mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject
This commit is contained in:
commit
d101124fb3
45
README.md
45
README.md
@ -33,23 +33,32 @@ LCTT的组成
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
目前活跃成员有:
|
||||
[wxy](https://github.com/wxy),
|
||||
[carolinewuyan](https://github.com/carolinewuyan),
|
||||
[vito-L](https://github.com/vito-L),
|
||||
[tinyeyeser](https://github.com/tinyeyeser),
|
||||
[woodboow](https://github.com/woodboow),
|
||||
[DeadFire](https://github.com/DeadFire),
|
||||
[flsf](https://github.com/flsf),
|
||||
[theo-l](https://github.com/theo-l),
|
||||
[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng),
|
||||
[boredivan](https://github.com/boredivan),
|
||||
[Linchenguang](https://github.com/Linchenguang),
|
||||
[gamelifedong](https://github.com/gamelifedong),
|
||||
[Maclauring](https://github.com/Maclauring),
|
||||
[lijhg](https://github.com/lijhg),
|
||||
[liuaiping](https://github.com/liuaiping),
|
||||
[younel0925](https://github.com/younel0925)。
|
||||
(更新于2013/10/3)
|
||||
[wxy](https://github.com/wxy),
|
||||
[carolinewuyan](https://github.com/carolinewuyan),
|
||||
[tinyeyeser](https://github.com/tinyeyeser),
|
||||
[vito-L](https://github.com/vito-L),
|
||||
[DeadFire](https://github.com/DeadFire),
|
||||
[flsf](https://github.com/flsf),
|
||||
[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng),
|
||||
[luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat),
|
||||
[woodboow](https://github.com/woodboow),
|
||||
[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi),
|
||||
[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater),
|
||||
[Linux-pdz](https://github.com/Linux-pdz),
|
||||
[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2),
|
||||
[theo-l](https://github.com/theo-l),
|
||||
[scusjs](https://github.com/scusjs),
|
||||
[Linchenguang](https://github.com/Linchenguang),
|
||||
[Vic020](https://github.com/Vic020),
|
||||
[l3b2w1](https://github.com/l3b2w1),
|
||||
[crowner](https://github.com/crowner),
|
||||
[boredivan](https://github.com/boredivan),
|
||||
[rogetfan](https://github.com/rogetfan),
|
||||
[willqian](https://github.com/willqian),
|
||||
[Maclauring](https://github.com/Maclauring),
|
||||
[small-Wood](https://github.com/small-Wood),
|
||||
[lijhg](https://github.com/lijhg),
|
||||
(更新于2013/11/13)
|
||||
|
||||
谢谢大家的支持!
|
||||
|
||||
@ -62,3 +71,5 @@ LCTT的组成
|
||||
* 2013/09/24 鉴于大家使用Github的水平不一,容易导致主仓库的一些错误,因此换成了常规的fork+PR的模式来进行翻译流程。
|
||||
* 2013/10/11 根据对LCTT的贡献,划分了Core Translators组,最先的加入成员是vito-L和tinyeyeser。
|
||||
* 2013/10/12 取消对LINUX.CN注册用户的依赖,在QQ群内、文章内都采用github的注册ID。
|
||||
* 2013/10/18 正式启动man翻译计划。
|
||||
* 2013/11/10 举行第一次北京线下聚会。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -4,9 +4,7 @@ Linux中grep命令的12个实践例子
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*12个grep命令的例子*
|
||||
|
||||
**grep**是每个**Linux**发行版都预装的一个强有力的文件样式搜索工具。无论何种原因,如果你的系统没有预装它的话,你可以很容易的通过系统的包管理器来安装它(**Debian/Ubuntu**系中的**apt-get**和**RHEl/CentOS/Fedora**系中的**yum**)。
|
||||
**grep**是每个**Linux**发行版都预装的一个强有力的文件模式搜索工具。无论何种原因,如果你的系统没有预装它的话,你可以很容易的通过系统的包管理器来安装它(**Debian/Ubuntu**系中的**apt-get**和**RHEl/CentOS/Fedora**系中的**yum**)。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install grep #Debian/Ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,7 +14,7 @@ Linux中grep命令的12个实践例子
|
||||
|
||||
###1.搜索和寻找文件
|
||||
|
||||
假设你已经在你的电脑上安装了一个全新的**Ubuntu**,你打算卸载**Python**。你浏览网页寻找教程,但是你发现存在两个不同版本的**Python**在使用,而你不知道你的**Ubuntu**安装器到底在你的系统中安装了哪个版本的Python,也不知道它安装了哪些模块。解决这个烦恼只需简单的运行以下命令:
|
||||
假设你已经在你的电脑上安装了一个全新的**Ubuntu**,然后你打算卸载**Python**。你浏览网页寻找教程,但是你发现存在两个不同版本的**Python**在使用,而你不知道你的**Ubuntu**安装器到底在你的系统中安装了哪个版本的Python,也不知道它安装了哪些模块。解决这个烦恼只需简单的运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -l | grep -i python
|
||||
|
||||
@ -32,11 +30,11 @@ Linux中grep命令的12个实践例子
|
||||
|
||||
grep还可以在一个或多个文件里用于搜索和过滤。让我们来看一个这样的情景:
|
||||
|
||||
你的**Apache网页服务器**出现了问题,你不得不从许多专业网站找一个发帖询问。好心的回复你的人让你粘贴你的**/etc/apache2/sites-available/default-ssl**文件内容。假如你能移除掉所有的注释行,那么对你,对帮你的人,以及所有阅读该文件的人,不是更容易发现问题吗?你当然可以很容易的做到!只需这样做就可以了:
|
||||
你的**Apache网页服务器**出现了问题,你不得不从许多专业网站里找一个发帖询问。好心回复你的人让你粘贴上来你的**/etc/apache2/sites-available/default-ssl**文件内容。假如你能移除掉所有的注释行,那么对你,对帮你的人,以及所有阅读该文件的人,不是更容易发现问题吗?你当然可以很容易的做到!只需这样做就可以了:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo grep -v "#" /etc/apache2/sites-available/default-ssl
|
||||
|
||||
选项**-v**是告诉**grep**命令反转它的输出结果,意思就是不输出匹配的项,做相反的事,打印出所有不匹配的项。这个例子中,有**#**的是注释行。
|
||||
选项**-v**是告诉**grep**命令反转它的输出结果,意思就是不输出匹配的项,做相反的事,打印出所有不匹配的项。这个例子中,有**#**的是注释行(译注:其实这个命令并不准确,包含“#”的行不全是注释行。关于如何精确匹配注释行,可以了解更多的关于正则表达式的内容。)。
|
||||
|
||||
###3.找出所有的mp3文件
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,21 +48,23 @@ grep还可以在一个或多个文件里用于搜索和过滤。让我们来看
|
||||
|
||||
###4.在搜索字符串前面或者后面显示行号
|
||||
|
||||
另外两个选项是-A和-B之间的切换,是用以显示匹配的行以及行号,分别控制在字符串前或字符串后显示。Man页给出了更加详细的解释,我发现一个记忆的小窍门:-A=after、-B=before。
|
||||
另外两个选项是-A和-B之间的切换,是用以显示匹配的行以及行号,分别控制在字符串前或字符串后显示的行数。Man页给出了更加详细的解释,我发现一个记忆的小窍门:-A=after、-B=before。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ifconfig | grep -A 4 etho
|
||||
$ sudo ifconfig | grep -B 2 UP
|
||||
|
||||
###5.在匹配字符串周围打印出行号
|
||||
grep命令的**-C**选项和例4中的很相似,不过打印的并不是在匹配字符串的前面或后面的行,而是打印出两个方向都匹配的行:
|
||||
|
||||
grep命令的**-C**选项和例4中的很相似,不过打印的并不是在匹配字符串的前面或后面的行,而是打印出两个方向都匹配的行(译注:同上面的记忆窍门一样:-C=center,以此为中心):
|
||||
$ sudo ifconfig | grep -C 2 lo
|
||||
|
||||
###6.计算匹配项的数目
|
||||
|
||||
这个功能类似于将**grep**输出的结果用管道传送给计数器(**wc**程序),grep内建的选项可以达到同样的目的:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ifconfig | grep -c inet6
|
||||
|
||||
###7.按给定字符串搜索文件
|
||||
###7.按给定字符串搜索文件中匹配的行号
|
||||
|
||||
当你在编译出错时需要调试时,**grep**命令的**-n**选项是个非常有用的功能。它能告诉你所搜索的内容在文件的哪一行:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -75,9 +75,9 @@ grep命令的**-C**选项和例4中的很相似,不过打印的并不是在匹
|
||||
假若你要在当前文件夹里搜索一个字符串,而当前文件夹里又有很多子目录,你可以指定一个**-r**选项以便于递归的搜索:
|
||||
$ sudo grep -r "function" *
|
||||
|
||||
###9.进行完全匹配搜索
|
||||
###9.进行精确匹配搜索
|
||||
|
||||
传递**-w**选项给grep命令可以在字符串中进行完全匹配搜索。例如,像下面这样输入:
|
||||
传递**-w**选项给grep命令可以在字符串中进行精确匹配搜索(译注:包含要搜索的单词,而不是通配)。例如,像下面这样输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ifconfig | grep -w “RUNNING”
|
||||
|
||||
@ -105,11 +105,10 @@ grep命令的**-C**选项和例4中的很相似,不过打印的并不是在匹
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo fgrep -f file_full_of_patterns.txt file_to_search.txt
|
||||
|
||||
这仅仅是**grep**命令的开始,你可能已经注意到,它对于实现各种各样的需求简直是太有用了。除了这种我们实施的只有一行的命令,**grep**还可以写成**cron**任务或者自动的**shell脚本**去执行。保持好奇心,试验一下**man页**的各个选项,为实现你的目的写出一些**grep表达式**吧。
|
||||
这仅仅是**grep**命令的开始,你可能已经注意到,它对于实现各种各样的需求简直是太有用了。除了这种我们运行的这种只有一行的命令,**grep**还可以写成**cron**任务或者自动的**shell脚本**去执行。保持好奇心,试验一下**man页**的各个选项,为实现你的目的写出一些**grep表达式**吧。
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/12-practical-examples-of-linux-grep-command/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Linux-pdz](https://github.com/Linux-pdz) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu每日小技巧——通过PPA升级你Ubuntu的LibreOffice到最新版
|
||||
Ubuntu每日小技巧:通过PPA升级你的LibreOffice
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
对于每一个你新安装的Ubuntu系统,你都会拥有一个可以让你办公的办公工具——LibreOffice。很多人都知道微软公司的的Word、Excel、PowerPoint和Outlook,但是很少有人知道LibreOffice。
|
||||
|
||||
LibreOffice靠来自全世界的志愿者来维护,由一个慈善基金会支持。它是Linux社区的一款主要的免费办公工具。它可以安装在Windows,Mac OS X和Linux等系统的计算机上。
|
||||
|
||||
就在5天前(译注:好吧,这个翻译稿拖了5天了~~,原文为“今天”),一个新的版本将面向公众开放了。Windows,Mac OS X和Linux用户可以直接从下载页面下载最新版本了。
|
||||
就在5天前(译注:好吧,这个翻译稿拖了5天了~~,原文为“今天”。),一个新的版本将面向公众开放了。Windows,Mac OS X和Linux用户可以直接从下载页面下载最新版本了。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu用户拥有添加LibreOffice软件仓库到自己的电脑来安装升级最新版的优势。如果你想要在最新版本可用时最快的得到它,这种方法将会很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,6 +30,6 @@ Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/11/daily-ubuntu-tipsupdate-to-libreoffice-latest-in-ubuntu-via-ppa/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[SCUSJS](https://github.com/scusjs) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[SCUSJS](https://github.com/scusjs) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
39
published/How to add icons to menus in Ubuntu 13.10.md
Normal file
39
published/How to add icons to menus in Ubuntu 13.10.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu 13.10中给菜单添加图标
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
通常,使用Ubuntu 13.10的用户会会对默认的程序、偏好和功能进行优化,才能得到更好的用户体验。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu的用户体验是可以优化调整的,因此用户可以通过一些工具来修改和调整那些默认设置,比如使用Ubuntu Tweak。
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,Ubuntu禁用了内部菜单的图标,即,右键点击桌面打开右键菜单时,菜单中只包含文本而且没有相应的图标。
|
||||
|
||||
不过,在Ubuntu 13.10的菜单中添加图标是很简单的:
|
||||
|
||||
- 安装Ubuntu Tweak
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:tualatrix/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install ubuntu-tweak
|
||||
|
||||
- 启动Ubuntu Tweak,并导航到`Tweaks-->Miscellaneous`
|
||||
- 选中 `Menus have icons`
|
||||
|
||||
**结果**:现在右键点击桌面,图标就会在菜单中显示, 图标显示也会在其他软件的右键菜单出现(例如, Nautilus, Firefox, Gedit中的菜单等等)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这样在最常用的右键菜单中加上新增的图标,菜单会更加清晰和美丽,特别是使用单色图标菜单显示图标时。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/how-add-icons-menus-ubuntu-1310
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Yu-Fei](http://blog.csdn.net/u011459130) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
||||
闭源优于开源的七个缘由?是这样吗?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这看起来似乎挺奇怪的,因为这样的观点来竟然自于OpenLogic的创办人,而该公司专注于在开源领域提供帮助。 但是事实上,闭源在某些情况下优于开源。
|
||||
|
||||
针对闭源……
|
||||
|
||||
###1. 出了问题,不用自己搞定
|
||||
|
||||
只要是软件,难保不出问题。要是开源软件出了这事儿,要么你自己,要么某个欠你人情债的工程师,总得有个人要花费时间排除bug。通览代码,求助于开源社区或者开源软件的供应商,通过这些手段来解决问题。
|
||||
|
||||
但是闭源呢,一旦你确定开发商代码出了问题,ok,你的工作到此为止! 你只需发个文件,等着就行了。当然,可能会等上几个月或者几年,问题才能得到解决,更甚者永远得不到答复。但是除此之外,你还能做什么呢。 把问题踢回去,放松,期待最好的解决方案,仅此而已。
|
||||
|
||||
###2. 不必担心贡献回流到社区
|
||||
|
||||
如果用的是开源软件, 很有可能, 你解决了一个bug或者做出了改善,之后你的代码就会进入到社区,随着时间的推移从而帮助测试或者维护。
|
||||
|
||||
闭源就不同了,你根本用不着给任何人做任何事情。当然,那是因为你接触不到代码,所以也修改不了,但是你可以针对遇到的问题创建自己的解决方案。你可以一直只针对同一个问题,改善再改善,一个版本接着一个版本,至少用不着跟社区打交道,为其他人提供更好的解决方法。
|
||||
|
||||
###3. 你不必考虑开源许可条款及规定事宜
|
||||
|
||||
对于开源,你必须遵循所使用的组件的许可条款。例如,想要搞明白Apache软件许可证和GPL之间的区别与联系,是需要花费一定的时间的。使用哪一种许可证取决于你所用的开源组件以及你如何使用这些组件(发布给第三方或者内部使用),据此都有不同的许可证可供应用(可附加到文档中进行说明)。
|
||||
|
||||
像OpenLogic这样的公司可以很容易地理解并遵守开源许可,但是针对闭源,你大可不必担心这类事情!你的供应商的许可协议把有关软件的所有的权利都收走了,如果没有你的公司的律师明确同意的情况下,你几乎是不可能的想以别的方式使用这些软件,想都不要想。当然,你还得考虑许可证数量、突如其来的软件合规性审计、随着时间的推移而恶化的条款、几乎难以理解的法律术语,但至少你不必了解如何使用开源组件。
|
||||
|
||||
###4. 你用不着为每个组件在众多选项中进行选择
|
||||
|
||||
针对数据库,Web服务器,应用服务器,编程语言,图形用户界面框架,类似的方面等等,开源都提供了大量的解决方案。在每一个特定的领域,你都可以找到运用不同的架构方法,使用各种语言构建的健壮的成品。找一款功能相似的工具很容易,这些工具都针对不同的使用场合进行了优化(性能、可扩展性、简洁之间的比较)。为了确信一个工具软件在既定场合下功能够满足需求,可以下载下来,试用一下。
|
||||
|
||||
使用闭源软件的话,你就用不着对付那么多的选择。你只需要在每个领域探索两三个大厂商提供的产品。如果供应商没有提供免费试用版本,或者很难说服你为试用品买单,甚至根本不和你签署试用协议,那你就节省时间了。
|
||||
|
||||
###5. 你不必四处找幻灯片
|
||||
|
||||
如果打算找一些软件的会议简报,架构图表,截图,以及其他相关的文档,这需要花费一定的时间。使用开源软件,你得读百科,访问论坛,还有邮件列表,才能获取到你需要的相关组件的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
使用闭源软件,一通电话就足够了,只需坐在自己舒适的办公室,会有西装革履的专业人士把PowerPoint演示文稿寄送到你的面前。当然,在你提供自己的联系方式之前,销售人员是不会给你打电话的。这样看来,至少自己没必要在网上搜索带有漂亮的图形的PPT。
|
||||
|
||||
###6. 你无需到处寻求技术支持
|
||||
|
||||
你可以得到来自开源社区,自己的工程师,或专业开源组织的帮助。这可能需要一些时间,以决定是否要服务等级协议(SLA)的支持,以便于在保证的时间内得到答复,就像从OpenLogic那里获得帮助一样,或者如果你可以自由的发问题到邮件列表,自己解决。
|
||||
|
||||
闭源就不同了,你根本不需要担忧从哪获得帮助。而且,你可能根本用不着和工程师当面交谈,只需要知道给谁打电话就OK了。
|
||||
|
||||
###7. 认输就行了
|
||||
|
||||
开源软件,总会有办法解决问题,打补丁,改善,强化,重构,升级,或者重写。没可能跟闭源那样,甩手走开。当然,你可以谩骂开发出这个导致问题的软件的社区,但是你仍然可以解决问题,从社区或者组织那里获得帮助,或者自己动手解决。 而对于商业供应商,那就远不能满足于骂一顿和花费一天的时间来找他们。
|
||||
|
||||
嗯,你都了解了。为甚么闭源优于开源的几条缘由。你还有要补充的吗?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://opensource.com/business/13/10/seven-reasons-closed-better-than-open-source
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[l3b2w1](https://github.com/l3b2w1) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 自从微软的反Linux、反开源战略备忘录泄露以来,已经整整过去了15个年头。让我们来回顾一下,这一战略是如何失败的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
15年前,当时临近万圣节,Eric S. Raymond发布了第一份“[万圣节档案(Halloween Documents)][1]”,文档揭露了微软专门针对Linux与开源的秘密战略。那时,“恐惧、未知与怀疑(fear, uncertainty and doubt - FUD)”这样的词汇第一次被收入辞典,到了今天,很多情况已经改变,而未曾改变的又有哪些?微软和开源世界今天能够和睦相处了吗?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,11 +19,12 @@
|
||||
今天,值得我们再次重温万圣节档案,提醒自己不要逃避开源世界的竞争。长远来看,开源软件开发模式能够大大地增进繁荣共享软件市场,而引入开源技术及其开发模式的公司,例如红帽,其发展远比那些因为“恐惧、未知与怀疑(FUD)”而固步自封的公司要好得多。如今的红帽已经拥有更加平稳的盈利潜力,在上文提到的多个开源领域都有持续的业务增长,例如云计算和大数据,相比之下,微软、甚至苹果,如果想要在这些领域有所扩展,则要在新的硬件种类方面面对高昂费用和更加危险的投资。
|
||||
|
||||
总结:不管是糖果还是软件,分享,都是前进的方向。万圣节快乐!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/halloween-documents-microsofts-anti-linux-strategy-15-yea
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
291
sources/10 basic examples of linux netstat command.md
Normal file
291
sources/10 basic examples of linux netstat command.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,291 @@
|
||||
[DONING]BY FingerLiu
|
||||
10 basic examples of linux netstat command
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Netstat ###
|
||||
|
||||
Netstat is a command line utility that can be used to list out all the network (socket) connections on a system. It lists out all the tcp, udp socket connections and the unix socket connections. Apart from connected sockets it can also list listening sockets that are waiting for incoming connections. So by verifying an open port 80 you can confirm if a web server is running on the system or not. This makes it a very useful tool for network and system administrators. So in this tutorial we shall be checking out few examples of how to use netstat to find information about network connections and open ports on a system.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a quick intro to netstat from the man pages
|
||||
|
||||
> netstat - Print network connections, routing tables, interface statistics, masquerade connections, and multicast memberships
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. List out all connections ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first and most simple command is to list out all the current connections. Simply run the netstat command with the a option.
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -a
|
||||
|
||||
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
|
||||
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
|
||||
tcp 0 0 enlightened:domain *:* LISTEN
|
||||
tcp 0 0 localhost:ipp *:* LISTEN
|
||||
tcp 0 0 enlightened.local:54750 li240-5.members.li:http ESTABLISHED
|
||||
tcp 0 0 enlightened.local:49980 del01s07-in-f14.1:https ESTABLISHED
|
||||
tcp6 0 0 ip6-localhost:ipp [::]:* LISTEN
|
||||
udp 0 0 enlightened:domain *:*
|
||||
udp 0 0 *:bootpc *:*
|
||||
udp 0 0 enlightened.local:ntp *:*
|
||||
udp 0 0 localhost:ntp *:*
|
||||
udp 0 0 *:ntp *:*
|
||||
udp 0 0 *:58570 *:*
|
||||
udp 0 0 *:mdns *:*
|
||||
udp 0 0 *:49459 *:*
|
||||
udp6 0 0 fe80::216:36ff:fef8:ntp [::]:*
|
||||
udp6 0 0 ip6-localhost:ntp [::]:*
|
||||
udp6 0 0 [::]:ntp [::]:*
|
||||
udp6 0 0 [::]:mdns [::]:*
|
||||
udp6 0 0 [::]:63811 [::]:*
|
||||
udp6 0 0 [::]:54952 [::]:*
|
||||
Active UNIX domain sockets (servers and established)
|
||||
Proto RefCnt Flags Type State I-Node Path
|
||||
unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 12403 @/tmp/dbus-IDgfj3UGXX
|
||||
unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 40202 @/dbus-vfs-daemon/socket-6nUC6CCx
|
||||
|
||||
The above command shows all connections from different protocols like tcp, udp and unix sockets. However this is not quite useful. Administrators often want to pick out specific connections based on protocols or port numbers for example.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. List only TCP or UDP connections ###
|
||||
|
||||
To list out only tcp connections use the t options.
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -at
|
||||
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
|
||||
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
|
||||
tcp 0 0 enlightened:domain *:* LISTEN
|
||||
tcp 0 0 localhost:ipp *:* LISTEN
|
||||
tcp 0 0 enlightened.local:36310 del01s07-in-f24.1:https ESTABLISHED
|
||||
tcp 0 0 enlightened.local:45038 a96-17-181-10.depl:http ESTABLISHED
|
||||
tcp 0 0 enlightened.local:37892 ABTS-North-Static-:http ESTABLISHED
|
||||
.....
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly to list out only udp connections use the u option.
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -au
|
||||
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
|
||||
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
|
||||
udp 0 0 *:34660 *:*
|
||||
udp 0 0 enlightened:domain *:*
|
||||
udp 0 0 *:bootpc *:*
|
||||
udp 0 0 enlightened.local:ntp *:*
|
||||
udp 0 0 localhost:ntp *:*
|
||||
udp 0 0 *:ntp *:*
|
||||
udp6 0 0 fe80::216:36ff:fef8:ntp [::]:*
|
||||
udp6 0 0 ip6-localhost:ntp [::]:*
|
||||
udp6 0 0 [::]:ntp [::]:*
|
||||
|
||||
The above output shows both ipv4 and ipv6 connections.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Disable reverse dns lookup for faster output ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the netstat command tries to find out the hostname of each ip address in the connection by doing a reverse dns lookup. This slows down the output. If you do not need to know the host name and just the ip address is sufficient then suppress the hostname lookup with the n option.
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -ant
|
||||
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
|
||||
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
|
||||
tcp 0 0 127.0.1.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
|
||||
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
|
||||
tcp 0 0 192.168.1.2:49058 173.255.230.5:80 ESTABLISHED
|
||||
tcp 0 0 192.168.1.2:33324 173.194.36.117:443 ESTABLISHED
|
||||
tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN
|
||||
|
||||
The above command shows ALL TCP connections with NO dns resolution. Got it ? Good.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. List out only listening connections ###
|
||||
|
||||
Any network daemon/service keeps an open port to listen for incoming connections. These too are like socket connections and are listed out by netstat. To view only listening ports use the l options.
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -tnl
|
||||
Active Internet connections (only servers)
|
||||
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
|
||||
tcp 0 0 127.0.1.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
|
||||
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
|
||||
tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can see only listening tcp ports/connections. If you want to see all listening ports, remove the t option. If you want to see only listening udp ports use the u option instead of t.
|
||||
Make sure to remove the 'a' option, otherwise all connections would get listed and not just the listening connections.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Get process name/pid and user id ###
|
||||
|
||||
When viewing the open/listening ports and connections, its often useful to know the process name/pid which has opened that port or connection. For example the Apache httpd server opens port 80. So if you want to check whether any http server is running or not, or which http server is running, apache or nginx, then track down the process name.
|
||||
|
||||
The process details are made available by the 'p' option.
|
||||
|
||||
~$ sudo netstat -nlpt
|
||||
Active Internet connections (only servers)
|
||||
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
|
||||
tcp 0 0 127.0.1.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1144/dnsmasq
|
||||
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 661/cupsd
|
||||
tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN 661/cupsd
|
||||
|
||||
When using the p option, netstat must be run with root privileges, otherwise it cannot detect the pids of processes running with root privileges and most services like http and ftp often run with root privileges.
|
||||
|
||||
Along with process name/pid its even more useful to get the username/uid owning that particular process. Use the e option along with the p option to get the username too.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo netstat -ltpe
|
||||
Active Internet connections (only servers)
|
||||
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State User Inode PID/Program name
|
||||
tcp 0 0 enlightened:domain *:* LISTEN root 11090 1144/dnsmasq
|
||||
tcp 0 0 localhost:ipp *:* LISTEN root 9755 661/cupsd
|
||||
tcp6 0 0 ip6-localhost:ipp [::]:* LISTEN root 9754 661/cupsd
|
||||
|
||||
The above example lists out Listening connections of Tcp type with Process information and Extended information.
|
||||
The extended information contains the username and inode of the process. This is a useful command for network administrators.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note** - If you use the n option with the e option, the uid would be listed and not the username.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Print statistics ###
|
||||
|
||||
The netstat command can also print out network statistics like total number of packets received and transmitted by protocol type and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
To list out statistics of all packet types
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -s
|
||||
Ip:
|
||||
32797 total packets received
|
||||
0 forwarded
|
||||
0 incoming packets discarded
|
||||
32795 incoming packets delivered
|
||||
29115 requests sent out
|
||||
60 outgoing packets dropped
|
||||
Icmp:
|
||||
125 ICMP messages received
|
||||
0 input ICMP message failed.
|
||||
ICMP input histogram:
|
||||
destination unreachable: 125
|
||||
125 ICMP messages sent
|
||||
0 ICMP messages failed
|
||||
ICMP output histogram:
|
||||
destination unreachable: 125
|
||||
... OUTPUT TRUNCATED ...
|
||||
|
||||
To print out statistics of only select protocols like TCP or UDP use the corresponding options like t and u along with the s option. Simple!
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Display kernel routing information ###
|
||||
|
||||
The kernel routing information can be printed with the r option. It is the same output as given by the route command. We also use the n option to disable the hostname lookup.
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -rn
|
||||
Kernel IP routing table
|
||||
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface
|
||||
0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
|
||||
192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Print network interfaces ###
|
||||
|
||||
The netstat command can also print out the information about the network interfaces. The i option does the task.
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -i
|
||||
Kernel Interface table
|
||||
Iface MTU Met RX-OK RX-ERR RX-DRP RX-OVR TX-OK TX-ERR TX-DRP TX-OVR Flg
|
||||
eth0 1500 0 31611 0 0 0 27503 0 0 0 BMRU
|
||||
lo 65536 0 2913 0 0 0 2913 0 0 0 LRU
|
||||
|
||||
The above output contains information in a very raw format. To get a more human friendly version of the output use the e option along with i.
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -ie
|
||||
Kernel Interface table
|
||||
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:16:36:f8:b2:64
|
||||
inet addr:192.168.1.2 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
|
||||
inet6 addr: fe80::216:36ff:fef8:b264/64 Scope:Link
|
||||
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
|
||||
RX packets:31682 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
|
||||
TX packets:27573 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
|
||||
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
|
||||
RX bytes:29637117 (29.6 MB) TX bytes:4590583 (4.5 MB)
|
||||
Interrupt:18 Memory:da000000-da020000
|
||||
|
||||
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
|
||||
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
|
||||
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
|
||||
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1
|
||||
RX packets:2921 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
|
||||
TX packets:2921 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
|
||||
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
|
||||
RX bytes:305297 (305.2 KB) TX bytes:305297 (305.2 KB)
|
||||
|
||||
The above output is similar to the output shown by the ifconfig command.
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Get netstat output continuously ###
|
||||
|
||||
Netstat can output connection information continuously with the c option.
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -ct
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will output tcp connections continuously.
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Display multicast group information ###
|
||||
|
||||
The g option will display the multicast group information for IPv4 and IPv6 protocols.
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -g
|
||||
IPv6/IPv4 Group Memberships
|
||||
Interface RefCnt Group
|
||||
--------------- ------ ---------------------
|
||||
lo 1 all-systems.mcast.net
|
||||
eth0 1 224.0.0.251
|
||||
eth0 1 all-systems.mcast.net
|
||||
lo 1 ip6-allnodes
|
||||
lo 1 ff01::1
|
||||
eth0 1 ff02::fb
|
||||
eth0 1 ff02::1:fff8:b264
|
||||
eth0 1 ip6-allnodes
|
||||
eth0 1 ff01::1
|
||||
wlan0 1 ip6-allnodes
|
||||
wlan0 1 ff01::1
|
||||
|
||||
### More examples of netstat command ###
|
||||
|
||||
Okay, we covered the basic examples of netstat command above. Now its time to do some geek stuff with style.
|
||||
|
||||
### Print active connections ###
|
||||
|
||||
Active socket connections are in "ESTABLISHED" state. So to get all current active connections use netstat with grep as follows
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -atnp | grep ESTA
|
||||
(Not all processes could be identified, non-owned process info
|
||||
will not be shown, you would have to be root to see it all.)
|
||||
tcp 0 0 192.168.1.2:49156 173.255.230.5:80 ESTABLISHED 1691/chrome
|
||||
tcp 0 0 192.168.1.2:33324 173.194.36.117:443 ESTABLISHED 1691/chrome
|
||||
|
||||
To watch a continous list of active connections, use the watch command along with netstat and grep
|
||||
|
||||
$ watch -d -n0 "netstat -atnp | grep ESTA"
|
||||
|
||||
### Check if a service is running ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to check if a server like http,smtp or ntp is running or not, use grep again.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo netstat -aple | grep ntp
|
||||
udp 0 0 enlightened.local:ntp *:* root 17430 1789/ntpd
|
||||
udp 0 0 localhost:ntp *:* root 17429 1789/ntpd
|
||||
udp 0 0 *:ntp *:* root 17422 1789/ntpd
|
||||
udp6 0 0 fe80::216:36ff:fef8:ntp [::]:* root 17432 1789/ntpd
|
||||
udp6 0 0 ip6-localhost:ntp [::]:* root 17431 1789/ntpd
|
||||
udp6 0 0 [::]:ntp [::]:* root 17423 1789/ntpd
|
||||
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 17418 1789/ntpd
|
||||
|
||||
So we found that ntp server is running. Grep for http or smtp or whatever you are looking for.
|
||||
|
||||
Well, that was most of what netstat is used for. If you are looking for more advanced information or want to dig deeper, read up the netstat manual (man netstat).
|
||||
|
||||
And do leave your feedback and suggestions in the comments box below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.binarytides.com/linux-netstat-command-examples/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[FingerLiu](https://github.com/FingerLiu) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
79
sources/Apache OpenOffice vs. LibreOffice.md
Normal file
79
sources/Apache OpenOffice vs. LibreOffice.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
||||
Apache OpenOffice vs. LibreOffice
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> The two open source office productivity suites are similar, yet one appears to have a slight advantage.
|
||||
|
||||
[Apache OpenOffice][1] and [LibreOffice][2] are the modern descendants of OpenOffice.org. For the last few years, almost all Linux distributions have included LibreOffice as their default office suite. However, in the past eighteen months, OpenOffice has reappeared, newly organized into an Apache project, and free software users now have the choice of two full-featured suites instead of one.
|
||||
|
||||
Users also have the difficulty of deciding between two almost-identical choices. The two diverged three years ago, and while that can be a long period in software development, in this case, the differences are only starting to become obvious. While considerable cleanup has gone on behind the scenes, the feature sets and underlying logic in both has mutated in only minor ways from the days of OpenOffice.org.
|
||||
|
||||
Here and there, you can find new features in the individual applications, especially in the Writer word processor. However, most of the differences are at a higher level, in support for formats and fonts, the policy towards extensions, and, most of all, in the efforts to modernize and standardize the interface.
|
||||
|
||||
### Differences in the Apps ###
|
||||
|
||||
Most of the features in LibreOffice's and OpenOffice's applications are the same. In Draw, there appear to be no difference at all. In Impress, the main difference is that LibreOffice's latest release includes support for controlling a slide show from an Android device. And although the selection of slide backgrounds differs between the two, either selection should be adequate unless you are looking for a favorite. Similarly, the greatest difference between the two versions of the Calc spreadsheet is that, in LibreOffice's, you can create data forms.
|
||||
|
||||
Even in Writer, the most popular application, the differences are generally in a minor key. In LibreOffice, the status bar at the bottom of the editing window now includes a word and character count. In addition, LibreOffice's comments can be anchored to paragraphs rather than a single point, and, in a correction of a longstanding bug, in footnotes now display besides the text to which they refer. LibreOffice also adds a simplified Find field, similar to one in a web browser, while omitting the option to insert a graphical horizontal line -- a feature that few must have used for the last decade or more.
|
||||
|
||||
### Formats and Fonts ###
|
||||
|
||||
Some of the more noticeable differences fall under the category of format and font support. For instance, OpenOffice continues to support saving to formats that have gone out of fashion, such as AportisDoc (Palm) and Pocket Word. It can open .docx files, but, unlike LibreOffice, not save to it.
|
||||
|
||||
LibreOffice also has the advantage in font support. The latest version supports OpenType, the preferred format for modern fonts because of its support for multiple languages and advanced typography. Even more importantly, by going to File -> Properties -> Fonts, you can embed fonts into the document, eliminating with a single click the need to ensure font compatibility.
|
||||
|
||||
Such features give LibreOffice a decided edge when exchanging files with Microsoft Office users. In general, neither OpenOffice nor LibreOffice interact best with Microsoft formats when a document is mostly text and contains a minimum of tables, draw objects, and complex formatting. In both, for example, you are best off sharing something like a brochure in .PDF format rather than the native Open Document Format.
|
||||
|
||||
However, if you do exchange native and Microsoft formats, LibreOffice has some decided advantages. Not only does it both read and write to recent Microsoft formats, but its advantages in font handling removes any need for font subsitution -- a major cause of problems when exchanging files. While other problems remain, such as differences in feature implementation, LibreOffice should generally be the more reliable handler of Microsoft Office files.
|
||||
|
||||
### Extension Policies ###
|
||||
|
||||
Both OpenOffice and LibreOffice support well-rounded collections of extensions that can be downloaded and added in minutes to enhance or alter features. In most cases, an extension that works with one will work with the other.
|
||||
|
||||
The difference is that, with LibreOffice, you don't have to install the most popular extensions. Instead, LibreOffice installs with them already enabled or integrated. These extensions include Lightproof, a basic grammar checker; Report Builder for summarizing and printing from data bases; Presentation Minimizer for reducing the size of presentations; Wiki Publisher for blogging, and Presentation Console for delivering slide shows, as well as a number of others.
|
||||
|
||||
All these extensions are available for OpenOffice as well. The difference is that, with OpenOffice, you need to know about them and deliberately find them. Effectively, this limitation makes a number of features unavailable to new users. When OpenOffice (and LibreOffice) have made such efforts in recent releases to provide useful modern templates and clip art, this omission is a crippling oversight, especially when it is so easily corrected.
|
||||
|
||||
### Interfaces in Transition ###
|
||||
|
||||
In the twelve years that Sun Microsystems and Oracle have owned the OpenOffice.org code, the interface, like so many features, was almost entirely neglected. The result is that today, both OpenOffice and LibreOffice are suites with a healthy set of features, but interfaces that are generally stuck in the mid-1990s. Some superficial aspects have been removed, but far more remains to be updated.
|
||||
|
||||
In the latest release, OpenOffice's efforts to overhaul the interface have been restricted largely to the sidebar, an feature that has to be specifically enabled in LibreOffice from Tools -> Options -> LibreOffice -> Advance, and is labeled as "experimental."
|
||||
|
||||
The sidebar is a collection of features, primarily for manual formatting. Since this use comes at the expense of encouraging the use of styles, as the logic of the code intends, it is easy to dismiss. However, at its best, the sidebar is an immense simplification of some of the tabs for formatting characters and paragraphs, such as the Border tab in all applications, and the Format tab for spreadsheet cells. With luck, its re-conceptualization of controls will eventually find its way to the menus and style dialogue windows.
|
||||
|
||||
LibreOffice has been even more adventuresome. For example, the task pane in Impress, while similar to the sidebar, summarizes most of the steps in slide design in the names of its tabs.
|
||||
|
||||
But it is the Writer editing window where most of LibreOffice's interface improvements have taken place. A word and character count has been added to the status bar at the bottom of the window, and the cramped sub-menus for managing and editing templates have been replaced with a stream-lined interface in which buttons replace drop-down menus.
|
||||
|
||||
Even more obvious, the main text frame has been reduced in LibreOffice to cross-hairs at the four corners. In the same way, headers and footers are invisible until you click where they should be, when four small right angles indicate their borders.
|
||||
|
||||
A less successful effort is a tab in LibreOffice's editing window for managing headers and footers. Aside from the fact that the tab encourages manual formatting, it has the annoying habit of hiding part of the first line of a new page as it is typed.
|
||||
|
||||
These efforts are far from complete, although LibreOffice has also rearranged options in a number of dialogue windows. At times, they make LibreOffice a disconcerting mixture of vintage interfaces and modern minimalism that can be disconcerting to move between. However, at least LibreOffice is trying to address the long-delayed problem of the interfaces -- something OpenOffice has not had much time to consider.
|
||||
|
||||
### Making a Choice ###
|
||||
|
||||
An average user, whose documents are rarely longer than two or three pages, would often have to check the title bar to be sure whether they were using LibreOffice or OpenOffice. However, depending on their needs, advanced users will probably find LibreOffice currently has a small, but definite advantage.
|
||||
|
||||
This advantage is hardly to be unexpected. For one thing, LibreOffice had many months to advance while OpenOffice was concerned with setting up governance and doing a code audit. These tasks might be useful and necessary, but they do not make for improvements in the code that ordinary users are likely to notice.
|
||||
|
||||
For another, the LibreOffice fork was begun largely by members of [Go-oo][3], an unofficial fork of OpenOffice.org that wanted to accelerate change. While Apache OpenOffice was forming, LibreOffice attracted talent around the world who wanted to code and were excited by the idea that everything was suddenly up for reconsideration.
|
||||
|
||||
Nobody has any done a census, but my impression is that when the OpenOffice.org community divided, the more adventurous contributors chose to focus on LibreOffice, although a few, such as the semi-independent documentation team, deliberately work for both projects.
|
||||
|
||||
However, the most important advantage for LibreOffice is what might be called the license-drain. That is, while the Apache License is compatible with LibreOffice's Lesser GNU General Public License, the Less GNU General Public License is incompatible with the Apache License. In other words, while LibreOffice can borrow code freely from OpenOffice, OpenOffice cannot borrow at all from LibreOffice. Strictly speaking, it must do clean-room implementations of features it wants to borrow from LibreOffice.
|
||||
|
||||
This situation may change, especially since Apache OpenOffice enjoys enormous name recognition compared to LibreOffice. Yet LibreOffice has quickly earned widespread support and has an active community that has done more in three years than OpenOffice.org managed in twelve.
|
||||
|
||||
For now, whether you use Apache OpenOffice or LibreOffice is likely to make very little difference unless you need a particular feature. However, I suspect that, unless something unexpected happens, LibreOffice's slight advantage is only going to widen. Whichever you decide on, you may want to schedule a re-evaluation in a few years' time.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.datamation.com/applications/apache-openoffice-vs.-libreoffice-1.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.openoffice.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.libreoffice.org/
|
||||
[3]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Go-oo
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Change Samba Workgroup And Computer Name
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Here’s another question new users to Ubuntu asked the most. The answer to the question is simple but when you’re new to anything, it takes time to fully understand it.
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s the question we received few days ago;
|
||||
|
||||
> How to change samba workgroup name and computer name in Ubuntu?
|
||||
|
||||
For most computer Ubuntu users, changing their computer name is the least thing on their list, let alone samba workgroup. A few power users may want to learn how to do this easily with using Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
When it comes to changing the computer name in Ubuntu, we’ve written a simple post on that which can be [found here][1]. Follow the this simple guide on [changing your computer name in Ubuntu][1] to accomplish your goal.
|
||||
|
||||
There maybe other ways to changing your PC name in Ubuntu but this is the easiest and fastest. For those using Ubuntu server, you can use vi or vim to edit the hostname and hosts files. Using vi or vim maybe difficult for most so only someone with knowledge of using these editors should use it.
|
||||
|
||||
To change Samba workgroup in Ubuntu, press **Ctrl – Alt – T** on your keyboard to open the terminal. When it opens, run the commands below to edit Samba’s configure file.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo gedit /etc/samba/smb.conf
|
||||
|
||||
When the file opens, make sure the line starting with workgroup in the [global] section has the word or value you want the workgroup to be. For example, if you want the workgroup to be UBGP, replace WORKGROUP with that and save the file. In most cases, you’ll have to restart the computer for the change to apply.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This is how you change your computer name as well as its workgroup in Ubuntu. Remember, if you are doing this to share or access Windows files and folders, you must also install Samba. Without Samba, it would be difficult sharing files with Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
To install Samba, run the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install samba
|
||||
|
||||
Please come back and check out other future tips about Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/11/daily-ubuntu-tips-change-samba-workgroup-and-computer-name/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/10/daily-ubuntu-tips-change-computer-name/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Get Geary, A Lightweight Email Reader In Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
As you may already know, Ubuntu comes with its own email client called Thunderbird that allows you to setup email accounts to send and receive emails. It also support IMAP protocol which services like Gmail, Yahoo Mail and Microsoft Outlook support.
|
||||
|
||||
Thunderbird is a great email client and does everything an email client supposed to do, but if you’re looking for an alternative that is lightweight and built around GNOME, then you may want to try Geary.
|
||||
|
||||
Geary is a free email program that lets you quickly and effortlessly read emails with a simple interface based around conversations. The entire discuss is read from a single pane without you having to click from one message to another.
|
||||
|
||||
Geary also support IMAP protocol which will let you send and receive emails using your online webmail accounts from Google, Yahoo and Microsoft.
|
||||
|
||||
For users with Ubuntu 13.10, Geary is already available from Ubuntu Software Center. All they have to do is run the commands below to install Geary.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install geary
|
||||
|
||||
For previous versions of Ubuntu, press **Ctrl – Alt – T** on your keyboard to open the terminal. When opens, run the commands below to add its PPA repository.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yorba/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
Next, run the commands below to update your system and install Geary.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install geary
|
||||
|
||||
When you launch Geary the first time, it wants you to setup email accounts from Gmail, Yahoo or Microsoft.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The setup is pretty easy, just enter your account info and Geary will attempt to automatically configure your account.
|
||||
|
||||
To uninstall Geary, first remove its PPA repository from your system by running the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository -r ppa:yorba/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
Then run the commands below to remove Geary.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove geary
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/11/daily-ubuntu-tips-get-geary-a-lightweight-email-reader-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
32
sources/Deciphering Top.md
Normal file
32
sources/Deciphering Top.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
Deciphering Top
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
When curious about the performance of a server, one of the first places I stop is "top". Top is not perfect, not by a long shot, but it does provide a decent point in time snapshot of the server, and attempts to answer the question of "what is going on right now?". Unfortunatly, the output of top can easily be misinterpreted if you do not have a good understanding of the different fields of data presented.
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not going to go through the [man page][2] for top, when you have the time and inclination it is always there waiting for you. What I would like to do is point out a few highlights of how I use it to get a quick overview of the system and hopefully get a direction I should go next. Top is often my first stop in troubleshooting, but it is rarely my only stop.
|
||||
|
||||
[][1]
|
||||
|
||||
The very first thing I look at in top is the load average, in the top right hand corner of the screen. The load average is computed based on a number of statistics gathered, but can generally be thought of as the amount of work the CPU is being asked to do. If your machine has a single CPU core, than a load average of one would mean that the machine was perfectly loaded and had sufficient power to accomplish all tasks during the time it was sampled. Likewise, if the load average is two, the single CPU machine was overloaded, and would have needed two available cores to accomplish the work it was being asked to do in the same amount of time. With todays 8, 16, and 32 core servers shipping, I need to think twice when considering the load average. If I need to check, I press "1" in top, which will drop down a list of all CPU cores so I can get a quick count for comparison.
|
||||
|
||||
The second item I check is the first process listed, and the ninth column over, labled "%CPU". The explanation for this column is novel:
|
||||
|
||||
> The task's share of the elapsed CPU time since the last screen update, expressed as a percentage of total CPU time. In a true SMP environment, if 'Irix mode' is Off, top will operate in 'Solaris mode' where a task's cpu usage will be divided by the total number of CPUs. You toggle 'Irix/Solaris' modes with the 'I' interactive command.
|
||||
|
||||
Clear as mud, right? The main idea to keep in mind is that if a single process has gone berzerk for one reason or antoher, it will probably show up listed first in top, with a rather extreme number for %CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
The next area I glance at is the "Cpu(s):" line, in the center of the header block. Specifically, I'm interested in the %us, which is user processes, %sy, for system processes, %id, which is idle time, and %wa, which is the percent of time the CPU had processes that were waiting on a response from an I/O stream to execute. This percentage should always be close to zero, and anything higher than 5% should be looked at closer.
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, I like to check the system up time, shown in the top left hand corner. If I'm having problems with a server, and the server was recently rebooted, there may be a correlation there, perhaps a daemon that didn't start.
|
||||
|
||||
All of these checks take only a few seconds. I may leave top running for a few minutes and watch the processes, CPU, and load if I'm just observing, but normally I'm in and out of top fairly quickly. Top is one of those fantastic sysadmin tools that is built to give you a quick overview of the health of your system, and allow you to quickly diagnose potential problems.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/deciphering-top
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/51724787@N06/10847969205/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linuxmanpages.com/man1/top.1.php
|
||||
67
sources/Five Examples Of The ping Utility.md
Normal file
67
sources/Five Examples Of The ping Utility.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
Five Examples Of The ping Utility
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### What is ping Utility? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Before going through some real world examples of the ping utility, let me explain what this commandline tool is and its purpose. The ping utility is used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. Its names comes from the active sonar method which is used to create a pulse of sound (ping) under the water and listening to echo requests from surrounding objects. This method is the best way to explain how the network ping utility works. The ping utility sends echo requests to a host and waits for an ICMP response.
|
||||
|
||||
Some Examples Of The ping Utility In Practice:
|
||||
|
||||
### Find Out The Ip Address Of A Host ###
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes you need the ip address of a host, you can use the ping tool like shown in Figure 1. Just type the ping command and after it type the hostname.
|
||||
|
||||
ping www.omgubuntu.com
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Find Out The Version Of The ping Utility You Are Using ###
|
||||
|
||||
The -V flag can be used to find out which version of the ping tool you have. Type the following command and it will display the current version of the ping utility.
|
||||
|
||||
ping -V
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see from Figure 2, I am using ping utility, iputils-sss20101006.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Exit Pinging ###
|
||||
|
||||
When you ping a machine with the ‘ping host’ command, pinging doesn’t stop and you have to pres CTRL+C to stop it, or you can use the -c (count) option to send a specified number of packets. When using the -c option, after the number of packets specified by the network admin (user whatever) is sent, the pinging process stops automatically instead of pressing CTRL+C.
|
||||
|
||||
ping -c 13 127.0.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
The above command is used to send 13 packets to my localhost.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As you can see from Figure 3 i did not press CTRL+C to exit pinging,it stopped automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
### Specify The Interval Between Packets ###
|
||||
|
||||
Did you know that ping sends a packet every second? Do you like to speed up or slow down? The -i option can be used to specify the interval between packets. Use the following commands to send packets very fast or very slow.
|
||||
|
||||
### Send A Packet Every 0.13 Seconds ###
|
||||
|
||||
ping -i 0.13
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Send A Packet Every 13 Seconds ###
|
||||
|
||||
ping -i 13
|
||||
|
||||
### Combine the -i option with -c option ###
|
||||
|
||||
ping -c 13 -i 3
|
||||
|
||||
It will take 39 seconds to send 13 packets with the specified interval of 3 seconds.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/five-examples-ping-utility/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to Install the Latest NVIDIA 331.20 Driver in Ubuntu 13.10
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**The installation of new NVIDIA drivers can be a problem sometimes, especially if you are not accustomed with the way things usually work on a Linux operating system.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This is where this tutorial will come in handy, to help regular users benefit from the most recent NVIDIA drivers, 331.20.
|
||||
|
||||
There are just a couple of ways of installing the NVIDIA driver on an Ubuntu system, the easy way and the hard way. The easy way is also the most straightforward, but it requires a working internet connection. This method will also introduce you into the beautiful world of PPAs.
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10, just like its predecessors, benefits from a large repository, but Canonical developers don’t upload the most recent version of the driver for several considerations. The most important is that it they don’t risk uploading a piece of software that has yet to be proven stable.
|
||||
|
||||
Fortunately, there is a PPA available that makes available the latest versions of the drivers, a day or two after the launch. Just enter the following command in a terminal (you will need root access):
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:xorg-edgers/ppa
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install nvidia-331
|
||||
|
||||
If you already have an older version of the driver you will need to replace the last command with sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
After the process has finished restart the computer and you’re set. The next time NVIDIA releases a new driver, you will only have to update the system, without adding the PPA.
|
||||
|
||||
The second method is a little more complicated, but you don’t need an Internet connection (you will need to download the driver at some point, but you don’t need the connection during the installation). We will be using the 64-bit driver as an example.
|
||||
|
||||
You will have to enter the virtual console with Ctrl + Alt + F1 and login into the system with the username and password. In here, you need to navigate to the location of your driver (for example Downloads) and enter the following commands
|
||||
|
||||
sudo service lightdm stop
|
||||
sudo chmod a+x NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-331.20.run
|
||||
sudo ./NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-331.20.run
|
||||
sudo reboot
|
||||
|
||||
This is it. Whatever method you choose, enjoy the latest NVIDIA drivers.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Install-the-Latest-NVIDIA-331-20-Drivers-in-Ubuntu-13-10-399182.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
@ -1,108 +0,0 @@
|
||||
(正在翻译 by whatever1992)
|
||||
How to Set Up Secure Remote Networking with OpenVPN on Linux, Part 1
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
It's always been prudent to wrap a warm comfy layer of encryption over your Internet travels to foil snoops of all kinds, and with our own government slurping up every bit wholesale it's more crucial than ever. OpenVPN is the top choice for protecting networking over untrusted networks. Today we'll learn a quick way to set up OpenVPN so you can securely access your home server when you're on the road.
|
||||
|
||||
A quick note on VPNs: there are many commercial VPNs that aren't worth the bits they're printed on. They're little better than SSL-protected Web sites, because they trust all clients. A true VPN (virtual private network) connects two trusted endpoints over untrusted networks. You can't just log in from whatever random PC you find, and this is good because (presumably) you understand that logging in to your private network from an infected host is a bad thing to do, no matter how secure the connection is. So you have to configure both your server and client.
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenVPN Quickstart ###
|
||||
|
||||
You need two computers on different subnets, like a wired and wireless PC on the same network (or a couple of Linux guests in Virtualbox), and you need to know the IP addresses of both PCs. Let's call our example computers Studio and Shop. Install OpenVPN on both of them. OpenVPN is included in most Linux distributions, so you can install it with your favorite package manager. This example is for Debian, Ubuntu, and their myriad descendants:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install openvpn openvpn-blacklist
|
||||
|
||||
That installs the server and a little program to check the blacklist of compromised keys. You must install the blacklist checker! Because once upon a time Debian distributed a [broken version of OpenSSL][1] which had a broken random number generator, so keys created with this are assumed to be too vulnerable to trust. The random number generator was not really random, but predictable. This happened way back in 2008, and everyone who used the defective OpenSSL was supposed to hunt down and replace their weak keys. Even though it's been over five years, it's cheap insurance to use the blacklist checker.
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's test it by creating an unencrypted tunnel between our two PCs. First ping each machine to make sure they're talking to each other. Then make sure that OpenVPN is not running, because we're going to start it manually:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps ax|grep openvpn
|
||||
|
||||
If it is, kill it. Let's say that Studio's IP address is 192.168.1.125, and Shop's is 192.168.2.125. Open an unencrypted tunnel from Studio to Shop:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo openvpn --remote 192.168.2.125 --dev tun0 --ifconfig 10.0.0.1 10.0.0.2
|
||||
|
||||
Then from Shop to Studio:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo openvpn --remote 192.168.1.125 --dev tun0 --ifconfig 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
When you make a successful connection you'll see something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 ******* WARNING *******: all encryption and authentication
|
||||
features disabled -- all data will be tunnelled as cleartext
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 TUN/TAP device tun0 opened
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 do_ifconfig, tt->ipv6=0, tt->did_ifconfig_ipv6_setup=0
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 /sbin/ifconfig tun0 10.0.0.1 pointopoint 10.0.0.2 mtu 1500
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 UDPv4 link local (bound): [undef]
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 UDPv4 link remote: [AF_INET]192.168.2.125:1194
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 Peer Connection Initiated with [AF_INET]192.168.2.125:1194
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 Initialization Sequence Completed
|
||||
|
||||
"Initialization Sequence Completed" are the magic words that confirm you did it right. You should be able to ping back and forth with the tunnel addresses, ping 10.0.0.1 and ping 10.0.0.2. When you build your tunnel you may use whatever IP addresses you want that don't overlap with your existing network. To close your tunnel press Ctrl+c.
|
||||
|
||||
Just for fun open an SSH session over your tunnel. Figure 1 shows a successful SSH login over a VPN tunnel, and it also demonstrates the fancy Message of the Day from [Put a Talking Cow in Your Linux Message of the Day][1]:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh carla@10.0.0.2
|
||||
|
||||
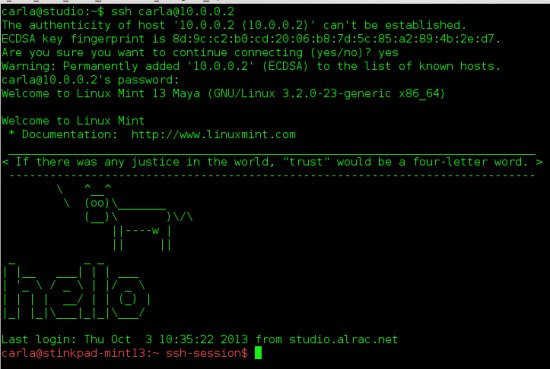
|
||||
|
||||
*Figure 1: A successful SSH session over a VPN tunnel, and a fancy MOTD.*
|
||||
|
||||
Hurrah, it works!
|
||||
|
||||
### Encrypted VPN Tunnel ###
|
||||
|
||||
This is all fun and exciting, but pointless without encryption, so we'll set up a simple static key configuration. It's not as strong as a proper public key infrastructure (PKI) with root certificates and revocations and all that good stuff, but it's a good-enough solution for the lone nerd needing to call home from the road. OpenVPN helpfully includes a command to create the static key, so create a directory to store the key in, create the key, and make it read-only for the file owner:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir /etc/openvpn/keys/
|
||||
$ sudo openvpn --genkey --secret /etc/openvpn/keys/static.key
|
||||
$ sudo chmod 0400 /etc/openvpn/keys/static.key
|
||||
|
||||
This is a plain-text key that you can open in a text editor and look at if you're curious, and you can name it anything you want; you don't have to call it "static.key". Copy this key to both computers-- yes, the same key. It's not a private-public key pair, but just one single shared key.
|
||||
|
||||
Now we'll create some simple barebones configuration files for each computer. (On Debuntu etc. there are no default configuration files, but rather a wealth of example files in/usr/share/doc/openvpn/.) In my little test tab Studio is the server, and Shop is the wandering laptop that will log into the server. My server configuration file is/etc/openvpn/studio.conf, and this is all it has:
|
||||
|
||||
# config for Studio
|
||||
dev tun
|
||||
ifconfig 10.0.0.1 10.0.0.2
|
||||
secret /etc/openvpn/keys/static.key
|
||||
|
||||
Make this file readable and writable only to the file owner:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chmod 0600 /etc/openvpn/studio.conf
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration file on the client is similar, with the addition of the IP address of the server:
|
||||
|
||||
# config for Shop
|
||||
dev tun
|
||||
ifconfig 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.1
|
||||
secret /etc/openvpn/keys/static.key
|
||||
remote 192.168.1.125
|
||||
|
||||
Mind the order of your IP addresses on the ifconfig line, because they need to be in the order of local > remote. Now fire up OpenVPN on the server, specifying the server configuration file, and do the same on your client:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo openvpn /etc/openvpn/studio.conf
|
||||
$ sudo openvpn /etc/openvpn/shop.conf
|
||||
|
||||
You'll see the same "Initialization Sequence Completed" message for a successful connection, and you must also look for the absence of this message, which should have appeared when you created your un-encrypted tunnel:
|
||||
|
||||
******* WARNING *******: all encryption and authentication features disabled
|
||||
|
||||
Firewalls and Dynamic IP Addresses
|
||||
|
||||
OpenVPN itself is simple to configure. The biggest hassles are dealing with firewalls and dynamic IP addresses. There are a skillion different firewalls in the world, so I shall leave it as your homework to figure out how to get through it safely. OpenVPN wants port 1194, and then you'll want to have a forwarding rule that points to the computer you want to access.
|
||||
|
||||
Dynamic IP addresses are another hassle. [Dyn.com][3] is an inexpensive way to manage dynamic IP assignment from your ISP. Or you might be able to pay your ISP a few bucks to get a static address.
|
||||
|
||||
At this point you could stop and call it good, because you can manually start OpenVPN on your server and leave it waiting for you, take your laptop out into the world, and connect to your server whenever you want. However, there are some refinements we can add such as daemonizing OpenVPN on the server, using Network Manager to make the connection automatically, and the biggest missing piece in OpenVPN howtos: how to access your remote resources. So come back next week for the rest of the story.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/743590-secure-remote-networking-with-openvpn-on-linux
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.debian.org/security/2008/dsa-1571
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/741573-put-a-talking-cow-in-your-linux-message-of-the-day
|
||||
[3]:http://dyn.com/dns/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
[Being translated by bazz2]
|
||||
How to Set Up Secure Remote Networking with OpenVPN on Linux, Part 2
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Greetings fellow Linux users, and welcome to the second part of our glorious OpenVPN series. When last we met we learned how to set up a [simple OpenVPN encrypted tunnel][1] between a home server and a remote node, such as a laptop. Today we're adding refinements such as how to daemonize OpenVPN so we don't have to start it manually, use Network Manager for easy connecting to our remote server, and access services.
|
||||
@ -90,4 +91,4 @@ via: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/745233-how-to-set-up-secure-remote-net
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/743590-secure-remote-networking-with-openvpn-on-linux
|
||||
[2]:http://10.0.0.1/drupal
|
||||
[3]:http://10.0.0.1/owncloud
|
||||
[3]:http://10.0.0.1/owncloud
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,56 +0,0 @@
|
||||
|
||||
**【晨光】翻译中**
|
||||
|
||||
How to add kernel boot parameters via GRUB on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The Linux kernel can be supplied with various parameters during boot time or at run time. These parameters customize the default behavior of the kernel, or inform the kernel about hardware configuration. Kernel parameters can be changed at run time by modifying files in /proc or /sys, while certain kernel parameters need be passed to the kernel at boot time by a boot loader such as GRUB or LILO.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I will describe **how to add kernel boot parameters via GRUB on Linux**.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to change or add kernel parameters when you are using GRUB boot loader, you can edit GRUB config file. The following are distro-specific ways to add kernel boot parameters to a GRUB config file.
|
||||
|
||||
### Add Kernel Boot Parameters on Debian or Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to add kernel parameters during boot time on a Debian based system, edit GRUB config template at /etc/default/grub. Add a kernel parameter in the form of “name=value” in GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT variable.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo -e /etc/default/grub
|
||||
|
||||
> GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="...... name=value"
|
||||
|
||||
Then run the following command to actually generate a GRUB config file.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo update-grub
|
||||
|
||||
If the command update-grub is not found, you can install it as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install grub2-common
|
||||
|
||||
### Add Kernel Boot Parameters on Fedora ###
|
||||
|
||||
To add kernel parameters during boot time on Fedora, edit GRUB config template at /etc/default/grub. Add a kernel parameter in the form of “name=value” in GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX variable.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo -e /etc/default/grub
|
||||
|
||||
> GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="...... name=value"
|
||||
|
||||
Then run the following command to generate a GRUB2 config file.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
### Add Kernel Boot Parameters on CentOS ###
|
||||
|
||||
To add kernel parameters during boot on CentOS, directly edit a GRUB config file located at /boot/grub/grub.conf. In the config file, look for the entry describing the default Linux image used. The string “default=N” at the top of the config file indicates which entry is the default image.
|
||||
|
||||
[][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Under the default image entry, append a kernel parameter to the line starting with “kernel /vmlinuz-”. A kernel parameter should be formatted as “name=value”.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2013/11/add-kernel-boot-parameters-via-grub-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10618657834/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
||||
How to create desktop shortcut or launcher on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
If you have a program you use regularly on Linux desktop, you may want to create a "desktop shortcut", so you can launch the program by simply clicking on the shortcut. While most GUI programs automatically create their desktop shortcut during installation, some GUI programs or terminal applications may require you to set up associated shortcuts manually.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I will describe **how to create a desktop shortcut or launcher on various Linux desktops**.
|
||||
|
||||
A desktop shortcut is represented by a corresponding .desktop file which contains meta information of a given app (e.g., name of the app, launch command, location of icon file, etc.). Desktop shortcut files are placed in **/usr/share/applications** or **~/.local/share/applications**. The former directory stores desktop shortcuts that are available for every user, while the latter folder contains shortcuts created for a particular user only.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a Desktop Shortcut From the Command Line ###
|
||||
|
||||
To manually create a desktop shortcut for a particular program or command, you can create a .desktop file using any text editor, and place it in either /usr/share/applications or ~/.local/share/applications. A typical .desktop file looks like the following.
|
||||
|
||||
[Desktop Entry]
|
||||
Encoding=UTF-8
|
||||
Version=1.0 # version of an app.
|
||||
Name[en_US]=yEd # name of an app.
|
||||
GenericName=GUI Port Scanner # longer name of an app.
|
||||
Exec=java -jar /opt/yed-3.11.1/yed.jar # command used to launch an app.
|
||||
Terminal=false # whether an app requires to be run in a terminal.
|
||||
Icon[en_US]=/opt/yed-3.11.1/icons/yicon32.png # location of icon file.
|
||||
Type=Application # type.
|
||||
Categories=Application;Network;Security; # categories in which this app should be listed.
|
||||
Comment[en_US]=yEd Graph Editor # comment which appears as a tooltip.
|
||||
|
||||
Besides manually create .desktop file, there are various desktop-specific ways to create an application shortcut, which I am going to cover in the rest of the tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a Desktop Shortcut on GNOME Desktop ###
|
||||
|
||||
In GNOME desktop, you can use gnome-desktop-item-edit to configure a desktop shortcut easily.
|
||||
|
||||
$ gnome-desktop-item-edit ~/.local/share/applications --create-new
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, gnome-desktop-item-edit will automatically create a desktop launcher file in ~/.local/share/applications. To customize icon location and other info, you may have to edit the .desktop file manually afterward.
|
||||
|
||||
If gnome-desktop-item-edit is not available (e.g., on Ubuntu), you can install it as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install --no-install-recommends gnome-panel
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a Desktop Shortcut on KDE Desktop ###
|
||||
|
||||
kickoff is the default application launcher in KDE desktop. Adding a new application shortcut to kickoff is straightforward.
|
||||
|
||||
First right-click on kickoff icon located at the left bottom corner of your desktop, and then choose "Edit Applications" menu.
|
||||
|
||||
[][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Click on an appropriate category (e.g., "Utilities") under which you want to create a shortcut, and click on "New Item" button on the top. Type in the name of the app.
|
||||
|
||||
[][2]
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, fill in the meta information of the app being launched by the shortcut.
|
||||
|
||||
[][3]
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a Desktop Shortcut on Xfce Desktop ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you are on Xfce desktop, right-click on the desktop background, and then select "Create Launcher" menu. Then fill out the details of the shortcut.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a Desktop Shortcut on Cinnamon Desktop ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you are on Linux Mint Cinnamon desktop, you can create an application launcher by right-clicking on the desktop background, and selecting "Create Launcher" menu.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a Desktop Shortcut on LXDE Desktop ###
|
||||
|
||||
On LXDE desktop, simply right click on the desktop background, and choose "Create New Shortcut".
|
||||
|
||||
[][4]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2013/11/create-desktop-shortcut-launcher-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10848506344/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10848418496/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10848506284/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10848922593/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
这几天盖帽了 -.- Luox
|
||||
KDE and Canonical Conflict Over Mir Finally Bursts into Open
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The conflict that has been brewing between the KDE developers and Canonical has finally exploded in a flurry of statements which show just how many problems the Mir display server has caused.
|
||||
@ -30,4 +31,4 @@ via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/KDE-and-Canonical-Conflict-Over-Mir-Finally-
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Mark-Shuttleworth-Says-That-Mir-Opponents-Have-Formed-the-Open-Source-Tea-Party-392793.shtml
|
||||
[2]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/KDE-Developer-and-President-of-KDE-e-v-Upset-Because-Mark-Shuttleworth-Is-Ignoring-Him-396623.shtml
|
||||
[3]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Major-KDE-Developer-Says-Goodbye-to-Ubuntu-396429.shtml
|
||||
[3]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Major-KDE-Developer-Says-Goodbye-to-Ubuntu-396429.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,108 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Options in Linux RPM Command to Query Packages
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
RPM is RedHat Package Manager, used to install/remove/update and query the packages in Red Hat based linux. RHEL and the systems based on it uses rpm command to do that. The following example demonstrates the use of rpm query feature and shows different ways you can query rpm database and restore configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
I have included the SSH package to in the example commands.
|
||||
|
||||
### Query RPM Database and Packages ###
|
||||
|
||||
**1、 To query the whole RPM database, use the following command.**
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -qa
|
||||
plymouth-0.8.3-27.el6.x86_64
|
||||
pciutils-libs-3.1.10-2.el6.i686
|
||||
netcf-libs-0.1.9-3.el6.x86_64
|
||||
..
|
||||
…
|
||||
..
|
||||
Output Truncated
|
||||
|
||||
**2、 You can identify the package from which SSH is installed by using grep on the above example.**
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -qa |grep ssh
|
||||
libssh2-1.4.2-1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
openssh-askpass-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
libssh2-1.4.2-1.el6.i686
|
||||
openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
openssh-clients-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
openssh-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
|
||||
The output shows other packages related to ssh but you have to still identify that which package is actually installing SSH. To further break it down see the next example.
|
||||
|
||||
**3、 Check the installed package of SSH a) from sshd daemon b) from it’s configuration file.**
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -qf /etc/init.d/sshd
|
||||
openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
# rpm -qf /etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||
openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see the ssh is installed from the openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64 package. You can use rpm -qf command both on daemon and a configuration file. Both will output the package it is installed from.
|
||||
|
||||
**4、 Now that you have the package name, you may want to explore more on it and want to know what are the various files this package contains. For that use rpm -ql command.**
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -ql openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
/etc/pam.d/ssh-keycat
|
||||
/etc/pam.d/sshd
|
||||
/etc/rc.d/init.d/sshd
|
||||
/etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||
/etc/sysconfig/sshd
|
||||
/usr/libexec/openssh/sftp-server
|
||||
/usr/libexec/openssh/ssh-keycat
|
||||
/usr/sbin/.sshd.hmac
|
||||
/usr/sbin/sshd
|
||||
/usr/share/doc/openssh-server-5.3p1
|
||||
/usr/share/doc/openssh-server-5.3p1/HOWTO.ssh-keycat
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man5/moduli.5.gz
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man5/sshd_config.5.gz
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man8/sftp-server.8.gz
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man8/sshd.8.gz
|
||||
/var/empty/sshd
|
||||
|
||||
he above output is showing all the files that this package installed on the system. Now let’s even break it down and we only want to see the configuration files and document files supplied with this package.
|
||||
|
||||
**5、 To list only the configuration files use the rpm -qc command.**
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -qc openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
/etc/pam.d/ssh-keycat
|
||||
/etc/pam.d/sshd
|
||||
/etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||
/etc/sysconfig/sshd
|
||||
|
||||
**6、 To list only documentation files use rpm -qd command**
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -qd openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
/usr/share/doc/openssh-server-5.3p1/HOWTO.ssh-keycat
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man5/moduli.5.gz
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man5/sshd_config.5.gz
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man8/sftp-server.8.gz
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man8/sshd.8.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Consider a situation in which you want to configure a service, but you don’t know where to find the configuration files. As an example, Consider the above example: Use **rpm -qf rpm -qf /etc/init.d/sshd** to find out from what package the **/etc/ssh/sshd_config** file originated. It should show you the **openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64** package. Use **rpm -ql openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64** to show a list of all the files in this package. As you can see, the names of many files are displayed, but the output is not very useful.
|
||||
|
||||
Now use **rpm -qc openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64** to show just the configuration files used by this package. This shows a list of four files only and gives you the absolute path of [/etc/ssh/sshd_config file][1] to start configuring the service.
|
||||
|
||||
**7、 Restore configuration file from RPM Package, without reinstalling a package.**
|
||||
|
||||
If for some reason a file has been damaged or got deleted from system, you can start with the **rpm -qf** query option to find out from what package the file originated. Next use **rpm2cpio | cpio -idmv** to extract the files from the package. Consider the ssh example:
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming that the **/etc/ssh/sshd_config** file has been deleted and you may not want to reinstall ssh, Restore the file using the steps below.
|
||||
|
||||
* Use rpm -qf /etc/init.d/sshd This command shows that the file comes from the openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64 Package.
|
||||
|
||||
* Download the Openssh rpm from it’s source
|
||||
|
||||
* Copy openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64 package file to /tmp directory or any other directory of your choice.
|
||||
|
||||
* Use rpm2cpio |cpio -idmv to extract the package.
|
||||
|
||||
The command you used in the above step created a few subdirectories in /tmp. You can now copy it to its original location.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/rpm-command-query/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linoxide.com/how-tos/disable-ssh-direct-login/
|
||||
@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by l3b2w1
|
||||
Linux Desktop In The Enterprise: Ubuntu Vs. Windows
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The "year of the Linux desktop" has been prophesied by Linux supporters almost every year for the last decade. This was once a lofty goal in the Microsoft-dominated enterprise, but times are changing. Linux has grown into a formidable competitor in the smartphone and cloud computing markets, which has caught Microsoft off guard. More importantly, Google, IBM, Red Hat, Facebook, and Netflix have made huge investments into Linux innovations.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, with shrinking technology budgets and rising Microsoft licensing fees, it's time for IT to seriously consider desktop Linux deployment as an alternative to Windows. The timing for this couldn't be better: Windows 8.1 was just released, as was the latest version of Ubuntu, 13.10. Windows XP has just five months of support left, so companies need to make the switch to something new. Ubuntu may just have what companies need to support their desktop OS needs. I'll look at various considerations for making the Linux desktop switch, including training and support, as well as potential complications.
|
||||
|
||||
I know that Ubuntu has lost some of the favor it once enjoyed in the open source community. Canonical, the creators of Ubuntu, have made some unpopular choices, including changing the display manager -- the base component of the graphical interface in Linux-- to the internally developed Mir instead of Wayland. However, Ubuntu remains completely open source and offers the most painless install of any Linux distribution or even Windows version, for that matter. Canonical also offers paid support, which may be needed in enterprise environments.
|
||||
|
||||
There has always been the argument that end users will need retraining if they switch over to a new desktop interface. Microsoft's controversial decision to overhaul the familiar interface for Windows 8.1 now requires just as much training as switching to Linux. Ubuntu's Unity desktop has evolved into a user friendly interface that is arguably more easily understood by end users than Windows 8.1.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, compare how a user shuts down the system in each operating system. In all recent versions of Ubuntu, it starts with one click in the right corner of the screen, where the symbol for on-off is located. A menu drops down and one more click shuts down the machine. Windows 8.1 requires a right-click on the Start button, where a menu drops down allowing for a shutdown. This was a vast improvement over Windows 8, which required a trip to the charms bar, but still not as obvious as an icon located directly on the screen.
|
||||
|
||||
End-user training for applications is a less complex task nowadays, thanks to the Windows versions of many popular open source applications. Users may already be familiar with Firefox, LibreOffice, Pidgin, and VLC Media Player on Windows. Commercial applications used in business, such as Skype and Adobe Acrobat, function just like their Windows equivalents. Cloud-based applications such as Google Drive or Microsoft Office 365 work well on Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
Legacy Windows applications can be accessed through the familiar Citrix client or open source RDP clients. Companies also can use open source virtualization products such as VirtualBox to run the most stubborn legacy Windows applications.
|
||||
|
||||
On the support front, many technicians will remember the earlier days of Linux when hardware support was extremely limited. That simply is not the case anymore.
|
||||
|
||||
Linux hardware support is oftentimes better than the latest versions of Windows. Many hardware vendors have been dropping driver support for newer versions of Windows. The open source drivers in Linux can be kept up to date by anyone in the developer community, so a lot of older hardware is fully supported in the latest versions of Ubuntu. This fact, plus Ubuntu's lower system requirements, will allow companies to extend the life of hardware once destined for the recycling bin.
|
||||
|
||||
While there are upsides to a Linux desktop replacement program, there are some potential difficulties companies should consider. While many technicians have already been using Linux or will be motivated by the prospect of learning new skills, there also will be technicians who have spent a lot of time developing a comfort level managing Windows and may be reluctant to embrace the change.
|
||||
|
||||
Citing salary trends is one way to address this potential issue. The salaries of positions with Linux skills requirements are rising at nearly double the rate of other technical professionals, according to Dice.
|
||||
|
||||
Companies under stringent compliance requirements may have difficulties switching over to Linux. For example, HIPAA requires encryption that meets FIPS-140-2 requirements. Most open source encryption projects do not have sponsors to get them through the NIST certification to meet this requirement. Open source may actually be more secure than proprietary software because of the number of people that have reviewed the source code, but surprisingly that doesn't matter in the world of compliance.
|
||||
|
||||
Businesses need to understand their compliance requirements and develop a plan for training IT staff before deciding to move forward with a full conversion. But overall, Ubuntu Linux has matured into a viable alternative to proprietary operating systems in the enterprise. The effort companies put into a Linux desktop replacement program will be worth the savings in licensing fees. Next year may finally be the “year of the Linux desktop.”
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> Joseph Granneman has more than 20 years of technology experience, primarily focused in health care information technology. He is CIO for Rockford Orthopedic Associates in Rockford, Ill., and an active independent author, presenter and professor in the health care information technology and information security fields. Granneman has been active in many standards groups, including developing the early frameworks for Health Information Exchange as part of the Health Information Security and Privacy Security Working Group for Illinois. He was also a volunteer for the Certification Commission for Health Information Technology (CCHIT) Security Working Group, which developed the information security standards for ARRA certification of electronic medical records.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.networkcomputing.com/data-networking-management/linux-desktop-in-the-enterprise-ubuntu-v/240163564
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Mikko Hypponen: Open Source Software Will Make the World More Secure
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Open source software can be one answer to combating the global surveillance of innocent citizens, said security expert Mikko Hypponen in his keynote last week at [LinuxCon and CloudOpen Europe][1] in Edinburgh.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Mikko Hypponen, chief research officer at F-Secure in Finland, spoke at LinuxCon and CloudOpen Europe 2013 in Edinburgh.*
|
||||
|
||||
Advances in computing and the rise of global networks have made the storage and transmission of data cheap and easy. This has created unparalleled connectivity, progress and innovation, Hypponen said. But it’s also enabled large-scale access to that data as demonstrated by the NSA’s PRISM program, made public this year in a series of top-secret document leaks by former U.S. government contractor Edward Snowden.
|
||||
|
||||
“In the last few years we've realized data is cheap. We never have to delete anything anymore, ever,” said Hypponen, chief research officer at F-Secure in Finland. “This has enabled lots of great things but also global wholesale blanket surveillance.”
|
||||
|
||||
Such access to our personal data, including cell phone records, geolocation, email and search engine queries, may be warranted in some cases, Hypponen said.
|
||||
|
||||
“I do believe some surveillance is OK,” he said. “If there's an investigation into finding a school shooter or drug lord or member of a terrorist cell… we should have the technical means of doing that. But we must first have the suspicion.”
|
||||
|
||||
But collecting the communications and personal data of “everyone” is not only a violation of privacy, but a threat to democracy, Hypponen said.
|
||||
|
||||
“Even if you don't have a problem with our government today, we don't know what the government will be 20 years from now,” he said. ”If they have 20 years of your search data, they'll find something illegal or embarrassing to twist your hand.”
|
||||
|
||||
Though the leaks have caused some IT professionals to question the safety of their data stored with and routed through U.S. service providers, avoiding these companies and services won’t solve the problem, Hypponen said. Neither can each country afford the time and expense of building its own alternatives.
|
||||
|
||||
Working across international boundaries, developers should band together to build secure and reliable software and services that prevent back-door tampering and ensure users’ privacy, Hypponen said.
|
||||
|
||||
“I suggest that open source provides a solution to this problem,” he said. “Then countries don't have to work alone. It will be secure, open and free.”
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/200-libby-clark/745585-mikko-hypponen-open-source-software-will-make-the-world-more-secure
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://events.linuxfoundation.org/events/linuxcon-europe
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
|
||||
Outreach Program for Women Seeks New Linux Kernel Interns
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The interns who worked with The Linux Foundation as part of the [FOSS Outreach Program for Women][1] this summer come from diverse backgrounds and levels of experience, but they now have at least one thing in common (besides their gender). They can all add “Linux kernel hacker” to their resume.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Outreach Program for Women ranked among the top contributors to Linux kernel 3.12. Source: LWN.net.*
|
||||
|
||||
Lisa Nguyen, Xenia Ragiadakou, Elena Ufimtseva, Laura Vasilescu and Tulin Izer were among the seven women out of 41 applicants who received $5,000 stipends each as part of the first group of OPW interns sponsored by the Linux Foundation. They worked full time with kernel developers at Intel, Oracle, and Citrix for three months and tackled projects that included the x86 boot process and vNUMA topolgy. They were also able to take advantage of a $500 travel scholarship to attend and speak at LinuxCon in New Orleans or Edinburgh.
|
||||
|
||||
“It's not often that I'd get to say, 'I volunteered at LinuxCon North America, spoke at LinuxCon North America, and met Linus Torvalds in three days!" said Nguyen, whose internship focused on Xen block drivers with Konrad Rzeszutek Wilk at Oracle.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to learning how to build and submit kernel patches, making new friends and colleagues and generally conquering their fears, the interns made significant contributions to the Linux kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
“I'm not scared touching kernel code anymore,” said Izer, who worked with Peter P. Waskiewicz Jr. at Intel on parallelizing the x86 boot process. “This was my first contribution to an open source project and I'm really proud of it. I intend to keep doing this for a long time.”
|
||||
|
||||
### Top Kernel Contributors ###
|
||||
|
||||
As a group, OPW was listed as a top contributor to the 3.11 kernel, coming in No. 13 with 230 changesets submitted, according to the [August kernel report on LWN][2]. And intern Xenia Ragiadakou was among the top 10 most active developers contributing 100 changesets to 3.11.
|
||||
|
||||
“My main project was to add trace events and write a trace-cmd plugin for parsing the traces in human readable format to facilitate xhci (driver) debugging,” said Ragiadakou, who worked with Intel kernel developer Sarah Sharp on the project. “I learned how to use git, how to use static code analysis tools, how to send patches, how to tune my debug logs, how the usb subsystem is assembled, how xhci driver is implemented.”
|
||||
|
||||
On the 3.12 kernel, OPW again ranked among the top companies contributing, this time at No. 11 with 19,649 lines of code changed, [according to LWN's][3] analysis in October. That represents 2.7 percent of all changes made during this latest development cycle.
|
||||
|
||||
After their internships ended in September, most of the women have continued to work on the projects they started and plan to keep it up.
|
||||
|
||||
“I think it's cool to be a kernel contributor and I wanted to do this for some time,” said Vasilescu, who worked with Carolyn Wyborny and Anjali Singhai at Intel on features for ethtool in the igb driver.
|
||||
|
||||
“I still have to learn how to stop. Sometimes, oh well, often, I cannot stop,” said Ufimtseva, who worked on vNUMA topolgy for paravirtual guests in Xen with Stefano Stabellini, Dario Fargiolli and George Dunlap at Citrix. “I keep working and later it contributes into the quality of code. But it is so engaging!”
|
||||
|
||||
The deadline for the next round of Linux kernel internships is Nov. 11. Applicants should have some basic knowledge of C or C++ and boolean algebra. Some experience with operating systems, Linux/Unix, and Git is nice but not required. For more information on the available projects and how to apply, visit the [OPW page on Kernel Newbies][4].
|
||||
|
||||
### Lisa Nguyen ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Lisa Nguyen worked on Xen block drivers with Konrad Rzeszutek Wilk at Oracle.**
|
||||
|
||||
I earned multiple college degrees in Computer Science, Digital Forensics, and Information Security before I became an OPW kernel intern. I have used Linux continuously for the past two years, and I have taken multiple roles in the Linux community including project manager, manpage author, LinuxCon session coordinator, and kernel contributor.
|
||||
|
||||
**Why did you apply to work on the Linux kernel with the OPW?**
|
||||
|
||||
I wanted a challenge and move out of my comfort zone. I wanted to give software development another chance, because I dealt with confidence issues in the past. One day, I decided that I wanted to pursue a career in Linux instead of becoming a digital forensics analyst. The timing couldn't have been better when I read about the OPW program through the Linux Foundation's post on Google+ and thought, "What do I have to lose if I don't try?"
|
||||
|
||||
### Elena Ufimtseva ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Elena Ufimtseva worked on vNUMA topolgy for paravirtual guests in Xen with Stefano Stabellini, Dario Fargiolli, George Dunlap at Citrix.**
|
||||
|
||||
I worked as a Linux system admin for quite some time and there were different projects I was a part of. I graduated with a Master Degree in Computer Science at St.-Petersburg University in Russian Federation.
|
||||
|
||||
**Why did you apply to work on the Linux kernel with the OPW?**
|
||||
|
||||
I felt I want to create software, system software, low-level. Not java :). I had that feeling that I can work on complex problems and solve them. I always check on latest Linux news and I think the one that truly caught my attention was Greg's presentation at Google a few years ago about Linux kernel development community organization and patches application process. I thought 'wow, that sounds great!'
|
||||
|
||||
### Laura Vasilescu ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Laura Vasilescu worked with Carolyn Wyborny and Anjali Singhai on features for ethtool in the igb driver.**
|
||||
|
||||
I consider myself a geek and I have a huge interest for improving the education system (especially in Romania). As a student, I volunteered myself as an undergraduate teaching assistant at my university and as a member of the Romanian Open Source Education Association. My technical expertise is in networking, operating systems and low-level programming.
|
||||
|
||||
**Why did you apply to work on the Linux kernel with the OPW?**
|
||||
|
||||
I think is cool to be a kernel contributor and I wanted to do this for some time.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tulin Izer ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Tulin Izer worked with Peter Waskiewicz at Intel on parallelizing the x86 boot process. **
|
||||
|
||||
I'm from Turkey. I'm a computer engineering student at Galatasaray University in Istanbul. This is my final year.
|
||||
|
||||
**Why did you apply to work on the Linux kernel with the OPW?**
|
||||
|
||||
I was interested in operating systems and programming in C but I didn't have any experience with kernel development, I thought this would be a good place to start.
|
||||
|
||||
### Xenia Ragiadakou ###
|
||||
|
||||
Currently I study Computer Science at the University of Crete. I have finished some other studies in the past, on Economics and on Eastern Europe Studies. The reason that I decided to change field once again is because I got bored. I don't know how that sounds. I realized that my organism needed something more applicable, creative and dynamic. So, I decided to enter the Computer Science department. Now, my spirit rests peaceful :) I think coding suits me perfectly. It 's like a game and also I enjoy the developers' mentality.
|
||||
|
||||
**Why did you apply to work on the Linux kernel with the OPW?**
|
||||
|
||||
I wanted since a long time to participate in an open source project but i was thinking that I'm not competent enough to do so. There were three factors that drove me to apply. 1) The fact that OPW is aimed at women made me feel more comfortable. 2) The fact that there were projects on linux kernel because I like working on systems. 3) The fact that the introduction to Linux kernel development was smooth and took place quite early, during the application process.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/200-libby-clark/746687-outreach-program-for-women-seeks-new-linux-kernel-interns/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.gnome.org/OutreachProgramForWomen
|
||||
[2]:http://lwn.net/Articles/563977/
|
||||
[3]:http://lwn.net/Articles/570483/
|
||||
[4]:http://kernelnewbies.org/OPWIntro
|
||||
@ -1,131 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Recoll: Text Search Tool For Unix And Linux Desktops
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[Recoll][1] is a text search tool for Unix and Linux desktops. Recoll finds keywords inside documents as well as file names.
|
||||
|
||||
Recoll will do the following for you.
|
||||
|
||||
- It can search any document format.
|
||||
- Supports wild card characters.
|
||||
- Search based on files author, type, size and format etc.
|
||||
- will search on all storage places such as files, archive members, email attachments etc.
|
||||
- supports Desktop and Website integration
|
||||
- Firefox extension is available to index visited web pages history.
|
||||
- One click will open the document inside a native editor or display a text preview.
|
||||
- The software is free, open source, and licensed under the GPL.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Recoll On Ubuntu / Linux Mint ###
|
||||
|
||||
Recoll is available in the Ubuntu repositories, However it is better to add Recoll repository and install the latest version.
|
||||
|
||||
Add Recoll repository using command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:recoll-backports/recoll-1.15-on
|
||||
|
||||
Update the package list with command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
Now install Recoll using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install recoll
|
||||
|
||||
For other distros, see the [download page][2] to download and install it from source.
|
||||
|
||||
### Launch Recoll ###
|
||||
|
||||
Recoll can be launched either from Dash or Menu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
At first launch, you’ll be asked to do indexing your whole home directory. This will take a while depending upon the size of your Home directory and no of files you have. Press the Start indexing now button.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Also you can adjust the indexing configuration and indexing schedule, if you want to more control of indexing. To do so, simply click on the Indexing configuration or Indexing schedule links. If you want to do it later, you can access these tools from the Preferences menu.
|
||||
|
||||
Once the indexing is done, you can start searching files/folders. The result will be displayed according to the exact relevancy and with a small snippet of the matched content.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration ###
|
||||
|
||||
As i noted above, you can adjust the Recoll indexing function if you want more control.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two configuration sections in the Recoll tool.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Index configuration
|
||||
|
||||
2. Index schedule
|
||||
|
||||
Let us see a short description of above sections.
|
||||
|
||||
**Index Configuration** is the section where you want to include directories or exclude the paths from indexing. By default Home directory will be included in the index. You can just remove and add some specific directory(s) for indexing.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Also you can define the web history queue and the max size of the web store.
|
||||
|
||||
**Index schedule** is the section where you want to define a schedule to automate batch indexing runs, or start real time indexing when you log in.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Recoll supports two indexing schedule:
|
||||
|
||||
**Cron Scheduling** – decides at what time indexing should run and installs the crontab entry.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As per the above screenshot, the recoll cron job will run on every day at 12 am. After setting up the cron job, click enable to make it active.
|
||||
|
||||
**Real time indexing start up** – decide if real time indexing will be started when you log in.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
By enabling this option, the recoll daemon will start on every reboot. Be mindful that this settings is applicable only for default index.
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Search ###
|
||||
|
||||
Hope you knew enough about Recoll now. It is time to search some files/folders. The beauty of this application is it finds keywords inside documents as well as file names.
|
||||
|
||||
In the Recoll interface, enter the search term(query) on the top right search box and click Search button.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As you see in the above picture, the result will be displayed with exact relevant contents, a small snippet and preview option of the matched contents. You can directly open the searched file by clicking on the Open button or preview it before opening using the Preview button.
|
||||
|
||||
Also you can filter the results according to their categories such as “media”, “message”, “other”, “presentation”, “spreadsheet” and “text” etc. Moreover you can choose the search results that should match “Any term”, “All terms”, “File name” or “Query language”.
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Search ###
|
||||
|
||||
Click the Advanced Search icon on the Menu bar or go to **Tools -> Advanced Search**. This will open a new window. From here you’ll be able to search more advanced with clauses. For example i am searching for files that contains matches keyword as “hp” and filename as “storage”.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This will find and displays the files that contains the keyword as “hp” and file name as “storage”.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Unity Desktop And Website Integration ###
|
||||
|
||||
This application supports desktop and website integration. If you want to integrate this with your Ubuntu Unity desktop, install **recoll-lens** with following command.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install recoll-lens
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that the Lens is limited to showing at most 20 results. If you want get more than 20 search results, edit **rclsearch.py**, change the “**if actual_results >= 20:**” line.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using Firefox browser and want to search the website history that you visit everyday, you can use [this firefox extension][3]. This extension works together with Recoll to index the websites that you visit all day. After installing this extension, enable it from the Web history tab of Recoll Index Configuration.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
All Linux distributions has built-in search function in their file manager to find files/folders as easy as possible. For those who aren’t not happy with the built-in search functionality and looking for an advanced text search tool, then Recoll is a worth trying tool. For me, this tool is lot easier and more powerful for basic and as well as advanced searches.
|
||||
|
||||
Cheers!
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/recoll-text-searching-tool-linux-desktops/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.recoll.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.lesbonscomptes.com/recoll/download.html
|
||||
[3]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/recollfirefox/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
(translating by whatever1992)
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat prepares for 64-bit ARM servers
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> ARM processors could lead to server racks with thousands of nodes, the Red Hat ARM chief predicts
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
NearTan占坑
|
||||
SBackup: A Simple Backup Solution For Your Linux Desktop
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**SBackup**, Simple Backup, is an Open Source, easy to use backup solution intended for desktop use. It can backup any subset of files and folders. All configuration is accessable via Gnome interface. File and paths can be included and excluded directly or by regex, It supports local and as well as remote backups. Though it looks simple, it has many features to meet the advanced backup functionality.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
|
||||
crowner挖的无底洞,争取早日填上
|
||||
Save, Access And Quickly Paste Text Snippets With This Nifty Unity Launcher Tool
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Repeatedly typing out certain information – like e-mail or home addresses, verbose terminal commands, and well timed quotes from cult TV shows – can be a chore.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Snippets – Handy Way to Access Stored Text*
|
||||
|
||||
Thankfully there are tools out there to help.
|
||||
|
||||
*‘Snippets’* is one such utility for Unity. It’s a simple Launcher item that lets you save and store excerpts in a text file, then, when needed, select them from a Unity Quicklist to copy them the clipboard.
|
||||
|
||||
Now before anyone throws their underwear at me in disgust, I’m well aware Snippets is not unique – or the first – in offering this sort of feature. But what it is unique in doing is offering it through a Unity Launcher item.
|
||||
|
||||
Features-wise, the tool is simple enough, offering:
|
||||
|
||||
- Ability to add & access snippets stored in .txt file
|
||||
- View stored snippets in quicklist
|
||||
- Click snippets to copy them to clipboard
|
||||
- Option to add current clipboard item to .txt file
|
||||
|
||||
While it’s not a “live” clipboard manager – it only lists items you specifically add; it does not present a history of your most recent clipboard items – it is still a handy little tool.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Install Snippets for Unity ###
|
||||
|
||||
To make use of this nifty Snippets launcher item you’ll need to first install the command-line clipboard tool xclip. Hit the button below to get it from the Software Center.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Click to Install XClip in Ubuntu][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Next up, download the following ‘Snippets‘ archive. This contains everything else needed to use the app.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download ‘Snippets’ Unity Launcher Script][2]
|
||||
|
||||
When the archive has downloaded fully you’ll want to extract it. Enter the resulting folder and hit Ctrl+H to reveal hidden files. Move the folder ‘.snippets-launcher‘ to your Home folder. **The utility won’t work if this step isn’t followed**.
|
||||
|
||||
Next step is to install the launcher item. This is taken care of by a script inside the folder you just moved, but it doesn’t have executable permissions (needed to install it) so we’ll need to first take care of that, too.
|
||||
|
||||
Open a new Terminal window and enter the following commands carefully:
|
||||
|
||||
cd .snippets-launcher/ && chmod +x snippets.sh
|
||||
|
||||
./snippets.sh
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it; Snippets should now be ready to use. Open the Unity Dash to search for the Snippets item and drag it onto the launcher.
|
||||
|
||||
- Left click on the launcher item opens the text file where you add your snippets
|
||||
- Right click on the launcher item opens the quick list
|
||||
|
||||
Options in the quicklist:
|
||||
|
||||
- Left click on a snippet to add it to the clipboard
|
||||
- Left click ‘Date’ to copy the current date
|
||||
- Click ‘Add Clipboard Content’ to add current item to .txt file
|
||||
- After adding items to .txt file click ‘Update Launcher’
|
||||
|
||||
For more information on the lazy-making tool, [head over to the Ubuntu Forums thread][3] where its developer, “Stinkeye”, will be happy to help.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/10/unity-launcher-clipboard-snippets-item
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:apt://xclip
|
||||
[2]:https://www.dropbox.com/s/ha6lngizmz78srv/snippets%20by%20stinkeye.tar.gz
|
||||
[3]:http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=2184916
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
Suse Linux Enterprise expands regular support to 10 years
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Suse expands general support on customer requests**
|
||||
|
||||
Suse Linux Enterprise (SLE) version 11 and up will come with 10 years of general support instead of the seven years offered up to now, in a move that matches services from competitors.
|
||||
|
||||
"We will move to a new life cycle of Suse Linux Enterprise," said Nils Brauckmann, president and general manager for Suse, during his keynote at the Susecon 2013 conference in Lake Buena Vista, Florida. A [video][1] of the keynote was posted on YouTube.
|
||||
|
||||
"Suse Linux Enterprise 11 is the first major version to receive 10 years of general support followed by 3 years of extended support (LTSS). We consider this the new standard Suse Linux Enterprise life cycle going forward, covering versions 12 and on as well," said Gerald Pfeifer, senior director of Suse product management and operations, in an email Wednesday. Suse sells open-source Linux software to businesses.
|
||||
|
||||
Suse offers different packages for extended support. Extending the support to 13 years will cost US$60,000 for up to 100 servers and $80,000 for up to 500 servers, said Pfeifer. Support for an unlimited number of servers can be extended for $125,000 he said, adding that these are standard prices that Suse has been using for several years.
|
||||
|
||||
By moving from a seven-plus-three-year support cycle to a 10-plus-three-year support cycle, customers get more time under general support, Brauckmann said during his keynote. The decision to increase the support cycle was made a couple of weeks ago and is a direct reaction to customer requests, he added.
|
||||
|
||||
Suse's general support extension follows Red Hat's move in January last year to extend the life cycle of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 5 and 6 from seven to 10 years, in response to enterprise customer demand.
|
||||
|
||||
Oracle Linux, which is based on RHEL, expanded its life cycle support from eight to 10 years in February last year. CentOS, an Enterprise Linux distribution that is based on a rebuild of RHEL, has also been offering 10-year support as a standard for a while.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.itworld.com/operating-systems/382610/suse-linux-enterprise-expands-regular-support-10-years
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T0W4izFu_WM
|
||||
@ -1,124 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating-------------geekpi
|
||||
|
||||
19 The Linux Kernel: Configuring the Kernel Part 15
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Aloha! In this article of the Linux kernel series, we are still configuring drivers for USB networking. Then, we will move on to input devices.
|
||||
|
||||
First, we can enable/disable the "Multi-purpose USB Networking Framework" which allows connecting laptops to desktop systems.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, the ASIX USB-to-Ethernet adapter driver can be enabled/disabled (ASIX AX88xxx Based USB 2.0 Ethernet Adapters).
|
||||
|
||||
Then, there is another ASIX adaptor driver (ASIX AX88179/178A USB 3.0/2.0 to Gigabit Ethernet).
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Generally, it is best to add adapter drivers as modules.
|
||||
|
||||
The Communication Device Class specification is offered in the driver (CDC Ethernet support (smart devices such as cable modems)). This specification is for USB modems. The Linux system recognizes this USB networking interface as an Ethernet interface and will be designated as "ethX" where "X" is the Ethernet device number.
|
||||
|
||||
Next is a specification similar to the above (CDC EEM support). CDC EEM stands for Communication Device Class Ethernet Emulation Model.
|
||||
|
||||
The CDC Network Control Model (NCM) also has a driver that offers the specification (CDC NCM support).
|
||||
|
||||
The driver providing the CDC MBIM (Mobile Broadband Interface Model) specification is also available for the Linux kernel (CDC MBIM support).
|
||||
|
||||
Next, there are several vendor/device specific drivers for various USB networking devices and chipsets.
|
||||
|
||||
After those, there is a generic driver for USB network devices that do not require any special drivers (Simple USB Network Links (CDC Ethernet subset)).
|
||||
|
||||
Again, there are some more drivers for device/vendor specific devices.
|
||||
|
||||
FUN FACT: Linux was used to make the special effects for the movie "Titanic" by James Cameron.
|
||||
|
||||
"CDC Phonet support" is for USB Nokia modems that use Phonet.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we can move on to Wireless LAN drivers which use the 802.11 specification.
|
||||
|
||||
Mainly, there is a list of vendor/device specific drivers.
|
||||
|
||||
"SoftLED Support" controls the LEDs that are associated with the Wifi cards/devices.
|
||||
|
||||
Some chipsets support SDIO as seen by this driver (Atheros ath6kl SDIO support). SDIO is an extension of the Secure Digital specification for wireless SD cards. SDIO stands for Secure Digital Input/Output.
|
||||
|
||||
Kernel developers may also notice that some wireless devices can support QoS. QoS stands for Quality of Service. This feature gives network transmissions priority. Assume two sets of data need to be sent over a network. Only one can go first. QoS will send the most important data first.
|
||||
|
||||
FUN FACT: Technically, Linux is not an operating system. Linux is the kernel while GNU/Linux is the operating system.
|
||||
|
||||
The "Generic HDLC layer" is needed for WAN cards. HDLC stands for High-Level Data Link Control. This is a data link layer protocol.
|
||||
|
||||
Raw HDLC can be used with the "Raw HDLC support" driver enabled.
|
||||
|
||||
The "Raw HDLC Ethernet device support" driver allows the HDLC layer to emulate Ethernet.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The cHDLC driver offers a HDLC extension also called Cisco HDLC (Cisco HDLC support).
|
||||
|
||||
The Linux kernel also has a driver for "Frame Relay support" for HDLC. Frame Relay is a Layer 2 protocol.
|
||||
|
||||
HDLC can also support PPP (Synchronous Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) support) and X.25 (X.25 protocol support).
|
||||
|
||||
Next, this driver offers Frame Relay the ability to use DLCI (Frame Relay DLCI support).
|
||||
|
||||
The "LAPB over Ethernet driver" creates a device file that permits the user to make a LAPB point-to-point connection to another computer via Ethernet. The device file is usually /dev/lapb0 for the first of such device.
|
||||
|
||||
X.25 frames can be sent over telephone lines with this driver (X.25 async driver). Specifically, this driver allows X.25 to use asynchronous serial lines.
|
||||
|
||||
A special driver is needed for ISA SBNI12-xx cards (Granch SBNI12 Leased Line adapter support). These cards are inexpensive substitutes for leased line modems.
|
||||
|
||||
The next driver allows parallel connections to carry scheduled traffic (Multiple line feature support). This allows the Linux system to more efficiently manage parallel connection on SBNI12 adapters. Some Linux users claim this driver doubles their speed. However, I have never tested this to know for myself.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, "IEEE 802.15.4 drivers" can be configured. This is for slow WAN devices. This is a standard that controls the media and physical layers of the wireless network. This specification uses different frequencies in different continents. For example, in Europe, such wireless devices will use the 868.0-868.6MHz frequency.
|
||||
|
||||
The first setting in this category is for a fake LR-WPAN driver (Fake LR-WPAN driver with several interconnected devices). LR-WPAN stand for Low-Rate Wireless Personal Area Network.
|
||||
|
||||
FUN FACT: Only about 2% of the current kernel was written by Linus Torvalds.
|
||||
|
||||
The vmxnet3 virtual Ethernet used by VMware requires this driver (VMware VMXNET3 ethernet driver). When making a kernel for a large number of users, it is best to enable this as a module because someone may want to use the Ethernet on VMware.
|
||||
|
||||
The Hyper-V virtual network needs this driver (Microsoft Hyper-V virtual network driver). You may be wondering if this is the same Hyper-V virtual network by Microsoft. It is and yes, Linux supports Hyper-V.
|
||||
|
||||
The digital telephone service, ISDN, is supported by this driver (ISDN support). ISDN stands for Integrated Services Digital Network. In France, ISDN is known as RNIS which stands for Réseau numérique à intégration de services. With an ISDN adapter, a computer can start and accept voice calls. This allows computers to be used as answering machines or some other telephone service device. ISDN can also carry video information.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we can move on to input devices (Input device support). These are devices that give the computer information. Mice and keyboards are the most commonly used and known input devices. Scanners are another example of input devices.
|
||||
|
||||
First, there is a driver that supports various haptic/tactile feed-back devices (Support for memoryless force-feedback devices). For instance, many game controllers vibrate which is haptic/tactile feed-back.
|
||||
|
||||
Some input devices check on the status of the hardware (Polled input device skeleton). Such behavior requires this driver.
|
||||
|
||||
Input devices that use sparse keymaps need this driver (Sparse keymap support library). A keymap is the layout information for keyboards.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, this is another keymap (Matrix keymap support library).
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: When making a kernel for a broad user group, include most or all input devices as modules because the developer usually does not know what type of devices the users may plugin to the computer.
|
||||
|
||||
FUN FACT: A Vanilla Kernel is a Linux kernel in its original, unchanged state.
|
||||
|
||||
The "Mouse interface" makes two different device files for the mouse. The two device files are /dev/input/mouseX and /dev/input/mice.
|
||||
|
||||
This next driver makes a psaux device file that is an alias to /dev/input/mice (Provide legacy /dev/psaux device). The psaux device file is /dev/psaux.
|
||||
|
||||
If the system has a digitizer, then the horizontal resolution needs to be set (Horizontal screen resolution) and then the vertical resolution (Vertical screen resolution). A digitizer is the type of touch-screen that supports touch-pens that allow users to draw. Other touch-screens cannot support such complex input.
|
||||
|
||||
The next driver supports joysticks and gamepads (Joystick interface). This driver creates the /dev/input/jsX files.
|
||||
|
||||
The "Event interface" driver allows input devices to be accessible via /dev/input/eventX.
|
||||
|
||||
The "Event debugging" driver outputs all input events to the system's log. Do not enable this for any reason other than debugging systems. Obviously, for performance reasons, but the main reason I recommend this be disabled is for security purposes. All key-presses are plainly logged including passwords.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, a list of various keyboard drivers are listed for configuration (Keyboards) followed by mouse drivers (Mice) and then joystick/gamepad drivers (Joysticks/Gamepads).
|
||||
|
||||
After that, various drivers for specific tablet hardware/vendors are listed (Tablets). After that is the driver list for "Touchscreens".
|
||||
|
||||
The last set of input device drivers is a list of miscellaneous drivers for specific hardware and vendors (Miscellaneous devices).
|
||||
|
||||
The next article of this series will discuss input ports. Do not forget to read the other articles of this series and this website. Mahalo!
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE TO FANS: Thank you** for all of your kind emails telling me how much you all love these articles.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-15.4793/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,118 +0,0 @@
|
||||
20 The Linux Kernel: Configuring the Kernel Part 16
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Welcome to the next Linux kernel article. In this article, we will discuss the input/output ports.
|
||||
|
||||
First, the "i8042 PC Keyboard controller" driver is needed for PS/2 mice and AT keyboards. Before USB, mice and keyboards used PS/2 ports which are circular ports. The AT keyboard is an 84-key IBM keyboard that uses the AT port. The AT port has five pins while the PS/2 port has six pins.
|
||||
|
||||
Input devices that use the COM port (sometime called RS232 serial port) will need this diver (Serial port line discipline). The COM port is a serial port meaning that one bit at a time is transferred.
|
||||
|
||||
The TravelMate notebooks need this special driver to use a mouse attached to the QuickPort (ct82c710 Aux port controller).
|
||||
|
||||
Parallel port adapters for PS/2 mice, AT keyboards, and XT keyboards use this driver (Parallel port keyboard adapter).
|
||||
|
||||
The "PS/2 driver library" is for PS/2 mice and AT keyboards.
|
||||
|
||||
"Raw access to serio ports" can be enabled to allow device files to be used as character devices.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, there is a driver for the "Altera UP PS/2 controller".
|
||||
|
||||
The PS/2 multiplexer also needs a driver (TQC PS/2 multiplexer).
|
||||
|
||||
The ARC FPGA platform needs special driver for PS/2 controllers (ARC PS/2 support).
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: I want to make it clear that the PS/2 controllers that are discussed in this article are not Sony's game controllers for their PlayStation. This article is discussing the 6-pin mouse/keyboard ports. The controller is the card that holds the PS/2 ports.
|
||||
|
||||
The "Gameport support" driver offers support for the 15-pin gameport. Gameport was the 15-pin port used by many input gaming devices until the invention of the USB port.
|
||||
|
||||
The next driver is for gameports on ISA and PnP bus cards (Classic ISA and PnP gameport support). ISA stands for Industry Standard Architecture and was a parallel bus standard before PCI. PnP stands for Plug-and-Play and was a common standard before ISA.
|
||||
|
||||
"PDPI Lightning 4 gamecard support" provides a driver for a proprietary gamecard with gameports.
|
||||
|
||||
The SoundBlaster Audigy card is a proprietary gameport card (SB Live and Audigy gameport support).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The ForteMedia FM801 PCI audio controller has a gameport on the card (ForteMedia FM801 gameport support). This driver only supports the gameport.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we can move on to "Character devices". Character devices transfer data character by character.
|
||||
|
||||
First, TTY can be enabled or disabled (Enable TTY). Removing TTY will save a lot of space, but TTY is needed for terminals and such. Unless you know what you are doing, do not disabled TTY.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE TO MY FANS: If you know of a reason for disabling TTY, could you post the answer below and share with us. Mahalo!
|
||||
|
||||
Next, support for "Virtual terminals" can be enabled/disabled. Again, a lot of space can be saved, but virtual terminals are very important.
|
||||
|
||||
This next driver supports font mapping and Unicode translation (Enable character translations in console). This can be used to convert ASCII to Unicode.
|
||||
|
||||
Virtual terminals can be used as system consoles with this driver (Support for console on virtual terminal). A system console manages the logins and kernel messages/warnings.
|
||||
|
||||
Virtual terminals must channel through a console driver to interact with the physical terminal (Support for binding and unbinding console drivers). Before the virtual terminal can do so, the console driver must be loaded. When the virtual terminal is closed, the console terminal must be unloaded.
|
||||
|
||||
The next driver provides support for Unix98 PTY (Unix98 PTY support). This is Unix98 pseudo terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
FUN FACT: The Linux kernel allows a filesystem to be mount many times in many places at once.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, "Support multiple instances of devpts" can be supported. The devpts filesystem is for pseudo-terminal slaves.
|
||||
|
||||
Legacy support for PTY can also be enabled (Legacy (BSD) PTY support).
|
||||
|
||||
The max amount of legacy PTYs in use can be set (Maximum number of legacy PTY in use).
|
||||
|
||||
The next driver can be used to offer support to serial boards that the other drivers fail to support (Non-standard serial port support).
|
||||
|
||||
Next, there are some drivers for specific boards and cards.
|
||||
|
||||
The GSM MUX protocol is supported with this driver (GSM MUX line discipline support (EXPERIMENTAL)).
|
||||
|
||||
The next driver enables the kmem device file (/dev/kmem virtual device support). kmem is usually used for kernel debugging. kmem can be used to read certain kernel variables and states.
|
||||
|
||||
The Stallion cards have many serial ports on them (Stallion multiport serial support). This driver specifically supports this card.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we can move on to drivers for serial devices. As stated before, serial devices transfer one bit at a time.
|
||||
|
||||
The first driver is for standard serial port support (8250/16550 and compatible serial support).
|
||||
|
||||
Plug-and-Play also exists for serial ports with this driver (8250/16550 PNP device support).
|
||||
|
||||
The following driver allows the serial ports to be used for connecting a terminal to be used as a console (Console on 8250/16550 and compatible serial port).
|
||||
|
||||
Some UART controllers support Direct Memory Access (DMA support for 16550 compatible UART controllers). UART stands for Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter. UART controllers convert serial to parallel and vice versa.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, this driver offers support for standard PCI serial devices (8250/16550 PCI device support).
|
||||
|
||||
16-bit PCMCIA serial devices are supported by this driver (8250/16550 PCMCIA device support). Remember, PCMCIA is a PC-card that is usually used in laptops.
|
||||
|
||||
The maximum number of supported serial ports can be set (Maximum number of 8250/16550 serial ports) and then the maximum that are registered during boot-up (Number of 8250/16550 serial ports to register at runtime).
|
||||
|
||||
For extended serial abilities like HUB6 support, enable this driver (Extended 8250/16550 serial driver options).
|
||||
|
||||
A special driver is needed to support more than four legacy serial ports (Support more than 4 legacy serial ports).
|
||||
|
||||
Serial interrupts can be shared when this driver is used (Support for sharing serial interrupts).
|
||||
|
||||
Serial port IRQs can be autodetected using this driver (Autodetect IRQ on standard ports).
|
||||
|
||||
RSA serial ports are also supported by the Linux kernel (Support RSA serial ports). RSA stands for Remote Supervisor Adapter. RSA is an IBM-specific hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, there are various vendor/device specific divers.
|
||||
|
||||
This is a TTY driver that uses printk to output user messages (TTY driver to output user messages via printk). Printk (print kernel) is a special piece of software that usually prints the boot-up messages. Any string that is displayed by printk is usually put in the /var/log/messages file. The shell command "dmesg" displays all strings that were used by printk.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we can enable/disable support for parallel printers (Parallel printer support).
|
||||
|
||||
The next driver allows a printer to be used as a console (Support for console on line printer). This means kernel messages will be literally printed at the printer. Normally when the word "print" was used in this article series, it meant putting data on the screen. This time, this literally means putting the data on paper.
|
||||
|
||||
The following driver makes the device files at /dev/parport/ (Support for user-space parallel port device drivers). This allows some processes to access.
|
||||
|
||||
Again, the Linux kernel has many features and drivers, so we will discuss more drivers in the next article. Mahalo!
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE TO FANS: We are getting close to the end of the configuration process. I still have a list of all of the suggested Linux kernel topics that many of you wanted to know about. Some of the topics include installing the kernel, managing modules, adding 3rd-party drivers, and all of the other very interesting suggestions and requests.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-16.4835/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
||||
Translating----------------geekpi
|
||||
|
||||
21 The Linux Kernel: Configuring the Kernel Part 17
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Aloha! This next article will cover various drivers.
|
||||
|
||||
First, the "virtio console" is a virtual console that is used with hypervisors.
|
||||
|
||||
The "IPMI top-level message handler" is a message manager for the IPMI system. IPMI stands for Intelligent Platform Management Interface. IPMI is an interface for managing the system via network without using a shell.
|
||||
|
||||
"/dev/nvram support" permits the system to read and write memory in the real time clock's memory. Generally, this feature is used for saving data during a power loss.
|
||||
|
||||
The next driver supports the Siemens R3964 packet protocol (Siemens R3964 line discipline). This is a device-to-device protocol.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we can move on to PCMCIA character devices. However, most of the drivers here are vendor/device specific.
|
||||
|
||||
The RAW driver allows block devices to be bound to the device files /dev/raw/rawN (RAW driver (/dev/raw/rawN)). The advantage to this is efficient zero-copy. However, most software will still prefer to access the storage through /dev/sd** or /dev/hd**.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, the maximum number of RAW devices can be supported is set.
|
||||
|
||||
The following driver makes the device file /dev/hpet (HPET - High Precision Event Timer).
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Many of you may be wondering why enabling these device file matter. Well, these device files serve as an interface between the software and hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
The HPET timers can be mapped with this driver (Allow mmap of HPET). Mapping is the process of making a list of address in memory of devices and files. The files can then be found faster by getting the address from the memory and then commanding the hard-drive to get the data from the address.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The "Hangcheck timer" is used to detect whether of not the system has locked-up.
|
||||
This timer watches for locked-up processes. As soon as a process freezes, a timer starts. After the timer goes off, if the process has not restarted or closed, then the timer will force the process to close.
|
||||
|
||||
Linus Torvalds Quote: Portability is for people who cannot write new programs.
|
||||
|
||||
The TPM security chip that uses Trusted Computing Group's specification will need this driver (TPM Hardware Support).
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we can move on to I2C devices. I2C stands for Inter-Integrated Circuit and is spoken as "eye two see". However, some people say "eye squared see". I2C is a serial bus standard.
|
||||
|
||||
Some old software used I2C adapters as class devices, but software now does not do that (Enable compatibility bits for old user-space). So, this driver will offer backwards compatibility for older software.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, the I2C device files can be made (I2C device interface).
|
||||
|
||||
I2C can support multiplexing with this driver (I2C bus multiplexing support).
|
||||
|
||||
I2C can support GPIO-controlled multiplexing with this driver (GPIO-based I2C multiplexer).
|
||||
|
||||
Various tests can be performed on I2C and SMBus with this driver for developers (I2C/SMBus Test Stub).
|
||||
|
||||
The I2C system will produce debugging messages with this feature enabled (I2C Core debugging messages).
|
||||
|
||||
The next driver produces additional I2C debugging messages (I2C Algorithm debugging messages).
|
||||
|
||||
Linus Torvalds Quote: The main reason there are no raw devices [in Linux] is that I personally think that raw devices are a stupid idea.
|
||||
|
||||
The following driver will cause the I2C drivers to produce debugging messages (I2C Bus debugging messages).
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we have Serial Peripheral Interface support (SPI support). SPI is a synchronous serial protocol used on SPI buses.
|
||||
|
||||
After that, there is a driver for High speed synchronous Serial Interface support (HSI support). HSI is a synchronous serial protocol.
|
||||
|
||||
PPS can also be supported by the Linux kernel (PPS support).
|
||||
|
||||
The "IP-over-InfiniBand" driver allows IP packets to be transported over InfiniBand.
|
||||
|
||||
After that, there is a debugging driver for IP-over-InfiniBand (IP-over-InfiniBand debugging).
|
||||
|
||||
SCSI's RDMA protocol can also travel over InfiniBand (InfiniBand SCSI RDMA Protocol).
|
||||
|
||||
There is also an extension for the iSCSI protocol to transmit over InfiniBand (iSCSI Extensions for RDMA (iSER)).
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes, errors occur in the core system that the whole system must know (EDAC (Error Detection And Correction) reporting). This driver sends the core errors to the system. Generally, such low-level errors are reported in the processor and then seen by this driver to let other system processes know about or handle the error.
|
||||
|
||||
This driver provides legacy support for EDAC to use older versions of sysfs (EDAC legacy sysfs).
|
||||
|
||||
EDAC can be set to send debugging information to the logging system of Linux (Debugging).
|
||||
|
||||
Linus Torvalds Quote: Nobody actually creates perfect code the first time around, except me.
|
||||
|
||||
The Machine Check Exceptions (MCEs) are converted to a readable form via this driver (Decode MCEs in human-readable form (only on AMD for now)).
|
||||
MCEs are hardware errors detected by the CPU. MCEs usually trigger kernel panics.
|
||||
|
||||
The decoding process for MCE to a readable form can be injected to test error handling (Simple MCE injection interface over /sysfs).
|
||||
|
||||
The next driver allows errors to be detected in memory and then corrected (Main Memory EDAC (Error Detection And Correction) reporting).
|
||||
|
||||
Next, there are many drivers that detect and correct errors on specific hardware sets.
|
||||
|
||||
Linus Torvalds Quote: Theory and practice sometimes clash. And when that happens, theory loses. Every single time.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we can move on to the "Real Time Clock". This is commonly abbreviated "RTC". The RTC keeps track of time.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The next setting allows us to make the Linux system use the time from the RTC as the time on the "wall clock" (Set system time from RTC on startup and resume). The wall clock is the clock on the desktop or the time seen using the "date" command.
|
||||
|
||||
Alternately, the wall clock can get the time from an NTP server and then sync with the RTC (Set the RTC time based on NTP synchronization).
|
||||
|
||||
Some systems have more than one RTC, so the user must set which is the default (RTC used to set the system time).
|
||||
It is best to make the first one (/dev/rtc0) the primary clock.
|
||||
|
||||
Debugging abilities can be set for the RTC system (RTC debug support).
|
||||
|
||||
The RTC can use various interfaces for giving the operating system the current time. Using sysfs will require this driver (/sys/class/rtc/rtcN (sysfs)) while using proc will require this driver (/proc/driver/rtc (procfs for rtcN)). Special RTC character devices can be made and used (/dev/rtcN (character devices)). The shell command "hwclock" uses /dev/rtc, so the RTC character devices are needed.
|
||||
|
||||
The next driver allows interrupts of the RTC to be emulated on the /dev/ interface (RTC UIE emulation on dev interface). This driver reads the clock time and allows the new time to be retrieved from /dev/.
|
||||
|
||||
The RTC system can be tested with the test driver (Test driver/device).
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we will discuss the Direct Memory Access system.
|
||||
DMA is the process of hardware accessing the memory independently of the processor. DMA increases system performance because the processor will have less to do if the hardware is performing more tasks for itself. Otherwise, the hardware would be waiting for the processor to complete the task.
|
||||
|
||||
The debugging engine is for debugging the DMA system (DMA Engine debugging).
|
||||
|
||||
Next, there are many vendor/device specific drivers for DMA support.
|
||||
|
||||
Some DMA controllers support big endian reading and writing with this driver (Use big endian I/O register access).
|
||||
|
||||
Big endian refers to the arrangement of the binary code. The number system used in English speaking countries places the largest end of the number on the left. For example, in the number 17, the most left numbers place is the tens place which is larger than the ones place. In big endian, each byte is arranged with the largest portion on the left. A byte is eight bits. Example: 10110100. Each place has a value of 128, 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, and 1 respectively. So the byte mentioned converts to the decimal number 180.
|
||||
|
||||
The DMA system can use the network to reduce CPU usage (Network: TCP receive copy offload).
|
||||
|
||||
The "DMA Test Client" is used for testing the DMA system.
|
||||
|
||||
In the next article, we will discuss the display/video drivers. Mahalo!
|
||||
|
||||
REFERENCE: The quotes from Linus Torvalds came from this site: [http://en.wikiquote.org/wiki/Linus_Torvalds][1]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-17.4875/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikiquote.org/wiki/Linus_Torvalds
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu vs. openSUSE: Weighing different styles of corporate control
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
*Ubuntu and openSUSE approach their Linux distros in much different ways. Which do you prefer?*
|
||||
|
||||
It's no secret that a rather large portion of Linux development is funded by companies with a financial interest in seeing Linux be improved. (And, by "Linux," I mean "All the various pieces and parts that make up a complete Linux-based system.") But there is a pretty major difference between how various companies go about that.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take a look at two high-profile examples: Ubuntu and openSUSE.
|
||||
|
||||
Both are distributions of Linux. Both are large, long-standing and highly successful projects with a large community of both volunteers and paid workers. Yet the difference between the two is fairly extreme, and highly important.
|
||||
|
||||
For Ubuntu, the primary direction is set by the team at Canonical and its head-master, Mark Shuttleworth. Examples such as Unity (Ubuntu's in-house user interface) and Mir (Ubuntu's in-house display server) quickly jump to mind when talking about how Canonical really “steers the ship” of Ubuntu. Goals, projects and priorities put into place by the parent company are, in many cases, simply non-negotiable (so to speak). Ubuntu's Unity user interface, for example, was a must-have for Canonical as it was part of their broader strategy. Some community members love it. Some hate it. But, either way, it's happening.
|
||||
|
||||
But is that bad? I'm not really convinced that it is either good or bad. It's simply how it is with that particular project and company.
|
||||
|
||||
Contrast that with openSUSE, who also has a "corporate master" in the form of, well, SUSE. The key difference there being that SUSE has a commercial offering in the form of "SUSE Linux Enterprise." And, while there is a great deal of technical overlap between openSUSE (the community Linux distro) and SUSE Linux Enterprise (the commercial offering)...the two are not, technically, the same.
|
||||
|
||||
Which means that SUSE, as a company, can afford to take a more “hands-off” approach to working with openSUSE. Sure, they have a vested interest in seeing key bits of technology (such as, say, Btrfs) be improved, tested and packaged with the community distro – as they may wish to include it in the commercial offering – but the separation between the community and commercial systems provides them with a bit more flexibility, in this regard, than Canonical presently has.
|
||||
|
||||
This is similar to the way Red Hat works with the Fedora project, and seems to be a generally successful approach as a mechanism for a company that sells enterprise-level Linux systems to utilize a community Linux distro as a foundation.
|
||||
|
||||
I'll be honest. I see benefits and drawbacks to both models. Both have their challenges in terms of organization and management (and public perception). And, in all reality, there is more in common than not with the two approaches.
|
||||
|
||||
I'd love to hear your thoughts on this. Do you prefer to have a singular captain at the helm of your community-based Linux distro (sort of a "benevolent dictator")? Or do like the big decisions of your Linux distro to be a bit more community-driven? Should companies behind a given flavor of Linux rule with an iron fist, or be more hands-off? Leave your thoughts in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.networkworld.com/community/node/84250
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,13 +1,13 @@
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu 13.10上安装Linux内核 3.12
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu 13.10 用户不必再羡慕地看着新的Linux内核发布,他们也可以相对轻松地更新他们的系统。**
|
||||
**Ubuntu 13.10 的用户不必再用羡慕的眼神看着新版Linux内核发布,他们也可以相对轻松地更新他们的系统。**
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical公司一贯的做法是,在一整个开发周期中始终使用一个Linux内核。例如,Ubuntu 13.10始终基于Linux内核 3.11,但现在已经推出一个新的稳定的Linux内核3.12。
|
||||
Canonical公司一贯的做法是,在整个开发周期中始终使用一个Linux内核。例如,Ubuntu 13.10始终基于Linux内核 3.11,但现在已经推出一个新的稳定的Linux内核3.12。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu用户只有等到14.04 LTS发布以后,才能得到一个较新版本的Linux内核,但到那之前他们也可以选择安装新的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
不过,我们必须从一开始就提醒你。Canonical不建议你更新除官方渠道以外的比其他版本的Linux内核。这不是一个完全安全的过程,你以后可能会遇到问题,甚至系统故障。但另一方面,你的系统性能可能会得到提升。
|
||||
不过,我们必须从一开始就提醒你。Canonical不建议你更新官方渠道以外的Linux内核版本。这不是一个完全安全的过程,你以后可能会遇到问题,甚至系统故障。但另一方面,你的系统性能可能会得到提升。
|
||||
|
||||
你将要下载的内核来自Canonical公司,这意味着它已经在.deb格式。你不需要再自己编译。打开一个终端,导航到Downloads文件夹,输入以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,14 +15,14 @@ Ubuntu用户只有等到14.04 LTS发布以后,才能得到一个较新版本
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v3.12-saucy/linux-headers-3.12.0-031200-generic_3.12.0-031200.201311031935_amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
如果你有一个32位的操作系统,你也可以下载32位版本。可见只需替换链接中的64bit为32bit即可[here][1].
|
||||
如果你有一个32位的操作系统,你也可以下载32位版本。可见只需替换链接中的64bit为32bit即可,[点此下载][1].
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你将像运行任何其它程序一样运行这些.deb文件。在你下载软件包的同一个终端,输入下面的命令(你需要root权限才能正常运行):
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg -i linux-image-3.12.0-031200-generic_3.12.0-031200.201311031935_amd64.deb
|
||||
sudo dpkg -i linux-headers-3.12.0-031200-generic_3.12.0-031200.201311031935_amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
安装完后,你需要重启系统。瞧,新的Linux内核就在那里了。好消息,旧的内核仍然存在,如果你要删除3.12版的内核,只需使用众所周知命令。
|
||||
此过程结束后,你需要重启系统。瞧,新版本的Linux内核更新成功。好消息是,旧版本内核仍然存在,如果你要删除3.12版的内核,只需使用众所周知命令。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get purge linux-image-3.12.0-031200-generic_3.12.0-031200.201311031935_amd64.deb
|
||||
sudo apt-get linux-headers-3.12.0-031200-generic_3.12.0-031200.201311031935_amd64.deb
|
||||
@ -34,8 +34,8 @@ Ubuntu用户只有等到14.04 LTS发布以后,才能得到一个较新版本
|
||||
|
||||
来源于: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Install-Linux-Kerrnel-3-12-in-Ubuntu-13-10-397013.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[coolpigs](https://github.com/coolpigs) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[coolpigs](https://github.com/coolpigs) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v3.12-saucy/
|
||||
[1]:http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v3.12-saucy/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu13.10中安装最新版的NVIDIA 331.20驱动
|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||
**有时候安装新版本的NVIDIA驱动会遇到一些麻烦,尤其是当你不习惯Linux系统中的运作方式时。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这时候,这篇教程就能起到作用了,它能帮助普通用户从最新版的NVIDIA驱动331.20中获益。
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu系统中有两种方法安装NVIDIA驱动,一种是简单方法,另一种是困难方法。简单方法也是最为直截了当的,但是需要你能够连接网络。这种方法也会把你带入PPA的美妙世界中去。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10像它的前辈们一样,有一个很大的软件仓库可供使用,但是Canonical的开发者们由于种种考虑并不上传最新版的驱动。最重要的是他们不会冒险去上传一款未被证明其稳定性的软件。
|
||||
|
||||
幸运的是,我们有PPA可供使用,PPA中有最新版的驱动程序可供使用,而且里面的驱动会在官方放出新驱动一两天后就添加进去。只需在终端中敲入一下命令即可(当然你需要拥有root权限):
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:xorg-edgers/ppa
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install nvidia-331
|
||||
|
||||
假如你已经安装了一个旧版本的驱动,你需要用**sudo apt-get dist-upgrade**命令替换上面命令中的最后一条命令。
|
||||
|
||||
完成这些步骤之后重启你的电脑,新驱动就安装好了。在下一次NVIDIA更新驱动时,你只需更新系统就可以,无需添加PPA。
|
||||
|
||||
第二种方法有点复杂,但是你可以不用联网(你需要先把驱动下载下来,在安装的时候不再需要联网)。我们将使用64位版本的驱动最为例子讲解。
|
||||
|
||||
你必须按Ctrl+Alt+F1组合键进入真正的终端(译注:原文中为虚拟终端,但实际上按这个组合键进入的是真正的终端),然后使用用户名和密码登录。接下俩,你需要用cd命令进入你放置驱动的位置(例如Downloads目录)然后输入以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo service lightdm stop
|
||||
sudo chmod a+x NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-331.20.run
|
||||
sudo ./NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-331.20.run
|
||||
sudo reboot
|
||||
|
||||
这样就搞定了。无论你选择使用什么方法,享受最新版的NVIDIA驱动吧。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Install-the-Latest-NVIDIA-331-20-Drivers-in-Ubuntu-13-10-399182.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Linux-pdz](https://github.com/Linux-pdz) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
OpenVPN 安全手册[part 1]
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
一直以来,我们在互联网上传输信息时,都谨慎地为这些信息加密,以防内容泄露出去,特别是在政府的干预下,为网络上每个字节都进行加密已经变得空前重要了。在这种情况下,OpenVPN 是保障网络信息安全的首选。今天我们就来学习一下如何架设 OpenVPN,使你可以在任何场所都能安全地访问家里的服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
VPN 小贴士:很多商业的 VPN 根本不值它们的售价,它们的安全性只比通过 SSL 保护的网站高一点点,原因是它们的安全意识还不够强,认为世上所有人都是值得信任的。而一个真正意义上的 VPN 认为在充满危险的互联网上只存在两个值得信任的终端 —— 即真正要建立连接的那两个。用户不能随便找一台 PC 机就能登录进 VPN,因为你的 VPN 如果能被随随便便的一台 PC 登录进来,不管它们建立的连接有多么安全,这都称不上是一件好事情。所以你必须在你的客户端和服务器端都要好好地配置一下 VPN 服务。
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenVPN 快速入门 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你需要两台不同子网下的计算机,比如一台连着光缆的 PC 和一台连着 Wifi 的 PC(或者是 VitualBox 虚拟机上的多台客户机),并且你要知道它们的 IP 地址。这里分别为这两台计算机命名为“Studio”和“Shop”,都给它们安上 OpenVPN。OpenVPN 支持大多数 Linux 发行版,所以你只要用你手头的安装包管理软件就行。本文的包管理器是 Debian、Ubuntu 以及它们的衍生版中使用的 apt-get,下面安装 OpenVPN:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install openvpn openvpn-blacklist
|
||||
|
||||
上面的步骤安装了 OpenVPN 服务器和一个用于检查外泄密钥的黑名单的程序。请务必安装这个黑名单检查器,因为有一次 Debian 发布了一个[有漏洞的 OpenSSL 软件][1],这个软件里的随机码生成器会产生不可信任的密钥 —— 产生的这些密钥不是真正的随机数,它们可以被预测到。这件事发生在2008年,当时所有使用了这个软件的人都需要修改他们这个不是秘密的密钥。即使5年过去了,我们还是建议使用这个黑名单检查器 —— 这是份廉价的保险。
|
||||
|
||||
现在让我们试着为两台 PC 机创建一个不加密的通道。首先互 ping 一下确保它们能连通,然后让 OpenVPN 处于关闭状态(别着急,我们会在后面手动启动它):
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps ax|grep openvpn
|
||||
|
||||
如果 openvpn 这个后台进程存在,那就 kill 了它。这里假设“Studio”这台 PC 的 IP 是192.168.1.125,“Shop”的 IP 是192.168.2.125。现在在“Studio”端开启一个未加密的连接到“Shop”端:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo openvpn --remote 192.168.2.125 --dev tun0 --ifconfig 10.0.0.1 10.0.0.2
|
||||
|
||||
然后开一个从“Shop”到“Studio”的连接:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo openvpn --remote 192.168.1.125 --dev tun0 --ifconfig 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
连接成功的话你会看到类似下面的信息:
|
||||
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 ******* WARNING *******: all encryption and authentication
|
||||
features disabled -- all data will be tunnelled as cleartext
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 TUN/TAP device tun0 opened
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 do_ifconfig, tt->ipv6=0, tt->did_ifconfig_ipv6_setup=0
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 /sbin/ifconfig tun0 10.0.0.1 pointopoint 10.0.0.2 mtu 1500
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 UDPv4 link local (bound): [undef]
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 UDPv4 link remote: [AF_INET]192.168.2.125:1194
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 Peer Connection Initiated with [AF_INET]192.168.2.125:1194
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 Initialization Sequence Completed
|
||||
|
||||
看到“Initialization Sequence Completed”这句话时,说明你的操作成功了。这时你应该能够 ping 通两个隧道的 IP:ping 10.0.0.1 和 ping 10.0.0.2。当你建立隧道的时候,你无需在意你所在的网络,你可以为你的隧道指定任何 IP 地址。关闭隧道请按 Ctrl+c。
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以利用这个隧道打开一个 SSH 会话了。图1显示了通过 VPN 隧道登录 SSH 的例子,这个图也显示了有趣的 Message of the Day(MOTD)图片,图片来自于博客《[在你的 Linux 系统上放一张奶牛的 MOTD 图片][2]》:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh carla@10.0.0.2
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*图1:成功通过 VPN 隧道建立 SSH 会话,并显示了有趣的 MOTD 图片*
|
||||
|
||||
哼哼哈𠯋,它运行得不错。
|
||||
|
||||
### 加密后的 VPN 隧道 ###
|
||||
|
||||
目前为止,我们玩得还不赖,但是没有使用加密技术,一切都毫无意义,所以我们需要建立一个简单的静态密钥配置文件。不像公钥基础设施(PKI),有着根认证中心、可撤消认证等安全措施,我们的加密机制没有那么强悍,但是对于仅仅想远程到家里的用户来说,已经足够了。OpenVPN 有提供创建静态密钥的命令,我们可以建立目录、建立密钥文件,并将文件设为只读模式:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir /etc/openvpn/keys/
|
||||
$ sudo openvpn --genkey --secret /etc/openvpn/keys/static.key
|
||||
$ sudo chmod 0400 /etc/openvpn/keys/static.key
|
||||
|
||||
这是个明文密钥,你可以利用文本编辑器打开密钥文件读取到它,文件名可以随意,不一定非得叫“static.key”。将这个密钥拷到需要通信的两台电脑上,呵呵,这是对称加密,而不是公钥加密。
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们要在两台电脑上完成基本的配置。(在非类 Ubuntu 的系统中,OpenVPN 没有提供默认的配置文件,但是在 /usr/share/doc/openvpn/ 目录下会为你提供一个配置文件的样本。)在我的实验中,“Studio”是服务器端,“Shop”是一台笔记本电脑,用于登录到“Studio”中。我的服务器端的配置文件是 /etc/openvpn/studio.conf,它的配置信息如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# config for Studio
|
||||
dev tun
|
||||
ifconfig 10.0.0.1 10.0.0.2
|
||||
secret /etc/openvpn/keys/static.key
|
||||
|
||||
将配置文件设为只有拥有者有读写权限:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chmod 0600 /etc/openvpn/studio.conf
|
||||
|
||||
客户端的配置文件内容类似,只是多了服务器端的 IP 地址:
|
||||
|
||||
# config for Shop
|
||||
dev tun
|
||||
ifconfig 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.1
|
||||
secret /etc/openvpn/keys/static.key
|
||||
remote 192.168.1.125
|
||||
|
||||
注意 ifconfig 那行的 IP 地址的顺序,本地的 IP 要放在远程的 IP 之前。现在启动服务器端的 OpenVPN,指定服务器端配置文件,客户端操作雷同:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo openvpn /etc/openvpn/studio.conf
|
||||
$ sudo openvpn /etc/openvpn/shop.conf
|
||||
|
||||
成功建立连接后,你还会看到“Initialization Sequence Completed”这句话,但你不会再看到这句 WARNING(这句话会在你建立了未加密的隧道时出现):
|
||||
|
||||
******* WARNING *******: all encryption and authentication features disabled
|
||||
|
||||
### 防火墙和动态 IP 地址 ###
|
||||
|
||||
OpenVPN 本身是比较容易配置的,最麻烦的是处理防火墙和动态 IP 地址。防火墙种类众多,对于如何配置防火墙不拦截你的隧道,我把这个话题当作家庭作业留给你自己解决:P。OpenVPN 的端口是1194,你可以在防火墙上设置一个转发规则,用于将消息转发到你的目标服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来处理另一件麻烦事:动态 IP 地址。[Dyn.com][3]可以提供一个廉价的方法,为你管理 ISP 分配给你的动态 IP,或者你也可以向你的 ISP 支付一笔费用,从而得到一个静态 IP。
|
||||
|
||||
至此,你可以宣告工作完成了,接下来的任务就是手动开启服务器端的 OpenVPN,让它一直运行在那里,等待你的登录。你可以将你的笔记本拿到外面,并随时随地随心所欲地连接到服务器。然而,关于 OpenVPN 的操作,我还有一些重要的知识点要讲,比如如何为 OpenVPN 设置开机启动,如何利用 Network Manager 自动建立连接,以及这篇 OpenVPN 教程中最重要的一块:如何访问你的远程服务器上的资源。我们下周见。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/743590-secure-remote-networking-with-openvpn-on-linux
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.debian.org/security/2008/dsa-1571
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/741573-put-a-talking-cow-in-your-linux-message-of-the-day
|
||||
[3]:http://dyn.com/dns/
|
||||
@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
|
||||
|
||||
如何在Uburtu 13.10中添加图标到菜单栏
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,使用Ubuntu 13.10,用户会遇到一个优化了的设置关于默认应用程序,偏好和功能,默认授权用户接受一个强大坚实的电脑技术。
|
||||
|
||||
Uburtu表达它自己的特点是可变化的,因此,用户可以借助直观友好的帮助工具修改和调整默认设置,就像Ubuntu Tweak。
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,Ubuntu禁用内部菜单的图标,意思是,右键点击桌面,打开右键菜单,菜单只包含文本条目而且没有图标。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,在Ubuntu 13.10的菜单中添加图标是很简单的:
|
||||
|
||||
- 安装Ubuntu Tweak
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:tualatrix/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install ubuntu-tweak
|
||||
|
||||
- 启动Ubuntu Tweak,并导航到`Tweaks-->Miscellaneous`
|
||||
- 选中 `Menus have icons`
|
||||
|
||||
**其结果是**:现在右键点击桌面, 图标在菜单中显示, 图标启动功能调整也可以在其他右键菜单实现, 等等(例如, Nautilus, Firefox, Gedit中的菜单等等).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
而次要的, 在最常用的右键菜单中加上新增的图标将更加清晰和美丽,增加它们漂亮的级别,特别的是当菜单显示图标时,是在图标主题特征为单色图标。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/how-add-icons-menus-ubuntu-1310
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Yu-Fei](http://blog.csdn.net/u011459130) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
如何在linux上通过GRUB添加内核参数
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以在linux内核启动时为其提供各种各样的参数。这些参数可以自定义内核默认的行为,或者通知内核关于硬件的配置信息。内核参数应在内核启动时通过引导装载程序如GRUB或LILO传递给内核。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我将会描述**如何在linux上通过GRUB添加内核参数**。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在使用GRUB引导装载程序,想修改或添加内核参数,你可以编辑GRUB配置文件。下面是针对特定发行版在GRUB的配置文件中添加内核启动参数的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Debian或Ubuntu上添加内核启动参数###
|
||||
|
||||
在基于Debian的系统上,如果你想在系统启动时添加内核参数,你可以编辑 /etc/default/grub 目录下的GRUB配置模板。在 GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT 变量中以 “name=value” 的格式添加内核参数。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo -e /etc/default/grub
|
||||
|
||||
> GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="...... name=value"
|
||||
|
||||
然后运行下面的命令来生成一个GRUB的配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo update-grub
|
||||
|
||||
如果无法找到 update-grub 命令,你可以通过下面的命令安装它。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install grub2-common
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Fedora上添加内核启动参数 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在Fedora上,想要在启动时添加内核参数,你可以编辑 /etc/default/grub目录下的 GRUB 配置模板。在 GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX 变量中以 “name=value” 的格式添加内核参数。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo -e /etc/default/grub
|
||||
|
||||
> GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="...... name=value"
|
||||
|
||||
然后运行下面的命令生成 GRUB2 配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
### 在CentOS上添加内核启动参数 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS上,想要在启动时添加内核参数,你可以直接编辑GRUB配置文件 /boot/grub/grub.conf。在配置文件中,找到描述默认使用的Linux映像的条目。文件中最顶行的字符串 “default=N”会指示哪一个条目是默认的映像。
|
||||
|
||||
[][1]
|
||||
|
||||
找到默认的映像条目后,在以 “kernel /vmlinuz-” 开头的那一段的结尾附加上内核参数。参数的格式为 “name=value” 。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2013/11/add-kernel-boot-parameters-via-grub-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Linchenguang](https://github.com/Linchenguang) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10618657834/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
Linux企业级桌面版:Ubuntu Vs Windows
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
过去的10年中,Linux的众多支持者几乎每年都预言当年会是“linux桌面版之年”。对微软主导的企业来说,这曾经是一个崇高的目标,但时代在变。在智能手机和云计算市场领域,Linux已经发展壮大成为一个顽强的竞争对手,打了微软一个措手不及。更重要的是,Google,IBM,Red Hat,Facebook, 还有Netflix等公司正在对linux的研发创新投入巨资。
|
||||
|
||||
现在, 随着技术预算缩水,微软授权费上涨,IT界是时候应该认真考虑一下了,部署桌面版Linux,替代Windows。这是个最佳时机,Windows 8.1刚发布,Ubuntu 13.10也同时发布。对Windows XP的支持也只剩下5个月时间。IT公司需要切换到新的环境。Ubuntu利用公司的需求来支持他们桌面版操作系统的需求。
|
||||
我会考虑几个促成向桌面版linux转换的因素,包括培训和支持,还有一些潜在的复杂性问题。
|
||||
|
||||
我知道Ubuntu已经失去了它曾经在开源社区享有的青睐。Canonical,Ubuntu的开创者,做出了几个不受欢迎的决策,包括改变屏幕管理器 -- linux图形界面的基本组件 -- 用内部开发的Mir替换掉Wayland。然而,Ubuntu的仍然是完全开源的,并提供任何Linux发行版甚至Windows版本的软件,安装起来最为省事。
|
||||
Canonical还提供付费支持,这可能是企业级环境所需要的。
|
||||
|
||||
一直存在这样的争论,如果切换到一个新的桌面的话,最终用户需要再培训。微软做出了争议性决策,针对Windows 8.1,对熟悉的界面全面整改,这种举措造成的影响就是,转向linux需要更多的培训。 Ubuntu Unity 桌面已经演变为用户友好的界面,比之Windows 8.1,更易于被终端用户所理解。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,比较一下用户在各个操作系统中关闭系统的方式。所有最近的Ubuntu版本,关闭系统只需点击一下屏幕右上角打开-关闭的图标。Windows 8.1则需要右击开始按钮,然后出现一个下拉菜单,从中找到关闭电源的选项。相较于Windows 8,这是个巨大的进步。Windows 8还得费劲去找相关的入口。总不如屏幕上只需一个图标来得直接。
|
||||
|
||||
多亏了许多流行的开源应用的Windows版本,对使用这些应用软件的终端用户的培训过也不是什么复杂的任务。用户已经熟悉了Windows上的Firefox, LibreOffice, Pidgin, 以及VLC媒体播放器。用于商业的应用,比如Skype和Adobe Acrobat,功能实现跟Windows上的基本相同。基于云的应用,比如Google Drive 和 Microsoft Office 365,在Ubuntu上都可以正常使用。
|
||||
|
||||
传统的Windows应用程序可以通过熟悉的Citrix或者开源RDP的客户端获取。公司可以使用开源的虚拟产品,比如VirtualBox,运行一些顽固的老掉牙的Windows应用。
|
||||
|
||||
On the support front, many technicians will remember the earlier days of Linux when hardware support was extremely limited. That simply is not the case anymore.
|
||||
前端支持上,许多技术人员还记得,在Linux刚刚起步的那些时日,硬件支持极其有限。如今形势已经转变了。
|
||||
|
||||
如今对Linux的硬件支持通常比对最新的Windows版本的支持还要理想。许多硬件供应商已经放弃了对Windows新版本的驱动支持。Linux下的硬件驱动可以由开源社区的任何一个人维护更新,因此最新版Ubuntu都支持许多旧的硬件。有基于此,再加上Ubuntu较低的系统需求,公司可以延长都已经进了回收站的硬件的使用寿命。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然Linux的桌面替代品存在它的优势,但是企业也应该考虑到一些潜在的困难。尽管许多技术人员正在使用linux,也为学习新的技术而欢欣鼓舞,但是仍有一部分技术人员用Windows进行开发工作很长时间了,已经习惯了,再去拥抱新的变化,对他们来说,或许不是那么得情愿。
|
||||
|
||||
援引薪酬的走向是一个解决潜在的问题的办法。相比于其他专业技术人员,Linux技能要求的职位薪酬上涨近一倍的速度,来自Dice的说法。
|
||||
|
||||
对严格遵守协议的公司来说,切换到Linux可能会遇到困难。例如,HIPAA要求加密,以满足FIPS-140-2的要求。大多数开源加密项目没有赞助商帮助他们通过NIST认证以满足这一要求。开源代码实际上可能因为有许多人已审查,会比专有软件更安全,但令人惊讶的是,在协议的世界中,这一点无关紧要。
|
||||
|
||||
在决定全面迁移之前,企业需要了解他们的规则要求,并制定一个计划,培训IT人员。但总体而言,相比于企业级私有操作系统, 作为一个切实可行的选择,Ubuntu Linux已然成熟。考虑到版权费用的花销,公司在Linux桌面替换项目中的投入是值得的。下一年或许就是“linux桌面版之年”。
|
||||
|
||||
> Joseph Granneman拥有超过20年的技术经验,主要专注于医疗信息技术。他是罗克福德,伊利诺伊州罗克福德骨科协会的CIO,医疗保健信息技术和信息安全领域一个活跃的独立作家,主持人和教授。Granneman一直活跃在许多的组织群体,包括发展健康信息交换的早期框架,该框架是卫生伊利诺斯州的保健信息安全和隐私安全工作组的一部分。他也是健康信息技术认证委员会(CCHIT)安全工作组的一名志愿者,该工作组负责制定ARRA认证的电子病历信息安全标准。
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.networkcomputing.com/data-networking-management/linux-desktop-in-the-enterprise-ubuntu-v/240163564
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/l3b2w1) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
米科·哈普宁:开源软件使世界更安全
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
安全专家米科·哈普宁(Mikko Hypponen)于上周在爱丁堡举行的[LinuxCon and CloudOpen Europe][1]会议上的主题演讲中说:"开源软件可以作为一个方法来打击全球监视无辜居民的行为。"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*米科·哈普宁,芬兰F-Secure的首席研究员,在爱丁堡举行的LinuxCon and CloudOpen Europe 2013会议上讲话。*
|
||||
|
||||
计算和全球网络增加的进步使得存储和传输数据变得便宜且简单。哈普宁说这创造了无比的连通性、进步和创新。但是同样使得大规模的数据被访问到就像NSA的棱镜项目演示的那样,这事件随着前美国政府员工爱德华·斯诺登(Edward Snowden)泄漏的一系列顶级机密文件而公开。
|
||||
|
||||
哈普宁,芬兰F-Secure的首席研究员说:"前几年我们已经意识到数据是廉价的。我们永远不必再删除任何数据。这促成了很多伟大的事情但同样也引发了大规模地毯式的监视。"
|
||||
|
||||
哈普宁说:"这些监视会访问我们的个人数据,包括电话记录、地理位置、电子邮件和搜索引擎请求,有些可能是被授权的。"
|
||||
|
||||
他说:"我相信一些监控是好的。如果有有一项研究来找出校园枪击者或者毒枭或者恐怖组织成员等等。我们应该已经有技术手段这么做。但是我们首先必须必须持有怀疑。"
|
||||
|
||||
哈普宁说:"但是收集通信和每个人的个人数据不仅是对隐私的侵犯还是对民主的威胁。"
|
||||
|
||||
他说:"即使你如今对政府认为没问题,但是我们不知道政府会在今后的20年怎么样。如果他们有你20年的搜索数据,他们会找出一些非法的或者令人尴尬的理由来扭曲你的手。"
|
||||
|
||||
哈普宁说:"虽然泄漏事件使得一些IT专家质疑他们的数据存储的安全性和经由美国服务商的的路由,但避免这些公司和服务不能解决问题。同样不能每个国家都花费和金钱来建造他们自己的替代品。"
|
||||
|
||||
哈普宁说:"要跨越国际边际地工作,开发者应该团结起来建造一个安全和可靠的软件和服务来放置后门篡改和用户隐私。"
|
||||
|
||||
他说:"我建议开源软件对这个问题提供一个解决方案。那么国家就不必独自工作。这将会变得安全、开放和免费。"
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/200-libby-clark/745585-mikko-hypponen-open-source-software-will-make-the-world-more-secure
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://events.linuxfoundation.org/events/linuxcon-europe
|
||||
109
translated/Options in Linux RPM Command to Query Packages.md
Normal file
109
translated/Options in Linux RPM Command to Query Packages.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
|
||||
用来查询安装包的Linux RPM选项
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
RPM是RedHat的包管理器,用来安装/卸载/升级和查询基于RedHta Linux的安装包。RHEL和基于它的系统使用rpm命令这么做。以下是一些例子来演示rpm的查询和展示你可以用不同的方法来查询rpm数据库和还原配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
我已经包含了SSH包在示例命令中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 查询RPM数据库和包 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**1、 在整个RPM数据库中查询,使用下面的命令**
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -qa
|
||||
plymouth-0.8.3-27.el6.x86_64
|
||||
pciutils-libs-3.1.10-2.el6.i686
|
||||
netcf-libs-0.1.9-3.el6.x86_64
|
||||
..
|
||||
…
|
||||
..
|
||||
Output Truncated
|
||||
|
||||
**2、 你可以确定在上面的例子中有哪些SSH包已经安装通过grep命令**
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -qa |grep ssh
|
||||
libssh2-1.4.2-1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
openssh-askpass-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
libssh2-1.4.2-1.el6.i686
|
||||
openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
openssh-clients-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
openssh-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
|
||||
输出显示了一些关于SSH的包但是你仍需确定哪个包真正安装了SSH。为了更近一步,请看下面的示例。
|
||||
|
||||
**3、 检查已安装的SSH包 a) 通过sshd守护进程 b) 通过它的配置文件**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -qf /etc/init.d/sshd
|
||||
openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
# rpm -qf /etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||
openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
|
||||
如你所见ssh是通过openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64包安装的,你可以在守护进程或者配置文件中使用rpm -qf命令。两者都会输出包从哪里安装。
|
||||
|
||||
**4、 现在你有了包名,你可能想要探索更多并想要知道包中包含了哪些不同的文件。这种情况下,使用rpm -ql命令**
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -ql openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
/etc/pam.d/ssh-keycat
|
||||
/etc/pam.d/sshd
|
||||
/etc/rc.d/init.d/sshd
|
||||
/etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||
/etc/sysconfig/sshd
|
||||
/usr/libexec/openssh/sftp-server
|
||||
/usr/libexec/openssh/ssh-keycat
|
||||
/usr/sbin/.sshd.hmac
|
||||
/usr/sbin/sshd
|
||||
/usr/share/doc/openssh-server-5.3p1
|
||||
/usr/share/doc/openssh-server-5.3p1/HOWTO.ssh-keycat
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man5/moduli.5.gz
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man5/sshd_config.5.gz
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man8/sftp-server.8.gz
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man8/sshd.8.gz
|
||||
/var/empty/sshd
|
||||
|
||||
上面的输出显示了所有该包在系统中安装的文件。现在让我们更进一步,我们只想要看到该包提供的配置文件和文档。
|
||||
|
||||
**5、 只显示配置文件,使用rpm -qc命令**
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -qc openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
/etc/pam.d/ssh-keycat
|
||||
/etc/pam.d/sshd
|
||||
/etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||
/etc/sysconfig/sshd
|
||||
|
||||
**6、 只列出文件,使用rpm -qd命令**
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -qd openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64
|
||||
/usr/share/doc/openssh-server-5.3p1/HOWTO.ssh-keycat
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man5/moduli.5.gz
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man5/sshd_config.5.gz
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man8/sftp-server.8.gz
|
||||
/usr/share/man/man8/sshd.8.gz
|
||||
|
||||
考虑一种情况你想要配置一个服务,但是你不知道哪里找到配置文件。举例来说,考虑上面的例子:使用**rpm -qf rpm -qf /etc/init.d/sshd**来找出 **/etc/ssh/sshd_config**这个文件源于哪个包。这应该会给你显示**openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64**包。使用**rpm -ql openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64**来显示包中所含的所有文件。如你所见,许多文件名显示了出来,但是输出并不非常有用。
|
||||
|
||||
现在使用**rpm -qc openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64** 来只显示这个包的配置文件。这只会显示4个文件并给出了[/etc/ssh/sshd_config file][1]的绝对路径来开始配置服务。
|
||||
|
||||
**7、 从PRM包还原配置文件,而不重新安装包。**
|
||||
|
||||
如果由于一些原因文件损坏或者从系统中删除了,你可以以**rpm -qf**开头来找出文件存在于哪个包。接下来使用**rpm2cpio | cpio -idmv**来从包中解压出文件。考虑ssh的例子。
|
||||
|
||||
假设**/etc/ssh/sshd_config**文件已经删除并且你不希望重装ssh,按以下步骤来还原文件。
|
||||
|
||||
* 使用rpm -qf /etc/init.d/sshd 这个命令会显示文件来自于openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64包。
|
||||
|
||||
* 从它的源中下载Openssh的rpm包。
|
||||
|
||||
* 复制openssh-server-5.3p1-84.1.el6.x86_64包到/tmp目录或者其他任何你选择的目录。
|
||||
|
||||
* 使用rpm2cpio |cpio -idmv解压包。
|
||||
|
||||
上面步骤中你使用的命令会在/tmp下面创建一个子目录。你现在可以复制到它的原始目录。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/rpm-command-query/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linoxide.com/how-tos/disable-ssh-direct-login/
|
||||
@ -1,18 +1,17 @@
|
||||
Package Management Using YUM In Red Hat Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在红帽Linux中使用YUM包管理器
|
||||
===
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Yum** is a utility provided in RHEL based systems to install,remove and search packages. It can do lot more than just installing and removing and that’s what I will demonstrate in this article.
|
||||
**YUM**是RHEL系系统中提供的一个安装,卸载和搜索软件包的工具。它能做的不仅仅是安装、卸载软件包,它能做的还有更多,下面我们将在本文中为你展示。
|
||||
|
||||
Yum installs the package dependencies automatically, for example yum install httpd will install https apache server and it’s required dependencies automatically. Something that is not that easy while installing through rpm. with rpm you have to download all the required dependencies and then install accordingly.
|
||||
YUM可以自动安装软件包的依赖,例如当你使用yum安装http时,它还会自动安装https apache服务以及它依赖的软件包。通过rpm软件包安装时就没有这么方便咯(译注:就是不会自动处理软件包依赖问题咯!),你必须下载所有它依赖的软件包,然后依序安装它们。
|
||||
|
||||
The yum utility fetches the package information from a hosted repository (usually by the OS vendor). A repository is basically a collection of rpm’s that are supposed to work on a particular architecture. For example there would be a separate repository for 32 and 64 bit systems, and same goes with RHEL Version 5 and Version 6. You can host your local repository and configure yum to search,install packages from the local repository. In the following examples I will show you some other stuff we can do with yum rather than install and remove but for the sake of understanding I will use httpd package for exempts on my Amazon EC2 RHEL 6.4 server.
|
||||
yum工具从远端服务器上的软件仓库(通常由系统提供商提供)内获取软件包的信息。一个软件仓库基本上是被认为能在特定架构上运行的一系列rpm软件包的集合。例如,对于32位和64位系统各有一个软件仓库,还有针对RHEL5以及RHEL6的软件仓库。你也可以建立一个本地仓库,配置你的yum让其从你的本地仓库里搜索安装软件包。在接下来的例子中,我将想你展示一些yum除了在安装和卸载软件之外可以做的其它事情。为了理解起见,我将在我的Amazon EC2 RHEL 6.4服务器上使用httpd软件包最为例子。
|
||||
|
||||
### Search package from repository ###
|
||||
###从软件仓库里搜索软件包
|
||||
# yum search httpd
|
||||
|
||||
# yum search httpd
|
||||
|
||||
Loaded plugins: amazon-id, rhui-lb, security
|
||||
Loaded plugins: amazon-id, rhui-lb, security
|
||||
=============================================== N/S Matched: httpd ==========
|
||||
httpd.x86_64 : Apache HTTP Server
|
||||
httpd-devel.i686 : Development interfaces for the Apache HTTP server
|
||||
@ -22,24 +21,24 @@ The yum utility fetches the package information from a hosted repository (usuall
|
||||
mod_dav_svn.x86_64 : Apache httpd module for Subversion server
|
||||
mod_dnssd.x86_64 : An Apache HTTPD module which adds Zeroconf support
|
||||
|
||||
For a more detailed output use the below command:
|
||||
想获得详细的输出信息,可以使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum provides httpd
|
||||
|
||||
# yum provides httpd
|
||||
|
||||
Loaded plugins: amazon-id, rhui-lb, security
|
||||
Loaded plugins: amazon-id, rhui-lb, security
|
||||
httpd-2.2.15-26.el6.x86_64 : Apache HTTP Server
|
||||
Repo : rhui-REGION-rhel-server-releases
|
||||
Matched from:
|
||||
|
||||
**yum provides */httpd** Searches in yum packages to find the package that contains a httpd.
|
||||
|
||||
### Provide a list of all Package Groups. ###
|
||||
*yum provides httpd*在软件仓库里搜索含有httpd的软件包
|
||||
|
||||
# yum grouplist
|
||||
###提供所有软件组列表
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will show you the installed and available package group. You can install an individual package group with group install option. For example we will install package group PHP Support. This package group contains the required php packages.
|
||||
# yum grouplist
|
||||
|
||||
# yum groupinstall PHP Support
|
||||
以上命令将为你显示已经安装的以及可用的软件组。你可以安装一个的软件组并可对组内软件进行选择。例如,我们将安装一个PHP支持的软件组。这个软件组内包含PHP需要的软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum groupinstall PHP Support
|
||||
|
||||
Loaded plugins: amazon-id, downloadonly, rhui-lb, security
|
||||
Setting up Group Process
|
||||
@ -125,9 +124,9 @@ The above command will show you the installed and available package group. You c
|
||||
|
||||
Complete!
|
||||
|
||||
### Install package using YUM ###
|
||||
###使用YUM安装软件包
|
||||
|
||||
A package can be installed using yum install command as below:
|
||||
可以使用yum命令安装软件包,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install httpd
|
||||
|
||||
@ -168,28 +167,28 @@ A package can be installed using yum install command as below:
|
||||
Installed size: 3.6 M
|
||||
Is this ok [y/N]: y
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see yum added additional packages with httpd installation. This is called the dependency resolution done by yum.
|
||||
如你所见,在安装httpd时yum安装了额外的软件包。这叫做被yum完成的依赖解析。
|
||||
|
||||
If you want yum not to prompt for the [y/N] option. Use **yum install -y httpd**
|
||||
假如你不想让yum弹出[y/N]选项,可以使用**yum install -y httpd**
|
||||
|
||||
**Update an existing package using yum update command.**
|
||||
**使用yum命令更新一个已存在的软件包**
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update httpd
|
||||
Loaded plugins: amazon-id, rhui-lb, security
|
||||
Setting up Update Process
|
||||
No Packages marked for Update
|
||||
|
||||
That means the httpd package is the latest version in the yum’s repository.
|
||||
这意味着你系统中安装的httpd软件包已经是yum软件仓库里的最新版本的了。
|
||||
|
||||
**Update all packages on the server.**
|
||||
**更新系统中所有的软件包**
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update
|
||||
# yum update
|
||||
|
||||
the above command will update all the packages including kernel package to the latest version that means your OS will be updated to the latest provided by RHEL.
|
||||
以上的命令将根系你系统上的所有软件包到最新版本,包括内核软件包,这意味着你的系统更新到了RHEL提供的最新版本了。
|
||||
|
||||
### Download RPM without installing ###
|
||||
###下载RPM软件包但是不安装
|
||||
|
||||
Use yum to download RPM package from RHN or CentOS repository without installing it. You have to install a plugin for yum first to have yum download the rpm only. The utility name is yum-downloadonly and can be installed through yum as below:
|
||||
使用yum从RHEL或者CentOS的软件仓库里下载RPM软件包但是不安装。你首先需要下载一个插件让yum只下载rpm软件包而不安装。插件名字叫downloadonly,可以通过yum安装,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install yum-downloadonly
|
||||
Loaded plugins: amazon-id, rhui-lb, security
|
||||
@ -228,19 +227,19 @@ Use yum to download RPM package from RHN or CentOS repository without installing
|
||||
|
||||
Complete!
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can just download a package from repository without installing it by using this command:
|
||||
现在你就可以从软件仓库里只下载软件包而不安装了,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install httpd-devel –downloadonly
|
||||
# yum install httpd-devel -downloadonly
|
||||
|
||||
By default packages are downloaded to **/var/cache/yum/<arch\>** directory but you can download them a specified location by adding another option to yum command
|
||||
默认情况下软件包会被下载到**/var/cache/yum/<arch\>**目录,但是你可以添加额外选项将其下载到指定位置
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install httpd-devel –downloadonly –downloaddir=/opt
|
||||
# yum install httpd-devel -downloadonly -downloaddir=/opt
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a rpm of a package but you don’t have the dependencies and you do not know where to get that. you can still have yum to install that rpm and get the required dependencies from the repository. Let’s install the httpd-devel-2.2.15-29.el6_4.x86_64 RPM that we just downloaded.
|
||||
假如你有一个rpm软件包但是没有它所依赖的软件包,你不知道到哪去得到它所依赖的软件包。你仍然可以通过yum安装这个rpm软件包然后从软件仓库里得到它所依赖的软件包。让我们安装刚刚下载的httpd-devel-2.2.15-29.el6_4.x86_64 RPM软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum localinstall /opt/httpd-devel-2.2.15-29.el6_4.x86_64.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
Loaded plugins: amazon-id, downloadonly, rhui-lb, security
|
||||
# yum localinstall /opt/httpd-devel-2.2.15-29.el6_4.x86_64.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
Loaded plugins: amazon-id, downloadonly, rhui-lb, security
|
||||
Setting up Local Package Process
|
||||
Examining /opt/httpd-devel-2.2.15-29.el6_4.x86_64.rpm: httpd-devel-2.2.15-29.el6_4.x86_64
|
||||
Marking /opt/httpd-devel-2.2.15-29.el6_4.x86_64.rpm to be installed
|
||||
@ -344,11 +343,11 @@ If you have a rpm of a package but you don’t have the dependencies and you do
|
||||
|
||||
Complete!
|
||||
|
||||
### Removing packages using yum. ###
|
||||
###使用yum卸载软件包
|
||||
|
||||
yum remove Remove a package.
|
||||
格式为yum remove 要卸载的软件包。举例如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum remove httpd
|
||||
# yum remove httpd
|
||||
Failed to set locale, defaulting to C
|
||||
Loaded plugins: amazon-id, downloadonly, rhui-lb, security
|
||||
Setting up Remove Process
|
||||
@ -399,9 +398,9 @@ yum remove Remove a package.
|
||||
|
||||
Complete!
|
||||
|
||||
### List all installed packages ###
|
||||
###列出所有安装的软件包
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to list all the installed packages then you can use yum list installed command. This is useful in combination with grep or to check whether a specific package has been installed. This is similar to query installed packages with rpm -qa command.
|
||||
假如你要列出你系统上安装的所有软件包,你可以使用命令yum list installed。这条命令结合grep命令是非常有用的,可以用来检查某个特定的软件包是否已被安装。这与使用rpm -qa命令询问已经安装的软件包相似。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum list installed
|
||||
Loaded plugins: amazon-id, downloadonly, rhui-lb, security
|
||||
@ -427,10 +426,10 @@ If you want to list all the installed packages then you can use yum list install
|
||||
.
|
||||
Output Truncated.
|
||||
|
||||
### List the available repository from which packages are being queried, installed and updated. ###
|
||||
###列出用于搜索、安装和更新软件包的可用软件仓库
|
||||
|
||||
# yum repolist
|
||||
|
||||
# yum repolist
|
||||
|
||||
Loaded plugins: amazon-id, downloadonly, rhui-lb, security
|
||||
repo id repo name status
|
||||
rhui-REGION-client-config-server-6 Red Hat Update Infrastructure 2.0 Client Configuration Server 6 4
|
||||
@ -442,6 +441,6 @@ If you want to list all the installed packages then you can use yum list install
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/package-management-yum-redhat-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[Linux-pdz](https://github.com/Linux-pdz) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
|
||||
Recoll:针对Unix和Linux桌面的文本搜索工具
|
||||
===
|
||||
[Recoll][1]是一个Unix和Linux桌面的文本搜索工具。Recoll可以既可以搜索文件名还可以搜索文件内的关键字。
|
||||
|
||||
Recoll可以为你做到以下这些。
|
||||
|
||||
- 它可以搜索任何格式的文件
|
||||
- 支持通配符
|
||||
- 可以搜索依据文件的作者、类型、大小和格式等条件进行搜索
|
||||
- 可以搜索存储在任何位置的文件,例如文件、归档文件、邮件附件等
|
||||
- 支持桌面和网站集成
|
||||
- 火狐插件可以支持索引web页的历史
|
||||
- 点击一下搜索结果就可以在本地编辑器内打开或者显示预览
|
||||
- 它是自由开源的,在GPL许可下发布
|
||||
|
||||
###在Ubuntu/Linux Mint上安装Recoll
|
||||
|
||||
Recoll在Ubuntu仓库里可以找到。然而,最好添加Recoll的仓库以便安装最新版本。
|
||||
|
||||
使用命令添加Recoll仓库:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository
|
||||
|
||||
使用命令更新软件源:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
现在就可以使用下面的命令安装Recoll。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install recoll
|
||||
|
||||
对于其它的发行版,可以去[下载页面][2]下载源代码并编译安装。
|
||||
|
||||
###启动Recoll
|
||||
|
||||
Recoll可以从Dash或者菜单中启动。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
第一次启动时,你需要索引整个家目录。依据你家目录里储存的东西的多少这将需要多少不等的时间。按下**Start indexing now**按钮开始索引。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
假如你想更多的自定义索引,可以调整索引配置和索引计划。要做到这一点,只需要点击一下**Indexing configuration**或者**Indexing schedule**链接。假如你要稍后再去配置,你可以在首选项菜单里配置这些选项。
|
||||
|
||||
一旦索引完成,你就可以搜索文件/文件夹了。结果将根据相关性和匹配的一小部分内容而展现。
|
||||
|
||||
###配置
|
||||
|
||||
正如上面我提到的,假如你想更多的控制索引的细节,你可以调节Recoll的索引功能。
|
||||
在Recoll的工具中有两个配置项
|
||||
|
||||
1.索引配置
|
||||
2.索引计划
|
||||
|
||||
让我们来看一下上面这两个的简短描述。
|
||||
|
||||
**索引配置**可以让你索引时决定包含哪些目录以及排除哪些目录。默认情况下索引时将包含整个家目录。你可以在这儿从索引中添加或移除目录。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你也可以决定web历史记录索引以及储存web页面的最大容量。
|
||||
|
||||
**index schedule**则是可以让制定一个计划以便于进行自动索引或者当你登陆如系统后就进行实时索引。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Recoll支持两种索引计划:
|
||||
|
||||
**Cron任务** - 决定什么时候开始运行以及写入Crontab键值。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
以上这个屏幕截图中,Recoll的cron任务会在每天上午12点的时候执行。设置完cron任务后,点击enable键激活它就可以咯。
|
||||
|
||||
**开启实时索引** - 决定是否当你登陆入系统后进行实时索引。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
激活这一选项,recoll的守护程序都会随系统启动。要注意的是这一选项只有在默认索引设置的情况下才可用。
|
||||
|
||||
###基本搜索
|
||||
|
||||
现在你已经对Recoll了解的足够多了。是时候去搜索一下文件或者文件夹了。这个应用的美妙之处就在于它既可以搜索文件名还可以搜索文件内的关键词。
|
||||
|
||||
在Recoll的用户界面中,在顶部右边的搜索栏中键入要搜索的关键字,然后点击Search按钮。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如你在上图所见,精确相关的内容将会显示还能预览到一小部分内容。你可以点击Open按钮直接打开搜索到的文件,或者在打开它之前使用预览按钮预览它。
|
||||
|
||||
你还可以过滤搜索结果,使用分类例如,媒体、消息、其它、演示文档、电子表格或者文本等。更重要的是,你还可以通过选择使搜索结果匹配任一项、全部项、文件名或者语言等来过滤搜索结果。
|
||||
|
||||
###高级搜索
|
||||
|
||||
点击菜单栏中的高级搜索图标或者前往**Tools->Advanced Search**。这将打开一个新的对话窗口。在这儿你可以附加更多的限制条件来进行搜索。例如我可以搜索文件内容里含有关键字“hp”以及文件名为“storage”的文件。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这将找到并显示文件内含有关键字“hp”且文件名为“storage”的文件。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
###Unity桌面以及网站集成
|
||||
|
||||
这个应用支持桌面集成以及网站集成。假如你要把它集成到你的Ubuntu的Unity桌面中去,你可以用下面的命令安装**recoll-lens**。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install recoll-lens
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,lens限制显示结果最多显示20条。假如你要显示更多数目的搜索结果,编辑**rclsearch.py**,修改“**if actual_results >= 20:**”这一行就可以咯。
|
||||
|
||||
假如你使用火狐浏览器,要去搜索你每天访问的浏览历史,你可以使用这个[火狐扩展][3]。这个火狐扩展可以和Recoll一起工作去索引你全天浏览的网站。在安装完这个扩展之后,在Recoll的索引配置中从web历史标签页中激活它就可以咯。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
所有的Linux都在他们的文件管理器中内建了搜索功能以便于尽可能容易的搜索文件/文件夹。对于那些不喜欢内置的搜索的功能以及想要寻找更加高级的文本搜索工具的人来说,Recoll是个值得一试的工具。对于我来说,这真是个容易使用且功能强大的工具,对基本搜索如此,对高级搜索也是如此.
|
||||
|
||||
欢呼吧!
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/recoll-text-searching-tool-linux-desktops/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Linux-pdz](https://github.com/Linux-pdz) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.recoll.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.lesbonscomptes.com/recoll/download.html
|
||||
[3]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/recollfirefox/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
用这个**漂亮的集成启动程序工具**保存,访问和快速粘贴文本片段Save, Access And Quickly Paste Text Snippets With This Nifty Unity Launcher Tool
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**反复键入特定的信息 - 如电子邮件地址或家庭地址,详细的终端命令,及时发送用户喜爱的电视节目的资讯 - 可是件苦差事。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Snippets – 方便的访问存储的文本的方法*
|
||||
|
||||
谢天谢地,这个世界上有一些工具可以帮助我们(做这些事儿)。
|
||||
|
||||
*‘Snippets’* 是Unity中这样的组件之一。 这是一个简单的启动程序小工具,它让你在一个文件中保存和存储摘下来的内容,然后当你需要的时候从Unity的一个快速列表里复制到剪贴板。
|
||||
|
||||
在有人因为厌恶而想我扔内衣之前,我深知Snippets不是唯一的 – 甚至不是第一个 – 提供这一系列功能的。但是它独特的是通过Unity启动器项目来提供这一系列功能。
|
||||
|
||||
(这个软件具有)非常聪明的特征,它足够简单,提供以下功能:
|
||||
|
||||
- 添加,访问存储在txt文件中的文本段
|
||||
- 在快速列表里查看保存的文本段
|
||||
- 点击文本段就可以复制到剪贴板
|
||||
- 提供了把剪贴板中的内容保存到txt文件的选项
|
||||
|
||||
尽管它不是一个“活(智能)”的剪贴板管理工具 – 它只是列出了你特别添加的项目;它不会列出你最近的剪贴板项目历史,它仍然是一个非常方便的小工具。
|
||||
|
||||
###怎样为Unity安装Snippets###
|
||||
|
||||
想要使用这个漂亮的启动器项目,你需要先安装一个命令行剪贴板工具XClip。点击下面的按钮(链接)从软件中心安装。
|
||||
- [点击以在Ubuntu里安装XClip][1]
|
||||
|
||||
下一步,下载下面的‘Snippets‘压缩文件。这包含了剩余所有的使用这个应用所需要的东西。
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download ‘Snippets’ Unity Launcher Script][2]
|
||||
|
||||
当这个压缩文件下完之后你就可以解压了。进入生成的文件夹,然后按Ctrl+H显示隐藏的文件。移动文件夹‘.snippets-launcher‘到你的主文件夹中。**如果不这么做,这个组件将无法正常工作。**
|
||||
|
||||
下一步是安装启动器项目。这是被一个你刚搬到文件夹里面的脚本关照的,但它不具有可执行的权限(需要安装),因此,我们首先需要关照它一下。
|
||||
|
||||
打开一个新的终端窗口在里面小心的键入下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
cd .snippets-launcher/ && chmod +x snippets.sh
|
||||
|
||||
./snippets.sh
|
||||
|
||||
就是这样;Snippets应该已经整装待发了。打开Unity Dash搜索Snippets然后把它拖到启动器上去:
|
||||
|
||||
- 左键点击启动器打开可以添加你的文本段的文本文件
|
||||
- 右键点击启动器上的项目打开快速列表
|
||||
|
||||
快速列表里的选项:
|
||||
|
||||
- 左键点击文本段以添加到剪贴板
|
||||
- 左键点击“日期”可以复制当前日期
|
||||
- 点击“添加剪贴板内容”可以把当前剪贴板中的内容加入到txt文件中
|
||||
- 在添加一个项目到.txt文件后点击“更新启动器”
|
||||
|
||||
更多关于这个懒人的工具信息尽在[Ubuntu论坛][3],在那里它的开发者,“Stinkeye”,会很高兴地提供帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/10/unity-launcher-clipboard-snippets-item
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[crowner](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:apt://xclip
|
||||
[2]:https://www.dropbox.com/s/ha6lngizmz78srv/snippets%20by%20stinkeye.tar.gz
|
||||
[3]:http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=2184916
|
||||
@ -1,47 +0,0 @@
|
||||
闭源(或者看起来似乎)优于开源的七个缘由
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
开源在某些情况下优于开源,看起来似乎挺奇怪的,因为这样的观点来竟然自于OpenLogic的创办人,而该公司专注于在开源领域提供帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
针对闭源……
|
||||
|
||||
**1. 出了问题,不用自己搞定。**
|
||||
|
||||
只要是软件,难保不出问题。要是开源软件出了这事儿,要么你自己,要么某个欠你人情债的工程师,总得有个人要花费时间排除bug。通览代码,求助于开源社区或者开源软件的供应商,通过这些手段来解决问题。
|
||||
但是闭源呢,一旦你确定开发商代码出了问题,ok,你的工作到此为止! 你只需发个文件,等着就行了。
|
||||
当然,可能会等上几个月或者几年,问题才能得到解决,更甚者永远得不到答复。但是除此之外,你还能做什么呢。 把问题踢回去,放松,期待最好的解决方案,仅此而已。
|
||||
|
||||
**2. 不必担心贡献回流到社区。**
|
||||
|
||||
如果用的是开源软件, 很有可能, 你解决了一个bug或者做出了改善,之后你的代码就会进入到社区,随着时间的推移从而帮助测试或者维护。闭源就不同了,你根本用不着给任何人做任何事情。当然,那是因为你接触不到代码,所以也修改不了,但是你可以针对遇到的问题创建自己的解决方案。你可以一直只针对同一个问题,改善再改善,一个版本接着一个版本,至少用不着跟社区打交道,为其他人提供更好的解决方法。
|
||||
|
||||
**3. 你不必考虑开源许可条款及规定事宜。**
|
||||
|
||||
针对开源,你必须遵循所使用的组件的许可条款。例如,想要搞明白Apache软件许可证和GPL之间的区别与联系,是需要花费一定的时间的。使用哪一种许可证取决于你所用的开源组件以及你如何使用这些组件(发布给第三方或者内部使用),据此都有不同的许可证可供应用(可附加到文档中进行说明)。像OpenLogic这样的公司可以很容易地理解并遵守开源许可,但是针对闭源,你大可不必担心这类事情!你的供应商的许可协议把有关软件的所有的权利都收走了,如果没有你的公司的律师明确同意的情况下,打算以独有的方式使用软件几乎是不可能的,想都不要想。当然,你还得对付许可证计数,突如其来的软件合规性审计,随着时间的推移而恶化的条款,几乎难以理解的法律术语,但至少你不必了解如何使用开源组件。
|
||||
|
||||
**4. 你用不着为每个组件在众多选项中进行选择**
|
||||
|
||||
针对数据库,Web服务器,应用服务器,编程语言,图形用户界面框架,类似的方面等等,开源都提供了大量的解决方案。在每一个特定的领域,你都可以找到运用不同的架构方法,使用各种语言构建的健壮的成品。找一款功能相似的工具很容易,这些工具都针对不同的使用场合进行了优化(性能、可扩展性、简洁之间的比较)。为了确信一个工具软件在既定场合下功能够满足需求,可以下载下来,试用一下。使用闭源软件的话,你就用不着对付那么多的选项。你只需要在每个领域探索两三个大厂商提供的产品。如果供应商没有提供免费试用版本,或者很难说服你为试用品买单,甚至签署试用协议,那你就节省时间了。
|
||||
|
||||
**5. 你不必四处找幻灯片**
|
||||
|
||||
如果打算找一些会议简报,架构图表,截图,以及其他软件相关的文档,这需要花费一定的时间。使用开源软件,你得读百科,访问论坛,还有邮件列表,才能获取到你需要的相关组件的信息。使用闭源软件,一通电话就足够了,只需坐在自己舒适的办公室,会有西装革履的专业人士把PowerPoint演示文稿寄送到你的面前。
|
||||
当然,你得预先提供自己的联系方式,销售人员是不会不给你打电话的。这样看来,至少自己没必要粗略地在网上搜索漂亮的图形。
|
||||
|
||||
**6. 你无需到处寻求技术支持**
|
||||
|
||||
你可以得到来自开源社区,自己的工程师,或专业开源组织的帮助。这可能需要一些时间,以决定是否要服务等级协议(SLA)的支持便于在保证的时间内得到答复,就像从OpenLogic那里获得帮助一样,或者如果你觉得随意的话可以张贴问题到邮件列表,自己解决。闭源就不同了,你根本不需要担忧从哪获得帮助。而且,你可能根本用不着和工程师当面交谈,只需要知道给谁打电话就OK了。
|
||||
|
||||
**7. 认输就行了**
|
||||
|
||||
开源软件,总会有办法解决问题,打补丁,改善,强化,重构,升级,或者重写。没可能跟闭源那样,甩手走开。当然,你可以谩骂开发出这个导致问题的软件的社区,但是你仍然可以解决问题,从社区或者组织那里获得帮助,或者自己动手解决。
|
||||
|
||||
嗯,你都了解了。为甚么闭源优于开源的几条缘由。你还有要补充的吗?
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://opensource.com/business/13/10/seven-reasons-closed-better-than-open-source
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/l3b2w1) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
|
||||
戴文的Linux内核专题:19 配置内核 (15)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你好!在这篇Linux系列文章中,我们将继续配置USB网络驱动。接着我们将进入输入设备。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们可以启用/禁用"Multi-purpose USB Networking Framework",这允许连接笔记本到桌面系统上。
|
||||
|
||||
下面,可以启用/禁用ASIX USB-to-Ethernet适配器驱动(ASIX AX88xxx Based USB 2.0 Ethernet Adapters)。
|
||||
|
||||
那么,还有一个ASIX适配器驱动(ASIX AX88179/178A USB 3.0/2.0 to Gigabit Ethernet)。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:通常地,最好将适配器驱动作为模块加入。
|
||||
|
||||
通信设备类规范(Communication Device Class specification)在这个驱动中提供(CDC Ethernet support (smart devices such as cable modems))。这个规范用于USB调制解调器。Linux系统可以将USB网络接口识别为以太网网络接口并且指定为"ethX",这里的"X"是以太设备编号。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一个与上面类似的规范(CDC EEM support)。CDC EEM代表的是"Communication Device Class Ethernet Emulation Model"(通信设备类以太网仿真模型)。
|
||||
|
||||
CDC网络控制模型(NCM)同样有一个驱动提供了规范(CDC NCM support)。
|
||||
|
||||
这个驱动提供了"CDC MBIM (Mobile Broadband Interface Model)"规范同样也在Linux内核中(CDC MBIM support)。
|
||||
|
||||
下面,有一些供货商/设备特定驱动用于不同的USB网络设备和芯片组。
|
||||
|
||||
在这之后,有一个用于USB网络设备的通用驱动,它不需要任何特殊的驱动(Simple USB Network Links (CDC Ethernet subset))。
|
||||
|
||||
再说一次,还有更多的驱动用于供货商特定设备。
|
||||
|
||||
有趣的事实:Linux被用于制作James Cameron的电影"泰坦尼克"的特效。
|
||||
|
||||
"CDC Phonet support"是用于使用Phonet的Nokia USB调制解调器。(译注:Phonet是Nokia开发的面向数据包的通信协议,仅用于Nokia maemo/meego产品)
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们可以进入使用802.11规范的无线局域网驱动了。
|
||||
|
||||
主要地,这里有一个供货商/设备特定驱动列表。
|
||||
|
||||
"SoftLED Support"控制着关于Wifi卡/设备的LED灯。
|
||||
|
||||
一些芯片组支持的SDIO在这个驱动中(Atheros ath6kl SDIO support)。SDIO是用于无线SD卡的SD(Secure Digital)规范的扩展。SDIO代表的是"Secure Digital Input/Output"
|
||||
|
||||
内核开发者可能注意到一些无线设备可以支持QoS。QoS代表"Quality of Service"(服务质量)。这个特性给予网络传输优先级。假设需要通过网络传输两组数据。只有一个可以先发送。QoS会先发送最重要的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
有趣的事实:技术上来说,Linux并不是一个操作系统。Linux是一种内核而GNU/Linux是操作系统。。
|
||||
|
||||
WAN卡需要"Generic HDLC layer"。HDLC代表"High-Level Data Link Control"(高级数据链路控制)。这是一个数据链路层协议。
|
||||
|
||||
原生HDLC可以通过"Raw HDLC support"驱动启用。
|
||||
|
||||
"Raw HDLC Ethernet device support"驱动允许HDLC层模拟以太网。
|
||||
|
||||
cHDLC驱动提供了一个HDLC的扩展,同样也称作Cisco HDLC(Cisco HDLC support)。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux内核同样也提供了一个HDLC的"Frame Relay support"(帧中继)驱动。帧中继是2层协议。
|
||||
|
||||
HDLC同样支持PPP(Synchronous Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) support)和X.25(X.25 protocol support)。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,这个驱动提供了DLCI下的帧中继(Frame Relay DLCI support)。
|
||||
|
||||
"LAPB over Ethernet driver"创建一个允许用户在以太网上使用LAPB的点到点连接到另一台计算机的设备文件。这个设备文件对于第一个此类设备通常是/dev/lapb0。
|
||||
|
||||
用这个驱动,X.25帧可以通过电话线发送(X.25 async driver)。特别地,这个驱动允许X.25使用异步串行。
|
||||
|
||||
对于ISA SBNI12-xx有一种特殊的驱动(Granch SBNI12 Leased Line adapter support)。这种卡对于租用线路的调制解调器是一种便宜的替代。
|
||||
|
||||
下一个驱动允许使用并行连接携带已安排的流量(Multiple line feature support)。这允许Linux系统更加有效地在SBNI12适配器上管理并行连接。一些Linux用户声称这个驱动双倍加速了他们的速度。然而,这个我没有亲身测试了解。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,可以配置"IEEE 802.15.4 drivers"。这个是对于慢速WAN设备。这是一个控制媒体和无线网络物理层的标准。这个规范在不同的大洲使用不同的频率。不如,在欧洲,这类无线设备会使用868.0-868.6MHz的频率。
|
||||
|
||||
这个目录中的第一个设定是fake LR-WPAN驱动(Fake LR-WPAN driver with several interconnected devices)。LR-WPAN代表"Low-Rate Wireless Personal Area Network"(低速无线个人网络)。
|
||||
|
||||
有趣的事实:目前内核中只有大约2%的代码是由Linus Torvalds写的。
|
||||
|
||||
VMware使用vmxnet3虚拟以太网需要这个驱动(VMware VMXNET3 ethernet driver)。当在为大量用户编译内核时,最好将这个启用为一个模块,因为一些人可能并不希望在VMware上使用以太网。
|
||||
|
||||
Hyper-V虚拟网络需要这个驱动(Microsoft Hyper-V virtual network driver)。你可能想知道这个是否与微软的Hyper-V相同。使得,Linux支持Hyper-V。
|
||||
|
||||
数字电话服务ISDN由这个驱动提供(ISDN support)。ISDN代表"Integrated Services Digital Network"(综合业务数字网)。在法国,ISDN被称为RNIS,代表" Réseau numérique à intégration de services"。有一台ISDN适配器,计算机可以开始并接收语音呼叫。这允许计算机用来做因待机或者其他一些电话服务设备。ISDN同样也可以携带视频信息。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们可以进入输入设备了(Input device support)。这些是给计算机信息的设备。鼠标和键盘是最常被使用和了解的输入设备。扫描仪是另外一种输入设备的例子。
|
||||
|
||||
首先是一个支持不同触觉反馈设备的驱动(Support for memoryless force-feedback devices)。比如,许多游戏控制器的震动就是一种触觉反馈。
|
||||
|
||||
一些输入设备会检测硬件的状态(Polled input device skeleton)。这类行为需要这个驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
使用稀疏键盘映射的输入设备需要这个驱动(Sparse keymap support library)。键盘映射是键盘的布局信息。
|
||||
|
||||
下面,是另外一种键盘映射(Matrix keymap support library)。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:当为广泛的用户组编译内核时,包含大多数或者全部输入设备作为模块,因为通常不知道用户可能插到计算机上的设备类型。
|
||||
|
||||
有趣的事实:Vanilla内核就是Linux自己的原始内核,是未改变的状态。
|
||||
|
||||
"Mouse interface"对于鼠标创建了两个不同的设备文件。这两个设备文件是/dev/input/mouseX 和 /dev/input/mice。
|
||||
|
||||
下一个驱动创建了一个psaux设备文件并且它是/dev/input/mice的别名 (Provide legacy /dev/psaux device)。psaux设备文件是/dev/psaux。
|
||||
|
||||
如果系统有一块数位板,那么需要设置水平分辨率(Horizontal screen resolution)和垂直分辨率(Vertical screen resolution)。数位板是一种支持允许用户绘画的触控笔的触摸屏。另外的触摸屏无法支持如此复杂的输入。
|
||||
|
||||
下一个驱动支持操纵杆和游戏手柄(Joystick interface)。这个驱动会创建/dev/input/jsX文件。
|
||||
|
||||
"Event interface"驱动允许输入设备通过dev/input/eventX访问。
|
||||
|
||||
"Event debugging"驱动会输出所有的输入事件到系统日志中。除了要调试系统否则不要以任何理由启用它。显然地,这么做为了性能原因,但是我这么建议禁用的主要原因是安全目的。所有的按键都会被明文记录下来包括密码。
|
||||
|
||||
下面,列出了不同的键盘(Keyboards)配置驱动,接下来是鼠标(Mice)驱动和操纵杆和游戏手柄(joystick/gamepad)驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
在这之后,列出了不同特定的平板硬件/供货商的不同驱动(Tablets)。在这之后是触摸屏的驱动列表。
|
||||
|
||||
最后一组输入设备驱动是对于特定硬件和供货商的杂项驱动列表(Miscellaneous devices)。
|
||||
|
||||
这个系列的下一篇文章会讨论输入端口。不要忘记阅读这个系列的其他文章和这个网站。谢谢!
|
||||
|
||||
**致粉丝: 谢谢**你们的邮件告诉我你们对这些文章的喜爱。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-15.4793/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,117 @@
|
||||
戴文的Linux内核专题:20 配置内核 (16)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
欢迎来到下一篇Linux内核文章。在本篇里,我们将讨论输入/输出端口。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,PS/2鼠标和AT键盘需要"i8042 PC Keyboard controller"驱动。在USB之前,鼠标和键盘使用圆形端口的PS/2端口。AT键盘是一种84键使用AT端口的IBM键盘。AT端口有5针而PS/2口有六针。
|
||||
|
||||
使用COM口(有时也称RS232串口)的输入设备需要这个驱动(Serial port line discipline)。COM是一种串口,意味着每次传输一位。
|
||||
|
||||
TravelMate笔记本需要这个特殊的驱动来使用连接到QuickPort的鼠标(ct82c710 Aux port controller)。
|
||||
|
||||
对于PS/2 mice、AT keyboards 和 XT keyboards的并口适配器使用这个驱动(Parallel port keyboard adapter)。
|
||||
|
||||
"PS/2 driver library"用于PS/2鼠标和AT键盘。
|
||||
|
||||
可以启用"Raw access to serio ports"来允许设备文件作为字符文件来使用。
|
||||
|
||||
下面,下面有一个用于"Altera UP PS/2 controller"的驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
PS/2复用同样需要一个驱动(TQC PS/2 multiplexer)。
|
||||
|
||||
ARC FPGA平台对于PS/2控制器需要特殊的驱动(ARC PS/2 support)。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:我想要说清楚这篇文章中讨论的PS/2空孩子气并不是Sony的PlayStation上的游戏控制器。这篇文章讨论的是6针鼠标/键盘端口。控制器是一种有PS/2端口的卡。
|
||||
|
||||
"Gameport support"提供对15针gameport的支持。gameport是一种曾经被很多游戏设备使用直到USB端口的发明的15针口。
|
||||
|
||||
下一个驱动是在ISA或者PnP总线卡上的gameport驱动(Classic ISA and PnP gameport support)。ISA代表"Industry Standard Architecture"(工业标准架构)并且它是一种在PCI之前的并行总线标准。PnP代表"Plug-and-Play"(即插即用)并且他是一种在ISA之前的通用标准。
|
||||
|
||||
"PDPI Lightning 4 gamecard support"提供了一个有gameport的游戏卡的专有驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
SoundBlaster Audigy卡是一种专有gameport卡(SB Live and Audigy gameport support)。
|
||||
|
||||
ForteMedia FM801 PCI音频控制器在卡上有一个音频控制器(ForteMedia FM801 gameport support)。这个驱动只支持gameport。
|
||||
|
||||
下一步,我们可以进入"Character devices"。字符设备以字符传输数据。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,可以启用/禁用TTY(Enable TTY)。移除TTY会节约很多空间,但是许多终端和这类设备需要TTY。除非你知道你在做什么,否则不要禁用TTY。
|
||||
|
||||
致我的粉丝:如果你知道一个禁用TTY的理由,你能在下面发表你的答案并与我们共享么?谢谢!
|
||||
|
||||
下一步,可以启用/禁用"Virtual terminals"(虚拟终端)。再说一次,这个可以节约很多空间,但是虚拟终端很重要。
|
||||
|
||||
下一个驱动支持字体映射和Unicode转换(Enable character translations in console)。这用于转换ASCII到Unicode。
|
||||
|
||||
虚拟终端可以用这个驱动作为系统控制台(Support for console on virtual terminal)。系统控制台管理着登陆和内核信息/警告。
|
||||
|
||||
虚拟终端必须通过控制台驱动与物理终端交互(Support for binding and unbinding console drivers)。在虚拟终端可以这么做之前,控制台驱动必须被加载。当虚拟终端关闭后,控制台终端必须被卸载。
|
||||
|
||||
下一个驱动提供了对Unix98 PTY驱动的支持(Unix98 PTY support)。这是Unix98伪终端。
|
||||
|
||||
有趣的事实:Linux内核允许某个文件系统一次在很多地方被多次挂载。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,可以支持"Support multiple instances of devpts"(译注:允许多个"devpts"文件系统实例)。devpts文件系统用于伪终端的slave。
|
||||
|
||||
过时的PTY同样可以启用(Legacy (BSD) PTY support)。
|
||||
|
||||
可以设置最大数量的使用中的过时PTS(Maximum number of legacy PTY in use)。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的驱动可以用于提供对其他驱动不支持的串口的支持 (Non-standard serial port support)。
|
||||
|
||||
下面有一些用于特定板和卡的驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
这个驱动支持GSM MUX协议(GSM多路复用)(GSM MUX line discipline support (EXPERIMENTAL))。
|
||||
|
||||
下一个驱动启用kmen设备文件(/dev/kmem virtual device support)。kmem通常用于内核调试。kmem可以用于读取某些内核变量和状态。
|
||||
|
||||
Stallion卡上面有许多串口Stallion multiport serial support)。这个驱动特别支持这块卡。
|
||||
|
||||
下面,我们可以进入到串行设备驱动了。如前所述,串行设备每次传输一位。
|
||||
|
||||
第一个驱动用于标准串口支持(8250/16550 and compatible serial support)。
|
||||
|
||||
在这个驱动下,即插即用(Plug-and-Play)同样存在于串口中(8250/16550 PNP device support)。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的驱动允许串口用于连接一个终端后作为控制台(Console on 8250/16550 and compatible serial port)。
|
||||
|
||||
一些UART控制器支持直接内存访问(DMA support for 16550 compatible UART controllers)。UART代表的是"Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter"(通用异步收发)。UART控制器转换串行到并行,反之亦然。
|
||||
|
||||
下一步,这个驱动提供了标准PCI串行设备支持(8250/16550 PCI device support)。
|
||||
|
||||
16位PCMCIA串行设备由这个驱动支持(8250/16550 PCMCIA device support)。记住,PCMCIA是一种通常使用于笔记本的PC卡。
|
||||
|
||||
可以设置最大数量支持的串口(Maximum number of 8250/16550 serial ports),接着是在启动中注册的最大数量(Number of 8250/16550 serial ports to register at runtime)。
|
||||
|
||||
为了扩展像HUB6的串行能力,启用这个驱动(Extended 8250/16550 serial driver options)。
|
||||
|
||||
一个特殊驱动用于支持多于4种的过时串口(Support more than 4 legacy serial ports)。
|
||||
|
||||
当启用这个驱动后,可以共享串口中断(Support for sharing serial interrupts)。
|
||||
|
||||
使用这个驱动可以自动检测串口中断请求(Autodetect IRQ on standard ports)。
|
||||
|
||||
RSA串口同样也在Linux内核中支持(Support RSA serial ports)。RSA代表的是"Remote Supervisor Adapter"(远程管理适配器)。RSA是一种IBM特定的硬件。
|
||||
|
||||
下面,有不同的供应商/设备特定驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
下面有一个使用printk输出用户信息的TTY驱动(TTY driver to output user messages via printk)。printk(print kernel)是一种通常打印启动信息的特殊软件。任何由printk显示的字符串通常在/var/log/messages文件里。shell命令"dmesg"显示所有被printk使用的字符串。
|
||||
|
||||
下面,我们可以启用/禁用并口打印机的支持(Parallel printer support)。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来的驱动允许打印机作为一个控制台(Parallel printer support)。这意味着内核消息会被逐字地由打印机打印。通常地在这个系列中使用"print"(打印)这个单词时,意味这将输出信息到屏幕上。而这次,字面上的意思是将数据输出在纸上。
|
||||
|
||||
以下的驱动使设备文件在/dev/parport/中(Support for user-space parallel port device drivers)。这使得一些进程可以访问。
|
||||
|
||||
再说一次,Linux内核有许多特性和驱动,所以我们还会在下一篇文章中继续讨论更多的驱动。谢谢!
|
||||
|
||||
致粉丝:我们正在接近配置过程的终点。我有一张你们很多人想知道的内核话题列表。这些话题包含了安装内核、管理模块、加入第三方驱动、还有许多其他有趣的建议和要求。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-16.4835/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user