您用的是DHCP的话,请选择Automatic (DHCP) addresses only", 这样的话才能输入DNS服务器。然后只要重连网络便可。
+
+您可以访问这条[链接][5]来测试您连接到了OpenDNS了没。
+
+如果您想设置开机启动DNSCrypt,可以自建一个init的脚本,如果您用的是Ubuntu,可以参考下面的。
+
+**Arch Linux的用户可以通过[AUR][6]来安装DNSCrypt-proxy** (内含rc.d脚本)
+
+### Ubuntu下的DNSCrypt ###
+
+如果您想在Ubuntu设置开机启动,您可以使用这个[Upstart脚本][7]。
+
+注: 在Ubuntu 12.04版在127.0.0.1有个本地的DNS cache 服务器(dnsmasq)在跑,所以已经把改脚本改成让DNSCrypt使用127.0.0.2了, 所以按照上面的教程,应该把127.0.0.1换成127.0.0.2了。
+
+要安装此脚本请使用以下的指令(要首先解压下下来的压缩文件):
+
+ sudo cp dnscrypt.conf /etc/init/
+ sudo ln -s /lib/init/upstart-job /etc/init.d/dnscrypt
+
+然后用这个指令来启动:
+
+ sudo start dnscrypt
+
+现在DNSCrypt就应该是开机自启了,如果您想停止的话,可以使用:
+
+ sudo stop dnscrypt
+
+[下载DNSCrypt][8] (.deb、 .rpm以及源码都可供下载哦!)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.webupd8.org/2012/02/encrypt-dns-traffic-in-linux-with.html
+
+译者:[213edu](https://github.com/213edu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://blog.opendns.com/2012/02/16/tales-from-the-dnscrypt-linux-rising/
+[2]:http://www.opendns.com/technology/dnscrypt/
+[3]:https://github.com/opendns/dnscrypt-proxy
+[4]:http://download.dnscrypt.org/dnscrypt-proxy/
+[5]:http://www.opendns.com/welcome
+[6]:http://aur.archlinux.org/packages.php?ID=54702
+[7]:http://webupd8.googlecode.com/files/dnscrypt-0.2.tar.gz
+[8]:https://github.com/opendns/dnscrypt-proxy/downloads
diff --git a/published/201406/20140620 How to enable testing and unstable repository on Debian.md b/published/201406/20140620 How to enable testing and unstable repository on Debian.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e506e95088
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140620 How to enable testing and unstable repository on Debian.md
@@ -0,0 +1,159 @@
+如何在Debian中启用测试版/不稳定版的软件库
+================================================================================
+为何要启用测试版/不稳定版?
+
+测试版/不稳定版的Debian给开发者提供了一个比当前稳定版更新的环境以及软件。你们注意到了么?其实这些稳定版啊不稳定版啊神马的都是别名,比方说稳定版其实就是Debian的稳定发行版,而测试版将会是下一个Debian的稳定发行版(当然那是测试后的事了)。截至发稿为止,当前Debian的稳定发行版是Wheezy 7.x,将会成为下一个稳定版的测试版则是Jessie。
+
+当你需要一款应用的最新版本的时候,启用测试版/不稳定版将会是不二的选择。当初我因为工作需要,要安装个Apache的 2.4.x到我的Debian Wheezy。测试版需要的是2.4.x的,可是我的软件库里面只有2.2.x的。所以最好的解决方案当时是将测试版下下来啦。
+
+通常来说当我们想尝试最新版本的应用时,都应该只在测试版软件库中搜索。
+
+在这篇文章里我将教大家如何在不弄坏你系统的前提下设置好测试、不稳定版的Debain系统并在上面安装软件。
+
+> Stable < Testing < Unstable (稳定 < 测试版 < 不稳定版)
+> Wheezy < Jessie < Sid
+
+### 1. 设置测试版/不稳定版的apt源 ###
+
+第一步是把测试版/不稳定版的源加到你的sources.list文件里。在Debian Wheezy系统上,/etc/apt/sources.list理应长得像这样:
+
+ $ cat /etc/apt/sources.list
+
+----------
+
+ ...
+ deb http://security.debian.org/ wheezy/updates main
+ deb http://http.us.debian.org/debian/ wheezy main
+ deb-src http://security.debian.org/ wheezy/updates main
+ ...
+
+把你repo服务器的链接记下来,比如:http://http.us.debian.org/debian/
+
+这个repo服务器将会是离你最近的一个服务器; 在不同的地理位置会有不同的url,这个将会用于下一步。
+
+如果想加测试/不稳定源,则需要在sources.list文件加上这些东西:
+
+ # Testing repository - main, contrib and non-free branches
+ deb http://http.us.debian.org/debian testing main non-free contrib
+ deb-src http://http.us.debian.org/debian testing main non-free contrib
+
+
+ # Testing security updates repository
+ deb http://security.debian.org/ testing/updates main contrib non-free
+ deb-src http://security.debian.org/ testing/updates main contrib non-free
+
+
+ # Unstable repo main, contrib and non-free branches, no security updates here
+ deb http://http.us.debian.org/debian unstable main non-free contrib
+ deb-src http://http.us.debian.org/debian unstable main non-free contrib
+
+格式将会是
+
+ deb
+ (deb <上一步弄的服务器或镜像url> )
+
+当然啦,除了用testing或者unstable这么烂的词,也能使用他们的发行版代号,比如Jessie或者Sid
+
+ deb http://http.us.debian.org/debian jessie main non-free contrib
+ deb http://security.debian.org/ jessie/updates main contrib non-free
+ deb http://http.us.debian.org/debian sid main non-free contrib
+
+### 2. 钉住 apt!这非常重要 ###
+
+> 在加了测试/不稳定的repo之后,当你更新系统的时候所有安装过并且可用的软件就会立马更新,而后你的系统就被你玩火自焚了。
+
+所以需要设置一些规则,以便选定的软件包在正常的更新时不会被更新到一个不稳定的测试版本。
+
+我们需要使用“钉住APT”的方式来告诉apt系统,除了我们希望使用测试版或不稳定版的特定软件包之外,其它的总是使用稳定版的软件包来更新。
+
+可以通过如下两个文件之一来设置如何设置APT的优先级来“钉住”。
+
+ /etc/apt/preferences
+ 或
+ /etc/apt/preferences.d/my_preferences
+
+打开这两个文件之一(如果没有的话就创建一个),然后输入如下内容:
+
+ Package: *
+ Pin: release a=stable
+ Pin-Priority: 700
+
+ Package: *
+ Pin: release a=testing
+ Pin-Priority: 650
+
+ Package: *
+ Pin: release a=unstable
+ Pin-Priority: 600
+
+前面我们提到过,稳定版指的是你当前的debian版本,测试版是下一个,而不稳定版则是更远的将来发行版。上面的设置中最主要的是优先级(Pin-Priority)。当前的稳定版应该有最高的优先级,这就是说,正常的apt-get操作只会从当前的稳定版的软件库(现在是wheezy)里面安装软件。
+
+#### 更新包缓存 ####
+
+在增加了新的软件库和指定了优先规则后,需要更新一下包缓存。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+
+#### 确认APT规则 ####
+
+我们必须确认“钉住”的设置正确,优先级也没问题。使用 apt-cache 的 policy 参数来检查:
+
+ $ apt-cache policy apache2
+ apache2:
+ Installed: (none)
+ Candidate: 2.2.22-13
+ Version table:
+ 2.4.7-1 0
+ 600 http://http.us.debian.org/debian/ unstable/main amd64 Packages
+ 2.4.6-3 0
+ 650 http://http.us.debian.org/debian/ testing/main amd64 Packages
+ 2.2.22-13 0
+ 700 http://http.us.debian.org/debian/ wheezy/main amd64 Packages
+
+如上的输出,确认在wheezy 稳定版中, 2.2.22 版本的Apache是选定的版本,它有最高的优先级。
+
+### 3. 从测试版/不稳定版软件库中安装软件 ###
+
+现在可以从测试版或不稳定版中选择一个特定的软件来安装它了。假如说我们要从测试版软件源中安装 apache2。
+
+有两个不同的方法,并且其结果也有所不同。
+
+#### 方式一 ####
+
+ # apt-get install apache2/testing
+
+上述命令会从测试版软件库中安装 apache2,并从稳定版软件库中安装其依赖包(稳定版通过apt规则确定)。这个命令在某些情况下会失败,比如安装的软件包(apache2)所需的依赖包在稳定版软件库中没有更新到可以支持该软件时。
+
+#### 方式二 ####
+
+ # apt-get -t testing install apache2
+
+上述命令会从测试版软件库中安装apache2,并从测试版软件库中安装其依赖包。这要比上面的命令工作的更好。
+
+所以,要安装较新的软件包,直接从测试版/不稳定版的软件库中安装就行了。注意,优先级号码不只是一个数字而已,还有其特定意义。可以查看 apt_preferences的man页面了解更多:
+
+ $ man 5 apt_preferences
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+使用“钉住”方式的测试版/不稳定版的软件库是一个获取较新版本软件包的一个好办法,不过其实并不推荐使用它们。如果弄错了,可能会从也许不兼容的分支上下载软件包,这会把你的系统搞乱。
+
+一个更好的方式是,使用向后移植的软件库来安装更新的包。它从测试版和不稳定版的软件库中获取较新版本的软件包,但是为当前的稳定版软件库而编译。所以,对于 debian wheezy来说,你可以使用wheezy-backports 软件库。访问http://backports.debian.org/ 了解更多。
+
+### 资源 ###
+
+- [https://wiki.debian.org/AptPreferences][1]
+- [https://wiki.debian.org/DebianTesting][2]
+- [https://www.debian.org/security/][3]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.binarytides.com/enable-testing-repo-debian/
+
+译者:[213edu](https://github.com/213edu) [wxy](https://github.com/wxy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://wiki.debian.org/AptPreferences
+[2]:http://wiki.debian.org/DebianTesting
+[3]:http://www.debian.org/security/
diff --git a/published/201406/20140625 Canonical Debuts 'Orange Box' for Ubuntu OpenStack Cloud Demos.md b/published/201406/20140625 Canonical Debuts 'Orange Box' for Ubuntu OpenStack Cloud Demos.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5a16cec25b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/20140625 Canonical Debuts 'Orange Box' for Ubuntu OpenStack Cloud Demos.md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+Ubuntu的Orange Box首次亮相
+================================================================================
+
+> Orange Box现已推出,它是一个便携的服务器集群,Canonical用它来演示和培训基于Ubuntu的OpenStack云。
+
+
+
+Canonical刚刚发布的Orange Box是一个便携式服务器集群,该公司用来展示[OpenStack][1],[MAAS][2],[Juju][3]和其它的基于Ubuntu Linux的云服务。
+
+下面是它的介绍。
+
+对于刚刚接触到它的人来说,重要的是要了解Orange Box不是什么:它不是一台Canonical用来盈利的硬件产品。到目前为止,该公司并无表示计划大规模销售这些设备。如果你真的想[买一款][4]的话,大概价格为$12,900,这个价格来自其合同制造商[TranquilPC Limited][5]。
+
+从大的方面来说,Orange Box是一个说服企业在基于Ubuntu的云计算投入资金的工具。Canonical的创始人马克·沙特尔沃思[上个月宣布了][6]Ubuntu OpenStack的战略,这是该战略的一个关键组成部分,更是该公司提供的称作[Jumpstart][7]的OpenStack的培训计划的一部分。
+
+作为Jumpstart的一部分,Canonical会将Orange Box借给合作伙伴,以便他们的员工可以在Ubuntu集群上练习配置OpenStack和相关软件。Canonical的工作人员也将在培训期间提供咨询。
+
+不过除开培训的目的不谈,Orange Box[看起来真的很酷][8]。它装有10个[英特尔NUC][9],总计集成了160GB的RAM,1200GB的存储空间和10个酷睿i5处理器,这种设备在一个袖珍空间内提供了相当强大的计算能力。
+
+
+
+更好的是,Orange Box通过预装软件为启动基于Ubuntu的云技术打下了良好基础。
+
+不过,对于Canonical来说,真正的考验是确保企业能够从Orange Box中获益。借出它们不只是为了让合作伙伴们体验一下不错的硬件设备,而是为了通过一个真正令人信服的方式体验Ubuntu的云,以吸引IT决策者选择Ubuntu所建立的下一代云基础设施。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://thevarguy.com/ubuntu/062314/canonical-debuts-orange-box-ubuntu-openstack-cloud-demos
+
+译者:[乌龙茶](https://github.com/yechunxiao19) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://openstack.org/
+[2]:https://maas.ubuntu.com/
+[3]:http://juju.ubuntu.com/
+[4]:http://www.tranquilpcshop.co.uk/ubuntu-orange-box/
+[5]:http://www.tranquilpcshop.co.uk/
+[6]:http://thevarguy.com/ubuntu/051614/shuttleworth-highlights-ubuntu-openstack-cloud-innovations
+[7]:http://www.ubuntu.com/cloud/tools/jumpstart
+[8]:http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2014/06/hands-on-with-canonicals-orange-box-and-a-peek-into-cloud-nirvana/
+[9]:http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/nuc/overview.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/8 examples of findmnt command to check mounted file systems on Linux.md b/published/201406/8 examples of findmnt command to check mounted file systems on Linux.md
similarity index 95%
rename from translated/tech/8 examples of findmnt command to check mounted file systems on Linux.md
rename to published/201406/8 examples of findmnt command to check mounted file systems on Linux.md
index 39fc2db478..5df7ae3052 100644
--- a/translated/tech/8 examples of findmnt command to check mounted file systems on Linux.md
+++ b/published/201406/8 examples of findmnt command to check mounted file systems on Linux.md
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-Linux 中 findmnt 命令检查已挂载的文件系统的8个实例
+findmnt 命令的八个应用实例
================================================================================
### 已挂载的文件系统和设备 ###
-linux 中更常用的检查已挂载的文件系统的是 mount 命令,不仅用于列出已挂载的设备,而且可以在需要的时候挂载和卸载。这有一个叫做 findmnt 的超赞命令,它可以用于快速查看挂载位置和选项。
+linux 中常用的检查已挂载的文件系统的是 mount 命令,不仅用于列出已挂载的设备,而且可以在需要的时候挂载和卸载。另外还有一个叫做 findmnt 的超赞命令,它可以用于快速查看挂载位置和选项。
### 安装findmnt ###
@@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ Findmnt 可以打印出只基于类型的特定的文件系统,例如 ext4,
/sys/fs/cgroup/systemd systemd cgroup rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,name=systemd
/run/user/1000/gvfs gvfsd-fuse fuse.gvfsd-fuse rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,user_id=1000,group_id=1000
-看起来非常整洁
+看起来非常整洁(译注,亲爱的读者你也这样觉得么?)。
#### 7. 通过源设备查找 ####
diff --git a/translated/tech/Bash Getopts--Scripts with Command Line Options.md b/published/201406/Bash Getopts--Scripts with Command Line Options.md
similarity index 97%
rename from translated/tech/Bash Getopts--Scripts with Command Line Options.md
rename to published/201406/Bash Getopts--Scripts with Command Line Options.md
index da9c2c42d9..1d4e812272 100644
--- a/translated/tech/Bash Getopts--Scripts with Command Line Options.md
+++ b/published/201406/Bash Getopts--Scripts with Command Line Options.md
@@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
-CNprober 翻译完成
-
Bash Getopts - 让你的脚本支持命令行参数
================================================================================
@@ -152,7 +150,7 @@ Bash Getopts - 让你的脚本支持命令行参数
via: http://tuxtweaks.com/2014/05/bash-getopts/
-译者:[daisy_love_daisy](https://github.com/CNprober) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者: CNprober \ 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/Collectl--An Advanced All-in-One Performance Monitoring Tool for Linux.md b/published/201406/Collectl--An Advanced All-in-One Performance Monitoring Tool for Linux.md
similarity index 94%
rename from translated/tech/Collectl--An Advanced All-in-One Performance Monitoring Tool for Linux.md
rename to published/201406/Collectl--An Advanced All-in-One Performance Monitoring Tool for Linux.md
index 3d450bafec..88615017b6 100644
--- a/translated/tech/Collectl--An Advanced All-in-One Performance Monitoring Tool for Linux.md
+++ b/published/201406/Collectl--An Advanced All-in-One Performance Monitoring Tool for Linux.md
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-Collectl: 一个高级全能的 Linux 性能监控工具
+Collectl: Linux 性能监控的全能冠军
================================================================================
对于一个 Linux 系统管理员来说确保自己管理的系统处于一个良好的状态是其首要责任。Linux 系统管理员可以找到有很多工具来帮助自己监控和显示系统中的进程,例如 top 和 htop ,但是这些工具都不能与 **collectl** 相媲美。
@@ -8,8 +8,7 @@ Collectl: 一个高级全能的 Linux 性能监控工具
**collectl**是一款非常优秀并且有着丰富的命令行功能的实用程序,你可以用它来采集描述当前系统状态的性能数据。不同于大多数其它的系统监控工具,collectl 并非仅局限于有限的系统度量,相反,它可以收集许多不同类型系统资源的相关信息,如 cpu 、disk、memory 、network 、sockets 、 tcp 、inodes 、infiniband 、 lustre 、memory、nfs、processes、quadrics、slabs和buddyinfo等。
-使用 **collectl** 的另一个好处就是它可以替代那些有特殊用途的工具如 top、ps、iotop 等还有其它许多这样的工具。那么 **collectl** 有什么特性而使其成为一个有用的工具呢?
-
+使用 **collectl** 的另一个好处就是它可以替代那些特定用途的工具如: top、ps、iotop 等等其它工具。那么 **collectl** 有什么特性而使其成为一个有用的工具呢?
经过许多研究后,我总结了 collectl 的命令行功能的一些非常重要的特性。
@@ -33,7 +32,6 @@ Collectl: 一个高级全能的 Linux 性能监控工具
### 如何在Linux上安装collectl###
-
**collectl**可以在所有的 Linux 发行版上运行,唯一需要的就是 perl 语言,所以在安装 **collectl** 之前,一定要确保你的电脑上已经安装了**Perl**。
#### 对于Debian/Ubuntu/Linux Mint ####
@@ -50,8 +48,7 @@ Collectl: 一个高级全能的 Linux 性能监控工具
### 一些关于collectl的实例 ###
-
-collectl 工具安装完成之后,你可以轻松得在终端运行它,你甚至不需要任何选项。下面的命令将会以简短的人性化的格式显示cpu、硬盘和网络信息。
+collectl 工具安装完成之后,你可以轻松地在终端运行它,你甚至不需要指定任何选项。下面的命令将会以简短易读的格式显示cpu、硬盘和网络信息。
# collectl
@@ -70,16 +67,15 @@ collectl 工具安装完成之后,你可以轻松得在终端运行它,你
22 4 993 1615 0 0 56 3 1 2 0 3
-正如上面终端上所显示的,我们很容易观察该命令输出的系统度量值,因为它只显示一整行。
-
+正如上面终端上所显示的,我们很容易观察该命令输出的系统度量值,因为它每次以一行显示。
不加任何参数执行 collectl 会显示下面子系统的信息
- cpu
-- disks
-- network
+- 磁盘
+- 网络
-**提示**:在这里,一个子系统是每一种可以测量的系统资源。
+**提示**:在这里,一个子系统就是每一种可以测量的系统资源。
你也可以显示除slabs以外各个子系统的统计数据,这要结合下面的 **-all** 选项来实现。
@@ -99,9 +95,7 @@ collectl 工具安装完成之后,你可以轻松得在终端运行它,你
15 1 753 1276 361 391 1G 175M 1G 683M 193M 1G ssslkjjebbk 0 0 40 3 1 2 0 3 0 0 0 0 623 0 0 0 8160 240829 0 0 0 0
-
-但是,你如何用它来监控 cpu 的使用情况呢? ‘s’ 选项可以用来控制需要收集和回放的数据。
-
+但是,你如何用它来监控 cpu 的使用情况呢? ‘-s’ 选项可以用来控制哪个子系统的数据需要收集和回放。
例如下面的命令可以用来对cpu使用情况进行一个总结。
@@ -140,7 +134,7 @@ collectl 工具安装完成之后,你可以轻松得在终端运行它,你
11 2 795 1285 0 0 0 0 2 14 1 14
-你可以很容易地理解默认选项是“**cdn**”,它代表cpu、硬盘和网络数据。运行添加这个选项的 collectl 命令的输出和“**collectl -scn**”的输出一样。
+你可以很容易就明白默认选项是“**cdn**”,它代表cpu、硬盘和网络数据。运行带这个选项的 collectl 命令的输出和“**collectl -scn**”的输出一样。
如果你想采集内存的数据,用下面的命令。
@@ -201,7 +195,7 @@ collectl 工具安装完成之后,你可以轻松得在终端运行它,你
对于我们普通大众来说记住这些选项很困难,所以在这里,我整理出了一个列表来总结这个工具支持的选项。
-- **b** – buddy info (memory fragmentation)
+- **b** – buddy info (内存碎片)
- **c** – CPU
- **d** – Disk
- **f** – NFS V3 Data
@@ -213,7 +207,7 @@ collectl 工具安装完成之后,你可以轻松得在终端运行它,你
- **s** – Sockets
- **t** – TCP
- **x** – Interconnect
-- **y** – Slabs (system object caches)
+- **y** – Slabs (系统对象缓存)
对于一个系统管理员或者一个 Linux 用户来说很重要的一种数据就是硬盘的使用情况。下面的命令可以帮你监控硬盘使用情况。
@@ -233,7 +227,7 @@ collectl 工具安装完成之后,你可以轻松得在终端运行它,你
0 0 0 0
-你也可以使用“**-sD**”选项来采集单个硬盘的数据,但是你必须知道全部硬盘的信息不会被报告。
+你也可以使用“**-sD**”选项来采集单个硬盘的数据,不过你必须知道这就不会显示全部硬盘的信息。
# collectl -sD
@@ -333,7 +327,7 @@ collectl 工具中有许多选项,但是仅用一篇文章来介绍肯定是
22 root 0 2 0 S 0 0 0 0.00 0.00 0 00:00.00 0 0 0 0 kintegrityd
-我确信许多系统管理员将会喜欢这个工具并且在充分利用它后会感受到它的强大。如果你想增进你对 collectl 的了解,从而达到新的层面,你可以去参阅 collectl 的 man 手册并勤加练习。
+我确信许多系统管理员将会喜欢这个工具并且在充分使用它后会感受到它的强大。如果你想增进你对 collectl 的了解,从而达到新的层面,你可以去参阅 collectl 的 man 手册并勤加练习。
在你的终端键入下面的命令开始阅读吧。
diff --git a/translated/tech/Fix Adobe Flash Player Issue In Chromium In Ubuntu 14.04.md b/published/201406/Fix Adobe Flash Player Issue In Chromium In Ubuntu 14.04.md
similarity index 67%
rename from translated/tech/Fix Adobe Flash Player Issue In Chromium In Ubuntu 14.04.md
rename to published/201406/Fix Adobe Flash Player Issue In Chromium In Ubuntu 14.04.md
index dcde5182f8..26f2236856 100644
--- a/translated/tech/Fix Adobe Flash Player Issue In Chromium In Ubuntu 14.04.md
+++ b/published/201406/Fix Adobe Flash Player Issue In Chromium In Ubuntu 14.04.md
@@ -2,21 +2,21 @@
================================================================================
[安装Ubuntu 14.04之后,先要做的几件事情][1]中其中一项是安装Adobe Flash Player。一般来说,如果安装了[Ubuntu Restricted Extras][2],Flash Player应该可以工作而且你应该能够在网上观看在线视频,比如You Tube等网站上。
-这不是Chromium和Ubuntu 14.04结合使用的原因。当你用其他的网页浏览器比如火狐、Chrome时,你可以轻松地播放You Tube等网站视频,在Chromium中你将会看到Adobe Flash player缺失插件的通知:
+其实这不是因为Chromium是在Ubuntu 14.04上使用才出现的问题。当你用其他的网页浏览器比如火狐、Chrome时,你可以轻松地播放You Tube等网站视频,但在Chromium中你将会看到Adobe Flash player缺失插件的通知:
-**Adobe Flash Player is required to display some elements on this page. Install plug-in..**
+> **Adobe Flash Player is required to display some elements on this page. Install plug-in..**

### 只有在Chromium中出现flash player问题的原因: ###
-只有在Chromium中发生这个问题的原因是,之前Chromium使用Netscape Plugin API构架来支持Flash,从Ubuntu 14.04开始,[Chromium将会停止使用Netscape Plugin API][3]。今后,你将要面对Chromium中Adobe Flash Player的问题。
+只有在Chromium中发生这个问题的原因是,之前Chromium使用Netscape Plugin API构架来支持Flash,从Ubuntu 14.04开始,[Chromium将会停止使用Netscape Plugin API][3]。因此,我们才遇到Chromium的Adobe Flash Player的问题。
-现在,为什么这个问题没有发生在其他浏览器上?答案是,因为它们使用 Flash Player 11.2。
+那么,为什么这个问题没有发生在其他浏览器上?答案是,因为它们使用 Flash Player 11.2。
### 修复Chromium上Adobe Flash Player的问题: ###
-修复这个问题,我们将使用Pepper Flash Player,一个来自Google更安全更稳定的版本的Flash Player。在Ubuntu 14.04的源里有[Adobe Flash Player Pepper 安装器][4]。这个安装器下载Google Chrome,提取出Pepper Flash Player然后建立给Chromium使用。
+修复这个问题,我们应该使用Pepper Flash Player,一个来自Google更安全更稳定的版本的Flash Player。在Ubuntu 14.04的源里有[Adobe Flash Player Pepper 安装器][4]。这个安装器会下载Google Chrome,提取出Pepper Flash Player然后设置给Chromium使用。
要在Ubuntu 14.04安装Pepper Flash Player,打开一个终端,使用下面的命令:
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@
via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-flash-player-issue-chromium-in-ubuntu-14-04/
-译者:[linuhap](https://github.com/linuhap) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[linuhap](https://github.com/linuhap) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201406/Guide To Install Ubuntu 14.04 In Dual Boot Mode With Windows 8 Or 8.1 UEFI.md b/published/201406/Guide To Install Ubuntu 14.04 In Dual Boot Mode With Windows 8 Or 8.1 UEFI.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ea718cc18a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/Guide To Install Ubuntu 14.04 In Dual Boot Mode With Windows 8 Or 8.1 UEFI.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+在UEFI模式下安装Ubuntu 14.04与Windows 8/8.1双启动
+================================================================================
+
+
+之前我已经写过关于[如何安装Ubuntu Linux和Windows 7][1]以及8的双启动,但是那些教程不包含那些预装Windows 8的系统。那些较新的预装了Windows 8或Windows 8.1的系统使用了UEFI来替代BIOS。这使得安装双启动变得和之前的常规方法有点不同。在这个教程中,我们将看到**如何在UEFI模式下安装Ubuntu 14.04与Windows 8/8.1双启动**。
+
+这个教程是在一台新买的戴尔灵越 7437(酷睿i7第四代处理器, 256GB SSD,8GB内存以及内置1GB(共享内存) Intel显卡)上演示的。为了使你能够成功安装UEFI下Linux和Windows 8的双启动,我会提到你需要做的所有步骤。如果你已经完成这些步骤中的部分步骤,直接跳到下一步。如果你有个全新的系统,那就更好了。
+
+在这里提到的这些步骤也适用于其它基于Ubuntu的Linux发行版,如Linux Mint,Elementary OS等等。不多说,让我们来看看如何在启用了UEFI安全启动的Windows 8系统上双启动Linux。
+
+### 让 Ubuntu 14.04 和 Windows 8 双启动: ###
+
+要在一个UEFI系统上安装Ubuntu有多方面的前提条件。让我们来一个一个看:
+
+#### 第一步:做个备份 [可选] ####
+
+做个备份总是个不错的选择,防止你把系统弄糟了。网上有众多文章教你如何备份系统。你可以参照[这个教程][2]。
+
+#### 第二步:创建一个Ubuntu的USB启动盘/光盘启动盘 ####
+
+你需要做的下一件事是创建一个USB启动盘或光盘启动盘。我推荐在Windows下使用[Universal USB Installer][3]创建一个Linux OS的USB启动盘。
+
+#### 第三步:为Ubuntu划分一块安装分区 ####
+
+假设你有一个全新的系统,我们要做的第一件事是创建一个分区来安装Linux。我系统中的256GB磁盘出厂时就有若干个分区,但主要是用来备份及其它目的的。主分区是安装了Windows 8.1的C盘,约有220GB。
+
+如果你也像这样只有一个分区,你需要从中分割出一些空间给Linux。如果你有若干空间大小足够的分区,可以使用它们中除C盘外的任意盘,因为安装时会抹掉其中的数据。
+
+要在Windows 8中创建分区,需要使用磁盘管理工具。你可以通过在控制面板中搜索‘磁盘’找到磁盘管理工具。
+
+
+
+在磁盘管理工具中,右键点击你想划分并缩小的卷。在我的演示中,我选择C盘的卷进行缩小,划分出未分配空间:
+
+
+
+缩小后出现的未分配空间就放在那里好了,不用对其分区和格式化。我们会在安装Ubuntu时用到它。
+
+#### 第四步:在Windows中禁用快速启动 [可选] ####
+
+为了实现快速启动,Windows 8引进了叫做“快速启动”的新特性。尽管不是强制要求,最好还是将其禁用。
+
+打开**控制面板 > 硬件与声音 > 电源选项 > 选择电源按钮的功能 > 更改当前不可用的设置**,取消选中**启用快速启动(推荐)**。
+
+#### 第五步:禁用Windows 8 and 8.1的安全启动(secure boot) ####
+
+这是最重要的步骤。Windows 8新的安全启动(secure boot)原本是针对rootkit病毒的安全特性,但它也阻止了Windows和Linux的双启动。为了实现Windows和Linux的双启动,我们必须在UEFI中禁用安全启动(secure boot)。
+
+可以参见:[如何在 Win8 上禁用 UEFI 安全引导以安装Linux][4]。
+
+#### 第六步:安装Ubuntu,与Windows 8共存 ####
+
+一旦你禁用了安全启动(secure boot),那就是时候安装Ubuntu了。我希望你像第二步中提到的一样创建了一个USB启动盘。插入U盘,然后从U盘启动系统。
+
+要从USB启动,需要在Windows中选择从USB启动的选项。从电脑设置(像UEFI)中选择选项或在点击“重新启动”的时候按住Shift键。
+
+当你用USB启动盘启动后,你会看到试用(try)或者安装(install)Ubuntu的选择,这里要点击“安装”。另外在屏幕上不多的设置选项里面,你可以选择你用的语言。接下来是关于硬盘空间,电源和网络连接等等的一些检查。只需点击**继续**。
+
+
+
+安装窗口中你需要注意的是**安装类型(Installation Type)**。选择这里的**其它选项(Something else)**:
+
+
+
+还记得我们事先划分的未分配空间吗?我们将用它来创建根分区( / ),交换空间(Swap)以及家目录(Home)。选择空闲(free space)然后点击加号(+)。
+
+
+
+它会给你提供创建Linux分区的选项。我们正在创建根分区 /。10到20GB空间就足够了。选择大小(Size),然后选择Ext 4作为文件系统以及 /(意思是根)作为挂载点(Mount point)。
+
+
+
+点击确定会回到分区界面。下一步我们创建交换空间(Swap)。像之前一样,再次点击加号(+)。这次我们选择作为交换空间(Swap area)。建议的交换空间大小是物理内存的两倍。
+
+
+
+以同样的方式创建家目录(Home)。给它分配最大的空间(实际上是给它分配剩余的所有空间),因为这是你会用来存储音乐,图片以及下载的文件的位置。
+
+
+
+分配好了根分区( / ),交换空间(Swap)和家目录(Home)之后,点击**现在安装(Install Now)**:
+
+
+
+好了,你现在基本上以及赢得了这场战役了~露出胜利的微笑吧~接下来你会被要求设置用户名密码等等。基本上你现在只需点击下一步。
+
+一旦安装完成,重新启动电脑,你应该会看到紫色的grub欢迎界面。尽情享受Ubuntu和Windows 8的双启动模式吧。(译注:对于可能出现grub系统选择中没有Windows 8选项或是无法正常启动的情况,可搜索Boot Repair工具的使用)
+
+我希望这份指南能够帮你实现Ubuntu和Windows 8的UEFI模式双启动。虽然这篇文章是为Ubuntu写的,它对其它的Linux OS应该也有所帮助。欢迎提出任何问题与建议。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://itsfoss.com/install-ubuntu-1404-dual-boot-mode-windows-8-81-uefi/
+
+译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://itsfoss.com/install-ubuntu-dual-boot-mode-windows/
+[2]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/6-safest-ways-to-backup-restore-your-files-in-windows-7-8/
+[3]:http://www.pendrivelinux.com/universal-usb-installer-easy-as-1-2-3/
+[4]:http://linux.cn/article-3061-1.html
diff --git a/published/201406/How To Install 'California' Calendar App in Ubuntu 14.04.md b/published/201406/How To Install 'California' Calendar App in Ubuntu 14.04.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c92e1dee93
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/How To Install 'California' Calendar App in Ubuntu 14.04.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+Ubuntu 14.04上怎样安装‘California’ 日历应用
+================================================================================
+
+
+**当非盈利软件服务商Yorba宣称它上个月开始开发名为‘California’的桌面日历应用程序时,我们很兴奋——我们在自己的头条里面说“正当其时!”**
+
+Yorba在背后支撑着注重用户体验的电子邮件客户端软件‘Geary’以及华丽的照片管理软件‘Shotwell’,因此,我们自然有理由非常期望他们能够进军linux系统上的生产力软件主流软件。
+
+尽管 **California 尚未稳定** 到可以发布到正式的发行版本,但现在可以通过该公司的日常开发的PPA安装到ubuntu系统中。
+
+### 迄今取得的进展 ###
+
+“*Neeeeeyaaaaaaaawwnnn!*” — 那是飞机即将降落在旧金山国际机场的一段警告声音.
+
+是的,California 正在积极的开发中,该软件尚未完成,也没有稳定到满足每个人每天使用,但是
+如果你愿意搞定一些bug的话,你可以在ubuntu 14.04上安装这款应用程序。
+
+是否这样做取决于你的想法。
+
+当前的构建(如,在写本文时的)提供了本地管理以及Google 日历和web日历(.ICS)的基本支持。事件可以甚至在GNOME桌面的日期/时间小程序中显示.
+
+#### 自然语言输入 ####
+
+当你第一次打开California 软件时,呈现在你面前的是当月概要,目前还没有按星期,年,议程去查看的方法,起码我没找到。你可以使用导航按钮而切换月份.
+
+可以通过点击工具栏中的日历图标创建新的日历(*如 ‘工作‘, ‘宠物照料‘*)及打开/关闭它。当所有的日历都展现在主窗口时,每个日历通过不同颜色来视觉区分。
+
+要创建新的事件,点击‘+’图标, 然后在弹出的输入框中使用**自然语言输入**,输入你想要提交事件的描述(译注:显然你得用英语)。例如, 输入内容“*Bake Sansa Stark A Lemon Cake on Wednesday 2.45 PM*”将在周三的这个时间(14:45)加入该事件。
+
+
+
+我希望这个功能变得更加完善些。现在,尽管它能够精准定位日期,但不支持重复性事件的创建
+(e.g., via “*Skype chat with Sam every Tuesday at 7 AM*“)也不能识别地点或人物(e.g., “*Coffee with Penelope on Monday 12 PM at Boston Tea Party*“)。
+
+要修改正确些,你可以在网格视图上双击它们来完善和编辑创建好条目。这将打开一个包含附加字段、时间选择、日期格式等的窗口。
+
+#### 不够完善 ####
+
+如果说有一些缺陷,那就是在外观上(这个阶段的bugs和欠缺的功能可以被忽略)。虽然在 Adwaita 主题下看来已经很棒了,不过在 Ubuntu 默认主题下它看起来糟透了。
+
+这不是Yorba(或GNOME)的错误,而是Ubuntu开发团队仍然没有在Compiz里面增加对GNOME新的GTK标题栏的支持,现在还在使用 Unity 来渲染窗口。
+
+California 在ubuntu系统上完全可用,这个问题只是在发行版升级之后。 这个问题没有影响到Ubuntu GNOME或Linux Mint。
+
+### 在ubuntu14.04中安装California ###
+
+如果你没注意先前的提醒,我们再次重申:California 尚未稳定,正处于积极的开发中。
+
+这个[Yorba Daily PPA][2] 也包含了最新(未稳定)的Shotwell和Geary版本。将这个PPA安装到你的系统中将能够使这些软件也更新了。
+
+ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yorba/daily-builds
+ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install california
+
+另一个安全试用这个软件的方法是,[直接下载来自PPA的.deb安装包][3]:
+
+- [Download California for Ubuntu 14.04 (64bit)][4]
+- [Download California for Ubuntu 14.04 (32bit)][5]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/05/california-calendar-app-hits-yorba-daily-ppa
+
+译者:[hunanchenxingyu](https://github.com/hunanchenxingyu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/04/yorba-california-calendar-app-linux
+[2]:https://launchpad.net/~yorba/+archive/daily-builds/
+[3]:https://launchpad.net/~yorba/+archive/daily-builds/+packages
+[4]:https://launchpad.net/~yorba/+archive/daily-builds/+files/california_0.1.0-0%7E188%7Eubuntu14.04.1_amd64.deb
+[5]:https://launchpad.net/~yorba/+archive/daily-builds/+files/california_0.1.0-0%7E188%7Eubuntu14.04.1_i386.deb
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/201406/How To Remove Drive Icons From Unity Launcher In Ubuntu 14.04 [Beginner Tips].md b/published/201406/How To Remove Drive Icons From Unity Launcher In Ubuntu 14.04 [Beginner Tips].md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fde49451b8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/How To Remove Drive Icons From Unity Launcher In Ubuntu 14.04 [Beginner Tips].md
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+[小白技巧]在Ubuntu 14.04中,如何从Unity启动器上移除盘符图标
+=======================================================
+
+一个读者发来的问题:在Ubuntu 14.04系统中,我如何从Unity启动器上移除这些盘符图标?我从来不使用它,然而它占用着启动器的位置。
+
+默认情况下,无论你挂载与否,系统上所有分区的盘符图标都会显示在Unity启动器上。事实上它可能会使 Unity 启动器的位置变得拥挤。刚刚接触 Ubuntu 的小白可能对如何将这些盘符移去感觉比较困扰,但是实际上这很容易。
+
+要从Ubuntu 14.04系统的Untiy启动器上永久地移除盘符图标,右键点击盘符,然后选择"Unlock from Launcher"即可。
+
+
+
+就这样。你不需要做更多操作了。即使分区被挂载,在Unity启动器上你再也看不到盘符图标了。我希望这能帮到你。如果你有任何问题可以随时问我。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+via: http://itsfoss.com/remove-drive-icons-from-unity-launcher-in-ubuntu/
+
+译者:[lousam](https://github.com/lousam) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201406/How to Install Windows 8.1 and Ubuntu 14.04 LTS on the Same Computer.md b/published/201406/How to Install Windows 8.1 and Ubuntu 14.04 LTS on the Same Computer.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3d35be0670
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/How to Install Windows 8.1 and Ubuntu 14.04 LTS on the Same Computer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+如何在同一台计算机上安装Windows 8.1和Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
+================================================================================
+
+
+
+**一些Windows用户,希望试试Linux操作系统,而不用删除他正在使用的系统。令人高兴的是,想尝试下Linux是非常简单的,而且Linux操作系统也能和其他操作系统在同一台机器上和平共处。**
+
+举个例子,如果你是Windows用户,想试试Ubuntu,这个过程实际上是相当简单的,用户只需要付出一点小小的努力即可,这个过程中稍微注意一点就行了。
+
+在PC上正常安装一个操作系统并不复杂,甚至是Ubuntu和其它Linux也一样简单。在大多数情况下,用户单击对话框的“下一步”,按照流程进行即可。当你想保留PC上的原来的操作系统时(并不特指Windows),还需要多一点操作才行,但是很简单。
+
+在Linux下刻录一个ISO镜像是很容易的,有好几个程序可以提供这样的功能。而在Windows下,你可以将Ubuntu刻录到DVD或制作成USB启动盘(这样更好一些)。要将Ubuntu正确复制到一个USB设备,你将需要下载名为[Win32 Disk Imager 0.9.5][1]一个小工具。它具有一个简单的界面,是完全自动的。
+
+在重启机器以安装Ubuntu前,你要给Ubuntu一些可用的磁盘空间,而且给Ubuntu一个磁盘分区是不够的。你将需要两个,一个放Ubuntu本身(大约10GB,如果你不想安装太多的应用的话,就足够了),第二个是交换分区(类似于Windows的页面文件),它的大小一般是你的内存的两倍。你不需要格式化它们,只要他们是可用的就行。如果你在第二块空闲硬盘安装Ubuntu,那就更简单了。
+
+插上USB启动盘并重新启动。你会得到一个提示,询问是“试用”还是“安装”。选择“安装”并选择安装方式:安装Ubuntu和Windows 8并存(或任何你拥有的其他版本),用Ubuntu替换Windows 8,或者别的选项。
+
+你可以选择“和Windows 8并存安装”,但你也许不喜欢安装程序自动处理的方式。你也可以选择“其它(Something Else)”来手动控制安装过程。
+
+找到你给Ubuntu保留的空闲分区(安装程序无法读取和显示Windows卷的名称,所以你要小心别选错了),双击它,选择ext4文件系统,和“/”作为默认的安装点。
+
+现在选择另外的那个较小的分区,选择swap分区类型。就这些了。当你点击下一步,安装程序将启动,你将要输入用户名,密码和其他信息。
+
+当你启动你之后,将得到一个简单的列表,可以选择你要启动的操作系统。
+
+尽情享受!
+
+------------------
+
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Install-Windows-8-1-and-Ubuntu-14-04-LTS-on-the-Same-Computer-440356.shtml
+
+译者:[CHINAANSHE](https://github.com/CHINAANSHE) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.softpedia.com/get/CD-DVD-Tools/Data-CD-DVD-Burning/Win32-Disk-Imager.shtml
diff --git a/published/201406/How to download webcomics from the command line on Linux.md b/published/201406/How to download webcomics from the command line on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9efaa73c7a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/How to download webcomics from the command line on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
+Linux + 漫画迷 = 二次元世界?
+================================================================================
+你是否从来都没有错过xkcd上的漫画连载?及时地阅读到网络漫画。或者你是否想过从你喜欢的网站上备份所有漫画连载?如你所愿,开源社区将为你提供解决方案:使用命令行程序从终端上下载所有你喜欢的漫画连载。
+
+在我们开始之前,请记住一点,你下载的漫画连载仅供个人使用,在没有授权的情况下是不可以散播出去的。如果你确实喜欢该作者的作品,请支持通过捐赠或购买正版商品获得。
+
+### 在Linux中安装Dosage
+
+有一个下载漫画连载的开源程序叫[dosage][1]。由于该程序是用python写的,所以安装漫画连载工具的方式有几种。今天我们就从一种简单的方法开始吧。
+
+第一步,你需要[安装pip][2](LCTT译注,这是一个用于安装和管理python包的工具),并确保你的python版本在2.7.0至3.3区间。接下来使用pip安装dosage。
+
+ $ sudo pip install dosage
+
+如果pip不能以某种方式来找到相关包(例如Ubuntu14.04系统),可以使用下列命令来找到。
+
+ $ sudo pip install http://wummel.github.io/dosage/dist/dosage-2.13.tar.gz
+
+dosage将会自动创建一个名为“Comics”新的文件夹。
+
+### Dosage的基本用法
+
+dosage的基本用法如下所述。使用dosage,你可以在数据库中找到你喜欢阅读的网络漫画,当最新一期的连载发布时,你可以及时获取最新一期。从某种意义来说,无论你在网络漫画中订阅多少连载,dosage都会确保一期不落地帮你把没有读过的漫画连载下载下来。
+
+下载和阅读你的离线网络漫画,首先要用以下命令将它们列出:
+
+ $ dosage -l
+
+现在,我们可以看到dosage将2000多套漫画从数据库列出。我个人建议用下面的这个命令来查找我们想要看的漫画:
+
+ $ dosage -l | grep [keyword]
+
+这样就会返回所有包含关键字标题的漫画了。
+
+一旦你确定列表中哪一本漫画是你想要阅读的,使用以下命令订阅这本漫画:
+
+ $ dosage [name of the webcomic]
+
+
+
+订阅漫画时会自动在"Comics"目录下创建子目录,并把最新的连载漫画下载到在里边。
+
+如果你不仅仅想下载最新连载的漫画而是完整的一部,那么你使用以下的命令就可以了:
+
+ $ dosage -a [name of the comic]
+
+最后,订阅了几本网络漫画之后,你可以使用下面这条简单的命令,方便地下载到这几本漫画的所有更新:
+
+ $ dosage @
+
+如果你不想错过每天的漫画更新,你可以每天执行这条命令确保不会错过。
+
+### Dosage的高级用法
+
+玩了一天dosage,你也许想知道它的更多使用方法。这需要你掌握更多的命令语法和快捷入门。
+
+如果你想在xkcd上下载更多的漫画连载,你应该会看到一条dosage拒绝的提示(使用成人选项,确认你的年龄):
+
+ use the --adult option to confirm your age
+
+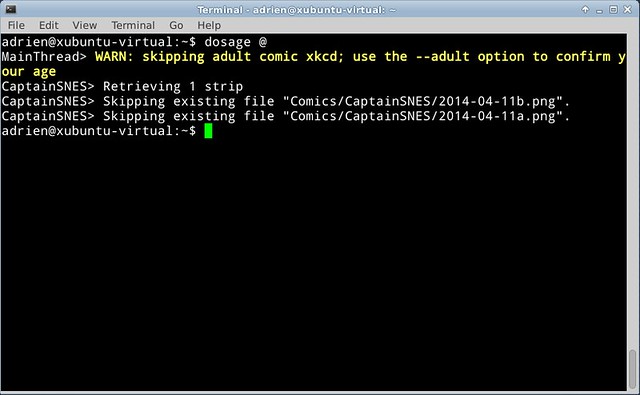
+
+因为默认情况下,dosage会忽略任何标记为仅限18岁以上的成年人浏览的网络漫画(由于某些原因,xkcd也属于其中的一个)。如果你已经成人了,请输入:
+
+ $ dosage --adult xkcd
+
+从之前的例子,你也许注意到'@'这个参数代表你所有已经下载的漫画书。而这个'@@'这个参数则是表示dosage数据库中的所有漫画书。
+
+ $ dosage @@
+
+上面的命令会下载dosage所知道的每一本漫画的最新连载。
+
+如果你想获取漫画从开始到特定的某一天的连载,你可以使用以下命令:
+
+ $ dosage -a [name of the comic]:[year-month-day]
+
+举个例子,我们想看《Calvin and Hobbes》2014年之前的所有连载,运行这条命令:
+
+ $ dosage -a calvinandhobbes:2014-01-01
+
+最后,对于所有想自己做些开发的人来说,dosage可以在下载时生成rss,json和html日志文件。
+
+ $ dosage -o [type] [name of the comic]
+
+在以上命令中,,[type]可以是rss,json或者html,[name of comic]也可以只用'@'。例如,用'html'参数就会创建一个漂亮的HTML代码,以看到所有已经下载到的漫画连载。
+
+下面的命令会下载所有关于Calvin and Hobbes的连载并生成一个网页,可以在你的浏览器中看到一个漂亮的网页,呈现出所有连载漫画。
+
+ $ dosage -o html -a calvinandhobbes
+
+
+
+最后,我会建议你[阅读手册][3]获取更多相关信息。dosage的确是一个非常简洁的工具,它为广大网页漫画迷们服务。我很好奇地想知道像创建出一个json文件来下载连载漫画的这种创意是怎么诞生的?
+
+你还有其它更好的取代dosage的工具么?或者说你是这些工具的粉丝并且用得非常过瘾,那就在评论里推荐给我们吧。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/04/download-webcomics-command-line-linux.html
+
+译者:[disylee](https://github.com/disylee) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://wummel.github.io/dosage/
+[2]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-pip-linux.html
+[3]:http://wummel.github.io/dosage/dosage.1.html
diff --git a/published/201406/How to launch applications differently with Gnome-Pie on Linux desktop.md b/published/201406/How to launch applications differently with Gnome-Pie on Linux desktop.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8fe5b3090c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/How to launch applications differently with Gnome-Pie on Linux desktop.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+Linux桌面上的小饼饼,让启动应用分外不同!
+================================================================================
+
+最近,你能听到很多关于Ubuntu新的Unity界面的抱怨。我记得,当Unity开始兴起的时候,我正好离开Archlinux。然而,Unity间接地导致了一个后果:随着人们对它不满意,人们开始关注其他的桌面环境和Linux发行版。而如果你的系统支持Unity,没有人会反对将它弄得更顺眼些。
+
+所以今天我向你推荐一个绝对原创的程序启动器: Gnome-Pie。你们可能会认为他的灵感来自魔兽世界插件"OPie"。因为他们有着相似的概念: 键盘快捷方式可以打开圆形"菜单",您可以从中选择一个应用程序或命令来启动。这种设计背后的主要思想是用户不必记住命令,但需要记住他的方向和操作。它的饼形设计让指针可以用同样的距离启动每个应用程序。再加上我们还有如此多自定义组合键,极大的提高效率并且最大限度地实现了人机工程学。
+
+### 安装Gnome-Pie ###
+
+在Ubuntu上,Gnome-Pie 可以从universe仓库中获得, 但是,某些原因,这个版本不是很稳定,常常会崩溃。作为一个备选方案,我建议你从官方的源进行下载。
+
+ $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:simonschneegans/testing
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get install gnome-pie
+
+在Fedora, 你可以使用以下命令:
+
+ $ sudo yum install gnome-pie
+
+对于Archlinux, 你可以在[AUR][1]找到它。
+
+### Gnome-Pie的基本用法 ###
+
+默认的,Gnome-Pie有一个比较可靠的初始配置。首先,你可以使用 **Ctrl + Alt + a** 调出,它将显示你的系统的基本应用程序。
+
+
+
+接下来, 按下 **Ctrl+Alt+b** 调出第二个圆,这将显示你的文件管理器的书签。
+
+
+
+第三个,也许是最有用的,它会显示你的应用程序菜单,按下 **Ctrl + Alt + 空格** 可调出。
+
+
+
+第四个,仅用于控制音乐播放器。你可以猜到,快捷键是 **Ctrl + Alt + m**。
+
+
+
+第五个,你可以快速访问重新启动、 关机和注销命令 (**Ctrl + Alt + q**,我猜q是代表退出吧)。
+
+
+
+最后,第六个,你可以用Pie来控制窗口,可以最小化、 规模、 关闭, 等等. 并且,快捷键是 **Ctrl+Alt+w**。
+
+
+
+虽然我发现这种默认设置已经是相当令人满意,几乎和预置的启动器一样好。然而,如果让我鸡蛋里找骨头,我会说一些快捷方式很难用一只手执行。大多数情况是,我们用两只手打开菜单,然后再回到鼠标以选择该选项。太不爽了。
+
+然而,我们在用 Linux!谁会在乎默认设置?自定义才是王道。Gnome-Pie将为你提供优良的服务。通过配置,你可以编辑现有的Pie,改变程序图标,设计自己的Pie,改变主题,甚至将另外一个Pie菜单作为一个子菜单。
+
+[][2]
+
+你甚至可以编辑它来访问 URL、 自由设置热键、运行你自己的命令。惟一的缺憾可能是它缺少Widgets。
+
+
+
+总之,相较于传统的基于文本的启动器,Gnome-Pie是一个相当有吸引力的可视化应用程序。我很喜欢他的自定义键盘和鼠标组合键,让我想起了我在War3或者LOL中的神级操作。如果玩家使用这种操作方式,它可以为你带来方便和高效。如果你想节约桌面空间,我甚至建议你不要将预置的启动器放到桌面上。总之,我甚至敢说它可以替代Gnome。
+
+你觉得怎么样?你在所有相信世界上有这么好的东西吗?或者说,随着新的Gnome shell出现,Gnome-Pie开始失去竞争力?欢迎评论。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/launch-applications-differently-gnome-pie-linux-desktop.html
+
+译者:[MikeCoder](https://github.com/MikeCoder) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/gnome-pie/
+[2]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14247093043/
diff --git a/translated/tech/How to manage Linux containers with Docker on Ubuntu.md b/published/201406/How to manage Linux containers with Docker on Ubuntu.md
similarity index 96%
rename from translated/tech/How to manage Linux containers with Docker on Ubuntu.md
rename to published/201406/How to manage Linux containers with Docker on Ubuntu.md
index e6be840633..94925b9649 100644
--- a/translated/tech/How to manage Linux containers with Docker on Ubuntu.md
+++ b/published/201406/How to manage Linux containers with Docker on Ubuntu.md
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
================================================================================
当前,完全硬件虚拟化技术(KVM、Xen、Hyper-V 等)能在一个物理主机上很好地运行多个互相独立的操作系统,但这也带来一些问题:性能不佳,资源浪费,系统反应迟缓等。有时候对用户来说,完全的硬件虚拟化并不是最好的选择。
-一种替代方案是使用轻量级虚拟化技术 —— 所谓的 [Linux Container 容器][1] (LXC),它提供的是系统级虚拟化。与跑虚拟机相比,LXC 可以在一个轻量级沙箱容器里面跑多个 Linux 操作系统。当你需要设置一些易于克隆的开发环境、测试环境,或想在安全沙盒里安装应用时,LXC 就非常有用了。
+一种替代方案是使用轻量级虚拟化技术 —— 所谓的 [LinuX Container 容器][1] (LXC),它提供的是系统级虚拟化。与跑虚拟机相比,LXC 可以在一个轻量级沙箱容器里面跑多个 Linux 操作系统。当你需要设置一些易于克隆的开发环境、测试环境,或想在安全沙盒里安装应用时,LXC 就非常有用了。
[Docker][2] 是一个开源工具,可以让用户方便地布署 Linux Container 容器。Docker 很快变成了 container 技术的非官方标准,从而被 [Ubuntu][3] 和 [Red Hat][4]等众多发行版吸收进去。
@@ -25,8 +25,8 @@
下一步是编辑 Docker 配置文件,确定 Docker 可执行文件的路径:
$ sudo vi /etc/default/docker.io
-
-> DOCKER="/usr/bin/docker.io"
+
+ DOCKER="/usr/bin/docker.io"
重启 Docker 服务:
@@ -102,7 +102,7 @@ Docker 使用 Linux 桥接技术与其他容器通信,以及连通外网。安
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/manage-linux-containers-docker-ubuntu.html
-译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/How to manage ip addresses and subnets with phpIPAM.md b/published/201406/How to manage ip addresses and subnets with phpIPAM.md
similarity index 77%
rename from translated/tech/How to manage ip addresses and subnets with phpIPAM.md
rename to published/201406/How to manage ip addresses and subnets with phpIPAM.md
index a934939bb6..94f1587d5d 100644
--- a/translated/tech/How to manage ip addresses and subnets with phpIPAM.md
+++ b/published/201406/How to manage ip addresses and subnets with phpIPAM.md
@@ -1,13 +1,12 @@
-Translating by GOLinux ...
-
如何使用phpIPAM来管理IP地址和子网
================================================================================
-通常,网络或系统管理员有责任来管理所管理的网络下的一个或多个子网。例如,当一个网段分配了/24子网,那么该子网就有254个IP地址可以用于不同目的。要跟踪某个IP被分配到了哪个主机,就需要某种文件编制。最简单的方法,就是使用一个电子表格来记录IP地址的分配信息。此方法对于只有一个管理员,并且网络很小的情况下比较奏效。然而,对于多个大型网络而言,依赖于电子表格并不方便,而且十分容易出错。更糟糕的是,如果有多个管理员参与管理,更新电子表格就十分麻烦了,因为每个管理员可能生成各种不同版本的文档记录。
-一种系统地管理IP地址分配的方式是使用网络化的IP地址管理工具。不仅仅是因为网络化管理工具能在任何地方访问并管理,而且其后端数据库也能保证所有更新能正确同步并实时生效。尽管有许多可用的网络化应用工具,但我们将在此教程中关注如何来安装[phpIPAM][1](IP地址管理工具)。phpIPAM是一个开源、高效的IP地址管理应用软件,有着以下一些特性。
+通常,网络或系统管理员有责任来管理其所管理的网络下的一个或多个子网。例如,当一个网段分配了/24子网,那么该子网就有254个IP地址可以用于不同用途。要跟踪某个IP被分配到了哪个主机,就需要通过某种方式记录下来。最简单的方法,就是使用一个电子表格,如Excel来记录IP地址的分配信息。此方法对于只有一个管理员,并且网络很小的情况下比较奏效。然而,对于多个大型网络而言,依赖于电子表格并不方便,而且十分容易出错。更糟糕的是,如果有多个管理员参与管理,更新电子表格就十分麻烦了,因为每个管理员可能生成各种不同版本的文档记录。
+
+一种系统地管理IP地址分配的方式是使用网络化的IP地址管理工具。不仅仅是因为网络化管理工具能在任何地方访问并管理,而且其后端数据库也能保证所有更新能正确同步并实时生效。尽管有许多可用的网络化应用工具,但我们将在此教程中关注如何来安装[phpIPAM][1](IP Address Manager IP地址管理工具)。phpIPAM是一个开源、高效的IP地址管理应用软件,有着以下一些特性。
- 同时支持IPv4和IPv6(和其它工具不同,它对IPv6支持得很好)
-- 内建IPv4和IPv6计算器
+- 内建的IPv4和IPv6计算器
- 支持无类域间路由(CIDR)标记
- 支持MySQL数据库
- 子网嵌套
@@ -22,18 +21,23 @@ Translating by GOLinux ...
可访问[http://demo.phpipam.net][2]查看phpIPAM演示网站。
在本教程中,我们将**在Ubuntu环境中使用Apache来配置phpIPAM**。
+
### 在Ubuntu上安装phpIPAM ###
+
首先,使用apt-get来安装需要的软件包。
# apt-get install apache2 mysql-server php5 php5-gmp php-pear php5-mysql php5-ldap wget
+
如果MySQL是首次安装,请使用以下命令来设置root密码。
# mysqladmin -u root password NEWPASSWORD
+
phpIPAM可以安装在任何Web服务器目录中,我们将会安装到Apache Web服务器的根目录下的/phpipam/子目录中。
下载phpIPAM软件包。
# wget http://kent.dl.sourceforge.net/project/phpipam/phpipam-1.0.tar
+
将软件包解压到Web服务器相应目录。
# cp phpipam-1.0.tar /var/www/
@@ -64,13 +68,15 @@ phpIPAM可以安装在任何Web服务器目录中,我们将会安装到Apache
需要在提供的.htaccess文件中指定基准目录。
# vim /var/www/phpipam/.htaccess
-
-> RewriteBase /phpipam/
+---
+ RewriteBase /phpipam/
### 准备Apache Web服务器 ###
-phpIPAM需要为该操作重写模块,该模块可以在Ubuntu或Debian机器上使用以下命令来启用。
+
+phpIPAM的运行需要Apache 的 Rewrite模块,该模块可以在Ubuntu或Debian机器上使用以下命令来启用。
# a2enmod rewrite
+
接下来,需要修改Apache的默认配置。请添加/修改你的配置,使它看起来像下面这样。
# vim /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default
@@ -89,48 +95,57 @@ phpIPAM需要为该操作重写模块,该模块可以在Ubuntu或Debian机器
# service apache2 restart
### 完成安装 ###
+
我们可以使用浏览器来完成phpIPAM的安装。将浏览器地址指向URL: http:///phpIPAM,将会显示以下phpIPAM安装页面。我们可以开始自动化数据库安装。
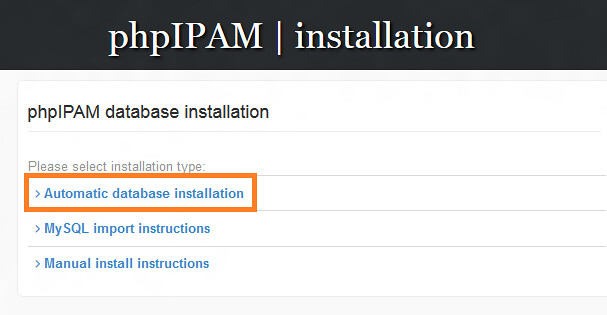
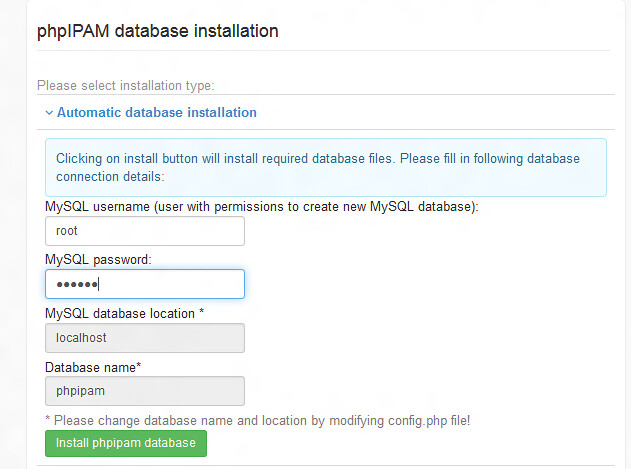
-现在,phpIPAM应该已经起来,并正在运行了,我们可以使用以下默认凭证来登录。
+现在,phpIPAM应该已经起来,并正在运行了,我们可以使用以下默认用户来登录。
- **URL**: http:///phpipam
- **User**: Admin
- **Pass**: ipamadmin
### 使用phpIPAM管理IP地址 ###
+
在本教程的剩下部分,我们将引领你进入phpIPAM的子网和IP地址管理。
+
#### 创建区域 ####
+
让我们从为我们的网络创建区域开始吧。点击“管理” > “区域”。
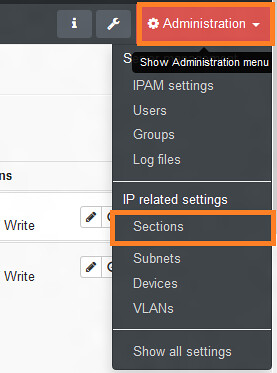
-点击“添加区域”。现在我们可以为我们的添加的区域取个你想要的名称了,填上区域的详细情况。
+点击“添加区域”。现在我们可以为我们的添加的区域取个你想要的名称了(如:"Our Network"),填上区域的详细情况。
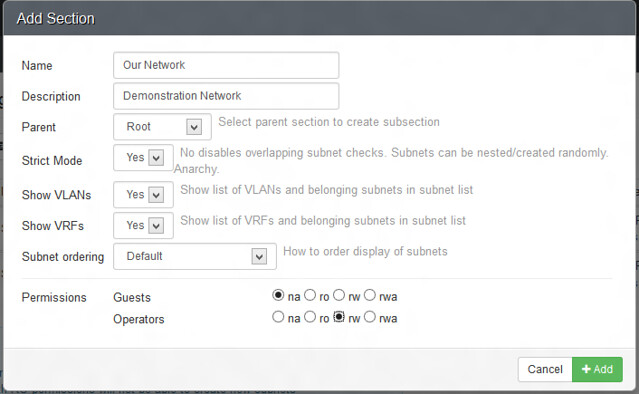][3]
#### 创建子网 ####
-接下来,在“我们的网络”区域下添加一个新的子网172.16.1.0/24。点击“我们的网络” > “添加子网”
+
+接下来,在上面场景的区域“Our Network”下添加一个新的子网172.16.1.0/24。点击“Our Network” > “添加子网”
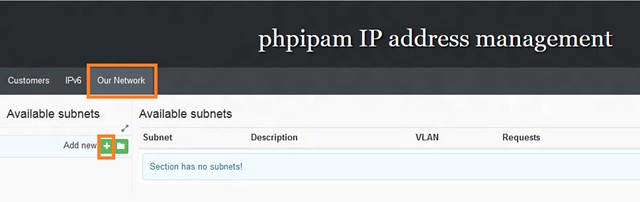
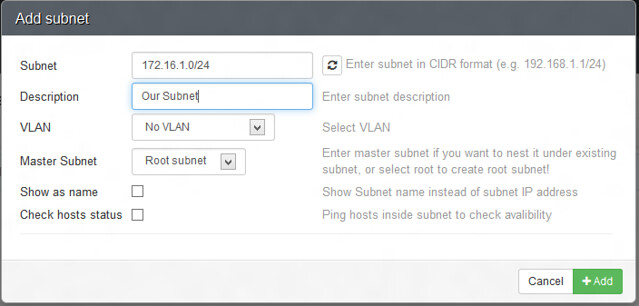
-现在,我们可以很容易地在子网中添加IP地址了。一种方法是逐个来添加它们,phpIPAM提供了一个可供选择的方法:扫描所有主机并自动添加,这一点都不麻烦。它可以扫描位于同一广播域下的本地子网,也可以通过路由扫描到远程子网。在选择一个子网后,像下面这样点击“扫描子网中的新主机”来扫描IP地址。
+现在,我们可以很容易地在子网中添加IP地址了。一种方法是逐个来添加它们,phpIPAM提供了一个可选的方法:扫描所有主机并自动添加,这一点都不麻烦。它可以扫描位于同一广播域下的本地子网,也可以通过路由扫描到远程子网。在选择一个子网后,像下面这样点击“扫描子网中的新主机”来扫描IP地址。
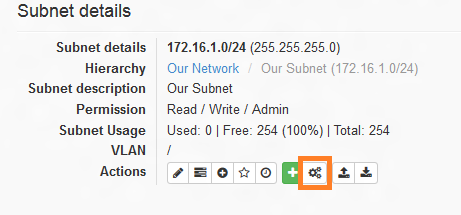][4]
在扫描完成后,发现的IP地址可以通过点击底部“添加发现的主机”按钮来将IP地址添加到数据库。
+
#### 创建IPv6子网 ####
+
可以通过相似的步骤来创建IPv6子网,像下面截图中展示的那样来指定IPv6网络。
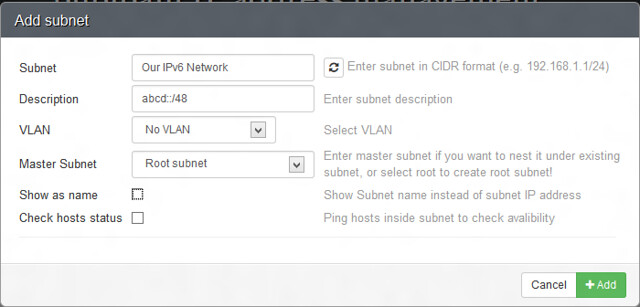
所有用于IPv4的工具也可以用于IPv6.
+
#### 创建嵌套子网 ####
+
phpIPAM也提供了创建嵌套子网的选项,可以用于IPv4和IPv6。例如,我们将172.16.1.0/24 IP区块划分成4个更小的子网(/26),每个子网用于组织内特定的部门。在选择/24子网后,我们可以使用“添加新的嵌套子网”按钮来创建嵌套子网。截图中展示了添加嵌套子网的图标。
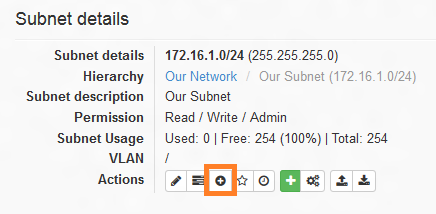[5]
@@ -140,7 +155,8 @@ phpIPAM也提供了创建嵌套子网的选项,可以用于IPv4和IPv6。例
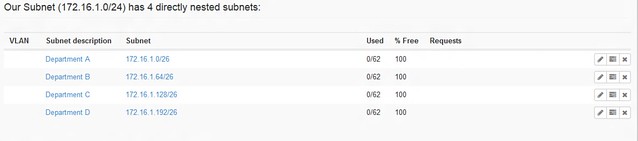[6]
#### 添加用户和组 ####
-首先,我们将为“我们的网络”创建一个具有读/写权限的组。这项工作可以通过选择“管理” > “组” > “创建组”来完成。
+
+首先,我们将为区域“Our Network”创建一个具有读/写权限的组。这项工作可以通过选择“管理” > “组” > “创建组”来完成。
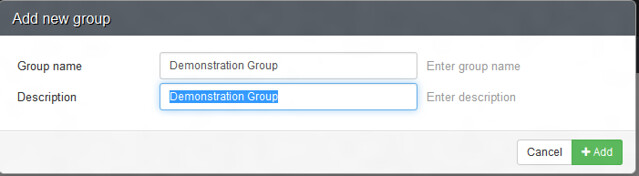
@@ -159,11 +175,12 @@ phpIPAM也提供了创建嵌套子网的选项,可以用于IPv4和IPv6。例
最后小结,phpIPAM是一个多样化的IP地址管理工具,可以用于IPv4和IPv6。本教程仅关注基本内容,以帮助你开始使用该工具。你一定要测试所有可用的特性,如使用IP地址计算器,添加设备,VLAN和VRF,以及使用.xls导入/导出。
希望本教程对你有所帮助。
+
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/manage-ip-addresses-subnets-phpipam.html
-译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201406/How to manage passwords from the command line on Linux.md b/published/201406/How to manage passwords from the command line on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..aa4f6e5a78
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/How to manage passwords from the command line on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
+如何在Linux上使用命令行管理密码
+================================================================================
+
+在基于密码的认证在网络盛行的今天,你可能需要或者已经使用了某种密码管理工具来跟踪管理你正在使用的所有密码。有各种各样的在线或离线服务或者软件工具用于完成此类事情,而这些工具因复杂程度、用户界面或者目标环境(如企业或终端用户)的不同而各不相同。例如,有一些是为终端用户开发基于图形化的密码管理器,如[KeePass(X)][1]。
+
+对于那些不想要依赖图形化进行密码管理的用户,笔者将会讲述如何在命令行下使用 [pass][2]来管理密码,**这是一个简单的用于命令行管理密码的工具**。
+
+该密码工具实际上是一个shell脚本编写的前端,其中调用了几个其它工具(如gpg,pwgen,git,xsel)来使用OpenGPG管理用户的密码信息。各个密码使用gpg工具进行加密,并存储到本地密码仓库中。密码信息可以通过终端或者自清除的剪贴板工具使用。
+
+该密码工具相当灵活,并且使用起来及其简单。你可以将每个密码信息存储到一个OpenGPG保护的普通文本文件,并且将不同的密码文件分组多个类目中。它支持bash自动补全特性,因此可以很方便地使用TAB键来补全命令或者很长的密码名称。
+
+
+### 在Linux上安装pass ###
+
+在Debian,Ubuntu或者Linux Mint上安装pass:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install pass
+ $ echo "source /etc/bash_completion.d/password-store" >> ~/.bashrc
+
+
+在Fedora上安装pass:
+
+ $ sudo yum install pass
+ $ echo "source /etc/bash_completion.d/password-store" >> ~/.bashrc
+
+在CentOS上安装pass,首先[启用EPEL仓库][3],然后执行以下命令:
+
+ $ sudo yum install pass
+ $ echo "source /etc/bash_completion.d/password-store" >> ~/.bashrc
+
+在Archlinux上安装pass:
+
+ $ sudo pac -S pass
+ $ echo "source /etc/bash_completion.d/password-store" >> ~/.bashrc
+
+### 初始化本地密码仓库 ###
+
+在使用密码工具之前,你需要执行一次初始化步骤,该步骤包括创建一个GPG密钥对(如果你还没有)以及一个本地密码仓库。
+
+首先,通过以下步骤创建一个GPG密钥对(即:公钥/私钥)。如果已经创建了自己的GPG密钥对,可以跳过此步骤。
+
+ $ gpg --gen-key
+
+执行该步骤,会询问你如下问题。如果你不确定,可以选择接受默认回答。作为密钥生成部分,你将要为你的密钥创建一个加密口令,这个口令实际上是你访问存储在本地密码仓库中的任何密码信息时的主密码。成功创建密钥对后,创建的密钥对会存储在~/.gnupg目录中。
+
+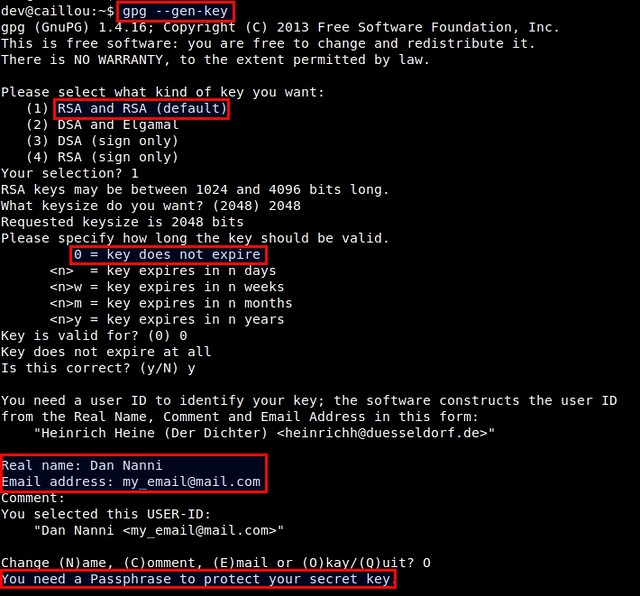
+
+接下来,运行以下命令来初始化本地密码仓库。下面的,输入之前创建密钥对时的关联电子邮件地址。
+
+ $ pass init
+
+该命令会在~/.password-store目录中创建一个密码仓库。
+
+### 在终端使用pass管理密码 ###
+#### 插入新密码信息 ####
+
+要将新的密码信息插入到本地密码仓库中,请遵循以下命令格式:
+
+ $ pass insert
+
+是你定义的专有名称,并且可以分级(如 "finance/tdbank", "online/gmail.com")。在这种情况下,密码信息可以存储到~/.password-store目录下对应的子目录中。
+
+如果你想要分多行插入密码信息,请像以下命令一样使用"-m"选项。以你自己喜欢的任何格式来输入密码信息,然后按Ctrl+D来结束。
+
+ $ pass insert -m
+
+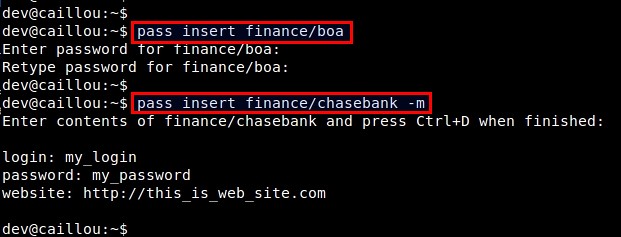
+
+#### 查看所有密码名称列表 ####
+
+要查看所有存储的密码名称列表,只需输入"pass"命令:
+
+ $ pass
+
+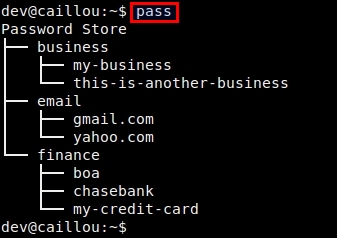
+
+#### 从密码仓库中取回密码信息 ####
+
+要访问特定密码列表中的内容,只需使用以下命令:
+
+ $ pass
+
+例如:
+
+ $ pass email/gmail.com
+
+会要求你输入密码口令来解锁密钥。
+
+如果你想要将密码复制到剪贴板,而不是显示到终端屏幕上,使用以下命令:
+
+ $ pass -c email/gmail.com
+
+当密码被复制到剪贴板,剪贴板在45秒后会被自动清空。
+
+#### 在密码仓库中生成并存储新密码 ####
+
+使用`pass`命令,你也可以生成一个新的随机密码,该密码可用于任何目的。pass工具将会使用pwgen工具来生成一个好的随机密码。你可以指定密码的长度,或者生成带或不带符号的密码。
+
+例如,要生成一个具有10个字符不带符号的密码,并将它存储到 "email/new_service.com"列表中:
+
+ $ pass generate email/new_service.com 10 -n
+
+#### 移除密码信息 ####
+
+要移除现存的密码信息是很容易的:
+
+ $ pass rm email/gmail.com
+
+小结一下,pass是及其灵活,便于携带,并且更为重要的是,易于使用。对于正在寻找能简单而行之有效地、安全地、并且不依赖图形化管理任何私人信息的工具的人,笔者强烈推荐pass。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/manage-passwords-command-line-linux.html
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/08/how-to-manage-multiple-passwords-on-linux.html
+[2]:http://www.zx2c4.com/projects/password-store/
+[3]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
diff --git a/published/201406/How to monitor Nginx web server from the command line in real time.md b/published/201406/How to monitor Nginx web server from the command line in real time.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0aa26102b1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/How to monitor Nginx web server from the command line in real time.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+ngxtop:在命令行实时监控 Nginx 的神器
+================================================================================
+Nginx网站服务器在生产环境中[运行][1]的时候需要进行实时监控。实际上,诸如[Nagios][2], Zabbix, Munin 的网络监控软件是支持 Nginx 监控的。
+
+如果你不需要以上软件提供的综合性报告或者长期数据统计功能,只是需要一种快速简便的办法去监控 Nginx 服务器的请求的话,我建议你采用一个叫 [ngxtop][3] 的命令行工具。
+
+
+你马上就会发现 ngxtop 从界面和名称都借鉴了著名的top命令。ngxtop 是通过分析 Nginx 或者其他的日志文件,使用类似 top 命令的界面实时展示出来的。你可以说你知道的其他高端监控工具,但是在简洁这方面 ngxtop 无疑是最好的。简单就意味着不可替代。
+
+本指南中,我将介绍如何使用 ngxtop 实时监控 Nginx 网站服务器。
+
+### Linux 上安装 ngxtop ###
+
+首先在 Linux 系统中安装依赖库[pip][4](LCTT译注:ngxtop是用python编写的)。
+
+然后使用如下命令安装 ngxtop。
+
+ $ sudo pip install ngxtop
+
+### ngxtop 使用 ###
+
+基本使用方法如下:
+
+ ngxtop [options]
+ ngxtop [options] (print|top|avg|sum)
+ ngxtop info
+
+这里是一些通用选项。
+
+- **-l **: 指定日志文件的完整路径 (Nginx 或 Apache2)
+- **-f **: 日志格式
+- **--no-follow**: 处理当前已经写入的日志文件,而不是实时处理新添加到日志文件的日志
+- **-t **: 更新频率
+- **-n **: 显示行号
+- **-o **: 排序规则(默认是访问计数)
+- **-a ..., --a ...**: 添加表达式(一般是聚合表达式如: sum, avg, min, max 等)到输出中。
+- **-v**: 输出详细信息
+- **-i **: 只处理符合规则的记录
+
+
+以下是一些内置变量,他们的含义不言自明。
+
+- body_bytes_send
+- http_referer
+- http_user_agent
+- remote_addr
+- remote_user
+- request
+- status
+- time_local
+
+### 使用 ngxtop 监控 Nginx ###
+
+ngxtop 默认会从其配置文件 (/etc/nginx/nginx.conf) 中查找 Nginx 日志的地址。所以,监控 Nginx ,运行以下命令即可:
+
+ $ ngxtop
+
+这将会列出10个 Nginx 服务,按请求数量排序。
+
+显示前20个最频繁的请求:
+
+ $ ngxtop -n 20
+
+
+
+获取Nginx基本信息:
+
+ $ ngxtop info
+
+
+
+你可以自定义显示的变量,简单列出需要显示的变量。使用 "print" 命令显示自定义请求。
+
+ $ ngxtop print request http_user_agent remote_addr
+
+
+
+显示请求最多的客户端IP地址
+
+ $ ngxtop top remote_addr
+
+
+
+显示状态码是404的请求
+
+ $ ngxtop -i 'status == 404' print request status
+
+
+
+除了Nginx,ngtop 还可以处理其他的日志文件,比如 Apache 的访问文件。使用以下命令监控 Apache 服务器:
+
+ $ tail -f /var/log/apache2/access.log | ngxtop -f common
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/06/monitor-nginx-web-server-command-line-real-time.html
+
+译者:[shipsw](https://github.com/shipsw) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2014/01/compile-install-nginx-web-server.html
+[2]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/monitor-common-services-nagios.html
+[3]:https://github.com/lebinh/ngxtop
+[4]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-pip-linux.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/How to set up a web-based lightweight system monitor on Linux.md b/published/201406/How to set up a web-based lightweight system monitor on Linux.md
similarity index 77%
rename from translated/tech/How to set up a web-based lightweight system monitor on Linux.md
rename to published/201406/How to set up a web-based lightweight system monitor on Linux.md
index 505adae447..ce7ea9416f 100644
--- a/translated/tech/How to set up a web-based lightweight system monitor on Linux.md
+++ b/published/201406/How to set up a web-based lightweight system monitor on Linux.md
@@ -1,17 +1,19 @@
-在Linux上配置基于web的轻量级系统监控
+Monitorix :支持服务器和树莓派的轻量级系统监控系统
================================================================================
-有时候,我们作为普通用户或者系统管理员,需要知道系统运行是否良好。与系统状态相关的许多问题,都可以通过检查活动服务生成的日志文件来获得答案。然而,即便对于历经数个春秋的系统管理员而言,要检查日志文件的每个细节都不是件容易的事。这也是为什么他们依赖于监控软件的原因,监控软件能够从不同的源收集信息,并以易于理解的格式给出分析报告,如图表、可视化图像、统计数据等。
+有时候,无论是普通用户还是系统管理员,都需要知道系统运行是否良好。与系统状态相关的许多问题,都可以通过检查运行的服务所生成的日志文件来获得答案。然而,即便对于干过几年的系统管理员而言,要检查日志文件的每个细节都不是件容易的事。这也是为什么他们依赖于监控软件的原因,监控软件能够从不同的源收集信息,并以易于理解的格式给出分析报告,如图表、可视化图像、统计数据等。
+
+市面上流传着许多复杂的系统监控软件,诸如[Cacti][1], [Nagios][2], Zabbix, Munin此类。在本文中,我们向您介绍一个轻量级的监控工具——Monitorix,该工具设计用于在Linux/BSD上监控系统资源和许多熟知的第三方应用程序。由于专为资源有限的嵌入式系统而优化,Monitorix以使用简单,消耗内存资源少而著称。它内建了一个HTTP服务器用于提供web界面,并使用RRDtool数据库来存储时间序列统计数据,RRDtool可以很容易地和任何脚本语言整合,如Perl,Python,shell脚本,Ruby等。
-市面上流传着许多复杂的系统监控软件,诸如[Cacti][1], [Nagios][2], Zabbix, Munin此类。在本文中,我们选取了一个轻量级的监控工具——Monitorix,该工具设计用于在Linux/BSD上监控系统资源和许多熟知的第三方应用程序。由于专为资源有限的嵌入式系统而优化,Monitorix以使用简单,消耗内存资源少而著称。它内建了一个HTTP服务器用于提供web界面,并使用PRDtool来存储时间序列统计数据,该PRDtoo可以很容易地和任何脚本语言整合,如Perl,Python,shell脚本,Ruby等。
### 主要特性 ###
+
这里列出了Monitorix的主要特性。要查看完整列表,请参阅[官方网站][3]
-- 系统负载和系统服务需求
+- 当前系统负载和系统服务
- CPU/GPU温度传感器
-- 磁盘温度和健康
+- 磁盘温度和健康度
- 网络/端口流量和网络状况统计
- 邮件统计
-- Web服务器统计(Apache,Nginx,Light图片的)
+- Web服务器统计(Apache,Nginx,Lighttpd)
- MySQL负载和统计
- Squid代理统计
- NFS服务器/客户端统计
@@ -28,8 +30,7 @@
$ sudo yum install monitorix
-
-要配置Monitorix,打开/etc/monitorix/monitorix.conf配置文件,并修改选项。关于Monitorix的配置文件细节,可以查阅[http://www.monitorix.org/documentation.html][6]。
+要配置Monitorix,打开`/etc/monitorix/monitorix.conf`配置文件,并修改选项。关于Monitorix的配置文件细节,可以查阅[http://www.monitorix.org/documentation.html][6]。
默认情况下,内建的HTTP服务器监听8080端口。因此,确保你的防火墙没有阻止TCP 8080端口。
@@ -40,9 +41,10 @@
启动你喜爱的Web浏览器,然后通过http://:8080/monitorix来访问Monitorix的Web界面。
### 在Archlinux上安装并配置Monitorix ###
+
在Archlinux上,可以从[AUR][7]上下载Monitorix包。
-默认情况下,Archlinux上是禁用内建HTTP服务器的。要启用内建的HTTP服务器,请编辑/etc/monitorix.conf文件的如下区块。
+默认情况下,在Archlinux上是禁用了其内建HTTP服务器的。要启用内建的HTTP服务器,请编辑/etc/monitorix.conf文件的如下区块。
enabled = y
@@ -65,10 +67,11 @@
打开你喜欢的Web浏览器,然后通过http://:8080/monitorix来访问Monitorix的Web界面。
### 在Debian和Ubuntu上安装并配置Monitorix ###
+
对于Debian家族,Monitorix可以通过两种方式安装:手工安装或通过第三方软件仓库。
+
#### 手工安装(用于Debian) ####
-Install all dependent packages first.
首先安装所有依赖包。
$ sudo apt-get install rrdtool perl libwww-perl libmailtools-perl libmime-lite-perl librrds-perl libdbi-perl libxml-simple-perl libhttp-server-simple-perl libconfig-general-perl libio-socket-ssl-perl
@@ -82,6 +85,7 @@ Install all dependent packages first.
$ sudo service apache2 reload
#### 通过软件仓库安装 (用于Ubuntu) ####
+
在/etc/apt/source.list中添加以下行来启用Izzysoft仓库。
deb http://apt.izzysoft.de/ubuntu generic universe
@@ -100,14 +104,15 @@ Install all dependent packages first.
$ sudo service monitorix start
-要配置Monitorix,请使用文本编辑器编辑/etc/monitorix/monitorix.conf,并重启Monitorix服务。
+要配置Monitorix,请使用文本编辑器编辑`/etc/monitorix/monitorix.conf`,并重启Monitorix服务。
$ sudo service monitorix restart
-用于Ubuntu的内建Web服务器默认将被启用。要从Web查看监控结果,在你喜爱的Web浏览器中访问http://8080/monitorix。
+用于Ubuntu的内建Web服务器默认启用。要从Web查看监控结果,在你喜爱的Web浏览器中访问http://8080/monitorix。
### 在Raspberry Pi上安装并配置Monitorix ###
-如果想要在Raspberry Pi(基于Debian)上安装Monitorix,你不能使用上面提到的Izzysoft仓库,因为它不提供Monitorix的ARM端口。取而代之的是,你可以参照如下基于Debian的手工安装。
+
+如果想要在Raspberry Pi(基于Debian)上安装Monitorix,你不能使用上面提到的Izzysoft仓库,因为它不提供Monitorix的ARM移植。取而代之的是,你可以参照如下基于Debian的手工安装。
首先,安装需要的软件包。
@@ -125,7 +130,7 @@ Install all dependent packages first.
安装完成后,我们需要像下面这样对Monitorix配置稍作修改。
-用你喜爱的文本编辑器打开/etc/monitorix/monitorix.conf,向下滚动文本直到你找到。搜索“raspberrypi = n”,并用“y”替换“n”,这将启用对Raspberry Pi时钟频率、温度和电压的监控。
+用你喜爱的文本编辑器打开`/etc/monitorix/monitorix.conf`,向下滚动文本直到你找到。搜索“raspberrypi = n”,并用“y”替换“n”,这将启用对Raspberry Pi时钟频率、温度和电压的监控。
编辑完成后,重启Monitorix服务。
@@ -159,7 +164,7 @@ Monitorix主屏幕:
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/web-based-lightweight-system-monitor-linux.html
-译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/How to take a screenshot from the command line on Linux.md b/published/201406/How to take a screenshot from the command line on Linux.md
similarity index 75%
rename from translated/tech/How to take a screenshot from the command line on Linux.md
rename to published/201406/How to take a screenshot from the command line on Linux.md
index c422f5e414..2681c03ff2 100644
--- a/translated/tech/How to take a screenshot from the command line on Linux.md
+++ b/published/201406/How to take a screenshot from the command line on Linux.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
-如何从Linux命令行截屏
+ 如何从Linux命令行截屏
================================================================================
-Linux上有着许多不同口味儿的截屏工具,包括桌面环境专用的截屏程序(如: KSnapshot for KDE,gnome-screenshot for GNOM,Screenshooter for Xfce),或者是通用的截屏程序(如 Shutter)。而Scort("SCReen shOT"的缩写)是最独一无二的截屏工具之一,它是一个**命令行截屏工具**。虽然它的界面十分简约,但Scrotas在功能上和其它专用的基于GUI的屏幕捕获工具一样强大。举个例子,Scrot支持延时截屏,截屏调整品质/大小,命令行传递等功能。如果你是那些命令行迷中的一个,Scrot应该是你加入兵器库中的又一实用工具。在这个教程中,我将会描述**如何在命令行中用Scrot截屏**。
+Linux上有着许多不同口味儿的截屏工具,包括桌面环境专用的截屏程序(如: KDE里面的KSnapshot,GNOME里面的gnome-screenshot,Xfce的Screenshooter),或者是通用的截屏程序(如 Shutter)。而Scort("SCReen shOT"的缩写)是最独一无二的截屏工具之一,它是一个**命令行截屏工具**。虽然它的界面十分简约,但Scrot在功能上和其它专用的基于GUI的屏幕捕获工具一样强大。举个例子,Scrot支持延时截屏,截屏调整品质/大小,命令行传递等功能。如果你是那些热衷命令行的爱好者之一,Scrot应该是你加入兵器库中的又一实用工具。在这个教程中,我将会描述**如何在命令行中用Scrot截屏**。
### 在Linux中安装Scrot ###
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ Linux上有着许多不同口味儿的截屏工具,包括桌面环境专用的
### 用Scrot截屏 ###
-在这个教程的剩余部分,我会描述如何通过几种不同方法用Scrot截屏。
+在这个教程的下面的部分,我会描述如何通过几种不同方法用Scrot截屏。
#### 1. 截下整个桌面 ####
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ Scrot允许你在桌面选择一个特定的窗口或定义一个矩形区域来
$ scrot -s
-运行这个命令后,继续用你的鼠标单击任意窗口或画出一个矩形,它能够触发对选定窗口/区域的屏幕截取。
+运行这个命令后,继续用你的鼠标单击任意窗口或画出一个矩形,它能够触发对选定窗口/区域的屏幕截取。(LCTT译注,还要使用鼠标,伐快乐)
有时候你选定的区域或窗口可能会被桌面的其它窗口部分遮挡。在这种情况下,你在截屏前需要一点时间来清理那个部分。那正是延迟截屏能够帮到你的,就像下面所描述的那样。
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ Scrot允许你发送保存的截屏图像给任意一个命令作为它们的输
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/take-screenshot-command-line-linux.html
-译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/How to take full length screenshots of websites via terminal.md b/published/201406/How to take full length screenshots of websites via terminal.md
similarity index 85%
rename from translated/tech/How to take full length screenshots of websites via terminal.md
rename to published/201406/How to take full length screenshots of websites via terminal.md
index 5e9542b741..dc8a5ad379 100644
--- a/translated/tech/How to take full length screenshots of websites via terminal.md
+++ b/published/201406/How to take full length screenshots of websites via terminal.md
@@ -1,8 +1,7 @@
-如何在终端为网页截取一个完整长度的截图
+如何在终端下截取一个完整长度的网页截图
================================================================================

-这是一个名叫 **Tsamis Konstantinos** 的访客所发的帖子。他是一个 Linux 和开源软件的狂热用户,也是 Unixmen 的常客。你可以通过他的邮箱 **tsamis73@gmail.com** 联系他:
与其记笔记或是把看到的内容发送给其他人,我们更经常通过截屏来帮助我们记忆。
但是通常情况下,如果一个网页超出了屏幕高度,我们就得用多张截图去截取其全部内容。
@@ -19,7 +18,7 @@
$ sudo yum install gnome-web-photo
但是对于 CentOS 和其他 RedHat 分支的用户,请注意 `gnome-web-photo` 依赖 GTK+ 3.0 这个软件包。
-也就是说 `gnome-web-photo` 是和 CentOS/RHEL 6 自带的 GNOME 2 不相兼容的。
+也就是说 `gnome-web-photo` 是和 **CentOS/RHEL 6 自带的 GNOME 2 不相兼容的**。
要为一个网页截图:
@@ -45,7 +44,7 @@
$ gnome-web-photo -t 0 --mode=print http://www.unixmen.com output.pdf
-注意这个应用并不兼容 **.jpg** 格式。
+注意这个应用并不支持 **.jpg** 格式。
这个应用应该对各类用户都有所帮助。我经常对网页进行缩略图和完整长度的截图,希望对你也有所帮助。
diff --git a/sources/tech/How to use LVM in Linux.md b/published/201406/How to use LVM in Linux.md
similarity index 51%
rename from sources/tech/How to use LVM in Linux.md
rename to published/201406/How to use LVM in Linux.md
index 859b2867c9..6679df3ba7 100644
--- a/sources/tech/How to use LVM in Linux.md
+++ b/published/201406/How to use LVM in Linux.md
@@ -1,43 +1,41 @@
-Vic020 在被关,我就急
-
-How to use LVM in Linux
+Linux LVM简明教程
================================================================================
-Logical Volume Manager (LVM) is a versatile disk management system that can easily be used in Linux or similar operating systems. Traditional partitions are created in fixed sizes, and resizing them is a tedious process. On the other hand, LVM creates and manages "logical" volumes off of physical hard disks, and provides administrators the flexibility to extend and shrink logical volumes easily on demand without damaging stored data. Additional hard disks can be added to LVM at will, further increasing existing logical volumes. LVM does not need reboot as long as the kernel is aware of the existence of a partition.
+逻辑卷管理LVM是一个多才多艺的硬盘系统工具。无论在Linux或者其他类似的系统,都是非常的好用。传统分区使用固定大小分区,重新调整大小十分麻烦。但是,LVM可以创建和管理“逻辑”卷,而不是直接使用物理硬盘。可以让管理员弹性的管理逻辑卷的扩大缩小,操作简单,而不损坏已存储的数据。可以随意将新的硬盘添加到LVM,以直接扩展已经存在的逻辑卷。LVM并不需要重启就可以让内核知道分区的存在。
-LVM uses a hierarchical structure as it can be seen in the following diagram.
+LVM使用分层结构,如下图所示。
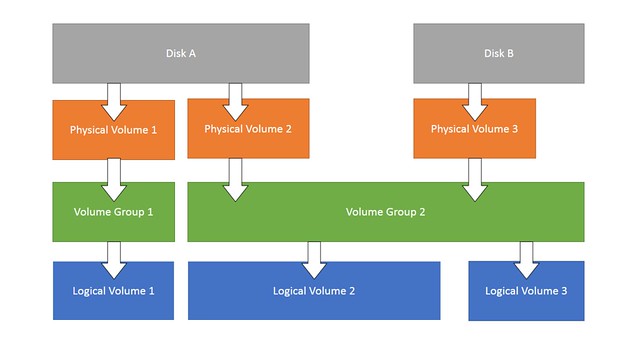
-At the top, we have physical volumes. One or more physical volumes are used to create a volume group. Logical volumes are then created from these volume groups. As long as there is space available in the volume group, we can create logical volumes from the volume group. File system is created on these logical volumes, which are then mounted and accessible in the operating system.
+图中顶部,首先是实际的物理磁盘及其划分的分区和其上的物理卷(PV)。一个或多个物理卷可以用来创建卷组(VG)。然后基于卷组可以创建逻辑卷(LV)。只要在卷组中有可用空间,就可以随心所欲的创建逻辑卷。文件系统就是在逻辑卷上创建的,然后可以在操作系统挂载和访问。
-### LVM Test Scenario ###
+### LVM测试说明 ###
-This tutorial will describe **how to use LVM to create and manage LVM volumes in Linux**. The tutorial will be divided into two parts. In the first part, we will create several logical volumes on one hard disk, and mount them in /lvm-mount directory. We will then resize the created volumes. In the second part, we will add additional volumes created from a second hard disk to LVM.
+本文将介绍**怎么在linux中创建和管理LVM卷**。我们将会分成两个部分。第一个部分,我们首先要在一个硬盘上创建多个逻辑卷,然后将它们挂载在/lvm-mount目录。然后我们将要对创建好的卷调整大小。而第二部分,我们将会从另外一块硬盘增加额外的卷到LVM中。
-### Preparing Disk Partitions ###
+### 准备磁盘分区 ###
-Disk partitions are created using fdisk. We will create three partitions of 1 GB each, though identical sized partitions are not mandatory. Also, the partitions are created as type '8e' to make them compatible with LVM.
+通过使用fdisk,创建磁盘分区。我们需要创建3个1G分区,注意,并不要求分区的大小一致。同样,分区需要使用‘8e’类型来使他们可用于LVM。
# fdisk /dev/sdb
----------
- Command (m for help): n ## new
+ Command (m for help): n ## 新建
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
- p ## primary
+ p ## 主分区
- Partition number (1-4): 1 ## partition number
- First cylinder (1-1044, default 1): ## hit enter
- Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-1044, default 1044): +1G ## size
+ Partition number (1-4): 1 ## 分区号
+ First cylinder (1-1044, default 1): ## 回车用默认的1
+ Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-1044, default 1044): +1G ## 大小
- Command (m for help): t ## change type
+ Command (m for help): t ## 改变类型
Selected partition 1
- Hex code (type L to list codes): 8e ## code for LVM
+ Hex code (type L to list codes): 8e ## LVM 的分区代码
Changed system type of partition 1 to 8e (Linux LVM)
-We repeat the same steps to create two other partitions. After the partitions are created, we should get an output similar to this:
+重复上面的操作来创建其他两个分区。分区创建完成后,我们应该有类似如下的输出:
# fdisk -l
@@ -48,15 +46,15 @@ We repeat the same steps to create two other partitions. After the partitions ar
/dev/sdb2 133 264 1060290 8e Linux LVM
/dev/sdb3 265 396 1060290 8e Linux LVM
-### Preparing Physical Volumes ###
+### 准备物理卷(PV) ###
-The newly created partitions are used to store physical volumes. LVM can work with different sized physical volumes.
+刚创建的分区是用来储存物理卷的。LVM可以使用不同大小的物理卷。
# pvcreate /dev/sdb1
# pvcreate /dev/sdb2
# pvcreate /dev/sdb3
-Physical volumes can be verified using the following command. The following section contains partial output. "/dev/sdb2" is a new physical volume of "1.01 GiB".
+使用下列命令检查物理卷的创建情况。下面截取部分输出。"/dev/sdb2"是一个新的"1.01 GiB"物理卷。
# pvdisplay
@@ -73,17 +71,17 @@ Physical volumes can be verified using the following command. The following sect
Allocated PE 0
PV UUID jszvzz-ENA2-g5Pd-irhV-T9wi-ZfA3-0xo092
-Physical volumes can be deleted using the following command.
+使用下列命令可以删除物理卷。
# pvremove /dev/sdb1
-### Preparing Volume Groups ###
+### 准备卷组(VG) ###
-The following command creates a volume group named 'volume-group1' by using the physical volumes /dev/sdb1, /dev/sdb2 and /dev/sdb3.
+下列命令用来创建名为'volume-group1'的卷组,使用/dev/sdb1, /dev/sdb2 和 /dev/sdb3创建。
# vgcreate volume-group1 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdb2 /dev/sdb3
-Volume groups can be verified using the following command.
+使用下列命令可以来验证卷组。
# vgdisplay
@@ -110,19 +108,19 @@ Volume groups can be verified using the following command.
Free PE / Size 774 / 3.02 GiB
VG UUID bwd2pS-fkAz-lGVZ-qc7C-TaKv-fFUC-IzGNBK
-We can view used/total size of the volume group from the output. Logical volumes take the space of the volume group. As long as there is free space available in the volume group, we can create logical volumes.
+从输出中,我们可以看见卷组的使用量/总量。物理卷给卷组提供空间。只要在这个卷组中还有可用空间,我们就可以随意创建逻辑卷。
-Volume groups can be deleted using the following command.
+使用下列命令删除卷组。
# vgremove volume-group1
-### Creating Logical Volumes ###
+### 创建逻辑卷(LV) ###
-The following command creates a logical volume named 'lv1' of size 100MB. We are using small sized partitions to reduce processing time. The logical volume will take its space from the volume group defined earlier.
+下列命令创建一个名为'1v1'、大小为100MB的逻辑卷。我们使用小分区减少执行时间。这个逻辑卷使用之前创建的卷组的空间。
# lvcreate -L 100M -n lv1 volume-group1
-Logical volumes can be verified using the command lvdisplay.
+逻辑卷可使用lvdisplay命令查看。
# lvdisplay
@@ -143,42 +141,42 @@ Logical volumes can be verified using the command lvdisplay.
- currently set to 256
Block device 253:2
-Now that the logical volume is ready, we can format and mount the logical volume like any other ext2/3/4 partition.
+现在逻辑卷已经准备好了,我们可以格式化和挂载逻辑卷,就像其它ext2/3/4分区一样!
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/volume-group1/lv1
# mkdir /lvm-mount
# mount /dev/volume-group1/lv1 /lvm-mount/
-Once the logical volume is mounted, we can access it by reading/writing to the mount point /lvm-mount/. To create and mount additional logical volumes, we can repeat this process.
+一旦逻辑卷挂载,我们就可以到挂载点 /lvm-mount/ 上读写了。要创建和挂载其它的逻辑卷,我们重复这个过程。
-Finally, we can delete any logical volume with lvremove.
+最后,使用lvremove我们可以删除逻辑卷。
# umount /lvm-mount/
# lvremove /dev/volume-group1/lv1
-### Expanding an LVM Volume ###
+### 扩展一个LVM卷 ###
-The ability to resize a logical volume is the best part about using LVM. This section will discuss how we can expand an existing logical volume. We will be expanding the previously created logical volume 'lv1' to 200 MB.
+调整逻辑卷大小的功能是LVM最有用的功能。这个部分会讨论我们怎么样扩展一个存在的逻辑卷。下面,我们将会扩展先前创建的逻辑卷‘lv1’扩大到200MB。
-Note that after resizing a logical volume, we also need to resize the file system to match. This extra step varies depending on which file system is created in the volume. In this tutorial, we created ext4 file system on 'lv1', so the instruction here focused on ext4 file system (it is compatible with ext2/3 file system as well). The sequence of the commands is important.
+注意,调整逻辑卷大小之后,也需要对文件系统调整大小进行匹配。这个额外的步骤各不相同,取决于创建文件系统的类型。在本文中,我们使用'lv1'创建了ext4类型的文件系统,所以这里的操作是针对ext4文件系统的。(ext2/3文件系统也类同)。命令的执行顺序是很重要的。
-First, we unmount the volume.
+首先,我们卸载掉lv1卷
# umount /lvm-mount/
-Then, the size of the volume is set to be 200M.
+然后,设置卷的大小为200M
# lvresize -L 200M /dev/volume-group1/lv1
-Next, the disk is checked for errors.
+接下来,检查磁盘错误
# e2fsck -f /dev/volume-group1/lv1
-After that, the ext4 information is updated.
+运行以下命令扩展文件系统以后,ext4信息就更新了。
# resize2fs /dev/volume-group1/lv1
-The logical volume should be extended to 200 MB by now. We can verify it by checking the LV status.
+现在,这个逻辑卷应该已经扩展到200MB了。我们检查LV的状态来验证。
# lvdisplay
@@ -199,27 +197,27 @@ The logical volume should be extended to 200 MB by now. We can verify it by chec
- currently set to 256
Block device 253:2
-Now the logical volume can be mounted again, and be used just like any partition.
+现在,这个逻辑卷可以再次挂载,同样这个方法也可用于其他分区。
-### Shrinking an LVM Volume ###
+### 缩减一个LVM卷 ###
-This section will cover the method of reducing the size of an LVM. The sequence of the commands is important. Again, this instruction is valid for ext2/3/4 file system.
+这章节介绍缩减LVM卷大小的方法。命令的顺序同样重要。并且,下列命令对ext2/3/4文件系统同样有效。
-Note that reducing the size of the logical volume to a value less than stored data will end in loss of data.
+注意减少逻辑卷的大小值若小于储存的数据大小,存储在后面的数据会丢失。
-First, the volume is unmounted.
+首先,卸载掉卷。
# umount /dev/volume-group1/lv1
-Then, the volume is checked for errors.
+然后,检测磁盘错误。
# e2fsck -f /dev/volume-group1/lv1
-Next, the ext4 information is updated.
+接下来缩小文件系统,更新ext4信息。
# resize2fs /dev/volume-group1/lv1 100M
-After that, the logical volume is reduced.
+完成以后,减少逻辑卷大小
# lvresize -L 100M /dev/volume-group1/lv1
@@ -229,7 +227,7 @@ After that, the logical volume is reduced.
> Reducing logical volume lv1 to 100.00 MiB
> Logical volume lv1 successfully resized
-Finally, the updated size of the logical volume is verified.
+最后,验证调整后的逻辑卷大小。
# lvdisplay
@@ -250,11 +248,11 @@ Finally, the updated size of the logical volume is verified.
- currently set to 256
Block device 253:2
-### Expanding a Volume Group ###
+### 扩展一个卷组 ###
-This section will cover the method of expanding a volume group by adding a new physical volume to the volume group. Let us assume that our volume group 'volume-group1' is full, and needs to be expanded. Our current hard disk (sdb) does not have any spare partitions, and we have added another hard disk (sdc). We will see how we can expand the volume group by adding a partition from sdc.
+本节将讨论扩展卷组的方法,将一个物理卷添加到卷组。让我们假设我们的卷组'volume-group1'已经满了,需要扩大。手上的硬盘(sdb)已经没有其他空闲分区,我们添加了另外一个硬盘(sdc)。我们将看到如何把sdc的分区添加到卷组以扩展。
-To check the current state of VG.
+检测现在卷组状态
# vgdisplay volume-group1
@@ -281,7 +279,7 @@ To check the current state of VG.
Free PE / Size 749 / 2.93 GiB
VG UUID bwd2pS-fkAz-lGVZ-qc7C-TaKv-fFUC-IzGNBK
-First, we create a 2 GB partition sdc1 of type LVM (8e) as explained earlier in the tutorial.
+首先,我们创建一个2GB分区sdc1,类型为LVM(8e),如教程前所述。
# fdisk /dev/sdc
@@ -305,15 +303,15 @@ First, we create a 2 GB partition sdc1 of type LVM (8e) as explained earlier in
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
-Then, we create a physical volume /dev/sdc1.
+然后,我们创建一个物理卷 /dev/sdc1
# pvcreate /dev/sdc1
-Now that the physical volume is ready, we can simply add it to the existing volume group 'volume-group1'.
+现在,物理卷已经准备好了,我们可以简单地将它增加到已存在的卷组'volume-group1'上。
# vgextend volume-group1 /dev/sdc1
-We can verify it using vgdisplay.
+使用vgdisplay来验证(可以看到卷组大小已经增大)。
# vgdisplay
@@ -340,16 +338,16 @@ We can verify it using vgdisplay.
Free PE / Size 1262 / 4.93 GiB
VG UUID bwd2pS-fkAz-lGVZ-qc7C-TaKv-fFUC-IzGNBK
-Note that although we have used a separate disk for demonstration, any disk of type '8e' can be used for expanding a volume group.
+注意,尽管我们使用一个单独的磁盘做示范,其实只要是‘8e’类型的磁盘分区都可以用来扩展卷组。
-To sum up, LVM is a very powerful tool for creating and managing resizable partitions. In this tutorial, we have seen how dynamic partitions can be created and used using LVM. We have also seen the method of expanding/reducing the logical volumes and volume groups, and adding new hard disks to LVM.
+总结一下,LVM是一个非常给力的工具,用来创建和管理可变大小的分区。本文中,我们已经看见了动态分区如何在LVM中创建和使用。我们也看见了扩展/缩小逻辑卷和卷组的方法,和如何增加一个新的磁盘到LVM。
-Hope this helps.
+希望对你有帮助。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/use-lvm-linux.html
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[Vic___](http://www.vicyu.net) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/How to verify DDOS attack with netstat command on Linux Terminal.md b/published/201406/How to verify DDOS attack with netstat command on Linux Terminal.md
similarity index 94%
rename from translated/tech/How to verify DDOS attack with netstat command on Linux Terminal.md
rename to published/201406/How to verify DDOS attack with netstat command on Linux Terminal.md
index ef84a1cd2e..d8a9be547e 100644
--- a/translated/tech/How to verify DDOS attack with netstat command on Linux Terminal.md
+++ b/published/201406/How to verify DDOS attack with netstat command on Linux Terminal.md
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ Dos攻击或者DDos攻击目的是使服务器或者网络资源耗尽,使其
netstat命令的用户手册描述其作用是用来显示网络连接、路由表、接口统计、伪连接和组播成员的。
-## 一些例子和解释 ##
+### 一些例子和解释 ###
netstat -na
@@ -47,18 +47,19 @@ netstat命令的用户手册描述其作用是用来显示网络连接、路由
列出所有连接到本机80端口的IP地址和其连接数。80端口一般是用来处理HTTP网页请求。
-## 如何减少DOS攻击 ##
+### 如何减少DOS攻击 ###
一旦你获得攻击服务器的IP地址你就可以使用以下命令拒绝此IP的所有连接。
iptables -A INPUT 1 -s $IPADRESS -j DROP/REJECT
注意,你需要将 $IPADRESS 替换成需要拒绝连接的IP地址。
+
执行完以上命令后,使用以下命令结束所有的httpd连接以清理系统。
killall -KILL httpd
- 然后执行以下命令重启httpd服务。
+然后执行以下命令重启httpd服务。
service httpd start #RedHat 系统
@@ -70,7 +71,7 @@ netstat命令的用户手册描述其作用是用来显示网络连接、路由
via: http://linuxaria.com/howto/how-to-verify-ddos-attack-with-netstat-command-on-linux-terminal
-译者:[shipsw](https://github.com/shipsw) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[shipsw](https://github.com/shipsw) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/Install SoundCloud In Ubuntu 14.04.md b/published/201406/Install SoundCloud In Ubuntu 14.04.md
similarity index 61%
rename from translated/tech/Install SoundCloud In Ubuntu 14.04.md
rename to published/201406/Install SoundCloud In Ubuntu 14.04.md
index 19a7b37f80..dc727f3885 100644
--- a/translated/tech/Install SoundCloud In Ubuntu 14.04.md
+++ b/published/201406/Install SoundCloud In Ubuntu 14.04.md
@@ -1,20 +1,23 @@
Ubuntu 14.04安装声云(SoundCloud)
================================================================================
-[SoundCloud][1]是一个发现交流音乐或印地音乐的很棒的平台。如果你是声云(SoundCloud)的粉丝,你可以在Ubuntu 14.04,或者其早期版本以及Linux Mint、Elementary OS等其它Linux发行版中作为“桌面应用”来尝试。
+[SoundCloud][1]是一个发现alternate音乐和 indi音乐的很棒的平台。如果你是声云(SoundCloud)的粉丝,你可以在Ubuntu 14.04,或者其早期版本以及Linux Mint、Elementary OS等其它Linux发行版中作为“桌面应用”来尝试。
要**在Ubuntu 14.04中安装声云(SoundCloud)**,我们将使用与[在Ubuntu中安装Google Keep][2]相同的方法来安装。上次我们使用Google Chrome来安装Google Keep,而这次我们将使用Firefox来安装声云(SoundCloud)。
+
### 在Ubuntu 14.04和Linux Mint中安装声云(SoundCloud): ###
+
由于Ubuntu(以及大多数其它Linux发行版)预装了Firefox,只需打开Firefox并转到该地址:[https://marketplace.firefox.com/][3]。
-Firefox应用市场是Chrome商店的替代品,里面提供了一些用于Firefox智能手机OS的应用,和Firefox网页浏览器一样。在Firefox应用市场中搜索声云(SoundCloud),点击安装(install)来安装,并作为Web应用添加到Ubuntu中。
+Firefox应用市场是Chrome商店的替代品,类似于Firefox网页浏览器的应用市场,里面提供了一些用于Firefox智能手机OS的应用。在Firefox应用市场中搜索声云(SoundCloud),点击安装(install)来安装,并作为Web应用添加到Ubuntu中。

-一旦完成,你可以通过在Unity Dash中搜索声云(SoundCloud)应用来启动它。下图展示了Ubuntu 14.04 Unity中该应用的外观:
+完成后,你可以通过在Unity Dash中搜索声云(SoundCloud)应用来启动它。下图展示了Ubuntu 14.04 Unity中该应用的外观:

### 卸载从Firefox应用市场安装的声云(SoundCloud)应用 ###
-不要过于兴奋了。该桌面没有整合声音菜单,我也不能对桌面通知持相同看法,但是这的确比Web应用要好,至少我是这么认为的。但是如果你感到不满意,那么就卸载它吧,这在Ubuntu中也很容易。
+
+不要过于兴奋了。该桌面没有整合声音菜单,桌面通知也一样没有,但是这的确比Web版应用要好,至少我是这么认为的。但是如果你感到不满意,那么就卸载它吧,这在Ubuntu中也很容易。
运行声云(SoundCloud),在Unity启动器上**右击**声云(SoundCloud)图标,然后点击**卸载应用(uninstall app)**。
@@ -26,7 +29,7 @@ Firefox应用市场是Chrome商店的替代品,里面提供了一些用于Fire
via: http://itsfoss.com/install-soundcloud-ubuntu-1404/
-译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201406/Linux Pros' Top Command Line Secrets.md b/published/201406/Linux Pros' Top Command Line Secrets.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..816583a130
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/Linux Pros' Top Command Line Secrets.md
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
+Linux大神们的顶级命令行秘诀
+================================================================================
+
+
+**好吧**,Linux博客圈这里这周相对比较平静,给网民们一个拖了很久的机会集体喘口气吧,去享受一下龙舌兰、燕尾服、鸡尾酒带来的欢快吧,然后评估一下过去几周来发生的和自由开放软件相关的事件吧。
+
+“你是否曾经在听一张专辑的时候想过‘伙计,这听起来不错,但是我希望它能经常从用户空间过渡到内核空间去!’”粉丝们在Facebook上写道,“我们会全力支持你的。我们的专辑现在完全可以作为一个可加载的Linux内核模块来播放。”
+
+Linux女孩曾经认为她自己已经完全进入Linux世界了,但是她现在却意识到她的想法是错误的。谢谢你们,粉丝们,是你们让生活一直这么有趣!
+
+### ‘命令行秘诀’ ###
+
+
+
+说到有趣,没什么比围坐在吧台前谈论行业内的事情来度过平静的一周更带劲了,而上周搞了一次。Linux博客圈内的生活很惬意。
+
+座谈会内容是《Linux之声》——那本炫目出世的新杂志,读者也许记得它是[去年年底发布的][6]——而谈话的主题恰恰就是[命令行秘诀][7]
+
+Linux女孩太激动了。
+
+### ‘它打算渲染大多数网页’ ###
+
+“有很多使用命令行的真正的好理由,”《Linux之声》的策划者写道,“它是让你和计算机进行交互的强大而简明的方法“
+
+“然而,我想花点时间来看看它里头一些更为晦涩的用法(有人会说毫无意义,不值得去做了)。“他们补充说。
+
+杂志首先列出的是elinks网页浏览器:“它可能看起来没有它的竞争对手那样光彩照人,但它的目标是能够渲染大多数网页。”他们解释道,“它也有着极客时尚,当你需要快速检查你是否能从只能通过SSH访问的计算机上去访问网页时,它就会派上用场了。“
+
+之后谈到的包含了从维基百科上查阅一些定义等其它一些实用的小建议。
+
+### '对维护很重要' ###
+
+“命令行的小技巧很有趣,真的很有趣。”比如,Google+博主亚历桑德鲁:埃伯索尔满怀热情地说,“但是他们忘了[cowsay][8],它可以用来在黑漆漆的终端里博你一笑。“
+
+”命令行对于维护很重要。“他补充说,”大家可以使用bash脚本来自动化,只需按几个快捷键(或者只要一个就行)来完成复杂的任务。”
+
+其它命令行秘诀,埃伯索尔会把它们放进原来的列表的包括sl(蒸汽机车),以及这些[这些奇怪的点子][9]:
+
+ * % cat "food in cans"
+ cat: can't open food in cans
+ * % nice man woman
+ No manual entry for woman.
+ * % [Where is Jimmy Hoffa?
+ Missing ].
+ * % make love
+ Make: Don't know how to make love. Stop.
+ * % man: why did you get a divorce?
+ man:: Too many arguments.
+
+### '最珍贵的精华' ###
+
+“命令行秘诀?根本没这玩意。”博主[罗伯特:伯格森][10]告诉Linux女孩道,”失望了吧,新手?那就猛敲‘help’吧。还想要点提示?随便‘man’个什么吧。想更多来点不同?敲‘ls /bin /sbin /usr/bin /usr/sbin | less’,随便捡几个宝贝命令出来,整晚地‘man’去吧。我已经干那活超过十年了,到现在还玩得不亦乐乎。”
+
+伯格森记不得多久以前他发现了‘ssh’,但是“它是自由/开源软件世界中最璀璨的宝石了。“他说。
+
+”ssh的强大力量在于,你可以在一台计算机上输入命令获得快乐,你更可以在100台计算机上干同样的事情来获得100倍的快乐。“他补充道,”当然,要输入100次命令可不是闹着玩的。所以,学习一下通过ssh安全地无密码登陆,可以让ssh的远程登陆透明化。“
+
+### '带着尊重来用吧' ###
+
+当然,”就像干任何快乐的事一样,有人会沉迷于搞破坏。“伯格森警告道,”作为root用户,你可以输入命令来删除所有的东西,或者把这一切搞乱。“
+
+”这是核弹按钮,就像全球领袖处理世界事务一样,在按下那个键之前一定要三思而后行,评估干这事所产生的结果,带着尊重和高尚的动机来使用它。“他补充道。
+
+”我曾经删除了一个文件系统,因为我的大拇指在输入一个命令时不小心蹭到了空格键。“伯格森总结道,”坦白地说,这种蠢事我只干过一次。“
+
+### '很强大' ###
+
+Google+博主贡萨洛:贝拉斯科C不那么热情。
+
+“即使[GUI][11]工具更易用,在*nix领域,命令行仍然很强大。“他告诉Linux女孩,”甚至一些高级MacOS用户也用它们。”
+
+对于贡萨洛:贝拉斯科C他自己而言,“我想要掌握的唯一一些命令是进程控制和杀死命令,想要使用ctrl+alt+退格键,因为我可以用来处理给我造成麻烦的那个进程,我还想要掌握tar.gz文件的管理——那玩意到现在还让我头痛。“他说。
+
+#### '你正在做错事' ####
+
+最后一点,但并非不重要,SoylentNews博主hairyfeet有一个完全不同的观点。
+
+“我只想谈一件事情来充实一下命令行界面这个报道:如果你不干IT,而且做着一些重复的事情,而这些事情只是很简单、很原始地去记录一些有用的事情,但你还在用命令行,那么‘你在走一条不归路’“hairyfeet告诉Linux女孩,”命令行界面没什么神奇——它只是1970年代以来的一个图形化界面!“
+
+今天,有很多“有用的图形化界面,这要多亏了CPU速度的提升和内存的增加,而不是一美元店里的廉价手表——我们甚至有IDE和脚本语言,大大超过70年代那些古董,可以在广域网或者局域网上工作,并与操作系统最底层交互,一切都在变得更易用,这多亏了智能感应和自动完成这样的技术。“他解释说,”所以上天作证,如果你不是那3%的系统管理员,工作在以字节计数的世界里,你会把那一堆垃圾从陈年旧帐中翻出来?
+
+这是Hairyfeet的最佳命令行建议?“不要——被21世纪那些不切实际的想法所左右,学学怎样真正来使用语言和工具吧。“他总结道,”让命令行成为泡影,把软盘都扔进历史的垃圾桶吧。“
+
+> 本文作者Katherine Noyes总是尽忠职守扮演好她的Linux女孩,那件斗篷她从2007穿到现在了。作为一个白天举止温和的女记者,她晚上像逛夜店一样,为了搜寻最新的小道消息,在Linux博客圈上灌水。你也能在 [Twitter][12]和[Google+][13]上找到她。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/80437.html?rss=1
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.computer.org/portal/web/pressroom/Linus-Torvalds-Named-Recipient-of-the-2014-IEEE-Computer-Society-Computer-Pioneer-Award
+[2]:http://www.ieee.org/
+[3]:http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/80386.html
+[4]:https://www.facebook.com/netcatband/posts/755205877853161?stream_ref=10
+[5]:http://www.netcat.co/
+[6]:http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/79448.html
+[7]:http://www.linuxvoice.com/commandline-secrets/
+[8]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cowsay
+[9]:https://www.linux.com/community/blogs/133-general-linux/10408
+[10]:http://mrpogson.com/
+[11]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GUI
+[12]:http://twitter.com/noyesk
+[13]:https://plus.google.com/+KatherineNoyes?rel=author
diff --git a/published/201406/Linux Terminal--Dstat monitoring tools.md b/published/201406/Linux Terminal--Dstat monitoring tools.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..198db278cc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/Linux Terminal--Dstat monitoring tools.md
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+Linux终端下 dstat 监控工具
+================================================================================
+
+dstat 是一个可以取代vmstat,iostat,netstat和ifstat这些命令的多功能产品。dstat克服了这些命令的局限并增加了一些另外的功能,增加了监控项,也变得更灵活了。dstat可以很方便监控系统运行状况并用于基准测试和排除故障。
+
+dstat可以让你实时地看到所有系统资源,例如,你能够通过统计IDE控制器当前状态来比较磁盘利用率,或者直接通过网络带宽数值来比较磁盘的吞吐率(在相同的时间间隔内)。
+
+dstat将以列表的形式为你提供选项信息并清晰地告诉你是在何种幅度和单位显示输出。这样更好地避免了信息混乱和误报。更重要的是,它可以让你更容易编写插件来收集你想要的数据信息,以从未有过的方式进行扩展。
+
+Dstat的默认输出是专门为人们实时查看而设计的,不过你也可以将详细信息通过CSV输出到一个文件,并导入到Gnumeric或者Excel生成表格中。
+
+###特性###
+
+- 结合了vmstat,iostat,ifstat,netstat以及更多的信息
+- 实时显示统计情况
+- 在分析和排障时可以通过启用监控项并排序
+- 模块化设计
+- 使用python编写的,更方便扩展现有的工作任务
+- 容易扩展和添加你的计数器(请为此做出贡献)
+- 包含的许多扩展插件充分说明了增加新的监控项目是很方便的
+- 可以分组统计块设备/网络设备,并给出总数
+- 可以显示每台设备的当前状态
+- 极准确的时间精度,即便是系统负荷较高也不会延迟显示
+- 显示准确地单位和和限制转换误差范围
+- 用不同的颜色显示不同的单位
+- 显示中间结果延时小于1秒
+- 支持输出CSV格式报表,并能导入到Gnumeric和Excel以生成图形
+
+### 安装方法 ###
+
+Ubuntu/Mint和Debin系统:
+
+本地软件库中有相关安装包,你可以用下面命令安装:
+
+ # sudo apt-get install dstat
+
+RHEL/Centos和Fedora系统:
+
+你可以在romforge软件库中添加有相关安装包,参照[指导][2],使用如下命令很简单就能进行安装:
+
+ # yum install dstat
+
+ArchLinux系统:
+
+相关软件包在社区资源库中,你可以用这个命令来安装:
+
+ # pacman -S dstat
+
+###使用方法 ###
+
+dstat的基本用法就是输入dstat命令,输出如下:
+
+
+
+这是默认输出显示的信息:
+
+**CPU状态**:CPU的使用率。这项报告更有趣的部分是显示了用户,系统和空闲部分,这更好地分析了CPU当前的使用状况。如果你看到"wait"一栏中,CPU的状态是一个高使用率值,那说明系统存在一些其它问题。当CPU的状态处在"waits"时,那是因为它正在等待I/O设备(例如内存,磁盘或者网络)的响应而且还没有收到。
+
+**磁盘统计**:磁盘的读写操作,这一栏显示磁盘的读、写总数。
+
+**网络统计**:网络设备发送和接受的数据,这一栏显示的网络收、发数据总数。
+
+**分页统计**:系统的分页活动。分页指的是一种内存管理技术用于查找系统场景,一个较大的分页表明系统正在使用大量的交换空间,或者说内存非常分散,大多数情况下你都希望看到page in(换入)和page out(换出)的值是0 0。
+
+**系统统计**:这一项显示的是中断(int)和上下文切换(csw)。这项统计仅在有比较基线时才有意义。这一栏中较高的统计值通常表示大量的进程造成拥塞,需要对CPU进行关注。你的服务器一般情况下都会运行运行一些程序,所以这项总是显示一些数值。
+
+默认情况下,dstat每秒都会刷新数据。如果想退出dstat,你可以按"CTRL-C"键。
+
+需要注意的是报告的第一行,通常这里所有的统计都不显示数值的。
+
+这是由于dstat会通过上一次的报告来给出一个总结,所以第一次运行时是没有平均值和总值的相关数据。
+
+但是dstat可以通过传递2个参数运行来控制报告间隔和报告数量。例如,如果你想要dstat输出默认监控、报表输出的时间间隔为3秒钟,并且报表中输出10个结果,你可以运行如下命令:
+
+ dstat 3 10
+
+在dstat命令中有很多参数可选,你可以通过man dstat命令查看,大多数常用的参数有这些:
+
+- -l :显示负载统计量
+- -m :显示内存使用率(包括used,buffer,cache,free值)
+- -r :显示I/O统计
+- -s :显示交换分区使用情况
+- -t :将当前时间显示在第一行
+- –fs :显示文件系统统计数据(包括文件总数量和inodes值)
+- –nocolor :不显示颜色(有时候有用)
+- –socket :显示网络统计数据
+- –tcp :显示常用的TCP统计
+- –udp :显示监听的UDP接口及其当前用量的一些动态数据
+
+当然不止这些用法,dstat附带了一些**插件**很大程度地扩展了它的功能。你可以通过查看/usr/share/dstat目录来查看它们的一些使用方法,常用的有这些:
+
+- -–disk-util :显示某一时间磁盘的忙碌状况
+- -–freespace :显示当前磁盘空间使用率
+- -–proc-count :显示正在运行的程序数量
+- -–top-bio :指出块I/O最大的进程
+- -–top-cpu :图形化显示CPU占用最大的进程
+- -–top-io :显示正常I/O最大的进程
+- -–top-mem :显示占用最多内存的进程
+
+
+举一些例子:
+
+查看全部内存都有谁在占用:
+
+ dstat -g -l -m -s --top-mem
+
+显示一些关于CPU资源损耗的数据:
+
+ dstat -c -y -l --proc-count --top-cpu
+
+###如何输出一个csv文件###
+
+想输出一个csv格式的文件用于以后,可以通过下面的命令:
+
+ # dstat –output /tmp/sampleoutput.csv -cdn
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linuxaria.com/howto/linux-terminal-dstat-monitoring-tools
+
+译者:[disylee](https://github.com/disylee) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://linuxaria.com/tag/network
+[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-and-enable-rpmforge-repository-in-rhel-centos-6-5-4/
diff --git a/published/201406/Making Linux Feel at Home.md b/published/201406/Making Linux Feel at Home.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..64f115d2e8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/Making Linux Feel at Home.md
@@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
+让Linux宾至如归
+================================================================================
+**采用小企鹅不管是对于小企业还是大企业而言,都是一个明智的选择。Linux曾经被认为是业余爱好者的操作系统,但是经历了很长一段历程后,现在它成了企业级系统。它很稳定,而且很安全。Linux易于定制,而且有庞大的社区提供帮助。这只是迁移到Linux桌面的部分理由。**
+
+
+
+迁移到一个不同的系统,从来都不是件容易的事。继续开着窗户(Windows),或吃着苹果(MacIntosh)可能是个令人沮丧且代价高昂的体验。花钱升级新的硬件来赶上高贵的新软件时髦,这往往是毫无价值的做法。
+
+在家里或一个小型的办公环境中运行一个Linux发行版,这是个有益的尝试,它可以带来开支的节约和效率的提升。对于企业环境而言,采用Linux服务器系统来替代微软基础架构常常是个明智的商业选择。
+
+然而,放弃熟悉操作系统下的舒适环境的过程看起来比实际更具挑战性。个人用户和中小型企业可以分阶段迁移到Linux桌面。软件是免费的,而用户已有的硬件是可以支持Window和Linux架构的。
+
+许多更大型的企业已经跑起了它们自己的Linux服务器仓库和完整的Linux桌面应用,这里它更容易适应。基于云的软件的使用使得办公室人员在使用他们的工作站工作时意识不到有很大的改变。
+
+“是否迁移到Linux取决于使用情况。如果在家里使用,或者从事开发,那么你会想使用Linux中所有可用的功能。那是没脑子的想法。迁移到另外一个操作系统从来没有一帆风顺的。没有哪种使用情况可以适合所有场合,它取决于用户基础。“麦克 瓦伊塔尔,[Talkpoint][1]首席技术官,告诉LinuxInsider。
+
+在中小型企业中和企业客户一起工作,瓦伊塔尔发现,利用新技术的个人用户和公司领导者的数量在增长,这些新技术将他们吸引到Linux中来。
+
+### 舒适度期望值 ###
+
+这些Linux技术之一就是Chrome OS,还有现在由基于Linux的Chrome操作系统驱动的廉价笔记本。
+
+由于用户已经熟悉Google的Chrome浏览器,或者开源的Chronium浏览器项目,使用Chromebook或者基于云的运载系统使得迁移到Linux变得小菜一碟。
+
+“忽略使用的操作系统,其中一个问题是浏览器的能力。我们已经发现,用户85%的时间花在浏览器中”[Splashtop][2]的共同创立者及产品管理高级副总裁托马斯.邓这样对LinuxInsider说。
+
+邓发现,那些有着快速学习曲线、能适应较新技术的人对此越来越有兴趣。人们使用多种多样的产品。因此迁移到一个与他们在其它设备上使用过的系统类似的系统,会使得迁移更平稳。
+
+### Chrome迎合潮流 ###
+
+移动设备用户,不管是在家中还是工作中,越来越精通Linux,而他们根本不知道这是个什么系统。他们在几个操作系统间切换。伴随着熟练程度的提高,开源环境也越发让人感觉舒适。通过云平台来分发跨平台软件,这是一个附加的迁移措施。
+
+“Google正在做的是与办公套件相关的一些真正有趣的事情。Google现在正在它的Chrome OS上敞开大门。”瓦伊塔尔说。
+
+对于关闭窗户(Windows),敞开大门(Chrome OS),一个很好的例子是它的公司内部使用Chrome驱动的工具。例如,Talkpoint使用ChromeBox设备。
+
+“那就为多媒体团队和传统的AV用户敞开了大门。我们看到该技术上的很多进展。”瓦伊塔尔解释说。
+
+### 平板打破传统 ###
+
+另外一个Linux设备为迁移到桌面OS铺平道路的例子是安卓系统的流行。加上这个为智能手机和平板电脑改良的Linux发行版。
+
+“对于迁移到Linux的人而言,人们对平板界面感到很舒服,尤其是在对Windows 8界面感到不满之后。我认识的每个人都试着回到Windows 7。”瓦伊塔尔说。
+
+### 云计算具有Linux影响力 ###
+
+人们希望使用像MS Offcie这样熟悉的生产工具来进行文字处理。而在Windows平台上,开源产品不怎么被人熟知。因此,在开始迁移到完整的Linux桌面之前,先整合开源工具到原有平台会很有帮助。邓解释道。
+
+随着Google Docs和Google Chrome浏览器的流行,Windows用户不知道开源的趋势正在发生改变。他指出。
+
+“让迁移到Linux变得方便的另外一条路是迁移到云端,使用云端应用。”邓说。“对用户进行教育,是将用户迁移到Linux的最有效的方式。Chromebook正大量被采用,这是一条迁移到Linux便捷的道路。”
+
+### 小企鹅威猛 ###
+
+聘请Tux,Linux的吉祥物小企鹅,对于小企业和大企业来说都是明智的选择。它是一个成熟、稳定而又灵活的操作系统,绝对可以帮你干活。据肖恩.塞乐,[视觉解决方案][3]高级产品经理说。
+
+“对于小型商业公司,运行Linux来替代其它操作系统是令人信服的选择,而且也带来优势,当然这取决于你的公司的需求。”塞乐告诉LinuxInsider。
+
+它曾经被认为是业余爱好者的操作系统,但是经历了很长一段历程后,现在它成了企业级系统。它很稳定,而且很安全。Linux易于定制,而且有庞大的社区提供帮助。这只是迁移到Linux桌面的部分理由。
+
+### 商业加分 ###
+
+利用更多的社区支持模式可以节约成本,塞乐说。Linux可以获得免费的社区支持,也可以付费订阅完整的技术支持。一些Linux版本也有硬件和软件认证这些东西,这些对于某些工作环境是很重要的。
+
+例如,小型商业公司和大型企业可以完整地免费运行像CentOS或者OpenSuse这样的发行版,或者也可以从[Red Hat][4]或者Suse来整合付费的版本。即便是一个完整的订阅服务,Linux也比Windows或者传统的Unix提供了更低的总拥有成本,以及更好的投资回报,塞乐解释道。
+
+“我相信,让小型企业来切身体验一下Linux很有意义。”塞乐补充道,“由于在社区以及像IBM和Red Hat这样的公司的帮助下,开源软件总体上正以快速的步伐帮助推动革新,Linux有一个光明的前途。”
+
+### 小心爽一把 ###
+
+操作系统在家庭和工作场所有不同的忠实用户。就拿BDNA的CTO沃克.怀特来说吧。他在家里使用Linux作为桌面操作系统,但是他的家人却对他热衷的东西并不买账。
+
+“我的家人用Mac之类的。他们盲目追随市场营销和功能炒作,而根本不考虑性能之类的东西。我在家里进行一个人的圣战,试着策反更多的人来加入Linux阵营。”怀特告诉LinuxInsider。
+
+在他的公司里有类似的死忠派在奋斗,他说道,他公司里Linux桌面使用并不普遍 —— 但他们为Linux在工作中更广泛地部署打下了基础。
+
+BDNA在内部使用Google应用很多。公司也在把越来越多的东西迁移到基于云计算的产品中。无论如何,这会给筹备中的工作更多的支持。
+
+“当我切换到想OpenOffice这样的应用时,该操作必须真正实现无缝操作以捕获更多人的心。从纯市场角度看,开发者需要稍稍改变一下游戏规则。苹果赢得了年轻孩子和30岁年轻一代的心。我经常在我公司听到这样的想法。”他说。
+
+### 小企鹅对战苹果 ###
+
+增加新的硬件设备是高端的MacBook Pro的特点,怀特解释道。尽管他们主要使用的工具是在线工具,BDNA的职员还是想要华而不实的,高度宣传的硬件。
+
+为了打破这种观念,他不得不将操作系统和硬件的功能分离。战役的一部分是将用户与操作系统本身隔离。而这只有在企业同时有在线和离线的生产力应用程序才会发生,据怀特说。
+
+“即使是使用文件管理器这样简单的事情,也应该将注意力放在操作系统允许我们在我们使用的应用里头做什么,而不是操作系统本身。”他说。
+
+### 爽到极点 ###
+
+操作系统多大程度上控制计算机用户?这个问题对于迁移到Linux而言很关键,怀特说。
+
+想想Chromebook以及安卓手机和平板的不断成功,消费者真的需要知道他们正在运行Linux么?
+
+“我认为迁移到Linux以及Linux在家里成功的关键在于,我们可以在线做多少事情。”怀特说,“因为我在家里使用Linux,所以我看到了其中的优势。”
+
+你是否启用家庭消费者层面的设置,或是转向家庭或小企业用户设置,重点在于用户可以兼容他们使用的工具和功能。这里头包括像共享和创建文档,以及与之相关的事情,他说明道。
+
+### 迁移措施 ###
+
+对于市场而言,软件和硬件生产商需要减少对操作系统的关注。例如,Chromebook正以苹果销售MacBook类似的方式获得大众认可。Google与其说是在贩卖Linux操作系统,倒不如说它是在销售应用,怀特回答道。
+
+“开发者真正需要做的是改变工作重点,让用户和Linux相处融洽,而不是让他们停留在使用非Windows,或者非Mac操作系统的踌躇上。不管你用什么,必须可以让它做你想让它做的事。像Chromebook这样的事物正是秉承了这样的观点,将Linux操作系统本身掩盖了起来。”他指出。
+
+计算机生产商必须首先开始打破“它是Windows”或者“它是Mac”这样的模式。到那个时候,迁移到Linux的数量才会大幅攀升,怀特总结道。
+
+“这无关操作系统品牌,”他说,“而在于运行该操作系统的设备所能做的事。”
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/80415.html
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.talkpointcommunications.com/
+[2]:http://www.splashtop.com/
+[3]:http://www.visionsolutions.com/
+[4]:http://www.redhat.com/
+[5]:http://www.bdna.com/
+[6]:http://www.openoffice.org/
+[7]:
+[8]:
+[9]:
+[10]:
+[11]:
+[12]:
+[13]:
+[14]:
+[15]:
+[16]:
+[17]:
+[18]:
+[19]:
+[20]:
diff --git a/published/201406/Open Source's Cult Of Personality Is Dying--Thankfully.md b/published/201406/Open Source's Cult Of Personality Is Dying--Thankfully.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ae25e4e17a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/Open Source's Cult Of Personality Is Dying--Thankfully.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+谢天谢地,开源软件中的个人崇拜正在消亡!
+================================================================================
+“开源之神圣独裁者”越来越少了,不过没事!
+
+Roy Rubin这位流行的电子商务开源项目[Magento][1]的联合创始人,从这一2008年启动的项目中功成身退后在[这周说出了][2]上面这样的话语。
+
+
+
+这已经不是第一次一个开源项目的领导者出走项目了,但值得注意的是对于它带来的反响是:没啥大的反应。
+
+并不是因为Rubin对于Magento项目不重要,实际上他非常重要。六年来,Rubin实际上是Magento项目的灵魂。但是开源软件一直在成长,它一直在削弱个人对其的影响。当然没人希望Linux的创始人Linus Torvalds不小心被车撞了,在这点上我们是[爱他][3]的。但是另外一方面其实我们并不太在意。
+
+但是并不总是这样的。
+
+### 崇拜开源之神圣独裁者! ###
+
+在好的一面,成功的开源项目一直以来都和伟大的领导者密不可分。对一个充满活力又有独立思想的一个开发团体施加影响,必定是众口难调的事情。在一个专门的开源项目当中不同的观点会产生各种不同的路线(在代码层上,管它叫做“分支”),通常这时候,要么是“开源之神圣独裁者”,要么是项目领袖,将会介入,施展自己的领导才能让开发人员团结在一起。
+
+“[开源之神圣独裁者 BDFL][0]”这个词[可能第一个用于Python项目的领导者Guido von Rossum][4]。它现在也被用到了Linux的发明人Linus Torvalds身上,以及Ubuntu的领导者Mark Shuttleworth和其他人身上。有时候另外两个人也会冠以这个称号,比如[Django][5]项目的Adrian Holovaty和Kaplan-Moss。(LCTT译注:BDFL,benevolent dictator for life ,由LCTT 核心译者 Viz 建议译作“开源之神圣独裁者”。)
+
+在他们影响力最大的时候,这些领袖离开项目会对项目的将来产生灾难性的影响,这展现出这些伟大领导者与项目之间紧密的关联。但是,有时候,也不总是这样。Django的领导者[去了其他的项目][6],但是Django依然不断前行着,像Python、Lucene(领导者Doug Cutting)、Jboss(领导者Marc Fleury)和其他很多的项目也是这样。
+
+现在开源软件研发的团体依然围绕着伟大的领导者,但我们似乎并不像曾经的那样依赖他们了。开源软件的“个人崇拜”正在褪色,也有可能已经消亡了,但是接下来会怎么样呢?
+
+### Apache和开源社区的崛起 ###
+
+是的,社区开始崛起了。我意识到我在做出一些自以为是的论调,但是根据我在开源项目15年的经验来说,我观察到开源软件项目从非常严格的控制阶段缓慢的转向了松散的开源团体,他们经常是因为兴趣才互相合作的。
+
+当然并不清楚是先有 BSD/Apache之类的许可证的“鸡”还是后有开源软件相互合作的“蛋”,这两个很明显的一起改变了开源软件的运作模式。
+
+当然还是需要“开源之神圣独裁者”。举个例子,当自由GNU还不是一个项目时,很难想象如果没有了Richard Stallman会是怎么样。相反的,很容易想象Apache Hadoop如果没有领导会怎么样…,等等,好像Hadoop真的没有人领导…
+
+如果真的要说答案的话,那就是这里每个人或者[许多人][7]。当然Hadoop由Doug Cutting启动,但是它已经发展成了一个公司和个人(不过大多数的公司雇佣了这些人)的协作的社区。
+
+OpenStack与之类似,[被涉及的公司所主导][8],如果某一个Openstack的开发者离开了,Openstack依然能够继续。因此,对于一个成员正在增加的开源项目来说,这种类似是确信无疑的。
+
+### 未来不需要“开源之神圣独裁者”吗? ###
+
+并不是说在以后的开源项目中不需要领导者。需要,但是越来越多的开源项目转为团体之间的合作,失去他们的风险消失了。坦白的说,即使公司们没有深入的参入进来,Apache许可证的项目反正也不依赖“开源之神圣独裁者”们。
+
+Photo of Richard Stallman [courtesy of Friprog on Flickr][9]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://readwrite.com/2014/05/02/open-source-magento-roy-rubin-bdfl#feed=/hack&awesm=~oDgSTEdnXAjUv0
+
+译者:[jiajia9linuxer](https://github.com/jiajia9linuxer) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://magento.com/
+[2]:http://magento.com/blog/magento-news/note-roy-and-mark#.U2JhPK1dVii
+[3]:http://www.serverwatch.com/server-news/if-linus-torvalds-got-hit-by-a-bus-would-linux-die.html
+[4]:http://www.artima.com/weblogs/viewpost.jsp?thread=235725
+[5]:https://www.djangoproject.com/
+[6]:http://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2014/01/on-the-reign-of-benevolent-dictators-for-life-in-software/283139/
+[7]:http://hadoop.apache.org/who.html
+[8]:http://activity.openstack.org/dash/releases/
+[9]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/friprog/
+[0]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Benevolent_dictator_for_life
diff --git a/published/201406/Pros' Secrets and Red Hat 7 and PCLinuxOS 2014.05 Reviews.md b/published/201406/Pros' Secrets and Red Hat 7 and PCLinuxOS 2014.05 Reviews.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a9c9d21cce
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/Pros' Secrets and Red Hat 7 and PCLinuxOS 2014.05 Reviews.md
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+点评 Redhat RHEL 7和PclinuxOS 2014.05
+=================
+
+在最近的Distrowatch杂志上,Jesse Smith尝试了一下RHEL 7桌面版本。在安装上,“从RHEL安装介质启动到一个图形化的系统安装界面,RHEL用了和最近发布的Fedora一样的新的Anaconda安装方式。就我个人来说新的安装方式是一种倒退”他说道。这没啥大不了的,他猜测在桌面版本就是这样的吧。Smith说他希望有一种图形化的软件包管理工具,因为用户只能在命令行下使用YUM源,只能使用标准的默认库。之后,GNOME shell登录崩溃了,只能使用KDE登录。虽然有些困惑但是他非常喜欢新的防火墙配置工具。请看他的[详细报告][2]。
+
+**在**ZDNet.com上,Jamie Watson对新发布的PCLinuxOS 2014.05发表了自己的看法。他说道:
+
+> 这是个有趣的看法,你可能从它的名字当中想到它包含了很多软件,补丁,驱动在非标准的分支中。最有趣的一点是,基于活动聚焦的虚拟桌面配置。这种趋势使PCLinuxOS使用起来既有趣又简单,提供了以下的桌面环境,个性化的图标:
+
+> 互联网:浏览器,邮件,聊天工具
+
+> 工作:office、kile、scribus
+
+> 娱乐:游戏
+
+> 多媒体:音乐,视频的编辑和创作
+
+> 图形和图像:浏览,编辑和创作
+
+> 管理:系统管理任务
+
+
+“PCLinuxOS始终使用原来的安装方式,它来源于Mandriva/Mandrake安装方式”Watson提到。它还带来了新的内核,最新的软件,和多样化互动的界面。[他总结道][3]:“这个新发布的PcLinuxOS版本很不错”。另外Watson在几周前也测试过了Ubuntu、Debian和LMDE。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ostatic.com/blog/pros-secrets-and-red-hat-7-and-pclinuxos-2014-05-reviews
+
+译者:[jiajia9linuxer](https://github.com/jiajia9linuxer) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/Linux-Pros-Top-Command-Line-Secrets-80437.html
+[2]:http://distrowatch.com/weekly.php?issue=20140512#feature
+[3]:http://www.zdnet.com/hands-on-with-pclinuxos-2014-05-kde-and-lxde-the-linux-with-something-for-everyone-7000029297/
+[4]:http://www.zdnet.com/testing-ubuntu-debian-and-lmde-on-my-new-notebook-7000029202/
diff --git a/translated/tech/Start Practising Linux ip command and Avoid the Habit of Using ifconfig.md b/published/201406/Start Practising Linux ip command and Avoid the Habit of Using ifconfig.md
similarity index 76%
rename from translated/tech/Start Practising Linux ip command and Avoid the Habit of Using ifconfig.md
rename to published/201406/Start Practising Linux ip command and Avoid the Habit of Using ifconfig.md
index e748fbd29e..9394ecd351 100644
--- a/translated/tech/Start Practising Linux ip command and Avoid the Habit of Using ifconfig.md
+++ b/published/201406/Start Practising Linux ip command and Avoid the Habit of Using ifconfig.md
@@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
-开始练习Linux的ip命令,避免使用ifconfig的习惯
+试试Linux下的ip命令,ifconfig已经过时了
================================================================================
-linux的**ip**命令和**ifconfig**类似,但前者功能更强大,并旨在取代后者。使用ip命令,只需一个命令,你就能很轻松地执行一些网络管理任务。ifconfig是网络工具中已被废弃使用的一个命令,许多年前就已经没有维护了。许多命令的功能被保留在iproute2套件里以提供更多特性。
+linux的**ip**命令和**ifconfig**类似,但前者功能更强大,并旨在取代后者。使用ip命令,只需一个命令,你就能很轻松地执行一些网络管理任务。ifconfig是net-tools中已被废弃使用的一个命令,许多年前就已经没有维护了。iproute2套件里提供了许多增强功能的命令,ip命令即是其中之一。

-要安装ip,请下载**iproute2套装工具** [点击这里][1]。不过,大多数Linux发行版已经预装了iproute2工具。
+要安装ip,请[点击这里][1]下载**iproute2套装工具** 。不过,大多数Linux发行版已经预装了iproute2工具。
-你也可以使用git命令来下载源代码:
+你也可以使用git命令来下载最新源代码来编译:
$ git clone https://kernel.googlesource.com/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/shemminger/iproute2.git
@@ -34,15 +34,15 @@ linux的**ip**命令和**ifconfig**类似,但前者功能更强大,并旨在
### 列出路由表条目 ###
-ip路由对象的命令还可以帮助你查看网络中的路由数据包并设置你的路由表。第一个条目是默认的路由条目,你可以随意改动它。
+ip命令的路由对象的参数还可以帮助你查看网络中的路由数据,并设置你的路由表。第一个条目是默认的路由条目,你可以随意改动它。
-在这个例子中,有一些路由条目。这个结果显示有几个设备通过不同的网络接口连接起来。它们包括WIFI、以太网和一个点对点连接。
+在这个例子中,有几个路由条目。这个结果显示有几个设备通过不同的网络接口连接起来。它们包括WIFI、以太网和一个点对点连接。
$ ip route show

-假设现在你有一个IP地址,你需要知道路由包从哪里来。可以使用下面的路由选项:
+假设现在你有一个IP地址,你需要知道路由包从哪里来。可以使用下面的路由选项(译注:列出了路由所使用的接口等):
$ ip route get 10.42.0.47
@@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ ip路由对象的命令还可以帮助你查看网络中的路由数据包并设

-当你需要获取一个特定网络接口的信息时,在网络接口名字后面添加选项**ls**即可。多次添加选项**-s**会给你这个特定接口更详细的信息。特别是在网络连接中排除故障时,这会非常有用。
+当你需要获取一个特定网络接口的信息时,在网络接口名字后面添加选项**ls**即可。使用多个选项**-s**会给你这个特定接口更详细的信息。特别是在排除网络连接故障时,这会非常有用。
$ ip -s -s link ls p2p1
@@ -76,9 +76,9 @@ ip路由对象的命令还可以帮助你查看网络中的路由数据包并设

-### 监控网络连接消息 ###
+### 监控netlink消息 ###
-也可以使用ip命令查看网络连接消息。monitor选项允许你查看网络设备的状态。比如,所在局域网的一台电脑根据它的状态可以被分类成REACHABLE或者STALE。使用下面的命令:
+也可以使用ip命令查看netlink消息。monitor选项允许你查看网络设备的状态。比如,所在局域网的一台电脑根据它的状态可以被分类成REACHABLE或者STALE。使用下面的命令:
$ ip monitor all
@@ -88,7 +88,7 @@ ip路由对象的命令还可以帮助你查看网络中的路由数据包并设
你可以使用ip命令的up和down选项来激某个特定的接口,就像ifconfig的用法一样。
-在这个例子中,当ppp0接口被激活和在它被停止和再次激活之后,你可以看到相应的路由表条目。这个接口可能是wlan0或者eth0.将ppp0更改为你可用的任意接口即可。
+在这个例子中,当ppp0接口被激活和在它被停止和再次激活之后,你可以看到相应的路由表条目。这个接口可能是wlan0或者eth0。将ppp0更改为你可用的任意接口即可。
$ sudo ip link set ppp0 down
@@ -109,11 +109,12 @@ ip路由对象的命令还可以帮助你查看网络中的路由数据包并设
### 小结 ###
对于网络管理员们和所有的Linux使用者们,ip命令是必备工具。是时候抛弃ifconfig命令了,特别是当你写脚本时。
+
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/use-ip-command-linux/
-译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201406/TechView--Linus Torvalds Inventor of Linux.md b/published/201406/TechView--Linus Torvalds Inventor of Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3e0cf8a92c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/TechView--Linus Torvalds Inventor of Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
+技术视点:李纳斯·托沃兹,Linux的缔造者
================================================================================

> 我们的第一个谈话对象是[李纳斯·托沃兹][1],Linux的传奇缔造者以及开源革命的先驱。托沃兹生于芬兰的赫尔辛基,是诗人奥尔·托沃兹的孙子。尽管他更喜欢告诉人们,他的名字来自于《花生漫画》中的角色,但事实是他是以李纳斯·鲍林——一位两次诺贝尔奖获得者的名字来命名的。他的计算机经历是从一台Commodore计算机上开始的,后来换成了Sinclair和IBM的386。他起初使用的是Minix操作系统,后来换成了他自己的Linux操作系统。托沃兹的妻子托芙是六次芬兰全国空手道冠军,婚后他们定居在加利佛尼亚的圣何塞,育有三个女儿。
**技术视点(TV)**:在当今的技术中,有什么令你感兴趣?
**托沃兹**:我差不多是个“鼠目寸光”的家伙,所以相对于那些更空洞的“大潮流”,我对实实在在的技术创新更感兴趣。
我很关注硬件厂商的新产品和最新的芯片,而最能吸引我的(因为毕竟我是个做软件的)是那些开发出新的算法和软件来充分利用这些新功能的人。
**TV**:那在当今科技中,什么会让你感到恼火?它是怎么以及为什么让你愤怒?
**托沃兹**:我不会用“愤怒”这个词,但是如果真要说技术领域中有什么让人反感的,那无疑是对那些头顶光环的“领袖”们的赞美。
是的,这种情况也发生在我身上。但是我很不喜欢人们把我以及我所说的话太当回事。我认为,现在流行的“个人崇拜”相当令人不安,即使是对于乔布斯,埃里森,盖茨等众所周知的领袖来说,这个现象也不正常。我希望更多的人能有自主思考,并能意识到技术发展实际上来源于遍布全球的那些默默无闻的伟大工程师的共同智慧。
我理解人们渴望明星,而这种事也不仅仅发生在技术世界中(嘿,我的确希望这事在技术世界中要比娱乐行业来得少 ;) ),但是,这还是有点令人沮丧。
**TV**:相比Red Hat和SuSE,你为什么没有抓住商业授权的机遇?难道如果Linux不开源,它就不会成为Linux了吗?你能谈谈更多情况吗?你是否曾在此事上感到过后悔?
**托沃兹**:我肯定不会因为任何事情自责。我现在身在一个令人羡慕的位置上,我能干我喜欢的事情,并赢得大家的尊重。况且,以前一文不得的时候我就很享受我的工作,而现在我从工作中得到了不错的报酬
我相信,很少有人能有机会做与众不同的事情,让我来告诉你吧,这种感觉真不错。对于商业,我从来都不感兴趣。对我来说,那些把Linux商业化的人替我做了我从没有动力做的事情。而这项工作的确需要人做,也很有益。因此,事实上我很感谢那些商业机构,它们让我能集中精力干我想干的那部分事情。
**TV**:在当今的科技界,你尊敬的人有哪些?为什么?
**托沃兹**:哈!这个问题又绕回了我对于“个人崇拜”的看法,对“让我们找个人并把他神化”这种事,我一点兴趣都没有。
所以,相比列出来个人名单,我更尊敬像EFF这样的组织,甚至有时候只是观念和想法。因为它们不是要单纯获取自身利益,而是努力去做一些实质性的事情来让技术在一个更大的蓝图中更好地发挥作用。
在个人层面上,我更喜欢那些不自骄自傲,同时又在他们的本职工作上干得很好的人。如果一定要我说一些知名人士,我想我更愿意成为斯蒂芬·沃兹尼克那样的人,我想这也是我尊敬他的原因。
**TV**:就谷歌和微软而言,你认为哪个更成功?为什么?
**托沃兹**:我认为,相对胜利者来说,两家公司竞争的过程才是更有趣的。
在谷歌和微软的竞争中,我真的不认为两家公司本身比技术的变革更为有趣。这种变革的本质是从对单个计算机的控制转向对成千上万独立计算机的整合。
**TV**:你认为像科技灾难、互联网泡沫崩溃以及电信业崩盘这样的事为什么会发生?我们在今后怎样来防止它们再发生?
**托沃兹**:实际上,我对此类事情持相反的看法,而且我认为没有必要去防止它们再次发生。
我坚信我们应该努力去挑战极限,而不是追求百分之百的稳定和理性
大多数技术发展都不是有规律可循的,有的像火山爆发,有的事后可能被认为是夸大其词,有的刚出来时一点都不讨人喜欢。但事实上,如果太过努力去保持理性和避免做蠢事,就会扼杀创造力。
我个人认为,真正稳定可靠的发展模式不是持续的微创新,而是通过超载和崩溃带来的系统演替。持续的微创新虽然看起来是一个好的选择,但是不经历超载和崩溃,你怎么可能发现系统的极限,并对它进行改进呢?
**TV**:技术在未来会怎样改变我们的生活?你会和其它领域的领军者一起创建新技术吗,比如生物信息学?
**托沃兹**:我个人的理论是,技术对我们的生活的改变,远没有我们构建技术来适应我们的生活来得多。
这就是为什么你看不到飞行汽车等科幻小说中受欢迎的东西——但是相反,你却看到了利用技术来降低成本,使得一些此前就存在但是却因为成本因素不能大规模应用或者量身定制的事情被更多人接受。
因此,技术很少直接改变我们的生活本身——虽然它往往意味着更多的人能获得那些以前罕见的或只限于土豪们的东西。
真正的改变发生在当某些事物变得如此廉价并且随手可得,从而改变了你的行为的时候。而在很多方面,这些行为上的改变要比技术本身来得更有趣。
例如,互联网带来的一大革命,是让你可以用极低的成本找到志趣相投的人并与他们进行交流。而且,我认为许多真正的改变正是来自于当人们无需付出太多努力就能找到其他对同一事物有相同兴趣的人时,他们的习惯会如何改变。
因此,你发现了所有的这些专业兴趣小组,许多人都在花大量时间讨论那些最神秘的问题,他们刚刚发现这些问题很有趣——这些事,你在之前不一定能实际去做,因为那时真的很难找到和你一样在某些不同寻常的专业上感兴趣的人并进行讨论。
而我认为那是生活真正改变的方式——不是因为任何新技术的出色特性,而完全是因为技术降低边际成本后带来的惊喜。
**TV**:就你而言,谁是当今科技界最举足轻重的人物?
**托沃兹**:我想大量的技术由消费市场推动,而不再是由军方或商业需求推动这一点很说明问题。我也常常认为,许多公司正在推进的愚蠢事情(特别是DRM)都忽略了一个事实:任何技术上最重要的人,最终总是“用户”。
因此,就我而言,我认为你的问题的答案是“用户”,或者叫“消费者”,而这确实是最重要的部分,因为用户正是市场需求和商业成功的根源。
**TV**:请谈一些你个人的观点吧,比如宗教?政治?
**托沃兹**:我完全是一个虔诚的——无神论者。我发现人们似乎认为宗教带给人道德和对自然的敬畏,但事实上我认为它反而把这两方面都削弱了。它给了人们借口说“哇,世界是被创造出来的”,而创世是神秘而不可测的。我更欣赏的说法是“哇,真让人难以置信,这样的事情竟然会首先发生”。具有讽刺意味的是,在许多欧洲国家,国家和宗教已经从法律意义上结合在了一起。
我现在是一位美国公民,并且我也拥有投票权。但是,坦率地说,我不支持任何政党,因为我的个人骄傲不允许我和任何政党有关联。
**TV**:谢谢,李纳斯!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.huffingtonpost.com/billrobinson/techview-linus-torvalds-i_b_5338844.html
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[reinoir](https://github.com/reinoir),mahua
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linus_Torvalds
diff --git a/translated/tech/Turn Off Bluetooth By Default In Ubuntu 14.04 [Quick Tip].md b/published/201406/Turn Off Bluetooth By Default In Ubuntu 14.04 [Quick Tip].md
similarity index 75%
rename from translated/tech/Turn Off Bluetooth By Default In Ubuntu 14.04 [Quick Tip].md
rename to published/201406/Turn Off Bluetooth By Default In Ubuntu 14.04 [Quick Tip].md
index a2b828550a..133ce762ed 100644
--- a/translated/tech/Turn Off Bluetooth By Default In Ubuntu 14.04 [Quick Tip].md
+++ b/published/201406/Turn Off Bluetooth By Default In Ubuntu 14.04 [Quick Tip].md
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-在Ubuntu 14.04中默认关闭蓝牙[快速秘诀]
+如何在Ubuntu 14.04中默认关闭蓝牙
================================================================================

@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
### 在Ubuntu 14.04中默认关闭蓝牙: ###
-打开一个终端并使用以下命令来安装[gksu][2](如果你还没有安装它的话)。
+打开一个终端并使用以下命令来安装[gksu][2](如果你还没有安装它的话)(译注:如果你已经有了gksu,那么可以使用它;如果还没有,也不想安装,那你使用sudo一样可以)。
sudo apt-get install gksu
@@ -32,13 +32,13 @@ gksu是用来在以root权限运行程序时输入密码的程序。当你已经
这一小部分只是对我们做了什么进行简短的解释。您并不一定要阅读完这一部分。您可以直接跳到评论部分留下您的建议和感谢 :)
-rc.local文件是用来记录在系统启动的时候运行的各种shell命令的。这些命令是用户定义的。在一个干净的安装中,rc.local文件中没有任何命令。我们做的就是在这里面加入命令 **rfkill block bluetooth**。[rfkill][3]是一个用来查询各种开关,按钮和底层系统接口状态的工具。我们在rc.local中使用这个命令来在每次启动的时候软关闭(译注:与其对应的是硬关闭,指通过硬件开关来关闭)蓝牙。我希望这些能把原理解释的清楚一点。
+rc.local文件是用来记录在系统启动的时候运行的各种shell命令的。这些命令是用户定义的。在一个新的安装中,rc.local文件中没有任何命令。我们做的就是在这里面加入命令 **rfkill block bluetooth**。[rfkill][3]是一个用来查询各种开关,按钮和底层系统接口状态的工具。我们在rc.local中使用这个命令来在每次启动的时候软关闭(译注:与其对应的是硬关闭,指通过硬件开关来关闭)蓝牙。我希望这些能把原理解释的清楚一点。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
via: http://itsfoss.com/turn-off-bluetooth-by-default-in-ubuntu-14-04/
-译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/201406/Ubuntu Linux Community Manager Jono Bacon Leaves Canonical.md b/published/201406/Ubuntu Linux Community Manager Jono Bacon Leaves Canonical.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b3558a2816
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/Ubuntu Linux Community Manager Jono Bacon Leaves Canonical.md
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+Ubuntu Linux社区经理Jono Bacon离开Canonical公司
+================================================================================
+
+
+Canonical——Ubuntu Linux背后的公司,其任职已久的社区经理将离职。[Jono Bacon][1],一直是 Ubuntu 业界最熟悉的面孔之一,他将在[XPRIZE基金会][2]任新职。
+
+Bacon于2006年加入Canonical,从[其博客可知][3]他是在收到XPRIZE的录用通知后决定离开Canonical的,XPRIZE[自称][4]为“创新引擎”和“造福人类的催化剂”。他将会在XPRIZE就任社区主管,施展他过去八年中在帮助协调Ubuntu社区方面所获得的能力。
+
+虽然Bacon在Canonical不是直接负责商业或者发展方面,但是他的离开对于Ubuntu和开源界来说都是一件大事儿,在Ubuntu和开源界实际社区参与比行政头衔更重要。与Ubuntu的创始人和Canonical的前CEO [Mark Shuttleworth][5]一起,Bacon是早期Ubuntu生态系统项目的领军人物之一。
+
+Bacon可以说在塑造Ubuntu的很多方面比Jane Silber更有影响力。Jane Silber自2010年一直是Canonical的CEO,但是他在公共场合的出面一般是很少的。
+
+Bacon带领的团队包括Daniel Holbach,David Planella,Michael Hall,Nicholas Skaggs和Alan Pope。Bacon说,他们将会接手他社区领袖的工作。然而,尚不清楚的是Canonical是否会填补他留的社区经理职位。
+
+也许Canonical不会。在很多方面,维持一个社区领袖与开源精神格格不入,开源精神往往赞扬的是分散的、用户主导的社区组织。一些Ubuntu的粉丝可能会因Bacon离职的新闻而感到恐慌。
+
+不过,Bacon帮助指导过Ubuntu社区度过一系列的危机——从Canonical将Ubuntu软件中心设计为一个商店的失败尝试,到与Fedora群体的摩擦,到关于将Amazon.com搜索特性植入到新的Ubuntu的争议。他在Ubuntu的生态系统上留下了光辉业绩,没有他这一切将完全不同。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://thevarguy.com/ubuntu/052214/ubuntu-linux-community-manager-jono-bacon-leaves-canonical
+
+译者:[linuhap](https://github.com/linuhap) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.jonobacon.org/
+[2]:http://www.xprize.org/
+[3]:http://www.jonobacon.org/2014/05/19/goodbye-canonical-hello-xprize/
+[4]:http://www.xprize.org/about/who-we-are
+[5]:http://markshuttleworth.com/
+[6]:http://thevarguy.com/ubuntu/ubuntu-software-store-will-your-kids-try-it
+[7]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/tensions-between-ubuntu-fedora-mount-over-new-website
+[8]:http://thevarguy.com/var-guy/controversy-erupts-over-amazon-search-ubuntu-1210
diff --git a/published/201406/What Heartbleed Teaches Us--Be An Open Source Contributor, Not Just A User.md b/published/201406/What Heartbleed Teaches Us--Be An Open Source Contributor, Not Just A User.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..20555f7924
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201406/What Heartbleed Teaches Us--Be An Open Source Contributor, Not Just A User.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+心脏流血教给我们的:成为开源的贡献者而不仅是个用户
+================================================================================
+
+
+> 如果你的公司依赖像OpenSSL这样的开源软件,是时候主动点了。
+
+心脏流血漏洞让开源社区如芒在背。
+
+ComputerWorld的Richi Jennings [抨击说][1]“又一个非常可怕的开源失败。”(他是要做标题党么?)ZDNet的Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols不像是作秀反开源,却仍旧将心脏流血漏洞[渲染为][2]“开源软件的最遭时刻”。而最后,ZDNet的Chris Duckett则务实地[倡议][3]:“商业公司(应该)筹集资金来避免心脏流血再次发生。”
+
+而实际上,企业资金并不是解决心脏流血事件的最终答案 。你才是!
+
+想要避免开源失败的公司应该不仅仅是开源软件的用户,还要是贡献者。
+
+### 贡献者乘坐头等舱 ###
+
+贡献者能够引导特定的项目。他们占据主动,而不是被动接受。大多数企业缺乏资源参与他们所使用的所有开源项目,但每家公司都可以资助给那些真正关系到他们的项目。并且资助得越多,得到的好处越大。
+
+开源就是一个不断给予的礼物,尤其是给予那些对开源反哺的人们。
+
+我在MongoDB的同事[Adam Comerford让这点更有说服力][4]:如果你看看第一批得知Heartbleed漏洞的[时间线] [5],那些第一批得知的(如谷歌)有一个相当大的优势。如Comford所说的,这些公司有一个显著的优势就是他们可以在bug还未大规模传开的时候率先采取措施保护他们的系统。
+
+
+鉴于早期了解像Heartbleed之类问题的优势,Comerford问:“我如何确保我在这类问题的早期通知列表里面?”
+
+
+如果你依赖于专有软件,你有一个答案:向卖方支付大量的金钱,并希望他适时地响应。但是,如果你正在使用开源软件,有一个更多选择: “要么有大量的员工给[开源项目]做贡献 ,或者...有认识主要贡献者的员工(我们可以找找,他们大多也会贡献其他开源软件项目,像其他的极客和呆瓜一样。“
+
+Comerford断言说,好处不止这样:
+
+> 这有很多好处 - 除了让问题及早通知,让手头上的专家来应付这些棘手的更新,以评估你的风险,甚至可能在公众知道之前内部解决问题。在确定项目的方向上你还可以得到重视的回馈,可以影响到关键特性的优先级。最终,你会得到社区的善意,使产品变得更好,并有可能成为其它的聪明贡献者的工作目标。
+
+换句话说,参与进来。成员有特权,主要的特权可能就是信息。
+
+### 选择在哪贡献 ###
+
+同样,没有一家公司有足够的资源来有效地促进所有它所使用的项目,这就是为什么Comerford建议对关键项目上这么做的原因:
+
+> 如果你要人们列出在企业中所有开源关键技术,你可能会得到一张很长的名单。然后,告诉他们,他们将必须清点人工和预算来支持清单上的每一种技术的话(并验证它) - 它可能会迅速缩水。
+
+如果你是一个AMD那样的芯片公司,给Linux内核贡献基本驱动程序和其他代码很可能是强制性的。给LibreOffice贡献可能不是。或者,如果你判断你的未来在Hadoop上进行深层数据分析,你应该贡献Hadoop,即使你依旧免费使用OpenSSL社区的成果。比如Dish Networks公司,它的[ CIO告诉上周在开放商业会上的人们][6],他们正在将重要的数据从关系型数据库转到Apache的Kafka,那他最好研究Kafka的代码,即使他不贡献给Apache HTTP服务器项目。
+
+每家公司都有其优先级,以及这些优先级应该以严肃的承诺而确立。
+
+这是确保这些项目安全的一部分办法。而另一部分,它是一种形成影响力指引的方式。但同时,红帽公司CEO[Jim Whitehurst][7]早在2008年声明,它是显著减少IT花费的办法:
+
+> 今天编写的绝大多数软件是企业编写的,不得转售。并且绝大多数是从来没有真正使用过。IT软件开发中的浪费是巨大的....最终,开源给全世界的客户提供价值,我们不仅需要让我们的客户作为开源产品的用户,而且真正加入开源和参与在开发社区。
+
+
+Comerford坚持认为:“如果我在业务中使用开源软件,我应该雇开发人员来积极给软件做贡献,如果他们自己不是核心开发者,那就雇佣核心开发者。 ”这是充分利用开源软件的关键:给它做贡献,不只是使用它。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://readwrite.com/2014/05/14/heartbleed-open-source-contribution-users
+
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://blogs.computerworld.com/encryption/23767/heartbleed-openssl-open-source-fail
+[2]:http://www.zdnet.com/heartbleed-open-sources-worst-hour-7000028420/
+[3]:http://www.zdnet.com/openssl-needs-corporate-funding-to-avoid-heartbleed-repeat-7000028385/
+[4]:http://comerford.cc/wordpress/2014/04/15/my-conclusion-heartbleed-timeline/
+[5]:http://www.smh.com.au/it-pro/security-it/heartbleed-disclosure-timeline-who-knew-what-and-when-20140415-zqurk.html
+[6]:http://blogs.wsj.com/cio/2014/05/06/dish-looks-to-open-source-software-after-database-failure/
+[7]:http://www.cnet.com/news/red-hat-solve-enterprise-waste-through-open-source/
diff --git a/translated/tech/Why htop Command Compete Linux top Command.md b/published/201406/Why htop Command Compete Linux top Command.md
similarity index 77%
rename from translated/tech/Why htop Command Compete Linux top Command.md
rename to published/201406/Why htop Command Compete Linux top Command.md
index 3709009735..d24d530d10 100644
--- a/translated/tech/Why htop Command Compete Linux top Command.md
+++ b/published/201406/Why htop Command Compete Linux top Command.md
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-为什么 Linux 的 htop 命令优于 top 命令
+为什么 Linux 的 htop 命令完胜 top 命令
================================================================================
在 Linux 系统中,top 命令用来显示系统中正在运行的进程的实时状态,它显示了一些非常有用的信息,比如 CPU 利用情况、内存消耗情况,以及每个进程情况等。但是,你知道吗?还有另外一个命令行工具 'htop',它与传统的 top 命令功能一样,但它有更加强大的功能及能显示更多的信息。这篇文章,我们会用实例来讨论这个 'htop' 命令。
@@ -12,11 +12,11 @@
### 首先明白它的输出 ###
-**htop 命令**以典型的格式来显示信息。下面是 HTOP 的输出快照:
+**htop 命令**以直观的格式来显示信息。下面是 HTOP 的输出快照:

-如果你观察窗口的左上角部分,你会看到显示的是 CPU 负载、内存消耗及交换空间的实时信息,右上角包含的是任务、平均负载及系统运行时间的信息。
+如果你观察窗口的左上角部分,你会看到显示的是 CPU 负载、内存消耗及交换空间的实时信息,右上角包含的是任务、线程、平均负载及系统运行时间的信息。
平均负载部分提供了三个数字,这仅仅表示的是过去的5分钟、10分钟和15分钟系统的平均负载而已,在单核的系统中,平均负载为1表示的是百分之百的 CPU 利用率。最后,运行时间 (uptime)标示的数字是从系统启动起到当前的运行总时间。
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@
### 1. 用 F2 键编辑配置 ###
-该 HTOP 命令提供了许多自定义选项,你所要做的就是从主窗口中按下 F2 键。
+htop 命令提供了许多自定义选项,你所要做的就是从主窗口中按下 F2 键。
下面所示的是可用的自定义选项:
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@
### 2. 通过 F9 键发送信号 ###
-HTOP 命令提供了某种功能,通过此功能您可以很容易地在 HTOP 窗口内给一个进程发送任意的信号。您需要做的就是按下 F9 键。
+htop 命令可以让你很容易地在 htop 窗口内给一个进程发送任意的信号。按下 F9 键即可。

@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ HTOP 命令提供了某种功能,通过此功能您可以很容易地在 HTOP
### 3. 显示进程的树状视图 ###
-HTOP 命令也提供了进程的树状视图查看功能。您需要做的就是按下 F5 键。
+htop 命令也提供了进程的树状视图查看功能。按下 F5 键切换。
下面是 htop 显示树形视图信息的例子:
@@ -52,17 +52,17 @@ HTOP 命令也提供了进程的树状视图查看功能。您需要做的就是
### 4. 通过 F3 键搜索进程 ###
-HTOP 命令提供了易用的方式来搜索进程。您需要做就是按下 F3 键,一个文本框就会出现在窗口底部。
+htop 命令提供了易用的方式来搜索进程。按下 F3 键,一个文本框就会出现在窗口底部。
下面是例子:

-如您所见,一条名为‘搜索’的文本提示框在窗口底部出现了,您可以在这儿输出进程的名字然后回车搜索。如果找到,它会在列出的进程列表里选中此进程。
+如您所见,一条名为‘搜索’的文本提示框出现在窗口底部,您可以在这儿输入进程的名字然后回车搜索。如果找到,它会在列出的进程列表里高亮选中此进程。
### 5. 通过空格键来设置颜色标注进程条目 ###
-在系统中运行着的实时进程视图中,要追踪某个进程是个大问题。因为整个列表在不停的刷新着,进程的排列顺序也在变动着。为了这个问题, HTOP 提供了一个很简单的解决方案:颜色标注。是的,你可以标注一个进程条目,它会以不同的颜色显示,因此要追踪它就变得容易了。
+在系统中运行着的实时进程视图中,要追踪某个进程是个大问题。因为整个列表在不停的刷新着,进程的排列顺序也在变动着。为了这个问题, htop 提供了一个很简单的解决方案:颜色标注。是的,你可以标注一个进程条目,它会以不同的颜色显示,因此要追踪它就变得容易了。
要标注某个进程条目,需要做的就是选中此条目,然后按下‘空格’键。例如,在下面的截图示例中,我已经颜色标注了三个进程条目:
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ HTOP 命令提供了易用的方式来搜索进程。您需要做就是按下 F3
- **-s 选项** : 按指定的列排序。例如,**htop -s PID** 命令会按 PID 列的大小排序来显示。
- **-u 选项** : 显示指定的用户的进程信息列表。例如,**htop -u himanshu** 命令会只显示出用户名为 himanshu 的相关进程。
-- **-d 选项** : 设置刷新的延迟时间。例如,**htop -d 100** 命令会使输出在1秒后才会刷新(参数 -d 可以考虑是十分之一秒的时间)。
+- **-d 选项** : 设置刷新的延迟时间。例如,**htop -d 100** 命令会使输出在1秒后才会刷新(参数 -d 的单位是10微秒)。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
diff --git a/published/20140607 How to turn Vim into a full-fledged IDE.md b/published/20140607 How to turn Vim into a full-fledged IDE.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6705ceefc3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140607 How to turn Vim into a full-fledged IDE.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+如何将Vim打造成一个成熟的IDE
+================================================================================
+
+如果你稍微写过一点代码,就能知道“集成开发环境”(IDE)是多么的便利。不管是Java、C还是Python,当IDE会帮你检查语法、后台编译,或者自动导入你需要的库时,写代码就变得容易许多。另外,如果你工作在Linux上,你也会知道Vim在进行文本编辑的时候是多么的方便。所以,你可能会想从Vim中也获取这些IDE特性。
+
+事实上,很少有方法可以帮你做到。有些人可能会想到试着把Vim打造成C语言IDE的,比如[c.vim][1];也有把Vim集成到Eclipse里的 [Eclim][2] 。但是我想要告诉你的是一个更加通用的,只用插件实现的方案。你肯定不想因为安装了太多的面板和特性而让你的编辑器变得臃肿不堪。只用插件实现的方案可以让你只选择那些你想要集成到Vim的特性。这样做的额外的一个好处是,这个IDE不是专门针对某一种语言的,可以让你写任何类型的代码。下面就来看一下我的 **把IDE特性带进Vim的前10款插件** 吧。
+
+### 先来个福利: Pathogen ###
+
+首先,可能不是所有人都熟悉Vim的插件,并知道该怎么安装这些插件。所以,我推荐的第一个插件就是[Pathogen][3],因为这个插件会让你更容易安装其他插件。如果你要安装另外的没有在这里列出来的插件,用Pathogen会变得非常简单。它的[官方页面][3]的文档写的非常好,去下载安装一个吧。接下来插件的安装也会变得容易很多。
+
+### 1. SuperTab ###
+
+
+
+我们习惯于IDE的第一个原因就是它的自动补全功能。所以,我喜欢这个非常方便的,给了Tab键“超能力”的 [SuperTab][5] 插件。
+
+### 2. Syntastic ###
+
+
+
+如果你需要使用一种以上的语言进行编程,有时候是非常容易混淆不同语言之间的语法的。幸运的是,[syntastic][6] 会帮你检查,然后告诉你是否应该加上圆括号或者方括号,或者告诉你在某个地方,你忘了一个分号。
+
+### 3. Auto Pairs ###
+
+另外一件让程序员们抓狂的事是:我是不是少加了最后一个括号?!每个人都讨厌用手指去数那些隔的非常远的括号。为了处理这个问题,我用 [Auto Pairs][7] 插件,这个插件会自动插入和格式化方括号和圆括号。
+
+### 4. NERD Commenter ###
+
+如果你在找一个可以支持多种程序语言的注释代码的快捷键,你可以试试 [NERD Commenter][8]。即使你不是程序员,我也非常非常推荐这款插件,因为它会让你在注释bash脚本或者其他任何东西的时候都会变得非常高效。
+
+### 5. Snipmate ###
+
+任何一个程序员都知道,好的码农写代码,杰出的码神重用代码。[snipmate][9]可以容易的插入代码片段到你的文件里面,大大的减少了你敲键盘的次数。它默认的包含了很多各种语言的代码片段,你也可以非常容易的添加你自己的。
+
+### 6. NERDTree ###
+
+
+
+管理一个大的项目时,把代码分散到不同的文件里面是非常好的主意。也是一个基本的编码原则。[NERDTree][10] 是一个不错的可以直接在Vim里使用的文件浏览器,它可以让你随时想到所有的文件。
+
+### 7. MiniBufferExplorer ###
+
+
+
+为了打造一个文件浏览器,支持同时打开多个文件,没有什么比一个好的缓冲区管理器更重要了。[MiniBufferExplorer][11] 就可以非常漂亮和高效地完成这个工作。它甚至为你的缓冲区设置了不同的颜色和切换快捷键。
+
+### 8. Tag List ###
+
+
+
+当你同时有多个文件打开时,很容易忘了你都在这些文件里添加了什么。为了防止你忘记,[Tag List][12] 这个代码查看器将会用一种漂亮简洁的格式展示其中的的变量和函数。
+
+### 9. undotree ###
+
+
+
+对于我们之中那些喜欢undo,redo然后又undo某些更改,然后依据这些来查看整个编辑完成过程的人来说, [undotree][13] 是一个不错插件,可以以一棵树的形式看到你的undo和redo历史。这个功能跟代码完全没有关系,所以这是我非常喜欢的一个插件。
+
+### 10. gdbmgr ###
+
+最后,但并非不重要,每个人都在某个时刻需要一个调试器。如果你喜欢gdb,那么[gbdmgr][14]就是为你准备的,因为它集成了那个著名的调试器到Vim中。
+
+总结一下,不管你是不是一个疯狂的coder,能有一些额外的Vim功能在手总是非常方便的。像我在简介里说到的,如果你不需要,你不用安装这里所有的这些插件。或者你想要安装另外的也行,这些其实只是一个基础入门级的插件。
+
+你在用Vim的什么插件?或者你想完善这个前10列表么?请在评论里告诉我们吧。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/06/turn-vim-full-fledged-ide.html
+
+译者:[love\_daisy\_love](https://github.com/CNprober) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=213
+[2]:http://eclim.org/
+[3]:https://github.com/tpope/vim-pathogen
+[4]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14332189422/
+[5]:https://github.com/ervandew/supertab
+[6]:https://github.com/scrooloose/syntastic
+[7]:https://github.com/jiangmiao/auto-pairs
+[8]:https://github.com/scrooloose/nerdcommenter
+[9]:https://github.com/garbas/vim-snipmate
+[10]:https://github.com/scrooloose/nerdtree
+[11]:http://www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=159
+[12]:http://www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=273
+[13]:https://github.com/mbbill/undotree
+[14]:http://vim.sourceforge.net/scripts/script.php?script_id=4104
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/20140609 Has Microsoft really changed its attitude toward open source.md b/published/20140609 Has Microsoft really changed its attitude toward open source.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4cc490ad1c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140609 Has Microsoft really changed its attitude toward open source.md
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+微软真的改变对开源软件的态度了吗?
+================================================================================
+> **在今天的开源软件摘要中:微软或许没有对开源软件有一个新的态度,就像安卓和windows的对抗,Cinnamon和Unity在Ubuntu14.04的对抗。**
+
+微软因为以前对开源软件的态度而臭名昭著,但是公司改建后对开源软件发出了积极的信号。CNet报道了微软对开源软件认知的行为的改变。
+
+> [CNet][1]消息:
+> 虽然微软资助开源软件有一些时间了,并且那些曾经反对开源软件的领导者们已经退出了或者不在位了。开源软件现在用在遍布全世界的公司当中,但这些与微软帝国无关。
+> 一些新的想法反映了企业顶层的一些变化,今年二月初Satya Nadella代替鲍尔默成为了微软CEO,Nadella已经给微软带来了一些新的东西改变了微软以前的一些束缚。
+>
+> [更多报道][2]
+>
+> 
+>
+> 微软和开源社区
+> Image credit: [Curako's Blog][3]
+
+我是一个持悲观态度的人,但是我认为微软和开源软件之间的信任关系是有待确定的。一个新的CEO和些许改变或许会改变微软在开源世界中的存在状态,但是对于微软这么大的企业来说改变并不容易,所以对于开源的世界来说微软是否真的改变还有待确定。
+
+我也从来不会忘记微软用“欢迎,扩大,压死”的策略来打翻其他的竞争软件,光这一条凡是微软参合的开源项目就必须瞪大眼睛,或许这家公司真的改了,但如果没有呢!我们还是用几年时间来观察下吧。
+
+### 安卓对抗windows ###
+
+ZDNet曾经报道过使用数量最多的Linux发行版本,不过现在桌面环境仍然是windows的天下,但是安卓今年很可能会是用户数量最大的用户终端操作系统。
+
+> [ZDNet][4]报道:
+>
+> 如果桌面和平板依旧像预期增长的销量,安卓平板渐渐蚕食苹果的市场,PC市场继续萎缩,安卓在2014年末很有可能成为终端用户数量最多的操作系统,而且不算安卓PC。
+>
+> 总而言之,安卓几乎统治了Linux终端用户。你可能不会想把它作为桌面使用,尽管Intel和AMD努力在让它变成现实,但是安卓正在变成使用量第一的终端操作系统。
+
+>
+> [更多消息][4]
+>
+> 
+> Image credit: [ZDNet][4]
+
+上面提到的并不算真的惊喜,移动终端的革命发展了接近10年了。桌面依然还像原来那样重要,微软也确实没有真正的在乎过移动设备。即使现在,微软在艰难的推他的手机和平板,他仍旧认为移动终端市场并不重要。
+
+谷歌严重的破坏了微软在移动领域的努力,而现在他在桌面市场又对微软发起了挑战。从chrome OS到安卓,谷歌给微软一连串的打击,如果你查看下Amazon最受欢迎的[台式机][5]和[笔记本][6]的话,你会看到很多chrome OS的电脑甚至是装有安卓的PC。所以人们的购买需求在变得多样化,并不局限在windows一家了。
+
+### Cinnamon和Unity在Ubuntu14.04上的对抗 ###
+
+Tech Republic发表了一篇文章介绍了如何在Ubuntu14.04上安装Cinnamon,研究了一下Ubuntu14.04上用Cinnamon替换unity的可行性。
+
+> [Tech Republic][7]报道:
+>
+> 如果你寻求性能为主不需要其他有特色的可自定义的桌面,Cinnamon适合你。Cinnamon是一个直观简洁的桌面,任何人都可以使用,不论你是IT工作者还是你的老妈妈。它非常的简单易用。Cinnamon很平淡,不会和你开什么玩笑,也不会让你感到有惊奇的感觉,但这就是它所注重的。它只会给桌面带来在标准层面上带来实用性,它不求突破,不耍花招,不加条条框框。
+>
+> Cinnamon是一个很平凡的桌面,它只集成了最好的功能并且把它们集成到一起,完美整合到一块。如果你可以用一个看起来和用起来都点老掉牙,但是性能很好的桌面的话,Cinnamon完全适合你。如果你喜欢各种花哨的界面和看起来很现代的感觉,Cinnamon可能就不适合你了。
+
+> [ 更多消息][7]
+>
+> 
+>
+> Image credit: [Tech Republic][7]
+
+我是站在Cinnamon这边的,Unity有自己的长处,但是我从来没用习惯过。Cinnamon更接近传统桌面,我用起来不错!
+
+但是在别人眼里,漂亮的桌面总是很受欢迎。Linux最大的特色就是提供很多很多不同的选择,如果你真不知道Unity和Cinnamon该选择谁,你就用自己最喜欢的就行了。
+
+你赞成那些呢?请在下方留下你的评论吧
+
+作者的观点和ITworld无关!
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.itworld.com/open-source/421894/has-microsoft-really-changed-its-attitude-toward-open-source
+
+译者:[jiajia9linuxer](https://github.com/jiajia9linuxer) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.cnet.com/news/dead-and-buried-microsofts-holy-war-on-open-source-software/
+[2]:http://www.cnet.com/news/dead-and-buried-microsofts-holy-war-on-open-source-software/
+[3]:http://curako.wordpress.com/2010/12/06/the-uneasy-alliance-free-software-vs-open-source/
+[4]:http://www.zdnet.com/the-five-most-popular-end-user-linux-distributions-7000030058/http://www.zdnet.com/the-five-most-popular-end-user-linux-distributions-7000030058/
+[5]:http://www.amazon.com/Best-Sellers-Electronics-Desktop-Computers/zgbs/electronics/565098/?_encoding=UTF8&camp=1789&creative=390957&linkCode=ur2&tag=fnh-20&linkId=REWXUPB7SQXPDSOL
+[6]:http://www.amazon.com/Best-Sellers-Computers-Accessories-Laptop/zgbs/pc/565108/?_encoding=UTF8&camp=1789&creative=390957&linkCode=ur2&tag=fnh-20&linkId=POG3J2CFBHDWBAVL
+[7]:http://www.techrepublic.com/article/is-cinnamon-a-worthy-replacement-for-ubuntu-unity/
diff --git a/published/20140610 The Best Linux Distribution for New Users.md b/published/20140610 The Best Linux Distribution for New Users.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2c8d5f7819
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140610 The Best Linux Distribution for New Users.md
@@ -0,0 +1,159 @@
+适合新用户的最佳的Linux发行版
+================================================================================
+这个争论无疑给许多Linux用户带来了麻烦。争论的焦点一般不是哪个发行版是真正最适合新用户的,而是哪个发行版受这些争论者的喜爱。如果我们撇开个人喜爱,我们会看到更清楚的一面。但即使这样,明确的结论也会受到被新用户的需求和期望的影响。考虑到这点,我决定采取一个不同的方法来找出“对新用户来说最好的发行版”。我评判最好发行版的标准不仅是易用,而且还要具有由日益增长的移动界面风格所带来的现代设计理念。
+
+对于这次评测,我们对发行版有如下要求:
+
+- 非常友好
+- 包括,开箱即用,所有常用的应用程序
+- 包括某个形式的应用程序商店
+- 提供一个时尚的用户界面
+
+让我解释一下各个标准
+
+### 用户友好 ###
+
+这是一个备受争议的话题。但事实的真相是——新用户必须能够选择某种风格的Linux并开始使用,只需要很少或不需要解释。如果必须很出太多解释,那么这个发行版便不是用户友好的。我不喜欢那些操作系统,但是几乎任何用户都可以在近乎零指导的情况下坐在Windows 7或OS X桌面前并开始使用它。这是每一个Linux桌面都应当争取去做的。
+
+### 常用应用程序 ###
+
+安装好系统后用户不应该再去安装必需的程序。那么什么是必需的呢?每年列表都会变短。目前,必备的程序列表如下:
+
+- 网页浏览器:Chrome或者Firefox(对不起,根本不需要其他的浏览器)
+- 电子邮件客户端:Thunderbird是显而易见的选择。
+- Office办公套件:LibreOffice。就这样。
+- 音乐播放器:播放本地文件以及连接到流媒体服务(比如Spotify)。
+
+这是几乎所有用户需要的应用程序的简表。
+
+### 应用程序商店 ###
+
+由于移动设备需求的日益增长,用户已经习惯了应用商店。Linux有应用商店很长时间了(Synaptic是最古老的一个)。没有一个经深思熟虑做的应用商店,用户将会挣扎于在Linux环境中添加软件。毫无疑问,这一点至关重要。
+
+### 时尚的界面 ###
+
+我已经多次提到移动设备的美化。由于iOS和Android,用户越来越喜欢时尚的界面。Linux的桌面需要进行效仿并且用独特的、时尚的和易用的界面来吸引用户注意力。旧的风格在支持多触控的移动世界里不再有影响力。
+
+## 排名前三的发行版 ##
+
+以文中的标准,哪个发行版本满足了(或超过)我们的需求?首先,让我们来审查一下前三名的候选者。以下哪个满足了(或超过)标准。
+
+### Ubuntu ###
+
+[Ubuntu Linux][1]一直是用户友好型Linux的王者。开箱即用,寻找一个比它更迷人和易用的桌面(Unity)有点困难,甚至是对于那些对平台不熟悉的人也是这样的。它的桌面布局虽然与众不同,但却是合乎逻辑和很直观的。对于在桌面环境中添加一个最强大的搜索工具,在Linux中Ubuntu Unity应当获得最高成就。
+
+### Linux Mint ###
+
+如果认为有一个篡夺王位的发行版,那它就是[Linux Mint][2]。Linux Mint做了更多桌面的标准方法,但是图层华丽且多变使其从老旧的桌面隐喻中脱颖而出。Linux Mint基于Ubuntu,所以它得益于“老大哥”Ubuntu的稳定性和可靠性。
+
+### Linux Deepin ###
+
+用户友好型列表中的新成员是[Linux Deepin][3]。这个相对较新的受欢迎的发行版来自中国,而且应该正视它所带来的成就。为什么这样说?因为它使得Linux桌面转变为艺术美;同时也保持了高水平的用户友好性。我期待它的新版本发布将是个大事件。Linux Deepin使用的是GNOME 3桌面并将它重组得完全不同的,完全不可思议。
+
+## 各发行版的比分 ##
+
+在最佳的竞争者名单中,我们来比较一下每一个标准和等级。每个发行版的比分如下:对于每个标准,发行版排名从高到底(第一名得一分,最后一名得三分)。最后,总分决定谁是冠军——最低得分获胜。
+
+### 用户友好性 ###
+
+这可能是最严密的分类和最艰难的判别。每个发行版以不同的方法在用户友好性上都各有优势。最后,我的排名是:
+
+1. Linux Mint
+
+2. Ubuntu Linux
+
+3. Linux Deepin
+
+为什么是这样呢?Mint仅有微小的优势,因为它的开始按钮,任务栏和桌面图标仍然使用旧的桌面风格。胜者的优势很微小,Ubuntu和Linux Deepin要求的学习曲线近乎为零——甚至是对于小白们。
+
+### 常用的应用程序 ###
+
+这一类别难以判断的唯一原因是因为每个发行版都包括所有必要的应用程序。虽然Linux Deepin目前提供的是金山Office(一个最好的移动办公套件解决方案之一),它计划在2014发行版本中默认使用LibreOffice。
+
+关于常用程序的我的一个问题是音乐播放器。虽然我在线听过很多音乐(使用Spotify客户端),但当我播放本地音乐时,总是使用Clementine。他们的默认播放器是:
+
+- Ubuntu: Rhythmbox
+- Linux Mint: Banshee
+- Linux Deepen: DMusic.
+
+三者中,Banshee(图1)提供了最多的功能,DMusic(图2)提供了最好的界面,(令人惊讶的)Rhythmbox(图3)目前最不稳定。
+
+
+
+banshee
+
+
+
+dmusic
+
+
+
+rhythmbox
+
+所以,他们得分多少?如下:
+
+1. Linux Mint
+
+2. Ubuntu Linux
+
+3. Linux Deepin
+
+### 应用程序商店 ###
+
+如果不分析这部分将难进行。为什么呢?因为对于新用户应用商店可以轻易成就或是毁掉一个Linux发行版。总会有应用需求而且没有用户想经过命令行的重重考验。每个发行版都有自己的应用商店。
+
+- Ubuntu: Ubuntu软件中心
+- Mint: 软件管理器
+- Linux Deepin: Deepin软件中心
+
+应该说,这些工具中的每一个都是基于Ubuntu软件中心的。奇怪的是Ubuntu软件中心却正好排在最底。主要原因是Ubuntu软件中心太慢了——甚至在一个非常强大的机器上。
+
+我将应用商店排名设为如下:
+
+1. Linux Deepin
+
+2. Linux Mint
+
+3. Ubuntu Linux
+
+每个应用商店有非常相似的功能。Linux Deepin获得第一的原因有两个:界面易于控制而且程序开启速度远远快于Ubuntu软件中心和Mint软件管理器。
+
+### 时尚的界面 ###
+
+在这部分Linux Mint远远落后。尽管它提供了一个华美的界面和有很浅的学习曲线,但相比之下它仍然是一个非常过时的桌面。甚至在强大的硬件(有强大的显卡)上,Linux Mint仍然很容易被看成是来自90年代末的桌面。为了评判结果,我们必须看看是Ubuntu Linux还是Linux Deepin能带我们走进未来。胜者是:
+
+1. Linux Deepin
+
+2. Ubuntu Linux
+
+3. Linux Mint
+
+Linux Deepin使用GNOME 3来制作一个使用起来很漂亮的GNOME和OSX的混合体,你会认为你在处理一件互动的艺术品。
+
+## 总冠军 ##
+
+虽然这是很初步的,对新用户来说最好的Linux发行版顺序应该是:
+
+1. Linux Mint的总得分是7
+
+2. Linux Deepin的总得分是8
+
+3. Ubuntu Linux的总得分是9
+
+如果你想知道关于这篇文章的作者观点,要知道:我已经使用Ubuntu Linux很多年了(而且仍在用)。我最近一直在说“如果有一个Linux发行版能动摇我使用Ubuntu的想法,它便是Linux Deepin。”虽然我很欣赏Linux Mint,但我只是用它来进行测试。当说到对新用户最好的Linux发行版,Linux Mint是显而易见的赢家。
+
+这件事真正的真相是——你在使用这些桌面中任何一个都不会错。他们都各有所长。如果你追求真正的美丽,使用Linux Deepin吧。如果你想要漂亮外观与易用结合,那就使用Ubuntu Linux。如果你只想要简单而且并不在乎漂亮的外观,那就用Linux Mint。不管你选哪一个,这都是三赢的局面。
+
+你怎么认为?你会如何排这三个桌面的名次?或者,你是否会写一个不同的Linux发行版,该发行版在外表上来说对新用户最好的?(还有原因是什么?)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linux.com/news/software/applications/775873-the-best-linux-distribution-for-new-users/
+
+译者:[linuhap](https://github.com/linuhap) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.ubuntu.com/
+[2]:http://www.linuxmint.com/
+[3]:http://www.linuxdeepin.com/index.en.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/20140611 HTG Explains--What is Unix and Why Does It Matter.md b/published/20140611 HTG Explains--What is Unix and Why Does It Matter.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..086568b98b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140611 HTG Explains--What is Unix and Why Does It Matter.md
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
+什么是Unix以及它为什么这么重要?
+================================================================================
+
+
+大多数操作系统可以被划分到两个不同的家族。除了微软的基于Windows NT的操作系统外,几乎所有其他的都可以追溯到Unix。
+
+Linux,Mac OS X,Android,iOS,Chrome OS,PlayStaion 4上运行的Orbis OS,运行在路由器上的各种固件,所有这些操作系统通常都被称为“类Unix”操作系统。
+
+### Unix的设计现在都还在应用 ###
+
+Unix在20世纪60年代中晚期诞生于AT&T的贝尔实验室中。最初发布的Unix中的一些重要设计因素到如今都还在使用。
+
+其中一个设计是“Unix哲学”,建立小的模块化的应用,只做一件事情并把它做好。如果你对Linux终端很熟悉的话,应该对这个不陌生-系统提供了大量的应用,可以通过[管道或其他特性][1]形成不同的组合来完成更复杂的任务。甚至图形界面程序也经常会在后台调用更简单的应用去做比较耗时的任务。这种模式也让[建立终端脚本][2]更为简单,通过文本把一些简单工具结合起来去做复杂的事情。
+
+Unix还设计了一个单一的文件系统,程序可以通过它互相通讯。这也是[为什么在Linux里说“一切都是文件”][3]-包括硬件设备文件,和提供系统信息及其他数据的特殊文件。这也是为什么只有Windows系统中才有磁盘盘符,这是从DOS继承过来的-在其他操作系统中,所有文件都是一个单一目录结构中的一部分。
+
+
+
+### 那些从Unix派生出的系统 ###
+
+类似任何可以往前追溯40年的历史,Unix的历史和它的派生系统一片混乱。为了简单,我们把Unix的派生系统大致分成两组。
+
+一组Unix派生系统是学术界开发的。
+
+首先是BSD(伯克利软件发布版),一个开源的类Unix操作系统。BSD如今还存在于FreeBSD,NetBSD和OpenBSD等系统中。NeXTStep基于最初版的BSD开发,苹果的Mac OS X基于NeXTStep,iOS基于Mac OS X。许多其他操作系统,包括运行在PlayStation 4上的Orbis OS,也源于各种BSD操作系统。
+
+Richard Stallman建立GNU项目的目的是为了反对AT&T的Unix软件协议条款日渐严格的限制。MINIX是一个类Unix操作系统,为教育目的而实现的,而Linux则是受到了MINIX的启发。[我们今天所熟悉的Linux其实应该叫GNU/Linux][4],因为它是由Linux内核和大量GNU应用组成的。GNU/Linux不是直接从BSD继承下来的,但是它继承了Unix的设计而且根植于学术界。如今许多操作系统,包括Android,Chrome OS,Steam OS,以及数量巨大的在各种设备上使用的嵌入式操作系统,都基于Linux。
+
+另一组是商用的Unix操作系统。AT&T UNIX,SCO UnixWare,Sun Microsystem Solaris,HP-UX,IBM AIX,SGI IRIX-许多大型企业都希望建立并授权自己版本的Unix。它们如今并不常见,但其中一些仍然存在。
+
+
+
+图片致谢: [Wikimedia Commons][5]
+
+### DOS和Windows NT的崛起 ###
+
+许多人希望Unix能够成为工业标准操作系统,但是DOS和“IBM PC兼容”计算机却最终人气爆发而普及开来。微软的DOS也成为众多DOS系统中最成功的一个。DOS完全没有参照Unix,这也是[为什么Windows使用反斜杠划分文件路径,而其他所有系统都使用正斜杠][6]。这个决定是在早期的DOS系统中做出的,而之后的Windows版本继承了这一设定,就像BSD,Linux,Mac OS X,和其他类Unix操作系统继承了许多Unix设计因素一样。
+
+Windows 3.1,Windows 95,Windows 98,和 Windows ME都是建立在DOS的基础上。当时微软已经在开发一个更现代更稳定的操作系统,叫做Windows NT-意思是“Windows新技术”。Windows NT最终通过Windows XP应用到普通计算机用户中,但是之前它都只用于针对企业用户的Windows 2000和Windows NT。
+
+如今所有微软的操作系统都基于Windows NT内核。Windows 7,Windows 8,Windows RT,Windows Phone 8,Windows Server,以及Xbox One上的操作系统都在使用Windows NT内核。不像其他大多数操作系统那样,Windows NT没有被开发成一个类Unix操作系统。
+
+当然,微软也不是完全从零开始的。为了维护DOS和旧版本Windows软件的兼容性,Windows NT继承了许多DOS里的设定,比如磁盘盘符,反斜杠区分文件路径,正斜杠作为命令行参数开关。
+
+
+
+### 为什么它影响很大 ###
+
+不知道你有没有看过Mac OS X终端或是文件系统,有没有注意到它们和Linux是如此相似,而又和Windows是如此不同?好吧,原因是-Mac OS X和Linux两个都是类Unix操作系统。
+
+了解了这点历史,就可以帮助你理解什么是“类Unix”操作系统,以及为什么这么多操作系统看起来都差不多,而Windows却那么与众不同。这也可以解释为什么Linux极客对Mac OS X上的终端会感觉如此熟悉,而[Windows 7上的Command Prompt和PowerShell][7]相对于其他命令行环境显得格格不入。
+
+这只是一点快速掠过的历史,帮助了解是如何发展到今天的,而不用陷入到细节中。如果你想了解更多,可以找到许多关于Unix历史的整本的书籍。
+
+图片致谢: [Peter Hamer on Flickr][8], [Takuya Oikawa on Flickr][9], [CJ Sorg on Flickr][10]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.howtogeek.com/182649/htg-explains-what-is-unix/
+
+译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.howtogeek.com/110150/become-a-linux-terminal-power-user-with-these-8-tricks/
+[2]:http://www.howtogeek.com/107217/how-to-manage-processes-from-the-linux-terminal-10-commands-you-need-to-know/
+[3]:http://www.howtogeek.com/117939/htg-explains-what-everything-is-a-file-means-on-linux/
+[4]:http://www.howtogeek.com/139287/the-great-debate-is-it-linux-or-gnulinux/
+[5]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Unix_history.svg
+[6]:http://www.howtogeek.com/181774/why-windows-uses-backslashes-and-everything-else-uses-forward-slashes/
+[7]:http://www.howtogeek.com/163127/how-powershell-differs-from-the-windows-command-prompt/
+[8]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/peter-hamer/2876612463/
+[9]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/takuyaoikawa/2060554607/
+[10]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/cjsorg/2726088549/
diff --git a/published/20140612 What is a good text editor on Linux.md b/published/20140612 What is a good text editor on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4a987268e3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140612 What is a good text editor on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+优秀的Linux文本编辑器
+================================================================================
+
+想要挑起狂热Linux爱好者之间的激烈争辩吗?那就问问他们最喜欢的文本编辑器是什么吧。在开源社区中,选择一个用来写文本,或者更进一步,用来写代码的编辑器,比选择一个球队或者游戏控制器还要重要。但是任何一个Linux新手都不该为过多的建议和各种各样的煽动而感到焦虑不安,取而代之,先去试着熟悉熟悉一堆不同的文本编辑器吧。所以今天我将要给你建议一个简单主题的列表,里面的编辑器都可以在Linux下编辑文本。这个列表不包括那些成熟的只用来编程的IDE,也不包括那些专门进行LaTex排版的编辑器。如果你对后者感兴趣,我可以建议你去看看[这里][1].
+
+### 1. Vim & Emacs ###
+
+
+
+让我们直接从这两个“大咖”开始。当有人在一个聊天室里问关于Linux下的编辑器时,会有一个人立马回答[Vim][2],然后会有另外一个说[Emacs][3]。(LCTT译注:这就是V党和E党啊~)之所以会这样,理由很充分。这两个都是非常强大的编辑器,有很多的特性,很多插件,很强大的社区支持。如果你一点都不熟悉它们的话,要描述清楚它们强大的功能是有点困难。但是简单来讲,它们允许你在文本中快速移动,简单地做出大量的修改,记录宏以及你能想到基本上任何疯狂的编辑方式。这两个编辑器共同的缺点是,不可避免地花时间去学习。讲完这点之后,我不会陷入到哪一个更好的争论中去,但是我真的想建议每一个人至少学习这两者之一。
+
+
+
+### 2. Sublime Text & Lime & Atom ###
+
+
+
+一款叫做[Sublime Text][4]的文本编辑器在过去几年逐渐兴起。一些人可能会将它视为Vim或者Emacs的友好版,专为编程而设计的。事实上,它保持了一些与Vim和Emacs的相似特性。比如,批量编辑和函数跳转都会让人或多或少想起Emacs或者[一个充满活力的Vim][5]。然而,它保留了更多的可视性并且更加容易使用。同样,大量的插件吸引大家进行个性化定制。(LCTT译注:实际上,译者认为Sublime Text与其说是像Vim或Emacs,不如说更像是Mac上的编辑器神器textmate。另外,Sublime Text的发展最近已经陷入停滞了。)
+
+Sublime Text唯一的“污点”是它的许可证:如果你只使用开源软件的话,你可以放弃它了。(LCTT译注:但是Sublime Text可以全功能一直试用下去,没有一点区别,只是如果你觉得应该支持的话,付费比较好,虽然挺贵。)为此,最近出现了一个雄心勃勃的克隆版 [Lime][6] 。这个软件正处在重度开发当中,但是它的理念是:跟Sublime Text相似的用户体验,但是带着开源的韵味。对于Lime,除了满满的期待没有更多要说的了。
+
+距现在更近的,GitHub以开源形式发布了[Atom][7],展开了与Sublime Text正式的竞争。Atom打包了所有你想要的文件跳转,代码片段使用等特性,提供一个完整特性的编辑器而不是简单的编辑框。使用HTML,CSS和集成Node.js环境,可以轻易地定制文本处理过程,这正是它的魅力所在。这其实已经要涉及到IDE的定义了,我们的列表最多会覆盖到这里。(LCTT译注:好吧,我觉得从Sublime Text转移出来的最佳出口就是Atom。)
+
+
+
+### 3. Gedit & Kate & Mousepad & Leafpad ###
+
+
+
+如果不谈这些超级厉害的神器,我们可以转向我认为的“桌面环境经典版”编辑器。这些编辑器感觉上更加的传统,有些也可以用插件进行强化,但是它们的重点是输入简单。如果你头脑里有一些想法想要在忘记之前赶快记下来(我必须怪罪那些视频游戏让我的注意力变得短暂)。你不需要学习Vim或者Sublime Text的快捷键。你只需要一些空白的地方进行输入。这类编辑器的好处是它们或多或少的和你的桌面环境集成在一起。在这一类编辑器中,Gnome 下的 [Gedit][8] 和 KDE下的 [Kate][9] 都很好的集成在桌面系统中,可以通过插件进行个性化定制。比如,更容易的进行LaTeX排版。[Mousepad][10] 和 [Leafpad][11] 更适合于轻量级的桌面,比如Xfce和LXDE。它们在某种程度上很像Windows的记事本。所以,如果你需要的是灵活和便捷,请选择它们。
+
+
+
+### 4. Nano & Qute ###
+
+
+
+另外一个流行的文本编辑器“大家族”是“无打扰编辑器”。如果你喜欢在后台持续地开着Facebook或者Twitter,或者每5分钟就收一次邮件,你就会知道把注意力集中在那篇明天要交的散文,或者这些还没编译通过的代码是多么困难的事。如果是这样,你需要一个编辑器,它可以占满整个屏幕空间,并且屏蔽掉所有的其它事情。
+
+也许这类编辑器里面最不受欢迎的是Nano。如果你想屏蔽所有分心的事,关掉X server(LCTT译注:关掉桌面,只用文字终端界面,Nano就是工作在这种模式下。实际上这时nano就是接管了X Server的工作。)。这是最简单和直接的方式。事实上,《权力游戏(Game of Thrones)》的作者Geogge R. R. Martin最近就在[一次采访][13]中说他使用一个类似DOS Word的文本处理程序写他的小说。
+
+如果你想要一款更顺眼一点的编辑器,你可以试试我的最爱:[Qute][14]。没有酷炫的特性,也许有一点LaTeX排版使它开起来更美观,但是重点其实是在它的界面的。它提供了一个舒适的导航和编辑体验。如果你对终端感觉不太舒服,Qute是个不错的选择。
+
+
+
+
+### 5. LibreOffice & Calligra & Abiword ###
+
+
+
+最后,办公套件也是文本编辑器。我不确定你能否轻松使用办公套件编程,但是它确实更适合纯文本编辑,也比LaTeX更容易学习。在这类编辑器中,[LibreOffice][15] 和 [Calligra][16] 不能避而不谈。这两个编辑器因为它们丰富的特性和响亮的名声成为这类编辑器中的巨兽。这两者我都喜欢,但是很多人明确的偏向于前者。如果你怀念微软的Word处理软件,你会有自己的选择。稍处下风的[Abiword][17]相对前面的两个是一个轻量级的选择。如果你的目的只是编辑一个文本文档,不关心电子表格或者数据库,Abiword的特性可以达到理想的效果。
+
+
+
+简单总结一下,如果我仅有一条建议给你,那么就是选择你周围的人正在使用的编辑器。如果因为某些疯狂的理由,每一个你周围的人都用LibreOffice写C程序,或者用Sublime Text写小说,而你也要做同样的事,你应该跟随潮流。原因就是当你遇到一个问题需要帮助的时候,他们可以更容易的给你提供帮助。
+
+你最喜欢的文本编辑器是什么?你都用它来做什么?请在评论中和我们分享吧。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/06/good-text-editor-linux.html
+
+译者:[love\_daisy\_love](https://github.com/CNprober) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2014/04/latex-editor-software-linux.html
+[2]:http://www.vim.org/
+[3]:https://www.gnu.org/software/emacs/
+[4]:http://www.sublimetext.com/
+[5]:http://xmodulo.com/2014/06/turn-vim-full-fledged-ide.html
+[6]:http://limetext.org/
+[7]:https://atom.io/
+[8]:https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Gedit
+[9]:http://kate-editor.org/
+[10]:http://www.home.unix-ag.org/bmeurer/xfce/apps.html
+[11]:http://tarot.freeshell.org/leafpad/
+[12]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14415259703/
+[13]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X5REM-3nWHg
+[14]:http://www.inkcode.net/qute
+[15]:https://www.libreoffice.org/
+[16]:http://www.calligra-suite.org/
+[17]:http://www.abisource.com/
+
diff --git a/published/20140616 How to Rescue a Non-booting GRUB 2 on Linux.md b/published/20140616 How to Rescue a Non-booting GRUB 2 on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..52c6df035e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140616 How to Rescue a Non-booting GRUB 2 on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
+如何拯救一台GRUB 2启动失败的Linux电脑
+================================================================================
+
+
+旧版GRUB我们使用了一段时间了,这个重要的Linux通用引导器的版本已经到了0.97。尽管旧版GRUB有很多的优点,但是它已经有点陈旧了,并且它的开发者也希望添加更多的功能,于是,GRUB 2 时代就要来了。
+
+GRUB 2 做了几个明显的改进。它可以从移动存储设备上启动,并且可以通过配置一个选项来进入系统BIOS。相对于将所有的配置都放到一个配置文件`/boot/grub/menu.lst`中 (现在默认是`/boot/grub/grub.cfg `),使用各种脚本来配置会更复杂。你不要直接编辑这个文件,那不是人干的事,太复杂了,我们需要使用其它的脚本来改变。我们卑微的人类可以编辑修改`/etc/default/grub`文件,它主要是控制Grub菜单的外观。我们还可以修改` /etc/grub.d/ `下的脚本,这些脚本用于启动操作系统、控制外部应用程序,如memtest 、os_prober和theming等等 。`./boot/grub/grub.cfg`是由`/etc/default/grub`和`/etc/grub.d/*`生成的。当你修改了某个地方,你必须要运行update-grub命令来生成它。
+
+好消息是,update-grub脚本可以可靠的检测内核、启动文件,并添加所有的操作系统,自动生成你的启动菜单,所以你不必手动的修改他们。
+
+我们还要学习如何解决两个常见的故障。当启动系统时,它会停在grub>提示上,这是一个完整的GRUB 2命令界面,所以不要惊慌。这意味着GRUB 2依旧可以正常启动和加载normal.mod模块(它和其他模块分别位于/boot/grub/[架构]/ 下),但没有找到你的grub.cfg文件。如果你看到grub rescue> 这意味着它无法找到normal.mod,因此它有可能找不到你的启动文件。
+
+这是如何发生的?因为内核可能改变驱动器分区号码的分配,或者您移动了您的硬盘驱动器,或者你手动改变一些分区,也有可能是安装一个新的操作系统或者移动一些文件。在这些情况下你的启动文件仍然存在,但GRUB不能找到他们。所以你可以在GRUB提示符中找到启动文件,设置它们的位置,然后启动您的系统并修复GRUB配置。
+
+### GRUB 2 命令行 ###
+
+GRUB 2 的命令界面和上一代GRUB中的一样强大。你可以用它来找到引导镜像,内核和根文件系统。事实上,它可以让你避开权限和其它访问控制,完全访问本地计算机上的所有文件。有些人可能会认为这是一个安全漏洞,但是你知道古老的UNIX的名言:有物理访问机器权限的人,就是拥有它的人。
+
+当你在` grub > `提示时,你有许多类似命令行界面的功能,如命令历史和tab补全。但是`grub rescue> `模式是受限的,没有命令历史,没有tab补全。
+
+如果你是在一个正常运作的系统上练习,那就当GRUB菜单出现时,可以按下C来打开GRUB命令行界面。你可以通过向上和向下光标键滚动你的菜单条目来停止启动倒计时。在GRUB命令行下做实验是安全的,因为做不了永久的修改,一切都是暂时的。如果你已经看到`grub > `或`grub rescue> `提示符,那就说明你的表现时刻到了。
+
+接下来的几个命令可以在`grub>`和`grub rescue`模式下运行。你应该运行的第一个命令是设置一个分页器,将长的命令分页。如下:
+
+ grub> set pager=1
+
+等号两侧必须不能出现空格。现在让我们做一点探索。输入`ls`来列出的GRUB识别的所有分区:
+
+ grub> ls
+ (hd0) (hd0,msdos2) (hd0,msdos1)
+
+msdos是什么?这意味着该系统具有老式的MS-DOS分区表,而不是全新的全局唯一标识符的分区表(GPT)。参见“[在Linux下使用新的GUID分区表,和古老的MBR说再见!][1]”。如果你正在运行的GPT,它会出现(hd0,GPT1)。现在让我们看看,使用ls命令查看你的系统里面有什么文件:
+
+ grub> ls (hd0,1)/
+ lost+found/ bin/ boot/ cdrom/ dev/ etc/ home/ lib/
+ lib64/ media/ mnt/ opt/ proc/ root/ run/ sbin/
+ srv/ sys/ tmp/ usr/ var/ vmlinuz vmlinuz.old
+ initrd.img initrd.img.old
+
+太好了,我们已经找到了根文件系统。你可以省略msdos和GPT的标签。如果没有加分区后面的斜杠/,则只会列出分区的信息。你可以用cat命令显示文件系统上的任何文件:
+
+ grub> cat (hd0,1)/etc/issue
+ Ubuntu 14.04 LTS \n \l
+
+在一个多引导系统上,通过/etc/issue文件可以知道这是哪个Linux系统。
+
+### 从 grub> 中启动###
+
+下面讲述如何设置启动文件并从`grub >`提示下启动系统。我们已经知道如何从Linux根文件系统(hd0,1)下运行ls命令,你可以一直寻找直到找到你的/boot/grub所在位置。然后运行以下命令,记得使用您自己的根分区,内核和initrd映像等参数:
+
+ grub> set root=(hd0,1)
+ grub> linux /boot/vmlinuz-3.13.0-29-generic root=/dev/sda1
+ grub> initrd /boot/initrd.img-3.13.0-29-generic
+ grub> boot
+
+第一行设置分区的根文件系统。第二行告诉GRUB您想要使用的内核位置。开始输入/boot/vmli,然后使用tab补完填写。输入`root= /dev/sdX`设置根文件系统位置。是的,这似乎是多余的,但如果你忘记了输入,你会得到一个kernel panic。你知道怎么找到正确的分区吗?hd0,1 即 /dev/sda1,hd1,1 即 /dev/sdb1,hd3,2 即 /dev/ sdd2。我想你可以自己推算剩下的了。
+
+第三行设置initrd文件,必须是和内核相同的版本号。
+
+最后一行启动系统。
+
+在一些Linux系统上,内核和initrd是被符号链接到当前的根文件系统的根目录,就像:
+
+ $ ls -l /
+ vmlinuz -> boot/vmlinuz-3.13.0-29-generic
+ initrd.img -> boot/initrd.img-3.13.0-29-generic
+
+所以,你也可以这样输入命令:
+
+ grub> set root=(hd0,1)
+ grub> linux /vmlinuz root=/dev/sda1
+ grub> initrd /initrd.img
+ grub> boot
+
+### 从grub rescue> 中启动 ###
+
+如果你处在grub rescue> 命令界面下,命令有所不同,你必须要先加载两个模块normal.mod 和 linux.mod。
+
+ grub rescue> set prefix=(hd0,1)/boot/grub
+ grub rescue> set root=(hd0,1)
+ grub rescue> insmod normal
+ grub rescue> normal
+ grub rescue> insmod linux
+ grub rescue> linux /boot/vmlinuz-3.13.0-29-generic root=/dev/sda1
+ grub rescue> initrd /boot/initrd.img-3.13.0-29-generic
+ grub rescue> boot
+
+在你加载了这两个模块之后tab补完的功能就可以用了。
+
+### 永久性的修复 ###
+
+当你成功地启动你的系统,运行这些命令来永久修复GRUB:
+
+ # update-grub
+ Generating grub configuration file ...
+ Found background: /usr/share/images/grub/Apollo_17_The_Last_Moon_Shot_Edit1.tga
+ Found background image: /usr/share/images/grub/Apollo_17_The_Last_Moon_Shot_Edit1.tga
+ Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-3.13.0-29-generic
+ Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-3.13.0-29-generic
+ Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-3.13.0-27-generic
+ Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-3.13.0-27-generic
+ Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-3.13.0-24-generic
+ Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-3.13.0-24-generic
+ Found memtest86+ image: /boot/memtest86+.elf
+ Found memtest86+ image: /boot/memtest86+.bin
+ done
+ # grub-install /dev/sda
+ Installing for i386-pc platform.
+ Installation finished. No error reported.
+
+当你运行 `grub-install` 时,记得GRUB是安装到整个硬盘驱动器的主引导扇区而不是到一个具体分区,所以不要加上像/dev/sda1一样的分区号。
+
+### 如果还是不能使用 ###
+
+如果你的系统是如此的倒霉,而且这个方式没有能起作用,那就尝试[超级GRUB2现场救援磁盘][2]吧。[官方GNU GRUB手册][3]也应该有所帮助。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/776643-how-to-rescue-a-non-booting-grub-2-on-linux
+
+译者:[MikeCoder](https://github.com/MikeCoder) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/730440-using-the-new-guid-partition-table-in-linux-good-bye-ancient-mbr-
+[2]:http://www.supergrubdisk.org/
+[3]:https://www.gnu.org/software/grub/manual/grub.html
diff --git a/published/20140616 Linux Screenshot App Shutter Updates with Bug Fixes, New Icon.md b/published/20140616 Linux Screenshot App Shutter Updates with Bug Fixes, New Icon.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..eaf3cccec7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140616 Linux Screenshot App Shutter Updates with Bug Fixes, New Icon.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+Linux 截屏软件 Shutter
+================================================================================
+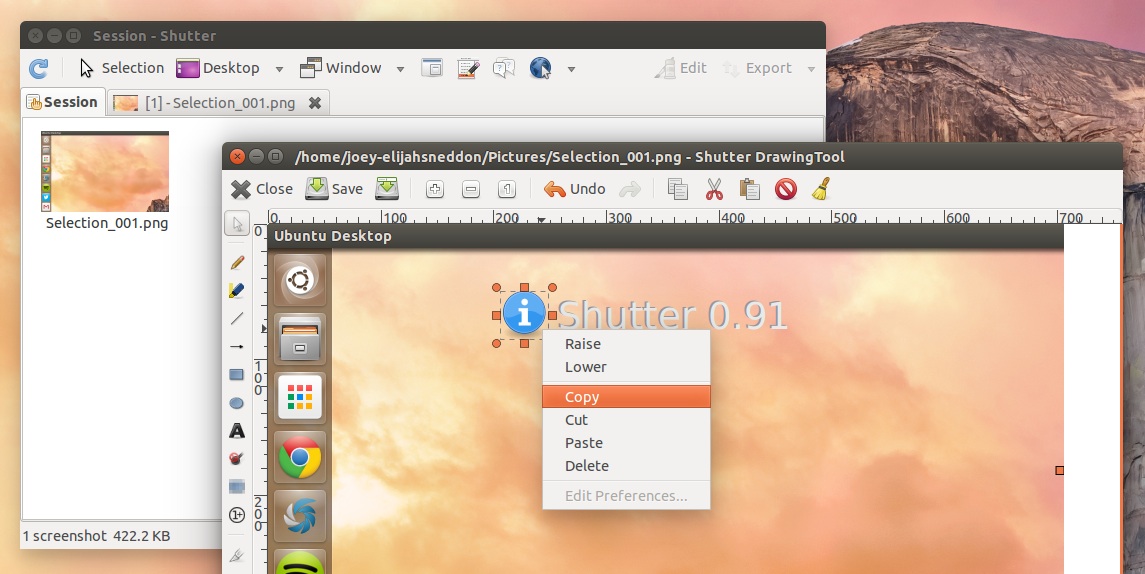
+
+**[Shutter][1],是一款Linux平台下广受欢迎的截屏软件。最近的更新中,该软件修复了若干bug,并且使用了新的应用图标。**
+
+这款开源并且功能强大的截屏工具可以让你选择桌面的任意区域、指定应用窗口或者整个屏幕区域来进行截屏。此外,你还可以添加注释、文本或者特效。
+
+0.91版本修复了若干明显的bug,包括在Ubuntu 14.04中缩略图无法正常地在应用切换栏中显示的问题。由于'imm.io'在今年早期停止了服务,所以此次更新还取消了将截图上传到Pixlr图像服务的选项。
+
+最后,这次更新突出了由 Lucas Romero Di Benedetto 精心设计的相机快门式应用图标。
+
+
+
+### 在Ubuntu环境下安装Shutter 0.91版本 ###
+
+升级到Shutter的最新版本是非常简单的——前提是你添加了该软件的PPA。[The Shutter PPA][2] 面向Ubuntu 12.04 LTS、13.10、14.04 LTS提供该软件最新稳定的发行版。
+
+ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:shutter/ppa
+
+ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install shutter
+
+不喜欢PPA?那么你也可以从该项目的主页下载Debian安装包。如果你使用的是Ubuntu 14.04 LTS系统,你可以点击下面的链接来下载安装包。
+
+- [下载适用于Ubuntu 14.04 LTS系统的Shutter 0.91][3]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/06/shutter-0-91-new-icon
+
+译者:[JonathanKang](https://github.com/JonathanKang) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://apps.ubuntu.com/cat/applications/shutter/
+[2]:https://launchpad.net/~shutter/+archive/ppa
+[3]:https://launchpad.net/~shutter/+archive/ppa/+files/shutter_0.91%7Eppa2%7Eubuntu14.04.1_all.deb
diff --git a/published/20140616 Managing Vim extensions with NeoBundle.md b/published/20140616 Managing Vim extensions with NeoBundle.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1246d99f7d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140616 Managing Vim extensions with NeoBundle.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+教你用NeoBundle管理Vim插件
+================================================================================
+[NeoBundle][1] 是一个 [Vim][2] 的插件管理器,以 [Vundle][3] 为基础(Vundle 是一个基于 [Pathogen][4] 的 Vim 插件管理器)。在之前的文章中,我[非常不推荐使用 Neobundle][5],原因是它当时还处于高速开发阶段(LCTT:意味着不稳定、变数大),并且当时它的英文文档很少。现在,已经过了一年多了,这两个问题都早已不再是问题。
+
+我们为什么要使用插件管理器?Vim 支持大量插件,但是由于它没有严格定义框架,插件的文件可以胡乱分布在不同目录下,导致用户管理起来会很困难(LCTT:当然,前提是你有很多插件,还有点小小的强迫症,觉得理一理这些插件心里会舒服点)。而一款插件管理器能让管理变得简单许多。Pathogen, Vundle 和 NeoBundle 的工作就是为不同插件建立一个目录,然后将这些目录扔到 ~/.vim/bundle 目录下。这个文件整理方法可以让你方便彻底地删除插件,使用 'rm -rf <插件目录>' 或直接在文件管理器里面把插件所在的目录删除就可以了,绝对绿色环保无残留。同时,这种方法还能最大程度避免插件与插件之间的不兼容性。
+
+NeoBundle 是一个基于 Vundle 的项目,如同 Vundle,它们都可以安装和升级插件。然而 NeoBundle 的说明文件上明确指出:“NeoBundle 不是一个稳定的插件管理器,如果你想要一个稳定的,请选择 Vundle”。最新的 release-note 上也有警告“可能会造成兼容性问题”——这是一个开发者写的注解,说明这个管理器还不能让人放心使用。
+
+所以,我们为什么要使用 NeoBundle?它都不能保证稳定运行!好吧,它还是有可取之处的。Vundle 只支持 [Git][6] 这种版本控制系统,而 NeoBundle 可以支持 [Subversion][7] 和 [Mercurial][8]。另一个原因是如果你不想插件升级时破坏你的 Vim 生态环境,你可以锁住 NeoBundle,让它只使用某个插件的固定版本。
+
+另外,NeoBundle 创建者,Shougo Matsuishita(LCTT:名字看着像日本人),正在将它的命令接口添加到其他插件项目,以便减少他们的命令使用量。现在 NeoBundle 支持3种插件:[unite.vim][9],Vim 使用的文件和缓存管理器;[vimshell.vim][10],Vim 使用的脚本程序;[vimproc.vim][11],运行于 vimshell.vim 中,用于对异步事件的支持。上面说的都是特殊案例,缺少英文文档,所以用户希望有人能完善它们。在正式使用它们之前,我们需要把注意力先集中在一些基本操作上。
+
+### 安装并初始化 NeoBundle ###
+
+NeoBundle 支持 Vim 7.2.051 或更高版本,需要 git 和 [cURL][12](用于下载文件)。你可以手动下载 NeoBundle,也可以使用 cURL 下载它在 GitHub 上的库。在你的 home 目录下使用如下命令,可以将 NeoBundle 插件下载到 .vim/bundle/neobundle.vim 目录里,然后 NeoBundle 就能管理它自己了。
+
+ curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Shougo/neobundle.vim/master/bin/install.sh | sh
+
+你还需要修改 .vimrc 文件。NeoBundle 的 GitHub 主页提供一个 .vimrc 范本,但是直接使用这个范本,NeoBundle 需要你安装5个可能不需要插件。如果不需要它们,你可以使用下面的最小配置:
+
+ if has('vim_starting')
+ set nocompatible
+ set runtimepath+=~/.vim/bundle/neobundle.vim/
+ call neobundle#begin(expand('~/.vim/bundle/'))
+ NeoBundleFetch 'Shougo/neobundle.vim'
+ call neobundle#end()
+ filetype plugin indent on
+
+上述配置的作用是:启动 NeoBundle 并且像其他插件一样升级自己。NeoBundle 默认从 GitHub 下载并升级,如果你正好在使用 GitHub,你只需要为这个插件指定维护者的用户名和路径。在上面的配置中,NeoBundleFetch 只需要指定为“Shougo/neobundle.vim”,而不是完整的 GitHub 路径。如果你想使用其他网站,比如是 Subversion 或 Mecurial 的网站,你就需要添加完整的 URL。
+
+如果你想安装其他插件,你可以使用下面的命令:
+
+ curl -k https://github.com/[项目维护者]/[插件路径] > ~/.vim/bundle/[插件路径]
+
+举个例子:你想安装 [vim-abolish][13],一个超级 NB 的文本搜索和替换插件,就使用下面的命令:
+
+ curl -k https://github.com/tpope/vim-abolish > ~/.vim/bundle/abolish
+
+如果要让它自动升级,在 NeoBundleFetch 那行下面添加一行:
+
+ NeoBundle 'tpope/vim-abolish'
+
+再介绍一个小技巧:你可以为插件指定一个分支或版本号。什么意思?NeoBundle 只会使用这个插件的某个分支或版本,而忽略其版本更新。如果你使用的某个插件处于高速开发过程,你就可以使用这个技巧,避免用到有 bug 的插件版本。举个例子:
+
+ NeoBundle 'Shougo/vimshell', { 'rev' : '3787e5' }
+
+还有一个技巧:在 .vimtc 文件内添加一行关于“NeoBundleCheck”的属性。NeoBundle 会根据配置检查没安装的插件,并提示你安装它们。你也可以使用命令“:NeoBundleInstall”(LCTT:这是要在 Vim 编辑器的命令模式下输入)来安装或升级插件。
+
+### NeoBundle 用法 ###
+
+很多 NeoBundle 命令用起来和 Vundle 类似,但命令的名字不一样。下面是 NeoBundle 命令的用法:
+
+- `:NeoBundleUpdate`:安装或升级插件,如果你手动把一个插件的目录删除了,这个命令会重新安装这个插件。在这个命令后面加上插件名称,就只升级一个插件;不加参数,会将所有己安装但没被记录在案的插件给记录下来。`:NeoBundleInstall` 命令效果相同。
+- `:NeoBundle {REPOSITORY URI} [[REVISION}] [,OPTIONS}]]`:将一个插件锁定到固定版本,防止胡乱升级。
+- `:NeoBundleList`:列出所有未初始化的插件。
+- `:NeoBundleClean`:进入交互界面,删除插件。
+
+这些命令在配合 unite.vim (LCTT:就是上面举过的32个例子之一)使用时,效果会稍微有些出入。你可以使用“:help neobundle”命令了解更多信息。
+
+### 是否使用 NeoBundle,自己决定 ###
+
+NeoBundle 是强大的工具,正处于高速开发状态。任何处于这种状态的项目,都会被帖上“有前途”和“不稳定”两个标签,看你自己怎么选。如果你想要最新的稳定版本的插件,NeoBundle 能够把 Vundle 和 Pathogen 甩出几条街。
+
+然而在线帮助文档已经给出警告,它不是个稳定的产品,不及时更新版本可能造成一些插件运行出错。最后,你需要在 .vimrc 文件为你的 Neoundle 和其他插件指定一个稳定的版本。记住这警告,然后你可以在使用这些尖端技术产品时游刃有余。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.openlogic.com/wazi/bid/348084/Managing-Vim-extensions-with-NeoBundle
+
+译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://github.com/Shougo/neobundle.vim
+[2]:http://olex.openlogic.com/packages/vim
+[3]:https://github.com/gmarik/Vundle.vim
+[4]:https://github.com/tpope/vim-pathogen
+[5]:http://www.openlogic.com/wazi/bid/262302/Three-tools-for-managing-Vim-plugins
+[6]:http://olex.openlogic.com/packages/git
+[7]:http://olex.openlogic.com/packages/subversion
+[8]:http://olex.openlogic.com/packages/mercurial
+[9]:https://github.com/Shougo/unite.vim
+[10]:https://github.com/Shougo/vimshell.vim/blob/master/doc/vimshell.txt
+[11]:https://github.com/Shougo/vimproc.vim/blob/master/doc/vimproc.txt
+[12]:http://olex.openlogic.com/packages/curl
+[13]:https://github.com/tpope/vim-abolish
diff --git a/published/20140617 9 Good Ways To Protect Your Linux System.md b/published/20140617 9 Good Ways To Protect Your Linux System.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7d7b3c477a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140617 9 Good Ways To Protect Your Linux System.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+保护你的Linux系统的九个老生常谈
+================================================================================
+在现在这个世道中,保障基于Linux的系统的安全是十分重要的。但是,你得知道怎么干。一个简单反恶意程序软件是远远不够的,你需要采取其它措施来协同工作。那么试试下面这些手段吧。
+
+
+
+### 1. 使用SELinux ###
+
+[SELinux][1]是用来对Linux进行安全加固的,有了它,用户和管理员们就可以对访问控制进行更多控制。SELinux为访问控制添加了更细的颗粒度控制。与仅可以指定谁可以读、写或执行一个文件的权限不同的是,SELinux可以让你指定谁可以删除链接、只能追加、移动一个文件之类的更多控制。(LCTT译注:虽然NSA也给SELinux贡献过很多代码,但是目前尚无证据证明SELinux有潜在后门)
+
+### 2. 订阅漏洞警报服务 ###
+
+安全缺陷不一定是在你的操作系统上。事实上,漏洞多见于安装的应用程序之中。为了避免这个问题的发生,你必须保持你的应用程序更新到最新版本。此外,订阅漏洞警报服务,如[SecurityFocus][2]。
+
+### 3. 禁用不用的服务和应用 ###
+
+通常来讲,用户大多数时候都用不到他们系统上的服务和应用的一半。然而,这些服务和应用还是会运行,这会招来攻击者。因而,最好是把这些不用的服务停掉。(LCTT译注:或者干脆不安装那些用不到的服务,这样根本就不用关注它们是否有安全漏洞和该升级了。)
+
+### 4. 检查系统日志 ###
+
+你的系统日志告诉你在系统上发生了什么活动,包括攻击者是否成功进入或试着访问系统。时刻保持警惕,这是你第一条防线,而经常性地监控系统日志就是为了守好这道防线。
+
+### 5. 考虑使用端口试探 ###
+
+设置[端口试探(Port knocking)][4]是建立服务器安全连接的好方法。一般做法是发生特定的包给服务器,以触发服务器的回应/连接(打开防火墙)。端口敲门对于那些有开放端口的系统是一个很好的防护措施。
+
+下面是来自 http://www.portknocking.org/ 的示意图:
+
+
+
+### 6. 使用Iptables ###
+
+Iptables是什么?这是一个应用框架,它允许用户自己为系统建立一个强大的防火墙。因此,要提升安全防护能力,就要学习怎样一个好的防火墙以及怎样使用Iptables框架。
+
+### 7. 默认拒绝所有 ###
+
+防火墙有两种思路:一个是允许每一点通信,另一个是拒绝所有访问,提示你是否许可。第二种更好一些。你应该只允许那些重要的通信进入。(LCTT译注:即默认许可策略和默认禁止策略,前者你需要指定哪些应该禁止,除此之外统统放行;后者你需要指定哪些可以放行,除此之外全部禁止。)
+
+### 8. 使用入侵检测系统 ###
+
+入侵检测系统,或者叫IDS,允许你更好地管理系统上的通信和受到的攻击。[Snort][3]是目前公认的Linux上的最好的IDS。
+
+### 9. 使用全盘加密 ###
+
+加密的数据更难窃取,有时候根本不可能被窃取,这就是你应该对整个驱动器加密的原因。采用这种方式后,如果有某个人进入到你的系统,那么他看到这些加密的数据后,就有得头痛了。根据一些报告,大多数数据丢失源于机器被盗。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=141368
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://selinuxproject.org/page/Main_Page
+[2]:http://www.securityfocus.com/rss/vulnerabilities.xml
+[3]:http://www.snort.org/
+[4]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Port_knocking
diff --git a/published/20140617 9 commands to check hard disk partitions and disk space on Linux.md b/published/20140617 9 commands to check hard disk partitions and disk space on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..77f5c5d637
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140617 9 commands to check hard disk partitions and disk space on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,235 @@
+Linux下掌控磁盘分区的九大神器
+================================================================================
+
+在这篇文章中,我们来了解一些用来检查你的系统分区的一些命令,这些命令将检查每个磁盘的分区情况和其它细节,例如总空间容量,已用完的空间和文件系统等。
+
+像fdisk,sfdisk和cfdisk命令这样的常规分区工具,不仅可以显示分区信息,还可以修改。
+
+### 1. fdisk ###
+
+Fdisk是检查磁盘上分区的最常用命令,fdisk命令可以显示分区和细节,如文件系统类型,但是它并不报告每个分区的字节大小。
+
+ $ sudo fdisk -l
+
+ Disk /dev/sda: 500.1 GB, 500107862016 bytes
+ 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 60801 cylinders, total 976773168 sectors
+ Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
+ Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
+ I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
+ Disk identifier: 0x30093008
+
+ Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
+ /dev/sda1 * 63 146801969 73400953+ 7 HPFS/NTFS/exFAT
+ /dev/sda2 146802031 976771071 414984520+ f W95 Ext'd (LBA)
+ /dev/sda5 146802033 351614654 102406311 7 HPFS/NTFS/exFAT
+ /dev/sda6 351614718 556427339 102406311 83 Linux
+ /dev/sda7 556429312 560427007 1998848 82 Linux swap / Solaris
+ /dev/sda8 560429056 976771071 208171008 83 Linux
+
+ Disk /dev/sdb: 4048 MB, 4048551936 bytes
+ 54 heads, 9 sectors/track, 16270 cylinders, total 7907328 sectors
+ Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
+ Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
+ I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
+ Disk identifier: 0x0001135d
+
+ Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
+ /dev/sdb1 * 2048 7907327 3952640 b W95 FAT32
+
+每个设备都单独显示其详细信息:容量大小,扇区数,设备ID及其包含的每个分区。
+
+### 2. sfdisk ###
+
+Sfdisk是另一种跟fdisk用途相似的实用工具,但具有更多的功能。它能够以MB为单位显示每个分区的大小。
+
+ $ sudo sfdisk -l -uM
+
+ Disk /dev/sda: 60801 cylinders, 255 heads, 63 sectors/track
+ Warning: extended partition does not start at a cylinder boundary.
+ DOS and Linux will interpret the contents differently.
+ Units = mebibytes of 1048576 bytes, blocks of 1024 bytes, counting from 0
+
+ Device Boot Start End MiB #blocks Id System
+ /dev/sda1 * 0+ 71680- 71681- 73400953+ 7 HPFS/NTFS/exFAT
+ /dev/sda2 71680+ 476938 405259- 414984520+ f W95 Ext'd (LBA)
+ /dev/sda3 0 - 0 0 0 Empty
+ /dev/sda4 0 - 0 0 0 Empty
+ /dev/sda5 71680+ 171686- 100007- 102406311 7 HPFS/NTFS/exFAT
+ /dev/sda6 171686+ 271693- 100007- 102406311 83 Linux
+ /dev/sda7 271694 273645 1952 1998848 82 Linux swap / Solaris
+ /dev/sda8 273647 476938 203292 208171008 83 Linux
+
+ Disk /dev/sdb: 1020 cylinders, 125 heads, 62 sectors/track
+ Warning: The partition table looks like it was made
+ for C/H/S=*/54/9 (instead of 1020/125/62).
+ For this listing I'll assume that geometry.
+ Units = mebibytes of 1048576 bytes, blocks of 1024 bytes, counting from 0
+
+ Device Boot Start End MiB #blocks Id System
+ /dev/sdb1 * 1 3860 3860 3952640 b W95 FAT32
+ start: (c,h,s) expected (4,11,6) found (0,32,33)
+ end: (c,h,s) expected (1023,53,9) found (492,53,9)
+ /dev/sdb2 0 - 0 0 0 Empty
+ /dev/sdb3 0 - 0 0 0 Empty
+ /dev/sdb4 0 - 0 0 0 Empty
+
+### 3. cfdisk ###
+
+Cfdisk是一个基于ncurses(提供字符终端处理库,包括面板和菜单)的带有交互式用户界面的Linux分区编辑器,它可以用来列出现有分区以及创建或修改这些分区。
+
+下面是一个如何使用Cfdisk来列出分区的例子。
+
+
+
+Cfdisk一次只能列出一个分区,所以如果你需要看某一磁盘的细节,可以把该磁盘的设备名作为Cfdisk的参数。
+
+ $ sudo cfdisk /dev/sdb
+
+### 4. parted ###
+
+Parted是另一个命令行实用程序,可以列出分区;如果需要的话,也可进行修改。
+
+下面是一个例子,列出了详细的分区信息。
+
+ $ sudo parted -l
+ Model: ATA ST3500418AS (scsi)
+ Disk /dev/sda: 500GB
+ Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
+ Partition Table: msdos
+
+ Number Start End Size Type File system Flags
+ 1 32.3kB 75.2GB 75.2GB primary ntfs boot
+ 2 75.2GB 500GB 425GB extended lba
+ 5 75.2GB 180GB 105GB logical ntfs
+ 6 180GB 285GB 105GB logical ext4
+ 7 285GB 287GB 2047MB logical linux-swap(v1)
+ 8 287GB 500GB 213GB logical ext4
+
+
+ Model: Sony Storage Media (scsi)
+ Disk /dev/sdb: 4049MB
+ Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
+ Partition Table: msdos
+
+ Number Start End Size Type File system Flags
+ 1 1049kB 4049MB 4048MB primary fat32 boot
+
+### 5. df ###
+
+Df是不是一个分区工具,但它打印出挂装文件系统的细节,Df可以列出甚至不是真实的磁盘分区的文件系统。
+
+这里是个简单的例子:
+
+ $ df -h
+ Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
+ /dev/sda6 97G 43G 49G 48% /
+ none 4.0K 0 4.0K 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
+ udev 3.9G 8.0K 3.9G 1% /dev
+ tmpfs 799M 1.7M 797M 1% /run
+ none 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock
+ none 3.9G 12M 3.9G 1% /run/shm
+ none 100M 20K 100M 1% /run/user
+ /dev/sda8 196G 154G 33G 83% /media/13f35f59-f023-4d98-b06f-9dfaebefd6c1
+ /dev/sda5 98G 37G 62G 38% /media/4668484A68483B47
+
+只有以 /dev 开始的文件系统才是实际的设备或分区。
+
+可以使用grep命令来筛选出实际的硬盘分区或文件系统。
+
+ $ df -h | grep ^/dev
+ /dev/sda6 97G 43G 49G 48% /
+ /dev/sda8 196G 154G 33G 83% /media/13f35f59-f023-4d98-b06f-9dfaebefd6c1
+ /dev/sda5 98G 37G 62G 38% /media/4668484A68483B47
+
+要只显示真正的磁盘分区与分区类型,可以这样使用Df:
+
+ $ df -h --output=source,fstype,size,used,avail,pcent,target -x tmpfs -x devtmpfs
+ Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
+ /dev/sda6 ext4 97G 43G 49G 48% /
+ /dev/sda8 ext4 196G 154G 33G 83% /media/13f35f59-f023-4d98-b06f-9dfaebefd6c1
+ /dev/sda5 fuseblk 98G 37G 62G 38% /media/4668484A68483B47
+
+请注意,Df只显示已挂载的文件系统或分区,并不是所有。
+
+### 6. pydf ###
+
+它是用Python写的Df的改进版本,以易读的方式打印出所有磁盘分区。
+
+ $ pydf
+ Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
+ /dev/sda6 96G 43G 48G 44.7 [####.....] /
+ /dev/sda8 195G 153G 32G 78.4 [#######..] /media/13f35f59-f023-4d98-b06f-9dfaebefd6c1
+ /dev/sda5 98G 36G 61G 37.1 [###......] /media/4668484A68483B47
+
+另外,pydf被限制为仅显示已挂载的文件系统。
+
+### 7. lsblk ###
+
+列出了所有的块存储设备,包括磁盘分区和光盘驱动器。细节包括所有分区/块总大小和挂载点。
+
+它不会报告分区上的已使用和空闲磁盘空间。
+
+ $ lsblk
+ NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
+ sda 8:0 0 465.8G 0 disk
+ ├─sda1 8:1 0 70G 0 part
+ ├─sda2 8:2 0 1K 0 part
+ ├─sda5 8:5 0 97.7G 0 part /media/4668484A68483B47
+ ├─sda6 8:6 0 97.7G 0 part /
+ ├─sda7 8:7 0 1.9G 0 part [SWAP]
+ └─sda8 8:8 0 198.5G 0 part /media/13f35f59-f023-4d98-b06f-9dfaebefd6c1
+ sdb 8:16 1 3.8G 0 disk
+ └─sdb1 8:17 1 3.8G 0 part
+ sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
+
+
+如果没有挂载点,这就意味着文件系统未安装,而对于cd/dvd这意味着没有插入光盘。
+
+lsblk能够显示每个设备的更多信息,如标签和型号,更多请查看信息手册。
+
+### 8. blkid ###
+
+显示块设备(分区和存储介质)属性,例如UUID和文件系统类型,不报告分区空间。
+
+ $ sudo blkid
+ /dev/sda1: UUID="5E38BE8B38BE6227" TYPE="ntfs"
+ /dev/sda5: UUID="4668484A68483B47" TYPE="ntfs"
+ /dev/sda6: UUID="6fa5a72a-ba26-4588-a103-74bb6b33a763" TYPE="ext4"
+ /dev/sda7: UUID="94443023-34a1-4428-8f65-2fb02e571dae" TYPE="swap"
+ /dev/sda8: UUID="13f35f59-f023-4d98-b06f-9dfaebefd6c1" TYPE="ext4"
+ /dev/sdb1: UUID="08D1-8024" TYPE="vfat"
+
+### 9. hwinfo ###
+
+hwinfo是一个通用的硬件信息的工具,可以用来打印出磁盘和分区表,但是输出不再像上面的命令那样打印每个分区的详细信息。
+
+ $ hwinfo --block --short
+ disk:
+ /dev/sda ST3500418AS
+ /dev/sdb Sony Storage Media
+ partition:
+ /dev/sda1 Partition
+ /dev/sda2 Partition
+ /dev/sda5 Partition
+ /dev/sda6 Partition
+ /dev/sda7 Partition
+ /dev/sda8 Partition
+ /dev/sdb1 Partition
+ cdrom:
+ /dev/sr0 SONY DVD RW DRU-190A
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+parted的输出可以得到简洁而完整的不同分区的概述、其上的文件系统以及总空间。pydf和df它们一样,只是被限制为只显示已挂载文件系统。
+
+fdisk和sfdisk显示完整大量的信息,需要花些时间来解释。cfdisk是一个交互式分区工具,每次显示一个单一的设备。
+
+来尝试下这些命令吧,别忘了在下面评论哟!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.binarytides.com/linux-command-check-disk-partitions/
+
+译者:[tenght](https://github.com/tenght) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20140617 How to Share Files Between Windows, Mac, and Linux PCs on a Network.md b/published/20140617 How to Share Files Between Windows, Mac, and Linux PCs on a Network.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..72ff9e4851
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140617 How to Share Files Between Windows, Mac, and Linux PCs on a Network.md
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
+如何通过网络在Windows、MAC和Linux之间共享文件
+================================================================================
+
+
+家庭[文件共享][1]曾经是一个噩梦,即使在不同的Windows版本之间—— 甚至不考虑Mac和Linux!但现在这些操作系统可以相互通信并且无需特殊软件就可共享文件。
+
+我们之前使用SMB协议来做到这点。Windows使用SMB来做文件共享,同时Mac和Linux发行版都内置支持SMB。Microsoft甚至给开源Samba项目[提交过补丁][2]来改进它!
+
+### 在Windows上共享文件夹 ###
+
+既然其他操作系统不能访问家庭组,您需要[启用Windows老式的文件共享][3]。要做到这点,打开控制面板进入网络和共享> 更改高级共享设置。启用“网络发现”和“文件与打印共享”。
+
+如果你想要无需密码访问共享文件夹你还需要微调一下其它选项。
+
+
+
+在Windows Explorer或者File Explorer中找到你想共享的文件夹,右键点击,选择属性。点击共享标签,并使用这里的选项来共享和配置文件夹的权限。
+
+
+
+### 在Windows上访问共享文件夹 ###
+
+在Windows Explorer或者File Explorer中访问网络面板来浏览其他计算机共享给你的文件。你会看到正确配置后的Mac和Linux计算机在Windows PC机附近出现了。双击一台计算机来查看它的共享文件。
+
+
+
+如果你知道计算机名或者IP地址,你同样可以直接连接到这台计算机上,只需要在Windows Explorer或者File Explorer中输入\\计算名后按下回车就可以了。如果你希望直接通过IP地址连接,只需要将计算机名换成IP地址就可以了
+
+
+
+### 在Mac OS X 上共享文件夹 ###
+
+你需要在你的Mac上启用网络文件共享来共享文件。点击桌面左上角的苹果logo,并选择系统偏好。点击共享图标并启用文件共享。点击选项按钮,并确认“使用SMB共享文件和文件夹”已经启用。
+
+在共享文件夹那列中选择添加要共享的文件夹。使用用户列来选择哪些用户和组可以访问和写入它们
+
+
+
+### 在 Mac OS X 访问共享目录###
+
+打开Finder,在屏幕顶部的菜单中点击Go,选择连接到服务器,输入下面的地址,用Windows计算机名代替COMPUTERNAME:smb://COMPUTERNAME。你同样可以输入计算机IP来代替计算机名。
+
+
+
+你会被提醒你应该用相应的凭证来验证或者以访客方式登录。连接完成后,在Finder的侧边栏的共享列中就会出现这台计算机,
+
+要在你每次登录后自动链接到共享文件夹,打开系统偏好窗口并进入用户与组 > 登录项。从finder中的共享列中的网络共享拖拽到登录项列表中
+
+
+
+### 在 Linux 中共享文件夹 ###
+
+在Linux上使用你桌面文件管理器来共享文件夹。这里,我们使用Ubuntu 14.04上的Nautilus,不过其他文件管理器上的过程应该是相似的。
+
+打开文件管理器,在想要共享的文件上右键,选择属性。点击本地网络共享标签并对这个文件启用共享。如果这是你第一次启用共享,你会被提示要求安装Samba软件——这在你提供密码的时候会自动显示。
+
+在安装完Samba软件后配置共享设置- 确认点击创建共享按钮来开始共享文件夹。
+
+
+
+### 在 Linux 上访问共享文件夹 ###
+
+你的Linux桌面文件管理器可能包含了一个网络浏览器,它可以用来定位并访问在本地网络的共享文件夹。
+
+在文件管理器的侧边栏点击浏览网络选项。接着双击Windows网络选项,双击你的工作组(默认是WORKFROUP),双击邻近的计算机来浏览它的共享文件。
+
+
+
+要直接连接到一台计算机,选中Nautilus中的“连接到服务器”选项,并输入像这样的远程计算机地址:smb://COMPUTERNAME
+
+
+
+不过在你连接时,你可能需要使用具有访问远程计算机权限的用户名和密码来验证。这依赖于你是否启用了访客访问以及你如何设置你的文件夹共享权限。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.howtogeek.com/191116/how-to-share-files-between-windows-mac-and-linux-pcs-on-a-network/
+
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.howtogeek.com/166407/how-to-easily-share-files-between-nearby-computers/
+[2]:http://www.samba.org/samba/news/developers/ms-patch.html
+[3]:http://www.howtogeek.com/school/windows-network-sharing/lesson3/
diff --git a/published/20140617 How to use Linux lsblk Command to List Block Device Information.md b/published/20140617 How to use Linux lsblk Command to List Block Device Information.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..76c62e647b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140617 How to use Linux lsblk Command to List Block Device Information.md
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
+使用Linux的lsblk命令列出块设备信息
+================================================================================
+**lsblk**(列出块设备)命令用于列出所有可用块设备的信息,但是,它**不会列出RAM盘的信息**。块设备有硬盘,闪存盘,CD-ROM等等。
+
+### 如何安装lsblk ###
+
+lsblk命令包含在util-linux-ng包中,现在该包改名为util-linux。这个包带了几个其它工具,如dmesg。要安装lsblk,请在[此处][1]下载util-linux包。
+
+### Fedora中安装lsblk ###
+
+Fedora用户可以通过以下方法来安装该包:
+
+ $ sudo yum install util-linux-ng
+
+该命令有几个选项:
+
+### 默认选项 ###
+
+lsblk命令默认情况下将以树状列出所有块设备。打开终端,并输入以下命令:
+
+ $ lsblk
+
+输出如下:
+
+
+
+7个栏目名称如下:
+
+**NAME** : 这是块设备名。
+
+**MAJ:MIN** : 本栏显示主要和次要设备号。
+
+**RM** : 本栏显示设备是否可移动设备。注意,在本例中设备sdb和sr0的RM值等于1,这说明他们是可移动设备。
+
+**SIZE** : 本栏列出设备的容量大小信息。例如298.1G表明该设备大小为298.1GB,而1K表明该设备大小为1KB。
+
+**RO** : 该项表明设备是否为只读。在本案例中,所有设备的RO值为0,表明他们不是只读的。
+
+**TYPE** :本栏显示块设备是否是磁盘或磁盘上的一个分区。在本例中,sda和sdb是磁盘,而sr0是只读存储(rom)。(LCTT译注,此处sr0的RO项没有标记为1,可能存在一些错误?)
+
+**MOUNTPOINT** : 本栏指出设备挂载的挂载点。
+
+### 列出所有设备 ###
+
+默认选项不会列出所有空设备。要查看这些空设备,请使用以下命令:
+
+ $ lsblk -a
+
+该选项将列出所有设备,包括空设备在内。
+
+
+
+### 列出设备权限和属主 ###
+
+lsblk命令也可以用于列出一个特定设备的拥有关系,同时也可以列出组和模式。可以通过以下命令来获取这些信息:
+
+ $ lsblk -m
+
+
+
+### 列出指定设备 ###
+
+该命令也可以只获取指定设备的信息。这可以通过在提供给lsblk命令的选项后指定设备名来实现。例如,你可能对了解以字节显示你的磁盘驱动器大小比较感兴趣,那么你可以通过运行以下命令来实现:
+
+ $ lsblk -b /dev/sda
+
+或者,以下命令等同:
+
+ $ lsblk --bytes /dev/sda
+
+### 以列表形式列出不带头的设备 ###
+
+你也可以组合几个选项来获取指定的输出。例如,你也许想要以列表格式列出设备,而不是默认的树状格式。你可能也对移除不同栏目名称的标题感兴趣。可以将两个不同的选项组合,以获得期望的输出,命令如下:
+
+ $ lsblk -nl
+
+或者,你可以使用下面的长选项,它们也能给出相同的输出。
+
+ $ lsblk --noheadings --list
+
+
+
+### 列出SCSI设备 ###
+
+要获取SCSI设备的列表,你只能使用-S选项。该选项是大写字母S,不能和-s选项混淆,该选项是用来以颠倒的顺序打印依赖的。
+
+ $ lsblk -S
+
+
+
+lsblk列出SCSI设备,而-s是逆序选项(LCTT译注:将设备和分区的组织关系逆转过来显示),其将给出如下输出。输入命令:
+
+ $ lsblk -s
+
+或者
+
+ $ lsblk --inverse
+
+
+
+你可以使用lsblk来获取关于你的块设备的更多信息,自己把它试着显示出来吧!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-lsblk-command/
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:ftp://ftp.kernel.org/pub/linux/utils/util-linux/
diff --git a/published/20140617 Make Ubuntu 14.04 Look Like Mac With Zukimac Theme.md b/published/20140617 Make Ubuntu 14.04 Look Like Mac With Zukimac Theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..106aa37301
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140617 Make Ubuntu 14.04 Look Like Mac With Zukimac Theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+在 Ubuntu 上体验 Mac 风格
+================================================================================
+
+
+虽然 Ubuntu Unity 本身已经是一款很漂亮的桌面了,但世界各地还是有很人被 Mac OS X 的外观所震撼。如果您恰好是其中之一,要获得 Mac OS X 一样外观体验,是不需要丢掉 Ubuntu 的,相反,您可以对它来个美化改造,**使 Ubuntu 14.04 看起来就像 Mac OS X**。
+
+### 让 Ubuntu 14.04 看起来像 Mac OS X ###
+
+要使 Ubuntu 美化成 Mac 的样子,我们得使用 Zukimac 主题。
+
+- 从后面的链接获得 Zukimac 主题包:[下载 Zukimac Theme for Ubuntu 14.04][1]
+- 解压下载的 Zip 包,解压后会出现 Zukimac 和 Zukimac-ml 两个目录文件。把这些目录拷贝到您的 home 目录下的 .themes 文件夹中。进入 Home 目录中,按下快捷键 Ctrl+H 可以显示所有隐藏的文件,如果没有 .themes 文件夹,需要创建一个。
+- 使用 [Unity Tweak Tool 来改变主题][2].
+
+就这些操作。Zukimac 提供了一些基本的 Mac OS 系统的外观和视窗感觉。下面是带有默认的 OS X Maveric 壁纸的外观。
+
+
+
+### Ubuntu 14.04 中获得更多 Mac 体验 ###
+
+通常,您可以**安装像 Plank 或 Docky 这样的 dock 启动面板**。在 Ubuntu 14.04 中要安装 Plank 可以使用下面的命令:
+
+ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ricotz/docky
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install plank
+
+安装完 dock 启动面板后,您也可以安装 **Synapse indicator 来代替模拟 Mac 中的 Spotlight**。使用来自于 Noobslabs 的 PPA 源来安装 Synapse indicator,如下示:
+
+ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/apps
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install indicator-synapse
+
+不想安装上面的两软件的话,您也可以安装 **Slingscold launcher,用来代替模拟 Mac OS X 的启动面板**。在 Ubuntu 14.04 中,使用上面提到的 Noobslabs 的 PPA 源来安装 Slingscold 启动面板,如下示:
+
+ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/apps
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install slingscold
+
+老实说,我是个狂热的 Ubuntu 迷,我喜欢 Ubuntu 默认的 Unity 主题样式外观。此外,还有很多[关于 Ubuntu 14.04 的漂亮图标主题样式][3] 可用来美化默认的外观。但正如我上面提到的仍有很多用户喜欢 Mac OS X 的主题样式,我希望这篇文章能帮助到他们,使其能把 Ubuntu 14.4 装扮成 Mac OS X 的样式。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-1404-mac-zukimac-theme/
+
+译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://gnome-look.org/content/show.php/Zukimac?content=165450
+[2]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-install-themes-in-ubuntu-13-10/
+[3]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/20140618 20 things to do after installing Linux Mint 17 Qiana Cinnamon.md b/published/20140618 20 things to do after installing Linux Mint 17 Qiana Cinnamon.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..56f5f7b82a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140618 20 things to do after installing Linux Mint 17 Qiana Cinnamon.md
@@ -0,0 +1,297 @@
+安装Linux Mint 17后要做的20件事
+================================================================================
+### Linux Mint 17 Qiana Cinnamon ###
+
+Linux Mint 17已经[发布][1],定名为Qiana。Mint是Linux最佳发行版之一,它定位于桌面用户,关注可用性和简洁。它携带了风格迥异的桌面环境,如Mate以及Cinnamon,并基于不同的发行版,如Ubuntu或Debian。
+
+在本文中,我们使用的是Linux Mint 17的cinnamon版本。要获取更多关于Cinnamon版本的信息(包括下载链接),可以访问 - http://linux.cn/article-3260-1.html
+
+下载适合你系统的正确的iso,烧录成dvd,或者也可以制作成usb启动盘来启动。安装完毕,是时候来使用一些优化工具和基本应用程序来优化系统性能和体验,让你系统激情澎湃吧!
+
+### 1. 更新系统 ###
+
+第一件事情是重中之重,就是让你的系统保持时刻最新。赶紧在终端中运行以下命令吧。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get upgrade
+
+或者,你也可以使用更新管理器(mintUpdate)来干这事,你可以在菜单(Menu)> 管理(Administration)中找到它。
+
+
+
+### 2. 找回旧壁纸 ###
+
+每个Linux Mint发行版都自带了一套最新的漂亮的壁纸。但是,你也可以安装先前版本中的壁纸。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install mint-backgrounds-*
+
+### 3. 多安装些浏览器 ###
+
+Linux Mint 17默认安装了firefox,你也可以获得更多的浏览器,如Chronium和Google Chrome。
+
+Chronium浏览器可以在仓库中获取。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install chromium-browser
+
+至于Google Chrome,请访问google.com/chrome下载deb包,并使用gdebi来安装。
+
+ # 64 位
+ $ wget https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb
+ $ sudo gdebi google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb
+
+ # 32 位
+ $ wget https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_current_i386.deb
+ $ sudo gdebi google-chrome-stable_current_i386.deb
+
+### 4. 安装Flash Player ###
+
+Mint上默认安装adobe flash插件包(adobe-flashplugin),因此,你可以在Firefox中畅玩flash游戏,也可以尽情享受网页版视频了。
+
+Google Chrome现在使用了基于flash player的Pepper API,而且该插件也内建于Chrome中,因此,你也不需要为它额外做任何事情了。
+
+然而对于Chronium,基于flash player的Pepper没有被囊括进来(因为它不是个自由组件),所以你需要手动安装了。
+
+安装以下包来为Chronium安装pepper flash player。它会自动从Google Chrome浏览器中下载pepper flash player并加入到Chronium中。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install pepperflashplugin-nonfree
+
+上面的命令应该帮你将flash player安装到Chronium里头了。万一下载失败,你可以使用下面的命令重新进行安装。
+
+ $ sudo dpkg-reconfigure pepperflashplugin-nonfree
+
+### 5. 安装多媒体解码 ###
+
+受限的额外包可以帮你安装大多数基本的解码,可以让你播放像mp3这样的格式。它也会帮你安装微软字体。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install ubuntu-restricted-extras
+
+要启用加密dvd的回放,请安装以下包。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install libdvdread4
+ $ sudo /usr/share/doc/libdvdread4/install-css.sh
+
+### 6. 安装专有驱动 ###
+
+如果你有一张Nvidia或者ati的图形卡,或者broadcom的无线网卡,那么请安装厂商提供的专有驱动,这些驱动会为你带来最佳的硬件性能。
+
+要安装Nvidia驱动,你可以参照先前的这篇文章
+
+[如何在Linux Mint上安装最新的Nvidia驱动][3]
+
+### 7. 安装Dropbox ###
+
+Linux mint仓库已经提供了dropbox的客户端软件包,所以你不必满世界找了。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install dropbox python-gpgme
+
+如果你还是比较喜欢从官方网站下载,那么翻墙可直达[https://www.dropbox.com/install?os=lnx][4],请遵照说明下载用于Ubuntu的deb安装包。(LCTT译注:墙内用户还是忽视此条吧。)
+
+Copy是另外一个云存储解决方案,它也有本地Linux客户端。详情可查阅[copy.com][5],它也有[ppa仓库][6]。
+
+### 8. Skype ###
+
+Skype可以在Ubuntu canonical合作仓库中找到。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install skype
+
+### 9. 安装rar和其它归档工具 ###
+
+要想在Nemo这样的文件管理器中通过上下文菜单创建rar归档,请安装rar工具。安装rar的同时,也可安装其它几个包以增加对其它归档格式的支持。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install unace p7zip-rar sharutils rar arj lunzip lzip
+
+### 10. 安装剪贴板管理器 ###
+
+剪贴板管理器允许你维护和访问通过像Ctr+C这样的操作拷贝的项目历史,gnome下有很多的剪贴板管理器,像diodon,clipit,glipper,parcellite。
+
+Diodon在cinnamon桌面上似乎存在一些问题,在历史列表增长时会出现滚动条。Clipit和Gipper工作得很好,你也可以安装
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install glipper
+ # 或者
+ $ sudo apt-get install clipit
+
+然后,你可以从应用程序菜单中启动它们,它们应该会在你每次登录时启动。
+
+### 11. 优化桌面 ###
+
+#### 1. 修复系统托盘上的日期格式 ####
+
+在底部面板右边的时间小程序只显示了时间,它也可以设置显示日期。右击底部面板右边的日期-时间小程序,然后点击配置,选中标有“使用自定义日期格式”的选框,然后填入
+
+ %B %e, %I:%M %p
+
+这会以带有AM/PM的12小时格式显示月份名称、日期和时间。
+
+#### 2. 安装主题、扩展、小程序、桌面组件 ####
+
+为你的桌面搞一些好东西玩玩。你可以在桌面区域放置一些桌面组件,在面板上放些小程序,为桌面效果添加一些扩展,以及为桌面设计安装一些主题。
+
+去系统设置吧,点击指定的图标,你可以看见一个可供选择的列表。点击“在线获取更多”标签来下载更多的好东西。
+
+#### 3. 修改Firefox的搜索引擎 ####
+
+你也许注意到,Firefox默认选择了Yahoo搜索引擎,而搜索引擎列表中并没有Google。点击“管理搜索引擎” > 获取更多搜索引擎,它会带你去[http://www.linuxmint.com/searchengines.php][7]。
+
+向下拉动滚动条到商业搜索引擎部分,找到并点击Google图标。进入下一页后,再次点击搜索引擎列表,而这次你会看到“添加Google”选项,点击它就可以用上Google搜索了。(LCTT译注:墙内用户也请忽略此条。怒!)
+
+### 12. 优化字体渲染 ###
+
+Linux mint默认使用Dejavu Sans字体,它看起来真普通啊。你可以使用Droid和Noto字体获得好看得多视觉享受。请参照我们先前的教程,它会一步一步带你渐入佳境。[如何在Linux Mint上获得华丽好看的字体][8]
+
+### 13. Guake下拉终端 ###
+
+下拉终端让你可以通过点击单个键来访问终端,Guake就是这其中之一,它用于基于gtk的桌面。下拉终端按要求显示/隐藏,并保持运行,因此你无需从菜单或者启动器中打开终端了。这对于热衷于终端的人来说,这是一个必不可少的工具。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install guake
+
+Guake需要配置,以便在每次登陆时启动。首先,找到guake命令的路径。
+
+ $ which guake
+ /usr/bin/guake
+
+现在,把它添加到启动程序列表中。出门左拐,请往系统设置 > 启动程序,然后点击添加。在对话框中填写
+
+> 名称 - Guake下拉终端
+> 命令 - /usr/bin/guake
+
+点击添加。现在Guake已经跑到你的运行程序列表中去了,并每次会自动启动。
+
+### 14. Uget下载管理器 ###
+
+Uget是一个简洁而健壮的跨平台下载管理器,在Linux上工作得很好。虽然它缺少分段下载文件功能,但是仍然是一个十分稳定的下载管理器。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install uget
+
+### 15. Deluge BitTorrent客户端 ###
+
+Linux Mint自带了Transmission,这是个简洁而高效的torrent客户端。如果正在寻找一个更有特色的torrent客户端,那么你可以试试deluge或者vuze(正式名称是azureus),还可以试试qbittorent。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install deluge-torrent
+
+### 16. Hardinfo - 系统信息工具 ###
+
+Hardinfo是一个十分便利的GUI工具,它可以用来报告大量完整的系统硬件信息。你可以通过它来集中查看处理器、内存、存储设备、网络配置、打印机、usb设备、声音/视频适配器等等信息。它具有测试和评估系统性能的功能。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install hardinfo
+
+### 17. 安装MATE桌面环境 ###
+
+除了Cinnamon,Linux Mint还自带了另一个流行的桌面环境MATE(Maatay)桌面。如果你想试试,那么就来安装吧。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install mint-meta-mate
+
+现在你可以在登陆屏幕选择MATE会话了。
+
+### 18. 让其它分区可写 ###
+
+如果你有其它ext分区,比如想用来存储和备份文件,那么你需要让它们可写,以免每次都要使用root特权。
+
+首先,使用gksudo在文件管理器里打开分区挂载目录
+
+ $ gksudo nemo
+
+导航到分区目录,右击去往属性 > 权限标签
+
+赋予“目录访问” - 创建和删除文件权限给用户、组和其它。
+
+赋予“文件访问” - 读和写权限给用户、组和其它。
+
+对于NTFS分区,你不需要做此事。
+
+### 19. 安装Conky ###
+
+Conky是一个轻量级系统监控工具,它通过桌面图形组件显示系统各种资源的统计数据,如cpu、内存、网络等。它不是必须的,但是可以让你的桌面更加绚丽夺目。
+
+ $ sudo apt-add-repository -y ppa:teejee2008/ppa
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get install conky-manager
+
+从应用程序菜单启动Conky管理器,并添加组件到桌面。也可以选中开机启动选项来让Conky开机启动。
+
+### 20. 安装一些游戏 ###
+
+Linux确实有一些酷爽的游戏,很具娱乐性,而且是免费的。注意,某些游戏像supertuxkart和0ad要求专用的图形处理器以优化性能。
+
+ # 0ad - 像帝国时代那样的策略游戏
+ $ aptitude search 0ad
+
+ # supertuxkart - 赛车游戏
+ $ aptitude search supertuxkart
+
+ # openarena
+ $ aptitude search openarena
+
+仓库中还有更多的游戏可供你安装,像Alien arena, secret maryo chronicles, supertux, frozen bubbles等等。
+
+### 清除 ###
+
+做完这一切后,请为系统进行一次大扫除,移除一些不必要的包。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get autoremove
+
+### 注 ###
+
+#### 为Google Chrome/Chronium提供Java小程序支持 ####
+
+默认情况下已经安装了"icedtea-plugin",用以为firefox提供java小程序支持。
+
+然而,Chrome和Chronium却不再支持基于NPAPI的插件。因此java小程序,在没有获得基于Pepper api的java插件前,java小程序是不能在这些浏览器中工作的。要查看更多信息,请往[这里][9]。
+
+#### 更多应用程序 ####
+
+如果你正在为你的Mint盒子寻找更多的应用程序,那么这里列出了一部分更好的应用程序,所有这些都可以在软件管理器中安装。
+
+* Opera - 网页浏览器
+* Gnome Encfs Manager - 管理使用Encfs加密的文件和文件夹
+* Smplayer - 多媒体播放器
+* Rhythmbox, Clementine - 音乐播放器
+* Openshot, Kdenlive - 视频编辑器
+* Audacity - 音频编辑器
+* Inkscape - 图形和图像编辑
+* Gparted - 分区编辑器
+* Gufw - 防火墙配置工具
+* qBittorrent, Vuze - Torrent客户端
+* Gwenview - 图像浏览
+* Team viewer - 远程桌面
+* Tv-maxe - 查看电视频道
+* Grub Customizer - 修改GRUB启动菜单设置
+* Linrunner TLP - 电源管理工具,对笔记本节电很有用
+* Virtualbox - 虚拟化
+* Kazam, recordMyDesktop - 桌面录像/演示
+* Bleachbit - 通过删除旧的/临时文件释放磁盘空间
+* Cheese - 使用网络摄像头拍照
+* Shutter - 带有众多功能的屏幕截图工具
+
+那么,请选择你喜欢的那些,并尽情享受Linux Mint吧!!
+
+### 资源 ###
+
+下载最新Linux Mint
+[http://www.linuxmint.com/download.php][10]
+
+社区教程
+[http://community.linuxmint.com/tutorial][11]
+
+Linux Mint论坛
+[http://forums.linuxmint.com/][12]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.binarytides.com/better-linux-mint-17-cinnamon/
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://blog.linuxmint.com/?p=2626
+[2]:http://blog.linuxmint.com/?p=2626
+[3]:http://www.binarytides.com/install-nvidia-drivers-linux-mint-16/
+[4]:http://www.dropbox.com/install?os=lnx
+[5]:http://copy.com/?r=DSwtSd
+[6]:http://launchpad.net/~paolorotolo/+archive/copy
+[7]:http://www.linuxmint.com/searchengines.php
+[8]:http://www.binarytides.com/optimize-fonts-linux-mint/
+[9]:http://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/chromium-browser/+bug/1309508
+[10]:http://www.linuxmint.com/download.php
+[11]:http://community.linuxmint.com/tutorial
+[12]:http://forums.linuxmint.com/
diff --git a/published/20140619 How To Flush Linux or UNIX DNS Cache.md b/published/20140619 How To Flush Linux or UNIX DNS Cache.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cace021b2a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140619 How To Flush Linux or UNIX DNS Cache.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+如何在 Linux/Unix/Mac 下清除 DNS 查询缓存
+================================================================================
+
+
+我在Linux下使用拨号连接上网,频繁的拨号断线造成DNS的问题。我如何在Linux/Unix发行版下使用shell命令清除DNS缓存?
+
+
+在MS-Windows下,你可以使用[ipconfig命令来清除dns缓存][1]。然而,Linux和Unix提供了不同的方法来清除缓存。Linux可以运行 nscd 或者 BIND 或者 dnsmasq 作为名称服务缓存守护进程。大型或者工作组服务器可能使用BIND或者dnsmasq作为专用缓存服务器来加速查询。
+
+### 如何: 清除 nscd dns 缓存 ###
+
+Nscd 会缓存libc发起的名称服务的请求。如果把检索NSS数据看做很慢,那么nscd能够显著加快连续访问同一数据的速度,并能提高整个系统的性能。只需重启nscd即可刷新缓存:
+
+ $ sudo /etc/init.d/nscd restart
+
+或
+
+ # service nscd restart
+
+或
+
+ # service nscd reload
+
+这个守护进程给最常用的名称服务请求提供了高速缓存。默认的配置文件/etc/nscd.conf,其决定了高速缓存守护进程的行为。
+
+### 清除 dnsmasq dns 缓存 ###
+
+[dnsmasq的是一个轻量级的DNS][2]、TFTP和DHCP服务器。它的目的是给局域网提供配对的DNS和DHCP服务。 dnsmasq接受DNS查询,并从一个小的本地高速缓存应答它们或将其转发到一个真正的递归DNS服务器。该软件也被安装在很多便宜的路由器上来缓存DNS查询。只需重新启动dnsmasq的服务来清除DNS缓存:
+
+ $ sudo /etc/init.d/dnsmasq restart
+
+或者
+
+ # service dnsmasq restart
+
+### 清除BIND缓存服务器的dns缓存 ###
+
+一台BIND缓存服务器从另一台服务器(区域主)响应主机的查询而获得信息,然后保存(缓存)数据到本地。您所要做的就是重启BIND以清除其缓存:
+
+ # /etc/init.d/named restart
+
+你也可以使用下面rndc命令来清除所有的缓存:
+
+ # rndc restart
+
+或者
+
+ # rndc exec
+
+BIND v9.3.0 及其以上版本支持一个清除一个特定域名的所有记录缓存的命令:rndc flushname。本例中刷新cyberciti.biz相关域的所有记录:
+
+ # rndc flushname cyberciti.biz
+
+同样也可以清除BIND View。比如,LAN和WAN的View可以用下面的命令清除:
+
+ # rndc flush lan
+ # rndc flush wan
+
+### 给 Mac OS X Unix 用户的提示 ###
+
+Mac下用root用户输入下面的命令:
+
+ # dscacheutil -flushcache
+
+或者
+
+ $ sudo dscacheutil -flushcache
+
+如果你正在使用OSX 10.5 或者更早的版本,尝试使用下面的命令:
+
+ lookupd -flushcache
+
+### 关于 /etc/hosts 文件的一个提示 ###
+
+/etc/hosts用作静态查询主机的表格。你需要在类Unix操作系统下依据你的要求移除并且/或者更新它:
+
+ # vi /etc/hosts
+
+#### 示例输出: ####
+
+ 127.0.0.1 localhost
+ 127.0.1.1 wks01.WAG160N wks01
+ # The following lines are desirable for IPv6 capable hosts
+ ::1 ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
+ fe00::0 ip6-localnet
+ ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix
+ ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
+ ff02::2 ip6-allrouters
+ 10.37.34.2 build
+ 192.168.1.10 nas01
+ 192.168.1.11 nas02
+ 192.168.1.12 nas03
+ #192.168.2.50 nfs2.nixcraft.net.in nfs2
+ #192.168.2.51 nfs1.nixcraft.net.in nfs1
+ 172.168.232.50 nfs1.nixcraft.net.in nfs1
+ 172.168.232.51 nfs2.nixcraft.net.in nfs2
+ 192.168.1.101 vm01
+
+### 参考 ###
+
+相关: 在Windows Vista / XP中用ipconfig 命令[清除 DNS 缓存][3]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/rhel-debian-ubuntu-flush-clear-dns-cache/
+
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://theos.in/windows-vista/flush-dns-cache-with-ipconfig/
+[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/how-do-i-improve-dns-performance-on-linuxwindows-desktop.html
+[3]:http://theos.in/windows-vista/flush-dns-cache-with-ipconfig/
diff --git a/published/20140620 How Many Languages Do Developers Need To Know.md b/published/20140620 How Many Languages Do Developers Need To Know.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d241b85e4f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140620 How Many Languages Do Developers Need To Know.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+到底开发者需要掌握多少门语言?
+================================================================================
+
+
+> 诸如Apple、Facebook及Google这样的大公司正在开发他们自己的编程语言,开发者们被迫只有适应。
+
+前不久的世界开发者大会上,Apple公布了它的新开发语言[Swift][1]。这是最近大型技术公司们开发的一大波新语言中的最新成员,这些新语言某种程度上都是专门应用于他们自己的平台。
+
+对iOS开发者,Apple有Swift;而[Facebook 有 Hack][2] —— 一门用于后端开发的语言。与此同时,Google已经拥有了它自己的Javascript替代者 Dart,以及一门新的通用编程语言Go。
+
+这一波又一波的新语言,给开发者们带来了许多问题。也许其中最严重的问题正如我一位同事[Adriana Lee][3]在Apple发布Swift后所说:
+
+> (开发者们到底还得学习多少门语言?)
+> ——Adriana Lee (@adra_la) [June 2, 2014][4]
+
+### 计算机语言的通天塔 ###
+
+目前已经存在的[编程语言有数百种][5],同时还有更多的语言正在涌现。其中许多都是被设计用在相对较窄的应用程序范围内,大多数甚至从未走出过项目小组的范围。
+
+与此类似,大技术公司开发的新语言其实也是伴随着公司一起成长的。[通用语言的鼻祖,C语言][6],就源于上世纪70年代初的AT&T贝尔实验室。Java,目前作为Android app开发的主要语言,诞生于上世纪90年代[Sun公司的Microsystems系统][7]。
+
+发展到现在,不同之处在于,公司们拥抱新语言、从而想要延伸的特定商业目标的范围不一样了 —— 这一过程同时建立了一个忠心耿耿的开发者基础,他们被牢牢锁定在了某个公司的特定平台上。这类一石二鸟的战略,最早可以追溯到Sun对Java的采用,当时公司就将其作为了挑战微软PC桌面统治地位的一种手段。(事情虽然没有像Sun计划的那样发展下去,但在Google转向Android之前,Java大体上也算是在企业中间件系统中找到了自己的一席之地。)
+
+这么看来,Apple的Swift其目标也就很明确了。Swift应该不会辜负公司前期的大肆宣传,通过磨平Objective-C那粗糙的毛边,看起来它能够成功简化iOS app开发者的开发过程。但是同样还是这些开发者,他们却需要学习一门新语言的输入和输出,而这些功能很可能在其他地方都不会用到。
+
+### 大公司们为什么要重复造轮子 ###
+
+“不要重复造轮子”这一哲学在绝大多数开发者心中根深蒂固,大公司们对此却并不买账。那他们为何不只是修改下现有语言用于新的用途呢?
+
+答案很简单,公司们发明他们自己的语言,是因为他们有这个能力。设计一门新语言可能很复杂,但对资源要求却并不很高。困难之处也就在对其提供支持,包括提供软件资源(共享代码库、API、编译器、文档等)以及赢得开发者的心意。大公司们在这两方面尤其擅长。
+
+还有一个事实,现有语言通常很难硬塞进如今的复杂代码框架中。举个栗子,[Facebook决定发明的Hack][8],就是一个普遍适用于Web开发的[脚本语言PHP][9]的超集合(superset)。
+
+Facebook的Hack最近已经比较普遍,其主要目标就是改进代码的稳定性,针对这一目的,它强制在程序运行之前对数据类型进行检测。这样的检测确保了一个程序,比方说,不会将一个整数解析为一个字符串,这样的错误如果捕获不到很可能会导致不可预知的后果。在Hack中,这些检测会预先执行,以便程序员能够在程序上线前早早发现这样的错误。
+
+据Facebook的Hack项目组核心成员Julien Verlaguet透露,公司之前尝试过用一门现有语言实现更高效的编程。但是Facebook的大部分代码都是由PHP编写的,公司实际上已经建立了一个支持PHP及其分支的软件架构。即使能够让PHP同其他语言编写的代码协同工作,实现的难易程度和运行速度都无法满足要求。
+
+“比如说我们尝试用Scala重写PHP代码库,”Verlaguet说。“Scala是一门设计优秀的漂亮语言,但是它与PHP完全不兼容。每次我需要从Scala的代码库部分调用PHP的时候,都会损失性能。我们很愿意使用一门现有语言,但是对于我们来说,这条路行不通。”
+
+于是,Facebook发明了Hack,它与PHP一样能够共用公司现有的架构。Verlaguet介绍说,Facebook的代码库主体已经从PHP迁移到了Hack,同时公司将Hack开源,希望独立开发者们能够帮公司找到Facebook以外的用途。
+
+“你仍然可以使用PHP,”他说,“但是我们希望你有使用Hack的欲望。”
+
+### 谁说了算 ###
+
+公司和开发者之间有一种微妙的平衡。公司可以按照自己的喜好发明语言。但是如果开发者都不愿使用这门语言,那就没人用了,公司以外的人也就没人愿意将自己的职业生涯托付给这家公司。
+
+公司在开发过程中同时使用不同的语言,这并不少见。例如,你可能用Objective-C开发iOS app,但却用Java开发Android app。对开发者来说,这从来都不是症结所在,因为Objective-C和Java都是通用面向对象语言。它们用途广泛适用于很多场合。
+
+然而,Hack、Dart、Go和Swift,到目前为止,仍然只适用于严格特定公司的编程解决方案,往往和公司选择的编程环境相对应。诚然,现在下结论可能还太早。比方说Hack,就可以用在一些后端的实现中;它只是太新了,以至于Facebook还没有任何数据供人们如此使用。
+
+不是开发者不能学习多门语言。事实上,大多数人已经掌握了多门语言。这好比罗曼斯语(由拉丁语演变而成的语言),如果你会说西班牙语,再去学法语就比那些不会西班牙语的人简单许多。与此类似,如果你已经会Java,再学Ruby或Perl就简单得多。如果你会PHP,基本上就已经学会了Hack。
+
+与此相反,学习多门语言更多的是一个习惯问题。如果Java已经解决了你的问题,你就不再有动机去学Ruby。如果你用Objective-C编写iOS app感觉很爽,你就不会有强烈的意愿去学Swift。
+
+另外,对于一些开发者来说,封闭生态系统的语言只会使每个人的生活变得更糟。例如,自由设计师Jack Watson-Hamblin就告诉我说,像Apple这样强势推出Swift,其实是在冒险增加程序员的负担,同时将开发者社区割裂开来:
+
+> 程序员掌握多门语言固然重要,但是不断强迫他们紧跟新语言,却是行不通的。如果我正在开发一个简单的跨平台app,我可不想被迫掌握四门语言再来完成它。如果真的需要,我也只想使用一门语言。
+
+Watson-Hamblin就主张说,当每家公司都为了自家需要发明自己的语言时,程序员的注意力被分散,开发的视野也局限于一种,这只会拖慢整个开发进程。他说,“如果拿公司负责一门语言与负责一个开源社区相比较,这两者的区别就好比一家大企业与一个初创小公司的区别”。社区生来就更加灵活,适应能力更强。
+
+当然,Apple有[许多非常好的理由推出Swift从零开始][10],就像当初Facebook发明Hack的时候一样。我并不是说,大公司不会强迫开发者接受这种改变,在这方面,有些公司一直都很让人讨厌。
+
+“新语言的发明,伴随着霸权的支配,”Verlaguet说,“被迫不停追赶,确实令人沮丧,但另一方面,你又多了一种解决问题的新语言。反过来想想,要是全世界的程序员都用同样一门语言做所有事情,即使啥都凑合着能干,这门语言也一定干得不怎么样”。
+
+题图来自于[Flickr user Ruiwen Chua][11],CC 2.0
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://readwrite.com/2014/06/17/apple-swift-facebook-hack-google-dart
+
+译者:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://developer.apple.com/swift/
+[2]:http://readwrite.com/2014/03/20/facebook-new-programming-language-hack
+[3]:http://readwrite.com/author/adriana-lee#awesm=~oGfPbJlSrFBamJ
+[4]:https://twitter.com/adra_la/statuses/473537386266112000
+[5]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_programming_languages
+[6]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C_(programming_language)
+[7]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Java_(programming_language)
+[8]:http://readwrite.com/2014/03/20/facebook-new-programming-language-hack
+[9]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PHP
+[10]:http://blog.erratasec.com/2014/06/why-it-had-to-be-swift.html#.U58BJI1dXtA
+[11]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/ruiwen/3260095534
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/20140620 Tips to Push Your Git Skills to the Next Level.md b/published/20140620 Tips to Push Your Git Skills to the Next Level.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6b0f5ada87
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140620 Tips to Push Your Git Skills to the Next Level.md
@@ -0,0 +1,188 @@
+已经会用Git了?不会这十招怎么行
+================================================================================
+
+之前我们发了一些教程让你熟悉[Git基础][1]和[在团队合作环境中使用Git][2].我们讨论的这些Git命令足够让一个开发者在Git的世界里生存下去。在这篇教程里,我们试着探索如何高效地管理你的时间以及如何充分利用Git提供的特性。
+
+> 注意:这里介绍的命令中有的包含方括号(例如:`git add -p [file_name]`)。在这些例子中,你应该用你自己的数字、标识符等替代方括号里的内容,并且去掉方括号。
+
+### 1. Git自动补全 ###
+
+如果你在命令行环境中运行Git命令,每次都手动地逐个输入命令是一件很无聊的事。为此,你可以花几分钟时间配置一下Git命令的自动补全功能。
+
+在*nix系统运行下列命令下载自动补全脚本:
+
+ cd ~
+ curl https://raw.github.com/git/git/master/contrib/completion/git-completion.bash -o ~/.git-completion.bash
+
+然后,添加下面的行到你的~/.bash_profile文件:
+
+ if [ -f ~/.git-completion.bash ]; then
+ . ~/.git-completion.bash
+ fi
+
+尽管我之前已经提到过,但我还是想再强调一下:如果你想使用完整的Git特性,你绝bi应该切换到命令行环境。
+
+### 2. 在Git中忽略文件 ###
+
+你是不是对出现在你Git库里面的编译生成文件(比如`.pyc`)感到很无语?或者你是不是很厌恶不小心将他们添加到了Git?直接看这里,这里有一个方法可以让你告诉Git忽略所有这些文件和目录。只需要创建一个名字为`.gitignore`的文件,里面列出你不想要Git跟踪的文件和目录。可以用感叹号(!)列出例外情况。
+
+ *.pyc
+ *.exe
+ my_db_config/
+
+ !main.pyc
+
+### 3. 谁动了我的代码? ###
+
+当事情出了乱子时立马责怪别人这是人类的天性。如果你的服务器程序不能正常工作了,要找出罪魁祸首是非常简单的--只需要执行`git blame`。这个命令告诉你文件里的每一行的作者是谁,最后改动那一行的提交,以及提交的时间戳。
+
+ git blame [file_name]
+
+
+
+在下面的截图里,你可以看到在一个更大的库里这个命令的输出是什么样的:
+
+
+
+### 4. 查看库的历史 ###
+
+在之前的教程里,我们已经看过了如何使用`git log`命令。不管怎样,有3个选项你应该知道。
+
+- **--oneline** - 压缩每次的提交信息,只保留一个缩减的Hash值和说明文字,然后把这些都展示在一行里。
+- **--graph** - 这个选项将在左边画出一个文字界面的提交历史图。如果你只有一个分支,用这个选项查看历史时是没什么意义的。
+- **--all** - 显示所有分支历史。
+
+这是这3个选项合起来使用的效果:
+
+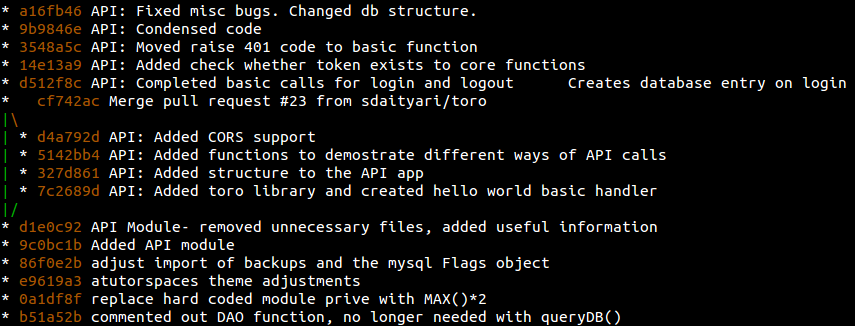
+
+### 5. 不要丢失对某个提交的跟踪 ###
+
+假设你提交了一些不需要的东西,然后你进行了hard重置回到之前的状态。后来,你发现在这个过程中你丢失了其他一些重要的信息,你想要把这些信息找回来,或者至少可以查看一下这些信息。这就需要`git reflog`帮忙。
+
+简单的`git log`只能告诉你最近的提交,这个提交的父提交,父提交的父提交,等等。但是`git reflog`是一个HEAD指向的提交的列表。记住,这个列表依赖于你自己的本地操作环境,它不是库的一部分,也不包含在push或者merge中。
+
+如果执行`git log`命令,可以看到提交历史,这是我的库的一部分:
+
+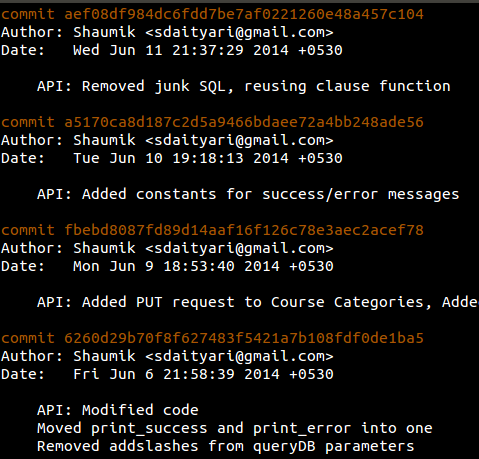
+
+但是,`git reflog`命令显示了一个被我用hard重置丢掉的提交(`b1b0ee9`-`HEAD@{4}`).
+
+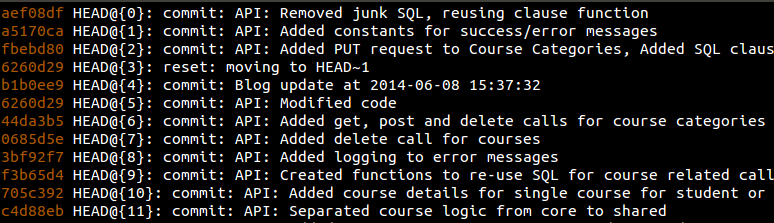
+
+### 6. 暂存文件的一部分更改以便进行一次提交 ###
+
+通常依据特性来提交是一个好的实践方法,意思是说,每一个提交都只添加一个特性或者修复一个bug。想一下如果你一次修复了两个bug或者添加了两个特性但是都还没有逐个提交该怎么办。这种场景下,你可以将他们一起提交。但是有一个更好的办法:单独暂存这些文件,然后分开提交。
+
+让我们假设你对一个文件做了多个更改,然后想让这些更改分开提交。这时,我们用带`-p`的添加命令。
+
+ git add -p [file_name]
+
+我们来试试这种用法。我添加了3个新行到`file_name`,但是我只想让第1行和第3行出现在我的提交里。让我们看看`git diff`的输出是什么样的。
+
+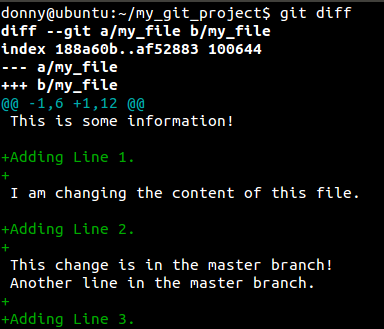
+
+然后,我们看看带`-p`选项的`add`命令会发生什么。
+
+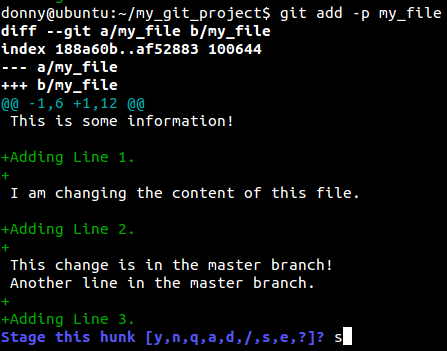
+
+看起来Git认为所有的更改都是同一个目的的一部分,所以把他们分组到同一个块里。这时,你可以:
+
+- 输入 y 暂存块
+- 输入 n 不暂存块
+- 输入 e 手动编辑块
+- 输入 d 退出或者跳转到下一个文件
+- 输入 s 分割块
+
+在我们这个例子中,我们想把这个块分割成更小的部分,然后选择其中一些忽略另外一些。
+
+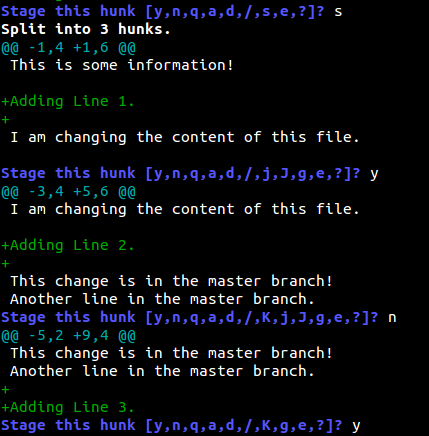
+
+如你所见,我们已经逐个添加了第1和第3行,忽略了第2行。你可以看到库的状态并且进行一次提交。
+
+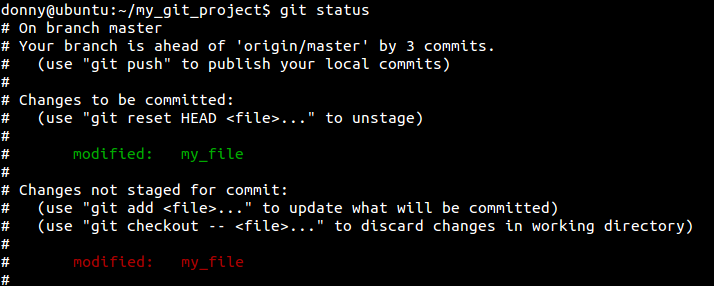
+
+### 7. 合并多个提交 ###
+
+为了进行核查或者发起一个合并请求(这经常发生在开源项目里),对代码进行了修改提交。但在最后代码被接受之前,你也许会需要修改你的代码。于是你修改代码,但是下一次核查的时候又一次需要进行修改。不知不觉中,你就已经有了好几个提交。理论上你应该用rebase命令把他们合并起来。
+
+ git rebase -i HEAD~[number_of_commits]
+
+如果你想合并最后的两次提交,你应该运行下面的命令。
+
+ git rebase -i HEAD~2
+
+一旦你运行这个命令,你将进入一个交互式界面,它将询问你想要合并哪些提交。你`pick`(拣选)最近的提交然后`squash`(合并)旧的提交。
+
+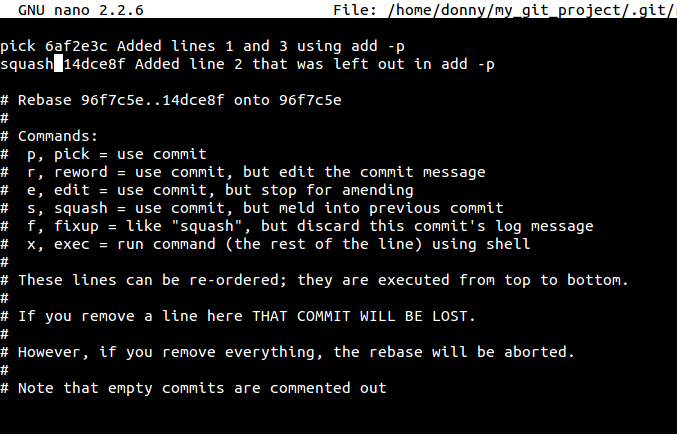
+
+接着你应该提供一个对新提交的说明。这个过程会重写你的提交历史。
+
+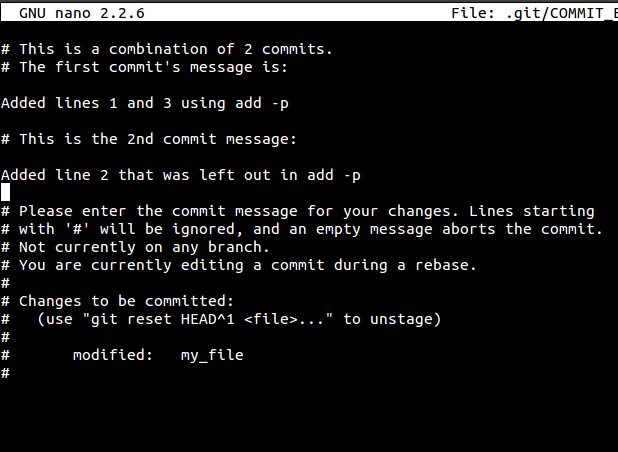
+
+### 8. 储藏没有提交的更改 ###
+
+假设你正在修复一个bug或者添加一个特性,突然你被要求展示一下你的工作成果。你现在的工作还没有完成,不够进行一次提交。这时,`git stash`命令可以用来急救一下。Stash命令跟踪你所有的更改,然后把他们储藏起来以便以后使用。命令如下-
+
+ git stash
+
+可以多次储藏更改,查看储藏列表,你可以运行下面的命令:
+
+ git stash list
+
+
+
+如果你想取消储藏,覆盖当前的更改,你可以通过下面的命令使用储藏:
+
+ git stash apply
+
+在最后的这个截图里,你可以看到每个储藏都有一个标识符,是一个唯一的数字(尽管在这里我们只有一个储藏)。如果你想使用某个储藏,你在apply命令后面加上这个唯一的标识符:
+
+ git stash apply stash@{2}
+
+
+
+### 9. 检查丢失的提交 ###
+
+尽管`reflog`是一种检查丢失提交的方法,大型的库里却不太实用。这个时候,应该用`fsck`(文件系统检查)命令。
+
+ git fsck --lost-found
+
+
+
+这里你可以看到一个丢失的提交。你可以通过`git show [commit_hash]` 查看提交的更改或者通过运行`git merge [commit_hash]`命令进行恢复。
+
+`git fsck`跟`reflog`命令相比有一个优点。假设你删除了一个远程分支,然后clone了这个库。用`fsck`命令你可以找到并且恢复这个删除的远程分支。
+
+### 10. 最佳选择 ###
+
+之前我已经存记下了那些最优雅的Git命令。但是目前为止,`cherry-pick`命令是我最喜欢的Git命令,因为它直白的名字和实用的功能!
+
+最简单的情况下,`cherry-pick`从另一个分支里选出单独的一个提交,然后合并到当前分支。如果你正并行工作在两个或者更多的分支上,你也许会发现一个存在于所有分支上的bug。如果你解决了一个分支上的这个bug,你可以拣选这个对应的提交应用到其他分支上,而不会弄乱其他文件或者提交。
+
+让我们来考虑一个可以使用这个命令的场景。我有两个分支,我想拣选`b20fd14: Cleaned junk`这个提交到另一个分支上。
+
+
+
+我切换到想要应用这个拣选出来的提交的分支,然后运行下面的命令:
+
+ git cherry-pick [commit_hash]
+
+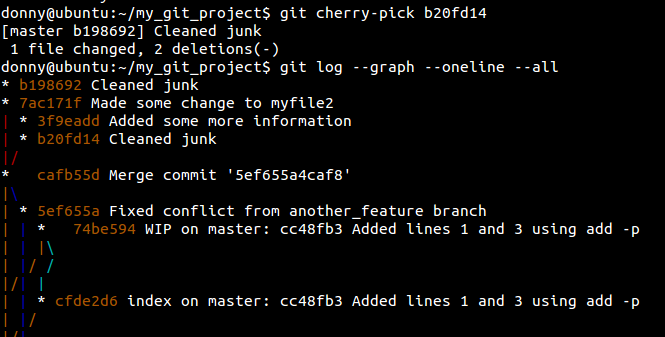
+
+尽管这次我们很干净的用了`cherry-pick`命令,但你应该知道这个命令经常会引起冲突,所以请小心使用。
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+到了这里,我们结束了这个能使你Git能力提升一个级别的列表。Git是最好的版本控制器,它能完成你能想象到的任何事情。所以,经常试着用Git挑战你自己。一不小心你就会学到很多新东西。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.sitepoint.com/10-tips-git-next-level/
+
+译者:[love\_daisy\_love](https://github.com/CNprober) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.sitepoint.com/git-for-beginners/
+[2]:http://www.sitepoint.com/getting-started-git-team-environment/
diff --git a/published/20140623 Advanced Directory Navigations Tips and Tricks in Linux.md b/published/20140623 Advanced Directory Navigations Tips and Tricks in Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8fe22e65f4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140623 Advanced Directory Navigations Tips and Tricks in Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+Linux 目录导航技巧
+================================================================================
+
+目录当行是命令行系统的基础概念.虽然不是什么难以理解的东西,但是知道一些技巧能够丰富你的经验并且提高工作效率.在这篇文章中,我们会讨论这些小技巧。
+
+### 我们已经知道的东西 ###
+
+在开始高级技巧之前,有一些必须知道的基本命令:
+
+- ‘pwd’显示当前目录
+- ‘cd’ 改变当前目录
+- ‘cd’ 跟两个点(cd ..)能返回父目录
+- ‘cd’ 跟着相对目录就能直接切换当相对目录下
+- ‘cd’ 跟着绝对目录就能切换到绝对目录下
+
+### 高阶技巧 ###
+
+这节将介绍几个技巧方便你进行目录的切换
+
+### 从任何地方回到home目录 ###
+
+虽然使用‘cd /home/<你的主目录>’, 不是什么大麻烦, 但是有一种方法直接打‘cd’ 就能回到你的主目录.
+
+例子:
+
+ $ pwd
+ /usr/include/netipx
+ $ cd
+ $ pwd
+ /home/himanshu
+
+所以无论你在哪个目录下,都能这么干,然后回到home目录。
+
+**注意**- 如果要切换到某个其它的指定用户的目录下, 就使用 ‘cd ~user_name'
+
+### 用cd - 在目录间切换 ###
+
+假设你的当前工作目录是这样的:
+
+ $ pwd
+ /home/himanshu/practice
+
+如果你想切换到 **/usr/bin/X11**, 然后又想回到之前的目录。 你会怎么做? 最直接的 :
+
+ $ cd /usr/bin/X11
+ $ cd /home/himanshu/practice/
+
+虽然这样行得通,但是要记住这些复杂的目录就太笨了。这种情况下使用 ‘cd -’ 命令就行.
+
+使用 ‘cd -’的第一步和上面的例子是一样的, 你可以 cd 到你想要切换到的<路径>下,但是回到之前的目录用 ‘cd -’就可以。
+
+ $ cd /usr/bin/X11
+ $ cd -
+ /home/himanshu/practice
+ $ pwd
+ /home/himanshu/practice
+
+如果你想再次回到刚刚访问的目录(在这个例子中是/usr/bin/X11),再使用'cd -'就可以。但是这个命令只会记住上一次访问的目录,这是一个缺点。
+
+### 用 pushd 和 popd 来切换目录 ###
+
+
+
+如果你对'cd -'非常了解了的话,你会发现这个命令只能帮助你在两个目录之间移动,但是很多场景下需要在很多目录之间切换。比如你要从A切换到B再到C然后又想回到A。
+
+一般来说,你需要打出A的完整路径,但是如果这个路径非常复杂,将是非常烦人的一件事,特别是在你的切换非常频繁的话。
+
+一些场景下可以使用 ‘pushd’ 还有 ‘popd’ 命令。 ‘pushd’ 将一个目录存到内存中,‘popd’ 将目录从内存中去除,并且转换到那个目录下。
+
+例如:
+
+ $ pushd .
+ /usr/include/netipx /usr/include/netipx
+ $ cd /etc/hp/
+ $ cd /home/himanshu/practice/
+ $ cd /media/
+ $ popd
+ /usr/include/netipx
+ $ pwd
+ /usr/include/netipx
+
+使用‘pushd’ 命令存储当前的工作目录 (用 .表示), 然后切换到各种各样的目录去。为了返回之前的目录,只要使用 ‘popd’命令就行了。
+
+(LCTT译注:显然,pushd和popd 是堆栈式操作,你可以push多个目录,然后逐一pop出来,自己试试吧。)
+(LCTT译注:我们之前介绍的[autojump][1],更加智能,不过需要安装一下。)
+
+**注意**- 你也可以使用不带参数的 ‘pushd’ 来切换到之前存储的目录, 但是不会像 ‘popd’ 一样去除这个目录。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/directory-navigations-tips-tricks/
+
+译者:[ggaaooppeenngg](https://github.com/ggaaooppeenngg) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://linux.cn/article-3401-1.html
diff --git a/published/20140623 How to disable Ipv6 on Ubuntu or Linux Mint or Debian.md b/published/20140623 How to disable Ipv6 on Ubuntu or Linux Mint or Debian.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4b63c6df0f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140623 How to disable Ipv6 on Ubuntu or Linux Mint or Debian.md
@@ -0,0 +1,137 @@
+如何在Ubuntu,Linux Mint,Debian上禁用IPv6
+================================================================================
+### IPv6 ###
+
+IPv6是寻址方案IPv4的下一个版本,被用来给域名分配数字地址。
+
+IPv6比IPv4支持更多的地址。然而,它还没有被广泛支持,还在被接受的过程中。
+
+### 你的系统支持IPv6么? ###
+
+为了支持IPv6,需要很多事情。首先你需要系统/操作系统支持IPv6。Ubuntu,Linux Mint,和大多是现代发行版都支持它。如果你看一下ifconfig指令的输出,你就会看见你的网络接口被分配了IPv6地址。
+
+ $ ifconfig
+ eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:1c:c0:f8:79:ee
+ inet addr:192.168.1.2 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
+ inet6 addr: fe80::21c:c0ff:fef8:79ee/64 Scope:Link
+ UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
+ RX packets:110880 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
+ TX packets:111960 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
+ collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
+ RX bytes:62289395 (62.2 MB) TX bytes:25169458 (25.1 MB)
+ Interrupt:20 Memory:e3200000-e3220000
+
+ lo Link encap:Local Loopback
+ inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
+ inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
+ UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1
+ RX packets:45258 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
+ TX packets:45258 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
+ collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
+ RX bytes:4900560 (4.9 MB) TX bytes:4900560 (4.9 MB)
+
+看一下行“inet6 addr”。
+
+接下来你需要一个支持ipv6的路由器/调制解调器。此外,你的ISP也必须支持IPv6。
+
+除了检查网络设备的每一部分,最好查出你是否可以通过IPv6访问网站。
+
+有很多网站可以检测你的网络连接是否支持IPv6. 这里就是个例子:[http://testmyipv6.com/][1]
+
+下面是在内核中启用IPv6的参数:
+
+ $ sysctl net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6
+ net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 0
+
+ $ sysctl net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6
+ net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 0
+
+ $ sysctl net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6
+ net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 0
+
+同样可以在proc文件中检查
+
+ $ cat /proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/all/disable_ipv6
+ 0
+
+注意这里的变量是控制IPv6的“禁用”。所以设置1就会禁用IPv6。
+
+### 如果它不支持就禁用IPv6 ###
+
+如果你的网络设备中不支持IPv6,那最好就全部禁用它们。为什么?因为这会引起域名查询延迟,在网络连接中不必要地尝试连接到IPv6地址导致延迟等等问题。
+
+我也遇到过像这样的问题,apt-get命令偶尔会尝试连接到IPv6地址失败接着检索IPv4地址。看一下下面的输出。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ Ign http://archive.canonical.com trusty InRelease
+ Ign http://archive.canonical.com raring InRelease
+ Err http://archive.canonical.com trusty Release.gpg
+ Cannot initiate the connection to archive.canonical.com:80 (2001:67c:1360:8c01::1b). - connect (101: Network is unreachable) [IP: 2001:67c:1360:8c01::1b 80]
+ Err http://archive.canonical.com raring Release.gpg
+ Cannot initiate the connection to archive.canonical.com:80 (2001:67c:1360:8c01::1b). - connect (101: Network is unreachable) [IP: 2001:67c:1360:8c01::1b 80]
+
+ .....
+
+像这样的错误在最近的Ubuntu中更频繁了,或许它比以前更频繁地尝试使用IPv6地址。
+
+我在其他的应用上也注意到了相似的问题,如Hexchat,同样Google Chrome也会有时会在查询域名的时候花费更长的时间。
+
+所以最好的方案是完全禁用IPv6来摆脱这些事情。这只需要一点点配置但可以帮助你解决很多你系统上的很多问题。用户甚至反应这可以加速网络。
+
+#### 禁用 IPv6 - 方案1 ####
+
+编辑文件 - /etc/sysctl.conf
+
+ $ sudo gedit /etc/sysctl.conf
+
+在文件的最后加入下面的行。
+
+ # IPv6 disabled
+ net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
+ net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1
+ net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 1
+
+保存并关闭
+
+重启sysctl
+
+ $ sudo sysctl -p
+
+再次检查ifconfig的输出,这里应该没有IPv6地址了。
+
+ $ ifconfig
+ eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:5f:28:8b
+ inet addr:192.168.1.3 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
+ UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
+ RX packets:1346 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
+ TX packets:965 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
+ collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
+ RX bytes:1501691 (1.5 MB) TX bytes:104883 (104.8 KB)
+
+如果不行,尝试重启系统并再次检查ifconfig
+
+#### 禁用 IPv6 - GRUB 方案 ####
+
+IPv6同样可以通过编辑grub配置文件禁用。
+
+ $ sudo gedit /etc/default/grub
+
+查找包含"GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX"的行,并如下编辑:
+
+ GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="ipv6.disable=1"
+
+同样可以加入名为"GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT"的变量,这同样有用。保存并关闭文件,重新生成grub配置。
+
+ $ sudo update-grub2
+
+重启,现在IPv6应该就已经禁用了。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.binarytides.com/disable-ipv6-ubuntu/
+
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) ,校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://testmyipv6.com/
diff --git a/published/20140623 How to speed up directory navigation in a Linux terminal.md b/published/20140623 How to speed up directory navigation in a Linux terminal.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4653fdca7e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140623 How to speed up directory navigation in a Linux terminal.md
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
+自动补完不算什么,一键直达目录才是终极神器!
+================================================================================
+
+在命令行中切换目录是最常用的操作,不过很少有比一遍又一遍重复“cd ls cd ls cd ls ……”更令人沮丧的事情了。如果你不是百分百确定你想要进入的下一个目录的名字,那么你不得不使用ls来确认,然后使用cd来进入你想要进的那一个。所幸的是,现在大量的终端和shell语言提供了强大的自动补全功能来处理该问题。但是,你仍然需要一直疯狂地敲击TAB键来干这事。如果你和我一样懒惰,你一定会对autojump感到惊喜。
+
+autojump是一个命令行工具,它允许你可以直接跳转到你喜爱的目录,而不用管你现在身在何处。
+
+### 在Linux上安装autojump ###
+
+在Ubuntu或Debian上安装autojump:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install autojump
+
+要在CentOS或Fedora上安装autojump,请使用yum命令。在CentOS上,你需要先[启用EPEL仓库][1]才行。
+
+ $ sudo yum install autojump
+
+在Archlinux上安装autojump:
+
+ $ sudo pacman -S autojump
+
+如果你找不到适合你的版本的包,你可以从[GitHub][2]上下载源码包来编译。
+
+### autojump的基本用法 ###
+
+autojump的工作方式很简单:它会在你每次启动命令时记录你当前位置,并把它添加进它自身的数据库中。这样,某些目录比其它一些目录添加的次数多,这些目录一般就代表你最重要的目录,而它们的“权重”也会增大。
+
+现在不管你在哪个目录,你都可以使用下面的语法来直接跳转到这些目录:
+
+ autojump [目录的名字或名字的一部分]
+
+注意,你不需要输入完整的名称,因为autojump会检索它的数据库,并返回最可能的结果。
+
+例如,假定我们正在下面的目录结构中工作。
+
+
+
+那么下面的命令将直接让你跳到/root/home/doc下,不管你当前位置在哪里。
+
+ $ autojump do
+
+如果你也很讨厌打字,那么我推荐你为autojump起个别名,或者使用默认的别名。
+
+ $ j [目录的名字或名字的一部分]
+
+另外一个引人注目的功能是,autojump支持zsh和自动补完。如果你不确认哪里是不是你要跳转的地方,敲击TAB键就会列出完整路径。
+
+还是同样的例子,输入:
+
+ $ autojump d
+
+然后敲击tab键,将会返回/root/home/doc或者/root/home/ddl。
+
+最后,对于高级用户,你可以访问目录数据库,并修改它的内容。可以使用下面的命令来手动添加一个目录:
+
+ $ autojump -a [目录]
+
+如果你突然想要把当前目录变成你的最爱和使用最频繁的文件夹,你可以在该目录通过命令的参数 i 来手工增加它的权重
+
+ $ autojump -i [权重]
+
+这将使得该目录更可能被选择跳转。相反的例子是在该目录使用参数 d 来减少权重:
+
+ $ autojump -d [权重]
+
+要跟踪所有这些改变,输入:
+
+ $ autojump -s
+
+这会显示数据库中的统计数据。而以下:
+
+ $ autojump --purge
+
+命令将会把不再存在的目录从数据库中移除。
+
+简言之,autojump将会受到所有命令行高级用户的欢迎。不管你是在ssh进一台服务器,还是仅仅想要追随复古潮流,敲更少的键来减少导航时间总是件好事。如果你真的热衷于此类工具,你也肯定也想看看[Fasd][3],它应该会给你一个惊喜,我们下次再介绍它。
+
+你觉得autojump怎么样?你会经常用它么?发表一下你的评论吧。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/06/speed-up-directory-navigation-linux-terminal.html
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
+[2]:https://github.com/joelthelion/autojump
+[3]:https://github.com/clvv/fasd
diff --git a/published/20140624 How to sync Microsoft OneDrive on Linux.md b/published/20140624 How to sync Microsoft OneDrive on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f2b8423e07
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140624 How to sync Microsoft OneDrive on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+逝去的纪念:如何在Linux中同步微软 OneDrive
+================================================================================
+【编者注】:本文译文完成之后不久,OneDrive 就成了中国人的昨日黄花了。编者想了想,还是发出来罢,仅以此文纪念我们逝去的这个、那个、以及这些和那些。也许若干年后我们回忆起来,我们曾经有过那么多那些,而当时却挑三拣四,没有珍惜,如果再给我一次机会……
+
+---
+
+[OneDrive][1](以前称为SkyDrive)是微软的一个广受欢迎的云存储产品。目前OneDrive为每一个新注册用户提供7GB免费存储空间。正如你所想,OneDrive与微软其他软件产品很好地集成。微软还提供了一个独立的OneDrive客户端,它会自动备份照相机拍摄的图片和视频到OneDrive。但你猜怎么着。该客户端可用于除Linux的各大PC/移动平台。
+
+“OneDrive在任何设备,任何时间”?哦,不,这还不行。
+
+不过不要失望。开源社区已经已经拿出了解决方案。 Boilermaker写的[onedrive-d][2]可以完成这项工作。作为监测守护进程运行,onedrive-D可自动将本地文件夹同步到OneDrive云存储。
+
+I在本教程中,我将介绍**如何在Linux上使用onedrive-d同步微软OneDrive**。
+
+### 在linux上安装onedrive-d ###
+
+虽然onedrive-d最初是为Ubuntu/ Debian开发的,但它仍然支持CentOS/ Fedora/ RHEL。
+
+安装就像输入下面的命令一样容易。
+
+ $ git clone https://github.com/xybu92/onedrive-d.git
+ $ cd onedrive-d
+ $ ./inst install
+
+### 第一次配置 ###
+
+安装之后,你需要进行一次性配置来授予onedrive-d对您OneDrive账户的读/写权限。
+
+首先,创建将用于对远程OneDrive账户同步的本地文件夹。
+
+ $ mkdir ~/onedrive
+
+接着运行下面的命令开启一次性配置。
+
+ $ onedrive-d
+
+它接着会弹出如下onedrive-d的设置窗口。在“Location”选项中,选择你之前创建的本地文件夹。在“Authentication”选项中,你会看见“You have not authenticated OneDrive-d yet”(“你还没有授权OneDrive-d”)的信息。现在点击"Connect to OneDrive.com"按钮。
+
+
+
+它会弹出一个新窗口来要求你登录OneDrivecom。
+
+
+
+登录OneDrive.com之后,你会被要求授权onedrive-d访问。选择“Yes”。
+
+
+
+回到先前的设置窗口,你会看到之前的状态已经变成了You have connected to OneDrive.com"(“你已经连接到了OneDrive.com”)。点击“OK”完成。
+
+
+
+### 与OneDrive同步一个本地文件夹 ###
+
+这里有两种方法来使用onedrice-d将本地文件夹与OneDrive存储同步。
+
+一种是“手动使用命令行来同步OneDrive”。就是当你需要与你的OneDrive账户同步时运行如下命令:
+
+ $ onedrive-d
+
+`onedrive-d`接着将扫描本地文件夹与OneDrive帐户的内容并使两者同步。这意味着要么上传一个在本地文件夹新添加的文件,或者从远程OneDrive帐户下载最新发现的文件。如果你从本地文件夹删除任何文件,相应的文件将自动在与OneDrive帐户同步后被删除。反之亦然。
+
+一旦同步完成,你可以使用Ctrl-C中断onedirve-d的前台进程。
+
+
+
+另一种方法是将onedrive-d作为一个始终运行的守护进程在开机时自动启动。在这种情况下,后台守护进程会同时监视本地文件夹和OneDrive账户,以使它们保持同步。要做到这一点,只需将onedrive-D加入到你桌面的[自动启动程序列表][3]中就行了。
+
+当onedrive-D作为守护进程在后台运行时,你会在桌面状态栏中看到OneDrive图标,如下图所示。每当同步更新被触发,你就会看到一个桌面通知。
+
+
+
+要注意的是:根据作者所言,onedrive-d仍在积极开发中。这并不能用于任何形式的生产环境。如果您遇到任何bug,请随时提交一份[bug报告][4]。你的贡献,笔者将不胜感激。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/06/sync-microsoft-onedrive-linux.html
+
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/go/onedrive
+[2]:http://xybu.me/projects/onedrive-d/
+[3]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/start-program-automatically-linux-desktop.html
+[4]:https://github.com/xybu92/onedrive-d/issues?state=open
diff --git a/published/20140624 Open Source Multimedia Converter Curlew 0.1.22.3 Is Out.md b/published/20140624 Open Source Multimedia Converter Curlew 0.1.22.3 Is Out.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8fe7018a07
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140624 Open Source Multimedia Converter Curlew 0.1.22.3 Is Out.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+开源多媒体转换器Curlew 0.1.22.3发布了
+================================================================================
+
+
+**Curlew是linux下的一款容易使用,开源多媒体转换器,现在的版本是0.1.22.3。**
+
+
+Curlew可以转换超过100种不同的格式、显示文件的详细信息、转换预览、插入字幕等等。
+
+此次更新包括:该软件打开时会记住上次的窗口大小和位置、增加了丢失了的对话框图标、在系统挂起前会主动同步文件系统。
+
+这个程序需要的依赖环境包括:Python 2.7及其以上 (但是不兼容3.x)、python-gobject 3.0、gir1.2-gtk 3.0、 ffmpeg 0.8、libav-tools 0.8、 mencoder、libavcodec-extra、xdg-utils和mediainfo等。
+
+来自noobslab.com的兄弟们提供一种通过PPA来简单地安装这个应用的方法。你要做的是在命令行下输入少量的命令(你需要有root权限才行)
+
+ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/apps
+ sudo apt-get update
+ sudo apt-get install curlew
+
+查看官方[更新日志][1]来获取完整的特性与更新列表。
+
+你可以下载Curlew 0.1.22.3 的软件包:
+
+- [Ubuntu 14.04 DEB ALL][2][ubuntu_deb] [172 KB]
+- [tar.gz][3][sources] [152 KB]
+
+记住这是一个开发版因此不应该安装在生产机器上。它只用于测试。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Open-Source-Multimedia-Converter-Curlew-0-1-22-3-Is-Out-448028.shtml
+
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://gtk-apps.org/content/show.php/Curlew?content=155664
+[2]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/curlew/files/curlew-0.1.22.3/curlew_0.1.22.3ubuntu14.04_all.deb/download
+[3]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/curlew/files/curlew-0.1.22.3/curlew-0.1.22.3.tar.gz/download
diff --git a/published/20140624 Top500 Supercomputer Remains Stuck at 33.86 Petaflops Each s - 翻译.md b/published/20140624 Top500 Supercomputer Remains Stuck at 33.86 Petaflops Each s - 翻译.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6a6808f4d9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140624 Top500 Supercomputer Remains Stuck at 33.86 Petaflops Each s - 翻译.md
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+超算TOP 500的计算性能仍然保持在 33.86 千万亿次/秒
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+天河2号一年以前第一次跳上世界超算舞台,拥有了当时世界上最强计算机的皇冠。当时,天河2号被评测为 33.86 petaflops (千万亿次/秒)。
+
+整整一年后天河-2 性能指数仍旧保持不变,它仍然坐在世界上最强超级计算机的头把交椅上。
+
+
+
+在 2013 年 6 月时,世界上第二快的超级计算机是安置于美国能源部橡树岭国家实验室的 Cray Titan。一年前,Titan可飙至 17.59 petaflops。Titan的优秀表现,正如同天河-2一样, 到了2014 年 6 月仍然保持住了他的地位。
+
+事实上,在最近的一年中,世界上顶尖的前 10 超级计算机的性能排名几乎没有任何改变,至少根据世界超算 500 强名单来看是这样的。
+
+如果看看名单底部,在超算排行榜的第500名,是德国Deutcher Wetterdienst 的Cray XC30 ,其性能已经逼近 133.7 teraflops (万亿次/秒)。
+
+TOP500 网站[指出][1],"最新名单上的最后的一个系统其实以前处在20年前世界 500 强排行榜中384位"。"这说明这二十年中列表变化不大。
+
+
+再次,列表有 85.4%的超级计算机都是英特尔芯片占主导地位的,而 IBM Power 处理器拥有 8%的市场份额。AMD 的占有率目前仅为 6%。
+
+
+就芯片架构来说,53.6%的超算都使用 8 个或更多核心的CPU, 13.4%的超算则是 10 个或更多的核心的CPU。
+
+再来看看网络互联,Infiniband和以太网拆分了整个市场。在 2014 年 6 月名单上,Infiniband占据了系统的 44.4%。
+
+相比之下,据报道千兆以太网有 25.4%的市场份额, 万兆以太网拥有 15%,合计占以太网整体份额的 40.4%。
+
+惠普和 IBM 再次占领了超级计算供应商的列表。惠普现在占有 36.4%的份额,而 IBM 占有 35.2%。Cray 排名降低,位列第三,占有10.2%的市场份额。
+
+虽然在世界前 500 的超级计算机榜单排名里面硬件供应商们,芯片体系架构,核心数量和互联方式竞争激烈,但是在选择操作系统的时候,毫无疑问的是,97%的超算都安装了linux操作系统,即top500超算榜单上的485个超算都安装了linux系统。
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.serverwatch.com/server-news/top500-supercomputer-remains-stuck-at-33.86-petaflops.html
+
+译者:[owen-carter](https://github.com/owen-carter) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://top500.org/blog/lists/2014/06/press-release/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/20140625 Betty--Translate English Phrases Into Linux Commands.md b/published/20140625 Betty--Translate English Phrases Into Linux Commands.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..83784a07e5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140625 Betty--Translate English Phrases Into Linux Commands.md
@@ -0,0 +1,201 @@
+Betty:通过大白话执行Linux命令
+================================================================================
+
+**Betty** 是一个将类英语短语翻译成Linux命令的开源工具。这个项目的主要目的是让大家可以通过输入自然语言来使用强大的Linux系统。让我们来看一下它是怎么工作的。
+
+### 安装 ###
+
+Betty的安装非常简单直接。首先确认你已经安装了下面这些依赖包[LCTT译注,需要安装至少Ruby1.9以上版本]。
+
+#### 对于基于Debian的系统:####
+
+ sudo apt-get install git curl ruby
+
+####对于基于RPM的系统:####
+
+ yum install git curl ruby
+
+现在用git工具把Betty库clone到你自定义的任何路径。这里我克隆到我的home目录,**例如 /home/sk/**.
+
+ git clone https://github.com/pickhardt/betty
+
+添加betty的别名到你的bashrc配置文件。
+
+ sudo nano ~/.bashrc
+
+将下列行添加到文件的末尾:
+
+ alias betty="/home/sk/betty/main.rb"
+
+确保你已经正确地设置好了betty的路径。
+
+好了,现在是时候和betty好好地玩耍了。
+
+### 用法 ###
+
+你应该在英语短语之前加上单词“betty” [LCTT译注,你自然可以用你的小甜心的名字来替换这个不是知道是谁的Betty :>]。你也许已经知道,如果我们想知道在系统中我们的用户名,应该运行下面的命令:
+
+ whoami
+
+输出是这样的:
+
+ sk
+
+如你所见,我当前登录的用户名是 **sk**. 现在我也可以通过下面的betty命令获取相同的结果。
+
+ betty whats my username
+
+输出是这样的:
+
+ Betty: Running whoami
+ sk
+
+真的好酷,是不是?Betty理解我输入的“whats my username”短语,然后运行“whoami”命令,最后输出结果。
+
+让我们也来看其他命令。
+
+如果你的输入不够准确,Betty也能以多种方式回应你。例如,我们运行下面的命令:
+
+ betty whats my name
+
+Betty不确定她应该查找系统用户名还是用户全名。这种情况下,她会询问你多个问题来找到准确的结果。如你下面所见,Betty问我想要运行哪一条命令(whoami 还是 finger $(whoami) | sed 's/.*:*//;q')[LCTT译注,需要你的系统已经安装finger]。我只想知道我的用户名,所以我选择数字**1**。
+
+ Betty: Okay, I have multiple ways to respond.
+ Betty: Enter the number of the command you want me to run, or N (no) if you don't want me to run any.
+ [1] whoami
+ Gets your system username.
+ [2] finger $(whoami) | sed 's/.*: *//;q'
+ Gets your full name.
+ 1
+ Betty: Running whoami
+ sk
+
+### 压缩和解压缩文件夹 ###
+
+如果你想要压缩一个文件或者文件夹,用下面的命令。例如,我想压缩我home目录下的“test”文件夹。
+
+ betty compress test/ test.tar.gz
+
+输出是这样的:
+
+ Betty: Running tar -czvf test.tar.gz test/
+ test/
+ test/home/
+ test/home/sk/
+ test/home/sk/test/
+ test/home/sk/test/sample
+
+类似的,我们可以用下面的命令来解压缩一个归档文件。
+
+ betty uncompress test.tar.gz
+
+输出是这样的:
+
+ Betty: Running mkdir test && tar -zxvf test.tar.gz -C test
+ test/
+ test/home/
+ test/home/sk/
+ test/home/sk/test/
+ test/home/sk/test/sample
+
+### 完整的Betty命令行列表 ###
+
+Betty工具有一些命令格式。如果你输入“what is my user name”而不是“whats my username”,它是不能识别的。所以,你只能输入Betty支持的英语短语。
+
+下面给出一个Betty支持的完整的命令行列表。
+
+ Count:
+ betty how many words are in this directory
+ betty how many characters are in myfile.py
+ betty count lines in this folder
+ (Note that there's many ways to say more or less the same thing.)
+
+ Config:
+ betty change your name to Joe
+ betty speak to me
+ betty stop speaking to me
+
+ Datetime:
+ betty what time is it
+ betty what is todays date
+ betty what month is it
+ betty whats today
+
+ Find:
+ betty find me all files that contain california
+
+ Internet:
+ betty download http://www.mysite.com/something.tar.gz to something.tar.gz
+ betty uncompress something.tar.gz
+ betty unarchive something.tar.gz to somedir
+ (You can use unzip, unarchive, untar, uncompress, and expand interchangeably.)
+ betty compress /path/to/dir
+
+ iTunes:
+ betty mute itunes
+ betty unmute itunes
+ betty pause the music
+ betty resume itunes
+ betty stop my music
+ betty next song
+ betty prev track
+ betty what song is playing
+ (Note that the words song, track, music, etc. are interchangeable)
+
+ Fun:
+ betty go crazy
+ betty whats the meaning of life
+ ...and more that are left for you to discover!
+
+ Map:
+ betty show me a map of mountain view
+
+ Meta:
+ betty what version are you (or just betty version)
+ betty whats your github again
+
+ Permissions:
+ betty give me permission to this directory
+ betty give anotheruser ownership of myfile.txt
+
+ Process:
+ betty show me all processes by root containing grep
+ betty show me all my processes containing netbio
+
+ Sizes:
+ betty show size for myfile.txt
+
+ Spotify:
+ betty play spotify
+ betty pause spotify
+ betty next spotify
+ betty previous spotify
+
+ User:
+ betty whats my username
+ betty whats my real name
+ betty whats my ip address
+ betty who else is logged in
+ betty whats my version of ruby
+
+ Web queries:
+ betty turn web on
+ betty please tell me what is the weather like in London
+
+对Linux初级使用者来说,Betty似乎是一个非常nice的工具。希望这个工具对你也会非常有用。
+
+Cheers!
+
+源代码:
+
+- [Betty Homepage][1]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/betty-translate-english-phrases-linux-commands/
+
+译者:[love\_daisy\_love](https://github.com/CNprober) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://github.com/pickhardt/betty
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/20140625 Create A '.deb Pacakge Repository' at Sourceforge.net Using 'Reprepro' Tool in Ubuntu.md b/published/20140625 Create A '.deb Pacakge Repository' at Sourceforge.net Using 'Reprepro' Tool in Ubuntu.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7c3686fd36
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140625 Create A '.deb Pacakge Repository' at Sourceforge.net Using 'Reprepro' Tool in Ubuntu.md
@@ -0,0 +1,203 @@
+在Ubuntu下如何创建远程".deb"包仓库
+================================================================================
+**Reprepro**是一款小巧的命令行工具来方便地创建并管理**.deb**仓库。今天我们会展示给你如何使用reprepro简单地创建一个Debian包仓库,并使用**rsync**上传到Sourceforge.net。
+
+
+
+### 步骤 1: 安装Reprepro并生成key ###
+
+首先,安装所有需要的包,使用下面的apt-get命令。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install reprepro gnupg
+
+现在你需要使用gnupg生成一个gpg key,这里使用下面的命令。
+
+ $ gpg --gen-key
+
+它会询问你一些问题,比如你想要哪种key、key的有效期、如果你不知道如何回答,只需点击**回车** 来选择默认选项(建议)
+
+当然,它会询问你用户名和密码,在脑海中记住这些,因为我们会在之后需要它。
+
+ gpg (GnuPG) 1.4.14; Copyright (C) 2013 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
+ This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
+ There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
+
+ Please select what kind of key you want:
+ (1) RSA and RSA (default)
+ (2) DSA and Elgamal
+ (3) DSA (sign only)
+ (4) RSA (sign only)
+ Your selection?
+ RSA keys may be between 1024 and 4096 bits long.
+ What keysize do you want? (2048)
+ Requested keysize is 2048 bits
+ Please specify how long the key should be valid.
+ 0 = key does not expire
+ = key expires in n days
+ w = key expires in n weeks
+ m = key expires in n months
+ y = key expires in n years
+ Key is valid for? (0)
+ Key does not expire at all
+ Is this correct? (y/N) Y
+
+ You need a user ID to identify your key; the software constructs the user ID
+ from the Real Name, Comment and Email Address in this form:
+ "Heinrich Heine (Der Dichter) "
+
+ Real name: ravisaive
+ Email address: tecmint.com@gmail.com
+ Comment: tecmint
+ You selected this USER-ID:
+ "Ravi Saive (tecmint) "
+
+ Change (N)ame, (C)omment, (E)mail or (O)kay/(Q)uit? O
+ You need a Passphrase to protect your secret key.
+
+ We need to generate a lot of random bytes. It is a good idea to perform
+ some other action (type on the keyboard, move the mouse, utilize the
+ disks) during the prime generation; this gives the random number
+ generator a better chance to gain enough entropy.
+
+ +++++
+ gpg: key 2EB446DD marked as ultimately trusted
+ public and secret key created and signed.
+
+ gpg: checking the trustdb
+ gpg: 3 marginal(s) needed, 1 complete(s) needed, PGP trust model
+ gpg: depth: 0 valid: 1 signed: 0 trust: 0-, 0q, 0n, 0m, 0f, 1u
+ pub 2048R/2EB446DD 2014-06-24
+ Key fingerprint = D222 B1C9 342E 5911 02B1 9147 3BD6 7918 2EB4 46DD
+ uid Ravi Saive (tecmint)
+ sub 2048R/7EF2F750 2014-06-24
+
+现在你的key已经生成了,要检查一下,用root权限运行这条命令。
+
+ $ sudo gpg --list-keys
+
+#### 示例输出 ####
+
+ /home/ravisaive/.gnupg/pubring.gpg
+ ----------------------------------
+ pub 2048R/2EB446DD 2014-06-24
+ uid ravisaive (tecmint)
+ sub 2048R/7EF2F750 2014-06-24
+
+### 步骤 2: 创建一个包仓库并导出key ###
+
+我们现在要开始创建仓库,首先你需要创建一些文件夹,我们的仓库会放在**/var/www/apt**目录,让我们先创建这些目录。
+
+ $ sudo su
+ # cd /var/www
+ # mkdir apt
+ # mkdir -p ./apt/incoming
+ # mkdir -p ./apt/conf
+ # mkdir -p ./apt/key
+
+你现在需要将key导出到仓库文件夹,运行:
+
+ # gpg --armor --export username yourmail@mail.com >> /var/www/apt/key/deb.gpg.key
+
+注意:用你之前步骤中输入的用户名代替username,用你的email代替上面的yourmail@mail.com。
+
+我们需要在**/var/www/apt/conf**创建一个文件“**distributions**”。
+
+ # touch /var/www/apt/conf/distributions
+
+加入下面这几行到distributions这个文件中并保存。
+
+ Origin: (你的名字)
+ Label: (库的名字)
+ Suite: (stable 或 unstable)
+ Codename: (发布的代码名,比如 trusty)
+ Version: (发布的版本,比如 14.04)
+ Architectures: (软件包所支持的架构, 比如 i386 或 amd64)
+ Components: (包含的部件,比如 main restricted universe multiverse)
+ Description: (描述)
+ SignWith: yes
+
+接下来我们会创建仓库树,运行这些命令:
+
+ # reprepro --ask-passphrase -Vb /var/www/apt export
+
+#### 示例输出 ####
+
+ Created directory "/var/www/apt/db"
+ Exporting Trusty...
+ Created directory "/var/www/apt/dists"
+ Created directory "/var/www/apt/dists/Trusty"
+ Created directory "/var/www/apt/dists/Trusty/universe"
+ Created directory "/var/www/apt/dists/Trusty/universe/binary-i386"
+ FF5097B479C8220C ravisaive (tecmint) needs a passphrase
+ Please enter passphrase:
+ Successfully created '/var/www/apt/dists/Trusty/Release.gpg.new'
+ FF5097B479C8220C ravisaive (tecmint) needs a passphrase
+ Please enter passphrase:
+ Successfully created '/var/www/apt/dists/Trusty/InRelease.new'
+
+### 步骤 3: 在新创建的仓库中加入包 ###
+
+现在准备你的**.deb**包来加入到仓库中。进入 **/var/www/apt**目录,你每次要加包的时候都必须这么做。
+
+ # cd /var/www/apt
+ # reprepro --ask-passphrase -Vb . includedeb Trusty /home/ravisaive/packages.deb
+
+**注意**:用你在distributions文件中输入的仓库代号来代替**trusty** ,并且用包的路径替换**/home/username/package.deb**,你会被要求输入密码。
+
+#### 示例输出####
+
+ /home/ravisaive/packages.deb : component guessed as 'universe'
+ Created directory "./pool"
+ Created directory "./pool/universe"
+ Created directory "./pool/universe/o"
+ Created directory "./pool/universe/o/ojuba-personal-lock"
+ Exporting indices...
+ FF5097B479C8220C ravisaive (tecmint) needs a passphrase
+ Please enter passphrase:
+ Successfully created './dists/Trusty/Release.gpg.new'
+ FF5097B479C8220C ravisaive (tecmint) needs a passphrase
+ Please enter passphrase:
+ Successfully created './dists/Trusty/InRelease.new'
+
+你的包已经加入了仓库,如果要移除它的话采用如下命令:
+
+ # reprepro --ask-passphrase -Vb /var/www/apt remove trusty package.deb
+
+当然你需要用你的包名与仓库代号来修改命令。
+
+### 步骤 4: 上传仓库到Sourceforge.net ###
+
+要上传仓库到**Sourceforge.net**,你当然需要一个可用的账号与一个可用的项目,让我假设你想要上传仓库到**http://sourceforge.net/projects/myfoo/testrepository**,这里的myfoo是项目名(UNIX上的名称,不是URL,不是标题),testrepository是你想要上传文件到这上面的目录,这里我们会使用[rsync 命令][1]。(LCTT译注:当然你也可以上传到其它的支持Http/Rsync的服务器上,以提供远程软件库的服务。)
+
+ # rsync -avP -e ssh /var/www/apt/ username@frs.sourceforge.net:/home/frs/project/myfoo/testrepository/
+
+**注意**:用你在sourceforge.net上的用户名代替username,用你的项目的UNIX名称代替myfoo,用你想要存储的文件夹代替testrepository。
+
+现在你的仓库(包括设置和key等等)上传到了**http://sourceforge.net/projects/myfoo/testrepository**。
+
+要把它加入到一个已装好的系统,首先你需要导入仓库key,它实际上就是**/var/www/apt/key/deb.gpg.key**,但是这是一个本地路径,使用你的仓库的其它用户不能添加到他们的系统中,这就是为什么我们要导入来自sourceforge.net的key的原因。
+
+ $ sudo su
+ # wget -O - http://sourceforge.net/projects/myfoo/testrepository/apt/key/deb.gpg.key | apt-key add -
+
+你现在可以非常轻松地把仓库加入到系统中了,打开**/etc/apt/sources.list**,并加入下面这行:
+
+ deb http://sourceforge.net/projects/myfoo/testrepository/apt/key/deb.gpg.key trusty main
+
+**Note**:用你的项目的UNIX类型名称代替myfoo,用你的仓库代码代替trusty,用你上传存储的文件夹代替testrepository,用你在distributionsj加入的仓库组件代替main。
+
+接下来,运行下面的命令来更新仓库列表。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+
+**祝贺你**! 你的软件仓库已经激活了!你现在可以非常简单地在你需要的时候安装包了。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/create-deb-pacakge-repository-in-ubuntu/
+
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/rsync-local-remote-file-synchronization-commands/
diff --git a/published/20140625 Keep an eye on these 5 new features in RHEL 7.md b/published/20140625 Keep an eye on these 5 new features in RHEL 7.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..debd55dcb5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140625 Keep an eye on these 5 new features in RHEL 7.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+RHEL 7值得注意的5个新特性
+================================================================================
+> RHEL 7 支持Docker容器,systemd,兼容微软的身份管理和支持高达500TB的XFS文件系统。
+
+
+
+在前一个主版本发布3年之后,经过至少6个月的[公开测试][1],RHEL(Red Hat Enterprise Linux)版本7终于发布了。这次更新表明了红帽子公司对于在RHEL中添加最新的以企业和数据为中心的特性的兴趣。这里列举了其中5个最吸引人眼球的新特性。
+
+### 1. Docker ###
+
+RHEL 7中最大的新特性就是[紧密集成][2]了广受欢迎的应用程序虚拟化技术[Docker][3]。随着[Docker 1.0发布][4],把它集成到RHEL 7里正是恰逢其时。
+
+用Docker包装的应用程序可以独立于操作系统,所以它们可以在操作系统之间移植并且正常运行。RHEL 7打算尽可能高效地使用Docker,以防止应用程序竞争资源或者为使用哪种运行时环境而困惑。
+
+从RHEL的Docker路线图上的长期计划表来看,这可能会超越操作系统本身,发展成一系列的Docker容器,它可以支持用最小的开销部署一个系统。这个被称为"[Atomic项目][5]"的计划还处于早期阶段,红帽公司准备首先将它部署在他的Fedora Linux发行版,仅仅当做对前沿技术的测试。
+
+### 2. Systemd ###
+
+引入systemd进程管理器可能引起系统管理员和Linux专家之间激烈的争论。systemd就被开发用于替代自专用Unix出现以来就在使用的init系统,它使得启动过程中装载服务更加高效。
+
+因为systemd可能会带来一些不适,红帽公司没有马上在RHEL上使用systemd。早在2010发布的Fedora版本15就已经包含了systemd作为默认项目,这给了红帽公司一次很好的了解systemd在真实世界的运行的经验。同样,systemd也没有孤立地加入RHEL 7,而是作为这个OS大计划的一部分。例如,红帽公司希望通过使用systemd加强对RHEL 7中Docker容器的支持。
+
+### 3. 默认使用 XFS ###
+
+第3个主要的改变是使XFS成为RHEL默认的文件系统,尽管这可能不那么引人瞩目。
+
+最初由Silicon Graphics International(硅谷图形公司)创建的XFS在Linux系统上用做生产环境已经很长时间了。在RHEL 7上它将支持高达500TB的文件系统。RHEL 6默认使用ext4,尽管它有XFS选项。红帽子的竞争对手Suse Linux [也支持XFS][6],尽管它安装时[默认使用ext3][7]。
+
+非常不幸的是,没有真正的方法可以将RHEL目前使用的其他文件系统,比如ext4或者btrfs移植到XFS。只能备份然后重建(来进行移植)。
+
+### 4. 兼容微软的身份管理 ###
+
+就算是那些不是微软系统粉丝的管理员也对微软目录服务保持一定的尊重。RHEL 7添加了两个关键的特性以优化处理微软目录服务(AD)的方式。跨域认证现在可以在RHEL 7和微软目录服务之间建立,所以目录服务用户可以直接访问Linux侧的资源,不需要再进行一次登录。RHEL 7另一个目录服务相关的附加特性,是基于DNS信息自动发现和加入目录服务(或者其他红帽子认证服务)。
+
+### 5. 性能监控(PCP:Performance Co-Pilot) ###
+
+进行性能调整的时候看不到实时数据就像是开着一辆挡风玻璃被刷上了油漆的车,所以RHEL 7添加了一个新的性能监控系统PCP([Performance Co-Pilot][8]),PCP最初由Silicon Graphics International(硅谷图形)[创建][9],但是现在它是RHEL 7的一部分。除了监控和记录系统状态,PCP还为其他子系统提供获取数据的API和工具集,比如正如你猜到的,刚刚介绍的systemd。
+
+遵循这个思路,另一个次要的附加特性:新的性能配置文件。RHEL 6已经有符合特殊应用场景的调整RHEL的配置文件。RHEL 7不仅默认有一个新的性能最大化的配置文件,而且包含另一个新的平衡性能表现和能源消耗的配置文件。
+
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via:http://www.infoworld.com/t/linux/keep-eye-these-5-new-features-in-rhel-7-244023
+
+译者:[love\_daisy\_love](https://github.com/CNprober) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.infoworld.com/t/linux/red-hat-enterprise-linux-7-beta-now-available-232520
+[2]:http://www.infoworld.com/t/application-virtualization/red-hat-fast-tracks-docker-apps-enterprise-linux-238122
+[3]:http://www.infoworld.com/t/application-virtualization/docker-unleashed-app-portability-gets-boost-231716
+[4]:http://www.infoworld.com/d/application-development/review-docker-10-ready-prime-time-243935
+[5]:http://www.projectatomic.io/
+[6]:https://www.suse.com/products/server/technical-information/
+[7]:https://www.suse.com/products/server/technical-information/
+[8]:http://developerblog.redhat.com/2013/11/19/exploratory-performance-pcp/
+[9]:http://oss.sgi.com/projects/pcp/index.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/20140626 Joy of Programming--Fail Fast.md b/published/20140626 Joy of Programming--Fail Fast.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..047cd1bf9d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140626 Joy of Programming--Fail Fast.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+编程的乐趣:快速终止!
+================================================================================
+
+
+> 当软件出现问题的时候,它应该以一种很容易引起注意的方式马上终止。这种“快速终止”的方式值得借鉴,我们会在这期专栏里谈谈这个重要的概念。
+
+一开始,“快速终止”看上去是一种会影响可靠性的不好的实践——为什么一个系统在还可以继续运行的时候要崩溃(或者说终止)?对于这个,我们需要理解,快速终止是和Heisenbugs(对于不易复现bug的一种称呼)紧密联系在一起的。
+
+考虑一下Bohrbugs(对于能够重现的bug的一种称呼),它们在一个给定输入的条件下总是会出现,比如,访问空指针。这类问题很容易测试、复现并修复。而如今,所有有经验的程序员应该都面对过这样的情形:导致崩溃的bug在重启软件后就不再出现了。不管花多少时间或努力去重现问题,那个bug就是跟我们捉迷藏。这种bug被称为Heisenbugs。
+
+花在寻找、修复和测试Heisenbugs上的努力比起Bohrbugs来说,要高出一个数量级。一种避免Heisenbugs的策略是将它们转化为Bohrbugs。怎么做呢?预测可能导致Heisenbugs的因素,然后尝试将它们变成Bohrbugs。是的,这并不简单,而且也并不是一定可行,但是让我们来看一个能产生效果的特殊例子。
+
+并发编程是Heisenbugs经常出现的一个典范。我们的例子就是一个Java里和并发相关的问题。在遍历一个Java集合的时候,一般要求只能通过Iterator的方法对集合进行操作,比如remove()方法。而在遍历期间,如果有另一个线程尝试修改底层集合(因为编程时留下的错误),那么底层集合就可能会被破坏(例如,导致不正确的状态)。
+
+类似这种不正确的状态会导致不确定的错误——假如我们幸运的话(实际上,这很不幸!),程序可以继续执行而不会崩溃,但是却给出错误的结果。这种bug很难重现和修复,因为这一类的程序错误都是不确定的。换句话说,这是个Heisenbug。
+
+幸运的是,Java Iterators会尝试侦测这种并发修改,并且当发现时,会抛出异常`ConcurrentModificationException`,而不是等到最后再出错——那样也是没有任何迹象的。换句话说,Java Iterators也遵从了“快速终止”的方法。
+
+如果一个`ConcurrentModificationException`异常在正式版软件中发生了呢?根据在Javadoc里对这个异常的说明,它“只应该被用于侦测bug”。换句话说,`ConcurrentModificationException`只应该在开发阶段监听和修复,而不应该泄漏到正式代码中。
+
+好吧,如果正式软件确实发生了这个异常,那它当然是软件中的bug,应当报告给开发者并修复。至少,我们能够知道曾经发生过一次针对底层数据结构的并发修改尝试,而这是软件出错的原因(而不是让软件产生错误的结果,或是以其他现象延后出错,这样就很难跟踪到根本原因)。
+
+“防止崩溃”的途径就意味着开发健壮的代码。一个很好的编写容错代码的例子就是使用断言。很可惜的是,关于断言的使用有大量不必要的公开争论。其中主要的批评点是:它在开发版本中使用,而在发布版中却被关掉的。
+
+不管怎么样,这个批评是错误的:从来没有说要用断言来替代应该放到发布版软件中的防御式检查代码。例如,断言不应该用来检查传递给函数的参数是否为空。相应的,应该用一个if语句来检查这个参数是否正确,否则的话抛出一个异常,或是提前返回,来适合上下文。然而,断言一般可以用于额外检查代码中所作出的假设,这些假设应该一直为真才正常。例如,用一个语句来检查在进行了入栈操作后,栈应该不是空的(例如,对“不变量”的检查)。
+
+所以,快速终止,随时中断,那么你就走在开发更加健壮代码的道路上了。
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via:http://www.opensourceforu.com/2011/12/joy-of-programming-fail-fast/
+
+译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025) 校对:[ReiNoir](https://github.com/reinoir)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:
+[2]:
+[3]:
+[4]:
+[5]:
+[6]:
+[7]:
+[8]:
+[9]:
+[10]:
+[11]:
+[12]:
+[13]:
+[14]:
+[15]:
+[16]:
+[17]:
+[18]:
+[19]:
+[20]:
diff --git a/published/20140630 How to access popular search engines from the command line on Linux.md b/published/20140630 How to access popular search engines from the command line on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b56cd66aa9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140630 How to access popular search engines from the command line on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
+主流搜索引擎闯入Linux命令行世界
+================================================================================
+(LCTT译注:这里,我们姑且认为您身处能够访问Internet的地方!)
+
+为什么会有人要从终端搜索互联网上的东西?我不清楚,这里头可能有许多的原因。但是,因为没人要求答案总比没人知道答案少令人失望一点。这里,列出了一些流行的搜索引擎的命令行工具,可以让你们通过Linux终端来访问它们。
+
+### 1. Google ###
+
+让我们从一个巨头开始吧:Bing!好吧,只是开个玩笑,事实上应该是Google。坦白讲,你根本不需要使用命令行工具来进行Google搜索。只需要简简单单的一个命令:
+
+ $ xdg-open https://www.google.com/search?q="[query]"
+
+
+它会打开网页浏览器,并转到合适的搜索页面。然而,如果你想要的是从终端窗口查看搜索结果,而不是打开什么网页浏览器,那么我推荐你使用[cli-google][1]。它是一个超级老古董了(最后一次更新是在2009年),但我喜欢它。这是一个简单而直接的应用,它会忠实地干好它应该干的事。
+
+安装完cli-google后,你就可以开始用它来搜索了,它的输出是那样的五彩斑斓。你也可以调整搜索结果的数量和你想要的语言,你只需要在终端中敲入:
+
+ $ google
+
+就可以看到所有的选项了。
+
+
+
+### 2. YouTube ###
+关于Google,有太多的东西要放进列表来。我会尽量简明扼要,但绝不会放过该有的。对于许多人而言,YouTube是他们快速查找相关内容视频的首选。要在终端中完成此事,我则钟情于[mps-youtube][2]。这个软件可以让你在终端中搜索、下载视频,创建播放列表,以及查看关于视频的评论。安装完mps-youtube后,你可以使用下面的命令来启动:
+
+ $ mpsyt
+
+然后,输入 h 来查看选项。要查看简明用法,你可以像下面这样:
+
+ /[query]
+
+来搜索你想知道的一切,然后输入视频的编号来听听它的声音,或者输入:
+
+ i [video-number]
+
+来看看相关信息,也可以输入:
+
+ d [video-number]
+
+来下载它。如果你觉得光听还不过瘾,这里还有更好玩的:
+
+ set player mplayer
+ set show_video True
+
+现在,你可以在另外一个窗口里头用mplayer来播放视频了。
+
+
+
+### 3. 维基百科 ###
+与Google一样,对于维基百科,我也喜欢一个古老的脚本,它干的不赖:[cliWiki][3]。安装完后,赶紧运行一下看看:
+
+ $ cliwiki
+
+然后,你就可以输入你想要搜索的内容了。如果有直接匹配的条目,终端中就会显示相关页面了。哈,输出内容可真够长的,建议你还是用less命令来看吧。当然,这不是最高效的方法,但你的母的只是想要查看与关键词相关的文本,那这就是你想要的。
+
+
+
+### 4. 海盗湾 ###
+现在,让我们聊聊龌龊的东西。网上有很多意想不到的(也许你不觉得)工具,可以帮助你在命令行下查找海盗湾上的种子。而在这其中,[pirate-get][4]是我的最爱。它里面蕴藏了大量的选项,你可以通过下面的命令来发现它们:
+
+ $ pirate-get -h
+
+但是还是简单一些吧:
+
+ $ pirate-get --color -c [category] [query]
+
+以上命令会返回与查询内容相关的特定搜索类目中的结果,输出结果也是彩色的!那里头,程序会提示你输入你想要的结果的编号,输入后就可以从磁链上下载种子了。简单又容易,仅限于没有版权的资料哦!
+
+
+
+### 5. Twitter ###
+Twitter是迎合潮流的一个很好的搜索引擎。我们已经在[如何在命令行中访问Twitter][5]一文中介绍了它的用法,但是我个人更喜欢[TTYtter][6]。该工具及其强大,它应该有它自身的一席之地,而不再仅仅用于简单搜索了。但在这里,我只想把它当作搜索引擎使用。安装并配置完后,你就可以登陆进去,并使用下面的命令来搜索了:
+
+ /search [query]
+
+界面在视觉上有点粗糙,但是你很快会习惯的。注意,这里头只能用普通的文字,也可以用哈希标记。
+
+
+
+最后来小结一下吧,这里列出了我认为人们使用最多5大搜索引擎,这些搜索引擎都可以通过命令行来访问。这里Google图像和Google地图可能缺席了,但我想这些可能不能很好适应控制台环境吧。我也想要寻找一个音乐搜索引擎,但是没有找到对于本列表“有价值的”。就像你可能已经注意到的那样,列表中的工具在功能和选项上是良莠不齐的:其中一些很简单,而另外一些则功能很复杂。但不管怎么说,最后它们都还是完成了它们的任务。
+
+列表中错失了哪些搜索引擎?你还知道哪些没有提到过的工具呢?请在文章评论中告诉我们吧。
+
+----------
+
+#### Adrien Brochard ####
+
+我是一位来自法国的Linux爱好者。在尝试了多个发行版后,我最后认可了Archlinux。然而,我一直在试着通过积累一些知识和技巧来改善我的系统。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/06/access-popular-search-engines-command-line-linux.html
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://github.com/henux/cli-google
+[2]:https://github.com/np1/mps-youtube
+[3]:https://github.com/AnirudhBhat/cliWiki.py
+[4]:https://github.com/vikstrous/pirate-get
+[5]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/access-twitter-command-line-linux.html
+[6]:http://www.floodgap.com/software/ttytter/
diff --git a/published/20140630 KDE Connect Adds Android File Sending, Touchpad Emulation.md b/published/20140630 KDE Connect Adds Android File Sending, Touchpad Emulation.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0ff2f836a6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140630 KDE Connect Adds Android File Sending, Touchpad Emulation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+KDE Connect增加了安卓文件发送、触摸板模拟等功能
+================================================================================
+
+
+
+通过安卓版的KDE和Plasma Desktop可以将所连接设备的触摸屏当作电脑的触摸板使用。(注:Plasma 是KDE项目提供的所有图形环境总称。目前有三个Plasma子项目:Plasma Desktop用于传统的桌面电脑和笔记本电脑、Plasma Netbook用于上网本,以及Plasma Active用于平板电脑。)
+
+这个新附加的无线输入设备可以作为一般的鼠标使用,不过仍然不支持像双指划动或双指右击这样的多点触摸。(LCTT译注:双指右击指在触摸板上双指同时双击,代表鼠标右键点击)
+
+安卓的共享方式现在支持KED Connect,允许你从安卓发送文件到你的桌面,也可以通过Dolphin文件管理的菜单或者用命令行推送文件的方式,从桌面发送文件到安卓。
+
+在[iOS 8 和 OS X Yosemite][1]、 [Android ‘L’ 和 Chrome OS][2]上的类似支持,计划在这个秋天首次亮相。
+
+本次更新的版本修复了很多的漏洞,包括很多的改进和对FreeBSD系统的支持。
+
+完整的特性如下:
+
+- 在安卓和KDE之间共享文件
+- 用平板电脑模拟触摸板
+- 在桌面接收来自安卓4.3以上版本的通知
+- 共享剪切板支持手机和PC之间的拷贝、粘贴
+- 可以遥控桌面上选定的媒体播放器
+- 电池状态
+- WI-FI连接共享
+- RSA加密
+
+### KDE Connect 0.7版下载 ###
+
+从Google Play和F-Droid商店可以免费下载到KDE Connect Android的应用。
+
+- [ 从Google Play下载KDE Connect][3]
+
+为了能用到这些最新特征,你需要安装Plasma的最新版本KDE Connect(0.7版)。撰写本文时,还没有提供deb安装包和PPA源。不过可以在Kubuntu 14.04 LTS上通过安装源码来安装,或用以下介绍方式[戳这里][4]。
+
+- [下载KDE Connect 0.7源代码][5]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+点击: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/06/kde-connect-android-notifications-linux-desktop
+
+译者:[bookjoy](https://github.com/bookjoy) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/06/os-x-10-10-feature-ubuntu-already
+[2]:http://www.omgchrome.com/android-apps-notifications-call-alerts-chromebook/
+[3]:https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.kde.kdeconnect_tp
+[4]:https://albertvaka.wordpress.com/2014/06/28/awesome-contributions-to-kde-connect/#comment-1175
+[5]:http://download.kde.org/unstable/kdeconnect/0.7/src/kdeconnect-kde-0.7.tar.xz.mirrorlist
diff --git a/published/20140630 New Linux Podcast App 'Vocal' Hits Beta, Ready for Testing.md b/published/20140630 New Linux Podcast App 'Vocal' Hits Beta, Ready for Testing.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..68ae48fdb2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140630 New Linux Podcast App 'Vocal' Hits Beta, Ready for Testing.md
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+Linux 播客软件‘Vocal’进入Beta阶段,准备测试
+================================================================================
+**在四月份我们就被一款叫做['Vocal'][1]的Ubuntu下的播客软件吸引了,但它从一个漂亮的草图到能真正可用,还有一段路要走,而你则可以帮助我们测试一下Vocal。**
+
+该软件的开发者,Nathan Dyer已经完成了一个beta版本,仍然不够稳定,其中还有很多功能也未完成,但它已经可以通过专用的PPA在Ubuntu 14.04 LTS以及14.10版本下进行测试了。
+
+新闻的发布者宣称,这个beta版本只能**安装在下一代Elementary OS桌面的系统中**。并且自从Elementary OS不再为用户提供官方的Beta预览版后,让测试这事更加的麻烦了。
+
+对于Unity、GNOME或者KDE来说试试也许并不太难,我想大概。如果你是Ubuntu的用户,想要试用Vocal,首先得安装不稳定版的Elementary OS的PPA,通常我们都不是很建议这样做。
+
+Dyer建议感兴趣的用户等待下一代的Elementary OS桌面的beta版本开发完毕吧。
+
+现在,我们只能望梅止渴了。
+
+
+
+Vocal Beta 在 Elementary OS中(图: Dyer)
+
+因为Vocal是开源的,那将没有任何东西能阻挡它被完美的移植到类似Unity的主流Linux桌面系统中。
+
+了解更多请访问[开发者的Blog][1]、[查看最新版本][2]或者在Launchpad.net上[查看Vocal的最新信息][3]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/06/linux-podcast-app-vocal-hits-preview-kicker
+
+译者:[nd0104](https://github.com/nd0104) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/04/vocal-podcast-manager-linux
+[2]:http://nathandyer.me/2014/06/28/vocal-beta-released-daily-ppa-available/
+[3]:https://launchpad.net/~nathandyer/+archive/vocal-daily
+[4]:https://launchpad.net/vocal
diff --git a/published/20140630 Ubuntu 14.04 LTS--Customizing Unity.md b/published/20140630 Ubuntu 14.04 LTS--Customizing Unity.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..eb3726fe6f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140630 Ubuntu 14.04 LTS--Customizing Unity.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+Ubuntu 14.04 LTS: 定制 Unity
+================================================================================
+虽然Unity桌面管理器自从伴随 Ubuntu 11.10首次发布以来表现出了强劲的性能,并在可用性上迈进了一大步,但是有人对自定义其外观和行为所带的限制感到反感。我们现在来看看如何自定义Unity,让你重拾自己掌控桌面的感觉。
+
+### Unity中的可用定制项目 ###
+
+在ubuntu 14.04中,Unity 有一些以前没有的可定制项。登入你的 Unity,进入“设置”并选择“显示”,你将看到以下画面:
+
+
+
+Ubuntu 14.04 LTS 显示和 Unity 设置
+
+你看到的大多数项目相比 Ubuntu 11.01 而言都是新的,而且一些相比较上一个版本的 Ubuntu13.10 也是新的。从Ubuntu13.10开始,Ubuntu加入了可以改变菜单栏和标题栏大小的新特性。
+
+Unity中所特有的一个特性是我们能够打开或者关闭的“粘性边缘”功能,它能让你的鼠标停止在多显示器组的每个屏幕的边缘,它使光标暂时停在边缘,仿佛是鼠标卡住了一样,我们可以选择关闭它。(LCTT译注,其实我觉得挺有用的,可以避免无意中切换到其他工作桌面,不要关闭)
+
+在“设置”中选择“外观”选项,可以看到如下画面。
+
+
+
+Ubuntu 14.04 LTS 显示和Unity设置
+
+这里我们可以看到一个人们最渴望在 Unity 启动器栏中包含的功能-能够改变启动器大小。虽然在Ubuntu 11.10及以后的各种版本中可以通过多种方法实现这个特性,但将其放入外观设置中使其显得更加正式。我喜欢它能将启动器图标缩小直至16的功能(我们接下来所要讲到的工具仅能支持最小调至24)。
+
+### Unity Tweak Tool-强大! ###
+
+在Unity首次伴随Ubuntu 11.10发布的几天之内这款工具就跟着出现了,只是你得大费周折去自己把它安装好而且在Unity升级时它可能会损坏。
+
+然而现在它被正式添加进了Ubuntu的默认软件仓库并且会在Unity更新时同时更新。它附带大量的定制项,那么我们就来安装它吧:
+
+ sudo apt-get install unity-tweak-tool
+
+安装好,启动后你将看到如下画面:
+
+
+
+正式的Unity Tweak Tool
+
+这款工具它集大量Unity桌面定制项目于一体。这些定制项大多能通过默认的Unity设置,命令行操作或者是即使是编辑有时候也很难寻找到的配置文件来实现。
+
+我们可以改变启动器栏,网页小程序和面板的行为,可以在Unity菜单中搜索等等。所有的都通过着一个工具来实现。花些时间去挖掘适合你的选项-Unity Tweak Tool-学习它,和它一起生活,爱上它(如果你使用Unity,这是起码的)
+
+### 结尾的一些想法 ###
+
+Ubuntu 14.04 LTS 越来越被人们视作Linux上的典型的Desktop,(对不起,Canonical,你还没有摆脱Linux身份),Linux Desktop不仅可以作为偶尔使用Linux的那些人(的确有这样的事)的选择,也适用于骨灰级linux专家。
+
+比之前没有工具,功能可以定制,或是通过配置文件修改定制但是有可能被之后个更新所破坏,现在对于Unity桌面我们就拥有了更多的控制权。Unity桌面性能强劲可靠,又通过Unity Tweak Tool加入一些特色元素,使得它的外观也酷极了!!!
+
+请给我们你的想法或者点击链接发表你对Unity桌面的评论,我们将有兴趣知道你是如何使用Ubuntu 14.04 LTS 的。
+
+
+----------
+
+#### Terrence T. Cox ####
+
+开发者,Linux倡导者,开源爱好者。 进入这个技术领域很久,被认为经验丰富,但从未感到厌倦。
+[Twitter][1]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://linuxacademy.com/blog/linux/ubuntu-14-04-lts-customizing-unity/
+
+译者:[Love-xuan](https://github.com/Love-xuan) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://twitter.com/mourngrymtc/
diff --git a/published/20140701 Command Line Tuesdays--Part Two.md b/published/20140701 Command Line Tuesdays--Part Two.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6f1113c7cd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140701 Command Line Tuesdays--Part Two.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+命令行星期二 —— 第二篇
+================================================================================
+Hi,极客们!
+
+让我们来更新一下我们的记忆。[上周][1],我们学习了一些基础命令,了解了shell是什么,同时介绍了我们CLI的星期二系列。
+
+今天的菜单将提供点别的东西:通过文件系统导航。
+
+现在,我设法找到最好的图片是从一个叫[devopsbootcamp][2]的网站。你可以在上面找到他们其余的教程。但无论如何,这是一个关于Linux根文件系统的看起来非常不错的图。
+
+
+
+例如,在上面的图片说明中,你的用户目录(你通常用来存储你的电影,音乐,文档等)是位于/home文件夹下。 /home文件夹位于/。然后,/下有个 /etc 文件夹,其中文件大部分为配置文件。无论如何,你可以在这里找到详细的描述,因为我们将进入这些文件夹来了解他们的功能,直到我们开始使用和配置它们。今天是仅用于导航。而关于这一点,让我们来开始今天的第一个命令...
+
+### pwd ###
+
+pwd,或者 ‘Print Working Directory’,当你觉得在文件丛林之中迷失了方向时是一个非常有用的命令。在任何给定时刻,键入pwd命令,瞧!这是你到达这个文件夹的完整路径。在电影《异次元杀阵(The Cube)》里的那些家伙总在用它,这些笨蛋!
+
+
+
+
+想象一下,自己在一个巨大的公寓里面从一个房间走到另一个房间房间,迷路了。 pwd就像面包屑指引着你到你的出发点,这样你就不会在文件夹迷宫里面失去你的方向!
+
+
+
+### cd ###
+
+现在你学习了如果想知道自己在哪个目录的pwd命令的用法。现在,你要做的下一步骤就是移动到另一个目录。比方说,你在你的home文件夹下有一个文件夹(目录),你要将你的绝密的东东放到里面。要这样做,你需要使用用'cd'命令。 cd,或‘Change Directory’,将改变所处目录的位置。你怎么使用它呢?简单,键入cd和你的文件夹路径。比方说,例如,你想从你的主文件夹进入你的Hello Kitty图片集。你输入‘cd /home/username/Hello\ Kitty’。
+
+正如你看到的,我们并没有只使用文件夹名称的空格键。这是因为终端将无法识别它。每当你要导航到它的名称中有空格的文件夹,你**用反斜杠字符,后跟空格**代替它。您也可以不使用反斜杠+空格选项,只是把**整个文件夹名称加引号**,例如,cd /home/username/ "Hello Kitty"。
+
+
+
+自己尝试一下。使用cd导航到不同的目录,同时,键入pwd命令,看看一切工作是否如期望的那样。
+
+### 肖茨先生的快捷键 ###
+
+肖茨先生提醒我们也有一些可用的快捷键。
+
+如果你仅键入cd,不带路径,你的终端将从你的工作目录(无论是不是)切换到你的/home文件夹。
+
+同样地,如果你键入 cd `~user_name` 它会带你到你指定的特定用户的主文件夹。
+
+### 下周 ###
+
+下周,我们将进入到下一章 - 我们将学习如何列出文件和目录,查看文本文件和文件的内容,因此会比之前我们已经学习的有更多的工作,但我希望你将会有足够的时间。一条命令又一条命令,如果你没有时间自己学习的话,那让我们在几个月内一起学习基础知识吧!
+
+同时,记得...
+
+### …玩得开心! ###
+
+P.S.:感谢bwl的评论,我们修正了一个在目录名称中包含空格的文本的一个错误。
+
+P.P.S:GreatEmerald还增加了有关文件层次结构的一些新信息。您可以在[意见][3]中阅读。
+
+感谢你们的贡献和更正
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://news.opensuse.org/2014/06/24/command-line-tuesdays-part-two/
+
+译者:[乌龙茶](https://github.com/yechunxiao19) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://linux.cn/article-3300-1.html
+[2]:http://devopsbootcamp.readthedocs.org/
+[3]:https://news.opensuse.org/2014/06/24/command-line-tuesdays-part-two/comment-page-1/#comment-99186
diff --git a/published/20140701 Here Are 5 Amazing Ascii Art Generators.md b/published/20140701 Here Are 5 Amazing Ascii Art Generators.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..010b688802
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140701 Here Are 5 Amazing Ascii Art Generators.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+五个超赞的字符艺术生成器!
+================================================================================
+
+
+ASCII是一个非常吸引人的字符编码系统,在计算机,通讯设备,以及其他设备中,通过它来用代码表示字符。新生代的人可能会觉得它已经过时了,但是那些熟悉它的人会懂得ASCII是多么的独特。我们在这里为你准备了五个超赞的ASCII字符艺术生成器。
+
+### 1.[GlassGiant ASCII Art][1] ###
+
+这个小程序可以把图片转换成ASCII文字艺术-一堆胡乱堆在一起的文字,数字和符号,看上去没有任何意义,直到你往后站一步去看完整的画面。它也没有什么实际的用途,只是看上去非常简洁灵巧。
+
+### 2.[ASCII Art Generator][2] ###
+
+ASCII字符艺术是一种在电脑上把可打印字符作为图片元素来拼接展现一幅图像的艺术活动。你所需要做的只是上传你的图片,然后它会帮你转成ASCII字符艺术。
+
+### 3.[Ascii.mastervb][3] ###
+
+ASCII字符艺术来源于7比特ASCII字符标准。ASCII字符艺术曾经在70-80年代很流行。在那个时候,计算机系统都还是基于字符的。这个程序可以非常快地把图片转换成ASCII字符。
+
+### 4.[IMG2TXT][4] ###
+
+这个脚本可以将GIF,JPG或PNG的链接转换成ASCII字符或是带颜色的HTML。
+
+### 5.[picascii][5] ###
+
+它可以把图片转换成ASCII文本或是HTML。要做转换,你只需要输入链接地址或是选择一张你电脑上的图片(gif/jpeg/png)。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=142480
+
+译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://glassgiant.com/ascii/
+[2]:http://www.ascii-art-generator.org/
+[3]:http://ascii.mastervb.net/
+[4]:http://www.degraeve.com/img2txt.php
+[5]:http://picascii.com/
diff --git a/published/20140701 How To Add Multiple Timezones In Ubuntu 14.04 [Quick Tip].md b/published/20140701 How To Add Multiple Timezones In Ubuntu 14.04 [Quick Tip].md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..48fae9f0be
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140701 How To Add Multiple Timezones In Ubuntu 14.04 [Quick Tip].md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+[小白技巧]如何在Ubuntu 14.04中添加多个时区时间
+================================================================================
+如果你需要和多时区时间打交道的话,你一定希望你的电脑时钟可以显示多个时区的时间。作为一个移居国外的人,我需要关注法国和印度的时间。在Ubuntu系统中,你可以进行简易的设置来添加多时区时间。
+
+在这次的使用技巧中,我们会了解到 **如何在Ubuntu 14.04系统中添加多时区时间**。
+
+### 在Ubuntu 14.04系统中添加多时区时间 ###
+
+打开系统设置(按下标有微软徽标的按键,在Dash中搜索“系统设置”),进入“时间&日期”选项。
+
+接下来,进入**时钟**标签页,找到**其他时区时间**选项,然后点击**选择地区**按钮。
+
+
+
+在新打开的窗口中,你可以**输入一个地区**,之后相应的结果会在下面显示出来。选择你想添加的地区,然后**点击下面的加号标志(+)**来添加。
+
+
+
+完成了这些工作之后,你就可以在系统时钟处看到其他地区的时间了。
+
+
+
+体验下Ubuntu多时区时钟给你带来的便捷吧。:)
+
+----------
+
+
+
+#### 关于 Abhishek ####
+
+我叫Abhishek Prakash,是It's F.O.S.S的创始人。我获得了通信系统工程硕士学位。我是一个狂野的Linux爱好者和开源痴迷者。我在使用Ubuntu系统并且希望和大家分享知识和经验。出了Linux,我还很喜欢经典侦探悬疑电影。我是阿加莎-克里斯蒂的超级粉丝。你可以在[Google Plus][g]上添加我到你的好友圈,也可以[在twitter上关注 @abhishek_pc][t]。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://itsfoss.com/add-multiple-timezones-ubuntu-1404/
+
+译者:[JonathanKang](https://github.com/JonathanKang) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[g]:https://plus.google.com/u/0/110180944531110746460
+[t]:https://twitter.com/abhishek_pc
diff --git a/published/20140702 Automotive Grade Linux Released for Open Source Cars.md b/published/20140702 Automotive Grade Linux Released for Open Source Cars.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cdd5a9a454
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140702 Automotive Grade Linux Released for Open Source Cars.md
@@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
+安装体验开源车载系统Automotive Grade Linux
+================================================================================
+> Linux基金会和他的合作伙伴本周发布了Automotive Grade Linux的第一个版本,这是一个在连网汽车内部使用的开源平台。
+
+
+
+随着本周 [Automotive Grade Linux][1](AGL)的第一个版本的发布,这个在物联网时代专为汽车定制的Linux发行版将转变为一个新的生态系统。
+
+AGL是由Linux基金会发起的合作项目,Linux基金会汇集了来自汽车行业,通信,计算硬件,学术界和其他领域的合作伙伴。AGL的第一个版本于6月30号发布在网上并且在可[免费下载][5],这个开源操作系统基于[Tizen IVI][4]。Tizen IVI是一个基于Linux的平台,它被用于为广泛的设备提供操作系统解决方案,从智能手机,到电视,汽车,笔记本电脑。
+
+
+
+在第一个版本中,AGL提供了一系列的功能和为汽车(或其他车辆)部署定制的应用程序,包括:
+
+- 主屏幕
+- 仪表盘
+- 谷歌地图
+- 暖通空调
+- 媒体回放
+- 新闻阅读器
+- 音响控制
+- 蓝牙手机
+- 智能设备连接集成
+
+Linux基金会和他的参与AGL项目的合作伙伴希望这个解决方案将帮助确保未来“连网汽车”使用开源软件以提供下一代娱乐,导航和其他车内使用的工具。“公开和合作是促进一个公共的,标准的汽车平台发展的关键,以便这个产业可以更快速地实现供连网汽车使用的愿望。”Linux基金会的汽车总经理Dan Cauchy这样说。
+
+Cauchy补充道,Linux基金会期望AGL是一个良好的开端,其合作者希望在以后的版本中能加入“一些额外的功能和特点。”
+
+## 下载和安装测试 ###
+
+### 下载 ###
+
+可以从此下载镜像:http://content.linuxfoundation.org/auto/downloads/images/
+
+支持在PC上测试,也提供了Vmware镜像。
+
+### 安装在X86上 ###
+
+**创建一个USB启动盘**
+
+1. 下载GPartd Live 镜像的压缩文件:http://gparted.sourceforge.net/download.php 。
+2. 使用FAT32文件系统格式化一个最少8GB的U盘。
+3. 解压 GPartd Live镜像的压缩包,并复制全部内容到U盘。保持完整的目录格式,比如你可以确认GPL这个文件是不是在U盘的根目录。
+4. 把U盘变成可启动的,根据你使用的系统不同而不同:
+ a) Linux: 执行U盘里 utils/linux 目录下的 makeboot.sh 。
+ b) Windows: 执行U盘里 utils\win32 目录下的 makeboot.bat 。
+5. 按 脚本提示执行。
+6. 复制 [AGL 演示镜像][6]到U盘。
+
+**安装到机器上**
+
+注意:这会破坏你的机器上的所有数据!所以请确保机器上的硬盘上的数据是无用的。
+
+1. 使用刚刚制作好的 GPartd U盘启动系统。
+2. 默认运行 GPartd (所有选项直接回车确认即可)
+3. 打开一个终端,并复制镜像内容到机器的硬盘:
+ gunzip -c agl-demo_1-0.img.gz | dd of=/dev/sda bs=16M
+4. 关闭终端。
+5. 在 GPartd 窗口,刷新设备。
+6. 将 /dev/sda3 的大小扩展到整个硬盘的可用空间。
+7. 关机。
+8. 拔下U盘。
+9. 重启!
+
+
+### 创建VMware虚拟机 ###
+
+在 64位Windows 7和32位Windows XP上的 VMware Player 5 测试通过。
+
+1. 下载 VMWare Player: http://www.vmware.com/products/player
+2. 解压缩 [AGL VMWare image][7]
+3. 在 VMware 中增加新的虚拟机:
+
+ 1. 选择“我将稍后安装操作系统”
+ 2. 使用 'Linux' -> 'Fedora'
+ 3. 给个名字,比如: tizen-ivi-2.0
+ 4. 创建一个新的磁盘,不过这个磁盘我们稍后会删除并重建一个新的
+ (将\ 作为 IDE(0:0) 设备添加)
+ 5. 创建好虚拟机之后,然后“编辑虚拟机设置”
+ 6. (可选)取消CD/DVD的“启动后连接”的选项(除非你的宿主机上有这个设备)
+ 7. (可选)取消打印机的“启动后连接”的选项
+ 8. 删除虚拟机当前的硬盘
+ 9. 添加一个新的硬盘
+ 10. 选择“使用已有的虚拟磁盘”,使用那个解压缩得到文件
+ 11. 当第一次启动虚拟机时,如果询问你是否要升级当前格式时,选择“保持现在的格式”
+4. 运行:
+ 1. 启动虚拟机
+ 2. 系统启动后显示一个黑屏,在桌面上任何地方右键点击并打开一个终端
+ 3. 运行如下命令
+ ./start_demo.sh
+ 这会调整屏幕分辨率,打开声音,启动node.js引擎,并最终显示界面。
+
+### 更多的演示截图 ###
+
+请参看我们之前的一篇文章:http://linux.cn/article-3324-1.html
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/070114/automotive-grade-linux-released-open-source-cars
+
+译者:[linuhap](https://github.com/linuhap) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://automotive.linuxfoundation.org/
+[2]:http://linuxfoundation.org/
+[3]:http://automotive.linuxfoundation.org/
+[4]:https://www.tizen.org/
+[5]:http://automotive.linuxfoundation.org/node/add/downloads
+[6]:http://content.linuxfoundation.org/auto/downloads/images/agl-demo-x86-1.0.img.gz
+[7]:http://content.linuxfoundation.org/auto/downloads/images/agl-demo-vmware-1.0.vmdk.bz2
+
diff --git a/published/20140702 Command Line Tuesdays--Part Three.md b/published/20140702 Command Line Tuesdays--Part Three.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5f7478e869
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140702 Command Line Tuesdays--Part Three.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+命令行星期二 —— 第三篇
+================================================================================
+今天,肖茨先生将带领我们游历文件系统的第一部分。我们将学到如何访问、列出目录内的文件,以及首次介绍一些选项的运用。OK,让我们开始学习这周的第一个命令。
+
+### ls ###
+
+ls 是一个用来列出目录内文件的命令。通过添加**选项**来实现多种不同的用途。简单起见,你可以只需键入 ls 。但是,你也可以在命令后面添加一个选项,它会帮助你修饰你的命令。如果你想要随意摆弄一些信息时,这会帮到你的。举例来说,当你要从一个命令的大量输出中找寻指定信息,你可以用选项缩小范围来实现。
+
+这就是选项的基础概念。我们可以用下面书写格式表示:
+
+ command(命令) -option(选项) argument(参数)
+
+命令,恩...,我们可以输入 pwd、 ls, 或者我们到目前为止所有学过的命令。
+
+以上我们已经阐述了选项的目的。但是我们需要注意一下书写格式:在前头添加一个破折号。所以,如果选项为 l, 你需要在命令后键入**-l**。
+
+**参数**是一个命令的操作对象(在这个例子中,它是一个目录,我们将会学到如何浏览它们)。
+
+接着,让我们尝试在主目录里尝试用 ls 命令列出 /etc 目录内容。这次我们先不添加选项。
+
+
+
+就这样,列出了一大堆的文件。它们还根据颜色进行了分类。蓝色的是目录,白色的为普通文件,绿色的似乎是某种 shell 脚本文件。除此之外,还有其他不同的颜色来代表不同的文件类型。
+
+接下来,你可以在刚才的命令里添加 -l 选项。添加选项 -l 后也会列出同样的文件和目录,但是以长格式方式输出。如果你需要查看更多信息的话,这个选项将是不错的选择。
+
+
+
+### 长格式 ###
+
+这样,用了长格式后,你可以看到更详细的信息,以及在每行开头类似-rw-r--r-- 令人抓狂的标示。实际上,这只是一种组合,代表了各种意义的信息。
+
+
+
+(File Name)就是文件的名称。(Modification time)是文件最后修改的时间。(Size) 用 byte 计量的文件大小。(Group) 是组的名称,和拥有者一起构成文件权限。(Owner) 是文件拥有者的名称。最最重要的…
+
+###…文件权限 ###
+
+文件权限在长格式每一行的开端都显得非常的杂乱。第一个字符代表文件类型。如果是 'd' , 意味着它是一个目录。如果是 '-' , 意味着它是一个一般文件。接下来的三个字符分别代表拥有者的可读, 可写 ,可执行的权限。再接着三个字符表示组成员的享有的文件权限,而最后三个字符表示其他人(既不是拥有者也不是同组)对文件的享有权限。
+
+例如,如果有个文件在长格式下显示为:-rw-r--r--, 这说明这是个普通文件(首字符 '-'),拥有者享有可读可写权限,但是没有可执行权限,导致拥有者无法执行该文件(首字符'-'后'rw-'),用户组和其他用户只享有可读权限(你不难发现'r--'字段在后面出现了两次 。如果用户组是 'rwx' 而不是 'r-',则意味着它们可读,可写,可执行)。
+
+ls 的下个选项是 ls -la .. ,-a 它会列出所有的文件,包括隐藏文件。在通常情况下,隐藏文件是不可见的。用长格式列出当前工作目录下的父目录的所有文件。
+
+### less ###
+
+less 是一个可以显示你的文本文件的命令。举例来说,你要在 /etc 下找寻名为 os-release 的文本文件。你可以使用 ls /etc 成功实现,而现在你想要阅读它的内容。
+
+你只需要使用 less /etc/os-release。
+
+
+
+..就这样了。
+
+你要如何控制 less 呢?
+
+简单的, 你只需要动动键盘就行了!
+
+less 一次只会显示一个页面的文本。往前翻页你需要按 **Page Up**, 或者 **'b'**。往后翻页你可以按**Page Down**, 或者 **空格**。大写的**G**会跳转到文本的末尾,**1G**会跳转到文本的开端。**/字符**会在文本内搜索指定字符(例如,如果你输入 /suse ,它会找寻所有文本含有的 suse 并标记出来)。n 会重复执行你的搜索,**h**会显示所有的选项(h,即帮助的意思)。
+
+
+
+按q退出 less 命令。
+
+### file ###
+
+file 会显示文件的类型,是否是你要找的 ASCII 文本,还是 jpg 图片,bash 脚本等。让我们用 /etc/os-release 执行练习。
+
+
+
+这样,如你所见,os-release 是一个 ASCII 文本文件。 请尝试其他文件,并观察结果。
+
+下回见了,记住…
+
+…一定要玩的开心啊!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://news.opensuse.org/2014/07/01/command-line-tuesdays-part-three/
+
+译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20140702 How to check MySQL storage engine type on Linux.md b/published/20140702 How to check MySQL storage engine type on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ef16572047
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140702 How to check MySQL storage engine type on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+[小白技巧]如何在Linux上检查MySQL数据表的存储引擎类型
+================================================================================
+> **提问**: 我想要知道我的MySQL数据库是MyISAM还是Innodb类型。我该如何检查MySQL数据库表的类型?
+
+MySQl主要使用两种存储引擎:**MyISAM 和 Innodb**。MyISAM是非事务的,因此拥有读取更快,然而InnoDB完全支持细颗粒度的事务锁定(比如:commit/rollback)。当你创建一张新的MySQL表时,你要选择它的类型(也就是存储引擎)。如果没有选择,你就会使用与预设置的默认引擎。
+
+如果你想要知道已经存在的MySQL数据表的类型,这里有几种方法达到。
+
+### 方法一 ###
+
+如果你可以访问phpMyAdmin,你可以从phpMyAdmin找出默认的数据库类型。从phpMyAdmin中选中数据库来查看它的表列表。在“Type”一列的下面,你会看到每个表的数据表类型。
+
+
+
+### 方法二 ###
+
+如果你可以直接登录MySQL服务器,另外一种鉴别存储引擎的方法是登录MySQL服务器后运行下面的MySQL命令:
+
+ mysql> SELECT ENGINE FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = 'my_database' AND TABLE_NAME = 'my_table';
+
+上面的命令会显示在'my_database'数据库中'my_table'表的引擎类型。
+
+### 方法三 ###
+
+还有一种检查引擎的方法是使用mysqlshow,是一种命令行下的显示数据库信息的工具。mysqlshow在[MySQL 客户端安装包][1]中有。要使用mysqlshow,你需要提供MySQL服务器登录凭据。
+
+下面的命令会显示特定的数据库信息。在“Engine”一列下面,你可以看到每个表使用的引擎。
+
+ $ mysqlshow -u -p -i
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/check-mysql-storage-engine-type-linux.html
+
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/06/how-to-install-mysql-server-and-client-on-linux.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/20140702 How to create sosreport in linux (RHEL 5.X or RHEL 6.X).md b/published/20140702 How to create sosreport in linux (RHEL 5.X or RHEL 6.X).md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..00569b6586
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140702 How to create sosreport in linux (RHEL 5.X or RHEL 6.X).md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+如何用sosreport在Linux上创建诊断信息
+================================================================================
+**Sosreport**是**RHEL / CentOS**上的一个命令,它会收集**系统配置**和你linux机器上的诊断信息,如正在运行的内核版本、加载的模块和系统和服务配置文件之类的信息。这个命令同样可以运行外部的程序来收集更多的信息,并存储这些输出到一个结论文档中。
+
+Sosreport在你需要获得redhat的技术支持时需要它。Redhat的支持工程师会要求你服务器上的sosreport来用于故障排除。
+
+要运行sosreport,需要安装**sos** 包。sos包是大多是linux的默认安装包中的一部分。如果因为某种原因没有安装,那么运行下面的yum命令来安装**sos 包** :
+
+ # yum install sos
+
+### 生成报告 ###
+
+打开终端输入sosreport命令:
+
+ # sosreport
+
+这条命令正常情况下会在**几分钟**里完成。根据本地配置,在某些情况下,某些选项可能需要更长的时间才能完成。一旦完成,sosreport将在**/ tmp目录**目录中生成一个压缩文件。不同版本使用不同的压缩方案(** gz,bz2,或xz**)。该文件应提供给红帽的支持代表(在开放的情况下通常作为附件)。
+
+**注意**:sosreport需要root权限才能运行。
+
+### sosreport命令中不同的选项: ###
+
+sosreport命令有一个**模块化结构**,并允许用户启用和禁用模块,并通过在命令行指定模块。要**列出可用的模块**(插件),请使用以下命令:
+
+ # sosreport -l
+
+要禁用一个模块,用逗号隔开的列表传给-n/–skip-plugins选项。比如要kvmand 、amd这两个模块:
+
+ # sosreport -n kvm,amd
+
+各个模块可以通过-k选项提供额外的选项。例如,在Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5中安装的sos rpm模块默认收集“rpm -Va”的输出。因为这是个耗时行为,因此可以通过下面的命令禁用:
+
+
+ # sosreport -k rpm.rpmva=off
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/how-to-create-sosreport-in-linux/
+
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/20140703 How to find and kill misbehaving MySQL queries.md b/published/20140703 How to find and kill misbehaving MySQL queries.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..848d466fdd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140703 How to find and kill misbehaving MySQL queries.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+怎样把坏的MySQL查询找到并杀死?
+================================================================================
+
+有时,关系型相关数据库系统的复杂性会把你搞晕,不过幸运的是,使用MySQL工具来管理查询就就可以避免这些复杂性。 在本教程中,我将向你们展示 **怎样去查找并杀掉任何非法的MySQL查询**。
+
+为了浏览当前正在运行的查询,登陆到MySQL终端,然后运行‘show processlist’命令:
+
+ mysql> show processlist;
+
+ +--------+--------+-----------------+---------+---------+-------+-------+------------------+-----------+---------------+-----------+
+ | Id | User | Host | db | Command | Time | State | Info | Rows_sent | Rows_examined | Rows_read |
+ +--------+--------+-----------------+---------+---------+-------+-------+------------------+-----------+---------------+-----------+
+ | 78233 | root | 127.0.0.1:37527 | mysql | Sleep | 16474 | | NULL | 6 | 6 | 6 |
+ | 84546 | root | 127.0.0.1:48593 | mysql | Sleep | 13237 | | NULL | 2 | 2 | 2 |
+ | 107083 | root | 127.0.0.1:56451 | mysql | Sleep | 15488 | | NULL | 1 | 121 | 121 |
+ | 131455 | root | 127.0.0.1:48550 | NULL | Query | 0 | NULL | show processlist | 0 | 0 | 0 |
+ +--------+--------+-----------------+---------+---------+-------+-------+------------------+-----------+---------------+-----------+
+ 4 rows in set (0.03 sec)
+
+首先你应该查看'Time'项,这里记录了进程执行 "做其当做的事情" 操作的秒数。‘command’项处于‘Sleep’
+状态的进程表示其正在等待接受查询,因此,它并没有消耗任何资源。对于其他任何进程而言,‘Time’超过一定的秒数表明出现问题。
+
+在上面的例子中,唯一运行的查询是我们的‘show processlist’命令。让我们来看看如果我们有一个写的很烂的查询是怎么样的:
+
+ mysql> show processlist;
+
+ +--------+--------+-----------------+-----------+---------+-------+--------------+----------------------------------+-----------+---------------+-----------+
+ | Id | User | Host | db | Command | Time | State | Info | Rows_sent | Rows_examined | Rows_read |
+ +--------+--------+-----------------+-----------+---------+-------+--------------+----------------------------------+-----------+---------------+-----------+
+ | 78233 | root | 127.0.0.1:37527 | example | Sleep | 18046 | | NULL | 6 | 6 | 6 |
+ | 84546 | root | 127.0.0.1:48593 | example | Sleep | 14809 | | NULL | 2 | 2 | 2 |
+ | 107083 | root | 127.0.0.1:56451 | example | Sleep | 17060 | | NULL | 1 | 121 | 121 |
+ | 132033 | root | 127.0.0.1:54642 | example | Query | 27 | Sending data | select max(subtotal) from orders | 0 | 0 | 0 |
+ | 133933 | root | 127.0.0.1:48679 | NULL | Query | 0 | NULL | show processlist | 0 | 0 | 0 |
+ | 134122 | root | 127.0.0.1:49264 | example | Sleep | 0 | | NULL | 0 | 0 | 0 |
+ +--------+--------+-----------------+-----------+---------+-------+--------------+----------------------------------+-----------+---------------+-----------+
+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
+
+啊哈!现在我们看到有一个查询运行了将近30秒。如果我们不想让它的进程继续运行,可以将它的'Id'传递给kill命令:
+
+ mysql> kill 132033;
+ Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
+ mysql>
+
+(注意 由于我们没有改变任何数据,MySQL总是报告0行被影响。)
+
+明智的使用kill命令能够清除积压的查询。然而,要记住的是,那不是一种永久的方法 - 如果这些查询来自你的程序,你需要去重写它们,或者将继续看到相同的问题不断出现。
+
+### 另请参阅 ###
+
+关于不同‘命令’的MySQL文档:
+
+- [https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/thread-commands.html][1]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/find-kill-misbehaving-mysql-queries.html
+
+译者:[hunanchenxingyu](https://github.com/hunanchenxingyu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/thread-commands.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/20140709 Command Line Tuesdays--Part Four.md b/published/20140709 Command Line Tuesdays--Part Four.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4fce09d33d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140709 Command Line Tuesdays--Part Four.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+命令行星期二——第四部分
+===================
+
+大家好。新的一周,新的冒险!
+
+今天,我们将会学习使用四个相当简单的命令去操作文件。好,废话少说,我们开始吧。
+
+在开始学习这些命令之前,我们先稍微说些题外话,讲讲“通配符”的用处。
+
+###通配符###
+
+使用图形工具区复制、粘贴、新建目录等操作也许很容易,但是若想完成一些更复杂的任务,例如仅仅将一个目录下的所有.html文件复制到另一个目录中、或者只复制在某个目录中不存在的文件,这时命令行也许会比较方便。我们回到通配符的学习中,通配符是shell的基本功能,它是一个由一些特殊字符组成的集合,它让你可以用一些简单的规则来选择出某些文件。(通配符可以出现在文件名中,用于指定文件名的字符个数和字母的大/小写等规则)。
+
+如下表 :
+
+
+
+下面是肖茨先生给出的一些实例,如下表:
+
+
+
+如果你使用一个包含文件名参数的命令,你就可以使用通配符。
+
+###cp###
+
+cp是一个用于复制文件或者目录的命令,它的用法相当的简单。进入到你想复制的文件所在的目录,然后使用如下命令
+
+`cp file1 file2` -复制一个文件
+
+或者
+
+`cp file1 file2 ... directory` -从当前工作目录复制多个文件到指定的目录。
+
+下表是肖茨先生给出的cp命令的一些选项:
+
+
+
+###mv###
+
+mv是今天的第二个命令,我们可以使用mv来重命名一个文件或目录,或者移动一个文件或目录。我们可以这样使用mv命令。
+
+`mv filename1 filename2` -若想将文件filename1重命名为filename2。
+
+或者
+
+`mv file directory` -若想将一个文件移动到某个目录。
+
+下表是一些mv命令的实例
+
+
+
+###rm###
+
+rm命令是用于删除文件或目录,它的用法比较直接,如下:
+
+`rm file`
+
+或者
+
+`rm -r driectory`
+
+这里也有一个包含rm其他选项的表
+
+
+
+但是,使用rm命令时要小心点。因为并没有撤销删除的选项,因此使用rm命令式要格外的小心,避免对你的系统造成不必要的破坏。
+
+###mkdir###
+
+mkdir是用于创建目录.它是今天最简单的一个命令:
+
+`mkdir directory`
+
+看,目录成功创建了!
+
+这是本周的内容,下周二再见,致以最真诚的问候!
+
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------
+via: https://news.opensuse.org/2014/07/08/command-line-tuesdays-part-four/
+
+译者:[cvsher](https://github.com/cvsher) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20140709 How To Disable Overlay Scrollbars in Ubuntu 14.04.md b/published/20140709 How To Disable Overlay Scrollbars in Ubuntu 14.04.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..360f9ca5cb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140709 How To Disable Overlay Scrollbars in Ubuntu 14.04.md
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+[小技巧]如何在Ubuntu14.04中禁用叠加滚动条
+================================================================================
+
+
+Hello 伙计们,
+
+这是一个如何在Ubuntu中禁用叠加滚动条的小技巧。注意,在本文中讲的不是删除叠加功能,而是告诉你如何启用或禁用它。
+
+### 禁用 ###
+
+打开终端并执行以下命令
+
+ gsettings set com.canonical.desktop.interface scrollbar-mode normal
+
+更改后会立即生效:
+
+
+
+### 启用 ###
+
+ gsettings reset com.canonical.desktop.interface scrollbar-mode
+
+
+
+Enjoy!
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Enock Seth Nyamador][1]
+
+我穿着--[0-0]--(比基尼?), 一个开源的瘾君子。一个发展中的非洲geek。我是一个菜鸟开发者和一个有追求的摄影师。想提供给我什么或者是小贴士,请随时与我联系。我随时准备开发和照片。干杯!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/disable-overlay-scrollbars-ubuntu-14-04-quick-tip/
+
+译者:[Vito](https://github.com/vito-L) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/seth/
+
diff --git a/published/20140709 Red Hat Announces Availability of its OpenStack Platform 5.md b/published/20140709 Red Hat Announces Availability of its OpenStack Platform 5.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6d038b032e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140709 Red Hat Announces Availability of its OpenStack Platform 5.md
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+红帽公司发布 OpenStack Platform 5
+================================================================================
+
+
+红帽公司[宣布][1]在RHEL上推出OpenStack Platform5,这是基于OpenStack开源云的第三个企业级发行版。该版本不仅开发了一些新功能,针对的用户群体也大为增多,如高大上的云用户、电信企业、互联网服务供应商(ISP)、公有云服务供应商等。
+
+OpenStack Platform 5是基于最新的Openstack Icehouse的发行版,并且针对云计算技术做了大量的修改和优化工作而来的。
+
+这个最新的发行版有3年的技术支持周期,[我选择了使用][2]它是考虑到红帽公司在Linux系统上对用户无以伦比的技术支持,红帽公司对其OpenStack Platform 5的技术支持服务将是促使企业购买的关键之一。
+
+对于红帽公司是否会支持OpenStack的其他发行版尚未有定论,但一份OpenStack用户调查已经显示[90%的OpenStack开发人员并没有在RHEL上使用OpenStack][3],而是选用了Ubuntu或者CentOS Linux和其虚拟化技术。
+
+OpenStack Platform 5的最新功能:
+
+> **支持和VMware基础架构的整合**,结构包含虚拟化、管理、网络和存储。
+用户一般会使用已经在使用的VMware vSphere资源,比如虚拟化驱动作为OpenStack (Nova)的计算节点,再使用上层的OpenStack Dashboard(Horizon)对节点进行管理。
+同样的,RHEL OpenStack Platform 5也支持VMware的NSX插件,作为OpenStack NetWorking (Neutron)对网络进行管理,支持VMware虚拟磁盘(VMDK)以插件形式存在,作为OpenStack Block Storage(Cinder)来使用。
+>
+
+> **对云资源的使用,采取了更好的布置。**服务器组让计算散布到OpenStack云的服务节点上,这让分布式应用有了更强的弹性,对于复杂的应用,也能起到降低通信延迟,提高运算性能的作用。
+>
+
+> **对虚拟机更好的支持,支持加密,满足美英国家对信息安全的要求** 使用RHEL 7中提供的半虚拟化随机数生成器,在用户程序中也添加进这个工具,可以更好的加密质量和性能提升。
+
+> **提升协议栈的互通性**红帽公司宣称,Neutron中新开发的模块化的网络技术将简化OpenStack的部署。这种技术将允许用户在OpenStack中部署多种网络方案来解决异构网络的访问。
+
+红帽公司虚拟化和OpenStack产品线总经理 Redhesh Balakrishnan说到:
+
+> “我们看到越来越多的企业级用户或服务供应商选择OpenStack作为私有云平台,RHEL OpenStack Platform 5不只是一个基于OpenStack Icehouse产品,我们还开发了很多简单易用的功能,增强了产品的可靠性。
+在未来三年内,我们要让用户看到,RHEL OpenStack Platform 5所提供的功能和技术支持服务,将为他们部署的应用保驾护航,让用户对我们的产品充满信心。
+
+我敢跟你打赌,--三年的技术支持服务--将是企业用户在竞争激烈的云平台领域选择红帽的关键点。并且,毋庸置疑,红帽公司把自己的未来放在了云计算,放在了OpenStack Platform上面。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ostatic.com/blog/red-hat-announces-availability-of-its-openstack-platform-5
+
+译者:[nd0104](https://github.com/nd0104) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.marketwatch.com/story/red-hat-announces-general-availability-of-red-hat-enterprise-linux-openstack-platform-5-2014-07-08
+[2]:http://ostatic.com/blog/why-red-hats-openstack-support-must-be-as-inclusive-as-possible
+[3]:http://www.openstack.org/blog/2013/11/openstack-user-survey-october-2013/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/20140711 Linux Basics--How To Find Size of Directory Commands.md b/published/20140711 Linux Basics--How To Find Size of Directory Commands.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..28d56c3faa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140711 Linux Basics--How To Find Size of Directory Commands.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+Linux基础:如何在命令行中查看目录的大小
+=====================================================================
+
+这是写给Liunx新用户的一系列文章中的第一篇,在这系列文章我将会写一些对新用户来说非常好用的**Linux基础命令**。
+
+**注意**:本文的目标读者是仅有小量甚至是没有任何Linux命令行使用经验的读者。
+
+>作为一个Linux的新用户,我怎样可以在命令行终端中查看某个目录的属性?
+
+###要求###
+
+唯一的要求是**du**命令行工具。du基本上是所有Linux发行版本默认提供的工具。用以下的命令来检查你的系统中是否可以使用du命令:
+
+ man du
+
+**du** 命令用于输出文件的空间使用情况。
+
+###使用du###
+
+不带任何参数的运行du命令会显示当前工作目录以及其子目录的文件名和所占用的空间大小(以字节为单位)。
+
+ du
+
+
+
+使用**-h**参数以对用户友好的方式输出文件大小,即分别以**K, M**和**G**来表示**Kb,Mb**和**Gb**
+
+ du -h
+
+
+
+若想查看某个特定目录的文件大小,则在du命令中指定要查看的目录名,如下:
+
+ du -h Mapmaker
+
+
+
+使用 **-c** 参数来查看目录所占用磁盘空间的总大小
+
+ du -ch
+
+
+
+使用 **-s** 参数只输出指定目录占用空间的大小
+
+ du -sh Mapmaker Sandbox
+
+
+
+使用 man du 查看du命令更多参数的用法
+
+ man du
+
+
+
+知道du命令更多的用法?请分享给我和其他人。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/linux-basics-find-size-directory-commands/
+
+译者:[cvsher](https://github.com/cvsher) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
diff --git a/published/20140711 ncdu--NCurses Disk Usage Analyzer.md b/published/20140711 ncdu--NCurses Disk Usage Analyzer.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5f9ebf05cd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140711 ncdu--NCurses Disk Usage Analyzer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+ncdu – 基于ncurses库的磁盘使用分析器
+================================================================================
+[Ncdu][1] (NCurses Disk Usage) 是一个基于Ncurses库的du命令的界面。它通过大家熟知的[du][2]命令,为用户提供一个快速且容易被使用的界面。它可以显示磁盘使用的百分比,且允许你使用ncurses库的方式在目录之间导航。
+
+
+
+### 安装 ###
+
+ncdu已经被移植到大多数linux发行版本,可从官方资源库中安装.
+
+Arch / Manajaro 及其衍生版:
+
+ sudo pacman -S ncdu
+
+
+
+Ubuntu / Debian / Linux Minut 及其衍生版:
+
+ sudo apt-get install ncdu
+
+Fedora 及其衍生版:
+
+ sudo yum install ncdu
+
+在[这里][3]可以找到其他的发行版。
+
+### 使用 ncdu ###
+
+键盘操作:
+
+
+- up, k — 向上移动光标
+- down, j – 向下移动光标
+- right/enter — 打开选定的目录
+- left, <, h — 打开父目录
+- n — 按文件名排序(升序/降序)
+- s — 按文件大小排序(升序/降序)
+- C – 按项目数排序(升序/降序)
+- d – 删除选定的文件或目录
+- t — 排序时将目录放在文件前面
+- g – 以图形方式显示百分比
+
+为使用ncdu,请打开终端并且运行
+
+ ncdu
+
+开始扫描目录.
+
+
+
+当扫描完成后,你能够很容易的看到文件/目录的大小.
+
+
+
+确认删除文件:
+
+
+
+在[这里][4] 阅读ncdu命令手册或运行:
+
+ man ncdu
+
+**荣誉**: 有两位读者**BasketCase**和**Sama Vim**在阅读“[Linux基础:如何在命令行中查看目录的大小][5]”之后 向我们推荐了这个Ncdu工具。
+
+
+Enjoy!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/ncdu-ncurses-disk-usage-analyzer/
+
+译者:[hunanchenxingyu](https://github.com/hunanchenxingyu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://dev.yorhel.nl/ncdu
+[2]:http://www.unixmen.com/linux-basics-find-size-directory-commands/
+[3]:http://dev.yorhel.nl/ncdu
+[4]:http://dev.yorhel.nl/ncdu/man
+[5]:http://linux.cn/article-3473-1.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/20140714 Canonical and Ubuntu Helped Munich Save Millions of Dollars by Ditching Microsoft Products.md b/published/20140714 Canonical and Ubuntu Helped Munich Save Millions of Dollars by Ditching Microsoft Products.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3f5658e2cb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140714 Canonical and Ubuntu Helped Munich Save Millions of Dollars by Ditching Microsoft Products.md
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+放弃微软产品,慕尼黑省下数百万美元
+=================================================
+
+
+**慕尼黑这座城市已经成为了从微软产品转向开源的,最突出的城市管理案例之一,而且Canonical公司和ubuntu为这次变革起了很大的作用。**
+
+慕尼黑成功脱离了微软的依赖,但是他们为这次摆脱过程付出了价值不菲的代价。从微软产品转向开源的好处看起来似乎很昂贵,但是转变的成本比之后的产品升级显著要低,不仅如此,在未来,我们会发现这种做法更便宜。
+
+当你在像慕尼黑城市这种大城市,尝试从一个专有解决方法转向开源的时候,这可并不容易。因为慕尼黑拥有22个组织单位,每个单位都有自己的IT部门,更不要说各部门之间不同版本的应用程序。
+
+地方政府不能只采用一个Linux发行版本。第一次的尝试是在2006年伴随着Debian的回归,但是特定的操作系统并没有一个可预测的发布时间表。这就是新操作系统LiMux产生的原因,一个基于ubuntu的操作系统。
+
+“LiMux/开源项目是漫长而又反复的,但是经过几年时间运行这种大型Linux,我们意识到ubuntu才是最能满足我们需求的平台。通过结合开源软件的低成本和自由,加以对我们需要的硬件和应用程序的持续支持,这种做法才是这个项目成功的关键因素之一。当然,最终要还有我们的市府在项目上始终给予的高度支持。”慕尼黑项目经理Peter Hofmann[说道][1]。
+
+截至2013年,如果只考虑升级成本的话,这个项目帮助慕尼黑节省了€1000万(1360万美元)。如果我们能量化官方支持软件和其余隐藏成本的话,这个数额显得有些多。
+
+眼下,慕尼黑14000台PC机运行着LiMux,而且数量还在持续增长。这很有可能影响其余德国城市在未来也这么做,尤其是慕尼黑的邻居。
+
+慕尼黑当局采用了13年才完成这次变革,但是最终事实证明,这样做可以省下一大笔资金,而且证明了Linux实际上是整个城市IT基础设施又好有免费的解决方案。
+
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Canonical-and-Ubuntu-Helped-Munich-Save-Millions-of-Dollars-By-Ditching-Microsoft-Products-450571.shtml
+
+ 译者:[su-kaiyao](https://github.com/su-kaiyao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+ 本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+ [1]:https://insights.ubuntu.com/2014/07/07/ubuntu-and-open-source-help-the-city-of-munich-save-millions/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/20140718 Git 2.0.2 Version Control System Now Available for Download.md b/published/20140718 Git 2.0.2 Version Control System Now Available for Download.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e13c2d8f60
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140718 Git 2.0.2 Version Control System Now Available for Download.md
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+Git 2.0.2版本控制系统现在可供下载使用了
+==================================================================================================================================================
+
+
+
+**Git 2.0.2如今已正式发布。这是一个免费和开源的分布式版本控制系统,因其处理速度和效率的优势,它可以处理大大小小各种项目。**
+
+新的Git 2.0.x分支保持着带来大量更新的传统,它整合了大量的改变和修正。这个最新的更新只是维护版,但是它的功能特性的确有一些有趣的修改。
+
+根据开发者的描述:"git submodule sync(git子模块的同步)"的文档中提到的子命令可以使用"--recursive"(递归)的选项;在.gitignore中跟踪引用反斜杠的空格的处理不当已经被纠正;对"git repack"命令的更新,将不再错误地复制那些被.keep标签标记的pack目录下的对象。
+
+还有,"git clone -b brefs/tags/bar"不再认为git遵循一个单一的tag,尽管它是一个分支的名称;"%G(G后面没有跟任何东西)"是一个无效的漂亮的格式说明符,现在的解析器不再对它进行解析;用于避免增加相同替代对象的存储的代码经过了两次修正,而且其余的几个修正也已经完成。
+
+想要查看完整的改变列表,查看[changelog][1]。
+
+下载Git 2.0.2:
+
+- [tar.gz][1][sources] [4.70 MB]
+- [Debian/Ubuntu DEB ALL][2][ubuntu_deb] [0 KB]
+- [Red Hat/Fedora/Mandriva/openSUSE RPM noarch][3][rh_rpm] [0 KB]
+
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Git-2-0-2-Version-Control-System-Now-Available-for-Download-451147.shtml
+
+译者:[su-kaiyao](https://github.com/su-kaiyao) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://github.com/git/git/blob/master/Documentation/RelNotes/2.0.2.txt
+[2]:https://github.com/git/git/archive/v2.0.2.tar.gz
+[3]:http://git-scm.com/download/linux
+[4]:http://git-scm.com/download/linux
+
diff --git a/published/20140722 The Native Dropbox Linux Client Debuts New Qt Interface.md b/published/20140722 The Native Dropbox Linux Client Debuts New Qt Interface.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..449f842479
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140722 The Native Dropbox Linux Client Debuts New Qt Interface.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+Dropbox原生Linux客户端首次展示QT界面
+================================================================================
+**Dropbox原生Linux客户端的最新试验版首次展示了全新的QT界面。**
+
+Dropbox表示这次的UI重写,将同时应用到Windows和Linux,将修复“大量”长期遗留下来的错误和问题。这个跨平台的工具也将整体提升性能。
+
+在全新的设置向导和登录界面(见下面的图片)旁边是几个重新设计过的启动画面。
+
+
+登录界面
+
+
+设置界面
+
+
+欢迎界面
+
+### 目前还不稳定 ###
+
+Dropbox开发人员提醒参与测试的人,目前大部分新界面“还很粗糙”,在使用中可能会碰到大量的界面问题。新界面还不能配合一些辅助工具一起工作,例如屏幕阅读器。
+
+
+
+新UI使用了(目前)系统自带的QT界面主题。它本身也不算很丑,不过在Ubuntu桌面上看起来不怎么合适,特别是和之前的版本比较。据说内存占用也变多了,在空闲情况下有时候会从60MB一下子跳到178MB。那些使用低端设备的人应该忍耐一下试用这个版本的诱惑-至少在这个特别的问题解决之后。
+
+Dropbox 2.11.0 (试验版本) for Linux的完整改动日志:
+
+- 用QT重写了Windows & Linux界面
+- 在移动和重命名文件后会尝试识别
+- 新的设置/登录体验
+- 更快上传小文件
+- 新的启动画面
+
+### 下载Dropbox Linux Build 2.11.x ###
+
+想尝鲜的话,可以通过下面的链接下载和你系统对应的安装包。
+
+- [Dropbox Experimental (64bit) Offline Linux Installer][1]
+- [Dropbox Experimental (32bit) Offline Linux Installer][2]
+
+下载完后,解压到主目录。它默认是隐藏的,所以打开终端,’`cd`‘到‘`.dropbox-dist/dropbox-lnx`‘目录下,然后运行‘`./dropbox start`‘。
+
+演示Dropbox终端操作的gif动画:
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/dropbox-experimental-linux-build-qt-rewrite
+
+原文作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a] 译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
+[1]:https://d1ilhw0800yew8.cloudfront.net/client/dropbox-lnx.x86_64-2.11.0.tar.gz
+[2]:https://d1ilhw0800yew8.cloudfront.net/client/dropbox-lnx.x86-2.11.0.tar.gz
diff --git a/published/20140724 Oracle Linux 7.0 OS Has XFS as Default File System and Unbreakable Enterprise Kernel Release 3.md b/published/20140724 Oracle Linux 7.0 OS Has XFS as Default File System and Unbreakable Enterprise Kernel Release 3.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2fe8583af8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/20140724 Oracle Linux 7.0 OS Has XFS as Default File System and Unbreakable Enterprise Kernel Release 3.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+Oracle Linux 7.0发布!
+===
+
+
+**Oracle已经发布了Oracle Linux 7.0操作系统,新系统带来了大量的新特性,比如“第三代坚不可摧的内核 UEK”(Unbreakable Enterprise Kernel Release 3)和一个新的默认文件系统**
+
+为了这次新的发行版的发布,Oracle的开发者们已经放出过两个预览版,现在最终版终于来了。果然,它有着大量的改进,其中包括使用新的XFS作为默认的文件系统**[注:原文为操作系统,应该是笔误]**,可选的Btrfs文件系统,Linux Containers (LXC), DTrace,Ksplice,加强版Xen和UEK R3。
+
+作为广泛流行的文件系统EXT4的对抗者,XFS有一个显著优势。它所允许用户的文件系统的大小达到了500TB,这比你在EXT4文件系统中所能达到最大值的十倍还多。唯一的缺点是单个文件的大小最大仅为16TB。
+
+这个发行版的一大特色是它支持两种内核。一个是红帽兼容性内核(RHCK),基于Linux内核版本3.10,第二个是Oracle自己的内核版本“第三代坚不可摧的内核”(UEK R3),版本号从3.8.13开始,因为它基于3.8的Linux内核。你或许还记得Linux内核3.8.x已经寿终正寝,但是看来Oracle一直在维护着自己的分支。
+
+“已经能够从Oracle软件发布云上下载了,Oracle Linux 7可以免费下载和部署。所有的bug修复和安全勘误会被发布到Oracle的公共yum服务器上,不管有没有付费,用户都能安装同样的代码,并且从免费到付费的迁移十分简单,无需重新安装。”
+
+“当发布最新的Linux更新,工具以及推送给客户和参与者新功能的时候,需要为现代化的数据中心提供企业级的解决方案。为此最新的发行版是构建在Oracle对OpenStack这样的新兴技术提供支持的基础上,”从官方声明可以看出。
+
+通过变更记录来看,Ksplice已经为了实现零宕机的内核完成了安全更新和bug修复,systemd也成了新的系统管理工具,Grub2现在是默认的启动引导程序,并且支持新的固件类型(比如UEFI),还有一个加强版Anaconda安装器,一个新的Apache Web服务器,支持GPT,和大量的安全特性被添加进来。
+
+更多关于最新的Oracle Linux发行版的详细内容可以参考官方[声明][1]。
+
+立即下载Oracle Linux 7.0:
+
+
+- [Oracle Enterprise Linux 6.5 (ISO) 64-bit][2][iso] [3 GB]
+- [Oracle Enterprise Linux 6.5 (ISO) 32-bit][3][iso] [3.60 GB]
+- [Oracle Enterprise Linux 7.0 (ISO) 64-bit][4][iso] [4.50 GB]
+
+
+---------------------------------
+
+原文: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Oracle-Linux-7-0-OS-Has-XFS-as-Default-File-System-and-Unbreakable-Enterprise-Kernel-Release-3-451894.shtml
+
+作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
+译者:[guodongxiaren](https://github.com/guodongxiaren)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
+[1]:http://www.oracle.com/us/corporate/press/2245947
+[2]:http://mirrors.dotsrc.org/oracle-linux/OL6/U5/i386/OracleLinux-R6-U5-Server-i386-dvd.iso
+[3]:http://mirrors.dotsrc.org/oracle-linux/OL6/U5/x86_64/OracleLinux-R6-U5-Server-x86_64-dvd.iso
+[4]:https://edelivery.oracle.com/linux/
diff --git a/published/Encrypting Your Cat Photos.md b/published/Encrypting Your Cat Photos.md
new file mode 100755
index 0000000000..9e80a36d30
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/Encrypting Your Cat Photos.md
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
+给猫咪照片加密
+================================================================================
+事实上,我的硬盘上不存在那种不愿意被别人看到的东西,只存有一些猫咪的照片、一些记录着想写的书的想法的文本文件,或者是一些短篇故事的文本,也有一些写了一半的 NaNoWriMo 小说文件。简单的说,我的硬盘就没有加密的必要,因为没有什么可隐藏的。可问题是,我们错误的把“隐私的渴望”跟“要隐藏某东西”两概念混淆在一起。比如说我生活的美国,我们视隐私权利是理所当然的事,但不包括那些传统所认为的“某人的隐藏色情或炸弹”。隐私考虑的是一些平常的事情。
+
+我居住在密歇根州。这儿的冬天很冷,我趋向于把温度设置在华氏 75 度左右。对您们来说这个温度可能高了,但在我的家里刚好合适。多亏我的家是属于私有的,我的邻居不可能知道我们保持了这么高的温度,否则一但他们看到冬天如此“浪费”能源的家庭,这些邻居心里会很不平衡的。事实上,本地条规中有一条明确指出任何超过华氏 60 度的就算是生态浪费。我并不想与这种僵老的条例较真,所以我仅仅想保守我们舒适的房子的秘密。我们并不想隐藏任何事情,但也并不是任何事情都要让外人知道。
+
+很明显,我举的例子有点弱智,但我希望的是这能引起大家的思考。现代的 Linux 系统很容易的就可以对我们的数据进行加密,并且很可靠,所以为什么不好好利用利用呢?
+
+### 加密原理? ###
+
+我不会涉及太多关于加密原理的细节,但要明白最基本的原理,即使是最简单的实现,这是必须的。要加密和解密一个文件,需要两把“钥匙”。一把是私钥,正如名字所示,属于私有的。我宁愿把私钥看作是真实的钥匙——你想要多少就可造出多少,但这样做是不明智的。同样的,私钥你造的越多,某些不怀好意的人得到其中一把的机率就越大,他们就会闯入你的公寓(额,我的意思是指那些文件)。
+
+公钥更像是锁的样子,只有你能(用你的私钥)打开此锁。这公钥任何人都可以得到,你可以将它张贴在网站上、把它放在你的 E-mail 中、甚至纹在你的背上。其它人想创建一个只有你能访问的文件,就可以使用此公钥来加密。
+
+这种一对多(LCTT译注:指别人可以加密多个文件,而只有你的一个私钥才能解密)的情况也有个很酷的副作用。如果你用你的私钥来加密一些东西,任何人都可以用你提供的公钥来解密它们。这听起来很傻,但这种情景很有用。虽然加密的文件不能免于被窥视,但是它能保证此文件确实来自于你而没有被恶意改动过。用你的公钥能解密的文件仅仅只能是用你私钥加密过的。用这种方式,用私钥加密的文件即是数字“签名”文件。(LCTT译注:既然是任何人都可以用公钥解密,其实加密没有意义,相反,仅仅用你的私钥做一个签名指纹,别人只需要用你的公钥来验证该签名是否一致即可判断是否来自你。)
+
+(LCTT译注:其实本文此处所述的加密解密、签名校验等原理不完全正确,和实际的非对称加密情形有所差异,不过比较容易理解和类比。)
+
+#### 通用加密步骤: ####
+
+1. 你有一个文件想要发送给苏茜 ,所以你得使用苏茜的公钥来加密,这样就只有 苏茜才能打开这个文件,但苏茜没有办法知道是谁给她发送的文件。因为任何一个人都可以用她的公钥来加密文件。
+2. 因此,你得把你的文件用苏茜的公钥和你的私钥都加密。苏茜将不得不解密两次,但她知道它是来自于你的文件。(LCTT译注:实际上应该是用你的私钥要做签名,生成一小段签名指纹,而不是对已经加密的文件再次加密。)
+3. 苏茜接收到此文件后会用能证明来自于你的公钥来解密第一层。(LCTT译注:校验签名,确认来自你的私钥的签名正确。)
+4. 然后用她的私钥来解密第二层的密码,这是唯一的能够将原始文件进行解密的钥匙了(因为你是用她的公钥来加密的)。
+
+当然,这情景就是用来安全传输文件的加密手段。这也是加密你的文件(或者分区)相当常用及简单的方法。就让我们开始来对文件进行加密吧,因为大多数人都想加密他们的系统。
+
+### 始于简 ###
+
+在深入更复杂的各种加密设置操作前,我们先做简单的对文件加密例子。能处理加密的应用程序有很多很多,事实上,对文件和系统进行加密的各种可用软件选择,很容易就会让我们变得焦头烂额。现在,我们就使用一款很基本的(但非常强大)命令行工具来对文件加密。 GPG (英文名:Gnu Privacy Guard)是一款对商业软件 PGP(英文名:Pretty Good Protection)的开源实现软件。它具有加密、签名及管理多个密钥等功能。用例子说明,让我们简单的加密一个文件吧。
+
+我们假设你有一个名叫 secret_manifesto.txt 的文件,它包含有关于生命、宇宙及一切事物的秘密。使用 GPG,你只需要一个密码就可以加密此文件。使用密码远比使用公钥和私钥对简单,因为它只是用你的密码加密。虽然这比较容易让你的文件遭受到破解(比如使用彩虹表或其他黑客工具暴力破解),但像它的名字中所宣称的:这是相当不错的保护。要加密你的文件,可以这样做:
+
+ # gpg -c secret_manifesto.txt
+ Enter passphrase:
+ Repeat passphrase:
+
+一但完成,在相同的目录下就会多出个新的文件,它默认的名字是 secret_manifesto.txt.gpg 。这是一个二进制文件,这意味着它真的比较小,但是要将其内容拷贝/粘贴到电子邮件(e-mail)或 即时消息(IM) 就不可能了(LCTT译注:当然你可以使用附件方式。)。要使其便于拷贝等操作,可以添加 -a 标志,这将创建一个只包含 ASCII 码文本的加密文件:
+
+ # gpg -a -c secret_manifesto.txt
+ Enter passphrase:
+ Repeat passphrase:
+ # ls -l
+ -rw-rw-r-- 1 spowers spowers 6 Nov 23 1:26 secret_manifesto.txt
+ -rw-rw-r-- 1 spowers spowers 174 Nov 23 1:27 secret_manifesto.txt.asc
+ -rw-rw-r-- 1 spowers spowers 55 Nov 23 1:26 secret_manifesto.txt.gpg
+
+注意到现在多了一个以 .asc 为扩展名的文件。它是个纯文本文件,从上面的代码段示例可以看到它比二进制的加密文件还大,当然比原文本文件就大的更多了。一但你把文件加密了,也确实想要对些信息保密,最明智的就是把原文本文件删除掉。(LCTT译注:千万记住密码啊,否则谁也帮不了你了——你得自己破解自己的密码啦:>)
+
+要解密文件,你需要再一次使用 GPG 程序。不管是二进制的还是 ASCII 文件,使用相同的命令就可以解密。如下所示:
+
+ # gpg secret_manifesto.txt.asc
+ gpg: CAST5 encrypted data
+ Enter passphrase:
+ gpg: encrypted with 1 passphrase
+ File `secret_manifesto.txt' exists. Overwrite? (y/N)
+
+注意到上面的例子中,我没有删除源文本文件,所以 GPG 给出了是否覆盖选项提示。一但操作完成,我的未加密的源文件又回来了。如果你仅仅只有一两个文件要保护,那基于命令行的 GPG 程序正是你所需的。但如果你想实现在系统上指定一个区域,任何保存到这区域的的文件都会自动加密的话,就有点复杂了。可这也并不是非常的困难,让我们用一个非常简单的示范例子来讲解吧。
+
+### 加密 USB 驱动盘 ###
+
+如我前面提到的,要加密有很多可选的方式方法。加密磁盘分区最通用的一种方法是 LUKS(Linux Unified Key Setup) 系统。一个使用 LUKS 格式化分区的 USB 驱动盘可以被大多数系统自动识别到。实际上,如果你使用的是像 Ubuntu 桌面这样的桌面环境系统的话,加密 USB 驱动盘其实就是在格式化过程中简单的勾选上一个复选框而已。虽然这是加密 USB 盘最容易让人接受的方式,但我还是想演示如何在命令行下进行加密,因为这种方式可以让你明白在加密的后面具体发生了什么。
+
+#### 步骤 1: 识别您的 USB 驱动盘。 ####
+
+在您插入 USB 驱动盘后,如果在终端输入 `dmesg` 命令,将会显示出所有的系统信息,包括刚插入的 USB 驱动盘的设备名字。 确保设备标识是正确的,因为后面要进行的操作会破坏驱动盘上的所有数据。您也不想一不小心就格式化掉正常的磁盘吧。(虽然不用提醒,但我还是要说,确保您的 USB 驱动盘已经没有你想保留的数据,因为这是一个破坏性的过程。)
+
+#### 步骤 2: 对 USB 驱动盘进行分区。 ####
+
+假设,在您的系统上 USB 驱动盘是 /dev/sdb 这个设备,您需要在这个驱动上创建一个单分区(LCTT译注:设备是sdb,其上可以有多个分区,分别叫sdb1、sdb2等等)。我们使用 fdisk 命令。下面是 fdisk 必须的交互操作。一般地,用 o 命令来创建一个新的空分区,然后用 w 命令来保存设置。然后重新运行 fdisk 命令,并用 n 命令来创建一个新的主分区,接下来保持默认的以使用整个设备空间:
+
+ # sudo fdisk /dev/sdb
+
+ Command (m for help): o
+ Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x1234567.
+ Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
+ After that, of course, the previous content won't be recoverable.
+
+ Command (m for help): w
+ The partition table has been altered!
+
+ # sudo fdisk /dev/sdb
+ Command (m for help): n
+ Command action
+ e extended
+ p primary partition (1-4)
+ p
+ Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
+ Using default value 1
+ First sector (2048-1016522, default 2048):
+ Using default value 2048
+ Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-1016522, default 1016522):
+ Using default value 1016522
+
+ Command (m for help): w
+ The partition table has been altered!
+
+现在你的 USB 驱动盘有了一个单分区了(/dev/sdb1),但还没有文件系统,这正是我们所想要的,因为 LUKS 系统需要在创建文件系统前在您的分区上创建一个加密层。因此,在创建文件系统之前,就让我们在分区上先创建一个 LUKS 层吧,可以使用 cryptsetup 程序。如果您还没有安装 cryptsetup 的话,可以搜索您系统发布版本的仓库源,里面就有。下面就开始创建 LUKS 加密分区层:
+
+ # cryptsetup luksFormat /dev/sdb1
+
+ WARNING!
+ ========
+ This will overwrite data on /dev/sdb1 irrevocably.
+
+ Are you sure? (Type uppercase yes): YES
+ Enter LUKS passphrase:
+ Verify passphrase:
+
+按照提示的操作,一定要确保记得您的密码!注意,这儿的“密码单词”不仅仅只表示一个单词。这只是一个习惯,因而得名,设置的越长越复杂,越难被破解。
+
+一但上面的操作完成,就创建好了一个加密的分区,但它还没有被挂载或格式化。要做的第一步就是挂载分区,可以再一次使用 cryptsetup 工具:
+
+ # cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/sdb1 my_crypto_disk
+ Enter passphrase for /dev/sdb1:
+
+当输入完密码后,您输入名字的设备就会像虚拟硬盘一样被挂载上。通常,它挂载在 /dev/mapper/设备名 的目录下,所以这个例子所示的分区就挂载到了 /dev/mapper/my_crypto_disk 目录。
+
+现在这个设备就可当做未加密的卷来访问了。 只要它一被挂载,就跟其它未加密的卷是一样的了,这就意味着您想要使用它的话就需要先建立文件系统:
+
+ # mkfs.vfat /dev/mapper/my_crypto_disk -n my_crypto_disk
+ mkfs.vfat 3.0.9 (31 Jan 2010)
+
+现在磁盘的功能完备了,可以像其它磁盘一样正常挂载使用了。实际上,如果你使用的是现代的图形用户界面系统的话,只要你把 USB 驱动盘一插入计算机,将会提示您输入密码,然后就自动挂载上了。退出的时候跟普通盘一样,里面存储的数据会被加密,直到下次输入密码。在命令行里使用 cryptsetup 卸载以及重加密驱动盘也是很简单的:
+
+ # cryptsetup luksClose my_crypto_disk
+
+### 这仅仅只是冰山一角 ###
+
+写这篇文章,我的目的是希望剥开加密后面的秘密。加密和解密单个文件很简单,要加密整个 USB 驱动盘也不是太困难(如果使用的是图形用户界面工具就更容易了)。对于大多数系统的发布版本来说,在安装过程中就可以对整个 home 目录进行加密。加密是对您的整个 home 目录起作用,然而有些问题就需要特别处理了。例如,您没登陆时就运行的任务在大多数情况下是不会访问您的 home 目录的,但如果您有调度任务需要访问 home 目录的话,应该进行修改,让其访问系统中其它目录的数据。我觉得在安全和便利之中平衡的中庸之道还是加密 USB 驱动盘,然后在上面存储个人资料。
+
+我必须警告您,一但您考虑到安全的问题,就会想要把任何东西都加密起来。这不是什么坏的事情,但是像要对 home 目录加密这种情况,是会碰到一些问题的。如果您使用不同系统的话,跨平台访问也是个大问题。像这种情况,我强烈建议您使用 [TrueCrypt][1]。在前期的文章片段里我提到过 TrueCrypt,它是一款开源的,跨平台的加密系统软件。可以对文件、文件夹、分区等等进行加密,同时可以在任何系统中访问加密的数据。像 Windows、Mac 及 Linux 客户端都可以使用。社区也有大力的支持。(LCTT译注:悲惨的是,棱镜门事件之后,TrueCrypt的作者已经放弃了该产品,并且强烈建议大家也不要使用,具体可以参考本站的一些相关消息。所以痛失TrueCrypt之后,我们还有哪些替代品?)
+
+希望对文件进行加密的目的并不是为了隐藏某些东西。就像即使您有个好邻居,最好夜里也得锁门一样,对您的个人数据进行加密也是个很正常的举动。如果您想在网上与大家分享你的 Whiskerton 先生戴着可爱的小豆豆帽子的照片的话,这是您的权利。但其它的人,比如他们索检你硬盘的时候,就不需要让他们看到了。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/encrypting-your-cat-photos
+
+译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.truecrypt.org/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/published/Raspberry Pi s Eben Upton--How We're Turning Everyone Into DIY Hackers.md b/published/Raspberry Pi s Eben Upton--How We're Turning Everyone Into DIY Hackers.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5953df559e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/Raspberry Pi s Eben Upton--How We're Turning Everyone Into DIY Hackers.md
@@ -0,0 +1,192 @@
+树莓派的联合创始人访谈——我们是怎么让大家都成为DIY黑客的
+================================================================================
+> 请记住它是为喜欢折腾的人准备的只要35美元的计算机
+
+
+我永远不会忘记我第一次看到树莓派的情形。那个小巧的,信用卡大小的计算机,性能却足够强劲,可以作为一般家用PC,媒体中心,电视游戏机,或是其他任何你能够想像的东西。只有35美元的价格,它是任何年龄段的动手爱好者都可以拥有的小东西,可以在上面捣腾硬件和软件试验,而不用担心会弄坏昂贵的家庭电脑。
+
+[Eben Upton][1],是树莓派基金会的共同创始人,通常被誉为这个神奇机器背后的魔法师。在剑桥大学的计算机实验室攻读哲学博士学位的时候,他费尽苦心地手工打造了树莓派的原型机。
+
+如今,Upton是树莓派基金会下面贸易公司的CEO,监督着树莓派的生产和销售,目前销量已经达到250万台。
+
+### 天上的派 ###
+
+ReadWrite网: 一开始是什么让你对技术这么感兴趣?它又是如何偶然地引导你创建树莓派项目的?
+
+**Eben Upton**: 在我还是孩子的时候就开始对技术感兴趣了。我有个对工程技术有很大兴趣的父亲,他自己不是工程师,而是一个英语老师。我们的房子里经常到处堆着各种电子器件,在还不知道这些东西是干嘛的时候,我就开始摆弄了。都是些小玩意,比如在床头装个灯,在“关灯”后还可以继续看书之类的。
+
+
+
+之后我有了一台计算机。在英国,我们把这种机器叫做[BBC微计算机][2],实际上是8位单片机,做教学用的。我们在学校的时候接触到这种机器,我之后就学会了编程,而且还蛮喜欢的。
+
+这些机器在学校里并不一定是用来编程的,或者说他们根本不是用来编程的,一般都运行教学软件。但是我却给它编程,之后我还买了一台回家,在我买了这台BBC微机后,我就泡在了房间里,再没出来过。[笑]
+
+编程对于小孩来说太神奇了。当你还是小孩的时候,并没有太多力量。没有听话的随从,反而身边有很多的限制。编程最伟大的地方在于,这是一个可以让你随心所欲的小世界。而这当然让我无法抗拒。
+
+我一直都对科学和数学,以及理科感兴趣。我在我的BBC微机上做了大量的计算和编程,之后我拥有了一台Commodore Amiga。
+
+在大学里我学习了物理,工程和计算机科学。这是激发树莓派项目想法的原因,因为当我在学校呆了10年的时候[当时在读博士学位],我发现那些新来的孩子们在他们小时候并没有机会获得这方面的经验。你也许仍然能拥有乐高玩具,但是它不是我们要的梯子。
+
+在一定程度上我们把身后的梯子撤掉了。我们造出了这些非常复杂而且用户友好的计算机给小孩使用,或者不仅仅是计算机,还包括电视游戏机,电话和平板,以及一些家用电器。但是,人们却没有机会自己动手改一改。所以实际上,树莓派是回到最初的一种尝试,当然也不会过于原始,希望找到在过去25年里计算机发展中迷失掉的那种感觉。
+
+**RW:** 你需要克服的最大的障碍有哪些?
+
+**EU:** 好吧,我们没有任何投资者,当然这也是一件好事情。我们从2006年就开始尝试做这件事情,你可以看到它花了我们很长时间才把树莓派从一个想法变成一件能卖的东西。在价格和性能之间或是价格和可编程性之间找到平衡,是一件很重要的事情。
+
+另外一件麻烦事是募集资金。我们是非营利组织,所以我们得去找人赞助,而这最后都变成了董事会中的几个人自掏腰包。我们有25万美元的启动资金是从我和其他几个成员自己借的。所以我觉得,当初这样做还挺有勇气。
+
+
+
+### 从东方到西方 ###
+
+为了找到价格合适的生产方式,我们选了一条不同寻常的路线。通常人们生产更传统的产品时,当量不大的时候都会选择在本地生产,然后[制造商]再制定较高的价格。大多数都能获得比树莓派丰厚的利润。
+
+所以他们开始会在西方生产。然后,为了追求更高的利润,当产品有一定的量就会想减少生产成本,所以转到远东地区。
+
+我们的问题是,因为我们没有足够的利润来支撑这种模式的订单,所以我们在中国制造了第一批产品。当然一开始会有一点不好的预感。我一点也不了解中国制造,最后,我们把价值5万美元的芯片和5万美元现金交给一个香港人,他需要还给我们2000片可以工作的树莓派。
+
+之后交期出现了延时,我们甚至都开始相信自己被骗了。然后终于有一天,现在250万台树莓派中最早的2000台放在托板上来到了门口。
+
+那个UPS快递员从卡车里拖出一个托板,并拉到我们车库里。托板上放着2000台树莓派,它们中每一台都比我小时候用过的计算机强多了。我们随机抽查了几台,都可以完美地工作。
+
+所以我觉得还挺幸运,中国你懂的。然后我们的产品终于开始有量了,我们选择了跟其他所有人不同的方向。我觉得这是这个项目中的另一个决定性时刻,我们认识到,以目前的订单量,我们可以用和在中国同样的成本在西方生产。所以我们可以回归,把所有的生产制造搬回威尔士,也是我出生的地方。像是一个美妙的圆圈。
+
+**RW:** 有没有一些树莓派的前身没有被制造出来的?
+
+**EU:** 有的,我们做了许多不同的原型机。我们希望做出一个可以编程,也能吸引小朋友兴趣的东西。“吸引小朋友兴趣”意味着,在某些方面要足够强大。比如,播放视频,玩游戏,以及上网。
+
+我们有许多能够达到价格目标和可编程目标的原型,但是等我们确定一个合适的方案,它足够强大能够吸引孩子们的热情,已经挺晚了,都到2010年底2011年初了。
+
+### 派是从哪儿烤好的 ###
+
+**RW:** 跟我们说说发明树莓派的故事
+
+**EU:** 我们尝试过基于所谓的微控制器技术做了几台机器。不知道你有没有听过一个叫Arduino的[开源电子原型]平台?它们的性能跟Arduino是一个级别的,优点是很容易买到,是常用的元器件,非常便宜,也很容易掌握。
+
+
+
+所以我们试了一下。最后的成品只能从技术上来说还是计算机,你可以把它接到电视机或其他显示设备上。但是,它太原始了,很明显不能吸引孩子们的兴趣。这个是一号原型机,它在爱尔兰一家博物馆的叫“失败”的展览中展出[笑]。我下个月会去看看。它现在被装载一个玻璃盒子里,作为一次辉煌失败的典型。
+
+好的一面是它是手工制作的,你不可能手工制作一块现代的树莓派。但是,这个原型太原始了,你实际上可以把所有器件手工焊接到一起,它就是我一个星期里做好的,是个挺好的小玩具。
+
+我在大学里呆了差不多10年以后,进入到一家叫Broadcom的公司工作,总部在南加利福尼亚但是在剑桥有个大办公室,主要生产手机芯片。然后,我意识到这种手机芯片非常适合,它是制作像派这样的设备的非常合适的平台,因为它有优秀的图形性能。
+
+我基于Broadcom开发工具制作了一个原型。这次的原型非常强大,也有更多功能,价格也差不多。不过问题是,它有一套定制的开发环境,而不是一个标准的平台。
+
+我们得写自己的SD卡驱动,自己的文件系统,自己的文本编辑器。你会发现你得做大量基础工作,虽然最后你能够得到一个强大的可编程的平台,但是它却是完全非标准的[而且]和其他设备完全不一样。从而无法重用那些已经在台式机系统中已经做过的工作。这个是二号原型机。
+
+真正的突破是三号原型机。我们从Broadcom拿到了另一种应用了ARM处理器的芯片,可以直接运行标准Linux。我们意识到终于可以做出能够满足所有的需求的机器了,这就是我们推向市场的产品。
+
+### 黑一黑下一代黑客 ###
+
+**RW:** 八岁的孩子就开始用树莓派做项目了。这在你意料中吗,还是说让你意外了?
+
+**EU:** 八岁是很好的年纪。我想每个人都会把自己开始编程的年龄定义成合适的年龄。我就是八岁开始编程的。某种程度上来说,孩子们所需要的只是年龄大到拥有相对完整的认知技能,或者说是解决问题的技能。也许在学校学一点数学就够了。
+
+
+
+年龄大到可以计划任务,编程就是终极的计划任务。还是得有一定的智力基础去做这个事情。八岁的时候,大多数孩子在自己的思维上已经非常成熟了。另外还需要敏捷的身手,对更小的孩子来说还存在一个问题就是,他们还不够灵巧去使用键盘。
+
+所以说,八岁是很好的年纪。你有合适的身体,有合适的心智,而且还处于生命中能轻松学习新知识的时候。你的大脑还具有非常大的可塑性,可以学习语言。。。
+
+我的意思是,你要是想让你的小孩学习法语的话,八岁就开始教他,不要等到16岁才开始。正式的计算机教育有一个历史性的缺点,就是太晚开始了,然后就很惊讶为何学生们理解起来概念有困难。所以我认为越早接触越好,而八岁是奇妙的年纪。八岁,十岁,十二岁,十二岁可能都有点晚了。
+
+我们基金会的CEO,[Lance][3] [Howarth],对初级教育特别热心。他真的认为这是一个实际的机会来做点非常特别的事情。
+
+**RW:** 所以这是树莓派项目的目的,让小孩子们编程?
+
+**EU:** 我想我们一直认为可以让孩子们玩编程只是举个例子。但是树莓派的目的是把这个东西做出来看看谁会买它。我们一直相信至少有一部分年轻的孩子会觉得它令人激动。现在我们已经有知识宽度和规模来支持孩子们玩它了。
+
+[仅仅]做出一个像树莓派的平台和提供相关支持是有很大区别的,如果只是做出来的话,你会发现有1%的八岁孩子会喜欢它并且玩起来,不管你提供多或者少的支持。
+
+我觉得现在基金会的一个实际的机会是,我们已经可以承担得起开发教材了,我们还可以提倡培训这方面的教师。有个机会是我们可以吸引比1%更多的孩子。还有个机会是吸引那些没有独自处理复杂技术问题倾向的机灵小孩。如果能够提供良好的教程和让他们感兴趣的教材,就能够吸引10%,20%,50%,甚至更多的孩子。
+
+我们认为80年代是[学习编程]的黄金年代,而实际上,只有很少一部分人学习编程并达到一定深度。大部分人也许可以写个几行,但是能够编写大型程序的还是很少见。
+
+所以我认为我们目前有一个实际的机会,因为我们可以参与到教材和教师培训的级别,我们也许可以超越80年代。现在有更多的参与者,两性之间也更平等。在80年代,编程很大程度上是男孩们的事情,而这也能反映到我们的工程师社区构成上。我觉得现在有个很好的机会,让更多的女孩子接触电脑编程。这个是挂在枝头上垂得最低的果子了,做到这个,人数马上增加了一半。
+
+机会有很多,我对树莓派最满意的地方就是我们已经有点规模可以吸引部分人的注意了。
+
+### 每个人的派 ###
+
+**RW:** 关于像派这样的项目的潜在需求,对于你来说意味着什么?是不是有一天我们都会变成DIY黑客?
+
+**EU:** 是的,我意思是,就是这样的。有非常大的这种需求。而且我认为有一条通向制作者社区的纽带。美国的制作者社区比英国成熟多了。我们也确实在举办制作者集会和黑客空间,但是差不多比美国落后了5年左右。
+
+所以在开始讨论树莓派之后我发现了一件事情,在它获得国际关注的时候,我们发现我们受到一些非常稳定的社区的成员的追捧,他们喜欢各种各样的DIY活动:编织,或者,你知道的,木工。
+
+所以,这也是为树莓派带来意外增长的其中一个因素。制作者们把它当作用来构建自己项目的模块。这太棒了!
+
+**RW:** 你怎么看现在出现的主流硬件黑客文化?
+
+**EU:** 我觉得,这太美妙了,不是吗?这是在软件工程领域里完全无法想到的。我接触这些之前就有软件背景,所以,实际上人们用树莓派制作的大多数很酷的东西都是硬件相关的,让我很惊讶。当然现在没那么吃惊了,不过一开始是有的。
+
+
+
+我认为这是非常积极的趋势,基于所有这些因素。因为它给孩子们带来了相关的经验。在我看来,在屏幕上移动一下像素还是很酷的,不过事实上,它没有像80年代那样酷了。我觉得,在现实世界里移动一些物体,比如机器人,对于现在的孩子来说是非常酷的。
+
+当有更多实用性的时候,就会吸引更多的女孩。确实存在一种潜在趋势,尝试和设计针对女孩子的科技活动。不过实际上这并不是关于女孩子,而是关于扩展用户的迫切要求。
+
+有这样一小段-我之前谈过的关于有1%的小孩会觉得抽象的计算机编程很有趣。“让我们开始学习变量!”我就是他们其中一个。但是,那只是很小一部分,而且看起来更大部分是男孩子。我不知道是不是文化因素或其他的,但是看起来这个世界就是这样的。
+
+在人们谈论追求实用性来吸引女孩子的时候,根本不关女孩子的事。而是吸引那一小部分男孩之外的所有人。不仅仅吸引女孩,也包括其他男孩。
+
+从教育的角度来看有一件美妙的事情是,在现实世界里应用计算机做点实际的东西,自然而然会比仅仅在计算机本身上面做点事情有用多了。所以,这就提供了一个方式来吸引女孩子进入这个领域,同样也可以吸引更多的男孩子进入这个领域。
+
+不再是一个人很好。能够加入到这波兴趣的浪潮中,和许多制作现实世界东西的人一起,也是很精彩的事情。我认识一个南加利福尼亚的小伙,他有两个兴趣就是倒腾派和制作他的锁链甲。有人做这些事情本身就是一件很美妙的事情。
+
+### 分享你的派 ###
+
+**RW:** 关于吸引比1%更多人的“实用”项目,能举个例子吗?
+
+**EU:** 整个机器人技术领域就是个很好的例子。有很多人基于派来制作小型机器人,让它们四周跑跑或做点事情。特别是现在,我们增加了摄像头模块,可以一定程度上实现计算机视觉。
+
+我觉得其他基于摄像头的项目也会变得更活跃。那些从事野外摄影的人们,以及从事缩时摄影的人们,因为有了这个25美元的摄像头模块,应用范围宽了许多。还有红外版本的模块,所以你可以在晚上拍摄野生动物-写脚本在晚上拍摄相片,然后选择保存里面包含了动作的。这些都非常好。
+
+我特别喜欢应用到高空气球的任何项目。环境监控-有一些英国的高中学生在IndieGoGo发起了一个叫[AirPi][4]的项目,这是一个污染监控防御系统,底层将用到树莓派。所以会有许多这样的项目,你可以用派来处理物理的,或化学的,或者生物的事情。-这些都是我认为有实用性的事情。这种项目也更容易向孩子们证明,这是值得他们关注的项目。
+
+**RW:** 我们什么时候可以看到树莓派C型?
+
+**EU:** 暂时还没有计划。我们目前都还在处理软件工作。我觉得我们还有机会通过调整软件来大幅提升系统性能,再优化一下。
+
+如果我们现在就启动制作C型,将会抛弃250万使用目前平台的用户。所以我觉得,至少现在,我们决心要继续软件工作,因为这可以帮到所有已经在这个领域里的人。我们感觉通过软件优化还有很大的性能提升空间。
+
+显然,我们同时也必须做一点[硬件方面]的事情。我真的不知道具体在什么时候。如果到了2017,2018,我们还在销售树莓派B型的话,那也挺糟糕的。但是,我认为我们也许在一年后再认真考虑后面要做什么。
+
+**RW:** 很多人的项目同时用到了派和Arduino(一个DIY电子调试工具套件)。你在设计派的时候,有考虑类似Arduino的工具吗?
+
+**EU:** 实际上没有,但是我们很早就意识到,媒体可能会倾向于把我们和Arduino看作竞争者。对于这件事情我们有点多疑,我觉得,因为我认为派和Arduino分别处理不同的事情,而且他们都做得很好。
+
+我们并没有把它设计成配合Arduino工作,但是Arduino被设计成配合家用PC一起工作。所以,我们实际上为Arduino制作了一台非常低功耗的家用PC。所以好吧,只是巧合,我猜。
+
+**RW:** 你在家里用树莓派做什么?工作中呢?
+
+**EU:** 在家里,我把它当作一个媒体中心;这是树莓派一个非常普通的应用。有趣的事,有些从事消费电子的人,把它当作消费电子来用。我当然也是其中之一。
+
+在工作中,我总是没有我想要的那么多时间来玩玩树莓派。通常在工作的时候如果在用派的话,那是因为我需要测试刚拿到的一些软件更新。大多数时候我用它来检查我花钱请的承包人是否把工作做好了。
+
+我真心希望明年会有更多休息时间。有时我感觉,除了媒体中心之外,我参与制作了这么神奇的玩具,但是因为它太成功了,我都没有时间去好好玩玩它。
+
+不过,看到这么多的人喜欢它,看到它被出现在各种不同的地方,也是很开心的。我听说在《生活大爆炸》中提到了我们,我要去找找是哪一集。它出现在所有的这些不可思议的地方。真是非常开心,看到这么多人把它放在心上,开始用它做点事情。
+
+承蒙树莓派基金会提供Eben Upton的图片;
+
+树莓派图片来自Flickr用户:[Johan Larsson][5], [Clive Darra][6], [Pete Sneekes][7], [Luca Sbardella][8]和[Ashley Basil][9]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://readwrite.com/2014/04/08/raspberry-pi-eben-upton-builders
+
+译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://twitter.com/EbenUpton
+[2]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BBC_Micro
+[3]:http://www.raspberrypi.org/welcome-lance/
+[4]:http://airpi.es/
+[5]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/johanl/8384790662
+[6]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/osde-info/8626662243
+[7]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/p8/7950485168
+[8]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/sbardella/7473604878
+[9]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/28438417@N08/8006786385/in/photolist-dcwSD8-d8PKa3-bmosVm-bmosWG-bz3YJF-e8NRQD-btyqN1-dorXrE-hTF7id-hTF7jL-hTF4mJ-hTF4jj-hTF4q1-hTF7jA-hTF7gj-gKRLrn-ftALdo-c7Qnjs-c7Qnyh-c7QmZj-c7QnY1-c7QmNY-cu8zs3-cu8BWm-cu8u5S-cu8yC3-cu8DBN-cu8wRq-cu8xNL-cu8CJj-cu8tss-cu8BcG-cu8uVL-cu8AoW-hTF7dU-hTEzCr-hTFBCp-hTFBvR-hTFBBH-hTF4hA-hTF7c1-hTEzza-hTFBM2-cdtf1b-bz7n87-gKQSJ7-gKQUko-ds8x8q-dqweVP-cVwvJq
diff --git a/translated/The Linux Kernel/25 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 21.md b/published/The Linux Kernel/25 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 21.md
similarity index 88%
rename from translated/The Linux Kernel/25 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 21.md
rename to published/The Linux Kernel/25 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 21.md
index 03d3ce0196..32b67ad644 100644
--- a/translated/The Linux Kernel/25 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 21.md
+++ b/published/The Linux Kernel/25 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 21.md
@@ -1,20 +1,20 @@
戴文的Linux内核专题:25 配置内核 (21)
================================================================================
-
+
-大家好!本篇我们将会配置Linux内核的网路文件系统支持。网络文件系统是一个通过网络远程访问计算机的远程文件系统。
+大家好!本篇我们将会配置Linux内核的网络文件系统支持。网络文件系统是一个可以通过网络远程访问计算机的远程文件系统。
-首先,"NFS client support"驱动允许linux系统使用NFS网络文件系统。这里还有3个不同版本的NFS - (NFS client support for NFS version 2)、 (NFS client support for NFS version 3)、 (NFS client support for NFS version 4) 和 (NFS client support for NFSv4.1)。如果你有一个处理NFS的网络,找出你正在使用NFS的版本,或者启用所有的NFS驱动。
+首先,"NFS client support"驱动允许linux系统使用NFS网络文件系统。这里还有3个不同版本的NFS - (NFS client support for NFS version 2)、 (NFS client support for NFS version 3)、 (NFS client support for NFS version 4) 和 (NFS client support for NFSv4.1)。如果你有一个使用NFS的网络,找出你正在使用NFS的版本,或者启用所有的NFS驱动。
-交换空间并不需要在本地存储单元上。这个驱动允许Linux使用NFS作为远程交换空间(Provide swap over NFS support)。
+交换空间并不需要总在本地存储单元上。这个驱动允许Linux使用NFS作为远程交换空间(Provide swap over NFS support)。
NFS系统可以通过缓存系统加速 (Provide NFS client caching support)。这是一个本地缓存。
-启用这个驱动允许DNS对NFS服务器使用主机名(Use the legacy NFS DNS resolver)。
+启用这个驱动允许NFS服务器使用DNS解析器(Use the legacy NFS DNS resolver)。
"NFS server support"给予需要满足这个需求的服务器提供了NFS的特性。其他一些NFS驱动包括(NFS server support for NFS version 3) 和 (NFS server support for NFS version 4)。
-"NFS server manual fault injection"驱动是一个调试驱动,它允许开发者让NFS服务器认为在NFS上发生了一个错误。特别地,这是用于测试服务器如何处理NFS错误。
+"NFS server manual fault injection"驱动是一个调试驱动,它允许开发者让NFS服务器认为在NFS上发生了一个错误。特别地,这用于测试服务器如何处理NFS错误。
"Secure RPC: Kerberos V mechanism"被用于RPC安全调用。由于安全原因,没有这个特性,NFS无法被加入到内核中。
@@ -26,8 +26,7 @@ CIFS是一个用于Samba和Windows服务器的虚拟文件系统(CIFS support (a
有两个特性被用于调试或监视CIFS驱动(CIFS statistics) 和 (Extended statistics)。
-
-一个特殊的需要在有LANMAN安全的服务器上需要(Support legacy servers which use weaker LANMAN security)。LANMAN或者LM哈希是一种有一些弱点的特殊的密码哈希函数。
+要在服务器上支持LANMAN安全需要一个特定的驱动(Support legacy servers which use weaker LANMAN security)。LANMAN或者LM哈希是一种较弱的特殊的密码哈希函数。
CIFS在被挂载到安全服务器上之前需要Kerberos票据(Kerberos/SPNEGO advanced session setup)。这个驱动提供了CIFS使用能够提供票据的用户空间工具的能力。
@@ -37,7 +36,7 @@ CIFS在被挂载到安全服务器上之前需要Kerberos票据(Kerberos/SPNEGO
CIFS有两个其他的调试工具(Enable CIFS debugging routines) 和 (Enable additional CIFS debugging routines)。
-CIFS有"DFS feature support",它允许共享在被移除后仍可以访问。DFS代表"Distributed FileSystem"(分布式文件系统)。
+CIFS有"DFS feature support",它允许共享在被移除后仍可以访问。DFS代表"Distributed FileSystem"(分布式文件系统)。
SMB2是CIFS的一个提升替代品(SMB2 network file system support)。SMB2代表的是"Server Message Block version 2"(服务器消息块第2版)。
@@ -85,7 +84,7 @@ Linux内核有一个实验性的驱动,通过9P2000协议访问Plan 9资源(Pl
这个设定分会启用/禁用普遍不需要或者废除的符号 (Enable unused/obsolete exported symbols)。然而,一些模块可能需要这些符号。启用这个会增加内核的大小。Linux用户很少会需要这些符号。通常上,禁用这个特性,除非你了解一个重要的模块需要这个符号。
-如果启用这个shehi,内核会在用户内核头上执行健康检查(Run 'make headers_check' when building vmlinux)。
+如果启用这个设施,内核会在用户内核头上执行健康检查(Run 'make headers_check' when building vmlinux)。
在编译期,这个特性会检查无效的引用(Enable full Section mismatch analysis)。
@@ -115,6 +114,6 @@ Linux内核有一个实验性的驱动,通过9P2000协议访问Plan 9资源(Pl
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-21.4988/
-译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/The Linux Kernel/26 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 22.md b/published/The Linux Kernel/26 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 22.md
similarity index 93%
rename from translated/The Linux Kernel/26 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 22.md
rename to published/The Linux Kernel/26 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 22.md
index a2e77c064f..ff43c1f0ac 100644
--- a/translated/The Linux Kernel/26 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 22.md
+++ b/published/The Linux Kernel/26 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 22.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
戴文的Linux内核专题:26 配置内核 (22)
================================================================================
-
+
你好!本篇我们将继续配置"kernel hacks",接着我们会配置整个安全系统。
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ Alpha和s390处理器需要配置下一个特性(Force weak per-cpu definitions)
"Latency measuring infrastructure"驱动提供了延迟检测工具LatencyTop,以找出用户空间中由于内核执行/任务而被阻碍/干扰的对象。
-下面,我们有一个子菜单名为"Tracers",它包含了不同追踪器的列表。追踪器是一段监视不同内核函数的代码。每次某个特定的函数启动,追踪器将被调用来检测函数。
+下面,我们有一个子菜单名为"Tracers",它包含了不同追踪器的列表。追踪器是一段监视不同内核函数的代码。每次某个特定的函数启动,追踪器将被调用来检测函数。
下面的模块用来测试红黑树库的性能(Red-Black tree test)。红黑树是一个排序和搜索算法。
@@ -28,9 +28,9 @@ printk()函数可以用来打印不同的调试信息,如果这个特性启用
Atomic64自我测试检查系统是否支持原子操作(Perform an atomic64_t self-test at boot)。这是一个32位系统执行64位操作。
-这个驱动提供了对于所有可能的RAID6恢复系统的自我测试(Self test for hardware accelerated raid6 recovery)。
+这个驱动提供了对于所有可能的RAID6恢复系统的自检(Self test for hardware accelerated raid6 recovery)。
-注意:自我测试是底层测试并且在绝大多数系统硬件和软件开启和执行前侦查软件。自我测试搜索硬件,失败的设备等等。自我测试也可能被编成应用测试它本身。
+注意:自检是底层测试并且在绝大多数系统硬件和软件开启和执行前侦查软件。自检搜索硬件,失败的设备等等。自检也可能被编成应用以测试它本身。
在"Kernel Hacking"菜单中(如果你是用的是像ncurses那样的菜单接口),有一个名为"Sample kernel code"的子菜单。在以后的文章中,我们会讨论如何实现自定义/自制内核模块。只要记住这里是启用你自己的模块。
@@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ printk()打印不同的消息到dmsg的启动界面,但是在串行和控制
下面的驱动提供了对"copy_from_user()"系统调用的基本测试(Strict copy size checks)。copy_fcrom_user()从用户空间拷贝数据块到内核空间中。
-这里还有一个自我测试;它用于NNI(NMI Selftest)。
+这里还有一个自检;它用于NMI(NMI Selftest)。
现在,我们会进入"Security Options",如果你使用像ncurses的基于菜单的接口时。第一个选项允许访问内核中存储的键和验证令牌(Enable access key retention support)。这有很多原因用到,像访问加密文件系统。
@@ -114,6 +114,6 @@ Yama是另外一个LSM(Yama support)。如果启用这个特性Yama可以与另
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-22.5017/
-译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/The Linux Kernel/27 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 23.md b/published/The Linux Kernel/27 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 23.md
similarity index 95%
rename from translated/The Linux Kernel/27 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 23.md
rename to published/The Linux Kernel/27 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 23.md
index c1d766f56b..5a10971a31 100644
--- a/translated/The Linux Kernel/27 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 23.md
+++ b/published/The Linux Kernel/27 The Linux Kernel--Configuring the Kernel Part 23.md
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
戴文的Linux内核专题:27 配置内核 (23)
================================================================================
-
+
-欢迎来到内核配置的下一章!本篇中我们会配置密码API,虚拟化和运行库。密码学指的是在需要的计算机之间加密和安全通信。用户可能加密数据以保证是收件人而不是黑客收到数据。
+欢迎来到内核配置的下一章!本篇中我们会配置密码API,虚拟化和运行库。密码学指的是在需要的计算机之间加密和安全通信的科学。用户可能加密数据以保证是收件人而不是黑客收到数据。
Linux内核需要在内核中启用"Cryptographic algorithm manager"(密码算法管理器)。这个特性提供了操作内核的加密特性所需的软件。
@@ -93,7 +93,7 @@ CORDIC algorithm - 双曲线和三角函数。
JEDEC DDR data - JEDEC双倍数据速率SD-RAM规范
-你猜怎么了?我们已经完成便宜内核。在23篇之后,我敢肯定这是你的感觉 -
+你猜怎么了?我们已经完成配置内核。在23篇之后,我敢肯定这是你的感觉 -
视频链接:[http://www.youtube.com/embed/barWV7RWkq0?wmode=opaque][1]
@@ -107,7 +107,7 @@ JEDEC DDR data - JEDEC双倍数据速率SD-RAM规范
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-23.5112/
-译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/The Linux Kernel/28 The Linux Kernel--Compiling and Installing.md b/published/The Linux Kernel/28 The Linux Kernel--Compiling and Installing.md
similarity index 58%
rename from translated/The Linux Kernel/28 The Linux Kernel--Compiling and Installing.md
rename to published/The Linux Kernel/28 The Linux Kernel--Compiling and Installing.md
index 40f655885b..cb5b9a500d 100644
--- a/translated/The Linux Kernel/28 The Linux Kernel--Compiling and Installing.md
+++ b/published/The Linux Kernel/28 The Linux Kernel--Compiling and Installing.md
@@ -1,32 +1,32 @@
戴文的Linux内核专题:28 编译与安装
================================================================================
-
+
-你好!在花费了大量的时间在配置你需要的内核后,你现在可以编译它了。源代码是纯文本形式的C代码。这对人来可读但是对机器不这样。编译会将代码转换成计算机可理解的一种称之为二进制码的形式(1是 [开],0 是 [关])。编译同样会将所有内核代码文件变成一个内核的文件。
+你好!在花费了大量的时间在配置你需要的内核后,你现在可以编译它了。源代码是纯文本形式的C代码。这对人来可读但是对机器可不是这样。编译会将代码转换成计算机可理解的一种称之为二进制码的形式(1是 [开],0 是 [关])。编译同样会将所有内核代码文件变成一个内核的文件。
-为了编译内核,在内核源代码相同目录下,在终端内输入"make"。这会花费一些时间。一旦完成,模块必须通过"make modules"来编译。为了从一开始就简化编译过程,输入"make; make modules"。这会先编译接着是模块,而不用用户再回来输入"make modules"。
+为了编译内核,在内核源代码相同目录下,在终端内输入"make"。这会花费一些时间。完成之后,必须通过"make modules"来编译模块。为了从一开始就简化编译过程,输入"make; make modules"。这会先编译接着是模块,而不用用户再回来输入"make modules"。
-
+
警告:在你安装一个内核时,备份所有的重要数据,确保有一份/boot目录备份在FAT32的存储卡上。这可以在如果安装失败后帮助修复系统。FAT32不会存储权限,因此它更容易被用作live盘来还原数据。记住设置原始文件权限和可执行位。
一旦编译已经成功完成,我们可以安装内核到本地系统中(我会马上解释如何在其他系统上安装内核[交叉编译])。在相同的终端下,在编译完成后,输入"make install"。这会在/boot目录下存放一些文件。"vmlinuz"(或者其他相似的名字)是内核自身。"initrd"是基于内存的文件系统,它被置于内存中且在启动中使用。"System-map"包含了一张内核符号列表。这些全局变量和函数用于内核代码。"config" 是内核的配置文件。grub.cfg会自动更新。然而,有些bootloder需要手动配置。内核安装器会自动配置Grub,LILO和SysLinux bootloder。像BURG这类bootloder需要手动配置。模块的安装同样需要输入"make modules install"。
-
+
注:内核和模块的安装可以写在一行-“make install && make modules_install”。
-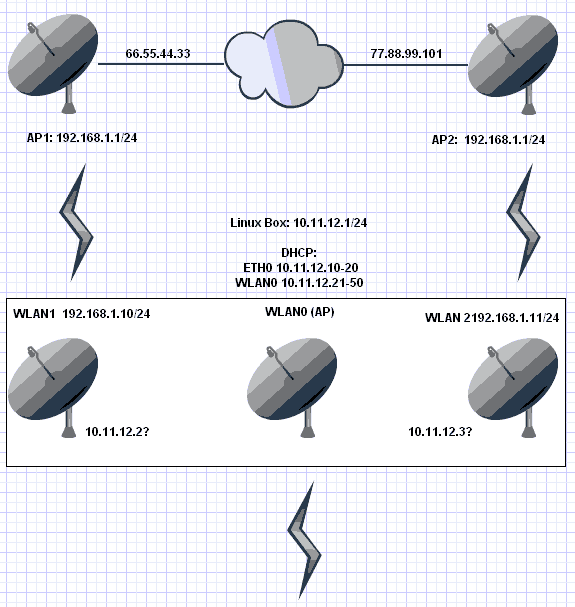
+
一旦上面的过程完成了,用户可以通过重启系统并在开机后在终端内输入"uname -r"来确保内核已经安装。如果系统无法启动或者uname报告你预期外的版本号,这个问题可能众多问题之一引起。或者是bootloader没有正确设置,特性/配置冲突,编译失败,不正确的安装,或者其他原因。找出问题源头最好的方法是查看系统日志(如果系统已经启动到足以产生日志)。"dmsg"是一个在屏幕上打印内核日志的命令。查看错误、警告或者未预料的结果。如果系统没有启动或者没有足够启动完全来生成日志,使用live linux盘来执行诊断和修复。如果所有的都失败了,再次编译内核并确保你已经用root或者"sudo"安装了内核。
注:最好的修复系统的方式是使用live Linux发行版来移除新的/损坏的内核,接着手动修复Grub文件(或者复制一个备份)。
-一些Linux用户也喜欢安装文档,但这并不是必要。对于那些想要安装文档的用户,输入这行,这里的version是你的内核版本号 "install -d /usr/share/doc/linux-VERSION && cp -r Documentation/* /usr/share/doc/linux-VERSION"(VERSION 是内核版本号)。很明显,这需要root特权。
+一些Linux用户也喜欢安装内核文档,但这并不是必要。对于那些想要安装文档的用户,输入这行,这里的version是你的内核版本号 "install -d /usr/share/doc/linux-VERSION && cp -r Documentation/* /usr/share/doc/linux-VERSION"(VERSION 是内核版本号)。很明显,这需要root特权。
-为了编译一个如你目前内核一样特性的内核,输入这条命令"zcat /proc/config.gz > .config"。这个文件可能不存在,如果是这样,你可能需要询问你发行版/内核的开发者这个文件。"zcat"命令解压并写入数据到一个".config"文件中。记住在你希望的地方输入".config"。这个文件放置在Linux内核目录下并允许它替换当前的文件。接着,像往常一样编译安装你的内核。
+要是想编译一个如你目前内核一样特性的内核,输入这条命令"zcat /proc/config.gz > .config"。这个文件可能不存在,如果是这样,你可能需要询问你发行版/内核的开发者这个文件。"zcat"命令解压并写入数据到一个".config"文件中。记住把".config"放到合适的位置。这个文件应该放置在Linux内核目录下,并允许它替换当前的文件。接着,像往常一样编译安装你的内核即可。
-交叉编译稍微有点不同。为目标系统配置内核。确保内核配置完后,它在脑海中交叉配置过了。当交叉编译时,需要熟悉两条术语。"Host"是执行编译的系统,"Target"是接收新内核的系统。确保主机系统有合适的编译器。比如,对于ARM系统的交叉编译,用户需要在主机系统上有gcc-arm-linux-gnueabi。通常来说,开发这可以在他们的包管理器上搜寻或者Googledao合适/最好的适合他们需要的交叉编译器。特定的用于ARM系统交叉编译的命令是"make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi-"。"ARCH=arm"指的是目标处理器的类型,"CROSS_COMPILE"指明了交叉编译器。注意交叉编译器前面缺少了"gcc-"并以破折号结束。这是用户在使用交叉编译器作为参数使用时必须使用的格式。模块可以通过输入"make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi- modules".交叉编译。为了在目标系统上安装内核,复制内核文件夹到目标系统上。一旦文件已在目标系统上并在该目录下打开了终端,输入"make install && make modules_install"。当然你必须是root或者使用"sudo"。
+交叉编译稍微有点不同。为目标系统配置内核。确保内核配置完后,它是以交叉编译配置的。当交叉编译时,需要熟悉两条术语。"Host"是执行编译的系统,"Target"是接收新内核的系统。确保Host主机系统有合适的编译器。比如,对于ARM系统的交叉编译,用户需要在主机系统上有gcc-arm-linux-gnueabi。通常来说,开发者可以在他们的包管理器上搜寻或者Google到合适/最好的适合他们需要的交叉编译器。比如用于ARM系统交叉编译的命令是"make ARCH=arm CROSS\_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi-"。"ARCH=arm"指的是目标处理器的类型,"CROSS\_COMPILE"指明了交叉编译器。注意交叉编译器前面缺少了"gcc-"并以连字符结束。这是用户在使用交叉编译器作为参数使用时必须使用的格式。模块可以通过输入"make ARCH=arm CROSS\_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi- modules"来交叉编译。为了在目标系统上安装内核,将内核文件夹复制到目标系统上。一旦文件已在目标系统上并在该目录下打开了终端,输入"make install && make modules_install"。当然你必须是root或者使用"sudo"。
信息:Kernel.org放了一个支持的交叉编译器列表([https://www.kernel.org/pub/tools/crosstool/][1])。
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@
make && make modules && make install && make modules_install
-#### 做一个更新的版本或者重混你的内核: ####
+#### 做一个更新的版本或者重整你的内核: ####
zcat /proc/config.gz > .config && make && make modules && make install && make modules_install
@@ -50,7 +50,7 @@
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-compiling-and-installing.5208/
-译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/sources/news/20140527 4MLinux 9.0 Beta Is a 55 MB Operating System That Has It All.md b/sources/news/20140527 4MLinux 9.0 Beta Is a 55 MB Operating System That Has It All.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 6e6c1ec9f4..0000000000
--- a/sources/news/20140527 4MLinux 9.0 Beta Is a 55 MB Operating System That Has It All.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,42 +0,0 @@
-4MLinux 9.0 Beta Is a 55 MB Operating System That Has It All
-================================================================================
-
-
-**4MLinux, a mini Linux distribution that is focused on the 4Ms of computing, Maintenance (system rescue Live CD), Multimedia (e.g., playing video DVDs), Miniserver (using the inetd daemon), and Mystery (Linux games), has advanced to version 9.0 Beta.**
-
-4MLinux is one of the smallest distributions in the world that are still able to provide users with a desktop environment and a number of applications that can make this OS something to be used on a daily basis.
-
-Most of the minimalistic Linux operating systems don't usually provide such a plethora of applications right from the start, especially if we keep in mind that the distro only weighs a little over 55MB.
-
-“The main features in this release are maintenance (MBR and GPT partitioning software, 4MLinux Backup Scripts 9.0, ClamAV 0.98.3), multimedia (MPlayer SVN-r37146, FFmpeg Git-2014-04-10), a mini server (FTP, HTTP, SSH, SFTP), and mystery (a set of small games).”
-
-“The X Window System is based on X.Org Server 1.15.1, Mesa 10.1.3, JWM 2.2.2, and the FOX toolkit 1.6.49. Fully automatic installation of the ‘vanilla’ versions of LibreOffice 4.2.4, Java RE 7u55, and VirtualBox 4.3.12 is also supported. The size of the ISO image is about 55 MB,” said the developer on his blog.
-
-As you can see, most of the packages provided are very new, like VirtualBox, LibreOffice, Mesa, Ffmpeg, ClamAV, and so on. If you have any doubts about this release, you can always start it in a virtual machine and take it for a spin.
-
-What's interesting is the fact that users can stop the booting process right before the X Server kicks in and use the system in command line, which is actually a nice change of pace.
-
-The developer will now start to release all the other distributions that he is building around this major update, like Allinone, Gaming, Server, Media, Rescue, and so on. Keep in mind that you can install any of these Linux distros from the main launcher with the help of a very simple piece of software.
-
-Users will also find that most of the applications that you need are available in the repositories and that the 4MLinux distro can be turned into any of the flavors mentioned above just by downloading the appropriate packages.
-
-A complete list of changes and updates can be found in the official [announcement][1].
-
-### Download 4MLinux 9.0 Beta: ###
-
-- [4MLinux 8.2 (ISO)][2][iso] [53.90 MB]
-- [4MLinux 9.0 Beta (ISO)][3][iso] [53 MB]
-
-Remember that this is a development version and it should NOT be installed on production machines. It is intended for testing purposes only.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/4MLinux-9-0-Beta-Is-a-55-MB-Operating-System-that-Has-It-All-443946.shtml
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://4mlinux-releases.blogspot.ro/2014/05/4mlinux-90-beta-released.html
-[2]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/linux4m/files/8.0/updates/8.2/livecd/4MLinux-8.2.iso/download
-[3]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/linux4m/files/9.0/livecd/4MLinux-9.0.iso/download
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/news/20140527 Apache Tomcat 7.0.54 Now Available for Download.md b/sources/news/20140527 Apache Tomcat 7.0.54 Now Available for Download.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c7e2643879..0000000000
--- a/sources/news/20140527 Apache Tomcat 7.0.54 Now Available for Download.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
-alim0x translating
-
-Apache Tomcat 7.0.54 Now Available for Download
-================================================================================
-
-
-**Apache Tomcat 7.0.54, an open source software implementation of the Java Servlet and JavaServer Pages technologies, developed under the Java Community Process, is now available for download.**
-
-It's been a while since the latest Apache Tomcat release, but this only means that the devs had more time to get more fixes and changes into the software. This is a source package, so regular users don't really need it.
-
-According to the changelog, the custom UTF-8 decoder has been fixed, more options have been added for managing the FIPS mode in the AprLifecycleListener, an infinite loop has been avoided if an application calls session.invalidate() from the destroyed session, removing an MBean notification listener now reverts all the operations performed when adding an MBean notification listener, and information about finished deployment and its execution time has been added to the log files.
-
-Also, a few additional locations where, theoretically, a memory leak could occur have been patched, the authentication of users when using the JAASMemoryLoginModule has been fixed, and a regression in the handling of back-slash has been corrected.
-
-A complete list of changes, fixes, and new features can be found in the official changelog, inside the source archive.
-
-### Download Apache Tomcat 7.0.54 (violetagg): ###
-
-- [tar.gz (6.0.39 Stable)][1][binary] [6.70 MB]
-- [tar.gz (6.0.39 Stable)][2][sources] [3.40 MB]
-- [tar.gz (7.0.52 Development)][3][binary] [8 MB]
-- [tar.gz (7.0.52 Development)][4][sources] [4.40 MB]
-- [zip (8.0.3 Beta Development)][5][binary] [8.10 MB]
-- [tar.gz (8.0.3 Beta Development)][6][sources] [4.40 MB]
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Apache-Tomcat-7-0-54-Now-Available-for-Download-443862.shtml
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://mirrors.hostingromania.ro/apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-6/v6.0.39/bin/apache-tomcat-6.0.39.tar.gz
-[2]:http://mirrors.hostingromania.ro/apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-6/v6.0.39/src/apache-tomcat-6.0.39-src.tar.gz
-[3]:http://www.apache.org/dist/tomcat/tomcat-7/v7.0.52/bin/apache-tomcat-7.0.52.tar.gz
-[4]:http://www.apache.org/dist/tomcat/tomcat-7/v7.0.52/src/apache-tomcat-7.0.52-src.tar.gz
-[5]:http://mirrors.hostingromania.ro/apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-8/v8.0.3/bin/apache-tomcat-8.0.3.tar.gz
-[6]:http://mirrors.hostingromania.ro/apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-8/v8.0.3/src/apache-tomcat-8.0.3-src.tar.gz
diff --git a/sources/news/20140702 CoreOS Linux ending the upgrade cycle.md b/sources/news/20140702 CoreOS Linux ending the upgrade cycle.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ca6dea9964
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/news/20140702 CoreOS Linux ending the upgrade cycle.md
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+CoreOS Linux ending the upgrade cycle
+CoreOS Linux结束升级周期
+================================================================================
+> CoreOS发布了他的Linux发行版的商用支持版,并且宣称将废除手动更新。
+
+国际数据集团新闻社消息——CoreOS发布了商用Linux发行版,以期能简化系统管理员的生活。这个Linux发行版可持续进行自动更新,不需要进行重大升级。
+
+CoreOS提供其同名的Linux发行版做为商业服务,开始为一个月100美元。
+
+“商家现在可以开始考虑将CoreOS作为他们系统团队的延伸,对于企业Linux客户,这将是他们会需要的最后一次迁移。”CoreOS的创始人和CEO在一份声明中这样说。
+
+商业Linux订阅并不是什么新鲜事:[Red Hat][2]和[Suse][3]都在为他们各自的发行版提供商业订阅。
+
+因为这些以Linux为基础的公司使用的应用程序和库都是开源和免费提供的,所以订阅的费用不包括软件本身,而收费来自更新,漏洞修复,集成以及发生问题时的技术支持。
+
+CoreOS公司声称,CoreOS将会和这些发行版不同,它将不会有重大更新,而这些更新通常需要一次更新更新所有的包。它的更新和新特征将会在就绪后自动。。。。CoreOS will be different from these distributions, the company asserted, in that there will be no major updates, which typically require updating all the packages in the distribution at once. Instead, updates and new features will be streamed automatically to the copy of the OS and applied as soon as they are ready.
+
+The service offers a dashboard, called CoreUpdate, that provides controls for designating which software packages should get updated, should the administrator not want all the packages to be updated automatically.
+
+CoreUpdate can manage multiple machines at once, and offers a roll-back capability should an update cause issues.
+
+Launched last December, CoreOS was designed to [focus][4] on an emerging use of the open-source OS kernel -- that of powering lots of cloud-based virtual servers.
+
+The average CoreOS instance was designed to consume only less than half of what other Linux distributions typically consume. All applications that run on the distribution run in Docker virtualized containers, so they can be started almost instantaneously.
+
+The distribution can be updated more easily [due to its novel use of two partitions][5]. One can contain the current version of the OS while the OS is being updated in the other, smoothing the process of upgrading a package, or the entire distribution.
+
+The CoreOS service can be run on-premises, or through Amazon, Google and Rackspace cloud services.
+
+CoreOS also announced Monday that it received $8 million in backing from the Kleiner Perkins Caulfield and Byers venture capital firm. The company has previously gotten investment from Sequoia Capital and Fuel Capital.
+
+----------
+
+Joab Jackson covers enterprise software and general technology breaking news for The IDG News Service. Follow Joab on Twitter at [@Joab_Jackson][6]. Joab's e-mail address is [Joab_Jackson@idg.com][7]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.computerworld.com/s/article/9249460/CoreOS_Linux_ending_the_upgrade_cycle?taxonomyId=122
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://coreos.com/products/managed-linux/plans/
+[2]:http://www.redhat.com/about/subscription/
+[3]:https://www.suse.com/support/programs/subscriptions/
+[4]:http://www.networkworld.com/article/2177120/cloud-computing/coreos-linux-distro-lands-on-the-google-cloud-platform.html
+[5]:https://coreos.com/using-coreos/updates/
+[6]:http://twitter.com/Joab_Jackson
+[7]:Joab_Jackson@idg.com
diff --git a/sources/news/20140709 Dwarf Fortress Sees First New Release In 2 Years.md b/sources/news/20140709 Dwarf Fortress Sees First New Release In 2 Years.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f958f829a7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/news/20140709 Dwarf Fortress Sees First New Release In 2 Years.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+Dwarf Fortress Sees First New Release In 2 Years
+================================================================================
+
+
+[Dwarf Fortress][1] is a single-player fantasy game. You can control a dwarven outpost or an adventurer in a randomly generated, persistent world. The kicker is that the graphics are all text, no actual graphics. There are of course mods to make it graphical however.
+
+I have to say I don't get the fuss at all with this one. The interface is confusing and it's not nice to look at, but I am guessing with plenty of graphical mods it could get pretty good considering everything you can do in it. I understand it will have a massive amount of replayability due to generating a new world each time, but it just doesn't look inviting to someone who hasn't played a game like it before.
+
+This new release is the first in 2 years and has massive changes as you might imagine. See the [full rundown here][1].
+
+What do people see in it exactly? I know plenty of you play it as the amount of people to email it in was crazy. I'm just going to sit back and let the "omg your crazy" comments come in.
+
+
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/dwarf-fortress-sees-first-new-release-in-2-years.3997
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.bay12games.com/dwarves/index.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/news/20140714 IPFire 2.13 Core 77 Linux Firewall Distro Brings Major OpenVPN Improvements.md b/sources/news/20140714 IPFire 2.13 Core 77 Linux Firewall Distro Brings Major OpenVPN Improvements.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cae86c7be8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/news/20140714 IPFire 2.13 Core 77 Linux Firewall Distro Brings Major OpenVPN Improvements.md
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+IPFire 2.13 Core 77 Linux Firewall Distro Brings Major OpenVPN Improvements
+================================================================================
+
+
+**Michael Tremer, a developer for the ipfire.org team, has announced that IPFire 2.13 Core 79, a new stable build of the popular Linux-based firewall distribution, is now out with some exciting new features.**
+
+IPFire is a modular Linux distribution, which means that it can be deployed as a firewall, a proxy server, or a VPN gateway. The main concern of the developers is security and every step has been taken in order to ensure that users can feel really safe when using this operation system.
+
+The developers are saying in the official [announcement][1] that the “Core Update 79 is finally arriving with many bug fixes and enhancements. Among the big changes with this update are lots feature enhancements that massively increase the security level of OpenVPN connections, some enhancements of the web user interface and a lot more awesome stuff under the hood.”
+
+The IPFire devs had another huge release a few months ago and it looks like they have made another one, this time focusing on the improvement of the OpenVPN features and a few other aspects.
+
+“The certificate authority that can be created on the OpenVPN page now uses much better hashes to protect the integrity of itself. The CA root certificate uses a SHA512 hash and a RSA key with length of 4096 bit. All new created host certificates use a RSA key with 2048 bit length and a SHA256 hash. Additionally, a set of Diffie-Hellman parameters can be generated for better protection of the session keys. The length of the pregenerated DH parameters can be chosen in the web interface,” also noted the devs.
+
+According to the changelog, the cipher that is used for each net-to-net connection can now be changed, the hash function is now configurable with a few options like SHA2 (512, 384, and 256-bit), Whirpool (512 bit), and SHA1 (160 bit), and the tls-auth option can be enabled, which uses a HMAC function.
+
+The Linux kernel used by the distribution has also been updated in this release and the OS now packs the 3.10.44 version. This should bring support for new hardware, a number of security fixes, and more stability.
+
+Also, snort (the Intrusion Detection System) has been updated to version 2.9.6.1, the new firewall GUI now supports blocking access to the GREEN firewall interface, the PIE packet scheduler has been added, and the default size of the root partition has been increased.
+
+The developers recommend all users of IPFire to upgrade their distributions. More details can be found on the official website.
+
+Download IPFire 2.13 Core 79:
+
+- [IPFire 2.15 Core 79][1] (ISO)[iso] [126 MB]
+- [IPFire 3.0 Alpha 1][2] (ISO)[iso] [76 MB]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/IPFire-2-13-Core-77-Linux-Firewall-Distro-Brings-Major-OpenVPN-Improvements-450605.shtml
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.ipfire.org/news/ipfire-2-15-core-update-79-released
+[2]:http://downloads.ipfire.org/releases/ipfire-2.x/2.15-core79/ipfire-2.15.i586-full-core79.iso
+[3]:http://www.rowie.at/ipfire/iso/ipfire-3.0-alpha1.i686.iso
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/news/20140714 LFTP 4.5.3 File Transfer Software Is for People Who Love the Terminal.md b/sources/news/20140714 LFTP 4.5.3 File Transfer Software Is for People Who Love the Terminal.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bd30878420
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/news/20140714 LFTP 4.5.3 File Transfer Software Is for People Who Love the Terminal.md
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+LFTP 4.5.3 File Transfer Software Is for People Who Love the Terminal
+================================================================================
+
+
+**LFTP 4.5.3, a sophisticated file transfer program with a command-line interface that supports FTP, HTTP, FISH, SFTP, HTTPS, and FTPS protocols, has been released and is ready for download.**
+
+Every operation made with LFTP is reliable, which means that, if any non-fatal error occurs, the operation is retried automatically. The software supports numerous protocols, but it can also handle a few other tasks, such as BitTorrent downloads, SRV DNS records, job queuing, bookmarks, aliases, and many more.
+
+“lftp has shell-like command syntax allowing you to launch several commands in parallel in background (&). It is also possible to group commands within () and execute them in background. All background jobs are executed in the same single process. You can bring a foreground job to background with ^Z (c-z) and back with command ‘wait’ (or ‘fg’ which is alias to ‘wait’),” reads the official website.
+
+According to the changelog, a new setting ftp:site has been added, the http body is not uncompressed when the Contrent-Type is compressed, the source address of DHT replies is now checked, and the disconnected torrent peers are now discarded after only a timeout.
+
+A complete list of changes and improvements can be found in the official [announcement][1].
+
+Download LFTP 4.5.3:
+
+- [LFTP 4.5.3 tar.xz][2][sources] [1.40 MB]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/LFTP-4-5-3-File-Transfer-Software-Is-for-People-Who-Love-the-Terminal-450596.shtml
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://lftp.yar.ru/news.html
+[2]:http://lftp.yar.ru/ftp/lftp-4.4.15.tar.xz
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/news/20140718 OpenMorrowind 0.31.0 RPG Remake Is Already Looking Great.md b/sources/news/20140718 OpenMorrowind 0.31.0 RPG Remake Is Already Looking Great.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b3202309a9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/news/20140718 OpenMorrowind 0.31.0 RPG Remake Is Already Looking Great.md
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+OpenMorrowind 0.31.0 RPG Remake Is Already Looking Great
+================================================================================
+
+
+**OpenMW, an open source implementation of The Elder Scrolls 3: Morrowind game engine and functionality, is now at version 0.31.0 and packs lots of new features.**
+
+OpenMW, or OpenMorrowind, is a project that aims to bring one of best role-playing games ever created into the open source world, but not by simple porting. The makers of this title have been working non-stop in the last months and it seems that the game is really starting to take shape.
+
+Half a year ago, players couldn't do much in OpenMW, but now a lot of features have been integrated, and it's almost playable if you don't expect too much. Even with all the changes in place, the version number indicates that the development is moving rather slowly and numerous problems still remain. It will take a long time until the game reaches a stable version, but when it gets there, it's going to be an awesome RPG.
+
+“The OpenMW team is proud to announce the release of version 0.31.0! This release includes implementation of many smaller features that have been sorely missing, as well fixes for a ridiculous amount of bugs. Many thanks to our developers for their relentless attention to detail. Some optimization has made it into this release, let us know if you see any increased performance,” reads the announcement on the official website.
+
+A number of important changes have been made and lots of new stuff has been added. For example, a periodic cleanup/refill has been added, precipitation and weather particles are now ready in the engine, the dialog has been merged, saving missing creature state is now working properly, the murder crime has been implemented, a number of sneak skill enhancements have been added, and animated main menu support has been implemented.
+
+Also, the clouds and weather have been modified to better match vanilla Morrowind, the background tracks are no longer repeating, the dead body collision behavior has been improved, and lots of other fixes have been implemented.
+
+A complete list of changes and new features can be found in the official [announcement][1]. Users must legally own and install the game before they can use OpenMW – as it is intended – to play Morrowind.
+
+Download OpenMW 0.31.0:
+
+- [tar.gz][2][sources] [3.20 MB]
+- [tar.gz (64-bit)][3][binary] [33.40 MB]
+- [tar.gz (32-bit)][4][binary] [33.10 MB]
+- [Ubuntu PPA Repository][5][ubuntu_deb] [0 KB]
+- [Arch Linux Package][6][binary] [0 KB]
+- [Debian PPA Repository][7][debian_deb] [0 KB]
+
+OpenMW aims to be a full-featured reimplementation of the Morrowind engine capable to work natively on all supported platforms and to support all existing content, including Tribunal, Bloodmoon, and all user-created mods.
+
+Keep in mind that this is not a stable version and bugs might still appear.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/OpenMorrowind-0-31-0-RPG-Remake-Is-Already-Looking-Great-451120.shtml
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://openmw.org/2014/openmw-0-31-0/
+[2]:https://github.com/OpenMW/openmw/archive/openmw-0.31.0.tar.gz
+[3]:https://github.com/OpenMW/openmw/releases/download/openmw-0.31.0/openmw-0.31.0-Linux-64Bit.tar.gz
+[4]:https://github.com/OpenMW/openmw/releases/download/openmw-0.31.0/openmw-0.31.0-Linux.tar.gz
+[5]:https://launchpad.net/~openmw/+archive/openmw
+[6]:https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/?O=0&K=openmw
+[7]:http://forum.openmw.org/viewtopic.php?f=20&t=1298
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/news/20140718 Time to Upgrade--Ubuntu 13.10 Support Ends Today.md b/sources/news/20140718 Time to Upgrade--Ubuntu 13.10 Support Ends Today.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..68dbc2d138
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/news/20140718 Time to Upgrade--Ubuntu 13.10 Support Ends Today.md
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+nd0104 is translate
+Time to Upgrade: Ubuntu 13.10 Support Ends Today
+================================================================================
+
+
+**It’s had a fair old run, but after 9 months basking in the sun today marks the end of official support for Ubuntu 13.10 ‘Saucy Salamander’.**
+
+> Despite the name ‘Saucy’, the changes on offer were rather bland
+
+Those still running it should look at upgrading to the most recent stable release, Ubuntu 14.04 LTS. Launched back in April, it will be supported with updates on the desktop all the way until mid-April 2019.
+
+Support for the server version of Ubuntu 13.10 also formally ends today.
+
+### Saucy Loses Flavour ###
+
+Ubuntu 13.10 came out last October with Canonical pledging to provide a full 9 months of ongoing security and bug fixes on the desktop. As of July 17 these updates will cease and no further updates or backported packages will be provided.
+
+Canonical’s [recommended upgrade path][1] is to 14.04, a transition that can be handled directly on the desktop itself through the Software Updater application or via the command line through the ‘`do-release-upgrade`‘ command.
+
+Saucy in name, but bland in nature, 13.10 is far from being one of Ubuntu’s more remarkable releases — [as evidenced by many of the online reviews at the time][2].
+
+It was, however, notable for inflicting(注:这个单词原文有删除线) introducing Smart Scopes to the Unity Dash, adding a keyboard indicator for faster language layout switching, and being the first release to integrate `Ubuntu One Single Sign-on` into the installation experience.
+
+For a natty visual rundown of all that debuted with it you can watch the compilation video below.
+
+Youtobe 视频地址:[http://www.youtube.com/embed/1EiRQ-znEcI?feature=oembed][3]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/ubuntu-13-10-support-ends-today
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://help.ubuntu.com/community/TrustyUpgrades
+[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/10/ubuntu-13-10-press-reaction
+[3]:http://www.youtube.com/embed/1EiRQ-znEcI?feature=oembed
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/news/20140722 Budgie Desktop 5.1 Is a Superb New Desktop Environment for Conservative Users.md b/sources/news/20140722 Budgie Desktop 5.1 Is a Superb New Desktop Environment for Conservative Users.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..882bb67481
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/news/20140722 Budgie Desktop 5.1 Is a Superb New Desktop Environment for Conservative Users.md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+Budgie Desktop 5.1 Is a Superb New Desktop Environment for Conservative Users
+================================================================================
+
+
+**The developer of Evolve OS, Ikey Doherty, has made a new desktop environment called Budgie Desktop and released a new version of it.**
+
+Evolve OS hasn't been launched yet, but the developer is actively working on it. Instead of adopting an existing desktop environment, he decided that it would be better to make his own. It's based on GNOME and uses quite a few GNOME packages, but it looks very different. In fact, it follows the same paradigm as MATE and Cinnamon, although Budgie seems to be a little more modern and polished.
+
+It's quite interesting to see that a critical piece of technology is released before the operating system that it's going to serve, but potential users don't have to be completely taken by surprise. To that effect, a [PPA][1] has been put in place for Ubuntu 14.04 LTS and Ubuntu 14.10, although it's not official. Also, the Arch Linux users will find the new desktop environment in the AUR repository.
+
+“Almost all of the changes since v4 have been related to the panel. It’s been completely rewritten in Vala, lowering the maintenance overhead and significantly reducing the barrier of entry for new contributors. So, when your update comes through later on (hopefully) today through OBS if you use it, or for Evolve OS users you already have the update, you should only see minor visual differences. The idea was not to change the look, but to rewrite what was there and make it moar better.”
+
+“The rewrite into Vala took quite some effort, but has immediately paid off. In the future all of the desktop will be rewritten to use Vala, and being the ‘second write’ – we do things better the second time around,” says Ikey Doherty in the release [announcement][2].
+
+Even if the desktop environment looks pretty advanced, judging by the version number, there is still room for improvements. The developer has promised that the next release in the series, 6.x, will allow users to write plugins in any language supported by libpeas, and that includes C, Vala, JavaScript, and Python.
+
+Users will also notice that some of the main elements from Budgie Desktop have remained in place, like the position of the menu and the size of the icons. In the future, it will be possible to change them, but for now, users need to contend with what's available.
+
+Even in this incipient phase, Budgie Desktop 5.1 looks better than many of the alternatives that can be found right now on other OSes.
+
+Download the source package right now for Ubuntu and Arch Linux:
+
+- [GIT sources][3][sources] [0 KB]
+- [Ubuntu 14.04 PPA Repository][4][ubuntu_deb] [0 KB]
+- [Arch Linux binary][5][binary] [0 KB]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Budgie-Desktop-5-1-Is-a-Superb-New-Desktop-Environment-For-Conservative-Users-451477.shtml
+
+原文作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
+[1]:https://launchpad.net/~sukso96100/+archive/ubuntu/budgie-desktop
+[2]:https://evolve-os.com/2014/07/20/budgie-desktop-v5-1-released/
+[3]:https://github.com/evolve-os/budgie-desktop/
+[4]:https://launchpad.net/~sukso96100/+archive/ubuntu/budgie-desktop?field.series_filter=trusty
+[5]:https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/budgie-desktop-git
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/news/20140725 GOG.com Now Supports Linux.md b/sources/news/20140725 GOG.com Now Supports Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a20343e2dd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/news/20140725 GOG.com Now Supports Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
+GOG.com Now Supports Linux!
+================================================================================
+> 50 games for the free OS available right NOW!
+
+[][1]
+
+A while ago, [we've announced our plans][2] to add Linux support as one of the features of our digital platform, with 100 games on the launch day sometime this fall. We've put much time and effort into this project and now we've found ourselves with over 50 titles, classic and new, prepared for distribution, site infrastructure ready, support team trained and standing by, and absolutely no reason to wait until October or November. We're still aiming to have at least 100 Linux games in the coming months, but we've decided not to delay the launch just for the sake of having a nice-looking number to show off to the press. It's not about them, after all, it's about you. So, one of the most popular site feature requests on our [community wishlist][3] is granted today: Linux support has officially arrived on GOG.com!
+
+The first 50+ titles we've have in store for you come from all the corners of our DRM-Free catalog. Note that we've got many classic titles coming officially to Linux for the very first time, thanks to the custom builds prepared by our dedicated team of penguin tamers. That's over twenty fan-favorite GOG.com classics, like [FlatOut][4]&[Flatout 2][5], , [Darklands][6], or [Realms of the Haunting][7] we've personally ushered one by one into the welcoming embrace of Linux gamers. That's already quite a nice chunk of our back-catalog, and you can expect more from our dedicated Linux team soon!
+
+Now, for the recent titles. We've got some indie games with native Linux versions that finally find their well-deserved spot in our store. Among them, debuting on Linux, [CLARC][8] - a well received original comedic Sci-Fi puzzler. On top of that, be on the lookout for two new additions to the GOG.com catalog: [Gods Will Be Watching][9] (coming in a couple of hours) and [Unrest:Special Edition][10] (Linux build coming right up!), both of them very fresh and intriguing. This is the very first time we can provide you with all the PC versions of a premiere game, and we will continue to do so in the future. If there's a Linux version of a title we're releasing, our aim is to deliver it to you Day-1. But enough about us, let's talk about the games. Here's what you can be playing on Linux today:
+
+- [**Anomaly Warzone Earth**][11]
+- [**Ascendant**][12]
+- [**Bionic Dues**][13]
+- [**Blake Stone: Aliens of Gold**][14] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Blake Stone: Planet Strike**][15] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Bloodnet**][16] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Braveland**][17]
+- [**CLARC**][18] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Darklands**][19] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Darwinia**][20]
+- [**Defcon**][21]
+- [**Don't Starve + DLC**][22]
+- [**Dragonsphere**][23] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Duke Nukem 3D: Atomic Edition**][24]
+- [**FlatOut**][25] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Flatout 2**][26] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Fragile Allegiance**][27] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Gemini Rue**][28]
+- [**Gods Will Be Watching**][29]
+- [**Hammerwatch**][30]
+- [**Hocus Pocus**][31] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Kentucky Route Zero**][32]
+- [**The Last Federation**][33]
+- [**Legend of Grimrock**][34]
+- [**Litil Divil**][35] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Long Live the Queen**][36]
+- [**MouseCraft**][37]
+- [**Multiwinia**][38]
+- [**Normality**][39] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Pinball Gold Pack**][40] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Pinball World**][41] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Pirates! Gold Plus**][42] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Realms of the Haunting**][43] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Rex Nebular and the Cosmic Gender Bender**][44] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Rise of the Triad: Dark War**][45] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Shattered Haven**][46]
+- [**The Shivah HD**][47]
+- [**Sid Meier's Colonization**][48] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Sid Meier's Covert Action**][49] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Sir, You Are Being Hunted**][50]
+- [**Slipstream 5000**][51] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Space Pirates and Zombies**][52]
+- [**Spacechem**][53]
+- [**Stargunner**][54] - first time on Linux!
+- [**SteamWorld Dig**][55]
+- [**Super Hexagon**][56]
+- [**Surgeon Simulator 2013**][57]
+- [**Sword of the Samurai**][58] - first time on Linux!
+- [**Teslagrad**][59]
+- [**Unrest:Special Edition**][60] (Linux build on the way!)
+- [**Uplink**][61]
+- [**VVVVVV**][62]
+
+As if this wasn't exciting enough, we've put more than half of these titles on a [special promo][63]! Head out to the [promo page][64] and find out which of them you can get up to 75% off until Tuesday, 9:59AM GMT. Of course, all of the games from the list above that you already own will be updated with Linux versions with no additional cost for you, just as you might have expected from GOG.com.
+
+"OK, but how will Linux support actually work on GOG.com" - you might ask. For both native Linux versions, as well as special builds prepared by our team, GOG.com will provide distro-independent tar.gz archives and support convenient DEB installers for the two most popular Linux distributions: Ubuntu and Mint, in their current and future LTS editions. Helpful and responsive customer support has always been an important part of the GOG.com gaming experience. We wouldn't have it any other way when it comes to Linux, and starting today our helpdesk offers support for our official Linux releases on Ubuntu and Mint systems.
+
+Diversity and freedom of choice have always been an important part of the GOG.com way. We're very glad that we could improve our service with the addition of the free (and DRM-Free) alternative to the commercial operating systems. Talking with gamers is just as important, so we're counting on your feedback! If you've got any questions, suggestions, or run into any trouble, just tell us in the forum thread below this post. Just please be gentle, this is [our very first time][65] with Linux. Happy launch day, everyone!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.gog.com/news/gogcom_now_supports_linux
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.gog.com/promo/linux_launch_promo_240714
+[2]:http://www.gog.com/news/gogcom_soon_on_more_platforms
+[3]:http://www.gog.com/wishlist/site#search=linux
+[4]:http://www.gog.com/game/flatout
+[5]:http://www.gog.com/game/flatout_2
+[6]:http://www.gog.com/game/darklands
+[7]:http://www.gog.com/game/realms_of_the_haunting
+[8]:http://www.gog.com/game/clarc
+[9]:http://www.gog.com/game/gods_will_be_watching
+[10]:http://www.gog.com/game/unrest_special_edition
+[11]:http://www.gog.com/game/anomaly_warzone_earth
+[12]:http://www.gog.com/game/ascendant
+[13]:http://www.gog.com/game/bionic_dues
+[14]:http://www.gog.com/game/blake_stone_aliens_of_gold
+[15]:http://www.gog.com/game/blake_stone_planet_strike
+[16]:http://www.gog.com/game/bloodnet
+[17]:http://www.gog.com/game/braveland
+[18]:http://www.gog.com/game/clarc
+[19]:http://www.gog.com/game/darklands
+[20]:http://www.gog.com/game/darwinia
+[21]:http://www.gog.com/game/defcon
+[22]:http://www.gog.com/game/dont_starve
+[23]:http://www.gog.com/game/dragonsphere
+[24]:http://www.gog.com/game/duke_nukem_3d_atomic_edition
+[25]:http://www.gog.com/game/flatout
+[26]:http://www.gog.com/game/flatout_2
+[27]:http://www.gog.com/game/fragile_allegiance
+[28]:http://www.gog.com/game/gemini_rue
+[29]:http://www.gog.com/game/gods_will_be_watching
+[30]:http://www.gog.com/game/hammerwatch
+[31]:http://www.gog.com/game/hocus_pocus
+[32]:http://www.gog.com/game/kentucky_route_zero_season_pass
+[33]:http://www.gog.com/game/last_federation_the
+[34]:http://www.gog.com/game/legend_of_grimrock
+[35]:http://www.gog.com/game/litil_divil
+[36]:http://www.gog.com/game/long_live_the_queen
+[37]:http://www.gog.com/game/mousecraft
+[38]:http://www.gog.com/game/multiwinia
+[39]:http://www.gog.com/game/normality
+[40]:http://www.gog.com/game/pinball_gold_pack
+[41]:http://www.gog.com/game/pinball_world
+[42]:http://www.gog.com/game/pirates_gold_plus
+[43]:http://www.gog.com/game/realms_of_the_haunting
+[44]:http://www.gog.com/game/rex_nebular_and_the_cosmic_gender_bender
+[45]:http://www.gog.com/game/rise_of_the_triad__dark_war
+[46]:http://www.gog.com/game/shattered_haven
+[47]:http://www.gog.com/game/the_shivah
+[48]:http://www.gog.com/game/sid_meiers_colonization
+[49]:http://www.gog.com/game/sid_meiers_covert_action
+[50]:http://www.gog.com/game/sir_you_are_being_hunted
+[51]:http://www.gog.com/game/slipstream_5000
+[52]:http://www.gog.com/game/space_pirates_and_zombies
+[53]:http://www.gog.com/game/spacechem
+[54]:http://www.gog.com/game/stargunner
+[55]:http://www.gog.com/game/steamworld_dig
+[56]:http://www.gog.com/game/super_hexagon
+[57]:http://www.gog.com/game/surgeon_simulator_2013
+[58]:http://www.gog.com/game/sword_of_the_samurai
+[59]:http://www.gog.com/game/teslagrad
+[60]:http://www.gog.com/game/unrest_special_edition
+[61]:http://www.gog.com/game/uplink_hacker_elite
+[62]:http://www.gog.com/game/vvvvvv
+[63]:http://www.gog.com/promo/linux_launch_promo_240714
+[64]:http://www.gog.com/promo/linux_launch_promo_240714
+[65]:http://youtu.be/qBxbPts5tOk
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/news/20140728 CoreOS Stable Release.md b/sources/news/20140728 CoreOS Stable Release.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..49880f3a4b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/news/20140728 CoreOS Stable Release.md
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+Translating by lfzark
+CoreOS Stable Release
+================================================================================
+First off, [Happy SysAdmin Day][1]. We think we have a pretty good SysAdmin surprise in store for you today as we are announcing the CoreOS stable release channel. Starting today, you can begin running CoreOS in production. This version is the most tested, secure and reliable version available for users wanting to run CoreOS. This is a huge milestone for us. Since our first alpha release in August 2013:
+
+- 191 releases have been tagged
+- Tested on hundreds of thousands of servers on the alpha and beta channels
+- Supported on 10+ platforms, ranging from bare metal to being primary images on Rackspace and Google
+
+It is a big day for us here at CoreOS, as we have been working hard to deliver the stable release. Of course, we couldn’t do this without the community so thank you for all of your support and contributions to the project.
+
+[CoreOS 367.1.0][2], our first version on the stable channel, includes the following:
+
+- Linux 3.15.2
+- Docker 1.0.1
+- Support on all major cloud providers, including Rackspace Cloud, Amazon EC2 (including HVM), and Google Compute Engine
+- Commercial support via [CoreOS Managed Linux][3]
+
+This is a great opportunity to read about our [Update Philosophy][4] if you haven't already done so.
+
+Please note: The stable release is not including etcd and fleet as stable, this release is only targeted at the base OS and Docker 1.0. etcd/fleet stable support will be in subsequent releases.
+
+For those of you who want to start running CoreOS in production be sure to review our quick [Switching Release Channels][5] guide. As you're booting new machines, be sure to base them off your desired channel from the beginning.
+
+Finally, thanks to the community for your support. We can’t wait to hear your feedback. For those looking for additional support of running CoreOS in production, be sure to check out our [Managed Linux][6] offerings, as we have a full support team in place ready to answer any questions you may have.
+
+Happy SysAdmin Day, and thank you for making the web awesome.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://coreos.com/blog/stable-release/
+
+作者:Alex Polvi
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://sysadminday.com/
+[2]:https://coreos.com/releases/#367.1.0
+[3]:https://coreos.com/products/managed-linux/
+[4]:https://coreos.com/using-coreos/updates/
+[5]:https://coreos.com/docs/cluster-management/setup/switching-channels/
+[6]:https://coreos.com/products/managed-linux/
diff --git a/sources/news/How has the Press Reacted to Ubuntu 14.04--We Round Up the Reviews.md b/sources/news/How has the Press Reacted to Ubuntu 14.04--We Round Up the Reviews.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 68499986ea..0000000000
--- a/sources/news/How has the Press Reacted to Ubuntu 14.04--We Round Up the Reviews.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,59 +0,0 @@
-translating --------------------------- by jutzyn
-How has the Press Reacted to Ubuntu 14.04? We Round Up the Reviews
-================================================================================
-
-
-**The release of Ubuntu 14.04 just before the Easter holiday arrived gave tech journalists and bloggers an extended period in which to play with the newest long-term support release.**
-
-But what did they make of it?
-
-### Press Reaction ###
-
-The last few years have seen each successive release of Ubuntu greeted by fewer and fewer pixels (as opposed to column inches).
-
-As an LTS, the recommended choice for home users and enterprise deployments alike, does 14.04 buck the trend?
-
-> ‘Reviews from mainstream tech publications and news site are once again thin on the ground.’
-
-In short: not really. Reviews from mainstream tech publications and news site are once again thin on the ground. Whether it’s that this release has little newsworthy to offer (outside of extended support and a few extras that only enthusiasts are likely to care about) or whether there’s an increasing weariness about covering an established product that has, by and large, remained a niche interest is not for me to postulate.
-
-But while there’s no mention of the Trusty Tahr on the BBC News website or in the technology section of The Guardian, it didn’t arrive totally unnoticed. What press reaction there has been, has been positive.
-
-#### Quote, Unquote ####
-
-ZDNet offers up a [detailed overview][1], describing the release as “solid and stable”. While noting that it features ‘no big changes’ the reviewer, Terry Ralph-Knight, goes on to declare Ubuntu as being “**pretty hard to beat**”.
-
-> ‘Terry Ralph-Knight of Zdnet declares Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
-
-Over at TechRepublic Jack Wallen, in his concise overview, [says Trusty][2] ‘wows through subtlety‘.
-
-Jon Gold of **Network World** conveys the salient [changes with a slideshow][3]. On the subject of improved HiDPI support Gold notes that this “could prove important as 4K screens begin to gain traction in the market.”
-
-Tech site The Inquirer [covers the release][4] from the ‘Windows XP Alternative’ angle, but noted it is a ‘natty bit of kit in its own right’.
-
-> ‘Other coverage tended to regurgitate the official Canonical press release’
-
-Other coverage tended to regurgitate the Canonical press release that trumpets the lure for Windows XP users and businesses; touts the ‘optimised for multi-touch trackpads and touchscreen’ angle; and touches on the co-release of new 14.04-based tablet and phone builds.
-
-Of these, **Engadget** and **PCAdvisor** cover the [above points concisely][5], while Jon Brodkin of Ars Technica [distills the essentials points in depth][6] with added insight from an email conversation he had with Rick Spencer, VP of Engineering at Canonical.
-
-The decision to refer to Ubuntu Touch as merely ‘Ubuntu’ (something that while technically true forgoes a distinction still warranted) confused a few reporters, with many inferring that the screenshots of the desktop version accompanying their articles is what will be shipping on tablets later this year.
-
-As we have previously reported, the ‘Unity 8′-based version of Ubuntu will be sold preinstalled on tablets from unknown OEMs later this year.
-
-In all the reception has been positive, if a little lacking. But what critics think matters not a jot — it’s you, the user whose opinion is the true decider. Have you upgraded yet?
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/04/press-reaction-ubuntu-14-04
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://www.zdnet.com/ubuntu-14-04-lts-trusty-tahr-review-solid-and-stable-but-no-big-changes-7000028437/
-[2]:http://www.techrepublic.com/article/ubuntu-14-04-wows-through-subtlety/
-[3]:http://www.networkworld.com/slideshow/149046/first-look-ubuntu-1404-lts.html
-[4]:http://www.theinquirer.net/inquirer/news/2340343/ubuntu-1404-lts-desktop-arrives-this-week-as-windows-xp-alternative#%C2%A0
-[5]:http://www.pcadvisor.co.uk/news/software/3512604/ubuntu-1404-lts-plays-better-with-high-res-displays-forms-ubuntus-tablet-backbone/
-[6]:http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2014/04/ubuntu-14-04-will-power-first-commercially-available-ubuntu-tablets/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/10 Linux Platforms Meant For Embedded Systems.md b/sources/talk/10 Linux Platforms Meant For Embedded Systems.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c47ab5d26f..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/10 Linux Platforms Meant For Embedded Systems.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,65 +0,0 @@
-这年头 就是要多占坑 No grown-ups will ever understand that this is a matter of so much importance!
-10 Linux Platforms Meant For Embedded Systems
-==========================================
-Linux has a wide variety of uses. The platform is used by many for simple home use, while it is also the chosen platform for programmers and hackers. In addition, Linux is widely used in embedded systems and there are distributions that are tailored specifically to such systems. Here are 10 Linux platforms that can work great on embedded systems!
-
-
-
-### 1. [Ampro Embedded Linux][1] ###
-
-This is a free and open source reduced footprint operating system that has been derived from Ubuntu packages.
-
-### 2. [BlueCat Linux from Lynx][2] ###
-
-This Linux-based distribution is a part of the Lynx suite and is meant for embedded systems.
-
-### 3. [CacheGuard OS][3] ###
-
-CacheGuard OS is an integrated Security solution based on a custom-hardened version of Linux built from scratch and specially designed to manage Web traffic.
-
-### 4. [Darma NAS OS][4] ###
-
-This distribution has an SSL-based encrypted client server and a Java-based graphical user interface.
-
-### 5. [DIET-PC][5] ###
-
-This is an open source thin client software kitset that allows users to build network appliances.
-
-### 6. [ELinOS][6] ###
-
-This distribution provides a number of technologies for users working on embedded systems. It is a pretty popular Linux platform for these systems.
-
-### 7. [eLux][7] ###
-
-This one has a pretty simple and easy-to-use interface and offers the unique situation where neither the client nor the administrator needs to have any knowledge in Linux.
-
-### 8. [eLux NG][8] ###
-
-This one adds new models to the list of supported processors for eLux.
-
-### 9. [Embedded Coyote Linux][9] ###
-
-This Firewall and VPN server-based on Coyote Linux has been the platform of choice for many.
-
-### 10. [Embedded Debian Project][10] ###
-
-This project aims to make the Debian GNU/Linux the first choice for embedded systems.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=137612
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://www.ampro.com/company/News/04_08_08_Ampro_Reveals_Ubuntu_Embedded_Linux.htm
-[2]:http://www.lynuxworks.com/embedded-linux/embedded-linux-virtualization.php
-[3]:http://www.cacheguard.com/cacheguard-os.html
-[4]:http://nas.darma.com/
-[5]:http://www.dietpc.org/
-[6]:http://www.sysgo.com/products/elinos-embedded-linux/
-[7]:http://www.myelux.com/index.htm?Unicon_Session=32bf53f198c94ba2ac2ce1ea45211754
-[8]:http://www.myelux.com/eluxng.htm
-[9]:http://www.myelux.com/eluxng.htm
-[10]:http://www.emdebian.org/
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140527 A Complete Historical Timeline of Linux Evolution.md b/sources/talk/20140527 A Complete Historical Timeline of Linux Evolution.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 68639168c3..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/20140527 A Complete Historical Timeline of Linux Evolution.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,140 +0,0 @@
-CNprober 翻译中
-
-A Complete Historical Timeline of Linux Evolution
-================================================================================
-
-
-Linux is Everywhere, at home, offices, colleges, labs and space stations. But it was not the dominant force in the past it is now, it all started as a hobby by a Finish student. Linux has evolved from a hobby into a computing revolution. We present you with the most complete historical timeline of Linux Evolution on the web spanning over 23 years.
-
-### 1991 ###
-
-**25 August** : The 21 year old Finnish student Linus Benedict Torvalds announced his work on a free operating system in the comp.os.minix Usenet newsgroup.
-
-**1 September** : Linux 0.01 was released on the net.
-
-### 1992 ###
-
-**5 January** : The Linux kernel was relicensed under the GNU GPL with the [v0.12 release][1]. The initial license forbade commercial use. After the change the distribution and sale of possibly modified and unmodified versions of Linux became possible, provided that all those copies be released under the same license and be accompanied by the complete corresponding source code. In a [later interview][2] Linus made the following statement about the license change:
-
- " Making Linux GPL’d was definitely the best thing I ever did."
-
-**29 January** : Andrew S. Tanenbaum posted [LINUX is obsolete][3] to the comp.os.minix mailing list. The debate, which is considered a flame war by some people, was about Linux and kernel architecture in general. Tanenbaum argued that microkernels are superior to monolithic kernels and that therefore Linux is obsolete.
-
-**5 April** : The first Linux newsgroup, comp.os.linux, is proposed and started by Ari Lemmke.
-
-**21 May** : Peter MacDonald announces SLS, the first standalone Linux install. It was installable by floppy disk and included such cutting-edge features as TCP-IP networking support and the X Window System. At least 10MB of space on disk was recommended.
-
-### 1993 ###
-
-**17 June** : Slackware was released by Patrick Volkerding. [Slackware][4] is considered to be the first broadly successful Linux distribution and is still in use today.
-
-**16 August** : Ian Murdock (the ian in Debian) released the 1st version of the Debian Linux distribution. Debian is one of the most influential Linux distros, being the basis of MEPIS, Mint, Ubuntu and many others.
-
-**19 August** : Matt Welsh’s Linux Installation and Getting Started, version 1 is released. This is the first book on Linux.
-
-### 1994 ###
-
-**14 March** : [Version 1.0 of the Linux kernel][5] was released. It supported single-processor i386-based computer systems. Within the 3 years of its existence the kernel code base had grown to 176,250 lines of code.
-
-**26 March** : The first issue of Linux Journal is published. This issue featured an interview with Linus Torvalds and articles written by Phil Hughes, Robert “Bob” Young, Michael K. Johnson, Arnold Robbins, Matt Welsh, Ian A.
-
-**15 August** : William R. Della Croce, Jr. files for the trademark “Linux” and it is registered in September. Della Croce has no known involvement in the Linux community yet sends letters out to prominent Linux companies demanding money for use of the trademark “Linux”. In 1997 the matter was settled by the assignment of the mark to Linus Torvalds on behalf of all Petitioners and Linux users.
-
-**3 November** : Red Hat co-founder Marc Ewing announced the availability of the Red Hat Software Linux on CD-ROM, a commercial product that shipped for a retail price of $49.95 and included 30 days of installation support. Red Hat became the [first $1 billion open source company][6] in 2012.
-
-### 1995 ###
-
-**4 April** : Linux Expo, the first Linux-specific tradeshow and conference series, launches and becomes the most popular and well-attended annual Linux show for the next several years. The price for entry into the exhibit hall and a pass to the conferences was $4. After three years Red Hat takes over organization and becomes the major sponsor.
-
-### 1996 ###
-
-**9 May** : The Tux mascot was created by Larry Ewing in 1996 after an initial suggestion made by Alan Cox and further refined by Linus Torvalds on the Linux kernel mailing list. The concept of the Linux mascot being a penguin came from Linus Torvalds, who claims to have contracted penguinitis after being gently nibbled by a penguin.
-
-**9 June** : [Version 2.0 of the Linux Kernel][7] was released. It was a significant improvement over the earlier versions being the first stable kernel to support multiple processors in a single system (SMP) and more processor types. Linux becomes a serious alternative for many companies. You can read an in advance [review of Linux Version 2.0][8] that was published in August 1996 in the Linux Journal to learn more about the improvements.
-
-**14 October** : Matthias Ettrich founded the KDE project in 1996 as he was troubled by the inconsistency of applications running on the Unix desktop.
-
-### 1997 ###
-
-**9 January** : Bliss, first “Linux Virus” was discovered. Bliss does not circumvent the security of the system, it relies on people with privilege to do something dumb and reminds users to install digitally signed software from trustworthy sites only and to check signatures before installing.
-
-“In fact it’s probably easier to write a virus for Linux because it’s open source and the code is available. So we will be seeing more Linux viruses as the OS becomes more common and popular.” —Wishful thinking from McAfee.
-
-### 1998 ###
-
-**1 May** : The Google search engine was launched. Not only is it one of the best search engines around, but it’s based on Linux and features a Linux-specific search page.
-
-**4 December** : A report from IDC says that Linux shipments rose by more than 200% in 1998, and its market share rose by more than 150%. Linux has a 17% market share and a growth rate unmatched by any other system on the market.
-
-### 1999 ###
-
-**9 February** : Linux and BSD users unite for “Windows Refund Day”. They visit Microsoft, hoping to return the unused Windows licenses that they were forced to acquire when they purchased a computer system bundled with the OS.
-
-**3 March** : Another influential desktop environment arrives in the Linux World, [the GNOME desktop][9]. GNOME is the default desktop environment in several major Linux distributions like Debian, Fedora, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, and SUSE Linux Enterprise Desktop.
-
-### 2000 ###
-
-**4 February** : The latest IDC report suggests that Linux now ranks as the “second-most-popular operating system for server computers”, with 25% of the server operating system sales in 1999. Windows NT is first with 38% and NetWare ranks third with 19%.
-
-**11 March** : Motorola Computer Group announces the release of its HA Linux distribution. This distribution is aimed at telecommunications applications that require very high amounts of uptime; it includes hot-swap capability and is available for the i386 and PowerPC architectures.
-
-**23 March** : Ericsson announces its “Screen Phone HS210” product—a Linux-based telephone with a touchscreen that can be used for e-mail, web browsing, etc. Ericsson and Opera Software also announce that Ericsson’s (Linux-based) HS210 Screen Phone will incorporate the Opera web browser.
-
-**30 September** : Knoppix was one of the first Linux live distributions when initially released by Linux consultant Klaus Knopper.
-
-### 2001 ###
-
-**3 January** : The US National Security Agency (NSA) releases SELinux under the GPL. SELinux offers an additional layer of security checks in addition to the standard UNIX-like permissions system.
-
-### 2003 ###
-
-**6 March** : The SCO Group (SCO) announced that they were suing IBM for $1 billion, claiming that IBM transferred SCO trade secrets into Linux. Later SCO began numerous legal claims and threats against many of the major names in the computer industry, including HP, Microsoft, Novell, Silicon Graphics, Sun Microsystems and Red Hat. The jury case was decided on 30 March 2010 in Novell’s favour
-
-### 2004 ###
-
-**20 October** : [Ubuntu][10] came into life with the unusual version number 4.10, referring to its release date in October 2004 and the odd code name Warty Warthog. Ubuntu’s development is led by Canonical Ltd., a company owned by Mark Shuttleworth. While not being a major contributor to the kernel, Ubuntu plays an important part in the adoption of Linux on desktops and laptops.
-
-### 2007 ###
-
-**6 June** : ASUS announced two Eee PC models at Computex Taipei 2007: the 701 and 1001. The 1st Eee PCs came pre-installed with Xandros Linux, a lightweigt distribution optimized for small displays based on Debian.
-
-**8 August** : Linux Foundation was founded in 2007 by the merger of the [Open Source Development Labs][11] (OSDL) and the [Free Standards Group][12] (FSG). The Linux Foundation sponsors the work of Linux creator Linus Torvalds and is supported by leading Linux and open source companies, including prominent technology corporations such as Fujitsu, HP,IBM, Intel, NEC, Oracle, Qualcomm, Samsungand developers from around the world.
-
-**5 November** : Instead of announcing a Gphone as speculated beforehand, [Google announced][13] the Open Handset Alliance and [Android][14] calling it "the first truly open and comprehensive platform for mobile devices".
-
-### 2009 ###
-
-**29 January** : In January 2009 the New York Times stated: “More than 10 million people are estimated to run Ubuntu today”.
-
-### 2011 ###
-
-**11 May** : Google announced the Chromebook at the Google I/O conference 2011. Chromebooks are laptops running the so-called cloud operating system Chrome OS, that is based on the Linux kernel.
-
-**21 June** : Linus Torvalds announces the release of Linux 3.0.
-
-### 2013 ###
-
-**13 December** : Valve Corporation announces its Linux-based operating system SteamOS for video game consoles.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.linuxfederation.com/complete-historical-timeline-linux-evolution/
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/Historic/old-versions/RELNOTES-0.12
-[2]:http://j.mp/fs-pragmatist
-[3]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tanenbaum%E2%80%93Torvalds_debate
-[4]:http://www.slackware.com/
-[5]:https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v1.0/
-[6]:http://www.informationweek.com/software/operating-systems/red-hat-first-$1-billion-open-source-company/d/d-id/1103616
-[7]:https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v2.0/
-[8]:http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/1311
-[9]:http://www.gnome.org/
-[10]:http://www.ubuntu.com/
-[11]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_Source_Development_Labs
-[12]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Free_Standards_Group
-[13]:http://googleblog.blogspot.com/2007/11/wheres-my-gphone.html
-[14]:http://www.android.com/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140607 Four Awesome Free Alternatives to Ubuntu One Cloud Storage.md b/sources/talk/20140607 Four Awesome Free Alternatives to Ubuntu One Cloud Storage.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e699df2cae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140607 Four Awesome Free Alternatives to Ubuntu One Cloud Storage.md
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+Four Awesome Free Alternatives to Ubuntu One Cloud Storage
+================================================================================
+
+
+Be honest: news that [Canonical is shuttering its Ubuntu One cloud storage service][1] came as a shock, right?
+
+After four years of serving each and every Ubuntu user with a few gigabytes of free space in which to store their documents, music and photos, Canonical have decided to close it down. The service will cease operating as normal from June, and all files will be deleted permanently this July.
+
+While the reasons behind its closure make sense for the company in lieu of it broader ambitions elsewhere, there’s no getting away from the fact that if you used it daily, you’re going to be left a little peeved.
+
+> ‘…there is an army of alternatives able to pick up where Ubuntu One has left off’
+
+Thankfully there is an army of alternatives able to pick up where Ubuntu One has left off. Most, if not all, offer more space, better features and are generally more reliable than Canonical’s aged offering. In fact, it seems like everyone and their pet cat now offers free cloud storage.
+
+It’s partly because of the fierce competition between these services, what CEO Jane Silber refers to as the “free storage wars”, that the Ubuntu One offering wasn’t able to find its footing.
+
+But the promise of some free space and a means of syncing to it through the desktop does not mean they’re all equal, or worthy of entrusting with your data. Which alternatives are worth pursuing? Let’s take a look.
+
+
+Dropbox Indicator on Ubuntu – Comes In Handy
+
+### Dropbox ###
+
+#### Best all rounder ####
+
+Who hasn’t heard of Dropbox? As the granddaddy of cloud storage, it was the first service to both popularise and implement desktop-to-server syncing in a way that felt productive and not cumbersome.
+
+Its success was buoyed by a generous referral scheme offering you extra space for signing others up, and extensive cross-platform support. Dropbox makes it easy to hop between devices and OSes and retain access to your files. Other features include public folders that let you share items with other people, regardless of whether they use the service, and near-instantaneous syncing of files as and when they’re changed.
+
+256-bit AES encryption and two-step verification mean your files are pretty safe and secure.
+
+For Ubuntu users Dropbox provides a native application that integrates tightly with the default file manager Nautilus. It offers an indicator applet for monitoring, sharing and managing sync; file and folder emblems; and some handy right-click menu options for quick sharing.
+
+- **2GB** Free Space
+- Referral Scheme
+- Paid plans start from $9.99/m for 100GB
+- **Multi-platform support** (Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, Blackberry & Linux)
+
+> - [Learn More on the Dropbox Website][2]
+
+
+Insync Integrates Google Drive on Linux
+
+### Google Drive ###
+
+#### Best for space and features ####
+
+If you use Gmail or Google Docs then you’ll have, at some point or another, interacted with Google Drive. The search giant’s cloud service offers 15GB of free space in which to store your files, folders, photos and the like. These can be accessed from virtually any device with internet access and a fairly recent web browser or through dedicated mobile and desktop apps.
+
+One of the neat things about Drive is that certain files do not count towards your free space quota; e.g., Google Docs files. Neither do files others have shared with you. Better still, any photos you upload to Google+ that have a resolution less than 2048 x 2048 are also hosted and synced gratis.
+
+But Drive offers more than just space for your stuff. You also gain tight integration with Google’s own services, like Gmail, Google Docs and Google+.
+
+While it’s not the easiest alternative to use on Ubuntu owing to a lack of official native support, there are a number of third party tools that allow you to sync your files locally and have all changes made uploaded back. The most popular third part app is InSync. It’s not free (costing a one-off fee of $15 for the basic account) but it is by far the best way to use it.
+
+- 15GB Free Space
+- Paid plans start from $2.99/m for 100GB
+- Official apps for Windows, Mac, iOS and Android
+- Integrated into Chrome OS
+- Unofficial applications for Linux
+
+> - [Learn More on the Google Drive Website][3]
+
+
+Copy running on Ubuntu
+
+### Copy ###
+
+#### Best for Security Conscious ####
+
+If popularity was based solely on the number of referral links that are posted in our comments section, then Copy would win the title hands down.
+
+It may be less well known than other entrants on this list, but Copy, which is run by cloud enterprise giant Barracuda Networks, touts its robust security benefits the loudest.
+
+Like Dropbox, Copy uses AES 256-bit encryption on all files but, unlike Dropbox, doesn’t not rely on third-party servers as all files are stored on the company’s own servers.
+
+“With advanced features like secure sharing, source validation, and identity verification, you can breathe easy knowing your content can only be seen by the people you want,” they promise on their website.
+
+Another of its unique advantages is that shared files and folders can be assigned to a single user so that they don’t count against the data storage limit for other users. Or, if preferred, the load can be shared between parties so that, for example, a 10GB file shared between 4 people would count as 2.5GB/each, rather than, as on Dropbox, 10GB each.
+
+Google Drive offers something similar in that only the ‘sharer’ of a file has it count against their storage.
+
+For desktop integration Copy spoil Linux users. The service supports native integration with **Nautilus, Thunar** and **Caja**, including sync folders and right-click options. An indicator applet/system tray item provides further control options, including a handy list of recently changed files.
+
+- 15GB Free Space
+- Referral scheme
+- Paid plans start from $9.99/m for 250GB
+- Multi-platform support (Windows, Mac, iOS, Android & Linux)
+
+> - [Learn More on the Copy Website][4]
+
+
+Manage File Sync Yourself
+
+### ownCloud ###
+
+#### Best for privacy ####
+
+If you’d rather not trust your data in other people’s hands but still want the convenience of a “personal cloud”, ownCloud is a free and open source cloud storage platform you can host yourself.
+
+Like with other cloud storage services, ownCloud lets you sync and share your files across Windows, OS X, Linux, Android, and iOS. It also comes with calendar integration, photo gallery sharing, built-in support for (mounting) additional storage devices/services – e.g., FTP servers, Dropbox and Amazon S3 – and a slew of “apps” that can be added for additional features in the web interface, including a PDF viewer, text editor, and version control.
+
+Packages are available for a number of distributions, including Ubuntu from 12.04 to 13.10.
+
+> - [Learn More on the ownCloud Website][5]
+
+Chances are some of you reading this will have you own favourite, so don’t take the four picks above as set in stone. Other options worth exploring before committing include [SpiderOak][6], Microsoft [OneDrive][7] and [Box][8].
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/04/three-alternatives-ubuntu-one
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/04/canonical-axe-ubuntu-one-file-music-services-grab-data-now
+[2]:http://dropbox.com/
+[3]:http://drive.google.com/
+[4]:https://www.copy.com/home/
+[5]:http://owncloud.org/
+[6]:https://spideroak.com/
+[7]:https://onedrive.live.com/
+[8]:https://www.box.com/
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140607 Raspberry Pi In Schools.md b/sources/talk/20140607 Raspberry Pi In Schools.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..131a046d42
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140607 Raspberry Pi In Schools.md
@@ -0,0 +1,178 @@
+Raspberry Pi In Schools
+================================================================================
+> Teaching the world to code is a noble goal, but how is it going to work in practice?
+
+Two years ago, when the Raspberry Pi launched, it was with the intention of improving IT education in the UK. Since then more powerful, better connected or cheaper boards have come onto the market, but the Pi retains its position as the white knight of ICT teaching.
+
+Why? Because of the community of users that has grown up around it. To find out more we travelled west to Manchester, venue for the second annual Jamboree – a festival of educators, makers and messer-abouters focussed on highlighting how engaging the Pi can be. There, we met 75% of the Raspberry Pi Foundation’s education team – Ben Nuttall, Clive Beale and Carrie Anne Philbin – to discuss IT teaching in the UK.
+
+
+
+**LV**: So, Raspberry Pi education team, we were saying earlier that the obvious place to start is with the UK government’s Year of Code initiative, but that seems far too negative to being with!
+
+**Carrie Anne**: Yeah, but there’s so much to say about it!
+
+**Clive**: I think it’s a fantastic initiative, which just represents everything we stand for, blah, blah, blah, blah, blah!
+
+**LV**: Should we just leave that then?
+
+**Clive**: I mean the main issue is how the media portray computing, which is a brilliant, creative, rigorous, hard, challenging, fun thing, to just reduced to ‘this code’. ‘We must learn to code.’ ‘You better learn code or you’re a rubbish teacher.’ Which of course is not the case at all, it’s so much more than that. And so the teachers are running around now thinking the sky’s falling because they think that by September 2014, if they can’t code, then they’ve failed and they’ll think their kids have failed, and it’s a really bad message. There hasn’t been a simple message to say this is not the case, get out into the playground with some chalk and make a maze and do some computing, to teach them how to use a computer. No politician has stepped in to say this is not the case and they haven’t asked teachers who would tell them this isn’t the case. And that’s the problem. Where are the teachers? Where are the people that are actually teaching?
+
+**LV**: As you’ve just left teaching to join the Raspberry Pi Foundation, what are your thought Carrie Anne?
+
+**Carrie Anne**: It feels like a lot longer than two months, it feels like an eternity!
+
+**Clive**: Is that bad?
+
+**Carrie Anne**: No no, not at all! Because teachings so fast paced in that you’re seeing the results of what you’re doing in class straight away, whereas being out of the classroom for the past two months and working the Foundation, I can’t actually see the impact I’m having, but obviously people are talking to me and saying I am having an impact. It’s just very different to what I was seeing before. Clive always said there’s a massive difference between teaching and being a teacher. There are a lot of people we talk to who run Raspberry Jams, workshops, CoderDoJos and that kind of thing, and they always say ‘Oh, it’s really easy, you just do this, this and this.’ And it’s like, great, but you’ve got kids coming to you that *want* to learn this stuff. Imagine a class where you’ve got a bunch of kids who aren’t interested or engaged by this subject and actually teaching is much harder…
+
+**Clive**: Maybe 15 year olds on a Friday afternoon…
+
+**Carrie Anne**: Yes, a six-period day, end of the week…
+
+**Clive**: Ofsted saying, ‘Why haven’t your kids developed after 20 minutes in your lesson? Why haven’t they progressed?’. It’s very different.
+
+**Carrie Anne**: It’s very different, yep.
+
+**LV**: So you have some idea of how things should be done because of your recent experience?
+
+**Carrie Anne**: Yes.
+
+> The Raspberry Jams have done an excellent job of bringing people together from all walks of life
+
+**LV**: Are we, in general as a society, doing the right things?
+
+**Carrie Anne**: I think so. I think what’s been really nice about the Raspberry Pi community is that is gives back to the community. So there are experts, there are people who love what they do, who are reaching out to teachers and reaching out to children by running workshops and clubs and things. And it’s actually that collaboration that produces the best materials and produces the best way to move forward with the new curriculum. I mean, the work I did as a teacher producing the Sonic Pi was a team of work. That was because I worked with, yes an academic, but he was an expert. He wanted to develop a teaching environment that I could use with my students to teach tech-based programing in a fun and engaging way, that engaged both genders and engaged both low ability students and high ability students. It’s a tech-based programming language, which is important at Key Stage 3 where you need to not just be able to teach Scratch, you need to teach a tech-based language that’s nice bridge between Starch and something like Python, which we can teach later on. So, yeah, I think we are moving in the right direction. It would be nicer if the powers that be…
+
+**Clive**: It would be nice to see that as a microcosm of how these things actually happen. So as an academic has a brilliant idea and they’re very good at what they do, and then they come to a teacher and say ‘How can we make this useful in the classroom?’, ‘How can we get assessment in there?’, which schools needs frankly, ‘How do we make it robust?’, ‘How can we test it?’. And isn’t that a weird idea, to actually ask the people that teach how we should do that? It hasn’t happened really. But, yes, as Carrie says, we’re going in the right direction, certainly. The community and third parties are doing more to push it along.
+
+**LV**: From someone outside a little bit, it kind of looks like this community has sort of spontaneously developed around the Raspberry Pi. Has this always been there or has it just become more obvious now?
+
+**Carrie Anne**: I think it’s always been there. I was a teacher so when Raspberry Pi first came out I got one. It got it and then I was like, this is brilliant! Someone’s developed something for education. A Linux box that we can use in the classroom. It’s cheap, it’s brilliant!
+
+**Clive**: And mess about with.
+
+**Carrie Anne**: Yeah, it’s going to be great! And then I was like, right, so where are the resources to go with it? Ah, there aren’t any. Then I was like, so where can I go and find some? The first obvious place was Raspberry Jam. There are people running events where they’re doing stuff. So I thought I’ll go along and speak to some people, and see what’s available. And it was through that that I met people to work with, and they’d formed that themselves, the enthusiasts from throughout the community around the Raspberry Pi.
+
+**Clive**: It’s been a focus, hasn’t it? There’s been a lot of people sort of hanging around, saying ‘Look, I like tinkering, I like messing, I like coding, I like making’, and this thing appeared which was cheap and cheerful and fantastic to play around with, and I think it was a focus. It was waiting to happen really.
+
+
+Carrie Ann Philbin, The Raspberry Pi Foundation’s Education Pioneer
+
+**LV**: Was there anything equivalent to Raspberry Jams before the Raspberry Pi came along for people and teachers to come together?
+
+**Carrie Anne**: Well teachers tend to generally get together through things like TeachMeets and through Twitter, and those kinds of chat tools. There are ways that you can get together, but that’s more talking about teaching practice. Like the different ways you can use a sentence. It’s very teachery, it wasn’t specific to teaching computing.
+
+**Clive**: I think hardware-wise, Raspberry Pi was in the right place and the right time.
+
+**Ben**: The Jams done a really good job of bringing people together. The people, like myself, who were attending user groups that are interested in tech and really passionate about it, have got a chance to share that interest with the wider community. There were families coming in, teachers coming in, and they were just sharing what they were doing. And the skills they already had, and I was already programming in Python and things like that just on the desktop, and the Pi came along and it opened up this way of plugging into the real world and all the other things the Pi brings with it. Just being about to use those skills and pass them on, I got myself involved in Education through that.
+
+**LV**: So you weren’t a teacher before then?
+
+**Ben**: No, I was a software developer.
+
+**Carrie Anne**: This is what’s great about the education team at Raspberry Pi. It’s 50% ex-teachers and 50% software developers. We need people like Ben and Dave (Honess).
+
+**Ben**: Yes, some people have ideas for things and think this could be an engaging exercise, but they may not know exactly how to deliver it, or how it’s going to work. They might not know how exactly a teacher is supposed to produce something to use that, but they have an end goal and working with someone else can help achieve that.
+
+**Clive**: Yeah, you’re right, the real key is the mix. So you’re getting teachers and engineers and developers and families. Before, they might have been on a Linux user group, they might have been a teacher group, and you’re just bringing a bunch of different people together and that just (to use a horrible word!) synergizes stuff.
+(Everyone LOL)
+
+**Clive**: Yes, I did it! I said synergizes! I’m buying a copy of the magazine now.
+
+**Carrie Anne**: There’s something that comes about from getting all those different types of people together is that it breeds this wonderful learning environment that you cannot reproduce. Like, you were running a Picamera workshop this morning. So that was run by people who run Jams who are from industry. And what was really nice is that there were teachers and there were people who had come for the Jamboree from industry that were helping the teachers do stuff. And there was this environment that was like, it’s ok to not know something, it’s ok to ask a question, it’s ok to get it wrong and make mistakes. And that’s really powerful because sometimes teachers are afraid perhaps of saying they don’t know.
+
+**Ben**: So at this workshop, we gave people an intro to building a real application around the camera. So it’s not just ‘Oh, there’s a camera and you can take pictures’. It was ‘Ok, let’s plug in a button, and attach that to the Pi and let’s make that be the button for the camera’. And just a simple intro like that opens up a world of possibilities. Sometimes a lot of these things like the Jam, just gives you a lot of inspiration. Or if you see something in a magazine or online, or on Twitter, and you think somebody’s done that with the Pi, I’d really like to do that project in my garden or I’d like to do that myself and twist it and use some of the libraries they’ve used or used some of the codebase they’ve used and take it in their own direction.
+
+**Clive**: Like it’s not a button, it’s a sensor for when your parents walk into your bedroom, it then tweets it as they walk in.
+
+**Ben**: And everyone’s got a different way of thinking. If you’re in classroom of 30 kids and you show them how to make a button do this, each of them is thinking ‘Oh I can make a such and such’. They’ll all have a different idea. And some of them will just go straight home and make one. And some of them would need a lot more guidance.
+
+> Every teacher needs more time off their timetable to develop their skills
+
+**LV**: Are there some kids that just don’t get it at all?
+
+**Ben**: I think there’s something for everyone, but they might not find it straight away. If you delivered a term’s worth of content for a class, with a good scope of different projects, I’d be surprised if there was one kid that wasn’t interested in any of it or didn’t find any of it engaging.
+
+**Clive**: It’s almost an antidote for kids not getting it. With teaching music, you’ll have people that are level 5 or 6 while others can’t read music. Because computing is creative and engaging, we don’t all have to become master coders. With Scratch, it’s a visual language and you’ll find that quite often you’ll get what are classed as low ability kids that just rip into that and do fantastic things because it’s the first time they’ve been allowed to get ideas out of their heads and make something with it. And before, if they’ve had problems with writing and numeracy, they haven’t been able to do that. There are case studies with young boys that aren’t very good at reading and writing but they start telling stories when you give them an environment where they can actually do these things. So it’s brilliant tool to actually fight the opposite. It’s not that they don’t get it. There’s something for everybody.
+
+
+Linux Voice’s Andrew Gregory asks Clive Beale a tough question
+
+**LV**: Pre-Raspberry Pi, in the dark ages of about 5 years ago, before the ICT revolution, what would those children be doing? Would they have responded to ICT at all?
+
+**Carrie Anne**: In a classroom, you have a network of computers that are all on lockdown. You’ve got your network administrator and team of technicians, and they do a wonderful job and I certainly wouldn’t slate them – I was a technician once. But we were living in a time where you had to lock down the internet, which I disagree with, I think it should be open. And all the computers, you can’t execute any files on them, so you can’t actually teach any programming on them. So that was a problem for me.
+
+**LV**: Is that changing?
+
+**Carrie Anne**: I think it is changing, and will change with the new curriculum. For me as a teacher, what was great when the Raspberry Pi came along is that I don’t actually need those computers around the outside any more.
+
+**LV**: So you don’t need permission.
+
+**Carrie Anne**: Here’s my box full of Pis, let’s just get them out.
+
+**Clive**: I’ll install what you want, do what I want.
+
+**Carrie Anne**: Yeah, you can break it. And that’s ok, you just flash it and start again.
+
+**Clive**: In 1997, they put the C back in ICT and suddenly it became this thing that you had to teach. The curriculum wasn’t really that bad. A lot of people moan about it, but if you actually sat down and read it, it was quite flexible and did let you do take control and make programming and coding interesting. But because resources are so important to schools, you just ended up doing the easy things.
+
+**LV**: But when you said about kids using Scratch and becoming motivated to do other things, that would never have happened before the Raspberry Pi came along.
+
+**Clive**: Yes, it was more just following what the teacher said, ‘And now we’re going to write a letter to the cinema’ or something. That’s like giving someone a Ferrari and saying you’ve just got to drive in this room for half an hour. So you’ve given them this fantastic tool for exploration and creativity, and you’re saying we’ve got to do this. Whereas with the computing thing, especially things like Scratch, just lets them think, ‘Ok, I can do a movie, I can do a little flip frame animation, or you know what, I can actually make a game’. And then suddenly they’re doing stuff that they haven’t had the opportunity to do.
+
+**Carrie Anne**: Yeah, and I think that ICT curriculum was about 12 years out of date. It was created and it wasn’t updated.
+
+> you can break it. And that’s ok, you just flash it and start again
+
+**LV**: Obviously quite a lot has changed in computing education according to the media over the last couple of years in the UK. Broadly speaking, it is getting better?
+
+**Carrie Anne**: Yes.
+
+**LV**: What are the parts that pushed it to be better.
+
+**Carrie Anne**: I think the teachers. They’re the ones in the classroom that have to teach the curriculum. When I became a teacher, I was already working in a school and I kept putting it off becoming a teacher because the curriculum bored me. But then I realised that, when I actually got into the classroom, I was able to put my own spin on it. I think it started with the teachers. Those people saying we want a new curriculum, we want to teach this and it’s engaging the kids and they’re learning something. I think it started there and then I think industry picked up on the fact that that was happening and they wanted more industry experts. And then the government got involved and it snowballed really.
+
+**Clive**: Scratch was a big word-of-mouth thing wasn’t it. It was about mid-2000 when it came out, and suddenly you just found that any teacher worth their salt was using it for their ICT curriculum because it taught about control.
+
+**Carrie Anne**: HTML as well. HTML has been on the curriculum for years. We’ve been teaching HTML in Notepad for years.
+
+**LV**: What are going to be the big things pushing it forward over the next few years?
+
+**Carrie Anne**: I think more of the same really. It’ll be teachers, it’s always the teachers. They’re the ones that come to the Jamboree and this kind of thing, and learn from people like Ben and that sort of collaboration. That’s where it starts. The teachers see what can be done, and they start doing it, and they’ll be more of that. And there are initiatives like code clubs and the Master Teachers are great.
+
+**Clive**: Teachers are meeting up more when before may not have been getting together.
+
+**Ben**: And as well as there being a more content, I think they’ll be convergence of a lot of this stuff. So, because the Raspberry Pi doesn’t have any official resources right now, some people are going off and writing their own. I think they’ll be a convergence of people pulling their ideas together and there’ll be a more centralised system for that. And we’ll be helping the community out with that.
+
+**Clive**: ‘We’ll be at the forefront of that’, is that quote!
+
+**LV**: You haven’t mentioned government policy, or anything like that at all. Is that a negative thing or just by-the-by?
+
+**Clive**: I was at the Westminster forum yesterday and they had a chap from the DFE there, and I couldn’t resist it, so I got the mic and said you haven’t really taken it seriously have you? He turned round and said, we have *really* take it seriously. This idea that we can just bring in a new program of study and saying ‘Oh, aren’t we wonderful’, because Eric Schmidt’s speech and going over that, and suddenly we’re made it all better for you. But you haven’t, you just seemed to have done something that a lot of teachers are now scared of. So there’s a lot of work to do, and we’re really positive. But no, the government have not, in my personal opinion, given the money or the support or the thought behind this. If you go to Jersey, it’s such a great contrast. 6 million pounds, 100 thousand people on the island – the size of Cambridge. Compared to the 53 million in England and parts of the UK. This is in England initially, it’s not in Scotland and Wales. They’re got the infrasture, fibre to the door in every school, linking into businesses, £2 million CPD for teachers, well that’s practically what the government pay for the whole of England. So, have you taken it seriously, no. I think they’ve completing underestimated what’s involved. They thought the teachers would just pick it up and have the time and resources, which we don’t have the time for.
+
+**Carrie Anne**: Maggie Philbin has been leading a UK digital skills taskforce, of which I’m part the team. We’re looking at where the skill shortages are and what are digital skills. Because there’s going to a whole group of kids who are now 14 to 16 who are going to leave the education system who haven’t had new programs like these. They were on the old program, so we’re looking at who will be deskilled and what we can do about that. So hopefully that report will inform government policy.
+
+**Ben**: There must be a generation of people that don’t have their own website.
+
+**LV**: If there’s one thing you could change about government policy, what would it be?
+
+**Clive**: It really is to do with support for teachers. This idea that teachers would be able to, especially primary school teachers where you have to teach a range of subjects, suddenly go off, and even the guy yesterday said, well there’s loads of third party resources, but you’ve still got to go out and get them and try them out and learn and bring them all together.
+
+**Carrie Anne**: Time. One of the biggest recommendations that I would say is time. Every teacher needs more time off their timetable to develop their skills, especially in an area like this that they perhaps think they’re weak. Because it takes a while to set things up and start your learning. As a teacher, you get like a 30 period timetable, you’re teaching for about 22 lessons of that with about 7 free periods, but some of those you’ll be covering for another lesson and some of those I need to plan my lesson and mark. They need time.
+
+**Clive**: If you look at science, so if you’re a chemistry or biology teacher at secondary, there’s a scheme where you can re-skill to physics and they will give you free periods, huge bursary, and they’ll also take you off timetable one day a week to go off and go to other schools and retrain, and maybe pay for the cover. And this is the government doing this, and if you do this, this and this, you come out as an accredited physics teacher. So they took that seriously, but yet here’s a brand new subject and they’re expecting people just to pick up and run with it, and it’s completely inadequate.
+
+**Carrie Anne**: But it’s not just time to learn something, it’s also time to go and meet industry people. Like go to a company and be in there and work and learn from them, and see what the world is like. Because some people, they went through education, went to university and became a teacher, so they’ve never left this school environment and they’ve got no idea of what the world of work is like.
+
+**Ben**: I think there are some people in the current government that seem to think there should just be this package, and this is what you should deliver as your syllabus this year. Everyone is treated the same. Each teacher has their own class, and they’re all different, with different ways of engaging their interest. It needs to be tailored, so the teacher needs to take that material, and perhaps look on our site in the next year and say, well this one looks quite suitable for my class, or this one might be a good one to do.
+
+**Clive**: It’s so long term. The government also do not understand that this is long term. So if you’re going to start teaching at 5 about algorithms and a bit of code and Scratch, what happens further down the line. The secondary school teacher will be saying, I can’t teach them Scratch anymore, which is what we do in Year 7 at the moment. So it’s actually quite a long term thing and things will continue to change over the next several years until that pipeline becomes full. And they’ve unbelievably said here’s £2 million, do some training for September 2014. What’s 2014 got to do with it? This is five, six, seven years down the line.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxvoice.com/education-education-education/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140609 Out in the Open--The Little-Known Open Source OS That Rules the Internet of Things.md b/sources/talk/20140609 Out in the Open--The Little-Known Open Source OS That Rules the Internet of Things.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3f70d6cd07
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140609 Out in the Open--The Little-Known Open Source OS That Rules the Internet of Things.md
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+Translating by toknow-gh Out in the Open: The Little-Known Open Source OS That Rules the Internet of Things
+================================================================================
+
+Image: Adnk/[Wikipedia][1]
+
+You can connect almost anything to a computer network. Light bulbs. Thermostats. Coffee makers. Even badgers. Yes, badgers.
+
+Badgers spend a lot of time underground, which make it difficult for biologists and zoologists to track their whereabouts and activities. GPS, for example, doesn’t work well underground or in enclosed areas. But about five years ago, University of Oxford researchers Andrew Markham and Niki Trigoni [solved that problem][2] by inventing a wireless tracking system that can work underground. Their system is clever, but they didn’t do it alone. Like many other scientists, they turned to open source to avoid having to rebuild fundamental components from scratch. One building block they used is an open source operating system called [Contiki][3].
+
+“Contiki was a real enabler as it allowed us to do rapid prototyping and easily shift between different hardware platforms,” says Markham, now an associate professor at the University of Oxford.
+
+Contiki isn’t nearly so well-known as Windows or OS X or even Linux, but for more than a decade, it has been the go-to operating system for hackers, academics, and companies building network-connected devices like sensors, trackers, and web-based automation systems. Developers love it because it’s lightweight, it’s free, and it’s mature. It provides a foundation for developers and entrepreneurs eager to bring us all the internet-connected gadgets the internet of things promises, without having to develop the underlying operating system those gadgets will need.
+
+Perhaps the biggest thing Contiki has going for it is that it’s small. Really small. While Linux requires one megabyte of RAM, Contiki needs just a few kilobytes to run. Its inventor, Adam Dunkels, has managed to fit an entire operating system, including a graphical user interface, networking software, and a web browser into less than 30 kilobytes of space. That makes it much easier to run on small, low powered chips–exactly the sort of things used for connected devices–but it’s also been ported to many older systems like the Apple IIe and the Commodore 64.
+
+
+Adam Dunkels. Photo: Sara Arnald
+
+Contiki will soon face competition from the likes of Microsoft, which recently [announced Windows for the Internet of Things][4]. But while Microsoft’s new operating system will be free for devices less than 9 inches in size, it won’t be open source. And Contiki has an 11-year head start.
+
+Contiki started in 2003, but its roots stretch to Dunkels’ days as a computer science student at Mälardalen University in Sweden. In 2000, he was working on a project to use wireless sensors to track hockey players’ vital signs and display them on a screen the crowd could see. “We convinced them to have this thing up their nose so we could measure their breathing rates,” Dunkels recalls.
+
+To make the sensors work correctly, Dunkels had to write software would enable them to interact with a computer network. He called the resulting code [LwIP][5], for “light weight internet protocol.” Although LwIP is still used in many microcontrollers and other products today, Dunkels decided it wasn’t quite lightweight enough. In 2003, he created microIP, which evolved into Contiki. The OS was an immediate hit with researchers and hobbyists, and has in recent years attracted commercial users including [Rad-DX][6] radiation detection devices and [Zolertia][7] noise monitoring system.
+
+While Nest, the web connected thermostat company [Google acquired for $3.2 billion][8] in January, has come to define the Internet of Things, Dunkels notes that many companies have been using network-connected devices for years in applications including industrial and building automation. “With something like CES you see all the consumer stuff, but there are just so many different aspects of this,” Dunkel says.
+
+But consumer technology companies are beginning to embrace Contiki as well. The [LiFX][9] “smart light bulb” is using the operating system, for example, as is the Nest competitor [Tado][10].
+
+To help support the burgeoning commercial usage of Contiki, Dunkels left his job as a professor at the Swedish Institute of Computer Science and founded [Thingsquare][11], a startup focused on providing a cloud-based back-end for Contiki devices. The idea is to make it easy for developers to connect their hardware devices with smartphones and the web. Thingsquare manages the servers, and provides all the software necessary to manage a device over the web.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.wired.com/2014/06/contiki/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Contiki-ipv6-rpl-cooja-simulation.png
+[2]:http://www.cs.ox.ac.uk/projects/WILDSENSING/
+[3]:http://www.contiki-os.org/
+[4]:http://www.wired.com/2014/04/free-windows/
+[5]:https://savannah.nongnu.org/projects/lwip/
+[6]:http://www.dtectsystems.com/rad-DX_page.html
+[7]:http://zolertia.com/home
+[8]:http://www.wired.com/2014/01/googles-3-billion-nest-buy-finally-make-internet-things-real-us/
+[9]:http://lifx.co/
+[10]:http://www.tado.com/de-en/
+[11]:http://www.thingsquare.com/
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140610 GitHub redesigns its Windows app to put your work front and center, adds emoji and gif support.md b/sources/talk/20140610 GitHub redesigns its Windows app to put your work front and center, adds emoji and gif support.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..7ee2f2f2c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140610 GitHub redesigns its Windows app to put your work front and center, adds emoji and gif support.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+GitHub redesigns its Windows app to put your work front and center, adds emoji and gif support
+================================================================================
+
+
+GitHub today [released][1] version 2.0 of its Windows app, which it markets as “the easiest way to use Git and GitHub on Windows.” The new version features a more streamlined design, new GitHub local features, and some general speed improvements. You can grab the new version now directly form [windows.github.com][2] (if you already have GitHub for Windows, it will update automatically).
+
+GitHub released its Windows app back in [May 2012][3], and has made improvements in three minor releases since. Today’s major 2.0 release comes more than two years after the app’s debut, and aims to inject new life into the app.
+
+GitHub executives told me they saw a major bump in terms of interest for the client with the 1.3 release that was more of an overall increase rather than just a spike associated with new versions. They are naturally hoping for a repeat of this jump with the 2.0 release.
+
+GitHub 2.0 for Windows is supposed to be simpler and cleaner, and aims to put more focus and the developer and their work. For the sake of comparison, here’s how the previous 1.3 version looked like:
+
+
+
+Here is the 2.0 release (the company emphasizes that your work is now ” front and center”):
+
+
+
+Previously, there were two different views available. The company has slimmed that down so developers no longer need to move back and forth between their projects.
+
+This is largely accomplished by adding a sidebar that reduces the need to navigate through menus and options. In short, your local repositories are always available on the left, plus you can create, clone, and publish repositories without having to navigate to a new screen. Your repositories are also grouped by where they originated from, so work projects (think GitHub Enterprise) are easy to distinguish from personal ones, and you can easily switch between them.
+
+The new design aside, GitHub for Windows now lets you pick an ignore file template for your project when you create a repository. It also supports including emoji and gifs in your commit messages.
+
+It’s worth noting that the aforementioned performance improvements should be felt around the app in general. Unfortunately, GitHub wasn’t able to share any benchmarks regarding the speed bumps.
+
+All in all, this is a big redesign aimed at improving the user experience. GitHub executives tell TNW the new design language aims is a “GitHub Metro style” that takes the “best parts of Metro as well as Android and iOS.” Whether or not that’s a good thing will likely come down to personal preference.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://thenextweb.com/dd/2014/06/09/github-redesigns-windows-app-put-work-front-center-adds-emoji-gif-support/?tnw_rfl=tw
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://github.com/blog/1844-say-hello-to-github-for-windows-2-0
+[2]:http://windows.github.com/
+[3]:http://thenextweb.com/apps/2012/05/21/github-releases-its-windows-app-at-last/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140610 How does the cloud affect the everyday linux user.md b/sources/talk/20140610 How does the cloud affect the everyday linux user.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..66ff726ffb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140610 How does the cloud affect the everyday linux user.md
@@ -0,0 +1,195 @@
+How does the cloud affect the everyday linux user?
+================================================================================
+### Introduction ###
+
+Cloud computing is one of those terms you hear about and see all the time whether it is in the national newspapers, online news websites, podcasts, technical blogs, technical news sites or on radio and television.
+
+It is a fairly woolly term that encompasses so many things but what exactly is it?
+
+> **Cloud computing** is a term used to refer to a model of network computing where a program or application runs on a connected server or servers rather than on a local computing device such as a PC, tablet or smartphone. Like the traditional client-server model or older mainframe computing,[1] a user connects with a server to perform a task. The difference with cloud computing is that the computing process may run on one or many connected computers at the same time, utilizing the concept of virtualization. With virtualization, one or more physical servers can be configured and partitioned into multiple independent “virtual” servers, all functioning independently and appearing to the user to be a single physical device. Such virtual servers are in essence disassociated from their physical server, and with this added flexibility, they can be moved around and scaled up or down on the fly without affecting the end user. The computing resources have become “granular”, which provides end user and operator benefits including on-demand self-service, broad access across multiple devices, resource pooling, rapid elasticity and service metering capability.[2]
+
+The above quote was obviously taken from Wikipedia.
+
+In the past we either used dumb terminals to connect to a mainframe or more recently desktop computers connected to applications on in-house servers which in turn connected to databases also kept on site.
+
+The management of the desktops, applications and servers were all local and all had to be supported by the company who owned them.
+
+Whilst this might be great for software houses it isn’t good business for other companies such as banks, insurance companies and oil companies. Information Technology is not a banking function in the same way catering isn’t a function of drilling oil out of the ground.
+
+Large companies have long since outsourced many functions to dedicated companies. For example outside catering companies provide the staff canteen and we all know about the offshore call centres handling customer calls for the banks.
+
+IT has also become an offshore function with a number of support and development functions shipped out to China, India, Malaysia and Eastern Europe.
+
+Cloud computing is different to the typical model in that it is all about virtualisation. It is about putting applications on virtual servers which could all be in one location or could be thousands of miles apart but the point is it doesn’t matter because it is somebody else’s job to make sure they work.
+
+> In common usage the term “the cloud” has become a shorthand way to refer to cloud computing infrastructure.[4] The term came from the cloud symbol that network engineers used on network diagrams to represent the unknown (to them) segments of a network.[5] Marketers have further popularized the phrase “in the cloud” to refer to software, platforms and infrastructure that are sold “as a service”, i.e. remotely through the Internet.
+
+This article is therefore all about the cloud and what it means for the everyday linux user and what it can do for you and what, if any, pitfalls are there.
+
+From an end user and home user point of view, cloud computing has basically come to mean any service that is hosted online.
+
+So here goes, which cloud services are useful for an everyday linux user?
+
+### Email ###
+
+I would be very surprised if you are reading this and you don’t have an email account.
+
+PC Advisor magazine analysed the top 6 emails services back in March, 2014 consisting of Outlook, GMail, Yahoo, iCloud, AOL and GMX.
+
+### Office Suites ###
+
+As well as an email client one of the most commonly used tools required by everyone is an office suite.
+
+In the past people would toddle off down to PC World, buy a computer and come home with a great big machine and half a dozen CDs containing 5 programs you definitely won’t use and Microsoft Works which was a cheap and virtually useless cut down version of Microsoft Office.
+
+Now you don’t even need an office suite on your computer even though there are some great free choices out there including LibreOffice and Kingsoft.
+
+The obvious choices are of course Google Docs and Office 365. Does Office 365 work for Linux? Well this article from PC Pro in 2012 seems to suggest that it does.
+
+
+
+I don’t believe everything I read though so I signed up to Office 365 to see what would happen.
+
+Signing up was free for a month and I was presented with a list of online applications that I could use which included Word, Excel and Outlook.
+
+
+
+All looked to be going well. I started Microsoft Word, chose a template to use and then of course it didn’t work at all.
+
+Office 365 isn’t yet supported on Linux and to be honest you don’t need it. Move on.
+
+
+
+Google Docs works and for home use it is perfect. There are hundreds of templates for the word processing and presentation tools and the spreadsheet application does most things although it doesn’t really replace Excel because you haven’t got hundreds of wannabe developers creating naff macros and VBA scripts everywhere.
+
+
+
+Another alternative to Office 365 is Zoho.
+
+Similar to Google Docs, Zoho includes a word processor, spreadsheet tool, presentation tool and mail.
+
+There are finance and CRM tools as well.
+
+
+
+The interface for the tools is actually very nice and clean.
+
+Services such as Google Docs and Zoho also give you the power of collaboration.
+
+Documents can be shared and worked on by different people in different locations.
+
+This site provides a good list of alternative choices to Google Docs and Zoho.
+
+### Online File Storage ###
+
+Another good service provided by Google Docs and Zoho is the ability to store the documents and files you create online.
+
+There are other services however such as Dropbox that are used to exclusively store your documents in the cloud.
+
+The benefit of storing files with services like Dropbox is that if your house is burgled or catches fire then you have an offshore backup that remains intact. You can also access your files anywhere.
+
+Dropbox is free for up to 2 gigabytes of use. If you have a lot more data, and most of us do nowadays, then there is a $ 9.99 monthly plan that is available allowing for 100 gigabytes. There is also a business version available from $ 15 a month.
+
+There are of course alternatives to Dropbox and this site provides a list of the best online backup solutions.
+
+### Photos ###
+
+Since the introduction of digital cameras and more recently smart phones, more and more of us have memory cards full of photos.
+
+I bet that at some point or other that you have lost photos because your phone died and the photos were on the phone and not the memory card or you lost your phone losing pictures of your child’s sports day or another important occasion.
+
+Losing a phone is never a good thing. If you are clever you will have set up some sort of security because most people have their phones synchronised with their email accounts, Facebook, Twitter and even online banking.
+
+All it takes to fix a lost phone is to change the passwords to all of the above accounts but lost photos are just not possible to recover and are a little bit more upsetting when lost.
+
+One solution of course is to backup to your computer. This is of course a good first step but occasionally laptops break as well and you are back to square one.
+
+Online photo storage sites are great resources because not only do they keep your photos safe you can also share them with whoever you choose to, eliminating the need to get 5 copies of the same photo developed to send to mum, nan, sister, aunty and mother-in-law.
+
+The solution I like to use is Google’s Picasa but many of you will have heard of services like Flickr as well.
+
+Lifehacker has a list of the five best photo sharing services.
+
+Remember though that just because they are called photo sharing services doesn’t mean you have to share them. You can keep them just to yourself.
+
+### Music ###
+
+The first record that I was ever given was a 12 inch vinyl version of “Kings of the wild frontier” by “Adam and the Ants” back in the early 1980s.
+
+As the 1980s progressed the long play records were replaced by cassettes and just as I had accumulated a decent number of cassettes the compact disc became the thing to have.
+
+Hundreds of compact discs later and MP3 file sharing became the norm and it even became the legal way of doing things.
+
+Nothing sits still with technology and the future is now with audio streaming services such as Spotify.
+
+Spotify is free to use but is supported with the inclusion of adverts. In this regard it is like having your own personal radio station where you choose the playlist. Of course you can pay a monthly fee and have the adverts removed altogether.
+
+There are dozens of similar services including Grooveshark and last.fm.
+
+Techradar has a list of 7 alternatives to Spotify.
+
+### Film ###
+
+The first film I ever watched in the Cinema was Dumbo. The first video I ever watched was “Krull” which contained a young Dulph Lundgren. The format of the video was on Beta Max. (My next door neighbour had one).
+
+My dad came home one day with a video recorder from Radio Rentals and my sister and I used to take it in turns to pick a video to hire from the video store. I remember my first choice being “The Black Hole”.
+
+As with music time moves on. Just as you get large units full of movies, some genius comes along and develops DVDs and then they come out with Bluerays.
+
+Now of course video streaming is the order of the day especially if you have a decent enough internet connection.
+
+The most commonly known services are Netflix and Lovefilm.
+
+This website has a list of good alternatives to Netflix. Not all of these services (including Netflix) work seamlessly on Linux.
+
+### Gaming ###
+
+Music, films and now gaming have moved to the online arena.
+
+Gaming is of course more difficult. Music is relatively low cost in terms of bandwidth and although films require a little more, the stream just needs to remain steady to get a clear picture.
+
+Games need to run at a consistently high frame rate to be playable and unless you have a decent connection it probably isn’t even worth trying.
+
+Current services offering a cloud gaming service include OnLive and StreamMyGame.
+
+This site contains a list of 6 online gaming services to rival OnLive.
+
+### Pitfalls ###
+
+Cloud computing isn’t free from issues.
+
+There is the obvious problem of hacking. If someone gets access to your online banking or your email then you have a real problem.
+
+What about online file storage? There is currently the high profile case of Megaupload.com.
+
+Megaupload.com was essentially a file storage site for storing large files. The problem is that a lot of people used the service to share copyright material and the US authorities came down like a ton of bricks and the service was shut down.
+
+Now a lot of people losing files would perhaps be expecting the inevitable but what about people who genuinely did nothing wrong. Their data has been lost. The US authorities refusing to give it back.
+
+Finally there is the subject of service maintenance. If your email went down for a day could you cope? What about 3 days? What about a month? You are at the mercy of the service provider.
+
+A lot has been made about large companies losing data and there has also been a lot of noise regarding heartbleed which is a vulnerability found in SSL left unpatched for years.
+
+If you have services hosted for you online then you are relying on technical support staff to do their job properly and if they don’t you could be at the mercy of hackers, hardware failures and poor backup and recovery maintenance.
+
+### Summary ###
+
+Cloud computing has really become the buzz term for any online service. Your web browser is a client connecting to a server or clusters of servers hosted anywhere in the world. The point is that you don’t care. You don’t need to know.
+
+Generally speaking I have barely touched the surface. We all use the cloud everyday and most of us don’t even think about it.
+
+How does the cloud affect the everyday linux user? It turns out quite a bit.
+
+Is the cloud a good or bad thing? Neither. Each service has to be judged on it’s own merits.
+
+The term “The Cloud” is just something marketing people and the technical press get excited about. Anyone remember when they kept using the term “Web 2.0″?
+
+Thankyou for reading.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxnews.pro/how-does-the-cloud-affect-the-everyday-linux-user/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140611 Little Known Apache Mesos Project Helps Mesosphere Raise $10M From Andreessen Horowitz.md b/sources/talk/20140611 Little Known Apache Mesos Project Helps Mesosphere Raise $10M From Andreessen Horowitz.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ede3ae1edf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140611 Little Known Apache Mesos Project Helps Mesosphere Raise $10M From Andreessen Horowitz.md
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+Little Known Apache Mesos Project Helps Mesosphere Raise $10M From Andreessen Horowitz
+================================================================================
+
+
+[Mesosphere][1], the company trying to build a business around the little-known open source [Apache Mesos][2] project, just racked up a $10 million investment from Andreessen Horowitz. Here’s why it attracted that kind of cash.
+
+Mesos, software for automatic scaling, was in fact built around five years ago and is already in use on more than 50,000 cores at Twitter, according to Florian Leibert, CEO and co-founder of Mesosphere. EBay, AirBnB, Netflix and HubSpot are also fans.
+
+While those big Web companies have discovered Mesos, the technology isn’t widely known among enterprises. But it could fill a need for companies which are trying to adopt some of the techniques available to them in public clouds on their internal data centers.
+
+Mesos manages clusters of machines, automatically scaling apps as needed. It requires a small bit of software on each machine – the software uses zero processing power and “negligible” memory, according to Liebert — which coordinates with a master scheduler. The software on each machine reports information about the capacity of the virtual machine or bare metal server to the scheduler, which allocates jobs to available machines.
+
+“If a task goes down and it doesn’t report back, the master knows to reschedule it and knows where it has resources,” said Matt Trifiro, senior vice president at Mesosphere.
+
+Mesos can automatically scale a variety of jobs including Hadoop databases, nodes running Ruby on Rails, and Cassandra.
+
+Using Mesos, Hubspot slashed its Amazon Web Services bill in half, said Liebert. That’s because Mesos efficiently assigns workloads to available machines.
+
+However, Mesos might be most appealing to businesses that are trying to essentially create an AWS-like environment internally, said Jay Lyman, an analyst at 451 Research. AWS offers some [tools for automatic scaling][3]. But many businesses are still shy about running everything on public cloud infrastructure. At the same time, they don’t want to block their developers from taking advantage of the capabilities available in public clouds like AWS. They’d like to make those capabilities available on their private clouds.
+
+“You’re seeing the interface of AWS-style strategy meets the old guard and command and control and stability,” he said.
+
+Mesos can run in both a private cloud and AWS, offering businesses the opportunity to most efficiently use their internal cloud and fallover to AWS when they need to scale.
+
+Mesos has some shortcomings in that regard, however. It [doesn’t run][4] any Windows or legacy apps like SAP, for instance.
+
+However, “if a team is contemplating cloud, they’re probably pretty deep into Linux already,” said Lyman.
+
+In the future, it’s possible Mesosphere could support Windows. Initially, technologies like Puppet and Chef only supported Linux too, Lyman noted. “It speaks to the early nature of Mesosphere. It’s pretty immature right now,” he said.
+
+Mesosphere is targeting the many enterprises that are building more and more apps running on Linux and modern programming languages as well as the first generation Web 2.0 companies like Twitter and Netflix that didn’t have technology like Mesos when they first launched. “Those are the two most common early adopter profiles,” Trifiro said.
+
+Before the end of the year, Mesosphere hopes to release commercial products with documentation, earning revenue from support and licensing. It has built a large-scale orchestration tool called Marathon and supports Docker integration. It’s currently offering packaged Mesos distributions for free in hopes of seeding the market.
+
+Mesosphere is also currently working with a handful of early customers. It helped HubSpot get going with its use of Mesos.
+
+Mesosphere isn’t alone in going after this use case. Rightscale, Scalr and Enstratius, now owned by Dell, all offer some version of scaling or cloud management technology. Mesosphere argues that Mesos, and the company’s own technologies, go above and beyond what’s on the market to create server clusters that essentially operate as one machine. The new investment from Andreessen could help it gain momentum.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://thenewstack.io/little-known-apache-mesos-project-helps-mesosphere-raise-10m-from-andreessen/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://mesosphere.io/
+[2]:http://mesos.apache.org/
+[3]:http://aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/
+[4]:http://mesosphere.io/learn/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140611 Red Hat's CEO Sees Open Source Cloud Domination.md b/sources/talk/20140611 Red Hat's CEO Sees Open Source Cloud Domination.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9e57a2533a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140611 Red Hat's CEO Sees Open Source Cloud Domination.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+Red Hat's CEO Sees Open Source Cloud Domination
+================================================================================
+Red Hat CEO Jim Whitehurst sees the business opportunity of a generation in what he calls a computing paradigm shift from client server to cloud architectures. “In those paradigm shifts, generally new winners emerge,” says Whitehurst and he intends to make sure Red Hat is one of those winners. His logic is sound and simple: disruptive technologies like the cloud that arise every couple decades level the playing field between large, established firms and smaller, innovative challengers since everyone, from corporate behemoth to a couple guys in a garage, starts from the same spot and must play by the same unfamiliar and changeable rules. With the cloud “there’s less of an installed based and an opportunity for new winners to be chosen,” Whitehurst adds. His mission is “to see that open source is the default choice for next generation architecture” and that Red Hat is the preferred choice, particularly for enterprise IT, of open source providers.
+
+The case for open source dominating the cloud rests on the fact that it’s already the foundation for many popular cloud services and enterprise applications. Whitehurst aptly notes that outside of Microsoft Azure, the underlying infrastructure of all the major public cloud services is built upon open source software. Furthermore, software like Linux, Apache, MySQL, WordPress and many others are already widely used and trusted by most enterprises. “In many cases [open source] already is the default choice for next generation architectures, but it hasn’t fully driven itself through the traditional enterprise data center,” he says. Cloud software is the next and most important software category up for open source disruption.
+
+
+
+Yet open source is still saddled with a reputation for widely variable software quality and support, something the recent OpenSSL Heartbleed bug only reinforced. However Whitehurst contends that strong enterprise adoption of Red Hat’s Linux distribution and it’s training and skills certification programs lends credibility to a similar plan for the cloud: [Red Hat’s Cloud Partner Program][1]. He believes such insurance policies alleviate enterprise IT’s fears of adopting open source software for both internal, private clouds and external public cloud services. Red Hat wants its imprimatur to be the Good Housekeeping seal of approval for open source in general and cloud software in specific, namely IT’s assurance that their applications will work and the service is trustworthy and reliable.
+
+Red Hat’s strategy to make open source clouds safe for the enterprise is mirrors that used to break into the market for enterprise server software. There, “Job one for Red Hat is making sure our operating system and layers above that work well on anyone’s infrastructure underneath,” says Whitehurst. Red Hat is applying this same model of polishing, integrating and supporting open source software to cloud stacks. “One of the most important parts about cloud, public, private or hybrid, is a sense that you can confidently run your applications,” says Whitehurst and he believes Red Hat’s track record on Linux and other open source products will carry over to make Red Hat “the enterprise choice” for cloud architectures.
+
+### Cloud isn’t just virtualization 2.0 ###
+
+One of the conundrums for OpenStack advocates like Whitehurst is the entrenchment of Microsoft and VMware in the enterprise market. Although virtual servers are a prerequisite for clouds, they’re sufficient. Countering the notion that enterprise clouds are just a natural extension of virtualized servers and storage, Whitehurst argues that by setting new rules for infrastructure and application design, cloud infrastructure is more than just the natural evolution of server virtualization.
+
+
+
+Whitehurst draws an important distinction between traditional client-server and cloud-optimized applications. “One of the big questions will be how much of this [cloud adoption] is moving traditional Windows workloads, which frankly were written as stateful apps in the first place. [Instead] are we talking about a new generation of applications that are actually built with elasticity and scalability in mind.” Whitehurst clearly believes cloud infrastructure is much more appropriate for the latter and that in such Greenfield scenarios, OpenStack and other open source software have established themselves as the preferred platform. Contrasting OpenStack, based on the Linux KVM hypervisor and VMware or Microsoft using their proprietary virtual machine platforms, Whitehurst says, “Longer term, nobody really cares what the hypervisor is, you just expect it to work and bluntly, as long as Red Hat supports you on it, why do you have to care,” adding “more and more, you’ll see the hypervisor mattering less and less.” Of course, VMware and Microsoft probably agree, both having moved their energies to building more sophisticated management platforms and making the hypervisor a baseline feature.
+
+But in Whitehurst’s view of the world, traditional virtualization platforms like VMware or Microsoft Hyper-V are legacy infrastructure designed for yesterday’s client-server software, not the sort of distributed, rapidly relocatable, elastically scalable applications that define the era of big data, SaaS and social software. “I’m not sure what good you get out of putting Exchange on a cloud,” he quips. Instead, he says this new generation of cloud-optimized applications are the sweet spot for OpenStack. According to Whitehurst, “If you look at where most new applications are getting built, and therefore where so much of the innovation around languages, frameworks and management paradigms are happening, it’s around an open infrastructure.” But there’s obviously some selection bias in Whitehurst’s account, as he lives in an open source world where it’s easy to be unaware, overlook or ignore the innovation happening on proprietary cloud platforms like Azure, AWS and vCloud.
+
+In sum, Whitehurst hopes and expects OpenStack to do to VMware what Linux did to Windows: to become the first choice of cloud-savvy startups and if not the default choice, at least an accepted and respectable alternative within the enterprise. In my next column I’ll explain that even for an open source champion like Whitehurst, OpenStack versus VMware vCloud or Microsoft Azure isn’t an either/or choice and how he sees the fundamental notion of cloud computing as based on virtual machines as an design model likely to change.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.forbes.com/sites/kurtmarko/2014/06/08/red-hat-ceo-open-source-clouds/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.redhat.com/partners/become/cloud/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140612 Linux hiring frenzy--Why open source devs are being bombarded with offers to jump ship.md b/sources/talk/20140612 Linux hiring frenzy--Why open source devs are being bombarded with offers to jump ship.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4115b21b64
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140612 Linux hiring frenzy--Why open source devs are being bombarded with offers to jump ship.md
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+Linux hiring frenzy: Why open source devs are being bombarded with offers to jump ship
+================================================================================
+> Summary: Figures from the Linux Foundation suggest skills shortages across disciplines and throughout Europe.
+
+Nine out of ten (87 percent) of hiring managers in Europe have "hiring Linux talent" on their list of priorities and almost half (48 percent) say they are looking to hire people with Linux skills within the next six months.
+
+But while they either need or want to hire more people with Linux skills, the data from the Linux Foundation suggests that this is easier said than done. Almost all — 93 percent — of the managers surveyed said they were having difficulty finding IT professionals with the Linux skills required and a quarter (25 percent) said they have "delayed projects as a result".
+
+All of this makes it a good time to be a Linux expert.
+
+Seven out of 10 Europe-based Linux professionals have received calls where they were pitched new positions in the past six months, and a third said they had received more calls than in the previous six months. One in three are looking to move anyway, and over half of them said it would be fairly or very easy. Salary is the biggest reason to move jobs, followed by work-life balance and the chance to gain additional skills.
+
+Employers are trying harder to keep hold of staff too: In the past six months, 29 percent of Linux professionals say they have been offered a higher salary from their current employers, while a quarter said they’ve been offered a flexible work schedule and one in five have been extended additional training opportunities or certification.
+
+The Linux Foundation, a non-profit organisation which supports the growth of Linux, and Dice Holdings, which provides career sites for technology professionals, produced the research which covers Europe and the US.
+
+In terms of the specific skills organisations are looking for people with the developer (69 percent) and enterprise management (51 percent) skills. These are followed by 32 percent of respondents who are looking for people with a combination of development and operations skills (DevOps), and 19 percent who are in management/IT management.
+
+The Linux Job Report has been produced for the last three years by the Linux Foundation and Dice but this is the first time that a specific report on European skills has been separated out of the worldwide report. Some 893 Linux professionals responded to the survey across Europe.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.zdnet.com/linux-hiring-frenzy-why-open-source-devs-are-being-bombarded-with-offers-to-jump-ship-7000030418/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140612 The Companies That Support Linux--Rackspace.md b/sources/talk/20140612 The Companies That Support Linux--Rackspace.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..20b5f7964b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140612 The Companies That Support Linux--Rackspace.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+The Companies That Support Linux: Rackspace
+================================================================================
+[][1]
+
+[Rackspace][1] has lately been in the news for its stock market gains and a [potential acquisition][2]. But over the past 16 years the company has become well known, first as a web hosting provider built on Linux and open source, and later as a [pioneer of the open source cloud][3] and founder of the OpenStack cloud platform.
+
+In May, Rackspace became a [Xen Project][4] member and was one of [three companies to join the Linux Foundation][5] as a corporate member, along with CoreOS and Cumulus Networks.
+
+“Many of the applications and infrastructure that we need to run for internal use or for customers run best on Linux,” said Paul Voccio, Senior Director of Software Development at Rackspace, via email. “This includes all the popular language frameworks and open virtualization platforms such as Xen, LXC, KVM, Docker, etc.”
+
+In this Q&A, Voccio discusses the role of Rackspace in the cloud, how the company uses Linux, why they joined the Linux Foundation, as well as current trends and future technologies in the data center.
+
+### Linux.com: What is Rackspace? ###
+
+Paul Voccio: Rackspace is the managed cloud specialist and founder of OpenStack, the open-source operating system for the cloud. Hundreds of thousands of customers look to Rackspace to deliver the best-fit hybrid cloud solutions for their IT needs, leveraging a product and services portfolio that allows workloads to run where they perform best – whether on the public cloud, private cloud, dedicated servers, or a combination of platforms.
+
+As a managed cloud pioneer, we give our customers 24x7 access to cloud engineers for everything from planning and architecting to building and operating clouds through our award-winning Fanatical Support®. We help customers successfully architect, deploy and run their most critical applications. Or, more plainly put, we’re cloud specialists so you don’t have to be. We are headquartered in San Antonio, Texas, and operate a global support and engineering organization with data centers on four continents.
+
+### How and why do you use Linux? ###
+
+Rackspace uses Linux because it provides a stable and flexible platform for our customers' workloads. Our customers trust us to support their mission-critical applications and we need reliable infrastructure – including software and hardware – to meet their expectations. If you look under the hood in our dedicated environments or in our expansive cloud infrastructure, you'll find Linux running there.
+
+Many of the applications and infrastructure that we need to run for internal use or for customers run best on Linux. This includes all the popular language frameworks and open virtualization platforms such as Xen, LXC, KVM, Docker, etc. Running combinations of these platforms give us the stability and performance we demand for the Rackspace Cloud. Our Cloud Servers product runs OpenStack services that manage tens of thousands of hypervisors – all running Linux.
+
+Using Linux also allows us to tap into a community of experts to solve problems. When we have an issue, we're comfortable asking questions. When we have a solution, we enjoy sharing it with the community. At Rackspace, we understand how to work and contribute in an open community and Linux has many opportunities to build relationships with other groups that have similar goals.
+
+### Why did you join the Linux Foundation? ###
+
+Joining the Linux Foundation allows us to show our support and engage the Linux community in new ways. We've learned plenty from running Linux in highly demanding environments at a large scale and we're eager to share those experiences. Other members of the community have probably run into different challenges than we have and this gives us a greater opportunity to learn from them as well.
+
+### What interesting or innovative trends are you witnessing in the data center and what role does Linux play in them? ###
+
+Virtualization and automation have changed how companies deploy hardware and software. Linux gives us several virtualization options and these allow us to automate more of our infrastructure deployments and maintenance tasks. Automation and configuration management frameworks allow us to reduce our costs, improve our testing capabilities, and bring products to market faster. The majority of these open source automation frameworks run best on Linux servers.
+
+### How is Rackspace participating in that innovation? ###
+
+We leverage several open-source Linux-based tools and projects to deliver great customer outcomes. One of our largest efforts in this area is with OpenStack. It's the software that runs our public and private clouds and we're actively engaged with the community to improve it. We're using Linux to find new ways to scale our large virtualization platform and deliver infrastructure to customers quickly.
+
+The open-source nature of Linux inspires us to share the majority of these discoveries with the community. Our customers can improve OpenStack and those improvements will eventually make it into our product offering. We make contributions to a countless number of open source projects either as a company or as individual Rackers (our employees are called "Rackers") and many of these projects are designed to run on Linux.
+
+### What other future technologies or industries do you think Linux and open source will increasingly become important in and why? ###
+
+The move to software-defined infrastructure is a big shift. Customers already have access to virtualization platforms like Xen that allow them to define their infrastructure with software. Software-defined networking is quickly becoming more mature and scalable. However, customers want the ability to have a software defined datacenter at their fingertips. This may involve physical servers, virtual servers, and virtual networks that need high performance with flexible configurations. Many of the current technologies are designed to run on Linux due to technology already available in the kernel or userland frameworks provided by the community.
+
+### Are you hiring? ###
+
+From hacking on kernels to supporting thousands of virtual machines – we are always looking for talented admins, developers and engineers. You can find more information at Rackertalent.com.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/200-libby-clark/775890-the-companies-that-support-linux-rackspace/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.rackspace.com/
+[2]:http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2014-05-15/rackspace-hires-morgan-stanley-to-evaluate-options.html
+[3]:http://www.informationweek.com/cloud/infrastructure-as-a-service/9-more-cloud-computing-pioneers/d/d-id/1109120
+[4]:http://www.xenproject.org/
+[5]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/news-media/announcements/2014/05/new-linux-foundation-members-advance-massively-scalable-secure
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140616 Valve SteamOS--A Linux-based Gaming Operating System Announced.md b/sources/talk/20140616 Valve SteamOS--A Linux-based Gaming Operating System Announced.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a65c9c609d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140616 Valve SteamOS--A Linux-based Gaming Operating System Announced.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+乌龙茶 占坑
+Valve SteamOS: A Linux-based Gaming Operating System Announced
+================================================================================
+
+
+The year of Linux on the desktop or living room is here. Today Valve software announced SteamOS, a free Linux-based gaming operating system designed for the TV, DIY enthusiast and the living room. From the announcement page:
+
+> As we've been working on bringing Steam to the living room, we’ve come to the conclusion that the environment best suited to delivering value to customers is an operating system built around Steam itself. SteamOS combines the **rock-solid architecture of Linux with a gaming experience** built for the big screen. It will be available soon as a free stand-alone operating system for living room machines.
+
+### More about SteamOS ###
+
+- Hundreds of great games are already running natively on SteamOS. More AAA titles coming natively to SteamOS in 2014.
+- You can stream games from your desktop and stream those games over your home network to your TV via a SteamOS machine.
+- You can play all your Windows and Mac games on your SteamOS machine, too.
+- Stream music and video with the SteamOS media services.
+- In SteamOS, Valve have achieved significant performance increases in graphics processing, and Valve working on audio performance and reductions in input latency at the operating system level. Game developers are already taking advantage of these gains as they target SteamOS for their new releases.
+- You can modify or replace any part of the software or hardware you want. No more lock-ins.
+- Valve are working on improving Linux kernel, drivers and debugging tools. This is a great news for both developers and users.
+- Standard parental controls for games and streaming services.
+
+### Input lag over a network... a horrible experience? ###
+
+Streaming games over the internet adds the the network latency. However, SteamOS machine and TV will be in a local network. This will keep delay to minimum including encoding and decoding video between the two systems. This is just a guess and I will wait for the reviews.
+
+I think Valve is following Android model. User will get consistent environment for all your devices or you can build your own device. SteamOS will be available soon as a free download for users and as a freely licensable operating system for manufacturers. For more information see [SteamOS][1] announcement page.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/linux-games/valve-announces-linux-based-steamos/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://store.steampowered.com/livingroom/SteamOS/
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140617 7 Improvements The Linux Desktop Needs.md b/sources/talk/20140617 7 Improvements The Linux Desktop Needs.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9a5c215d2e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140617 7 Improvements The Linux Desktop Needs.md
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+7 Improvements The Linux Desktop Needs
+======================================
+
+In the last fifteen years, the Linux desktop has gone from a collection of marginally adequate solutions to an unparalleled source of innovation and choice. Many of its standard features are either unavailable in Windows, or else available only as a proprietary extension. As a result, using Linux is increasingly not only a matter of principle, but of preference as well.
+
+Yet, despite this progress, gaps remain. Some are missing features, others missing features, and still others pie-in-the sky extras that could be easily implemented to extend the desktop metaphor without straining users' tolerance of change.
+
+For instance, here are 7 improvements that would benefit the Linux desktop:
+
+### 7. Easy Email Encryption
+
+These days, every email reader from Alpine to Thunderbird and Kmail include email encryption. However, documentation is often either non-existent or poor.
+
+But, even if you understand the theory, the practice is difficult. Controls are generally scattered throughout the configuration menus and tabs, requiring a thorough search for all the settings that you require or want. Should you fail to set up encryption properly, usually you receive no feedback about why.
+
+The closest to an easy process is [Enigmail][1], a Thunderbird extension that includes a setup wizard aimed at beginners. But you have to know about Enigmail to use it, and the menu it adds to the composition window buries the encryption option one level down and places it with other options guaranteed to mystify everyday users.
+
+No matter what the desktop, the assumption is that, if you want encrypted email, you already understand it. Today, though, the constant media references to security and privacy have ensured that such an assumption no longer applies.
+
+### 6. Thumbnails for Virtual Workspaces
+
+Virtual workspaces offer more desktop space without requiring additional monitors. Yet, despite their usefulness, management of virtual workspaces hasn't changed in over a decade. On most desktops, you control them through a pager in which each workspace is represented by an unadorned rectangle that gives few indications of what might be on it except for its name or number -- or, in the case of Ubuntu's Unity, which workspace is currently active.
+
+True, GNOME and Cinnamon do offer better views, but the usefulness of these views is limited by the fact that they require a change of screens. Nor is KDE's written list of contents, which is jarring in the primarily graphic-oriented desktop.
+
+A less distracting solution might be mouseover thumbnails large enough for those with normal vision to see exactly what is on each workspace.
+
+### 5. A Workable Menu
+
+The modern desktop long ago outgrew the classic menu with its sub-menus cascading across the screen. Today, the average computer simply has too many applications to fit comfortably into such a format.
+
+The trouble is, neither of the major alternatives is as convenient as the classic menu. Confining the menu into a single window is less than ideal, because you either have to endure truncated sub-menus or else continually resize the window with the mouse.
+
+Yet the alternative of a full-screen menu is even worse. It means changing screens before you even begin to work, and relying on a search field that is only useful if you already know what applications are available -- in which case you are almost better off launching from the command line.
+
+Frankly, I don't know what the solution might be. Maybe spinner racks, like those in OS X? All I can say for certain is that all alternatives for a modern menu make a carefully constructed set of icons on the desktop seem a more reasonable alternative.
+
+### 4. A Professional, Affordable Video Editor
+
+Over the years, Linux has slowly filled the gaps in productivity software. However, one category in which it is still lacking is in reasonably priced software for editing videos.
+
+The problem is not that such free software is non-existent. After all, [Maya][2] is one of the industry standards for animation. The problem is that the software costs several thousand dollars.
+
+At the opposite end of the spectrum are apps like Pitivi or Blender, whose functionality -- despite brave efforts by their developers -- remain basic. Progress happens, but far more slowly than anyone hopes for.
+
+Although I have heard of indie directors using native Linux video editors, the reason I have heard of their efforts is usually because of their complaints. Others prefer to minimize the struggle and edit on other operating systems instead.
+
+### 3. A Document Processor
+
+At one extreme are users whose need for word processing is satisfied by Google Docs. At the other extreme are layout experts for whom Scribus is the only feasible app.
+
+In-between are those like publishers and technical writers who produce long, text-oriented documents. This category of users is served by [Adobe FrameMaker][3] on Windows, and to some extent by LibreOffice Writer on Linux.
+
+Unfortunately, these users are apparently not a priority in LibreOffice, Calligra Words, AbiWord, or any other office suite. Features that would provide for these users include:
+
+- separate bibliographic databases for each file
+- tables that are treated like styles in the same way that paragraphs and characters are
+- page styles with persistent content other than headers or footers that would appear each time the style is used
+- storable formats for cross-references, so that the structure doesn't need to be recreated manually each time that it is needed
+
+Whether LibreOffice or another application provides these features is irrelevant comparing to whether they are available. Without them, the Linux desktop is an imperfect place for a large class of potential users.
+2. Color-Coded Title Bars
+
+Browser extensions have taught me how useful color coded tabs can be for workspaces. The titles of open tabs disappear when more than eight or nine or open, so the color is often the quickest visual guide to the relation between tabs.
+
+The same system could be just as useful on the desktop. Better yet, the color coding might be preserved between sessions, allowing users to open all the apps needed for a specific task at the same time. So far, I know of no desktop with such a feature.
+
+### 1. Icon Fences
+
+For years, Stardock Systems has been selling a Windows extension called [Fences][4], which lets icons be grouped. You can name each group and move the icons in it together. In addition, you can assign which fence different types of files are automatically added to, and hide and arrange fences as needed.
+
+In other words, fences automate the sort of arrangements that users make on their desktop all the time. Yet aside from one or two minor functions they share with KDE's Folder Views, fences remain completely unknown on Linux desktops. Perhaps the reason is that designers are focused on mobile devices as the source of ideas, and fences are decidedly a feature of the traditional workstation desktop.
+
+### Personalized Lists
+
+As I made this list, what struck me was how few of the improvements were general. Several of these improvement would appeal largely to specific audiences, and only one even implies the porting of a proprietary application. At least one is cosmetic rather than functional.
+
+What this observation suggests is that, for the general user, Linux has very little left to add. As an all-purpose desktop, Linux arrive some years ago, and has been diversifying ever since, until today users can choose from over half a dozen major desktops.
+
+None of that means, of course, that specialists wouldn't have other suggestions. In addition, changing needs can make improvements desirable that nobody once cared about. But it does mean that many items on a list of desirable improvements will be highly personal.
+
+All of which raises the question: what other improvements do you think would benefit the desktop?
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/7-improvements-the-linux-desktop-needs-1.html
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/thunderbird/addon/enigmail/
+[2]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autodesk_Maya
+[3]:http://www.adobe.com/products/framemaker.html
+[4]:http://www.stardock.com/products/fences/
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140617 Does Linux Lack a Killer App.md b/sources/talk/20140617 Does Linux Lack a Killer App.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..dce3b05415
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140617 Does Linux Lack a Killer App.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+(翻译中 by runningwater)
+Does Linux Lack a Killer App?
+================================================================================
+
+
+**What Linux needs most is games, said Hyperlogos blogger Martin Espinoza. However, "if you were trying to narrow it down to one app, it would probably still be Photoshop. For all the talk of how great GIMP has become, usability is still an abject nightmare, and in spite of the OSS community's self-back-patting regarding documentation, there is no documentation for GIMP which is not pathetic."**
+
+Well the days are heating up here in the Linux blogosphere, and FOSS fans are flocking to the Broken Windows Lounge as much for the frosty air-conditioning as for the conversation.
+
+Even Linux Girl, whose days generally involve far more pavement-pounding than she'd like, has found herself seeking solace in the blogobar's arctic climes far more often than she probably should.
+
+It's a good thing she has been, though, or she might have missed the latest juicy debate. "What killer app is Linux missing?" was the question that [kicked things off][1], and the discussion has been escalating ever since.
+
+"The Free Software world is incredibly rich, and covers pretty much all bases," **Linux Voice's** Mike Saunders began. "We have a wealth of desktop, server, development and multimedia tools to choose from -- some of which are the best in their field.
+
+"But what is missing?" Sanders went on provocatively. "Is there a killer app that prevents you from running Linux 24x7 on your main machine?"
+
+There was a momentary lull in the conversation around the bar as patrons pondered the suggestion. Linux Girl tried to enjoy the fleeting peace, but it didn't last for more than an instant.
+
+### 'Depends on What You Do' ###
+
+
+
+"A long time ago Linux needed a lot of things," Google+ blogger Alessandro Ebersol offered. "These days, when every software and the kitchen sink are migrating to the cloud, everything is going to be multiplatform.
+
+"I would say we lacked games, but that also is being taken care of," Ebersol said. "So I don't feel that we desperately need a killer app anymore."
+
+The killer app "depends on what you do with your computer," consultant and [Slashdot][2] blogger Gerhard Mack opined. "If you are drafting, then the killer app is Autocad. But for other industries the killer app will be something else."
+
+### 'The Enterprise Space' ###
+
+Google+ blogger Kevin O'Brien had a similar view.
+
+"There isn't much left on the consumer level," O'Brien said. "I could maybe gripe about games or Nvidia drivers, and I don't really see anything that can replace Quicken. But for me the big difference maker is in the enterprise space.
+
+"Microsoft owns that, and there is nothing that compares to Outlook/Exchange server, Sharepoint, etc.," he asserted. "I suspect part of the reason is that there are not a lot of open source developers who really care about that stuff."
+
+### 'The Tide Is Changing' ###
+
+It's not so much a "missing app" situation as a "not-enough-critical-mass" kind of problem, Google+ blogger Gonzalo Velasco C. suggested.
+
+Many more people use Linux today than did five years ago, he noted; at the same time, many are tied to non-Linux-friendly applications.
+
+"'Everybody' uses $kype, but we have half a dozen apps for that in GNU/Linux, from the simple and very useful Pidgin (my favorite) to Ekiga and similar VoIP apps," Gonzalo Velasco C. explained. "Some users still claim they need Photo$hop and don't take the time to master and suggest improvements for GIMP, Inkscape, Bender and others."
+
+Games used to be missing, "but the tide is changing, mainly -- but not only -- because of Valve's brave SteamOS movement," he added.
+
+### 'Retail Shelf Space' ###
+
+"I don't think there are any 'killer' apps these days," blogger [Robert Pogson][3] agreed. "In Debian GNU/Linux, there are 40K packages. My main PC has only 3K installed and I lack nothing. I have multiple browsers, editors, compilers/interpreters, platforms, and with virtual machinery like KVM, I can play with multiple operating systems and different versions of software as needed.
+
+"I can treat multiple machines as if they were a single machine from anywhere on the LAN," Pogson added. "I can access resources on any node on the LAN from any machine. What more do I need?"
+
+That said, "several professionals have told me that video and image editors in GNU/Linux are a bit weak," he noted. "GIMP is being improved in bit-depth, so that should be covered. Lightworks will eventually be released as FLOSS, so video should be covered."
+
+Nevertheless, "these are tiny niches in IT," he pointed out. "Many ordinary folks go decades without using those other special applications, so I don't think this is anything holding GNU/Linux back."
+
+The real killer in the market, however, is lack of shelf space in retail stores, Pogson asserted. "Where that is covered, GNU/Linux thrives."
+
+### 'Linux Has Lost Out to OS X' ###
+
+Chris Travers, a [blogger][4] who works on the [LedgerSMB][5] project, had a different perspective.
+
+"I don't think that it is a question of killer apps," he began. "The real issue is that on the desktop, Linux has generally lost out to OS X, while it is increasingly dominating the server market along with the BSDs. People who use Linux on the desktop tend to be looking for openness."
+
+What Linux needs is either "the momentum of Microsoft or the smooth UI and attention to detail of OS X," Travers said. "These may come over time."
+
+### The Documentation Problem ###
+
+Linux isn't missing one killer app -- "what it's missing is polish, as always," [Hyperlogos][6] blogger Martin Espinoza opined. "No desktop environment for Linux has the polish of Windows XP, let alone Windows 7.
+
+"Move away from the bloat and oversimplicity of GNOME or from the widget salad of [KDE][7] to what, Xfce or LXDE, with their perfectly horrible file managers and primitive panels?" Espinoza added. "GNOME is the only DE that ever got close, and then they decided to remove all the complexity and eliminate their reason to exist."
+
+Windows is just "a nicer place to hang out," he asserted.
+
+Still, if Linux is missing anything for broader acceptance, "that is games," Espinoza said. "If you were trying to narrow it down to one app, it would probably still be Photoshop. For all the talk of how great GIMP has become, usability is still an abject nightmare, and in spite of the OSS community's self-back-patting regarding documentation, there is no documentation for GIMP which is not pathetic."
+
+GIMP "might be able to do most of the things Photoshop can do, but I'll probably never know," Espinoza concluded. "I suppose if I spent hours trolling fora I could find out how to use GIMP. This failing is shared by most OSS projects, including the ones that think they're really well-documented."
+
+### 'Ease of Use and Support' ###
+
+Ease of use and support are the "killer app" SoylentNews blogger hairyfeet named.
+
+"Oh, a freshly installed Linux distro LOOKS nice, it works great; the problem is it doesn't CONTINUE to look nice or work great," he explained. "First update and whoops! Wireless no longer can use WPA V2. Second update? Whoops, say goodbye to sound, as Pulse has puked. First 'upgrade'? Uh oh, hope you didn't need that!
+
+"THIS is what Windows and OS X have that Linux doesn't: the ease of use and support," hairyfeet concluded. "As long as it takes 15+ Linux releases to equal the same support cycle a single Windows release gets? Then I'm sorry, but your product is just not in the same league -- you are comparing HS baseball to the majors."
+
+### 'Windows 8' ###
+
+Last but not least, [Linux Rants][8] blogger Mike Stone had a surprising suggestion.
+
+"The killer app that Linux has been missing all these years is Windows 8," Stone quipped.
+
+"Seriously, I don't think there is a particular app that can be the 'killer app,'" he said. "Linux needs to have more mainstream application support, and that's going to mean Photoshop and Microsoft Office at the minimum. Thankfully, Microsoft has done their best to make Office less relevant, and most people don't need Photoshop."
+
+Linux "could be reaching critical mass, and I was only partially joking when I said Windows 8 earlier," he concluded. "The application base in Linux is starting to arrive, and the current version of Windows is remarkably unpopular. Fingers crossed we see some motion here soon."
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via:
+
+译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.linuxvoice.com/voice-of-the-masses-what-killer-app-is-linux-missing/
+[2]:http://slashdot.org/
+[3]:http://mrpogson.com/
+[4]:http://ledgersmbdev.blogspot.com/
+[5]:http://www.ledgersmb.org/
+[6]:http://hyperlogos.org/
+[7]:http://www.kde.org/
+[8]:http://linuxrants.com/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140619 Fire Phone Dynamic Perspective tracks eyes for 3D UI.md b/sources/talk/20140619 Fire Phone Dynamic Perspective tracks eyes for 3D UI.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..65b0e250d1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140619 Fire Phone Dynamic Perspective tracks eyes for 3D UI.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+Fire Phone Dynamic Perspective tracks eyes for 3D UI
+================================================================================
+
+
+3D on phones is back, and it's Amazon giving it a try this time with Dynamic Perspective on the new [Fire Phone][1]. Eschewing a "true" 3D display as we've seen before, the Fire Phone's system instead uses four front-facing cameras to track the user's eyes, and adjusts the on-screen UI so that the various layers shift around to give the impression of 3D.
+
+A combination of physically tilting the phone and moving your head as you hold it can be used to navigate through the interface and apps. So, tilting the Fire Phone can scroll through the browser, rather than having to swipe around with a fingertip.
+
+youtube视频链接地址:[http://www.youtube.com/embed/iB75HJe8eiI][2]
+
+Similarly, with a carousel of items in Amazon's store on the phone, tilting the handset left and right pans through the products.
+
+youtube视频链接地址:[http://www.youtube.com/embed/lwj0hlE8CJc][3]
+
+In ebooks, the Kindle app can scroll through according to how you're holding it. The settings can be switched between adjusting speed depending on how extreme the tilt angle is, or locking it to a fixed rate if you'd rather have things be predictable.
+
+### This is the Amazon Fire Phone ###
+
+Maps, too, get Dynamic Perspective support. Moving the Fire Phone around can show what's "hiding" behind 3D buildings or on different layers. Tilting can also be used to open up menus, in games for motion control, and even to navigate between the now-playing and lyrics UIs in the Prime Music app.
+
+
+
+All that 3D didn't come easy, though. Based on the fact that every face is different, with variations in hair color, shape, whether they wear glasses, and other factors, Amazon had to put Dynamic Perspective through some serious testing.
+
+
+
+In the companies labs, that involved a somewhat nightmarish rubber head on a stick, but then Amazon expanded that to use real-world data from thousands of photos of people. The use of four cameras means that, no matter what may be blocking the screen, the Fire Phone should be able to spot the user properly.
+
+youtube视频链接地址:[http://www.youtube.com/embed/X-wPOq27iXk][5]
+
+Whether it'll all work as Bezos says, or be something owners quickly turn off, remains to be seen. We'll know more when we spend some hands-on time with the Fire Phone soon.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.slashgear.com/fire-phone-dynamic-perspective-tracks-eyes-for-3d-ui-18334229/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.slashgear.com/tags/fire-phone
+[2]:http://www.youtube.com/embed/iB75HJe8eiI
+[3]:http://www.youtube.com/embed/lwj0hlE8CJc
+[4]:http://www.slashgear.com/this-is-the-amazon-fire-phone-18334195/
+[5]:http://www.youtube.com/embed/X-wPOq27iXk
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140619 Red Hat designs RHEL for a decade-long run.md b/sources/talk/20140619 Red Hat designs RHEL for a decade-long run.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..baf39438f5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140619 Red Hat designs RHEL for a decade-long run.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+Red Hat designs RHEL for a decade-long run
+================================================================================
+> The newly released RHEL 7 includes Docker containers and the new terabyte-scaled XFS file system
+
+IDG News Service - Knowing how system administrators enjoy continuity, Red Hat has designed the latest release of its flagship Linux distribution to be run, with support, until 2024.
+
+Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 (RHEL 7), the completed version of which was shipped Tuesday, also features a number of new technologies that the company sees as instrumental for the next decade, including the Docker Linux Container system and the advanced XFS file system.
+
+"XFS opens the door for a new class of business analytics, big data and data analytics," said Mark Coggin, Red Hat senior director of product marketing.
+
+The last major update to RHEL, RHEL 6, was released in November 2010. Since then, server software has been used in an increasingly wide variety of operational scenarios, including providing the basis for bare metal servers, virtual machines, IaaS (infrastructure-as-a-service) and PaaS (platform-as-a-service) cloud packages.
+
+Red Hat will support RHEL 7 with bug fixes and commercial support for up to 10 years. The company generally releases a major version of RHEL every three years.
+
+In contrast, Canonical's Ubuntu LTS (long-term support) distributions are supported for five years. Suse Enterprise Linux [is also supported][1], in most aspects, for up to 10 years,
+
+This is the first edition to include Docker, a container technology [that could act as a nimbler replacement][2] to full virtual machines used in cloud operations. Docker provides a way to package an application in a virtual container so that it can be run across different Linux servers.
+
+Red Hat expects that containers will be widely deployed over the next few years as a way to package and run applications, thanks to their portable nature.
+
+"Customers have told us they are looking for a lighter weight version of developing applications. The applications themselves don't need a full operating system or a virtual machine," Coggin said. The system calls are answered by the server's OS and the container includes only the necessary support libraries and the application. "We only put into that container what we need," he said.
+
+Containers are also easier to maintain because users don't have to worry about updating or patching the full OS within a virtual machine, Coggin said.
+
+Red Hat is also planning a special stripped-down release of RHEL, now code-named RHEL Atomic, which will be a distribution for just running containers. Containers that run on the regular RHEL can easily be transferred to RHEL Atomic, once that OS is available. They will also run on Red Hat OpenShift PaaS.
+
+Red Hat is also supporting Docker through its switch in RHEL 7 to the systemd process manager, replacing Linux's long used init process manager. Systemd "gives the administrator a lot of additional flexibility in managing the underlying processes inside of RHEL. It also has a tie back to the container initiative and is very integral to the way the processes are stood up and managed in containers," Coggin said.
+
+Red Hat has switched the default file system in RHEL 7 to XFS, which is able to keep track of up to 500TBs on a single partition. The previous default file system, ext4, was only able to support 50TBs. Ext4 is still available as an option, as well as another of other file systems such as GFS2 and Btrfs (under technology preview).
+
+Red Hat has added greater interoperability with the Microsoft Windows environment. Organizations can now use Microsoft Active Directory to securely authenticate users on Red Hat systems. Tools are also included in RHEL 7 to offer Red Hat credentials for Windows servers.
+
+"Customers have thousands of Windows servers and thousands of RHEL servers, and they to need ways to integrate the two," Coggin said.
+
+The installation process has been sped up as well, thanks to an update to the Anaconda installer, which now allows administrators to preselect server configurations on the start of the installation process. The inclusion of the industry standard OpenLMI (Open Linux Management Infrastructure), which allows the administrator to manage services at a granular level through a standardized API (application programming interface).
+
+"OpenLMI is another important way of improving stability and efficiency by helping to manage systems better," Coggin said.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.computerworld.com/s/article/9248988/Red_Hat_designs_RHEL_for_a_decade_long_run?taxonomyId=122
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://www.suse.com/support/policy.html
+[2]:http://www.infoworld.com/d/virtualization/docker-all-geared-the-enterprise-244020
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140619 What will your business look like in 2030.md b/sources/talk/20140619 What will your business look like in 2030.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d30888bede
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140619 What will your business look like in 2030.md
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
+What will your business look like in 2030?
+================================================================================
+
+
+lya Pozin is a serial entrepreneur, writer, and investor. He is the founder of online video entertainment platform [Pluto.TV][1], social greeting card company [Open Me][2], and digital marketing agency [Ciplex][3].
+
+The year is 2030, and you’re walking into the front doors of your company. What will it look like, what functions will your employees be performing and how will you stack up against the competition?
+
+You might not be considering the future, but remember that [25 years ago][4], only 15 percent of US households had a personal computer. While 73 percent of online adults currently have a social media account, social media barely existed 15 years ago.
+
+Technology is always changing, and with it come disruptions to industries, companies and the employment marketplace. The future is closing in, but is your company ready?
+
+### Why should you be worried? ###
+
+In business, to stop moving forward means your company is stagnating; for many companies, stagnation equates to eventual death. Companies clinging to outmoded and outdated business practices eventually run into major problems. There are examples everywhere in the marketplace, from struggling BlackBerry phones to Kodak slowly shuttering its film business.
+
+According to [futurist and TED talk speaker Thomas Frey][5], two billion jobs will disappear by 2030 thanks to shifting technologies and changing needs. You can’t afford to be behind the pack when the future comes calling.
+
+### What will 2030 look like? ###
+
+
+
+Recently, the [Canadian Scholarship Trust][6], as part of its Inspired Minds campaign, [put together a list of the jobs][7] we might all be hiring for in 2030. These jobs range from “Company Culture Ambassador” to – get this! – “Nostalgist.”
+
+Taking CST’s lead, I spoke to some entrepreneurs and innovators in different fields, from medicine to marketing, to see their predictions for how businesses will be run in the future. Hopping in our time travel machine, here’s a glimpse at what 2030 might look like:
+
+### Cloud-based ###
+
+“Everything will be cloud-based with faster speeds,” said Marjorie Adams, [AQB][8] CEO and President. “The technologies coming out now will be better defined and connected. While innovation from the business side could be a lot slower-going than the consumer side, we will have a lot more data to understand real needs.”
+
+### Automated ###
+
+Google is already leading the way with the self-driving car, but automation might creep into other aspects of our lives in the future.
+
+“Home automation will be very different in 2030,” said Andrew Thomas, co-founder of [SkyBell Technologies, Inc][9] .“We’ll all have brain-sensing headbands and glasses and we’ll just ‘think’ about locking the door or turning off the lights. Our fridge will email the store when we’re low on food and our self-driving cars will go pick up the groceries for us!”
+
+### Human curated ###
+
+As more and more options become available to consumers, we’ll all become overwhelmed by choice. Human curation will come back into vogue for everything from music to online video.
+
+We’re already seeing the trend start now with [Apple’s acquisition][10] of human curated music service Beats. After all, do you really think apps are [smarter than you][11]?
+
+### Socially-connected ###
+
+If you can’t watch the latest episode of Scandal or Game of Thrones, it’s common sense to stay off your Facebook and Twitter feeds.
+
+“Imagine a media environment 15 years into the future where no object or entertainment venue is out of reach for second-screen integration with social media,” said Jared Feldman, CEO and founder of [Mashwork][12]. “Social platforms like Facebook and Twitter might as well be agnostic at this point in time since consumers will have aggregated all of their digital social life into consolidated user profiles designed to curate multiple feeds and allow for single-source user engagement.”
+
+### Targeted ###
+
+Already advertising is becoming more and more targeted to consumers needs thanks to big data and algorithms. Don’t expect this trend to move backwards, at least according to [FlexOne][13] CEO Matthijs Keij.
+
+“Advertisers will know more about you than you yourself. Which products you like, how to improve your personal and work life, and even how to be more healthy. Sounds a little like Huxley’s Brave New World? Maybe…but consumers might actually like it.”
+
+### How do your prepare? ###
+
+
+
+Preparing for the future might seem impossible, but you don’t need a crystal ball to keep abreast of changes. It’s important to always keep up with trends and emerging technology, both in the economy in general and within your industry in particular.
+
+Go to conferences, attend industry talks, and make time for industry trade shows. Pay attention to the new technology entering your sector, and don’t turn your nose up at something new just because it’s different than the way things have always been.
+
+Understand your customers and know what they need, because the future is looking more consumer-focused than ever before, even in segments like healthcare. “The paradigm is shifting to a more “consumer-centric” model,” said Robert Grajewski, CEO of [Edison Nation Medical][14]. “Healthcare as a whole will shift to this individual care focus.”
+
+Companies that understand their core competencies and their consumer needs will have a leg up on the competition.
+
+As more digital natives come of age and flock into the economy, some highly skilled fields will see consumers picking up additional skills.
+
+“By 2030 virtually everyone will be a designer, equipped with knowledge of the hottest mega trends and ripe and ready to replace those who can’t keep up with the latest software,” said Ashley Mady, CEO of [Brandberry][15].
+
+“The best way to prepare for this inevitable shift in the design world is to focus on creative, big picture thinking over production, which will soon become a commodity. Designers should remain innovative by developing their own adaptable brands and technology that will grow alongside the quickly evolving world we live in.”
+
+Finally, it’s important to be open, curious, and willing to pivot. New technologies are going to come along to improve, and sometimes complicate, your business. You need to be willing to embrace these new paradigms, or you risk your company becoming obsolete.
+
+What do you think? How do you plan to prepare for the future? Share in the comments!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://thenextweb.com/entrepreneur/2014/06/18/will-business-look-like-2030/?utm_campaign=share%20button&utm_content=What%20will%20your%20business%20look%20like%20in%202030?&awesm=tnw.to_q3L0P&utm_source=copypaste&utm_medium=referral
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://pluto.tv/
+[2]:http://www.openme.com/
+[3]:http://www.ciplex.com/
+[4]:http://www.cnbc.com/id/101611509
+[5]:http://www.futuristspeaker.com/2012/02/2-billion-jobs-to-disappear-by-2030/
+[6]:http://www.cst.org/
+[7]:http://careers2030.cst.org/jobs/
+[8]:http://www.aqb.com/
+[9]:http://www.skybell.com/
+[10]:http://thenextweb.com/apple/2014/05/28/apple-confirms-acquisition-beats/
+[11]:http://thenextweb.com/apps/2013/10/19/i-let-apps-tell-me-how-to-live-for-a-day/
+[12]:http://mashwork.com/
+[13]:http://www.flxone.com/
+[14]:http://www.edisonnationmedical.com/
+[15]:http://www.brandberry.com/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140620 Linux Poetry Explains the Kernel Line By Line.md b/sources/talk/20140620 Linux Poetry Explains the Kernel Line By Line.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e46e7d34e3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140620 Linux Poetry Explains the Kernel Line By Line.md
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
+Linux Poetry Explains the Kernel, Line By Line
+================================================================================
+> Editor's Note: Feeling inspired? Send your Linux poem to [editors@linux.com][1] for your chance to win a free pass to [LinuxCon North America][2] in Chicago, Aug. 20-22. Be sure to include your name, contact information and a brief explanation of your poem. We'll draw one winner at random from all eligible entries each week through Aug. 1, 2014.
+
+
+
+Software developer Morgan Phillips is teaching herself how the Linux kernel works by writing poetry.
+
+Writing poems about the Linux kernel has been enlightening in more ways than one for software developer Morgan Phillips.
+
+Over the past few months she's begun to teach herself how the Linux kernel works by studying text books, including [Understanding the Linux Kernel][3], Unix Network Programming, and The Unix Programming Environment. But instead of taking notes, she weaves the new terminology and ideas she learns into poetry about system architecture and programming concepts. (See some examples, below, and on her [Linux Poetry blog][4].)
+
+It's a “pedagogical hack” she adopted in college and took up again a few years ago when she first landed a job as a data warehouse engineer at Facebook and needed to quickly learn Hadoop.
+
+“I could remember bits and pieces of information but it was too rote, too rigid in my mind, so I started writing poems,” she said. “It forced me to wrap all of these bits of information into context and helped me learn things much more effectively.”
+
+The Linux kernel's history, architecture, abundant terminology and complex concepts, are rich fodder for her poetry.
+
+“I could probably write thousands of poems about just one subsystem in the kernel,” she said.
+
+### Why learn Linux? ###
+
+
+Phillips publishes on her Linux Poetry blog.
+
+Phillips started her software career through a somewhat unconventional route as a physics major in a research laboratory. Instead of writing journal articles she was writing Python scripts to parse research project data on active galactic nuclei. She never learned the fundamentals of computer science (CS), but picked up the information on the job, as the need arose.
+
+She soon got a job doing network security research for the Army Research Laboratory in Adelphi, Maryland, working with Linux. That was her first foray into the networking stack and the lower levels of the operating system.
+
+Most recently she worked at Facebook until about six months ago when she moved from the Silicon Valley back to Nashville, near her home state of Kentucky, to work for a software startup that helps major record labels manage their business.
+
+“I have all this experience but I suffer from a thing that almost every person who doesn’t have an actual background in CS does: I have islands of knowledge with big gaps in between,” she said. “Every time I'd come across some concept, some data structure in the kernel, I'd have to go educate myself on it.”
+
+A few weeks ago her frustration peaked. She was trying to do a form of message passing between web application processes and a web socket server she had written and found herself having to brush up on all the ways she could do interprocess communication.
+
+“I was like, that's it. I'm going to start really learning everything I should have known starting at the bottom up with the Linux kernel,” she said. “So I bought some textbooks and started reading.”
+
+
+
+### What she's learned ###
+
+Over the course of a few months of reading books and writing poems she's learned about how the virtual memory subsystem works. She's learned about the data structures that hold process information, about the virtual memory layout and how pages are mapped into memory, and about memory management.
+
+“I hadn't thought about a lot of things, like that a system that's multiprocessing shouldn’t bother with semaphores,” she said. “Spin locks are often more efficient.”
+
+Writing poems has also given her insight into her own way of thinking about the world. In some small way she is communicating not just her knowledge of Linux systems, but also the way that she conceptualizes them.
+
+“It's a deep look into my mind,” she said. “Poetry is the best way to share these abstract ideas and things that we can't possibly truly share with other people.”
+
+Writing a Linux poem
+
+The inspiration for her Linux poems starts with reading a textbook chapter. She hones the topics down to the key concepts that she wants to remember and what others might find interesting, as well as things she can “wrap a conceptual bubble around.”
+
+A concept like demand paging is too broad to fit into a single poem, for example. “So I'm working my way down deeper in it,” she said. “Instead I'm looking at writing a poem about the actual data structure where process memory is laid out and then mapped into a page map.”
+
+She hasn't had any formal training writing poetry, but writes the lines so that they are visually appealing and have a nice rhythm when they're read aloud.
+
+In her poem, “The Reentrant Kernel,” Phillips writes about an important property in software that allows a function to be paused and restarted later with the same result. System calls need to have this reentrant property in order to make the scheduler run as efficiently as possible, Phillips explains. The poem also includes a program, written in C style pseudocode, to help illustrate the concept.
+
+Phillips hopes her Linux poetry helps her increase her understanding enough to start contributing to the Linux kernel.
+
+“I've been very intimidated for a long time by the idea of submitting a patch to the kernel, being a kernel hacker,” she said. “To me that's the pinnacle of success.
+
+“My ultimate dream is that I can gain a good enough understanding of the kernel and C to submit a patch and have it accepted.”
+
+ The Reentrant Kernel
+
+ A reentrant function,
+ if interrupted,
+ will return a result,
+ which is not perturbed.
+
+ int global_int;
+ int is_not_reentrant(int x) {
+ int x = x;
+ return global_int + x; },
+ depends on a global variable,
+ which may change during execution.
+
+ int global_int;
+ int is_reentrant(int x) {
+ int saved = global_int;
+ return saved + x; },
+ mitigates external dependency,
+ it is reentrant, though not thread safe.
+
+ UNIX kernels are reentrant,
+ a process may be interrupted while in kernel mode,
+ so that, for instance, time is not wasted,
+ waiting on devices.
+
+ Process alpha requests to read from a device,
+ the kernel obliges,
+ CPU switches into kernel mode,
+ system call begins execution.
+
+ Process alpha is waiting for data,
+ it yields to the scheduler,
+ process beta writes to a file,
+ the device signals that data is available.
+
+ Context switches,
+ process alpha continues execution,
+ data is fetched,
+ CPU enters user mode.
+
+注:上面代码内文本发布时请参考原文排版(第一行着重,全部居中)
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/200-libby-clark/777473-linux-poetry-explains-the-kernel-line-by-line/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:editors@linux.com
+[2]:http://events.linuxfoundation.org/events/linuxcon-north-america
+[3]:http://shop.oreilly.com/product/9780596005658.do
+[4]:http://www.linux-poetry.com/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140623 9 ASCII Games You'll Want to Play Again and Again.md b/sources/talk/20140623 9 ASCII Games You'll Want to Play Again and Again.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cc1cf60b2b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140623 9 ASCII Games You'll Want to Play Again and Again.md
@@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
+9 ASCII Games You'll Want to Play Again and Again
+================================================================================
+Modern Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) offer exceptional gaming capabilities, and have contributed to the trend of astonishing leaps in graphics fidelity. There is not a year that has gone by without a game being released that makes significant advances in technical graphics wizardry. Computer graphics have been advancing at a staggering pace. At the current rate of progress, in the next 10 years it may not be possible to distinguish computer graphics from reality.
+
+Personally, these developments do not overly interest me. I find little fascination playing games that focus so much on the visuals they neglect the essential elements. Too often the storyline and game play has been compromised for visual quality. Most of my favourite games are somewhat deficient in the graphics department. Gameplay is always king in my eyes.
+
+Linux has an excellent library of free games many of which are released under an open source license. The vast majority of these games are aesthetically pleasing. Popular games often have full motion video, vector graphics, 3D graphics, realistic 3D rendering, animation, texturing, a physics engine, and much more. Early computer games did not have these graphic techniques. The earliest video games were text games or text-based games that used text characters rather than vector or bitmapped graphics.
+
+Text-based games often receive little coverage in the Linux press. However, there are some real ASCII gems out there waiting to be explored which are immensely addictive and great fun to play.
+
+The idiom 'don't judge a book by its cover' can be extended to 'don't judge a computer game by its graphics'. Whilst the games featured in this article have extremely basic graphics, they have many redeeming qualities beyond evoking fond memories of the early days of computer gaming.
+
+There are no fancy graphics here, just great gameplay coupled with the urge of always having just one more play.
+
+
+
+
+
+The first game in this roundup is UnNetHack, a fork of NetHack, originally based on the hugely popular roguelike game NetHack. NetHack was first released in 1987, and is considered by many gamers to be one of the best gaming experiences the computing world offers.
+
+UnNetHack adds a number of enhancements to NetHack, such as additional monsters, more levels, a few new objects, additional dangers, more challenging gameplay, and most importantly more entertainment than vanilla NetHack. It offers a tutorial to help new players get started.
+
+Be warned, UnNetHack is fiendishly addictive.
+
+- Website: [sourceforge.net/apps/trac/unnethack][1]
+- Authors: Patric Mueller
+- License: Nethack General Public License
+- Version Number: 5.1.0
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+Empire is a simulation of a full-scale war between two emperors, the computer and you. Naturally, there is only room for one, so the object of the game is to destroy the other. The computer plays by the same rules that you do.
+
+This game is the ancestor of all the multiplayer 4X simulations out there, including Civilization and Master of Orion. The classic game from the 1980s uses text mode graphical output, drawing your units, cities and the world in color. Commands are issued using the keyboard.
+
+The world on which the game takes place is a square rectangle containing cities, land, and water. Cities are used to build armies, planes, and ships which can move across the world destroying enemy pieces, exploring, and capturing more cities. The objective of the game is to destroy all the enemy pieces, and capture all the cities.
+
+The game starts by assigning you one city and the computer one city. Cities can produce new pieces. Every city that you own produces more pieces for you according to the cost of the desired piece. The typical play of the game is to issue the Automove command until you decide to do something special. During movement in each round, the player is prompted to move each piece that does not otherwise have an assigned function.
+
+- Website: [www.catb.org/~esr/vms-empire][2]
+- Authors: Chuck Simmons, Eric S. Raymond
+- License: GNU GPL v2
+- Version Number: 1.12
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+Intricacy is an addictive, open source, networked, video puzzle game. It is written in Haskell, using the Curses and SDL libraries.
+
+Intricacy runs directly from the command-line, and provides a turn-based, abstract puzzle game where the players need to pick locks, simply by coordinating a couple of tools in order to manipulate the lock’s mechanism. Constructing and solving difficult puzzles within certain strict design constraints is both challenging and good fun.
+
+The catch is that you will be able to pick locks that are designed by other players. It has multi-platform support, with binaries for both Linux and Windows.
+
+- Website: [mbays.freeshell.org/intricacy][3]
+- Authors: Chuck Simmons, Eric S. Raymond
+- License: GNU GPL v3
+- Version Number: 0.2.6.3
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+XorCurses is a puzzle game set inside a series of mazes. It is a remake of XOR by Astral Software, a game published in 1987 and released on the popular home computers of the day including the Commodore 64, ZX Spectrum, Atari ST, and Amiga. XOR is a pure puzzle game with no random or arcade elements.
+
+In some respects, XorCurses is a regression from the graphics of the old 8 bit computers as it uses even more simplistic graphics, with coloured ASCII characters instead of pixel based graphics.
+
+XorCurses attempts to faithfully recreate that game for Linux, with particular attention placed on the behaviour of the objects within the original game.
+
+The basic premise of Xor is to roam around a series of mazes collecting all of the blue masks and then finding the exit. You have two player-shields to aid you and you can use either one at any time and switch between them. The first few levels are easy to progress, but the rest are progressively harder to solve. A particularly challenging and difficult puzzle game that will keep you engaged for hours.
+
+- Website: [www.jwm-art.net/dark.php?p=XorCurses][4]
+- Authors: James W. Morris
+- License: GNU GPL
+- Version Number: 0.2.2
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+Goblin Hack is an open source roguelike OpenGL-based smooth-scrolling ASCII graphics game. The game is inspired by the likes of NetHack, but faster with fewer keys.
+
+Goblin Hack has a simple interface that appears to appeal to players of all ages, and fires their imagination in today's world of over-rendered games.
+
+Players can choose one of several classes before being thrown into the first floor of a randomized, ongoing dungeon.
+
+- Website: [goblinhack.sourceforge.net][5]
+- Authors: Neil McGill
+- License: GNU GPL v2
+- Version Number: 1.18
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+Curse of War is a fast-paced real time strategy game released under an open source license. It is implemented using C and ncurses. There is also an SDL version available.
+
+The core game mechanics turns out to be quite close to WWI-WWII type of warfare, however, there is no explicit reference to any historical period.
+
+Unlike most real time strategy games, in Curse of War players do not control units, but instead they concentrate on high-level strategic planning: Building infrastructure, securing resources, and moving armies.
+
+A multiplayer mode is available. Computer opponents differ in personality, and it affects the way they fight.
+
+- Website: [a-nikolaev.github.io/curseofwar][6]
+- Authors: Alexey Nikolaev
+- License: GNU GPL v3
+- Version Number: 1.2.0
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+Brogue is an open source Roguelike game for Mac OS X, Windows, Linux, iOS and Android.
+
+Brogue is a direct descendant of Rogue, a dungeon crawling video game first developed by Michael Toy and Glenn Wichman around 1980. Unlike other popular modern roguelikes, Brogue favors simplicity over complexity, while trying to ensure that the interactions between components are interesting and varied.
+
+Your goal is to travel to the 26th subterranean floor of the dungeon, retrieve the Amulet of Yendor and return with it to the surface. For the truly skillful who desire further challenge, depths below 26 contain three lumenstones each, items which confer an increased score upon victory.
+
+Brogue is a challenging game, but still great fun to play. Try not to be disheartened by the difficulty of the game; with some application, Brogue will become very addictive.
+
+- Website: [sites.google.com/site/broguegame][7]
+- Authors: Brian Walker
+- License: GNU Affero GPL
+- Version Number: 1.7.3
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+DiabloRL is a roguelike "unmake" of the popular Blizzard game Diablo 1 classic RPG to a turn-based ASCII roguelike.
+
+The game was created for the 7 Day Roguelike Competition, but has since been expanded with magic items, spells, more classes and levels, as well as fast travelling to known locations, and high scores.
+
+DiabloRL gives you a choice of classes, the Warrior, Rogue, or Sorcerer. Each of these has different starting and maximum stats, as well as completely different play styles.
+
+- Website: [diablo.chaosforge.org][8]
+- Authors: Kornel Kisielewicz, Chris Johnson and Mel'nikova Anastasia
+- License: GNU GPL
+- Version Number: 0.5.0
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+Cataclysm is an open source post-apocalyptic roguelike, set in the countryside of fictional New England after a devastating plague of monsters and zombies. It is a continuation of Whale's original Cataclysm, which expands it with numerous new creatures, buildings, gameplay mechanics and many other features.
+
+While some have described it as a "zombie game", there's far more to Cataclysm than that. Struggle to survive in a harsh, persistent, procedurally generated world. Scavenge the remnants of a dead civilization for for food, equipment, or, if you're lucky, a vehicle with a full tank of gas to get you the hell out of Dodge. Fight to defeat or escape from a wide variety of powerful monstrosities, from zombies to giant insects to killer robots and things far stranger and deadlier, and against the others like yourself, that want what you have...
+
+Cataclysm is very different from most roguelikes in many ways. Rather than being set in a vertical, linear dungeon, it is set in an unbounded, 3D world. This means that exploration plays a much bigger role than in most roguelikes, and the game is much less linear. As the map is so huge, it is actually completely persistant between games. If you die, and start a new character, your new game will be set in the same game world as your last. Like in many roguelikes, you will be able to loot the dead bodies of previous characters; unlike most roguelikes, you will also be able to retrace their steps completely, and any dramatic changes made to the world will persist into your next game.
+
+- Website: [en.cataclysmdda.com][9]
+- Authors: Kevin Granade
+- License: Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
+- Version Number: 0.A
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20140621060017503/9ASCIIGames.html
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://sourceforge.net/apps/trac/unnethack/
+[2]:http://www.catb.org/~esr/vms-empire/
+[3]:http://mbays.freeshell.org/intricacy/
+[4]:http://www.jwm-art.net/dark.php?p=XorCurses
+[5]:http://goblinhack.sourceforge.net/
+[6]:http://a-nikolaev.github.io/curseofwar/
+[7]:https://sites.google.com/site/broguegame/
+[8]:http://diablo.chaosforge.org/
+[9]:http://en.cataclysmdda.com/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140624 Staying free--should GCC allow non-free plug ins.md b/sources/talk/20140624 Staying free--should GCC allow non-free plug ins.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d2865199fc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140624 Staying free--should GCC allow non-free plug ins.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+Staying free – should GCC allow non-free plug ins?
+================================================================================
+> Arguments in favour of the use of non-free plug-ins in GCC have again been raised on GCC mailing-lists, but are trumped by the arguments for GCC as a vehicle for free software development
+
+Once again, Gcc and its lack of modularity has been raised as an issue and contrasted with LLVm, the new compiler on the block. GCC is huge and venerable: 5 million lines, 30 years, and growing. LLVM, in contrast, is relatively youthful and modular and allows free and proprietary languages to be added as modules.
+
+The core of LLVM is ‘open source’. GCC is copyleft and unreservedly free software and doesn’t allow plug-ins or other means to add proprietary extensions to the GCC code. The argument, as delivered by Eric Raymond, is that “FSF can no longer prevent proprietary vendors from plugging into a free compiler to improve their tools. That horse has left the barn; the strategic goal of the anti-plug-in policy has been definitively busted.”
+
+LLVM has been sponsored by Apple as a replacement for GCC on OS X and Apple hardware and has grown in popularity, especially among users of the BSDs. Advocates of LLVM see it as a putative replacement for GCC in the wider market for applications developers and mobile devices. The argument against GCC is that its complexity, and the commitment of its developers to copyleft licensing, constrains the possibilities for proprietary developers, who do not want to release their language or architectural specifications under a copyleft licence. Apple, of course, has a long history of antipathy to free software, and doesn’t allow applications licensed under copyleft licences to be distributed through its App Store.
+
+To this extent, the argument between LLVM and GCC is a retread of the historic differences between GNU/Linux and the BSDs, between ‘open source’ and free software. Open source developers allow the code to be reused in any context, free or proprietary. Free software is restrictive in that it insists that the code, and any modifications to the code, must remain free in perpetuity. Advocates of free software would argue that the integrity of copyleft licensing has been instrumental in the spread of GCC, and has taken Linux and free software into places it would not otherwise have reached, and that free software cannot be bought or corrupted by commercial or corporate interests. Open source advocates argue that open source is more free because the user has no restrictions and can do what he or she likes, including developing closed source versions of the code.
+
+Since the beginning, the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) was vital to the spread of free software. Compilers were a rare and expensive commodity and the compilers of the proprietary software companies were rife with ‘features’ that were non-compliant with ANSI programming standards. Porting software between different machines and operating systems was an unnecessarily complicated task. GCC, the first truly free cross-platform compiler, commoditised this process.
+
+GCC was a breakthrough product for applications developers and mobile device developers – not just those who were committed to the idea of free software. Not only was GCC free and portable, its ubiquity and commonality across different architectures made it easier to port software between machines and to expect robust and consistent results – as the likes of John Gilmore, Michael Tiemann and David Henkel- Wallace were to discover when they made GCC and its development the key selling point of Cygnus Solutions, the first company to make money by selling free software.
+
+The primary technical difference between LLVM and GCC emerges in the separation between the modules that form the ‘front ends’, ‘middle end’ and ‘back ends’ of both GCC and LLVM. ‘Front ends’ are used to interpret the code specific to the translation of a particular language. The ‘middle end’ optimises the translated code. The ‘back ends’ take the optimised code and apply the results to a specific target architecture. LLVM separates these modules into distinct entities, but for semantic and historical reasons, GCC obfuscates the separation between the modules.
+
+Perhaps untypically for a free software project, it is a difficult process to add a new language or architecture to GCC and the adding of proprietary plug-ins is not allowed. There is little clear separation between the modules, and the path of least resistance is to add any feature under a free software licence. The early ports of C++ and Objective C (via Apple) are cited as examples where the original developers might have preferred to keep the code in-house and proprietary, and instead released the code as free software.
+
+In contrast, LLVM has allowed, or perhaps even encouraged, the addition and development of proprietary languages and architectures – one example being Nvidia’s NVCC for GPU computing, based on Clang and LLVM. The source code of NVCC is inaccessible to free software or ‘open source’ developers.
+
+Richard Stallman’s [take on this][1] is characteristically resolute: “In the free software movement, we campaign for the freedom of the users of computing. The values of free software are fundamentally different from the values of open source, which make‘bettercode’theultimategoal. IfGCCwere to change from a free compiler into a platform for non-free compilers, it would no longer serve the goal of freedom very well.
+
+“The Clang and LLVM developers reach different conclusions from ours because they do not share our values and goals. They object to the measures we have taken to defend freedom because they see the inconvenience of them and do not recognise (or don’t care about) the need for them. I would guess they describe their work as ‘open source’ and do not talk about freedom.”
+
+The GCC developers are unlikely to compromise on the licensing terms. While LLVM is fashionable among certain sectors of industry, because it is young and new and has been quicker to jump on developing trands in programming languages, the prevailing wind is towards greater openness, and GCC’s resolve to be incorruptible and free from commercial interests, may be the greater asset in the long term. The Unix companies learnt something from the Unix wars of the Eighties and Nineties. Languages and operating systems are tools, and are better open and shared. GCC is free software and belongs to nobody.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxuser.co.uk/features/staying-free-should-gcc-allow-non-free-plug-ins
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://lwn.net/articles/582241
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140626 Linux Administration--A Smart Career Choice.md b/sources/talk/20140626 Linux Administration--A Smart Career Choice.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..924056cdd1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140626 Linux Administration--A Smart Career Choice.md
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+Linux Administration: A Smart Career Choice
+================================================================================
+
+
+> This is a good year for IT professionals with a number of new jobs in emerging technologies like Big Data and Analytics, and Social Mobile Analytics and Cloud (SMAC) as employers look to strengthen their technological force.
+
+If we were to believe the reports by [Dice.com][1] and Linux foundation released in mid Feb, 2014, this year will be a high octane year for Linux professionals and aspirants particularly. Thus it only makes sense to be future-ready and find out about the details of career opportunities such as that of a Linux administrator.
+
+Dice.com, the leading job site for tech professionals and Linux Foundation did a comprehensive survey to find out about the advantage Linux professionals have in the current technology landscape. The findings were heavily skewed in favor of those who are looking for a good job opportunity on Linux platform.
+
+While seventy seven percent of hiring managers surveyed consider hiring Linux talent as one of their top priorities (up from 70 percent in 2013), 64 percent of professionals chose to work with Linux owing to its ubiquitous nature in the present day technology infrastructure. More than nine in ten recruitment manager is planning to hire a Linux professional in the next six months. This demand is surely going to translate in form of a lot of interview calls from employers. Most hiring managers also agree to the fact that it is rather difficult to find experienced professionals, and those who have the right mix of skills, knowledge, certifications and experience are being aggressively recruited.
+
+### Why Linux administration? ###
+
+The findings of this report make it clear that Linux professionals are amongst the most sought after in the current tech market. However, a more interesting finding of the report is that amongst all the skills, the hiring managers are most actively seeking system administration, with 58 percent confirming they were on look out of professionals with good system administration skills. The reason is quite simple. There aren’t too many good system administrators out there, which is also driving the salaries of system admins northwards.
+Getting started in Linux administration
+
+Armed with all this data, it wouldn’t come as surprise if you decide right away to pursue a career in Linux administration. So, how do you become a pro Linux system admin? Well, the right mix of certification, education and experience will obviously land you the perfect Linux job, but if you are clueless about a place to start, then a degree in computers is what you should be looking at. This could be B.Tech with Computer Science or IT as specialisation or Bachelors in Computer Application or even a Bachelor in Science with IT as specialisation will do. This would actually make you familiar with the various aspects of computer science as a subject, likes of programming, hardware, and software. This understanding would come handy in the advancement of your career, when you climb the next ladder through certifications.
+
+### Certifications ###
+
+It is widely believed that IT certifications do help one in career advancement. However, it ultimately boils down to selecting the right certification to gain the maximum RoI. There are many Linux based certifications, the most famous of which is Red Hat Certification Program, which teaches general Linux related skills along with specific system administration skills.
+
+In addition to the vendor sponsored certifications, there is a vendor-independent Linux Professional Institute Certification offered by Linux Professional Institute, a non-profit organisation based in Toronto, Canada.
+
+These exams can be taken by anyone irrespective of their nationalities. The LPI programs have three level hierarchies that include LPIC-1: Junior Level Linux Administration, LPIC-2: Advanced Level Linux Administration and LPIC 3: Senior Level Linux Administration. In order to be considered seriously for any system administrator job opportunity in one must possess at least one of the above described certifications. The LPI also has partnerships with SUSE, which is the vendor for a famous enterprise operating system going by the same name. CompTIA, which is a global IT certification agency also provided a Linux+ certification which was phased out after an agreement between LPI and CompTIA.
+
+### Salaries and Benefits ###
+
+The compensations for Linux administrators are generally on the higher side. As per PayScale, the annual median salary is around INR 3 lacs for entry level professionals (as updated on 27th March, 2014). With experience, there is an exponential increase in the salary levels as individuals with 5+ years of experience getting annual packages in seven figures.
+Well, with the grass being greener for Linux professionals this year, you won’t get a better opportunity or time for pursuing career as a Linux system administrator.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.opensourceforu.com/2014/04/career-overview-linux-administrator/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://dice.com/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140701 Easy File Comparisons With These Great Free Diff Tools.md b/sources/talk/20140701 Easy File Comparisons With These Great Free Diff Tools.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..92dbf74103
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140701 Easy File Comparisons With These Great Free Diff Tools.md
@@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
+Easy File Comparisons With These Great Free Diff Tools
+================================================================================
+by Frazer Kline
+
+File comparison compares the contents of computer files, finding their common contents and their differences. The result of the comparison is often known as a diff.
+
+diff is also the name of a famous console based file comparison utility that outputs the differences between two files. The diff utility was developed in the early 1970s on the Unix operating system. diff will output the parts of the files where they are different.
+
+Linux has many good GUI tools that enable you to clearly see the difference between two files or two versions of the same file. This roundup selects 5 of my favourite GUI diff tools, with all but one released under an open source license.
+
+These utilities are an essential software development tool, as they visualize the differences between files or directories, merge files with differences, resolve conflicts and save output to a new file or patch, and assist file changes reviewing and comment production (e.g. approving source code changes before they get merged into a source tree). They help developers work on a file, passing it back and forth between each other. The diff tools are not only useful for showing differences in source code files; they can be used on many text-based file types as well. The visualisations make it easier to compare files.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+Meld is an open source graphical diff viewer and merge application for the Gnome desktop. It supports 2 and 3-file diffs, recursive directory diffs, diffing of directories under version control (Bazaar, Codeville, CVS, Darcs, Fossil SCM, Git, Mercurial, Monotone, Subversion), as well as the ability to manually and automatically merge file differences.
+
+Meld's focus is on helping developers compare and merge source files, and get a visual overview of changes in their favourite version control system.
+
+Features include
+
+- Edit files in-place, and your comparison updates on-the-fly
+- Perform twoand three-way diffs and merges
+- Easily navigate between differences and conflicts
+- Visualise global and local differences with insertions, changes and conflicts marked
+- Built-in regex text filtering to ignore uninteresting differences
+- Syntax highlighting (with optional gtksourceview)
+- Compare two or three directories file-by-file, showing new, missing, and altered files
+- Directly open file comparisons of any conflicting or differing files
+- Filter out files or directories to avoid seeing spurious differences
+- Auto-merge mode and actions on change blocks help make merges easier
+- Simple file management is also available
+- Supports many version control systems, including Git, Mercurial, Bazaar and SVN
+- Launch file comparisons to check what changes were made, before you commit
+- View file versioning statuses
+- Simple version control actions are also available (i.e., commit/update/add/remove/delete files)
+- Automatically merge two files using a common ancestor
+- Mark and display the base version of all conflicting changes in the middle pane
+- Visualise and merge independent modifications of the same file
+- Lock down read-only merge bases to avoid mistakes
+- Command line interface for easy integration with existing tools, including git mergetool
+- Internationalization support
+- Visualisations make it easier to compare your files
+
+- Website: [meldmerge.org][1]
+- Developer: Kai Willadsen
+- License: GNU GPL v2
+- Version Number: 1.8.5
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+注:上面这个图访问不到,图的地址是原文地址的小图的链接地址,发布的时候在验证一下,如果还访问不到,不行先采用小图或者网上搜一下看有没有大图
+
+DiffMerge is an application to visually compare and merge files on Linux, Windows, and OS X.
+
+Features include:
+
+- Graphically shows the changes between two files. Includes intra-line highlighting and full support for editing
+- Graphically shows the changes between 3 files. Allows automatic merging (when safe to do so) and full control over editing the resulting file
+- Performs a side-by-side comparison of 2 folders, showing which files are only present in one file or the other, as well as file pairs which are identical, equivalent or different
+- Rulesets and options provide for customized appearance and behavior
+- Unicode-based application and can import files in a wide range of character encodings
+- Cross-platform tool
+
+- Website: [sourcegear.com/diffmerge][2]
+- Developer: SourceGear LLC
+- License: Licensed for use free of charge (not open source)
+- Version Number: 4.2
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+xxdiff is an open source graphical file and directories comparator and merge tool.
+
+xxdiff can be used for viewing the differences between two or three files, or two directories, and can be used to produce a merged version. The texts of the two or three files are presented side by side with their differences highlighted with colors for easy identification.
+
+This program is an essential software development tool that can be used to visualize the differences between files or directories, merge files with differences, resolving conflicts and saving output to a new file or patch, and assist file changes reviewing and comment production (e.g. approving source code changes before they get merged into a source tree).
+
+Features include:
+
+- Compare two files, three files, or two directories (shallow and recursive)
+- Horizontal diffs highlighting
+- Files can be merged interactively and resulting output visualized and saved
+- Features to assist in performing merge reviews/policing
+- Unmerge CVS conflicts in automatically merged file and display them as two files, to help resolve conflicts
+- Uses external diff program to compute differences: works with GNU diff, SGI diff and ClearCase's cleardiff, and any other diff whose output is similar to those
+- Fully customizable with a resource file
+- Look-and-feel similar to Rudy Wortel's/SGI xdiff, it is desktop agnostic
+- Features and output that ease integration with scripts
+
+- Website: [furius.ca/xxdiff][3]
+- Developer: Martin Blais
+- License: GNU GPL
+- Version Number: 4.0
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+Diffuse is an open source graphical tool for merging and comparing text files. Diffuse is able to compare an arbitrary number of files side-by-side and offers the ability to manually adjust line-matching and directly edit files. Diffuse can also retrieve revisions of files from bazaar, CVS, darcs, git, mercurial, monotone, Subversion and GNU Revision Control System (RCS) repositories for comparison and merging.
+
+Features include:
+
+- Compare and merge an arbitrary number of files side-by-side (n-way merges)
+- Line matching can be manually corrected by the user
+- Directly edit files
+- Syntax highlighting
+- Bazaar, CVS, Darcs, Git, Mercurial, Monotone, RCS, Subversion, and SVK support
+- Unicode support
+- Unlimited undo
+- Easy keyboard navigation
+
+- Website: [diffuse.sourceforge.net][]
+- Developer: Derrick Moser
+- License: GNU GPL v2
+- Version Number: 0.4.7
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+Kompare is an open source GUI front-end program that enables differences between source files to be viewed and merged. Kompare can be used to compare differences on files or the contents of folders. Kompare supports a variety of diff formats and provide many options to customize the information level displayed.
+
+Whether you are a developer comparing source code, or you just want to see the difference between that research paper draft and the final document, Kompare is a useful tool.
+
+Kompare is part of the KDE desktop environment.
+
+Features include:
+
+- Compare two text files
+- Recursively compare directories
+- View patches generated by diff
+- Merge a patch into an existing directory
+- Entertain you during that boring compile
+
+- Website: [www.caffeinated.me.uk/kompare/][5]
+- Developer: The Kompare Team
+- License: GNU GPL
+- Version Number: Part of KDE
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/2014062814400262/FileComparisons.html
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://meldmerge.org/
+[2]:https://sourcegear.com/diffmerge/
+[3]:http://furius.ca/xxdiff/
+[4]:http://diffuse.sourceforge.net/
+[5]:http://www.caffeinated.me.uk/kompare/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140702 The People Who Support Linux--Hacking on Linux Since Age 16.md b/sources/talk/20140702 The People Who Support Linux--Hacking on Linux Since Age 16.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e29f2e03fe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140702 The People Who Support Linux--Hacking on Linux Since Age 16.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+Translating by Alisa-annie
+The People Who Support Linux: Hacking on Linux Since Age 16
+================================================================================
+
+
+Pretty much all of the projects in software developer [Yitao Li's GitHub repository][1] were developed on his Linux machine. None of them are necessarily Linux-specific, he says, but he uses Linux for “everything.”
+
+For example: “coding / scripting, web browsing, web hosting, anything cloud-related, sending / receiving PGP signed emails, tweaking IP table rules, flashing OpenWrt image into routers, running one version of Linux kernel while compiling another version, doing research, doing homework (e.g., typing math equations in Tex), and many others...” Li said via email.
+
+Of all the projects in his repository his favorite is a school project developed in C++ with libpthread and libfuse to understand and correctly implement PAXOS-based distributed locking, key-value service, and eventually a distributed filesystem. He tested it using a number of test scripts on both single-core and multi-core machines.
+
+“One can learn something about distributed consensus protocol by implementing the PAXOS protocol correctly (or at least mostly correctly) such that the implementation will pass all the tests,” he said. “And of course once that is accomplished, one can also earn some bragging rights. Besides, a distributed filesystem can be useful in many other programming projects.”
+
+Li first started using Linux at age 16, or about 7.47 years ago, he says, using the website [linuxfromscratch.org][2], with numerous hints from the free, downloadable Linux From Scratch book. Why?
+
+“1. Linux is very hacker-friendly and I do not see any reason for not using it,” he writes. “2. The prefrontal cortex of the brain becoming well-developed at age 16 (?).”
+
+[][3]
+
+He now works for eBay, mostly coding in Java but working sometimes with Hadoop, Pig, Zookeeper, Cassandra, MongoDB, and other software that requires a POSIX-compliant platform. He supports the Linux community by contributing to Wikipedia pages and forums on Linux-related subjects. And by becoming an individual member of The Linux Foundation.
+
+He keeps up with the latest Linux developments and has recently been impressed by the new "-fstack-protector-strong" option for GCC 4.9 and later.
+
+“It's not directly related to any of my projects, but it was important for both security and performance reasons,” he said. “It's much more efficient than "-fstack-protector-all" with little impact on security, while providing better stack-overflow protection coverage compared to that of the "-fstack-protector" option.”
+
+Welcome to the Linux Foundation Yitao!
+
+Learn more about becoming an [individual member of The Linux Foundation][3]. The foundation will donate $25 to Code.org for every new individual member who joins during June.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Libby Clark][4]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/200-libby-clark/778559-the-people-who-support-linux-hacking-on-linux-since-age-16
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://github.com/yl790
+[2]:http://linuxfromscratch.org/
+[3]:https://www.linuxfoundation.org/about/join/individual
+[4]:http://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/41373/catid/200-libby-clark
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140723 Linux System Administration Skills are Changing.md b/sources/talk/20140723 Linux System Administration Skills are Changing.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..87ce32c6a1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140723 Linux System Administration Skills are Changing.md
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+Linux System Administration Skills are Changing
+================================================================================
+When was the last time you compiled a kernel? For many of the latest generation of Linux admins, the answer is really simple: never. I am one of those, provided we don't count a few times I tried it just for fun, then couldn't see why I would need a custom kernel and went back to my out-of-the-box kernel.
+
+For many of the longer-time Linux admins and engineers this may seem laughable, but it is a reality: As Linux adoption grows in the enterprise, a new generation of Linux admins is created that has extremely good technical skills, but lacks these 'simple' low level skills seen by many as fundamental to being a good Linux admin. We can build a high performance, highly available web infrastructure that uses the latest of the latest techniques, but don't ask us to fix a non-booting Linux machine: our advice will be to ditch it and set up a new vm.
+
+Over the past decade or so, we have seen some interesting trends. Linux became a commodity in the enterprise, and as that happened the various distributions became powerful yet flexible enough to remove the need for the average admin to ever have to do low level things like compiling a kernel.
+
+Next, we welcomed virtual machine technology as a commodity, which added another layer of abstraction. Users of clouds like amazon or VPS providers will possibly never have to deal with deploying Linux on bare metal. As hybrid and private clouds are becoming common as well, many enterprise admins will also not have to deal with this kind of thing anymore, they will just log into a web interface and spin up 5 more apache vm's.
+
+The newest two trends add even more abstraction: configuration management and the seemingly brand new (yet not new at all) containerization with tools like docker. Whenever a client asks us at [OlinData][1] to configure a Linux machine, our first action will be to set up [Puppet][2]. With our trusted library of well-functioning Puppet modules, that is very easy and will cost me less time then doing this manually.
+
+For example with Puppet, I can install Apache on a new machine as simple as this:
+
+ node 'web01.olindata.com' {
+ include apache
+ apache::vhost{ 'www.olindata.com':
+ docroot => '/var/www/olindata'
+ }
+ }
+
+Depending on the environment, I don't even have to log into the machine anymore. Deploying this code through Continuous Deployment tools like [Jenkins][3] will allow me to deploy my infrastructure code automatically as it passes the tests I set up.
+
+### SysAdmin skills move up the stack ###
+
+Even as we move toward higher levels of abstraction, ongoing Linux training is still highly valuable and desirable for admins today and will be well into the future. Knowing the fundamentals is key but as abstraction removes some of the old tasks, this requires sysadmins to move up further in the stack and enhance their skills in the higher level tools and practices. It is critical for a sysadmin to become familiar with the tools that enable these higher levels of abstraction. It pushes them to become more skilled in things like coding so that they can do more with these "new" tools.
+
+Will the need for low(er) level linux skills ever go away completely? Of course not. We still have many other uses for Linux then just the commodity server deployments. Also, people will still benefit hugely from knowing how to do lower level operations in their everyday work. On top of that, with demonstrable Linux skills on your resume, I (and many other employers with me) will always prefer you over candidates that don't have them. You never know when you need those low-level skills!
+
+
+----------
+
+
+Walter Heck is CEO and Founder of OlinData, an authorized Linux Foundation training partner. Here's a list of [scheduled official Linux Foundation courses by OlinData][4].
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linux.com/news/enterprise/systems-management/780956-linux-system-administration-skills-are-changing
+
+原文作者:[Walter Heck][a]
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/59207
+[1]:http://olindata.com/
+[2]:http://puppetlabs.com/
+[3]:http://jenkins.org/
+[4]:http://www.olindata.com/training/upcoming?technology=295
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140724 Best Linux Browsers.md b/sources/talk/20140724 Best Linux Browsers.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fe3960a89a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140724 Best Linux Browsers.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+Love-xuan翻译中
+Best Linux Browsers
+================================================================================
+> Pros and cons of the best browsers for the Linux desktop, including Firefox, Chrome and other browsers.
+
+Choosing the best Linux browser for your needs requires just a bit of homework: Web browsers for the Linux desktop have evolved over the years, just as they have for other popular desktop platforms. With this evolution, both good and bad revelations have been discovered. Revelations from new functionality, to broken extensions, and so forth. In this article, I'll serve as your guide through these murky waters to help you discover the best in Linux browsers.
+
+### **Firefox** ###
+
+– [Firefox][1] has long been a friendly browser for Linux users. Accessible on both 32bit and 64bit Linux installs, Firefox also offers extensive extensions to choose from. It's a fast loading, easy to navigate Web browser that has found itself in a popular place with Linux users.
+
+**The good**: It's easily installed from most common Linux software repositories, if not already installed on the distro by default. Thousands of extensions to choose from to make your Firefox browser more fully featured. Nearly every website on the Web (including government and banking sites) render properly.
+
+Also important: Firefox respects your privacy. In addition to a straight forward privacy policy, they're not in the "same business" as Google. Therefore, most users feel more comfortable allowing Firefox to see their daily browsing activities whereas other browsers, might have more profit-driven interests. Firefox is also great for web developers, thanks to its element inspection tool, built right into the browser.
+
+**The bad**: Not too long ago, I was finding that Firefox's frequent updates were breaking my extensions. This meant I needed to verify that my favorite extensions were compatible with new Firefox updates BEFORE I updated my browser.
+
+To be blunt, this caused me to rethink which browser would be my default tool to browse the Internet. In fairness, Mozilla does post a blog post with each browser update for extension developers. In these posts, developers are told what has changed and what needs to be done to keep things working smoothly.
+
+### **Chrome/Chromium** ###
+
+– Google promotes its browser named [Chrome][2], however I tend to put [Chromium][3] into the same group as Chrome since Chromium is used as its base for development. Unlike Firefox, Chrome/Chromium was late to the game for Linux. Linux users only considered it worth trying at the time due to the fact that Chrome/Chromium was perceived by many as being the fastest browser.
+
+**The good**: Even today, Chrome/Chromium is considered pretty fast. Even with the recent updates made to other competing browsers, Chrome/Chromium hasn't lost its speed. Extensions for Chrome/Chromium are plentiful and even better, updates to the browser have no affect on said extensions. This means that, unlike Firefox, I haven't dealt with extension incompatibilities. Like Firefox, Chrome/Chromium also has an element inspection tool, built right into the browser. After trying syncing options with other browsers, only Chrome/Chromium has proven itself to be truly idiot-proof. Without question, Chrome/Chromium syncing is the best in the browser space, from my perspective.
+
+**The bad**: Chrome/Chromium doesn't always render pages correctly. Be it rare, some sites like Ebay don't always render correctly. Case in point, if I create a new Ebay submission, I find there are buttons missing in some cases. I've also found that sometimes Chrome/Chromium can lockup completely if an open tab is rendering heavy script. Sites like Google Plus and Facebook are the most common offenders.
+
+### **Qupzilla** ###
+
+– When it comes to lightweight browsers, I've found [Qupzilla][4] to be among the most awesome. Based on Webkit, it provides decent rendering support while maintaining a very small resource footprint.
+
+**The good**: Qupzilla is ideal for lightweight desktop environments where you need a modern browser capable of rendering pages correctly and generally providing a solid web browser experience. It's extremely lightweight and will run on older PCs without missing a beat. Access Keys and [GreaseMonkey][5] extensions are installed (but disabled) by default.
+
+Like Firefox and Chrome/Chromium, Qupzilla provides access to an element inspection tool as well. And finally, having [Adblock][6] installed by default makes this a clear lightweight winner for me.
+
+**The bad**: HTML5 video doesn't seem to work reliably. Also, in order to watch Flash videos, you must visit the preferences and uncheck Click to Flash in the Extensions, Webkit plugins area. This is a poorly thought out decision to essentially disable Flash out of the box, while HTML5 video remains completely broken.
+
+### **Midori** ###
+
+– I like to call [Midori][7] the lightweight Chrome alternative. Like Google's browser(s), Midori offers a minimalist experience with its "hamburger menu," which is nice as it takes up less browser space. Not only do you get a solid browsing experience without the usual browser politics found elsewhere, Midori is also quite fast.
+
+**The good**: Midori is fast, lightweight and feels familiar out of the box. I'm also happy to report that it renders pages correctly and works great with sites like YouTube. The best part, in my opinion, is the built-in functionality for creating browser profiles and actual launchable links for Web apps. For example, you can easily create a web app on your desktop for Gmail or Facebook. You can also setup user specific browser profiles as well, without creating new Linux user accounts.
+
+**The bad**: Despite mentioning user extensions for this browser, the selection available is less than impressive. Also, the browser layout takes a bit of getting used to. A trash can for previously visited websites – seriously?
+
+### **Opera** ###
+
+– [Opera][8] has long been one of the misunderstood browsers out there. Very early on, Opera provided Linux support despite being dismissed by the overall Linux community. In addition to being a compatible, fast web browser that has been nothing but good to Linux users, it's also a full of configurable options.
+
+**The good**: It's fast and it's full of user controllable settings. You can import and export everything from RSS feeds to email, and skin Opera with easy access to breathtaking themes. Plus, Opera offers an extensive library of extensions to choose from. Not to mention the ability to read RSS feeds and email, from your browser! Relive the days of the Mozilla Suite by using Opera's extended suite functionality. And perhaps best of all, Opera Turbo – super-charge your browser speed with selective compression to provide a faster experience.
+
+**The bad**: A nag for the Terms of Service on its first run. Also, Opera Turbo can slightly alter your browsing experience – YouTube for example, may not show a video's thumbnail. Opera also provides so many options that it can feel a bit overwhelming to the casual user. And lastly, it's a closed source browser that hasn't been well recognized for desktop use. Most folks think of Opera as a mobile browser only these days.
+
+### Which browser is right for you? ###
+
+With so many great choices, it can be a tough call to say which browser is right for you. Speaking for myself, I've found that I rely heavily on Firefox and Chromium due to specific extensions I put to work each day. For someone with a lower end system or netbook, my suggestion is to try Midori first and if that's not a fit, fallback to Qupzilla.
+
+So what about other web browsers for Linux? Such as the [Epiphany][9] browser or [Konqueror][10]? Browsers like these are great, but I feel strongly about the browsers I've shared above specifically. Each of the options listed above are browsers I use often and have found to be something I feel good about recommending to friends and family.
+
+That said, by all means, share any browsers you're passionate about in the Comments below so others can benefit from your preferred method of browsing the Web.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/best-linux-browsers-1.html
+
+原文作者:[Matt Hartley][a]
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.datamation.com/author/Matt-Hartley-3080.html
+[1]:https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/new/
+[2]:https://www.google.com/intl/en_us/chrome/browser/
+[3]:http://www.chromium.org/
+[4]:http://www.qupzilla.com/
+[5]:https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/greasemonkey/
+[6]:https://adblockplus.org/
+[7]:http://midori-browser.org/
+[8]:http://www.opera.com/
+[9]:https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Web
+[10]:http://www.konqueror.org/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140724 What are useful online tools for Linux.md b/sources/talk/20140724 What are useful online tools for Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..461ff0afef
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140724 What are useful online tools for Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,150 @@
+What are useful online tools for Linux
+================================================================================
+As you know, GNU Linux is much more than just an OS. There is literally a whole sphere on the Internet dedicated to the penguin OS. If you read this post, you are probably inclined towards reading about Linux online. Among all the pages that you can find on the subject, there are a couple of websites that every Linux adventurer should have in his bookmarks. These websites are more than just tutorials or reviews. They are real tools that you can access from anywhere and share with everyone. So today I shall propose you a non-exhaustive list of sixteen websites that should be in your bookmarks. Some of them can also be useful for Windows or Mac users: that's the extent of their reach.
+
+### 1. [ExplainShell.com][1] ###
+
+[][2]
+
+If you are interested in Linux command line, you should use this website. If you are not interested in Linux command line, you should use it even more as it will explain in detail how a command works. This could prevent you from launching a command detrimental to your computer, and is a good way to learn with a great interface.
+
+### 2. [BashrcGenerator.com][3] ###
+
+[][4]
+
+If you want to begin with Linux command line, or if you want to quickly get a customized shell prompt but not sure how, this website will generate for you PS1 prompt code to place your .bashrc file in your home directory. You can drag and drop the elements that you would like to see in your prompt, like your username and the current time, and the website will write the code for you. It's easy and very readable. Definitely a must for the lazy.
+
+### 3. [Vim-adventures.com][5] ###
+
+[][6]
+
+I only recently discovered this website, but it already sucked in many hours of my life. In short: a RPG game with Vim commands. Move your character in the isometric levels with the 'h,j,k,l' keys, gain new commands/abilities, collect keys, and learn how to use Vim proficiently very quickly.
+
+### 4. [Try Github][7] ###
+
+[][8]
+
+The pitch is simple: learn Git in 15 minutes. This website simulates a console, and walks you though the steps of collaborative editing. The interface is very stylish and the intention is worthy. The only downside is for the Git allergic. But it is definitely a good skill to have, and a good place to learn it.
+
+### 5. [Shortcutfoo.com][9] ###
+
+[][10]
+
+Another shortcut database, shortcutfoo is a bit more standard in its way to present its content to the user, but definitely more straight-forward than funny mini-games. The shortcuts of several programs are available and grouped by categories. As it might not be super complete for software like Vim, which is completely reliant on shortcuts, it is perfect for giving a quick tip or a general overview.
+
+### 6. [GitHub Free Programming Books][11] ###
+
+[][12]
+
+As you might guess from the URL, this is a collection of free online books about programming, written collaboratively using Git. The content is awesome and the authors deserve to be praised for such work. It might not be the easiest read at first, but it is one of the most instructive for sure. We can only hope that the movement will keep growing.
+
+### 7. [Collabedit.com][13] ###
+
+[][14]
+
+If you ever plan on giving a phone interview, you should check out collabedit beforehand. It allows you to create a document, select the programming language that you want to write in, and then share that document via the URL. The people opening the link will be able to freely interact in real time with the text, allowing you to judge their programming skills or just exchange snippets. It even comes with the proper syntax highlighting and a chat widget. In other words, it is the instant-Google Document of programmers.
+
+### 8. [Cpp.sh][15] ###
+
+[][16]
+
+This is one of those websites that extend beyond just Linux, but it is so useful that it deserves its place here. In short, an online development environment for C++. Just write your code in your navigator and run it. As a bonus, you get an auto-indentation feature, Ctrl+Z, and the possibility to share the URL with your buddy. This is just one of those crazy things that you can do from a simple browser.
+
+### 9. [Copy.sh][17] ###
+
+[][18]
+
+In continuation with crazy things that you can do from your browser, copy.sh lets you run a virtual machine online. Just that. It gained fame relatively recently, but the idea is just insane. From the navigator you can select among the defaults virtual images to run, or upload your own iso file. The code for that feat has been shared on [GitHub][19]. Just amazing.
+
+### 10. [Commandlinefu.com][20] ###
+
+[][21]
+
+We all keep a big snippet of command-line "gems" on our computer. commandlinefu's goal is to release those snippets to the world. As a collaborative database, it resembles the Wikipedia of the command line. Everyone is free to register and post their favorite command on the website for everyone else to see. You will then be able to access that knowledge from everywhere and share it with everyone. If you are interested in mastering the shell, commandlinefu also proposes great features like random commands and a news feed to learn something new every day.
+
+### 11. [Alias.sh][22] ###
+
+[][23]
+
+Another collaborative database, alias.sh (I love the URL) is a bit like commandlinefu but for shell aliases. You can share and discover useful aliases which will make your CLI experience so much better. I personally like the alias to get the dimensions of a picture.
+
+ function dim(){ sips $1 -g pixelWidth -g pixelHeight }
+
+All the seconds you save with alias.sh probably accumulate with time, and turn to years by the end of your life.
+
+### 12. [Distrowatch.com][24] ###
+
+[][25]
+
+Who does not know Distrowatch? Besides giving a precise ranking of Linux distributions based on their website popularity, Distrowatch is also a very useful database. Whether you are looking for a new distribution to try, or just curious, it presents an exhaustive account of every Linux you can find, with information like which default desktop environment it uses, or package system, or its default applications. And all the versions, and with easily accessible download links. In a word, the Linux database.
+
+### 13. [Linuxmanpages.com][26] ###
+
+[][27]
+
+Everything is in the URL: access the manual pages for popular commands from anywhere. Not really sure if this would actually be useful for Linux users as you can access that from your actual terminal, but the intent is remarkable.
+
+### 14. [AwesomeCow.com][28] ###
+
+[][29]
+
+This is maybe a bit less hardcore Linux, but definitely useful to some. Awesomecow is a search engine for finding alternatives to Windows software on Linux. It can be helpful for anyone migrating to the penguin, or nostalgic of a Windows program. I see this as a strength, showing that Linux can compete with the professional spheres when it comes sot software quality. Or at least try to.
+
+### 15. [PenguSpy.com][30] ###
+
+[][31]
+
+Before Steam started to show up on Linux, gaming was probably one of the penguin's weakness. But the website penguspy made the effort of fighting that weakness by collecting all Linux compatible games in a database with a sexy interface. Games can be sorted by categories, release dates, ratings, etc. I really hope that websites like this are not going to disappear because of Steam as it remains one of my favorites of this list.
+
+### 16. [Linux Cross Reference by Free Electrons][32] ###
+
+[][33]
+
+Finally, for all the experts and the curious, lxr is the anagram from Linux Cross Reference, and allows us to interactively view the Linux Kernel code online. The navigation is made easy via identifiers, and you can compare the different versions of the files with a standard diff markup. The interface is sober and straight-forward, and this is just a website that perfectly illustrates the concept of open source.
+
+To conclude, there are a lot more websites which deserve to be listed, and this might be a topic for a part two to this post. But this is a good start. It serves as an appetizer to what can be found online as tools for Linux users. If you have any other pages that you would like to share, following this thematic, do so in the comments. And maybe contribute to a sequel to this list.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/useful-online-tools-linux.html
+
+原文作者:[Adrien Brochard][a](I am a Linux aficionado from France. After trying multiple distributions, I finally settled for Archlinux. But I am always trying to improve my system by stacking up tips and tricks.)
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/adrien
+[1]:http://explainshell.com/
+[2]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14517716647/
+[3]:http://bashrcgenerator.com/
+[4]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14703872782/
+[5]:http://vim-adventures.com/
+[6]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14681149696/
+[7]:https://try.github.io/
+[8]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14517499739/
+[9]:https://www.shortcutfoo.com/
+[10]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14517499799/
+[11]:https://github.com/vhf/free-programming-books/blob/master/free-programming-books.md
+[12]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14517499989/
+[13]:http://collabedit.com/
+[14]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14681150086/
+[15]:http://cpp.sh/
+[16]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14700981001/
+[17]:http://copy.sh/v24/
+[18]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14517479870/
+[19]:https://github.com/copy/v86
+[20]:http://www.commandlinefu.com/
+[21]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14517495938/
+[22]:http://alias.sh/
+[23]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14701762124/
+[24]:http://distrowatch.com/
+[25]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14681149996/
+[26]:http://www.linuxmanpages.com/
+[27]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14704165765/
+[28]:http://awesomecow.com/
+[29]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14704165965/
+[30]:http://www.penguspy.com/
+[31]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14517495728/
+[32]:http://lxr.free-electrons.com/
+[33]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14712049464/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20140724 diff -u--What is New in Kernel Development.md b/sources/talk/20140724 diff -u--What is New in Kernel Development.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5089d370ff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20140724 diff -u--What is New in Kernel Development.md
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+diff -u: What's New in Kernel Development
+================================================================================
+Once in a while someone points out a POSIX violation in Linux. Often the answer is to fix the violation, but sometimes Linus Torvalds decides that the POSIX behavior is broken, in which case they keep the Linux behavior, but they might build an additional POSIX compatibility layer, even if that layer is slower and less efficient.
+
+This time, *Michael Kerrisk* reported a POSIX violation that affected file operations. Apparently, reading and writing to files during multithreaded operations could hit race conditions and overwrite each other's changes.
+
+There was some discussion over whether this was really a violation of POSIX, but ultimately, who cares? Data clobbering is bad. After Michael posted some code to reproduce the problem, the conversation focused on what to do to fix it. But Michael did make an argument that "Linux isn't consistent with UNIX since early times. (E.g., page 191 of the 1992 edition of Stevens APUE discusses the sharing of the file offset between the parent and child after fork(). Although Stevens didn't explicitly spell out the atomicity guarantee, the discussion there would be a bit nonsensical without the presumption of that guarantee.)"
+
+Al Viro joined Linus in trying to come up with a fix. Linus tried introducing a simple mutex to lock files so that write operations couldn't clobber each other, and Al offered his own refinements that improved on Linus' patch.
+
+At one point, Linus explained the history of the bug itself. Apparently, once upon a time the file pointer, which told the system where to write into the file, had been locked in a semaphore so only one process could do anything to it at a time. But, they took it out of the semaphore in order to accommodate device files and other non-regular files that ran into race conditions when users were barred from writing to them whenever they pleased.
+
+That was what introduced the bug. At the time, it slipped through undetected, because that actual reading and writing to regular files was still handled atomically by the kernel. It was only the file pointer itself that could get out of sync. And, because high-speed threaded file operations are a pretty rare need, it took a long time for anyone to run into the problem and report it.
+
+An interesting little detail is that, while Linus and Al were hunting for a fix, Al at one point complained that the approach Linus was taking wouldn't support certain architectures, including *ARM* and *PowerPC*. Linus' response was, "I doubt it's worth caring about. [...] If the ARM/PPC people end up caring, they could add the struct-return support to gcc."
+
+It's always interesting to see how corner cases crop up and get dealt with. In some cases, part of the fix has to happen in the kernel, part in GCC and part elsewhere. In this particular instance, Al felt the whole thing could be done in the kernel, and he was inspired to write his own version of the patch, which Linus accepted.
+
+*Andi Kleen* wanted to add low-level CPU event support to *perf*. The problem was that there could be tons of low-level events, and it varied widely from CPU to CPU. Even storing the possible events in memory for all CPUs would significantly increase the kernel's running size. So, hard-coding this information into the kernel would be problematic.
+
+He pointed out that the *OProfile* tool relied on publicly available lists of these events, though he said the OProfile developers didn't always keep their lists up to date with the latest available versions.
+
+To solve these issues, Andi submitted a patch that allowed perf to identify which event-list was needed for the particular CPU on the given system, and automatically download the latest version of that list from its home location. Then perf could interpret the list and analyze the events, without overburdening the kernel.
+
+There was various feedback to Andi's code, mostly to do with which directory should house the event-lists, and what the filenames should be called. The behavior of the code itself seemed to get a good reception. One detail that may turn out to be more controversial than the others was Andi's decision to download the lists to a subdirectory of the user's own home directory. Andi said that otherwise users might be encouraged to download the event-lists as the root user, which would be bad security practice.
+
+Sasha Levin recently posted a script to translate the *hexadecimal offsets *from stack dumps into meaningful line numbers that pointed into the kernel's source files. So something like "ffffffff811f0ec8" might be translated into "fs/proc/generic.c:445".
+
+However, it turned out that Linus Torvalds was planning to remove the hex offsets from the stack dumps for exactly the reason that they were unreadable. So Sasha's code was about to go out of date.
+
+They went back and forth a bit on it. At first Sasha decided to rely on data stored in the System.map file to compensate, but Linus pointed out that some people, including him, didn't keep their System.map file around. Linus recommended using /usr/bin/nm to extract the symbols from the compiled kernel files.
+
+So, it seems as though Sasha's script may actually provide meaningful file and line numbers for debugging stack dumps, assuming the stack dumps provide enough information to do the calculations.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/diff-u-whats-new-kernel-development-0
+
+原文作者:[Zack Brown][a]
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.linuxjournal.com/user/801501
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/Linux Pros' Top Command Line Secrets.md b/sources/talk/Linux Pros' Top Command Line Secrets.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a5759da8c6..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/Linux Pros' Top Command Line Secrets.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,112 +0,0 @@
-Linux Pros' Top Command Line Secrets
-================================================================================
-
-
-> "Command-line secrets? There aren't any such things," said blogger Robert Pogson. "Desperate newbie? Type 'help.' Still need a hint? Type 'man whatever.' Want more diversity? Type 'ls /bin /sbin /usr/bin /usr/sbin | less,' pick out a few gems and type 'man whatever' all night long. I've been at it more than a decade. Still having fun." Of course, "one can be addicted to the point of destruction."
-
-**W**ell it was a relatively quiet week here in the Linux blogosphere, giving residents a long-overdue opportunity to catch their collective breath, enjoy a few Tequila Tux cocktails and take stock of all the FOSS-related happenings that have taken place over the past few weeks.
-
-Among the highlights, for those who missed them, were [the awarding][1] of the [IEEE][2] Computer Society's 2014 Computer Pioneer Award to none other than Linus Torvalds; [the arrival][3] of Tails OS 1.0; and, perhaps most exciting of all, [the release][4] of Seattle-based band [netcat's][5] debut album as a Linux kernel module.
-
-"Are you ever listening to an album, and thinking 'man, this sounds good, but I wish it crossed from user-space to kernel-space more often!'" netcat wrote on its Facebook page. "We got you covered. Our album is now fully playable as a loadable Linux kernel module."
-
-Linux Girl thought she had seen it all here in the Linux world, but now she realizes she was wrong. Thank you, netcat, for keeping life interesting!
-
-### 'Command Line Secrets' ###
-
-
-
-Speaking of interesting, there's nothing like a little shop talk around the bar to pass the time during a quiet week, and last week afforded a dose of that as well. Life is good here in the Linux blogosphere!
-
-The forum was Linux Voice -- that shiny, new magazine alert readers may remember [launched late last year][6] -- and the topic was none other than [command line secrets][7].
-
-Linux Girl couldn't resist.
-
-### 'It Manages to Render Most Web Pages' ###
-
-"There are loads of really good reasons to use the command line," wrote the masterminds at Linux Voice. "It's the most powerful and concise method of interacting with your computer.
-
-"However, we decided to take a moment to look at some of its more obscure (and some would say pointless) uses," they added.
-
-Top of the magazine's list is the elinks Web browser: "It might not be as colorful as its more famous rivals, but it manages to render most Web pages," they explained. "As well has having geek-chic, it can come in handy when you just need to quickly check if a Web page is accessible from a computer you only have SSH access to."
-
-The list goes on from there to include looking up definitions on Wikipedia, among other tips.
-
-Down at the Broken Windows Lounge, patrons had plenty of suggestions of their own.
-
-### 'Great for Maintenance' ###
-
-"Very nice tips on CL commands, very nice," enthused Google+ blogger Alessandro Ebersol, for example. "But they forgot [cowsay][8], which is great for having some laughs in the darkness of a terminal."
-
-The command line "is great for maintenance," he added. "One can automate with bash scripts and make complex tasks with few (or just one) keystrokes."
-
-Other command line secrets Ebersol would add to the original list are sl (steam locomotive), along with [these nuggets][9]:
-
- * % cat "food in cans"
- cat: can't open food in cans
- * % nice man woman
- No manual entry for woman.
- * % [Where is Jimmy Hoffa?
- Missing ].
- * % make love
- Make: Don't know how to make love. Stop.
- * % man: why did you get a divorce?
- man:: Too many arguments.
-
-### 'The Most Precious Gem' ###
-
-"Command-line secrets? There aren't any such things," blogger [Robert Pogson][10] told Linux Girl. "Desperate newbie? Type 'help.' Still need a hint? Type 'man whatever.' Want more diversity? Type 'ls /bin /sbin /usr/bin /usr/sbin | less,' pick out a few gems and type 'man whatever' all night long. I've been at it more than a decade. Still having fun."
-
-Pogson doesn't remember how long ago he discovered 'ssh,' but "it's the most precious gem of the FLOSS world," he said.
-
-"The awesome power of ssh is that the joy you have with typing commands on one computer can allow you a hundred times the joy on 100 computers," he added. "Of course, it's not fun to type passwords 100 times, so learn to use secure passwordless logins with ssh to make logging in remotely transparent."
-
-### 'Use It With Respect' ###
-
-Of course, "just as with any pleasurable activity, one can be addicted to the point of destruction," Pogson warned. "As root, you can type commands to delete everything or otherwise mess things up.
-
-"This is the nuclear option, and just as world leaders should sit on their hands and think carefully before pushing the button, value this power and use it with respect and higher motivations," he added.
-
-"I once deleted a file system because my thumb dragged the space bar into a command," Pogson concluded. "I only did that once. Honest."
-
-### 'Very Powerful' ###
-
-Google+ blogger Gonzalo Velasco C. was no less enthusiastic.
-
-"Even though the [GUI][11] tools are easier, in the *nix universe, the command line remains very powerful," he told Linux Girl. "Even some power MacOS users use them."
-
-As for Gonzalo Velasco C. himself, "the only commands I would like to master are the process control and killing, to use with ctrl+alt+backspace, so I can handle the one process that is giving me trouble, and the tar.gz files management -- that to this very day remains a pain for me," he said.
-
-#### 'Ur Doing It Wrong' ####
-
-Last but not least, SoylentNews blogger hairyfeet had a different perspective altogether.
-
-"The only thing I would add to a story about CLI is this: If you aren't working in IT and performing repetitive tasks where having an extremely simplistic, primitive way to script something is useful, and yet you are still using CLI, then 'ur doing it wrong,'" hairyfeet told Linux Girl. "A CLI isn't magic -- it's a GUI from the 1970s!"
-
-Today there are "useful GUIs thanks to actually having more CPU and RAM than a dollar-store watch -- we even have IDEs and scripting languages that can run rings around that 70s throwback, work across the WAN or LAN and interact with the deepest levels of the OS, all while being easier to use thanks to technologies like intellisense and autocomplete," he explained. "So why in God's name, if you aren't one of the 3 percent who are administering systems where every single byte counts, would you be dragging that old pile of junk out of mothballs?"
-
-Hairyfeet's best CLI advice? "Don't -- join the rest of the planet in the 21st century and learn how to use real languages and tools," he concluded. "Let CLI join bubble memory and floppies on the dustbin of history."
-
-> atherine Noyes is always on duty in her role as Linux Girl, whose cape she has worn since 2007. A mild-mannered journalist by day, she spends her evenings haunting the seedy bars and watering holes of the Linux blogosphere in search of the latest gossip. You can also find her on [Twitter][12] and [Google+][13].
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/80437.html?rss=1
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://www.computer.org/portal/web/pressroom/Linus-Torvalds-Named-Recipient-of-the-2014-IEEE-Computer-Society-Computer-Pioneer-Award
-[2]:http://www.ieee.org/
-[3]:http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/80386.html
-[4]:https://www.facebook.com/netcatband/posts/755205877853161?stream_ref=10
-[5]:http://www.netcat.co/
-[6]:http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/79448.html
-[7]:http://www.linuxvoice.com/commandline-secrets/
-[8]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cowsay
-[9]:https://www.linux.com/community/blogs/133-general-linux/10408
-[10]:http://mrpogson.com/
-[11]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GUI
-[12]:http://twitter.com/noyesk
-[13]:https://plus.google.com/+KatherineNoyes?rel=author
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/Making Linux Feel at Home.md b/sources/talk/Making Linux Feel at Home.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 715a1996bb..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/Making Linux Feel at Home.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,135 +0,0 @@
-Linux-pdz重又复出,先占一坑哦!
-Making Linux Feel at Home
-================================================================================
-**Hiring Tux is a smart move for both small and large businesses. Linux once was considered a hobbyist's operating system, but it has come a long way and now is considered enterprise class. It is considered very stable and secure. Linux can easily be customized, and there is a huge community eager to help out. Those are just some of the reasons to migrate to the Linux desktop.**
-
-Migrating to a different operating system is never easy. Keeping the Windows opened or not chewing on a MacIntosh can be a frustrating and costly experience. Buying new upgraded hardware to keep up with costly new software releases is often an exercise in futility.
-
-Running a Linux distribution at home or in a small office environment can be a productive endeavor that brings cost savings and increased efficiency. Adopting a Linux server system instead of playing catch-up with a Microsoft infrastructure is often a smart business move for enterprise environments.
-
-However, the process of giving up a comfort zone around a familiar operating system often seems more of a challenge than it actually is. Individual users and SMBs can move into the Linux desktop in stages. The software is free, and users already have suitable hardware that can function with both platforms.
-
-Many larger enterprises already run their own Linux server silos and integrate Linux desktop use where it fits more easily. The growing use of cloud-based software lets office workers use their workstations without realizing any major change occurred.
-
-"Migrating to Linux is based on the use case. If you are home or are a developer, you are going to want to use all the power available in Linux. That is a no-brainer. There is no one easy way to migrate to another operating system. No one use case fits all. It is dependent on the user base," Mike Vitale, chief technology officer for [TalkPoint][1], told LinuxInsider.
-
-Working with enterprise clients in SMB environments, Vitale sees a growing movement of individual users and corporate leaders taking advantage of new technologies that draw them toward Linux.
-
-### Comfort Counts ###
-
-One of those Linux technologies is the Chrome OS and the low-cost laptop computers now powered by the Linux-based Chrome browser OS.
-
-For users already familiar with Google's Chrome browser or the open source Chromium browser project, using a Chromebook or cloud-based delivery system makes migrating to Linux an easy walk in the park.
-
-"One of the issues, regardless of which OS is used, is the browser capabilities. We have found that 85 percent of the time the user is in a browser," Thomas Deng, cofounder and senior vice president of product management for [Splashtop][2], told LinuxInsider.
-
-There's a growing interest in people adapting to newer technologies with quick learning curves, Deng observed. People use a variety of products. So migrating to an OS that resembles what they use on another device makes for a smoother transition.
-
-### hrome Craze Caters ###
-
-Mobile device users both at home and at work are becoming proficient with Linux without knowing it. They move back and forth among several operating systems. With that familiarity comes a comfort zone for open source. Using cross-platform software delivered from a cloud platform is an added migration measure.
-
-"What Google is doing is really interesting with the office suite. Google is opening the door with its Chrome OS now," said Vitale.
-
-A good example of opening doors while shutting Windows is how his company uses Chrome-driven tools in-house. For instance, TalkPoint uses the ChromeBox appliance.
-
-"That is opening the door for multimedia teams and traditional AV users. We are seeing a lot of inroads with that technology," Vitale explained.
-
-### Tablets Tackle Tradition ###
-
-Another instance of Linux devices paving the way for desktop OS migration is the popularity of the Android OS. Add to this the Linux distros retooled for smartphones and tablets.
-
-"As far as migrating people to Linux goes, people are getting more comfortable with the tablet interface, especially with their unhappiness over the Windows 8 interface. Everyone I know is trying to turn it back to Windows 7," said Vitale.
-
-### Cloud Has Linux Clout ###
-
-People expect to use their familiar productivity tools like MS Office for word processing. There is less familiarity with open source products on the Windows platform, so integrating open source before starting a move to fully implementing the Linux desktop helps, noted Deng.
-
-That trend of Windows users not knowing about open source is changing with the popularity of Google Docs and the Google Chrome browser, he pointed out.
-
-"What is also easing the transition to Linux is the shift to using cloud applications," Deng said. "Educating the user is the most effective way to move users into Linux. The Chromebook is becoming very widely adopted. It is an easy migration path into Linux."
-
-### Tux the Mighty ###
-
-Hiring Tux, the Penguin that is the Linux mascot, is a smart move for both small and large businesses. It is a mature, stable and flexible operating system that definitely can do the job, according to Shaun Seller, senior product manager at [Vision Solutions][3].
-
-"For a small business, running Linux is a compelling alternative to other operating systems and may provide advantages, depending on your business needs," Seller told LinuxInsider.
-
-It once was considered a hobbyist's operating system. Linux has come a long way and now is considered enterprise class. It is considered very stable and secure. Linux can easily be customized, and there is a huge community eager to help out, he said. Those are just some of the reasons to migrate to the Linux desktop.
-
-### Good Business Cents ###
-
-Leveraging more of the community support model can create cost savings, Seller said. Linux is available free with community support or through subscriptions that offer full technical support. Some Linux distributions also come with things like hardware and software certifications, which may be important for some work environments.
-
-For example, small businesses and larger enterprises can run a distribution such as CentOS or OpenSuse completely or in combination with a subscription-based version from [Red Hat][4] or Suse. Even with a full subscription model, Linux offers a lower total cost of ownership and better return on investment than Windows or traditional Unix, explained Seller.
-
-"I believe it makes sense for smaller businesses to take a close look at Linux," added Sellers. "Linux has a bright future, as open source software in general is helping drive innovation at a fast pace, with help and collaboration from the community, and companies like IBM and Red Hat."
-
-### Cozy but Cautious ###
-
-Operating systems can produce divided loyalties within families and workplaces. Take the case of Walker White, CTO of [BDNA][5]. He uses Linux as a desktop OS at home, but his family is not so enthusiastic about his computing passion.
-
-"My family members use Mac gear. They blindly follow the marketing ploys and the feature hype without any consideration of performance and such. I am on a personal holy war at home to try slipping more allegiance towards Linux," White told LinuxInsider.
-
-There are similar allegiance struggles in his company, he said, where the Linux desktop is not yet universally used -- but he is laying the foundation for a wider Linux deployment at work.
-
-BDNA uses the Google applications internally quite a bit. The company is migrating more and more things to cloud-based offerings. However, that will take more support from ongoing preparations.
-
-"When I switch over to applications like [OpenOffice][6], that operation has to be really seamless for it to start getting better adoption. From a pure marketing perspective, developers need to change the game a little bit. Apple is winning the hearts and minds of the young kids and the younger generations through their 30s. I see that attitude often at my company," he said.
-
-### Tux Takes On Apple ###
-
-Requests for new equipment are very specific to the high-end MacBook Pro, explained White. Even though the tools they mostly are using are based online, workers BDNA want the flashy, highly advertised hardware names.
-
-To break that view, he has to separate function from OS and hardware. Part of that battle is to insulate the user from the operating system itself. That can happen only when the industry has productivity applications both online and offline, according to While.
-
-"Even simple things like using file managers need to focus on not the OS but what that OS allows us to do within the apps that we use," he said.
-
-### Making Comfy Complete ###
-
-How much should an operating system control the computer user? That question is critical in migrating to Linux, said Whites.
-
-Consider the growing success of the Chromebook and Android phones and tablets. Do consumers really need to know they are running Linux?
-
-"I think the key to Linux migration and success of the Linux desktop in the home is tied to how much can we actually do online," White said. "Since I use Linux at home, I see the advantages."
-
-Whether you start at the consumer level at home or move up to the business user in the home or in a small business setting, it's important that users be comfortable with all of the tools and features they use. That includes things like sharing and creating documents, and everything that goes along with that, he explained.
-
-### Migrating Measures ###
-
-As for marketing, software and hardware makers need to put less emphasis on the operating system. For example, Chromebook is gaining acceptance in much the same way as Apple sells the MacBook. Google is not so much hawking a Linux OS as it is selling an appliance, White reasoned.
-
-"What developers really need to do is change the focus, so users get comfortable with Linux in their homes without dwelling on using a non-Windows or non-Mac operating system. Whatever you use has to be able to do the things you want it to do. Something like Chromebook does that with Linux under the covers," he pointed out.
-
-Computer makers must first start to break that mold of "it is Windows" or "it is a Mac." Until that happens, migrating to Linux will be a steep climb, White concluded.
-
-"It is not about branding the OS," he said. "It is about the capabilities of the devices the OS runs."
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/80415.html
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://www.talkpointcommunications.com/
-[2]:http://www.splashtop.com/
-[3]:http://www.visionsolutions.com/
-[4]:http://www.redhat.com/
-[5]:http://www.bdna.com/
-[6]:http://www.openoffice.org/
-[7]:
-[8]:
-[9]:
-[10]:
-[11]:
-[12]:
-[13]:
-[14]:
-[15]:
-[16]:
-[17]:
-[18]:
-[19]:
-[20]:
diff --git a/sources/talk/Open Source's Cult Of Personality Is Dying--Thankfully.md b/sources/talk/Open Source's Cult Of Personality Is Dying--Thankfully.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9779aeba3d..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/Open Source's Cult Of Personality Is Dying--Thankfully.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,57 +0,0 @@
-[小冰在此]
-Open Source's Cult Of Personality Is Dying—Thankfully
-================================================================================
-Roy Rubin, co-founder of the popular [Magento][1] open-source project, [announced this week][2] he is bowing out of the project he helped launch back in 2008.
-
-)
-
-It's not the first time the leader of an open-source project has stepped away from her project, but it's remarkable by its response: Relative silence.
-
-It's not because Rubin wasn't critical to Magento. He was. For six years, Rubin was the soul of Magento. But open source has grown up, and it's increasingly shedding its cult of personality. While no one wishes Linux founder Linus Torvalds gets hit by a bus, we're to the point that we, [like Linus][3], "won't care."
-
-But it wasn't always this way.
-
-### Worshipping The Benevolent Dictator ###
-
-Successful open-source projects have long been associated with strong leaders, and for good reason. Influencing a vibrant community of individually-minded developers can be the equivalent of herding cats. While differences of opinion on the direction a particular open-source project can turn into a parting of ways (and code, called a "fork"), more often than not a "benevolent dictator for life," or project leader, will step in, exert leadership and keep the community together.
-
-The term "benevolent dictator for life" (BDFL) [may have started with Guido von Rossum][4], the former Python development lead. It has since been applied to Linus Torvalds, the creator of Linux, as well as Mark Shuttleworth, Ubuntu's lead, among others. Sometimes two leaders on a project share the title, as did Adrian Holovaty and Jacob Kaplan-Moss for [Django][5].
-
-At their peak, the departure of any one of these leads would have wreaked havoc on the fortunes of the project, given how closely identified the projects were with these strong leaders. Over time, however, this has changed. The Django BDFLs [moved on to other projects][6], and Django kept chugging along. Ditto Python, Lucene (Doug Cutting), JBoss (Marc Fleury) and many other projects.
-
-While open source communities still rally around strong leaders, we don't seem to be as dependent on them as we once were. Open source's "cult of personality" faded, and perhaps has died altogether. But what happened?
-
-### Apache And The Rise Of Community ###
-
-Well, community did, for starters. I realize I'm making a somewhat subjective assertion here, but over the roughly 15 years I've been involved in open source, I've seen a gradual shift away from tightly-controlled free software projects to more loosely joined open-source communities, often with significant corporate interest.
-
-While it's not clear whether the open, BSD/Apache-style licensing "chicken" came before the corporate open source interest "egg," the two together have definitely changed how open source operates.
-
-This includes the need for a BDFL. For example, and while it's not a project, it's hard to imagine Free GNU without Richard Stallman. By contrast, it's pretty easy to imagine Apache Hadoop without... wait, who is in charge of Hadoop, anyway?
-
-The answer? Everyone. Or [many][7], rather. It started with Doug Cutting, but it has since grown to become a community of companies and individuals (but mostly companies that employ those individuals) working together.
-
-The same is true of OpenStack, which has a [host of companies involved][8]. If any particular OpenStack developer were to leave, the OpenStack show would go on. And it has thus far. The same is true of an increasing number of open-source projects.
-
-### A BDFL-Free Future? ###
-
-This isn't to suggest that leaders aren't needed in open source. They are. But as more open-source projects become communities of corporations, the risk of a BDFL leaving diminishes. Frankly, even if companies aren't heavily involved, projects with an Apache license may not be as dependent on a BDFL, anyway.
-
-Photo of Richard Stallman [courtesy of Friprog on Flickr][9]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://readwrite.com/2014/05/02/open-source-magento-roy-rubin-bdfl#feed=/hack&awesm=~oDgSTEdnXAjUv0
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://magento.com/
-[2]:http://magento.com/blog/magento-news/note-roy-and-mark#.U2JhPK1dVii
-[3]:http://www.serverwatch.com/server-news/if-linus-torvalds-got-hit-by-a-bus-would-linux-die.html
-[4]:http://www.artima.com/weblogs/viewpost.jsp?thread=235725
-[5]:https://www.djangoproject.com/
-[6]:http://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2014/01/on-the-reign-of-benevolent-dictators-for-life-in-software/283139/
-[7]:http://hadoop.apache.org/who.html
-[8]:http://activity.openstack.org/dash/releases/
-[9]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/friprog/
diff --git a/sources/talk/Pros' Secrets and Red Hat 7 and PCLinuxOS 2014.05 Reviews.md b/sources/talk/Pros' Secrets and Red Hat 7 and PCLinuxOS 2014.05 Reviews.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 8b66085b04..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/Pros' Secrets and Red Hat 7 and PCLinuxOS 2014.05 Reviews.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
-[小冰在此]
-Pros' Secrets and Red Hat 7 and PCLinuxOS 2014.05 Reviews
-================================================================================
-
-
-Today in Linux news Katherine Noyes scoured Linuxdom to find "Linux Pros' top command line secrets," if there's really such a thing argues one blogger. In other news, Jesse Smith reviewed new Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Release Candidate and Jamie Watson reviewed quietly released PCLinuxOS 2014.05.
-
-Katherine Noyes writes, "there's nothing like a little shop talk around the bar to pass the time during a quiet week, and last week afforded a dose of that as well." It was a post at the Linux Voice that got the ball rolling but one Robert Pogson is quoted as saying, "Command-line secrets? There aren't any such things." See if there's anything new [for you there][1].
-
-**In today's** Distrowatch Weekly, Jesse Smith takes RHEL 7 Workstation RC for a test drive. Of the installer he said, "Booting from the RHEL media brought up a graphical system installer. RHEL uses the same new Anaconda installer Fedora has been using in recent releases. Personally, I feel as though the new installer is a step backward." From there was little remarkable, although that's what you want in a workstation I suppose. Smith said he wished there was a graphical package manager because users only have YUM at the commandline and there's only the standard fare in the default stack. Later GNOME shell kept crashing upon KDE login... puzzling but he quite liked the new firewall configuration. See his [full report][2] here.
-
-**Over at** ZDNet.com, Jamie Watson reviewed recently released PCLinuxOS 2014.05. He said:
-
-> It is an interesting concept, as you might assume from the name it includes a lot of packages, applications and drivers which are not in the standard distribution. The really interesting bit, though, is the activity-focused virtual desktop configuration. The intention is to make using PCLinuxOS easy and fun, by providing the following desktops, each with its own specific wallpaper:
->
-> Internet — browser, email, chat, IM
-> Work — Office, kile, scribus
-> Play — games
-> Multimedia — music, video, editing and composing
-> Graphics and Images — scan, edit, draw
-> Administration — System management tasks
-
-"PCLinuxOS still uses the same installer they have had for as long as I can remember, which was originally derived from the Mandriva/Mandrake installer," observed Watson. He said it ships with a modern kernel, up-to-date software, and well behaved desktops. [He concludes][3], " this new PCLinuxOS release is very nice." Additionally, [Watson testdrove][4] Ubuntu, Debian, and LMDE last week as well.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://ostatic.com/blog/pros-secrets-and-red-hat-7-and-pclinuxos-2014-05-reviews
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/Linux-Pros-Top-Command-Line-Secrets-80437.html
-[2]:http://distrowatch.com/weekly.php?issue=20140512#feature
-[3]:http://www.zdnet.com/hands-on-with-pclinuxos-2014-05-kde-and-lxde-the-linux-with-something-for-everyone-7000029297/
-[4]:http://www.zdnet.com/testing-ubuntu-debian-and-lmde-on-my-new-notebook-7000029202/
diff --git a/sources/talk/Raspberry Pi s Eben Upton--How We're Turning Everyone Into DIY Hackers.md b/sources/talk/Raspberry Pi s Eben Upton--How We're Turning Everyone Into DIY Hackers.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b792ff744f..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/Raspberry Pi s Eben Upton--How We're Turning Everyone Into DIY Hackers.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,189 +0,0 @@
-Raspberry Pi's Eben Upton: How We're Turning Everyone Into DIY Hackers
-================================================================================
-> Inside the mind that prototyped a $35 computer for tinkerers.
-
-I’ll never forget my first time seeing a Raspberry Pi. The tiny, credit-card sized computer is powerful enough to operate as a home PC, a media center, a gaming console, or anything you can dream up. At only $35, it’s a bargain for tinkerers of all ages who want to try out hardware and software experiments without worrying about bricking their pricier family computers.
-
-[Eben Upton][1], cofounder of the Raspberry Pi Foundation, is generally credited as the magician behind this incredible machine. While working on his doctorate in philosophy at the University of Cambridge's computer laboratory, Upton painstakingly put together Raspberry Pi prototypes by hand.
-
-Today, Upton is CEO of the Raspberry Pi Foundation’s trading company, where he oversees production and sales of the Raspberry Pi. The foundation has now sold more than 2.5 million units.
-
-### Pi In The Sky ###
-
-ReadWrite: What got you really interested in technology in the first place? How did that lead you eventually to the Raspberry Pi project?
-
-**Eben Upton**: So I actually got started when I was a kid. I have a father who has a certain amount of interest in engineering. He’s not an engineer, he’s an English academic. There were always piles of electrical stuff around the house that I used to play with before I understood what it did. Little things like making a light to have by your bed so you could read after “lights out” and stuff.
-
-
-
-And then I got a computer. In the UK we have these machines called [BBC Microcomputers][2], which were 8-bit micros that were build for education. We had them at school, I got into programming at school, and I enjoyed it.
-
-These things weren’t necessarily in school for programming, or at least they didn’t tend to get used for programming. They would get used to run educational software. But I used to program on them. And then I bought one to program at home. I mean, the day I got my BBC micro, I went in my room, turned it on, and never came out again. [Laughs]
-
-Programming is amazing for a kid. When you’re a kid you don’t have a lot of power. You don’t have a lot of agency, a lot of control over the world around you. The great thing about programming is it’s a little world where you do whatever you want. And I certainly found that very compelling.
-
-I’d always been interested in science, math, kind of hard science subjects. Did a lot of computing, did a lot of programming on my BBC. I had a Commodore Amiga after that.
-
-At university I did a mixture of physics, engineering, and computer science. And then that really kind of led me to the Pi. Because after I’d been at university for a decade [while getting a doctorate], I realized that the kids who were arriving hadn’t had the chance to have that set of experiences as a child. You could still get Legos but … that ladder.
-
-We’d kind of pulled the ladder up after us. We built these very sophisticated and user-friendly computers for children to use now. Or not even computers—game consoles and phones and tablets, kind of appliances. But people were being denied that opportunity to tinker. So really Raspberry Pi is an attempt to get back—without kind of being too retro—some of what we kind of feel was lost from the evolution of computers over the last 25 years.
-
-**RW:** What were some of the biggest hurdles you had to overcome?
-
-**EU:** Well, we didn’t have any investors, so that was one nice thing. We’ve been trying to do this since 2006 so you can see it took us a long time to get from the idea of a Raspberry Pi to something you could sell. Finding something that had the right tradeoff between price and performance, or price and programmability was a big deal.
-
-Getting the money together. We’re a not-for-profit, so we had to go find some money, and there ended up being a few of us on the board of trustees just loaning money out of our own pockets. So we had about a quarter of a million dollars of startup funding which was entirely loans from me and a couple of other people. So having the guts to do that, I guess.
-
-
-
-### From East To West ###
-
-Finding a way to get it manufactured at the right price. We ended up taking an unusual route. Generally when people make more conventional products, what they do is make them locally, when they’re low volume. And they [manufacturers] charge a high price. Most people have thicker margins than Raspberry Pi.
-
-So what people do is manufacture in the west. Later on, in search of a squeeze, they got the volume and are looking to improve their production costs, so they go to the far east.
-
-The issue for us was that, because we didn’t have enough margin to support that kind of order, we built our very first units in China. Which was of course, at first a slightly daunting prospect. I knew nothing about manufacturing in China, and we ended up sending $50,000 of chips and $50,000 to some guy in Hong Kong. And he sent us back 2,000 working Raspberry Pis.
-
-It got to the point where there was a little bit of a delay and we were convinced that we’d gotten shafted. And then one day, the first 2,000 of now 2.5 million Raspberry Pis turned up on the doorstep on a pallet.
-
-This UPS guy comes out of his truck with a pallet and a pallet jack and jacks this pallet into the garage. It’s got 2,000 Raspberry Pis on it and each one of those is massively more powerful than any computer I had when I was a kid. And we were just picking them out at random out of the pallet just to sample them and they all worked perfectly.
-
-So getting lucky, I guess, with China, and then finally having got the volume, we went in the other direction from everyone else. I guess the other defining moment in the project was when we realized that, having got the volume, we could now build in the west for the same price we would have been able to build in China. So we were able to repatriate, to reshore all the manufacturing back to Wales, which is where I was born. Kind of a nice sort of circle.
-
-**RW:** Were there any precursors to the Pi that didn’t work out?
-
-**EU:** Yeah, we built a number of different prototype devices. We were trying to build something that was programmable but interesting to kids. “Interesting to kids” means kind of … powerful in some respects. Able to play video and games and go on the Web.
-
-We had a number of prototypes that met the price goal and the programmability goal, but it was only very late, post 2010 and 2011, that we were able to identify a path that allowed us to build something that was also powerful enough that kids were going to engage with it.
-
-### Whence The Pi Was Baked ###
-
-**RW:** Tell me about inventing the Raspberry Pi.
-
-**EU:** We tried building some units based on what you’d call microcontroller technology. I don’t know if you’ve come across an [open source electronics prototyping] platform called Arduino? Sort of a similar level of performance to the Arduino. The nice thing about those chips is they’re very available, they’re commodity parts, they’re very cheap and easy to get ahold of.
-
-
-
-So we tried that. And we ended up with something which was technically a computer—you plug it into your television and stuff. But it was kind of primitive and it was clear that kids weren’t going to engage with it. So that was prototype one, and that prototype is coming to a museum in Ireland in an exhibition called “Fail.” [Laughs] I’m going to go see it next month. It’s in a glass cabinet as an example of a glorious failure.
-
-The nice thing about that was that was hand built. You can’t really build a modern Raspberry Pi by hand. But this one was primitive enough that you could actually solder it together and I soldered it together in a week. And it was a nice little toy.
-
-After I’d been at university for a decade of so, I went to work for a company called Broadcom, which is based in southern California but has a big office in Cambridge. They make cellphone chips. And we realized that cell phone chips are quite a good fit. They’re quite a good platform for building a Pi-like device, since they have a lot of graphics performance.
-
-I built a prototype based on that, based on a Broadcom dev kit. And that was much more powerful, much more capable, again at the same price point. But the challenge we had with that was that it was really a custom environment. It wasn’t a standards based platform.
-
-We were writing our own SD card drivers, our own file system, our own text editor. You find yourself doing a lot of basic work and although you end up with a platform which is powerful and programmable, it's completely nonstandard [and] completely unlike any other machine. You don’t get to leverage any of the work that’s already been done by people on desktop platforms. That was prototype two.
-
-The real breakthrough for us was with prototype three. We got hold of another chip from Broadcom which had an ARM processor which was able to run standard Linux. That was really the point where we realized we had something that met all our goals. And that was the product we went to market with.
-
-### Hacking The Next Generation Of Hackers ###
-
-**RW:** Kids as young as eight have built projects using the Raspberry Pi. Did you intend that, or did it take you by surprise?
-
-**EU:** Eight is a good age. I think everyone defines the right age as being the age when they started programming. I was eight when I started programming. To some extent, all a child needs is to be old enough to have the relevant suite of cognitive skills, kind of problem solving type skills. A little bit of math maybe, at school.
-
-
-
-To be old enough to be able to plan activities—programming is the ultimate planned activity. You need to have the mental equipment to do that. By the age of eight, a lot of children are quite mature in their way of thinking. You also need mechanical dexterity; another challenge that younger children have is the lack of mechanical dexterity required to use a keyboard.
-
-So eight’s a great age. You’ve got the physical equipment, the mental equipment, and you’re still at that point in your life where you’re able to learn new things very easily. Your brain’s very plastic, you’re able to learn languages....
-
-I mean, if you want a child to learn French, start teaching them at eight, don’t start teaching them at 16. One of the weaknesses we have historically in our formal teaching of computing is we start people incredibly late, and then are surprised when people have difficulty picking up the concepts. So I think the younger you can get them the better and eight is a fantastic age. Eight, 10, 12—12 is maybe a little bit late.
-
-Our foundation CEO, [Lance][3] [Howarth], is particularly passionate about primary education. He really perceives a real opportunity there to do something quite special.
-
-**RW:** So that was an intention of the Raspberry Pi, to get really young kids programming?
-
-**EU:** I think we’ve always thought that young kids could do programming just by example. But the intention of the Raspberry Pi was to make this thing available and just see who buys it. We always believed that at least a subset of young children would find it exciting. Now we have the breadth and scale to get it to young kids with support.
-
-There’s a big difference between [just] making a platform like Raspberry Pi available and offering support for it. I think if you just make it available, you’ll find one percent of eight-year-olds will be the one percent who love that sort of thing and will get into it, regardless of how much or how little support you give them.
-
-I think the real opportunity for the foundation right now is that, since we can afford to pay for the development of educational material, we can afford to advocate for good training for teachers throughout this. There’s an opportunity to get more than one percent. There’s an opportunity to reach the bright kids who don’t quite have the natural inclination to personally tackle complicated technical tasks. If you give them good teaching and compelling material that’s relevant and interesting to them, you can reach ten percent, twenty percent, fifty percent, many more.
-
-We look back to the 1980s as this golden era [of learning to program], and in practice, only a very few percent of people were learning to program to any great degree. Most people could probably write a couple of lines. But doing any significant programming was still rare.
-
-I think the real opportunity for us now, because we can intervene on the material and teacher training levels, we can potentially blow past where we were in the 1980s. There’s much more participation, there’s much more gender equality. Programming was largely a boy’s activity in the 1980s, and that’s now reflected in the makeup of our engineering community. I think there’s a real opportunity to get more girls programming computers. That’s the lowest of low hanging fruit. If we do that, we instantly double the number of people.
-
-There are a lot of opportunities and I think the most satisfying thing for Pi is we’re kind of at the scale where we can start to attack some of them.
-
-### Pi For Everyone ###
-
-**RW:** What does that say to you about the potential demand for DIY projects like the Pi? Are we all going to be DIY hackers one day?
-
-**EU:** Yeah, I mean, that’s the thing. There is an enormous demand for it. And I think that there is a tie to the maker community. The maker community is much more developed in American than it is in the UK. We do have maker fairs and hackerspaces now, but it’s probably five years behind where it is in the U.S.
-
-So one thing we found when we started talking about Raspberry Pi, when it started getting international attention, we found we were launching into this very well established community of people who like doing all sorts of DIY activity: knitting, or, you know, woodworking.
-
-So that’s one of the things that led to that surprise increase in volume for the Pi. Makers who see it as a component they can use to build their projects. Which is great!
-
-**RW:** What do you think about the emergence of mainstream hardware-hacking culture?
-
-**EU:** I mean, it’s fantastic, right? It’s something we would never have predicted on the software engineering front. I’ve come to this stuff from a software background, so the fact that most of the cool stuff people do with the Raspberry Pi is hardware related is surprising to me. It’s not surprising to me anymore, but it was surprising to me originally.
-
-
-
-I think it’s a very positive trend, for all sorts of reasons. It’s positive because it provides children with relevant experiences. In my mind, moving pixels around on the screen is still cool, but in reality, it’s much less cool than it was in the 1980s. I think moving objects around in the world, like robots, is what’s cool for kids now.
-
-When you get more relevance, you attract more girls. There’s a really insidious tendency to try and design activities for girls around tech, and it actually isn’t about girls. It’s about appealing to a broader audience.
-
-There is this tiny segment—I’ve talked about the one percent, the kids who find the abstract computer programming exciting. “Let’s learn about variables!” And I was one of those kids. But that’s only a small number of people, and it seems to be boys, more often. I don’t know whether that’s a cultural thing or what but it just seems to be the way the world is.
-
-Quite often when people are talking about pursuing relevance in order to attract girls, it’s not about attracting girls at all. It’s about attracting anyone other than that tiny little sliver of boys. You’re not just attracting girls, you’re attracting all the other boys as well.
-
-One of the wonderful things from an education standpoint is that part of actually doing stuff in the real world with a computer is automatically more relevant than just doing things on the computer itself. So it gives you a route to attract girls into the subject, it gives you a route to track more than one percent of boys into the subject.
-
-It’s great not to be alone. It’s fantastic to be launching into this tidal wave of interest, of people doing stuff in the real world. I know a guy in southern California whose two hobbies are Pi hacking and making his own chainmail. It’s just a wonderful thing that people are doing that sort of stuff.
-
-### Sharing The Pi ###
-
-**RW:** Can you give me an example of the sort of “relevant” projects that attract more than the one percent?
-
-**EU:** The whole broad area of robotics is one. There are just vast numbers of people using the Pi as a base to make little robots that run around and do stuff, particularly now that we have the camera module, which acts as kind of computer vision.
-
-I think other camera-based projects as well tend to get a lot of play. People doing wildlife photography type things, people doing time lapse photography, a wide range of stuff because we have this $25 camera module, and an infrared version so you can do nighttime animal photography—writing scripts to take pictures at night and save away the ones that have some motion in them. So those ones are nice.
-
-I’m particularly fond of anything that has to do with high altitude ballooning. Environmental monitoring—there are some high school kids in the UK who did an IndieGoGo called [AirPi][4], which is a pollution monitoring shield that would sit on top of the Pi. So lots of those things that let you do physics or chemistry or biology using the Pi—those are the things that I think have relevance. Those are the things that are much easier to justify to the bulk of kids as a thing that’s worth paying attention to.
-
-**RW:** When will we be seeing a Raspberry Pi Model C?
-
-**EU:** We have no plans at the moment. We are mostly doing software work at the moment. I think we’ve discovered that there is a large amount of performance gain available by nickel and diming the software, buffing it a little bit.
-
-If we go and make a Model C, we orphan 2.5 million people who are committed to the current platform. So I think we are, at least for now, pretty committed to trying to do software work because that helps all of those people who are in the field. We feel there is still significant performance gain available through software optimization.
-
-Obviously, we’ll have to do something [about hardware] at some point. I don’t really known when. If we’re still shipping the Pi Model B in 2017, 2018, that would be bad. But I think we’re probably a year away from giving any serious consideration to what to do next.
-
-**RW:** Lots of people are building projects using both the Pi and Arduino, the DIY electronics-hacking kit. Did you design Pi with kits like Arduino in mind?
-
-**EU:** Not really, but we realized very early on there could sometimes be a tendency in the press to see us as a competitor to the Arduino. We were always skeptical, I think, as to whether that was really the case because I think the Pi and Arduino do different things and do them well.
-
-We didn’t design it to work with the Arduino, but the Arduino is designed to work with a house PC. We make a great low power house PC for the Arduino. So yeah, it was just lucky, I guess.
-
-**RW:** What do you use Raspberry Pi for at home? At work?
-
-**EU:** At home, I use it as a media center; that’s a fairly common use of the Pi. It’s an interesting thing that you have people doing actual consumer electronics, using it as a piece of consumer electronics. And I’m certainly one of those.
-
-I don’t have anywhere near as much time to play with it at work as I would like. Usually when I get a Pi at work it’s because I’m testing some new piece of software that I’ve commissioned. Mostly I’m just using it to check that the contractors I’ve paid to do work have done a good job.
-
-I’m really hoping that I will get some more downtime over the next year. Sometimes it feels like, aside from the media center, I’ve been involved with making this fantastic toy, and because it’s been so successful I don’t get much time to play with it.
-
-But it’s really gratifying to see how many people are having fun with it, to see it show up in different places. I understand we got mentioned on The Big Bang Theory, I need to track down the episode. It shows up in all these unusual places. It’s really nice to see how many people have taken it to heart and started doing stuff with it.
-
-Eben Upton image courtesy of the Raspberry Pi Foundation; Raspberry Pi images by Flickr users [Johan Larsson][5], [Clive Darra][6], [Pete Sneekes][7], [Luca Sbardella][8] and [Ashley Basil][9]
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://readwrite.com/2014/04/08/raspberry-pi-eben-upton-builders#awesm=~oBGnazhOCOfaUd
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:https://twitter.com/EbenUpton
-[2]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BBC_Micro
-[3]:http://www.raspberrypi.org/welcome-lance/
-[4]:http://airpi.es/
-[5]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/johanl/8384790662
-[6]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/osde-info/8626662243
-[7]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/p8/7950485168
-[8]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/sbardella/7473604878
-[9]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/28438417@N08/8006786385/in/photolist-dcwSD8-d8PKa3-bmosVm-bmosWG-bz3YJF-e8NRQD-btyqN1-dorXrE-hTF7id-hTF7jL-hTF4mJ-hTF4jj-hTF4q1-hTF7jA-hTF7gj-gKRLrn-ftALdo-c7Qnjs-c7Qnyh-c7QmZj-c7QnY1-c7QmNY-cu8zs3-cu8BWm-cu8u5S-cu8yC3-cu8DBN-cu8wRq-cu8xNL-cu8CJj-cu8tss-cu8BcG-cu8uVL-cu8AoW-hTF7dU-hTEzCr-hTFBCp-hTFBvR-hTFBBH-hTF4hA-hTF7c1-hTEzza-hTFBM2-cdtf1b-bz7n87-gKQSJ7-gKQUko-ds8x8q-dqweVP-cVwvJq
diff --git a/sources/talk/The Open Source Witch Hunts Have Returned.md b/sources/talk/The Open Source Witch Hunts Have Returned.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b924d67b98..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/The Open Source Witch Hunts Have Returned.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,60 +0,0 @@
-[小冰在此]
-The Open Source Witch Hunts Have Returned
-================================================================================
-
-
-> The open source community has been turning on itself lately, just like the good old days.
-
-Open source has gone soft. We used to pass the time with hangings of the ideologically impure, but of late we've had this weird obsession with sharing code and innovation.
-
-Fortunately, this streak of pragmatism was bound to end. In the past few weeks, we've picketed Mozilla for supporting DRM and pilloried Red Hat for competing against OpenStack rivals. The community that once spent years counting the number of free software angels that were bumped off the [Open Core][1] pin is back to eating its own.
-
-And oh, how we missed it!
-
-### Red Hat Rewinds To 2003 ###
-
-Red Hat, arguably the poster child for open source idealism, has come under fire in the past week for—wait for it!—refusing to support its competitors. ReadWrite's Jodi Mardesich [does an excellent job uncovering][2] the accusations and Red Hat's labored defense, but ultimately, the real issue is this:
-
-Red Hat doesn't want to support competitors, and its OpenStack competitors don't like that much.
-
-In what other universe would this even be news?
-
-### Mozilla Becomes A Mudblood ###
-
-The problem for Red Hat is that it has such a strong track record of open source idealism that it's an easy target if it looks like it's coloring outside the lines. But Mozilla, if anything, offers an even bigger target.
-
-Mozilla, for its part, committed the cardinal sin of serving its users. The organization that recently went through a bout of self-immolation over its ousted CEO's politics has been called on the carpet for agreeing to embed DRM technology in the otherwise pure Firefox browser code so that its users can—gasp!—watch videos on the Web.
-
-No, really. People want to watch videos and Mozilla prefers they watch those videos in its browser. Stop the presses!
-
-Ever ready to make much of others' ideological failings, the Free Software Foundation [blasted Mozilla][3], expressing its "deep disappoint[ment]" in Mozilla because its "decision compromises important principles in order to alleviate misguided fears about loss of browser market share."
-
-After all, why should Mozilla bother with such silly things as, you know, actually being useful to customers?
-
-Not to be outdone in the moralizing department, the [Electronic Frontier Foundation tsktsk's the decision][4], lamenting that "the last holdout for the open web has fallen." It goes on to argue that Mozilla's capitulation "changes the industry by accepting DRM" because such "repeated compromises to the needs of DRM advocates by tech company after tech company [are] transforming [the personal computer industry] into a sector that is dominated by established interests and produces locked-down devices, monitored and managed by everyone but their users."
-
-Well, maybe. Or maybe, as Mozilla chair [Mitchell Baker explains][5] without such capitulation "Firefox users would need to use another browser every time they want to watch a controlled video, and that calls into question the usefulness of Firefox as a product."
-
-Um, yes.
-
-### A Return To Our Ideological Roots ###
-
-However much we may want to force others to live by our absolutist ideals, the reality is that others may have different priorities. As free software gave way to open source, its more pragmatic cousin, a fixed fetish on "the one true way" to license software, also withered.
-
-And yet, such ideological handwringing is useful, if not always convenient or pleasant. As much as I prefer the pragmatism of open source/Apache Software Foundation crowd, there's great benefit in the grating reminders of what's at stake from the more ideologically minded free software/GPL group. Software freedom actually does matter.
-
-As such, and despite my sarcastic tone above, I simultaneously dread and welcome a return to the constant self-flagellation of the free and open-source software communities. It makes open source less collaborative and more fractious, but it may also make it more powerful and relevant for decades to come.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://readwrite.com/2014/05/21/open-source-witch-hunt-mozilla-openstack-redhat#feed=/hack&awesm=~oEYDhxfP0Qv5hE
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_core
-[2]:http://readwrite.com/2014/05/16/red-hat-openstack-mirantis-rhel-support
-[3]:http://www.fsf.org/news/fsf-condemns-partnership-between-mozilla-and-adobe-to-support-digital-restrictions-management
-[4]:https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2014/05/mozilla-and-drm
-[5]:https://blog.mozilla.org/blog/2014/05/14/drm-and-the-challenge-of-serving-users/
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/03 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/03 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9e09fc8503
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/03 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+From left to right: Android 0.9’s home screen, add drawer, and shortcut deletion interfaces.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+### Android 0.9, Beta—hey, this looks familiar! ###
+
+Six months after Milestone 5, in August 2008, [Android 0.9 was released][1]. While the Android 0.5 milestone builds were "early looks," by now 1.0 was only two months away. Thus, Android 0.9 was labeled "beta." On the other side of the aisle, Apple already released its second version of the iPhone—the iPhone 3G—a month prior. The second-gen iPhone brought a second-gen iPhone OS. Apple also launched the App Store and was already taking app submissions. Google had a lot of catching up to do.
+
+Google threw out a lot of the UI introduced in Milestone 5. All the artwork was redone again in full-color, and the white square icon backgrounds were tossed. While still an emulator build, 0.9 offered something that looked familiar when compared to a released version of Android. Android 0.9 had a working desktop-style home screen, a proper app drawer, multiple home screens, a lot more apps, and fully functional (first-party only) widgets.
+
+Milestone 5 seemingly had no plan for someone installing more than 21 apps, but Android 0.9 had a vertically scrolling app drawer accessible via a gray tab at the bottom of the screen. Back then, the app drawer was actually a drawer. Besides acting as a button, the gray tab could be pulled up the screen and would follow your finger, just like how the notification panel can be pulled down. There were additional apps like Alarm Clock, Calculator, Music, Pictures, Messaging, and Camera.
+
+This was the first build with a fully customizable home screen. Long pressing on an app or widget allowed you to drag it around. You could drag an app out of the app drawer and make a home screen shortcut or long press on an existing home screen shortcut to move it.
+
+0.9 is a reminder that Google was not the design powerhouse it is today. In fact, some of the design work for Android was farmed out to other companies at the time. You can see one sign of this in the clock widget, which contains the text “MALMO," the home town of design firm [The Astonishing Tribe][2].
+
+
+The “Add to Home" dialog in Android 0.9.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+There were only three widgets: Clock, Picture frame, and Search. The Search widget didn't even have a proper icon in the list—it used the Picture icon. Perhaps the most interesting item here was a "Purchased pictures" option in the wallpaper choices—a leftover from the days when purchasing ringtones on a dumbphone was a common occurrence. Google was either planning on selling wallpapers, or it was already adding a carrier at some point. The company never went through with the plan.
+
+
+A collection of widgets, an open folder, renaming a folder, and the copy/paste menu.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The left screen, above, shows the widgets for Google Search and pictures. Search didn't do anything other than give you a box to type in—there was no auto complete or additional UI. Typing in the box and hitting "Go" would launch the browser. The bottom row of icons revealed a few options for "shortcuts" from the long press menu, which created icons that opened an app to a certain screen. Individual contacts, browser bookmarks, and music playlists were all shortcuts that could all be added to the home screen in 0.9.
+
+"Folders" was an option under the shortcuts heading despite not being a shortcut to anything. Once a blank folder was created, icons could be dragged into it and rearranged. Unlike today, there was no indication of what was in a folder; it was always a plain, white, empty-looking icon.
+
+0.9 was also the first Android version to have OS-level copy/paste support. Long pressing on any text box would bring up a dialog allowing you to save or recall text from the clipboard. iOS didn't support copy/paste until almost two years later, so for a while, this was one of Android's big differentiators—and the source of many Internet arguments.
+
+
+From left to right: Android 0.9’s new menu, recent apps, power options, and lock screen.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Android 0.9 was really starting to show its maturity. The home screen had a full set of menu items, including a settings option (although it didn't work yet) and a search button (because Google likes it when you search). The menu design was already in the final form that would last until Android 2.3 swapped it to black.
+
+Long pressing on the hardware home button brought up a 3x2 grid of recent apps, a design that would stick around until the release of Android 3.0. Recent Apps blurred the exposed background, but that was strangely applied here and not on other popups like the "Add to home" dialog or the home screen folder view. The power menu was at least included in the blurry background club, and it was redesigned with icons and more commonly accepted names for functions. The power menu icons lacked padding, though, appearing cramped and awkward.
+
+Android 0.9 featured a lock screen, albeit a very basic one. The black and gray lock screen had no on-screen method of unlocking—you needed to hit the hardware menu button.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/3/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2008/08/robotripping-hands-on-with-the-android-sdk-beta/
+[2]:http://www.tat.se/
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/04 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/04 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d6b2090654
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/04 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+Android 0.9 showing off a horizontal home screen—a feature that wouldn’t make it to later versions.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+While it's hard to separate emulator and OS functionality, Android 0.9 was the first version to show off horizontal support. Surprisingly, almost everything supported horizontal mode, and 0.9 even outperforms KitKat in some respects. In KitKat, the home screen and dialer are locked to portrait mode and cannot rotate. Here, though, horizontal support wasn't a problem for either app. (Anyone know how to upgrade a Nexus 5 from KitKat to 0.9?)
+
+This screenshot also shows off the new volume design used in 0.9. It dumped the old bell-style control that debuted in Milestone 3. It was a massive, screen-filling interface. Eventually, the redesign in Android 4.0 made it a bit smaller, but it remained an issue. (It's extremely annoying to not be able to see a video just because you want to bump up the volume.)
+
+
+The new notification panel, which ditched the application shortcut and added a top section.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+In just about every Android version, the notification panel gets tweaked, and 0.9 was no exception. The battery indicator was redrawn and changed to a darker shade of green, and the other status bar icons switched to black, white, and gray. The left area of the status bar was brilliantly repurposed to show the date when the panel was open.
+
+A new top section was added to the notification panel that would display the carrier name ("Android" in the case of the emulator) and a huge button labeled "Clear notifications," which allowed you to finally remove a notification without having to open it. The application button was canned and replaced with the time the notification arrived, and the "latest events" text was swapped out for a simpler "notifications." The empty parts of the panel were now gray instead of white, and the bottom gripper was redesigned. The pictures seem misaligned on the bottom, but that was because Milestone 5's notification panel had white space around the bottom of the panel. Android 0.9 goes all the way to the edge.
+
+
+The browsers of 0.9 and 0.5, showing the new, colorless menus.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The browser now loaded an actual website for the home page instead of the locally stored faux-Google of Milestone 5. The WebKit version rose up to 525.10, but it didn't seem to render the modern Google.com search button correctly. All throughout Android 0.9, the menu art from Milestone 5 was trashed and redrawn as gray icons. The difference between these screens is pretty significant, as all the color has been sucked out.
+
+The "more" list-style menu grew a little taller, and it was now just a plain list with no icons. Android 0.9 gained yet another search method, this time in the browser menu. Along with the home screen widget, home screen menu button, and browser homepage, that made four search boxes. Google never hid what its prime business was, even in its OS.
+
+
+From left to right: Android 0.9’s browser showing off the zoom controls, find-in-page interface, browser windows, and the settings.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Android 0.9 brought tons of browser improvements. The zoom controls were thankfully reworked from the crazy vertical controls to simpler plus and minus buttons. Google made the common-sense decision of moving the controls from the center of the screen to the bottom. In these zoom controls, the Android struggle with consistency became apparent. These appeared to be the only round buttons in the OS.
+
+0.9's new "find in page" feature could highlight words in the page. But overall, the UI was still very rough—the text box was much taller than it should be, and the "done" button with a checkbox was a one-of-a-kind icon for this screen. "Done" was basically a "close" button, which means it should probably have been a right-aligned "X" button.
+
+The main OS didn't have a settings screen in this build, but the browser finally had its own settings screen. It featured desktop-style options for pop ups, javascript, privacy and cookies, saved passwords and form data. There was even Google Gears integration (remember [Google Gears?][1]).
+
+
+The dialer and in-progress call screen with the menu open.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Dialer and Contacts in Android 0.9 were actually the same app—the two icons just opened different tabs. Attaching contacts to the dialer like this suggested the primary purpose of a smartphone contact was still for calls, not to text, e-mail, IM, or look up an address. Eventually Google would fully embrace alternative smartphone communications and split up contacts and dialer into separate apps.
+
+Most of the dialer weirdness in Milestone 5 was wiped out in Android 0.9. The "minimizing" tabs were replaced with a normal set of dark/light tabs. The speech bubble backspace button was changed to a normal backspace icon and integrated into the number display. The number buttons were changed to circles despite everything else in the OS being a rounded rectangle (at least the text was vertically aligned this time). The company also fixed the unbalanced "one," "star," and "pound" keys from Milestone 5.
+
+Tapping on the number display in Android 0.9 would start a call. This was important, as it was a big step in getting rid of the hardware "Call" and "End" keys on Android devices. The incoming call screen, on the other hand, went in the complete opposite direction and removed the on-screen “Answer" and “Decline" buttons present in Android 0.5. Google would spend the next few versions fumbling around between needing and not needing hardware call buttons on certain screens. With Android 2.0 and the Motorola Droid, though, call buttons were finally made optional.
+
+All of the options for the in-call screen were hidden under the menu button. Milestone 5 didn't support a proximity sensor, so it took the brute force route of disabling the touch screen during a call. 0.9 was developed for the G1, which had a proximity sensor. Finally, Google didn't have to kill the touch sensor during a call.
+
+
+The individual contacts screen and edit contacts screen for Android 0.9 and 0.5.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Milestone 5 had confusing labels for some contact information, like e-mail only being labeled "primary" instead of something like “primary e-mail." Android 0.9 corrected this with horizontal headers for each section. There were now action icons for each contact type on the left side, too.
+
+The edit contact screen was now a much busier place. There were delete buttons for every field, per-contact ringtones, an on-screen "more info" button for adding fields, a checkbox to send calls directly to voicemail, and "Save and "discard changes" buttons at the bottom of the list. Functionally, it was a big improvement over the old version, but it still looked very messy.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/4/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.tat.se/
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/05 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/05 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6cf77007e2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/05 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+The main alarm screen, setting an alarm, the calculator, and the calculator advanced functions screen.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Android 0.9 gave us the first look at the Alarm and Calculator apps. The alarm app featured a plain analog clock with a scrolling list of alarms on the bottom. Rather than some kind of on/off switch, alarms were set with a checkbox. Alarms could be set to repeat at certain days of the week, and there was a whole list of selectable, unique alarm sounds.
+
+The calculator was an all-black app with glossy, round buttons. Through the menu, it was possible to bring up an additional panel with advanced functions. Again consistency was not Google’s strong suit. The on-press highlight on the pi key was red—in the rest of Android 0.9, the on-press highlight was usually orange. In fact, everything used in the calculator was 100 percent custom artwork limited to only the calculator.
+
+
+Google Maps with the menu open and the new directions interface.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Google Maps actually worked in Android 0.9—the client could connect to the Google Maps server and pull down tiles. (For our images, remember that Google Maps is cloud based. Even the oldest of clients will still pull down modern map tiles, so ignore the actual map tiles pictured.) The Maps menu got the same all-gray treatment as the browser menu, and the zoom controls were the same as the browser too. The all-important "My Location" button finally arrived, meaning this version of Maps supported GPS location.
+
+The directions interface was revamped. The weird speech bubbles with misaligned plus buttons were swapped out for a more communicative bookmark icon, the swap field button moved to the left, and the go button was now labeled "Route."
+
+
+The Google Maps layers selector, search history, and the now-broken street view mode.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+"Layers" was renamed "Map Mode" and switched to a radio button list. Only one map type was available at a time—you couldn't see traffic on the satellite view, for instance. Buried in the menu was a hastily thrown together search history screen. History seemed like only a proof-of-concept, with giant, blurry search icons that rammed up against search terms on a transparent background.
+
+Street View used to be a separate app (although it was never made available to the public), but in 0.9 it was integrated into Google Maps as a Map Mode. You could drag the little pegman around, and it would display a popup bubble showing the thumbnail for Street View. Tapping on the thumbnail would launch Street View for that area. At the time, Street View showed nothing other than a scrollable 360 degree image—there was no UI on the interface at all.
+
+
+Our first look at the Google Maps search interface. These shots show the search bar, the results in a list, the results in a map, and a business page.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Android 0.9 also gave us our first look at the texting app, called "Messaging." Like many early Android designs, Messaging wasn't sure if it should be a dark app or a light app. The first visible screen was the message list, a stark black void of nothingness that looked like it was built on top of the settings interface. After tapping on “New Message" or one of the existing conversations, though, you were taken to a white and blue scrolling list of text messages. The two connected screens couldn’t be more different.
+
+
+The SMS app’s chat window, attachment screen, chat list, and setting.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Messaging supported a range of attachments: you could tack on pictures, audio, or a slideshow to your message. Pictures and audio could be recorded on the fly or pulled from phone storage. Another odd UI choice was that Android already had an established icon for almost everything in the attach menu, but Messaging used all-custom art instead.
+
+Messaging was one of the first apps to have its own settings screen. Users could request read and delivery reports and set download preferences.
+
+
+The slideshow creator. The right picture shows the menu options.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The "slideshow" option in attachments would actually launch a fully featured slideshow creator. You could add pictures, choose the slide order, add music, change the duration of each slide, and add text. This was complicated enough to have its own app icon, but amazingly it was buried in the menu of the SMS app. This was one of the few Android apps that was completely unusable in portrait mode—the only way to see the picture and the controls was in landscape. Strangely, it would still rotate to portrait, but the layout just became a train wreck.
+
+
+The Music player’s main navigation page, song list, album list, and “now playing" screen.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Android 0.9 was the first to bring a music app to Android. The primary screen was mostly just four big, chunky navigation buttons that would take you to each music view. At the bottom of the app was a "now playing" bar that only contained the track name, artist, and a play/pause button. The song list had only a bare minimum interface, only showing the song name, artist, album and runtime. Album art was the only hope of seeing any color in this app. It was displayed as a tiny thumbnail in the album view and as a big, quarter-screen image in the Now Playing view.
+
+Like most parts of Android in this era, the interface may not have been much to look at, but the features were there. The Now Playing screen had a button for a playlist queue that allowed you to drag songs around, shuffle, repeat, search, and choose background audio.
+
+
+The “Pictures" all album view, individual album view, and a single picture view.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The photo gallery was simply called "Pictures." The initial view showed all your albums. The two default ones were "Camera" and a large unified album called "All pictures." The thumbnail for each album was made up of a 2x2 grid of pictures, and every picture got a thick, white frame.
+
+The individual album view was about what you would expect: a scrolling grid of pictures. You couldn't swipe through individual pictures—large left and right arrows flanking the individual picture had to be tapped on to move through an album. There was no pinch-zoom either; you had to zoom in and out with buttons.
+
+
+Picture editing! These screenshots show an open menu, the “more" menu, cropping, and the settings.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+"Pictures" looked simple until you hit the menu button and suddenly accessed a myriad of options. Pictures could be cropped, rotated, deleted, or set as a wallpaper or contact icon. Like the browser, all of this was accomplished through a clumsy double-menu system. But again, why do two related menus look completely different?
+
+Android 0.9 came out a mere two months before the first commercial release of Android. That was just enough time for app developers to make sure their apps worked—and for Google to do some testing and bug squashing before the big release.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/5/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/06 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/06 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..72b753a658
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/06 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+The T-Mobile G1
+Photo by T-Mobile
+
+### Android 1.0—introducing Google Apps and actual hardware ###
+
+By October 2008, Android 1.0 was ready for launch, and the OS debuted on the [T-Mobile G1][1] (AKA the HTC Dream). The G1 was released into a market dominated by the iPhone 3G and the [Nokia 1680 classic][2]. (Both of those phones went on to tie for the [best selling phone][3] of 2008, selling 35 million units each.) Hard numbers of G1 sales are tough to come by, but T-Mobile announced the device broke the one million units sold barrier in April 2009. It was way behind the competition by any measure.
+
+The G1 was packing a single-core 528Mhz ARM 11 processor, an Adreno 130 GPU, 192MB of RAM, and a whopping 256MB of storage for the OS and Apps. It had a 3.2-inch, 320x480 display, which was mounted to a sliding mechanism that revealed a full hardware keyboard. So while Android software has certainly come a long way, the hardware has, too. Today, we can get much better specs than this in a watch form factor: the latest [Samsung smart watch][4] has 512MB of RAM and a 1GHz dual-core processor.
+
+While the iPhone had a minimal amount of buttons, the G1 was the complete opposite, sporting almost every hardware control that was ever invented. It had call and end call buttons, home, back, and menu buttons, a shutter button for the camera, a volume rocker, a trackball, and, of course, about 50 keyboard buttons. Future Android devices would slowly back away from thousand-button interfaces, with nearly every new flagship lessening the number of buttons.
+
+But for the first time, people saw Android running on actual hardware instead of a frustratingly slow emulator. Android 1.0 didn't have the smoothness, flare, or press coverage of the iPhone. It wasn't as capable as Windows Mobile 6.5. Still, it was a good start.
+
+
+The default app selection of Android 1.0 and 0.9.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The core of Android 1.0 didn't look significantly different from the beta version released two months earlier, but the consumer product brought a ton more apps, including the full suite of Google apps. Calendar, Email, Gmail, IM, Market, Settings, Voice Dialer, and YouTube were all new. At the time, music was the dominant media type on smartphones, the king of which was the iTunes music store. Google didn't have an in-house music service of its own, so it tapped Amazon and bundled the Amazon MP3 store.
+
+The most important addition to Android 1.0 was the debut of Google's store, called "Android Market Beta." While most companies were content with calling their app catalog some variant of "app store"—meaning a store that sold apps and only apps—Google had much wider ambitions. It went with the much more general name of "Android Market." The idea was that the Android Market would not just house apps, but everything you needed for your Android device.
+
+
+The first Android Market client. Screenshots show the main page, “my downloads," an app page, and an app permissions page.
+Photo by [Google][5]
+
+At the time, the Android Market only offered apps and games, and developers weren't even able to charge for them. Apple's App Store had a four-month head start on the Android Market, but Google's big differentiator was that Android's store was almost completely open. On the iPhone, apps were subject to review by Apple and had to meet design and technical guidelines. Potential apps also weren't allowed to duplicate the stock functionality. On the Android Market, developers were free to do whatever they wanted, including replacing the stock apps. The lack of control would turn out to be a blessing and a curse. It allowed developers to innovate on the existing functionality, but it also meant even the trashiest applications were allowed in.
+
+Today, this client is another app that can no longer communicate with Google's servers. Luckily, it's one of the few early Android apps [actually documented][6] on the Internet. The main screen provided links to the common areas like Apps, Games, Search, and Downloads, and the top section had horizontally scrolling icons for featured apps. Search results and the "My Downloads" page displayed apps in a scrolling list, showing the name, developers, cost (at this point, always free), and rating. Individual app pages showed a brief description, install count, comments and ratings from users, and the all-important install button. This early Android Market didn’t support pictures, and the only field for developers was a description box with a 500-character limit. This made things like maintaining a changelog very difficult, as the only spot to put it was in the description.
+
+Right out of the gate, the Android Market showed permissions that an app required before installing. This is something Apple wouldn't get around to implementing until 2012, after an iOS app was caught [uploading entire address books][7] to the cloud without the user's knowledge. The permissions display gave a full rundown of what permissions an app was using, although this version railroaded users into agreeing. There was an “OK" button, but no way to cancel other than the back button.
+
+
+Gmail showing the inbox, the inbox with the menu open.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The next most important app was probably Gmail. Most of the base functionality was here already. Unviewed messages showed up in bold, and labels displayed as colored tags. Individual messages in the Inbox showed the subject, author(s), and number of replies in a conversation. The trademark Gmail star was here—a quick tap would star or unstar something. As usual for early versions of Android, the Menu housed all the buttons on the main inbox view. Once inside a message, though, things got a little more modern, with "reply" and "forward" buttons as permanent fixtures at the bottom of the screen. Individual replies could be expanded and collapsed just by tapping on them.
+
+The rounded corners, shadows, and bubbly icons gave the whole app a "cartoonish" look, but it was a good start. Android's function-first philosophy was really coming through here: Gmail supported labels, threaded messaging, searching, and push e-mail.
+
+
+Gmail’s label view, compose screen, and settings on Android 1.0.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+But if you thought Gmail was ugly, the Email app took it to another level. There was no separate inbox or folder view—everything was mashed into a single screen. The app presented you with a list of folders and tapping on one would expand the contents in-line. Unread messages were denoted with a green line on the left, and that was about it for the e-mail interface. The app supported IMAP and POP3 but not Exchange.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/6/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2008/10/android-g1-review/
+[2]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nokia_1680_classic
+[3]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_best-selling_mobile_phones#2008
+[4]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/04/review-we-wear-samsungs-galaxy-gear-and-galaxy-fit-so-you-dont-have-to/
+[5]:http://android-developers.blogspot.com/2008/08/android-market-user-driven-content.html
+[6]:http://android-developers.blogspot.com/2008/08/android-market-user-driven-content.html
+[7]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2012/02/path-addresses-privacy-controversy-but-social-apps-remain-a-risk-to-users/
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/07 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/07 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2be62866ad
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/07 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+Both screens of the Email app. The first two screenshots show the combined label/inbox view, and the last shows a message.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The message view was—surprise!—white. Android's e-mail app has historically been a watered-down version of the Gmail app, and you can see that close connection here. The message and compose views were taken directly from Gmail with almost no modifications.
+
+
+The “IM" applications. Screenshots show the short-lived provider selection screen, the friends list, and a chat.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Before Google Hangouts and even before Google Talk, there was "IM"—the only instant messaging client that shipped on Android 1.0. Surprisingly, multiple IM services were supported: users could pick from AIM, Google Talk, Windows Live Messenger, and Yahoo. Remember when OS creators cared about interoperability?
+
+The friends list was a black background with white speech bubbles for open chats. Presence was indicated with colored circles, and a little Android on the right hand side would indicate that a person was mobile. It's amazing how much more communicative the IM app was than Google Hangouts. Green means the person is using a device they are signed into, yellow means they are signed in but idle, red means they have manually set busy and don't want to be bothered, and gray is offline. Today, Hangouts only shows when a user has the app open or closed.
+
+The chats interface was clearly based on the Messaging program, and the chat backgrounds were changed from white and blue to white and green. No one changed the color of the blue text entry box, though, so along with the orange highlight effect, this screen used white, green, blue, and orange.
+
+
+YouTube on Android 1.0. The screens show the main page, the main page with the menu open, the categories screen, and the videos screen.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+YouTube might not have been the mobile sensation it is today with the 320p screen and 3G data speeds of the G1, but Google's video service was present and accounted for on Android 1.0. The main screen looked like a tweaked version of the Android Market, with a horizontally scrolling featured section along the top and vertically scrolling categories along the bottom. Some of Google's category choices were pretty strange: what would the difference be between "Most popular" and "Most viewed?"
+
+In a sign that Google had no idea how big YouTube would eventually become, one of the video categories was "Most recent." Today, with [100 hours of video][1] uploaded to the site every minute, if this section actually worked it would be an unreadable blur of rapidly scrolling videos.
+
+The menu housed search, favorites, categories, and settings. Settings (not pictured) was the lamest screen ever, housing one option to clear the search history. Categories was equally barren, showing only a black list of text.
+
+The last screen shows a video, which only supported horizontal mode. The auto-hiding video controls weirdly had rewind and fast forward buttons, even though there was a seek bar.
+
+
+YouTube’s video menu, description page, and comments.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Additional sections for each video could be brought up by hitting the menu button. Here you could favorite the video, access details, and read comments. All of these screens, like the videos, were locked to horizontal mode.
+
+"Share" didn't bring up a share dialog yet; it just kicked the link out to a Gmail message. Texting or IMing someone a link wasn't possible. Comments could be read, but you couldn't rate them or post your own. You couldn't rate or like a video either.
+
+
+The camera app’s picture taking interface, menu, and photo review mode.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Real Android on real hardware meant a functional camera app, even if there wasn't much to look at. That black square on the left was the camera interface, which should be showing a viewfinder image, but the SDK screenshot utility can't capture it. The G1 had a hardware camera button (remember those?), so there wasn't a need for an on-screen shutter button. There were no settings for exposure, white balance, or HDR—you could take a picture and that was about it.
+
+The menu button revealed a meager two options: a way to jump to the Pictures app and Settings screen with two options. The first settings option was whether or not to enable geotagging for pictures, and the second was for a dialog prompt after every capture, which you can see on the right. Also, you could only take pictures—there was no video support yet.
+
+
+The Calendar’s month view, week view with the menu open, day view, and agenda.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Like most apps of this era, the primary command interface for the calendar was the menu. It was used to switch views, add a new event, navigate to the current day, pick visible calendars, and go to the settings. The menu functioned as a catch-all for every single button.
+
+The month view couldn't show appointment text. Every date had a bar next to it, and appointments were displayed as green sections in the bar denoting what time of day an appointment was. Week view couldn't show text either—the 320×480 display of the G1 just wasn't dense enough—so you got a white block with a strip of color indicating which calendar it was from. The only views that provided text were the agenda and day views. You could move through dates by swiping—week and day used left and right, and month and agenda used up and down.
+
+
+The main settings page, the Wireless section, and the bottom of the about page.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Android 1.0 finally brought a settings screen to the party. It was a black and white wall of text that was roughly broken down into sections. Down arrows next to each list item confusingly look like they would expand line-in to show more of something, but touching anywhere on the list item would just load the next screen. All the screens were pretty boring and samey looking, but hey, it's a settings screen.
+
+Any option with an on/off state used a cartoony-looking checkbox. The original checkboxes in Android 1.0 were pretty strange—even when they were "unchecked," they still had a gray check mark in them. Android treated the check mark like a light bulb that would light up when on and be dim when off, but that's not how checkboxes work. We did finally get an "About" page, though. Android 1.0 ran Linux kernel 2.6.25.
+
+A settings screen means we can finally open the security settings and change lock screens. Android 1.0 only had two styles, the gray square lock screen pictured in the Android 0.9 section, and pattern unlock, which required you to draw a pattern over a grid of 9 dots. A swipe pattern like this was easier to remember and input than a PIN even if it did not add any more security.
+
+
+The Voice Dialer, pattern lock screen, low battery warning, and time picker.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+oice functions arrived in 1.0 with Voice Dialer. This feature hung around in various capacities in AOSP for a while, as it was a simple voice command app for calling numbers and contacts. Voice Dialer was completely unrelated to Google's future voice products, however, and it worked the same way a voice dialer on a dumbphone would work.
+
+As for a final note, low battery popup would occur when the battery dropped below 15 percent. It was a funny graphic, depicting plugging the wrong end of the power cord into the phone. That wasn't (and still isn't) how phones work, Google.
+
+Android 1.0 was a great first start, but there were still so many gaps in functionality. Physical keyboards and tons of hardware buttons were mandatory, as Android devices were still not allowed to be sold without a d-pad or trackball. Base smartphone functionality like auto-rotate wasn't here yet, either. Updates for built-in apps weren't possible through the Android Market the way they were today. All the Google Apps were interwoven with the operating system. If Google wanted to update a single app, an update for the entire operating system needed to be pushed out through the carriers. There was still a lot of work to do.
+
+### Android 1.1—the first truly incremental update ###
+
+
+All of Android 1.1’s new features: Search by voice, the Android Market showing paid app support, Google Latitude, and the new “system updates" option in the settings.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Four and a half months after Android 1.0, in February 2009, Android got its first public update in Android 1.1. Not much changed in the OS, and just about every new thing Google added with 1.1 has been shut down by now. Google Voice Search was Android's first foray into cloud-powered voice search, and it had its own icon in the app drawer. While the app can't communicate with Google's servers anymore, you can check out how it used to work [on the iPhone][2]. It wasn't yet Voice Actions, but you could speak and the results would go to a simple Google Search.
+
+Support for paid apps was added to the Android Market, but just like the beta client, this version of the Android Market could no longer connect to the Google Play servers. The most that we could get to work was this sorting screen, which lets you pick between displaying free apps, paid apps, or a mix of both.
+
+Maps added [Google Latitude][3], a way to share your location with friends. Latitude was shut down in favor of Google+ a few months ago and no longer works. There was an option for it in the Maps menu, but tapping on it just brings up a loading spinner forever.
+
+Given that system updates come quickly in the Android world—or at least, that was the plan before carriers and OEMs got in the way—Google also added a button to the "About Phone" screen to check for system updates.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/7/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.youtube.com/yt/press/statistics.html
+[2]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y3z7Tw1K17A
+[3]:http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2009/02/google-tries-location-based-social-networking-with-latitude/
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/08 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/08 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3bd0c3a8c5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/08 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+Android 1.5’s on-screen keyboard showing the suggestion bar while typing, the capital letters keyboard, the number and symbols screen, and an additional key popup.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+### Android 1.5, Cupcake—a virtual keyboard opens up device design ###
+
+In April 2009, almost three months after the release of 1.1, Android 1.5 was released. It was the first Android version to have a public, marketed code name: Cupcake. From here on out, Android releases would have alphabetical, snack-themed names.
+
+The most important Cupcake addition was easily the on-screen keyboard. For the first time, it was possible for OEMs to build a slate-style Android device without a thousand hardware keyboard keys and a complicated slide mechanism.
+
+Android's key labels could switch between uppercase and lowercase, depending on if caps lock was on or not. While it was off by default, there was an option to turn on the suggestion bar, which appeared along the top edge of the keyboard. Keys with ellipses in the popup, like the "u," above, could be held down to input [diacritical marks][1], which would display in a popup. The keyboard could switch to numbers and alternate characters, and long pressing on the period key would bring up even more punctuation.
+
+
+Composite images of the app lineup in 1.5 and 1.1 and the notification panels from each version.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+New icons were added for the new "Camcorder" functionality, and Google Talk was broken out from IM into its own separate app. The Amazon MP3 and Browser icons were redesigned, too. The Amazon MP3 icon was changed primarily because Amazon was planning on launching other Android apps soon, and the "A" icon was far too generic. The browser icon was easily the worst in Android 1.1, so it was changed and no longer resembled a desktop OS dialog box. The last app drawer change was to "Pictures," which was renamed to "Gallery."
+
+The notification panel was redesigned again as well. The panel background got a weave texture, and the gradients on notifications were smoothed out. Android 1.5 had a lot of little design changes to core OS pieces that affected all apps. On the "Clear notifications" button, you could see the new system-wide button style, which had a gradient, a thinner outline, and less shadowing than the old version.
+
+
+The “Add to Home" dialog boxes in 1.5 and 1.1.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Third-party widgets were another headline feature of Cupcake, and they still remain one of Android's defining features. Developers could bundle a home screen widget along with their apps that would either control or display information from that app. Google showed off a few new widgets of its own, too, with the Calendar and Music apps.
+
+
+Left: a screenshot of the calendar widget, music widget, and a row of live folders. Center: the folder list. Right: an open view of the “contacts with phone numbers" live folder.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+On the left screenshot, above, you can see the new Calendar and Music icons. The Calendar widget could only show a single event for the day, and tapping it would open the calendar. It wouldn't let you choose what calendars to display, and widgets weren't resizable—it only ever looked like this. The music widget was blue—despite the music app not having a drop of blue in it—and showed the song and artist name, along with play and next buttons.
+
+Also in the left shot, the first three folders on the bottom row were a new feature called "Live Folders." These were accessible under the new top-level "Folders" section in the "Add to Home" menu, which you can see in the center picture. Live Folders showed the content of an application without having to open that application. The ones that came with Cupcake were all contacts-related, showing all of the user's contacts, contacts with phone numbers, or starred contacts.
+
+Rather than icons, Live Folders used a simple list view that popped up over the home screen. Contacts were just for starters, Live Folders was a whole API that developers could use. Google demoed a folder of books from the Google Books app, and it was possible to have an RSS feed or top stories from a website as a live folder. Live folders were one of the few Android ideas that didn't work out, and the feature was shut down in Honeycomb.
+
+
+The camcorder and camera UI, with on-screen shutter buttons.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+If you couldn't tell from the new "Camcorder" icon, video recording was added to Android in 1.5. The two icons, camera and camcorder, were actually the same app, and you could jump between the two of them with an option in the menu labeled "Switch to camera" and "Switch to camcorder." Video quality on the T-Mobile G1 was not that great. A test video on "High" quality output; a .3GP video file with a resolution of 352 x 288 and a lagtastic frame rate of 4 FPS.
+
+Along with the new video feature, the Camera app saw a few much-needed UI tweaks. A thumbnail in the top left showed the last picture that was taken, and tapping on it would jump to the camera roll in the Gallery. The circle icon on the top right of both screens was an on-screen shutter button, meaning that, post 1.5, Android devices no longer required a hardware camera button.
+
+This interface was actually much closer to the Android 4.2 design than many of the subsequent camera apps. While later designs would add silly leather textures and more controls to the camera, Android went back to basics with later designs, and that 4.2 redesign shares a lot in common with this. What was a primitive layout in Android 1.5 became a minimal, full-screen viewfinder in Android 4.2.
+
+
+Google Talk running in the Google Talk app versus Google Talk running in the IM app.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Android 1.0's IM app was used for Google Talk functionality, but in Android 1.5, Google Talk was broken off into its own app. Support for it in the IM app was removed. Google Talk (above, left) was clearly based on the IM app (above, right), but as soon as the stand alone app was released in 1.5, work on the IM app was abandoned.
+
+The new Google Talk app had a redesigned status bar, presence lights on the right side, and a redesigned mobile icon, which was a gray monogram of the bugdroid. The blue compose bar switched to a more sensible gray in the chat view, and the message backgrounds changed from light green and white to light green and green. With a stand alone app, Google could add Gtalk-only features like chatting "off the record," which would stop Gmail from saving a copy of every chat.
+
+
+The calendar in Android 1.5 got a lot lighter.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The calendar dumped the ugly white squares on a black background and changed to an all-light app. The background of everything became white, and day-of-the-week headers were changed to blue. The individual appointment blocks switched from a small color strip to entirely colored, and the text changed to white. This will be the last time the calendar is touched for a long time.
+
+
+From left to right: the browser’s new controls, the zoomed-out magnifying view, and highlighting text for copy/pasting.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Android 1.5 changed the zoom controls system-wide. Instead of two big circles, the zoom controls became two halves of a rectangle with rounded corners. These new controls applied to the browser, Google Maps, and the gallery.
+
+The browser had lots of work done on the zoom functionality. After zooming in or out, the "1x" button would return you to the standard zoom level. The button in the bottom right corner would zoom all the way out of the page and display a magnifying rectangle over the page, which you can see in the center image. Grabbing the rectangle and releasing it would zoom that part of the page to a "1x" view. Android didn't have acceleratable scrolling, which made the max scrolling speed pretty slow—this was Google's solution for navigating a long webpage.
+
+Another addition to the browser was the ability to copy text on a webpage—previously you could only copy text from an input box. Selecting "copy text" from the menu would activate highlight mode, and dragging your finger over text in a Web page would highlight it. The G1’s trackball was very handy for super-precise movement like this and could control the mouse cursor. There were no draggable handles, and as soon as you lifted your finger off the screen, Android would copy the text and remove the highlight, so you had to be ridiculously precise to get any use out of the copy feature.
+
+The browser in Android 1.5 would crash a lot—much more than in previous versions. Just viewing Ars Technica in desktop mode would crash the browser, as did many other sites.
+
+
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The default lock screen and pattern lock screen both changed their empty, black backgrounds to the same wallpaper as the home screen.
+
+The lighter background on the pattern unlock screen revealed the sloppy job Google did on the alignment of the circles. The white circles were nowhere near centered inside the black circles—basic alignment issues like this continued to be a frequent problem for Android in these early days.
+
+
+The YouTube uploader, contacts thumbnails, the auto rotate setting, and the new music design.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+
+The HTC Magic, the second Android device, and the first without a hardware keyboard.
+Photo by HTC
+
+> #### Google Maps is the first built-in app to hit the Android Market ####
+>
+> While this article is (mostly) organizing app updates by Android version for simplicity's sake, there are a few outliers that deserve special recognition. On June 14, 2009, Google Maps was the first packed-in Android app to be updated via the Android Market. While every other app required a full system release to be updated, Maps was broken out of the OS, free to receive out-of-cycle updates whenever a new feature was ready.
+>
+> Moving apps out of the core OS and onto the Android Market would be a big focus for Google going forward. In general, OTA updates were a big initiative—they required the cooperation of the OEM and the carrier, both of which could drag their feet. Updates also didn’t make it to every device. Today, the Android Market gives Google a direct line to every Android phone with no such interference from outside parties.
+>
+> These were problems for a later date, though. In 2009, Google had only two unskinned phones to support, and the early Android carriers were seemingly responsive to Google’s update needs. This early move would prove to be a very proactive decision on Google’s part. At first, the company went this route only with its most important properties—Maps and Gmail—but later it would port the majority of the packed-in apps to the Android Market. Later initiatives like Google Play Services even brought app APIs out of the OS and into Google’s store.
+>
+> As for the new Maps at the time, it gained a new directions interface, along with the ability to give mass transit and walking directions. For now, directions were given on a plain black list—turn-by-turn-style navigation would come later.
+>
+> June 2009 was also the time Apple launched the third iPhone—the 3GS—and the third version of iPhone OS. iPhone OS 3's headline features were mostly catch-up items like copy/paste and MMS support. Apple's hardware was still nicer, and the software was smoother, more cohesive, and better designed. Google's insane pace of development was putting it on a path to parity though. iPhone OS 2 launched just before the Milestone 5 build of Android 0.5, which makes five Android releases in the span of the yearly iOS release cycle.
+
+Android 1.5 gave the YouTube app the ability to upload videos to the site. Uploading was accomplished by sharing a video from the Gallery to the YouTube app, or by opening a video directly from the YouTube app. This would bring up an upload screen, where the user would set things like the video title, tags, and access rights. Photos could be uploaded to Picasa, Google's original photo site, in a similar fashion.
+
+There were little tweaks all over the OS. Favorite contacts now showed a picture in the contacts list (although regular contacts were still pictureless). The third picture shows the new auto-rotate option in the settings—this was also the first version to support automatically switching orientations based on readings from the devices’ internal sensors.
+
+Cupcake did a great job of improving Android, particularly in terms of hardware options. The on-screen keyboard meant a hardware keyboard was no longer necessary. Auto rotate brought the OS a little closer to the iPhone, and an on-screen camera shutter button meant that hardware camera buttons were now optional, too. Shortly after the release of 1.5, a second Android device came out that would show the future direction of the platform: the HTC Magic. The Magic (right) didn’t have a hardware keyboard or a camera button. It was a solid, slider-less slate device that relied on Android’s on-screen buttons to get the job done.
+
+Android flagships started with the most buttons possible—a hardware qwerty phone—and slowly began whittling the button count down over time. While the Magic was a big step, eliminating an entire keyboard and a camera button, it still used start and end call buttons, four system buttons, and a trackball.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/8/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diacritic
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/09 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/09 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c629e9cc75
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/09 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+The new Android Market—less black, more white and green.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+### Android 1.6, Donut—CDMA support brings Android to any carrier ###
+
+The fourth version of Android—1.6, Donut—launched in September 2009, five months after Cupcake hit the market. Despite the myriad of updates, Google was still adding basic functionality to Android. Donut brought support for different screen sizes, CDMA support, and a text-to-speech engine.
+
+Android 1.6 is a great example of an update that, today, would have little reason to exist as a separate point update. The major improvements basically boiled down to new versions of the Android Market, camera, and YouTube. In the years since, apps like this have been broken out of the OS and can be updated by Google at any time. Before all this modularization work, though, even seemingly minor app updates like this required a full OS update.
+
+The other big improvement—CDMA support—demonstrated that, despite the version number, Google was still busy getting basic functionality into Android.
+
+The Android Market was christened as version "1.6" and got a complete overhaul. The original all-black design was tossed in favor of a white app with green highlights—the Android designers were clearly using the Android mascot for inspiration.
+
+The new market was definitely a new style of app design for Google. The top fifth of the screen was dedicated to a banner logo announcing that this app is indeed the “Android Market." Below the banner were buttons for Apps, Games, and Downloads, and a search button was placed to the right of the banner. Below the navigation was a thumbnail display of featured apps, which could be swiped through. Below that were even more featured apps in a vertically scrolling list.
+
+
+The new Market design, showing an app page with screenshots, the apps categories page, an app top list, and the downloads section.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The biggest addition to the market was the inclusion of app screenshots. Android users could finally see what an app looked like before installing it—previously they only had a brief description and user reviews to go on. Your personal star review and comment was given top billing, followed by the description, and then finally the screenshots. Viewing the screenshots would often require a bit of scrolling—if you were looking for a well-designed app, it was a lot of work.
+
+Tapping on App or Games would bring up a category list, which you can see in the second picture, above. After picking a category, more navigation was shown at the top of the screen, where users could see "Top paid," "Top free," or "Just in" apps within a category. While these sorta looked like buttons that would load a new screen, they were really just a clunky tabbed interface. To denote which "tab" was currently active, there were little green lights next to each button. The nicest part of this interface was that the list of apps would scroll infinitely—once you hit the bottom, more apps would load in. This made it easy to look through the list of apps, but opening any app and coming back would lose your spot in the list—you’d be kicked to the top. The downloads section would do something the new Google Play Store still can't do: simply display a list of your purchased apps.
+
+While the new Market definitely looked better than the old market, cohesion across apps was getting worse and worse. It seemed like each app was made by a different group with no communication about how all Android apps should look.
+
+
+The Camera viewfinder, photo review screen, and menu.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+For instance, the camera app was changed from a full-screen, minimal design to a boxed viewfinder with controls on the side. With the new camera app, Google tried its hand at skeuomorphism, wrapping the whole app in a leather texture roughly replicating the exterior of a classic camera. Switching between the camera and camcorder was done with a literal switch, and below that was the on-screen shutter button.
+
+Tapping on the previous picture thumbnail no longer launched the gallery, but a custom image viewer that was built in to the camera app. When viewing a picture the leather control area changed the camera controls to picture controls, where you could delete, share a picture, or set the picture as a wallpaper or contact image. There was still no swiping between pictures—that was still done with arrows on either side of the image.
+
+This second picture shows one of the first examples of designers reducing dependence on the menu button, which the Android team slowly started to realize functioned terribly for discoverability. Many app designers (including those within Google) used the menu as a dumping ground for all sorts of controls and navigational elements. Most users didn't think to hit the menu button, though, and never saw the commands.
+
+A common theme for future versions of Android would be moving things out of the menu and on to the main screen, making the whole OS more user-friendly. The menu button was completely killed in Android 4.0, and it's only supported in Android for legacy apps.
+
+
+The battery and TTS settings.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Donut was the first Android version to keep track of battery usage. Buried in the "About phone" menu was an option called "Battery use," which would display battery usage by app and hardware function as a percentage. Tapping on an item would bring up a separate page with relevant stats. Hardware items had buttons to jump directly to their settings, so for instance, you could change the display timeout if you felt the display battery usage was too high.
+
+Android 1.6 was also the first version to support text-to-speech (TTS) engines, meaning the OS and apps would be able to talk back to you in a robot voice. The “Speech synthesizer controls" would allow you to set the language, choose the speech rate, and (critically) install the voice data from the Android market. Today, Google has its own TTS engine that ships with Android, but it seems Donut was hard coded to accept one specific TTS engine made by SVOX. But SVOX’s engine didn’t ship with Donut, so tapping on “install voice data" linked to an app in the Android Market. (In the years since Donut’s heyday, the app has been taken down. It seems Android 1.6 will never speak again.)
+
+
+From left to right: new widgets, the search bar UI, the new notification clear button, and the new gallery controls.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+There was more work on the widget front. Donut brought an entirely new widget called "Power control." This comprised on/off switches for common power-hungry features: Wi-FI, Bluetooth, GPS, Sync (to Google's servers), and brightness.
+
+The search widget was redesigned to be much slimmer looking, and it had an embedded microphone button for voice search. It now had some actual UI to it and did find-as-you-type live searching, which searched not only the Internet, but your applications and history too.
+
+The "Clear notifications" button has shrunk down considerably and lost the "notifications" text. In later Android versions it would be reduced to just a square button. The Gallery continues the trend of taking functionality out of the menu and putting it in front of the user—the individual picture view gained buttons for "Set as," "Share," and "Delete."
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/9/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/10 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/10 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f01a0a0f7f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/10 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+注:youtube视频地址
+
+
+### Android 2.0, Éclair—blowing up the GPS industry ###
+
+Forty-one days—that was how much time passed between Android 1.6 and 2.0. The first big version number bump for Android launched in October 2009 [on the Motorola Droid][1], the first "second generation" Android device. The Droid offered huge hardware upgrades over the G1, starting with the massive (at the time) 3.7 inch, 854×480 LCD. It brought a lot more power, too: a (still single-core) 600Mhz TI OMAP Cortex A8 with 256MB of RAM.
+
+
+The Motorola Droid stares into your soul.
+
+The most important part of the Droid, though, was the large advertising campaign around it. The Droid was the flagship device for Verizon Wireless in the US, and with that title came a ton of ad money from America's biggest carrier. Verizon licensed the word "droid" from Lucasfilm and started up the ["Droid Does" campaign][2]—a shouty, explosion-filled set of commercials that positioned the device (and by extension, Android) as the violent, ass-kicking alternative to the iPhone. The press frequently declared the T-Mobile G1 as trying to be an “iPhone Killer," but the Droid came out and owned it.
+
+Like the G1, the Droid had a hardware keyboard that slid out from the side of the phone. The trackball was gone, but some kind of d-pad was still mandatory, so Motorola placed a five-way d-pad on the right side of the keyboard. On the front, the Droid switched from hardware buttons to capacitive touch buttons, which were just paint on the glass touchscreen. Android 2.0 also finally allowed devices to do away with the “Call" and “End" buttons. So together with the demotion of the d-pad to the keyboard tray, the front buttons could all fit in a nice, neat strip. The result of all this streamlining was the best-looking Android device yet. The T-Mobile G1 looked like a Fisher-Price toy, but the Motorola Droid looked like an industrial tool that you could cut someone with.
+
+
+The lock and home screens from 2.0 and 1.6.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Some of Verizon's grungy ad campaign leaked over to the software, where the default wallpaper was changed from a calm, watery vista to a picture of dirty concrete. The boot animation used a pulsing, red, Hal 9000 eyeball and the default notification tone shouted "[DRRRRROOOOIIIIDDDD][3]" every time you received an e-mail. Éclair was Android’s angsty teenager phase.
+
+One of the first things Android 2.0 presented to the user was a new lock screen. Slide-to-unlock was patented by Apple, so Google went with a rotary-phone-inspired arc unlock gesture. Putting your finger on the lock icon and sliding right would unlock the device, and sliding left from the volume icon would silence the phone. A thumb naturally moves in an arc, so this felt like an even more natural gesture than sliding in a straight line.
+
+The default homescreen layout scrapped the redundant analog clock widget and introduced what is now an Android staple: a search bar at the top of the home screen. SMS Messaging and the Android Market were also given top billing in the new layout. The app drawer tab was given a sharp redesign, too.
+
+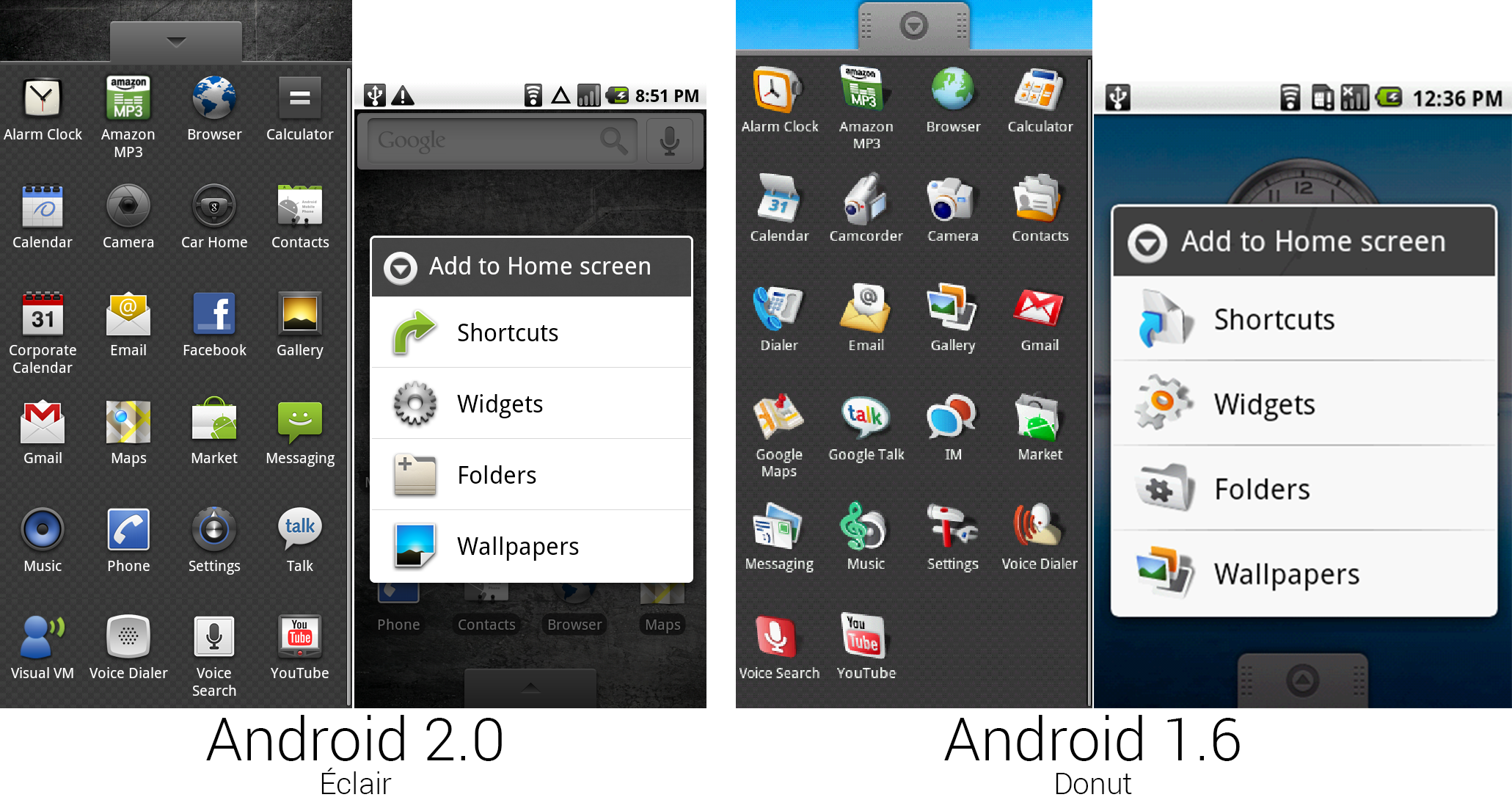
+The app drawers and pictures of the “Add to Home" menus.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Android was developed at such a breakneck pace in the early days that the Android Team could never really plan for future devices when making interface art. The Motorola Droid—with its 854×480 LCD—was a huge bump up in resolution over the 320×480 G1-era devices. Nearly everything needed to be redrawn. Starting from scratch with interface art would pretty much be the main theme of Android 2.0.
+
+Google took this opportunity to redesign almost every icon in Android, going from a cartoony look with an isometric perspective to straight-on icons done in a more serious style. The only set of icons that weren't redrawn were the status bar icons, which now look very out of place compared to the rest of the OS. These icons would hang around from Android 0.9 until 2.3.
+
+There were a few changes to the app lineup as well. Camcorder was merged into the camera, the IM app was killed, and two new Google-made apps were added: Car Home, a launcher with big buttons designed for use while driving, and Corporate Calendar, which is identical to the regular calendar except it supports Exchange instead of Google Calendar. Weirdly, Google also included two third-party apps out of the box: Facebook and Verizon's Visual VM app. (Neither works today.) The second set of pictures displays the “Add to Home screen" menu, and it received all new art, too.
+
+
+A Places page, showing the “Navigate" option, the Navigation disclaimer, the actual Navigation screen, and the traffic info screen.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Beyond a redesign, the clear headline feature of Android 2.0 was Google Maps Navigation. Google updated Maps to allow for free turn-by-turn navigation, complete with a point of interest search and text to speech, which could read the names of streets aloud just like a standalone GPS unit. Turning GPS navigation from a separate product into a free smartphone feature pretty much [destroyed][4] the standalone GPS market overnight. TomTom’s stock dropped almost 40 percent during the week of Android 2.0’s launch.
+
+But navigation was pretty hard to get to at first. You had to open the search box, type in a place or address, and tap on the search result. Next, after tapping on the "Navigate" button, Google showed a warning stating that Navigation was in beta and should not be trusted. After tapping on "accept," you could jump in a car, and a harsh-sounding robot voice would guide you to your destination. Hidden behind the menu button was an option to check out the traffic and accidents for the entire route. This design of Navigation hung around forever. Even when the main Google Maps interface was updated in Android 4.0, the Android 2.0 stylings in the Navigation section hung around until almost Android 4.3.
+
+Maps would also show a route overview, which contained traffic data for your route. At first it was just licensed by the usual traffic data provider, but later, Google would use information from Android and iOS phones running Google Maps to [crowd source traffic data][5]. It was the first step in Google's dominance of the mobile map game. After all, real-time traffic monitoring is really just a matter of how many points of data you have. Today, with hundreds of millions of Google Maps users across iOS and Android, Google has become the best provider of traffic data in the world.
+
+With Maps Navigation, Android finally found its killer app. Google was offering something no one else could. There was finally an answer to the "Why should I buy this over an iPhone?" question. Google Maps didn't require PC-based updating like many GPS units did, either. It was always up-to-date thanks to the cloud, and all of those updates were free. The only downside was that you needed an Internet connection to use Google Maps.
+
+As was greatly publicized during the [Apple Maps fiasco][6], accurate maps have become one of the most important features of a smartphone, even if no one really appreciates them when they work. Mapping the world is really only solvable with tons of person power, and today, Google’s “Geo" division is the largest in the company with more than [7,000 employees][7]. For most of these people, their job is to literally drive down every road in the world with the company’s camera-filled Street View cars. After eight years of data collection, Google has more than [five million miles][8] of 360-degree Street View imagery, and Google Maps is one of the biggest, most untouchable pillars of the company.
+
+
+The Car Home screen, and, because we have room, a horizontal version of Navigation.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Along with Google Maps Navigation came "Car Home," a large-buttoned home screen designed to help you use your phone while driving. It wasn't customizable, and each button was just a shortcut to a standard app. The Motorola Droid and its official [car dock accessory][9] had special magnets that would automatically trigger Car Home. While docked, pressing the hardware home button on the Droid would open Car Home instead of the normal home screen, and an on-screen home button led to the normal home screen.
+
+Car Home, while useful, didn’t last long—it was cut in Android 3.0 and never came back. GPS systems are almost entirely used in cars while driving, but encouraging users to do so with options like “search," which would bring up a keyboard, is something that Google’s lawyers probably weren’t very fond of. With [Apple’s CarPlay][10] and Google’s [Open Automotive Alliance][11], car computers are seeing a resurgence these days. This time, though, there is more of a focus on safety, and government organizations like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration are on board to help out.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/10/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2009/12/review-of-the-motorola-droid/
+[2]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e52TSXwj774
+[3]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UBL47tHrvMA
+[4]:http://techcrunch.com/2009/10/28/googles-new-mobile-app-cuts-gps-nav-companies-at-the-knees/
+[5]:http://googleblog.blogspot.com/2009/08/bright-side-of-sitting-in-traffic.html
+[6]:http://arstechnica.com/apple/2012/09/apple-ceo-tim-cook-apologizes-for-ios-6-maps-promises-improvements/
+[7]:http://www.businessinsider.com/apple-has-7000-fewer-people-working-on-maps-than-google-2012-9
+[8]:https://developers.google.com/events/io/sessions/383278298
+[9]:http://www.amazon.com/Motorola-Generation-Vehicle-Charger-Packaging/dp/B002Y3BYQA
+[10]:http://arstechnica.com/apple/2014/03/ios-in-the-car-becomes-carplay-coming-to-select-dashboards-this-year/
+[11]:http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2014/01/open-automotive-alliance-aims-to-bring-android-inside-the-car/
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/11 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/11 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..94a9e762e8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/11 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+The redesigned Dialer and Contacts pages.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The rounded tabs in the contacts/dialer app were changed to a sharper, more mature-looking design. The dialer changed its name to "Phone" and the dial pad buttons changed from circles to rounded rectangles. Buttons for voicemail, call, and delete were placed at the bottom. This screen is a great example of Android’s lack of design consistency in the pre-3.0 days. Just on this screen, the tabs used sharp-cornered rectangles, the dial pad used rounded rectangles, and the sides of the bottom buttons were complete circles. It was a grab bag of UI widgets where no one ever tried to make anything match anything else.
+
+One of the new features in Android 2.0 was "Quick Contacts," which took the form of contact thumbnails that were added all over the OS. Tapping on them would bring up a list of shortcuts to contact that person through other apps. This didn't make as much sense in the contacts app, but in something like Google Talk, being able to tap on the contact thumbnail and call the person was very handy.
+
+
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Android 2.0 was finally equipped with all the on-screen buttons needed to answer and hang up a call without needing a hardware button, and the Droid took advantage of this and removed the now-redundant buttons from its design. Android’s solution to accept or reject calls was these left and right pull tabs. They work a lot like slide-to-unlock (and would later be used for slide-to-unlock)—a slide from the green button to the right would answer, and a slide from the red button to the left would reject the call. Once inside a call, it looked a lot like Android 1.6. All the options were still hidden behind the menu button.
+
+Someone completely phoned-in the art for the dialpad drawer. Instead of redrawing the number "5" button from Android 1.6, they just dropped in bold text that said "Dialpad" and called it a day.
+
+
+The Calculator and Browser.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The calculator was revamped for the first time since its introduction in Android 0.9. The black glass balls were replaced with gradiented blue and black buttons. The crazy red on-press highlight of the old calculator was replaced with a more normal looking white outline.
+
+The browser's tiny website name bar grew into a full, functional address bar, along with a button for bookmarks. To save on screen real estate, the address bar was attached to the page, so the bar scrolled up with the rest of the page and left you with a full screen for reading. Android 1.6's unique magnifying rectangle zoom control and its associated buttons were tossed in favor of a much simpler double-tab-to-zoom gesture, and the browser could once again render arstechnica.com without crashing. There still wasn't pinch zoom.
+
+
+The camera with the settings drawer open, the flash settings, and the menu over top of the photo review screen.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The camera app gained an entire drawer on the left side, which opened to reveal a ton of settings. The Motorola Droid was one of the first Android phones with an LED flash, so there was a setting for flash control, along with settings like scene mode, white balance, effects, picture size, and storage location (SD or Internal).
+
+On the photo review screen, Google pared down the menu button options. They were no longer redundant when compared to the on-screen options. With the extra room in the menu, all the options fit in the menu bar without needing a "more" button.
+
+
+The “accounts" page of the e-mail app, the new combined inbox, the account & sync page from the system settings, and the auto brightness setting.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The e-mail app got a big functionality boost. The most important of which is that it finally supported Microsoft Exchange. The Android 2.0 version of Email finally separated the inbox and folder views instead of using the messy mashed-together view introduced in Android 1.0. Email even had a unified inbox that would weave all your messages together from different accounts.
+
+The inbox view put the generic Email app on even ground with the Gmail app. Combined inbox even trumped Gmail's functionality, which was an extremely rare occurrence. Email still felt like the unwanted stepchild to Gmail, though. It used the Gmail interface to view messages, which meant the inbox and folders used a black theme, and the message view oddly used a light theme.
+
+The bundled Facebook app had an awesome account sync feature, which would download contact pictures and information from the social network and seamlessly integrate it into the contacts app. Later down the road when Facebook and Google stopped being friends, [Google removed this feature][1]. The company said it didn't like the idea of sharing information with Facebook when Facebook wouldn't share information back, thus a better user experience lost out to company politics.
+
+(Sadly, we couldn't show off the Facebook app because it is yet another client that died at the hands of OAuth updates. It's no longer possible to sign in from a client this old.)
+
+The last picture shows the auto brightness control, which Android 2.0 was the first version to support. The Droid was equipped with an ambient light sensor, and tapping on the checkbox would make the brightness slider disappear and allow the device to automatically control the screen brightness.
+
+As the name would imply, Android 2.0 was Google's biggest update to date. Motorola and Verizon brought Android a slick-looking device with tons of ad dollars behind it, and for a time, “Droid" became a household name.
+
+### The Nexus One—enter the Google Phone ###
+
+
+
+In January 2010, the first Nexus device launched, appropriately called the "[Nexus One][2]". The device was a huge milestone for Google. It was the first phone designed and branded by the company, and Google planned to sell the device directly to consumers. The HTC-manufactured Nexus One had a 1GHz, single-core Qualcomm Snapdragon S1 SoC, 512MB of RAM, 512MB of storage, and a 3.7-inch AMOLED display.
+
+The Nexus One was meant to be a pure Android experience free of carrier meddling and crapware. Google directly controlled the updates. It was able to push software out to users as soon as it was done, rather than having to be approved by carriers, who slowed the process down and were not always eager to improve a phone customers already paid for.
+
+Google sold the Nexus One [directly over the Web][3], unlocked, contract-free, and at the full retail price of $529.99. While the Nexus One was also sold at T-Mobile stores on-contract for $179.99, Google wanted to change the way the cell phone industry worked in America with its online store. The idea was to pick the phone first and the carrier second, breaking the control the wireless oligarchy had over hardware in the United States.
+
+Google's retail revolution didn't work out though, and six months after the opening on the online phone store, Google shut the service down. Google cited the primary problem as low sales. In 2010, Internet shopping wasn't the commonplace thing it is today, and consumers weren't ready to spend $530 on a device they couldn’t first hold in their hands. The high price was also a limiting factor; smartphone shoppers were more used to paying $200 up front for devices and agreeing to a two-year contract. There was also the issue of the Motorola Droid, which came out only three months earlier and was not significantly slower. With the Droid’s huge marketing campaign and "iPhone Killer" hype, it already captured much of the same Android enthusiast market that the Nexus One was gunning for.
+
+While the Nexus One online sales experiment could be considered a failure, Google learned a lot. In 2012, it [relaunched its online store][4] as the "Devices" section on Google Play.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/11/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://techcrunch.com/2011/02/22/google-android-facebook-contacts/
+[2]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2010/01/nexus-one-review/
+[3]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2010/01/googles-big-news-today-was-not-a-phone-but-a-url/
+[4]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2012/04/unlocked-samsung-galaxy-nexus-can-now-be-purchased-from-google/
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/12 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/12 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6f7058c56a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/12 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+### Android 2.1—the discovery (and abuse) of animations ###
+
+Android 2.1 came out with the launch of the Nexus One, which was only three months after the release of 2.0. The new OS wasn't a huge release, so it still kept the codename "Éclair." Android development was chugging along at an unheard-of pace, with Google averaging a new OS release every two-and-a-half months over the last 15 months.
+
+Thanks mostly to the marketing efforts of Verizon and the "Droid" line of phones, Android was gaining in popularity. The OS was still considered ugly, though, and while the Android engineers at the time seemed to have almost no formal design training, in Android 2.1 they tried to spruce things up a bit by slathering on heavy-handed animation effects wherever they could. The result was an OS that seemed to be desperately trying to prove that it could do animation effects. Many of the new additions felt more like tech demos than user-experience improvements.
+
+
+The lock and home screens from Android 2.1 and 2.0.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Android 2.0's rotary dial lock screen was kicked to the curb after only one version and replaced with the same pull tabs the incoming call screen used. The lock screen clock was an attempt at a uniquely Android font, but as typefaces go, it was pretty hideous looking.
+
+One of the biggest features in Android 2.1 was "Live Wallpapers"—interactive or moving images that could be set as the wallpaper. The default Live Wallpaper was a grid of squares with blue, red, yellow, and green lights continually streaking across it. Tapping on the screen would send lights firing out in all four directions from the center of your tap. While Live Wallpapers looked neat (and was a unique feature over the iPhone), the animated backgrounds sucked up battery power and CPU cycles. It seemed to make the whole phone run a little slower.
+
+On the home screen, the default Google Search widget was given a lot more padding and now sits centered in its row. Page indicators now lived in the bottom left and right corners of the screen, and the number of home screen pages jumped from three to five. The app drawer tab at the bottom was replaced with an icon showing a grid of squares, a metaphor that Google still uses today.
+
+
+A picture showing the app drawer design and a composite image showing the app selection for Android 2.1 and 2.0.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+With the new app drawer icon came a totally new app drawer. Instead of a tabbed container that lifted up from the bottom of the screen, the app drawer displayed as a full-screen interface. The carbon fiber weave was removed, and the background switched to a plain black background—a decision that would stick around all the way up to KitKat.
+
+Google decided to add a floating, semi-transparent home icon to the bottom of the app drawer to give people an easy way out of the full-screen tab interface. This could be seen as a precursor to the on-screen home button that was introduced in Android 4.0.
+
+The app drawer was given a tacky graphics effect, too. While scrolling, the icons at the top and bottom of the list would bend inward and appear to move deeper into the phone, sort of like the opening scroll in Star Wars.
+
+There were a few changes to the icons. "Amazon MP3" and "Alarm Clock" both lost their first names, along with their premium alphabetical real-estate at the top of the app drawer. Two new apps showed up: News and Weather, and Google Voice, which was Google's telecommunication service. Since the Nexus One was not a Verizon phone, Verizon's Visual Voicemail app was dumped.
+
+
+The revamped clock app.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Along with the name change, the clock app got a total revamp. Tapping on the clock shortcut no longer opened the alarms page; instead it went to a "desk clock" interface (left picture, above) with a background that matched the wallpaper. The clock used the same font from the lock screen, pulling in weather from the new News And Weather app.
+
+The new alarm page cleaned up a lot of the weirder design decisions made in the old version. The analog clock and selectable clock designs were dead. The checkboxes were replaced with a green on/off light, which was much easier to parse than "gray check/green check." While it might be hard to see from the thumbnail (click for a bigger version), the old alarm design displayed AM and PM next to the time. The 2.1 design did away with that, only showing the relevant meridian. A digital clock was placed at the bottom, and the clock icon took you back to the desk clock interface.
+
+
+The Gallery and individual image screens from 2.1 and 2.0.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Google's desire to improve the look of Android was most evident in the 2.1 Gallery, which was all about heavy-handed animation effects and transparencies. When the app opened, individual pictures flew in from the top of the screen and shuffled into little piles that made up an album. When opening an album, the picture stack separated, and the photos slid into a grid formation. Everything you touched would pop open, squish, and stretch like a spring-loaded piece of Jell-o.
+
+There was no "normal" background for the Gallery. It would randomly pick a picture on the screen and heavily distort it for use as a background image. When that picture scrolled off-screen, it would pick a new background image, so the tone of the background always matched your pictures.
+
+The top left of the screen housed a breadcrumbs bar. It displayed your current location and any folders between you and the main screen—it could be thought of as an early precursor to the "Up" button that would debut in Android 3.0. In the top right was a link to the camera app, which still sported the same faux-leather design that debuted in Android 1.6—the two designs could not be more different.
+
+While the camera was another weird, one-off design, never was the wild UI disparity between Android apps more apparent than in the new Gallery. It didn't use Android buttons, menus, or any of the existing UI paradigms. It even hid the status bar in every screen—you could barely tell you were looking at Android.
+
+In the individual photo view, you could finally swipe between images, which removed the need for chunky left and right arrows. For some reason, the color-matched background wasn't on this screen. It was the only part of the app where the background is black. Zoom controls were in the top-right (still no pinch zoom), and commands were held in a single strip along the bottom of the screen. Hitting the "menu" button (software or hardware) didn't bring up a 2×3 grid of options like every other app—the items in the bottom strip just changed from two options to three other options.
+
+
+The animation-filled Gallery app.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The first picture, above, shows an album view. You could scroll horizontally through a large album or use the fast scroll bar at the bottom of the screen. Long pressing on a picture (or, bizarrely, pressing the hardware menu button) would bring up a "checkbox" interface, where you could tap on several pictures to select them. After you've selected pictures, you could then batch share, delete, or rotate them.
+
+The menus on this screen and the next individual picture screen were semi-transparent speech bubbles that would spring out of their respective buttons when tapped on. Again, this was about as far away from the normal Android conventions as you could get. The Gallery was also one of the first apps to have an overscroll effect. When you hit the end of the photo wall, the entire surface would skew in the direction of the scrolling.
+
+The 2.1 Gallery was the first photo client to show your cloud-stored Picasa photos along with local pictures. These were marked with a white camera shutter icon in the bottom left corner of a thumbnail. This would later become Google+ Photos.
+
+No Android app before or since had looked like the gallery. There was good reason for that—it wasn’t made by Google! The app was farmed out to Cooliris, who didn't bother following a single existing Android UI paradigm. While the app was usable, all the animations and effects made it seem like a case of style over substance.
+
+
+The "News and Weather" app showing... the news and weather.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Compare the Gallery to the other new Android 2.1 app: News And Weather. While the Gallery was a transparency-filled animation fest, News And Weather was all about dark gradients and contrasting colors. This app powered the weather display on the desk clock app, and it even came with a home screen widget. The first screen just showed the weather and a six-day forecast for your current location. Along the top of the screens were tabs, next to the city name was a small "i" button that would bring up a temperature and precipitation graph. You could slide your finger along the graph to get exact temperatures and precipitation for any given minute.
+
+The big innovation in this app was swipeable tabs, an idea that would eventually become a standard Android UI convention. After the weather were a bunch of user configurable news tabs, and besides tapping on the tabs to switch to them, you could just swipe horizontally across the screen and the tab would change. The news tabs all showed a list of news headlines that were almost always truncated to the point that you had no idea what the story was about. When opening a webpage from this app, it didn't load the browser. Instead, it opened the story within the app complete with a weird white border.
+
+
+Google Maps showing off some Labs features, the new widget designs, the only screen we can access in Google Voice, and the new tabbed music design.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Widgets in 2.1 were all redesigned, with almost everything receiving a black gradient, and made better use of the available space. The clock changed back to a circle, and the calendar got a blue top, which matched the app a little more closely. Google Voice will start up, but the sign-in is broken—this is as far as you can get.
+
+The oft-neglected Music app got a minor update. The four-button home screen was removed completely, and tabs for each music display mode were added to the top of the screen. This meant when opening the app, you were immediately presented with a list of music, instead of a navigational page. Unlike the News and Weather app, these newly installed tabs here could not be swiped between.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via:
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/13 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/13 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..85c04441ac
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/13 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+
+### Android 2.1, update 1—the start of an endless war ###
+
+Google was a major launch partner for the first iPhone—the company provided Google Maps, Search, and YouTube for Apple’s mobile operating system. At the time, Google CEO Eric Schmidt was a member of Apple’s board of directors. In fact, during the original iPhone presentation, [Schmidt was the first person on stage][] after Steve Jobs, and he joked that the two companies were so close they could merge into “AppleGoo."
+
+While Google was developing Android, the relationship between the two companies slowly became contentious. Still, Google largely kept Apple happy by keeping key iPhone features, like pinch zoom, out of Android. The Nexus One, though, was the first slate-style Android flagship without a keyboard, which gave the device the same form factor as the iPhone. Combined with the newer software and Google branding, this was the last straw for Apple. According to Walter Isaacson’s biography on Steve Jobs, after seeing the Nexus One in January 2010, the Apple CEO was furious, saying "I will spend my last dying breath if I need to, and I will spend every penny of Apple's $40 billion in the bank, to right this wrong... I'm going to destroy Android, because it's a stolen product. I'm willing to go thermonuclear war on this."
+
+All of this happened behind closed doors, only coming out years after the Nexus One was released. The public first caught wind of this growing rift between Google and Apple when, a month after the release of Android 2.1, an update shipped for the Nexus One called “[2.1 update 1.][2]" The updated added one feature, something iOS long held over the head of Android: pinch-zoom.
+
+While Android supported multi-touch APIs since version 2.0, the default operating system apps stayed clear of this useful feature at the behest of Jobs. After reconciliation meetings over the Nexus One failed, there was no longer a reason to keep pinch zoom out of Android. Google pushed all their chips into the middle of the table, hit the update button, and was finally “all-in" with Android.
+
+With pinch zoom enabled in Google Maps, the Browser, and the Gallery, the Google-Apple smartphone war was on. In the coming years, the two companies would become bitter enemies. A month after the pinch zoom update, Apple went on the warpath, suing everyone and everything that used Android. HTC, Motorola, and Samsung were all brought to court, and some of them are still in court. Schmidt resigned from Apple’s board of directors. Google Maps and YouTube were kicked off of the iPhone, and Apple even started a rival mapping service. Today, the two players that were almost "AppleGoo" compete in smartphones, tablets, laptops, movies, TV shows, music, books, apps, e-mail, productivity software, browsers, personal assistants, cloud storage, mobile advertising, instant messaging, mapping, and set-top-boxes... and soon the two will be competing in car computers, wearables, mobile payments, and living room gaming.
+
+### Android 2.2 Froyo—faster and Flash-ier ###
+
+[Android 2.2][3] came out four months after the release of 2.1, in May 2010. Froyo featured major under-the-hood improvements for Android, all made in the name of speed. The biggest addition was just-in-time (JIT) compilation. JIT automatically converted java bytecode into native code at runtime, which led to drastic performance improvements across the board.
+
+The Browser got a performance boost, too, thanks to the integration of the V8 javascript engine from Chrome. This was the first of many features the Android browser would borrow from Chrome, and eventually the stock browser would be completely replaced by a mobile version of Chrome. Until that day came, though, the Android team needed to ship a browser. Pulling in Chrome parts was an easy way to upgrade.
+
+While Google was focusing on making its platform faster, Apple was making its platform bigger. Google's rival released the 10-inch iPad a month earlier, ushering in the modern era of tablets. While some large Froyo and Gingerbread tablets were released, Google's official response—Android 3.0 Honeycomb and the Motorola Xoom—would not arrive for nine months.
+
+
+Froyo added a two-icon dock at the bottom and universal search.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The biggest change on the Froyo homescreen was the new dock at the bottom, which filled the previously empty space to the left and right of the app drawer with phone and browser icons. Both of these icons were custom-designed white versions of the stock icons, and they were not user-configurable.
+
+The default layout removed all the icons, and it only stuck the new tips widget on the screen, which directed you to click on the launcher icon to access your apps. The Google Search widget gained a Google logo which doubled as a button. Tapping it would open the search interface and allow you to restrict a search by Web, apps, or contacts.
+
+
+The downloads page showing the “update all" button, the Flash app, a flash-powered site where anything is possible, and the “move to SD" button.
+Photo by [Ryan Paul][4]
+
+Some of the best additions to Froyo were more download controls for the Android Market. There was now an “Update all" button pinned to the bottom of the Downloads page. Google also added an automatic updating feature, which would automatically install apps as long as the permissions hadn't changed; automatic updating was off by default, though.
+
+The second picture shows Adobe Flash Player, which was exclusive to Froyo. The app plugged in to the browser and allowed for a “full Web" experience. In 2010, this meant pages heavy with Flash navigation and video. Flash was one of Android's big differentiators compared to the iPhone. Steve Jobs started a holy war against Flash, declaring it an obsolete, buggy piece of software, and Apple would not allow it on iOS. So Android picked up the Flash ball and ran with it, giving users the option of having a semi-workable implementation on Android.
+
+At the time, Flash could bring even a desktop computer to its knees, so keeping it on all the time on a mobile phone delivered terrible performance. To fix this, Flash on Android's browser could be set to "on-demand"—Flash content would not load until users clicked on the Flash placeholder icon. Flash support would last on Android until 4.1, when Adobe gave up and killed the project. Ultimately Flash never really worked well on Android. The lack of Flash on the iPhone, the most popular mobile device, pushed the Internet to eventually dump the platform.
+
+The last picture shows the newly added ability to move apps to the SD card, which, in an era when phones came with 512MB of internal storage, was sorely needed.
+
+
+The car app and camera app. The camera could now rotate.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The camera app was finally updated to support portrait mode. The camera settings were moved out of the drawer and into a semi-transparent strip of buttons next to the shutter button and other controls. This new design seemed to take a lot of inspiration from the Cooliris Gallery app, with transparent, springy speech bubble popups. It was quite strange to see the high-tech Cooliris-style UI design grafted on to the leather-bound camera app—the aesthetics didn't match at all.
+
+
+The semi-broken Facebook app is a good example of the common 2x3 navigation page. Google Goggles was included but also broken.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Unlike the Facebook client included in Android 2.0 and 2.1, the 2.2 version still sort of works and can sign in to Facebook's servers. The Facebook app is a good example of Google's design guidelines for apps at the time, which suggested having a navigational page consisting of a 3x2 grid of icons as the main page of an app.
+
+This was Google's first standardized attempt at getting navigational elements out of the menu button and onto the screen, where users could find them. This design was usable, but it added an extra roadblock between launching an app and using an app. Google would later realize that when users launch an app, it was a better idea to show them content instead of an interstitial navigational screen. In Facebook for instance, opening to the news feed would be much more appropriate. And later app designs would relegate navigation to a second-tier location—first as tabs at the top of the screen, and later Google would settle on the "Navigation Drawer," a slide-out panel containing all the locations in an app.
+
+Also packed in with Froyo was Google Goggles, a visual search app which would try to identify the subject of a picture. It was useful for identifying works of art, landmarks, and barcodes, but not much else. These first two setup screens, along with the camera interface, are all that work in the app anymore. Today, you can't actually complete a search with a client this old. There wasn't much to see anyway; it was a camera interface that returned a search results page.
+
+
+The Twitter app, which was an animation-filled collaboration between Google and Twitter.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Froyo included the first Android Twitter app, which was actually a collaboration between Google and Twitter. At the time, a Twitter app was one of the big holes in Android's app lineup. Developers favored the iPhone, and with Apple's head start and stringent design requirements, the App Store's app selection was far superior to Android's. But Google needed a Twitter app, so it teamed up with the company to get the first version out the door.
+
+This represented Google's newer design language, which meant it had an interstitial navigation page and a "tech-demo" approach to animations. The Twitter app was even more heavy-handed with animation effects than the Cooliris Gallery—everything moved all the time. The clouds at the top and bottom of every page continually scrolled at varying speeds, and the Twitter bird at the bottom flapped its wings and moved its head left and right.
+
+The Twitter app actually featured an early precursor to the Action Bar, a persistent strip of top-aligned controls that was introduced in Android 3.0 . Along the top of every screen was a blue bar containing the Twitter logo and buttons like search, refresh, and compose tweet. The big difference between this and the later action bars was that the Twitter/Google design lacks an "Up" button in the top right corner, and it actually uses an entire second bar to show your current location within the app. In the second picture above, you can see a whole bar dedicated to the location label "Tweets" (and, of course, the continuously scrolling clouds). The Twitter logo in the second bar acted as another navigational element, sometimes showing additional drill down areas within the current section and sometimes showing the entire top-level shortcut group.
+
+The 2.3 Tweet stream didn't look much different from what it does today, save for the hidden action buttons (reply, retweet, etc), which were all under the right-aligned arrow buttons. They popped up in a speech bubble menu that looked just like the navigational popup. The faux-action bar was doing serious work on the create tweet page. It housed the twitter logo, remaining character count, and buttons to attach a picture, take a picture, and a contact mention button.
+
+The Twitter app even came with a pair of home screen widgets. The big one took up eight slots and gave you a compose bar, update button, one tweet, and left and right arrows to view more tweets. The little one showed a tweet and reply button. Tapping on the compose bar on the large widget immediately launched the main "Create Tweet," rendering the "update" button worthless.
+
+
+Google Talk and the new USB dialog.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Elsewhere, Google Talk (and the unpictured SMS app) changed from a dark theme to a light theme, which made both of them look a lot closer to the current, modern apps. The USB storage screen that popped up when you plugged into a computer changed from a simple dialog box to a full screen interface. Instead of a text-only design, the screen now had a mutant Android/USB-stick hybrid.
+
+While Android 2.2 didn’t feature much in the way of user-facing features, a major UI overhaul was coming in the next two versions. Before all the UI work, though, Google wanted to revamp the core of Android. Android 2.2 accomplished that.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/13/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9hUIxyE2Ns8#t=3016
+[2]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2010/02/googles-nexus-one-gets-multitouch/
+[3]:http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2010/07/android-22-froyo/
+[4]:http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2010/07/android-22-froyo/
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/14 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/14 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2825d7eee8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/14 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+### Voice Actions—a supercomputer in your pocket ###
+
+In August 2010, a new feature “[Voice Actions][1]" launched in the Android Market as part of the Voice Search app. Voice Actions allowed users to issue voice commands to their phone, and Android would try to interpret them and do something smart. Something like "Navigate to [address]" would fire up Google Maps and start turn-by-turn navigation to your stated destination. You could also send texts or e-mails, make a call, open a Website, get directions, or view a location on a map—all just by speaking.
+
+注:youtube视频地址
+
+
+Voice Actions was the culmination of a new app design philosophy for Google. Voice Actions was the most advanced voice control software for its time, and the secret was that Google wasn’t doing any computing on the device. In general, voice recognition was very CPU intensive. In fact, many voice recognition programs still have a “speed versus accuracy" setting, where users can choose how long they are willing to wait for the voice recognition algorithms to work—more CPU power means better accuracy.
+
+Google’s innovation was not bothering to do the voice recognition computing on the phone’s limited processor. When a command was spoken, the user’s voice was packaged up and shipped out over the Internet to Google’s cloud servers. There, Google’s farm of supercomputers pored over the message, interpreted it, and shipped it back to the phone. It was a long journey, but the Internet was finally fast enough to accomplish something like this in a second or two.
+
+Many people throw the phrase “cloud computing" around to mean “anything that is stored on a server," but this was actual cloud computing. Google was doing hardcore compute operations in the cloud, and because it is throwing a ridiculous amount of CPU power at the problem, the only limit to the voice recognition accuracy is the algorithms themselves. The software didn't need to be individually “trained" by each user, because everyone who used Voice Actions was training it all the time. Using the power of the Internet, Android put a supercomputer in your pocket, and, compared to existing solutions, moving the voice recognition workload from a pocket-sized computer to a room-sized computer greatly increased accuracy.
+
+Voice recognition had been a project of Google’s for some time, and it all started with an 800 number. [1-800-GOOG-411][1] was a free phone information service that Google launched in April 2007. It worked just like 411 information services had for years—users could call the number and ask for a phone book lookup—but Google offered it for free. No humans were involved in the lookup process, the 411 service was powered by voice recognition and a text-to-speech engine. Voice Actions was only possible after three years of the public teaching Google how to hear.
+
+Voice recognition was a great example of Google’s extremely long-term thinking—the company wasn't afraid to invest in a project that wouldn’t become a commercial product for several years. Today, voice recognition powers products all across Google. It’s used for voice input in the Google Search app, Android’s voice typing, and on Google.com. It’s also the primary input interface for Google Glass and [Android Wear][2].
+
+The company even uses it beyond input. Google's voice recognition technology is used to transcribe YouTube videos, which powers automatic closed captioning for the hearing impaired. The transcription is even indexed by Google, so you can search for words that were said in the video. Voice is the future of many products, and this long-term planning has led Google to be one of the few major tech companies with an in-house voice recognition service. Most other voice recognition products, like Apple’s Siri and Samsung devices, are forced to use—and pay a license fee for—voice recognition from Nuance.
+
+With the computer hearing system up and running, Google is applying this strategy to computer vision next. That's why things like Google Goggles, Google Image Search, and [Project Tango][3] exist. Just like the days of GOOG-411, these projects are in the early stages. When [Google's robot division][4] gets off the ground with a real robot, it will need to see and hear, and Google's computer vision and hearing projects will likely give the company a head start.
+
+
+The Nexus S, the first Nexus phone made by Samsung.
+
+### Android 2.3 Gingerbread—the first major UI overhaul ###
+
+Gingerbread was released in December 2010, a whopping seven months after the release of 2.2. The wait was worth it, though, as Android 2.3 changed just about every screen in the OS. It was the first major overhaul since the initial formation of Android in version 0.9. 2.3 would kick off a series of continual revamps in an attempt to turn Android from an ugly duckling into something that was capable of holding its own—aesthetically—against the iPhone.
+
+And speaking of Apple, six months earlier, the company released the iPhone 4 and iOS 4, which added multitasking and Facetime video chat. Microsoft was finally back in the game, too. The company jumped into the modern smartphone era with the launch of Windows Phone 7 in November 2010.
+
+Android 2.3 focused a lot on the interface design, but with no direction or design documents, many apps ended up getting a new bespoke theme. Some apps went with a flatter, darker theme, some used a gradient-filled, bubbly dark theme, and others went with a high-contrast white and green look. While it wasn't cohesive, Gingerbread accomplished the goal of modernizing nearly every part of the OS. It was a good thing, too, because the next phone version of Android wouldn’t arrive until nearly a year later.
+
+Gingerbread’s launch device was the Nexus S, Google’s second flagship device and the first Nexus manufactured by Samsung. While today we are used to new CPU models every year, back then that wasn't the case. The Nexus S had a 1GHz Cortex A8 processor, just like the Nexus One. The GPU was slightly faster, and that was it in the speed department. It was a little bigger than the Nexus One, with a 4-inch, 800×480 AMOLED display.
+
+Spec wise, the Nexus S might seem like a tame upgrade, but it was actually home to a lot of firsts for Android. The Nexus S was Google’s first flagship to shun a MicroSD slot, shipping with 16GB on-board memory. The Nexus One had only 512MB of storage, but it had a MicroSD slot. Removing the SD slot simplified storage management for users—there was just one pool now—but hurt expandability for power users. It was also Google's first phone to have NFC, a special chip in the back of the phone that could transfer information when touched to another NFC chip. For now, the Nexus S could only read NFC tags—it couldn't send data.
+
+Thanks to some upgrades in Gingerbread, the Nexus S was one of the first Android phones to ship without a hardware D-Pad or trackball. The Nexus S was now down to just the power, volume, and the four navigation buttons. The Nexus S was also a precursor to the [crazy curved-screen phones][6] of today, as Samsung outfitted the Nexus S with a piece of slightly curved glass.
+
+
+Gingerbread changed the status bar and wallpaper, and it added a bunch of new icons.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+An upgraded "Nexus" live wallpaper was released as an exclusive addition to the Nexus S. It was basically the same idea as the Nexus One version, with its animated streaks of light. On the Nexus S, the "grid" design was removed and replaced with a wavy blue/gray background. The dock at the bottom was given square corners and colored icons.
+
+
+The new notification panel and menu.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The status bar was finally overhauled from the version that first debuted in 0.9. The bar was changed from a white gradient to flat black, and all the icons were redrawn in gray and green. Just about everything looked crisper and more modern thanks to the sharp-angled icon design and higher resolution. The strangest decisions were probably the removal of the time period from the status bar clock and the confusing shade of gray that was used for the signal bars. Despite gray being used for many status bar icons, and there being four gray bars in the above screenshot, Android was actually indicating no cellular signal. Green bars would indicate a signal, gray bars indicated “empty" signal slots.
+
+The green status bar icons in Gingerbread also doubled as a status indicator of network connectivity. If you had a working connection to Google's servers, the icons would be green, if there was no connection to Google, the icons turned white. This let you easily identify the connectivity status of your connection while you were out and about.
+
+The notification panel was changed from the aging Android 1.5 design. Again, we saw a UI piece that changed from a light theme to a dark theme, getting a dark gray header, black background, and black-on-gray text.
+
+The menu was darkened too, changing from a white background to a black one with a slight transparency. The contrast between the menu icons and the background wasn’t as strong as it should be, because the gray icons are the same color as they were on the white background. Requiring a color change would mean every developer would have to make new icons, so Google went with the preexisting gray color on black. This was a change at the system level, so this new menu would show up in every app.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/14/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2010/08/google-beefs-up-voice-search-mobile-sync/
+[2]:http://arstechnica.com/business/2007/04/google-rolls-out-free-411-service/
+[3]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/03/in-depth-with-android-wear-googles-quantum-leap-of-a-smartwatch-os/
+[4]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/02/googles-project-tango-is-a-smartphone-with-kinect-style-computer-vision/
+[5]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/12/google-robots-former-android-chief-will-lead-google-robotics-division/
+[6]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/12/lg-g-flex-review-form-over-even-basic-function/
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/15 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/15 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..078e106d1c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/15 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+Gingerbread's new keyboard, text selection UI, overscroll effect, and new checkboxes.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+One of the most important additions to Android 2.3 was the system-wide text selection interface, which you can see in the Google search bar in the left screenshot. Long pressing a word would highlight it in orange and make draggable handles appear on either side of the highlight. You could then adjust the highlight using the handles and long press on the highlight to bring up options for cut, copy, and paste. Previous methods used tiny controls that relied on a trackball or D-Pad, but with this first finger-driven text selection method, the Nexus S didn’t need the extra hardware controls.
+
+The right set of images shows the new checkbox design and overscroll effect. The Froyo checkbox worked like a light bulb—it would show a green check when on and a gray check when off. Gingerbread now displayed an empty box when an option is turned off—which made much more sense. Gingerbread was the first version to have an overscroll effect. An orange glow appeared when you hit the end of a list and grew larger as you pulled more against the dead end. Bounce scrolling would probably have made the most sense, but that was patented by Apple.
+
+
+The new dialer and dialog box design.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The dialer received a little more love in Gingerbread. It became darker, and Google finally addressed the combination of sharp corners, rounded corners, and complete circles that it had going on. Now every corner was a sharp right angle. All the dial pad buttons were replaced with a weird underline, like some faint leftovers of what used to be a button. You were never really sure if you were supposed to see a button or not—our brains wanted to imagine the rest of the square.
+
+The Wi-Fi network dialog is pictured to show off the rest of the system-wide changes. All the dialog box titles were changed from gray to black, every dialog box, dropdown, and button corner was sharpened up, and everything was a little bit darker. All these system-wide changes made all of Gingerbread look a lot less bubbly and more mature. The "all black everything" look wasn't necessarily the most welcoming color palette, but it certainly looked better than Android's previous gray-and-beige color scheme.
+
+
+The new Market, which added a massive green header.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+While not exclusive to Gingerbread, with the launch of the new OS came "Android Market 2.0." Most of the list design was the same, but Google covered the top third of the screen with a massive green banner that was used for featured apps and navigation. The primary design inspiration here was probably the green Android mascot—the color is a perfect match. At a time when the OS was getting a darker design, the neon green banner and white list made the Market a lot brighter.
+
+However, the same green background image was used across phones, which meant on lower resolution devices, the green banner was even bigger. Users complained so much about the wasted screen space that later updates would make the green banner scroll up with the content. At the time, horizontal mode was even worse—it would fill the left half of the screen with the static green banner.
+
+
+An app page from the Market showing the collapsible text section, the "My apps" section, and Google Books screenshots.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+App pages were redesigned with collapsible sections. Rather than having to scroll through a thousand-line description, text boxes were truncated to only the first few lines. After that, a "more" button needed to be tapped. This allowed users to easily scroll through the list and find things like pictures and "contact developer," which would usually be farther down the page.
+
+The other parts of the Android homescreen wisely toned down the green monster. The rest of the app was mostly just the old Market with new green navigational elements. Any of the old tabbed interfaces were upgraded to swipeable tabs. In the right Gingerbread image, swiping right-to-left would switch from "Top Paid" to "Top Free," which made navigation a little easier.
+
+Gingerbread came with the first of what would become the Google Play content stores: Google Books. The app was a basic book reader that would display books in a simple thumbnail grid. The "Get eBooks" link at the top of the screen opened the browser and loaded a mobile website where you could buy books.
+
+Google Books and the “My Apps" page of the Market were both examples of early precursors to the Action Bar. Just like the current guidelines, a stickied top bar featured the app icon, the name of the screen within the app, and a few controls. The layout of these two apps was actually pretty modern looking.
+
+
+The new Google Maps.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Google Maps (which, again, at this point was on the Android Market and not exclusive to this version of Android) now featured another action bar precursor in the form of a top-aligned control bar. This version of an early action bar featured a lot of experimenting. The majority of the bar was taken up with a search box, but you could never type into the bar. Tapping on it would open the old search interface from Android 1.x, with a totally different bar design and bubbly buttons. This 2.3 bar wasn't anything more than a really big search button.
+
+
+The new business pages, which switched from black to white.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Along with Places' new top billing in the app drawer came a redesigned interface. Unlike the rest of Gingerbread, this switched from black to white. Google also kept the old buttons with rounded corners. This new version of Maps helpfully displayed the hours of operation of a business, and it offered advanced search options like places that were currently open or thresholds for ratings and price. Reviews were brought to the surface, allowing a user to easily get a feel for the current business. It was now also possible to "star" a location from the search results and save it for later.
+
+
+The new YouTube design, which, amazingly, sort of matches the old Maps business page design.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The YouTube app seemed completely separate from the rest of Android, as if whoever designed this had no idea what Gingerbread would end up looking like. Highlights were red and gray instead of green and orange, and rather than the flat black of Gingerbread, YouTube featured bubbly buttons, tabs, and bars with rounded corners and heavy gradients. The new app did get a few things right, though. All the tabs could be horizontally swiped through, and the app finally added a vertical viewing mode for videos. Android seemed like such an uncoordinated effort at this stage. It’s like someone told the YouTube team “make it black," and that was all the direction they were given. The only Android entity this seemed to match was the old Google Maps business page design.
+
+Despite the weird design choices, the YouTube app had the best approximation yet of an action bar. Besides the bar at the top with an app logo and a few buttons, the rightmost button was labeled “more" and would bring up options that didn’t fit in the bar. Today, this is called the “Overflow" button, and it's a standard UI piece.
+
+
+The new Google Talk, which supported voice and video calls, and the new Voice Actions interface.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+One last update for Gingerbread came with Android 2.3.4, which brought a new version of Google Talk. Unlike the Nexus One, the Nexus S had a front-facing camera—and the redesigned version of Google Talk had voice and video calling. The colored indicators on the right of the friends list were used to indicate not only presence, but voice and video availability. A dot was text only, a microphone was text or voice, and a camera was text, voice, or video. If available, tapping on a voice or video icon would immediately start a call with that person.
+
+Gingerbread is the oldest version of Android still supported by Google. Firing up a Gingerbread device and letting it sit for a few minutes will result in a ton of upgrades. Gingerbread will pull down Google Play Services, resulting in a ton of new API support, and it will upgrade to the very newest version of the Play Store. Open the Play Store and hit the update button, and just about every single Google app will be replaced with a modern version. We tried to keep this article authentic to the time Gingerbread was released, but a real user stuck on Gingerbread today will be treated to a flood of anachronisms.
+
+Gingerbread is still supported because there are a good number of users still running the now ancient OS. Gingerbread's staying power is due to the extremely low system requirements, making it the go-to choice for slow, cheap phones. The next few versions of Android were much more exclusive and/or demanding on hardware. For instance, Android 3.0 Honeycomb is not open source, meaning it could only be ported to a device with Google's cooperation. It was also only for tablets, making Gingerbread the newest phone version of Android for a very long time. 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich was the next phone release, but it significantly raised Android’s systems requirements, cutting off the low-end of the market. Google is hoping to get cheaper phones back on the update track with 4.4 KitKat, which brings the system requirements back down to 512MB of RAM. The passage of time helps, too—by now, even cheap SoCs have caught up to the demands of a 4.0-era version of Android.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/15/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/16 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/16 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..91e0946078
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/16 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+### Android 3.0 Honeycomb—tablets and a design renaissance ###
+
+Despite all the changes made in Gingerbread, Android was still the ugly duckling of the mobile world. Compared to the iPhone, its level of polish and design just didn't hold up. On the other hand, one of the few operating systems that could stand up to iOS's aesthetic acumen was Palm's WebOS. WebOS was a cohesive, well-designed OS with several innovative features, and it was supposed to save the company from the relentless march of the iPhone.
+
+A year after launch though, Palm was running out of cash. The company never saw the iPhone coming, and by the time WebOS was ready, it was too late. In April 2010, Hewlett-Packard purchased Palm for $1 billion. While HP bought a product with a great user interface, the lead designer of that interface, a man by the name of Matias Duarte, did not join HP. In May 2010, just before HP took control of Palm, Duarte jumped ship to Google. HP bought the bread, but Google hired the baker.
+
+
+The first Honeycomb device, the Motorola Xoom 10-inch tablet.
+
+At Google, Duarte was named the Director of Android User Experience. This was the first time someone was publicly in charge of the way Android looked. While Matias landed at Google during the launch of Android 2.2, the first version he truly impacted was Android 3.0, Honeycomb, released in February 2011.
+
+By Google's own admission, Honeycomb was rushed out the door. Ten months prior, Apple modernized the tablet with the launch of the iPad, and Google wanted to respond as quickly as possible. Honeycomb was that response, a version of Android that ran on 10-inch touchscreens. Sadly, getting this OS to market was such a priority that corners were cut to save time.
+
+The new OS was for tablets only—phones would not be updated to Honeycomb, which spared Google the difficult problem of making the OS work on wildly different screen sizes. But with phone support off the table, a Honeycomb source drop never happened. Previous Android versions were open source, enabling the hacking community to port the latest version to all sorts of different devices. Google didn't want app developers to feel pressured to support half-broken Honeycomb phone ports, so Google kept the source to itself and strictly controlled what could and couldn't have Honeycomb. The rushed development led to problems with the software, too. At launch, Honeycomb wasn't particularly stable, SD cards didn't work, and Adobe Flash—one of Android's big differentiators—wasn't supported.
+
+One of the few devices that could have Honeycomb was [the Motorola Xoom][1], the flagship product for the new OS. The Xoom was a 10-inch, 16:9 tablet with 1GB of RAM and a dual-core, 1GHz Nvidia Tegra 2 processor. Despite being the launch device of a new version of Android where Google controlled the updates directly, the device wasn't called a "Nexus." The most likely reason for this was that Google didn't feel confident enough in the product to call it a flagship.
+
+Nevertheless, Honeycomb was a major milestone for Android. With an experienced designer in charge, the entire Android user interface was rebuilt, and most of the erratic app designs were brought to heel. Android's default apps finally looked like pieces of a cohesive whole with similar layouts and theming across the board. Redesigning Android would be a multi-version project though—Honeycomb was just the start of getting Android whipped into shape. This first draft laid the groundwork for how future versions of Android would function, but it also used a heavy-handed sci-fi theme that Google would spend the next few versions toning down.
+
+
+The home screens of Honeycomb and Gingerbread.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+While Gingerbread only experimented with a sci-fi look in its photon wallpaper, Honeycomb went full sci-fi with a Tron-inspired theme for the entire OS. Everything was made black, and if you needed a contrasting color, you could choose from a few different shades of blue. Everything that was made blue was also given a "glow" effect, making the entire OS look like it was powered by alien technology. The default background was a holographic grid of hexagons (a Honeycomb! get it?) that looked like it was the floor of a teleport pad on a spaceship.
+
+The most important change of Honeycomb was the addition of the system bar. The Motorola Xoom had no hardware buttons other than power and volume, so a large black bar was added along the bottom of the screen that housed the navigational buttons. This meant the default Android interface no longer needed specialized hardware buttons. Previously, Android couldn't function without hardware Back, Menu, and Home keys. Now, with the software supplying all the necessary buttons, anything with a touch screen was able to run Android.
+
+The biggest benefit of the new software buttons was flexibility. The new app guidelines stated that apps should no longer require a hardware menu button, but for those that do, Honeycomb detects this and adds a fourth button to the system bar that allows these apps to work. The other flexibility attribute of software buttons was that they could change orientation with the device. Other than the power and volume buttons, the Xoom's orientation really wasn't important. The system bar always sat on the "bottom" of the device from the user's perspective. The trade off was that a big bar along the bottom of the screen definitely sucked up some screen real estate. To save space on 10-inch tablets, the status bar was merged into the system bar. All the usual status duties lived on the right side—there was battery and connectivity status, the time, and notification icons.
+
+The whole layout of the home screen changed, placing UI pieces in each of the four corners of the device. The bottom left housed the previously discussed navigational buttons, the bottom right was for status and notifications, the top left displayed text search and voice search, and the top right had buttons for the app drawer and adding widgets.
+
+
+The new lock screen and Recent Apps interface.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+(Since the Xoom was a [heavy] 10-inch, 16:9 tablet, it was primarily meant to be used horizontally. Most apps also supported portrait mode, though, so for the sake of our formatting, we're using mostly portrait mode shots. Just keep in mind the Honeycomb shots come from a 10-inch tablet, and the Gingerbread shots come from a 3.7-inch phone. The densities of information are not directly comparable.)
+
+The unlock screen—after switching from a menu button to a rotary dial to slide-to-unlock—removed any required accuracy from the unlock process by switching to a circle unlock. Swiping from the center outward in any direction would unlock the device. Like the rotary unlock, this was much nicer ergonomically than forcing your finger to follow a perfectly straight path.
+
+The strip of thumbnails in the second picture was the interface brought up by the newly christened "Recent Apps" button, now living next to Back and Home. Rather than the group of icons brought up in Gingerbread by long-pressing on the home button, Honeycomb showed app icons and thumbnails on the screen, which made it a lot easier to switch between tasks. Recent Apps was clearly inspired by Duarte's "card" multitasking in WebOS, which used full-screen thumbnails to switch tasks. This design offered the same ease-of-recognition as WebOS's task switcher, but the smaller thumbnails allowed more apps to fit on screen at once.
+
+While this implementation of Recent Apps may look like what you get on a current device, this version was very early. The list didn't scroll, meaning it showed seven apps in portrait mode and only five apps in horizontal mode. Anything beyond that was bumped off the list. You also couldn't swipe away thumbnails to close apps—this was just a static list.
+
+Here we see the Tron influence in full effect: the thumbnails had blue outlines and an eerie glow around them. This screenshot also shows a benefit of software buttons—context. The back button closed the list of thumbnails, so instead of the normal arrow, this pointed down.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/16/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2011/03/ars-reviews-the-motorola-xoom/
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/17 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/17 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5422877252
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/17 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+The Honeycomb app lineup lost a ton of apps. This also shows the notification panel and the new quick settings.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The default app icons were slashed from 32 to 25, and two of those were third-party games. Since Honeycomb was not for phones and Google wanted the default apps to all be tablet-optimized, a lot of apps didn't make the cut. We lost the Amazon MP3 store, Car Home, Facebook, Google Goggles, Messaging, News and Weather, Phone, Twitter, Google Voice, and Voice Dialer. Google was quietly building a music service that would launch soon, so the Amazon MP3 store needed to go anyway. Car Home, Messaging, and Phone made little sense on a non-phone device, Facebook and Twitter still don't have tablet Android apps, and Goggles, News and Weather, and Voice Dialer were barely supported applications that most people wouldn't miss.
+
+Almost every app icon was new. Just like the switch from the G1 to the Motorola Droid, the biggest impetus for change was probably the bump in resolution. The Nexus S had an 800×480 display, and Gingerbread came with art assets to match. The Xoom used a whopping 1280×800 10-inch display, which meant nearly every piece of art had to go. But again, this time a real designer was in charge, and things were a lot more cohesive. Honeycomb marked the switch from a vertically scrolling app drawer to paginated horizontal drawer. This change made sense on a horizontal device, but on phones it was still much faster to navigate the app drawer with a flingable, vertical list.
+
+The second Honeycomb screenshot shows the new notification panel. The gray and black Gingerbread design was tossed for another straight-black panel that gave off a blue glow. At the top was a block showing the time, date, connection status, battery, and a shortcut to the notification quick settings, and below that were the actual notifications. Non-permanent notifications could now be dismissed by tapping on an "X" on the right side of the notification. Honeycomb was the first version to enable controls within a notification. The first (and at the launch of Honeycomb, only) app to take advantage of this was the new Google Music app, which placed previous, play/pause, and next buttons in its notification. These new controls could be accessed from any app and made controlling music a breeze.
+
+
+"Add to home screen" was given a zoomed-out interface for easy organizing. The search interface split auto suggest and universal search into different panes.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Pressing the plus button in the top right corner of the home screen or long pressing on the background would open the new home screen configuration interface. Honeycomb showed a zoomed-out view of all the home screens along the top of the screen, and it filled the bottom half of the screen with a tabbed drawer containing widgets and shortcuts. Items could be dragged out of the bottom drawer and into any of the five home screens. Gingerbread would just show a list of text, but Honeycomb showed full thumbnail previews of the widgets. This gave you a much better idea of what a widget would look like instead of an app-name-only description like "calendar."
+
+The larger screen of the Motorola Xoom allowed the keyboard to take on a more PC-style layout, with keys like backspace, enter, shift, and tab put in the traditional locations. The keyboard took on a blueish tint and gained even more spacing between the keys. Google also added a dedicated smiley-face button. :-)
+
+
+Gmail on Honeycomb versus Gmail on Gingerbread with the menu open. Buttons were placed on the main screen for easier discovery.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Gmail demonstrated all the new UI concepts in Honeycomb. Android 3.0 did away with hiding all the controls behind a menu button. There was now a strip of icons along the top of the screen called the Action Bar, which lifted many useful controls to the main screen where users could see them. Gmail showed buttons for search, compose, and refresh, and it put less useful controls like settings, help, and feedback in a dropdown called the "overflow" button. Tapping checkboxes or selecting text would cause the entire action bar to change to icons relating to those actions—for instance, selecting text would bring up cut, copy, and select all buttons.
+
+The app icon displayed in the top left corner doubled as a navigation button called "Up." While "Back" worked similarly to a browser back button, navigating to previously visited screens, "Up" would navigate up the app hierarchy. For instance, if you were in the Android Market, pressed the "Email developer" button, and Gmail opened, "Back" would take you back to the Android Market, but "Up" would take you to the Gmail inbox. "Back" might close the current app, but "Up" never would. Apps could control the "Back" button, and they usually reprogrammed it to replicate the "Up" functionality. In practice, there was rarely a difference between the two buttons.
+
+Honeycomb also introduced the "Fragments" API, which allowed developers to use a single app for tablets and phones. A "Fragment" was a single pane of a user interface. In the Gmail picture above, the left folder list was one fragment and the inbox was another fragment. Phones would show one fragment per screen, and tablets could show two side-by-side. The developer defined the look of individual fragments, and Android would decide how they should be displayed based on the current device.
+
+
+The calculator finally used regular Android buttons, but someone spilled blue ink on the calendar.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+For the first time in Android's history, the calculator got a makeover with non-custom buttons, so it actually looked like part of the OS. The bigger screen made room for more buttons, enough that all the calculator functionality could fit on one screen. The calendar greatly benefited from the extra space, gaining much more room for appointment text and controls. The action bar at the top of the screen held buttons to switch views, along with showing the current time span and common controls. Appointment blocks switched to a white background with the calendar corner only showing in the top right corner. At the bottom (or side, in horizontal view) were boxes showing the month calendar and a list of displayed calendars.
+
+The scale of the calendar could be adjusted, too. By performing a pinch zoom gesture, portrait week and day views could show between five and 19 hours of appointments on a single screen. The background of the calendar was made up of an uneven blue splotch, which didn't look particularly great and was tossed on later versions.
+
+
+The new camera interface, showing off the live "Negative" effect.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The giant 10-inch Xoom tablet did have a camera, which meant that it also had a camera app. The Tron redesign finally got rid of the old faux-leather look that Google came up with in Android 1.6. The controls were laid out in a circle around the shutter button, bringing to mind the circular controls and dials on a real camera. The Cooliris-derived speech bubble popups were changed to glowing, semi-transparent black boxes. The Honeycomb screenshot shows the new "color effect" functionality, which applied a filter to the viewfinder in real time. Unlike the Gingerbread camera app, this didn't support a portrait orientation—it was limited to landscape only. Taking a portrait picture with a 10-inch tablet doesn't make much sense, but then neither does taking a landscape one.
+
+
+The clock app didn't get quite as much love as other areas. Google just threw it into a tiny box and called it a day.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Tons of functionality went out the door when it came time to remake the clock app. The entire "Deskclock" concept was kicked out the door, replaced with a simple large display of the time against a plain black background. The ability to launch other apps and view the weather was gone, as was the ability of the clock app to use your wallpaper. Google sometimes gave up when it came time to design a tablet-sized interface, like here, where it just threw the alarm interface into a tiny, centered dialog box.
+
+
+The Music app finally got the ground-up redesign it has needed forever.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+While music received a few minor additions during its life, this was really the first time since Android 0.9 that it received serious attention. The highlight of the redesign was a don't-call-it-coverflow scrolling 3D album art view, called "New and Recent." Instead of the tabs added in Android 2.1, navigation was handled by a Dropbox box in the Action Bar. While "New and Recent" had 3D scrolling album art, "Albums" used a flat grid of albums thumbnails. The other sections had totally different designs, too. "Songs" used a vertically scrolling list of text, and "Playlists," "Genres," and "Artists" used stacked album art.
+
+In nearly every view, every single item had its own individual menu, usually little arrows in the bottom right corner of an item. For now, these would only show "Play" and "add to Playlist," but this version of Google Music was built for the future. Google was launching a Music service soon, and those individual menus would be needed for things like viewing other content from that artist in the Music Store and managing the cloud storage versus local storage options.
+
+Just like the Cooliris Gallery in Android 2.1, Google Music would blow up one of your thumbnails and use it as a background. The bottom "Now Playing" bar now displayed the album art, playback controls, and a song progress bar.
+
+
+Some of the new Google Maps was really nice, and some of it was from Android 1.5.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Google Maps received another redesign for the big screen. This one would stick around for a while and used a semi-transparent black action bar for all the controls. Search was again the primary function, given the first spot in the action bar, but this time it was an actual search bar you could type in, instead of a search bar-shaped button that launched a completely different interface. Google finally gave up on dedicating screen space to actual zoom buttons, relying on only gestures to control the map view. While the feature has since been ported to all old versions of Maps, Honeycomb was the first version to feature 3D building outlines on the map. Dragging two fingers down on the map would "tilt" the map view and show the sides of the buildings. You could freely rotate and the buildings would adjust, too.
+
+Not every part of Maps was redesigned. Navigation was untouched from Gingerbread, and some core parts of the interface, like directions, were pulled straight from Android 1.6 and centered in a tiny box.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/17/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/18 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/18 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2b795adba1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/18 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+Yet another Android Market redesign dips its toe into the "cards" interface that would become a Google staple.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The Android Market released its fourth new design in Android's two-and-a-half years on the market. This new design was hugely important as it came really close to Google's "cards" interface. By displaying Apps or other content in little blocks, Google could seamlessly transition its app design between screens of various sizes with minimal effort. Content could be displayed just like photos in a gallery app—feed the layout renderer a big list of content blocks, enable screen wrapping, and you were done. Bigger screens saw more blocks of content, and smaller screens only saw a few at a time. With the content display out of the way, Google added a "Categories" fragment to the right side and a big featured app carousel at the top.
+
+While the design was ready for an easily configurable interface, the functionality was not. The original shipping version of the market was locked to a landscape orientation and was Honeycomb-exclusive.
+
+
+The app page and "My Apps" interface.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+This new market sold not only apps, but brought Books and Movies rentals into the fold as well. Google was selling books since 2010; it was only ever through a Website. The new market unified all of Google's content sales in a single location and brought it one step closer to taking on Apple's iTunes juggernaut, though selling all of these items under the "Android Market" was a bit of a branding snafu, as much of the content didn't require Android to use.
+
+
+The browser did its best to look like Chrome, and Contacts used a two-pane interface.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The new Browser added an honest-to-goodness tabs strip at the top of the interface. While this browser wasn't Chrome, it aped a lot of Chrome's design and features. Besides the pioneering tabs-on-top interface, it added Incognito tabs, which kept no history or autocomplete records. There was also an option to have a Chrome-style new tab page consisting of thumbnails of your most-viewed webpages.
+
+The new Browser even synced with Chrome. After signing in to the browser, it would download your Chrome bookmarks and automatically sign in to Google Web pages with your account. Bookmarking a page was as easy as tapping on the star icon in the address bar. Just like Google Maps, the browser dumped the zoom buttons and went with all gesture controls.
+
+The contacts app was finally removed from the phone app and broken out into a standalone app. The previous contacts/dialer hybrid was far too phone-centric for how people use a modern smartphone. Contacts housed information for e-mails, IM, texting, addresses, birthdays, and social networks, so tying it to the phone app makes just as much sense as trying it to Google Maps. With the telephony requirements out of the way, contacts could be simplified to a tab-less list of people. Honeycomb went with a dual pane view showing the full contact list on the left and contacts on the right. This again made use of a Fragments API; a hypothetical phone version of this app could show each panel as a single screen.
+
+The Honeycomb version of Contacts was the first version to have a quick scroll feature. When grabbing the left scroll bar, you could quickly scroll up and down, and a letter preview showed your current spot in the list.
+
+
+The new YouTube app looked like something out of the Matrix.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+YouTube thankfully dumped the "unique" design Google came up with for 2.3 and gave the video service a cohesive design that looked like it belonged in Android. The main screen was a horizontally scrolling curved wall of video thumbnails that showed a most popular or (when signed in) personalized selection of videos. While Google never brought this design to phones, it could be considered an easily reconfigurable card interface. The action bar shined here as a reconfigurable toolbar. When not signed it, the action bar was filled with a search bar. When you were signed in, search shrank down to a button, and tabs for "Home," "Browse," and "Your Channel" were shown.
+
+
+Honeycomb really liked to drive home that it was a computer interface with blue scaffolding. Movie Studio completes the Tron look with an orange theme.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The lone new app in Honeycomb was "Movie Studio," which was not a self-explanatory app and arrived with no explanations or instructions. As far as we could tell, you could import video clips, cut them up, and add text and scene transitions. Editing video—one of the most time consuming, difficult, and processor-intensive things you can do on a computer—on a tablet felt just a little too ambitious, and Google would completely remove this app in later versions. Our favorite part of Movie Studio was that it really completed the Tron theme. While the rest of the OS used blue highlights, this was all orange. (Movie Studio is an evil program!)
+
+
+Widgets!
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Honeycomb brought a new widget framework that allowed for scrolling widgets, and the Gmail, Email, and Calendar widgets were upgraded to support it. YouTube and Books used a new widget that auto-scrolled through cards of content. By flicking up or down on the widget, you could scroll through the cards. We're not sure what the point of being constantly reminded of your book collection was, but it's there if you want it. While all of these widgets worked great on a 10-inch screen, Google never redesigned them for phones, making them practically useless on Android's most popular form factor. All the widgets had massive identifying headers and usually took up half the screen to show only a few items.
+
+
+The scrollable Recent Apps and resizable widgets in Android 3.1.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Later versions of Honeycomb would fix many of the early problems 3.0 had. Android 3.1 was released three months after the first version of Honeycomb, and it brought several improvements. Resizable widgets were one of the biggest features added. After long pressing on a widget, a blue outline with grabbable handles would pop up around it, and dragging the handles around would resize the widget. The Recent Apps panel could now scroll vertically and held many more apps. The only feature missing from it at this point was the ability to swipe away apps.
+
+Today, an 0.1 upgrade is a major release, but in Honeycomb, point releases were considerably smaller. Besides the few UI tweaks, 3.1 added support for gamepads, keyboards, mice, and other input devices over USB and Bluetooth. It also offered a few more developer APIs.
+
+
+Android 3.2's compatibility zoom and a typical stretched-out app on an Android tablet.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Android 3.2 launched two months after 3.1, adding support for smaller sized tablets in the seven- to eight-inch range. It finally enabled SD card support, which the Xoom carried like a vestigial limb for the first five months of its life.
+
+Honeycomb was rushed out the door in order to be an ecosystem builder. No one will want an Android tablet if the tablet-specific apps aren't there, and Google knew it needed to get something in the hands of developers ASAP. At this early stage of Android's tablet ecosystem, the apps just weren't there. It was the biggest problem people had with the Xoom.
+
+3.2 added "Compatibility Zoom," which gave users a new option of stretching apps to the screen (as shown in the right picture) or zooming the normal app layout to fit the screen. Neither option was ideal, and without the app ecosystem to support it, Honeycomb devices sold pretty poorly. Google's tablet moves would eventually pay off though. Today, Android tablets have [taken the market share crown from iOS][1].
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/18/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://techcrunch.com/2014/03/03/gartner-195m-tablets-sold-in-2013-android-grabs-top-spot-from-ipad-with-62-share/
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/19 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/19 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..32841f5be9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/19 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+Google Music Beta running on Gingerbread.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+### Google Music Beta—cloud storage in lieu of a content store ###
+
+While Honeycomb revamped the Google Music interface, the Music app didn't go directly from the Honeycomb design to Ice Cream Sandwich. In May 2011, Google launched "[Google Music Beta][1]," an online music locker that came along with a new Google Music app.
+
+The new Google Music app for 2.2 and up took a few design cues from the Cooliris Gallery, of all things, going with a changing, blurry image for the background. Just about everything was transparent: the pop-up menus, the tabs at the top, and the now-playing bar at the bottom. Individual songs or entire playlists could be downloaded to the device for offline playback, making Google Music an easy way to make sure your music was on all your devices. Besides the mobile app, there was also a Webapp, which allowed Google Music to work on any desktop computer.
+
+Google didn't have content deals in place with the record companies to start a music store yet, so its stop-gap solution was to allow users to store songs online and stream them to a device. Today, Google has content deals for individual song purchases and all-you-can-eat subscription modes, along with the music locker service.
+
+### Android 4.0, Ice Cream Sandwich—the modern era ###
+
+
+The Samsung Galaxy Nexus, Android 4.0's launch device.
+
+Released in October 2011, Android 4.0, Ice Cream Sandwich, got the OS back on track with a release spanning phones and tablets, and it was once again open source. It was the first update to come to phones since Gingerbread, which meant the majority of Android's user base went almost a year without seeing an update. 4.0 was all about shrinking the Honeycomb design to smaller devices, bringing on-screen buttons, the action bar, and the new design language to phones.
+
+Ice Cream Sandwich debuted on the Samsung Galaxy Nexus, one of the first Android phones with a 720p screen. Along with the higher resolution, the Galaxy Nexus pushed phones to even larger sizes with a 4.65-inch screen—almost a full inch larger than the original Nexus One. This was called "too big" by many critics, but today many Android phones are even bigger. (Five inches is "normal" now.) Ice Cream Sandwich required a lot more power than Gingerbread did, and the Galaxy Nexus delivered with a dual core, 1.2Ghz TI OMAP processor and 1GB of RAM.
+
+In the US, the Galaxy Nexus debuted on Verizon with an LTE modem. Unlike previous Nexus devices, the most popular model—the Verizon version—was under the control of a carrier, and Google's software and updates had to be approved by Verizon before the phone could be updated. This led to delays in updates and the removal of software Verizon didn't like, namely Google Wallet.
+
+Thanks to the software improvements in Ice Cream Sandwich, Google finally achieved peak button removal on a phone. With the on-screen navigation buttons, the capacitive buttons could be removed, leaving the Galaxy Nexus with only power and volume buttons.
+
+
+Android 4.0 shrunk down a lot of the Honeycomb design.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The Tron aesthetic in Honeycomb was a little much. Immediately in Ice Cream Sandwich, Google started turning down some of the more sci-fi aspects of the design. The sci-fi clock font changed from a folded over semi-transparent thing to a thin, elegant, normal-looking font. The water ripple touch effect on the unlock circle was removed, and the alien Honeycomb clock widget was scrapped in favor of a more minimal design. The system buttons were redesigned, too, changing from blue outlines with the occasional thick side to thin, even, white outlines. The default wallpaper changed from the blue Honeycomb spaceship interior to a streaky, broken rainbow, which added some much-needed color to the default layout.
+
+The Honeycomb system bar features were split into a two-bar design for phones. At the top was the traditional status bar, and at the bottom was the new system bar, which housed the three system buttons: Back, Home, and Recent. A permanent search bar was added to the top of the home screen. The bar persisted on the screen the same way the dock did, so over the five home screens, it took up 20 icon spots. On the Honeycomb unlock screen, the small inner circle could be moved anywhere outside the larger circle to unlock the device. In Ice Cream Sandwich, you had to actually hit the unlock icon with the inner circle. This new accuracy requirement allowed Google to add another option to the lock screen: a camera shortcut. Dragging the inner circle to the camera icon would directly launch the camera, skipping the home screen.
+
+
+A Phone OS meant a ton more apps, and the notification panel became a full-screen interface again.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The App drawer was still tabbed, but the "My Apps" tab from Honeycomb was replaced with "Widgets," which was a simple 2×3 thumbnail view of widgets. Like Honeycomb, this app drawer was paginated and had to be swiped through horizontally. (Android still uses this app drawer design today.) New in the app drawer was an Android Google+ app, which existed separately for some time. Along with it came a shortcut to "Messenger," the Google+ private messaging service. ("Messenger" is not to be confused with "Messaging," the stock SMS app.)
+
+Since we're back to a phone now, Messaging, News and Weather, Phone, and Voice Dialer returned, and Cordy, a tablet game, was removed. Our screenshots are from the Verizon variant, which, despite being a Nexus device, was sullied by crapware like "My Verizon Mobile," and "VZ Backup Assistant." In keeping with the de-Tronification theme of Ice Cream Sandwich, the Calendar and Camera icons now looked more like something from Planet Earth rather than alien artifacts. Clock, Downloads, Phone, and Android Market got new icons, too, and "Contacts" got a new icon and a new name, becoming "People."
+
+The Notification panel got a big overhaul, especially when compared to the [previous Gingerbread design][2]. There was now a top header featuring the date, a settings shortcut, and a "clear all." While first Honeycomb allowed users to dismiss individual notifications by tapping on an "X" in the notification, Ice Cream Sandwich's implementation was much more elegant: just swipe the individual notifications to the left or right and they cleared. Honeycomb had blue highlights, but the blue tone was all over the place. Ice Cream Sandwich unified almost everything to a single blue (hex code #33B5E5, if you want to get specific). The background of the notification panel was made transparent, and the "handle" at the bottom changed to a minimal blue circle with an opaque black background.
+
+
+The main page of the Android Market changed back to black.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The Market got yet another redesign. It finally supported portrait mode again and added Music to the lineup of content you can buy in the store. The new Market extended the cards concept that debuted in Honeycomb and was the first version to use the same application on tablets and phones. The cards on the main page usually didn't link to apps, instead pointing to special promotional pages like "staff picks" or seasonal promotions.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/19/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2011/05/hands-on-grooving-on-the-go-with-impressive-google-music-beta/
+[2]:http://cdn.arstechnica.net/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/32.png
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/20 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/20 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..30db4ce5c2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/20 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+Another Market design that was nothing like the old one. This lineup shows the categories page, featured, a top apps list, and an app page.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+These screenshots give us our first look at the refined version of the Action Bar in Ice Cream Sandwich. Almost every app got a bar at the top of the screen that housed the app icon, title of the screen, several function buttons, and a menu button on the right. The right-aligned menu button was called the "overflow" button, because it housed items that didn't fit on the main action bar. The overflow menu wasn't static, though, it gave the action bar more screen real-estate—like in horizontal mode or on a tablet—and more of the overflow menu items were shown on the action bar as actual buttons.
+
+New in Ice Cream Sandwich was this design style of "swipe tabs," which replaced the 2×3 interstitial navigation screen Google was previously pushing. A tab bar sat just under the Action Bar, with the center title showing the current tab and the left and right having labels for the pages to the left and right of this screen. A swipe in either direction would change tabs, or you could tap on a title to go to that tab.
+
+One really cool design touch on the individual app screen was that, after the pictures, it would dynamically rearrange the page based on your history with that app. If you never installed the app before, the description would be the first box. If you used the app before, the first section would be the reviews bar, which would either invite you to review the app or remind you what you thought of the app last time you installed it. The second section for a previously used app was “What’s New," since an existing user would most likely be interested in changes.
+
+
+Recent apps and the browser were just like Honeycomb, but smaller.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Recent apps toned the Tron look way down. The blue outline around the thumbnails was removed, along with the eerie, uneven blue glow in the background. It now looked like a neutral UI piece that would be at home in any time period.
+
+The Browser did its best to bring a tabbed experience to phones. Multi-tab browsing was placed front and center, but instead of wasting precious screen space on a tab strip, a tab button would open a Recent Apps-like interface that would show you your open tabs. Functionally, there wasn't much difference between this and the "window" view that was present in past versions of the Browser. The best addition to the Browser was a "Request desktop site" menu item, which would switch from the default mobile view to the normal site. The Browser showed off the flexibility of Google's Action Bar design, which, despite not having a top-left app icon, still functioned like any other top bar design.
+
+
+Gmail and Google Talk—they're like Honeycomb, but smaller!
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Gmail and Google Talk both looked like smaller versions of their Honeycomb designs, but with a few tweaks to work better on smaller screens. Gmail featured a dual Action Bar—one on the top of the screen and one on the bottom. The top of the bar showed your current folder, account, and number of unread messages, and tapping on the bar opened a navigation menu. The bottom featured all the normal buttons you would expect along with the overflow button. This dual layout was used in order display more buttons on the surface level, but in landscape mode where vertical space was at a premium, the dual bars merged into a single top bar.
+
+In the message view, the blue bar was "sticky" when you scrolled down. It stuck to the top of the screen, so you could always see who wrote the current message, reply, or star it. Once in a message, the thin, dark gray bar at the bottom showed your current spot in the inbox (or whatever list brought you here), and you could swipe left and right to get to other messages.
+
+Google Talk would let you swipe left and right to change chat windows, just like Gmail, but there the bar was at the top.
+
+
+The new dialer and the incoming call screen, both of which we haven't seen since Gingerbread.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Since Honeycomb was only for tablets, some UI pieces were directly preceded by Gingerbread instead. The new Ice Cream Sandwich dialer was, of course, black and blue, and it used smaller tabs that could be swiped through. While Ice Cream Sandwich finally did the sensible thing and separated the main phone and contacts interfaces, the phone app still had its own contacts tab. There were now two spots to view your contact list—one with a dark theme and one with a light theme. With a hardware search button no longer being a requirement, the bottom row of buttons had the voicemail shortcut swapped out for a search icon.
+
+Google liked to have the incoming call interface mirror the lock screen, which meant Ice Cream Sandwich got a circle-unlock design. Besides the usual decline or accept options, a new button was added to the top of the circle, which would let you decline a call by sending a pre-defined text message to the caller. Swiping up and picking a message like "Can't talk now, call you later" was (and still is) much more informative than an endlessly ringing phone.
+
+
+Honeycomb didn't have folders or a texting app, so here's Ice Cream Sandwich versus Gingerbread.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Folders were now much easier to make. In Gingerbread, you had to long press on the screen, pick "folders," and then pick "new folder." In Ice Cream Sandwich, just drag one icon on top of another, and a folder is created containing those two icons. It was dead simple and much easier than finding the hidden long-press command.
+
+The design was much improved, too. Gingerbread used a generic beige folder icon, but Ice Cream Sandwich actually showed you what was in the folder by stacking the first three icons on top of each other, drawing a circle around them, and using that as the folder icon. Open folder containers resized to fit the amount of icons in the folder rather than being a full-screen, mostly empty box. It looked way, way better.
+
+
+YouTube switched to a more modern white theme and used a list view instead of the crazy 3D scrolling
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+YouTube was completely redesigned and looked less like something from The Matrix and more like, well, YouTube. It was a simple white list of vertically scrolling videos, just like the website. Making videos on your phone was given prime real estate, with the first button on the action bar dedicated to recording a video. Strangely, different screens used different YouTube logos in the top left, switching between a horizontal YouTube logo and a square one.
+
+YouTube used swipe tabs just about everywhere. They were placed on the main page to browse and view your account and on the video pages to switch between comments, info, and related videos. The 4.0 app showed the first signs of Google+ YouTube integration, placing a "+1" icon next to the traditional rating buttons. Eventually Google+ would completely take over YouTube, turning the comments and author pages into Google+ activity.
+
+
+Ice Cream Sandwich tried to make things easier on everyone. Here is a screen for tracking data usage, the new developer options with tons of analytics enabled, and the intro tutorial.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Data Usage allowed users to easily keep track of and control their data usage. The main page showed a graph of this month's data usage, and users could set thresholds to be warned about data consumption or even set a hard usage limit to avoid overage charges. All of this was done easily by dragging the horizontal orange and red threshold lines higher or lower on the chart. The vertical white bars allowed users to select a slice of time in the graph. At the bottom of the page, the data usage for the selected time was broken down by app, so users could select a spike and easily see what app was sucking up all their data. When times got really tough, in the overflow button was an option to restrict all background data. Then, only apps running in the foreground could have access to the Internet connection.
+
+The Developer Options typically only housed a tiny handful of settings, but in Ice Cream Sandwich the section received a huge expansion. Google added all sorts of on-screen diagnostic overlays to help app developers understand what was happening inside their app. You could view CPU usage, pointer location, and view screen updates. There were also options to change the way the system functioned, like control over animation speed, background processing, and GPU rendering.
+
+One of the biggest differences between Android and the iOS is Android's app drawer interface. In Ice Cream Sandwich's quest to be more user-friendly, the initial startup launched a small tutorial showing users where the app drawer was and how to drag icons out of the drawer and onto the homescreen. With the removal of the off-screen menu button and changes like this, Android 4.0 made a big push to be more inviting to new smartphone users and switchers.
+
+
+The "touch to beam" NFC support, Google Earth, and App Info, which would let you disable crapware.
+
+Built into Ice Cream Sandwich was full support for [NFC][1]. While previous devices like the Nexus S had NFC, support was limited and the OS couldn't do much with the chip. 4.0 added a feature called Android Beam, which would let two NFC-equipped Android 4.0 devices transfer data back and forth. NFC would transmit data related to whatever was on the screen at the time, so tapping when a phone displayed a webpage would send that page to the other phone. You could also send contact information, directions, and YouTube links. When the two phones were put together, the screen zoomed out, and tapping on the zoomed-out display would send the information.
+
+In Android, users are not allowed to uninstall system apps, which are often integral to the function of the device. Carriers and OEMs took advantage of this and started putting crapware in the system partition, which they would often stick with software they didn't want. Android 4.0 allowed users to disable any app that couldn't be uninstalled, meaning the app remained on the system but didn't show up in the app drawer and couldn't be run. If users were willing to dig through the settings, this gave them an easy way to take control of their phone.
+
+Android 4.0 can be thought of as the start of the modern Android era. Most of the Google apps released around this time only worked on Android 4.0 and above. There were so many new APIs that Google wanted to take advantage of that—initially at least—support for versions below 4.0 was limited. After Ice Cream Sandwich and Honeycomb, Google was really starting to get serious about software design. In January 2012, the company [finally launched][2] *Android Design*, a design guideline site that taught Android app developers how to create apps to match the look and feel of Android. This was something iOS not only had from the start of third-party app support, but Apple enforced design so seriously that apps that did not meet the guidelines were blocked from the App Store. The fact that Android went three years without any kind of public design documents from Google shows just how bad things used to be. But with Duarte in charge of Android's design revolution, the company was finally addressing basic design needs.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/20/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2011/02/near-field-communications-a-technology-primer/
+[2]:http://arstechnica.com/business/2012/01/google-launches-style-guide-for-android-developers/
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/21 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/21 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..265e7a867b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/21 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+### Google Play and the return of direct-to-consumer device sales ###
+
+On March 6, 2012, Google unified all of its content offerings under the banner of "Google Play." The Android Market became the Google Play Store, Google Books became Google Play Books, Google Music became Google Play Music, and Android Market Movies became Google Play Movies & TV. While the app interfaces didn't change much, all four content apps got new names and icons. Content purchased in the Play Store would be downloaded to the appropriate app, and the Play Store and Play content apps all worked together to provide a fairly organized content experience.
+
+The Google Play update was Google's first big out-of-cycle update. Four packed-in apps were all changed without having to issue a system update—they were all updated through the Android Market/Play Store. Enabling out-of-cycle updates to individual apps was a big focus for Google, and being able to do an update like this was the culmination of an engineering effort that started in the Gingerbread era. Google had been working on "decoupling" the apps from the operating system and making everything portable enough to be distributed through the Android Market/Play Store.
+
+While one or two apps (mostly Maps and Gmail) had previously lived on the Android Market, from here on you'll see a lot more significant updates that have nothing to do with an operating system release. System updates require the cooperation of OEMs and carriers, so they are difficult to push out to every user. Play Store updates are completely controlled by Google, though, providing the company a direct line to users' devices. For the launch of Google Play, the Android Market updated itself to the Google Play Store, and from there, Books, Music, and Movies were all issued Google Play-flavored updates.
+
+The design of the Google Play apps was still all over the place. Each app looked and functioned differently, but for now, a cohesive brand was a good start. And removing "Android" from the branding was necessary because many services were available in the browser and could be used without touching an Android device at all.
+
+In April 2012, Google started [selling devices though the Play Store again][1], reviving the direct-to-customer model it had experimented with for the launch of the Nexus One. While it was only two years after ending the Nexus One sales, Internet shopping was now more common place, and buying something before you could hold it didn't seem as crazy as it did in 2010.
+
+Google also saw how price-conscious consumers became when faced with the Nexus One's $530 price tag. The first device for sale was an unlocked, GSM version of the Galaxy Nexus for $399. From there, price would go even lower. $350 has been the entry-level price for the last two Nexus smartphones, and 7-inch Nexus tablets would come in at only $200 to $220.
+
+Today, the Play Store sells eight different Android devices, four Chromebooks, a thermostat, and tons of accessories, and the device store is the de-facto location for a new Google product launch. New phone launches are so popular, the site usually breaks under the load, and new Nexus phones sell out in a few hours.
+
+### Android 4.1, Jelly Bean—Google Now points toward the future ###
+
+
+The Asus-made Nexus 7, Android 4.1's launch device.
+
+With the release of Android 4.1, Jelly Bean in July 2012, Google settled into an Android release cadence of about every six months. The platform matured to the point where a release every three months was unnecessary, and the slower release cycle gave OEMs a chance to catch their breath. Unlike Honeycomb, point releases were now fairly major updates, with 4.1 bringing major UI and framework changes.
+
+One of the biggest changes in Jelly Bean that you won't be able to see in screenshots is "Project Butter," the name for a concerted effort by Google's engineers to make Android animations run smoothly at 30FPS. Core changes were made, like Vsync and triple buffering, and individual animations were optimized so they could be drawn smoothly. Animation and scrolling smoothness had always been a weak point of Android when compared to iOS. After some work on both the core animation framework and on individual apps, Jelly Bean brought Android a lot closer to iOS' smoothness.
+
+Along with Jelly Bean came the [Nexus][2] 7, a 7-inch tablet manufactured by Asus. Unlike the primarily horizontal Xoom, the Nexus 7 was meant to be used in portrait mode, like a large phone. The Nexus 7 showed that, after almost a year-and-a-half of ecosystem building, Google was ready to commit to the tablet market with a flagship device. Like the Nexus One and GSM Galaxy Nexus, the Nexus 7 was sold online directly by Google. While those earlier devices had shockingly high prices for consumers that were used to carrier subsidies, the Nexus 7 hit a mass market price point of only $200. The price bought you a device with a 7-inch, 1280x800 display, a quad core, 1.2 GHz Tegra 3 processor, 1GB of RAM, and 8GB of storage. The Nexus 7 was such a good value that many wondered if Google was making any money at all on its flagship tablet.
+
+This smaller, lighter, 7-inch form factor would be a huge success for Google, and it put the company in the rare position of being an industry trendsetter. Apple, which started with a 10-inch iPad, was eventually forced to answer the Nexus 7 and tablets like it with the iPad Mini.
+
+
+4.1's new lock screen design, wallpaper, and the new on-press highlight on the system buttons.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The Tron look introduced in Honeycomb was toned down a little in Ice Cream Sandwich, and Jelly Bean took things a step further. It started removing blue from large chunks of the operating system. The hint was the on-press highlights on the system buttons, which changed from blue to gray.
+
+
+A composite image of the new app lineup and the new notification panel with expandable notifications.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The Notification panel was completely revamped, and we've finally arrived at the design used today in KitKat. The new panel extended to the top of the screen and covered the usual status icons, meaning the status bar was no longer visible when the panel was open. The time was prominently displayed in the top left corner, along with the date and a settings shortcut. The clear all notions button, which was represented by an "X" in Ice Cream Sandwich, changed to a stairstep icon, symbolizing the staggered sliding animation that cleared the notification panel. The bottom handle changed from a circle to a single line that ran the length of the notification panel. All the typography was changed—the notification panel now used bigger, thinner fonts for everything. This was another screen where the blue introduced in Ice Cream Sandwich and Honeycomb was removed. The notification panel was entirely gray now except for on-touch highlights.
+
+There was new functionality in the panel, too. Notifications were now expandable and could show much more information than the previous two-line design. It now showed up to eight lines of text and could even show buttons at the bottom of the notification. The screenshot notification had a share button at the bottom, and you could call directly from a missed call notification, or you could snooze a ringing alarm all from the notification panel. New notifications were expanded by default, but as they piled up they would collapse back to the traditional size. Dragging down on a notification with two fingers would expand it.
+
+
+The new Google Search app, with Google Now cards, voice search, and text search.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The biggest feature addition to Jelly Bean for not only Android, but for Google as a whole, was the new version of the Google Search application. This introduced "Google Now," a predictive search feature. Google Now was displayed as several cards that sit below the search box, and it would offer results to searches Google thinks you care about. These were things like Google Maps searches for places you've recently looked at on your desktop computer or calendar appointment locations, the weather, and time at home while traveling.
+
+The new Google Search app could, of course, be launched with the Google icon, but it could also be accessed from any screen with a swipe up from the system bar. Long pressing on the system bar brought up a ring that worked similarly to the lock screen ring. The card section scrolled vertically, and cards could be a swipe away if you didn't want to see them. Voice Search was a big part of the updates. Questions weren't just blindly entered into Google; if Google knew the answer, it would also talk back using a text-To-Speech engine. And old-school text searches were, of course, still supported. Just tap on the bar and start typing.
+
+Google frequently called Google Now "the future of Google Search." Telling Google what you wanted wasn't good enough. Google wanted to know what you wanted before you did. Google Now put all of Google's data mining knowledge about you to work for you, and it was the company's biggest advantage against rival search services like Bing. Smartphones knew more about you than any other device you own, so the service debuted on Android. But Google slowly worked Google Now into Chrome, and eventually it will likely end up on Google.com.
+
+While the functionality was important, it became clear that Google Now was the most important design work to ever come out of the company, too. The white card aesthetic that this app introduced would become the foundation for Google's design of just about everything. Today, this card style is used in the Google Play Store and in all of the Play content apps, YouTube, Google Maps, Drive, Keep, Gmail, Google+, and many others. It's not just Android apps, either. Many of Google's desktop sites and iOS apps are inspired by this design. Design was historically one of Google's weak areas, but Google Now was the point where the company finally got its act together with a cohesive, company-wide design language.
+
+
+Yet another YouTube redesign. Information density went way down.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Another version, another YouTube redesign. This time the list view was primarily thumbnail-based, with giant images taking up most of the screen real estate. Information density tanked with the new list design. Before YouTube would display around six items per screen, now it could only display three.
+
+YouTube was one of the first apps to add a sliding drawer to the left side of an app, a feature which would become a standard design style across Google's apps. The drawer has links for your account and channel subscriptions, which allowed Google to kill the tabs-on-top design.
+
+
+Google Play Service's responsibilities versus the rest of Android.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+### Google Play Services—fragmentation and making OS versions (nearly) obsolete ###
+
+It didn't seem like a big deal at the time, but in September 2012, Google Play Services 1.0 was automatically pushed out to every Android phone running 2.2 and up. It added a few Google+ APIs and support for OAuth 2.0.
+
+While this update might sound boring, Google Play Services would eventually grow to become an integral part of Android. Google Play Services acts as a shim between the normal apps and the installed Android OS, allowing Google to update or replace some core components and add APIs without having to ship out a new Android version.
+
+With Play Services, Google had a direct line to the core of an Android phone without having to go through OEM updates and carrier approval processes. Google used Play Services to add an entirely new location system, a malware scanner, remote wipe capabilities, and new Google Maps APIs, all without shipping an OS update. Like we mentioned at the end of the Gingerbread section, thanks to all the "portable" APIs implemented in Play Services, Gingerbread can still download a modern version of the Play Store and many other Google Apps.
+
+The other big benefit was compatibility with Android's user base. The newest release of an Android OS can take a very long time to get out to the majority of users, which means APIs that get tied to the latest version of the OS won't be any good to developers until the majority of the user base upgrades. Google Play Services is compatible with Froyo and above, which is 99 percent of active devices, and the updates pushed directly to phones through the Play Store. By including APIs in Google Play Services instead of Android, Google can push a new API out to almost all users in about a week. It's [a great solution][3] to many of the problems caused by version fragmentation.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/21/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2012/04/unlocked-samsung-galaxy-nexus-can-now-be-purchased-from-google/
+[2]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2012/07/divine-intervention-googles-nexus-7-is-a-fantastic-200-tablet/
+[3]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/09/balky-carriers-and-slow-oems-step-aside-google-is-defragging-android/
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/22 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/22 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..79cf7bd2a5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/22 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+### Android 4.2, Jelly Bean—new Nexus devices, new tablet interface ###
+
+The Android Platform was rapidly maturing, and with Google hosting more and more apps in the Play Store, there was less and less that needed to go out in the OS update. Still, the relentless march of updates must continue, and in November 2012 Android 4.2 was released. 4.2 was still called "Jelly Bean," a nod to the relatively small amount of changes that were present in this release.
+
+
+The LG-made Nexus 4 and Samsung-made Nexus 10.
+Photo by Google/Ron Amadeo
+
+Along with Android 4.2 came two flagship devices, the Nexus 4 and the Nexus 10, both of which were sold direct by Google on the Play Store. The Nexus 4 applied the Nexus 7 strategy of a quality device at a shockingly low price and sold for $300 unlocked. The Nexus 4 had a quad-core 1.5 GHz Snapdragon S4 Pro, 2GB of RAM and a 4.7-inch 1280×768 LCD. Google's new flagship phone was manufactured by LG, and with the manufacturer switch came a focus on materials and build quality. The Nexus 4 had a glass front and back, and while you couldn't drop it, it was one of the nicest-feeling Android phones to date. The biggest downside to the Nexus 4 was the lack of LTE at a time when most phones, including the Verizon Galaxy Nexus, came with the faster modem. Still, demand for the Nexus 4 greatly exceeded Google's expectations—the launch rush crashed the Play Store Web site on launch day. The device sold out in under an hour.
+
+The Nexus 10 was Google's first 10-inch Nexus tablet. The highlight of the device was the 2560×1600 display, which was the highest resolution in its class. All those pixels were powered by a dual core, 1.7GHz Cortex A15 processor and 2GB of RAM. With each passing month, it's looking more and more like the Nexus 10 is the first and last 10-inch Nexus tablet. Usually these devices are upgraded every year, but the Nexus 10 is now 16 months old, and there's no sign of the new model on the horizon. Google is doing well with smaller-sized 7-inch tablets, and it seems content to let partners [like Samsung][1] explore the larger end of the tablet spectrum.
+
+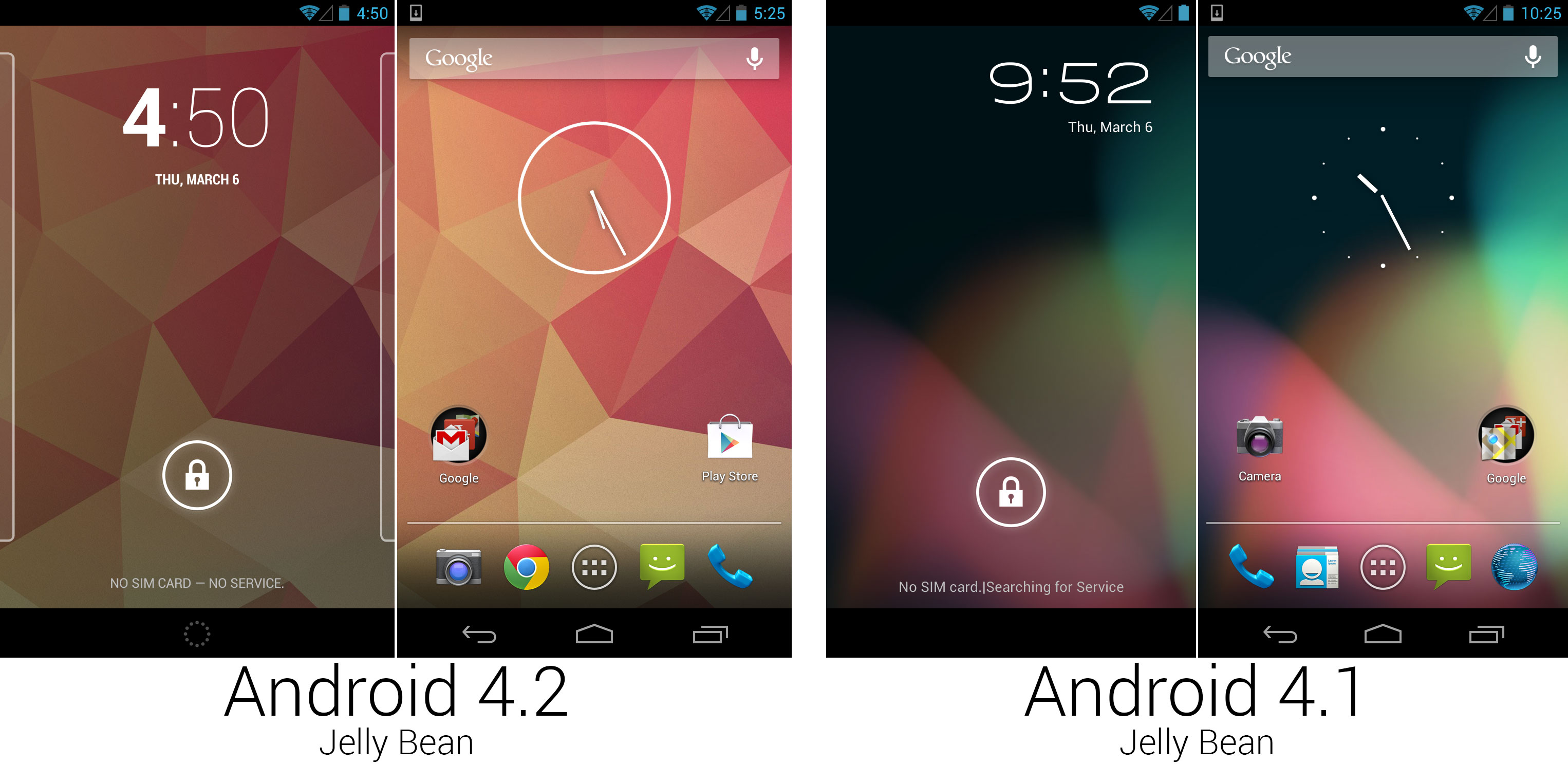
+The new lock screen, wallpaper, and clock widget design.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+4.2 brought lots of changes to the lock screen. The font was centered and used an extremely thick weight for the hour and a thin font for the minutes. The lock screen was now paginated and could be customized with widgets. Rather than a simple clock on the lock screen, users could replace it with another widget or add extra pages to the lock screen for more widgets.
+
+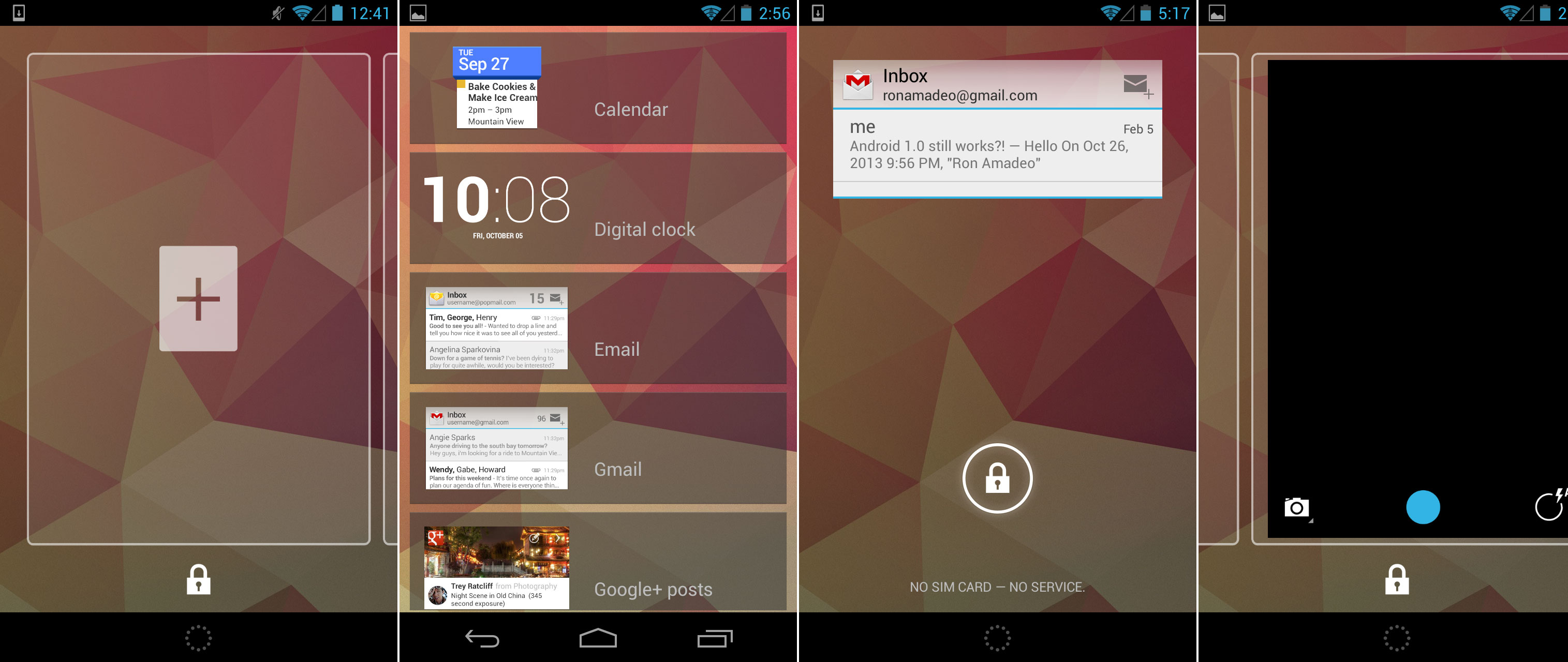
+The lock screen's add widget page, the list of widgets, the Gmail widget on the lock screen, and swiping over to the camera.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The lock screen now worked like a stripped-down version of the home screen. Page outlines would pop up on the left and right sides of the lock screen to hint to users that they could swipe to other pages with other widgets. Swiping to the left would show a simple blank page with a plus sign in the center, and tapping on it would bring up a list of widgets that were compatible with the lock screen. Lock screens were limited to one widget per page and could be expanded or collapsed by dragging up or down on the widget. The right-most page was reserved for the camera—a simple over would open the camera interface, but you weren't able to swipe back.
+
+
+The new Quick Settings panel and a composite image of the app lineup.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+One of the biggest additions to 4.2 was the new "Quick Settings" panel. Android 3.0 brought a way to quickly change power settings to tablets, and 4.2 finally brought that ability to phones. A new icon was added to the top right corner of the notification panel that would switch between the normal list of notifications and the new quick settings screen. Quick Settings offered faster access to screen brightness, network connections, and battery and data usage without having to dig through the full settings screen. The top level settings button in Android 4.1 was removed, and a square was added to the Quick Settings screen for it.
+
+There were lots of changes to the app drawer and 4.2's lineup of apps and icons. Thanks to the wider aspect ratio of the Nexus 4 (5:3 vs 16:9 on the Galaxy Nexus), the app drawer on that device could now show a five-wide grid of icons. 4.2 replaced the stock browser with Google Chrome and the stock calendar with Google Calendar, both of which brought new icon designs. The Clock and Camera apps were revamped in 4.2, and new icons were part of the deal. "Google Settings" was a new app that offered shortcuts to all the existing Google Account settings around the OS, and it had a unified look with Google Search and the new Google+ icon. Google Maps got a new icon, and Google Latitude, which was part of Google Maps, was retired in favor of Google+ location.
+
+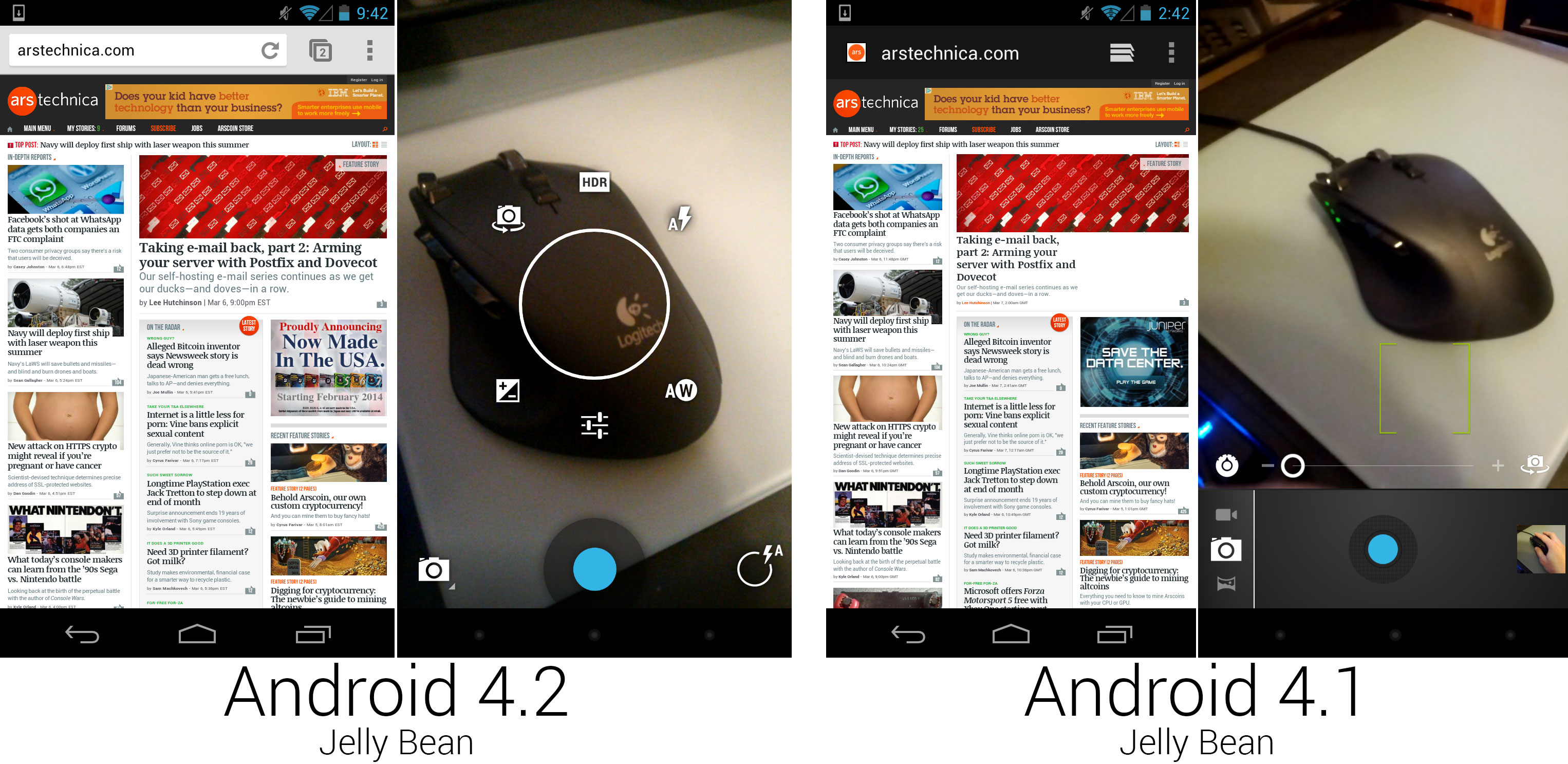
+The browser was replaced with Chrome, and the new camera interface with a full screen viewfinder.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The stock browser did its best Chrome imitation for a while—it took many cues from Chrome’s interface, many Chrome features, and was even using Chrome’s javascript engine—but by the time Android 4.2 rolled around, Google deemed the Android version of Chrome ready to replace the imitator. On the surface, it didn't seem like much of a difference; the interface looked different, and early versions of Chrome for Android didn't scroll as smoothly as the stock browser. Under the hood, though, everything was different. Development of Android's main browser was now handled by the Google Chrome team instead of being a side project of the Android team. Android's default browser moved from being a stagnant app tied to Android releases to a Play Store app that was continually updated. Today there is even a beta channel that receives several updates per month.
+
+The camera interface was redesigned. It was now a completely full-screen app, showing a live view of the camera and places controls on top of it. The layout aesthetic had a lot in common with the [camera design][2] of Android 1.5: minimal controls with a focus on the viewfinder output. The circle of controls in the center appeared when you either held your finger on the screen or pressed the circle icon in the bottom right corner. When holding your finger down, you could slide around to pick the options around the circle, often expanding out into a sub-menu. Releasing over a highlighted item would select it. This was clearly inspired by the Quick Controls in the Android 4.0 browser, but arranging the options in a circle meant your finger was almost always blocking part of the interface.
+
+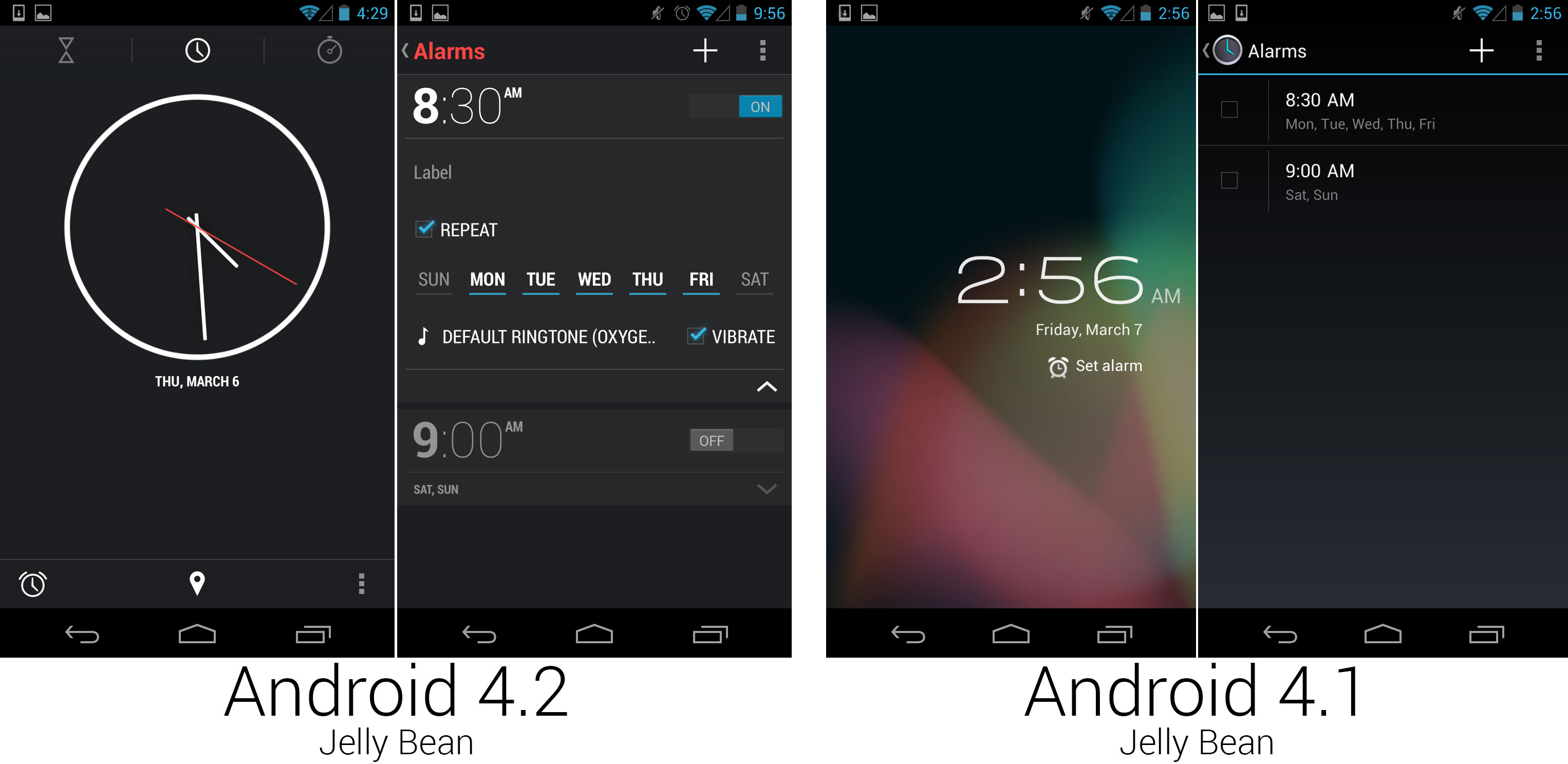
+The clock app, which went from a two-screen app to a feature-packed, useful application.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The clock application was completely revamped, going from a simple two-screen alarm clock to a world clock, alarm, timer, and stopwatch. The clock app design was like nothing Google introduced before, with an ultra-minimal aesthetic and red highlights. It seemed to be an experiment for Google. Even several versions later, this design language seemed to be confined only to this app.
+
+The clock's time picker was particularly well-designed. It showed a simple number pad, and it would intelligently disable numbers that would result in an invalid time. It was also impossible to set an alarm time without implicitly selecting AM or PM, forever solving the problem of accidentally setting an alarm for 9pm instead of 9am.
+
+
+The new system UI for tablets used a stretched-out phone interface.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The most controversial change in Android 4.2 was made to the tablet UI, which switched from a unified single bottom system bar to a two-bar interface with a top status bar and bottom system bar. The new design unified the phone and tablet interfaces, but critics said it was a waste of space to stretch the phone interface to a 10-inch landscape tablet. Since the navigation buttons had the whole bottom bar to themselves now, they were centered, just like the phone interface.
+
+
+Multiple users on a tablet, and the new gesture-driven keyboard.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+On tablets, Android 4.2 brought support for multiple users. In the settings, a "Users" section was added, where you could manage users on a device. Setup was done from within each user account, where Android would keep separate settings, home screens, apps, and app data for each user.
+
+4.2 also added a new keyboard with swiping abilities. Rather than just tapping each individual letter, users could now keep a finger on the screen the whole time and just slide from letter to letter to type.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/22/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/01/hands-on-with-samsungs-notepro-and-tabpro-new-screen-sizes-and-magazine-ui/
+[2]:http://cdn.arstechnica.net/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/device-2013-12-26-11016071.png
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/23 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/23 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e67dff87e6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/23 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+Another Play Store redesign! This one is very close to the current design and uses cards that make layout changes a piece of cake.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+### Out-of-cycle updates—who needs a new OS? ###
+
+In between Android 4.2 and 4.3, Google went on an out-of-cycle update tear and showed just how much Android could be improved without having to fire up the arduous OTA update process. Thanks to the [Google Play Store and Play Services][1], all of these updates were able to be delivered without updating any core system components.
+
+In April 2013, Google released a major redesign to the Google Play Store. Like most redesigns from here on out, the new Play Store fully adopted the Google Now aesthetic, with white cards on a gray background. The action bar changed color based on the current content section, and since the first screen featured content from all sections of the store, the action bar was a neutral gray. Buttons to navigate to the content sections were now given top billing, and below that was usually a promotional block or rows of recommended apps.
+
+In April 2013, Google released a major redesign to the Google Play Store. Like most redesigns from here on out, the new Play Store fully adopted the Google Now aesthetic, with white cards on a gray background. The action bar changed color based on the current content section, and since the first screen featured content from all sections of the store, the action bar was a neutral gray. Buttons to navigate to the content sections were now given top billing, and below that was usually a promotional block or rows of recommended apps.
+
+
+The individual content sections are beautifully color-coded.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The new Play Store showed off the real power of Google’s card design language, which enabled a fully responsive layout across all screen sizes. One large card could be stuck next to several little cards, larger-screened devices could show more cards, and rather than stretch things in horizontal mode, more cards could just be added to a row. The Play Store content editors were free to play with the layout of the cards, too; a big release that needed to be highlighted could get a larger card. This design would eventually trickle down to the other Google Play content apps, finally resulting in a unified design.
+
+
+Hangouts replaced Google Talk and is now continually developed by the Google+ team.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Google I/O, the company's annual developer conference, was usually where a new Android version was announced. But at the 2013 edition, Google made just as many improvements without having to update the OS.
+
+One of the biggest things announced at the show was an update to Google Talk, Google's instant messaging platform. For a long time, Google shipped four text communication apps for Android: Google Talk, Google+ Messenger, Messaging (the SMS app), and Google Voice. Having four apps that accomplished the same task—sending a text message to someone—was very confusing for users. At I/O, Google killed Google Talk and started their messaging product over from scratch, creating [Google Hangouts][2]. While initially it only replaced Google Talk, the plan for Hangouts was to unify all of Google's various messaging apps into a single interface.
+
+The layout of the Hangouts UI really wasn't drastically different from Google Talk. The main page contained your open conversations, and tapping on one opened a chat page. The design was updated, the chat page now used a card-style display for each paragraph, and the chat list was now a "drawer"-style interface, meaning you could open it with a horizontal swipe. Hangouts had read receipts and a typing status indicator, and group chat was now a primary feature.
+
+Google+ was the center of Hangouts now, so much so that the full name of the product was actually "Google+ Hangouts." Hangouts was completely integrated with the Google+ desktop site so that video and chats could be made from one to the other. Identity and avatars were pulled from Google+, and tapping on an avatar would open that person's Google+ profile. And much like the change from Browser to Google Chrome, core Android functionality was passed off to a separate team—the Google+ team—as opposed to being a side product of the very busy Android engineers. With the Google+ takeover, Android's main IM client now became a continually developed application. It was placed into the Play Store and received fairly regular updates.
+
+
+The new navigation drawer interface.
+Photo by [developer.android.com][3]
+
+Google also introduced a new design element for the action bar: the navigation drawer. This drawer was shown as a set of three lines next to the app icon in the top-right corner. By tapping on it or dragging from the edge of the screen to the right, a side-mounted menu would appear. As the name implies, this was used to navigate around the app, and it would show several top-level locations within the app. This allowed the first screen to show content, and it gave users a consistent, easy-to-access place for navigation elements. The nav drawer was basically a super-sized version of the normal menu, scrollable and docked to the right side.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/23/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/09/balky-carriers-and-slow-oems-step-aside-google-is-defragging-android/
+[2]:http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2013/05/hands-on-with-hangouts-googles-new-text-and-video-chat-architecture/
+[3]:https://developer.android.com/design/patterns/navigation-drawer.html
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/24 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/24 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b95ceb29c7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/24 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+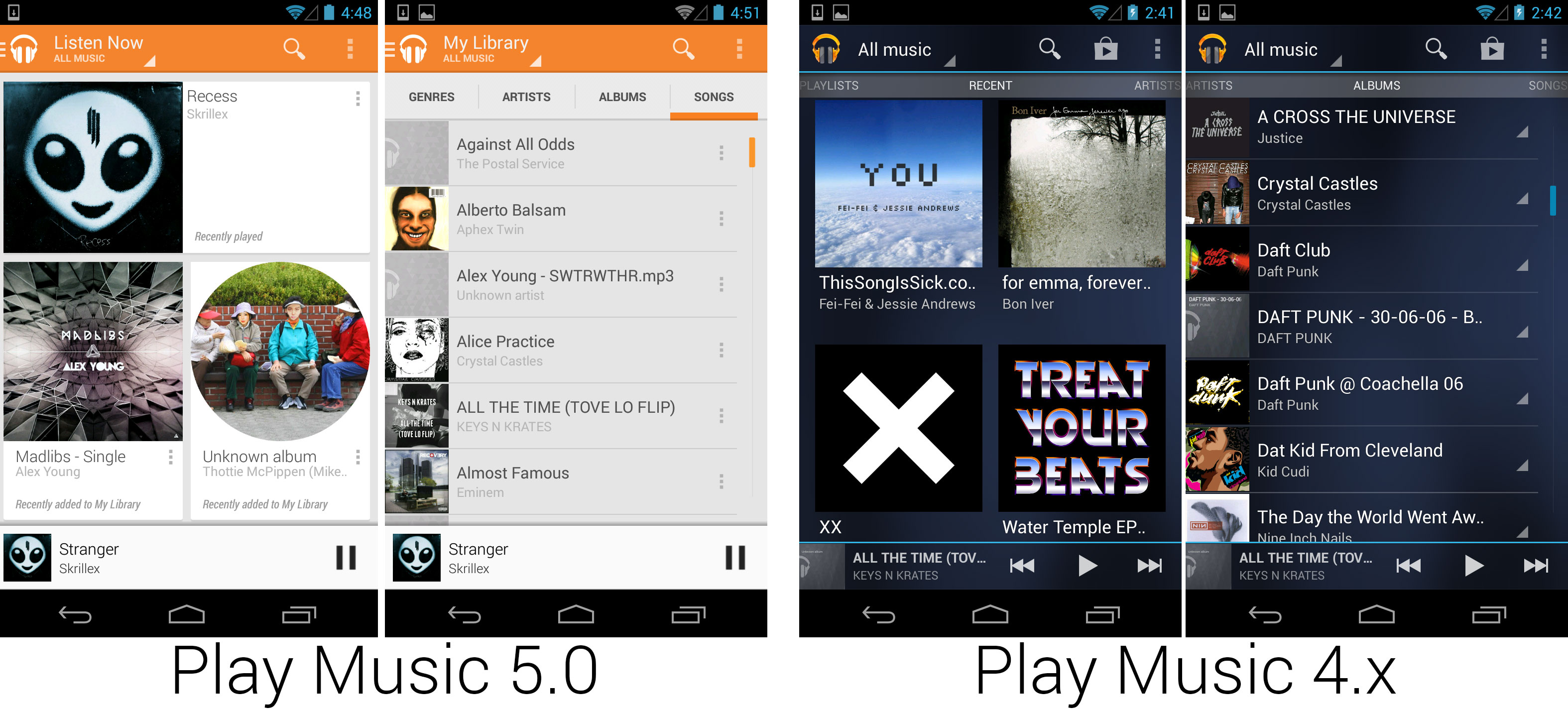
+The slick new Google Play Music app, which changed from Tron to a perfect match for the Play Store.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Another app update pushed out at I/O was a new Google Music app. The app was completely redesigned, finally doing away with the blue-on-blue design introduced in Honeycomb. Play Music's design was unified with the new Play Store released a few months earlier, with a responsive white card layout. Music was also one of the first major apps to take advantage of the new navigation drawer style. Along with the new app, Google launched Google Play Music All Access, an all-you-can-eat subscription service for $10 a month. Google Music now had a subscription plan, à la carte purchasing, and a cloud music locker. This version also introduced "Instant Mix," a mode where Google would cloud-compute a playlist of similar songs.
+
+
+A game showing support for Google Play Games. This lineup shows the Play Store game feature descriptions, the permissions box triggered by signing into the game, a Play Games notification, and the achievements screen.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Google also introduced "Google Play Games," a back-end service that developers could plug into their games. The service was basically an Android version of Xbox Live or Apple's Game Center. Developers could build Play Games support into their game, which would easily let them integrate achievements, leaderboards, multiplayer, matchmaking, user accounts, and cloud saves by using Google's back-end services.
+
+Play Games was the start of Google's big push into gaming. Just like standalone GPS units, flip phones, and MP3 players, smartphone makers were hoping standalone gaming devices would be turned into nothing more than a smartphone feature bullet point. Why buy a Nintendo DS or PS Vita when you had a smartphone with you? An easy-to-use multiplayer service would be a big part of this, and we've still yet to see the final consequence of this move. Today, Google and Apple are both rumored to be planning living room gaming devices.
+
+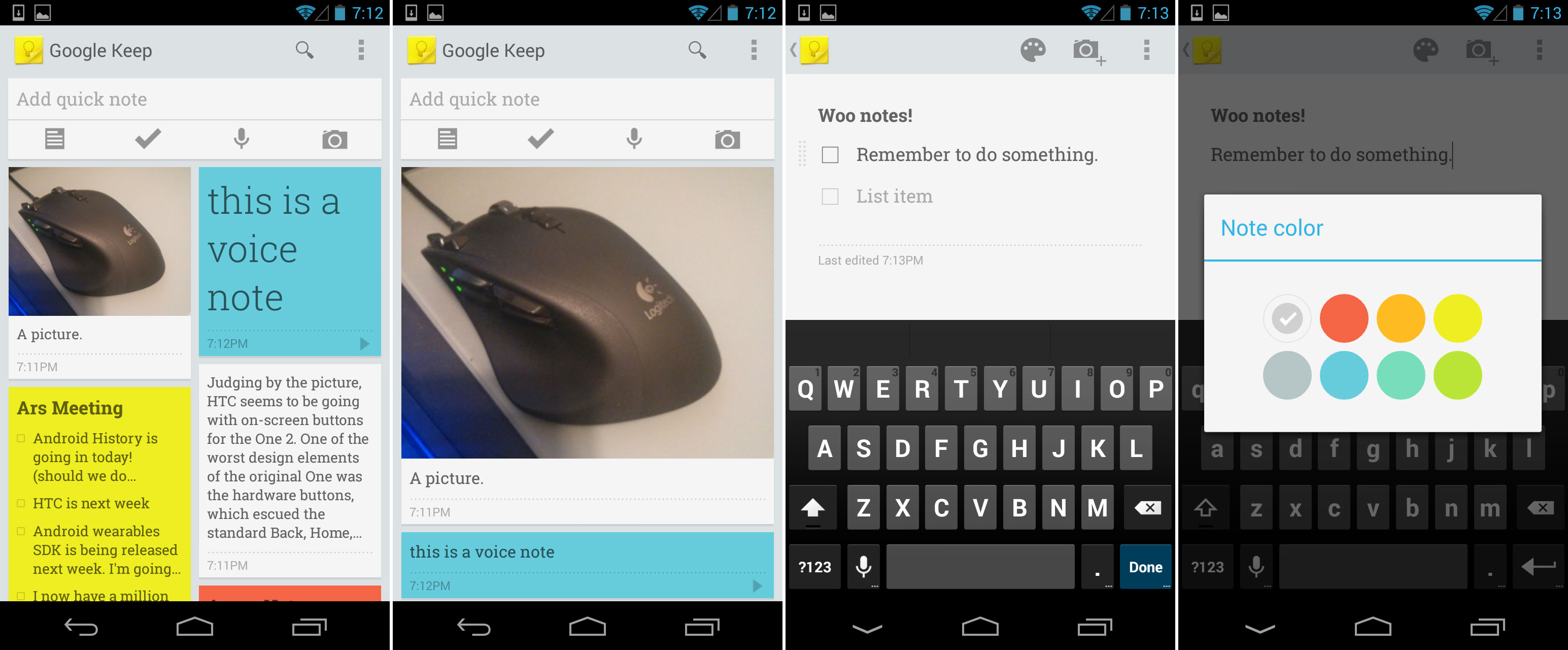
+Google Keep, Google's first note taking service since Google Notebook.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+It was clear some products were developed in time for presentation at Google I/O, [but the three-and-a-half hour keynote][1] was already so massive, some things were cut from being announced. Once the smoke cleared three days after Google I/O, Google introduced Google Keep, a note taking app for Android and the Web. Keep was a fairly straightforward affair, applying the responsive Google Now-style design to a note taking app. Users could change the size of the cards from a multi-column layout to a single column view. Notes could consist of plain text, checklists, voice note with automatic transcription, or pictures. Note cards could be dragged around and rearranged on the main screen, and you could even assign a color to a note.
+
+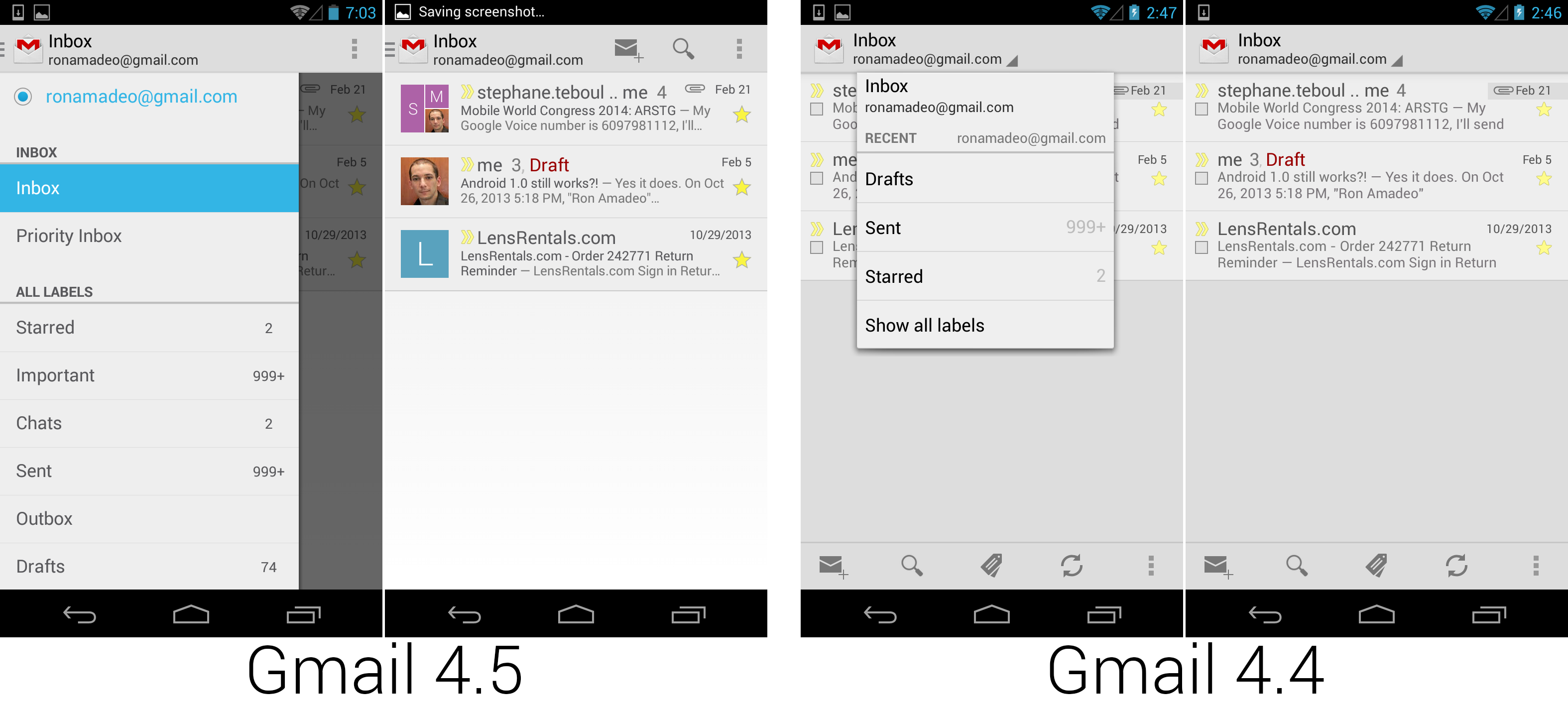
+Gmail 4.5, which switched to the new navigation drawer design and merged the action bars, thanks to some clever button elimination.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+After I/O, not much was safe from Google's out-of-cycle updating. In June 2013, Google released a redesigned version of Gmail. The headline feature of the new design was the new navigation drawer interface that was introduced a month earlier at Google I/O. The most eye catching change was the addition of Google+ profile pictures instead of checkboxes. While the checkboxes were visibly removed, they were still there, just tap on a picture.
+
+
+The new Google Maps, which switched to an all-white Google Now-style theme.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+One month later, Google released a completely overhauled version of Google Maps to the Play Store. It was the first ground-up redesign of Google Maps since Ice Cream Sandwich. The new version fully adopted the Google Now white card aesthetic, and it greatly reduced the amount of stuff on the screen. The new Google Maps seemed to have a design mandate to always show a map on the screen somewhere, as you’ll be hard pressed to find something other than the settings that fully covers the map.
+
+This version of Google Maps seemed to live in its own little design world. The white search bar “floated" above the map, with maps showing on the sides and top of the bar. That didn't really make it seem like the traditional Action Bar design. The navigation drawer, in the top left on every other app, was in the bottom left. There was no up button, app icon, or overflow button on the main screen.
+
+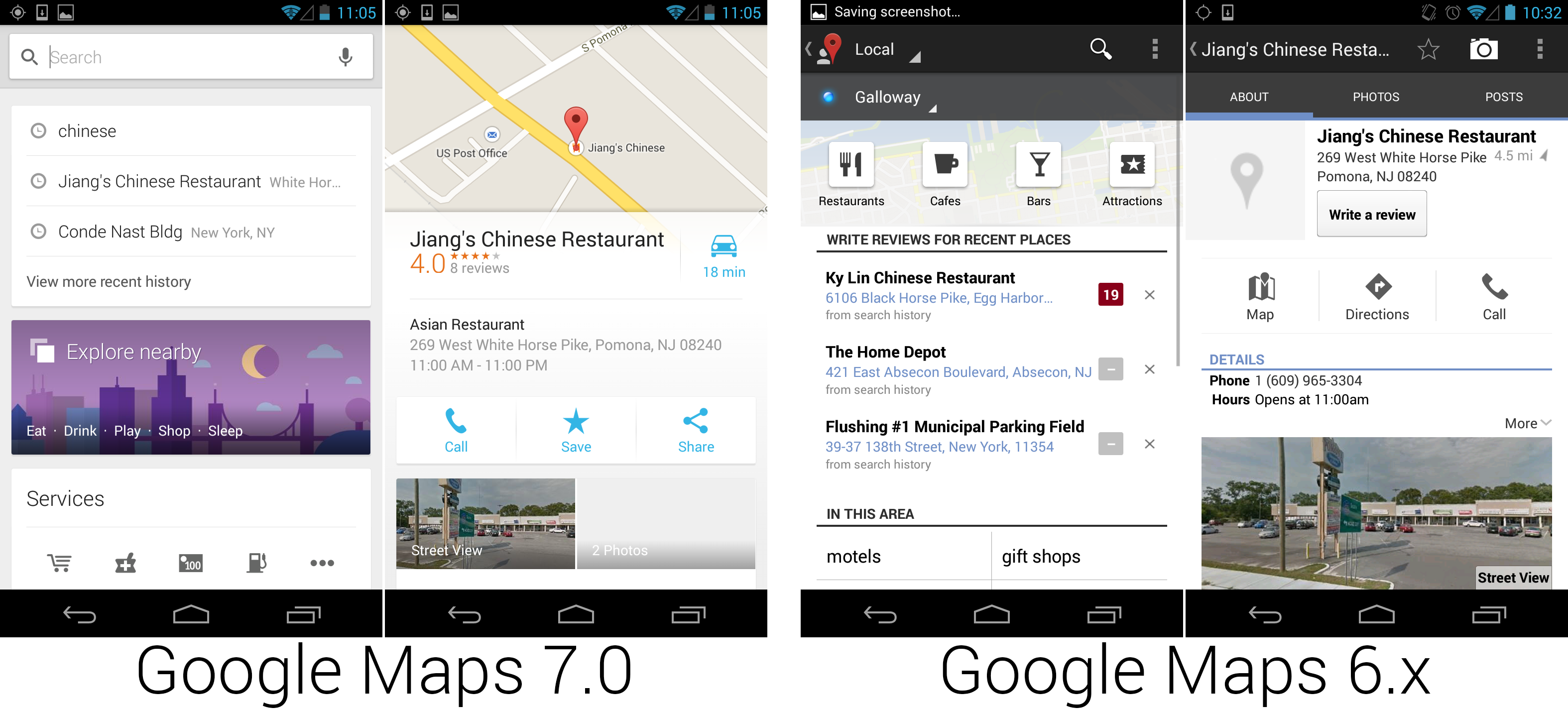
+The new Google Maps cut a lot of fat and displayed more information on a single screen.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The left picture shows what popped up when you tapped on the search bar (along with the keyboard, which had been closed). In the past, Google would show an empty page below a blank search bar, but in Maps, Google used that space to link to the new “Local" page. The “blank" search results displayed links to common, browsable results like restaurant listings, gas stations, and attractions. At the bottom of the results page was a list of nearby results from your search history and an option to manually cache parts of the map.
+
+The right set of images shows location page. The map shown in the top of the Maps 7 screenshot isn’t a thumbnail; that’s the full map view. In the new version of Google Maps, a location was displayed as a card that “floats" overtop of the main map, and the map was repositioned to center on the location. Scrolling up would move the card up and cover the map, and scrolling down would show the whole map with the result reduced to a small strip at the bottom. If the location was part of a list of search results, swiping left and right would move through the results.
+
+The location pages were redesigned to be much more useful at a glance. On the first page, the new version added critical information, like the location on a map, the review score, and the number of reviews. Since this is a phone, and the software will be dialing for you, the phone number was deemed pointless and was removed. The old version showed the distance to the location in miles, while the new version of Google Maps showed the distance in terms of time, based on traffic and preferred mode of transportation—a much more useful metric. The new version also put a share button front and center, which made coordination over IM or text messaging a lot easier.
+
+### Android 4.3, Jelly Bean—getting wearable support out early ###
+
+Android 4.3 would have been an incredible update if Google had done the traditional thing and not released updates between 4.3 and 4.2 through the Play Store. If the new Play Store, Gmail, Maps, Books, Music, Hangouts, Keep, and Play Games were bundled into a big brick as a new version of Android, it would have been hailed as the biggest release ever. Google didn't need to do hold back features anymore though. With very little left that required an OS update, at the end of July 2013, Google released the seemingly insignificant update called "Android 4.3."
+
+
+Android Wear plugging into Android 4.3's Notification access screen.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Google made no qualms about the low importance of 4.3, calling the newest release "Jelly Bean" (the third one in a row). Android 4.3's feature list read like a laundry list of things Google couldn't update from the Play Store or through Google Play Services, mostly consisting of low-level framework changes for developers.
+
+Many of the additions seemed to fit a singular purpose, though—Android 4.3 was Google's trojan horse for wearable computing support. 4.3 added support for Bluetooth Low Energy, a way to wirelessly connect Android to another device and pass data back and forth while using a very small amount of power—an integral feature to a wearable device. Android 4.3 also added a "Notification Access" API, which allowed apps to completely replicate and control the notification panel. Apps could display notification text and pictures and interact with the notification the same way users do—namely pressing action buttons and dismissing notifications. Doing this from an on-board app when you have the notification panel is useless, but on a device that is separate from your phone, replicating the information in the notification panel becomes much more useful. One of the few apps that plugged into this was "Android Wear Preview," which used the notification API to power most of the interface for Android Wear.
+
+The "4.3 is for wearables" theory explained the relatively low number of features in 4.3: it was pushed out the door to give OEMs time to update devices in time for the launch of [Android Wear][2]. The plan seems to have worked. Android Wear requires Android 4.3 and up, which has been out for so long now that most major flagships have updated.
+
+Android 4.3 was not all that exciting, but Android releases from here on out didn't need to be all that exciting. Everything became so modularized that Google could push updates out as soon as they were done through Google Play, rather than drop everything in one huge brick as an OS update.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/24/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://live.arstechnica.com/liveblog-google-io-2013-keynote/
+[2]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/03/in-depth-with-android-wear-googles-quantum-leap-of-a-smartwatch-os/
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/25 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/25 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..39eeb55768
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/25 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+The LG-made Nexus 5, the launch device for KitKat.
+
+Android 4.4, KitKat—more polish; less memory usage
+
+Google got really cute with the launch of Android 4.4. The company [teamed up with Nestlé][1] to name the OS "KitKat," and it launched on Halloween, October 31, 2013. Nestlé produced limited-edition Android-shaped KitKat bars, and KitKat packaging in stores promoted the new OS while offering a chance to win a Nexus 7.
+
+KitKat launched with a new Nexus device, the Nexus 5. The new flagship had the biggest display yet: a five-inch, 1920x1080 LCD. Despite the bigger screen size, LG—again the manufacturer for the device—was able to fit the Nexus 5 into the same dimensions as a Galaxy Nexus or Nexus 4.
+
+The Nexus 5 was specced comparatively to the highest-end phones at the time, with a 2.3Ghz Snapdragon 800 processor and 2GB of RAM. The phone was again sold unlocked on the Play Store, but while most phones with specs like this would go for $600-$700, Google sold the Nexus 5 for only $350.
+
+One of the most important improvements in KitKat was one you couldn't see: significantly lower memory usage. For KitKat, Google started a concerted effort to lower memory usage across the OS and bundled apps called "Project Svelte." After tons of optimization work and a "low memory" mode that disabled expensive graphical effects, Android could now run on as little as 340MB of RAM. Lower memory requirements were a big deal, because devices in the developing world—the biggest growth markets for smartphones—often ran on only 512MB of RAM. Ice Cream Sandwich's more advanced UI significantly raised the system requirements of Android devices, which left many low-end devices—even newly released low-end devices—stuck on Gingerbread. The lower system requirements of KitKat meant to bring these cheap devices back into the fold. With KitKat, Google hoped to finally kill Gingerbread (which, at the time of writing, is around 20 percent of the market). Just in case the lower system requirements weren't enough, there have even been reports that Google will [no longer license][2] the Google apps to Gingerbread devices.
+
+Besides bringing low-end phones to a modern version of the OS, Project Svelte's lower memory requirements were to be a boon to wearable computers, too. Google Glass [announced][3] it was also switching to the slimmer OS, and [Android Wear][4] ran on KitKat, too. The lower memory requirements in Android 4.4 and the notification API and Bluetooth LE support in 4.3 came together nicely to support wearable computing.
+
+KitKat also featured a lot of polish to the core OS interfaces that couldn't be updated via the Play Store. The System UI, Dialer, Clock, and Settings all saw updates.
+
+
+KitKat's transparent bars on the Google Now Launcher.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+KitKat not only got rid of the unpopular lines to the left and right sides of the lock screen—it completely disabled lock screen widgets by default! Google obviously felt multiple lock screens and multiple home screens were a little to complicated for new users, so lock screen widgets now needed to be enabled in the settings. The lopsided time here and in the clock app was switched to a symmetrical weight, which looked a lot nicer.
+
+In KitKat, apps had the ability to make the system and status bars transparent, which significantly changed the look of the OS. The bars now blended into the wallpaper and any other app that chose to enable transparent bars. The bars could also be completely hidden by any app via a new feature called “immersive" mode.
+
+KitKat was the final nail in the “Tron" coffin, removing almost all traces of blue from the operating system. The status bar icons were changed from a blue to a neutral white. The status and system bars on the home screen weren’t completely transparent; a dark gradient was added to the top and bottom of the screen so that the white icons would still be visible on a light background.
+
+
+Tweaks to Google Now and the folders.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The home screen that shipped with KitKat on the Nexus 5 was actually exclusive to the Nexus 5 for a few months, but it could now be on any Nexus device. The new home screen was called the "Google Now Launcher," and it was actually [the Google Search app][5]. Yes, Google Search grew from a simple search box to an entire home screen, and in KitKat, it drew the wallpaper, icons, app drawer, widgets, home screen settings, Google Now, and, of course, the search box. Thanks to Search now running the entire home screen, any time the home screen was open and the screen was on, voice commands could be activated by saying “OK Google." This was pointed out to the user with introductory “Say 'OK Google' text in the search bar, which would fade away after a few uses.
+
+Google Now was more integrated, too. Besides the usual swipe up from the system bar, Google Now was also the leftmost home screen. The new version brought some design tweaks as well. The Google logo was moved into the search bar, and the whole top area was compacted. A few card designs were cleaned up, and a new set of buttons at the bottom led to reminders, customization options, and an overflow button with settings, feedback, and help. Since Google Now was part of the home screen, it got transparent system and status bars, too.
+
+Transparency and “brightening up" certain parts of the OS were design themes in KitKat. Black was removed in the status and system bars by switching to transparent, and the black background of the folders was switched to white.
+
+
+A screenshot showing the new, cleaner app screen layout, and a composite image of the app lineup.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+The KitKat icon lineup changed significantly from 4.3. To be more dramatic, it was a bloodbath, with Google removing seven icons over the 4.3 loadout. Google Hangouts could handle SMS now, so the Messaging app was removed. Hangouts also took over Google+ Messenger duties, so that app shortcut was cut. Google Currents was removed as a default app, as it would soon be killed—along with Google Play Magazines—in favor of Google Play Newsstand. Google Maps was beaten back into a single icon, which meant Local and Navigation shortcuts were removed. The impossible-to-understand Movie Studio was cut, too—Google must have realized no one wants to edit movies on a phone. Thanks to the home screen “OK Google" hotword detection, the Voice Search icon was rendered redundant and removed. Depressingly, the long abandoned News & Weather app remained.
+
+There was a new app called “Photos"—really the Google+ app—which took over picture management duties. On the Nexus 5, the Gallery and Google+ Photos were pretty similar, but in newer builds of KitKat present on Google Play Edition devices, the Gallery was completely replaced by Google+ photos. Play Games was an interface for Google’s back-end multiplayer service—a Googly version of Xbox Live or Apple’s Game Center. Google Drive, which existed for years as a Play Store app, was finally made a default app. Google bought Quickoffice back in June 2012, now finally deeming the app acceptable for inclusion by default. While Drive opened Google Documents, Quickoffice opened Microsoft Office Documents. If keeping track, that was two document editing apps and two photo editing apps included on most KitKat loadouts.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/25/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/09/official-the-next-edition-of-android-is-kitkat-version-4-4/
+[2]:http://www.androidpolice.com/2014/02/10/rumor-google-to-begin-forcing-oems-to-certify-android-devices-with-a-recent-os-version-if-they-want-google-apps/
+[3]:http://www.androidpolice.com/2014/03/01/glass-xe14-delayed-until-its-ready-promises-big-changes-and-a-move-to-kitkat/
+[4]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/03/in-depth-with-android-wear-googles-quantum-leap-of-a-smartwatch-os/
+[5]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/11/google-just-pulled-a-facebook-home-kitkats-primary-interface-is-google-search/
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/The history of Android/26 - The history of Android.md b/sources/talk/The history of Android/26 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3f9e1427ba
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/The history of Android/26 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+The history of Android
+================================================================================
+
+The new "add to home screen" interface was definitely inspired by Honeycomb.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+KitKat added a nice throwback to Honeycomb with the home screen configuration screen. On the massive 10-inch screen of a Honeycomb tablet (right picture, above), long pressing on the home screen background would present you with a zoomed-out view of all your home screens. Widgets could be dragged from the bottom widget drawer into any home screen—it was very handy. When it came time to bring the Honeycomb interface to phones, from Android 4.0 all the way to 4.3, Google skipped this design and left it to the larger screened devices, presenting only a list of options after a long press (center picture).
+
+For KitKat though, Google finally came up with a solution. After a long press, 4.4 presented a slightly zoomed out view—you could see the current home screen and the screens to the left and right of it. Tapping on the “widgets" button would open a full screen list of widget thumbnails, but after long-pressing on a widget, you were thrown back into the zoomed-out view and could scroll through home screen pages and place the icon where you wanted. By dragging an icon or widget all the way past the rightmost home page, you could create a new home page.
+
+
+Contacts and the Keyboard both removed any trace of blue.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+KitKat was the end of the line for the Tron design. In most parts of the OS, any remaining blue highlights were removed in favor of gray. In the People app, blue was sucked out of the header and the letter separators in the contact list. The pictures swapped sides and the bottom bar was changed to a light gray to match the top. The Keyboard, which injected the color blue into nearly every app, was changed to gray-on-gray-on-gray. That wasn't a bad thing. Apps should be allowed to have their own color scheme—forcing a potentially clashing color on them via the keyboard wasn’t good design.
+
+
+The first three screenshots show KitKat's dialer, and the last one is 4.3.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Google completely revamped the dialer in KitKat, creating a wild new design that changed the way users thought about a phone. Actual numbers in the new dialer were hidden as much as possible—there wasn’t even a dial pad on the main screen. The primary interface for making a phone call was now a search bar! If you wanted to call someone in your contacts, just type their name in; if you wanted to call a business, just type the business name in and the dialer would search through Google Maps’ extensive database of phone numbers. It worked incredibly well and was something only Google could pull off.
+
+If searching for numbers wasn’t your thing, the app also intelligently displayed a listing for the previous phone call, your most-contacted people, and a link to all contacts. At the bottom were links to your call history, the now old school number pad, and the usual overflow button containing a settings page.
+
+
+Office stuff: Google Drive, which was now packed in, and the printing support.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+It was amazing it took this long, but in KitKat, Google Drive was finally included as a default app. Drive allowed users to create and edit Google Docs spreadsheets and documents, scan documents with the camera and upload them as PDFs, or view (but not edit) presentations. Drive, by this point, had a great, modern design with a slide-out navigation drawer and a Google Now-style card design.
+
+For even more mobile office fun, KitKat included an OS-level printing framework. At the bottom of the settings was a "Printing" screen, and any printer OEM could make a plugin for it. Google Cloud Print was, of course, one of the first supporters. Once your printer was hooked up to Cloud Print, either natively or through a computer with Chrome installed, you could print to it over the Internet. Apps needed to support the printing framework, too. Pressing the little "i" button on Google Drive would show information about the document and give you the option to print it. Just like a desktop OS, a print dialog would pop up with settings like copies, paper size, and page selection.
+
+
+The "Photos" section of the Google+ app, which replaced the Gallery.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Google+ Photos and the Gallery initially shipped together on the Nexus 5, but in a later build of KitKat on Google Play devices, the Gallery was axed and Google+ completely took over photo duties. The new app changed the photo app from a light theme to a dark theme, and Google+ Photos brought a modern navigation drawer design.
+
+Android had long included an instant upload feature, which would automatically backup all pictures on Google’s cloud storage, first on Picasa and later on Google+. The big benefit of G+ Photos over the Gallery was that it could finally manage those cloud-stored photos. Little cloud icons in the lower right of a photo indicated backup status, and it would fill from right to left to indicate an upload-in-progress. G+ photos brought its own photo editor along with support for a million of other Google+ photo features, like highlights, auto awesome, and, of course, sharing to Google+.
+
+
+Tweaks to the Clock app, which added an alarms tab and changed the time input dialog.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+Google changed the excellent time picker that was introduced in 4.2 to this strange clock interface, which was both slower and less precise than the old interface. First you were presented with a one-handed clock which you used to choose the hour, then that clock went away and another one-handed clock allowed you to choose the minute. Having to spin the minute hand or tap a spot on the clock face made it very difficult to pick times in non-five-minute increments. Unlike the old time picker, which required you to pick a time period, this just defaulted to AM (again making it possible to accidentally be off by 12 hours).
+
+### Today—Android everywhere ###
+
+
+Photo by Google/Sony/Motorola/Ron Amadeo
+
+What started out as a curious BlackBerry clone from a search engine company became the most popular OS in the world from one of the biggest titans in the tech industry. Android has become Google's de-facto consumer operating system, and it powers phones, tablets, Google Glass, Google TV, and more. [Parts of it][1] are even used in the Chromecast. In the future, Google will be bringing Android to watches and wearables with [Android Wear][2], and the [Open Automotive Alliance][3] will be bringing Android to cars. Google will be making a renewed commitment to the living room soon, too, with [Android TV][4]. The OS is such a core pillar of Google, that events that are supposed to cover company-wide products, like Google I/O, end up becoming Android launch parties.
+
+
+Top row: the Google Play content stores. Bottom row: the Google Play Apps.
+Photo by Ron Amadeo
+
+What was once the ugly duckling of the mobile industry has transformed so much it now [wins design awards][5] for its user interface. The design of things like Google Now have affected everything the company produces, with even the desktop sites like Search, Google+, YouTube, and Maps getting in on the card design unity. The design keeps evolving as well. Google's next plan is to [unify design][6] across not just Android, but all of its products. The goal is to take something like Gmail and make it feel the same, whether you're using it on Android, a desktop browser, or a watch.
+
+Google outsourced so many pieces of Android to the Play Store, that version releases are becoming less and less necessary. Google decided the best way to beat carrier and OEM update issues was to sidestep those roadblocks completely. From here on out, there isn't much left to include in an Android update other than core under-the-hood changes—but even many APIs have been pushed to Google Play Services. If you just look at version releases, it seems like Android development has slowed down from the peak 2.5-month release cycle. But the reality is Google can now continually push out improvements to the Play Store in a never-ending, somewhat subtler stream of updates.
+
+With 1.5 million activations per day, Android has no where to go but up. In the future, Android will be headed from phones and tablets to cars and watches, and the lower system requirements of KitKat will drive phones to even lower prices in the developing world. The bottom line? More and more people will get online. And for many of those people, Android will be not just their phone but their primary computing device. With Android leading the charge for Google in so many areas, the OS that started off as a tiny acquisition has become one of Google's most important products.
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/26/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://blog.gtvhacker.com/2013/chromecast-exploiting-the-newest-device-by-google/
+[2]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/03/in-depth-with-android-wear-googles-quantum-leap-of-a-smartwatch-os/
+[3]:http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2014/01/open-automotive-alliance-aims-to-bring-android-inside-the-car/
+[4]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/04/documents-point-to-android-tv-googles-latest-bid-for-the-living-room/
+[5]:http://userexperienceawards.com/uxa2012/
+[6]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/04/googles-next-design-challenge-unify-app-design-across-platforms/
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/Ubuntu Linux Community Manager Jono Bacon Leaves Canonical.md b/sources/talk/Ubuntu Linux Community Manager Jono Bacon Leaves Canonical.md
deleted file mode 100644
index f1c09dfd83..0000000000
--- a/sources/talk/Ubuntu Linux Community Manager Jono Bacon Leaves Canonical.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
-linuhap翻译中
-Ubuntu Linux Community Manager Jono Bacon Leaves Canonical
-================================================================================
-
-
-In a few days, Canonical, the company behind Ubuntu Linux, will bid farewell to its longtime community manager. [Jono Bacon][1], who has long been one of the most familiar faces in the Ubuntu world, is moving to a new position at the [XPRIZE Foundation][2].
-
-Bacon, who joined Canonical in 2006, [reported on his blog][3] that he decided to leave Canonical after receiving an offer from XPRIZE, which [describes itself][4] as "an innovation engine" and "catalyst for the benefit of humanity." He will work at XPRIZE as senior director of Community, bringing to bear the skills he acquired helping to coordinate the Ubuntu community over the last eight years.
-
-Although Bacon was not directly responsible for the business or development side of things at Canonical, his departure is significant for the Ubuntu and open source worlds, where executive titles have tended to matter less than actual community involvement. Alongside Ubuntu founder and former Canonical CEO [Mark Shuttleworth][5], Bacon was one of the leading figures in the Ubuntu ecosystem since the project's earlier days.
-
-Bacon was arguably even more influential in shaping many aspects of Ubuntu than Jane Silber, who has been Canonical's CEO since 2010, but whose public presence has generally been limited.
-
-The team Bacon led—which includes Daniel Holbach, David Planella, Michael Hall, Nicholas Skaggs and Alan Pope—will continue his community leadership work at Canonical after his departure, he said. It is not yet clear, however, whether Canonical will be filling the community manager position he leaves behind.
-
-Perhaps Canonical shouldn't. In many ways, maintaining an official community leader is at odds with the open source ethos, which tends to celebrate decentralized, user-driven community organization. Few Ubuntu fans are likely to panic at the news of Bacon's change of jobs.
-
-Still, Bacon has helped to guide the Ubuntu community through a slew of crises—from Canonical's [failed attempt][6] to style the Ubuntu Software Center as a store, to [friction with the Fedora crowd][7], to [controversy][8] over the Amazon.com search features built into modern Ubuntu. He has left a mark on the Ubuntu ecosystem, and it won't be quite the same without him.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://thevarguy.com/ubuntu/052214/ubuntu-linux-community-manager-jono-bacon-leaves-canonical
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://www.jonobacon.org/
-[2]:http://www.xprize.org/
-[3]:http://www.jonobacon.org/2014/05/19/goodbye-canonical-hello-xprize/
-[4]:http://www.xprize.org/about/who-we-are
-[5]:http://markshuttleworth.com/
-[6]:http://thevarguy.com/ubuntu/ubuntu-software-store-will-your-kids-try-it
-[7]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/tensions-between-ubuntu-fedora-mount-over-new-website
-[8]:http://thevarguy.com/var-guy/controversy-erupts-over-amazon-search-ubuntu-1210
diff --git a/sources/tech/10 Database Tools For Linux Users To Use!.md b/sources/tech/10 Database Tools For Linux Users To Use!.md
deleted file mode 100644
index fb6efadbcd..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/10 Database Tools For Linux Users To Use!.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,56 +0,0 @@
-GOLinux Translating ... !
-
-10 Database Tools For Linux Users To Use!
-================================================================================
-From content management systems to simple tables, databases are a part of every development project nowadays. That is why developers lay so much emphasis on using the right kind of database tools. Here are some that may be of help to you!
-
-
-
-#### 1. [Autotabla][1] ####
-
-Autotabla is a CGI web interface to your programs' SQL tables. Just provide an XML description of your schema, and you'll be able to create/modify/delete records. HTML output fully customisable through CSS. Database independence through Perl/DBI.
-
-#### 2. [Cruddy!][2] ####
-
-Cruddy! is an application of the CGI::CRUD framework that provides an instant web front-end CRUD interface to your database.
-
-#### 3. [myPhile][3] ####
-
-This is a customisable generic front-end for MySQL tables.
-
-#### 4. [NG-Admin][4] ####
-
-This is a content management tool for databases.
-
-#### 5. [phpMoAdmin][5] ####
-
-This is a MongoDB administration tool for PHP.
-
-#### 6. [phpMSAdmin][6] ####
-
-phpMSAdmin is a tool written in PHP that allows you to administer a Microsoft SQL Server through a web browser, without the need for Windows or the proprietary Enterprise Manager. It allows you to create/modify: databases, tables, views, triggers, etc.
-
-#### 7. [RockMongo][7] ####
-
-RockMongo, a MongoDB administration tool, written in PHP5, is Best in PHP world, more like PHPMyAdmin.
-
-#### 8. [WizMySQLAdmin][8] ####
-
-WizMySQLAdmin is a MySQL database manager like the most famous phpMyAdmin, but it's very simple to install and maintain. It's composed by only one file, and it support multiple databases and tables creation and manipulation.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=138307
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/autotabla/
-[2]:http://www.thesmbexchange.com/cruddy/
-[3]:http://efytimes.com/e1/companionway.net
-[4]:http://www.ng-marketing.com/wuerzburg/
-[5]:http://phpmoadmin.com/
-[6]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/phpmsadmin/
-[7]:http://rockmongo.com/
-[8]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/wizmysqadmin/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20140527 Ubuntu Users Will No Longer Have a Cinnamon PPA.md b/sources/tech/20140527 Ubuntu Users Will No Longer Have a Cinnamon PPA.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 16746f27f5..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20140527 Ubuntu Users Will No Longer Have a Cinnamon PPA.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
-Translating by GOLinux ...
-Ubuntu Users Will No Longer Have a Cinnamon PPA
-================================================================================
-
-
-**Many Ubuntu users have been employing a third-party repository to test Cinnamon without installing Linux Mint to do it, but it seems that that will no longer be possible in the future.**
-
-If you have an Ubuntu operating system, you are now able to test the Cinnamon desktop environment just by adding a PPA and installing the appropriate packages. This is as close as you can get to Linux Mint without actually installing another OS.
-
-Unfortunately, this functionality is about to disappear, but not because the main maintainer doesn't want to continue offering it. Apparently, the Ubuntu repositories will no longer keep older versions of GNOME packages, which Cinnamon requires, making it difficult, if not impossible, to install it through this method.
-
-“The stable PPA is indeed no longer being maintained. The nightly PPA is being kept for development purposes and should not be used on any sort of production machine (it can and will break at any time).”
-
-“To be honest, I don't have an alternative to offer Ubuntu users at the moment, apart from switching to a distribution that does support Cinnamon. There are many such distributions out there, and I'm only hoping for someone to (finally) step up on Ubuntu's side to provide proper packages to its users,” [said][1] Gwendal Le Bihan, the maintainer of the Cinnamon packages.
-
-This means that, for now, only an unstable PPA will be available, but it's only for testing. Users shouldn't employ it on their production machines, and soon the only way to see what Cinnamon looks like will be by installing Linux Mint (or Arch for that matter) or compile it for yourself.
-
-If you still want to install Cinnamon, the unstable PPA is available for Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (Trusty Tahr). All you have to do is to enter a few commands in a terminal (you will need to be root in order for it to work):
-
- sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gwendal-lebihan-dev/cinnamon-nightly
- sudo apt-get update
- sudo apt-get install cinnamon
-
-After the installation has been completed, all you have to do is to log out of the system and choose Cinnamon from the greeter.
-
-The Cinnamon desktop environment was developed as a GNOME shell fork with the aim to provide a simple and conservative alternative to everything that is offered right now. Many users are not happy with the direction taken by GNOME, Unity, and KDE and are looking for desktops that haven't strayed too much from the norm.
-
-It's possible that someone else will set up another PPA with all the required packages to make Cinnamon work with the upcoming Ubuntu 14.10, but that is unlikely.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Ubuntu-Users-Will-No-Longer-Have-a-Cinnamon-PPA-443933.shtml
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://askubuntu.com/questions/94201/how-do-i-install-the-cinnamon-desktop
diff --git a/sources/tech/20140528 Setup Backup Server Using Bacula And Webmin On Ubuntu 14.04.md b/sources/tech/20140528 Setup Backup Server Using Bacula And Webmin On Ubuntu 14.04.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 4927afbb5a..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20140528 Setup Backup Server Using Bacula And Webmin On Ubuntu 14.04.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,190 +0,0 @@
-Setup Backup Server Using Bacula And Webmin On Ubuntu 14.04
-================================================================================
-**Bacula** is an open source network backup solution that permits you to backup and restore the data’s from a local or group of remote networked computers. It is very easy in terms of installation and configuration with many advanced storage management features.
-
-In this tutorial, let us see how to install and configure Bacula on Ubuntu 14.04 server. My test box IP address is **192.168.1.250/24**, and hostname is **server.unixmen.local**. Well, now let me get us into the tutorial.
-
-### Install Bacula ###
-
-Bacula uses an SQL database to manage its information. We can use either MySQL or PostgreSQL database. In this tutorial, I use MySQL server.
-
-Enter the following command to install MySQL server.
-
- sudo apt-get update
- sudo apt-get upgrade
- sudo apt-get install mysql-server
-
-During MySQL installation, you’ll be asked to set the database administrator password. Enter the password and click Ok.
-
-
-
-Re-enter the password:
-
-
-
-Now, let us install bacula using the following command:
-
- sudo apt-get install bacula-server bacula-client
-
-By default, Bacula uses Postfix MTA. During installation, you’ll be asked to configure Postfix.
-
-
-
-Select Internet Site and click Ok.
-
-
-
-Enter server fully qualified name(FQDN):
-
-
-
-Now, select Yes to configure database for Bacula with dbconfig-common.
-
-
-
-Enter the MySQL database administrator password:
-
-
-
-Set password for bacula-director-mysql to register with the database server. If left blank, a random password will be generated.
-
-
-
-Re-enter the password:
-
-
-
-### Create Backup and Restore Directories ###
-
-Now, let us backup and restore directories.
-
- sudo mkdir -p /mybackup/backup /mybackup/restore
-
-Set permissions and ownership to the above directories:
-
- sudo chown -R bacula:bacula /mybackup/
- sudo chown -R 700 /mybackup/
-
-### Configure Bacula ###
-
-Bacula has many configuration files which we have to configure.
-
-**Update Bacula Director configuration:**
-
- sudo vi /etc/bacula/bacula-dir.conf
-
-Find the following section, and update the restore path. In our case,** /mybackup/restore** is my restore location.
-
- [...]
- Job {
- Name = "RestoreFiles"
- Type = Restore
- Client=server-fd
- FileSet="Full Set"
- Storage = File
- Pool = Default
- Messages = Standard
- Where = /mybackup/restore
- }
- [...]
-
-Scroll down to “list of files to be backed up” section, and set the path of the directory to backup. For this tutorial, I want to backup the “**/home/sk**” directory. So, I included this directory path in the “File” parameter.
-
- [...]
-
- # By default this is defined to point to the Bacula binary
- # directory to give a reasonable FileSet to backup to
- # disk storage during initial testing.
- #
- File = /home/sk
- }
- [...]
-
-Scroll down further, fins the section **Exclude** section. Set the list of directories to be excluded from the backup. Here, I excluded the backup folder **/mybackup** directory from being backed up.
-
- [...]
-
- # If you backup the root directory, the following two excluded
- # files can be useful
- #
- Exclude {
- File = /var/lib/bacula
- File = /nonexistant/path/to/file/archive/dir
- File = /proc
- File = /tmp
- File = /.journal
- File = /.fsck
- File = /mybackup
- }
- }
- [...]
-
-Save and close file.
-
-**Update Bacula Storage Daemon settings:**
-
-Edit **/etc/bacula/bacula-sd.conf**,
-
- sudo vi /etc/bacula/bacula-sd.conf
-
-Set the backup folder location. i.e **/mybackup/backup** in our case.
-
- [...]
-
- Device {
- Name = FileStorage
- Media Type = File
- Archive Device = /mybackup/backup
- LabelMedia = yes; # lets Bacula label unlabeled media
- Random Access = Yes;
- AutomaticMount = yes; # when device opened, read it
- RemovableMedia = no;
- AlwaysOpen = no;
- }
- [...]
-
-Now, check if all the configurations are valid as shown below. If the commands displays nothing, the configuration changes are valid.
-
- sudo bacula-dir -tc /etc/bacula/bacula-dir.conf
- sudo bacula-sd -tc /etc/bacula/bacula-sd.conf
-
-Once you done all the changes, restart all bacula services.
-
- sudo /etc/init.d/bacula-director restart
- sudo /etc/init.d/bacula-fd restart
- sudo /etc/init.d/bacula-sd restart
-
-That’s it. Now, bacula has been installed and configured successfully.
-
-### Manage Bacula Using Webmin ###
-
-Managing and working with Bacula via command line is bit difficult. So let use a graphical system administration tool called “webmin” to ease our tasks.
-
-Follow the below link to install Webmin on Ubuntu 14.04.
-
-- [Install Webmin on Ubuntu 14.04 LTS][1]
-注:此链接文章在另一篇里,如果也翻译发布了,那么可以更改这个链接地址
-
-Now, go to the Webmin interface using URL https://ip-address:10000. Go to the System tab on the left pane and click on the Module configuration link. If it not found under system, search it from the unused modules section.
-
-
-
-Select MySQL in the database section. Enter the MySQL database administrator password, and click Save button.
-
-
-
-That’s it. Now you’ll be able to configure Bacula from webmin easily. Start adding backup clients, volumes and schedule the jobs.
-
-
-
-Cheers!
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.unixmen.com/setup-backup-server-using-bacula-webmin-ubuntu-14-04/
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/install-webmin-ubuntu-14-04/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20140701 Get OpenVPN up and running, enjoy your privacy.md b/sources/tech/20140701 Get OpenVPN up and running, enjoy your privacy.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..54ee1ff9c2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20140701 Get OpenVPN up and running, enjoy your privacy.md
@@ -0,0 +1,499 @@
+Get OpenVPN up and running, enjoy your privacy
+================================================================================
+
+
+> We are fanatic supporters of privacy. Not so much because we have super secrets to hide, but because we consider privacy as a basic human right. So we believe that anytime anyone chooses to exercise that right on the net, then they should have unencumbered access to all the necessary tools and services. OpenVPN is such a service and there are also many tools (clients) which allow us to utilize and enjoy that service.
+
+By establishing a connection to an [OpenVPN][1] server, we basically create a secure communications channel between our device and the remote host OpenVPN runs on. Although traffic flowing between these two end-points can be intercepted, it is strongly encrypted and thus practically useless to the interceptor. In addition to the OpenVPN acting as the facilitator of this encrypted channel (or tunnel), we may configure the server to also play the role of our Internet gateway. By doing so, we can for example hook up to any open, inherently insecure WiFi network, then immediately connect to the remote OpenVPN server and start using any Internet-enabled application without worrying of prying eyes or bored administrators. (Note though that we still need to trust any administrator in the vicinity of the OpenVPN server. But more on that towards the end of the post.)
+
+This article is a step-by-step guide on how to setup OpenVPN on [Ubuntu Server 14.04 LTS][2]. The OpenVPN host computer may be a VPS in the cloud, a virtual machine running on one of our computers at home, or even that somewhat aged box we tend to forget we have.
+
+### Step 01 -- System Preparation ###
+
+We gain access to a command shell in the Ubuntu Server host, for example by remotely connecting to it via SSH, and immediately refresh the local repository database:
+
+ sub0@delta:~$ sudo apt-get update
+
+To perform any upgrades for all installed packages and the operating system itself, we type:
+
+ sub0@delta:~$ sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
+
+If a new kernel gets pulled in, a system reboot will be required. After refreshing and upgrading, it’s time to install OpenVPN:
+
+ sub0@delta:~$ sudo apt-get -y install openvpn easy-rsa dnsmasq
+
+Notice that we installed three packages with apt-get:
+
+- openvpn provides the core of OpenVPN
+- easy-rsa contains some handy scripts for key management
+- dnsmasq is the name server we’ll be using later on, when our OpenVPN server box/VM will assume the role of a router for all OpenVPN clients`
+
+### Step 02 -- Master certificate and private key for the Certificate Authority ###
+
+The most important –and admittedly the most crucial– step during the setup of an OpenVPN server, is the establishment of a corresponding Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). This infrastructure comprises the following:
+
+- A certificate (public key) and a private key for the OpenVPN server
+- A certificate and a private key for any OpenVPN client
+- A master certificate and a private key for the Certificate Authority (CA). This private key is used for signing the OpenVPN certificate as well as the client certificates.
+
+Beginning with the latter, we create a convenient working directory
+
+ sub0@delta:~$ sudo mkdir /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa
+
+and then copy easy-rsa’s files to it:
+
+ sub0@delta:~$ sudo cp -r /usr/share/easy-rsa/* /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa
+
+Before we actually create the keys for the CA, we open /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/vars for editing (we like the nano text editor but this is just our preference):
+
+ sub0@delta:~$ sudo nano /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/vars
+
+Towards the end of the file we assign values to a set of variables which are read during the creation of the master certificate and private key. Take a look at the variables we assigned values to:
+
+ export KEY_COUNTRY="GR"
+ export KEY_PROVINCE="Central Macedonia"
+ export KEY_CITY="Thessaloniki"
+ export KEY_ORG="Parabing Creations"
+ export KEY_EMAIL="nobody@parabing.com"
+ export KEY_CN="VPNsRUS"
+ export KEY_NAME="VPNsRUS"
+ export KEY_OU="Parabing"
+ export KEY_ALTNAMES="VPNsRUS"
+
+It goes without saying that you may assign different values, more appropriate for your case. Also take particular note of the last line, in which we set a value to the KEY_ALTNAMES variable. This line is not part of the original vars file but we nevertheless append it at the end of said file, or the build-ca script we’re going to run next will fail.
+
+To save the changes in vars we hit [CTRL+O] followed by the [Enter] key. To quit nano we hit [CTRL+X]. Now, we gain access to the root account and move on to building of the master certificate and private key:
+
+ sub0@delta:~$ sudo su
+ root@delta:/home/sub0# cd /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# source vars
+ NOTE: If you run ./clean-all, I will be doing a rm -rf on /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# sh clean-all
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# sh build-ca
+ Generating a 1024 bit RSA private key
+ ...++++++
+ ................++++++
+ writing new private key to 'ca.key'
+ -----
+ You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
+ into your certificate request.
+ What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
+ There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
+ For some fields there will be a default value,
+ If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
+ -----
+ Country Name (2 letter code) [GR]:
+ State or Province Name (full name) [Central Macedonia]:
+ Locality Name (eg, city) [Thessaloniki]:
+ Organization Name (eg, company) [Parabing Creations]:
+ Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) [Parabing]:
+ Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) [VPNsRUS]:
+ Name [VPNsRUS]:
+ Email Address [nobody@parabing.com]:
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa#
+
+In our example the default answers were used for all the questions. After the build-ca script finishes we have the file for the master certificate (keys/ca.crt) and also the file for the private key (keys/ca.key). The latter must be kept secret at all costs.
+
+### Step 03 -- Certificate and private key for the OpenVPN server ###
+
+Before we make a certificate and private key for our OpenVPN server, we need to pick a name for it. We decided to name ours “delta” and then ran the build-key-server script to get the keys:
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# sh build-key-server delta
+ Generating a 1024 bit RSA private key
+ ....++++++
+ ...++++++
+ writing new private key to 'delta.key'
+ -----
+ You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
+ into your certificate request.
+ What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
+ There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
+ For some fields there will be a default value,
+ If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
+ -----
+ Country Name (2 letter code) [GR]:
+ State or Province Name (full name) [Central Macedonia]:
+ Locality Name (eg, city) [Thessaloniki]:
+ Organization Name (eg, company) [Parabing Creations]:
+ Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) [Parabing]:
+ Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) [delta]:
+ Name [VPNsRUS]:deltaVPN
+ Email Address [nobody@parabing.com]:
+
+ Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
+ to be sent with your certificate request
+ A challenge password []:
+ An optional company name []:
+ Using configuration from /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/openssl-1.0.0.cnf
+ Check that the request matches the signature
+ Signature ok
+ The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows
+ countryName :PRINTABLE:'GR'
+ stateOrProvinceName :PRINTABLE:'Central Macedonia'
+ localityName :PRINTABLE:'Thessaloniki'
+ organizationName :PRINTABLE:'Parabing Creations'
+ organizationalUnitName:PRINTABLE:'Parabing'
+ commonName :PRINTABLE:'delta'
+ name :PRINTABLE:'deltaVPN'
+ emailAddress :IA5STRING:'nobody@parabing.com'
+ Certificate is to be certified until Apr 7 08:06:02 2024 GMT (3650 days)
+ Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y
+
+ 1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y
+ Write out database with 1 new entries
+ Data Base Updated
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa#
+
+The script successfully finished and we got a certificate (keys/delta.crt) as well as a private key (keys/delta.key) for our server. Note that the server certificate is signed by the CA’s private key.
+
+### Step 04 -- Diffie-Hellman parameters ###
+
+The secure passing of keys over an insecure communications channel is made possible thanks to a well-known technique involving the so called Diffie-Hellman parameters. To generate those we just type
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# sh build-dh
+ Generating DH parameters, 2048 bit long safe prime, generator 2
+ This is going to take a long time
+ .......................+.....................................+..
+ ...........................+..+.....................+...........
+ ..............................................+.................
+ .......................+........................................
+ ................................................+...............
+ .......................................++*++*++*
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa#
+
+The certificates, private keys and the file containing the Diffie-Hellman parameters we just generated, are all stored into the /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys directory. So up until now we have five files in total and in our case they are as follows:
+
+1. **ca.crt** – the certificate of the Certificate Authority
+2. **ca.key** – the private key of the CA
+3. **delta.crt** – the certificate of the OpenVPN server
+4. **delta.key** – the private key of the OpenVPN server
+5. **dh2048.pem** – the Diffie-Hellman parameters file
+
+In all likelihood, the keys for your own OpenVPN server are named differently. We now need to copy all files but the ca.key over to the /etc/openvpn directory:
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# cd keys
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys# cp ca.crt delta.crt delta.key dh2048.pem /etc/openvpn
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys# cd ..
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa#
+
+### Step 05 -- Certificates and private keys for the OpenVPN clients ###
+
+Let’s assume we’d like to connect to the OpenVPN server from our laptop. That’s actually a very common scenario and in order to be able to do so we first need to generate a certificate as well as a private key for the client, i.e. our laptop. There’s a script for that and it lives in the /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa directory:
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# source vars
+ NOTE: If you run ./clean-all, I will be doing a rm -rf on /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# ./build-key laptop
+ Generating a 1024 bit RSA private key
+ .......................................++++++
+ ...................................................................................................++++++
+ writing new private key to 'laptop.key'
+ -----
+ You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
+ into your certificate request.
+ What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
+ There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
+ For some fields there will be a default value,
+ If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
+ -----
+ Country Name (2 letter code) [GR]:
+ State or Province Name (full name) [Central Macedonia]:
+ Locality Name (eg, city) [Thessaloniki]:
+ Organization Name (eg, company) [Parabing Creations]:
+ Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) [Parabing]:
+ Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) [laptop]:
+ Name [VPNsRUS]:
+ Email Address [nobody@parabing.com]:
+
+ Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
+ to be sent with your certificate request
+ A challenge password []:
+ An optional company name []:
+ Using configuration from /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/openssl-1.0.0.cnf
+ Check that the request matches the signature
+ Signature ok
+ The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows
+ countryName :PRINTABLE:'GR'
+ stateOrProvinceName :PRINTABLE:'Central Macedonia'
+ localityName :PRINTABLE:'Thessaloniki'
+ organizationName :PRINTABLE:'Parabing Creations'
+ organizationalUnitName:PRINTABLE:'Parabing'
+ commonName :PRINTABLE:'laptop'
+ name :PRINTABLE:'VPNsRUS'
+ emailAddress :IA5STRING:'nobody@parabing.com'
+ Certificate is to be certified until Apr 7 18:00:51 2024 GMT (3650 days)
+ Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y
+
+ 1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y
+ Write out database with 1 new entries
+ Data Base Updated
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa#
+
+The base name we chose for the keys was “laptop”, so after the build-key finished we got keys/laptop.crt (certificate) and keys/laptop.key (private key). Those two keys for the particular client along with the CA’s certificate file go together, and it’s a good idea to copy them to a directory where our user (sub0) has full access to. We can, for example, create a new directory in the user’s home directory and copy those three files there:
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# mkdir /home/sub0/ovpn-client
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# cd keys
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys# cp ca.crt laptop.crt laptop.key /home/sub0/ovpn-client
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys# chown -R sub0:sub0 /home/sub0/ovpn-client
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys# cd ..
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa#
+
+The directory ovpn-client must be securely copied to our laptop. We are allowed to distribute those three files to more than one clients, as long as they are all ours. Of course, should we need a different certificate-private key couple, we run the build-key script again.
+
+### Step 06 -- OpenVPN server configuration ###
+
+In a little while our OpenVPN server will be up and running. But first, there are some configuration changes that need to be made. There’s a sample configuration file in /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files which is excellent for our setup. That file is named server.conf.gz:
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa# cd /etc/openvpn
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# cp /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files/server.conf.gz .
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# gunzip -d server.conf.gz
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# mv server.conf delta.conf
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn#
+
+As you can see, we copied server.conf.gz into the /etc/openvpn directory, uncompressed it and renamed it to delta.conf. You may choose any name you like for your OpenVPN server’s configuration file, as long as it has the “.conf” extension. Whatever the base name, we now open the configuration file with nano:
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# nano delta.conf
+
+Here are the changes and additions we should make.
+
+- First, we locate the lines
+
+ cert server.crt
+ key server.key
+
+and make sure they reflect the names of our OpenVPN server’s certificate and private key. In our case, those lines were changed into
+
+ cert delta.crt
+ key delta.key
+
+- We locate the line
+
+ dh dh1024.pem
+
+and replace “1024″ with “2048″:
+
+ dh dh2048.pem
+
+- At the end of the configuration file we add the following two lines:
+
+ push "redirect-gateway def1"
+ push "dhcp-option DNS 10.8.0.1"
+
+Those last two lines instruct the clients to use OpenVPN as the default gateway to the Internet, and also use 10.8.0.1 as the server to deal with DNS requests. Notice that 10.8.0.1 is the IP address of the tunnel network interface OpenVPN automatically creates upon startup. If the clients were to use any other server for name resolution, then we would have a situation in which all DNS requests were served from a possibly untrustworthy server. To avoid such DNS leaks, we instruct all OpenVPN clients to use 10.8.0.1 as the DNS server.
+
+We start our OpenVPN server like this:
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# service openvpn start
+
+By default, OpenVPN listens for connections on port 1194/UDP. One way to see that is with the netstat tool:
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# netstat -anup
+ Active Internet connections (servers and established)
+ Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
+ udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:54149 0.0.0.0:* 555/dhclient
+ udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:1194 0.0.0.0:* 3024/openvpn
+ udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:53 0.0.0.0:* 2756/dnsmasq
+ udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:68 0.0.0.0:* 555/dhclient
+ udp6 0 0 :::60622 :::* 555/dhclient
+ udp6 0 0 :::53 :::* 2756/dnsmasq
+
+All is well, though we have no properly configured DNS server for the clients yet.
+
+### Step 07 -- A DNS service for OpenVPN clients ###
+
+That’s why we’ve installed dnsmasq for. We open up its configuration file
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# nano /etc/dnsmasq.conf
+
+locate this line
+
+ #listen-address=
+
+and change it into the following one:
+
+ listen-address=127.0.0.1, 10.8.0.1
+
+We also locate this line
+
+ #bind-interfaces
+
+and delete the hash character on the left:
+
+bind-interfaces
+
+To make dnsmasq take these changes into account, we just restart the service:
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# service dnsmasq restart
+ * Restarting DNS forwarder and DHCP server dnsmasq [ OK ]
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn#
+
+As it is now, dnsmasq listens for DNS requests from the loopback (lo) and also from the tunnel (tun0) interface. The output of netstat confirms that:
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# netstat -anup
+ Active Internet connections (servers and established)
+ Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
+ udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:57219 0.0.0.0:* 638/dhclient
+ udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:1194 0.0.0.0:* 911/openvpn
+ udp 0 0 127.0.0.1:53 0.0.0.0:* 1385/dnsmasq
+ udp 0 0 10.8.0.1:53 0.0.0.0:* 1385/dnsmasq
+ udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:68 0.0.0.0:* 638/dhclient
+ udp6 0 0 :::39148 :::* 638/dhclient
+
+### Step 08 -- Router functionality ###
+
+We want the VM/box our OpenVPN server runs on to behave like a router, and that means that IP forwarding must be enabled. To enable it right now, from the root account we just type
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# echo "1" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
+
+To make this setting persistent across reboots we open up /etc/sysctl.conf
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# nano /etc/sysctl.conf
+
+locate the line
+
+ #net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
+
+and remove the hash character on the left:
+
+ net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
+
+There are also some iptables-related rules we should activate:
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# iptables -A FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# iptables -A FORWARD -s 10.8.0.0/24 -j ACCEPT
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# iptables -A FORWARD -j REJECT
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.8.0.0/24 -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn#
+
+And of course we want these rules activated every time Ubuntu boots up, so we add them inside /etc/rc.local:
+
+ #!/bin/sh -e
+ #
+ # rc.local
+ #
+ # This script is executed at the end of each multiuser runlevel.
+ # Make sure that the script will "exit 0" on success or any other
+ # value on error.
+ #
+ # In order to enable or disable this script just change the execution
+ # bits.
+ #
+ # By default this script does nothing.
+
+ iptables -A FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
+ iptables -A FORWARD -s 10.8.0.0/24 -j ACCEPT
+ iptables -A FORWARD -j REJECT
+ iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.8.0.0/24 -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
+
+ service dnsmasq restart
+
+ exit 0
+
+Please notice the line before the last one:
+
+service dnsmasq restart
+
+> This is crucial: During system startup dnsmasq tries to come up before OpenVPN does. But without OpenVPN there is no tunnel interface (tun0) present so naturally dnsmasq fails. A bit later, when /etc/rc.local is read the tun0 interface is present, so at this point we restart dnsmasq and everything is as it's supposed to be.
+
+### Step 09 -- Client configuration ###
+
+In Step 05 we created the directory ovpn-client inside our user’s home directory (/home/sub0, in our example). In there we have the CA certificate plus the client certificate and private key. There’s only one file missing and that’s the configuration file for the client. A sample file we can use is inside /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files:
+
+ root@delta:/etc/openvpn# exit
+ exit
+ sub0@delta:~$ cd ~/ovpn-client
+ sub0@delta:~/ovpn-client$ cp /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files/client.conf .
+ sub0@delta:~/ovpn-client$
+
+We open up client.conf for editing and immediately locate the following line:
+
+ remote my-server-1 1194
+
+This “my-server-1″ string is a placeholder and we are now going to replace it for our server’s public domain name or public IP. If we do have a public domain name already assigned to the server, then there’s nothing more to do than put it in place of my-server-1. Things get a tiny bit more involved if there’s no public domain name for our server. What’s the public IP for it? One way to find out is by typing the following:
+
+ sub0@delta:~/ovpn-client$ curl ipecho.net/plain ; echo
+
+(If instead of a numeric IP address you get an error, just wait a few seconds and try again.) So now we know our server’s public IP, but is it static or dynamic? Well, if we’re dealing with a server at home or even at the office, chances are it has a dynamic IP address. In that case it is advisable to use a free dynamic DNS service, such as the one provided by http://www.noip.com. In the case of NoIP, assuming we have chosen the free domain dnsalias.net then we may end up with a line like this
+
+ remote ovpn.dnsalias.net 1194
+
+where “ovpn” is the hostname we’ve given to the server. On the other hand, if our server is hosted in the cloud then it probably has a static public IP address. In that case, the remote directive inside client.conf will look like the following:
+
+ remote 1.2.3.4 1194
+
+There are two more lines we need to modify:
+
+ cert client.crt
+ key client.key
+
+In our case, the certificate and private key files for the client are named laptop.crt and laptop.key respectively, so our client.conf contains these two lines:
+
+ cert laptop.crt
+ key laptop.key
+
+After making sure the changes to client.conf are saved, we need to securely transfer the whole ovpn-client directory to the client. One way to do so is by using the scp command (secure copy or copy over SSH). An alternative is provided by the excellent and free FileZilla, which supports FTP over SSH connections (SFTP).
+
+### Step 10 -- Connecting and testing ###
+
+
+
+
+So how do we actually connect to the remote OpenVPN server? It all depends on the type of the device we have in hand and of course on the operating system is runs. In a bit we are going to examine the cases of four different OS families — or OS categories, if you will: Linux, Windows, OS X and iOS/Android. Note though that no matter the device or the OS, for the connection to be successful we need to be outside of the OpenVPN server’s local network. In addition, if there’s a firewall in front of the server –and it probably is– then we ought to put a new rule in place which essentially states something like this:
+
+*Redirect all incoming UDP packets for port 1194 to port 1194/UDP of the server’s public-facing network interface.*
+
+That’s some simple firewall rule, don’t you think? And without further ado, let’s establish our first connection to the fabulous OpenVPN server of ours.
+
+**Linux**. All we need is the openvpn package installed. One way to connect to the remote OpenVPN server is to fire up a terminal, change to the ovpn-client directory and from the root user account –or with the assistance of sudo– type something like this:
+
+ /usr/sbin/openvpn --config client.conf
+
+Anytime we want to terminate the connection we just hit [CTRL+C].
+
+**Windows**. A free OpenVPN client is the so called [OpenVPN Desktop Client][3]. The configuration file client.conf must be renamed to client.ovpn and that’s the file we should give to the OpenVPN Desktop Client. The application will read client.ovpn and create a new connection profile for the OpenVPN server.
+
+
+
+**OS X**. A free OpenVPN client for OS X is [tunnelblick][4]. There is also [Viscosity][5] which is commercial and happens to be our favorite. Viscosity will read client.conf and create a new connection profile for the remote server.
+
+iOS/Android. An excellent choice is OpenVPN connect. It is free of charge and available from the [App Store][6] as well as the Google [Play store][7].
+
+Regardless of the computing platform, sometimes we’d like to check if we’re actually using the OpenVPN server we think we’re using. One way to do that is by following this simple 4-step procedure:
+
+Prior to connecting to the OpenVPN server we…
+
+- visit a site such as [whatip.com][8] and take note of our public IP
+- visit [dnsleaktest.com][10, perform the standard test, take note of the name servers we’re using
+
+
+
+After connecting to the OpenVPN server we repeat the above two steps. If we get two different public IPs, this means we do go out on the net through the remote OpenVPN server. In addition, if we get two different sets of name servers, then there are no DNS leaks.
+
+### Final thoughts ###
+
+I use three different OpenVPN servers, all custom-made. One of them runs on the pfSense router at my home office in Thessaloniki, Greece. I use this server when I’m out of office and want secure access to the home LAN. The other two OpenVPN servers are hosted on two different VPSes, one in Reykjavik, Iceland, and the other in New Jersey, USA. Whenever I’m out and about and feel like using a random WiFi hotspot, I don’t even have to think of the security implications: I simply connect to the Reykjavik server and start surfing the web normally. There are also some times when I want to casually check out a service which is geographically restricted to the US. In these not-so-common cases the New Jersey server comes in handy, for when I connect to it I get a public IP from the U, S of A and hence access to that otherwise restricted service. It is worth noting that some service providers maintain blacklists with numerous well-known VPN companies. And that’s *exactly* one of the advantages of setting up your own OpenVPN server on a VPS provider of your choosing: It’s unlikely that this provider is blacklisted.
+
+No matter where the physical location of your server is, OpenVPN ensures that the traffic flow between the client and the server is strongly encrypted. What happens to the traffic leaving the OpenVPN server is another story. Depending on the application-layer protocol it may still be encrypted, but it could be unencrypted as well. So unless you have absolute control of the OpenVPN server and of the local network it belongs to, you cannot fully trust the administrator at the other end. The moral of this is apparent: If you really care about your privacy, then you should keep in mind that your own behavior may indeed undermine it.
+
+One example will hopefully get the point across. You have a well configured OpenVPN server in the cloud. You use any random WiFi hotspot anytime you feel like it and without the slightest bit of worry, thanks to that heroic OpenVPN server. Then you fire up your favorite mail client to get your email from this good, old mail server which still uses plain SMTP. Guess what? Your username and password leave the OpenVPN server in plain text, i.e. unencrypted. At the same time a bored administrator in the vicinity of the OpenVPN server could be easily sniffing-out your credentials and storing them in their ever-growing list named “random happy people.txt”.
+
+So what do you do? Simple. You continue using your OpenVPN server, but refrain from using applications which talk old and/or insecure protocols.
+
+Enjoy your brand new OpenVPN server!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://parabing.com/2014/06/openvpn-on-ubuntu/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Openvpn
+[2]:http://www.ubuntu.com/server
+[3]:http://swupdate.openvpn.net/downloads/openvpn-client.msi
+[4]:https://code.google.com/p/tunnelblick
+[5]:https://www.sparklabs.com/viscosity
+[6]:https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/openvpn-connect/id590379981?mt=8
+[7]:https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=net.openvpn.openvpn
+[8]:http://www.whatip.com/
+[9]:https://dnsleaktest.com/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20140702 Wine 1.7.21 (Development Version) Released--Install in RedHat and Debian Based Systems.md b/sources/tech/20140702 Wine 1.7.21 (Development Version) Released--Install in RedHat and Debian Based Systems.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fcf41447d8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20140702 Wine 1.7.21 (Development Version) Released--Install in RedHat and Debian Based Systems.md
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+2q1w2007翻译中
+Wine 1.7.21 (Development Version) Released – Install in RedHat and Debian Based Systems
+================================================================================
+Wine, a most popular and powerful open source application for Linux, that used to run Windows based applications and games on Linux Platform without any trouble.
+
+
+Install Wine (Development Version) in Linux
+
+**WineHQ** team, recently announced a new development version of **Wine 1.7.21**. This new development build arrives with a number of new important features and bug fixes.
+
+Wine team, keep releasing their development builds almost on weekly basis and adding numerous new features and fixes. Each new version brings support for new applications and games, making Wine a most popular and must have tool for every user, who want to run Windows based software in a Linux platform.
+
+According to the changelog, following key features are added in this release:
+
+- Added support for critical sections in the C runtime.
+- The Unicode data updated to Unicode 7.
+- Implemented support for interlaced PNG encoding.
+- Added an initial stub for the Package library.
+- And several bug fixes have been implemented.
+
+For more in-depth details about this build can be found at the official [changelog][1] page.
+
+This article guides you how to install most recent development version of **Wine 1.7.21** on **Red Hat** and **Debian** based systems such as CentOS, Fedora, Ubuntu, Linux Mint and other supported distributions.
+
+### Installing Wine 1.7.21 Development Version in Linux ###
+
+Unfortunately, there are no official Wine repository available for the **Red Hat** based systems and the only way to install Wine, is to compile it from source. To do this, you need to install some dependency packages such as gcc, flex, bison, libX11-devel freetype-devel and Development Tools, etc. These packages are must required to compile Wine from source. Let’s install them using following **YUM** command.
+
+#### On RedHat, Fedora and CentOS ####
+
+ # yum -y groupinstall 'Development Tools'
+ # yum -y install flex bison libX11-devel freetype-devel
+
+Next, download the latest development version of Wine (i.e. **1.7.21**) and extract the source tallball package using the following commands.
+
+ $ cd /tmp
+ $ wget http://citylan.dl.sourceforge.net/project/wine/Source/wine-1.7.21.tar.bz2
+ $ tar -xvf wine-1.7.21.tar.bz2 -C /tmp/
+
+Now, it’s time to compile and build Wine installer using the following commands as normal user. (**Note**: The installation process might take up-to **15-20** minutes depending upon your internet and hardware speed, during installation it will ask you to enter **root** password.
+
+**On 32-Bit Systems**
+
+ $ cd wine-1.7.21/
+ $ ./tools/wineinstall
+
+**On 64-Bit Systems**
+
+ $ cd wine-1.7.21/
+ $ ./configure --enable-win64
+ $ make
+ # make install
+
+#### On Ubuntu, Debian and Linux Mint ####
+
+Under **Ubuntu** based systems, you can easily install the latest development build of Wine using the official **PPA**. Open a terminal and run the following commands with sudo privileges.
+
+ $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ubuntu-wine/ppa
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get install wine 1.7 winetricks
+
+**Note**: At the time of writing this article, available version was **1.7.20** and the new build not yet updated in official Wine Repository, but the above instructions will install **1.7.21** when they made available.
+
+Once the installation completes successfully, you can install or run any windows based applications or games using wine as shown below.
+
+ $ wine notepad
+ $ wine notepad.exe
+ $ wine c:\\windows\\notepad.exe
+
+**Note**: Please remember, this is a development build and cannot be installed or used on production systems. It is advised to use this version only for testing purpose.
+
+If you’re looking for a most recent stable version of Wine, you can go through our following articles, that describes how to install most latest version on almost all Linux environments.
+
+- [Install Wine 1.6.2 (Stable) in RHEL, CentOS and Fedora][2]
+- [Install Wine 1.6.2 (Stable) in Debian, Ubuntu and Mint][3]
+
+### Reference Links ###
+
+- [WineHQ Homepage][4]
+
+----------
+
+
+
+#### Ravi Saive ####
+
+Owner at [TecMint.com][5]
+
+Simple Word a Computer Geek and Linux Guru who loves to share tricks and tips on Internet. Most Of My Servers runs on Open Source Platform called Linux.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-wine-in-linux/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.winehq.org/announce/1.7.21
+[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-wine-in-rhel-centos-and-fedora/
+[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-wine-on-ubuntu-and-linux-mint/
+[4]:http://www.winehq.org/
+[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20140711 How to use systemd for system administration on Debian.md b/sources/tech/20140711 How to use systemd for system administration on Debian.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..12e2ca24ff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20140711 How to use systemd for system administration on Debian.md
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
+[bazz2 hehe]
+How to use systemd for system administration on Debian
+================================================================================
+Soon enough, hardly any Linux user will be able to escape the ever growing grasp that systemd imposes on Linux, unless they manually opt out. systemd has created more technical, emotional, and social issues than any other piece of software as of late. This predominantly came to show in the [heated discussions][1] also dubbed as the 'Init Wars', that occupied parts of the Debian developer body for months. While the Debian Technical Comittee finally decided to include systemd in Debian 8 "Jessie", there were efforts to [supersede the decision][2] by a General Resolution, and even threats to the health of developers in favor of systemd.
+
+This goes to show how deep systemd interferes with the way of handling Linux systems that has, in large parts, been passed down to us from the Unix days. Theorems like "one tool for the job" are overthrown by the new kid in town. Besides substituting sysvinit as init system, it digs deep into system administration. For right now a lot of the commands you are used to will keep on working due to the compatibility layer provided by the package systemd-sysv. That might change as soon as systemd 214 is uploaded to Debian, destined to be released in the stable branch with Debian 8 "Jessie". From thereon, users need to utilize the new commands that come with systemd for managing services, processes, switching run levels, and querying the logging system. A workaround is to set up aliases in .bashrc.
+
+So let's have a look at how systemd will change your habits of administrating your computers and the pros and cons involved. Before making the switch to systemd, it is a good security measure to save the old sysvinit to be able to still boot, should systemd fail. This will only work as long as systemd-sysv is not yet installed, and can be easily obtained by running:
+
+ # cp -av /sbin/init /sbin/init.sysvinit
+
+Thusly prepared, in case of emergency, just append:
+
+ init=/sbin/init.sysvinit
+
+to the kernel boot-time parameters.
+
+### Basic Usage of systemctl ###
+
+systemctl is the command that substitutes the old "/etc/init.d/foo start/stop", but also does a lot more, as you can learn from its man page.
+
+Some basic use-cases are:
+
+- systemctl - list all loaded units and their state (where unit is the term for a job/service)
+- systemctl list-units - list all units
+- systemctl start [NAME...] - start (activate) one or more units
+- systemctl stop [NAME...] - stop (deactivate) one or more units
+- systemctl disable [NAME...] - disable one or more unit files
+- systemctl list-unit-files - show all installed unit files and their state
+- systemctl --failed - show which units failed during boot
+- systemctl --type=mount - filter for types; types could be: service, mount, device, socket, target
+- systemctl enable debug-shell.service - start a root shell on TTY 9 for debugging
+
+For more convinience in handling units, there is the package systemd-ui, which is started as user with the command systemadm.
+
+Switching runlevels, reboot and shutdown are also handled by systemctl:
+
+- systemctl isolate graphical.target - take you to what you know as init 5, where your X-server runs
+- systemctl isolate multi-user.target - take you to what you know as init 3, TTY, no X
+- systemctl reboot - shut down and reboot the system
+- systemctl poweroff - shut down the system
+
+All these commands, other than the ones for switching runlevels, can be executed as normal user.
+
+### Basic Usage of journalctl ###
+
+systemd does not only boot machines faster than the old init system, it also starts logging much earlier, including messages from the kernel initialization phase, the initial RAM disk, the early boot logic, and the main system runtime. So the days where you needed to use a camera to provide the output of a kernel panic or otherwise stalled system for debugging are mostly over.
+
+With systemd, logs are aggregated in the journal which resides in /var/log/. To be able to make full use of the journal, we first need to set it up, as Debian does not do that for you yet:
+
+ # addgroup --system systemd-journal
+ # mkdir -p /var/log/journal
+ # chown root:systemd-journal /var/log/journal
+ # gpasswd -a $user systemd-journal
+
+That will set up the journal in a way where you can query it as normal user. Querying the journal with journalctl offers some advantages over the way syslog works:
+
+- journalctl --all - show the full journal of the system and all its users
+- journalctl -f - show a live view of the journal (equivalent to "tail -f /var/log/messages")
+- journalctl -b - show the log since the last boot
+- journalctl -k -b -1 - show all kernel logs from the boot before last (-b -1)
+- journalctl -b -p err - shows the log of the last boot, limited to the priority "ERROR"
+- journalctl --since=yesterday - since Linux people normally do not often reboot, this limits the size more than -b would
+- journalctl -u cron.service --since='2014-07-06 07:00' --until='2014-07-06 08:23' - show the log for cron for a defined timeframe
+- journalctl -p 2 --since=today - show the log for priority 2, which covers emerg, alert and crit; resembles syslog priorities emerg (0), alert (1), crit (2), err (3), warning (4), notice (5), info (6), debug (7)
+- journalctl > yourlog.log - copy the binary journal as text into your current directory
+
+Journal and syslog can work side-by-side. On the other hand, you can remove any syslog packages like rsyslog or syslog-ng once you are satisfied with the way the journal works.
+
+For very detailed output, append "systemd.log_level=debug" to the kernel boot-time parameter list, and then run:
+
+ # journalctl -alb
+
+Log levels can also be edited in /etc/systemd/system.conf.
+
+### Analyzing the Boot Process with systemd ###
+
+systemd allows you to effectively analyze and optimize your boot process:
+
+- systemd-analyze - show how long the last boot took for kernel and userspace
+- systemd-analyze blame - show details of how long each service took to start
+- systemd-analyze critical-chain - print a tree of the time-critical chain of units
+- systemd-analyze dot | dot -Tsvg > systemd.svg - put a vector graphic of your boot process (requires graphviz package)
+- systemd-analyze plot > bootplot.svg - generate a graphical timechart of the boot process
+
+
+
+
+
+systemd has pretty good documentation for such a young project under heavy developement. First of all, there is the [0pointer series by Lennart Poettering][3]. The series is highly technical and quite verbose, and holds a wealth of information. Another good source is the distro agnostic [Freedesktop info page][4] with the largest collection of links to systemd resources, distro specific pages, bugtrackers and documentation. A quick glance at:
+
+ # man systemd.index
+
+will give you an overview of all systemd man pages. The command structure for systemd for various distributions is pretty much the same, differences are found mainly in the packaging.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/use-systemd-system-administration-debian.html
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://lists.debian.org/debian-devel/2013/10/msg00444.html
+[2]:https://lists.debian.org/debian-devel/2014/02/msg00316.html
+[3]:http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/systemd.html
+[4]:http://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/systemd/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20140714 Linux slabtop command--Display Kernel Slab Cache Information.md b/sources/tech/20140714 Linux slabtop command--Display Kernel Slab Cache Information.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8bb4e1f626
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20140714 Linux slabtop command--Display Kernel Slab Cache Information.md
@@ -0,0 +1,139 @@
+Linux slabtop command - Display Kernel Slab Cache Information
+================================================================================
+The Linux kernel needs to allocate memory for temporary objects such as task or device structures and inodes. The caching memory allocator manages caches of these types of objects. The modern Linux kernel implements this caching memory allocator to hold the caches called the slabs. Different types of slab caches are maintained by the slab allocator. This article concentrates on the slabtop command which shows real-time kernel slab cache information.
+
+### 1. Command Usage: ###
+
+The command is simple to use. Default execution does not mandate any arguments to the command. But it does require root privileges to access the kernel slab information. Executing the command as normal user gives following error:
+
+
+
+You can run it by prepending “sudo” with slabtop. The default output looks like:
+
+
+
+To quit from slabtop, just hit ‘q’ like you do for top command.
+
+### 2. Slabtop options: ###
+
+#### 2.1 Display Interval: ####
+
+By default slabtop refreshes every 3 seconds. But if you want, you can provide the refreshing interval in seconds with -d or --delay=N option:
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 2.2 Sort criteria: ####
+
+There are many fields in slabtop output. The -s or --sort=S option sorts the output according to the mentioned sort criteria. This option will be discussed in detail in the next section.
+
+#### 2.3 Output once: ####
+
+The -o or --once option does not refresh the output, instead it just throws the output once on STDOUT and exits.
+
+
+
+#### 2.4 Version info: ####
+
+The -V or --version displays the version of the command and exits.
+
+
+
+#### 2.5 Help: ####
+
+The common option, -h or --help displays usage of the command.
+
+
+
+### 3. Sort Criteria: ###
+
+The sort criteria determines which slab caches are displayed on top. Following are the sort criteria for slabtop:
+
+#### 3.1 ACTIVE: ####
+
+Caches can be sorted by number of active objects with “a”.
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 3.2 OBJ/SLAB: ####
+
+The Objects per Slab can be selected with “b”.
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 3.3 CACHE SIZE: ####
+
+For selecting cache size, you need to provide “c”.
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 3.4 SLABS: ####
+
+The number of slabs. Select it with “l”
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 3.5 Active Slabs: ####
+
+The number of Active Slabs. (Note that this is different from number of Active Objects described above.) Use “v” to sort according to this criteria.
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 3.6 NAME: ####
+
+Name of cache. Corresponding character is “n”
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 3.7 OBJS: ####
+
+To sort by number of objects, use “o”
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 3.8 Pages Per Slab: ####
+
+“p” will sort by pages per slab
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 3.9 OBJ SIZE: ####
+
+The object size is sorted by “s”
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 3.10 USE: ####
+
+“u” sorts by the cache utilization.
+
+
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/kernel-slab-cache-information/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20140714 Test read or write speed of usb and ssd drives with dd command on Linux.md b/sources/tech/20140714 Test read or write speed of usb and ssd drives with dd command on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..43ca1aa34e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20140714 Test read or write speed of usb and ssd drives with dd command on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,139 @@
+Test read/write speed of usb and ssd drives with dd command on Linux
+================================================================================
+### Drive speed ###
+
+The speed of a drive is measured in terms of how much data it can read or write in unit time. The dd command is a simple command line tool that can be used to read and write arbitrary blocks of data to a drive and measure the speed at which the data transfer took place.
+
+In this post we shall use the dd command to test and read and write speed of usb and ssd drives using the dd command.
+
+The data transfer speed does not depend solely on the drive, but also on the interface it is connected to. For example a usb 2.0 port has a maximum operational speed limit of 35 Mbytes/s, so even if you were to plug a high speed usb 3 pen drive into a usb 2 port, the speed would be capped to the lower limit.
+
+The same applies to SSD. SSD connect via SATA ports which have different versions. Sata 2.0 has a maximum theoretical speed limit of 3Gbits/s which is roughly 375 Mbytes/s. Whereas Sata 3.0 supports twice that speed.
+
+### Test Method ###
+
+Mount the drive and navigate into it from the terminal. Then use the dd command to first write a file using fixed sized blocks. Then read the same file out using the same block site.
+
+The general syntax of the dd command looks like this
+
+ dd if=path/to/input_file of=/path/to/output_file bs=block_size count=number_of_blocks
+
+When writing to the drive, we simply read from /dev/zero which is a source of infinite useless bytes. And when read from the drive, we read the file written earlier and send it to /dev/null which is nowhere. In the whole process, dd keeps track of the speed with which the transfer takes place and reports it.
+
+### SSD ###
+
+The SSD that we are using is a "Samsung Evo 120GB" ssd. It is a beginner level ssd that comes within a decent budget and is also my first SSD. It is also one of the best performing ssds, in the market.
+
+In this test the ssd is connected to a sata 2.0 port.
+
+#### Write speed ####
+
+Lets first write to the ssd
+
+ $ dd if=/dev/zero of=./largefile bs=1M count=1024
+ 1024+0 records in
+ 1024+0 records out
+ 1073741824 bytes (1.1 GB) copied, 4.82364 s, 223 MB/s
+
+Block size is actually quite large. You can try with smaller sizes like 64k or even 4k.
+
+#### Read speed ####
+
+Now read back the same file. However, first clear the memory cache to ensure that the file is actually read from drive.
+
+Run the following command to clear the memory cache
+
+ $ sudo sh -c "sync && echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches"
+
+Now read the file
+
+ $ dd if=./largefile of=/dev/null bs=4k
+ 165118+0 records in
+ 165118+0 records out
+ 676323328 bytes (676 MB) copied, 3.0114 s, 225 MB/s
+
+The Arch Linux wiki has a page full of information about the read/write speed of various SSDs from different vendors like Intel, Samsung, Sandisk etc. Check it out at the following url.
+
+[https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/SSD_Benchmarking][1]
+
+### USB ###
+
+In this test we shall measure the read and write speed of ordinary usb/pen drives. The drives are plugged to standard usb 2 ports. The first one is a sony 4gb usb drive and the second is a strontium 16gb drive.
+
+First plug the drive into the port and mount it, so that it is readable. Then navigate into the mount directory from the command line.
+
+#### Sony 4GB - Write ####
+
+In this test, the dd command is used to write 10,000 chunks of 8 Kbyte each to a single file on the drive.
+
+ # dd if=/dev/zero of=./largefile bs=8k count=10000
+ 10000+0 records in
+ 10000+0 records out
+ 81920000 bytes (82 MB) copied, 11.0626 s, 7.4 MB/s
+
+So the write speed is around 7.5 MBytes/s. This is a low figure.
+
+#### Sony 4GB - Read ####
+
+The same file is read back to test the read speed. Run the following command to clear the memory cache
+
+ $ sudo sh -c "sync && echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches"
+
+Now read the file using the dd command
+
+ # dd if=./largefile of=/dev/null bs=8k
+ 8000+0 records in
+ 8000+0 records out
+ 65536000 bytes (66 MB) copied, 2.65218 s, 24.7 MB/s
+
+The read speed comes out around 25 Mbytes/s which is a more or less the standard for cheap usb drives.
+
+> USB 2.0 has a theoretical maximum signaling rate of 480 Mbits/s or 60 Mbytes/s. However due to various constraints the maximum throughput is restricted to around 280 Mbit/s or 35 Mbytes/s. Beyond this the actual speed achieved depends on the quality of the pen drives and other factors too.
+
+And the above usb drive was plugged inside a USB 2.0 port and it achieved a read speed of 24.7 Mbytes/s which is not very bad. But the write speed lags much behind
+
+Now lets do the same test with a Strontium 16gb drive. Strontium is another very cheapy brand, although usb drives are reliable.
+
+#### Strontium 16gb write speed ####
+
+ # dd if=/dev/zero of=./largefile bs=64k count=1000
+ 1000+0 records in
+ 1000+0 records out
+ 65536000 bytes (66 MB) copied, 8.3834 s, 7.8 MB/s
+
+Strontium 16gb read speed
+
+ # sudo sh -c "sync && echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches"
+
+ # dd if=./largefile of=/dev/null bs=8k
+ 8000+0 records in
+ 8000+0 records out
+ 65536000 bytes (66 MB) copied, 2.90366 s, 22.6 MB/s
+
+The read speed is lower than the Sony drive.
+
+### Resources ###
+
+- [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/USB][2]
+- [https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/SSD_Benchmarking][1]
+
+----------
+
+
+
+About Silver Moon
+
+Php developer, blogger and Linux enthusiast. He can be reached at [m00n.silv3r@gmail.com][e]. Or find him on [Google+][g]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.binarytides.com/linux-test-drive-speed/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/SSD_Benchmarking
+[2]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/USB
+[e]:m00n.silv3r@gmail.com
+[g]:http://plus.google.com/117145272367995638274/posts
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20140715 Command Line Tuesdays--Part Five.md b/sources/tech/20140715 Command Line Tuesdays--Part Five.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e1c6be7948
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20140715 Command Line Tuesdays--Part Five.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+translating by cvsher
+Command Line Tuesdays – Part Five
+================================================================================
+Yes, you’ve guessed what time it is! It’s time to rrrrrrrrummmbleeeee! And this time, we’ll learn how to work with commands. So without further ado, let’s get to business.
+
+Mr Shotts states that until now, we worked with a few mysterious commands, arguments and options, and today is the day we shed a little light upon that mystery. We’ll learn the following commands and what they do: type, which, help and man. But first, let’s learn…
+
+### …what are commands? ###
+
+All great things come in fours, and it’s the same with commands. We can split them up into four categories:
+
+**1) An executable program:** a command can be an executable program. If you’ve ‘traveled’ across your file system in the previous lessons like you were supposed to, you probably visited the /usr/bin folder. You’ve seen quite a number of familiar names like transmission-gtk, deluge-gtk etc. What’s less important for us novices currently is that programs there can be compiled binaries or programs written in scripting languages. Point is, since they are executable programs, you can run them. Try it. Navigate to it, list the files inside, pick one and run it simply by typing its name.
+
+**2) A command built into the shell:** bash provides a number of commands internally called shell builtins. The cd command, for example, is a shell builtin, mr Shotts says.
+
+**3) A shell function:** miniature shell script, built into the environment. For the time being, we’ll just mention it, as it will be covered in the following weeks.
+
+**4) An alias:** commands you can define yourself, using other commands. Also coming in the following lessons.
+
+Now, it’s useful to know what type of command we’re dealing with. And we can find out using…
+
+### …type ###
+
+You can use **type + command** to inspect what kind of command is the command you’d like to use. You do it by simply typing: type command and you’ll get an output. For example:
+
+
+
+or
+
+
+
+…where we can see that the ‘ls’ command is actually an alias of ‘_ls’!
+
+### which ###
+
+Sometimes (but rarely on a desktop system, though) there are more versions of one executable installed on a machine. To find out the exact location of a given executable, we can use command which. Additionally, it only works with executable programs.
+
+
+
+Now, mostly every command has documentation that comes with it. So you’re somewhere doing your CLI thing, no access to the internet so you can’t bug geekos on the forums or IRC, and you need to find out how to exactly use a command. You can do it two ways. First being…
+
+### …help ###
+
+help command works with shell builtins (the second category we have mentioned above). So you can pick a shell builtin, like cd, for example, and simply type help cd. You’ll get a helpful page printed out in your terminal, so go ahead and read what cd has to offer. It shows in what ways you can use the command, what options you can use (it’s in square brackets, which means they are optional! Also, if there’s a vertical separator inside the square brackets, it means the options mentioned are mutually exclusive. Don’t use them together!)
+
+### –help ###
+
+help works only for the shell builtins. But most executables work with –help. As far as usage goes, it’s similar to help, but you have to type –help after the command you want to inspect. For example, transmission-gtk –help. Try it out, and see what options you can use with that executable etc.
+
+### man ###
+
+Most executables come with a formal documentation page. You can inspect it using the man command. You just enter man program, and see what it prints out. Pick any program on your computer, and try it out. For example, let’s try man transmission-gtk. You get a file opened, split into categories. It gives you information what the program is, what it does, how you can use it etc., but it doesn’t offer examples, as it’s not a tutorial.
+
+And we’re stoping to a halt there.
+
+I’d like to take a minute and thank everyone commenting and contributing to this section. You make this series vastly better, and I hope that with your help, us noobs will be able to use the CLI basics by the end of summer (just in time for 13.2 :) ). You guys are the best. Newbie users like me, who are feeling lost, stick with it. It will pay off in the end!
+
+And I’d also like to add a formal heads up: part six will not come next Tuesday, as I’ll sadly be away, so we’ll see/hear each other in 14 days, on July 29th. And until then…
+
+### …have a lot of fun! ###
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://news.opensuse.org/2014/07/15/command-line-tuesdays-part-five/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:
+[2]:
+[3]:
+[4]:
+[5]:
+[6]:
+[7]:
+[8]:
+[9]:
+[10]:
+[11]:
+[12]:
+[13]:
+[14]:
+[15]:
+[16]:
+[17]:
+[18]:
+[19]:
+[20]:
diff --git a/sources/tech/20140722 How to manage DigitalOcean VPS droplets from the command line on Linux.md b/sources/tech/20140722 How to manage DigitalOcean VPS droplets from the command line on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a96a4f9e74
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20140722 How to manage DigitalOcean VPS droplets from the command line on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,185 @@
+How to manage DigitalOcean VPS droplets from the command line on Linux
+================================================================================
+[DigitalOcean][1] is one of the [hottest][2] new kids in the block in the cloud VPS hosting market. While not offering as comprehensive service portfolio as Amazon Web Services and the likes, DigitalOcean is already a strong contender for the best Linux-based cloud VPS service targeted at small businesses and developers, thanks to their competitive pricing and user-friendly management interface.
+
+
+
+Whenever you need a web-facing server for your personal project, you can quickly spin up a "droplet" (nickname for a VPS instance at [DigitalOcean][3]). And kill it when it's not needed. No need to burn a hole in your pocket as you are charged for its up time. While DigitalOcean's web-based management interface is streamlined already, for those of you who are die-hard fans of command-line interface (CLI), there is a CLI-based droplet management tool called [Tugboat][4]. Thanks to this CLI tool, any complex droplet management task can easily be turned into a script.
+
+In this tutorial, I am going to describe **how to use Tugboat to manage DigitalOcean dropets from the command line**.
+
+### Install Tugboat on Linux ###
+
+To install Tugboat on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install ruby-dev
+ $ sudo gem install tugboat
+
+To install Tugboat on Fedora:
+
+ $ sudo yum install ruby-devel
+ $ sudo gem install tugboat
+
+To install Tugboat on CentOS, first [install or upgrade to the latest Ruby][5], because on CentOS 6.5 and earlier, the default Ruby does not meet the minimum version requirement (1.9 and higher) for Tugboat. Once you install Ruby 1.9 and higher, install Tugboat as follows.
+
+ $ sudo gem install tugboat
+
+### Configure Tugboat for the First Time ###
+
+After installation, it's time to go through one-time configuration, which involves authorizing Tugboat to access your DigitalOcean account.
+
+Go to [https://cloud.digitalocean.com/api_access][6], and create a new API key. Make a note of client ID and API key.
+
+
+
+Start authorization process by running:
+
+ $ tugboat authorize
+
+When prompted, enter your client ID and API key. It will ask you several other questions. You can accept default answers for now. We are going to customize the default settings later anyway.
+
+[][7]
+
+Now let's customize default droplet settings to reflect your typical use cases. For that, first check available droplet offerings (e.g., available images, regions, sizes).
+
+Running the command below will show you a list of available droplet images. Pick a default image to use, and make a note of the corresponding ID.
+
+ $ tugboat images --global
+
+
+
+Similarly, pick a default geographic location from available regions:
+
+ $ tugboat regions
+
+Also, choose a default droplet size from available RAM sizes:
+
+ $ tugboat sizes
+
+
+
+Now put your default choices in ~/.tugboat. For example, here I customize my default settings to 512MB Ubuntu 14.04 x64 to be created in New York region. Set "ssh_user" to root if you want to enable SSH via key authentication, which will be described shortly.
+
+ $ vi ~/.tugboat
+
+----------
+
+ ---
+ authentication:
+ client_key: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
+ api_key: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
+ ssh:
+ ssh_user: root
+ ssh_key_path: /home/dev/.ssh/id_rsa
+ ssh_port: '22'
+ defaults:
+ region: '4'
+ image: '3240036'
+ size: '66'
+ ssh_key: ''
+ private_networking: 'false'
+ backups_enabled: 'false'
+
+### Create and Add SSH Key to DigitalOcean ###
+
+A secure way to access your droplet instance is to SSH to the instance via [key authentication][8].
+
+In fact, you can automatically enable key authentication for your droplets by registering your SSH public key with [DigitalOcean][9]. Here is how to do it.
+
+First, generate a private/public SSH key pair (if you don't have one).
+
+ $ ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "your@emailaddress.com"
+
+Assuming that the generated key pair consists of: ~/.ssh/id_rsa (private key) and ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub (public key), go ahead and upload your public key by running:
+
+ $ tugboat add-key [name-of-your-key]
+
+You can give your key any name you like (e.g., "my-default-key"). When prompted, enter the path to your public key (e.g., /home/user/.ssh/id_rsa.pub). After key uploading is completed, verify the key is successfully added by running:
+
+ $ tugboat keys
+
+
+
+The key should also appear in DigitalOcean's [SSH key page][10]. If you want the key to be automatically used for your droplets, add the ID of your key to ~/.tugboat.
+
+ ssh_key: '182710'
+
+### Basic Usage of Tugboat ###
+
+Here are a few basic use cases of tugboat command line.
+
+1. Create a new droplet with default settings.
+
+ $ tugboat create
+
+2. Show a list of all active droplets.
+
+ $ tugboat droplets
+
+3. Display information about a droplet.
+
+ $ tugboat info
+
+[][11]
+
+4. Shutdown a droplet, and remove its image.
+
+ $ tugboat destroy
+
+5. Shutdown a droplet, but keep its image
+
+ $ tugboat halt
+
+6. Take a snapshot of a droplet. The droplet must be turned off first.
+
+ $ tugboat snapshot
+
+7. Resize (increase or decrease the RAM size of) a droplet. The droplet must be shutdown first.
+
+ $ tugboat resize -s
+
+If you want to know more about a particular command option, run:
+
+ $ tugboat help
+
+
+
+### Troubleshooting ###
+
+1. When I run tugboat command, it fails with the following error.
+
+ /usr/lib/ruby/site_ruby/1.8/rubygems/custom_require.rb:31:in `gem_original_require': /usr/lib/ruby/gems/1.8/gems/tugboat-0.2.0/lib/tugboat/cli.rb:12: syntax error, unexpected ':', expecting kEND (SyntaxError)
+
+Tugboat requires Ruby 1.9 and higher. You need to upgrade Ruby to solve this problem. For CentOS, refer to [this tutorial][12].
+
+2. When I try to install Tugboat with gem, I get the following error.
+
+/usr/local/share/ruby/site_ruby/rubygems/core_ext/kernel_require.rb:55:in `require': cannot load such file -- json/pure (LoadError)
+
+Install the following gem to fix the problem.
+
+ $ sudo gem install json_pure
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/manage-digitalocean-vps-droplets-command-line-linux.html
+
+原文作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/go/digitalocean
+[2]:http://news.netcraft.com/archives/2013/12/11/digitalocean-now-growing-faster-than-amazon.html
+[3]:http://xmodulo.com/go/digitalocean
+[4]:https://github.com/pearkes/tugboat
+[5]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/upgrade-ruby-centos.html
+[6]:https://cloud.digitalocean.com/api_access
+[7]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14685122101/
+[8]:http://xmodulo.com/2012/04/how-to-enable-ssh-login-without.html
+[9]:http://xmodulo.com/go/digitalocean
+[10]:https://cloud.digitalocean.com/ssh_keys
+[11]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14501627440/
+[12]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/upgrade-ruby-centos.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20140723 Fix Missing Speaker Icon From Moka Icon Theme.md b/sources/tech/20140723 Fix Missing Speaker Icon From Moka Icon Theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..28afbba227
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20140723 Fix Missing Speaker Icon From Moka Icon Theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+Fix Missing Speaker Icon From Moka Icon Theme [Quick Tip]
+================================================================================
+[Moka][1] is a beautiful icon theme. It has been constantly featured among the [best icon themes available for Ubuntu][2]. But there is little issue with Moka in Ubuntu 14.04. If you use Moka icons in Ubuntu 14.04 with Unity, you’ll find that speaker icon used for sound is missing:
+
+
+
+### Fix missing sound icon while using Moka icon theme ###
+
+Though you might have already added official Moka PPA but for the sake of checking, add it again:
+
+ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:moka/stable
+ sudo apt-get update
+
+Now, next step is to install monochrome panel icons. Use the following command to install it:
+
+ sudo apt-get install faba-mono-icons
+
+Once you have installed the Faba monochrome icons, change your icon theme from Moka to Faba. This will give you Moka icon theme along with beautiful monochrome icons in the top panel in Unity:
+
+
+
+I hope this helped you to fix the missing sound icon. Enjoy every bit and every sip of the Moka.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-missing-speaker-icon-from-moka/
+
+原文作者:[Abhishek][a]
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
+[1]:http://mokaproject.com/
+[2]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20140723 How to access SoundCloud from the command line in Linux.md b/sources/tech/20140723 How to access SoundCloud from the command line in Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d664593e6e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20140723 How to access SoundCloud from the command line in Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+How to access SoundCloud from the command line in Linux
+================================================================================
+If you enjoy music streaming and originally-created sounds, you cannot have missed [SoundCloud][1]. Based in Germany, this cloud streaming service is now famous and well-established for any music adventurer. And naturally, as a Linux enthusiast, you might wonder how to join your passion for Linux with your love for music. As a solution, I advise you to check out Soundcloud2000, **a command line client for SoundCloud** born out of the [Music Hack Day Stockholm '13][2].
+
+### Installation ###
+
+For Debian or Ubuntu users, install via:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install portaudio19-dev libmpg123-dev libncurses-dev ruby1.9.1-dev
+ $ sudo gem install soundcloud2000
+
+For Archlinux users, the package is available in [AUR][3].
+
+For Fedora users, install via:
+
+ $ sudo yum install portaudio-devel libmpg123-devel ncurses-devel ruby-devel
+ $ sudo gem install soundcloud2000
+
+For CentOS users, install or upgrade to the [latest Ruby/RubyGems][4] (1.9 and higher), enable [Repoforge repo][5], and install via:
+
+ $ sudo yum install portaudio-devel mpg123-devel
+ $ sudo gem install curses soundcloud2000
+
+And finally, go to the official github page for the sources.
+
+### Usage ###
+
+Soundcloud2000 is very easy to pick up. Some might even say simplistic. I like it for that sobriety and the effort of the three authors and contributors. Launch it via:
+
+ $ soundcloud2000
+
+From there, you will be welcomed with a splash screen:
+
+
+
+and then a list of songs:
+
+
+
+You can scroll through the list via the up and down keys, play a song with enter, pause/resume with the space bar, and fast forward/rewind with the right and left arrow keys. As you can see, nothing groundbreaking but definitely ergonomic.
+
+If the random list is too long to scroll through, you have an option to see all the tracks for a particular user by hitting the 'u' key and then typing his name.
+
+
+
+That is probably one of the major defaults of Soundcloud2000. While the navigation is not optimized, I have high hopes for improvements and support as the software is still very young.
+
+### Bonus ###
+
+Another alternative as a bonus: if you like the idea of using SoundCloud from a terminal, but do not want to install any additional software (or maybe you cannot), I advise you to go to [cmd.fm][6]. The website is a kind of camouflage for SoundCloud, as it hides it behind a shell interface.
+
+[][7]
+
+Type "help" for a list of commands, which is a lot longer than for Soundcloud2000. As examples, I noticed:
+
+- _genres to list all genres
+- _play random to play a random track
+- _pause to pause the current track
+- _playlist new to make a new playlist
+- _loop to loop current track
+- _cinema to watch and ASCII version of Star Wars which completely blew my mind.
+
+And it even supports auto-completion via the tabulation key for genres.
+
+To conclude, Soundcloud2000 is a neat program that does exactly what it is supposed to. We can forgive its current flaws as they are surely tied to its youth. I really hope that it will grow and include more features (and potentially get inspiration from cmd.fm).
+
+If you like the idea, I invite you to support the programmers, and if you like these kinds of initiatives, support [Music Hack Day][8] which mixes software development and music.
+
+What do you think of using SoundCloud from the command line? Please let us know in the comments.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/access-soundcloud-command-line-linux.html
+
+原文作者:[Adrien Brochard][a]
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/adrien
+[1]:https://soundcloud.com/
+[2]:https://www.hackerleague.org/hackathons/music-hack-day-stockholm-13/
+[3]:https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/ruby-soundcloud2000/
+[4]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/upgrade-ruby-centos.html
+[5]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/01/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
+[6]:https://cmd.fm/
+[7]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14494448218/
+[8]:http://new.musichackday.org/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20140723 Top 10 Fun On The Command Line.md b/sources/tech/20140723 Top 10 Fun On The Command Line.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c31d807dd5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20140723 Top 10 Fun On The Command Line.md
@@ -0,0 +1,116 @@
+Top 10! Fun On The Command Line
+================================================================================
+**If you just love making 'top 10'-type lists but are a little embarrassed to say so, tell people you're passionate about data exploration. To impress them even more, explain that you do your data exploration on the command line. But don't ruin the impression by telling them how easy that is!**
+
+In this article I'll do some data exploration with basic GNU/Linux tools and 'one-column tables', by which I mean simple lists. For more information on the commands used here, see their Linux 'man' pages, or ask for an explanation in the 'Comments' section.
+
+### Passwords ###
+
+The first list to explore is Mark Burnett's 2011 compilation of the [10000 most commonly used passwords][1]. The list is ordered most-frequent-first, and is one source of the widely known factoid that 'password' is the most commonly used password, with '123456' in second place. Here I've put the list in a file called passwords, and used the head command to show the first 10 lines:
+
+
+
+(Burnett explains how he collects his passwords [here][2]. Note that he converted all uppercase letters to lowercase in his list.)
+
+OK, so 'password' is top of the Burnett list. What about individual digits?
+
+
+
+Interesting. The digit '1' appears in the password list more than twice as often as the next most-used digit, '2', and the 10 digits are in numerical as well as popularity order, except for 0 and 9. And the top 10 letters?
+
+
+
+The most frequent letters in the passwords file are EARONISTLC. That's not too far off EAIRTONSLC, which is the frequency pattern in at least [one published table][3] of letter usage in common English words. Does this mean that most passwords are actually common English words, maybe with a few digits thrown in?
+
+To find out, I'll first convert passwords to a list of letters-only strings, then see how many of those strings are in an English dictionary.
+
+First I'll delete all the digits in passwords with a **sed** command, then delete all the punctuation marks, then all the blank lines. This creates a list of letters-only passwords. Then I'll prune that list with **sort** and **uniq** to get rid of any duplicates. (For example, 'abc1234def' and 'abc1!2!3!def!' both reduce to 'abcdef'.) According to the wc command, my pruning reduces the 10000 passwords to 8583 letters-only strings:
+
+
+
+For a handy English dictionary I'll use the file `usr/share/dict/american-english`, which came with my Debian Linux distribution. It contains 99171 words. I'll first convert this wordlist to lowercase-only with the **tr** command, then delete any duplicate entries with **sort** and **uniq** (like 'A' and 'a' both becoming 'a'). That reduces the wordlist to 97723 entries:
+
+
+
+I can now ask the comm command with the '-23' option to compare the two lists and report just the words in the letters-only file that are not found in the dictionary:
+
+
+
+The total is 3137, so at least 8583 - 3137 = 5446 'core' passwords in Burnett's lowercase-only list (about 63%) are either plain English words, or plain English words with some digits or punctuation marks added. I wrote at least because a big proportion of the 3137 strings are only slight modifications of plain English words or names, or words or names missing from the /usr/share dictionary. Among the LA's, for example, are 'labtec', 'ladyboy', 'lakeside', 'lalakers', 'lalala', 'laserjet', 'lasvegas', 'lavalamp' and 'lawman'.
+
+### Placenames ###
+
+In a previous [Linux Rain article][4], I described how I built a table of Australian placenames with more than 370 000 entries. Using it, I can now answer vital questions like 'Is Round Hill the most popular name for hills in Australia?' and 'Is Sandy Beach tops for beaches, and Rocky Creek for creeks?'
+
+The placename field in the gazetteer table is number 2, so here goes:
+
+
+
+Wow. I wasn't even close. (But note how I saved typing by using the **^string1^string2** command. It repeats the last command, but substitutes string2 for string1. Wonderful BASH trick!)
+
+Another burning question is how many placenames there are with 'Mile' in them, like 'Six Mile Creek', and how they rank:
+
+
+
+I've noticed a lot of Dead Horse Creeks in my Australian travels, and so has the gazetteer:
+
+
+
+### Species ###
+
+The third list to explore comes from a table I published this year of new Australian insect species named in the period 1961-2010. From the table I've pulled out all the 'species epithets', which are the second parts of genus-species combinations like Homo sapiens (you and me) and Apis mellifera (European honeybee).
+
+(Tech note: The insects table, which is available from the open data Zenodo repository at [https://zenodo.org/record/10481][5], includes subspecies. For my 'top 10' exercise I first isolated all the unique genus-species combinations, to avoid duplication from subspecies like Apis mellifera iberica, Apis mellifera intermissa, etc. The final species file has 18155 species epithets.)
+
+Most people who make jokes about scientific names use the '-us' ending, as in 'Biggus buggus'. What about entomologists? There are a couple of good, command-line ways to get the last 2 letters of a string, and here I've used both:
+
+
+
+Yep, entomologists prefer '-us', too. Next, I wonder how many species are named for my home State of Tasmania? (Below I ask head for the first 100 lines to make sure I get all the 'tasman' combinations.)
+
+
+
+How about Queensland?
+
+
+
+And generally speaking, what are the top 10 names in that insect species list?
+
+
+
+Hmm. Apart from the obvious 'australis' and 'australiensis', and the geographical 'occidentalis' (of the west), the other 7 epithets in the 10-most-popular list have been created by entomologists to honour other entomologists. (The epithet 'commoni' honors the Australian butterfly and moth specialist Ian F.B. Common, 1917-2006.)
+
+### Speechifying ###
+
+The commands used above work on simple lists. To make a simple list out a block of text, the command line is again your friend. For example, I've saved a rather filibustery [speech][6] in the Australian Senate on 16 July 2014 as the text file hansard. To split hansard into a list of words:
+
+
+
+And to look at word frequency in the speech:
+
+
+
+### Coming soon... ###
+
+Doing 'top 10' and other rankings from multi-column tables requires a few more command-line tools. I'll demonstrate their use in a future article.
+
+
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://thelinuxrain.com/articles/top-10-fun-on-the-command-line
+
+原文作者:Bob Mesibov(Bob Mesibov is Tasmanian, retired and a keen Linux tinkerer.)
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://xato.net/passwords/more-top-worst-passwords/#.U8eD13AvDy0
+[2]:https://xato.net/passwords/how-i-collect-passwords/#.U8eEdnAvDy0
+[3]:http://www.rinkworks.com/words/letterfreq.shtml
+[4]:http://www.thelinuxrain.com/articles/building-a-gazetteer-table-from-kml-files
+[5]:https://zenodo.org/record/10481
+[6]:http://parlinfo.aph.gov.au/parlInfo/search/display/display.w3p;db=CHAMBER;id=chamber%2Fhansards%2F232fa1a8-d7e8-4b22-9018-1a99b5a96812%2F0025;query=Id%3A%22chamber%2Fhansards%2F232fa1a8-d7e8-4b22-9018-1a99b5a96812%2F0000%22
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20140724 Camicri Cube--An Offline And Portable Package Management System.md b/sources/tech/20140724 Camicri Cube--An Offline And Portable Package Management System.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bcd2773a32
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20140724 Camicri Cube--An Offline And Portable Package Management System.md
@@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
+Camicri Cube: An Offline And Portable Package Management System
+================================================================================
+
+
+As we all know, we must have an Internet connection in our System for downloading and installing applications using synaptic manager or software center. But, what if you don’t have an Internet connection, or the Internet connection is dead slow? This will be definitely a headache when installing packages using software center in your Linux desktop. Instead, you can manually download the applications from their official site, and install them. But, most of the Linux users doesn’t aware about the required dependencies for the applications that they wanted to install. What could you do if you have such situation? Leave all the worries now. Today, we introduce an awesome offline package manager called **Camicri Cube**.
+
+You can use this package manager on any Internet connected system, download the list of packages you want to install, bring them back to your offline computer, and Install them. Sounds good? Yes, It is! Cube is a package manager like Synaptic and Ubuntu Software Center, but a portable one. It can be used and run in any platform (Windows, Apt-Based Linux Distributions), online and offline, in flashdrive or any removable devices. The main goal of this project is to enable the offline Linux users to download and install Linux applications easily.
+
+Cube will gather complete details of your offline computer such as OS details, installed applications and more. Then, just the copy the cube application using any USB thumb drive, and use it on the other Internet connected system, and download the list of applications you want. After downloading all required packages, head back to your original computer and start installing them. Cube is developed and maintained by **Jake Capangpangan**. It is written using C++, and bundled with all necessary packages. So, you don’t have to install any extra software to use it.
+
+### Installation ###
+
+Now, let us download and install Cube on the Offline system which doesn’t have the Internet connection. Download Cube latest version either from the [official Launchpad Page][1] or [Sourceforge site][2]. Make sure you have downloaded the correct version depending upon your offline computer architecture. As I use 64 bit system, I downloaded the 64bit version.
+
+ wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/camicricube/files/Camicri%20Cube%201.0.9/cube-1.0.9.2_64bit.zip/
+
+Extract the zip file and move it to your home directory or anywhere you want:
+
+ unzip cube-1.0.9.2_64bit.zip
+
+That’s it. Now it’s time to know how to use it.
+
+### Usage ###
+
+Here, I will be using Two Ubuntu systems. The original (Offline – no Internet) is running with **Ubuntu 14.04**, and the Internet connected system is running with **Lubuntu 14.04** Desktop.
+
+#### Steps to do On Offline system: ####
+
+From the offline system, Go to the extracted Cube folder. You’ll find an executable called “cube-linux”. Double click it, and Click Execute. If it not executable, set the executable permission as shown below.
+
+ sudo chmod -R +x cube/
+
+Then, go to the cube directory,
+
+ cd cube/
+
+And run the following command to run it.
+
+ ./cube-linux
+
+Enter the Project name (Ex.sk) and click **Create**. As I mentioned above, this will create a new project with complete details of your system such as OS details, list of installed applications, list of repositories etc.
+
+
+
+As you know, our system is an offline computer that means I don’t have Internet connection. So I skipped the Update Repositories process by clicking on the **Cancel** button. We will update the repositories later on an Internet connected system.
+
+
+
+Again, I clicked **No** to skip updating the offline computer, because we don’t have Internet connection.
+
+
+
+That’s it. Now the new project has been created. The new project will be saved on your main cube folder. Go to the Cube folder, and you’ll find a folder called Projects. This folder will hold all the essential details of your offline system.
+
+
+
+
+
+Now, close the cube application, and copy the entire main **cube** folder to any flash drive, and go to the Internet connected system.
+
+#### Steps to do on an Internet connected system: ####
+
+The following steps needs to be done on the Internet connected system. In our case, Its **Lubuntu 14.04**.
+
+Make the cube folder executable as we did in the original computer.
+
+ sudo chmod -R +x cube/
+
+Now, double click the file cube-linux to open it or you can launch it from the Terminal as shown below.
+
+ cd cube/
+ ./cube-linux
+
+You will see that your project is now listed in the “Open Existing Projects” part of the window. Select your project
+
+
+
+Then, the cube will ask if this is your project’s original computer. It’s not my original (Offline) computer, so I clicked **No**.
+
+
+
+You’ll be asked if you want to update your repositories. Click **Ok** to update the repositories.
+
+
+
+Next, we have to update all outdated packages/applications. Click on the “**Mark All updates**” button from the Cube’s tool bar. After that, click “**Download all marked**” button to update all updated packages/applications. As you see in the below screenshot, there are 302 packages needs to be updated in my case. Then, Click **Ok** to continue to download marked packages.
+
+
+
+Now, Cube will start to download all marked packages.
+
+
+
+We have completed updating repositories and packages. Now, you can download a new package if you want to install it on your offline system.
+
+#### Downloading New Applications ####
+
+For example, here I am going to download the **apache2** Package. Enter the name of the package in the **search** box, and hit Search button. The Cube will fetch the details of the application that you are looking for. Hit the “**Download this package now**” button, and click **Ok** to start download.
+
+
+
+Cube will start downloading the apache2 package with all its dependencies.
+
+
+
+If you want to search and download more packages, simply Click the button “**Mark this package**”, and do search the required packages. You can mark as many as packages you want to install on your original computer. Once you marked all packages, hit the “**Download all marked**” button on the top tool bar to start downloading them.
+
+After you completed updating repositories, outdated packages, and downloading new applications, close the Cube application. Then, copy the entire Cube folder to any flash drive or external hdd, and go back to your Offline system.
+
+#### Steps to do on Offline computer: ####
+
+Copy the Cube folder back to your Offline system on any place you want. Go to the cube folder and double click **cube-linux** file to launch Cube application.
+
+Or, you can launch it from Terminal as shown below.
+
+ cd cube/
+ ./cube-linux
+
+Select your project and click Open.
+
+
+
+Then a dialog will ask you to update your system, please click “Yes” especially when you download new repositories, because this will transfer all new repositories to your computer.
+
+
+
+You’ll see that the repositories will be updated on your offline computer without Internet connection. Because, we already have updated the repositories on the Internet connected system. Seems cool, isn’t it?
+
+After updating the repositories, let us install all downloaded packages. Click the “Mark All Downloaded” button to select all downloaded packages, and click “Install All Marked” to install all of them from the Cube main Tool bar. The Cube application will automatically open a new Terminal, and install all packages.
+
+
+
+If you encountered with dependency problems, go to **Cube Menu -> Packages -> Install packages with complete dependencies** to install all packages.
+
+If you want to install a specific package, Navigate to the List Packages, click the “Downloaded” button, and all downloaded packages will be listed.
+
+
+
+Then, double click the desired package, and click “Install this”, or “Mark this” if you want to install it later.
+
+
+
+By this way, you can download the required packages from any Internet connected system, and then you can install them in your offline computer without Internet connection.
+
+### Conclusion ###
+
+This is one of the best and useful tool ever I have used. But during testing this tool in my Ubuntu 14.04 testbox, I faced many dependency problems, and the Cube application is suddenly closed often. Also, I could use this tool only on a fresh Ubuntu 14.04 offline system without any issues. Hope all these issues wouldn’t happen on previous versions of Ubuntu. Apart from these minor issues, this tool does this job as advertised and worked like a charm.
+
+Cheers!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/camicri-cube-offline-portable-package-management-system/
+
+原文作者:
+
+
+
+[SK][a](Senthilkumar, aka SK, is a Linux enthusiast, FOSS Supporter & Linux Consultant from Tamilnadu, India. A passionate and dynamic person, aims to deliver quality content to IT professionals and loves very much to write and explore new things about Linux, Open Source, Computers and Internet.)
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
+[1]:https://launchpad.net/camicricube
+[2]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/camicricube/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20140724 Install Google Docs on Linux with Grive Tools.md b/sources/tech/20140724 Install Google Docs on Linux with Grive Tools.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6e49ffd618
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20140724 Install Google Docs on Linux with Grive Tools.md
@@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
+nd0104 is translate
+Install Google Docs on Linux with Grive Tools
+================================================================================
+Google Drive is two years old now and Google’s cloud storage solution seems to be still going strong thanks to its integration with Google Docs and Gmail. There’s one thing still missing though: a lack of an official Linux client. Apparently Google has had one floating around their offices for a while now, however it’s not seen the light of day on any Linux system.
+
+Thankfully, there is an alternative solution using Grive Tools. We’ve covered Grive once before when it was in its infancy, but it’s received a fair few upgrades since then thanks to Grive Tools and is now compatible with Fedora and OpenSUSE to cover a better selection of distros. Over the course of this tutorial, we’ll show you how to set up Grive Tools and get it syncing files to and from Google Drive on a regular basis, so your work is always perfectly backed up. With the death of Ubuntu One, it’s a great alternative to Canonical’s own cloud storage solution.
+
+
+Accesss your backed up Linux files from anywhere with an internet connection by making use of the Drive connection
+
+### Resources ###
+
+A Google account
+
+- [Grive Tools][1]
+
+### Step-by-step ###
+
+#### Step 01 Ubuntu repository ####
+
+Grive Tools is not included in Ubuntu or Ubuntu-based distros yet, so you’ll need to add a third-party repository to access it. Add this with:
+
+ $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:thefanclub/grive-tools
+
+Follow this up with the usual sudo apt-get update before we continue.
+
+#### Step 02 Ubuntu install ####
+
+After the apt-get update, Grive Tools will appear in the software centre. If you want to go there and install it you can, however as we already have a terminal open we might as well use:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install grive-tools
+
+#### Step 03 Fedora dependencies ####
+
+You’ll need to install some specific dependencies for OpenSUSE, Fedora and other RHEL-based distros. In Fedora specifically, open a terminal and install them with:
+
+ $ sudo yum install json-c json-c-devel qt-devel boost-devel openssl-devel libxslt libcurl libcurl-devel
+
+The same packages will need to be installed on the other distros.
+
+#### Step 04 Grive package ####
+
+Grive is not in the repositories of any of
+these distros, however binaries exist if you won’t want to build it from source. Go to RPMSEEK.com and search for Grive; look out for the version for your distro and download it.
+
+#### Step 05 Install the download ####
+
+Once downloaded, install the package; you can either do it graphical or install with:
+
+ $ sudo yum install grive-tools-1.9.noarch.rpm
+
+After that, go to the Resources link for Grive Tools and locate the Fedora package on the website: download this binary and install it alongside Grive.
+
+#### Step 06 Start the setup ####
+
+The method to actually get Grive and Grive Tools working on both systems is basically the same, so we’ll cover both at once while mentioning any extras that need to be done for a specific distro. The first thing you’ll need to do is look for Grive Setup in your list of programs.
+
+#### Step 07 Log into your account ####
+
+If you haven’t already created a Google account, you’ll need to get one sorted now before continuing. Otherwise, click Next to bring up a browser that will point you towards Google and ask you to log in. Make sure you’re logged in to the correct email address before continuing.
+
+#### Step 08 Connect your account ####
+
+You’ll be asked if the specific info it can look at is okay – you’ll need to confirm to continue, otherwise it can’t download or sync your Drive data. It will then give you a code to paste into a pop-up that launched when the browser opened.
+
+#### Step 09 Code input ####
+
+Press Next for Grive to accept the code. It will automatically open up a new Google Drive window and show your files being synced straight to your PC. This may take a while depending on how much you have stored on your account.
+
+#### Step 10 Desktop notifications ####
+
+Once the sync is complete, search again for Grive in your programs and look for Google Drive Indicator. Click on this and it will automatically launch a Dropbox-style toolbar notifier for Google Drive. This is also similar to the kind of notifier on desktops with an official client.
+
+#### Step 11 Access Google Drive ####
+
+You can quick access the contents of your Google Drive by finding the app of the same name in your program list. It links straight to your folder for ease of access, so you can add it to favourites or quick bar if you wish. There’s also an option to open it from the notifier.
+
+#### Step 12 Drive options ####
+
+You can access syncing options from the indicator to make sure Grive works as you want it to. Access them by clicking on the toolbar icon and select preferences. A couple of options you’d probably want checked are ‘Start Drive when computer turns on’, and ‘On screen notifications’.
+
+#### Step 13 Auto-syncing ####
+
+Unlike the official clients, you cannot select which folders do and do not get synced on your client. Depending on how you plan to use it, you can turn on Auto-sync so that everything is synced up and down at all times, or you can turn it off and sync manually when everything is ready.
+
+#### Step 14 Large file tip ####
+
+Google Drive – not just Grive – always seems to have issues with uploading larger files. We suggest splitting them up into smaller files using split on a compressed file to make them all a specific size. You can do it in a terminal with:
+
+ split -b 500m file.mp4 newfilename
+
+#### Step 15 File types ####
+
+One of the major things you may have noticed is which documents have and have not been downloaded by Grive. On the official clients, links will be added that can let you jump straight to pure Google Docs files, while files that are actually DOC, ODF or PDF will be downloaded outright to the system. Only the latter files are downloaded with Grive as they’re purely stored in the cloud on Drive. The upside is they’re properly stored locally and will still sync between the cloud and other systems.
+
+#### Step 16 Location ####
+
+Very simply, the Google Drive folder is kept in the home folder under Google Drive. If you’re using standard GNOME it’s actually opening the files in the GNOME file manager; for some reason it also does that in Unity and any non-GNOME desktop environment.
+
+#### Step 17 Backup to Grive ####
+
+One of the benefits of cloud storage for files is that the storage itself is off-site and difficult to lose. This makes it ideal for backing up other important documents and settings. The simplest and quickest way to do this is to periodically copy a file over to the Drive folder and watch it upload.
+
+#### Step 18 Better backup ####
+
+This is not the most efficient way to backup such files though; fortunately Linux comes with many tools to back up data that also includes backup scheduling thanks to cron. We’ll be using luckyBackup for this: find it in your package manager and install it.
+
+#### Step 19 Set up the backup ####
+
+Click Add to create a new task and name it however you wish. Keep the Type setting to ‘Backup Source inside Destination’, choose your Source and finally set the Destination as the Google Drive folder. Click OK to save it, followed by the checkbox next to the task to activate it.
+
+#### Step 20 First backup ####
+
+Click Run at the top to do the first backup operation. It will print out a verbose list of the files and operations and will inform you once it’s finished, along with any errors that occurred along the way. If you have automatic sync on, it will start uploading the backed up files to Drive.
+
+#### Step 21 Timed backup ####
+
+Click Done to return to the main menu. Click Profile followed by Schedule to bring up the scheduling dialog. The schedules are done by profiles, which can all contain a number of different backup tasks. Click Add to start creating a schedule for our Drive backup.
+
+#### Step 22 To schedule ####
+
+The schedule creates a cron job, so you can set it to occur on specific days of the week or specific months of the year and at what time the backup should occur. You can have it do so every hour at a specific minute past the hour if you need it to back up so frequently.
+
+#### Step 23 Reverse backup ####
+
+Google Drive helpfully keeps a record of past versions of files on its servers; however they do not extend forever. If you’re backing up or saving to the cloud you may want to consider creating a backup of the Drive files to your PC or network as well.
+
+#### Step 24 Driven ####
+
+While there are no official tools for Linux just yet, Grive and Grive Tools at least enable you to emulate what they should be relatively well. Look out for updates to Drive and Grive Tools to see if any new functions would work well for you.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxuser.co.uk/tutorials/install-google-docs-on-linux-with-grive-tools
+
+原文作者:Rob Zwetsloot
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.thefanclub.co.za/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/Encrypting Your Cat Photos.md b/sources/tech/Encrypting Your Cat Photos.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b4f3879239..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/Encrypting Your Cat Photos.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,143 +0,0 @@
-(翻译中 by runningwater)
-Encrypting Your Cat Photos
-================================================================================
-The truth is, I really don't have anything on my hard drive that I would be upset over someone seeing. I have some cat photos. I have a few text files with ideas for future books and/or short stories, and a couple half-written starts to NaNoWriMo novels. It would be easy to say that there's no point encrypting my hard drive, because I have nothing to hide. The problem is, we wrongly correlate a "desire for privacy" with "having something to hide". I think where I live, in America, we've taken our rights to privacy for granted. Rather than the traditional "he must be hiding porn or bombs", think about something a little more mundane.
-
-I live in Michigan. It's cold here in the winter, and I tend to keep my thermostat set around 75 degrees. That might seem high to you, but for my family, it's just right. Thanks to the privacy of my own home, my neighbors don't know how toasty warm we keep it. Some of those neighbors would be very upset to see how "wasteful" the Powers family is in the winter. In fact, there's one local man who makes it a point to let everyone know that anything over 60 degrees is ecologically wasteful. I don't want to get into a fight with Old Man Icebritches, so we just keep our comfortable house a secret. We don't have anything to hide, but it's not something everyone needs to know about.
-
-Obviously my example is silly, but hopefully it makes you think. Modern Linux allows us to encrypt our data easily and reliably, so why not take advantage of it?
-
-### How Does It Work? ###
-
-I won't go into too much detail about how encryption works, but a basic understanding is necessary for even the simplest implementation. To encrypt and decrypt a file, two "keys" are required. One is the private key, which is just that, private. I like to think of the private key as an actual key—you can make copies if you want, but it's not wise to do so. The more copies of your private keys you make, the more likely someone nefarious will get one and break into your apartment—er, I mean files.
-
-The public key is more like a schematic for a lock that only you can open (with your private key). You make this key available for anyone. You can post it on a Web site, put it in your e-mail, tattoo it on your back, whatever. When others want to create a file that only you can see, they encrypt it using your public key.
-
-This one-to-many scenario also has a cool side effect. If you encrypt something using your private key, anyone can decrypt it using your public key. This may sound silly, but what makes such a scenario useful is that although the encrypted file isn't protected from prying eyes, it is guaranteed to be from you. Only a file encrypted with your private key can be decrypted with your public key. In this way, encrypting something with your private key digitally "signs" the file.
-
-#### Usually it works like this: ####
-
-1. You have a file you want to send to Suzy, so you encrypt it with Suzy's public key. Only Suzy can open it, but there's no way for Suzy to know that you are the one who sent it, since anyone could encrypt a file with her public key.
-1. Therefore, you take the file you encrypted with Suzy's public key and encrypt that file with your private key. Suzy will have to decrypt the file twice, but she'll know it came from you.
-1. Suzy receives the file and decrypts the first layer with your public key, proving it came from you.
-1. Suzy then decrypts the second layer of encryption with her private key, as that's the only key able to decrypt the original file. (Because you originally encrypted it with her public key.)
-
-That scenario is when encryption is used for safely transferring files, of course. It's also quite common simply to encrypt your files (or partitions) so that no one can see them unless you decrypt them first. Let's start with file encryption, because that's what most people will want to do on their systems.
-
-### Starting Simple ###
-
-Before I go into more complex type setting, let's discuss simply encrypting a file. There are various programs to handle encryption. In fact, it's easy to get overwhelmed with the available options for file and system encryption. Today, let's use a basic (but very powerful) command-line tool for encrypting a file. GPG (Gnu Privacy Guard) is an open-source implementation of PGP (Pretty Good Protection). It allows encryption and signing, and manages multiple keys and so on. For this example, let's simply encrypt a file.
-
-Let's say you have a file called secret_manifesto.txt, which contains the secrets to life, the universe and everything. Using GPG, you can encrypt the file with a passphrase. Using a passphrase is far simpler than using a public and private key pair, because it's simply encrypted using your passphrase. This does make your file more susceptible to cracking (using rainbow tables or other hacking tools), but like the label on the tin says, it's Pretty Good Protection. To encrypt your file, you can do this:
-
- # gpg -c secret_manifesto.txt
- # Enter passphrase:
- # Repeat passphrase:
-
-Once complete, you'll have a new file in the same directory. It will be named secret_manifesto.txt.gpg by default. This is a binary file, which means it's fairly small, but it can't be copy/pasted into an e-mail or IM. For portability, you can add the -a flag, which will create an encrypted file that contains only ASCII text:
-
- # gpg -a -c secret_manifesto.txt
- # Enter passphrase:
- # Repeat passphrase:
- # ls -l
- -rw-rw-r-- 1 spowers spowers 6 Nov 23 1:26 secret_manifesto.txt
- -rw-rw-r-- 1 spowers spowers 174 Nov 23 1:27 secret_manifesto.txt.asc
- -rw-rw-r-- 1 spowers spowers 55 Nov 23 1:26 secret_manifesto.txt.gpg
-
- Notice there is now a file with .asc as the extension. This is text-only, but you can see in the code snippet that it's also much larger than the binary encrypted file, and much much larger than the original text file. Once you've encrypted your file, if you truly want to keep your information secret, it would be wise to delete the original text file.
-
-To decrypt the file, you'll again use the gpg program. The same command will decrypt either file, whether it's binary or ASCII:
-
- # gpg secret_manifesto.txt.asc
- # gpg: CAST5 encrypted data
- # Enter passphrase:
- # gpg: encrypted with 1 passphrase
- # File `secret_manifesto.txt' exists. Overwrite? (y/N)
-
-Notice in the example above, I hadn't deleted the original text file, so gpg gave me the option of overwriting. Once complete, I have my original file back, unencrypted. If you just have a file or two you want to protect, the command-line gpg program might be all you need. If you'd rather have an area on your system that automatically encrypts everything you save, it's a little more complicated. It's still not terribly difficult, but let's start with a fairly simplistic model.
-
-### Encrypting a USB Drive ###
-
-Like I mentioned earlier, there are many options when it comes to encryption. One of the more popular methods of encrypting partitions is the LUKS (Linux Unified Key Setup) system. A USB drive with a LUKS-formatted partition should be detected automatically by most systems. In fact, if you're using a desktop environment like Ubuntu Desktop, encrypting a USB drive is a simple check box during the formatting process. Although that's a perfectly acceptable way to encrypt your USB drive, I'm going to demonstrate how to do it on the command line, so you understand what's actually happening behind the scenes.
-
-#### Step 1: identify your USB drive. ####
-
-If you type `dmesg` after plugging in your USB drive, you should get all sorts of system information, including the device name of your freshly plugged-in USB device. Make sure you have the correct device identified, because what you're doing will destroy any data on the drive. You wouldn't want to format the wrong disk accidentally. (It should go without saying, but I'll say it anyway, make sure there's nothing on your USB drive that you want to save—this is a destructive process.)
-
-#### Step 2: partition the USB drive. ####
-
-Assuming that your USB drive is the /dev/sdb device on your system, you need to create a single partition on the drive. Let's use fdisk. Below is the interaction with fdisk required. Basically, you create a new empty partition with the o command, then write changes with w. Then, you'll restart fdisk and use the n command to create a new primary partition, using the defaults so that the entire drive is used:
-
- # sudo fdisk /dev/sdb
-
- Command (m for help): o
- Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x1234567.
- Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
- After that, of course, the previous content won't be recoverable.
-
- Command (m for help): w
- The partition table has been altered!
-
- # sudo fdisk /dev/sdb
- Command (m for help): n
- Command action
- e extended
- p primary partition (1-4)
- p
- Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
- Using default value 1
- First sector (2048-1016522, default 2048):
- Using default value 2048
- Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-1016522, default 1016522):
- Using default value 1016522
-
- Command (m for help): w
- The partition table has been altered!
-
-Now you have a USB drive with a single partition (/dev/sdb1), but there is no filesystem on it. That's exactly what you want, because the LUKS system creates an encryption layer on the partition before you put a filesystem on it. So before creating a filesystem, let's create the LUKS layer on the partition, using the cryptsetup program. If you don't have cryptsetup, search for it in your distribution's repository; it should be there. To create the LUKS encrypted partition layer:
-
- # cryptsetup luksFormat /dev/sdb1
-
- WARNING!
- ========
- This will overwrite data on /dev/sdb1 irrevocably.
-
- Are you sure? (Type uppercase yes): YES
- Enter LUKS passphrase:
- Verify passphrase:
-
-Follow the directions, and be sure to remember your passphrase! Note, that a "passphrase" is usually more than just a word. It's most often a phrase, thus the name. The longer the phrase, the tougher to crack.
-
-Once the process completes, you have an encrypted partition, but it's not mounted or formatted yet. The first step is to mount the partition, which again uses the cryptsetup utility:
-
- # cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/sdb1 my_crypto_disk
- Enter passphrase for /dev/sdb1:
-
-When you type in your passphrase, the device name you entered will be mounted like a virtual hard drive. Usually, it's mounted under /dev/mapper/devicename, so this example mounts a partition at /dev/mapper/my_crypto_disk.
-
-This device is now being accessed as an unencrypted volume. As long as it stays mounted, it will act like any other unencrypted volume. That means you need to write a filesystem to it if you want to use it:
-
- # mkfs.vfat /dev/mapper/my_crypto_disk -n my_crypto_disk
- mkfs.vfat 3.0.9 (31 Jan 2010)
-
-Now the drive is fully functional and can be mounted like any other disk. In fact, when you put the USB drive into your computer, if you have a modern GUI desktop, it should prompt you for a password and mount it automatically. Then you can eject it like a normal disk, and it will be encrypted until you next enter your passphrase. It's simple to unmount and, therefore, re-encrypt the drive on the command line too, using cryptsetup:
-
- # cryptsetup luksClose my_crypto_disk
-
-That's Only the Tip of the Iceberg
-
-In this article, my hope is to peel back some of the mystery behind encryption. It's simple to encrypt and decrypt a file. It's not too much more difficult (especially if you use the GUI desktop tools) to encrypt an entire USB drive. With most distributions, it's possible to encrypt the entire home directory during the installation process! When encryption is set up on your entire home directory, however, there are some issues you need to address. For example, jobs that run while you're not logged in most likely will not have access to your home directory. If you have cron jobs that need access to your home directory, you should rewrite them to access data elsewhere on the system. I find a happy medium between security and convenience is to encrypt a USB drive and store my personal data on it.
-
-Once you get the encryption bug, I must warn you, you'll want to start encrypting everything. That's not a bad thing, but like the home directory scenario, you'll run into a few snags. Cross-platform accessibility is a big one if you go between systems. For situations like that, I highly recommend [TrueCrypt][1]. I've mentioned TrueCrypt in UpFront pieces before, but it's basically an open-source, cross-platform encryption system that allows you to encrypt files, folders, partitions and more while being able to access that data on any system. Windows, Mac and Linux clients are all available, and the community has great support.
-
-You don't have to have something to hide in order to desire encryption for your files. Just like it's wise to lock your house at night, even if you live in a good neighborhood, it's a smart move to encrypt your personal data. If you want to share your photos of Mr Whiskerton in his cute little beanie hat with everyone on the Internet, that's your right. But others don't need to see those things if they're being nosey and poking around your hard drive!
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/encrypting-your-cat-photos
-
-译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://www.truecrypt.org/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/Guide To Install Ubuntu 14.04 In Dual Boot Mode With Windows 8 Or 8.1 UEFI.md b/sources/tech/Guide To Install Ubuntu 14.04 In Dual Boot Mode With Windows 8 Or 8.1 UEFI.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 7f391dd917..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/Guide To Install Ubuntu 14.04 In Dual Boot Mode With Windows 8 Or 8.1 UEFI.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,101 +0,0 @@
-GOLinux Translating!
-
-Guide To Install Ubuntu 14.04 In Dual Boot Mode With Windows 8 Or 8.1 UEFI
-================================================================================
-
-
-Previously I had written about [dual booting Ubuntu Linux with Windows 7][1] and 8 previously, But those tutorials did not cover systems that come with Windows 8 pre-installed. The newer systems that come with Windows 8 or Windows 8.1, have UEFI instead of BIOS. This makes thing a little different from the conventional way of dual booting. In this tutorial, we shall see **how to install Ubuntu Linux in dual boot mode with Windows 8 or Windows 8.1**.
-
-This tutorial is performed on a newly bought Dell Inspiron 7437 that has Core i7 fourth generation processor, 256 GB SSD, 8 GB RAM and built in 1 GB Intel graphics. I’ll cover all the steps you need to do in order to successfully dual boot Linux with Windows 8 UEFI. If you have already done some of these steps, just skip to the next one. If you have a fresh system, even better.
-
-The steps mentioned here are applicable to other Ubuntu based Linux distributions such as Linux Mint, Elementary OS etc. Cutting the chit-chat, let’s see how to dual boot Linux on a UEFI secure boot enabled Windows 8 system.
-
-### Dual boot Ubuntu 14.04 with Windows 8: ###
-
-There are various prerequisites to install Ubuntu on a UEFI system. Let’s see them one by one:
-
-#### Step 1: Make a backup [optional] ####
-
-It is always nice to make a back up, just in case if you mess up with the system. There are numerous articles on the web to show you how to backup your system. You can follow this tutorial [here][2].
-
-#### Step 2: Create a live USB/disk of Ubuntu ####
-
-The next thing you need to do is to create a live USB or disk. I recommend [Universal USB Installer][3] to create a live USB of Linux OS in Windows.
-
-#### Step 3: Make a partition where Ubuntu will be installed ####
-
-Assuming tat you have a fresh system, the first thing we need to do is to make partition to install Linux. The 256 GB in my system was already had several partitions from manufacturer but mainly for backup and other purposes. Main partition was C drive, of around 220 GB, where Windows 8.1 was installed.
-
-If you have just one partition like this, you need to make some free space out of it for Linux. If you have several partitions of considerable size, use any of them except C drive because it may erase the data.
-
-To make a partition in Windows 8, go to Disk Management tool. You can find disk management tool by searching for ‘disk’ in Control Panel.
-
-
-
-In the Disk Management tool, right click on the drive which you want to partition and select shrink volume. In my case, I shrank the C drive to make some free space:
-
-
-
-You can leave the free space as it is. We shall use it while installing Ubuntu.
-
-#### Step 4: Disable fast startup in Windows [optional] ####
-
-Windows 8 introduced a new feature called “fast startup” for quick boot. While it is not mandatory, it would be better to have it disabled.
-
-Go to **Control Panel > Hardware and Sound > Power Options > System Settings > Choose what the power buttons do** and uncheck the **Turn on fast startup box**.
-
-#### Step 5: Disable secureboot in Windows 8 and 8.1 ####
-
-This is the most important step. The new secure boot feature of Windows 8, originally intended for security feature for rootkit viruses, prevents dual booting of Windows with Linux. To dual boot Windows 8 with Linux, we must disable secure boot in UEFI.
-
-#### Step 6: Installing Ubuntu alongside Windows 8 ####
-
-Once you have disabled secure boot, it’s time to install Ubuntu. I hope you already created the live USB as mentioned in step 2. Plug in the USB and boot the system from it.
-
-To boot from USB, will have to choose boot from USB option from within Windows itself. Either with PC Setting (like for UEFI) or pressing shift key while clicking on Restart.
-
-Once you have booted in the live USB, you will be presented with option to try or install Ubuntu. Click on install. You will be presented with few screen options to choose the language. It will then do some checks on available space, power and internet connection etc. Just click on **Continue**.
-
-
-
-The main screen which you should pay attention to is **Installation Type**. Choose **Something else** here:
-
-
-
-Remember we had created some free space beforehand? We shall use the free space to create Root, Swap and Home. Select the free space and click on the + sign.
-
-
-
-It will provide you with option to create Linux partition. We are creating the Root partition. Any thing between 10-20 GB is more than sufficient for it. Choose the size, select Ext 4 as file type and / (means root) as the mount point.
-
-
-
-Clicking on OK in previous step will bring you to the partition screen. Next we will create swap. Like previously, click on the + sign again. This time use the file type as Swap area. Suggestible swap size is double of RAM.
-
-
-
-In similar fashion, create a Home partition. Allocate it maximum space (in fact allocate it rest of the free space) because this is where you’ll save music, pictures and downloaded files.
-
-
-
-Once you are ready with Root, Swap and Home, click on **Install Now**:
-
-
-
-Well, you have almost won the battle. You can smell victory now. Next you will be asked to set username password etc. Basically, you just need to click next now.
-
-Once the installation is completed, restart the computer, you should be welcomed by a purple grub screen. Enjoy Ubuntu along with Windows 8 in dual boot mode.
-
-I hope this guide helped you to dual boot Ubuntu with Windows 8 UEFI. Though this article is written for Ubuntu, it should be heloful for other Linux OS as well. Any questions or suggestions are always welcomed.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://itsfoss.com/install-ubuntu-1404-dual-boot-mode-windows-8-81-uefi/
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://itsfoss.com/install-ubuntu-dual-boot-mode-windows/
-[2]:http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/6-safest-ways-to-backup-restore-your-files-in-windows-7-8/
-[3]:http://www.pendrivelinux.com/universal-usb-installer-easy-as-1-2-3/
diff --git a/sources/tech/How to launch applications differently with Gnome-Pie on Linux desktop.md b/sources/tech/How to launch applications differently with Gnome-Pie on Linux desktop.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d5b9426c1d..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/How to launch applications differently with Gnome-Pie on Linux desktop.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,72 +0,0 @@
-Translating by GOLinux ...
-
-How to launch applications differently with Gnome-Pie on Linux desktop
-================================================================================
-The biggest complaint you can hear those days about Ubuntu is the new Unity interface. I remember leaving for Archlinux precisely when Unity started to rise, and when it was made clear that it was here to stay. However, Unity indirectly has led to good consequences: it allowed other distributions and other desktop environments to become more prominent as people were unhappy with it. If your system can support it, no one is against a bit of eye candy.
-
-So today I shall propose you a different type of application launcher which is definitely original: Gnome-Pie. Some of you may recognize the inspiration from the World of Warcraft addon "OPie." The concept is similar: a keyboard shortcut opens a circular "pie" from which you can select an application or a command to launch. The main idea behind that design is that a user does not have to remember the name of a command, but its direction. The fact that it is circular makes every application at the same distance from the pointer. Plus we get the combo that so many gamers adopted: left hand on the keyboard and right hand on the mouse. The two combined intend to minimize the amount of time needed and maximize the ergonomy.
-
-### Gnome-Pie Installation ###
-
-On Ubuntu, Gnome-Pie is available from the universe repository, but for some reason this version crashes at startup. Instead, I advise you to get it from the official PPA repository:
-
- $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:simonschneegans/testing
- $ sudo apt-get update
- $ sudo apt-get install gnome-pie
-
-On Fedora, use this command to install it:
-
- $ sudo yum install gnome-pie
-
-For Archlinux, the package is on [AUR][1].
-
-### Basic Usage of Gnome-Pie ###
-
-By default, Gnome-Pie comes with a very decent initial configuration. The first pie, summoned with Ctrl+Alt+a, displays your system's basic applications.
-
-
-
-The second pie, associated with Ctrl+Alt+b, brings your file manager's bookmarks.
-
-
-
-The third pie is maybe the most useful as it displays your application menu, callable by Ctrl+Alt+Space.
-
-
-
-The fourth pie is exclusively to control the music player. As you can guess, the shortcut is Ctrl+Alt+m.
-
-
-
-The fifth pie is a quick access to the reboot, shutdown, and log out commands (with Ctrl+Alt+q, q for quit I suppose).
-
-
-
-Finally, the sixth pie controls the windows, allowing you to minimize, scale, close, etc. And of course, the shortcut is Ctrl+Alt+w.
-
-
-
-I find this default setup already pretty satisfactory, almost as good as an out-of-the-box launcher. However, if I wanted to be picky, I would say that some shortcuts are hard to perform with just one hand, and it is kind of frustrating to use two hands to call a pie, and then go back to the mouse to select the option. But again I am being picky.
-
-However, we are on Linux! Who cares about the default? The whole point is to configure like crazy, and make the system our own. With Gnome-Pie, you are well served. The configuration screen lets you edit the current pies, change the shortcuts, select the icons, make your own pie, change the theme, and even make pie menu that summons another pie.
-
-[][2]
-
-You can even edit the pie to launch an URL, simulate a hotkey activation, or just your own command. The only thing that is potentially missing is the possibility to have widgets.
-
-
-
-In conclusion, Gnome-Pie is a quite attractive visual application launcher which differs from traditional text-based launchers. I really like the combo left hand on the keyboard and right hand on the mouse, which does indeed remind me of Warcraft or even Leagues of Legend. If players adopted this kind of system, it is because it is convenient and efficient. I would even advise it if you are trying to save some space on the screen, and don't want a launcher constantly on the screen. As a last word, I would even dare to say that it provides an interesting alternative to the awesome Gnome-Do.
-
-What do you think? Do you believe in eye candy at all? Or is Gnome-Pie out of the question since the new Gnome shell entered the competition? Please let us know in the comments.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/launch-applications-differently-gnome-pie-linux-desktop.html
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/gnome-pie/
-[2]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14247093043/
diff --git a/translated/talk/20140607 Got Linux--Add Proprietary Code.md b/translated/talk/20140607 Got Linux--Add Proprietary Code.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..667962c302
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/talk/20140607 Got Linux--Add Proprietary Code.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+
+Got Linux? Add Proprietary Code
+================================================================================
+
+
+> 对于一些产业来讲,在开源的Linux发行版上运行商业版的软件并不类外。--这很常见,例如,在华尔街,“华尔街上百分之九十九的应用依赖于商业版的软件。在我们运行在Linux上的产品中,Oracle是我们最喜欢的一种商业软件”, FSMLabs' President Victor Yodaiken说。
+
+迁移到Linux平台并不是一个非此即彼的提议。作为一个计算机平台,Linux是非常灵活的。它提供给用户一个自定义的软件菜单选项。
+
+一种选择是Linux桌面。家庭个人用户,SOHO 和 SMB 操作可以从众多的企业级Linux发行版中选择。Linux桌面系统提供了一个0成本或者成本很低的替代,相对于微软系统来讲,或者是基于Unix的苹果OS X系统依赖苹果硬件的局限性。
+
+另一个替换的办法是,让员工放弃linux桌面办公,取而代之,企业可以运行后台办公系统在Linux服务器上。Linux服务器在网络化和云计算领域有一个缜密和强大的空间。Linux服务器在很多企业中应用很广。
+
+第三个方法是运行一个完整的Linux商店,斯坦达德办公中心运作的软件在开源包,网络浏览,图形产生方面非常有用。开源的数据库应用和和后台软件及服务器连接相当频繁,在此方面,Linux不需要购入特殊硬件来支持。
+
+培训员工使用Linux桌面应用需求量很小。感谢工作者对跨平台软件的友好支持。例如LibreOffice 和 Open Office, 同样的,Chrome和 Firefox浏览器。前端办公交互很少漏掉。
+
+Linux很灵活。一个新的趋势是生产适合你企业需要的第三方软件。商业软件公司可以再编译必要的WIndow或者其它平台软件。他们也可以生产Linux任务应用将现成的资源和他们自己的代码结合到一起。
+
+“我相信这将是一个新的趋势,企业可以用第三方软件在Linux系统上进行开发。推动企业向Linux迁移并使用定制的软件的一个因素便是支付微软的专利费用的财政负担”,Dayan Jeremiah ,[Icewarp Pacific][1] 的 CEO 说。
+
+
+### Linux Does Proprietary ###
+
+一个公司向任何一个系统迁移的时候所面临的最大障碍是监测应用的通用性。在迁移到Linux上时,企业不得不保证软件在Liunx上通用。Jeremiah强调
+
+Linux操作系统有一个多类型和Linux桌面系统软件库。根据不同的行业,大量的开源社区可能没有为每一个特殊的任务指定一种方案。在这种情况下, 借助于第三方软件来推出自己的应用往往更节约成本。
+
+“使用第三方软件有助于保证兼容性,例如,我们可以混合和匹配软件组件来保证应用在Linux上运行” ,Jeremiah 说。
+
+### 旧的模型产生新模型 ###
+
+越来越多的专有软件公司,例如爱思华宝,建立特殊的软件来满足企业特殊的业务需求,他们将许多开源组件混合在一起使用。
+
+与微软的基础设施相比,不仅节省了许可成本,还节省了编码成本。
+
+“我们可以建立一个完整的软件方案,使用现成的Linux软件组件,整个解决方案往往更节省成本,高效,稳定。” Jermaih强调。
+
+Icewarp不开发专门的软件作为免费的开源项目,它不提供免费版,需要付费支持。你需要付费购买它。
+
+### 代码移植 ###
+
+把软件从一个平台移植到另一个平台并与Liunx兼容的一个障碍是Liunx的多样化,依据Jacob Loveless, CEO of [Lucera][2]的观点。Linux操作系统拥有一个通用kernel,但是有很多多样化。
+
+“当软件公司不得不在多个Linux系统中交叉编译时,问题进一步加深。”伴随着微软Exchange 服务器的类外,大多数数据库运行良好。Mysql和postSql可能是最突出的两个开源版本。
+
+在软件移植到Linux的最大挑战,是需要重新编译代码,通常有平台相关的事情你不得不去做。他说。
+
+例如,如果你有特殊的代码底层依赖,对于window来讲,.net 或者其它语言,运行在Linux的开源编译器并不总是兼容,因此你有很多软件工作需要重做,Loveless说道。
+
+另一个例子是使用数据库。你经常不得不连接到一个不同的数据库和一个不同的web服务器。
+
+有明确的工作要做,Loverless说道。
+
+### 许多还不够 ###
+
+在移植到Linux上时,另一个兼容性问题是开源软件公司的需求。
+
+没有足够的开源方案来解决企业的专业需求, IceWarp 的Jeremiah说,通常来讲,我们认为是足够的,目前还没有被专门的软件应用来提供,而第三方不能提供的软件。
+
+例如,IceWarp最近建立了一个特殊的Linux兼容应用,不需要额外的硬件采购,没有额外的许可费用。
+
+特殊的软件包括一个集群负载均衡。集群数据库和集群IP服务器,所有的这一切都运行在一个标准的红帽企业版Linux或者CentOS Linux.
+
+
+### 跟着钱走 ###
+
+在一些情况下,你可以跟着前找到Linux。有时它是Linux服务器在工业中有很高的用途。另一些时候,它是Linux桌面应用,或者两者都有。
+
+例如,在金融市场中,时间同步是关键。金融依靠分布式网络,用户不得不在指定的时间内完成交易。其它的应用需要在交易前进行精确的计时。这些功能需要精确的时间同步控制。Victor Yodaiken 说,[FSMLabs][3] 的总裁。
+
+当FSMLabs 开始开发时间同步软件,Yodaiken期待很快会拥有一个Windows版本。
+
+然而,被证实每一个在使用自动交易或者低延迟交易,甚至是采集高精度数据软件的人,都运行的是Linux系统,他告诉LinuxInsider.
+
+### 时间是昂贵的 ###
+
+FSMLabs 将专有的代码运行在Linux上,建立在Linux上的软件时间协议不适用同步时间在纳秒级别的应用,比如那些追踪股票,或者交易的需求。
+
+“我认为Linux的在Windows之上,因为Windows没有一个标准的API让你获取时间在毫秒级别以下。”所以Window并不是真的都好。你不得不拥有特殊的API,在Linux下。你不需要费力在你的应用程序上。Yodaiken 说。
+
+金融市场是第一个拥抱Linux的。许多早期的系统管理者来自80年代的[贝尔实验室][4],因此这是一个很成熟的市场,他说。
+
+### 满足需求 ###
+
+对于一些产业来说,在开源的Linux发型版上运行有专利的软件并不意外,这是很常见的。
+
+“华尔街99%的应用都运行在有专利的产品上。在我们运行在Linux的产品中,我们很喜欢Oracle,它有一个专利许可。”FSMLabs' Yodaiken说。
+
+一些市场运行Linux需要跟更多专业的软件,相比开源的产品,现存的开源软件不能满足他们的需求。这也就是为什么软件开发者为企业Linux提供商业的产品。他补充道。
+
+“这是很常见的,开源最适合大市场,这就是为什么他们具有广泛的需求。没有几人总是对的。如果他们不对,需要告诉他们” 他指出。
+
+### Linux纯粹主义是没有意义的 ###
+
+在Linux上运行完全免费开源的软件的观念是欠缺的,有时候你要运行专利软件。
+
+当一个专业的计算不需要进入广泛市场时,第三方软件开发者提供一个专有的,商业的或者闭源的解决方案。由于商业持续地适应Linux系统,绝对的开源将成为过去的事情。
+
+在Linux上拥有商业软件是相当普遍的,Yodaiken说,商人都不是纯粹主义者,他们只想解决问题。
+
+Jack M. Germain从早期的苹果二和PC的时候就一直在写计算机技术。他保留着一些原始的IBM PC和一些传统的DOC系统,和Windows盒子,他抛弃了共享程序,走向开源Linux世界.他运行一些Windows系统和Linux系统,经常不能决定是否用他的平板电脑或者安卓智能手机替代他的桌面系统或者便携式电脑。你可以在Google+上联系到他。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/80555.html
+
+译者:[jiajia9linuxer](https://github.com/jiajia9linuxer) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.icewarp.com/
+[2]:https://lucerahq.com
+[3]:http://www.fsmlabs.com/
+[4]:http://www.bell-labs.com/
diff --git a/translated/talk/20140624 Performance benchmarks--KVM vs. Xen.md b/translated/talk/20140624 Performance benchmarks--KVM vs. Xen.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e6abc80fe0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/talk/20140624 Performance benchmarks--KVM vs. Xen.md
@@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
+KVM和Xen的性能基准测试
+================================================================================
+在上周,我们讨论了 KVM 和 Xen 的性能上一些令人感兴趣的话题后,我打算自己做一些这方面的研究。我能找到的最新的资料,是来自[2013年 Phoronix Haswell 性能评测][1]上的基准测试。当然,还有[2011年的评测][2],由于 Xen 已经被收录进 Kernel 3.0,这些曾经都是热门话题。
+
+2011年的测试提供了[许多很好的基准报表][3],我尽最大努力把它们列出的属性重新测试一遍,但少测了两三个基准测试,原因是它们在未经特定优化的配置后跑出来的数据不是很好,或者它们需要跑很长时间才能得到结果。
+
+### 测试环境 ###
+
+测试环境由两台一模一样的超微服务器组成,都配备一颗[Intel 至强 E3-1220][4](4核,3.10GHz),24G 金士顿 DDR3 内存,4块西数 RE-3 160G 磁盘(组成 RAID10 阵列)。另外 BIOS 也是一模一样。
+
+所有测试项目(即实体机和虚拟机)都在 Fedora 20 (开 SELinux)上进行,并且测试过程中没有跑很多的不相关的服务。这里列一下相关服务的版本:
+
+- Kernel: 3.14.8
+- For KVM: qemu-kvm 1.6.2
+- For Xen: xen 4.3.2
+
+根文件系统是 XFS,使用默认配置。虚拟机使用 virt-manager 来创建(virt-mamager 也使用默认配置)。虚拟磁盘使用 raw 镜像,容量为 8GB,虚拟4颗 CPU。Xen 虚拟机使用 [PVHVM][5] 建立虚拟磁盘。
+
+### 警告 ###
+
+也许有人会考虑到 Fedora 是红帽公司所有,红帽一直在维护 KVM,而 Xen 则自从[在2009年红帽重新选择 KVM 作为虚拟化产品][6]后,再没得到这个公司的维护。在本测试中这个因素不会对结果产生任何影响,不过可以在心里稍微注意一下。
+
+不考虑资源竞争产生的影响。在大多数虚拟服务器上,你可以跑多个虚拟机,而这些虚拟机会争用 CPU 时间片、磁盘 IO、网络带宽等等资源。在本测试中也不考虑这些因素。一台虚拟机抢到资源少,性能就差,而另一台抢得多,性能就好(LCTT:它们的性能总和,就可以大致当作是 KVM 或 Xen 的性能了)。
+
+本测试运行在 Intel 的 CPU 上。如果使用的是 AMD 或 ARM,可能有些数据会不一样。
+
+### 结果 ###
+
+本测试使用裸机作为虚拟服务测试的基准设备。在不跑虚拟机的情况下,两台裸机的性能偏差不会大于0.51%
+
+在所有测试中,KVM 的性能相比宿主机而言下降了1.5%以内,除了两个测试。第一个是 7-zip 压缩,比宿主机慢了 2.79%。第二个就奇怪了,我们搭了一个邮件服务器,用 PostMark 测试其性能,结果表明 KVM 竟比宿主机快了4.11%。然后我在两台服务器中重新跑了几遍 PostMark 测试,结果性能差异基本不变,浮动在1%以内。由于我对 virtio 的内部机制没有很深的理解,我只能在以后再对这个怪现象进行进一步了解。
+
+Xen 的性能相对宿主机而言差异就比较大了。有3个测试性能下降在2.5%以内,剩下的性能下降率都是 KVM 的2~4倍。PostMark 测试的性能比 KVM 慢了14.41%,这结果令我大吃一惊。重新跑了下测试,性能差还是在14%左右。KVM 表现最好的两个测试:CPU 测试和 MAFFT 对齐测试,是 Xen 表现最差的。
+
+现在奉上一个总结表:
+
+
+
+
Best Value
Bare Metal
KVM
Xen
+
+
+
+
C-Ray
lower
35.35
35.66
36.13
+
+
POV-Ray
lower
230.02
232.44
235.89
+
+
Smallpt
lower
160
162
167.5
+
+
John the Ripper (Blowfish)
higher
3026
2991.5
2856
+
+
John the Ripper (DES)
higher
7374833.5
7271833.5
6911167
+
+
John the Ripper (MD5)
higher
49548
48899.5
46653.5
+
+
OpenSSL
higher
397.68
393.95
388.25
+
+
7-Zip
higher
12467.5
12129.5
11879
+
+
Timed MAFFT Alignment
lower
7.78
7.795
8.42
+
+
CLOMP
higher
3.3
3.285
3.125
+
+
PostMark
higher
3667
3824
3205
+
+
+如果需要完整数据,请查看[Goole Docs 电子表格][7]。
+
+### 结论 ###
+
+基于上面的测试环境,KVM 的性能损耗在2%以内,Xen 则只有3项损耗在2.5%以内,其他几项损耗都在5~7%之间。虽然 KVM 在 PostMark 测试中性能表现优异,但这个测试只是众多测试中的一项,如果想证明 KVM 确实在 I/O 处理方面很强悍,就需要更多测试。
+
+对我来说,我需要深入理解 KVM 和 Xen 在 I/O 处理上为什么会有这么大的差别。并且还需要跑一些压力测试,来证明虚拟机是否真的比宿主机表现得更出色。
+
+我鼓励读者通过使用[Phoronix 测试套件][8]来进行一些基准测试,你们可以找到一些能模仿你们工作环境的用例。如果你的工作环境是低 CPU 高 I/O,你可以找找套件里面的 I/O 压力测试。另一方面,如果你的工作是音频、视频转码,你可以试试套件里面的 x264 或 mp3 测试。
+
+更新:[Chris Behrens 指出][9],我忘了提到 Xen 虚拟机类型了。这里补充下,我使用的是 PVHVM 模型(LCTT:目前支持的模型包括 PV、HVM 和 PVHVM),因为在 Xen 4.3 中这个选拥有最好的性能。另外需要注意的是在 Xen 4.4 中可以使用 PVH,但是在 Fedora 20 中还没有使用 Xen 4.4。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://major.io/2014/06/22/performance-benchmarks-kvm-vs-xen/
+
+译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=article&item=intel_haswell_virtualization&num=1
+[2]:http://blog.xen.org/index.php/2011/11/29/baremetal-vs-xen-vs-kvm-redux/
+[3]:http://blog.xen.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/11/overview.png
+[4]:http://ark.intel.com/products/52269/Intel-Xeon-Processor-E3-1220-8M-Cache-3_10-GHz?q=e3-1220
+[5]:http://wiki.xen.org/wiki/Xen_Linux_PV_on_HVM_drivers
+[6]:http://www.infoworld.com/d/virtualization/red-hat-releases-first-kvm-support-rhel-54-376
+[7]:https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1kmudbOjCDUgfw76b8qP2GqNqF1ddlTOKyOjc0GmNOIE/edit?usp=sharing
+[8]:http://www.phoronix-test-suite.com/
+[9]:https://twitter.com/comstud/status/480785742730252288
diff --git a/translated/talk/20140723 110 Fun Open Source Games and Apps.md b/translated/talk/20140723 110 Fun Open Source Games and Apps.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..eb158faca7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/talk/20140723 110 Fun Open Source Games and Apps.md
@@ -0,0 +1,615 @@
+translating by disylee 20140701
+110 Fun Open Source Games and Apps
+110款开源游戏和应用
+================================================================================
+
+再次庆祝,伴随着一系列最好的开源游戏,我们庆祝这个夏天的到来。我们已经更新了[去年的列表][1]把新开发的添加进来,这样更好地把一些不再积极开发之中的旧游戏从列表中剔除。你会发现街机、平板、休闲、拼图、益智和第一人称射击游戏,音乐,赛车,角色扮演,冒险,模拟器和战略游戏等,它们也像一些应用程序一样并非真正的游戏但是仍然非常有趣。
+
+今年,比以往有更多的开源游戏可用于移动设备上,主要是安卓设备上。希望未来几年,这种趋势一直保存下去。
+
+请注意,这个列表是不按排名的。这些应用程序被放在目录中并按照字母顺序放在每个类别里。
+
+如果你想建议明年游戏列表的版本,请随时注意在下面的评论区提出。
+
+### Arcade Games ###
+>
+
+#### 1. [安迪的超级大公园][2] ####
+
+当你乘坐过山车时,你需要抓到气球并且避开障碍物。里面有25个等级,加上18个你可以解锁的等级以获取高分。可使用操作系统:Windows,Linux或者安卓。
+
+#### 2. [Armagetron Advanced][3] ####
+
+一个3D电子争霸克隆,这个游戏激起你去指导一个光周期直到你撞上一堵墙。它支持单机模式和16人参与的网络模式。可使用操作系统:Windows,Linux,OS X或者安卓。
+
+#### 3. 塔克大战夺取旗帜 ####
+
+众所周知的“战场夺旗”,“BZflag是一个流行的在线坦克游戏。自1992年开发以来,它具备3D图形化特征,多种游戏模式和多人竞争比赛等特征。可使用操作系统:Windows,Linux,OS X或者安卓。
+
+#### 4. [纵向卷轴射击游戏] [5] ####
+
+别让这个名字就把你愚弄了,这和Chromium browser浏览器无关。这是一款快节奏、顶部滚动射击的游戏,其难度在于设置,而且这个游戏不回超过15分钟。可使用操作系统:Windows,Linux。
+
+#### 5. [埃德加的传说][6] ####
+
+埃德加的传说是一个旧派的游戏平台,主角必须通过克服障碍和敌人来完成他的任务。它包含了很多不同的武器、很多不同等级。适用操作系统:Windows,Linux和OS X。
+
+#### 6. [JVGS][7] ####
+
+
+取代非常详细的图形,JVGS只要一个最低限度方法使其中画中人物跨越景观,看起来就像使用铅笔的手工绘制。在这个不寻常的游戏中,主角是一个失去记忆的诗人。适用操作系统:Windows,Linux和OS X。
+
+#### 7. [失重力][8] ####
+
+这是基于空间的街机射击游戏,玩家需要在8002年份中,他们必须完成各种各样的任务。但是,这个游戏不是免费的,游戏也可以在安卓和IOS中使用。适用操作系统有:Windows,Linux和OS X。
+
+#### 8. [Open Sonic][9] ####
+
+
+基于刺猬索尼克游戏,Open Sonic提供了合作的游戏,用户可以同时控制3个字符。其中只有2个级别可以在原始游戏中使用,但是很多游戏粉丝们已经建立了mods提供额外的发挥。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和OS X.
+
+#### 9. [Powermanga][10] ####
+
+类是于旧街机游戏Galaga,Powermanga是一款2D,顶部滚动的空间射击游戏。它拥有超过41个等级,并能够在旧的硬件上运行。适用操作系统:Linux。
+
+#### 10. [Scorched3D][11] ####
+
+Scorched3D是一款现代的基于DOS的游戏Scorched星球,最引人瞩目的是它出色的图形。你可以适用单机模式或者连接到许多网络服务器使用多玩家行动。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 11. [音速机器人大爆炸][12] ####
+
+另一款声波风格的平台游戏,SRB2是一种采用了Doom引擎内置的3D平台游戏。它包括了2个不同的游戏角色和超过20个等级。适用操作系统:Linux。
+
+#### 12. [SuperTux][13] ####
+
+SuperTux很像旧款的马里奥兄弟游戏,但是是以Linux的小企鹅成为主人公。这是一个2D横向卷轴的平台游戏,有9个不同的敌人和26个等级可以玩。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和OS X.
+
+#### 13. [Those Funny Funguloids][14] ####
+
+这是一款挑战玩家在太空手机蘑菇的游戏。该网站称:“在此之前从未听说过手机蘑菇。至少不是在外太空。真的,它更是一种生活而不是一个游戏。适用操作系统:Windows和Linux.
+
+
+#### 14. [Teeworlds][15] ####
+
+这个在线游戏把自己描述成一个“复古的多人射击游戏”。它是一个横向卷轴的2D游戏,支持多达16名选手和几个不同的游戏模式。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 15. [X摩托][16] ####
+
+在这个游戏中,你骑着一辆摩托车通过一个侧面滚动的风景区,同时收集草莓并避免高低不平的“破坏者”。这看起来是比较难!适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 16. [Yo Frankie!][17] ####
+
+通过混合开源3D动画工具创造的,呦羊羊特征角色是从开源电影Peach来的。玩家必须指导羊羊,糖滑翔机或者Momo,一只猴子,来回或者环绕并通过一个非常细致的3D环境中的障碍物。适用操作系统: Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+### 棋类游戏 ###
+
+#### 17. [Domination][18] ####
+
+基于Java支配带来的棋牌游戏可能会对你的PC或者安卓设备造成风险。最新版本中可以让你实时与你Google+的朋友通过谷歌游戏服务发挥多人游戏服务功能。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux, OS X和 Android.
+
+#### 18. [GNU 十五子棋][19] ####
+
+
+这个“世界级”十五子棋引擎让你每一次都更好地挑战它,并且它会分析你的战况来帮助你玩得更好。这个借口是非常好的图形化定制。适用操作系统:Windows,Linux和OS X。
+
+#### 19. [3D 拼字游戏][20] ####
+
+随着拼字游戏的变化,你可以选择自己的电路板——经典版本。Superscrabble是一款3D的拼字游戏,您可以通过它定制你自己的电路板。玩家可以对战AI或者连到在线服务器上进行多人游戏。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 20. [PokerTH][21] ####
+
+这是一个高质量的德州扑克牌应用程序,拥有优秀的、可定制的界面。想要在线玩或者看看你和其它对手的排名,只需要在Poker-Heroes.com在线注册。适用操作系统:Windows,Linux和OS X,Android系统。
+
+#### 21. [PySolFC][22] ####
+
+你知道吗,接龙有1000多种类型?这个强大的集合功能“使用52张国际格局甲板模式,比赛为78张Tarock夹板,8和10套装备,Ganjiafa游戏,花札游戏,棋牌游戏、麻将游戏和原始十六进制为基础的平台”。适用操作系统: Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+
+### 休闲益智游戏 ###
+
+#### 22. [2048][23] ####
+
+
+这个简单而上瘾的益智游戏,玩家围绕着方格里喜欢的数字组合。当你将组合数字累加到2048时,你就赢了。适用操作系统:在线,IOS或者安卓。
+
+
+#### 23. [台球][24] ####
+
+台球游戏的主要目的是当你不能够拥有一张可用的台球桌时,给现实中能够让你练习球杆运动。它拥有一个好看的3D界面,同时也可以在不具备良好图形界面的2D系统中运行。适用操作系统:Linux。
+
+
+#### 24. [立方火车][25] ####
+
+
+躺在连接隧道和桥梁的铁轨,然后机动绕过障碍物。你可以万很多内置等级的或者创建你属于自己的等级。适用操作系统:Windows,Linux或者OS X。
+
+#### 25. [谜语][26] ####
+
+类似于旧Oxyd和摇滚乐的游戏,谜语挑战者在相同的石头中找到迷宫,陷进,激光束和其他障碍。这个游戏拥有1000多个等级,这也是一款益智游戏,可能占用你一段很长时间。适用操作系统:Windows,Linux和OS X。
+
+
+
+#### 26. [Fish Fillets NG][27] ####
+
+在这个益智游戏中,玩家必须尝试分别在这70个等级中各找到一条安全路径。一路上,鱼类和其它水下居民提供相关用户的幽默解说。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 27. [冰冻泡泡][28] ####
+
+这是最古老的泡沫射击游戏中的一个,冰冻泡沫是以Linux小企鹅和多于100多个级别为特征的单机游戏。你也可以通过局域网或者互联网对阵2~5个玩家。适用操作系统:Windows和Linux。
+
+#### 28. [GnomeGames][29] ####
+
+这个集合汇聚了15个不同的休闲游戏,你可以在5分钟以内玩。它包括了数独,一个扫雷游戏,麻将,一个黑白棋版本等等。适用操作系统:Linux。
+
+#### 29. [切番茄][30] ####
+
+10分钟内,你可以粉碎多少个西红柿?这种“极端闲暇时间的活动”来自同一个叫做Those Funny Funguloids的团队。适用操作系统: Windows和 Linux.
+
+#### 30. [KDE 游戏][31] ####
+
+这是为KDE桌面准备的休闲游戏的集合。它包含了一个游戏纸牌的变化,一个高尔夫游戏,一个风险版本,扫雷艇,数度等等。适用操作系统:Windows和Linux。
+
+#### 31. [平衡球][32] ####
+
+在这个游戏中,玩家必须倾斜地板去引导球通过障碍球场。这个游戏包括很多级别,并且你可以设计自己的级别。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X。
+
+#### 32. [Pingus][33] ####
+
+你是否还话费数个小时玩旅鼠总动员来追忆的你90年代?如果这样的话,Pingus会更适合你。这是旅鼠的翻拍(企鹅取代了旅鼠)有77个级别。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 33. [易如反掌][34] ####
+
+这个益智游戏的特点是蚂蚁来推排成各种团的多米若骨牌。玩家必须让所有多米诺骨牌倒下,并通过出口,为的是发送一个特别的触发信号来进入新的等级。适用操作系统:Windows。
+
+#### 34. [Zaz][35] ####
+
+这是另一款泡沫射手游戏,Zaz挑战你沿着他们设定的路径击中球。其转折点是你的枪炮只能沿着一条路径移动,这样使事情变得有点难度了。适用操作系统:Windows和Linux。
+
+### 教育类游戏 ###
+
+#### 35. [ChildsPlay][36] ####
+
+这个游戏专门有5岁及一下的小孩设计,ChildsPlay帮助教一些发音,字母,数字和基础键盘技巧。它也包括了一些游戏,例如记忆,乒乓球和吃豆豆。适用操作系统:Windows,Linux和OS X。
+
+#### 36. [GBrainy][37] ####
+
+通过GBrainy的逻辑,训练你的词汇、数学和记忆游戏的意识。它充满了乐趣和教育意义,适合所有年龄段的人群。适用操作系统:Windows和 Linux.
+
+#### 37. [GCompris][38] ####
+
+专为2~10岁的儿童射击, GCompris 包括了超过100多种but的活动,其中大多数是教育类的。它包括数学,地理,科学,阅读,敲键盘和艺术游戏,再加上国际象棋,数独,记忆法等等。适用操作系统:Wwindows和Linux。
+
+#### 38. [TuxMath][39] ####
+
+在即将到来的彗星杀死企鹅之前迅速解决算数问题。这是一个简单的游戏用于强化小学学龄的数学真相。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+### 第一人称射击游戏 ###
+
+#### 39. [外星人竞技场][40] ####
+
+内置的“专为手榴弹攻击者的手榴弹,”外星人竞技场是一个激烈的充满复古题材的死亡争斗射击者。许多不同的网站为线上游戏提供了托管服务器,也有很多粉丝网站和玩家技巧等等。适用操作系统:Linux, Windows和 OS X.
+
+#### 40. [AssaultCube][41] ####
+
+由于它的轻量级,AssaultCube也可以在旧硬件上运行,除了拥有不错的真实感图形之外。它还支持单机模式和多玩家游戏模式,包括了26张不同的地图和12种不同的游戏模式。适用操作系统:Linux,Wwindows和OS X。
+
+#### 41. [经典 Nexuiz][42] ####
+
+下载量超过600万次,Nexuiz是最流行的开源射击游戏之一。几年前,该游戏是一个非开源版本创建的,但你可以从SourceForge的链接下载经典版本。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和OS X.
+
+#### 42. [OpenArena][43] ####
+
+这个多玩家游戏是雷蛇之锤3的克隆,它的特征是拥有13种不同的武器,51个竞技场和12类游戏。该程序的拥有者发出警告,“由于暴力和偶尔的不健康内容,它不适合17岁一下的孩子玩”。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 43. [Red Eclipse][44] ####
+
+这个休闲的第一人称射击游戏已经获得极高的评价。其特点包括跑酷,脉冲刺激,界面华丽,几种游戏模式和一个内置的关卡编辑。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 44. [Tremulous][45] ####
+
+这是一个屡获殊荣的游戏,一款混合了即时战略游戏元素的第一射击游戏。用户可以选择扮演外星人或者人类来永久消灭其它队的对手。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux, OS X和 XBox.
+
+#### 45. [TrueCombat][46] ####
+
+TrueCombat声称自己“也许永远是最好的免费战术写实的射击游戏。”这是一个2个对抗团队比赛的现代世界实战模拟器。请注意,为了使用它,你还需要德军总部:敌对势力。操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X。
+
+#### 46. [Unvanquished][47] ####
+
+从Tremulous分离出来,不可征服的人陷入“高度适应能力人类群体的先进技术。”在非常活跃的开发环境下,每个月提供了新的版本。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X。
+
+#### 47. [Warsow][48] ####
+
+这款自称在“在Web上节奏最快的运动”,Warsow是一个卡通射击游戏具有”猪尾巴火箭炮和携带赛伯朋克”的射击游戏。不想大多数射击游戏,它没有大量的血液和仇恨,更多强调的是运动。适用操作系统:Windows,Linux和OS x.
+
+#### 48. [Wolfenstein: Enemy Terriorty][49]
+
+虽然已经有好几个专有德军部队游戏,但这一个是开源的。这是一个第二次世界大战时间的游戏,其核心专门对抗盟军。适用操作系统:Windows,Linux,OS X。
+
+#### 49. [ Padman世界][50] ####
+
+基于Quake引擎,这个射手类似三角形状显得非常卡通化。这个游戏有相当多的在线服务器可以适用,或者您也可以离线玩。适用操作系统:Wwindows和Linux。
+
+#### 50. [Xonotic][51] ####
+
+Xonotic是经典版Nexuiz的分支。它拥有超过22种不同的地图,16种武器和大量不同的游戏模式。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和OS X.
+
+#### 51. [零导弹][52] ####
+
+部分第一人称射击手,部分坦克游戏,零导弹坐落在风景如画的山区环境,并已经拥有超过81个坦克体系可用。玩死斗,团队死斗或者独特的beaconstrike模式。适用操作系统:Windows、Linux 和 OS X。
+
+### 音乐类游戏 ###
+
+#### 52. [Frets on Fire][53] ####
+
+Frets on Fire这个游戏很多地方都很像“吉它英雄”这个游戏,它甚至可以起到播放“吉它英雄”里的歌曲(当然其它歌曲也同样可用)。如果你没有一个吉它控制器,别担心,你也可以适用键盘来玩。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 53. [StepMania][54] ####
+
+这是一个免费版本的跳舞机,挑战者可以停留在某个节奏去对应音乐的节拍。你既可以适用跳舞毯(如果你拥有的话)去挑,或者也可以适用键盘操作。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux/Unix, OS X或者 XBox.
+
+#### 54. [Ultrastar Deluxe][55] ####
+
+如果卡拉OK是你的菜,那么你就会喜欢Ultrastar Deluxe这个游戏了。在这个游戏中,你必须单独唱完一首歌并且是对应正确的节拍。它包含了超过10000歌曲。适用操作系统: Windows, Linux和OS X.
+
+### 赛车游戏 ###
+
+#### 55. [至尊小企鹅竞赛][56] ####
+
+Tux Racer是一款备受宠爱的旧款游戏,其特征是Linux小企鹅展示他的腹部滑下山。至尊小企鹅为现在的游戏玩家更新了这款经典游戏。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和OS X.
+
+#### 56. [Speed Dreams][57] ####
+
+这是TORCS自动赛车游戏的分支(见下文),其特征是一个更新过的UI界面和许多骑车和轨道。正如TORCS,视觉效果非常出色。适用操作系统:Windows和 Linux.
+
+#### 57. [SuperTuxKart][58] ####
+
+这个卡通赛车游戏的特点是Linux小企鹅和朋友们驾驶卡丁车。沿着轨道的指引前进,同时避开一堆障碍物的撞击。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 58. [TORCS][59] ####
+
+TROCS是"The Open Racing Care Simulator”的缩写,TORCS是一款拥有大量粉丝为基础的杰出的逼真赛车游戏。单独驾驶或与朋友在其中一条轨道中竞赛也是可选的。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+
+#### 59. [终极特技][60] ####
+
+由经典DOS游戏Stunts的启发,终极特技要求玩家去指导整个破碎的桥梁的车辆,跳跃,环绕等避开其它障碍。它允许提供一些选项通过更加疯狂的特技来设计自己的轨道。操作系统:Windows,Linux和OS X。
+
+
+#### 60. [VDrift][61] ####
+
+类似一款模拟器的赛车游戏,VDrift介绍玩家们赛车漂移的世界在一个真实的物理引擎中。它包含了超过45辆车,超过45条轨道,并且对各种控制器提供了支持。适用操作系统Wwindows,Linux,OS X。
+
+### 角色扮演和冒险游戏 ###
+
+#### 61. [穿越火线][62] ####
+
+有时被描述为NetHack 和 Gauntlet之间的穿越,穿越火线是一款非常旧派的图形街机冒险游戏。它拥有超过3000张不同的地图和超过150种不同的怪物。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 62. [Epic Inventor][63] ####
+
+Epic Inventor将自己描述成一个"横向卷轴动作的RPG游戏。"它类似于Minecraft,是一款简单的,像素化图形和开放式的游戏。适用操作系统:Windows和 Linux.
+
+#### 63[神剑:Morganna的复仇] [64] ####
+
+这款时空穿梭游戏让扮演你在未来海洋空间,玩家必须穿越回到亚瑟王和克莱特的年代。这个图形界面并没有什么特别的(想想 Minecraft),但是故事情节和游戏性都很赞。适用操作系统: Windows, Linux和OS X.
+
+#### 64. [火炬][65] ####
+
+受Diablo启发,这个角色扮演游戏的重点在于战斗。它仍然是一个开端版本但是依旧可以玩。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 65. [苏娜之吻][66] ####
+
+仅对成年人开发,这款"舌头在脸颊上的动作RPG"充满了“暴力、粗俗、裸体等主题”,也许你在其它游戏中很少看到。它提供了大量的动作和不断变化的景观。适用操作系统:Windows和 Linux.
+
+#### 66. [The Mana World][67] ####
+
+这是一款大型的多人在线角色扮演游戏(MMORPG),但事实没有想象中庞大。(在我写下这段文字的时候有31个人正在玩这个游戏。)尽管这样,创造一个不断扩大的世界充满了怪物、任务和迷你游戏是一个很好的尝试。适用操作系统:Windows,Linux和OS X。
+
+#### 67. [NetHack][68]注:此链接原文有错误,和上面的链接地址一样了 ####
+
+游戏史上经典之一,NetHack是一个带及其简单图形的复杂地牢履带。它被称为有史以来最好的100个视频之一。适用操作系统: Windows, Linux, 和经典Mac.
+
+#### 68. [PlaneShift][69] ####
+
+设置在Yliakum的梦幻世界,这是一个独特的在线角色扮演游戏,其特征是有10个不同的种族和一个拥有自己经济、政府、宗教和法律的发达国家。虽然可以试玩,但是这款游戏还处在早期的开发阶段。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+
+
+#### 69. [Ryzom][70] ####
+
+其中一个较好开源MMORPGS,获得Ryzom奖是设置在一个叫Atys的树状星球,其中有几种不同种族互动,有时候树状星球会发生冲突。你可以自由发回,但是那些选择订阅会得到特别的好处。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 70. [Stendhal][71] ####
+
+这个在线角色扮演游戏相比大多数同类游戏更友好。网站上解释,"你可能会被要求去帮助保护土地,拯救穷人,治愈病人,是别人获得快乐,解决难题,或者直接伸出援手。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和OS X.
+
+#### 71. [Summoning Wars][72] ####
+
+可以多达8个人一起玩的幻想角色扮演游戏。拖车这个游戏有一个拖车你可以同时在Youtube上看到它的动作。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+### 模拟类游戏 ###
+
+#### 72. [FlightGear][73] ####
+
+FlightGear是一个极其逼真、一流的飞行模拟器并且有竞争对手的专用软件。它包括了整个世界精准的地形和20,000多个机场还有众多栩栩如生的飞机模型。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux, OS X和其它。
+
+#### 73. [Golems][74] ####
+
+有了这个物理模拟器,你可以创建任何你想要的东西并看它在真实世界中如何表现。这是一个强大的基础学习机器,可以制造机器人,并发明各种玩意。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 74. [LinCity NG][75] ####
+
+基于原来的SimCity游戏,LinCity NG挑战玩家去建造一个可持续发展的大都市并拥有繁华的经济状况。需要注意的是,由于这个游戏是基于旧代码,所以它的图形化更像久的DOS游戏。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+
+#### 75. [Micropolis/OLPC SimCity][76] ####
+
+另一个SimCity的模仿者,Micropolis是一个基于Java开发的城市模拟器。它还具有相当老派的图形界面,而不是较新的3D外观模拟城市游戏。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 76. [Minetest][77] ####
+
+与Minecraft极其相似,Minetest被设置在基础构建的一个无垠世界中。玩家可以探索,矿山或者根据他们的需要制造一些新事物。适用操作系统: Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 77. [Pioneer][78] ####
+
+Pioneer描述自己为“一个孤独的太空冒险游戏”。它将玩家输送到一个开放式的世界里,这个世界里他们可以决定他们想做什么和去哪里。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 78. [Oolite][79] ####
+
+这个游戏是基于Elite,Oolite是一个太空模拟器,你可以与其它航天员进行进行交易或者参加一场战斗。这个游戏存在了相当长的一段时间,很多扩展操作系统可以使用。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 79. [OpenCity][80] ####
+
+这个3D城市模拟器并不是要成为一个模拟城市的克隆器,但是提供类似的玩家模式。这是相当基础的,但是很耐玩。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 80. [OpenTTD][81] ####
+
+基于豪华运输大亨,OpenTTD邀请玩家去简历一个运输帝国。它支持一次多达255个玩家并可以通过很多种方式去改善原来的TTD系统。适用操作系统: Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 81. [Rigs of Rods][82] ####
+
+#### 81. [Rigs of Rods][82] ####
+
+这个车辆模拟器具有一个独特的软体物理引擎拥有一批非常积极和热情的粉丝为基础。使用它来创造陆地,海洋或者空中骑车,可以带着它们驾驶或者飞往全国各地。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 82. [Simutrans][83] ####
+
+这个交通仿真器提供了连接到互联网在线游戏主机的选项。适用公车、卡车、火车、电车、船只、飞机、单轨铁车、磁悬浮列车或者其它交通工具将人们或者货物运送到他们想抵达的地方去。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 83. [Vega Strike][84] ####
+
+这是另一款太空模拟器可以让你星系中交易和战斗。你可以选择是否选择飞贸易路线,接受狩猎任务奖金,打海盗或者探索浩瀚的太空。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+### 战略游戏 ###
+
+#### 84. [0 A.D.][85] ####
+
+现在已经更新到了第16个alpha版本了。0 A.D.是一个屡获文明建设的游戏,这个游戏努力地在追溯历史的准确性。玩家可以选择迦太基人,凯尔特人,希腊人,伊比利亚人,孔雀王朝人,波斯人或者罗马人进行游戏。适用操作系统:Linux, Windows和 OS X.
+
+#### 85. [Advanced Strategic Command][86] ####
+
+这个回合制战略游戏是基于Battle Isle游戏系列。玩家在战斗网格景观可以适用单机游戏模式或者多人游戏模式。适用操作系统:Windows和 Linux.
+
+#### 86. [Battle for Wesnoth][87] ####
+
+这个回合制战术策略游戏将玩家置身于神话世界里,它们争取夺回王位。游戏中充斥着兽人、精灵、巫师和数以百计的其它充满梦幻的一个大环境。支持单人游戏和多人游戏。适用操作系统:Linux,Windows,OS X,IOS。
+
+#### 87. [BosWars][88] ####
+
+这个未来的实时战略游戏需要玩家建立能源存储和一个经济体系来支持其军事斗争。玩家可以可以通过局域网进行多人游戏来抵抗对手。适用操作系统:Windows,Linux和BSD,OS X。
+
+#### 88. [CommanderStalin][89] ####
+
+关于BosWars的变化是被设置在斯大林时期的苏联国家。为的是对不可避免的纳粹进行攻击做准备!适用操作系统:Windows和Linux。
+
+#### 89. [FreeCol][90] ####
+
+受游戏Colonization and Civilization的启发,FreeCol是一款回合制文明建设的战略游戏。你可是的新世界在1492年并通过建立一个独立和言论自由的国家取胜。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和OS X.
+
+#### 90. [FreeCiv][91] ####
+
+这也是一个在Civilization得到启发的游戏,这个回合制战略游戏开始在石器时期,结束于太空时期。它包括了50个可玩单元和541国家并附带了各种可玩场景。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 91. [FreeOrion][92] ####
+
+尽管这不是一个克隆或者翻拍,FreeOrion是一个松散的基于Master of Orion 的游戏。这是一个设置在太空的回合制战略游戏。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 92. [Glest][93] ####
+
+这个实时战略游戏中科技的力量和魔法的力量都在其中。虽然它任然提供下载,但是大多数Linux发行版本现在包含了Megaglest的分支(见下文)而不是这个旧的程序。适用操作系统:Windows和 Linux.
+#### 93. [Globulation 2][94] ####
+
+这个实时文明建设战略游戏用意在于减少微观管理并允许玩家集中精力于战略上。单机模式或者多用户模式游戏和关卡编辑器都是可用的。适用操作系统:Windows和 Linux.
+
+#### 94. [Hedgewars][95] ####
+
+这是一个更轻快的战略游戏,Hedgewars以“粉红刺猬从地狱深处战斗到太空深处”,总共31个环境,48张已经设置好的地图,还可以无限制随机生成张地图,55种武器,280种服装,最多支持8个玩家。适用操作系统:Linux, OS X和iOS.
+
+#### 95. [Kernel Panic][96] ####
+
+这款游戏设置在数字地形中,Kernel Panic是一款实时战略游戏,拥有Tron-like的图形界面。所有资源都是免费的,所以玩家不必担心楼宇经济,只需要于其它骇客在网络上斗争。适用操作系统:Linux和 Windows。
+
+#### 96. [Liquid War][97] ####
+
+追溯回2002年,Liquid War被评委最“最原始的Linux游戏”,但是仍然是值得一玩的。玩家尝试消耗敌人的能量来控制水军。适用操作系统: Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+
+#### 97. [MegaGlest][98] ####
+
+这个游戏是Glest的衍生,在原来的Tech和Magic上增加了5个新的队伍:埃及,印度,挪威人,波斯和罗马。它提供了17中不同的地图,有单机模式和多人游戏模式,并为新手提供了教程。适用操作系统:Windows和 Linux.
+
+#### 98. [Pax Brittanica][99] ####
+
+这是一款。最多可以支持4个玩家在战斗中使用同意键盘的潜艇战略游戏。这些空间简单易学(你只需适用一个按钮),但是这个游戏可以玩得非常激烈。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 99. [Spring: 1944][100] ####
+
+这是一款二战战略游戏提供了逼真的游戏单元和强度。供选择的游戏角色可以是美国,德国,苏联和英国。适用操作系统:Linux。
+
+#### 100. [UFO: Alien Invasion][101] ####
+
+在未来70年,一个秘密的组织正在为保卫地球不受狠毒的外星人侵略做战斗。玩家扮演人类或者外星人在单机模式或者多用户模式。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 101. [Unknown Horizons][102] ####
+
+在这个文明建设的战略游戏中,强调的是建设一个强大的经济体制,你需要在一个孤岛上利用屈指可数的定居者和资源为开始,去建造一个欣欣向荣的城市。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+
+#### 102. [Warzone 2100][103] ####
+
+你可以在核爆炸后重建地球吗?这个游戏提供了一个非常强大科技树并支持单人模式或者多人模式。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux,和OS X.
+
+#### 103. [Widelands][104] ####
+
+受Settlers II启发,Widelands是另外一款实时战略游戏,挑战玩家去建立一个文明国度。它的特点是具有3个部落,分别为野蛮人、帝国和亚特兰蒂斯,而不像大多数文明游戏,玩家并没有被告知每个单元要做什么,而是把下订单并委派给代表,更像一个统治者的角色。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 104. [Zero-K][105] ####
+
+在这个快速移动的实时战略游戏中,机器人军队进行着一场永无休止的战斗。主要功能包括超过100种不同的单元,一个精简的经济体系,逼真的物理引擎,地球化等等。适用操作系统: Windows和 Linux.
+
+#### 105. [Zombies][106] ####
+
+你能够在在僵尸杀了你之前杀死所有僵尸吗?这是一个回合制的游戏提供了令人上瘾的游戏和设置,允许玩家决定挑战的级别。适用操作系统:OS X、
+
+### 有趣的非游戏类 ###
+
+#### 106. [Celestia][107] ####
+
+对于想成为宇航员和初露头角的天文学家,这款游戏无疑是至臻完美的, Celestia可以让你看到太空,因为它会出现在任何时间和宇宙中的任何已知点。快速地到木星旅行或者画出你夜晚的观星图。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 107. [Electric Sheep][108] ####
+
+这个游戏的灵感来自于Philip K. Dick小说中 Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep(做电绵羊机器人的梦想)?这个屏幕通过创造抽象图案和花纹来保护您的系统连接到成千上万人的系统上。投票支持你喜欢的团,它们便会出现得更经常一些。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux, OS X, 安卓和 iOS.
+
+#### 108. [LCARS 24][109] ####
+
+如果你家里有一台旧的电脑(睡会没有),为何不把它变成一个星际旅行为主题。有了这个应用,你可以得到一个闹钟和文件管理器,从图形界面看来,就像来到了一个正规的企业。适用操作系统:Windows和 DOS.
+
+#### 109. [Stellarium][110] ####
+
+把你的PC变成一个天文馆。Stellarium可以在地球上随时从任何角度随时显示夜空,而且它使用许多天象仪器来为显示器供电。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+#### 110. [Tux Paint][111] ####
+
+Tux Paint可以让学龄前儿童很容易地在电脑上创建自己的“图画”。它的特征是有一个借口和大按钮,有趣的声音效果和友好的字符界面。适用操作系统:Windows, Linux和 OS X.
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/110-fun-open-source-games-and-apps-1.html
+
+译者:[disylee](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.datamation.com/open-source/101-most-fun-open-source-games-and-apps-1.html
+[2]:http://www.stuff-o-matic.com/asgp/
+[3]:http://armagetronad.org/index.php
+[4]:http://bzflag.org/
+[5]:http://chromium-bsu.sourceforge.net/
+[6]:http://www.parallelrealities.co.uk/p/legend-of-edgar.html
+[7]:http://www.penguspy.com/jvgs/
+[8]:http://www.nogravitythegame.com/classic/
+[9]:http://opensnc.sourceforge.net/home/index.php
+[10]:http://linux.tlk.fr/games/Powermanga/
+[11]:http://www.scorched3d.co.uk/
+[12]:http://www.srb2.org/
+[13]:http://supertux.lethargik.org/
+[14]:http://funguloids.sourceforge.net/
+[15]:http://www.teeworlds.com/
+[16]:http://xmoto.tuxfamily.org/
+[17]:http://www.yofrankie.org/
+[18]:http://domination.sourceforge.net/
+[19]:http://sourceforge.net/apps/mediawiki/scrabble/index.php?title=Main_Page
+[20]:http://sourceforge.net/apps/mediawiki/scrabble/index.php?title=Main_Page
+[21]:http://www.pokerth.net/
+[22]:http://pysolfc.sourceforge.net/
+[23]:http://gabrielecirulli.github.io/2048/
+[24]:http://www.nongnu.org/billiards/
+[25]:http://cubetrains.com/
+[26]:http://www.nongnu.org/enigma/
+[27]:http://fillets.sourceforge.net/
+[28]:http://www.frozen-bubble.org/
+[29]:http://live.gnome.org/GnomeGames
+[30]:http://tomatoes.sourceforge.net/about.html
+[31]:http://games.kde.org/
+[32]:http://neverball.org/
+[33]:http://pingus.seul.org/welcome.html
+[34]:http://pushover.sourceforge.net/
+[35]:http://zaz.sourceforge.net/
+[36]:http://www.schoolsplay.org/
+[37]:https://live.gnome.org/gbrainy
+[38]:http://gcompris.net/index-en.html
+[39]:http://tux4kids.alioth.debian.org/tuxmath/index.php
+[40]:http://icculus.org/alienarena/rpa/
+[41]:http://assault.cubers.net/
+[42]:http://www.alientrap.org/games/nexuiz
+[43]:http://openarena.ws/smfnews.php
+[44]:http://www.redeclipse.net/
+[45]:http://tremulous.net/
+[46]:http://www.truecombatelite.com/
+[47]:http://www.unvanquished.net/
+[48]:http://www.warsow.net/
+[49]:http://www.splashdamage.com/wolfet
+[50]:http://worldofpadman.net/website/news
+[51]:http://www.xonotic.org/
+[52]:http://www.zeroballistics.com/
+[53]:http://www.stepmania.com/
+[54]:http://www.stepmania.com/
+[55]:http://www.ultrastardeluxe.org/
+[56]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/extremetuxracer/
+[57]:http://www.speed-dreams.org/
+[58]:http://supertuxkart.sourceforge.net/
+[59]:http://torcs.sourceforge.net/
+[60]:http://www.ultimatestunts.nl/
+[61]:http://vdrift.net/
+[62]:http://crossfire.real-time.com/intro/index.html
+[63]:http://www.epicinventor.com/
+[64]:http://excaliburworld.com/emr/emr3/index.html
+[65]:http://flarerpg.org/media/
+[66]:http://lipsofsuna.org/
+[67]:http://themanaworld.org/
+[68]:http://themanaworld.org/
+[69]:http://www.planeshift.it/about.html
+[70]:http://www.ryzom.com/en/
+[71]:http://stendhalgame.org/
+[72]:http://sumwars.org/wiki/Main_Page
+[73]:http://www.flightgear.org/
+[74]:http://www.golemgame.com/
+[75]:http://lincity.sourceforge.net/
+[76]:https://code.google.com/p/micropolis/
+[77]:http://minetest.net/
+[78]:http://pioneerspacesim.net/
+[79]:http://www.oolite.org/
+[80]:http://www.opencity.info/
+[81]:http://www.openttd.org/en/
+[82]:http://www.rigsofrods.com/content/
+[83]:http://www.simutrans.com/
+[84]:http://vegastrike.sourceforge.net/
+[85]:http://play0ad.com/
+[86]:http://www.asc-hq.org/
+[87]:http://www.wesnoth.org/
+[88]:http://www.boswars.org/
+[89]:http://commanderstalin.sourceforge.net/
+[90]:http://www.freecol.org/
+[91]:http://freeciv.wikia.com/wiki/Main_Page
+[92]:http://freeorion.org/index.php/Main_Page
+[93]:http://glest.org/en/index.php
+[94]:http://globulation2.org/wiki/Main_Page
+[95]:http://www.hedgewars.org/
+[96]:http://springrts.com/wiki/Kernel_Panic
+[97]:http://www.ufoot.org/liquidwar/v5
+[98]:http://glest.org/en/index.php
+[99]:http://paxbritannica.henk.ca/
+[100]:http://spring1944.net/
+[101]:http://ufoai.org/wiki/News
+[102]:http://www.unknown-horizons.org/
+[103]:http://wz2100.net/
+[104]:http://wl.widelands.org/
+[105]:http://zero-k.info/
+[106]:http://codenautics.com/zombies/
+[107]:http://www.shatters.net/celestia/index.html
+[108]:http://community.electricsheep.org/
+[109]:http://lcars24.com/
+[110]:http://stellarium.org/
+[111]:http://tuxpaint.org/
diff --git a/translated/talk/TechView--Linus Torvalds Inventor of Linux.md b/translated/talk/TechView--Linus Torvalds Inventor of Linux.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 33bed191b7..0000000000
--- a/translated/talk/TechView--Linus Torvalds Inventor of Linux.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
-技术视点:李纳斯·托沃兹,Linux的缔造者
-================================================================================
-
-
-> 技术视点是技术视角(TechScape)的一个新的组成部分,其特色是与科技界的上层人士进行独家采访和长时间谈话,探讨科技动态。
-> 我们的第一个谈话对象是[李纳斯·托沃兹][1],Linux的传奇缔造者以及开源改革先驱。托沃兹生于芬兰的赫尔辛基,是诗人奥尔·托沃兹的孙子。尽管他更喜欢告诉人们,他的名字来自于“花生”里角色,但事实是他是以李纳斯·鲍林——两次诺贝尔奖获得者的名字来命名的。他的计算机经历是从康懋达公司的一台Amiga 500计算机上开始的,搬到辛克莱尔后又换到了IBM的386上。刚开始,他使用的是Minix操作系统,后来在该系统上衍生出了他自己的Linux操作系统。托沃兹和他的妻子托芙——六次芬兰全国空手道冠军结婚了,婚后他们定居在加利佛尼亚的圣何塞,育有三个女儿。
-
-**技术视点(TV)**:在当今科技中,什么令你感兴趣?
-
-**托沃兹**:我差不多是个“鼠目寸光”的家伙,所以相对于那些更空洞的“大潮流”,我对实在的新的零散的技术更感兴趣。
-我喜欢跟踪公司生产的新硬件,它们最新的芯片,而可能最能激励我的是(因为毕竟我是个做软件的)那些提出新的算法并开发新的软件来利用这些新功能的人。
-
-**TV**:那在当今科技中,什么真正让你感到生气?它怎么会让你生气,以及为什么让你生气?
-
-**托沃兹**:我不会用生气这个词,但是如果真要说技术市场中有什么让人反感的,那就是对那些最令人瞩目的“领袖”们的赞美。
-
-这里,当然也包括我。我认为,整个的“个人崇拜”相当令人不安。而且,我很痛恨把我以及我所说的话看得太重。对于乔布斯,埃里森,盖茨,凡是你说得出的人来讲也一样。我希望更多的人能自己思考,并且意识到技术实际上来自遍布全球的那些默默无闻的伟大的工程师中的一员。
-
-我理解人们想要并且需要一个焦点,而这种事也不仅仅发生在技术世界中(嘿,毫无疑问,我希望这事在技术世界中要发生得比娱乐行业来得少;)但是,这事仍然有点令人沮丧。
-
-**TV**:你是怎么错过“申请终身许可证的机会”,而其它像Red Hat,SuSE等等却抓住了这个机会?这是因为如果Linux不开源,它就不是Linux了?你能谈谈更多情况吗?你是否在此事上有点自甘堕落了?
-
-**托沃兹**:我当然不会因为任何事情自甘堕落。我有着令人羡慕的地位,我能干我喜欢的事情。而且,人们因此而尊重我。况且,我想要做的(而我已经做了)无偿工作也获得了酬劳。
-我想,很少有人会感觉到他们实际上已经有所不同,那么让我来告诉你吧,这种感觉真不错。对于商业方面,我从来都不感兴趣。而且,对我来说,那些可以采用Linux并把它商用的人和公司只是做了我从没有动力做的事情。而这项工作需要人做,也很有益。因此,事实上我很感谢那些商业实体:它们让我集中精力干我想干的那部分事情。
-
-**TV**:在当今的科技界,哪位是你尊敬的人?为什么?
-
-**托沃兹**:嗨!看看我对于整个“个人崇拜”的控诉吧。我只是并不对那种“让我们找个人并把他置于令人尊敬的地位上”的事情印象深刻。
-
-所以,与其个人扬名,我更高兴去做像EFF这样的事情,这些组织(有时候只是观念和想法)不是要试着去穷其一生提升他们自己,而是试着去做一些实质性的事情来给予帮助,让技术工作在一个更大的蓝图中变得更好。
-
-在个人层面上,我更喜欢那些不把他们太当一回事而又在他们的本质工作上干得很好的人。如果一定要我说一些知名人士,我想我更愿意成为斯蒂芬·沃兹尼克那样的人,而这也是我尊敬他的原因。
-
-**TV**:照你估计,当谷歌和微软都实现了各自的诺言,他们之间会发生什么?胜者又为什么会胜出?
-
-**托沃兹**:我不认为获胜的结果会和获胜的过程一样有趣。
-在整个谷歌和微软的竞争中,我真的不认为公司本身比改变技术环境来转移人们的视线更有趣。焦点从一个控制发生在单台机器上的公司转移到了更多关注整合大量独立机器的公司。
-
-**TV**:为什么你会认为像科技灾难,互联网泡沫崩溃以及电信业崩盘这样的事会发生?我们在今后怎样来防止它们再发生?
-
-**托沃兹**:实际上,我对此类事情持相反的看法,并且没有理由去“阻止它们反复”。
-
-我是坚信超越极限,但是我不太相信会完全稳定,而且百分百“正常”。
-
-大量真正的进展在井喷似的发生,而后来成了被称为“夸大宣传”以及其它不讨好的事情的一部分。但事情是,做了一些太难理解而且无聊的事情,而没有做些蠢事,这实在是事与愿违。
-我个人认为,稳定开发模型不是持续的增量改进,而是一连串的反应过度和崩溃。
-渐进增量改进常常可能看起来是更好的策略,但是如果你不是偶然地反应过度和崩溃,你又怎么知道你实际上是在超越极限呢?
-
-**TV**:技术在将来会怎样改变我们的生活?你会和其它部门的领袖们一起创建新技术吗,比如生物信息学?
-
-**托沃兹**:我个人的理论是,技术对我们的生活的改变没有我们构建技术来适应我们的生活来得多。
-
-这就是为什么你看不到飞行汽车等喜爱的装订本科幻小说中的的东西——但是相反,你却看到了利用技术来降低交易成本这类此前就存在的事情,但此前不能大规模应用或者量身定制(除了有时候是为了那些富得冒油的做)。
-
-因此,技术很少直接改变我们的生活本身——虽然它往往意味着更多的人能获得那些以前是罕见的或只限于暴富者的东西。
-真正的改变发生在当某些事物变得如此廉价并且遍地都是让你行为变得大不相同的时候。而在不同方面,这些行为上的改变要比技术本身来得更有趣。
-
-例如,互联网做真正做的一件事是让你寻找并与志趣相投的人交流的成本更低。而且,我认为大量的真正的改变正是从人们无需付出太多努力就能找到其他和你对同一事物有相同兴趣的人的时候,他们的习惯因此而改变中得以体现。
-因此,你发现了所有的这些专业兴趣小组,以及许多人正在花大量时间讨论最神秘的问题,这些问题他们刚刚发现很有趣——这些事,你在之前不一定能实际去做的,因为那时真的很难找到和你在某些不同寻常的专业上志趣相投人并进行讨论。
-
-而我认为那是生活真正改变的方式——而不是因为任何新技术的出色的特性,而是因为完全是技术降低增量成本后的无意的副作用。
-
-**TV**:据你估计,当今科技界谁是举足轻重的人物?
-
-**托沃兹**:我想大量的技术怎么会是由消费市场推动,而不再是由军方或甚至是商业需求推动这一点很说明问题。我也常常认为公司正在做的许多貌似愚蠢的事情(特别是DRM)似乎正忽略了一个事实:任何技术上最重要的人,他也最终总是个“用户”。
-
-因此,就我而言,我认为你的问题的答案是“用户”,或者叫“消费者”,而那个确实是最重要的部分,因为那个正是需求和实际商业成功的根源。
-
-**TV**:请谈一些你个人的观点,比如宗教?政治?
-
-**托沃兹**:我完全是一个宗教——无神论者。我发现人们似乎认为宗教带给人道德和感激自然的情感。事实上我认为,它反而把这两方面都削弱了。它给人们理由来说“哦,自然刚被创立”,以及创世行为是神奇的事情。我欣赏此事实“哇,真让人难以置信,竟然首先发生了这样的事情。”是啊,这是种讽刺。在许多欧洲国家,事实上国家和国家宗教之间具有法律约束力。
-
-我成了一位美国公民,并且我注册取得了在美国的投票权。我不支持任何政党,因为相当坦率地说,我有太多个人引以为豪的东西,不想和他们中的任何人有什么关联。
-
-**TV**:谢谢,李纳斯!
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.huffingtonpost.com/billrobinson/techview-linus-torvalds-i_b_5338844.html
-
-译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[reinoir](https://github.com/reinoir)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linus_Torvalds
-[2]:
-[3]:
-[4]:
-[5]:
-[6]:
-[7]:
-[8]:
-[9]:
-[10]:
-[11]:
-[12]:
-[13]:
-[14]:
-[15]:
-[16]:
-[17]:
-[18]:
-[19]:
-[20]:
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/talk/The Open Source Witch Hunts Have Returned.md b/translated/talk/The Open Source Witch Hunts Have Returned.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9810a8e258
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/talk/The Open Source Witch Hunts Have Returned.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+开源女巫狩猎归来!
+================================================================================
+
+
+> 开源软件社区已经做出了改变,就像之前的美好时光。
+
+开源软件已经变的温和了,之前我们有的那些不纯洁的想法,可是随后我们却奇怪的和别人分享自己的代码与创作。
+
+幸运的是,这种务实主义要结束了。在过去的几周当中,我们团结在Mozilla身边支持DRM版权保护以及嘲笑Red Hat和OpenStack之间的竞争。社区那些年如数家珍的开源软件明星和[Open Core][1]产生了冲突而被反噬了.
+
+多么怀念啊。
+
+
+### 2003年的Red Hat ###
+
+Red Hat,开源软件理想主义的典范,在几周前拒绝支持它的竞争对手。Jodi Mardesich做了[非凡的工作][2]却受到了指控以及Red Hat的回击。但是真实情况是:
+
+Red Hat不想支持它的竞争对手OpenStack
+
+在另外一边这难道算是新闻吗?
+
+
+### Mozilla变成了麻瓜 ###
+
+Red Hat作为开源软件理想主义的典范代表很容易成为各种带颜色攻击的目标,Mozilla其实是更大的一个目标。
+
+Mozilla承诺为用户服务的罪过,它最近进行了一场自我牺牲似的行动违背CEO的策略同意加入DRM的技术,即纯Firefox浏览器源码可以使用户观看视频。
+
+人们想看视频,Mozilla倾向于在它的浏览器中观看。
+
+最新消息,这一次失败,开源软件组织[批评了][3] Mozilla,深切表达了自己对于Mozilla的失望,因为这种决定妥协的态度会导致浏览器份额的降低。
+
+但是,Mozilla为什么要做这样的傻事呢,为了用户,你懂的。
+
+说教部门不甘示弱,[电子前沿基金会感叹][4]到开放网络最后的抗争已经失败了。它对Mozilla失败的做法争论道:“接受DRM会改变这个行业”!DRM的倡导者一再妥协,一个公司又一个公司(PC行业)演变成一个行业,它通过锁定装置,监视器,接受每一个人的管理建立自己的利益关系。
+
+[Mitchell Bake解释道][5],Mozilla可能并没有投降:“Firefox用户会需要使用另外的浏览器来观看他们自己想看的视频,这让人怀疑Firfox做一一个产品是否真的有用”。
+
+Um, yes.
+
+### 回到我们的思想源头 ###
+
+However much we may want to force others to live by our absolutist ideals, the reality is that others may have different 我们或许很专制的意图其他的东西活着,事实上他们却有着不同的优先度。免费的软件让步给开源软件,更加严格,更加固定“正确的方式”去获得授权。
+
+这种意识在目前还是有用的,但它并不总是方便和愉悦。我崇尚开源软件的实用主义,Apache软件基金会,这样有很大的好处提醒GPL组织在意识形态上的危机感。软件自由真的很重要。
+
+这么多悲观的言论,我自己也感到了恐惧,希望回到一个不断会自我鞭策的免费的开软软件的组织。这使开源软件协作变少而且更难驾驭,但是会变得更有力而且关乎未来。
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://readwrite.com/2014/05/21/open-source-witch-hunt-mozilla-openstack-redhat#feed=/hack&awesm=~oEYDhxfP0Qv5hE
+
+译者:[jiajia9linuxer](https://github.com/jiajia9linuxer) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_core
+[2]:http://readwrite.com/2014/05/16/red-hat-openstack-mirantis-rhel-support
+[3]:http://www.fsf.org/news/fsf-condemns-partnership-between-mozilla-and-adobe-to-support-digital-restrictions-management
+[4]:https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2014/05/mozilla-and-drm
+[5]:https://blog.mozilla.org/blog/2014/05/14/drm-and-the-challenge-of-serving-users/
diff --git a/translated/talk/The history of Android/01 - The history of Android.md b/translated/talk/The history of Android/01 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c312a38551
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/talk/The history of Android/01 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,201 @@
+安卓编年史
+================================================================================
+> 让我们跟着安卓从0.5版本到4.4的无尽迭代来看看它的发展历史。
+
+
+这些年来历代安卓的主屏幕。
+图片提供:Ron Amadeo
+
+安卓已经以不止一种形式陪伴了我们六年以上。在这段时间内,我们已经看到了不同于任何已有开发周期的,绝对惊人变化速度。当Google卷入智能手机的战场中时,它拿出了它的快速迭代,Web风格的更新周期,把它们应用到了开发的这个操作系统之中,而结果就是突击式的持续改进。近来,安卓项目甚至以前所未闻的六个月开发周期在运行,这可比它之前的开发周期慢。在安卓的第一年商业运作时,Google每两个半月就会发布一个新版本。
+
+注:youtube视频地址开始
+
+
+Google在2007年11月时对安卓最初的介绍。
+注:youtube视频地址结束
+
+同行业的其它公司和其相比,只能是以蜗牛的步伐在缓慢前进。微软每三到五年升级它的桌面操作系统,苹果对OS X和iOS以一年为一个更新周期。另外不是每个更新都是同等地位的。iOS在七年内有一个主要的设计上的大变动,而最新的Windows Phone 8看起来和Windows Phone 7十分相似。但在安卓上,如果用户能看到今年的任何东西看起来和去年一样,那简直是中彩票了一样。比如Play商店,五年内有五次的重新设计。对安卓来说那更是家常便饭。
+
+回头看看,安卓的存在是很模糊的。从其历史来看,现在它是个使用量巨大的操作系统。近十亿的设备销量,以及每天一百五十万左右的激活量——但Google是如何达到这种地步的?安卓现在如此水平的规模和成功,可能会让你觉得安卓从零开始到万众瞩目的英雄中覆盖到了方方面面。但事实上不是这样的。安卓在早期并不流行,以及直到安卓4.0屏幕截图还只能通过开发者工具实现。这两个因素意味着你无法轻易找到许多安卓早期版本的图片或信息。
+
+对于早期版本的缺乏覆盖问题现在称作*安卓早期版本正在消亡*。尽管像Windows 1.0这样的系统可以永远在你身边——只要找台旧电脑把它装上去就好了——安卓可以被认为是第一个基于云的操作系统。许多功能严重依赖Google的服务来实现。随着越来越少的人使用老版本的安卓,那些服务被逐渐关闭。当一个依赖云的应用其服务支持停止之后,它再也不能正常运作——应用崩溃并显示空白的屏幕,或直接无法启动。
+
+正是由于这种“[云腐烂][1]”现象,安卓回顾展在几年内不可能出现。早期版本的安卓没有了云的支持会是一个不能正常工作的破碎的空壳。尽管可以简单地认为这是早期版本安卓渐渐消失的一种方法,但这正是正在发生的。就在写到这里的时候,正有无数的应用因为服务器支持被关闭而失去作用。例如早期的谷歌地图和安卓市场客户端,已经不能和Google服务器交互。它们会弹出错误消息并崩溃或者是显示一个空白的界面。有些应用甚至在一个星期正常运行然后下个星期就宣告死亡,因为就在我们写下这篇文章的时候谷歌正在积极地关闭服务器!
+
+为了防止在滚滚历史里丢失掉更多关于安卓的过去,我们做了需要完成的工作。这里有20+个版本的安卓,七台设备,以及无数的屏幕截图被集合到一起。这就是安卓编年史,从最早的公开版本到罪行的KitKat。
+
+注:下面一块为文章链接列表,发布后可以改为发布后的地址
+----------
+
+### 目录 ###
+
+- [Android 0.5 Milestone 3——第一个公开版本][10]
+- [Android 0.5 Milestone 5——报废接口的领地][11]
+- [Android 0.9 Beta——嘿,这看起来很眼熟!][12]
+- [Android 1.0——谷歌应用的引入和实体硬件][13]
+- [Android 1.1——第一个真正的增量更新][14]
+- [Android 1.5 Cupcake——虚拟键盘打开设备设计的大门][15]
+- ----[谷歌地图———登陆安卓市场的第一个内置应用][16]
+- [Android 1.6 Donut——CDMA支持将安卓带给了各个运营商][17]
+- [Android 2.0 Éclair——带动GPS产业][18]
+- [The Nexus One——迎来Google Phone][19]
+- [Android 2.1——动画的大发现(以及滥用)时代][20]
+- ----[Android 2.1, update 1——无尽战争的开端][21]
+- [Android 2.2 Froyo——更快更华丽][22]
+- ----[语音操作——口袋里的超级电脑][23]
+- [Android 2.3 Gingerbread——第一个UI大变][24]
+- [Android 3.0 Honeycomb——平板和设计的新生][25]
+- ----[Google Music Beta——云存储的内容库][26]
+- [Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich——摩登时代][27]
+- ----[Google Play以及直接面向消费者销售设备的回归][28]
+- [Android 4.1 Jelly Bean——Google Now指明未来][29]
+- ----[Google Play服务——碎片化以及让系统版本(几乎)过时][30]
+- [Android 4.2 Jelly Bean——新Nexus设备,新平板界面][31]
+- ----[周期外更新——谁需要一个新系统?][32]
+- [Android 4.3 Jelly Bean——为可穿戴设备做好准备][33]
+- [Android 4.4 KitKat——更完美;更少的内存占用][34]
+- [今日安卓无处不在][35]
+
+----------
+
+### Android 0.5, Milestone 3——第一个公开版本 ###
+
+在我们开始在实体硬件上研究安卓之前,我们要从很早,很早以前的安卓时光开始说起。尽管1.0是第一个运行在实体硬件上的版本,但在那之前其实还有若干个只随SDK发布的模拟器beta版本。这些模拟器只用于开发的目的,所以它们不含任何谷歌应用,甚至是一些核心系统应用。但它们仍然是回顾安卓的发布前时光的最好渠道。
+
+
+模拟器默认的qwerty布局并运行Milestone 3。
+Ron Amadeo供图
+
+在异想天开的糖果版本代号和[与跨国食品公司跨界合作][2]之前,第一个安卓的公开发布版本的标签是“m3-rc20a”——“m3”代表“Milestone 3(里程碑3)”。尽管谷歌可能不会公布版本号——这个版本甚至没有一个设置应用来查看——浏览器用户标识识别为“Android 0.5”。
+
+在2007年11月,谷歌获得安卓两年,iPhone发布五个月之后,[安卓正式发布][3],第一个模拟器正式释出。回到那时候看,这个系统才刚处于起步阶段。它很容易就被认为“只是个黑莓的山寨而已”。模拟器使用了一个qwerty布局的皮肤以及320×240的显示屏,是一台[原型设备][4]的复制品。这台设备由HTC制造,通过一些早期的安卓账户可以得知这台设备的代号似乎是“Sooner”。但是Sooner从未正式上市。
+
+通过安卓早期[开发账号][5]得知,当苹果在2007年1月最终发布它革命性的智能手机后,谷歌不得不对安卓“从头来过”——包括放弃Sooner。考虑到Milestone 3模拟器在苹果的iPhone后近一年才推出,设备界面看起来还是那么像黑莓的模型是在是令人惊奇的事情。尽管在iPhone发布后的开发里任务毫无疑问地在优先保障下完成了,但模拟器仍然以被认为是“旧学院风”的界面发布。这使得它没能给人留下一个好的第一印象。
+
+在早期阶段,安卓按键布局看起来并没有最终确定下来。尽管第一台商业安卓设备使用了“主屏幕”,“后退”,“菜单”以及“搜索”作为标准的按键套件,模拟器上有一个空白的标记为“X”的键,你可能会认为是那是搜索键应该在的地方。“Sooner”原型机看起来更奇怪——它在第四个键上有个星形标记。
+
+
+从左到右:主屏幕,一个打开的通知,以及“应用”文件夹。
+Ron Amadeo供图
+
+在这里没有可以配置的主屏幕或小插件,仅仅只是简单的在底部有聚合图标的dock,可以循环或是点击。尽管已经有一些特性支持触摸屏,Milestone 3主要还是使用五向十字键——一个时至今日安卓仍然支持的不合时宜的设计。甚至早期的安卓都能够实现动画效果。图标在进入dock的中心窗口时会变大或缩小。
+
+在这时候一样也还没有通知栏。通知图标显示在顶部状态栏(上面图片中的微笑标志),打开它的唯一方法是在主屏幕按下十字键的上键。你无法通过点击微笑的图标来打开它,也无法从除主屏幕以外的地方打开通知。当通知被打开的时候,状态栏些许地扩展开,通知文本会显示在一个聊天气泡中。一旦你阅读完通知,你无法手动清除它——应用本身负责清除它的通知消息。
+
+应用抽屉的职责由一个dock左侧简单的“应用程序”文件夹负责。尽管有着不少标志性的功能,Milestone 3模拟器应用图标还不是十分完善。只有“浏览器”,“联系人” ,以及“地图”是这里面真正的应用。奇怪的是,“最近通话”被提升为一个独立的图标。因为这仅仅只是个模拟器,像闹钟,日历,拨号,计算器,照相机,相册,以及设置这样的智能手机核心功能的图标统统没有。硬件原型倒是有[其中的大部分][6],它还有一套谷歌应用出现并运行着。不幸的是我们没办法看到它们了。它们已经老到无论如何都连不上谷歌的服务器了。
+
+
+Milestone 3的浏览器菜单系统,壁纸界面,以及音量控制。
+Ron Amadeo供图
+
+这套现在已经过时的菜单系统出现并运行在Milestone 3上。点击实体菜单键会打开一个灰色带有蓝色梯度高亮的列表,通过实体键盘完成操作。在上面的截图中,你可以看到在浏览器中打开的菜单。进入二级菜单,像缩放菜单,一级菜单变成有些奇怪的透明状态。
+
+令人惊喜的是,多任务及后台应用在Milestone 3上已经可以运作了。离开应用而不关闭它——应用会保存状态,甚至写入文本保存。这个特性iOS直到2010年推出iOS 4才能与其相比,这就真正显示出了这两个平台的不同。iOS最初是作为一个封闭的平台而没有第三方应用,所以平台的鲁棒性并没有得到很大的关注。安卓是从头开始被构建成一个强大的应用软件平台,轻松开发应用是它创造出来背后的推动力之一。
+
+在安卓之前,谷歌已经通过[WAP网站][7]和[J2ME手机应用][8]向移动端开始迁移,这使得它们强烈地意识到移动开发的难度。据[The Atlantic][9],拉里佩奇曾这么描述公司在移动端的努力“我们有一系列超过100台手机,我们在每一台设备上都要构建一次我们的应用”。开发者们现在经常抱怨安卓的碎片化,但在安卓出现之前,问题要比现在糟糕很多。
+
+谷歌的平台战略实际上胜出了,iOS最终在不久后开始慢慢加入这些围绕应用的特性——多任务,跨应用分享,以及应用切换。
+
+
+当你在主屏幕按数字键弹出的拨号界面,来电,以及电话会议界面。
+Ron Amadeo供图
+
+尽管没有拨号图标,Milestone 3模拟器还是有办法拨号。按键盘上的任意键会打开左侧界面,这是拨号/联系人搜索混合界面。仅输入数字并点击绿色的实体拨号键来开始通话,输入字母会搜索联系人。但是联系人无法通过数字搜索。甚至直接点击一个号码也不会打开联系人。
+
+来电被显示成一个几乎全屏的令人愉快的透明背景弹窗。一旦进入通话,背景会变成深灰色,Milestone 3展现给用户一些令人惊奇的高级特性:静音,扬声器,保持,以及电话会议按钮。多方通话会显示成重叠,半透明的卡片状,用户有切换或者合并通话的选项可以选择。切换通话会触发一个漂亮的小卡片洗牌动画。
+
+
+联系人列表,打开一个联系人,编缉联系人,以及最近通话界面。
+Ron Amadeo供图
+
+联系人是一个质朴的,黑色和蓝色的姓名列表。联系人卡片中有个联系人头像的位置但是没办法设置一张图像上去(至少在模拟器中不行)。这里唯一的装饰是每个联系人名字左侧的XMPP状态点。传统来说一个保持在线的XMPP连接是安卓的核心,它的深度集成从Milestone 3就已经开始了。安卓使用XMPP来驱动一个24/7在线的与谷歌服务器之间的连接,驱动Google Talk,云到端消息推送,以及应用的安装和卸载信息。
+
+
+浏览器的假Google首页,地址栏,浏览历史界面。
+Ron Amadeo供图
+
+浏览器运行Webkit 419.3,它也被用在相同时代的像Mac OS X 10.4的Safari 2上。浏览器主页并不是Google.com,而是一个包含在安卓里的硬编码的home.html文件。它看起来就像是千年之前的Google.com。浏览器的OS X遗留还可以辨认出来,用了光滑的,Aqua风格的搜索按钮来渲染浏览器按钮。
+
+这个小小的黑莓风格的屏幕需要一个分离的地址栏,可以通过浏览器菜单里的“前往”选项打开。尽管自动补全不起作用,地址栏会在你输入的时候实时搜索你的浏览历史。右侧图片显示的是历史界面,它使用了略缩图来显示各个站点。当前的略缩图在其它两个之前,滑动它们会触发一个猛扑的动画效果。但在早期阶段,浏览器不支持多标签或窗口——你可以看到当前站点,那就是全部了。
+
+
+一个视频屏幕抓取导出的谷歌地图界面,方向界面,相册测试界面。
+Ron Amadeo供图
+
+在开始的时候,谷歌认识到在移动端地图将会非常重要,甚至在Milestone 5模拟器中内置了地图客户端。那个版本的谷歌地图是我们遇到的第一个死于云腐烂的。这个客户端无法从谷歌的服务器上载入信息,所以地图显示为一片空白,灰色的网格。没有什么能够运转。
+
+幸运的是,因为上面的第一张截图,我们能够从安卓启动视频中拼凑出准确的界面。旧的谷歌地图看起来完全是为非触摸设备准备的,实体键快捷方式列表排列在屏幕底部。这样在看地图时,或是在如果仅仅显示该点的地址的时候就不大清楚。
+
+隐藏在菜单之后的是搜索选项,方向,以及卫星和交通图层。中间的截图是方向的UI之一,你可以选择一个联系人的地址作为起点或者终点。但地图缺乏任何种类的集成GPS,你在哪都找不到“我的位置”这个按钮。
+
+尽管没有合适的相册,在右边是相册的测试界面,隐藏在“API Demos”应用里。图片可以向左向右滚动,但无法以全屏的方式打开一张照片。同样它也没有照片管理选项。它本质上就是个图片滚动界面的测试视图。
+
+
+时间设置和日历,有点字间距问题,以及以Ars为特色的垂直列表测试。
+Ron Amadeo供图
+
+同样模拟器中也没有设置应用,但是通过API Demos我们可以看到最初的日期时间设置界面。这个示例暴露出很多安卓没来得及处理的问题:到处都有的字间距问题,分钟数字间巨大的间隔,以及日历中星期日间不均等的间隔。尽管时间设置允许你单独更改每个数字,但除非你将当前日期移出本月到前一个或下一个月,否则你无法改变月份或年份。
+
+别忘了尽管这看起来像是一些被遗忘时代的恐龙级别遗留物,但这仅仅是六年前发布的。我们总趋向与适应科技的脚步。我们很容易将这样的东西看作是20年前的东西。比较一下2007年晚些时候这个时间段的桌面操作系统,微软尝试将Windows Vista售往全世界快要一年了,而苹果刚刚发布OS X 10.5 Leopard。
+
+最后一个关于Milestone 3的细节:谷歌在Milestone 3模拟器中给了Ars Technica一个快捷方式。打开“API Demos”应用并打开"Views," "Focus,"然后"Vertical"显示一个*this very Website*的头条测试列表。
+
+
+随Milestone 3,RC37a发布的更加现代,全触控风格的模拟器。
+Ron Amadeo供图
+
+两个月后,2007年12月,谷歌放出了一个Milestone 3的更新,带来了更大的480×320设备设置。这个更新的标签是“m3-rc37a”。软件看起来还是像黑莓一样,仅仅是带来了更多的屏幕分辨率支持。
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron是Ars Technica的评论编缉,专注于安卓系统和谷歌产品。他总是在追寻新鲜事物,还喜欢拆解事物看看它们到底是怎么运作的。
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/
+
+译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/how-we-found-and-installed-every-version-of-android/
+[2]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/09/official-the-next-edition-of-android-is-kitkat-version-4-4/
+[3]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2007/11/its-official-google-announces-open-source-mobile-phone-os-android/
+[4]:http://www.zdnet.com/blog/mobile-gadgeteer/mwc08-hands-on-with-a-working-google-android-device/860
+[5]:http://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2013/12/the-day-google-had-to-start-over-on-android/282479/
+[6]:http://www.letsgomobile.org/en/2974/google-android/
+[7]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/%E2%80%9D
+[8]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/%E2%80%9D
+[9]:http://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2013/12/the-day-google-had-to-start-over-on-android/282479/
+[10]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/1/#milestone3
+[11]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/2/#milestone5
+[12]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/3/#0.9
+[13]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/6/#1.0
+[14]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/7/#1.1
+[15]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/8/#cupcake
+[16]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/9/#Mapsmarket
+[17]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/9/#donut
+[18]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/10/#2.0eclair
+[19]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/11/#nexusone
+[20]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/12/#2.1eclair
+[21]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/13/#alloutwar
+[22]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/13/#froyo
+[23]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/14/#voiceactions
+[24]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/14/#gingerbread
+[25]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/16/#honeycomb
+[26]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/19/#music
+[27]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/19/#ics
+[28]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/21/#googleplay
+[29]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/21/#4.1jellybean
+[30]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/21/#playservices
+[31]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/22/#4.2jellybean
+[32]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/23/#outofcycle
+[33]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/24/#4.3jellybean
+[34]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/25/#kitkat
+[35]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/26/#conclusion
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
diff --git a/translated/talk/The history of Android/02 - The history of Android.md b/translated/talk/The history of Android/02 - The history of Android.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..696de0aa22
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/talk/The history of Android/02 - The history of Android.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+ 安卓编年史 02
+
+=============================================================================
+
+左边:里程碑 5,主屏幕展示了“All”按钮,两个dock图标,以及最近使用的四个应用。中间:主屏幕与打开的应用程序列表。右边:电源菜单。
+图片来自@Ron Amadeo
+
+###Android0.5, 里程碑 5——如今已经是报废接口的领地了 ### -
+
+“M5-RC14”构建后:也就是第一个仿真器发布,三个月之后Android迎来了她的首次重大革新。 2008年2月发布的“里程碑5”甩掉了发展中的黑莓界面,走向一个完全革新的设计——谷歌在手指触摸技术的第一次尝试。
+
+由于浏览器的用户代理字符串的使用,此版本仍然被识别为“Android0.5”,但里程碑 5与Android的第一个版本相比已经完全不一样了。几个核心的Android功能直接追踪他们的血统最终还是会回到这个版本。通知面板的布局和功能几乎已经整装待发,并且,除了样式变化外,菜单同样也存在于它的最终组成。安卓1.0距离该项目起航的时间仅仅只有八个月,一个操作系统的基础已经开始形成了。
+
+有一件东西绝对不会存在于最后的组成,那就是是主屏幕。这是一个不可配置的,单屏壁纸的应用程序的架子和空位。【译者注:"an app drawer and dock,",度娘直接是"应用程序的抽屉和码头,",没有搜到相关专业的词汇,求指点,感激。zsky@live.com】应用程序图标是天真活泼的,三种颜色的组合,由一个方形的、有圆角的白色背景包围着。应用程序的架子由在右下角的一个“All”按钮组成,轻按它,扩展的应用程序列表显示在了左边。这个“All”按钮正上面的是两个图标空位,“联系人”和“拨号器”分别获得了专属的永久主屏幕位置。然后上边有四个板块,它们是最近应用程序的早期版式,展示了最后访问的应用程序。没有了左画面或右画面,基座和最近的应用程序占用一整列,这种布局下21个正方形的应用程序才会填充满整个屏幕。模拟器仍然只选择同等最小的应用程序,但在实际的设备中,这样的设计并产生没有很好地工作效果。
+
+按住“end call”按钮会出现一个超级早期版本的电源菜单,您可以在最右边的图片中看到的。谷歌迄今为止没有正常的智能手机命名术语:对于“Turn Off Screen”最好地形容也许是“Lock screen”(虽然当时没有锁屏)和“Turn Off Radio”在今天被叫做“Airplane Mode”。
+
+
+从左至右依次为:令人惊喜的现代版通知面板,谷歌地图的菜单在打开着(地图已经不可用了),和新的适合手指操作的列表视图。
+照片来自@Ron Amadeo
+
+所有的方式都会回溯到里程碑 5,谷歌在那时就毫无疑问拥有通知面板的基本知识储备。就像在任何现代的智能手机里看到的一样,它能够从屏幕顶部下拉下来。目前的通知都显示在列表中。通知面板的第一个版本是不透明的白色薄片带着棱纹的的“handle”在底部,一个橙色的圆点在中心。通知是可触的,通过触摸可以打开该通知关联的应用程序。没有人被在此列表中垂直对齐的应用程序图标所困扰,不过也没关系,随着在接下来的更新,它已经是过去式了。
+
+点一下通知,进入一个在面板顶部的“on going”部分。在这个版本,这里似乎只包含打电话。在“Latest Event”里的通知只有打开相应的应用程序后才是清楚的。用户令人惊喜的通过内置的XMPP连接成功登录到谷歌talk。不过,虽然通知面板中显示“new chat message,”,其实这里并没有没有真正的即时消息应用程序。
+
+里程碑 5里的艺术设计全部都是新的。该应用程序图标被重新绘制,并且菜单从一个无聊的黑莓风格的文本列表转变为一个大格全彩色、卡通的图标。通知面板图标也从简单的、突兀的、白色的图标切换到一个天真活泼的绿色设计。当时在信号栏指示器下边有一个奇怪的黑线,几乎没有作用。早期开发版本的微小列表视图不适合手指使用,所以里程碑 5开发了全面强大的整体布局。
+
+
+拨号器,最近通话,和来电接听。
+照片来自@Ron Amadeo
+
+M5是第一个有一个拨号器的版本,即使她是一个相当难看的版本。数字被显示在包含一个奇怪的语音气泡风格的退格键里,看上去就像是从其他界面回收回来的。对齐问题随处可见。按钮上的数字没有正确的垂直排列,而且退格键的“X”也没有与对话框对齐。由于屏幕上没有的“dial”按钮,你甚至不能从拨号程序打个电话,一个硬件按钮也被托管了。
+
+里程碑 5 有几个选项卡式界面,所有这些都表明了一个非常奇怪的想法:标签应该如何工作。活跃的标签是白色的,而背景标签是拥有一小条白色在其边沿的黑色。后台标签应该是向下的“shrink”吗?切换标签时,是没有动画的。目前还不清楚这个设计试图想表达什么。
+
+在第二张图片中显示的最近通话记录项,是从顶级的应用程序降级到拨号器选项卡的。它丢弃了早期版本的疯狂十字丝UI,多亏了大块列表视图,现在所有必要的信息都是显示在一个正常的列表。
+
+不同于拨号器,来电画面只有即时屏幕上的按钮来接听和结束通话。奇怪的是,来电屏幕贴在显示器的底部,而不是顶部或中心。它可能是从旧的黑莓4:3屏幕遗留下来的。
+
+
+通话中,触摸屏不可用的显示错误信息,和暂停通话的第二个呼叫的呼叫屏幕。
+照片来自@Ron Amadeo
+
+通话中界面看起来正常,但在实践中毫无意义。今天,在通话中为了阻止你的脸按到屏幕按钮,手机近距离传感器一旦检测到相关信息会快速关闭屏幕。虽然里程碑 5不支持近距离传感器。谷歌的杂乱无章的解决方案是在通话过程中禁止整个触摸屏。与此同时,通话中的屏幕显然会彻底检查触摸功能。这时候是有大的,可触摸的按钮; *就是不让你摸!!*。
+
+M5在这里让旧里程碑3版本的几个回归者占据特色地位。许多旧的接口里有体面相貌的图标被替换成了文本。像“mute”按钮不再提供屏幕上的反馈,过去他们是活跃的。合并通话被完全切掉了。
+
+
+浏览器的主要菜单,浏览器的二级菜单,疯狂的变焦控制和窗口界面。
+照片来自@Ron Amadeo
+
+浏览器菜单中得到了一贯的触摸功能大修理,并且“more”按钮第一次出现。它充当一个[extra menu for your menu] [1]。而不是转动3x2的网格成3x4的网格,里程碑 5(和Android的许多后续版本一样)中使用很长的、滚动的列表来引出其他选项。不支持双指缩放(据说是[concession to Apple] [2]),因此Android运行着可笑的变焦控制外表,在上边第三张图片。而不是理智的比如是一个水平的、底部对齐变焦的控制,谷歌控制它直接出现在屏幕的中间。最后一张图片显示浏览器的“window”界面,允许你打开多个网页和两者之间轻松切换。
+
+
+谷歌地图的层级部分的屏幕,搜索界面,并指示屏幕。
+照片来自@Ron Amadeo
+
+谷歌地图仍然不能使用,但我们访问的小小UI却有了显著更新。你可以挑选地图图层,虽然只有两种可以选择:卫星和交通。顶部对齐的搜索界面隐藏了奇怪的状态栏,而底部对齐方向没有隐藏状态栏。指示的输入按钮被标有“Go”,而且搜寻的输入按钮被标有一个奇怪的弯曲的箭头。这样的例子不胜枚举,并演示了老同学的Android在最坏时候的情况:在同一个应用程序,它的外观和工作方式类似的两个功能,但这些都实现为完全相反的方向。
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron是Ars Technica的评论编辑,他专注于Android操作系统和谷歌的产品。他总是在寻找一个新的小工具,喜欢分解事物来看看它们是如何工作的。
+
+[@RonAmadeo][t]
+
+-------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------
+
+via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/2/
+
+译者:[cereuz](https://github.com/cereuz)邮箱:[cereuz](mailto:sunedo@qq.com)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://i.imgur.com/GIYGTnb.jpg
+[2]:http://www.businessinsider.com/steve-jobs-on-android-founder-andy-rubin-big-arrogant-f-2013-11
+[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
+[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
diff --git a/translated/talk/What Heartbleed Teaches Us--Be An Open Source Contributor, Not Just A User.md b/translated/talk/What Heartbleed Teaches Us--Be An Open Source Contributor, Not Just A User.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 4d825204ff..0000000000
--- a/translated/talk/What Heartbleed Teaches Us--Be An Open Source Contributor, Not Just A User.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
-心脏流血教给我们的:成为开源的贡献者而不仅是个用户
-================================================================================
-
-
-> 如果你的公司依赖像OpenSSL这样的开源软件,是时候主动点了。
-
-开源社区已经官方披上了它心脏流血衬衫。
-
-ComputerWorld的Richi Jennings [抨击说][1]“又一个非常可怕的开源失败。”(骗取更多的页面浏览量?)ZDNet的Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols没有公开反对开源软件,仍旧[设法称][2]心脏流血是开源软件的最遭时刻。" 最终ZDNet的Chris Duckett务实地[恳求][3]:"公司筹集资金来避免心脏流血再次发生。"
-
-而一个好的开始,企业资金并不是心脏流血的最终答案 。你才是。
-
-想要避免开源失败的公司应该不仅仅是开源软件的用户,还要是贡献者。
-
-### 贡献者乘坐头等舱 ###
-
-贡献者帮助引导特定的项目。他们开始行动,而不只是执行。大多数企业缺乏资源参与他们所使用的所有开源项目,但每家公司都可以投资给那些真正关系到他们的项目。并且投资得越多,得到的好处越大。
-
-开源就是坚持给那些会给予反馈项目补助的礼物。
-
-我MongoDB的同事[Adam Comerford让这点更有说服力][4]:如果你看看第一批得知Heartbleed的[时间线] [5],那些第一批得知的(如谷歌)有一个相当大的优势。如Comford所说的,这些公司有一个显著的优势就是他们可以在bug还大规模未知的时候率先采取措施保护他们的系统。
-
-
-既然知道早期了解像Heartbleed问题的优势,Comerford问:“我如何确保我在这类问题的早期通知列表里面?”
-
-
-如果你依赖于专有软件,你有一个答案:向卖方支付大量的金钱,并希望他适时地响应。但是,如果你正在使用开源软件,有一个扩展选项: “要么有大量的员工给[开源项目]做贡献 ,或者...有知道主要贡献者的员工(让我们面对他,他们大多会贡献其他开源软件项目,极客和书呆子八卦像其他人一样。“
-
-Comerford断言说:”好处不止这样“
-
-> 这有很多好处 - 除了让问题及早通知,你让手头上的专家来应付这些棘手的更新,以评估你的风险,甚至可能在公众知道之前内部解决问题。在设置项目的方向上你还可以得到尊重的声音,可以有权划分关键特性的优先级。最终,你会了解社区好的意愿,有助于使大家的产品变得更好,并成为让聪明的贡献者一起工作的目标。
-
-换句话说,参与进来。成员有特权,主要的特权可能就是信息。
-
-### 选择在哪贡献 ###
-
-同样,没有一家公司有足够的资源来有效地促进所有它所使用的项目,这就是为什么Comerford建议对关键项目上这么做的原因:
-
-> 如果你要人们列出在商业中所有开源关键技术,你可能会得到一张很长的名单。现在,告诉他们,他们将不得不清点数量和预算来支持清单上的每一种技术的(并证明它) - 它可能会迅速缩水。
-
-如果你是一个AMD那样的芯片公司,给Linux内核贡献基本驱动程序和其他代码很可能是强制性的。给LibreOffice贡献可能不是。或者,如果你赌你的未来在Hadoop上进行深层数据分析,你应该贡献Hadoop,即使你选择在OpenSSL社区免费乘车。如果你是Dish Networks,它的[ CIO告诉上周在开放商业会以上的人们][6],他们正在将重要的的工作载荷,关系型数据库转到Apache的Kafka,那他最好研究Kafaka的代码,即使他不贡献给Apache HTTP服务器项目。
-
-每家公司都有其优先级,以及这些优先级必须以严肃地给开源项目提交来证明。
-
-这是确保这些项目安全的一部分办法。而另一部分,它是一种影响方向的方式。但同时,红帽公司CEO[Jim Whitehurst][7]早在2008年声明,它是显著减少IT花费的办法:
-
-> 今天编写的绝大多数软件是企业编写的,不得转售。并且绝大多数是从来没有真正使用过。IT软件开发中的浪费是巨大的....最终,开源给全世界的客户提供价值,我们不仅需要让我们的客户作为开源产品的用户,而且真正加入开源和参与在开发社区。
-
-
-Comerford坚持认为:“如果我在业务中使用开源软件,如果他们自己不是核心开发者,我应该雇核心开发人员来积极给软件做贡献。 ”这是充分利用开源软件的关键:给它做贡献,不只是使用它。
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://readwrite.com/2014/05/14/heartbleed-open-source-contribution-users
-
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://blogs.computerworld.com/encryption/23767/heartbleed-openssl-open-source-fail
-[2]:http://www.zdnet.com/heartbleed-open-sources-worst-hour-7000028420/
-[3]:http://www.zdnet.com/openssl-needs-corporate-funding-to-avoid-heartbleed-repeat-7000028385/
-[4]:http://comerford.cc/wordpress/2014/04/15/my-conclusion-heartbleed-timeline/
-[5]:http://www.smh.com.au/it-pro/security-it/heartbleed-disclosure-timeline-who-knew-what-and-when-20140415-zqurk.html
-[6]:http://blogs.wsj.com/cio/2014/05/06/dish-looks-to-open-source-software-after-database-failure/
-[7]:http://www.cnet.com/news/red-hat-solve-enterprise-waste-through-open-source/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140616 How to diskless boot a Linux machine.md b/translated/tech/20140616 How to diskless boot a Linux machine.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..eddf0d8adb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140616 How to diskless boot a Linux machine.md
@@ -0,0 +1,151 @@
+如何无盘启动Linux
+================================================================================
+无盘启动意味着一台客户端电脑在启动操作系统时没有任何的磁盘存储介质。在这种情形之下,电脑能够通过网络从远程NFS服务器上加载内核和根文件系统。在这过程中可能会用到多种不同的方法来从NFS服务器上加载内核和根文件系统:RARP,BOOTP或是DHCP协议。在这个指导教程中,我会使用BOOTP/DHCP协议,因为它们能够被大多数的网卡所支持。
+
+### 无盘计算机的优势 ###
+
+想象一下你的办公室内有30台电脑,每一台都需要使用相同的应用程序。如果你作为管理这些电脑的管理员,你会怎么做?如果你在每一台电脑上安装应用程序,那只是在浪费你的时间。另一方面来说,一套无盘系统就能解决你的问题。有了一套无盘系统,你只需在中央NFS服务器上安装需要的程序,然后通过网络启动这30台客户机即可。
+
+### 需要什么 ###
+
+两台或更多的装备有支持DHCP协议的网卡的Linux电脑。这些将扮演NFS服务器角色的电脑应当配有硬盘,其它客户机不需要任何的硬盘。服务器和客户机需要连接到同一个本地网络之内。
+
+设置一个无盘系统共需要五步。
+
+1. 安装所需的包
+1. 配置TFTP服务器
+1. 配置DHCP服务器
+1. 配置NFS服务器
+1. 启动无盘客户机
+
+在这个指导教程中,我假设作为启动服务器的电脑运行的是 Ubuntu。如何你正在使用其它的Linux发行版,原理是一样的。
+
+### 第一步:安装所需的包 ###
+
+像下面这样使用 apt-get 命令来安装所有需要的包。
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install dhcp3-server tftpd-hpa syslinux nfs-kernel-server initramfs-tools
+
+### 第二步:配置TFTP服务器 ###
+
+TFTP服务器是一个小型FTP服务器,需要用它来在本地网络中的客户机和服务器之间自动传输启动文件。
+
+向/etc/default/tftpd-hpa中添加以下行:
+
+ RUN_DAEMON="yes"
+ OPTIONS="-l -s /var/lib/tftpboot/"
+
+接着,创建一个启动文件夹。
+
+ $ sudo mkdir -p /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg
+
+复制引导程序镜像。
+
+ $ sudo cp /usr/lib/syslinux/pxelinux.0 /var/lib/tftpboot
+
+像下面这样创建一个默认启动配置文件。
+
+ $ sudo vi /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
+
+----------
+
+ LABEL Ubuntu
+ KERNEL vmlinuz
+ APPEND root=/dev/nfs initrd=initrd.img nfsroot=10.10.101.1:/nfsroot ip=dhcp rw
+
+注意:
+
+- "root=/dev/nfs"表示服务器上的网络文件系统(不需要修改)。
+- "initrd=initrd.img"是一个用于系统启动的启动脚本。
+- "nfsroot=10.10.101.1/nfsroot"指明了服务器的IP地址以及NFS共享文件夹的名称。用你的服务器地址来替换掉IP地址。
+- "ip=dhcp"表示客户端电脑使用DHCP寻址方案。
+- "rw"表示NFS共享是可读/可写的。
+
+最后,重启TFTPD服务。
+
+ sudo /etc/init.d/tftpd-hpa restart
+
+### 第三步:配置DHCP服务 ###
+
+你还需要在NFS服务器上配置DHCP服务来允许使用/var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.0启动。假设你在使用10.10.101.0作为子网,你的配置可能看起来像下面这样子。
+
+ $ sudo vi /etc/dhcp3/dhcpd.conf
+
+----------
+
+ allow booting;
+ allow bootp;
+
+ subnet 10.10.101.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
+ range 10.10.101.2 10.10.101.254;
+ option broadcast-address 10.10.101.255;
+ option routers 10.10.101.1;
+ filename "/pxelinux.0";
+ }
+
+然后重启DHCP服务。
+
+ $ sudo service isc-dhcp-server restart
+
+### 第四步:配置NFS服务器 ###
+
+创建一个保存客户机根文件系统目录的文件夹。
+
+ $ sudo mkdir /nfsroot
+
+接着,设置NFS服务器导出客户机根文件系统。向/etc/exports添加以下行来实现。
+
+ /nfsroot *(rw,no_root_squash,async,insecure,no_subtree_check)
+
+运行下列命令来重新载入修改过的/etc/exports。
+
+ $ sudo exportfs -rv
+
+默认情况下,Ubuntu在initrd镜像中不提供网络启动支持。因此你需要创建一个新的initrd.img文件。首先添加下列行到/etc/initramfs-tools/initramfs.conf中。
+
+ BOOT=nfs
+ MODULES=netboot
+
+然后运行下列命令来创建一个新的initrd.img。
+
+ $ sudo mkinitramfs -o /var/lib/tftpboot/initrd.img
+
+将新的内核镜像文件复制到/var/lib/tftpboot中。
+
+ $ sudo cp /boot/vmlinuz-`uname -r` /var/lib/tfftpboot/vmlinuz
+
+是时候将整个根文件系统拷贝到/nfsroot中了。
+
+假设您使用的是一个全新的Ubuntu服务器安装,你只需将文件系统拷贝到NFS的根之中。
+
+ $ sudo cp -ax / /nfsroot
+
+然后通过文本编辑器打开/nfsroot/etc/fstab 并添加以下行。
+
+ /dev/nfs / nfs defaults 1 1
+
+文件夹/var/lib/tftpboot应拥有全局读写权限。否则客户机无法从网络启动。
+
+ $ sudo chmod -R 777 /var/lib/tfftpboot
+
+最后,为了避免任何服务器设置出现错误,我推荐对运行DHCP服务的网卡使用静态IP。举个例子,如果网卡名为eth0,你的/etc/network/interfaces中的配置应该看起来像这样:
+
+ iface eth0 inet static
+ address 10.10.101.1
+ netmask 255.255.255.0
+ broadcast 10.10.101.255
+ network 10.10.101.0
+
+### 第五步:启动无盘客户机 ###
+
+在您完成了服务器上的配置之后,从网络启动你的客户机。要从网络启动一般你只需修改BIOS设置中的启动优先顺序即可。
+
+如果客户机启动成功,您的无盘环境就配置好了。无需做任何修改就可以任意添加一台或多台客户端电脑。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/06/diskless-boot-linux-machine.html
+
+译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140620 11 Advance MySQL Database 'Interview Questions and Answers' for Linux Users.md b/translated/tech/20140620 11 Advance MySQL Database 'Interview Questions and Answers' for Linux Users.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9b95a5e4b2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140620 11 Advance MySQL Database 'Interview Questions and Answers' for Linux Users.md
@@ -0,0 +1,200 @@
+给linux用户的11个高级MySQL数据库面试问题和答案
+================================================================================
+我们已经发表了两篇MySQL的文章,非常感谢Tecmint社区的大力支持.这是MySQL面试系列的第三篇文章,并且在面试专栏中排第16.
+- [15个基本的MySQL面试问题][1]
+- [给中级人员的10个MySQL面试问题][1]
+
+
+
+感谢你们这一路上对我们的支持.这篇文章主要针对MySQL的实用性,讲面试方面的问题.
+
+### 1. 如何使用SELECT语句找到你正在运行的服务器的版本并打印出当前数据库的名称? ###
+**Ans**:下面的语句的结果会显示服务器的版本和当前的数据库名称
+
+ mysql> SELECT VERSION(), DATABASE();
+
+ +-------------------------+------------+
+ | VERSION() | DATABASE() |
+ +-------------------------+------------+
+ | 5.5.34-0ubuntu0.13.10.1 | NULL |
+ +-------------------------+------------+
+ 1 row in set (0.06 sec)
+
+在Database一栏中显示**NULL**是因为我们当前没有选择任何数据库.因此,使用下面的语句先选择一个数据库,就能看到相应的结果.
+
+ mysql> use Tecmint;
+
+ Reading table information for completion of table and column names
+ You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
+
+ Database changed
+
+----------
+
+ mysql> select VERSION(), DATABASE();
+
+ +-------------------------+------------+
+ | VERSION() | DATABASE() |
+ +-------------------------+------------+
+ | 5.5.34-0ubuntu0.13.10.1 | tecmint |
+ +-------------------------+------------+
+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
+
+### 2. 使用非运算符(!)从表"Tecmint"中列出除了user等于"SAM"的所有记录
+
+**Ans**:使用下面的语句
+
+ mysql> SELECT * FROM Tecmint WHERE user !=SAM;
+
+ +---------------------+---------+---------+---------+---------+-------+
+ | date | user | host | root | local | size |
+ +---------------------+---------+---------+---------+---------+-------+
+ | 2001-05-14 14:42:21 | Anthony | venus | barb | venus | 98151 |
+ | 2001-05-15 08:50:57 | TIM | venus | phil | venus | 978 |
+ +---------------------+---------+---------+---------+---------+-------+
+
+### 3. 是否能够使用非运算符(!)来实现'AND'运算
+
+**Ans**: 我们使用’=’号和OR运算符或者'!='和AND运算符,下面是'='和AND运算符的例子
+
+ mysql> SELECT * FROM mail WHERE user = SAM AND root = phil
+
+'!='和OR运算符的例子
+
+ mysql> SELECT * FROM mail WHERE user != SAM OR root != phil
+
+ +---------------------+---------+---------+---------+---------+-------+
+ | date | user | host | root | local | size |
+ +---------------------+---------+---------+---------+---------+-------+
+ | 2001-05-14 14:42:21 | Anthony | venus | barb | venus | 98151 |
+ +---------------------+---------+---------+---------+---------+-------+
+
+- = : 等于
+- != : 不等于
+- ! : 非运算符
+
+AND和OR在MySQL中被看作加入运算符
+
+### 4. IFNULL()语句在MySQL中有什么作用? ###
+
+**Ans**: **IFNULL**语句的使用使得MySQL中的查询更加精确。IFNULL()语句先测试它的的一个参数,若不为空就返回该参数的值,否则返回第二个参数的值
+
+ mysql> SELECT name, IFNULL(id,'Unknown') AS 'id' FROM taxpayer;
+
+ +---------+---------+
+ | name | id |
+ +---------+---------+
+ | bernina | 198-48 |
+ | bertha | Unknown |
+ | ben | Unknown |
+ | bill | 475-83 |
+ +---------+---------+
+
+### 5. 如果你只想知道从一个结果集的开头或者结尾开始的特定条数的行记录改如何实现?
+
+**Ans**: 我们可以用**LIMIT**和**ORDER BY**从句。
+
+#### 显示一行记录 ####
+
+ mysql> SELECT * FROM name LIMIT 1;
+
+ +----+------+------------+-------+----------------------+------+
+ | id | name | birth | color | foods | cats |
+ +----+------+------------+-------+----------------------+------+
+ | 1 | Fred | 1970-04-13 | black | lutefisk,fadge,pizza | 0 |
+ +----+------+------------+-------+----------------------+------+
+
+#### 显示5行记录 ####
+
+ mysql> SELECT * FROM profile LIMIT 5;
+
+ +----+------+------------+-------+-----------------------+------+
+ | id | name | birth | color | foods | cats |
+ +----+------+------------+-------+-----------------------+------+
+ | 1 | Fred | 1970-04-13 | black | lutefisk,fadge,pizza | 0 |
+ | 2 | Mort | 1969-09-30 | white | burrito,curry,eggroll | 3 |
+ | 3 | Brit | 1957-12-01 | red | burrito,curry,pizza | 1 |
+ | 4 | Carl | 1973-11-02 | red | eggroll,pizza | 4 |
+ | 5 | Sean | 1963-07-04 | blue | burrito,curry | 5 |
+ +----+------+------------+-------+-----------------------+------+
+
+#### 显示按照ORDER BY排序后的第一条记录 ####
+
+ mysql> SELECT * FROM profile ORDER BY birth LIMIT 1;
+
+ +----+------+------------+-------+----------------+------+
+ | id | name | birth | color | foods | cats |
+ +----+------+------------+-------+----------------+------+
+ | 9 | Dick | 1952-08-20 | green | lutefisk,fadge | 0 |
+ +----+------+------------+-------+----------------+------+
+
+### 6. Oracle 和 MySQL该如何选择? ###
+
+**Ans**: 它们都有各自的优点和缺点。
+
+#### 选择MySQL而不选orcale的原因 ####
+
+- 开源
+- 轻便快捷
+- 有命令行和图形界面
+- 能通过查询器进行数据库的管理
+
+### 7. MySQL中如何得到当前日期? ###
+
+**Ans**: 使用CURRENT_DATE()函数
+
+ mysql> SELECT CURRENT_DATE();
+
+ +----------------+
+ | CURRENT_DATE() |
+ +----------------+
+ | 2014-06-17 |
+ +----------------+
+
+### 8. MySQL中如何将表导出为XML文件? ###
+
+**Ans**: 使用'-e'(export)参数来把MySQL表或整个数据库导出到XML文件。当处理大型表的时候或许我们需要手动导出,但是只是导出小文件的话可以直接使用想phpMyAdmin这样的工具。
+
+ mysql -u USER_NAME –xml -e 'SELECT * FROM table_name' > table_name.xml
+
+上面的例子中USER_NAME是数据库的用户名,table_name是待导出为xml文件的表名,table_name.xml是存放数据的xml文件
+
+### 9. MySQL_pconnect是什么? 它和MySQL_connect有什么区别? ###
+
+**Ans**: MySQL_pconnect()打开一个永久的数据库连接,这意味着数据库不是在每次页面加载的时候被打开,因此我们不能使用MySQL_close()来关闭一个永久的连接
+
+MySQL_pconnect和MySQL_connect有一定的差别
+
+和MySQL_pconnect不同,MySQL_connect在每次页面被加载的时候打开,并且可以使用MySQL_close()语句来关闭连接
+
+### 10. 如何查看一个名为'mysql'的数据库中'user'表中的所有索引? ###
+
+**Ans**: 可以使用下面的语句
+
+ mysql> show index from user;
+ +-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
+ | Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+ +-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
+ | user | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | Host | A | NULL | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
+ | user | 0 | PRIMARY | 2 | User | A | 4 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
+ +-------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
+
+### 11. 什么是CSV表? ###
+
+**Ans**: CSV是逗号分隔值的缩写,也称为字符分隔值。CSV表中存放纯文本和表格数据。
+
+每一条记录使用具体的分隔符隔开(如逗号,分号,...),CSV表广泛的用来存放易于导入和导出的电话联系人,能够用来存放任何数量的纯文本。
+
+以上就是这次要将的内容。我还会带来其他的有趣的文章,向往你们喜欢。连接到Tecmint继续关注我们,不要忘了在评论栏中留下你们的宝贵意见。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/mysql-advance-interview-questions/
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/basic-mysql-interview-questions-for-database-administrators/
+[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-mysql-database-interview-questions-for-beginners-and-intermediates/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140624 Super Pi Brothers.md b/translated/tech/20140624 Super Pi Brothers.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..46630e216c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140624 Super Pi Brothers.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+超级树莓派兄弟
+================================================================================
+我已经不象以前那样玩那么多游戏了。虽然之前我当然花费了生命里的无数时间在任天堂,SNES,或是之后在我电脑上的第一人称射击游戏(只在Linux下,谢谢),如今,我更愿意把空余时间花在我累积起来的许多其他非游戏爱好上。但是最近,我发现自己又抹掉了Wii手柄上的灰尘,这样就可以玩一玩我重新购买的NES和SNES游戏了。不过问题是,这些游戏需要用到一些特别的控制器,而且我已经有一个修改过的SNES控制器可以通过USB连接。这已经有足够的理由让我去寻找一个更合适的方案。当然,我也可以简单地接上三个甚至四个手柄,然后在客厅里面堆满游戏。但是我已经习惯于把我的CD和DVD都提取成文件,然后在中心媒体服务器上挑选着听或是看。所以如果每次我想换游戏的时候,不用起身去翻游戏卡带,那就完美了。当然,这意味着得使用模拟器。尽管之前我在一个改动过的Xbox上成功过,不过可惜它已经不在我手上了。然后我觉得一定有什么人已经在树莓派上实现过这种平台,结果是肯定的,在简单地搜索和一些命令之后,我在一个剩下的树莓派上搭起来一个完美的怀旧游戏中心。
+
+树莓派项目的一个优点是,有大量的用户在使用相同的硬件。对我来说,这意味着我不用完整地参考别人的指引再根据自己的需求做出必要的改动,而只需要简单地完全按照别人的指导做就行了。在我这件事情上,我找到了RetroPie项目,它把你安装时需要用到的所有命令都包到了一个单一的大脚本中。在执行完后,你就完整地安装并配置好了RetroArch,它集成了所有的主流模拟器以及一个统一的配置方式,再加上一个在树莓派上开机启动的EmulationStation图形界面,通过它可以只用手柄就能方便地定位到你想玩的游戏。
+
+### 安装RetroPie ###
+
+在安装RetroPie之前,你可能需要确认一下你的Raspbian版本(树莓派默认的Linux发行版,这也是这个项目假设你在用的)是不是最新的,包括有没有新的固件。这只需要几个通用的`apt`命令。虽然,在这一步里你当然可以接个键盘到树莓派上,不过我觉得用`ssh`登录到树莓派上更方便。之后直接复制和粘贴下面的命令:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get -y upgrade
+
+现在树莓派已经更新到最新了,再确认一下是否安装了git和dialog,然后可以通过git来下载RetroPie:
+
+
+ $ sudo apt-get -y install git dialog
+ $ cd
+ $ git clone --depth=0
+ ↪git://github.com/petrockblog/RetroPie-Setup.git
+
+执行完上边的命令后会创建一个RetroPie-Setup目录,里面有主要的安装脚本。之后你只需要进去这个目录,并运行安装脚本:
+
+ $ cd RetroPie-Setup
+ $ chmod +x retropie_setup.sh
+ $ sudo ./retropie_setup.sh
+
+这个脚本会在终端里显示一个菜单(图1),在里面你可以选择二进制安装或是源码安装,配置RetroPie,或是更新RetroPie安装脚本和执行文件。之后选择二进制安装或是源码安装,任选一个。二进制安装会快一些,不过有些软件版本可能不是最新的。源码安装需要编译软件,所以用的时间会比较长,但是完成之后,所有的一切都是最新版的。我个人会选择二进制安装,因为我知道在碰到任何问题之后,随时都可以重新执行这个脚本再选择源码安装。
+
+
+
+#### 图1. RetroPie安装菜单 ####
+
+在vanilla Raspbian固件版本中,这一步会需要很长时间,因为有大量不同的包需要下载和安装。在安装完成之后,返回在RetroPie安装主界面中,在主菜单里选择SETUP,在之后的二级菜单里,你可以调整设置,例如是否开机启动EmulationStation(推荐打开)以及是否允许欢迎界面。在我这里,我两个都允许了,因为我希望这个设备是一个独立的模拟游戏机。不过你需要了解的是,如果你确实允许了EmulationStation开机自动启动,你仍然可以ssh登录到机器上然后执行原始的RetroPie安装配置脚本来改变这个设置。
+
+### 添加ROM ###
+
+你也可以在RetroPie设置界面添加ROM。如果你在菜单里选择了Samba方式,就可以在网络上找一个Samba共享目录,然后从里面拷贝ROM。如果通过U盘的方式,RetroPie会在插到树莓派的U盘上创建一个目录结构,分别对应不同的模拟器。在这之后,你就可以把U盘插到其他电脑上,然后把ROM拷贝到合适的目录里,当再插回树莓派的时候,它会自动同步文件。最后(我就是这么做的),你还可以使用scp或者rsync来拷贝ROM到~/RetroPie/roms/的合适目录下。举个例子,NES游戏需要拷贝到~/RetroPie/roms/nes/目录里。
+
+当你完成了配置并退出了RetroPie的设置脚本后,应该会想重启并进入EmulationStation,但是在那之前,你应该重新配置树莓派的内存空间,设为192或者128,运行命令:
+
+
+ $ sudo raspi-config
+
+然后选择高级设置,调整内存空间设定。之后就可以安全地重启了。
+
+### EmulationStation ###
+
+重启完之后,当看到EmulationStation界面时应该会很高兴,之后它会提示你设定控制杆,游戏手柄,或键盘按键,这样就可以控制EmulationStation菜单了。不过注意一下,这并不会影响手柄在游戏里的按键定义,只是用于控制EmulationStation菜单的。在设定完手柄后,你应该可以按下向右或向左方向键来切换不同的模拟器菜单了。在我这里,我将会在游戏里用到手柄上的所有按钮,所以我特别将另一个键盘上的键映射到菜单功能,这样在我玩完一个游戏后,不用重启树莓派就可以退出来。
+
+EmulationStation只会显示已经侦测到ROM的模拟器,所以,如果你还没有拷贝ROM的话,得先做这件事情,然后可能还得重启一下才会有效果。而且,默认情况下,你的手柄没有为任何游戏做配置,但是,如果你在EmulationStation里一直按向右键足够多次以后,会弹出输入设定界面,你可以在里面映射手柄按键。有一个亮点是,当你设定好按键后,它会相应地应用到其他模拟器中。
+
+就是这些了。在这之后,你可以浏览你收藏的各种游戏,然后按下绑定到确定的那个按键开始游戏。一开始我还担心树莓派可能不够强劲来玩我的游戏,但是直到现在,我试过地所有游戏都可以完美地运行。
+
+### 资源 ###
+
+RetroPie项目主页:[http://blog.petrockblock.com/retropie][1]
+
+RetroPie安装文档:[https://github.com/petrockblog/RetroPie-Setup][2]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/super-pi-brothers
+
+译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://blog.petrockblock.com/retropie
+[2]:https://github.com/petrockblog/RetroPie-Setup
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140702 How to install Raspberry Pi camera board.md b/translated/tech/20140702 How to install Raspberry Pi camera board.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..3ce4315ad5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140702 How to install Raspberry Pi camera board.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+如何安装树莓派摄像头模块
+==============================================================================
+[树莓派摄像头模块(Pi Cam)][1]发售于2013年5月。在首发时,Pi Cam配备了500万像素的传感器,通过排线链接树莓派上的CSI接口。第二次发布时,Pi Cam改名为[Pi NoIR][2]并配备了相同的传感器,不同之处在于第二版摄像头模块没有红外线过滤装置。因此使用第二版的摄像头模块可以观测到近红外线的波长(700 - 1000 nm),如同一个安全监控摄像机一样,当然实现红外线的感应牺牲了传感器的显色性。
+
+本文将会展示**如何在[树莓派][3]上安装摄像头模块**。我们会使用第一版摄像头模块来演示。在安装完摄像头模块之后,你将会使用三个应用来访问这个模块:raspistill, raspiyuv 和raspivid。其中前两个应用用来捕捉图像,第三个应用来捕捉视频。raspistill 工具会生成标准的图片文件例如 .jpg 图像,但是 raspiyuv 可以通过摄像头生成未处理的 raw 图像文件。
+
+### 安装树莓派摄像头模块 ###
+
+按照以下指示来安装树莓派摄像头模块:
+
+1. 找到 CSI 接口(CSI接口在以太网接口旁边),掀起深色胶带。
+
+2. 拉起 CSI 接口挡板。
+
+3. 将摄像头模块贴在透镜上的塑料保护膜撕掉。确保黄色部分的PCB(有字的一面)是安装完美的。
+
+4. 将排线插入CSI接口。记住,有蓝色胶带的一面应该面向以太网接口方向。在检查排线安装好了之后,将挡板拉下。
+
+
+
+好了,现在你的 Pi Cam 已经准备就绪来拍摄相片以及视频了。
+
+### 在树莓派上启用摄像头模块 ###
+
+在安装完摄像头模块之后,确认你已经升级了树莓派系统并应用了最新的固件。输入以下命令来更新:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get upgrade
+
+运行树莓派配置工具来激活摄像头模块:
+
+ $ sudo raspi-config
+
+移动光标至菜单中的 "Enable Camera",确认启用。完成之后重启树莓派。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+安装完摄像头模块后的完成照:
+
+
+
+### 通过摄像头模块拍照 ###
+
+在重启完树莓派后,我们就可以使用它了。输入以下命令通过摄像头模块拍摄照片:
+
+ $ raspistill -o keychain.jpg -t 2000
+
+这句命令会在执行 2000ms 之后捕捉图像。然后保存为 keychain.jpg。下面是一张由 下面是一张由 Pi Cam 拍摄的钥匙链。
+
+
+
+raspivid 工具用法差不多,从命令行运行 raspivid 工具。下面这句命令会按照默认配置(5秒,分辨率1920x1080,比特率 17Mbps)拍摄一段视频。
+
+ $ raspivid -o mykeychain.h264
+
+如果你想改变拍摄时长,只要通过 "-t" 选项来设置长度就行了。
+
+ $ raspivid -o mykeychain.h264 -t 10000
+
+使用 "-w" 和 "-h" 选项将分辨率降为 1280x720...
+
+ $ raspivid -o mykeychain.h264 -t 10000 -w 1280 -h 720
+
+raspivid 的输出是一段未压缩的 H.264 视频流,而且这段视频没有声音。因此这段视频需要转换在能被通常的视频播放器所播放。使用 gpac 包中所带有的 MP4Box 应用。
+
+在 Raspbian 上安装 gpac,输入命令:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install -y gpac
+
+然后将这段 raw 的 H.264 格式的视频流转换为30帧每秒的 .mp4 格式视频:
+
+ $ MP4Box -fps 30 -add keychain.h264 keychain.mp4
+
+视频长度为10秒,默认分辨率以及比特率。下面是一段通过 Pi Camera 拍摄的一段实例视频。
+
+注:youtube视频地址
+
+
+
+如果想要看到 raspistill, raspiyuv 和 raspivid 的完整命令行选项,直接运行以上命令(不加选项)就行了。
+
+
+----------------
+
+### [Kristophorus Hadiono][a] ###
+
+我是一个 Linux 爱好者。我在日常生活中使用 Linux,甚至在我给学生们教学的时候。我的梦想是成为一名优秀的作家。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/install-raspberry-pi-camera-board.html
+
+译者:[ThomazL](https://github.com/ThomazL) 校对:[校对者id](https://github.com/校对者id)
+
+本文由 [lctt](https://github.com/lctt/translateproject) 原创翻译,[linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/go/picam
+[2]:http://xmodulo.com/go/pinoir
+[3]:http://xmodulo.com/go/raspberrypi
+[a]:http://hadiono.org/blog
+
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140709 How to set up two-factor authentication for SSH login on Linux.md b/translated/tech/20140709 How to set up two-factor authentication for SSH login on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ac11963fbd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140709 How to set up two-factor authentication for SSH login on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+如何为Linux系统中的SSH添加双重认证
+================================================================================
+近来很多知名企业都出现了密码泄露,业内对多重认证的呼声也越来越高。在这种多重认证的系统中,用户需要通过两种不同的认证程序:提供他们知道的信息(如 用户名/密码),再借助其他工具提供用户所不知道的信息(如 用手机生成的一次性密码)。这种组合方式常叫做双因子认证或者两阶段验证。
+为了鼓励广泛采用双因子认证的方式,Google公司发布了[Google Authenticator][1],一款开源的,可基于开放规则(如 HMAP/基于时间)生成一次性密码的软件。这是一款跨平台软件,可运行在Linux, [Android][2], [iOS][3]。Google公司同时也支持插件式鉴别模块PAM(pluggable authentication module),使其能和其他也适用PAM进行验证的工具(如OpenSSH)协同工作。
+在本教程中,我们将叙述集成OpenSSH和Google提供的认证器实现**如何为SSH服务设置双因子认证**。我将使用一款[Android][4]设备来生成一次性密码,本教程中需要两样兵器:(1)一台运行着OpenSSH服务的Linux终端,(2)一台安卓设备。
+### 在Linux系统中安装Google Authenticator ###
+
+第一步需要在运行着OpenSSH服务的Linux主机上安装Google认证器。按照[安装指南] [5]的步骤安装Google认证器及其PAM模块。
+当Google认证器安装好后,你需要在Linux主机上创建验证密钥,并且在安卓设备上注册,注意这项配置操作是一次性的。我们将详细叙述如何完成这些操作:
+### 生成验证密钥 ###
+
+在Linux主机上运行Google认证器
+ $ google-authenticator
+
+你将看到一个QR码,它使用图形保存了我们数字形态的密钥。一会我们要用到它在安卓设备上完成配置。
+
+
+
+Google认证器会问一些问题,如果你不确定,就回答"Yes"。这个应急备用验证码(图中 emergency scratch codes)可以在你丢失被绑定的安卓设备的情况下恢复访问,并且设备也不再生成一次性密码。所以最好将应急备用验证码妥善保存。
+### 在安卓设备上运行Google认证器 ###
+
+我们需要在安卓设备上安装[Google Authenticator app][6]才能完成双因子认证,到Google Play下载并安装一个。在安卓设备上运行Google认证器,找到下图所示中的配置菜单。
+
+
+你可以选择"Scan a barcode" 或者"Enter provided key"选项。"Scan a barcode"允许你扫描QR码来完成密钥的输入,在此可能需要先安装扫描软件[Barcode Scanner app][7]。如果选择"Enter provided key"选项,你可以使用键盘输入验证密钥,如下图所示:
+
+
+无论采用上述两种选项的任何方式,一旦成功,你将看到注册成功提示和一次性密码,如下图所示:
+
+
+### 为SSH服务器用Google认证器 ###
+
+最终我们需要修改两个文件来完成集成Google认证器和OpenSSH服务这临门一脚。
+首先,修改PAM配置文件,命令和需添加的内容如下:
+ $ sudo vi /etc/pam.d/sshd
+
+----------
+
+ auth required pam_google_authenticator.so
+
+然后打开SSH配置文件,找到参数ChallengeResponseAuthentication,并启用它。
+ $ sudo vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
+
+----------
+
+ChallengeResponseAuthentication yes
+
+
+最后,重启SSH服务。
+在 Ubuntu, Debian, Linux Mint:
+
+ $ sudo service ssh restart
+
+在Fedora:
+
+ $ sudo systemctl restart sshd
+
+在CentOS 或 RHEL:
+
+ $ sudo service sshd restart
+
+### 验证双因子认证 ###
+
+在绑定的安卓设备上运行Google认证器,获得一个一次性验证码,该验证码30秒内有效,一旦过期,将重新生成一个新的验证码。
+
+
+现在和往常一样,使用SSH登录终端
+ $ ssh user@ssh_server
+
+当提示你输入验证码的时候,输入我们刚获得的验证码。验证成功后,再输入SSH的登录密码。
+
+
+双因子认证通过在用户密码前新增一层来有效的保护我们脆弱的用户密码。你可以使用Google认证器来保护我们其他的密码,如Google账户, WordPress.com, Dropbox.com, Outlook.com等等。是否使用这项技术,取决于我们自己,但采用双因子认证已经是行业的大趋势了。
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/two-factor-authentication-ssh-login-linux.html
+
+译者:[nd0104](https://github.com/nd0104) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://code.google.com/p/google-authenticator/
+[2]:https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.google.android.apps.authenticator2
+[3]:https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/google-authenticator/id388497605
+[4]:http://xmodulo.com/go/android_guide
+[5]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-google-authenticator-linux.html
+[6]:https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.google.android.apps.authenticator2
+[7]:https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.google.zxing.client.android
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140711 How To Enable Tab Complete Heroku Commands In Oh-My-Zsh.md b/translated/tech/20140711 How To Enable Tab Complete Heroku Commands In Oh-My-Zsh.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..b2cf8281aa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140711 How To Enable Tab Complete Heroku Commands In Oh-My-Zsh.md
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+如何在Oh-My-Zsh中启用Heroku命令tab按键补全功能
+================================================================================
+**Heroku**客户端是创建和管理Heroku应用的命令行界面工具。
+
+需求:
+
+- Heroku toolbelt
+- Oh-My-Zsh ([如何安装][1])
+
+本文不是讲关于hereku的知识,也不是讲关于heroku的使用细节,而是仅仅展示给用户他们怎样可以使用oh-my-zsh来方便地敲写命令。此外你还应该安装[heroku toolbelt][2]来进行本文的相应的操作。对于Ubuntu和Debian发行版,你可以通过运行下面的命令来安装:
+
+ wget -qO- https://toolbelt.heroku.com/install-ubuntu.sh | sh
+
+打开终端,用你在[这里]创建的用户登陆heroku:
+
+ heroku登陆
+ 输入您的Heroku认证。
+ 邮箱: enockseth@unixmen.com
+ 密码 (您的输入会被隐藏):
+ 认证成功。
+
+这显示heroku正在运行。
+
+使用你喜欢的文本编辑器打开**.zshrc**:
+
+ vim .zshrc
+
+
+
+git是唯一默认启用的插件。
+
+在下图显示的插件选择区添加**heroku**:
+
+
+
+重启终端,输入**heroku**,按下tab键,到此就搞定啦:
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/enable-tab-complete-heroku-commands-oh-zsh/
+
+译者:[JonathanKang](https://github.com/JonathanKang) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/install-oh-zsh-ubuntu-arch-linux-fedora/
+[2]:https://toolbelt.heroku.com/
+[3]:https://www.heroku.com/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140711 How to Install Lightweight Budgie Desktop in Ubuntu 14.04.md b/translated/tech/20140711 How to Install Lightweight Budgie Desktop in Ubuntu 14.04.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..af3e97bb4f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140711 How to Install Lightweight Budgie Desktop in Ubuntu 14.04.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+怎样在ubuntu 14.04上安装轻量级的Budgie桌面
+================================================================================
+**如果你在推特上关注了我们,你可能看见了我们最近分享的一张截图,和这张截图一起的还有对它所展示的桌面进行命名的邀请。 **
+
+你猜对了吗? 答案就是budgie —— 一种为基于openSUSE 的linux发行版Evolve OS所设计,但不仅仅只能用于 Evolve OS的简易桌面环境。
+
+
+
+我们第一次描写Budgie是在三月份,当时我们被它的整洁,小巧的美感,灵活的架构,还有重复使用在当今大多数发行版中所使用的GNOME 3.10 成熟技术中的公共部分和标堆栈的决定所折服。
+
+我对此项目的领导者LKey Doherty所作出的开发选择非常佩服。无可否认另起炉灶有它的优点,但决定从上游的项目获取帮助将可以整个项目进展得更快,无论是在发展方面(更轻的技术负担)还是在用户可使用方面(更容易在其它发行版上运行)。
+
+政治因素选择除外,这款桌面以干净,小巧向谷歌Chrome OS的Ash桌面表示敬意。如果你不介意有些许粗糙的边缘,那它值得你玩玩。那么怎样在Ubuntu安装Budgie呢?
+
+###非官方的PPA是不正式的 ###
+
+开源意味着如果你有一点终端使用知识的话,你就可以在获得Budgie桌面的源代码后进行编译,然后运行。
+
+但如果你很懒,想不费周折就在Ubuntu 14.04 LTS(或者一个基于它的发行版)运行Budgie,那么你可以通过比较容易的途径来实现。
+
+添加一个非官方的Unofficial PPA,刷新你的软件源然后进行安装。几分钟后在这个家庭中你将有一位名叫Bob的新叔叔,并且有一个新的桌面可以玩耍。
+
+###添加Budgie PPA ###
+
+将以下命令复制进一个打开的终端窗口,在提示过后输入你的密码(如果需要的话)
+
+ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:sukso96100/budgie-desktop
+ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install budgie-desktop
+
+### 登入Budgie会话 ###
+
+安装完成后你就可以在Unity欢迎界面的会话选择器中选择Budgie会话了。(别忘了以后要把选择项改回到稳定的桌面环境)
+
+### 注意 ###
+
+**budgie是不稳定,不完善的,它在Ubuntu上也没有被正式支持。它正在积极开发中,缺少一些特性,包括(但不仅仅只有这些):不支持网络管理,没有音量控制小程序(键盘工作良好),没有通知系统,无法将应用程序“固定”在任务栏。**
+
+它对UBUNTU的叠加滚动条和一些GTK主题的支持也不是很好,而且在使用upstart的发行版(例如ubuntu,即使它正在改变之中)中会话管理器(例如,注销,重启等等)将无法工作。
+
+一个应变方法是:禁用叠加滚动条,设置一个默认主题,通过在终端中使用以下命名来退出会话。
+
+ gnome-session-quit
+
+想着脑海中所有的这些警告,我建议想使用稳定的,可靠的系统的人现在暂时不要使用它。
+
+而作为狂热一族的业余体验呢?请在下面评论,让我们了解你的想法。我将退出而让Bob来接手。
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/install-budgie-evolve-os-desktop-ubuntu-14-04
+
+译者:[Love-xuan](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/03/budgie-desktop-chrome-os-like
+[2]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bob
+[3]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/02/ubuntu-debian-switching-systemd
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140711 How to simulate key press and mouse movement in Linux.md b/translated/tech/20140711 How to simulate key press and mouse movement in Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c7d9906f21
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140711 How to simulate key press and mouse movement in Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,131 @@
+在Linux中模拟击键和鼠标移动
+================================================================================
+你是否曾经拥有一个梦
+ ——你的计算机
+ 可以自动为你干活?
+或许,并非因为
+ 你刚看了终结者。
+然而,除此之外
+ 脚本和任务自动化
+ 是每个高级用户追寻的梦
+如果今天
+ 有许多的解决方案
+ 可以满足这个目标
+那么
+ 有时候
+ 就难以从那众多之中采撷那
+ 简洁、聪明而又高效的一个
+我
+ 不能假装
+ 是我自己发现了它
+而与此同时
+ 却偏爱着那个
+ 整洁的软体——xdotool
+其方法是如此直观
+ 正如它作为X11自动化工具的表露
+转换思想
+ xdotool可以通过读取文本文件
+ 模拟击键的旋律
+ 以及鼠标的曼舞
+
+
+### 让Xdotool在Linux定居 ###
+对于Ubuntu,Debian或者Linux Mint,你能够只做:
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install xdotool
+
+对于Fedora,请使用yum命令:
+
+ $ sudo yum install xdotool
+
+对于CentOS用户,可以在[EPEL repo][1]中找到该包。在启用EPEL仓库后,只要使用上面的yum命令就可以达成你的愿望。
+
+对于Arch用户,可在Community仓库中找到该包:
+
+ $ sudo pacman -S xdotool
+
+如果你还是找不到你的发行版的对应xdotool,你可以从它的[官方站点][2]下载。
+
+### Xdotool基本功 ###
+
+虽然xdotool是那样的直观,但它仍然是个脚本程序。因此,为了要正确地使用它,你还是得了解它的语法。不过敬请放心,相对于程序的功能而言,语法还是比较简单易学的。
+
+首先,模拟击键是很容易的。你可以从终端敲入下面的命令:
+
+ $ xdotool key [name of the key]
+
+如果你想要连接两个键,可以在它们之间使用“+”操作符。它看起来像这样:
+
+ $ xdotool key alt+Tab
+
+这两个组合键可以为你切换窗口。
+
+要想让xdotool帮你输入,可以使用以下命令:
+
+ $ xdotool type ''
+
+这些对于基本的击键而言已经足够了。但是,xdotool的众多长处之一,就是它可以获取特定窗口的焦点。它可以获取右边的窗口,然后在里面输入,同时阻止所有你记录的按键,让那些动作随风而逝吧。要获得该功能,一个简单的命令可以搞定:
+
+ $ xdotool search --name [name of the window] key [keys to press]
+
+该命令将在打开的窗口中搜索对应名称的窗口,并聚焦于该窗口,然后模拟击键。
+
+来点更高级的,但很有用哦,xdotool可以模拟鼠标移动和点击,看这命令:
+
+ $ xdotool mousemove x y
+
+你可以将光标定位到屏幕坐标(x,y)(像素)。你也可以使用“click”参数来组合:
+
+ $ xdotool mousemove x y click 1
+
+这会让鼠标移动到(x,y),然后点击鼠标左键。“1”代表鼠标左键,“2”则是滚轮,“3”则是右键。
+
+最后,一旦你这些命令根植于你脑海,你也许想要实际转储于文件来编辑并试着玩玩。鉴于此,就会有超过一个语句以上的内容了。你可以写的就是一个bash脚本了:
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+
+ xdotool [command 1]
+ xdotool [command 2]
+ etc
+
+或者你可以使用:
+
+ $ xdotool [filename]
+
+这里你将命令写入到一个独立的文件中,然后通过将文件名作为xdotool命令的参数。
+
+### 意外收获 ###
+
+作为本文的一个意外收获,这里是xdotool的一个具体实例。你可能听说过,也可能没听说过Bing,微软的搜索引擎。在后面的实例中,你从没听过Bing奖励吧:一个程序,可以让你用Bing积分兑取亚马逊的礼物卡和其它的一些礼物卡。要赚取这些积分,你可以每天在Bing上搜索累计达30次,每次搜索你都会获得0.5个积分。换句话说,你必须把Bing设为默认搜索引擎,并每天使用它。
+
+或者,你可以使用xdotool脚本,在这个脚本中,会自动聚焦到Firefox(你可以用你喜欢的浏览器来取代它),并使用fortune命令生成一些随机单词来实施搜索。大约30秒之内,你的日常搜索任务就完成了。
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+
+ for i in {1..30}
+ do
+ WID=`xdotool search --title "Mozilla Firefox" | head -1`
+ xdotool windowfocus $WID
+ xdotool key ctrl+l
+ xdotool key Tab
+ SENTENCE="$(fortune | cut -d' ' -f1-3 | head -1)"
+ xdotool type $SENTENCE
+ xdotool key "Return"
+ sleep 4
+ done
+
+
+下面来个小结吧:我真的很喜欢xdotool,即便它完整功能超越了本文涵盖的范围。这对于脚本和任务自动化而言,确实是种平易的方式。负面的问题是,它可能不是最有效率的一个。但我要再说一遍,它忠于职守了,而且学习起来也不是那么麻烦。
+
+你对xdotool怎么看呢?你是否更喜欢另外一个自动化工具,而不是它呢?为什么呢?请在评论中告诉我们吧。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/simulate-key-press-mouse-movement-linux.html
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
+[2]:http://www.semicomplete.com/projects/xdotool/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140714 Fix No Sound In Ubuntu 14.04 As HDMI Enabled BY Default.md b/translated/tech/20140714 Fix No Sound In Ubuntu 14.04 As HDMI Enabled BY Default.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5c1c39b23c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140714 Fix No Sound In Ubuntu 14.04 As HDMI Enabled BY Default.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+Ubuntu 14.04中修复默认启用HDMI后没有声音的问题
+================================================================================
+
+声音问题在Ubuntu中是老生常谈了。先前我已经在[修复Ubuntu中的“无声”问题][1]一文中写到了多种方法,但是我在此正要谈及的声音问题跟在另外一篇文章中提到的有所不同。
+
+因此,我安装了Ubuntu 14.04,实际上是重新安装了一遍。一如既往,我将[全新安装Ubuntu 14.04后要做的事][2]全部又重新做了一遍。然后,我意识到系统突然失声了。当我正侦查问题所在之时,我发现了一件奇怪的事情。我检查了[alsamixer][3],发现它的状况有点离奇。
+
+
+
+正如你能看到的,**alsamixer中默认设置了HDMI**。这意味着默认情况下将使用HDMI输出,而不是内置扬声器。这就是我从系统上内置扬声器无法获得声音的原因。
+
+使用下面的命令来检查alsamixer的状态:
+
+ alsamixer
+
+如果alsamixer默认设置成了HDMI或者其它声音输出,那就继续读下去吧,看看我们是怎么来修复这个问题的。
+
+### 修复默认设置成HDMI时Ubuntu的失声问题 ###
+
+现在来强制Ubuntu使用模拟输出来取代默认的HDMI,但我们还需要一点点信息。打开终端,然后使用下列命令:
+
+ aplay -l
+
+这会列出设备,卡号之类的东西。注意,向下检查模拟输出使用的卡和设备编号。我的输出如下所示:
+
+
+
+一旦你取得了所需的卡和设备编号,重新构建一个配置文件:
+
+ sudo gedit /etc/asound.conf
+
+上面的命令也会打开文件,将下面两行添加进去,当然将卡和设备编号替换成你自己的:
+
+ defaults.pcm.card 1
+ defaults.pcm.device 0
+
+保存文件,并重启计算机。现在,你应该听到声音了吧。需要提一下的是,这对所有的Linux发行版都有效,如Linux Mint,Elementary OS,Fedora,Arch Linux等等都可以。正如我之前所说,该“失声疗法”仅针对HDMI被设置为默认设备的情况。对于其它情况,你可以阅读[关于在Ubuntu和Linux Mint中修复失声问题这篇文章][4]。
+
+您可以尽情发表评论来告诉我这个方法是否有疗效,或者您有更好的方法来处理该问题,也可以告诉我。再见了!
+
+
+
+----------
+
+
+
+关于Abhishek
+
+我是Abhishek Prakash,It's F.O.S.S.的“创立者”,我有一个通信系统工程的硕士学位。我酷爱Linux和开源。我使用Ubuntu,信奉知识分享。除了Linux之外,我也喜爱经典的侦探推理小说,是Agatha Christie作品的超级粉丝。大家尽可以在[Google+][g]上将我圈进去,并追随[@abhishek_pc][t]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-sound-ubuntu-1404/
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://itsfoss.com/fix-sound-ubuntu-1304-quick-tip/
+[2]:http://itsfoss.com/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-14-04/
+[3]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alsamixer
+[4]:http://itsfoss.com/fix-sound-ubuntu-1304-quick-tip/
+[g]:https://plus.google.com/u/0/110180944531110746460
+[t]:https://twitter.com/abhishek_pc
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140714 Set Default Browser on Debian or Ubuntu Using Terminal.md b/translated/tech/20140714 Set Default Browser on Debian or Ubuntu Using Terminal.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..48d209653a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140714 Set Default Browser on Debian or Ubuntu Using Terminal.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+[快速技巧]利用终端在 Debian/Ubuntu 中设置默认浏览器
+================================================================================
+
+
+
+嘿,伙计们!
+
+在这篇文章中,我们将使用终端设置默认浏览器。
+
+虽然,使用浏览器主界面来设置默认浏览器很方便,但是有时,你需要远程来操作。
+
+要做到这一点,你只需打开终端,然后执行下述命令:
+```
+sudo update-alternatives --config x-www-browser
+```
+之后输入你想设置为默认浏览器的号码,这样就搞定了!
+
+截图如下:
+
+
+
+成功了吗?
+
+---
+via: http://www.unixmen.com/quick-tip-set-default-browser-debianubuntu-using-terminal/
+
+译者:[su-kaiyao](https://github.com/su-kaiyao) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140716 5 Simple Ways To Make Cinnamon Feel at Home on Ubuntu.md b/translated/tech/20140716 5 Simple Ways To Make Cinnamon Feel at Home on Ubuntu.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2e0a9ff50a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140716 5 Simple Ways To Make Cinnamon Feel at Home on Ubuntu.md
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+5个让Cinnamon桌面环境完美运行在ubuntu上的方法
+=======================================================================
+
+
+**Cinnamon桌面环境最新稳定版本发行了,[ubuntu用户可以去安装使用了][1]**
+
+在其安装后的基础上,我们可以做一些微调来拥有更棒的体验
+
+你的ubuntu如果没有安装Cinnamon,你可以参照我们之前的文章进行安装
+
+###更改Mint菜单图标###
+Mint菜单图标是Cinnamon的特色之一,它给予用户一种简单,快速,熟悉的方式来搜索,打开,组织应用程序,默认情况下,菜单使用启动程序项中的Linux
+Mint
+Logo。既然你是在ubuntu系统下使用它,而不是Mint,为什么不使用ubuntu熟悉的橙色朋友圈logo来替换原有的菜单图标呢?实现很简单
+
+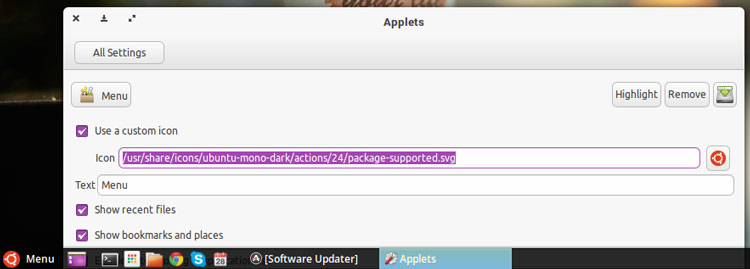
+
+想要改变Cinnamon菜单图标为ubuntu风格的,只需点击applet,选择‘config‘,在设置窗口,就会出现‘Use
+a custom icon‘,然后你就输入下面的路径来使用ubuntu logo了
+
+ /usr/share/icons/ubuntu-mono-dark/actions/24/package-supported.svg
+
+你可以使用任何支持的图片类型,只需要在刚才的填写区域写入正确的图片路径,或者点击后面的方框来打开文件选择器,选择你要使用的图标
+
+###尝试Cinnamon主题###
+
+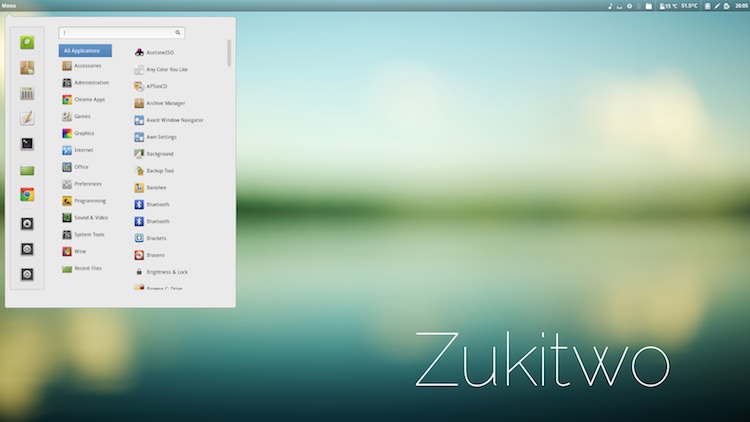
+
+和GNOME
+Shell一样,Cinnamon也支持自定义主题,我所说的主题并不只是应用程序的GTK主题和简单的窗口装饰,而是将面板,菜单,程序等等结合为一个整体的视觉风格
+
+Cinnamon主题可以被浏览,下载甚至不需要离开桌面的就触手可及 —
+无需下载或者手动安装:打开Cinnamon Settings tool中的Appearance
+pane,然后选择‘Online Themes‘
+
+下面是一些受欢迎的主题:
+
+- [**Android Holo**][2] — Android 4.x style theme
+- [**Zukitwo**][3] — Sleek, stylish and light
+- [**Minty**][4] — Dark theme with bold green accents
+- [**Metro**][5] — Based on the visual style of Windows 8.
+
+###找出你最喜欢的布局###
+
+我们统一认为应用程序发射器永远只是固定地待在屏幕的一侧,但是Cinnamon并没有这样的顾虑,它可以让你重新设计最符合你的桌面布局
+
+手动面板可以增加,编辑和移动,或选择三种预设的布局
+
+
+
+打开`Settings > Panel > Layout Options > Panel Layout`,然后下面这几个中选择
+
+- Traditional — 这是默认的布局,控制面板在屏幕的顶部
+- Flipped ——和Traditional一样,控制面板在屏幕顶部
+- Classic ——两个控制面板,一个在顶部,一个在底部
+
+你需要注销或者重启Cinnamon才能生效
+
+###添加面板小程序###
+
+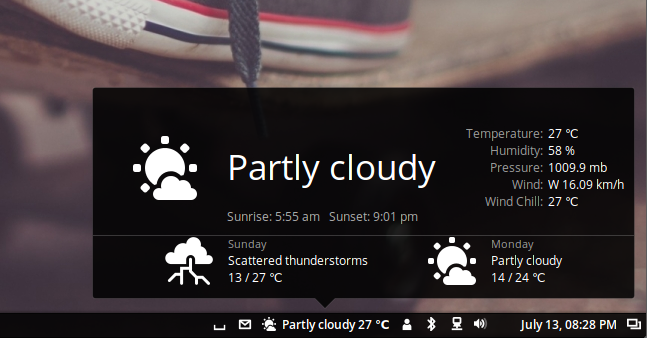
+
+Cinnamon和GNOE
+Shell一样具有可扩展性,丰富的社区插件和扩展程序提供了额外的特性和功能,比如天气,系统监测,窗口管理工具等,这些都可以被浏览,安装并能从桌面直接启动
+
+选择控制面板,右键点击要添加小程序,选择 ‘…Add Appls to the
+Panel‘,一些著名的小程序如下:
+
+- [**Weather**][6] - does what it forecasts (ho ho)
+- [**Stark Menu**][7] - Clone of the Windows 7 Start Menu
+- [**Screenshot**][8] — Easy way to grab screenshots with delay
+
+###改变日期的显示格式###
+
+
+
+Cinnamon的时间日期程序很方便,它可以让你很容易就记住日期
+
+但是它显示时间的默认格式是24小时制,但是我们很容易就能调整时钟格式
+
+右击然后选择‘Configure‘,在设置窗口中出现“Use a custom date
+format“的选择框上打勾,或者使用下面的几种格式(复制粘帖粗体字段)
+
+- **%B %e, %I:%M %p** (July 13, 7:19 PM)
+- **%m/%d/%Y** (07/13/2014)
+- **%l:%M %p** (7:19 PM)
+
+改变立马生效,如果中途发生了错误,你可以取消自定义时间格式选项恢复到默认状态
+
+###更多###
+
+在Cinnamon桌面环境中只有少部分定制选择供使用者使用,但是我们认为上述所讲的调整是不断探索的很好跳板,通过下面的评论栏让我们了解你最喜欢的调整是什么吧,你可以通过Facebook或者Google+
+
+----------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/5-things-installing-cinnamon-ubuntu
+
+译者:[su-kaiyao](https://github.com/su-kaiyao) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/new-cinnamon-ubuntu-14-04-ppa-stable
+[2]:http://cinnamon-spices.linuxmint.com/themes/view/122
+[3]:http://cinnamon-spices.linuxmint.com/themes/view/219
+[4]:http://cinnamon-spices.linuxmint.com/themes/view/25
+[5]:http://cinnamon-spices.linuxmint.com/themes/view/188
+[6]:http://cinnamon-spices.linuxmint.com/applets/view/17
+[7]:http://cinnamon-spices.linuxmint.com/applets/view/168
+[8]:http://cinnamon-spices.linuxmint.com/applets/view/35
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140716 7 dmesg Commands for Troubleshooting and Collecting Information of Linux Systems.md b/translated/tech/20140716 7 dmesg Commands for Troubleshooting and Collecting Information of Linux Systems.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..927e4773da
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140716 7 dmesg Commands for Troubleshooting and Collecting Information of Linux Systems.md
@@ -0,0 +1,195 @@
+在linux系统中处理故障和收集系统信息的7种‘dmesg’的用法
+==========================================================
+‘dmesg’命令显示linux内核的环形缓冲区信息,我们可以从中获得诸如系统架构,cpu,挂载的硬件,RAM等多个运行级别的大量的系统信息。当计算机启动时,系统内核(操作系统的核心部分)将会被加载到内存中。在加载的过程中会显示很多的信息,在这些信息中我们可以看到内核检测硬件设备。
+
+
+dmesg 命令的使用范例
+
+‘dmesg’命令设备故障的诊断是非常重要的。在‘dmesg’命令的帮助下进行硬件的连接或断开连接操作时,我们可以看到硬件的检测或者断开连接的信息。‘dmesg’命令在多数基于**Linux**和**Unix**的操作系统中都可以使用。
+
+下面我们展示一些最负盛名的‘dmesg’命令工具以及其实际使用举例。‘dmesg’命令的使用语法如下。
+
+ # dmesg [options...]
+
+### 1. 列出加载到内核中的所有驱动 ###
+
+我们可以使用如‘**more**’。 ‘**tail**’, ‘**less** ’或者‘**grep**’的文字处理工具来处理‘dmesg’命令的输出。由于dmesg日志的输出不适合在一页中完全显示,因此我们使用管道(pipe)将其输出送到more或者less命令中进行分页显示。
+
+ [root@tecmint.com ~]# dmesg | more
+ [root@tecmint.com ~]# dmesg | less
+
+### 输出 ###
+
+ [ 0.000000] Initializing cgroup subsys cpuset
+ [ 0.000000] Initializing cgroup subsys cpu
+ [ 0.000000] Initializing cgroup subsys cpuacct
+ [ 0.000000] Linux version 3.11.0-13-generic (buildd@aatxe) (gcc version 4.8.1 (Ubuntu/Linaro 4.8.1-10ubuntu8) ) #20-Ubuntu SMP Wed Oct 23 17:26:33 UTC 2013
+ (Ubuntu 3.11.0-13.20-generic 3.11.6)
+ [ 0.000000] KERNEL supported cpus:
+ [ 0.000000] Intel GenuineIntel
+ [ 0.000000] AMD AuthenticAMD
+ [ 0.000000] NSC Geode by NSC
+ [ 0.000000] Cyrix CyrixInstead
+ [ 0.000000] Centaur CentaurHauls
+ [ 0.000000] Transmeta GenuineTMx86
+ [ 0.000000] Transmeta TransmetaCPU
+ [ 0.000000] UMC UMC UMC UMC
+ [ 0.000000] e820: BIOS-provided physical RAM map:
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x0000000000000000-0x000000000009fbff] usable
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x00000000000f0000-0x00000000000fffff] reserved
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x0000000000100000-0x000000007dc08bff] usable
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x000000007dc08c00-0x000000007dc5cbff] ACPI NVS
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x000000007dc5cc00-0x000000007dc5ebff] ACPI data
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x000000007dc5ec00-0x000000007fffffff] reserved
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x00000000e0000000-0x00000000efffffff] reserved
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x00000000fec00000-0x00000000fed003ff] reserved
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x00000000fed20000-0x00000000fed9ffff] reserved
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x00000000fee00000-0x00000000feefffff] reserved
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x00000000ffb00000-0x00000000ffffffff] reserved
+ [ 0.000000] NX (Execute Disable) protection: active
+ .....
+
+### 列出所有被检测到的硬件 ###
+
+要显示所有被内核检测到的硬盘设备,你可以使用‘**grep**’命令搜索‘**sda**’关键词,如下:
+
+ [root@tecmint.com ~]# dmesg | grep sda
+
+ [ 1.280971] sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] 488281250 512-byte logical blocks: (250 GB/232 GiB)
+ [ 1.281014] sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] Write Protect is off
+ [ 1.281016] sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] Mode Sense: 00 3a 00 00
+ [ 1.281039] sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] Write cache: enabled, read cache: enabled, doesn't support DPO or FUA
+ [ 1.359585] sda: sda1 sda2 < sda5 sda6 sda7 sda8 >
+ [ 1.360052] sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] Attached SCSI disk
+ [ 2.347887] EXT4-fs (sda1): mounted filesystem with ordered data mode. Opts: (null)
+ [ 22.928440] Adding 3905532k swap on /dev/sda6. Priority:-1 extents:1 across:3905532k FS
+ [ 23.950543] EXT4-fs (sda1): re-mounted. Opts: errors=remount-ro
+ [ 24.134016] EXT4-fs (sda5): mounted filesystem with ordered data mode. Opts: (null)
+ [ 24.330762] EXT4-fs (sda7): mounted filesystem with ordered data mode. Opts: (null)
+ [ 24.561015] EXT4-fs (sda8): mounted filesystem with ordered data mode. Opts: (null)
+
+**注解** ‘sda’表示第一块 SATA硬盘,‘sdb’表示第二块SATA硬盘。若想查看IDE硬盘搜索‘hda’或‘hdb’关键词。
+
+### 3. 只输出dmesg命令的前20行日志 ###
+
+ [root@tecmint.com ~]# dmesg | head -20
+
+ [ 0.000000] Initializing cgroup subsys cpuset
+ [ 0.000000] Initializing cgroup subsys cpu
+ [ 0.000000] Initializing cgroup subsys cpuacct
+ [ 0.000000] Linux version 3.11.0-13-generic (buildd@aatxe) (gcc version 4.8.1 (Ubuntu/Linaro 4.8.1-10ubuntu8) ) #20-Ubuntu SMP Wed Oct 23 17:26:33 UTC 2013 (Ubuntu 3.11.0-13.20-generic 3.11.6)
+ [ 0.000000] KERNEL supported cpus:
+ [ 0.000000] Intel GenuineIntel
+ [ 0.000000] AMD AuthenticAMD
+ [ 0.000000] NSC Geode by NSC
+ [ 0.000000] Cyrix CyrixInstead
+ [ 0.000000] Centaur CentaurHauls
+ [ 0.000000] Transmeta GenuineTMx86
+ [ 0.000000] Transmeta TransmetaCPU
+ [ 0.000000] UMC UMC UMC UMC
+ [ 0.000000] e820: BIOS-provided physical RAM map:
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x0000000000000000-0x000000000009fbff] usable
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x00000000000f0000-0x00000000000fffff] reserved
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x0000000000100000-0x000000007dc08bff] usable
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x000000007dc08c00-0x000000007dc5cbff] ACPI NVS
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x000000007dc5cc00-0x000000007dc5ebff] ACPI data
+ [ 0.000000] BIOS-e820: [mem 0x000000007dc5ec00-0x000000007fffffff] reserved
+
+### 只输出dmesg命令最后20行日志 ###
+
+当我们插入可以出的硬件是在‘dmesg’命令后跟随‘tail’命令来输出‘dmesg’命令的最后20行日志是非常有用的。
+
+ [root@tecmint.com ~]# dmesg | tail -20
+
+ parport0: PC-style at 0x378, irq 7 [PCSPP,TRISTATE]
+ ppdev: user-space parallel port driver
+ EXT4-fs (sda1): mounted filesystem with ordered data mode
+ Adding 2097144k swap on /dev/sda2. Priority:-1 extents:1 across:2097144k
+ readahead-disable-service: delaying service auditd
+ ip_tables: (C) 2000-2006 Netfilter Core Team
+ nf_conntrack version 0.5.0 (16384 buckets, 65536 max)
+ NET: Registered protocol family 10
+ lo: Disabled Privacy Extensions
+ e1000: eth0 NIC Link is Up 1000 Mbps Full Duplex, Flow Control: None
+ Slow work thread pool: Starting up
+ Slow work thread pool: Ready
+ FS-Cache: Loaded
+ CacheFiles: Loaded
+ CacheFiles: Security denies permission to nominate security context: error -95
+ eth0: no IPv6 routers present
+ type=1305 audit(1398268784.593:18630): audit_enabled=0 old=1 auid=4294967295 ses=4294967295 res=1
+ readahead-collector: starting delayed service auditd
+ readahead-collector: sorting
+ readahead-collector: finished
+
+### 5. 搜索包含特定字符串的被检测到的硬件 ###
+由于‘dmesg’命令的输出实在太长了,在其中搜索某个特定的字符串是非常困难的。因此,有必要过滤出一些包含‘**usb**’ ‘**dma**’ ‘**tty**’ ‘**memory**’等字符串的日志行。[grep 命令][1] 的‘**-i**’选项表示忽略大小写。
+
+ [root@tecmint.com log]# dmesg | grep -i usb
+ [root@tecmint.com log]# dmesg | grep -i dma
+ [root@tecmint.com log]# dmesg | grep -i tty
+ [root@tecmint.com log]# dmesg | grep -i memory
+
+###输出###
+
+ [ 0.000000] Scanning 1 areas for low memory corruption
+ [ 0.000000] initial memory mapped: [mem 0x00000000-0x01ffffff]
+ [ 0.000000] Base memory trampoline at [c009b000] 9b000 size 16384
+ [ 0.000000] init_memory_mapping: [mem 0x00000000-0x000fffff]
+ [ 0.000000] init_memory_mapping: [mem 0x37800000-0x379fffff]
+ [ 0.000000] init_memory_mapping: [mem 0x34000000-0x377fffff]
+ [ 0.000000] init_memory_mapping: [mem 0x00100000-0x33ffffff]
+ [ 0.000000] init_memory_mapping: [mem 0x37a00000-0x37bfdfff]
+ [ 0.000000] Early memory node ranges
+ [ 0.000000] PM: Registered nosave memory: [mem 0x0009f000-0x000effff]
+ [ 0.000000] PM: Registered nosave memory: [mem 0x000f0000-0x000fffff]
+ [ 0.000000] please try 'cgroup_disable=memory' option if you don't want memory cgroups
+ [ 0.000000] Memory: 2003288K/2059928K available (6352K kernel code, 607K rwdata, 2640K rodata, 880K init, 908K bss, 56640K reserved, 1146920K highmem)
+ [ 0.000000] virtual kernel memory layout:
+ [ 0.004291] Initializing cgroup subsys memory
+ [ 0.004609] Freeing SMP alternatives memory: 28K (c1a3e000 - c1a45000)
+ [ 0.899622] Freeing initrd memory: 23616K (f51d0000 - f68e0000)
+ [ 0.899813] Scanning for low memory corruption every 60 seconds
+ [ 0.946323] agpgart-intel 0000:00:00.0: detected 32768K stolen memory
+ [ 1.360318] Freeing unused kernel memory: 880K (c1962000 - c1a3e000)
+ [ 1.429066] [drm] Memory usable by graphics device = 2048M
+
+### 6. 清空dmesg缓冲区日志 ###
+
+我们可以使用如下命令来清空dmesg的日志。该命令会清空dmesg环形缓冲区中的日志。但是你依然可以查看存储在‘**/var/log/dmesg**’文件中的日志。你连接任何的设备都会产生dmesg日志输出。
+
+ [root@tecmint.com log]# dmesg -c
+
+### 7. 实时监控dmesg日志输出 ###
+
+在某些发行版中可以使用命令‘tail -f /var/log/dmesg’来实时监控dmesg的日志输出。
+
+ [root@tecmint.com log]# watch "dmesg | tail -20"
+
+**结论**:dmesg命令在系统dmesg记录实时更改或产生的情况下是非常有用的。你可以使用man dmesg来获取关于dmesg更多的信息。
+
+----------
+
+
+
+Narad Shrestha
+
+- [Twitter profile][t]
+- [Facebook profile][f]
+- [Google+ profile][g]
+
+他在IT领域拥有超过10年的丰富经验,其中包括各种Linux发行版,开源软件和网络。 Narad始终坚持与人分享知识和自如的运用新技术。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/dmesg-commands/
+
+译者:[cvsher](https://github.com/cvsher) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/12-practical-examples-of-linux-grep-command/
+[t]:http://twitter.com/@nrdshrestha
+[f]:http://facebook.com/narad.shrestha.9
+[g]:http://plus.google.com/104542109955805873615?rel=author
+
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140716 How to analyze Squid logs with SARG log analyzer on CentOS.md b/translated/tech/20140716 How to analyze Squid logs with SARG log analyzer on CentOS.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..07a4fe6be9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140716 How to analyze Squid logs with SARG log analyzer on CentOS.md
@@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
+如何用CentOS上的SARG log分析其来分析Squid的log
+================================================================================
+[上一节教程][1]中,我们战士了如何在CentOS上使用Squid配置透明代理。Squid提供了很多有用的特性,但是分析一个原始Squid日志文件并不直接。比如,你如何分析下面Squid log中的时间戳和数字?
+
+ 1404788984.429 1162 172.17.1.23 TCP_MISS/302 436 GET http://facebook.com/ - DIRECT/173.252.110.27 text/html
+ 1404788985.046 12416 172.17.1.23 TCP_MISS/200 4169 CONNECT stats.pusher.com:443 - DIRECT/173.255.223.127 -
+ 1404788986.124 174 172.17.1.23 TCP_MISS/200 955 POST http://ocsp.digicert.com/ - DIRECT/117.18.237.29 application/ocsp-response
+ 1404788989.738 342 172.17.1.23 TCP_MISS/200 3890 CONNECT www.google.com:443 - DIRECT/74.125.200.106 -
+ 1404788989.757 226 172.17.1.23 TCP_MISS/200 942 POST http://clients1.google.com/ocsp - DIRECT/74.125.200.113 application/ocsp-response
+ 1404788990.839 3939 172.17.1.23 TCP_MISS/200 78944 CONNECT fbstatic-a.akamaihd.net:443 - DIRECT/184.26.162.35 -
+ 1404788990.846 2148 172.17.1.23 TCP_MISS/200 118947 CONNECT fbstatic-a.akamaihd.net:443 - DIRECT/184.26.162.35 -
+ 1404788990.849 2151 172.17.1.23 TCP_MISS/200 76809 CONNECT fbstatic-a.akamaihd.net:443 - DIRECT/184.26.162.35 -
+ 1404788991.140 611 172.17.1.23 TCP_MISS/200 110073 CONNECT fbstatic-a.akamaihd.net:443 - DIRECT/184.26.162.35 –
+
+SARG(或者说是Squid分析报告生成器)是一款基于web的工具,用于从Squid日志中生成报告。SARG提供了一个易于理解的由Squid处理的网络流量视图,并且它很容易设置与维护。在下面的教程中,我们会展示**如何在CentOS平台上设置SARG**。
+
+我们使用yum来安装安装必要的依赖。
+
+ # yum install gcc make wget httpd crond
+
+在启动时加载必要的服务
+
+ # service httpd start; service crond start
+ # chkconfig httpd on; chkconfig crond on
+
+现在我们下载并解压SARG
+
+ # wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/sarg/sarg/sarg-2.3.8/sarg-2.3.8.tar.gz?
+ # tar zxvf sarg-2.3.8.tar.gz
+ # cd sarg-2.3.8
+
+**注意**: 对于64位的Linux,log.c的源代码需要用下面的文件打补丁。
+
+ 1506c1506
+ < if (fprintf(ufile->file, "%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%"PRIi64"\t%s\t%ld\t%s\n",dia,hora,ip,url,nbytes,code,elap_time,smartfilter)<=0) {
+ ---
+ > if (fprintf(ufile->file, "%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%"PRIi64"\t%s\t%ld\t%s\n",dia,hora,ip,url,(int64_t)nbytes,code,elap_time,smartfilter)<=0) {
+ 1513c1513
+ < fprintf(fp_log, "%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%"PRIi64"\t%s\t%ld\t%s\n",dia,hora,user,ip,url,nbytes,code,elap_time,smartfilter);
+ ---
+ > fprintf(fp_log, "%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%"PRIi64"\t%s\t%ld\t%s\n",dia,hora,user,ip,url,(int64_t)nbytes,code,elap_time,smartfilter);
+ 1564c1564
+ < printf("LEN=\t%"PRIi64"\n",nbytes);
+ ---
+ > printf("LEN=\t%"PRIi64"\n",(int64_t)nbytes);
+
+如下继续并编译/安装SARG
+
+ # ./configure
+ # make
+ # make install
+
+SARG安装之后,配置文件可以按你的要求修改。下面是一个SARG配置的例子。
+
+ # vim /usr/local/etc/sarg.conf
+
+----------
+
+ access_log /var/log/squid/access.log
+ temporary_dir /tmp
+ output_dir /var/www/html/squid-reports
+ date_format e ## We use Europian DD-MM-YYYY format here ##
+ ## we don’t want multiple reports for single day/week/month ##
+ overwrite_report yes
+
+现在是时候测试运行了,我们用调试模式运行sarg来找出是否存在错误。
+
+ # sarg -x
+
+如果i一切正常,sarg会根系Squid日志,并在/var/www/html/squid-reports下创建报告。报告也可以在浏览器中通过地址http://<服务器IP>/squid-reports/访问
+
+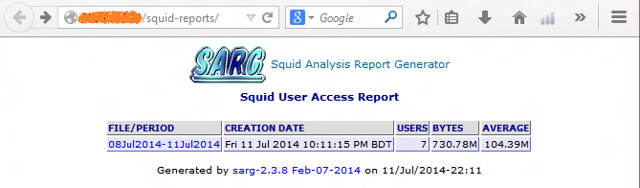
+
+
+
+、SARG可以用于创建每日、每周、每月的报告。时间范围用“-d”参数来指定,可能的值的形式可能为day-n、 week-n 或者 month-n,n的值向后天/周/月的数量。比如,使用week-1,SARG会生成前面一星期的报告。使用day-2,SARG会准备前面两天的报告。
+
+作为演示,我们会准备一个计划任务来每天运行SARG。
+
+ # vim /etc/cron.daily/sarg
+
+----------
+
+ #!/bin/sh
+ /usr/local/bin/sarg -d day-1
+
+文件需要可执行权限。
+
+ # chmod 755 /usr/local/bin/sarg
+
+现在SARG应该会每天准备关于Squid管理的流量报告。这些报告可以很容易地通过SARG网络接口访问。
+
+To sum up, SARG is a web based tool that analyzes Squid logs and presents the analysis in an informative way. System admins can leverage SARG to monitor what sites are being accessed, and to keep track of top visited sites and top users. This tutorial covers a working configuration for SARG. You can customize the configuration even further to match your requirements.
+总结一下,SARG一款基于网络的工具,它可以分析Squid日志,并以更详细的方式展示分析。系统管理员可以利用SARG来监视哪些网站被访问了,并跟踪访问量最大的网站和用户。本教程涵盖了SARG配置工作。你甚至可以进一步自定义配置来满足您的要求。
+
+希望这篇教程有用
+
+----------
+
+[Sarmed Rahman][w]
+
+- [Twitter 地址][t]
+- [LinkedIn 地址][l]
+
+Sarmed Rahman是一名在孟加拉国的IT专业人士。他坚持写作科学文章,并坚信技术可以通过分享提高。在他的空闲时间里,他爱好游戏与他的朋友在一起
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/analyze-squid-logs-sarg-log-analyzer-centos.html
+
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2014/06/squid-transparent-web-proxy-centos-rhel.html
+[w]:http://amar-linux.blogspot.com/
+[t]:http://twitter.com/SarmedRahman
+[l]:http://www.linkedin.com/in/sarmedrahman
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140716 How to check RPM package dependencies on Fedora or CentOS or RHEL.md b/translated/tech/20140716 How to check RPM package dependencies on Fedora or CentOS or RHEL.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c15bd5fdac
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140716 How to check RPM package dependencies on Fedora or CentOS or RHEL.md
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
+How to check RPM package dependencies on Fedora, CentOS or RHEL
+教你如何在Fedora,CentOS,RHEL中检查RPM包的依赖性
+================================================================================
+A typical RPM package on Red Hat-based systems requires all its dependent packages be installed to function properly.
+For end users, the complexity of such RPM dependency is hidden by package managers (e.g., yum or DNF) during package install/upgrade/removal process. However, if you are a sysadmin or a RPM maintainer, you need to be well-versed in RPM dependencies to maintain run-time environment for the system or roll out up-to-date RPM specs.
+我们都知道,在基于红帽的Linux系统中,一个RPM包,需要把先将它依赖的其他包安装好才能正常的工作。对于终端用户,RPM的安装、更新、删除中存在的依赖关系已经被工具透明化了(如 yum或 DNF等)。但如果你是系统管理员或者RPM包的管理员,你需要对RPM包中存在的依赖关系以及时更新、删除适当的包来保证系统的正常运行。
+In this tutorial, I am going to show **how to check RPM package dependencies**. Depending on whether a package is installed or not, there are several ways to identify its RPM dependencies.
+在本教程中,我将教大家**如何检查RPM包的依赖关系**无论这个包是否已经安装进操作系统中,我们都有一些办法来检查它们的依赖性。
+### Method One ###
+### 方法一 ###
+One way to find out RPM dependencies for a particular package is to use rpm command. The following command lists all dependent packages for a target package.
+使用RPM命令可以列出目标包所依赖的所有包,如下:
+ $ rpm -qR
+
+
+
+Note that this command will work only if the target package is already **installed**. If you want to check package dependencies for any **uninstalled** package, you first need to download the RPM package locally (no need to install it).
+注意,这种方法只适用于**已安装**的包。如果你需要检查一个**未安装**包的依赖关系,你需要把这个包先下载到本地来。
+To download a RPM package without installing it, use a command-line utility called `yumdownloader`. Install yumdownloader as follows.
+对于已在本地但未安装的包,可以使用叫做'yumdownloader'的工具,下面我们先安装yumdownloader:
+ $ sudo yum install yum-utils
+
+Now let's check RPM depenencies of a uninstalled package (e.g., tcpdump). First download the package in the current folder with yumdownloader:
+现在我们来检查一个未安装的RPM包的依赖关系(本列使用 tcpdump)。首先,我们使用yumdownloader把tcpdump的RPM包下载下来
+ $ yumdownloader --destdir=. tcpdump
+
+Then use rpm command with "-qpR" options to list dependencies of the downloaded package.
+然后再使用 "-qpR"参数显示该包的依赖关系。
+ # rpm -qpR tcpdump-4.4.0-2.fc19.i686.rpm
+
+### Method Two ###
+### 方法二 ###
+You can also get a list of dependencies for a RPM package using repoquery tool. repoquery works whether or not a target package is installed. This tool is included in yum-utils package.
+你可以使用repoquery工具来罗列包的依赖关系,这个工具包含在yum-utils中。
+ $ sudo yum install yum-utils
+
+To show all required packages for a particular package:
+显示目标包所依赖的包:
+ $ repoquery --requires --resolve
+
+
+
+For repoquery to work, your computer needs network connectivity since repoquery pulls information from Yum repositories.
+为让repoquery正常的工作,需要保持网络的畅通,应为repoquery需要在Yum库中查找信息。
+### Method Three ###
+### 方法三 ###
+The third method to show RPM package dependencies is to use rpmreaper tool.
+Originally this tool is developed to clean up unnecessary packages and their dependencies on RPM-based systems.
+rpmreaper has an ncurses-based intuitive interface for browsing installed packages and their dependency trees.
+第三个方法是使用rpmreaper工具。这个工具本来是用作清理系统中无用以及它们所依赖的包,rpmreaper有很直观的界面来展示已安装的包和它们依赖关系的树形图。
+To install rpmrepater, use yum command. On CentOS, you need to [set up EPEL repo][1] first.
+安装rpmrepater,在CentOS中,你需要先[设置好EPEL库][1]
+ $ sudo yum install rpmreaper
+
+To browser RPM dependency trees, simply run:
+只需运行rpmreaper就可以看到RPM包的依赖关系:
+ $ rpmreaper
+
+
+
+The rpmrepater interface will show you a list of all installed packages. You can navigate the list using up/down arrow keys.
+ Press "r" on a highlighted package to show its dependencies.
+ You can expand the whole dependency tree by recursively pressing "r" keys on individual dependent packages.
+ The "L" flag indicates that a given package is a "leaf", meaning that no other package depends on this package.
+ The "o" flag implies that a given package is in the middle of dependency chain.
+ Pressing "b" on such a package will show you what other packages require the highlighted package.
+rpmrepater会向用户显示已安装包的列表,你可以使用上/下箭头来滚动屏幕。
+你可以在指定包上使用"r"键来显示其依赖关系,循环在指定包上按下"r"键可以展示出余下的信息。
+"L"标志的意思是说这个包是一片“孤叶”,意思说说没有任何包依赖它。
+"o"标志是说这个包是整个依赖链的中间部分。
+按下"b"键会显示其他依赖于该包的其他包。
+### Method Four ###
+### 方法四 ###
+Another way to show package dependencies on RPM-based systems
+is to use rpmdep which is a command-line tool for generating a full package dependency graph of
+any installed RPM package. The tool analyzes RPM dependencies, and produce partially ordered package lists from
+topological sorting. The output of this tool can be fed into dotty graph visualization tool
+to generate a dependency graph image.
+还有一个办法是使用rpmdep工具,rpmdep是一个命令行工具,可以显示已安装包的完整包依赖关系图。该工具会分析RPM包的依赖性,从完整的排完序
+的拓扑图中摘取部分包的信息,形成列表展示给用户。该工具的输出结果可以直接使用到Dotty(可视化展示工具)中去。
+To install rpmdep and dotty on Fedora:
+在Fedora中安装rpmdep和dotty:
+ $ sudo yum install rpmorphan graphviz
+
+To install the same tools on CentOS:
+在CentOs中安装:
+ $ wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/rpmorphan/rpmorphan/1.14/rpmorphan-1.14-1.noarch.rpm
+ $ sudo rpm -ivh rpmorphan-1.14-1.noarch.rpm
+ $ sudo yum install graphviz
+
+To generate and plot a dependency graph of a particular installed package (e.g., gzip):
+生成包依赖的拓扑关系图:
+ $ rpmdep.pl -dot gzip.dot gzip
+ $ dot -Tpng -o output.png gzip.dot
+
+
+
+So far in this tutorial, I demonstrate several ways to check what other packages a given RPM package relies on.
+If you want to know more about .deb package dependencies for Debian-based systems,
+you can refer to [this guide][2] instead.
+教程到这个地方,我们用到了几种办法来检查包的依赖关系。如果您想知道如何在居于Debian的系统中检查.deb的包依赖关系,请阅读另外一篇[文档][2]
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/check-rpm-package-dependencies-fedora-centos-rhel.html
+
+译者:[nd0104](https://github.com/nd0104) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
+[2]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/07/how-to-check-package-dependencies-on-ubuntu-or-debian.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140716 Install Android 4.4 KitKat to Run Favourite Games and Applications in Linux.md b/translated/tech/20140716 Install Android 4.4 KitKat to Run Favourite Games and Applications in Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..39ad6b4648
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140716 Install Android 4.4 KitKat to Run Favourite Games and Applications in Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
+装X指南--在Linux上装个Android 4.4玩玩
+================================================================================
+**Android (x86)**项目致力于移植Android系统到X86处理器上,使用户可以更容易的在任何电脑上安装Android。他们通过使用android源码,增加补丁来使Android能够在X86处理器下工作,不单只是笔记本电脑和平板电脑。
+
+
+在Linux安装Android 4.4 KitKat
+
+几天前,项目组发布了最新的“Android KitKat 4.4 RC2”,下面,我将说明如何在VirtualBox上的安装过程,不过有一个小问题,安装完成Android后鼠标指针不工作了,我猜,如果你根据本教程将它安装成主系统,这个鼠标应该可以工作,否则我们只能使用键盘了。
+
+### 阶段 1: 在linux上安装VirtualBox ###
+
+**1.** 大多数的Linux发行版中,官方源都有VirtualBox,例如在Ubuntu中安装
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install virtualbox
+
+其他的Linux发行版,像**RHEL, CentOS and Fedora**,请参考下面文章来安装VirtualBox
+
+- [Install VirtualBox in RHEL, CentOS and Fedora][1]
+
+### 阶段 2: 下载并在VirtualBox中安装Android 4.4 kitkat ###
+
+**2.** 这步挺简单的,只是需要去[androud Sourceforge.net][2]项目下载 **Android 4.4 x86 Kit Kat**文件
+
+**3.** 为了安装**Android 4.4 kitkat**,首先,你需要引导刚刚下载.iso文件,启动 **VirtualBox**,创建一个新的虚拟机,然后跟着下面图片设置:
+
+
+创建新的虚拟设备
+
+**4.** 接下来,它会询问你新设备的内存大小,Android 4.4 kikat需要1G内存才能完美运行,但是由于我的电脑只有1G内存,我只能选择512MB。
+
+
+设置内存
+
+**5.** 选择“现在创建虚拟硬盘”(“Create a virtual hard drive now”)创建一个新的硬盘
+
+
+创建虚拟硬盘
+
+**6.** 它现在会询问你新虚拟硬盘的类型,选择**VDI**
+
+
+选择硬盘驱动类型
+
+
+选择存储方式
+
+**7.** 现在设置虚拟硬盘大小,你可以设置任何大小,但是除了未来安装Apps的空间,至少系统正确地安装需要**4G**。
+
+
+设置虚拟硬盘大小
+
+**8.** 现在你的新虚拟设备创建好了,可以引导下载的**.iso**文件了,右键刚刚创建的虚拟机,**设置** -> **存储** ,如下图,设置**android 4.4 kitkat RC2**的镜像文件。
+
+
+选择Android KitKat ISO
+
+**9.** Click on **OK**, and start the machine to boot the .iso image, choose “**Installation**” to start installing the system on the virtual machine.
+
+
+选择 Install Android Kit Kat
+
+**10.** 请选择一个分区来安装Android-x86
+
+
+选择 Partition Drive
+
+**11.** 如下图,你可以看见cfdisk界面,cfdisk是一个分区工具,我们将要使用它来创建一个新的硬盘分区,用来安装Android 4.4,现在,点击 “**New**”
+
+
+创建新分区
+
+**12.** 选择“**Primary**”作为分区类型
+
+
+选择主分区
+
+**13.** 接下来,设置分区大小
+
+
+设置分区大小
+
+**14.** 现在我们必须给硬盘创建新的引导使其能够写入新的分区表,点击“**Bootable**”给引导标记新的分区,你不会注意到有任何变化,但是引导标记将会自己给选中分区。
+
+
+制作分区引导
+
+**15.** 完成之后,点击“**Write**”对硬盘写入新的分区。
+
+
+应用新分区
+
+**16.** 它会询问你是否确认,输入“**yes**”并点击**Enter**
+
+
+确认分区改变
+
+**17.** 现在我们的新硬盘已经创建,点击 **Quit** 你就可以看来类似下图的显示,选中刚刚创建的用来安装Android 的分区,点击**Enter**
+
+
+选择分区安装Android
+
+**18.** 选择“**ext3**”作为硬盘文件系统并格式化
+
+
+选择Ext3分区类型
+
+
+格式化分区
+
+**19.** 它将会询问你时候需要安装GRUB启动器,当然选择**Yes**,如果不这样,你将不能启动新系统,所以选择**Yes**并点击**Enter**
+
+
+安装引导加载器 GRUB
+
+**20.** 最后,它会问你**/system**分区是否能写入,选择yes,它会在安装完系统后帮助你减少很多麻烦
+
+
+使分区能写入
+
+**21.** 安装将会开始它的任务,安装器结束工作后,选择重启,在我做测试的时候,“Run-Android x86”不起作用,所以你不得不重启。
+
+
+Android Kit kat 安装完成
+
+**22.** 我们已经安装完成**Android 4.4 KitKat RC2**,问题是VirtualBox将会继续引导**.iso**镜像文件而不是虚拟设备,所以为了修正这个问题,**设置** -> **存储** ->移除iso文件
+
+
+移除Android Kit Kat 镜像
+
+**23.** 你可以启动你的虚拟设备,运行你的Android系统了
+
+
+启动Android Kit Kat 系统
+
+
+Android标志界面
+
+**24.** 使用**Android**之前,你需要完成一个向导来配置一些事。你会看见如下屏幕,现在问题是,鼠标不能在**android 4.4 kitkat**工作,这意味着我们需要展示我们键盘的高超技巧了。首先,选择语言,你需要使用键盘**上**键和**下**键,到下一步,需要使用**右**键移动光标,选择**Enter**
+
+
+Android 欢迎界面
+
+
+选择WiFi网络
+
+
+创建Android Google账户
+
+
+注册Google账户
+
+
+设置日期和时间
+
+
+输入你的信息
+
+
+Android 4.4 Kit Kat 主界面
+
+
+安装 **Android x86**好处颇多,如果你没有智能手机而又想早点使用**Play Store**apps,怎么不试试安装android x86呢?结果怎样?你有想过android可以成为一个针对桌面功能的**实时操作系统**?
+
+----------
+
+
+
+[Hanny Helal][3]
+
+2010年,成为Linux和自由软件用户,已为自由软件贡献多个项目
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-android-kitkat-in-linux/
+
+译者:[Vic___](http://www.vicyu.net) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-virtualbox-on-redhat-centos-fedora/
+[2]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/android-x86/
+[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140716 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to define PATH environment variable for sudo commands.md b/translated/tech/20140716 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to define PATH environment variable for sudo commands.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..732eb2eadf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140716 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to define PATH environment variable for sudo commands.md
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+
+Linux 常见问题(有答案的哦)-- 如何为sudo命令定义PATH环境变量
+================================================================================
+>**问题**:我安装了一个程序到/usr/local/bin目录下,这个程序需要root权限才能执行,当我用sudo去执行它时,收到"sudo: XXXXX: command not found"的错误提示,不知道为什么/usr/local/bin没有被包含到PATH环境变量下面来,我该如何解决这个问题?
+
+当你使用sudo去执行一个程序时,处于安全的考虑,这个程序将在一个新的、最小化的环境中执行,也就是说,诸如PATH这样的环境变量,在sudo命令下已经被重置成默认状态了。
+所以当一个刚初始化的PATH变量中不包含你所要运行的程序所在的目录,你就会得到"command not found"的错误提示。
+
+为了改变PATH在sudo会话中的初始值,打开/etc/sudoers文件并编辑,找到"secure_path"一行,"secure_path"中包含的路径就将在sudo会话中的PATH变量中生效。
+
+添加所需要的路径(如 /usr/local/bin)到"secure_path"下,在开篇所遇见的问题就将迎刃而解。
+ Defaults secure_path = /sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin
+
+
+这个修改会即刻生效。
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/define-path-environment-variable-sudo-commands.html
+
+译者:[nd0104](https://github.com/nd0104) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140716 Simple Dock GNOME Shell Extension Puts Your Fave Apps On The Desktop.md b/translated/tech/20140716 Simple Dock GNOME Shell Extension Puts Your Fave Apps On The Desktop.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..187aa61777
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140716 Simple Dock GNOME Shell Extension Puts Your Fave Apps On The Desktop.md
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+“Simple Dock” GNOME Shell扩展乾坤大挪移,钟爱应用桌面展现
+================================================================================
+
+
+**我爱GNOME Shell,但是我痛恨的是话费力气从隐藏屏幕中找到我所钟爱的应用或者在我正运行的应用间切换。**
+
+这么说,好像听起来我是个老古董,像是一个UX勒德分子,也像是某个过分沉溺于Unity可用性瘾君子,但我,像阅读本文的许多人一样,喜欢将app启动器/切换器放到桌面上。这是一个熟悉、快速的工作方式。
+
+而GNOME Shell,从设计上看,却完全是个不同的世界。它将所有这一切隐藏起来 —— 从消息中心和通知,到工作区和应用列表。它是最小美学,包含这样的道理:帮助用户专注于最重要的部分。
+
+但是对我而言,我的桌面需要比一个美化的相框更多的东西。
+
+### GNOME Shell之美 ###
+
+抛开我自己的偏好,隐藏应用是GNOME Shell之美的一部分。它带来了默认的桌面体验:用户友好,稳健以及可预见性——而且也完全可扩展。因此,它也附带有大量的扩展组件以迎合不同用户的需要、职业和希望,包括传统应用菜单,桌面停靠栏,以及甚至是Ubuntu Unity Dash的复制品!
+
+在本文中,我仅仅关注那个能满足我需要的扩展:它有个恰如其分的名字**Simple Dock**。Simple Dock获取GNOME Shell应用网格以及收藏栏,并可以将它放到任何我想要放的不引人注目的位置:桌面上。
+
+目前为止,它只支持放置在屏幕底部,只提供了最小的设置项。虽然是最小的,但我觉得所有这些设置已经能满足我的需要:
+
+- 智能自动隐藏
+- 最小化/还原应用窗口
+- 拖放收藏
+- 覆盖活动启动按钮
+
+想要吗?如果你正在Ubuntu 13.10或更高版本上使用GNOME Shell,那么你可以使用它。只需在支持的浏览器(Firefox, GNOME Web之类)中访问下面的链接就可以导航到GNOME扩展页面,然后将页面上开个从“off”拖动到“on”上。
+
+- [GNOME Shell扩展中的Simple Dock][1]
+
+要调整Simple Dock设置,点击GNOME扩展页面上的齿轮图标,或者通过GNOME优化工具这样的桌面应用程序来设置。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/simple-dock-gnome-shell-extension
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://extensions.gnome.org/extension/815/simple-dock/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140718 Display Song Lyrics On Desktop In Ubuntu 14.04.md b/translated/tech/20140718 Display Song Lyrics On Desktop In Ubuntu 14.04.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..376a68f122
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140718 Display Song Lyrics On Desktop In Ubuntu 14.04.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+在 Ubuntu 桌面上显示歌词
+================================================================================
+
+
+除了免费的流媒体音乐外,我最喜欢[Spotify][1]的地方就是它的歌词插件了。有时候我听不懂一首歌里面的所有歌词,尤其是rap。[TuneWiki][2]插件在这种情况下就派得上用场了。但TuneWiki仅有支持Windows和iTune的插件,那我们在linux桌面上有什么选择呢?
+
+如果你使用过一段时间Linux桌面,你也许听过[OSD Lyrics][3]。它是一个显示桌面歌词的小程序。你可以借助一些音乐播放器来使用它,比如 Rythmbox,[Banshee][4],[Clementine][5]等等。
+
+### 在Ubuntu 14.04和Linux mint 17上安装OSD Lyrics ###
+
+两年以前 OSD Lyrics 在它的官方仓库中被积极地维护,但现在对它的开发已经停止了。尽管这个PPA已经不可用,但可以通过网络下载OSD Lyrics的安装包。虽然这些安装执行文件最初是为 Ubuntu 12.02 设计的,但这些文件也能在 Ubuntu 14.04 上良好地工作。我们一起看看怎么在 Ubuntu 14.04 和 Linux mint 17 上安装OSD Lyrics。
+
+[前往下载页下载OSDLyrics][6],根据你是使用[32位还是64位的ubuntu][7]来下载相应的.deb 文件。你会在网页的上方找到这些文件。
+
+
+
+下载完成后,双击它通过使用Ubuntu软件中心来安装。另外,你也可以使用[Gdebi ][8]来快速地安装.deb安装包。
+
+### 怎样在 Ububtu 和 linux mnit 上使用 OSD Lyrics 显示歌词 ###
+
+安装完成后,你可以从Unity Dash运行OSD Lyrics :
+
+
+
+首次运行时,OSD Lyrics会检测你的系统中能被它支持的播放器。你可以设定一个默认播放器,以后当你运行OSD Lyrics时它就会自动启动 。
+
+
+
+有一件事值得注意,那就是OSD Lyrics不像[Shazam][9]等软件一样,它不是通过音频来寻找歌词,而是通过比如名称,专辑,艺术家等信息来关联音乐文件。所以你得确保你的音乐文件的来源正当,或者是你得保持你的音乐文件的信息是正确并且是已经更新后的。
+
+如果OSD Lyrics辨认出了音乐文件,它就会用卡拉OK格式在桌面上显示歌词了:(译者注:OSD Lyrics可以自动在千千静听和虾米歌词站点在线下载歌词,这对我们中文用户来说是个福音)
+
+
+
+OSD Lyrics有大量设置选项,你可以改变歌词字体,文字大小等等。
+
+你认为 OSD Lyrics 怎么样?你还使用其它歌词插件吗?欢迎您和我们分享。
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://itsfoss.com/display-song-lyrics-desktop-ubuntu-1404/
+
+译者:[Love-xuan](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://itsfoss.com/install-spotify-ubuntu-1404/
+[2]:http://www.tunewiki.com/
+[3]:https://code.google.com/p/osd-lyrics
+[4]:http://banshee.fm/
+[5]:https://www.clementine-player.org/
+[6]:https://code.google.com/p/osd-lyrics/downloads/list
+[7]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-know-ubuntu-unity-version/
+[8]:http://itsfoss.com/install-deb-files-easily-and-quickly-in-ubuntu-12-10-quick-tip/
+[9]:http://www.shazam.com/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 1.md b/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 1.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..deb81ef193
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 1.md
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
+Linux 内核的测试和调试
+================================================================================
+### Linux 内核测试哲学 ###
+
+不管是开源还是闭源,所有软件的开发流程中,测试是一个重要的、不可或缺的环节,Linux 内核也不例外。开发人员自测、系统测试、回归测试、压力测试,都有各自不同的目的,但是从更高一个层次上看,这些测试的最终目的又是一样的:保证软件能一直运行下去,当有新功能加进去时,要保证新功能可以正常工作。
+
+在软件释出 release 版之前,不用回归测试就能保证稳定性,并且尽量避免在软件发布后被用户发现 bug。调试被用户发现的 bug 是一项非常浪费时间和精力的工作。因此测试是一项非常重要的工作。不像闭源和专有的操作系统,Linux 内核的开发过程是完全开放的。这种处理方式即是它的优点,也是它的缺点。多个开发者持续增加新功能、修 bug、不断集成与测试 —— 当环境有新的硬件或功能时,这种开发方式能够保证内核能持续工作。在开源项目中,开发者与用户共享测试的结果,这也是开源项目与闭源项目之间的一个很重要的差别。
+
+几乎所有 Linux 内核开发者都是活跃的 Linux 用户。内核测试人员不一定非得是内核开发者,相反,用户和开发者如果对新增的代码不是很熟悉,他们的测试效果会比代码开发人员自己测试的效果要好很多。也就是说,开发者的单元自测能验证软件的功能,但并不能保证在其他代码、其他功能、其他软件、硬件环境下面运行时会出现什么问题。开发者无法预料、也没有机会和资源来测试所有环境。因此,用户在 Linux 内核开发过程中起到非常重要的角色。
+
+现在我们已经了解了持续集成测试的重要性,接下来我们会详细介绍测试的知识。但在此之前,我还是向介绍一下开发的过程,以便让大家了解它是怎么工作的,以及如何把补丁打进内核主线。
+
+全世界共有3000多个内核开发者为 Linux 内核贡献代码,每天都有新代码添加到内核,结果是大概2个月就能产生一个稳定版和多个扩展的稳定版。新功能的开发与已发布的稳定版集成测试流程在同时进行。
+
+关于开发流程的详细描述,请参考[Greg Kroah-Hartman 的 Linux 内核开发的介绍][1]。
+
+这份教程适合与初学者以及有经验的内核开发者,如果你想加入到内核开发者行列,那么它也适合你。有经验的开发人员可以跳过那些介绍基础测试和调试的章节。
+
+这份教程介绍如何测试和调试 Linux 内核、工具、脚本以及在回归测试会集成测试中使用的调试机制。另外,本文还会介绍如何使用 git 把针对一个 bug 的补丁分离出来,在介绍介绍把你的补丁提交到内核的邮件列表之前需要做些什么。我将会使用 Linux PM 作为测试它调试的对象。尽管本文讨论的是 Linux 内核,但是介绍的方法适用于任何其他软件开发项目。
+
+### 配置开发与测试的系统 ###
+
+第一步,找一个满足你需求的开发环境,x86-64 是一个比较理想的选择,除非你必须用特别的架构。
+
+第二步,安装 Linux 发行版,我推荐 Ubuntu,所以本教程会介绍基于 Ubuntu 的配置过程。你可以参考[如何使用 Ubuntu][2] 来安装一个 Ubuntu 系统。
+
+在开发和测试环境,最好要保证你的 boot 分区有足够的空间来存放内核文件。你可以为 boot 分区留下 3GB 空间,或把 boot 分区直接放到根目录下,这样 boot 分区可以使用整个磁盘的空间。
+
+安装好操作系统后,确保 root 用户可用,确保你的用户可以使用 sudo 命令。你的系统也许已经安装了 build-essential,它是编译内核必备的软件包,如果没安装,运行下面的命令:
+
+ sudo apt-get install build-essential
+
+然后运行下面的命令,保证你的系统能够交叉编译内核。下面的 ncurses-dev 安装包是运行 make menuconfig 命令必须用到的。
+
+ sudo apt-get install binutils-multiarch
+
+ sudo apt-get install ncurses-dev
+
+ sudo apt-get install alien
+
+然后安装一些每个内核开发者都会用到的工具包:
+
+ sudo apt-get install git
+
+ sudo apt-get install cscope
+
+ sudo apt-get install meld
+
+ sudo apt-get install gitk
+
+如果你喜欢把内核通过交叉编译以支持非 x86_64 架构的环境,请参考[在 x86_64 上交叉编译 Linux 内核][3]。
+
+### 稳定的内核 ###
+
+使用 git 克隆一个稳定的内核,然后编译安装。你可以参考[Linux 内核结构][4]来找到最新的稳定版和开发主线。
+
+ git clone git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux-stable.git
+
+上面的步骤将会创建一个新的目录,名为 linux-stable,然后把源码下载到里面。
+
+你也可以直接下载压缩包并解压出源码,无需使用 git:
+
+ tar xvf linux-3.x.y.tar.xz
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/linux-kernel-testing-and-debugging?page=0,0
+
+译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://events.linuxfoundation.org/images/stories/pdf/als2012_gregkh.pdf
+[2]:http://howtoubuntu.org/
+[3]:http://linuxdriverproject.org/mediawiki/index.php/Cross-compiling_Linux_kernel_on_x86_64
+[4]:https://www.kernel.org/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 2.md b/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 2.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c21125a984
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 2.md
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
+Linux 内核测试与调试 - 2
+================================================================================
+### 编译安装稳定版内核 ###
+
+如果你用 git 下载源码,就执行以下命令:
+
+ cd linux-stable
+
+ git checkout linux-3.x.y
+
+如果是直接下载压缩文件,用以下命令进入源码目录:
+
+ cd linux-3.x.y
+
+如果你想把内核安装到自己的系统上,最安全的方法是使用你安装好的发行版拥有的配置文件。你可以在 /boot 目录找到当前发行版的内核配置文件:
+
+ cp /boot/config-3.x.y-z-generic .config
+
+运行下面的命令,可以在当前内核配置的基础上修改一些小地方,然后产生新的内核配置文件。比如说新的内核比你的 Ubuntu 发行版自带的内核多了些新功能,而你正好需要用到它们,这个时候你就要修改配置了。
+
+ make oldconfig
+
+完成配置后,就可以编译了:
+
+ make all
+
+完成编译后,安装这个新的内核:
+
+ sudo "make modules_install install"
+
+上面的命令安装新内核,并把新内核作为启动项添加到 grub 文件(LCTT:就是你下次开机时会多出一个开机选项)。好了你可以重启电脑,然后选择新的内核启动系统。等等!先别冲动,在重启电脑之前,我们保存下编译内核产生的日志,用于比较和查找错误(如果有错误发生的话):
+
+ dmesg -t > dmesg_current
+
+ dmesg -t -k > dmesg_kernel
+
+ dmesg -t -l emerg > dmesg_current_emerg
+
+ dmesg -t -l alert > dmesg_current_alert
+
+ dmesg -t -l crit > dmesg_current_alert
+
+ dmesg -t -l err > dmesg_current_err
+
+ dmesg -t -l warn > dmesg_current_warn
+
+正常的话,dmesg 不会输出 emerg, alert, crit 和 err 级别的信息。如果你不幸看到这些输出了,说明内核或者你的硬件环境有问题。
+
+再介绍一些重启前的需要执行的操作。谁也不能保证新内核能够正常启动,所以请不要潇洒地把老内核删除,至少保留一个稳定可用的内核在系统上。修改一下 /etc/default/grub 文件:
+
+使用 earlyprink=vga 作为内核启动选项,把系统早期启动的信息打印到显示屏上:
+
+ GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="earlyprink=vga"
+
+将 GRUB_TIMEOUT 的值设置成10秒到15秒之间的值,保证在开机启动的时候你有足够的时间来选择启动哪个内核:
+
+ 取消对 GRUB_TIMEOUT 的注释,并把它设置为10:GRUB_TIMEOUT=10
+ 注释掉 GRUB_HIDDEN_TIMEOUT 和 GRUB_HIDDEN_TIMEOUT_QUIET
+
+运行 update-grub 命令,更新 /boot 目录下的 grub 配置文件:
+
+ sudo update-grub
+
+现在可以重启系统了。新内核起来后,比较新老内核的 dmesg 信息,看看新的内核有没有编译错误。如果新内核启动失败,你需要通过老内核启动系统,然后分析下为什么失败。
+
+### 跟上节奏,永不落后(编译最新版内核) ###
+
+如果你想开上内核快车道,追求与时俱进,那就去下载 mainline 状态的内核或 linux-next 状态的内核(LCTT:读者可进入 kernel.org 获取代码,linux 代码被分为4种状态:mainline, stable, longterm, linux-next)。安装测试 mainline 状态或 linux-next 状态的内核,你就可以在正式发布之前帮助内核找到并修复里面的 bug。
+
+mainline 状态的内核源码:
+
+ git clone git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git
+
+linux-next 状态的内核源码:
+
+ git clone git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/next/linux-next.git
+
+编译安装这两种内核的步骤与编译安装稳定版内核一样。按之前讲过的步骤来就行了。
+
+### 打补丁 ###
+
+Linux 内核的补丁是一个文本文件,包含新源码与老源码之间的改变量。每个补丁只包含自己依赖的源码的增量,除非它被特意包含进一系列补丁之中。打补丁方法如下:
+
+ patch -p1 < file.patch
+
+ git apply --index file.patch
+
+两种方法都可以打补丁。但是,如果你要打的补丁包含一个新文件,git 命令不能识别这个新增的文件,也就是说这个新文件在 git 里面属于 untracked 文件(LCTT:玩 git 的人对这个会比较熟悉,就是文件处于未被跟踪的状态,你需要使用 git add 命令将文件放入暂存区)。git diff 命令不会将这个文件的增量显示出来,并且 git status 命令会显示这个文件处于 untracked 状态。
+
+大多数情况下,有个没被跟踪的文件,对于编译安装内核来说没什么问题,但是 git 操作就会出现一些问题了: git reset --hard 命令不会删除这个新加的文件,并且接下来的 git pull 操作也会失败。你有多种选择来避免上面所说的状况:
+
+选项1,不跟踪这个新文件:
+
+> 如果打补丁后新添加了文件,在 git reset --hard 前使用 git clean 命令来删除没有被跟踪的文件。举个例子,git clean -dfx 命令会强制删除未被跟踪的目录和文件,忽略在 .gitigniore 文件内规定的文件。如果你不在乎哪些文件会被删除,你可以使用 -q 选项让 git clean 命令进入安静模式,不输出任何处理过程。
+
+选项2,跟踪新文件:
+
+> 你可以在使用 git apply --index file.patch 命令后让 git 跟踪打完补丁后新产生的文件(LCTT:使用 git add 命令),就是让 git 把文件放入 index 区域。做完这个后,git diff 命令会将新文件的增量打印出来,git status 也会显示者这是一个正常的新增文件。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/linux-kernel-testing-and-debugging?page=0,1
+
+译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 3.md b/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 3.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0ba9c4a18c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 3.md
@@ -0,0 +1,124 @@
+Linux 内核测试与调试 - 3
+================================================================================
+### 基本测试 ###
+
+安装好内核后,试试能不能启动它。能启动的话,检查 dmesg 看看有没有隐藏的错误。试试下面的功能:
+
+- 网络(Wifi 或者网线)是否可用?
+- ssh 是否可用?
+- 使用 ssh 远程传输文件。
+- 使用 git clone 和 git pull 命令。
+- 用用网络浏览器。
+- 查看 email。
+- 使用 ftp, wget 等软件下载文件。
+- 播放音频视频文件。
+- 连上 USB 鼠标等设备。
+
+
+### 检查内核日志 ###
+
+使用 dmesg 查看隐藏的问题,对于定位新代码带来的 bug 是一个好方法。一般来说,dmesg 不会输出新的 crit, alert, emerg 级别的错误信息,也不应该出现新的 err 级别的信息。你要注意的是那些 warn 级别的日志信息。请注意 warn 这个级别的信息并不是坏消息,新代码带来新的警告信息,不会给内核带去严重的影响。
+
+- dmesg -t -l emerg
+- dmesg -t -l crit
+- dmesg -t -l alert
+- dmesg -t -l err
+- dmesg -t -l warn
+- dmesg -t -k
+- dmesg -t
+
+下面的脚本运行了上面的命令,并且将输出保存起来,以便与老的内核的 dmesg 输出作比较(LCTT:老内核的 dmesg 输出在本系列的第一篇文章中有介绍)。然后运行 diff 命令,查看新老内核 dmesg 日志之间的不同。脚本需要输入老内核版本号,如果不输入参数,它只会生成新内核的 dmesg 日志文件后直接退出,不再作比较(LCTT:话是这么说没错,但点开脚本一看,没输参数的话,这货会直接退出,连新内核的 dmesg 日志也不会保存的)。如果 dmesg 日志有新的警告信息,表示新发布的内核有漏网之鱼(LCTT:嗯,漏网之 bug 会更好理解些么?),这些 bug 逃过了自测和系统测试。你要看看,那些警告信息后面有没有栈跟踪信息?也许这里有很多问题需要你进一步调查分析。
+
+- [**dmesg 测试脚本**][1]
+
+### 压力测试 ###
+
+执行压力测试的一个好办法是同时跑三四个内核编译任务。下载各种版本的内核,同时编译它们,并记录时间。比较新内核跑压力测试和老内核跑压力测试所花的时间,然后可以定位新内核的性能。如果新内核跑压力测试的时间比老内核的更长,说明新内核的部分模块性能退步了。性能问题很难调试出来。第一步是找出哪里导致的性能退步。同时跑多个内核编译任务对检测内核整体性能来说是个好方法,但是这种方法涵盖了多个内核模块,比如内存管理、文件系统、DMA、驱动等(LCTT:也就是说,这种压力测试没办法定位到是哪个模块造成了性能的下降)。
+
+ time make all
+
+### 内核测试工具 ###
+
+我们可以在 Linux 内核本身找到多种测试方法。下面介绍一个很好用的功能测试工具集: ktest 套件
+
+ktest 是一个自动测试套件,它可以提供编译安装启动内核一条龙测试服务,也可以跑交叉编译测试,前提是你的系统有安装交叉编译所需要的软件。ktest 依赖于 flex 和 bison。详细信息请参考放在 tools/testing/ktest 目录下的文档,你可以自学成材。另外还有一些参考资料教你怎么使用 ktest:
+
+- [**ktest-eLinux.org**][2]
+
+### tools/testing/selftests 套件 ###
+
+我们来玩玩自测吧。内核源码的多个子系统都有自己的自测工具,到目前为止,断点、cpu热插拔、efivarfs、IPC、KCMP、内存热插拔、mqueue、网络、powerpc、ptrace、rcutorture、定时器和虚拟机子系统都有自测工具。另外,用户态内存的自测工具可以利用 test_user_copy 模块来测试用户态内存到内核态的拷贝过程。下面的命令演示了如何使用这些测试工具:
+
+编译测试:
+
+ make -C tools/testing/selftests
+
+测试全部:(有些测试需要 root 权限,你需要以 root 用户登入系统然后运行命令)
+
+ make -C tools/testing/selftests run_tests
+
+只测试单个子系统:
+
+ make -C tools/testing/selftests TARGETS=vm run_tests
+
+### tools/testing/fault-injection 套件 ###
+
+在 tools/testing 目录下的另一个测试套件是 fault-injection。failcmd.sh 脚本用于检测 slab 和内存页分配器的错误。这些工具可以测试内核能否很好地从错误状态中恢复回来。这些测试需要用到 root 权限。下面简单介绍了一些当前能提供的错误检测方法。随着错误检测方法的增加,这份名单也会不断增长。最新的名单请参考 Documentation/fault-injection/fault-injection.txt 文档。
+
+failslab (默认选项)
+
+ 产生 slab 分配错误。作用于 kmalloc(), kmem_cache_alloc() 等函数(LCTT:产生的结果是调用这些函数就会返回失败,可以模拟程序分不到内存时是否还能稳定运行下去)。
+
+fail_page_alloc
+
+ 产生内存页分配的错误。作用于 alloc_pages(), get_free_pages() 等函数(LCTT:同上,调用这些函数,返回错误)。
+
+fail_make_request
+
+ 对满足条件(可以设置 /sys/block//make-it-fail 或 /sys/block///make-it-fail 文件)的磁盘产生 IO 错误,作用于 generic_make_request() 函数(LCTT:所有针对这块磁盘的读或写请求都会出错)。
+
+fail_mmc_request
+
+ 对满足条件(可以设置 /sys/kernel/debug/mmc0/fail_mmc_request 这个 debugfs 属性)的磁盘产生 MMC 数据错误。
+
+你可以自己配置 fault-injection 套件的功能。fault-inject-debugfs 内核模块在系统运行时会在 debugfs 文件系统下面提供一些属性文件。你可以指定出错的概率,指定两个错误之间的时间间隔,当然本套件还能提供更多其他功能,具体请查看 Documentation/fault-injection/fault-injection.txt。 Boot 选项可以让你的系统在 debugfs 文件系统起来之前就可以产生错误,下面列出几个 boot 选项:
+
+- failslab=
+- fail_page_alloc=
+- fail_make_request=
+- mmc_core.fail_request=[interval],[probability],[space],[times]
+
+fault-injection 套件提供接口,以便增加新的功能。下面简单介绍下增加新功能的步骤,详细信息请参考上面提到过的文档:
+
+使用 DECLARE_FAULT_INJECTION(name) 定义默认属性;
+
+> 详细信息可查看 fault-inject.h 中定义的 struct fault_attr 结构体。
+
+配置 fault 属性,新建一个 boot 选项;
+
+> 这步可以使用 setup_fault_attr(attr, str) 函数完成,为了能在系统启动的早期产生错误,添加一个 boot 选项这一步是必须要有的。
+
+添加 debugfs 属性;
+
+> 使用 fault_create_debugfs_attr(name, parent, attr) 函数,为新功能添加新的 debugfs 属性。
+
+为模块设置参数;
+
+> 为模块添加一些参数,对于配置错误属性来说是一个好主意,特别是当新功能的应用范围受限于单个内核模块的时候(LCTT:不同内核,你的新功能可能需要不同的测试参数,通过设置参数,你的功能可以不必为了迎合不同内核而每次都重新编译一遍)。
+
+添加一个钩子函数到错误测试的代码中。
+
+> should_fail(attr, size) —— 当这个钩子函数返回 true 时,用户的代码就应该产生一个错误。
+
+应用程序使用这个 fault-injection 套件可以指定某个具体的内核模块产生 slab 和内存页分配的错误,这样就可以缩小性能测试的范围。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/linux-kernel-testing-and-debugging?page=0,2
+
+译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://linuxdriverproject.org/mediawiki/index.php/Dmesg_regression_check_script
+[2]:http://elinux.org/Ktest#Git_Bisect_type
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 4.md b/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 4.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..81334dfac1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 4.md
@@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
+Linux 内核测试和调试 - 4
+================================================================================
+### 自动测试工具 ###
+
+这里列出一些能满足不同需求的测试工具供你选择。本小节只是简单介绍个大概,并不提供详细操作指南。
+
+#### [AuToTest][1] ####
+
+> AuToTest 是一个全自动测试框架,存在的主要目的就是测试 Linux 内核,当然也可以用来测试其他东西,比如测试一块新硬件是否能稳定工作。AuToTest 是开源软件,以 GPL 方式授权,运行于 server-client 架构(即 C/S 架构)。你可以通过配置 server 端来对运行了 client 端的系统执行初始化、运行与监测工作,也可以自己在目标系统上让 client 运行起来。另外你可以为这个测试框架添加测试用例,详情请参考[AuToTest 白皮书][2]。
+
+#### Linaro Automated Validation Architecture ####
+
+> LAVA 自动测试框架用于自动安装于运行测试。举个例子:你在 LAVA 里面只需运行几个命令就可以跑 LTP(LCTT:Linux Test Project,中文是 Linux 测试计划,SGI发起并由IBM负责维护,目的是为开源社区提供测试套件来验证Linux的可靠性、健壮性和稳定性)。通过 LAVA 命令可以自动为你安装 LTP 所需要的所有依赖包,下载源码、编译编码、将 LTP 安装到某个独立的地方,方便卸载 LTP 时能移除所有二进制文件。安装好 LTP 后,运行 LAVA 命令时添加 'ltp' 选项就可以运行 LTP 测试任务了,它会将测试结果以文件方式保存下来,文件名包含测试名称、时间戳。这些测试结果可以留着供以后参考。这是个发现软件退化(如果软件退化了的话)的好方法。下面列出 LAVA 配合 LTP 使用的一些命令:
+
+显示 LAVA 支持的测试列表:
+
+ lava-test list-tests
+
+安装测试套件:
+
+ lava-test install ltp
+
+运行测试:
+
+ lava-test run ltp
+
+查看结果:
+
+ lava-test results show ltp-timestamp.0
+
+卸载测试套件:
+
+ lava-test uninstall ltp
+
+### 内核调试功能 ###
+
+Linux 内核本身包含很多调试功能,比如 kmemcheck 和 kmemleak。
+
+#### kmemcheck ####
+
+> kmemcheck 是一个动态检查工具,可以检测出一些未被初始化的内存(LCTT:内核态使用这些内存可能会造成系统崩溃)并发出警告。它的功能与 Valgrind 类似,只是 Valgrind 运行在用户态,而 kmemchecke 运行在内核态。编译内核时加上 CONFIG_KMEMCHECK 选项打开 kmemcheck 调试功能。你可以阅读 Documentation/kmemcheck.txt 来学习如何配置使用这个功能,以及如何看懂调试结果。
+
+#### kmemleak ####
+
+> kmemleak 通过类似于垃圾收集器的功能来检测内核是否有内存泄漏问题。而 kmemleak 与垃圾收集器的不同之处在于前者不会释放孤儿目标(LCTT:不会再被使用的、应该被释放而没被释放的内存区域),而是将它们打印到 /sys/kernel/debug/kmemleak 文件中。用户态的 Valgrind 也有一个类似的功能,使用 --leak-check 选项可以检测并报错内存泄漏问题,但并不释放这个孤儿内存。编译内核时使用 CONFIG_DEBUG_KMEMLEAK 选项打开 kmemcleak 调试功能。阅读 Documentation/kmemleak.txt 来学习怎么使用这个工具并读懂调试结果。
+
+### 内核调试接口 ###
+
+Linux 内核通过配置选项、调试用的 API、接口和框架来支持动态或静态的调试。我们现在就好好学习学习这些牛逼的功能,从静态编译选项开始讲。
+
+### 调试配置选项:静态编译 ###
+
+大部分 Linux 内核以及内核模块都包含调试选项,你只要在编译内核或内核模块的时候添加这个静态调试选项,程序运行时后就会产生调试信息,并记录在 dmesg 缓存中。
+
+### 调试的 API ###
+
+调试 API 的一个很好的例子是 DMA-debug,用来调试驱动是否错误使用了 DMA 提供的 API。它会跟踪每个设备的映射关系,检测程序有没有试图为一些根本不存在的映射执行“取消映射”操作,检测代码建立 DMA 映射后可能产生的“映射丢失”的错误。内核配置选项 CONFIG_HAVE_DMA_APT_DEBUG 和 CONFIG_DMA_API_DEBUG 可以为内核提供这个功能。其中,CONFIG_DMA_API_DEBUG 选项启用后,内核调用 DMA 的 API 的同时也会调用 Debug-dma 接口。举例来说,当一个驱动调用 dma_map_page() 函数来映射一个 DMA 缓存时,dma_map_page() 会调用debug_dma_map_page() 函数来跟踪这个缓存,直到驱动调用 dma_unmap_page() 来取消映射。详细内容请参考[使用 DMA 调试 API 检测潜在的数据污染和内存泄漏问题][3]。
+
+### 动态调试 ###
+
+动态调试功能就是你可以决定在程序运行过程中是否要 pr_debug(), dev_dbg(), print_hex_dump_debug(), print_hex_dump_bytes() 这些函数正常运行起来。什么意思?当程序运行过程中出现错误时,你可以指定程序打印有针对性的、详细的调试信息。这功能牛逼极了,我们不再需要为了添加调试代码定位一个问题,而重新编译安装内核。你可以指定 CONDIF_DYNAMIC_DEBUG 选项打开动态调试功能,然后通过 /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control 接口指定要打印哪些调试日志。下面分别列出代码级别和模块级别打印日志的操作方法:
+
+让 kernel/power/suspend.c 源码第340行的 pr_debug() 函数打印日志:
+
+ echo 'file suspend.c line 340 +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
+
+让内核模块在加载过程中打开动态调试功能:
+
+> 使用 modprobe 命令加在模块时加上 dyndbg='plmft' 选项。
+
+让内核模块的动态调试功能在重启后依然有效:
+
+> 编辑 /etc/modprobe.d/modname.conf 文件(没有这个文件就创建一个),添加 dyndbg='plmft' 选项。然而对于哪些通过 initramfs 加载的驱动来说,这个配置基本无效(LCTT:免费奉送点比较高级的知识哈。系统启动时,需要先让 initramfs 挂载一个虚拟的文件系统,然后再挂载启动盘上的真实文件系统。这个虚拟文件系统里面的文件是 initramfs 自己提供的,也就是说你在真实的文件系统下面配置了 /etc/modprobe.d/modname.conf 这个文件,initramfs 是压根不去理会的。站在内核驱动的角度看:如果内核驱动在 initramfs 过程中被加载到内核,这个驱动读取到的 /etc/modprobe.d/modname.conf 是 initramfs 提供的,而不是你编辑的那个。所以会有上述“写了配置文件后重启依然无效”的结论)。对于这种刁民,呃,刁驱动,我们需要修改 grub 配置文件,在 kernel 那一行添加 module.dyndbg='plmft' 参数,这样你的驱动就可以开机启动动态调试功能了。
+
+想打印更详细的调试信息,可以使用 dynamic_debug.verbose=1 选项。参考 Documentation/dynamic-debug-howto.txt 文件获取更多信息。
+
+### 设置追踪点 ###
+
+到目前为止,我们介绍了多种动态和静态调试方法。静态调试选项和静态调试钩子函数(比如 DMA Debug API)需要的编译过程打开或关闭,导致了一个难过的事实:需要重新编译安装内核。而动态编译功能省去了“重新编译”这件麻烦事,但是也有不足的地方,就是调试代码引入了条件变量,用于判断是否打印调试信息。这种方法可以让你在程序运行时决定是否打印日志,但需要执行额外的判断过程。“追踪点”代码只会在程序运行过程中使用“追踪点”功能才会被触发。也就是说,“追踪点”代码与上述说的两种方法都不一样。当用不到它时,它不会运行(LCTT:动态调试的话,代码每次都需要查看下变量,然后判断是否需要打印日志;而“追踪点”貌似利用某种触发机制,不需要每次都去查看变量)。当你需要用到它时,程序的代码会把“追踪点”代码包含进去。它不会添加任何条件变量来增加系统的运行负担。
+
+详细信息请参考[布置追踪代码的小技巧][4]。
+
+### “追踪点”的原理 ###
+
+追踪点使用“跳跃标签”,这是一种使用分支跳转的编码修正(code modification)技术。
+
+当关闭追踪点的时候,其伪代码看起来时这样的:
+
+ [ code1 ]
+ nop
+ back:
+ [ code2 ]
+ return;
+ tracepoint:
+ [ tracepoint code ]
+ jmp back;
+
+当打开追踪点的时候,其伪代码看起来时这样的:(注意追踪点代码出现的位置)
+
+ [ code1 ]
+ jmp tracepoint
+ back:
+ [ code2 ]
+ return;
+ tracepoint:
+ [ tracepoint code ]
+ jmp back;
+
+(LCTT:咳咳,解释解释上面两段伪代码吧,能看懂的大神请忽略这段注释。不使用追踪点时,代码运行过程是:code1->code2->return结束;使用追踪点时,代码运行过程是:code1->跳到tracepoint code执行调试代码->跳回code2->return结束。两段代码的唯一区别就是第二行,前者为 nop(不做任何操作),后者为 jmp tracepoint (跳到调试代码)。)
+
+### Linux 电源管理子系统的测试 ###
+
+使用静态调试、动态调试和追踪调试技术,我们来跑一下磁盘的电源管理测试。当系统被挂起时,内核会为磁盘创建一个休眠镜像,使磁盘进入休眠模式,当系统重新被唤醒时,内核又利用这个休眠镜像重新唤醒磁盘。
+
+设置挂起设备与唤醒设备需要的时间:
+
+ echo 1 > /sys/power/pm_print_times
+
+以 reboot 模式挂起磁盘:
+
+ echo reboot > /sys/power/disk
+ echo disk > /sys/power/state
+
+以 shutdown 模式挂起磁盘 —— 与 reboot 模式一样,只是重新唤醒磁盘的话还需要电源提供。
+
+ echo shutdown > /sys/power/disk
+ echo disk > /sys/power/state
+
+以 platform 模式挂起磁盘 —— 能测试更多内容,比如 BIOS 挂起和唤醒,会涉及到 ACPI 功能。我们推荐你使用这种方式,把 BIOS 也拉下水陪你玩挂起和唤醒游戏。
+
+ echo platform > /sys/power/disk
+ echo disk > /sys/power/state
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via:http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/linux-kernel-testing-and-debugging?page=0,3
+
+译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://autotest.github.io/
+[2]:https://github.com/autotest/autotest/wiki/WhitePaper
+[3]:http://events.linuxfoundation.org/sites/events/files/slides/Shuah_Khan_dma_map_error.pdf
+[4]:http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/july-2013-linux-kernel-news
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 5.md b/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 5.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ef868c8c26
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 5.md
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
+Linux 内核测试和调试 - 5
+================================================================================
+### 仿真环境下进行 Linux 电源管理子系统测试 ###
+
+Linux 电源管理子系统在仿真环境下提供5种测试方式。这些方式仅仅在内核各层之间运行休眠的代码而不是真正的让系统进入休眠状态。有些平台不能挂起系统,比如说我们需要模拟飞机的飞行环境,这时候使用这种仿真环境就非常有用处了。
+
+freezer - 测试停掉处理器:
+
+ echo freezer > /sys/power/pm_test
+ echo platform > /sys/power/disk
+ echo disk > /sys/power/state
+
+devices - 测试停掉处理器以及挂起设备:
+
+ echo devices > /sys/power/pm_test
+ echo platform > /sys/power/disk
+ echo disk > /sys/power/state
+
+platform - 测试停掉处理器、挂起设备以及平台全局控制方法(*)
+
+ echo platform > /sys/power/pm_test
+ echo platform > /sys/power/disk
+ echo disk > /sys/power/state
+
+processors - 测试停掉处理器、挂起设备和平台全局控制方法(*),以及关闭未启动的 CPU。
+
+ echo processors > /sys/power/pm_test
+ echo platform > /sys/power/disk
+ echo disk > /sys/power/state
+
+core - 测试停掉处理器、挂起设备和平台全局控制方法(*),关闭未启动的 CPU,以及挂起平台或系统的设备。注意:这个测试模式运行在 ACPI 系统。
+
+ echo core > /sys/power/pm_test
+ echo platform > /sys/power/disk
+ echo disk > /sys/power/state
+
+### Linux 电源管理子系统追踪事件 ###
+
+电源管理子系统在运行过程中支持多种追踪点和追踪事件。我将对如何使用这些追踪时间以及如何找到追踪信息作一个简单的介绍:
+
+在运行时开启电源管理事件:
+
+ cd /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/power
+ echo 1 > cpu_frequency/enable
+ cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/set_event
+ less /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace
+
+为内核启动的命令添加一个参数:
+
+ trace_event=cpu_frequency
+
+更多信息查看 Documentation/power/basic-pm-debugging.txt 以及同目录下其他的文档。
+
+### git bisect 命令 ###
+
+git bisect 是一个非常有用非常强大的工具,用于将 git 上的一个 commit 分离出来。我简单过一遍它的用法。
+
+下面是 git bisect 的用法:
+
+ git bisect start
+ git bisect bad # 当前版本是坏的
+ git bisect good v3.14-rc6 # 上个版本是好的
+
+一旦指定好好的版本和坏的版本,git bisect 就会开始把好坏两个版本之间的所有 commit 对半分,并将其中的一半提交 pull 下来。然后重新编译安装测试内核,并标记这个内核是好是坏。重复这个过程,知道某个你选好的 commit 被标记被好或者坏。我们可能需要测试多个内核版本,测到最后一个版本时,git bisect 会将一个 commit 标记为坏。下面的命令可以在 git bisect 分析过程中起到帮助作用:
+
+查看 bisect 操作的过程:
+
+ git bisect log
+
+重置 git bisect,标记错误时可以用到,保存 git log 的输出,重新操作上一次 bisect 的步骤:
+
+ git bisect reset
+
+重放 git bisect 操作过程:
+
+ git bisect replay git_log_output
+
+如果一个问题很清楚是在某个区域内,git bisect 命令可以定位到一个具体的内核源码树枝干上。举个例子,在调试一个镭龙显卡驱动的问题时,为 git bisect 指定 drivers/drm/radeon 参数,可以让 git bisect 只检索对 drivers/drm/radeon 里面的文件有修改的 commit。
+
+让 git bisect 只检索内核树的某个枝干:
+
+ git bisect start drivers/drm/radeon
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/linux-kernel-testing-and-debugging?page=0,4
+
+译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 6.md b/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 6.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..02a53bccd1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140718 Linux Kernel Testing and Debugging 6.md
@@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
+Linux 内核的测试和调试 - 6
+================================================================================
+### Linux 内核补丁测试 ###
+
+你试过自己写内核补丁吗?本节介绍在把你的补丁包提交到 Linux 邮箱列表之前,需要做哪些操作。另外我们还会介绍如何把它发送出去。
+
+写好代码后,编译它。把 make 过程产生的输出保存到文档中,查看新代码有没有警告信息。找到所有的警告信息,处理掉。当你的代码编译过程没有任何不正常的输出,安装这个内核,然后启动测试。如果启动正常,查看 dmesg 里面有没于错误,与老内核生成的 dmesg 日志做个比较。运行一些压力测试,请参考我们以前讲过的测试内容。如果这个补丁用于修复某个 bug,请确保真的已经修复了。如果真的修复了,请确保能通过系统测试。找出打你补丁的模块下面的回归测试工具,运行一下。如果补丁涉及到其他架构,你需要交叉编译然后测试一下。请通过下面的目录查找测试工具:
+
+- linux_git/Documentation
+- linux_git/tools/testing
+- 交叉编译参考:[在 x86_64 架构上交叉编译 Linux 内核:初学者教程][1]
+
+如果你对你的补丁测试结果感到很满意,你就可以提交补丁了。请确保提交 commit 的信息要描述得非常清楚。要让内核维护者和其他开发者看懂补丁所修改的内容,这一点非常重要。生成补丁后,执行 scripts/checkpatch.pl 脚本,找到 checkpatch 是产生的错误或警告(如果有的话),修复它们。重新生成补丁,直到补丁通过这个脚本的测试。重新测试这个补丁。将本补丁用于其他的内核源码上,保证不会有冲突产生。
+
+现在你做好提交补丁的准备了。先运行 scriptst/get_maintainer.pl 来确认你应该把补丁发给哪个内核维护者。注意不要以附件形式发送补丁,而是以纯文本形式粘贴在邮件里面。确保你的邮件客户端可以发送纯文本信息,你可以试试给自己发送一份补丁邮件来测试你的邮件客户端的功能。收到自己的邮件后,运行 checkpatch 命令并给自己的内核源码打上你的补丁。如果这两部都能通过,你就可以给 Linux 邮箱列表发送补丁了。使用 git send-email 命令是提交补丁最安全的方式,可以避免你的邮箱的兼容性问题。你的 .gitconfig 文件里面需要配置好有效的 smtp 服务器,详细操作参考 git 的帮助文档。
+
+更多提交补丁的规矩,请参考下面的资料:
+
+- linux_git/Documentation/applying-patches.txt
+- linux_git/Documentation/SubmitChecklist
+- linux_git/Documentation/SubmittingDrivers
+- linux_git/Documentation/SubmittingPatches
+- linux_git/Documentation/stable_kernel_rules.txt
+- linux_git/Documentation/stable_api_nonsense.txt
+
+下面是一些内核测试教程的资料:
+
+- [USB Testing on Linux][2]
+- [Linux Kernel Tester's Guide Chapter2][3]
+- [Linux Kernel Tester's Guide][4]
+- [Testing resources at eLinux.org][5]
+- [eLinux Debugging Portal][6]
+
+### 内核测试套件和项目 ###
+
+除我们讨论过的测试资源之外,这里还有很多测试项目值得介绍,包括开源的和厂家自己提供的。这些项目每一个都是针对特定领域的,比如嵌入式或者企业自己使用。我们简单过一下。
+
+[Linux 测试项目][7](LTP)测试套件是一系列工具的集合,用于测试内核的可靠性、健壮性和稳定性。你可以为这个项目添加自己的测试代码,并且 LTP 项目欢迎你贡献自己的代码。runltp 脚本默认情况下会测试下面的子系统:
+
+- 文件系统压力测试
+- 磁盘 IO 测试
+- 内存管理压力测试
+- IPC(进程间通信)测试
+- 调度器测试
+- 命令的功能性验证测试
+- 系统调用功能验证测试
+
+[**LTP-DDT**][8] 是一个基于 LTP 的测试应用(LCTT:就是 LTP 的阉割版么),专注于测试嵌入式设备驱动。
+
+[**Linux Driver Verification**][9] 这个项目的目标是提高 Linux 设备驱动的质量,它为设备驱动验证开发了集成环境平台,并且利用与时俱进的研究来增强验证工具的质量。
+
+### 一致性测试 ###
+
+如果你有将某个 Unix 平台下的应用一直到另一个平台的经验,你就能理解 [Linux Standard Base (LSB)][10] 和 LSB 一致性测试套件的重要性了。LSB 是 Linux Foundation 工作组创建的用于降低支持不同 Linux 平台所需要的开销,方法就是通过降低不同 Linux 发行版之间的差别,保证应用在不同发行版之间的可移植性。前事不忘后事之师,Unix 世界的分歧在 Linux 世界一定要避免。这就是为什么你可以把一个 rpm 包转化成 deb 包后还能安装并正常运行的秘密。
+
+### 静态分析工具 ###
+
+静态分析之所以会被称为“静态分析”,是因为这些工具只分析代码,并不执行它们。分析 Linux 内核代码的静态分析工具有很多,Sparse 是 Linus Torvalds 写的专门用于检查内核静态类型的工具。它是一个语义检查器,会为 C 语言的语义建立语义检析树,执行惰性类型评估。内核编译系统支持 sparse,并且为编译内核的命令提供开启 sparse 的选项。
+
+为内核所有需要重新编译的 C 文件执行 sparse 语义检查:
+
+ make C=1 allmodconfig
+
+为内核所有 C 文件(即使不需要重新编译)执行 sparse 语义检查:
+
+ make C=2 allmodconfig
+
+Sparse 的资源:
+
+- [Sparse Archive][11]
+- [Sparse How To][12]
+
+Smatch 分析程序代码的逻辑错误。它可以检测到诸如“为一个没锁上的 spinlock 执行解锁”的逻辑错误。内核源码支持 smatch:
+
+在 Linux 内核中运行 smatch:
+
+ make CHECK="~/path/to/smatch/smatch -p=kernel" C=1 bzImage modules | tee warns.txt
+
+请参考下面的资料来获取和编译 smatch。需要注意的是 smatch 是个正在发展的项目,架构会不断变化。
+
+- [**Smatch**][12]
+
+那么我们该怎么处理 Sparse 和 Smatch 所发现的语义和逻辑上的错误呢?一些错误可以被分离为日常问题或模块问题,可以轻易被解决。但是有些语义错误涉及到全局,因为剪切粘贴了一些代码。在一些环境中,当一些接口函数被废弃不再使用,或者仅仅做了写微小的修改,你就需要大规模更新源码。这时候你需要 Coccinelle 来帮忙。,Coccinelle 使用 SmPL 语言(语义包语言)来为 C 代码提供匹配和转换代码的功能。Coccinelle 的从一开始就作为 Linux 的附属产品持续发展的。
+
+举个例子:foo(int) 函数突然变成 foo(int, char \*) 函数,多出了一个输入参数(可以把第二个参数置为 null)。所有调用 foo() 函数的代码都需要更新了,这可能是个悲摧的体力活。但是使用 Coccinelle 的话,这项工作瞬间变得轻松,脚本会帮你找到调用 foo(parameter1) 的代码,然后替换成 foo(parameter1, NULL)。做完这些后,所有调用这个函数的代码都可以运行一遍,验证下第二个参数为 NULL 是否能正常工作。关于 Coccinelle 的更多信息,以及在不同项目中(当然,也包括 Linux 内核这个项目)的使用方法,请参考项目主页:[**Cocinelle**][13]。
+
+### 参考文献 ###
+
+本文涵盖了很多方面,这里列出一些参考文档供读者做进一步研究。
+
+- [KernelHacking][14]
+- [kernel Documentation][15]
+- [Linux Device Drivers, Third Edition][16]
+- [Dynamic Event Tracing in Linux Kernel][17]
+- [Kernel Testing: Tool and Techniques][18]
+
+### 鸣谢 ###
+
+感谢来自 Oracle 的 Khalid Aziz,审查校对并提供许多非常有价值的建议。感谢来自三星的 Mauro Chehab 和 Guy Martin,他们给了我多次反馈。感谢来自 Linux Foundation 的 Grey Kroah-Hartman 对本文的审阅。感谢来自三星的 Ibrahim Haddad,没有他的支持和鼓励,我可能还不会坐下来写出这篇文章。
+
+----------
+
+
+
+作者:[Shuah Khan][a]
+
+Shuah Khan 是三星公司开源组的高级 Linux 内核开发工程师。
+她为 Linux 内核中的 IOMMU、DMA、电源管理、PCIe 贡献代码,同时维护内核,为内核提供补丁包。Shuah 有多年 Unix 内核开发经验。她也为 OpenHPI 和 LLDP 项目作贡献。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/linux-kernel-testing-and-debugging?page=0,5
+
+译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://events.linuxfoundation.org/sites/events/files/slides/Shuah_Khan_cross_compile_linux.pdf
+[2]:http://www.linux-usb.org/usbtest/
+[3]:http://kernelnewbies.org/Linux_Kernel_Tester%27s_Guide_Chapter2
+[4]:http://www.kerneltravel.net/downloads/tester_guide.pdf
+[5]:http://elinux.org/Test_Systems
+[6]:http://elinux.org/Debugging_Portal
+[7]:http://ltp.sourceforge.net/documentation/how-to/ltp.php
+[8]:http://processors.wiki.ti.com/index.php/LTP-DDT
+[9]:http://linuxtesting.org/project/ldv
+[10]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/collaborate/workgroups/lsb
+[11]:http://codemonkey.org.uk/projects/git-snapshots/sparse/
+[12]:http://smatch.sourceforge.net/
+[13]:http://coccinelle.lip6.fr/
+[14]:http://kernelnewbies.org/KernelHacking
+[15]:http://kernelnewbies.org/Documents
+[16]:http://lwn.net/Kernel/LDD3/
+[17]:http://events.linuxfoundation.org/slides/lfcs2010_hiramatsu.pdf
+[18]:http://events.linuxfoundation.org/images/stories/slides/elc2013_porter.pdf
+[a]:http://www.linuxjournal.com/users/shuah-khan
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140718 Need Microsoft Office on Ubuntu--Install the Official Web Apps b/translated/tech/20140718 Need Microsoft Office on Ubuntu--Install the Official Web Apps
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..32991be99b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140718 Need Microsoft Office on Ubuntu--Install the Official Web Apps
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+需要在Ubuntu上安装微软办公软件?去安装官方的网络应用程序
+================================================== ==============================
+
+
+**这是微软办公软件及其一贯繁琐的文件指令,而不是每个人的一杯咖啡。同时这是许多工作和教育环境的主要依靠——无论是好还是坏**
+
+通过使用[LibreOffice的应用程序套件][1],阅读、编辑和保存这些专有指令出现在Ubuntu上是有着某种程度的可能。在作家中,Calc和Impress都不同程度的夸耀微软办公软件文件的协作性,但在我自己的实际操作经验中(谢天谢地,它很简洁!)它并不完美。
+
+时不时的,你会不得不使用微软办公软件,(虽然我们大多数人都心里向着开放标准,但是我们不应该无视实际问题)但你已经没有意愿去购买一个完整的微软办公软件许可证来运行这个窗口模拟器,那么微软的在线网络应用程序是完美的解决方法。
+
+###安装微软在线办公软件上的应用程序在Ubuntu###
+
+为了使从Ubuntu的桌面访问这些在线版本更容易,“Linux的网络应用程序项目”创造了一个小的、非官方的安装程序。它可以添加网络应用程序的快捷方式(“荣耀书签”)到您的应用程序启动器。
+
+
+
+通过快捷方式,相应的Microsoft Web应用程序在你默认的系统浏览器中打开,不可能有比这更精美的了。听起来漂亮吗?下面是你的应用程序的快捷方式:
+
+- 文档
+- 表格
+- 幻灯片
+- Outlook
+- OneDrive
+- 日历
+- OneNote
+- 通讯录
+
+该软件包还创建了一个新的应用程序类别来容纳这些链接,不但可以让您把这些快捷方式从其他应用程序单独分开来,而且是直接位于常见的“办公软件”应用程序下。
+
+这些都是必不可少的吗?不见得。他们有用吗?这取决于你的工作流程。但它是不错的选择吗?一定是的。
+
+你可以从下面的链接保存含有.deb文件安装程序,其中有安装链接。适用于Ubuntu14.04 LTS和更高版本。
+
+- [下载微软的在线办公应用(.deb)][2]
+
+###其他可选项###
+
+
+
+类似的替代方案是[安装Chrome官方网上应用商店的在线办公应用程序][3],然后添加应用程序启动器到Linux。这次短跑中仍然会为它们创建可启动的快捷方式,但那些可以被设置为打开自己的窗框,而且不需要安装任何第三方软件包。
+
+同时,谷歌最近在整合完整的Office功能(由于其购买了QuickOffice)[到自己的文档,幻灯片和床单应用][4]。Android应用程序Quickoffice退出了舞台,同时Chrome也实现了扩展。
+
+如果你是一个深度的谷歌网络硬盘/文档的用户,那么这个解决方案可能对你是更加好了。
+
+-------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/run-microsoft-office-web-apps-ubuntu-desktop
+
+译者:[cereuz](https://github.com/cereuz)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://www.libreoffice.org/
+[2]:https://docs.google.com/file/d/0ByQnaVw7riBQMjNCUFh4ZlM4Y0E/edit?usp=sharing
+[3]:http://www.omgchrome.com/microsoft-brings-office-online-chrome-web-store/
+[4]:http://www.omgchrome.com/quickoffice-chrome-extension-gets-name-change/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140722 10 Useful Interview Questions and Answers on Linux Commands.md b/translated/tech/20140722 10 Useful Interview Questions and Answers on Linux Commands.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..20a8ac5f78
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140722 10 Useful Interview Questions and Answers on Linux Commands.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+关于Linux命令的10个有用的面试问题及其答案
+==================================================================================================================================================
+Linux命令行,以及用户使用Linux命令进行Linux shell交互,是Linux最吸引人的地方,也是面试中最普遍的话题之一。在这篇文章中,我们将提出10个面试中很重要问题,这肯定能拓宽你的知识面
+
+ Linux Command Questions
+
+### 1. 如何停止一个正在运行的进程 ###
+
+**答案**:为了停止正在运行的进程,我们可以使用组合键 Ctrl+Z
+
+### 2. 什么是安装Linux所需的最小分区数量,以及如何查看系统启动信息? ###
+
+**答案**:单独一个/root分区足以执行所有的系统任务,但是强烈建议安装Linux时,需要至少三个分区:/root,/boot,/swap。一个IDE硬盘驱动器支持高达63个分区,SCSI硬盘驱动器支持超过15个分区
+
+为了检查启动信息,我们可以使用cat或者dmesg命令,如下所示:
+
+ #cat /var/log/messages
+
+OR
+
+ #dmesg
+
+### 3. 在你的Linux机器上更踪系统事件的守护进程名是什么?###
+
+**答案**:'syslogd',它负责更踪系统信息,并将更踪日志存储在特定的日志文件里
+
+### 4. 在/root分区运行'fsck'命令的最低要求是什么?###
+
+**答案**:/root分区必须挂载为只读模式,而不是读写模式
+
+### 5. 如何分层复制/home目录到另一个目录,你有什么办法?###
+
+**答案**:Linux的'cpio'命令起到了效果。'cpio'可以分层地复制文件和目录层次结构到另一个位置
+
+### 6. 在Linux中,怎样实现日志文件的自动替换?###
+
+**答案**:'logrotate'提供日志自动替换功能
+
+### 7. 你知道Linux中是谁在安排工作吗?###
+
+**答案**:使用'at'命令加上'-l'选项,就可以查出
+
+### 8. 如何在不解压tar包的前提下,查看包里的内容 ###
+
+**答案**:使用'tar -tvf'。选项‘t’(显示内容),‘v’(详细报告tar处理的文件信息),‘f’(使用档案文件或者设备)
+
+### 9. 什么是页面错误,它是怎么发生的?###
+
+**答案**:当一个程序请求内存中不存在的数据时,就会产生页面错误,导致的结果就是程序停止
+
+### 10. 什么叫在程序中返回代码?###
+
+**答案**:返回代码是shell的特性。返回代码显示了程序的状态,一个成功的程序执行后返回‘0’,&&可以用来决定那个应用程序先执行
+
+好了,文章要结束了。不久以后,我还会在这分享其余有趣文章的,记得和我们保持联系。还有,别忘了在评论栏里面向我们提供您的宝贵意见
+
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-interview-questions-and-answers-on-linux-commands/
+
+原文作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
+
+译者:[su-kaiyao](https://github.com/su-kaiyao) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
+
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140723 How to configure chroot SFTP in Linux.md b/translated/tech/20140723 How to configure chroot SFTP in Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..6847924e54
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140723 How to configure chroot SFTP in Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+在Linux中为SFTP配置chroot环境
+================================================================================
+在**某些环境**中,系统管理员想要允许极少数用户传输文件到Linux盒子中,而非ssh。要实现这一目的,我们可以使用**SFTP**,并为其构建chroot环境。
+
+### SFTP & chroot背景: ###
+
+**SFTP**是值**SSH文件传输协议(SSH File Transfer protocol)或安全文件传输协议(Secure File Transfer Protocol)**,它提供了任何可信数据流下的文件访问、文件传输以及文件管理功能。当我们为SFTP配置chroot环境后,只有被许可的用户可以访问,并被限制到它们的**家目录**中,或者我们可以这么说:被许可的用户将处于牢笼环境中,在此环境中它们甚至不能切换它们的目录。
+
+在本文中,我们将配置**RHEL 6.X** & **CentOS 6.X中的SFTP Chroot环境**。我们开启一个用户帐号‘**Jack**’,该用户将被允许在Linux盒子上传输文件,但没有ssh访问权限。
+
+### 步骤:1 创建组 ###
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# groupadd sftp_users
+
+### 步骤:2 分配附属组(sftp_users)给用户 ###
+
+如果用户在系统上不存在,使用以下命令创建:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# useradd -G sftp_users -s /sbin/nologin jack
+ [root@localhost ~]# passwd jack
+
+对于**已经存在的用户**,使用以下usermod命令进行修改:
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# usermod –G sftp_users -s /sbin/nologin jack
+
+**注意**:如果你想要修改用户的**默认家目录**,那么在useradd和usermod命令中使用‘**-d**’选项,并设置**合适的权限**。
+
+### 步骤:3 现在编辑配置文件 “/etc/ssh/sshd_config” ###
+
+ # vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
+ #comment out the below line and add a line like below
+ #Subsystem sftp /usr/libexec/openssh/sftp-server
+ Subsystem sftp internal-sftp
+
+ # add Below lines at the end of file
+ Match Group sftp_users
+ X11Forwarding no
+ AllowTcpForwarding no
+ ChrootDirectory %h
+ ForceCommand internal-sftp
+
+#### 此处: ####
+
+- **Match Group sftp_users** – 该参数指定以下的行将仅仅匹配sftp_users组中的用户
+- **ChrootDirectory %h** – 该参数指定用户验证后用于chroot环境的路径(默认的用户家目录)。对于Jack,该路径就是/home/jack。
+- **ForceCommand internal-sftp** – 该参数强制执行内部sftp,并忽略任何~/.ssh/rc文件中的命令。
+
+重启ssh服务
+
+ # service sshd restart
+
+### 步骤:4 设置权限: ###
+
+ [root@localhost ~]# chmod 755 /home/jack
+ [root@localhost ~]# chown root /home/jack
+ [root@localhost ~]# chgrp -R sftp_users /home/jack
+
+如果你想要允许jack用户上传文件,那么创建一个上传文件夹,设置权限如下:
+
+ [root@localhost jack]# mkdir /home/jack/upload
+ [root@localhost jack]# chown jack. /home/jack upload/
+
+### 步骤:5 现在尝试访问系统并进行测试 ###
+
+尝试通过ssh访问系统
+
+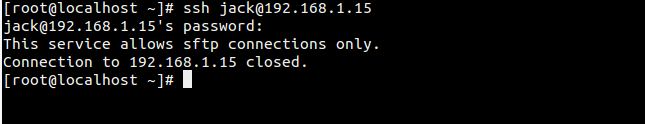
+
+正如下图所示,用户jack通过SFTP登录,而且因为chroot环境不能切换目录。
+
+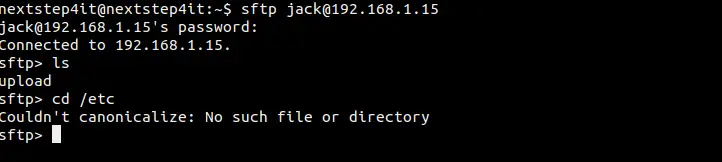
+
+现在进行**上传和下载**测试,如下图:
+
+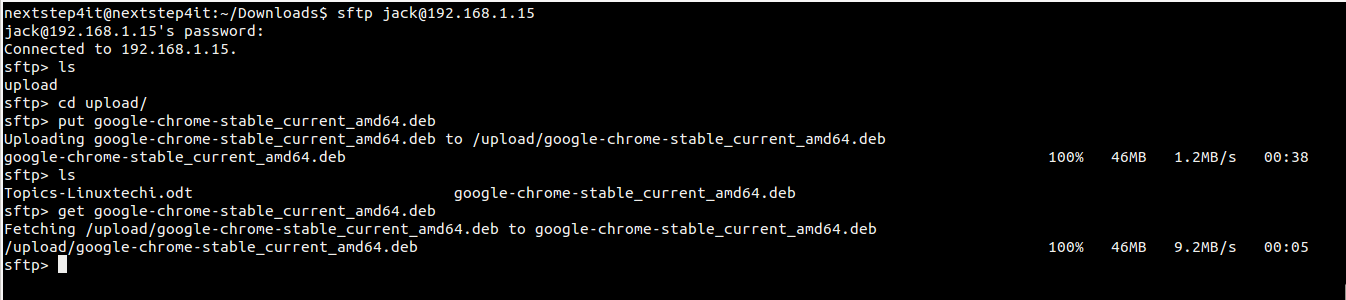
+
+正如上图所示,jack用户的上传下载功能都工作得很好。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/configure-chroot-sftp-in-linux/
+
+原文作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
+
+译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140724 How to Merge Directory Trees in Linux using cp Command.md b/translated/tech/20140724 How to Merge Directory Trees in Linux using cp Command.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2f9beebd09
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20140724 How to Merge Directory Trees in Linux using cp Command.md
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+在linux中怎样使用cp命令合并目录树
+================================================================================
+怎样将布局相似的两个目录树合并成新的目录树? 为理解该问题让我们思考下面的例子.
+
+假设dir1和dir2目录中分别有3个子目录a,b和c.目录布局如下所示:
+
+
+输入目录布局
+
+在目录a,b和c中有一些文件,tree命令的输出将能更好的说明:
+
+
+文件布局
+
+### 1. 使用cp命令创建合并: ###
+
+现在我们将这两个目录合并成一个新的目录,如"merged".完成上述操作最简单的方式就是递归
+复制目录,如下图所示:
+
+
+递归复制完成新的合并
+
+#### 1.1 cp命令和替换带来的问题: ####
+
+这种方式所带来的问题是该合并目录中所创建的文件为原文件的副本,并非原文件本身. 别急, (你可能正在问自己) 如果不是原文件又有什么问题? 为了回答你的问题,考虑下你有很多大文件的情况
+.那种情形下,复制所有的文件可能消耗数小时.
+
+现在让我们回到刚那问题上,且尝试使用mv命令而不是cp命令.
+
+
+企图使用mv命令进行合并操作
+
+这些目录不能被合并.因此我们不能像这样使用mv命令去合并目录.
+现在你该怎样将原文件保存到"merged"目录中?
+
+### 2. 方法: ###
+
+cp命令有一个非常有用的选项来帮助我们摆脱这种状况.
+cp命令的-l 或 --link选项能够创建硬链接而非原文件副本.让我们尝试一下.
+
+在我们尝试cp命令的硬链接选项前,让我们查看一下原文件的inode号码.
+可通过tree命令--inodes选项来查看inodes:
+
+
+原文件的inodes
+
+现在我们有了inodes的列表,对于cp命令可通过--link选项创建硬链接:
+
+
+使用硬链接合并的目录
+
+#### 2.1 验证文件: ####
+
+现在文件已经被复制,让我们验证一下inodes是否和原文件匹配:
+
+
+Verify Inodes
+
+#### 2.2 清除: ####
+
+
+正如你所看到的,这些文件的inodes和原文件的一样.现在 那问题已经被解决,且
+原文件已被复制到合并目录中.现在我们能够移除dir1和dir2目录.
+
+
+移除原始目录
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/merge-directory-trees-linux/
+
+原文作者:[Raghu][a]
+
+译者:[hunanchenxingyu](https://github.com/hunanchenxingyu) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/raghu/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/Building A Raspberry Pi VPN Part One--How And Why To Build A Server.md b/translated/tech/Building A Raspberry Pi VPN Part One--How And Why To Build A Server.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e58a8fab69..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/Building A Raspberry Pi VPN Part One--How And Why To Build A Server.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,324 +0,0 @@
-在树莓派上建立VPN~第一部分~:如何以及为何建立一个服务器
-================================================================================
-> 不要相信任何人,自己建立为Web数据加密的服务器从而躲过他人的窥视
-
-虽然免费,未加密的无线AP遍地都是,但是你不应该连接这些AP来登陆你的网银账户,除非你对他人的窥视毫不在意.那么对此的解决方案是什么呢?一个[虚拟专用网][1],也就是VPN(virtual private network).
-
-一个VPN可以使你的私用网络拓展至公共场所,因此即使你连接着星巴克的 Wi-Fi,你对网络浏览仍然保持着安全的加密.
-
-有很多方法来建立VPN,包括[免费以及付费的服务][2],但是每个解决方案都有其的优点以及缺点,取决于VPN服务商运作的方式和服务商提供的VPN选项.
-
-最简单以及最方便的保证数据安全的方法就是完全抛弃公共Wi-Fi.但是这个解决方案对于我来说有点极端了,一部分原因是在家里建立一个VPN服务器相对容易以及划算,你只需要一个便宜(35刀)小型的树莓派.
-
-我的树莓派与智能手机差不多大小,并且它拥有一个VPN服务器所有应有的功能.这意味着不管我在哪里,我可以通过安全的网络连接在家里的电脑和家里的内网来访问分享的文件以及媒体.这个服务器在我最近去波士顿的旅途中使生活变得十分美好,在旅途中我仍然可以观看储存在家里台式机上的视频.
-
-在这部分文章中,说实话我喜欢直接带给你们一个设置树莓派VPN的教程.问题是这个优秀教程并不存在,至少目前没有一个适合大部分电脑用户的优秀教程.虽然有无数关于如何搭建树莓派VPN的教程,极少教程会解释这么做的目的.
-
-我阅读了不少教程,并把好的部分整合入了这半篇教程中,来教授读者如何搭建树莓派VPN服务器.这个教程甚至连我都能理解,在如何搭建之后完成了为何搭建部分.最重要的是,我相信Eric Jodoin的VPN教程更适合那些专家,但它使我的大脑直接宕机了...
-
-那么跟随我钻进加密法的兔子洞并且开始学习吧,无论你有多么多疑,提出了创造VPNs的那个人更正是如此.
-
-### 材料 ###
-
-#### 硬件 ####
-
-
-
-**Raspberry Pi Model B**:以及使其工作所需要的所有硬件-一个常规电源供电器和一个放置的小盒子.小盒子可以避免意外的可以造成树莓派硬件损坏的短路-这个盒子甚至可以是一个自己折叠的纸板箱.
-
-**SD card**:我建议8GB及以上的容量,只是来保证你有必要的储存空间.像所有树莓派项目一样,SD卡上应该要预装上NOOBS.
-
-**CAT-5线**:这根线将连接树莓派的以太网接口至你的路由器的以太网接口.
-
-#### 软件 ####
-
-[Open VPN][3]:这是一个开源VPN服务,我们今天就要安装它.
-
-### 开始项目之前的准备 ###
-
-1) 你需要[准备好NOOBS][4]并且安装完[Raspbian][5].我在"鱼缸量化"项目中对此做过一个[一步步][6]的教程.因此你也可以在那里查看.
-
-2) 你需要为树莓派设置一个在你家内网中的静态IP地址.这一步骤取决于你路由器的型号,因此你可能需要阅读你的路由器的说明书来完成这一步.如果你还没有完成这一步,你可以参照ReadWrite的[教程][7].
-
-3) 你需要启用SSH.我们需要通过[SSH][8]与树莓派进行连接,一个使我们能够从另一台电脑连接树莓派的工具.通过这个方法,我们在这个项目中不需要再为树莓派单独设置一个显示屏以及无线键盘.再提一下,看看ReadWrite的[教程][9].
-
-4) 你需要将1194端口映射至树莓派的内网IP地址[UDP traffic][10],完成这一步的方法也决定于你路由器的型号,所以阅读路由器说明书吧.如果你想用另一个端口,没问题,只要将此教程中提及"TCP","UDP"的1194端口改为你需要的端口就行了.想必你也猜到了,ReadWrite为此也写了一篇[教程][11].
-
-你可以从上文看出,我们现在在建立一些树莓派的基础概念,这也是为什么在树莓派上搭建VPN对初学者来说不是一个适合的原因之一.
-
-### 简单的一些警告 ###
-
-我曾经喜欢直接拷贝网上教程中的代码,但是当我自己测试这篇教程时,我发现直接的复制粘贴代码会导致一些错误,原因是复制粘贴中出现的空行以及格式变化.如果你发现在此篇教程在实际操作时出现了一些问题,我的建议是先手动输入代码试试!
-
-### First Steps ###
-
-1) 启动并修改树莓派的密码.如果你还在使用树莓派的默认用户名(pi)和密码(respberry),那么接下来的安全教程就完全没有什么意义了.
-
-打开一个terminal/PuTTY 窗口输入:
-
- sudo passwd
-
-将用户名以及密码修改地既好记并难猜([微软对此有一些建议][12]),不然的话为什么要自找麻烦搭建一个私人网络呢?
-
-2) 为了树莓派的安全来进行软件包的升级.为此有两条命令:
-
- sudo apt-get update
-
- sudo apt-get upgrade
-
-这应该不会花太多时间,而且为我们排除了之后可能会产生的问题.
-
-3) 接下来我们需要这个开源软件(OpenVPN).输入:
-
- sudo apt-get install openvpn
-
-
-
-树莓派会寻求你的安装许可,因为这用掉一点点储存空间.但是由于我们已经准备了一张8GB及以上的SD卡,我们对此完全没问题.
-
-### 生成密钥 ###
-
-4) 你当然不想让任何发现你的VPN的人就可以连接,因此我们会为这个安全的地址准备一个来验证身份的密钥.这就像为你的家门准备一把锁一样.
-
-OpenVPN自带了Easy_RSA,一个轻量并容易的使用RSA加密方法的包.发明于1977年,RSA是第一个沿用至今可用的加密系统.加密的密钥是公开的,解密的密钥是保密的.如果你听说过比特币的工作原理,这些对你来说应该十分熟悉.
-
-通过使用Easy_RSA,你可以使用软件带有的算法来生成一个独一无二的密钥.
-
-首先获得树莓派的系统权限,就是将命令提示符中的"pi@raspberrypi"转换成"root@raspberrypi".
-
- sudo -s
-
-这句命令在现有的终端中再次创建了一个拥有root权限的终端实例.我们需要获得root权限的原因是,如果我们没有root权限,树莓派将不会允许我们创建密钥.
-
-接下来,输入:
-
- cp –r /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/easy-rsa/2.0 /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa
-
-在这句命令中,"cp"代表"复制","r"代表递归.这说明我们让电脑执行:复制这个目录以及此目录下的所有文件结构及文件.
-
-在**/2.0**和**/etc**中间的空格表示我们将第一个目录地址的文件(一个实例文件)拷贝至第二个目录地址,就是你让OpenVPN寻找密钥的地址.
-
- cd /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa
-
-5) 接下来,我们需要"cd",改变所在目录(change directory),来放置我们生成的Easy_RSA文件.一旦完成这步,我们需要打开文件**/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/vars**来编辑.我们可以使用nano: **nano /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/vars**,由于我们以及在此目录下了,我们可以使用简写:
-
- nano vars
-
-Nano在Raspbian中内建的文件编辑工具,当然也有其他工具提供给"科技通"们,不过我们将在此教程中只使用nano.
-
-现在,将你的 EASY_RSA 变量改为:
-
- export EASY_RSA="/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa"
-
-对我来说,这是在第13行.
-
-
-
-为什么要修改这个变量呢?其实这是你在回答计算机的问题"你想让文件生成在哪里?".在这个情况下,我们想要将其生成在我们保存的同一个目录,easy-rsa文件树的顶层.
-
-在vars文件中我们还可以做一件事,如果你对Innuminati阅读你的邮箱这件事十分偏执的话,你可以将加密方法从1024-bit改至2048-bit.在vars文件中,它明显的指出,"偏执狂请将此改为2048"("increase this to 2048 if you are paranoid").
-
-但是因为这个方法大大增长了生成密钥的时间,我们不会在这个教程中使用它.保持下面这个样子:
-
- export KEY_SIZE=1024
-
-按下**Control+X**来保存修改并推出nano.
-
-### 获取加密手段 ###
-
-6) 现在该搭建CA证书和Root CA证书了.
-
-在加密学中,一个授权机构(certificate authority (CA))是一个颁布电子证书的存在.电子证书证明公钥的所有者.
-
-你可能一直在使用它只是你自己不知道而已.举个例子,当我登陆我的网银账户时,我可以在网页地址前看到HTTPS字符.当我点击HTTPS前的锁时,我会看到一个叫做[GeoTrust][13]的公司验证了我网银页面的合法性,因此我知道这不是一个钓鱼欺诈网站.(当然最近的[Heartbleed漏洞][14]指出HTTPS并不是我们想得那么安全).
-
-在树莓派这个例子中,我作为我自己的授权机构,自己为OpenVPN签字,而不是通过一个第三方公司.
-
- cd /etc/openvon/easy-rsa
-
-现在我们又改变了所在目录,将下面命令一行接一行输入终端:
-
-**source ./vars** → 这个"source"加载你之前修改的文件(vars).
-
-**./clean-all** → 这会删除之前所有的密钥文件,如果有的话.如果在这个文件目录下有你不想删除的密钥文件(比如这是你第二次尝试这篇教程),跳过这条命令.
-
-**./build-ca** → 最后一条来生成你的授权机构.
-
-再输入第三条命令之后,树莓派会弹出一堆选项,你可以填写这些选项如果你愿意的话--国家名字,州名或省名,位置名,机构名,机构单位和电子邮件地址.如果你不想填写,只要在每个选项出现时按"enter"就行了,树莓派会使用默认值.下面的截屏展现了这些选项的长相:
-
-
-
-现在你可以为你的服务器命名了.我很创新地将其命名为"Server"...你可以取任意的名字,不过别忘记输入:
-
- ./build-key-server [Server_Name]
-
-再次,树莓派会给出一系列的选项,请随便输入,但注意以下几个选项:
-
-**Commom Name ** 必须是你为服务器取得名字.
-
-**A challenge password?** 必须留空.
-
-**Sign the certificate? [y/n]** 废话,你必须输入"y".
-
-你接下来会获得说明你的证书会在接下来的3650天中有效的信息.因此,如果你打算长期使用这个VPN的话,你必须在十年后重新走这个流程.
-
-**1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]** 明显,输入"y".
-
-
-
-6) 服务器端就这么设置好了.现在该为各位用户生成密钥了,或者说"客户".我为家里的计算机,平板,手机各生成了一个密钥,总共有5个.不要以为在所有客户端使用同样的密钥就可以节省时间,这样的话,一次只能有一个设备能访问VPN.
-
- ./build-key-pass UserName
-
-我发现采用用户名 Client1, Client2, Client3...十分方便
-
-
-
-在这之后,更多信息会弹出!
-
-**Enter PEM pass phrase** 设置其为你记得住的密码!他会让你输入两次,不会有几率输入错误.
-
-**A challenge password?** 必须留空!
-
-**Sign the certificate? [y/n]** 同样签十年.
-
- cd keys
-
- openssl rsa -in Client1.key -des3 -out Client1.3des.key
-
-留意我们使用des3加密生成的字符串文件,des3是一个复杂[加密算法][15]会在每一个数据块上运行3次,来防止骇客的暴力破解.OpenSSL 代表开源的加密套接字实现,是一个建立安全连接的标准方法.你需要为你生成的每一个客户端运行这一步.
-
-有人会说这一步完全没有必要,你可以跳过这一步.但是如果你通过Android或者iOS设备连接OpenVPN,那么你必须要做这一步,不然的话目前版本在解析你的密钥时会有一些困难产生.
-
- Enter pass phrase for Client1.key
-
-说实话,我用了和以前一样的密码.再输入一遍,就想说的那样.
-
-
-
-现在我们已经创建了服务器证书以及至少一个客户端证书,输入以下命令:
-
- cd /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/
-
-或者
-
- cd ..
-
-两种方法都会将你的所在目录带会/easy-rsa/.
-
-7) 现在该生成[Diffie-Hellman key exange][16]了.这是使你的VPN工作的关键代码,一个使两个没有准备的实例通过服务器交换密钥的协议.像RSA一样,这是现有的最早发明的加密系统.
-
- ./build-dh
-
-这一步会花一些时间,甚至比2048-bit加密还要慢.而且没有任何方法可以预测它运行的时间,因为这个算法使用的是随机数并寻找一些特定的关系.事实上,在我写这篇教程时,1024-bit加密只花了我5分钟.
-
-
-
-8) 最后,我们要实现OpenVPN内建的服务阻断攻击(Denial of Service -- DoS)防护.你可能已经知道服务阻断攻击是骇客找到你的服务器地址后很有效的攻击手段,这种攻击通过生成大量的访问请求来使你的服务器崩溃.
-
-输入以下代码来生成静态的HMAC([hash-based message authentication code][17])密钥:
-
- openvpn --genkey --secret keys/ta.key
-
-## 最后收尾 ##
-
-9) 我们已经生成了密钥以及来签名的授权机构.剩下的只是如何告诉OpenVPN如何配置这个服务器了.
-
-因为我们在树莓派上使用在没有图形用户界面的Linux操作系统,我们需要生成一个.conf (configuration) 文件来告诉OpenVPN如何配置服务器,而不是通过图形界面的选择.用nano打开.conf文件:
-
- nano /etc/openvpn/server.conf
-
-我们在这个目录下打开.conf文件的理由是,编辑完此文件会直接生成在/etc/openvpn的目录中.但是你刚刚打开的这个文件是空的.[将此地址中的配置复制入编辑器][18].在配置中我用大写字符注释了你必须要更改的地方,具体可以看注释.按下 Control+X 来保存文件.
-
-10) 让我们快速地编辑一下另一个配置文件.在默认配置下树莓派并不会映射网络流量,我们需要另一个配置文件来使树莓派启用对我们新建网络中的网络流量的映射.
-
- nano /etc/sysctl.conf
-
-在文档开头处有注释:"反注释下一行来启用IPv4中的数据包映射."("Uncomment the next line to enable packet forwarding for IPv4.").我在下面的截图中高亮了这部分.
-
-
-
-删除那一行前面的 # 来反注释这一行.这告诉树莓派要对IPv4的数据包进行映射.当你反注释了这一行,树莓派就拥有了作为互联网的中介而不是单单的接受者的权限,可以既接受并传输数据包.
-
-按下 Control+X 来保存修改.通过以下命令启用此配置:
-
- sysctl -p
-
-sysctl命令表示"[在运行中改变内核配置参数][19]".-p 告诉计算机重新加载你刚刚修改的配置文件.
-
-11) 到这一步我们以及配置完了一个拥有互联网访问权限的工作中的服务器.但是我们还不能用它,用为树莓派有内置的[防火墙][20]来限制传输入的网络连接.
-
-Raspbian的防火墙会在来路不明的互联网源头中保护你的树莓派.我们仍然需要防火墙来保护我们,但是我们要在防火墙中挖一个OpenVPN样子的洞,使OpenVPN的连接可以顺利通过.
-
-此外,Raspbian的防火墙会在重启后默认进行重置.我们需要创建一个简单的脚本使树莓派记住每次重启时对OpenVPN的连接进行允许.
-
- nano /etc/firewall-openvpn-rules.sh
-
-这是一个空文件,输入以下内容:
-
- #!/bin/sh
-
- iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.8.0.0/24 -o eth0 -j SNAT --to-source 192.168.XX.X
-
-不要忘记将默认IP地址改为你树莓派的IP地址!
-
-分解下这条命令: 10.8.0.0 是客户端连接树莓派VPN后树莓派的默认地址. "eth0"代表以太网接口. 将其改为"wlan0"如果你使树莓派用无线连接互联网, 当然我不建议你这么做. 按下 Control+X 保存编辑.
-
-为了安全考虑, 我们要改变**/etc/firewall-openvpn-rules.sh**的所有者,使此文件默认不可被运行. 首先将权限设定为[700][21] (所有者可以读,写,执行). 然后,我们会将此脚本的所有者改为root, 在Linux标准系统中, root代表系统管理员.
-
- chmod 700 /etc/firewall-OpenVPN-rules.sh
-
- chown root /etc/firewall-OpenVPN-ruels.sh
-
-12) 我们已经创建了一个在防火墙中开出OpenVPN形状的洞, 我们现在只需要将这个脚本注射入网络interface初始化的代码中, 然后它就会在每次开机时运行了.
-
- nano /etc/network/interfaces
-
-找到带有"iface eth0 inet dchp"的那一行. 我们需要在这行之后的缩进中加上一行. 下面是这两行, 一行新加入, 一行原来就存在, 在完成之后它应该差不多像这样:
-
- iface eth0 inet dhcp
-
- pre-up /etc/firewall-openvpn-rules.sh
-
-按下 Control+X 保存更改 (当你在使用nano的时候都应该这么做).
-
-最后, 在最后, 在最最后: 重启树莓派.
-
- sudo reboot
-
-恭喜你!! vpn服务器就这么搭建完成了, 当然如果没有客户端连接服务器的话, 服务器也没什么用, 因此你应该牢记你在第6步创建, 生成的用户名及密钥. 接下来你可以继续阅读这篇教程的[第二部分][22]来学习如何创建加密的客户端.
-
-树莓派的照片来自 [Tors][23]. 其他所有的截屏来自Lauren Ordini. 教程展示于ReadWrite.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://readwrite.com/2014/04/10/raspberry-pi-vpn-tutorial-server-secure-web-browsing
-
-译者:[ThomazL](https://github.com/ThomazL) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_private_network
-[2]:http://netforbeginners.about.com/od/readerpicks/tp/The-Best-VPN-Service-Providers.htm
-[3]:http://openvpn.net/
-[4]:http://learn.adafruit.com/setting-up-a-raspberry-pi-with-noobs/overview
-[5]:http://www.raspbian.org/
-[6]:http://readwrite.com/2014/03/04/raspberry-pi-quantified-fish-acquarium
-[7]:http://readwrite.com/2014/04/09/raspberry-pi-projects-ssh-remote-desktop-static-ip-tutorial?utm_content=readwrite3-orionautotweet&awesm=readwr.it_b1UN&utm_campaign=&utm_medium=readwr.it-twitter&utm_source=t.co#awesm=~oAXilI0BMOHsS3
-[8]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secure_Shell
-[9]:http://readwrite.com/2014/04/09/raspberry-pi-projects-ssh-remote-desktop-static-ip-tutorial
-[10]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User_Datagram_Protocol
-[11]:http://readwrite.com/2014/04/09/raspberry-pi-projects-ssh-remote-desktop-static-ip-tutorial?utm_content=readwrite3-orionautotweet&awesm=readwr.it_b1UN&utm_campaign=&utm_medium=readwr.it-twitter&utm_source=t.co#awesm=~oAXilI0BMOHsS3
-[12]:http://windows.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-vista/tips-for-creating-a-strong-password
-[13]:http://www.geotrust.com/
-[14]:http://readwrite.com/2014/04/08/heartbleed-openssl-bug-cryptography-web-security
-[15]:http://osxdaily.com/2012/01/30/encrypt-and-decrypt-files-with-openssl/#
-[16]:http://www.google.com/patents/US4200770
-[17]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hash-based_message_authentication_code
-[18]:https://gist.github.com/laurenorsini/9925434
-[19]:http://linux.about.com/library/cmd/blcmdl8_sysctl.htm
-[20]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Firewall_(computing)
-[21]:http://www.thinkplexx.com/learn/article/unix/command/chmod-permissions-flags-explained-600-0600-700-777-100-etc
-[22]:http://readwrite.com/2014/04/11/building-a-raspberry-pi-vpn-part-two-creating-an-encrypted-client-side#awesm=~oB89WBfWrt21bV
-[23]:http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Raspberry_Pi_Model_B_Rev._2.jpg
-
diff --git a/translated/tech/Building A Raspberry Pi VPN Part Two--Creating An Encrypted Client Side.md b/translated/tech/Building A Raspberry Pi VPN Part Two--Creating An Encrypted Client Side.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 65f01a335c..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/Building A Raspberry Pi VPN Part Two--Creating An Encrypted Client Side.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,150 +0,0 @@
-在树莓派上建立VPN~第二部分~:建立加密客户端
-================================================================================
-> 你已经成功搭建了一个工作中的VPN服务器! 现在该干什么了?
-
-欢迎来到ReadWrite的树莓派VPN搭建教程的第二部分!
-
-到现在为止, 我们已经很清楚地摆平了将你的树莓派变成了一个虚拟私人网络这个工作. 但是随着[未来安全漏洞对互联网生活的妥协][1], 让我们感觉拥有一个安全的服务器在你的身边越来越重要了. 通过这样, 你就可以不用担心有人在信息传输于你的电脑和互联网时拦截信息, 自由地写邮件以及传输数据了.
-
-[如果你看了此教程的第一部分][2], 你应该在你的树莓派上已经配置完一个拥有完全功能的VPN服务器了. 你可以在有免费WiFi时用这个服务器来传输加密信息了. 你也可以访问保存于你家里网络中已分享的文件以及媒体.
-
-只是, 你现在还无法访问. 我们现在已经为客户端(计算机和移动设备)创建了访问的密钥, 但是我们还没有告诉客户端服务器的访问地址, 如何连接, 以及用什么密钥访问.
-
-你应该记得, 我们已经为需要连接VPN的不同客户端创建了不同的密钥. 我们将客户端命名为 Client1, Client2 和 Client3.
-
-但是为每个客户端从零单独生成一个配置文件会造成很多不必要的麻烦, 这就是为什么我们需要使用[SANS institute][3]的Eric Jodoin写的巧妙的脚本. 这个脚本会帮助我们生成配置文件.
-
-### 跟随脚本 ###
-
-这个脚本会访问我们的默认设置, 从而为每一个客户端生成各自的配置文件. 我们需要做的第一件事是, 创建一个空的刻度文本文档并写入我们的默认配置.
-
- nano /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys/Default.txt
-
-写入下面的文本:
-
- client
-
- dev tun
-
- proto udp
-
- remote <你的公网ip地址> 1194
-
- resolv-retry infinite
-
- nobind
-
- persist-key
-
- persist-tun
-
- mute-replay-warnings
-
- ns-cert-type server
-
- key-direction 1
-
- cipher AES-128-CBC
-
- comp-lzo
-
- verb 1
-
- mute 20
-
-这个文档应该长的和下面的截屏差不多, 除了你应该填入你自己的公网ip地址之外. 你注意到了我已经把我的公网ip删除了, 当然这是为了保护我的隐私. 换句话说, 每个人的本地静态ip都差不多. 他们都以 "192.268." 起头.
-
-
-
-如果你没有一个公网ip的话, 你需要使用动态DNS服务来给你自己一个域名来代替公网ip. 我建议你使用免费服务[DNS Dynamic][4], 它允许你取自己选择的名字. 然后在你的树莓派上, 你需要运行DDclient来自动更新你的DDNS登记. 我在[这里][5]写过一篇完整的教程.
-
-同样, 按 Control+X 来保存文件并推出nano.
-
-接下来, 我们需要创建一个实际的脚本. 一个可执行脚本通常从shell启动, 可以自动化一些我们需要做的工作.
-
- nano /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys/MakeOPVN.sh
-
-[这里][6]是脚本文件, 由Jodoin编写. 将内容复制粘贴至编辑器(注意一下复制粘贴中产生的问题).
-
-你需要将执行权限赋予给这个脚本. 首先改变所在目录:
-
- cd /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys/
-
-然后给予其root权限. 如果你还记得第一部分教程的内容的话, Linux中的权限管理由[不同的3位数字][7]实现. 700表示"所有者可以读,写,执行".
-
- chmod 700 MakeOPVN.sh
-
-最后, 执行文件:
-
- ./MakeOPVN.sh
-
-在脚本运行途中, 他会要求你输入现有的客户端名称. 实例: "Client1". 注意只输入已经存在的客户端名称.
-
-如果一切运行良好的话, 你应该会看到下面这行字弹出:
-
- Done! Client1.opvn Successfully Created.
-
-为剩下的客户端都执行这一步.
-
-最后要做的事是将客户端连上树莓派, 然后你就可以从客户端下载文件了. 你需要使用一个SCP (Secure Copy Protocol)客户端来实现它. 在Windows中, 我推荐[WinSCP][8]. 我一直在mac中使用[Fugu][9].
-
-注意: 如果你没有连接SCP客户端的权限, 你需要为自己授权在此文件夹的读/写权限. 回到树莓派中输入:
-
- chmod 777 -R /etc/openvpn
-
-注意在你复制完文件后取消这一步, 从而其他人不能从这里下载文件! 完成之后将权限改为[600][10], 使树莓派的用户能读/写文件:
-
- chmod 600 -R /etc/openvpn
-
-完成后回到客户端.
-
-### 使用客户端软件 ###
-
-好了,困难的部分都结束了. 从这里开始我们需要将之前生成的脚本输入图形用户界面. 对PC, Android或者iOS手机来说, 你可以下载[OpenVPN Connect][11]. 但是这个软件没有mac版, 所以我尝试了[Tunnelblick][12]和[Viscosity][13].
-
-Tunnelblick 是免费的, 但是Viscosity在免费30天尝试之后需要9美刀来购买. 不管怎么样, 我们来尝试下将mac连入我们的服务器吧.
-
-在我的情况下, mac是我第5个连接VPN的客户端, 所以我生成的文件名叫做client5.opvn.
-
-下载可以在你的OS X版本下运行的Tunnelblick. 我在使用Mavericks, 所以我下载了[beta][14]版. 虽然这个软件有很多我看起来很好笑的语言弹出, 但这真的是一个合法的下载.
-
-
-
-然后它会问你, 你的配置文件是.opvn或.tblk. 如果你选择了.opvn它会带你将文件格式转换成Tunnelblick本地格式. 我把Client.opvn传送至Tunnelblick提供的文件夹, 然后把文件夹的名字改为了Client5.tblk.
-
-好啦, 你已经可以连接了. 点击屏幕右上方Tunnelblick的标志然后选择Client5.
-
-
-
-它会问你是否传输密码文本, 这个密码和上篇中我们生成各个客户端时使用的密码是同样的.
-
-
-
-如果你密码输入正确, 你会获得像上面这样的情况.
-
-尝试在咖啡厅, 图书馆或任何有免费WiFi的地方连接VPN. 通过使用VPN, 即使你连接的是公共网络, 你的数据仍然是安全的.
-
-教程展示于ReadWrite.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://readwrite.com/2014/04/11/building-a-raspberry-pi-vpn-part-two-creating-an-encrypted-client-side
-
-译者:[ThomazL](https://github.com/ThomazL) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://readwrite.com/2014/04/10/heartbleed-security-protect-yourself-data-passwords
-[2]:http://readwrite.com/2014/04/10/raspberry-pi-vpn-tutorial-server-secure-web-browsing
-[3]:http://www.sans.org/
-[4]:https://www.dnsdynamic.org/
-[5]:http://readwrite.com/2014/04/09/raspberry-pi-projects-ssh-remote-desktop-static-ip-tutorial
-[6]:https://gist.github.com/laurenorsini/10013430/revisions
-[7]:http://www.thinkplexx.com/learn/article/unix/command/chmod-permissions-flags-explained-600-0600-700-777-100-etc
-[8]:http://winscp.net/eng/index.php
-[9]:http://download.cnet.com/Fugu/3000-7240_4-26526.html
-[10]:http://linuxcommand.org/lts0070.php
-[11]:http://openvpn.net/
-[12]:https://code.google.com/p/tunnelblick/
-[13]:https://www.sparklabs.com/viscosity/
-[14]:https://code.google.com/p/tunnelblick/wiki/DownloadsEntry#Tunnelblick_Beta_Release
diff --git a/translated/tech/How To Install 'California' Calendar App in Ubuntu 14.04.md b/translated/tech/How To Install 'California' Calendar App in Ubuntu 14.04.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 2c23ceb382..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/How To Install 'California' Calendar App in Ubuntu 14.04.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
-Ubuntu 14.04上怎样安装‘California’ 日历应用
-================================================================================
-
-
-**当非盈利软件安装Yorba时表明它开始用在被称为‘California’的桌面日历应用程序中,在上个月的 那段时间里我们都很兴奋,我们在自己的头条中进行了声明.**
-
-那是非常好的理由,Yorba在背后支撑着用户体验好的电子邮件客户端软件‘Geary’以及照片管理软件‘Shotwell’.期望他们能够自然的成为linux系统的主流软件.
-
-尽管 **California 尚未稳定** 到保证一个正式的发行版本,但现在将公司日常开发的PPA(Personal Package Archives)安装到ubuntu系统中是可使用的.
-
-### 迄今取得的进展 ###
-
-“*Neeeeeyaaaaaaaawwnnn!*” — 那是飞机即将降落在旧金山国际机场的一段警告声音.
-
-是的,California 正在积极的开发中,该软件没有完成,也没有稳定到满足任何人每天使用,但是
-如果你能够很聪明的处理一些bug的话,你能够在ubuntu 14.04上安装这款应用程序
-
-是否这样做取决于你的需要.
-
-当前的构建提供了本地管理以及Google 日历和web日历的基本支持. 事件甚至在GNOME桌面
-的日期/时间小程序中显示.
-
-#### 自然语言输入 ####
-
-当你第一次打开California 软件时,当月的概要呈现在你的面前,目前还没有-至少我能够找到一种方法
-按星期,年,议程去查看. 尽管月份使用导航按钮,然而能够周期性的操作.
-
-通过点击工具栏中的日历图标创建新的日历(*e.g., ‘work‘, ‘pet schedule‘*)及打开/关闭. 当所有的日历都展现在主窗口时,每个日历分配的不同颜色能够带来视觉的区分.
-
-为了创建新的事件,点击‘+’图标, 然后在弹出的输入框中使用**自然语言输入**,输入你想要提交事件的描述. 例如, 输入内容“*Bake Sansa Stark A Lemon Cake on Wednesday 2.45 PM*”将嵌入新的条目在周三的这个时间(14:45).
-
-
-
-我不能等待这个功能变得更加完善。现在,尽管它能够精准定位日期,但不支持经常性事件的创建
-(e.g., via “*Skype chat with Sam every Tuesday at 7 AM*“)也不能填写地点或人物(e.g., “*Coffee with Penelope on Monday 12 PM at Boston Tea Party*“).
-
-为了能够更好的控制,你可以在网格视图上双击它们来完善和编辑创建好条目. 将打开一个包含附加字段、时间选择、日期格式等的窗口.
-
-#### 缺乏光芒 ####
-
-在外观上如果有一些缺陷被发现(这个阶段bugs和遗漏选项应该被忽略). 然而在 Adwaita看来已经很棒了,ubuntu默认主题下它看起来糟透了.
-
-这不是Yorba的错误(或GNOME) 只是Ubuntu开发团队不再增加主题来支持GNOME新的GTK标题栏以及‘光主题’的模式对话框
-
-California 在ubuntu系统上完全可用,恰巧运行在相似软件分发升级失败之后. 这个问题将不影响它们在ubuntu GNOME中的运行或第三方主题的切换
-
-
-### 在ubuntu14.04中安装California ###
-
-如果你掩饰先前的警告, 我们再次重声:California 尚未稳定,正处于积极的开发中.
-
-这个[Yorba Daily PPA][2] 包含最新(未稳定)的Shotwell和Geary版本. 将这个PPA安装到你的系统中将能够看到这些软件的更新.
-
- sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yorba/daily-builds
- sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install california
-
-可通过一个安全的方法来使用这个应用程序,便是[直接下载来自PPA的.deb安装包][3]:
-
-- [Download California for Ubuntu 14.04 (64bit)][4]
-- [Download California for Ubuntu 14.04 (32bit)][5]
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/05/california-calendar-app-hits-yorba-daily-ppa
-
-译者:[hunanchenxingyu](https://github.com/hunanchenxingyu) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/04/yorba-california-calendar-app-linux
-[2]:https://launchpad.net/~yorba/+archive/daily-builds/
-[3]:https://launchpad.net/~yorba/+archive/daily-builds/+packages
-[4]:https://launchpad.net/~yorba/+archive/daily-builds/+files/california_0.1.0-0%7E188%7Eubuntu14.04.1_amd64.deb
-[5]:https://launchpad.net/~yorba/+archive/daily-builds/+files/california_0.1.0-0%7E188%7Eubuntu14.04.1_i386.deb
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/How to Install Windows 8.1 and Ubuntu 14.04 LTS on the Same Computer.md b/translated/tech/How to Install Windows 8.1 and Ubuntu 14.04 LTS on the Same Computer.md
deleted file mode 100644
index da800a2694..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/How to Install Windows 8.1 and Ubuntu 14.04 LTS on the Same Computer.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
-如何在同一台计算机上安装Windows 8.1和Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
-================================================================================
-
-
-
-**许多Windows用户,正在去尝试使用Linux操作系统,并且不用删除其它正在使用的系统。他们知道Linux操作系统,很容易更好的对待共享的同一台计算机上的其他操作系统,会很高兴的。**
-
-如果你是Wi如果你是Windows用户,你想去安装Ubuntu。例如,程序实际上是相当简单的,需要一点小小的努力来自用户,他们只需要关注一下本程序。
-
-一种新的基于PC操作系统正常的安装并不复杂,Ubuntu和Linux同样也是。在大多数情况下,用户单击“下一步”对话框中,所有的都是按照这个脚本。当你想保存,也存在于相同的PC操作系统(不一定是Windows专门),更多的工作是必需的,但可以很容易。
-
-从Ubuntu Linux编写一个图像是容易的,这是可以做到的一些应用程序。在Windows你将需要Ubuntu任何一个dvd上或USB(最好是)。为了让Ubuntu正确复制到一个USB设备,你将需要下载一个小巧的工具称为Win32 Disk Imager 0.9.5。它具有一个简单的界面,它是完全自动的。
-
-现在,把Ubuntu安装重启之前,你可能要设置一些自由的空间,将用于Ubuntu,但一个分区是不够的。您将需要两个,一个Ubuntu本身的(大约10GB,如果你不想安装太多的应用的话,就足够了)和第二分区(Windows,pagefile等),这是増加你的内存。你不需要的他们,但他们都是免费的。如果你在第二HDD安装Ubuntu,那就更好了。
-
-插上USB和重新启动。你会得到一个提示试用或安装。选择安装并给你选择:安装Ubuntu和Windows 8(或任何你拥有版本),替换Windows 8与Ubuntu,或者别的什么。
-
-你可以选择安装在Windows 8,但你也许不喜欢,安装程序将为你选择。这是更好地打击其他手动安装。
-
-发现,你放置Ubuntu空闲分区(安装程序无法读取Windows卷名称),双击它,选择ext4文件系统,和“/”作为默认的安装点。
-
-现在选择较小的分区和选择交换文件。就这些了。当你点击下一步,安装程序将启动,你将要选择的名称,密码,和其他细节。
-
-下次当你启动你时将得到一个简单的操作系统,将让你选择你喜欢的操作系统列表。
-
-尽情享受!
-
-------------------
-
-via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Install-Windows-8-1-and-Ubuntu-14-04-LTS-on-the-Same-Computer-440356.shtml
-
-译者:[CHINAANSHE](https://github.com/CHINAANSHE) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://www.softpedia.com/get/CD-DVD-Tools/Data-CD-DVD-Burning/Win32-Disk-Imager.shtml
diff --git a/translated/tech/How to download webcomics from the command line on Linux.md b/translated/tech/How to download webcomics from the command line on Linux.md
deleted file mode 100644
index ba3e53bb81..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/How to download webcomics from the command line on Linux.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,106 +0,0 @@
-
-
-在Linux系统中,如何通过命令行变出二次元世界?
-================================================================================
-你是否从来都没有错过xkcd上的漫画连载?及时地阅读到网络漫画。或者你是否考虑过从你喜欢的网站上备份所有漫画连载?如你所愿,开源社区将为你提供解决方案:使用命令行程序从终端上下载所有你喜欢的漫画连载。
-
-
-在我们开始之前,请记住一点,你下载的漫画连载仅供个人使用,在没有授权的情况下是不可以散播出去的。如果你确实喜欢该作者的作品,请支持通过捐赠或购买正版商品获得。
-
-
-在Linux中安装Dosage
-
-
-有一个下载漫画连载的开源程序叫dosage。由于该程序是用python写的,所以安装漫画连载工具的方式有几种。今天我们就从一种简单的方法开始吧。
-
-第一步,你需要安装pip(用于安装和管理python包的工具),并确保你的python版本在2.7.0至3.3区间。接下来使用pip安装dosage。
-
- $ sudo pip install dosage
-
-如果pip不能以某种方式来找到相关包(例如Ubuntu14.04系统),可以使用下列命令来找到。
-
- $ sudo pip install http://wummel.github.io/dosage/dist/dosage-2.13.tar.gz
-
-dosage将会自动创建一个名为“Comics”新的文件夹。
-
-
-Dosage的基本用法
-
-dosage的基本用法可以被描述如下。使用dosage,你可以在数据库中找到你喜欢阅读的网络漫画,当最新一期的连载发布时,你可以几时获取最新一期。从某种意义来说,无论你在网络漫画中订阅多少连载,dosage都会确保一期不落地帮你把没有读过的漫画连载下载下来。
-
-下载和阅读你的离线网络漫画,首先要用以下命令将它们列出:
-
- $ dosage -l
-
-马上,我们可以看到dosage将2000多套漫画从数据库列出。我个人建议用下面的这个命令来查找我们想要看的漫画:
-
- $ dosage -l | grep [keyword]
-
-这样就会返回所有包含关键字标题的漫画了。
-一旦你确定列表中哪一本漫画是你想要阅读的,使用一下命令订阅这本漫画:
- $ dosage [name of the webcomic]
-
-
-
-订阅漫画时会自动生成一个名为"Comics"的目录,并把最新的连载漫画下载到在里边。
-如果你不仅仅像下载最新连载的漫画而是整一部,那么你使用一下的命令就可以了:
-
- $ dosage -a [name of the comic]
-
-最后,如果你订阅了几本网络漫画,你可以使用下面这条简单的命令,方便地下载到这几本漫画的所有更新:
-
- $ dosage @
-
-如果你不想错过每天的漫画更新,你可以每天执行这条命令确保不会错过。
-
-Dosage的高级用法
-
-玩了一天dosage,你也许想知道它的更多使用方法。这需要你掌握更多的命令语法和快捷入门。
-如果你想在xkcd上下载更多的漫画连载,你应该会看到一条dosage拒绝的提示(使用成人选项,确认你的年龄):
-
- use the --adult option to confirm your age
-
-
-
-因为默认情况下,dosage会为18岁以上的成年人忽略所有网络漫画中产生的冲突(xkcd只是其中的一个)。跳过这一步,请输入:
-
- $ dosage --adult xkcd
-
-从之前的例子,你也许注意到'@'这个参数几乎用于所有关于漫画书的下载。接下来这个'@@'这个参数是关于dosage数据库的所有漫画书。
-
- $ dosage @@
-
-上面的命令会下载dosage所知道的每一本漫画的最新连载。
-如果你想获取漫画开始到特定某一天的连载,你可以使用以下命令:
- $ dosage -a [name of the comic]:[year-month-day]
-
-举个例子,我们想看《Calvin and Hobbes》2014年之前的所有连载,运行这条命令:
-
- $ dosage -a calvinandhobbes:2014-01-01
-
-最终对所有想把连载作为个人用途的开发者,dosage会在下载连载时生成rss,json和html日志文件。
-
- $ dosage -o [type] [name of the comic]
-
-在以上命令中,,[type]可以是rss,json或者html,[name of comic]也可以只用'@'。例如,用'html'参数就回创建一个漂亮的HTML代码可以看到所有已经下载到的漫画连载。
-
-下面的命令会下载所有关于Calvin and Hobbes的连载并生成一个网页代码,在你的浏览器中看到一个漂亮的网页格式呈现出所有连载漫画。
- $ dosage -o html -a calvinandhobbes
-
-
-
-最后,我会建议你阅读手册3获取更多相关信息。dosage的确是一个非常简洁的工具,它为广大网页漫画迷们服务。我很好奇地想知道像创建出一个json文件来下载连载漫画的这种创意是怎么诞生的?
-
-你还有其它更好的工具来取代dosage?或者说你是这种可以取代dosage工具的粉丝并且用得非常过瘾,那就在评论里推荐给我们吧。
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/04/download-webcomics-command-line-linux.html
-
-译者:disylee(https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://wummel.github.io/dosage/
-[2]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-pip-linux.html
-[3]:http://wummel.github.io/dosage/dosage.1.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/How to manage passwords from the command line on Linux.md b/translated/tech/How to manage passwords from the command line on Linux.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d46f855051..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/How to manage passwords from the command line on Linux.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,141 +0,0 @@
-GOLinux翻译中
-
-How to manage passwords from the command line on Linux
-如何在Linux上使用命令行管理密码
-================================================================================
-With password-based authentication so prevalent online these days, you may need or already use some sort of password management tool to keep track of all the passwords you are using. There are various online or offline services or software tools for that matter, and they vary in terms of their sophistication, user interface or target environments (e.g., enterprises or end users). For example, there are a few GUI-based password managers for end users, such as [KeePass(X)][1].
-在基于密码的认证在网络盛行的今天,你可能需要或者已经使用了某种密码管理工具来跟踪管理你正在使用的所有密码。有各种各样的在线或离线服务或者软件工具用于完成此类事情,而这些工具因复杂程度、用户界面或者目标环境(如企业或终端用户)的不同而各不相同。例如,有一些是为终端用户开发基于图形化的密码管理器,如[KeePass(X)][1]。
-For those of you who do not want any kind of GUI dependency for password management, I will describe how to manage passwords from the command line by using [pass][2], **a simple command-line utility for password management**.
-对于那些不想要依赖图形化进行密码管理的用户,笔者将会讲述如何在命令行下使用 [pass][2]来管理密码,**这是一个简单的用于命令行管理密码的工具**。
-The pass utility is in fact a shell script frontend which uses several other tools (e.g., gpg, pwgen, git, xsel) to manage user's password info using OpenPGP. Each password is encrypted with gpg utility, and stored in a local password store. Password info can be retrieved either via terminal or self-clearing clipboard interface.
-该密码工具实际上是一个shell脚本编写的前端,其中调用了几个其它工具(如gpg,pwgen,git,xsel)来使用OpenGPG管理用户的密码信息。各个密码使用gpg工具进行加密,并存储到本地密码仓库中。密码信息可以通过终端或者自清除的剪贴板工具取回。
-The pass utility is quite flexible and extremely simple to use. You can store each password info in an OpenPGP-protected plain text file, and group different password files into multiple categories. It supports bash auto completion feature, so it is very convenient to fill in commands or long password names using TAB key.
-该密码工具相当灵活,并且使用起来及其简单。你可以将各个密码信息存储到一个OpenGPG保护的普通文本文件,并且将密码文件分组放到多个类目中。它支持bash自动补全特性,因此可以很方便地使用TAB键来补全命令或者很长的秘密名称。
-### Install pass on Linux ###
-### 在Linux上安装pass ###
-To install pass on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
-在Debian,Ubuntu或者Linux Mint上安装pass:
-
- $ sudo apt-get install pass
- $ echo "source /etc/bash_completion.d/password-store" >> ~/.bashrc
-
-To install pass on Fedora:
-在Fedora上安装pass:
-
- $ sudo yum install pass
- $ echo "source /etc/bash_completion.d/password-store" >> ~/.bashrc
-
-To install pass on CentOS, first [enable EPEL repository][3] and then run:
-在CentOS上安装pass,首先[启用EPEL仓库][3],然后执行以下命令:
-
- $ sudo yum install pass
- $ echo "source /etc/bash_completion.d/password-store" >> ~/.bashrc
-
-To install pass on Archlinux:
-在Archlinux上安装pass:
-
- $ sudo pac -S pass
- $ echo "source /etc/bash_completion.d/password-store" >> ~/.bashrc
-
-### Initialize Local Password Store ###
-### 初始化本地密码仓库 ###
-Before using pass utility, you need to do one-time initialization step which involves creating a GPG key pair (if you don't have one) and a local password store.
-在使用密码工具之前,你需要执行一次初始化步骤,该步骤包括创建一个GPG密钥对(如果你还没有)以及一个本地密码仓库。
-First, create a GPG key pair (i.e., public/private keys) as follows. If you already have your own GPG key pair, you can skip this step.
-首先,通过以下步骤创建一个GPG密钥对(即:公钥/私钥)。如果已经创建了自己的GPG密钥对,可以跳过此步骤。
-
- $ gpg --gen-key
-
-It will ask you a series of questions as shown below. If you are not sure, you can accept default answers. As part of key generation, you will set a passphrase for your secret key, which is essentially the master password required to access any password info stored in local password store. A successfully generated key pair will be stored in ~/.gnupg
-执行该步骤,会询问你如下问题。如果你不确定,可以选择接受默认回答。作为密钥生成部分,你将要为你的密钥创建一个加密口令,这个口令本质上是你访问存储在本地密码仓库中的任何密码信息时的主密码。成功创建密钥对后,创建的密钥对会存储在~/.gnupg目录中。
-
-
-Next, initialize the local password store by running the following command. For , enter the email address associated your GPG key created above.接下来,运行以下命令来初始化本地密码仓库。对于,输入上面创建密钥对时的关联电子邮件地址。
-
-
- $ pass init
-
-This command will create a password store under ~/.password-store directory.
-该命令会在~/.password-store目录中创建一个密码仓库。
-
-### Manage Passwords from a Terminal with pass ###
-### 在终端使用pass管理密码 ###
-#### Insert new password info ####
-### 插入新密码信息 ###
-To insert new password info into local password store, use the following format.
-要将新的密码信息插入到本地密码仓库中,请遵循以下命令格式:
-
- $ pass insert
-
- is an arbitrary name you define, and can be hierarchical (e.g., "finance/tdbank", "online/gmail.com"), in which case the password info will be created in corresponding sub-directories under ~/.password-store
-是你定义的专有名称,并且可以分级(如 "finance/tdbank", "online/gmail.com")。在这种情况下,密码信息可以存储到~/.password-store目录下对应的子目录中。
-If you want to insert password info as multi-lines, use "-m" option as follows. Type in password info in any format as you like, and press Ctrl+D to finish.
-如果你想要分多行插入密码信息,请像以下命令一样使用"-m"选项。以你自己喜欢的任何格式来输入密码信息,然后按Ctrl+D来结束。
-
- $ pass insert -m
-
-
-注:此图片暂时无法访问,不过可以直接访问flickr地址:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14129264286/ 文章发布的时候注意此处
-
-#### View a list of all password names ####
-#### 查看所有密码名称列表 ####
-
-To view the list of all stored password names, simply type "pass":
-要查看所有存储的密码名称列表,只需输入"pass"命令:
-
- $ pass
-
-
-
-#### Retrieve password info from password store ####
-#### 从密码仓库中取回密码信息 ####
-To access the content of a particular password listing, simply use the command below:
-要访问特定密码列表中的内容,只需使用以下命令:
-
- $ pass
-
-For example:
-例如:
-
- $ pass email/gmail.com
-
-You will be asked to enter the passphrase to unlock the secret key.
-会要求你输入密码口令来解锁密钥。
-
-If you want the password to be copied to the clipboard, instead of appearing in the terminal screen, use this command instead:
-如果你想要将密码复制到剪贴板,而不是显示到终端屏幕上,使用以下命令:
-
- $ pass -c email/gmail.com
-
-Once copied to the clipboard, the password will automatically be cleared from the clipboard after 45 seconds.
-一旦密码被复制到剪贴板,剪贴板在45秒后会被自动清空。
-
-#### Generate and store a new password in password store ####
-#### 在密码仓库中生成并存储新密码 ####
-With `pass`, you can also generate a new random password which you can use for any purpose. pass will use pwgen utility to generate a good random password. You can specify the length of a password, or generate a password with or without symbols.
-使用`pass`命令,你也可以生成一个新的随机密码,该密码可用于任何目的。pass工具将会使用pwgen工具来生成一个好的随机密码。你可以指定密码的长度,或者生成是否带有符号的密码。
-For example, to generate a 10-character password with no symbol, and store it under "email/new_service.com" listing:
-例如,要生成一个具有10个字符不带符号的密码,并将它存储到 "email/new_service.com"列表中:
-
- $ pass generate email/new_service.com 10 -n
-
-#### Remove password info ####
-#### 移除密码信息 ####
-Removing existing password info is easy:
-要移除现存的密码信息是很容易的:
-
- $ pass rm email/gmail.com
-
-To summarize, pass is extremely flexible, portable, and more importantly, easy to use. I highly recommend pass to anyone looking for a simple means to organize any kind of private info in a secure fashion, without relying on GUI dependency.
-针对以上小结,pass是及其灵活,便于携带,并且更为重要的是,易于使用的一个工具。对于正在寻找能简单而行之有效地,安全地并且不依赖图形化管理任何私人信息的工具的人,笔者强烈推荐pass。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/manage-passwords-command-line-linux.html
-
-译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/08/how-to-manage-multiple-passwords-on-linux.html
-[2]:http://www.zx2c4.com/projects/password-store/
-[3]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/Linux Terminal--Dstat monitoring tools.md b/translated/tech/Linux Terminal--Dstat monitoring tools.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c7b9b751af..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/Linux Terminal--Dstat monitoring tools.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,142 +0,0 @@
-
-
-Linux终端:Dstat监控工具
-================================================================================
-
-Dstat 是一个可以取代vmstat,iostat,netstat和ifstat这些命令的多功能产品。Dstat克服了这些命令的局限并增加了一些另外的功能,比如增加了运算能力和变得更灵活了。Dstat在很方便监控系统运行状况并用于基准测试和排除故障。
-
-
-Dstat可以让你实时地看到所有系统资源,例如,你能够通过中断IDE控制器来比较磁盘利用率,或者直接通过网络带宽数来比较磁盘的吞吐率(在相同的时间间隔内)。
-
-Dstat将以列表的形式为你提供选项信息并清晰地告诉你是在何种幅度和单位显示输出。这样更好地避免了信息混乱和误报。更重要的是,它让你更方便写插件来收集你想要的数据信息,并且这种方式会令你意想不到。
-
-
-Dstat的默认输出是专门为人们实时解释而设计的,然而你却可以将详细信息通过CSV输出到一个文件或导入到Gnumeric或者Excel生成表格。
-
-
-###特征###
-
-
-- 结合了vmstat,iostat,ifstat,netstat等信息
-- 实时显示统计情况
-- 运算结果在分析和排障时具有重要意义
-- 模块化设计
-- 使用python编写的,更方便扩展现有的工作任务
-- 容易扩展和添加你的计数器(请为此做出贡献)
-- 包含了许多扩展插件以方便添加计数器
-- 分组统计节点/网络设备总数
-- 显示每台设备说明
-- 极准确的时间帧,当系统负荷时不存在时间差
-- 显示准确地单位和限制转换过程中产生的错误
-- 用不同的颜色显示不同的单元内容
-- 显示中间结果延时小于1秒
-- 支持输出CSV格式报表,并能导入到Gnumeric和Excel生成表格
-
-### 安装方法 ###
-
-Ubuntu/Mint和Debin系统:
-本地软件库中有相关安装包,你可以用下面命令安装:
-
-
- # sudo apt-get install dstat
-
-
-RHEL/Centos和Fedora系统:
-你可以在romforge软件库中添加有相关安装包,参照[2】指导后,使用命令很简单就能进行安装:
- # yum install dstat
-
-ArchLinux系统:
-
-相关软件包在社区资源库中,你可以用这个命令来安装:
-
- # pacman -S dstat
-
-
-###使用方法 ###
-
-
-dstat的基本用法只是用dstat命令就会像这样输出:
-
-
-
-这是默认输出显示的信息:
-
-
-CPU状态:CPU的使用率。这项报告更有趣的部分是显示了用户,系统,和空闲,这更好地分析了CPU当前的使用状况。如果你看到"wait"一栏中,CPU的状态是一个高使用率值,那说明系统存在一些其它问题。当CPU的状态在"waits"时,那是因为它正在等待I/O设备(例如内存,磁盘或者网络)的响应而且还没有收到。
-
-
-**磁盘统计**:磁盘的读写操作,这一栏显示磁盘的读写总数。
-
-
-**网络统计**:网络设备发送和接受的数据,这一栏显示的网络收发数据的总数。
-
-
-**分页统计**:系统的分页活动。分页指的是一种内存管理技术用于查找系统场景,一个高水平的分页表明系统正在使用大量的交换空间,或者说内存非常分散,大多数情况下你都希望看到page in和page out的值是0 0。
-
-**系统统计**:这一项显示的是中断(int)和文本转换(csw)。如果你需要一个基线来比较他们的话,这项统计通常是唯一有用的。这一栏中较高的统计值通常表示大量的进程造成拥塞,需要对CPU进行关注。当你的服务器默认情况下正在运行一些程序时,那一项将会显示一些数值。
-
-
-默认情况下,dstat每秒都会刷新数据。如果想退出dstat,你可以按"control-C"键。
-
-需要注意的是报告的第一行通常所有统计都不显示数值的。
-
-
-这是由于dstat会通过上一次的报告来给出一个总结。所以第一次运行时是没有平均值和总值的相关数据。
-
-但是dstat可以通过传递2个参数运行输出来控制报告和报告数量之间的延迟。例如,如果你想要dstat输出默认统计,和报表输出的时间间隔未3秒钟,并且报表中输出10个结果,你可以运行如下命令:
-
-
- dstat 3 10
-
-
-在dstat命令中有很多参数可选,你可以通过man dstat命令查看,大多数常用的参数有这些:
-
-- -l = shows load statistics #显示加载统计量#
-- -m = shows the memory usage (used, buffer, cache, free) #显示内存使用率(包括used,buffer,cache,free值)#
-- -r = displays I/O statistics, #显示I/O统计#
-- -s = shows the swap usage #显示swap使用情况#
-- -t = puts the current time in the first column #将当前时间显示在第一行#
-- –fs = displays file system stats (includes amount of files and used inodes)#显示系统数据(包括文件总数量和inodes值)#
-- –nocolor = sometimes very useful…
-- –socket = shows interesting network statistics #显示感兴趣的网络数据#
-- –tcp = displays common TCP stats #显示常用的CPU统计#
-- –udp = shows you the listen and active figures for the UDP usage #显示你监听的和UDP用法中的一些动态数据#
-
-
-当然不止这些用法,dstat附带了一些**插件**很大程度地扩展了它的功能。你可以通过查看/usr/share/dstat目录来查看它们的一些使用方法,常用的有这些:
-
-- –disk-util = shows how much the disks are busy at the moment#显示某一时间磁盘的忙碌状况#
-- –freespace = shows the current disk usage#显示当前磁盘使用率#
-- –proc-count = displays the number of running processes#显示正在运行的程序数量#
-- –top-bio = points to the most expensive block I/O process #指出最大块I/O进程#
-- –top-cpu = draws the attention on the most expensive CPU process#图形化显示最值得引起注意的CPU进程#
-- –top-io = shows the most expensive “normal” I/O process#显示大多数正常的I/O进程#
-- –top-mem = displays the process using the most memory#显示占用最多内存的进程#
-
-
-举一些例子:
-
-查看全部内存都有谁在占用:
-
- dstat -g -l -m -s --top-mem
-
-显示一些关于CPU资源损耗的数据:
-
- dstat -c -y -l --proc-count --top-cpu
-
-
-###如何输出一个csv文件###
-在往后的使用中,想输出一个csv格式的文件可以通过下面的命令:
-
- # dstat –output /tmp/sampleoutput.csv -cdn
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://linuxaria.com/howto/linux-terminal-dstat-monitoring-tools
-
-译者:disylee (https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:http://linuxaria.com/tag/network
-[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-and-enable-rpmforge-repository-in-rhel-centos-6-5-4/
diff --git a/translated/tech/Update Enable Username On Indicator Panel In Ubuntu 14.04.md b/translated/tech/Update Enable Username On Indicator Panel In Ubuntu 14.04.md
deleted file mode 100644
index de34e16067..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/Update Enable Username On Indicator Panel In Ubuntu 14.04.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
-这是一个免费的MySQL客户端工具,基于浏览器,使用起来非常简单,其名称中的SIDU代表Select、Insert、Delete和Update操作,当然它能够完成更多的任务,支持火狐、IE、Opera、Safari和Chrome等浏览器,其界面体验酷似数据库前端软件图形化界面,支持MySQL、Postgres和SQLite数据库。
-
-下载地址:http://downloads.sourceforge.net/sidu/sidu31.zip
-
-Navicat Lite MySQL Admin Tool
-
-Navicat是一个快速、可靠和通用的数据库管理工具,旨在简化数据库管理、降低管理成本,满足数据库管理员、开发人员和中小型企业的需要。Navicat具有一个非常直观的图形化界面,让你可以更安全、更简单的创建、组织、访问和共享信息。
-
-Navicat for MySQL是一个强大的数据库管理和开发工具。它支持3.21及以上版本的所有MySQL数据库服务器,支持绝大多数最新的MySQL功夫能,其中包括触发器、存储过程、函数、事件、视图和管理用户等。Navicat Lite是针对非商业客户提供的免费下载