mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
Merge branch 'LCTT/master'
This commit is contained in:
commit
cd49f16e6a
@ -0,0 +1,316 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10安装后你要做的8件事
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 已经发布了,对于那些打算安装“纯净版”的用户,安装完系统后你可以考虑下面的8件事。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 安装一些绚丽的小零件 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**系统负载** 是系统监控工具GNOME里的一个小应用。它能在面板上展示出CPU、内存、网络使用、硬盘I/O等信息。点击下面的按钮从Ubuntu软件中心安装。
|
||||
|
||||
[][1]
|
||||
|
||||
或者通过命令行进行安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install indicator-multiload
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**CPU频率**是一款等效于“GNOME-CPU调频”的应用。你可以实时的调整CPU的频率。点击下面的按钮从Ubuntu软件中心安装。
|
||||
|
||||
[][2]
|
||||
|
||||
或者通过命令行安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install indicator-cpufreq
|
||||
|
||||
**我的天气**是一款显示当前天气的应用,它能显示5天内的预报并支持四大天气服务站点:OpenWeatherMap, Yahoo, Wunderground 和 World Weather Online。
|
||||
|
||||
通过命令行进行安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:atareao/atareao
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install my-weather-indicator
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[**Variety**][3]一款带有AppIndicator的应用,但是基本上你只需要配置一次就可以用指示器来使用此软件了。Variety是一款很酷的壁纸更换的应用,他能在设定的时间内自动下载并更换壁纸。用起来就有种高帅富的感觉。壁纸库每天都会有更新,你可以很快的切换到另外一个壁纸,收藏自己喜欢的壁纸,留着日后再用。
|
||||
|
||||
通过以下命令行安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:peterlevi/ppa
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install variety
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可能还需要一个剪切板管理器,试试**Diodon** 吧,这是款轻量型软件,支持文件、图像等。点击下面的按钮安装:
|
||||
|
||||
[][4]
|
||||
|
||||
或者通过命令行安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install diodon diodon-plugins
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 设置 Unity ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Unity Tweak Tool**让用户能改变一些Unity设置,比如:自动隐藏、窗口最大化、“触发角”、Dash、Unity启动器或平视显示器、改变GTK或图标主题、改变字体和大小,移动窗口控制器到右边等。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
点击下面的按钮从软件中心安装
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
或者通过命令行安装
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install unity-tweak-tool
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 隐私设置 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你应该知道可以通过默认的Dash来查看最近访问的文件和其他的一些文件。系统设置可以通过设置**“安全和隐私”**来选择显示的文件类型。这样就不用看到那些软件、文件夹之类的了。你也可以清除最近的记录。
|
||||
|
||||
此外你在使用搜索框的时候,可以设定不显示网络搜索的结果。但是这会屏蔽掉所有的网络信息。所以当你仅仅是想**“屏蔽购物推荐”**的话,你可以输入下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
gsettings set com.canonical.Unity.Lenses disabled-scopes "['more_suggestions-amazon.scope', 'more_suggestions-u1ms.scope', 'more_suggestions-populartracks.scope', 'music-musicstore.scope', 'more_suggestions-ebay.scope', 'more_suggestions-ubuntushop.scope', 'more_suggestions-skimlinks.scope']"
|
||||
|
||||
更多插件屏蔽,点击[此处][6]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
另外一种在Ubuntu 13.10中设置隐私的方法是使用**隐私指示器**,这是一款让你快捷设置启用/屏蔽Zeitgeist 或者在线搜索结果的软件,并能清除Zeitgeist日志和最近文件(显示先边栏的“最近”里面)。
|
||||
|
||||
[**下载 Privacy Indicator**][7](此网页中含有deb文件下载)
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 使用混合显卡功能###
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu的开发人员已经在Ubuntu 13.10 (和 12.04 LTS版 )中实现了混合显卡技术,下面你会看到相关设置的说明。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Nvidia Optimus**:不幸的是,Linux平台下Nvidia显卡驱动并不完全支持Optimus,[更多][8]。
|
||||
|
||||
但是Ubuntu 13.10用了“nvidia-prime”包来过渡。这个包使默认支持Intel显卡芯片的Optimus平台也支持Nvidia显卡。通过下面指令你能Nvidia显卡一直处于工作状态,就是说没有办法让它停止工作来节能了。这样笔记本就会功耗更大和过热--——**对我而言,我是不会 用这个的,除非过热的问题解决了**,如果没有解决的话,你可以取消这个设置。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
再次不幸的是,这不是唯一的问题。你会发现画面分割和热插拔并不工作。所以,如果你想用多个显示器的话。你需要手动的在xorg.conf进行设置。这样的好处就是,你可以玩那些不支持Intel显卡的游戏,用支持VDPAU的媒体播放器等。
|
||||
|
||||
即便如此,如果你还是想尝试一下的话,请确保你使用的是默认的显示管理器LightDM,并不是其他的,如GDN等。此外,如果你安装了Bumblebee,你需要卸载掉它:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get purge bumblebee* bbswitch-dkms
|
||||
|
||||
然后安装最新的Nvidia驱动和“nvidia-prime”:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install nvidia-319 nvidia-settings-319 nvidia-prime
|
||||
|
||||
最后重启电脑(重启X是不够)。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想撤销这些改变,你可以输入通过下面的指令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove nvidia-319 nvidia-settings-319 nvidia-prime
|
||||
|
||||
然后重启
|
||||
|
||||
**AMD 混合显卡**:我并没有测试过这个,因为我没有支持AMD显卡的系统,但是根据Ubuntu wiki上的[**HybridGraphics**][9]包说明,应该是没有问题。(再次申明,我并不确定,因为我没试过)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
要想在Ubuntu 13.10下获得合适的AMD显卡支持。你需要安装最新的 fglrx驱动和fglrx-pxpress:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install fglrx fglrx-pxpress
|
||||
|
||||
并重启电脑。重启X是没有用的
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 延长电池寿命 ###
|
||||
|
||||
有两个工具可以延长电池的寿命:laptop-mode-tools 和 TLP。这两个工具都是为了延长电池寿命,[**TLP**][10] 似乎效果更好一点,但是TLP仅有PPA,如果你不想添加APPs时,就安装 laptop-mode-tools吧。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:**不要同时安装laptop-mode-tools和TLP**
|
||||
|
||||
点击下面的按钮安装laptop-mode-tools。
|
||||
|
||||
[][11]
|
||||
|
||||
或者通过命令行安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install laptop-mode-tools
|
||||
|
||||
输入下面命令安装TLP:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:linrunner/tlp
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install tlp tlp-rdw
|
||||
sudo tlp start
|
||||
|
||||
这两个工具都不需要额外的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
另外一种节约电池的方法是**Bumblebee**(是允许在独显运行软件或游戏的工具),Bumblebee是一款支持笔记本上双显卡智能切换的软件。能停止Nvidia显卡,当你不需要使用的时候。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:如果你想在显卡自动切换技术的第4步采用混合显卡时,请不要安装Bumblebee**
|
||||
|
||||
点击下面的按钮进行安装:
|
||||
|
||||
[][12]
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install bumblebee bumblebee-nvidia
|
||||
|
||||
然后重启。
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu中有个禁止"optirun"工作的[**bug**][13]。通过下面的命令解决这个问题。
|
||||
|
||||
- 32位系统
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ln -s /usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libturbojpeg.so.0 /usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libturbojpeg.so
|
||||
|
||||
- 64位系统
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ln -s /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libturbojpeg.so.0 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libturbojpeg.so
|
||||
|
||||
当你想用Nvidia显卡时,运行:
|
||||
|
||||
optirun APP-EXECUTABLE
|
||||
|
||||
将"APP-EXECUTABLE"替换为你要运行的软件或者游戏的可执行文件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 安装 编解码器, Java 和 加密DVD播放 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果需要播放更多类型的音频视频文件,那就安装 **Ubuntu Restricted Extras** 吧
|
||||
|
||||
[][14]
|
||||
|
||||
或者输入下面的命令行:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install ubuntu-restricted-extras
|
||||
|
||||
我建议再安装一下“libavformat 和 libavcodec的无限制版”,这样当你使用一些编辑器或者转换器的时候就不会出现丢失编码丢失的情况。点击下面的按钮进行安装:
|
||||
|
||||
[][15]
|
||||
|
||||
或者输入一下命令行:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install libavformat-extra-53 libavcodec-extra-53
|
||||
|
||||
你可能需要Java,但是你得明确你到底需要的是什么,不少用户仅仅使用**OpenJRE**和java游览器插件,你可以点击下面的按钮安装:
|
||||
|
||||
[][16]
|
||||
|
||||
或者输入命令行:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install icedtea-7-plugin openjdk-7-jre
|
||||
|
||||
如果用于开发,你可能需要**OpenJDK**,点击下面的按钮进行安装:
|
||||
|
||||
[][17]
|
||||
|
||||
或者输入下面的命令行:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install openjdk-7-jdk
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如果你因为某些原因需要安装**Oracle Java**(包含JDK,JRE,游览器插件的包)时,你可以通过下面的命令进行安装[**Oracle Java 7**][18] :
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install oracle-java7-installer
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**加密DVD播放**: 由于现在很多安装包都能在官方的库中找到,或者有更好的替代物,Medibuntu也渐渐的[**被废弃**][19]了。但是在播放加密视频时仍然需要livdvdcss包。
|
||||
|
||||
输入以下指令启动加密DVD播放功能:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install libdvdread4
|
||||
sudo /usr/share/doc/libdvdread4/install-css.sh
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. 安装最新的 Rhythmbox 和 VLC ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu13.10中,Rhythmbox 和 VLC并没有升级到最新的版本,如果你想安装最新的版本,你可以使用PPAs
|
||||
|
||||
请注意:升级Rhythmbox后,里面的[**第三方插件**][20]将停止工作。Rhythmbox插件可以正常的运行。
|
||||
|
||||
**Rhythmbox**(Ubuntu 13.10下的版本:2.99.1,PPA中的版本:3.0.1):
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:jacob/media
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install rhythmbox
|
||||
|
||||
**VLC**(Ubuntu 13.10下的版本:2.0.8,PPA中的版本:2.1.0):
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:videolan/stable-daily
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install vlc
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Tweak Nautilus: 打开被禁用的递归搜索和文件快速预览 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在Nautilus V3.6之后,提前键入查找功能就被去除掉了。之后版本的搜索就只是在当前文件夹和其子文件下进行搜索。这用起来就很不爽了,如果你为此感到烦恼的话就安装Nautilus的补丁来启用[**被禁用的递归搜索**][21](你可以很方便的启用它)。
|
||||
|
||||
**用下面的命令将Nautilus升级到可以禁用递归搜过的版本**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:dr3mro/personal
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get upgrade
|
||||
nautilus -q
|
||||
|
||||
**然后使用下面的命令禁用递归搜索**
|
||||
|
||||
gsettings set org.gnome.nautilus.preferences enable-recursive-search false
|
||||
|
||||
如果你还想恢复递归搜索的功能,使用下面的命令行:
|
||||
|
||||
gsettings set org.gnome.nautilus.preferences enable-recursive-search true
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**GNOME Sushi**是一款快速预览的软件。点击下面的按钮安装。(会安装gnome-sushi 和 unoconv来实现预览)。
|
||||
|
||||
[][22]
|
||||
|
||||
或者输入命令行:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gnome-sushi unoconv
|
||||
|
||||
要使用这个软件,需选择一个文件(图片、文本文档、音乐文件等)然后点击SPACE按钮来预览。再次点击SPACE按钮或者关闭窗口可以关闭预览。
|
||||
|
||||
**现在!看完我们的介绍之后,你会选择哪个作为第一个安装的呢?**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.webupd8.org/2013/10/8-things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Timeszoro](https://github.com/Timeszoro) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:apt://indicator-multiload
|
||||
[2]:apt://indicator-cpufreq
|
||||
[3]:http://www.webupd8.org/2013/06/variety-wallpaper-changer-0415-released.html
|
||||
[4]:apt://diodon,diodon-plugins
|
||||
[5]:apt://unity-tweak-tool
|
||||
[6]:http://www.webupd8.org/2013/10/how-to-disable-amazon-shopping.html
|
||||
[7]:http://www.florian-diesch.de/software/indicator-privacy/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.webupd8.org/2013/08/using-nvidia-graphics-drivers-with.html
|
||||
[9]:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/X/Config/HybridGraphics#Known_issues
|
||||
[10]:http://www.webupd8.org/2013/04/improve-power-usage-battery-life-in.html
|
||||
[11]:apt://laptop-mode-tools
|
||||
[12]:apt://bumblebee,bumblebee-nvidia
|
||||
[13]:http://www.webupd8.org/2013/10/fix-bumblebee-libturbojpegso-issue-in.html
|
||||
[14]:apt://ubuntu-restricted-extras
|
||||
[15]:apt://libavformat-extra-53,libavcodec-extra-53
|
||||
[16]:apt://icedtea-7-plugin,openjdk-7-jre
|
||||
[17]:apt://openjdk-7-jdk
|
||||
[18]:http://www.webupd8.org/2012/01/install-oracle-java-jdk-7-in-ubuntu-via.html
|
||||
[19]:http://gauvain.pocentek.net/node/61
|
||||
[20]:http://www.webupd8.org/2012/08/rhythmbox-third-party-plugins-ubuntu-ppa.html
|
||||
[21]:http://www.webupd8.org/2013/09/how-to-disable-recursive-search-in.html
|
||||
[22]:apt://gnome-sushi,unoconv
|
||||
@ -1,22 +1,23 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu每日贴士 – 深入理解应用菜单和按钮
|
||||
Ubuntu每日小技巧 – 深入理解应用菜单和按钮
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ubuntu是一款很不错的操作系统。它基本上可以做到任何现代操作系统能做的事情,甚至有时候能做的更好。如果你是一个ubuntu新手,那么你现在还有很多不知道的事情。对于那些专家级用户来说十分普通的事情课能对你来说可能就不太普通了,因此这个“ubuntu每日贴士”系列旨在帮助你和新用户轻松设置管理ubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu有一个菜单栏。主菜单栏是在屏幕的顶端黑色条状栏,其包含了状态菜单或指示器和时间日期,音量键,应用菜单和窗口管理按钮。
|
||||
Ubuntu是一款很不错的操作系统。它基本上可以做到任何现代操作系统能做的事情,甚至有时候能做的更好。如果你是一个ubuntu新手,那么你现在还有很多不知道的事情。对于那些专家级用户来说十分普通的事情可能对你来说可能就不太普通了,因此这个“ubuntu每日小技巧”系列旨在帮助你和新用户轻松设置管理ubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
窗口管理按钮在主菜单(黑色条状栏)的左上角。当年你打开一个程序的时候,主菜单左上角的按钮包括关闭,最小化,最大化,和保存按钮叫做窗口管理按钮。
|
||||
Ubuntu有一个菜单栏。这个主菜单栏是在屏幕的顶端黑色条状栏,其包含了状态菜单或指示器和时间日期,音量键,应用的菜单和窗口管理按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
应用按钮位于窗口管理按钮的右侧。当它打开时显示应用菜单。
|
||||
窗口管理按钮在主菜单(黑色条状栏)的左上角。当年你打开一个程序的时候,主菜单左上角的按钮包括关闭、最小化、最大化、和恢复大小按钮,这些按钮叫做窗口管理按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
应用的菜单位于窗口管理按钮的右侧。当应用打开时才显示应用菜单。
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,ubuntu隐藏了窗口应用菜单和管理按钮,只有当你把鼠标放在左侧角里的时候才能看到。如果你打开一个程序但是找不到菜单,只需要把你的鼠标移动到屏幕左上角就可以使它显示出来。
|
||||
|
||||
如果这让你很困惑,而且你想关闭应用菜单而使每个程序都有自己的菜单的话,继续向下看。
|
||||
如果这让你很困惑,而且你想关闭(全局的)应用菜单而使每个程序都有自己的菜单的话,继续向下看。
|
||||
|
||||
运行以下命令以安装或删除应用菜单:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get autoremove indicator-appmenu
|
||||
|
||||
运行上面的命令将会删除应用菜单即全局菜单。现在,为了使改变生效,先退出然后再登陆回来。
|
||||
运行上面的命令将会删除应用菜单即全局菜单。现在,为了使改变生效,先退出然后再登录回来。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,当你打开一个ubuntu里面的程序的时候,每个程序就会用显示自己的菜单代替把它隐藏在全局菜单或主菜单里。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,10 +28,11 @@ Ubuntu有一个菜单栏。主菜单栏是在屏幕的顶端黑色条状栏,
|
||||
sudo apt-get install indicator-appmenu
|
||||
|
||||
使用愉快!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/09/daily-ubuntu-tips-understanding-app-menus-buttons/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[crowner](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[crowner](https://github.com/crowner) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
|
||||
各种 NoSQL 的比较
|
||||
================
|
||||
|
||||
即使关系型数据库依然是非常有用的工具,它们持续几十年的垄断地位就要走到头了。现在已经存在无数能撼动关系型数据库地位的 NoSQL,当然,这些 NoSQL 还无法完全取代它们。(也就是说,关系型数据库还是处理关系型事务的最佳方式。)
|
||||
即使关系型数据库依然是非常有用的工具,但它们持续几十年的垄断地位就要走到头了。现在已经存在无数能撼动关系型数据库地位的 NoSQL,当然,这些 NoSQL 还无法完全取代它们。(也就是说,关系型数据库还是处理关系型事务的最佳方式。)
|
||||
|
||||
NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所以软件架构师必须要在项目一开始就选好一款合适的 NoSQL。
|
||||
NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于不同的 SQL 数据库之间的区别,所以软件架构师必须要在项目一开始就选好一款合适的 NoSQL。
|
||||
|
||||
考虑到这种情况,本文为大家介绍以下几种 NoSQL 之间的区别:[Cassandra][], [Mongodb][], [CouchDB][], [Redis][], [Riak][], [Couchbase (ex-Membase)][], [Hypertable][], [ElasticSearch][], [Accumulo][], [VoltDB][], [Kyoto Tycoon][], [Scalaris][], [Neo4j][]和[HBase][]:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,9 +15,9 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
|
||||
**主要特性:** 保留 SQL 中一些用户友好的特性(查询、索引等)
|
||||
|
||||
**许可证:** AGPL (发起者: Apache)
|
||||
**许可证:** AGPL (驱动: 采用Apache许可协议)
|
||||
|
||||
**数据传输、存储的格式:** 自定义,二进制( BSON 文档格式)
|
||||
**数据传输格式:** 自定义,二进制( BSON 文档格式)
|
||||
|
||||
- 主/从备份(支持自动故障切换功能)
|
||||
- 自带数据分片功能
|
||||
@ -30,12 +30,19 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
- 在 32 位系统中,内存限制在 2.5GB
|
||||
- 空数据库占用 192MB 空间
|
||||
- 使用 GridFS(不是真正的文件系统)来保存大数据和元数据
|
||||
- 支持对数据建立索引
|
||||
- 数据中心意识
|
||||
- 支持对地理数据建立索引
|
||||
- 可用于数据中心
|
||||
|
||||
**应用场景:** 动态查询;需要定义索引而不是 map/reduce 功能;提高大数据库性能;想使用 CouchDB 但数据的 IO 吞吐量太大,CouchDB 无法满足要求。MongoDB 可以满足你的需求
|
||||
**应用场景:**
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:** 想布署 MySQL 或 PostgreSQL,但它们存在的预定义处理语句和预定义变量让你望而却步。这个时候,MongoDB 是你可以考虑的选项
|
||||
- 动态查询
|
||||
- 喜欢定义索引,而不是使用 map/reduce 功能
|
||||
- 高性能的大数据访问
|
||||
- 想使用 CouchDB 但数据变化频度太大
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:**
|
||||
|
||||
想布署 MySQL 或 PostgreSQL,但预先定义数据字典让你望而却步。这个时候,MongoDB 是你可以考虑的选项
|
||||
|
||||
###Riak 1.2版
|
||||
|
||||
@ -45,23 +52,28 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
|
||||
**许可证:** Apache
|
||||
|
||||
**数据传输、存储的格式:** HTTP/REST 架构,自定义二进制格式
|
||||
**数据传输格式:** HTTP/REST 架构,或自定义二进制格式
|
||||
|
||||
- 可存储 BLOB(binary large object,二进制大对象,比如一张图片、一个声音文件 —— 译者注)
|
||||
- 可在分部式存储和备份存储之间作协调
|
||||
- 可在分布式存储和复制存储之间作协调
|
||||
- 为了保证可验证性和安全性,Riak 在 JS 和 Erlaing 中提供提交前(pre-commit)和提交后(post-commit)钩子(hook)函数(你可以在提交数据前执行一个 hook,或者在提交数据后执行一个 hook —— 译者注)
|
||||
- JS 和 Erlang 提供映射和简化(map/reduce)编程模型
|
||||
- 使用 links 和 link walking 图形化数据库(link 用于描述对象之间的关系,link walking 是一个用于查询对象关系的进程 —— 译者注)
|
||||
- 使用 links 和 link walking ,用于图形化数据库(link 用于描述对象之间的关系,link walking 是一个用于查询对象关系的进程 —— 译者注)
|
||||
- 次要标记(secondaty indeces,开发者在写数据时可用多个名称来标记一个对象 —— 译者注),一次只能用一个
|
||||
- 支持大数据对象(Luwak)(Luwak 是 Riak 中的一个服务层,为大数据量对象提供简单的、面向文档的抽象,弥补了 Riak 的 Key/Value 存储格式在处理大数据对象方面的不足 —— 译者注)
|
||||
- 提供“开源”和“企业”两个版本
|
||||
- 提供“全文搜索”(可能就是允许用户在不提供 table/volume 等信息,对一个表进行文本字段的搜索,瞎猜的,望指正 —— 译者注)
|
||||
- 基于Riak搜索的全文检索、建立索引和查询
|
||||
- 正在将存储后端从“Bitcask”迁移到 Google 的“LevelDB”上
|
||||
- 企业版本提供多点备份(各点地位平等,非主从架构)和SNMP监控功能
|
||||
- 企业版本提供无主模式的多点复制(各点地位平等,非主从架构)和SNMP监控功能
|
||||
|
||||
**应用场景:** 假如你想要类似 Dynamo 的数据库,但不想要它的庞大和复杂;假如你需要良好的单点可扩展性、可用性和容错能力,但不想为多点备份买单。 Riak 能满足你的需求
|
||||
**应用场景:**
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:** 销售点数据收集;工厂控制系统;必须实时在线的系统;需要易于升级的网站服务器
|
||||
- 假如你想要类似 Dynamo 的数据库,但不想要它的庞大和复杂
|
||||
- 假如你需要良好的单点可扩展性、可用性和容错能力,但不想为多点备份买单。
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:**
|
||||
|
||||
销售点数据收集;工厂控制系统;必须实时在线的系统;需要易于升级的网站服务器
|
||||
|
||||
###CouchDB 1.2版
|
||||
|
||||
@ -73,25 +85,30 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
|
||||
**数据传输格式:** HTTP/REST
|
||||
|
||||
- 双向复制(一种同步技术,每个备份点都有一份它们自己的拷贝,允许用户在存储点断线的情况下修改数据,当存储节点重新上线时,CouchDB 会对所有节点同步这些修改 —— 译者注)
|
||||
- 双向复制!(一种同步技术,每个备份点都有一份它们自己的拷贝,允许用户在存储点断线的情况下修改数据,当存储节点重新上线时,CouchDB 会对所有节点同步这些修改 —— 译者注)
|
||||
- 支持持续同步或者点对点同步
|
||||
- 支持冲突检测
|
||||
- 支持主主互备(多个数据库时时同步数据,起到备份和分摊用户并行访问量的作用 —— 译者注)
|
||||
- 多版本并发控制(MVCC),写操作时不需要阻塞读操作(或者说不需要锁住数据库)
|
||||
- 向下兼容
|
||||
- 支持主主互备!(多个数据库实时同步数据,起到备份和分摊用户并行访问量的作用 —— 译者注)
|
||||
- 多版本并发控制(MVCC),写操作时不需要阻塞读操作(或者说不需要锁住数据库的读取操作)
|
||||
- 向下兼容以前版本的数据
|
||||
- 可靠的 crash-only 设计(所谓 crash-only,就是程序出错时,只需重启下程序,丢弃内存的所有数据,不需要执行复杂的数据恢复操作 —— 译者注)
|
||||
- 需要实时压缩数据
|
||||
- 视图(文档是 CouchDB 的核心概念,CouchDB 中的视图声明了如何从文档中提取数据,以及如何对提取出来的数据进行处理 —— 译者注):内嵌映射和简化(map/reduce)编程模型
|
||||
- 格式化的views字段:lists(包含把视图运行结果转换成非 JSON 格式的方法)和 shows(包含把文档转换成非 JSON 格式的方法)(在 CouchDB 中,一个 Web 应用是与一个设计文档相对应的。在设计文档中可以包含一些特殊的字段,views 字段包含永久的视图定义 —— 译者注)
|
||||
- 可能会提供服务器端文档验证的功能
|
||||
- 可能提供身份认证功能
|
||||
- 通过 _changes 函数实时更新数据
|
||||
- 能够进行服务器端文档验证
|
||||
- 能够提供身份认证功能
|
||||
- 通过 _changes 函数实时更新数据!
|
||||
- 链接处理(attachment:couchDB 的每份文档都可以有一个 attachment,就像一份 email 有它的网址 —— 译者注)
|
||||
- 有个 CouchApps(第三方JS的应用)
|
||||
- 有个 [CouchApps][1](第三方JS的应用)
|
||||
|
||||
**应用场景:** 用于随机数据量多、需要预定义查询的地方;用于版本控制比较重要的地方
|
||||
**应用场景:**
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:** 可用于客户关系管理(CRM),内容管理系统(CMS);可用于主主互备甚至多机互备
|
||||
- 用于随机数据量多、需要预定义查询的地方
|
||||
- 用于版本控制比较重要的地方
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:**
|
||||
|
||||
可用于客户关系管理(CRM),内容管理系统(CMS);可用于主主互备甚至多机互备
|
||||
|
||||
###Redis 2.4版
|
||||
|
||||
@ -101,25 +118,29 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
|
||||
**许可证:** BSD
|
||||
|
||||
**数据传输方式:** 类似 Telnet
|
||||
**数据传输格式:** 类似 Telnet 式的交换
|
||||
|
||||
- Redis 是一个内存数据库(in-memory database,简称 IMDB,将数据放在内存进行读写,这才是“快到掉渣”的真正原因 —— 译者注),磁盘只是提供数据持久化(即将内存的数据写到磁盘)的功能(这类数据库被称为“disk backed”数据库)
|
||||
- 当前不支持将磁盘作为 swap 分区,虚拟内存(VM)和 Diskstore 方式都没加到此版本(Redis 的数据持久化共有4种方式:定时快照、基于语句追加、虚拟内存、diskstore。其中 VM 方式由于性能不好以及不稳定的问题,已经被作者放弃,而 diskstore 方式还在实验阶段 —— 译者注)
|
||||
- 主从备份
|
||||
- 存储结构为简单的 key/value 或 hash 表
|
||||
- 但是操作比较复杂,比如:ZREVRANGEBYSCORE
|
||||
- 但是[操作比较复杂][2],比如:ZREVRANGEBYSCORE
|
||||
- 支持 INCR(INCR key 就是将key中存储的数值加一 —— 译者注)命令(对限速和统计有帮助)
|
||||
- 支持sets数据类型(以及 union/diff/inter)
|
||||
- 支持 lists (以及 queue/blocking pop)
|
||||
- 支持 hash sets (多级对象)
|
||||
- 支持 sorted sets(高效率的表,在范围查找方面有优势)
|
||||
- 支持事务处理
|
||||
- 支持事务处理!
|
||||
- 缓存中的数据可被标记为过期
|
||||
- Pub/Sub 操作能让用户发送信息
|
||||
- Pub/Sub 实现了消息订阅和推送!
|
||||
|
||||
**应用场景:** 适合布署快速多变的小规模数据(可以完全运行在存在中)
|
||||
**应用场景:**
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:** 股价系统、分析系统、实时数据收集系统、实时通信系统、以及取代 memcached
|
||||
- 适合布署快速多变的小规模数据(可以完全运行在存在中)
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:**
|
||||
|
||||
股价系统、分析系统、实时数据收集系统、实时通信系统、以及取代 memcached
|
||||
|
||||
##Google Bigtable 的衍生品
|
||||
|
||||
@ -131,7 +152,7 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
|
||||
**许可证:** Apache
|
||||
|
||||
**数据传输方式:** HTTP/REST (也支持 Thrift 开发框架)
|
||||
**数据传输格式:** HTTP/REST (也支持 Thrift 开发框架)
|
||||
|
||||
- 仿造 Google 的 BigTable
|
||||
- 使用 Hadoop 的 HDFS 文件系统作为存储
|
||||
@ -139,15 +160,20 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
- 查询条件被推送到服务器端,由服务器端执行扫描和过滤
|
||||
- 对实时查询进行优化
|
||||
- 高性能的 Thrift gateway(访问 HBase 的接口之一,特点是利用 Thrift 序列化支持多种语言,可用于异构系统在线访问 HBase 表数据 —— 译者注)
|
||||
- 使用 HTTP 通信协议,支持 XML、Protobuf 以及一些二进制文档结构
|
||||
- 使用 HTTP 通信协议,支持 XML、Protobuf 以及二进制格式
|
||||
- 支持基于 Jruby(JIRB)的shell
|
||||
- 当配置信息有更改时,支持 rolling restart(轮流重启数据节点)
|
||||
- 随机读写性能与 MySQL 一样
|
||||
- 一个集群可由不同类型的结点组成
|
||||
|
||||
**应用场景:** Hadoop 可能是在大数据上跑 Map/Reduce 业务的最佳选择;如果你已经搭建了 Hadoop/HDFS 架构,HBase 也是你最佳的选择。
|
||||
**应用场景:**
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:** 搜索引擎;日志分析系统;扫描大型二维非关系型数据表。
|
||||
- Hadoop 可能是在大数据上跑 Map/Reduce 业务的最佳选择
|
||||
- 如果你已经搭建了 Hadoop/HDFS 架构,HBase 也是你最佳的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:**
|
||||
|
||||
搜索引擎;日志分析系统;扫描大型二维非关系型数据表。
|
||||
|
||||
###Cassandra 1.2版
|
||||
|
||||
@ -157,7 +183,7 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
|
||||
**许可证:** Apache
|
||||
|
||||
**数据传输和存储方式:** Thrift 和自定义二进制 CQL3(即 Cassandra 查询语言第3版 —— 译者注)
|
||||
**数据传输格式:** Thrift 和自定义二进制 CQL3(即 Cassandra 查询语言第3版 —— 译者注)
|
||||
|
||||
- 可以灵活调整对数据的分布式或备份式存储(通过设置N,R,W之间的关系)(NRW是数据库布署模型中的概念,N是存储网络中复制数据的节点数,R是网络中读数据的节点数,W是网络中写数据的节点数。一个环境中N值是固定的,设置不同的WR值组合能在数据可用性和数据一致性之间取得不同的平衡,可参考 CAP 定理 —— 译者注)
|
||||
- 按列查询,按keys值排序后存储(需要包含你想要搜索的任何信息)(Cassandra 的数据模型借鉴自 BigTable 的列式存储,列式存储可以理解成这样,将行ID、列簇号,列号以及时间戳一起,组成一个Key,然后将Value按Key的顺序进行存储 —— 译者注)
|
||||
@ -169,9 +195,14 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
- 所有节点都相似,这点与 Hadop/HBase 架构不同
|
||||
- 可靠的跨数据中心备份解决方案
|
||||
|
||||
**应用场景:** 写操作多于读操作的环境(比如日志系统);如果系统全部由 JAVA 组成(“没人会因为使用了 Apache 许可下的产品而被炒鱿鱼”(此句貌似是网上有人针对“Apache considered harmful”一文所作的回应 —— 译者注))
|
||||
**应用场景:**
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:** 银行、金融机构;写性能强于读性能,所以 Cassandra 天生就是用来作数据分析的。
|
||||
- 写操作多于读操作的环境(比如日志系统)
|
||||
- 如果系统全部由 JAVA 组成(“没人会因为使用了 Apache 许可下的产品而被炒鱿鱼”(此句貌似是网上有人针对“Apache considered harmful”一文所作的回应 —— 译者注))
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:**
|
||||
|
||||
银行、金融机构;写性能强于读性能,所以 Cassandra 天生就是用来作数据分析的。
|
||||
|
||||
###Hypertable 0.9.6.5版
|
||||
|
||||
@ -181,7 +212,7 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
|
||||
**许可证:** GPL 2.0
|
||||
|
||||
**数据传输和存储的方式:** Thrift,C++库,或者 HQL shell
|
||||
**数据传输格式:** Thrift,C++库,或者 HQL shell
|
||||
|
||||
- 采用与 Google BigTable 相似的设计
|
||||
- 运行在 Hadoop HDFS 之上
|
||||
@ -193,9 +224,13 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
- 表在命名空间内定义
|
||||
- 使用 Hadoop 的 Map/reduce 模型
|
||||
|
||||
**应用场景:** 假如你需要一个更好的HBase,就用Hypertable吧。
|
||||
**应用场景:**
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:** 与HBase一样,就是搜索引擎被换了下;分析日志数据的系统;适用于浏览大规模二维非关系型数据表。
|
||||
- 假如你需要一个更好的HBase,就用Hypertable吧
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:**
|
||||
|
||||
与HBase一样,就是搜索引擎被换了下;分析日志数据的系统;适用于浏览大规模二维非关系型数据表。
|
||||
|
||||
###Accumulo 1.4版
|
||||
|
||||
@ -205,7 +240,7 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
|
||||
**许可证:** Apache
|
||||
|
||||
**数据传输和存储的方式:** Thrift
|
||||
**数据传输格式:** Thrift
|
||||
|
||||
- 另一个 BigTable 的复制品,也是跑在 Hadoop 的上层
|
||||
- 单元级安全保证
|
||||
@ -214,9 +249,13 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
- 使用 Hadoop 的 Map/reduce 模型
|
||||
- 支持在服务器端编程
|
||||
|
||||
**应用场景:** HBase的替代品
|
||||
**应用场景:**
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:** 与HBase一样,就是搜索引擎被换了下;分析日志数据的系统;适用于浏览大规模二维非关系型数据表。
|
||||
- HBase的替代品
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:**
|
||||
|
||||
与HBase一样,就是搜索引擎被换了下;分析日志数据的系统;适用于浏览大规模二维非关系型数据表。
|
||||
|
||||
##特殊用途
|
||||
|
||||
@ -228,7 +267,7 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
|
||||
**许可证:** GPL,AGPL(商业用途)
|
||||
|
||||
**数据传输和存储的方式:** HTTP/REST(或内嵌在 Java 中)
|
||||
**数据传输格式:** HTTP/REST(或内嵌在 Java 中)
|
||||
|
||||
- 可独立存在,或内嵌在 JAVA 的应用中
|
||||
- 完全的 ACID 保证(包括正在处理的数据)
|
||||
@ -244,9 +283,13 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
- 可运行脚本 Groovy 脚本
|
||||
- 在商用版本中提供在线备份,高级监控和高可用性功能
|
||||
|
||||
**应用场景:** 适用于用图形显示复杂的交互型数据。
|
||||
**应用场景:**
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:** 搜寻社交关系网、公共传输链、公路路线图、或网络拓扑结构
|
||||
- 适用于用图形显示复杂的交互型数据。
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:**
|
||||
|
||||
搜寻社交关系网、公共传输链、公路路线图、或网络拓扑结构
|
||||
|
||||
###ElasticSearch 0.20.1 版
|
||||
|
||||
@ -256,7 +299,7 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
|
||||
**许可证:** Apache
|
||||
|
||||
**数据传输和存储的方式:** 通过 HTTP 使用 JSON 进行数据索引(插件:Thrift, memcached)
|
||||
**数据传输格式:** 通过 HTTP 使用 JSON 进行数据索引(插件:Thrift, memcached)
|
||||
|
||||
- 以 JSON 形式保存数据
|
||||
- 提供版本升级功能
|
||||
@ -272,9 +315,13 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
- 可以维持自动的“统计组”(对调试很有帮助)
|
||||
- 只有一个开发者(kimchy)
|
||||
|
||||
**应用场景:** 当你有可伸缩性很强的项目并且想拥有“高级搜索”功能。
|
||||
**应用场景:**
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:** 可布署一个约会服务,提供不同年龄、不同地理位置、不同品味的客户的交友需求。或者可以布署一个基于多项参数的排行榜。
|
||||
- 当你有可伸缩性很强的项目并且想拥有“高级搜索”功能。
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:**
|
||||
|
||||
可布署一个约会服务,提供不同年龄、不同地理位置、不同品味的客户的交友需求。或者可以布署一个基于多项参数的排行榜。
|
||||
|
||||
##其他
|
||||
|
||||
@ -288,7 +335,7 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
|
||||
**许可证:** Apache
|
||||
|
||||
**数据传输和存储的方式:** 缓存和扩展(memcached + extensions)
|
||||
**数据传输格式:** 缓存和扩展(memcached + extensions)
|
||||
|
||||
- 通过 key 访问数据非常快(20万以上IOPS)
|
||||
- 数据保存在磁盘(不像 Memcache 保存在内存中 —— 译者注)
|
||||
@ -300,9 +347,13 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
- 支持 Map/reduce 模式
|
||||
- 支持跨数据中心备份
|
||||
|
||||
**应用场景:** 适用于低延迟数据访问系统,高并发和高可用系统。
|
||||
**应用场景:**
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:** 低延迟可用于广告定投;高并发可用于在线游戏(如星佳公司)。
|
||||
- 适用于低延迟数据访问系统,高并发和高可用系统。
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:**
|
||||
|
||||
低延迟可用于广告定投;高并发可用于在线游戏(如星佳公司)。
|
||||
|
||||
###VoltDB 2.8.4.1版
|
||||
|
||||
@ -312,7 +363,7 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
|
||||
**许可证:** GPL 3
|
||||
|
||||
**数据传输和存储的方式:** 专有方式
|
||||
**数据传输格式:** 专有方式
|
||||
|
||||
- 运行在内存的关系型数据库
|
||||
- 可以将数据导入到 Hadoop
|
||||
@ -320,9 +371,13 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
- 在 JAVA 环境中保存操作过程
|
||||
- 支持跨数据中心备份
|
||||
|
||||
**应用场景:** 适用于在大量传入数据中保证快速反应能力的场合。
|
||||
**应用场景:**
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:** 销售点数据分析系统;工厂控制系统。
|
||||
- 适用于在大量传入数据中保证快速反应能力的场合。
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:**
|
||||
|
||||
销售点数据分析系统;工厂控制系统。
|
||||
|
||||
###Scalaris 0.5版
|
||||
|
||||
@ -341,9 +396,13 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
- 支持分布式数据的一致性写操作
|
||||
- 根据 CAP 定理,数据一致性要求高于数据可用性(前提是在一个比较大的网络分区环境下工作)(CAP 定理:数据一致性consistency、数据可用性availability、分隔容忍partition tolerance是分布式计算系统的三个属性,一个分布式计算系统不可能同时满足全部三项)
|
||||
|
||||
**应用场景:** 如果你喜欢 Erlang 并且想要使用 Mnesia 或 DETS 或 ETS,但你需要一个能使用多种语言(并且可扩展性强于 ETS 和 DETS)的技术,那就选它吧。
|
||||
**应用场景:**
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:** 使用基于 Erlang 的系统,但是想通过 Python、Ruby 或 JAVA 访问数据库
|
||||
- 如果你喜欢 Erlang 并且想要使用 Mnesia 或 DETS 或 ETS,但你需要一个能使用多种语言(并且可扩展性强于 ETS 和 DETS)的技术,那就选它吧。
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:**
|
||||
|
||||
使用基于 Erlang 的系统,但是想通过 Python、Ruby 或 JAVA 访问数据库
|
||||
|
||||
###Kyoto Tycoon 0.9.56版
|
||||
|
||||
@ -365,9 +424,13 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
- 支持内存数据库在后端执行快照
|
||||
- 自动过期处理(可用来布署一个缓存服务器)
|
||||
|
||||
**应用场景:** 当你想要一个很精准的后端存储算法引擎,并且速度是刚需的时候,玩玩 Kyoto Tycoon 吧。
|
||||
**应用场景:**
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:** 缓存服务器;股价查询系统;数据分析系统;实时数据控制系统;实时交互系统;memcached的替代品。
|
||||
- 当你想要一个很精准的后端存储算法引擎,并且速度是刚需的时候,玩玩 Kyoto Tycoon 吧。
|
||||
|
||||
**使用案例:**
|
||||
|
||||
缓存服务器;股价查询系统;数据分析系统;实时数据控制系统;实时交互系统;memcached的替代品。
|
||||
|
||||
当然,上述系统的特点肯定不止列出来这么点。我只是列出了我认为很关键的信息。另外科技发展迅猛,技术改变得非常快。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -377,14 +440,9 @@ NoSQL 与 NoSQL 之间的区别,要远大于 SQL 与 SQL 之间的区别。所
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://kkovacs.eu/cassandra-vs-mongodb-vs-couchdb-vs-redis
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT][] 原创翻译,[Linux中国][] 荣誉推出
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID][] 校对:[校对者ID][]
|
||||
|
||||
[LCTT]:https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject
|
||||
[Linux中国]:http://linux.cn/portal.php
|
||||
[chenjintao]:http://linux.cn/space/chenjintao
|
||||
[校对者ID]:http://linux.cn/space/校对者ID
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[Cassandra]:http://cassandra.apache.org/
|
||||
[Mongodb]:http://www.mongodb.org/
|
||||
@ -400,3 +458,6 @@ via: http://kkovacs.eu/cassandra-vs-mongodb-vs-couchdb-vs-redis
|
||||
[Scalaris]:https://code.google.com/p/scalaris/
|
||||
[Neo4j]:http://neo4j.org/
|
||||
[HBase]:http://hbase.apache.org/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://couchapp.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://redis.io/commands
|
||||
@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ Torvalds并没有提到某个具体的公司,但之前[他曾对Google的Chrom
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.pcpro.co.uk/news/384934/torvalds-steamos-will-really-help-linux-on-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
263
published/di – Disk Information Utility, Better Than df.md
Normal file
263
published/di – Disk Information Utility, Better Than df.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,263 @@
|
||||
di - 比 df 更有用的磁盘信息工具
|
||||
===========================
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是个Linux命令行用户,你肯定会使用df命令检查文件系统的磁盘使用情况。尽管df是一个受欢迎的命令,但仍然不能提供一些高级的功能,如一个用户实际的磁盘可用空间,以及各种有用的显示格式等。还有另一个命令行实用工具可用,不仅提供了这些高级功能也提供了df的所有特性。在本文中,我们将讨论磁盘信息工具 -- **di**
|
||||
|
||||
**注释** - 如果你想了解 df 更多信息, 查看 [df命令教程][1].
|
||||
|
||||
## di - 磁盘信息工具
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
从这个di帮助手册页很明显的发现 di 提供了一些很有价值的特性,值得一试。让我们看一些这个工具实际使用的例子。
|
||||
|
||||
### 测试环境
|
||||
|
||||
- OS – Ubuntu 13.04
|
||||
- Shell – Bash 4.2.45
|
||||
- Application – di 4.30
|
||||
|
||||
## 一个简短的教程
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一些 di 工具的示例:
|
||||
|
||||
###1. 默认的输出
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下di命令生成人们易读的输出格式
|
||||
|
||||
这里有个示例:
|
||||
|
||||
$ di
|
||||
Filesystem Mount Size Used Avail %Used fs Type
|
||||
/dev/sda6 / 28.1G 20.2G 6.5G 77% ext4
|
||||
udev /dev 1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% devtmpfs
|
||||
tmpfs /run 300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
|
||||
所以你能发现用千兆字节(G)和兆字节(M)做磁盘使用情况的数据单位。这绝对是比 df 默认的输出产生的效果好。(译注:df也可以输出带类似单位的显示,只是需要额外加参数 -h)
|
||||
|
||||
###2. 用 -A 选项打印类似挂载点、特殊设备名称等全部字段
|
||||
|
||||
选项 -A可以用来极详细的打印挂载点,特殊设备名称等。
|
||||
|
||||
这里有个示例:
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -A
|
||||
Mount fs Type Filesystem
|
||||
Options
|
||||
Size Used Free %Used %Free
|
||||
Size Used Avail %Used %Free
|
||||
Size Used Avail %Used
|
||||
Inodes Iused Ifree %Iused
|
||||
/ ext4 /dev/sda6
|
||||
rw,errors=remount-ro
|
||||
28.1G 20.2G 8.0G 72% 28%
|
||||
28.1G 21.6G 6.5G 77% 23%
|
||||
26.7G 20.2G 6.5G 75%
|
||||
1884160 389881 1494279 21%
|
||||
/dev devtmpfs udev
|
||||
rw,mode=0755
|
||||
1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% 100%
|
||||
1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% 100%
|
||||
1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0%
|
||||
381805 571 381234 0%
|
||||
/run tmpfs tmpfs
|
||||
rw,noexec,nosuid,size=10%,mode=0755
|
||||
300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% 100%
|
||||
300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% 100%
|
||||
300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0%
|
||||
384191 549 383642 0%
|
||||
|
||||
所以你可以看到所有的字段,可以用于调试目的时打印输出。
|
||||
|
||||
###3. 用 -a选项打印所有挂载设备
|
||||
|
||||
这里是个示例:
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -a
|
||||
Filesystem Mount Size Used Avail %Used fs Type
|
||||
/dev/sda6 / 28.1G 20.2G 6.5G 77% ext4
|
||||
udev /dev 1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% devtmpfs
|
||||
devpts /dev/pts 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% devpts
|
||||
proc /proc 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% proc
|
||||
binfmt_misc /proc/sys/fs/bi 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% binfmt_misc
|
||||
tmpfs /run 300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /run/lock 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /run/shm 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /run/user 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
gvfsd-fuse /run/user/himan 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% fuse.gvfsd-fuse
|
||||
sysfs /sys 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% sysfs
|
||||
none /sys/fs/cgroup 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /sys/fs/fuse/co 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% fusectl
|
||||
none /sys/kernel/deb 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% debugfs
|
||||
none /sys/kernel/sec 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% securityfs
|
||||
|
||||
所以你能看到与所有设备相关的所有信息,被打印出来了。
|
||||
|
||||
###4. 用 -c 选项用逗号作为值的分隔符
|
||||
|
||||
选项 -c 用命令分隔的值将附上双引号
|
||||
|
||||
这里是个示例:
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -c
|
||||
s,m,b,u,v,p,T
|
||||
/dev/sda6,/,28.1G,20.2G,6.5G,77%,ext4
|
||||
udev,/dev,1.5G,0.0G,1.5G,0%,devtmpfs
|
||||
tmpfs,/run,300.2M,0.9M,299.3M,0%,tmpfs
|
||||
|
||||
如上,你可以看到打印了用逗号分隔符输出的值。(译注:这种输出便于作为其他程序的输入解析)
|
||||
|
||||
###5. 用 -g 选项通过千兆字节(G)打印大小
|
||||
|
||||
下面是个示例:
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -g
|
||||
Filesystem Mount Gibis Used Avail %Used fs Type
|
||||
/dev/sda6 / 28.1 20.2 6.5 77% ext4
|
||||
udev /dev 1.5 0.0 1.5 0% devtmpfs
|
||||
tmpfs /run 0.3 0.0 0.3 0% tmpfs
|
||||
|
||||
当然,你能看到所有与大小有关的值都用千兆字节(G)打印出来。
|
||||
|
||||
同样的你可以用 -k 和 -m 选项来分别的显示千字节(K)大小和兆字节(M)大小。
|
||||
|
||||
###6. 通过 -I 选项显示特定的文件系统类型的相关信息
|
||||
|
||||
假设你想显示只跟tmpfs文件系统相关的信息。下面将告诉你如何用 -I 选项完成任务。
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -I tmpfs
|
||||
Filesystem Mount Size Used Avail %Used fs Type
|
||||
tmpfs /run 300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /run/lock 5.0M 0.0M 5.0M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /run/shm 1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /run/user 100.0M 0.0M 100.0M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /sys/fs/cgroup 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
|
||||
Ok 你能看到只有tmpfs类型相关文件系统信息被输出并显示出来了。
|
||||
|
||||
###7. 用 -n 选项跳过标题行的输出
|
||||
|
||||
如果你正试图通过一个脚本(或程序)解析该命令的输出结果并希望 di 命令跳过显示的标题行,那么用 -n 选项是绝佳的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是个示例:
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -n
|
||||
/dev/sda6 / 28.1G 20.2G 6.5G 77% ext4
|
||||
udev /dev 1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% devtmpfs
|
||||
tmpfs /run 300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
|
||||
如上,你能发现输出中并没有显示标题行。
|
||||
|
||||
###8. 通过 -t 选项在文件系统列表底下再打印一行总计行
|
||||
|
||||
如果想要显示所有相关列的总数,用 -t 选项。
|
||||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -t
|
||||
Filesystem Mount Size Used Avail %Used fs Type
|
||||
/dev/sda6 / 28.1G 20.2G 6.5G 77% ext4
|
||||
udev /dev 1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% devtmpfs
|
||||
tmpfs /run 300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
Total 29.9G 20.2G 8.3G 72%
|
||||
|
||||
观察到最后一行的值为所有文件系统的统计数据。
|
||||
|
||||
###9. 通过 -s 选项 排序输出
|
||||
|
||||
-s选项可用于排序该命令的输出结果(译注:默认按照挂载点名称排序)
|
||||
|
||||
下面告诉你如何反向排序输出:
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -sr
|
||||
Filesystem Mount Size Used Avail %Used fs Type
|
||||
tmpfs /run 300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
udev /dev 1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% devtmpfs
|
||||
/dev/sda6 / 28.1G 20.2G 6.5G 77% ext4
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以在-s后添加子选项'r'逆序排序输出。
|
||||
|
||||
类似的,你可以使用 -s 选项做一些其他类型的排序.以下是摘自man手册供您参考:
|
||||
|
||||
-s 排序方式
|
||||
|
||||
可以指定排序方式。默认排序方式的按照挂载点的名称进行排序。支持如下的排序方式:
|
||||
m :按照挂载点名称排序(默认)
|
||||
n :不排序(即按照在挂载表/etc/fstab中的顺序)
|
||||
s :按照特殊设备名称
|
||||
t :按照文件系统类型
|
||||
r :逆序排序
|
||||
|
||||
排序方式可以组合使用,如: di --stsrm :按照类型、设备、挂载点逆序排序。di --strsrm :按照类型、设备逆序、挂载点逆序排序。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
###10. 通过 -f 选项指定输出格式
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过结合-f选项和其子选项指定输出格式字符串。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,用 -fm,打印挂载点的名称。
|
||||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -fm
|
||||
Mount
|
||||
/
|
||||
/dev
|
||||
/run
|
||||
|
||||
如上你可以看到只有挂载点的名字被打印出来。
|
||||
|
||||
同样的,打印文件系统的类型,用 -ft
|
||||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -ft
|
||||
fsType
|
||||
ext4
|
||||
devtmpf
|
||||
tmpfs
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想快速查找,这里有个其他可用的格式选项截图.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
更完整的选项,参考[di命令man文档][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### 下载/安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这里有一些关于di命令的重要链接:
|
||||
|
||||
- [主页][3]
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载链接][4]
|
||||
|
||||
命令行工具 di 也能通过apt、yum等命令在命令行下载和安装。Ubuntu用户也可以从Ubuntu 软件中心下载这个命令。
|
||||
|
||||
### 优点 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 提供了许多高级功能
|
||||
- 跨平台
|
||||
|
||||
### 缺点 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 在大多数的Linux发行版没有预装
|
||||
- 大量选项需要学习
|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
最后,di命令提供了一些非常有用的特性,比df命令更强大。如果你正在寻找一个类似df,但比df更强大的关于磁盘信息的命令行工具,那么di是最理想的选择。试试吧,包你满意!!!
|
||||
|
||||
**你试过di或任何其他类似df工具?请跟我们分享你的经验!**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://mylinuxbook.com/di-a-disk-information-utility/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.expertslogin.com/linux-command/linux-df-command/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.manpagez.com/man/1/di/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.gentoo.com/di/
|
||||
[4]:http://freecode.com/projects/diskinfo
|
||||
@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
|
||||
l3b2w1 translaing……
|
||||
10 Best Quotes from Linus Torvalds' Keynote at LinuxCon Europe
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Linus Torvalds and Dirk Hohndel on stage at LinuxCon Europe in Edinburgh.*
|
||||
|
||||
Linux creator Linus Torvalds took the stage today at [LinuxCon Europe][1] in Edinburgh with Intel’s Chief Linux and Open Source Technologist Dirk Hohndel to discuss the present and future of Linux and answer questions from the community. They covered a range of topics including the upcoming 3.12 kernel release, the ideal characteristics of a kernel maintainer, the issues that keep Linus up at night, gaming on the Linux desktop, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are 10 of Linus’s best quotes, in the order that he said them, from Wednesday morning’s keynote.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Linus is happy with the current timing of releases every 3 months because it allows developers to take their time building new features. If they miss the merge window, it’s not very long until the next one comes so they don’t feel rushed to send in their code.
|
||||
|
||||
**“Don't hurry your code. Make sure it works well and is well designed. Don't worry about timing.”**
|
||||
|
||||
2. The rapid pace of change also allows developers to merge their code quickly and move on.
|
||||
|
||||
**"Developers have the attention spans of slightly moronic woodland creatures."**
|
||||
|
||||
**3. “One of the most important things for a maintainer isn't that he's a super engineer. It’s that you're responsive and people can rely on you being there 24/7, 52 weeks a year.”**
|
||||
|
||||
It’s very difficult for a young developer to become a maintainer because it takes a few years for the community to trust that you’ll be around for a while. That said, once you’ve proven you’re reliable, it’s easy to become a maintainer because it’s a hard job. You have to be there all the time.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Dirk: “What keeps you up at night?”
|
||||
|
||||
Linus: Bugs in the code and other technical problems don’t worry him as much.
|
||||
|
||||
**“The thing with technology is if you do something stupid you can fix it.”**
|
||||
|
||||
5. What really keeps Linus up at night are the social issues and problems with the development process.
|
||||
|
||||
**“When tempers flare it can be really stressful for a few days. I have flare-ups and that works fine for me… Other people tend to mull over things. It eats at them for weeks on end, and those issues tend to be the painful ones.”**
|
||||
|
||||
6. Linus takes a Darwinistic view when it comes to convincing companies to contribute to the kernel or use open source software. They either see the benefits of open source or they suffer the economic consequences.
|
||||
|
||||
**“I do open source because it's fun and it works… Companies who work with the kernel community will waste less time and they'll just work better.”**
|
||||
|
||||
**7. “If you're a company that thinks your tiny change to the kernel is what gives you a competitive edge, you'll probably be facing economic problems. You'd be much better off worrying about making the best damn hardware for the lowest price.”**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Linux creator Linus Torvalds answers audience questions at LinuxCon Europe, 2013.*
|
||||
|
||||
8. He had a few things to say about the state of Linux on the desktop. It’s one area that Linux could still really see some improvement. But distribution infighting has become a problem.
|
||||
|
||||
**“I started Linux because I wanted to see it on the desktop... I wish people would work together better ... and make a really nice login screen.”**
|
||||
|
||||
9. Valve’s Steam for Linux is the best opportunity to help the Linux desktop, he said. They’ll do this by setting a standard for Linux distributions that want to enable gaming on their platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
**“It's the best model for standardization. Standards should not be people sitting in a smoky room… and writing papers. It's being successful enough to drive the market.”**
|
||||
|
||||
10. On diversity, Linus said he would like to see the kernel community grow to include more women and developers from different geographies.
|
||||
|
||||
**“We have very few women. But I'm not very worried. We used to have this discussion about not having enough Japanese developers. We can solve this but it will take time.”**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxfoundation.org/news-media/blogs/browse/2013/10/10-best-quotes-linus-torvalds-keynote-linuxcon-europe
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://events.linuxfoundation.org/events/linuxcon-europe
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
10 Years of Xen: Transforming a Dinosaur Into a Bird
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Xen Hypervisor development started at [Cambridge University][1] as part of the [Xenoserver][2] research project in the late 90’s. The goal of Xenoserver was ambitious:
|
||||
|
||||
The Xenoserver project is building a public infrastructure for wide-area distributed computing. We envisage a world in which Xenoserver execution platforms will be scattered across the globe and available for any member of the public to submit code for execution. The sponsor of the code will be billed for all the resources used or reserved during the course of execution. This will serve to encourage load balancing, limit congestion, and hopefully even make the platform self-financing.
|
||||
|
||||
Today, this model of computing is called cloud computing. And the Xen Hypervisor was - and indeed is today - instrumental in enabling the biggest cloud in production. Not only are Amazon Web Services and Rackspace Public cloud based on Xen. New large deployments such as [Verizon Public Cloud][3] also chose Xen as basis for their offering.
|
||||
|
||||
### Happy 10th Birthday ###
|
||||
|
||||
On October 21st, 2003 at the [19th ACM Symposium on Operating Systems Principles][4] the Xen Hypervisor was first revealed as an open source project to the public. Exactly 10 years ago. Time to wish the project a Happy 10th Birthday!
|
||||
|
||||
### The Burden of being First : Or what happened to the Dinosaurs? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes being the first open source project in its field can become a burden. Why? Because, community problems can build up unchecked. The simple fact is that lack of competition can cause complacency. This is what happened to the Xen Project. For the first few years of its life the project operated without governance, became insular, didn’t promote itself and failed to engage its users and contributors. When its first open source competitor - KVM - gathered steam, the community was slow to respond and change.
|
||||
|
||||
The effect of all this was that it was difficult to join the project and that the project did not play well with the Linux kernel, QEMU and Linux distros. In the end, the Xen community got a bad reputation. Ultimately this resulted in Canonical and RedHat dropping Xen support in favour of KVM. Add to the mix a failure to tell the world, when things did change. The bad reputation lingered and eventually the project was seen as a dinosaur by the open source community and technology press. Destined to be extinct in the near future.
|
||||
|
||||
### Evolving fast : The Dinosaur becomes a Bird ###
|
||||
|
||||
Not many open source projects recover from mistakes like the ones the Xen community made. The Xen Project managed to do this, through a combination of introducing good governance, active efforts to collaborate with other open source projects, rebooting marketing efforts and actively working with users and contributors to the project. In other words, the project had to
|
||||
Xen Project flying Panda
|
||||
|
||||
Let the Bird fly (or more correctly, give the Xen Project’s Panda wings).
|
||||
transform itself from a Dinosaur to a Bird. If you want to know how we did this, why not attend my LinuxCon EU session called [Xen Project : Lessons Learned][5]? Other sessions you may want to attend are [Securing your Xen based Cloud][6] and [Xen: Open Source Hypervisor Designed for Clouds][7].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Let the Bird fly (or more correctly, give the Xen Project’s Panda wings).*
|
||||
|
||||
### A peek into the Future : New Frontiers in Virtualization ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you look at the Xen Project now, you will find that the community is diverse and growing. On many counts, it is bigger and more diverse than it has ever been.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the interesting things that is happening in the Xen Community at the moment is adoption of the Xen Project’s software for non-traditional virtualization use-cases. This is mirroring a rise in activity by embedded companies in the Linux community in general. At the [Xen Project Developer Summit][8] later this week, we will see two Android VMs running on top of Xen on a Nexus 10, we will see first experiments in using Xen for In-Vehicle-Infotainment and automotive applications in general, and we will see how Xen can provide the high performance expected of hardware-based middlebox offerings such as firewalls and NATs.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, there is also plenty innovation in server virtualization and cloud. Let the Bird fly (or more correctly, give the Xen Project’s Panda wings).
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/news/enterprise/cloud-computing/743330-10-years-of-xen-transforming-a-dinosaur-into-a-bird/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/research/srg/netos/xen/index.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/research/srg/netos/xeno/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.techweekeurope.co.uk/news/verizon-public-cloud-launch-128724
|
||||
[4]:http://www.cs.rochester.edu/meetings/sosp2003/papers.shtml
|
||||
[5]:http://linuxconcloudopeneu2013.sched.org/event/68003c370760bcc2da7e3e8b59b6b50f
|
||||
[6]:http://linuxconcloudopeneu2013.sched.org/event/37ecfe02561cf264a02061d1927da26c
|
||||
[7]:http://linuxconcloudopeneu2013.sched.org/event/bdca1274d9799646cdf2934dbde94ccd
|
||||
[8]:http://www.linux.com/news/software/applications/742053-a-great-line-up-of-speakers-at-xen-project-developer-summit
|
||||
@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
|
||||
BetaPizza Hackaton Results
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Friday a week ago a [Beta Pizza Hackaton][1] took place at the SUSE offices and online. 121 people went over more than 580 bugs, screening 440 and fixing 140 of them. The contest was won by Stephan ‘coolo’ Kulow and Dominique ‘DimStar‘ Leuenberger, with top gold fixers Josef Reidinger and Michael Chang and a honorable mention for Antoine Saroufim.
|
||||
|
||||
## The BetaPizza Party Concept Turned Hackaton ##
|
||||
|
||||
Usually, the BetaPizza is as much about testing as about party. This time we added in the fixing of bugs as well! The SUSE engineers joined on Friday the 27th to catch and kill as many of these pesky little creatures as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
We set up some facilities:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- a [bug list prepared][2] in bugzilla, labeled as [GOLD][3], [SILVER][4] and [BRONZE][5] as part of a contest)
|
||||
- [a Google hangout][6]
|
||||
- a [#openSUSE-pizza-hackaton IRC channel on Freenode][7]
|
||||
|
||||
In the various offices, a local BetaPizzaMaster made sure a common room was reserved and pizza was available at the appropriate time.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Results and winners of the bug fixing contest ##
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s start our results section with some great statistics:
|
||||
|
||||
- **140** fixed (19 GOLD, 4 SILVER, 0 BRONZE, 117 OTHER)
|
||||
- **440** screened (46 GOLD, 19 SILVER, 0 BRONZE, 375 OTHER)
|
||||
- **121** participants (76 employees, 45 volunteer)
|
||||
|
||||
As we said in the initial article announcing the event, we have some SUSE provided prizes for top contributors. An evaluation committee was established with Richard Brown (openSUSE Board member), Frederic Crozat (SLE department, openSUSE contributor) and Michal Hrusecky (openSUSE Team) as members.
|
||||
|
||||
It was a tough decision, but in the end, the committee selected two hackers, well known to Factory contributors, as overall winners: Stephan ‘coolo’ Kulow and Dominique ‘DimStar’ Leuenberger. The committee furthermore awarded the top contributors working on the preselected golden bugs: Josef Reidinger and Michael Chang. The committee finally decided on a Honorable mention. This one goes to Antoine Saroufim, who was helping the GNOME team a lot with testing and providing feedback regarding various bugs and crashes over IRC.
|
||||
|
||||
So in the end, we have three awards with following winners:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Winners**: Stephan ‘coolo’ Kulow and Dominique ‘DimStar’ Leuenberger
|
||||
- **Top gold fixers**: Josef Reidinger and Michael Chang
|
||||
- **Honorable mention**: Antoine Saroufim
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Local experiences at the SUSE Offices
|
||||
|
||||
Taipei kicked off the long day, opening the hangout and working from a single room. Beijing had the biggest showing with 40 participants and 18 pizza’s eliminated though part of the Pizza eaters were kicking off [hackweek][8] and didn’t participate in the hackaton. The Pizza Master David Liang reports that the team enjoyed the IRC bot which reported the results of their work and other teams echo-ed this.
|
||||
|
||||
The Provo team noted that being in the last timezone meant being pretty lonely. Pizza Master Scott suggested we need to set up a teleportation unit and get everybody physically in one place next time. The openSUSE team is evaluating this option and suggestions for reasonably priced teleportation devices are welcome.
|
||||
|
||||
More testing?
|
||||
|
||||
All in all, we fixed lots of bugs, rid the world of some pizza (don’t worry, the world isn’t running out, and it’s [easy to make][9]) and had fun. But there’s more work to do – [openSUSE 13.1 RC1 is out][10] and we’re looking forward to more bug reports and fixes!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.opensuse.org/2013/10/15/betapizza-hackaton-results/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://news.opensuse.org/2013/09/25/beta-pizza-hackaton-starting-friday/
|
||||
[2]:https://bugzilla.novell.com/buglist.cgi?query_format=advanced&bug_status=UNCONFIRMED&bug_status=NEW&bug_status=ASSIGNED&bug_status=NEEDINFO&bug_status=REOPENED&bug_status=VERIFIED&resolution=---&product=openSUSE%2012.3&product=openSUSE%20Factory
|
||||
[3]:https://bugzilla.novell.com/buglist.cgi?field0-0-0=status_whiteboard&type0-0-0=substring&value0-0-0=GOLD
|
||||
[4]:https://bugzilla.novell.com/buglist.cgi?field0-0-0=status_whiteboard&type0-0-0=substring&value0-0-0=SILVER
|
||||
[5]:https://bugzilla.novell.com/buglist.cgi?field0-0-0=status_whiteboard&type0-0-0=substring&value0-0-0=BRONZE
|
||||
[6]:https://plus.google.com/events/csnu5vk431s6b2292dbi911vumc
|
||||
[7]:irc://freenode.net/#openSUSE-pizza-hackaton
|
||||
[8]:http://hackweek.suse.com/
|
||||
[9]:https://news.opensuse.org/2011/09/30/opensuse-pizza-parties-the-geeko-way/
|
||||
[10]:https://news.opensuse.org/2013/10/11/opensuse-13-1-rc-1-available-time-to-test/
|
||||
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Cloud tool Juju GUI 0.11 released with new features and enhancements
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Solid-as-a-rock desktops, polished phones and advanced cloud tools are the ground on which [Canonical][1] stands, company being characterized by speed in development, bold decisions and an overall innovative quality, innovation setting Canonical as a serious partner for Dell, HP and OpenStack Foundation, as well as delivering freshness and modernism in the IT world.
|
||||
|
||||
[Juju][2] is an Ubuntu technology that offers reliable service orchestration in the cloud, environment where it permits fast and productive deploying, scaling and managing of services, thus allowing its utilizers to deploy Wordpress, MongoDB, Ceph, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Juju can be harnessed via both command-line and intuitive GUI, latter expressed as Juju GUI.
|
||||
|
||||
[Juju GUI][3] is a fancy, user-friendly and intuitive web-based interface for Juju, allowing complex actions from within web-browsers, Juju GUI presenting itself as a hassle-free manner of using Juju's power.
|
||||
|
||||
Juju GUI has been [updated][4] to version **0.11**, introducing a significant amount of new features, as well as multiple fixes and optimizations, among which:
|
||||
|
||||
- support for upgrading/downgrading of service's charms
|
||||
- support to display both endpoints for relations
|
||||
- significantly decreased size of GUI distribution (therefore, increasing the speed of deployment)
|
||||
- optimized service positioning behavior
|
||||
- red-triangle marker added to recommended charms and bundles
|
||||
- removed faulty behaviors (such as newly-added units overlapping previously-added units)
|
||||
- accurate URLs for unit details
|
||||
- several enhancements
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Juju GUI can be tested and grasped on [https://jujucharms.com/sidebar/][5]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/cloud-tool-juju-gui-011-released-new-features-and-enhancements
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.canonical.com/
|
||||
[2]:https://juju.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[3]:https://launchpad.net/juju-gui
|
||||
[4]:http://jujugui.wordpress.com/2013/10/18/0-11-0-juju-gui-release/
|
||||
[5]:https://jujucharms.com/sidebar/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
(翻译中 by runningwater)
|
||||
Create And Manage Encrypted Folders in Linux With encfs
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
here are times when you want certain information on your computer protected from prying eyes. One way to protect your information is to encrypt your home directory. However, that does not protect your information when you are logged on to your computer. I've shown in the past how you can [use Cryptkeeper to create an encrypted folder on your system][1]. Cryptkeeper is a graphical front end to **encfs**. encfs allows you to create an encrypted folder and then mount it as a user filesystem using [FUSE][2]. In this tutorial I'll show how to use encfs from the command line to create and manage an encrypted folder on Linux.
|
||||
@ -60,7 +61,7 @@ What will you use encfs for? Let me know in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://tuxtweaks.com/2013/10/encrypted-folders-linux-encfs/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
|
||||
翻译中啦,Vic___
|
||||
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – How To Change Your Computer Name
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Another blog post that is geared towards new Ubuntu users or newbies. This post shows you how to easily change your computer name when using Ubuntu. Many users will never worry about changing their computer name or hostname in Ubuntu. In most cases, that’s the least of their worries.
|
||||
|
||||
Many will use the name that was created or given to the machine during Ubuntu installation. But for those new users who would like to know how to do it, continue below to learn how. This post isn’t for pros, it’s for newbies and users who are just starting out with Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
So, why would you want to change your computer name again? If you don’t have a good reason other than to learn how to do it, then don’t. If you want to do it for a good reason or learn how to do it, then do this.
|
||||
|
||||
Press **Ctrl – Alt – T** on your keyboard to open the terminal. When it opens, run the commands below to edit the hostname file using gedit.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo gedit /etc/hostname
|
||||
|
||||
Next, change whatever in there to be the new computer name. For example, if you want your computer name to be RDOMNU, delete what’s currently in there and type **RDOMNU** and save the file.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, run the commands below to open the hosts file.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo gedit /etc/hosts
|
||||
|
||||
Then change the value of the second line highlighted below to match your computer name you entered earlier. Save the file when you’re done.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
That’s it! Restart your computer and your machine will reflect the new name. This is how one changes the name of a Ubuntu machine.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/10/daily-ubuntu-tips-change-computer-name/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
Vic020翻译中
|
||||
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Resize Ubuntu Unity Launcher
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Here’s another tip for users who are new to Ubuntu. This series aims to help new users to Ubuntu configure and manage their computer easily. It’s not geared towards Ubuntu power users or pros, rather users who are just starting with Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Development version of GIMP presented with top-bottom-left-right configurable tabs
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[GIMP][1] is a powerful, advanced and complex image-editing application, permitting to both regular and professional skilled users to in-depth edit images via a massive amount of features, tools and functionalities.
|
||||
|
||||
It seems that the unstable development-only versions of **GIMP** are targeting interesting potential additions, including a more friendly and configurable manner of enjoying tabs in **GIMP**.
|
||||
|
||||
The official Google+ webpage of GIMP [shared][2] an interesting image with a **development** version of GIMP featuring adjustable tabs, essentially, allowing the user to set the tabs in GIMP on top, bottom, left and right areas, therefore, permitting an easy rearranging of tabs per-one's likeness.
|
||||
|
||||
The mentioned tweakable tabs are to be housed under the `Windows` menu, where the user is to be probably able to 1-click away select desired locations for tabs.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The exciting support has been created due to "**in some cases it's desirable to have tabs position configurable**, so Jehan Pagès did just that: the unstable branch now lets you choose where you want your tabs: top, bottom, left, or right sides".
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/development-version-gimp-presented-top-bottom-left-right-configurable-tabs
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.gimp.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://plus.google.com/116634837115748851709/posts/KuXpxUf8iVm
|
||||
@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
|
||||
GNOME Settings Daemon 3.10.1 Fixes Memory Leaks
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**The GNOME developers announced a few days ago that the first maintenance release of the stable GNOME Settings Daemon 3.10 package, a daemon run by all GNOME sessions to provide live access to configuration settings and the changes done to them, is available for download. **
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME Settings Daemon 3.10.1 is distributed as part of the recently released GNOME 3.10.1 desktop environment, and includes several memory leak fixes and small cleanups. Below is a detailed list with all the changes implemented in this stable release of GNOME Settings Daemon:
|
||||
|
||||
**Housekeeping:**
|
||||
|
||||
- The cache directories are no longer scanned if not needed;
|
||||
|
||||
**Keyboard:**
|
||||
|
||||
- The XKB group switching option is no longer set if not needed;
|
||||
|
||||
**Media-keys:**
|
||||
|
||||
- A gsettings key is now used for the maximum length of a screencast;
|
||||
|
||||
**Mouse:**
|
||||
|
||||
- Edge scrolling is now automatically enabled if two-finger scroll is not available;
|
||||
|
||||
**Power:**
|
||||
|
||||
- A test case has been added as no warning was provided on startup;
|
||||
- Notifications are now displayed on critical battery state;
|
||||
- The "keyboard Backlight is not available" warning has been fixed;
|
||||
- A mouse will no longer appear as the status icon;
|
||||
|
||||
**Updates:**
|
||||
|
||||
- Added a 'Not Now' button to the distribution upgrade notification;
|
||||
- Multiple notifications are no longer displayed when updates are available;
|
||||
- It now requires PackageKit 0.8.1 or higher in order to avoid complexity;
|
||||
|
||||
**Wacom:**
|
||||
|
||||
- A couple of crashes have been fixed;
|
||||
- Default area ordering has been fixed;
|
||||
- A failure to get area with the cursor device has been fixed;
|
||||
- Resetting the tablet area to default has been implemented;
|
||||
- OSD has been fixed;
|
||||
- Tablet PC setting has been removed as there's no UI (User Interface) for it;
|
||||
|
||||
**XRandR:**
|
||||
|
||||
- The temporary configurations generated by the FN+F7 keyboard shortcut or rotate buttons are no longer saved.
|
||||
|
||||
More details about this release can be found in the [official raw changelog][1].
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download GNOME Settings Daemon 3.10.1 tar.xz][2][sources] [1.60 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/GNOME-Settings-Daemon-3-10-1-Fixes-Memory-Leaks-393135.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/gnome-settings-daemon/3.10/gnome-settings-daemon-3.10.1.news
|
||||
[2]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/gnome-settings-daemon/3.10/gnome-settings-daemon-3.10.1.tar.xz
|
||||
@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
||||
GNOME Software 3.10.1 Fixes Bugs and Adds New Features
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**The GNOME Project has announced last evening, October 14, that the first maintenance release for the recently introduced GNOME Software application for the GNOME 3.10 desktop environment is available for download/upgrade.**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME Software 3.10.1 is a maintenance release that mostly fixes bugs reported by users who had the chance to test this new application, which was originally introduced with the release of the GNOME 3.10 desktop environment.
|
||||
|
||||
However, the new release of GNOME Software also introduces some new features, among which we can mention a loading icon for empty tiles, support for the new 16:9 screenshots format, support for per-repo icon directories, support the 'X-AppInstall-Package' extension in desktop files, and the IBus frameworks installed by default are marked as system apps.
|
||||
|
||||
The hardcoded ratings and screenshot plugins were removed from this version of GNOME Software, with the mention that they will not be available until the release of the GNOME 3.12 desktop environment, next year.
|
||||
|
||||
Among the bugs fixed in GNOME Software 3.10.1, we can mention re-implementation of the hover state to feature tile, strings in the AppData file are now translatable, memory corruption is now prevented when doing dedupe() more than once, notify::state is no longer transmitted from a thread, and the "Remove" option is now displayed for installed apps that are updatable.
|
||||
|
||||
Moreover, a critical error has been fixed in gs_string_replace(), some small memory leaks were fixed, a refcounting error, which could cause a crash, has been fixed, the application widget will no longer be removed twice when it changes state, and local applications have names, icons and comments.
|
||||
|
||||
Last but not least, the following translations have been updated in this release: Indonesian, Latvian, Brazilian Portuguese, Czech, Hungarian, Italian, Polish, Slovenian, Spanish, and Traditional Chinese. More details can be found in the official raw [changelog][1].
|
||||
|
||||
- [GNOME 3.10.1 tar.xz][2][sources] [1.40 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/GNOME-Software-3-10-1-Fixes-Bugs-and-Adds-New-Features-391284.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/gnome-software/3.10/gnome-software-3.10.1.news
|
||||
[2]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/gnome-software/3.10/gnome-software-3.10.1.tar.xz
|
||||
@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
|
||||
GNOME To Work On Wayland Accessibility Support
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Now that GNOME 3.10 has shipped and with it comes initial native Wayland support, GNOME developers are beginning to focus on the GNOME 3.12 release cycle and working on some of the open work items in Wayland enablement.
|
||||
|
||||
Matthias Clasen of Red Hat has written to the Wayland developers about improving the accessibility support. In the GNOME Wayland porting, among the accessibility items that will likely need to be implemented within the GNOME Shell Mutter Wayland compositor are input tweaks (slow keys / bounce keys), zoom and color adjustments, text protocol support for on-screen keyboards and the like, and other improvements for properly handling the on-screen keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||
In terms of why Clasen is bringing this GNOME work up with Wayland developers, "All of these features violate the careful separation between clients that Wayland maintains, so that probably calls for some privileged interface for ATs. I would appreciate feedback and discussion on this. Has anybody else thought about these problems already?"
|
||||
|
||||
The new mailing list thread can be found on [Wayland-devel][1].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTQ4NzI
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://lists.freedesktop.org/archives/wayland-devel/2013-October/011487.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
How to Set Up Secure Remote Networking with OpenVPN on Linux, Part 1
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
It's always been prudent to wrap a warm comfy layer of encryption over your Internet travels to foil snoops of all kinds, and with our own government slurping up every bit wholesale it's more crucial than ever. OpenVPN is the top choice for protecting networking over untrusted networks. Today we'll learn a quick way to set up OpenVPN so you can securely access your home server when you're on the road.
|
||||
|
||||
A quick note on VPNs: there are many commercial VPNs that aren't worth the bits they're printed on. They're little better than SSL-protected Web sites, because they trust all clients. A true VPN (virtual private network) connects two trusted endpoints over untrusted networks. You can't just log in from whatever random PC you find, and this is good because (presumably) you understand that logging in to your private network from an infected host is a bad thing to do, no matter how secure the connection is. So you have to configure both your server and client.
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenVPN Quickstart ###
|
||||
|
||||
You need two computers on different subnets, like a wired and wireless PC on the same network (or a couple of Linux guests in Virtualbox), and you need to know the IP addresses of both PCs. Let's call our example computers Studio and Shop. Install OpenVPN on both of them. OpenVPN is included in most Linux distributions, so you can install it with your favorite package manager. This example is for Debian, Ubuntu, and their myriad descendants:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install openvpn openvpn-blacklist
|
||||
|
||||
That installs the server and a little program to check the blacklist of compromised keys. You must install the blacklist checker! Because once upon a time Debian distributed a [broken version of OpenSSL][1] which had a broken random number generator, so keys created with this are assumed to be too vulnerable to trust. The random number generator was not really random, but predictable. This happened way back in 2008, and everyone who used the defective OpenSSL was supposed to hunt down and replace their weak keys. Even though it's been over five years, it's cheap insurance to use the blacklist checker.
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's test it by creating an unencrypted tunnel between our two PCs. First ping each machine to make sure they're talking to each other. Then make sure that OpenVPN is not running, because we're going to start it manually:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps ax|grep openvpn
|
||||
|
||||
If it is, kill it. Let's say that Studio's IP address is 192.168.1.125, and Shop's is 192.168.2.125. Open an unencrypted tunnel from Studio to Shop:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo openvpn --remote 192.168.2.125 --dev tun0 --ifconfig 10.0.0.1 10.0.0.2
|
||||
|
||||
Then from Shop to Studio:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo openvpn --remote 192.168.1.125 --dev tun0 --ifconfig 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
When you make a successful connection you'll see something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 ******* WARNING *******: all encryption and authentication
|
||||
features disabled -- all data will be tunnelled as cleartext
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 TUN/TAP device tun0 opened
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 do_ifconfig, tt->ipv6=0, tt->did_ifconfig_ipv6_setup=0
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 /sbin/ifconfig tun0 10.0.0.1 pointopoint 10.0.0.2 mtu 1500
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 UDPv4 link local (bound): [undef]
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 UDPv4 link remote: [AF_INET]192.168.2.125:1194
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 Peer Connection Initiated with [AF_INET]192.168.2.125:1194
|
||||
Wed Oct 16 2013 Initialization Sequence Completed
|
||||
|
||||
"Initialization Sequence Completed" are the magic words that confirm you did it right. You should be able to ping back and forth with the tunnel addresses, ping 10.0.0.1 and ping 10.0.0.2. When you build your tunnel you may use whatever IP addresses you want that don't overlap with your existing network. To close your tunnel press Ctrl+c.
|
||||
|
||||
Just for fun open an SSH session over your tunnel. Figure 1 shows a successful SSH login over a VPN tunnel, and it also demonstrates the fancy Message of the Day from [Put a Talking Cow in Your Linux Message of the Day][1]:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh carla@10.0.0.2
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Figure 1: A successful SSH session over a VPN tunnel, and a fancy MOTD.*
|
||||
|
||||
Hurrah, it works!
|
||||
|
||||
### Encrypted VPN Tunnel ###
|
||||
|
||||
This is all fun and exciting, but pointless without encryption, so we'll set up a simple static key configuration. It's not as strong as a proper public key infrastructure (PKI) with root certificates and revocations and all that good stuff, but it's a good-enough solution for the lone nerd needing to call home from the road. OpenVPN helpfully includes a command to create the static key, so create a directory to store the key in, create the key, and make it read-only for the file owner:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir /etc/openvpn/keys/
|
||||
$ sudo openvpn --genkey --secret /etc/openvpn/keys/static.key
|
||||
$ sudo chmod 0400 /etc/openvpn/keys/static.key
|
||||
|
||||
This is a plain-text key that you can open in a text editor and look at if you're curious, and you can name it anything you want; you don't have to call it "static.key". Copy this key to both computers-- yes, the same key. It's not a private-public key pair, but just one single shared key.
|
||||
|
||||
Now we'll create some simple barebones configuration files for each computer. (On Debuntu etc. there are no default configuration files, but rather a wealth of example files in/usr/share/doc/openvpn/.) In my little test tab Studio is the server, and Shop is the wandering laptop that will log into the server. My server configuration file is/etc/openvpn/studio.conf, and this is all it has:
|
||||
|
||||
# config for Studio
|
||||
dev tun
|
||||
ifconfig 10.0.0.1 10.0.0.2
|
||||
secret /etc/openvpn/keys/static.key
|
||||
|
||||
Make this file readable and writable only to the file owner:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chmod 0600 /etc/openvpn/studio.conf
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration file on the client is similar, with the addition of the IP address of the server:
|
||||
|
||||
# config for Shop
|
||||
dev tun
|
||||
ifconfig 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.1
|
||||
secret /etc/openvpn/keys/static.key
|
||||
remote 192.168.1.125
|
||||
|
||||
Mind the order of your IP addresses on the ifconfig line, because they need to be in the order of local > remote. Now fire up OpenVPN on the server, specifying the server configuration file, and do the same on your client:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo openvpn /etc/openvpn/studio.conf
|
||||
$ sudo openvpn /etc/openvpn/shop.conf
|
||||
|
||||
You'll see the same "Initialization Sequence Completed" message for a successful connection, and you must also look for the absence of this message, which should have appeared when you created your un-encrypted tunnel:
|
||||
|
||||
******* WARNING *******: all encryption and authentication features disabled
|
||||
|
||||
Firewalls and Dynamic IP Addresses
|
||||
|
||||
OpenVPN itself is simple to configure. The biggest hassles are dealing with firewalls and dynamic IP addresses. There are a skillion different firewalls in the world, so I shall leave it as your homework to figure out how to get through it safely. OpenVPN wants port 1194, and then you'll want to have a forwarding rule that points to the computer you want to access.
|
||||
|
||||
Dynamic IP addresses are another hassle. [Dyn.com][3] is an inexpensive way to manage dynamic IP assignment from your ISP. Or you might be able to pay your ISP a few bucks to get a static address.
|
||||
|
||||
At this point you could stop and call it good, because you can manually start OpenVPN on your server and leave it waiting for you, take your laptop out into the world, and connect to your server whenever you want. However, there are some refinements we can add such as daemonizing OpenVPN on the server, using Network Manager to make the connection automatically, and the biggest missing piece in OpenVPN howtos: how to access your remote resources. So come back next week for the rest of the story.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/743590-secure-remote-networking-with-openvpn-on-linux
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.debian.org/security/2008/dsa-1571
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/741573-put-a-talking-cow-in-your-linux-message-of-the-day
|
||||
[3]:http://dyn.com/dns/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
How to Set Up Secure Remote Networking with OpenVPN on Linux, Part 2
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Greetings fellow Linux users, and welcome to the second part of our glorious OpenVPN series. When last we met we learned how to set up a [simple OpenVPN encrypted tunnel][1] between a home server and a remote node, such as a laptop. Today we're adding refinements such as how to daemonize OpenVPN so we don't have to start it manually, use Network Manager for easy connecting to our remote server, and access services.
|
||||
|
||||
### Network Manager Integration ###
|
||||
|
||||
Network Manager is a nice OpenVPN client; just make sure you have the network-manager-openvpn plugin installed. We'll use our example configurations from part 1. Open your Network Manager configuration and find the window where you set up a new VPN connection. This looks different on KDE and GNOME, but the information you'll need is the same. When you start you need to see an OpenVPN connection type, like in figure 1; if you don't see this then the plugin is missing. (The figures are from GNOME.)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Figure 1: Creating a new OpenVPN client config in Network Manager.*
|
||||
|
||||
Figure 2 shows the main configuration screen. Starting from the top:
|
||||
|
||||
- Whatever name you want for this connection.
|
||||
- The Gateway is the IP address of your remote server.
|
||||
- Select Static Key from the dropdown menu,
|
||||
- Then use the filepicker to find the key you want to use.
|
||||
- This is not a directional key, so select None.
|
||||
- The remote and local IP addresses are your virtual OpenVPN addresses, from your /etc/openvpn/foo.conf files.
|
||||
- We did not set a password.
|
||||
- "Available to all users" or just you, whichever you want.
|
||||
|
||||
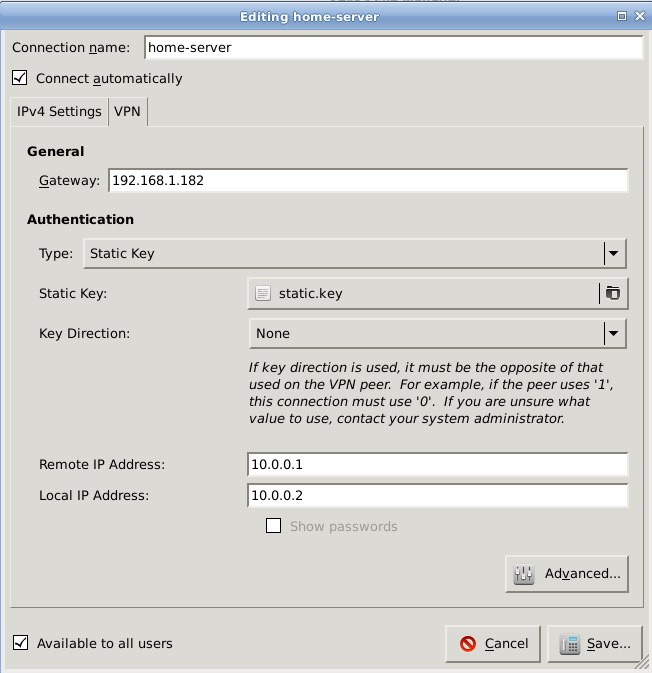
|
||||
|
||||
*Figure 2: Main Network Manager configuration for OpenVN client.*
|
||||
|
||||
Save, and then use Network Manager to connect. Easy peasey! Now you can connect and disconnect with the click of a button (figure 3).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Run OpenVPN Automatically ###
|
||||
|
||||
It's simple to start up OpenVPN manually, but you might want to daemonize it on your server for convenience, and to survive accidental reboots. On Debian/Ubuntu/great-thundering-herd-of-spawn distros this is handled automatically: when you install OpenVPN it's configured to automatically start at boot. So, after installation you need to reboot, or start the daemon with one of these commands:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/openvpn start
|
||||
$ sudo service openvpn start
|
||||
|
||||
The first command is the old-fashioned way, and the second command uses the service command. service first appeared in Red Hat Linux back in the olden days, and if your distro doesn't install it by default it's probably lurking in the repos if you want to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
Fedora uses the systemd init system, in contrast to Ubuntu which uses Upstart, and Debian still uses good old SysV init. If you have multiple OpenVPN configurations in /etc/openvpn you can start each one selectively in systemd, like this:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start systemctl start openvpn@studio.service
|
||||
|
||||
Where "studio.service" references our example /etc/openvpn/studio.conf file from part one. This invocation does not survive a reboot, so it's just like running openvpn /etc/openvpn/studio.conf, which is how we started OpenVPN sessions manually in part 1. You should be able to daemonize OpenVPN on systemd with chkconfig:
|
||||
|
||||
# service openvpn start
|
||||
# chkconfig openvpn on
|
||||
|
||||
That should daemonize OpenVPN in the usual way, which is as a monolithic daemon and not individually per .conf file in /etc/openvpn/. systemd supports the chkconfig and servicecommands so it should work. However, the distros that use systemd are quite variable, so if yours is different please let us know in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
### Strengthening Your Connection ###
|
||||
|
||||
OpenVPN is robust and is good at maintaining a persistent connection, even with service interruptions. You can make your connection even stronger by adding these lines to your .conf files on clients and server:
|
||||
|
||||
persist-tun
|
||||
persist-key
|
||||
|
||||
These are helpful for laptop users who disrupt their connection a lot with power-save and being on the move.
|
||||
|
||||
### Now What? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you have this all set up and working, what do you do with it? If you're used to using OpenSSH for remote operations you might be stuck in the SSH mindset of being able to log into specific machines and run applications. It doesn't work that way. Rather, think of OpenVPN as a virtual Ethernet cable to your server or LAN, all wrapped in a nice stout layer of encryption. You can run unencrypted and encrypted services over the same tunnel, and you only have to open a single hole in your firewall.
|
||||
|
||||
So you can run SSH in the way you're used to over your OpenVPN tunnel, and do remote administration and run applications. You can access network resources such as fileshares and Web applications. You can force all networking on the client to go through your VPN tunnel, but for this series I've assumed that you want to be able to use both your native and VPN networks.
|
||||
|
||||
So there you are on your trusty laptop and you can surf the Web, run SSH, do whatever you want on whatever network you're connected to. Then when you want to run something over your OpenVPN tunnel open it up and specify the IP address, like this:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh carla@10.0.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
Web applications are easy: point your Web browser to the virtual IP address of your OpenVPN server and log in as usual. For example, I run various Web services for testing on my home server. So I access Drupal at [http://10.0.0.1/drupal][2] and OwnCloud at [http://10.0.0.1/owncloud][3]. I use the nice gFTP graphical FTP client, so all I need to connect is the virtual IP address on the Host line, username, and password. Or use the command line:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ftp 10.0.0.1 21
|
||||
|
||||
You can administer your MySQL database from afar, using your own username and password:
|
||||
|
||||
$ mysql -h 10.0.0.1 -u admin -p
|
||||
|
||||
So the main thing you need to know is how to add the host specification to whatever command you want to run.
|
||||
|
||||
Obviously, this would all be easier with name services instead of having to use IP addresses, so one of these days we'll learn how to implement name services in OpenVPN. Meanwhile, please enjoy your nice secure OpenVPN tunnel.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/745233-how-to-set-up-secure-remote-networking-with-openvpn-on-linux-part-2
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/743590-secure-remote-networking-with-openvpn-on-linux
|
||||
[2]:http://10.0.0.1/drupal
|
||||
[3]:http://10.0.0.1/owncloud
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
|
||||
How to set up web-based network traffic monitoring system on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
When you are tasked with monitoring network traffic on the local network, you can consider many different options to do it, depending on the scale/traffic of the local network, monitoring platforms/interface, types of backend database, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
[ntopng][1] is an open-source (GPLv3) network traffic analyzer which provides a web interface for real-time network traffic monitoring. It runs on multiple platforms including Linux and MacOS X. ntopng comes with a simple RMON-like agent with built-in web server capability, and uses [Redis][2]-backed key-value server to store time series statistics. You can install ntopng network traffic analyzer on any designated monitoring server connected to your network, and use a web browser to access real-time traffic reports available on the server.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I will describe **how to set up a web-based network traffic monitoring system on Linux by using ntopng.**
|
||||
|
||||
### Features of ntopng ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Flow-level, protocol-level real-time analysis of local network traffic.
|
||||
- Domain, AS (Autonomous System), VLAN level statistics.
|
||||
- Geolocation of IP addresses.
|
||||
- Deep packet inspection (DPI) based service discovery (e.g., Google, Facebook).
|
||||
- Historical traffic analysis (e.g., hourly, daily, weekly, monthly, yearly).
|
||||
- Support for sFlow, NetFlow (v5/v9) and IPFIX through nProbe.
|
||||
- Network traffic matrix (who’s talking to who?).
|
||||
- IPv6 support.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install ntopng on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
The official website offers binary packages for [Ubuntu][3] and [CentOS][4]. So if you use either platform, you can install these packages.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to build the latest ntopng from [its source][5], follow the instructions below.
|
||||
|
||||
To build ntopng on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install libpcap-dev libglib2.0-dev libgeoip-dev redis-server wget
|
||||
$ tar xzf ntopng-1.0.tar.gz
|
||||
$ cd ntopng-1.0/
|
||||
$ ./configure
|
||||
$ make geoip
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
|
||||
In the above steps, “make geoip” will automatically download a free version of GeoIP databases with wget from maxmind.com. So make sure that your system is connected to the network.
|
||||
|
||||
To build ntopng on Fedora:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install libpcap-devel glib2-devel GeoIP-devel
|
||||
libxml2-devel redis wget
|
||||
$ tar xzf ntopng-1.0.tar.gz
|
||||
$ cd ntopng-1.0/
|
||||
$ ./configure
|
||||
$ make geoip
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
|
||||
To install ntopng on CentOS or RHEL, first [set up EPEL repository][6], and then follow the same instructions as in [Fedora][7] above.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure ntopng on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
After building ntopng, create a configuration directory for ntopng, and prepare default configuration files as follows. I assume that “192.168.1.0/24″ is the CIDR address prefix of your local network.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mkir /etc/ntopng -p
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo -e /etc/ntopng/ntopng.start
|
||||
|
||||
> --local-networks "192.168.1.0/24"
|
||||
>
|
||||
> --interface 1
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo -e /etc/ntopng/ntopng.conf
|
||||
|
||||
> -G=/var/run/ntopng.pid
|
||||
|
||||
Before running ntopng, make sure to first start redis, which is a key-value store for ntopng.
|
||||
|
||||
To start ntopng on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/redis-server restart
|
||||
$ sudo ./ntopng
|
||||
|
||||
To start ntopng on Fedora, CentOS or RHEL:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service redis restart
|
||||
$ sudo ./ntopng
|
||||
|
||||
By default, ntopng listens on TCP/3000 port. Verify this is the case using the command below.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo netstat -nap|grep ntopng
|
||||
|
||||
> tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 29566/ntopng
|
||||
|
||||
### Monitor Network Traffic in Web-Based Interface ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once ntopng is successfully running, go to http://<ip-address-of-host>:3000 on your web browser to access the web interface of ntopng.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the login screen of ntopng. Use the default username and password: “admin/admin” to log in.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few screenshots of ntopng in action.
|
||||
|
||||
Real-time visualization of top flows.
|
||||
|
||||
[][8]
|
||||
|
||||
Live statistics of top hosts, top protocols and top AS numbers.
|
||||
|
||||
[][9]
|
||||
|
||||
Real time report of active flows with DPI-based automatic application/service discovery.
|
||||
|
||||
Historic traffic analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
[][10]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2013/10/set-web-based-network-traffic-monitoring-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ntop.org/products/ntop/
|
||||
[2]:http://redis.io/
|
||||
[3]:http://apt.ntop.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://rpm.ntop.org/
|
||||
[5]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/ntop/files/ntopng/
|
||||
[6]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[7]:http://xmodulo.com/go/fedora_guide
|
||||
[8]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10487165303/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10486988416/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10486995114/
|
||||
@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Install Or Upgrade VMware Tools In Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Few days ago, VMware Workstation 10 was released. VMware Workstation is a virtualization software that lets you run multiple operating systems using a single host machine. With this software, you can run guest machines such as Windows XP, Vista 7 and 8 though 8.1. You can also run Linux operating systems, including Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
Because we use VMware Workstation to run some guest machines, we had to upgrade VMware tools on all of them. It is very important that you install VMware Tools in the guest operating system. That’s because the tool provides required support for shared folders, drag and drop operations, better graphic and improved performance.
|
||||
|
||||
This brief tutorial is going to show you what we did to install and upgrade all our guest machines that run under VMware Workstation. Other benefits that the tool provides is synchronization of time between the guest machine and the host, grabbing and releasing of the mouse, coping and pasting between the guest and hose machines and more.
|
||||
|
||||
To get started, open VMware Workstation and select the Ubuntu guest machine and start it or turn it on. Next, click **VM –> Install VMware Tools…** from the host menu.
|
||||
|
||||
For you information, I am running Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) but this method may work with previous versions.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
A virtual CD/DVD Rom should be mounted with VMware Tools archive. Next, run the commands below to extract the package to the temp directory.
|
||||
|
||||
tar -xvf /media/$USER/"VMware Tools"/VMwareTools*.gz -C /tmp
|
||||
|
||||
Next, run the below commands to begin the installation.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo /tmp/vmware-tools-distrib/vmware-install.pl
|
||||
|
||||
During the installation, just press the Enter key to accept the defaults when prompted. The tool will install itself along with any required packages.
|
||||
|
||||
When it’s done, restart your computer and begin enjoying your machine.
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/09/install-upgrade-vmware-tools-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux Won't Get Aura UI Stack Until Google Chrome 33
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
While Google's Chrome 32 web-browser will feature the Aura UI stack from Chrome OS, the Chrome desktop web-browser on Linux won't get the GPU-accelerated interface until one version later.
|
||||
|
||||
Aura is the UI stack used by Google Chrome OS that can fully take advantage of graphics processors where supported. The only native element/widget is the top-level window while everything else is handled by Chrome and composited by the program itself. Google's goal is to use the same UI stack across Windows, Linux, and Chrome OS (albeit not on OS X or other platforms). While Aura is designed to take advantage of modern GPUs, there is a pure software fallback mode too.
|
||||
|
||||
With Chrome 32, Aura will now be used as the UI stack. Windows 7 and Windows 8 systems will support the GPU acceleration code-path while Windows XP and Vista users will be limited to software-accelerated support. The Aura code-path also determines whether WebGL and Pepper-based Flash is using GPU support too.
|
||||
|
||||
As shared via the [Chromium Google Group][1] last week, the Linux version of Chromium now won't see Aura with GPU acceleration until version 33. In other words, the UI stack should arrive on Linux right around the end of the calendar year.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTQ4NzE
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://groups.google.com/a/chromium.org/forum/#!topic/chromium-dev/UMwGGgP0P9c
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
Linux's First Space Opera Game "The Mandate" Gets a Fabulous Trailer
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Perihelion Interactive has announced the release of the first gameplay trailer for one of the most promising space-related games on Kickstater, The Mandate.
|
||||
|
||||
According to its developers, The Mandate is a six-player, cooperative, sandbox sci-fi RPG that allows the players to control a huge ship, with hundreds of people on board.
|
||||
|
||||
The gameplay will change depending of the situation. While in space, it is similar to the one in Nexus: Jupite Incident, but The Mandate provides a full RPG experience.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, players will be able to board the ships they're attacking, playing from an isometric perspective, while the rest of the party is engaging other ships in space. Or better yet, they will have to protect their own ships in the same way.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
“The gameplay trailer begins with neutral starship Zukov issuing a distress signal after it is assaulted by pirates. This signal is intercepted by a player who is commanding battle squadron Azimov which is loyal to the Empress of The Mandate. The player engages the pirates giving them the chance to surrender and withdraw, but battle ensues. One rule, no quarter,” reads the official [announcement][1].
|
||||
|
||||
The game is built on the Unity3D engine, but it's still in its initial stages of development and the final product might look a lot different.
|
||||
|
||||
The studio is comprised of industry veterans who worked on important games such as Assassin's Creed, Assassin's Creed II, Mafia II, Far Cry 2, Age of Conan: Hyborian Adventures, Call of Duty 3, and The Secret World. More importantly, they are avid CRPG players, they like Battlestar Galactica, Star Trek, Babylon 5, and Firefly.
|
||||
|
||||
The developers from Perihelion Interactive LLC have managed to raise a third of the money, but they still have 34 days to go.
|
||||
|
||||
The game is expected to arrive in March 2015. If you are interested in this project, you can check out the official Kickstarter website.
|
||||
|
||||
youtube video:[http://www.youtube.com/embed/lf-lB51wlNo][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Linux-s-First-Space-Opera-Game-quot-The-Mandate-quot-Gets-a-Fabulous-Trailer-394858.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.kickstarter.com/projects/1964463742/the-mandate/posts
|
||||
[2]:http://www.youtube.com/embed/lf-lB51wlNo
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
LinuxCon/CloudOpen Goose Chase Ends in Tie for Grand Prize
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Hundreds of people raced to the finish in the first-ever LinuxCon/CloudOpen Goose Chase. From showing your cowsay to the coffee cup that fuels your Linux work, you - the community - showcased your competitive nature and passion for having fun. The competiton was fierce through the end, which resulted in a tie for Grand Prize for Round Two (round one wrapped up in October, and the [winners were announced][1] at LinuxCon and CloudOpen North America). Because there are two Grand Prize winners, we will not be awarding a First Prize.
|
||||
|
||||
The winners of Round Two are:
|
||||
|
||||
**Grand Prize: $500 Amazon Gift Card**
|
||||
|
||||
**Daniel German**, Canada
|
||||
|
||||
**Joao Paulo Rechi Vita**, Brazil
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Joao works for the Nokia Institute of Technology. His latest Linux project was adding BlueZ 5 bluetooth support to PulseAudio on the Linux desktop. He's attended LinuxCon in Japan, North America and Europe this year.
|
||||
|
||||
"I participated in the Goose Chase at LinuxCon North America and found it really fun, so when I was showing the pictures to my girlfriend back home I found the {online} Goose Chase and decided to join it as well. And as I expected, {it} was a lot of fun again, specially because this time some of the missions needed quite a bit of creativity to be accomplished."
|
||||
|
||||
**Second Prize, $50 Amazon Gift Card**
|
||||
|
||||
**Madalina-Ioana Alexe**, Romania
|
||||
|
||||
Madalina-Ioana works for Intel Romania on Tizen and attended the Gluster Community Day this week at LinuxCon Europe.
|
||||
|
||||
"I found it is a fun game, which is still suitable for geeks. It was a nice and funny experience and I found out that there are even more geeks like me."
|
||||
|
||||
Congratulations to all our winners and thank you so much for participating in the Goose Chase!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/185-jennifer-cloer/745263-linuxconcloudopen-goose-chase-ends-in-tie-for-grand-prize/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/200-libby-clark/737969-announcing-goose-chase-contest-winners-more-prizes-for-linuxcon-europe
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
Mikko Hypponen: Open Source Software Will Make the World More Secure
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Open source software can be one answer to combating the global surveillance of innocent citizens, said security expert Mikko Hypponen in his keynote last week at [LinuxCon and CloudOpen Europe][1] in Edinburgh.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Mikko Hypponen, chief research officer at F-Secure in Finland, spoke at LinuxCon and CloudOpen Europe 2013 in Edinburgh.*
|
||||
|
||||
Advances in computing and the rise of global networks have made the storage and transmission of data cheap and easy. This has created unparalleled connectivity, progress and innovation, Hypponen said. But it’s also enabled large-scale access to that data as demonstrated by the NSA’s PRISM program, made public this year in a series of top-secret document leaks by former U.S. government contractor Edward Snowden.
|
||||
|
||||
“In the last few years we've realized data is cheap. We never have to delete anything anymore, ever,” said Hypponen, chief research officer at F-Secure in Finland. “This has enabled lots of great things but also global wholesale blanket surveillance.”
|
||||
|
||||
Such access to our personal data, including cell phone records, geolocation, email and search engine queries, may be warranted in some cases, Hypponen said.
|
||||
|
||||
“I do believe some surveillance is OK,” he said. “If there's an investigation into finding a school shooter or drug lord or member of a terrorist cell… we should have the technical means of doing that. But we must first have the suspicion.”
|
||||
|
||||
But collecting the communications and personal data of “everyone” is not only a violation of privacy, but a threat to democracy, Hypponen said.
|
||||
|
||||
“Even if you don't have a problem with our government today, we don't know what the government will be 20 years from now,” he said. ”If they have 20 years of your search data, they'll find something illegal or embarrassing to twist your hand.”
|
||||
|
||||
Though the leaks have caused some IT professionals to question the safety of their data stored with and routed through U.S. service providers, avoiding these companies and services won’t solve the problem, Hypponen said. Neither can each country afford the time and expense of building its own alternatives.
|
||||
|
||||
Working across international boundaries, developers should band together to build secure and reliable software and services that prevent back-door tampering and ensure users’ privacy, Hypponen said.
|
||||
|
||||
“I suggest that open source provides a solution to this problem,” he said. “Then countries don't have to work alone. It will be secure, open and free.”
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/200-libby-clark/745585-mikko-hypponen-open-source-software-will-make-the-world-more-secure
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://events.linuxfoundation.org/events/linuxcon-europe
|
||||
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Modern terminal Final Term adds multiple-terminals per-window support
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[Final Term][1] is a modern terminal application that centers exciting capabilities and handy features into a beautiful interface, Final Term presenting itself as a significant advancement for the terminal metaphor.
|
||||
|
||||
Smart command completion with drop-down menu and case sensitive/insensitive ability, semantic text menus recognizing web URLs, IP addresses, PIDs, option to collapse commands, 8 / 16 / 256 colors support, drop-down look, accurate and proper window resizing with precise text repositioning come to present Final Term as an advanced, versatile terminal application.
|
||||
|
||||
Along with the already-existent pack of solid and exciting features, it seems that Final Term's development is targeting new features for inclusion, as in the case of the newly-announced **multiple terminals per window** support.
|
||||
|
||||
Essentially, the multiple-terminals-per-window allows the user to split the Final Term's window into multiple splits, splits then having the capacity to contain numerous tabs.
|
||||
|
||||
As seen in the below GIF, the modern terminal application features now a clickable menu containing *New Tab, Split Horizontally* and *Split Vertically*, clicking on *Split Horizontally*, splits the window horizontally, behavior followed by *Split Vertically*, too.
|
||||
|
||||
Yet, hitting the *New Tab* entry, continues to add new and new tabs into a portion/split of the Final Term's main window, therefore, permitting an advanced usage of the terminal application suitable for both regular and complex demands.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
A definitely interesting aspect of the mentioned feature is its drag & drop support, dragging a tab from one split and dropping it on another split, moves the tab on the other split and, thus, moves all commands and details from one side of the terminal to another preferred area of the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
The full article, including the programming-specific manner of implementing the handy features, is available on [http://blog.finalterm.org/2013/10/multiple-terminals-final-term-style.html][2]
|
||||
|
||||
Final Term's code is available on [https://github.com/p-e-w/finalterm][3]
|
||||
|
||||
**Worth mentioning**
|
||||
|
||||
At the moment, Final Term is work in progress.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/modern-terminal-final-term-adds-multiple-terminals-window-support
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://finalterm.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://blog.finalterm.org/2013/10/multiple-terminals-final-term-style.html
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/p-e-w/finalterm
|
||||
@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Rapid Photo Downloader 0.4.7 released with enhancements
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[Rapid Photo Downloader][1] is a free open-source powerful, versatile item downloader (photo and video), permitting to the user to download/copy images and videos from photography-wise devices,--as well as using regular folders from within the desktop--, to one's computer via a hassle-free, intuitive and robust experience.
|
||||
|
||||
A definitely interesting aspect of Rapid Photo Downloader is its nature, namely, being created by a photographer and, therefore, presenting itself as a photographer-centric utility with accordingly-exposed features and support.
|
||||
|
||||
Essentially, Rapid Photo Downloader allows the user to copy/move items from (for example) storage media used by photography machines, in order to remove the manual confuse manner of browsing through the photography machine' media and manually picking items.
|
||||
|
||||
Among its **features**, Rapid Photo Downloader comes with:
|
||||
|
||||
- auto-detection of camera-specific media via the Auto Detect button and exposing of contained items
|
||||
- ability to specify automatic file renaming with tweakable text (editable), date and time, filename, metadata, job code, sequences and real-time previews of to-be-generated item names
|
||||
- support to simultaneously download photos and images from multiple devices
|
||||
- optimized manner of rapidly downloading items
|
||||
- in-depth configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
Launching Rapid Photo Downloader, the user is to notice its elegant look centering clarity and user-friendliness, main window divided in three main areas: the top area housing `From` and `To`, middle area with items populating it and bottom-area featuring details and the actual `Download` button.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Copying (for example) items from a location to the `Pictures` and `Videos` folders is as simple as:
|
||||
|
||||
- under `From`, select the preferred source-like location (containing the about-to-be-copied items)
|
||||
- action that exposes the automatically-detected items on the dark middle-area
|
||||
- retaining the `Copy` button checked and hitting the bottom-bar's Download, downloads images to the `Pictures` folder and video-clips to `Videos`
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The result: by hitting the `Download` button, Rapid Photo Downloader automatically divides the photos from videos and copies images to a specific location and video-clips to a different location.
|
||||
|
||||
The about-to-be-copied items are checkable, allowing the user to uncheck certain files, files then fully ignored by the copying process.
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, the `Move` button is to be utilized for moving items from one location to another, action that removes the items from the source location and copies them to the new location (therefore, there is only one instance of the copied files).
|
||||
|
||||
Rapid Photo Downloader is a solid robust application, being able to successfully manage thousands of items, items properly exposed on its view, from where the user is able to act on them.
|
||||
|
||||
Rapid Photo Downloader has been updated to version **0.4.7**, introducing several fixes, including enhancements related to its usability under Ubuntu 13.10, as well as removed crashes and ability to download audio files associated with photos generated by specific cameras (such as Canon 1D series).
|
||||
|
||||
How do we **install** Rapid Photo Downloader 0.4.7?
|
||||
|
||||
Add the following **official** PPA (Ubuntu 12.04, Ubuntu 12.10, Ubuntu 13.04, Ubuntu 13.10, Ubuntu 14.04)
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:dlynch3/ppa
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install rapid-photo-downloader
|
||||
|
||||
In-depth **step-by-step** features, abilities and support are fully presented on [http://www.damonlynch.net/rapid/documentation/][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### Worth mentioning ###
|
||||
|
||||
While Rapid Photo Downloader 0.4.7 removes a bug affecting Ubuntu 13.10 and Ubuntu 12.10, there still may be likely for users to encounter freezes using Rapid Photo Downloader 0.4.7 under Ubuntu 13.10, situation in which the user is advised to use Rapid Photo Downloader under Ubuntu 12.04 (version unaffected by the mentioned bug).
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/rapid-photo-downloader-047-released-enhancements
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://damonlynch.net/rapid/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.damonlynch.net/rapid/documentation/
|
||||
@ -1,28 +0,0 @@
|
||||
SmartGit 5 Preview 4 Gets Some Greta Features
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**SmartGit, a graphical client for the version control systems Git and Mercurial with optimized workflows for multiple platforms, is now at version 5 Preview 4.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
SmartGit provides some very important features such as local working tree operations, push, pull, fetch for all protocols, tag and branch management, and much more.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the developers, the ability to configure multiple accounts even for the same provider has been added, the refresh toolbar button is now only enabled if a GitHub account is configured, Reveal Commit now also works on Pull Requests, notifications are a lot more obvious, and a lot more.
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the complete [changelog][1] for a list of bugfixes and other important new features.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download SmartGit (4.6.5 Stable) tar.gz][2][binary] [28 MB]
|
||||
- D[ownload SmartGit (5 Preview 4 Development) tar.gz][3][sources] [19 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
Remember that this is a development version and it should NOT be installed on production machines. It is intended for testing purposes only.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/SmartGit-5-Preview-4-Gets-Some-Greta-Features-393093.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.syntevo.com/smartgithg/changelog-eap.txt
|
||||
[2]:http://www.syntevo.com/smartgit/download.html?all=true
|
||||
[3]:http://www.syntevo.com/smartgithg/early-access?file=smartgithg/smartgithg-generic-5-preview-4.tar.gz
|
||||
@ -1,237 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating-------------------geekpi
|
||||
|
||||
03 The Linux Kernel: Drivers
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Drivers are small programs that enable the kernel to communicate and handle hardware or protocols (rules and standards). Without a driver, the kernel does not know how to communicate with the hardware or handle protocols (the kernel actually hands the commands to the BIOS and the BIOS passes them on the the hardware). The Linux Kernel source code contains many drivers (in the form of source code) in the drivers folder. Each folder within the drivers folder will be explained. When configuring and compiling the kernel, it helps to understand the drivers. Otherwise, a user may add drivers to the kernel that they do not need or leave out important drivers. The driver source code usually includes a commented line that states the purpose of the driver. For example, the source code for the tc driver has a single commented line that says the driver is for TURBOchannel buses. Because of the documentation, users should be able to look at the first few commented lines of future drivers to learn their purpose.
|
||||
|
||||
There are different terms that should be understood so that the information below is understandable. An I/O device is an Input/Output device. A modem and network card are examples of this; they send and receive data. A monitor is an output device - information only comes out. A keyboard, mouse, and joystick are input only - data goes into the system. Storage devices store data. Examples of these include SD cards, Hard-drives, CD-roms, memory cards, etc. The CPU (also called a processor) is the "brain" or "heart" of the computer. Without this single processing chip, the computer cannot function. A motherboard (mainboard) is a small board with printed circuits that connect to the components that are on the board. The board and the components are essential to the functionality of a computer. Many computer users say that the motherboard is the heart of the computer (the motherboard holds the CPU). The motherboard contains ports for peripherals. Peripherals include the input, output, and storage devices. A bus is the circuitry of the motherboard and connection to peripherals. Network devices deal with the connection of two or more computers. Ports are devices that users can plug another device or cable into. For example, users would plug a FireWire memory stick into a FireWire port; an Ethernet cable would go into an Ethernet port. Optical discs are read using lasers that read off of reflective surfaces that will either scatter or reflect the laser light. A common optical disk is the DVD. Many systems are 32-bit or 64-bit systems; this refers to the number of bits of registers, address buses, or data buses. For instance, on a 64-bit motherboard, the data buses (the silver lines going between components) have sixty-four lines running parallel to the same destination. Memory addresses are addresses to the memory in the form of bits (ones and zeros). So, a 32-bit memory address contains thirty-two ones and zeros that give the location of a spot on the memory.
|
||||
|
||||
Many of the drivers are generic driver meaning that a generic keyboard driver will allow the kernel to handle nearly every keyboard. However, some drivers are specialized. Apple and Commodore, for instance, have made specialized hardware for their Apple computer and Amiga system, respectively. The Linux kernel contains drivers for many devices like Smartphones, Apples, Amiga systems, Sony's Playstation3, Android tablets, and many others.
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that some drivers overlap categories. For instance, radio drivers exist in the net folder and the media directory.
|
||||
|
||||
**accessibility** - These drivers offer support for accessibility devices. In Linux kernel 3.9.4, only one driver is in this folder, and that is the braille device driver.
|
||||
|
||||
**acpi** - The Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) drivers manage power usage.
|
||||
|
||||
**amba** - Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture (AMBA) is a protocol for the management and interconnection in a System-on-Chip (SoC). A SoC is a single chip that contains many or all essential components of a computer in one chip. The AMBA drivers in this folder allow the kernel to run on these chips.
|
||||
|
||||
**ata** - This directory contains drivers for PATA and SATA devices. Serial ATA (SATA) is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to storage devices like hard-drives. Parallel ATA (PATA) is a standard for connecting storage devices like hard-drives, floppy drives, and optical disc drives. PATA is commonly known as IDE.
|
||||
|
||||
**atm** - Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a standard for telecommunications. There are a variety of drivers in here from PCI bridges (they connect to PCI buses) and Ethernet controllers (integrated circuit chip that controls Ethernet communications).
|
||||
|
||||
**auxdisplay** - This folder provides three drivers - LCD framebuffer driver, LCD Controller driver, and a LCD driver. These drivers manage Liquid Crystal Display monitors. LCD monitors are the screens that ripple when pressed. NOTE: The screen can be damaged when pressed, so do not poke of push on LCD screens.
|
||||
|
||||
**base** - This is an important directory that contains essential base drivers for firmware, the system bus, hypervisor abilities, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
**bcma** - These are drivers for buses that use a protocol that are based on the AMBA protocol. These new buses are made by Broadcom.
|
||||
|
||||
**block** - These drivers provide the kernel with support for block devices like floppy-disk readers, SCSI tapes, block devices over TCP, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
**bluetooth** - Bluetooth is a secure wireless standard for Personal Area Networks (PANs). The bluetooth drivers are in this folder and allow the system to use the different bluetooth devices. For example, a bluetooth mouse lacks a cable, and the computer has a dongle (small USB receiver). The Linux system must be able to understand the mouse signals that are coming in through the dongle. Otherwise, the bluetooth device would not work.
|
||||
|
||||
**bus** - This directory contains three drivers. One converts the ocp interface protocol to scp protocol. The other is a driver for interconnection between devices and the third driver is error handling for interconnection.
|
||||
|
||||
**cdrom** - Two drivers exist in this directory. One is for cd-roms - this includes reading and writing DVDs and CDs. The driver second is for gd-roms (Gigabyte Disc Read-Only Memory). A GD is an optical disc with a 1.2GB storage capacity. This is like a large CD or small DVD. GDs are commonly used in Dreamcast game consoles.
|
||||
|
||||
**char** - Character device drivers are stored here. Character devices transmit data one character at a time. Some included drivers in the folder are printers, PS3 flash ROM storage driver, Toshiba SMM drivers, and random number generator driver.
|
||||
|
||||
**clk** - These drivers are for the system clock.
|
||||
|
||||
**clocksource** - These drivers use the clock as a timer.
|
||||
|
||||
**connector** - These drivers supply the kernel with the ability to know when processes fork and execute as well as changing the UID (User ID), GID (Group ID), and SID (session ID) using what is called a proc connector. The kernel needs to know when process fork (run multiple tasks in the CPU) and execute. Otherwise, the kernel may have inefficiencies in managing resources.
|
||||
|
||||
**cpufreq** - These drivers control the CPU by changing power consumption.
|
||||
|
||||
**cpuidle** - These drivers manage the idleness of the CPU/s. If the system uses multiple CPUs, then one of the drivers will try to keep the idleness the same.
|
||||
|
||||
**crypto** - These drivers provide cryptographic features like encryption.
|
||||
|
||||
**dca** - Direct Cache Access drivers allow the kernel to access the CPU cache. The CPU cache is like a RAM storage built into the CPU chip. The CPU cache is faster than the RAM chip. However, the CPU cache has a much lower space capacity than the RAM. The CPU stores the most important and executed code on this cache system.
|
||||
|
||||
**devfreq** - This driver provides a Generic Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS) Framework which changes the CPU frequency as needed to conserve energy. This is known as CPU throttling.
|
||||
|
||||
**dio** - The Digital Input/Output bus drivers allow the kernel to use DIO buses.
|
||||
|
||||
**dma** - The Direct memory access (DMA) driver allows devices to access without needing the CPU. This reduces the load on the CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
**edac** - The Error Detection And Correction drives help reduce and correct errors.
|
||||
|
||||
**eisa** - The Extended Industry Standard Architecture drivers provide EISA bus support to the kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
**extcon** - The EXTernal CONnectors driver detects changes in the ports when a device is plugged in. For instance, extcon will detect if a user plugs in a USB drive.
|
||||
|
||||
**firewire** - These drivers control FireWire devices which are USB-like devices made by Apple.
|
||||
|
||||
**firmware** - These drivers communicate with the firmware of the device like the BIOS (the Basic Input Output System firmware of a computer). The BIOS is used to boot up the operating system and control the hardware and firmware of the device. Some BIOS systems allow user's to overclock the CPU. Overclocking is making the CPU operate at a faster speed. The CPU speed is measured in MHz (Mega-Hertz) or GHz. A CPU with a clock speed of 3.7GHz is significantly faster than a 700MHz processor.
|
||||
|
||||
**gpio** - General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) is a generic pin on a chip whose behavior can be controlled by the user. The drivers here control GPIO.
|
||||
|
||||
**gpu** - The drivers in this folder control the Video Graphics Array (VGA), Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), and Direct Rendering Manager (DRM). VGA is the 640×480 resolution analog computer displays or simply the resolution standard. A GPU is a processor for graphics. DRM is a rendering system for Unix systems.
|
||||
|
||||
**hid** - These drivers provide support for USB Human Interface Devices.
|
||||
|
||||
**hsi** - This driver offers the kernel the ability to access the cellular modem on the Nokia N900.
|
||||
|
||||
**hv** - These drivers provide Key Value Pair (KVP) functionality to Linux systems.
|
||||
|
||||
**hwmon** - The HardWare MONitoring drivers allow the kernel to get the readings from sensors in the hardware. For example, the CPU has a thermometer. The kernel can then keep track of the temperature and change the fan speed accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
**hwspinlock** - The hardware spinlock drivers allow systems to use two or more processors that are different or a single processor with two or more different cores.
|
||||
|
||||
**i2c** - I2C drivers enable the I2C protocol which handle low-speed peripherals attached to the motherboard. The System Management Bus (SMBus) driver manages SMBuses which is a single two-wire bus for lightweight communication.
|
||||
|
||||
**ide** - These drivers are for PATA/IDE devices like cdroms and hard-drives.
|
||||
|
||||
**idle** - This driver manages the idleness of Intel processors.
|
||||
|
||||
**iio** - The Industrial I/O core drivers handle analog to digital or digital to analog converters.
|
||||
|
||||
**infiniband** - Infiniband is a high-performance port used by enterprise datacenters and some supercomputers. The drivers in this directory support Infiniband hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
**input** - This directory contains many drivers. All of the drivers deal with input and some include drivers for joysticks, mice, keyboards, gameport (old joystick connectors), remotes, haptic controllers, headphone buttons, and many others. Joysticks today use USB ports, but in the 1980s and 1990s, joysticks plugged into gameports.
|
||||
|
||||
**iommu** - Input/Output Memory Management Unit (IOMMU) drivers manage the IOMMU which is a form of Memory Management Unit (MMU). The IOMMU connects a DMA-capable I/O bus to the RAM. The IOMMU is the bridge between devices and access to the RAM without help from the CPU. This helps to reduce the processors load.
|
||||
|
||||
**ipack** - Ipack stands for IndustryPack. This driver is for a virtual bus that allows operations between carrier and mezzanine boards.
|
||||
|
||||
**irqchip** - These drivers allow interrupt requests (IRQ) which are hardware signals sent to the processor that temporarily stop a running program for a special program(called an interrupt handler) to run instead.
|
||||
|
||||
**isdn** - These drivers support Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) which is a set of communication standards for simultaneous digital transmission of voice, video, data, and other network services using traditional circuits of the telephone network.
|
||||
|
||||
**leds** - These drivers support LEDS.
|
||||
|
||||
**lguest** - The lguest drivers manage interrupts that are used with guest operating system. Interrupts are hardware or software signals that interrupt the CPU for important tasks. The CPU then gives the hardware or software some processing resources.
|
||||
|
||||
**macintosh** - Drivers for Apple devices belong in this directory.
|
||||
|
||||
**mailbox** - The driver in this folder (pl320-pci) manages connections for mail systems.
|
||||
|
||||
**md** - The Multiple Devices driver supports RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) - a system of many hard-drives sharing or replicating data.
|
||||
|
||||
**media** - The media drivers offer support in radios, tuners, video capturers, DVB standards for digital television, etc. The drivers also support various media devices that plug in through USB or FireWire ports.
|
||||
|
||||
**memory** - This important driver supports the RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
**memstick** - This driver supports Sony memorysticks.
|
||||
|
||||
**message** - These drivers are to be used with LSI PCI chip/adapter(s) running LSI Fusion MPT (Message Passing Technology) firmware. LSI stands for Large-Scale Integration which are integrated circuits with tens of thousands of transistors per chip.
|
||||
|
||||
**mfd** - MultiFunction Device (MFD) drivers provide support for multifunction devices which are devices that provide multiple services like email, fax, copy machine, scanner, and printer. The drivers in here also add a generic MCP (Multimedia Communications Port) layer which is a protocol for MFDs.
|
||||
|
||||
**misc** - This directory contains miscellaneous drivers that do not fit in any other category like light sensor drivers.
|
||||
|
||||
**mmc** - MultiMediaCard (MMC) drivers handle the MMC standard that is used in flash memory cards.
|
||||
|
||||
**mtd** - Memory technology devices (MTD) are drivers used in Linux for interacting with flash memory like a Flash Translation Layer. Other block and character drivers do not map the same way flash memory devices operate. Although USB memory cards and SD cards are flash drives, they do not use this driver because they are hidden from the system behind a block device interface. This driver is a generic flash drive driver for new flash devices.
|
||||
|
||||
**net** - The network drivers provide network protocols like Appletalk, TCP, and others. The drivers also support modems, USB 2.0 Ethernet Devices, and radio devices.
|
||||
|
||||
**nfc** - This driver is the interface between Texas Instrument's Shared Transport Layer and NCI core.
|
||||
|
||||
**ntb** - The Non-Transparent Bridging driver provides non-transparent bridging in PCI express (PCIe) systems. PCIe is a high-speed expansion bus standard.
|
||||
|
||||
**nubus** - NuBus is a 32-bit parallel computer bus. The driver supports this Apple device.
|
||||
|
||||
**of** - This driver provides OF helpers which are procedures for creating, accessing and interpreting the device tree. The Device Tree is a data structure for describing hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
**oprofile** - This driver profiles the whole system from drivers to user-space processes (applications running under the user's name). This helps developers find performance problems.
|
||||
|
||||
**parisc** - These drivers are for PA-RISC devices which are made by HP. PA-RISC is a specific instruction set for processors.
|
||||
|
||||
**parport** - The Parport drivers provides parallel-port support under Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
**pci** - These drivers offer PCI bus services.
|
||||
|
||||
**pcmcia** - These are laptop motherboard drivers.
|
||||
|
||||
**pinctrl** - These drivers handle pin control devices. Pin controllers can disable and enable I/O devices.
|
||||
|
||||
**platform** - This directory contains drivers for the different computer platforms like Acer, Dell, Toshiba, IBM, Intel, ChromeBooks, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
**pnp** - The Plug-aNd-Play drivers allow users to plug in a device, like a USB device, and use it immediately without the need to manually configure the device.
|
||||
|
||||
**power** - The power drivers allow the kernel to measure the battery power, detect chargers, and power management.
|
||||
|
||||
**pps** - Pulse-Per-Second drivers control an electrical pulse rate that is used for time keeping.
|
||||
|
||||
**ps3** - These are the drivers for Sony's game console - Playstation3.
|
||||
|
||||
**ptp** - Picture Transfer Protocol (PTP) drivers support a protocol for transferring images from digital cameras.
|
||||
|
||||
**pwm** - Pulse-width modulation (PWM) drivers control the pulse of the electricity to devices, mainly motors like the CPU fan.
|
||||
|
||||
**rapidio** - RapidIO drivers manage the RapidIO architecture which is a high-performance packet-switched, interconnect technology for interconnecting chips on a circuit board, and also circuit boards to each other using a backplane.
|
||||
|
||||
**regulator** - The regulator drivers regulate the electricity, temperature, and any other regulator hardware that may exist on a system.
|
||||
|
||||
**remoteproc** - These drivers manage remote processors.
|
||||
|
||||
**rpmsg** - These drivers control Remote Processor MeSsaginG buses which can support a number of drivers. These buses supply the messaging infrastructure, facilitating client drivers to write their own wire-protocol messages.
|
||||
|
||||
**rtc** - The Real Time Clock (RTC) drivers allow the kernel to read the clock.
|
||||
|
||||
**s390** - The drivers are for the 31/32-bit mainframe architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
**sbus** - The SPARC-based buses are managed by these drivers.
|
||||
|
||||
**scsi** - SCSI drivers allow the kernel to use the SCSI standard with peripheral devices. For instance, Linux would be using a SCSI driver when it transmits data with a SCSI hard-drive.
|
||||
|
||||
**sfi** -The Simple Firmware Interface (SFI) drivers allow firmware to send tables of information to the operating system. These tables of data are called SFI tables.
|
||||
|
||||
**sh** - These drivers are for SuperHyway buses.
|
||||
|
||||
**sn** - These drivers add support for IOC3 serial ports.
|
||||
|
||||
**spi** - These drivers handle the Serial Peripheral Interface Bus (SPI bus) which is a synchronous serial data link standard that operates in full duplex mode. Full duplex mode is seen when two devices can both send and receive information at the same time. Duplex refers to two-way communication. Devices communicate in master/slave mode (device configuration).
|
||||
|
||||
**ssb** - Sonics Silicon Backplane drivers provide support for a mini-bus used on various Broadcom chips and embedded devices.
|
||||
|
||||
**staging** - This directory contains numerous subdirectories with many drivers. All of the contained drivers are drivers that need more development before being added to the mainstream kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
**target** - These are drivers for SCSI targets.
|
||||
|
||||
**tc** - These are drivers for TURBOchannel. TURBOchannel is a 32-bit open bus developed by the Digital Equipment Corporation. These buses are commonly used in DECstations.
|
||||
|
||||
**thermal** - The thermal drivers make sure that the CPU stays cool.
|
||||
|
||||
**tty** - The tty drivers manage the connection to a physical terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
**uio** - This driver allows the user to make drivers that run in the user space instead of the kernel space. This keeps the user's driver from causing the kernel to crash.
|
||||
|
||||
**usb** - The USB drivers allow the kernel to use USB ports. Flash drivers and memory cards already contain firmware and a controller, so these drivers allow the kernel to use the USB ports and talk to the USB device.
|
||||
|
||||
**uwb** - The Ultra-WideBand driver manages very low energy level radio devices for short-range, high-bandwidth communications.
|
||||
|
||||
**vfio** - The VFIO driver allows devices to access the userspace.
|
||||
|
||||
**vhost** - This driver is for a virtio server in the host kernel. This is used for virtualization.
|
||||
|
||||
**video** - Video drivers are needed to manage the graphics card and monitor.
|
||||
|
||||
**virt** - These drivers are for virtualization.
|
||||
|
||||
**virtio** - This driver allows virtio devices to be used over a virtual PCI device. This is used for virtualization.
|
||||
|
||||
**vlynq** - This driver controls a proprietary interface developed by Texas Instruments. These are broadband products, like WLAN and modems, VOIP processors, and audio and digital media processor chips.
|
||||
|
||||
**vme** - VMEbus is a bus standard originally developed for the Motorola 68000 line of processors.
|
||||
|
||||
**w1** - These drivers control one-wire buses.
|
||||
|
||||
**watchdog** - This driver manages the watchdog timer which is a timer that is used to detect and recover from malfunctions.
|
||||
|
||||
**xen** - This driver is for the Xen hypervisor system. A hypervisor is software or hardware that allows users to run multiple operating systems on a single computer. This means that the xen code would allow users to have two or more Linux system running on one computer at the same time. Users could also run Windows, Solaris, FreeBSD, or some other operating system on the Linux system.
|
||||
|
||||
**zorro** - This driver offers support for the Zorro Amiga buses.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-drivers.4205/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
4
sources/The Linux Kernel/04 The Linux Kernel--Security.md
Normal file → Executable file
4
sources/The Linux Kernel/04 The Linux Kernel--Security.md
Normal file → Executable file
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
Translating--------------geelpi
|
||||
|
||||
04 The Linux Kernel: Security
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
@ -34,4 +36,4 @@ via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-security.4223/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,101 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 ‘Saucy Salamander’ Final has been released! | Installation Instructions With Screenshots
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Finally, the most expected distribution in Linux World, **Ubuntu 13.10 ‘Saucy Salamander’** final has been released, there is **no official release announcement yet**, but the [download page of Saucy has been updated][1] with the final packages. Just like most of you, We also expected it very long. This awesome distribution has come with plenty of new features and improvements.
|
||||
|
||||
**Download**
|
||||
|
||||
- **[Download Ubuntu 13.10 ‘Saucy Salamander’][1]**
|
||||
|
||||
If you have already a previous release of Ubuntu, and want to upgrade to the latest 13.10 version, then please follow our [step by step guide upgrade to Ubuntu 13.10 Saucy Salamander][2].
|
||||
|
||||
You can also Download the Getting Started Manual from the following link.
|
||||
|
||||
- **[Getting Started With Ubuntu 13.10][3]**
|
||||
|
||||
**What’s New in Ubuntu 13.10?**
|
||||
|
||||
- Kernel 3.11
|
||||
- Unity 7
|
||||
- Search hundreds of different online sources directly from the Dash.
|
||||
- Filter Dash results in several different ways.
|
||||
- [Smart Scopes][5]
|
||||
- Add or remove scopes from the Dash to customize your experience.
|
||||
- Browse messages from your social networks with the new Friends scope.
|
||||
- Comes with the latest OpenStack cloud platform (Code name: Havana).
|
||||
- Enhanced support for Linux Containers ([LXC][6]).
|
||||
- Get work done in style with LibreOffice 4.0, now with new, modern presentation templates and built-in support for Ubuntu’s integrated menu bar.
|
||||
|
||||
**Install steps of Ubuntu 13.10 for Newbies**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Press Continue:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Choose the first option and continue:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Here we have 3 options:
|
||||
|
||||
1- Install Ubuntu alongside them, this mean if you have windows installed on your hard drive, ubuntu will be installed alongside windows.
|
||||
|
||||
2- Erase Disk and install Ubuntu : **Be careful** because choosing this option will erase all the data on your hard disk. Only use it if you are testing in an old computer or if you have an empty hard drive
|
||||
|
||||
3- Something else: You can use this option if you have many partitions on your hard drive, use the empty one then to install Ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you choosed “something else” in the previous screen, You will got this screen, as you see in my case i chooses the free space on my hard disk :
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Choose your language:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enter your name, username, password …etc.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you don`t have an Ubuntu One account, choose “Login Later”.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Installation will start now.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now installation is done. Press reboot and enjoy the new release of Ubuntu 13.10 Saucy Salamander.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ok, you have successfully installed Ubuntu 13.10, What’s now? Well, We have made a comprehensive guide about [Top things to do after installing Ubuntu 13.10 Saucy Salamander][6]. This guide will help you to enhance Ubuntu 13.10 further for day to day activities and it contains lot of interesting insight and ideas about what you can and should do after a successful installation.
|
||||
|
||||
Still having some issues? well, don’t hesitate to contact us via [our brand new forum][7] or [IRC chat channel][8].
|
||||
|
||||
Cheers!!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/ubuntu-13-10-saucy-salamander-released-screenshots/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/saucy/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.unixmen.com/upgrade-ubuntu-13-04-raring-ubuntu-13-10-saucy-salamander/
|
||||
[3]:http://ubuntu-manual.org/
|
||||
[4]:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/SmartScopes1304Spec
|
||||
[5]:http://lxc.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.unixmen.com/top-things-installing-ubuntu-13-10/
|
||||
[7]:http://ask.unixmen.com/BB/
|
||||
[8]:http://ask.unixmen.com/BB/chat.php
|
||||
@ -1,65 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10: It just works
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Find out why Jack Wallen thinks that Ubuntu 13.10 is a solid, reliable platform that just works. Do you agree? **
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
I've been using Ubuntu for a very long time. I was one of the few in the media who adopted Unity as my primary desktop interface. In fact, I've grown so used to Unity that I have trouble finding any form of efficiency in other desktops. So, naturally, when a new Ubuntu release is about to be unleashed upon the world, I grab a beta and install it.
|
||||
|
||||
The hype surrounding the upcoming 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) was fairly significant. Leading this charge was the much-anticipated switch to Xmir. Well, thanks to a few show-stopping issues (such as dual-monitor support), Xmir has been pushed back to 14.04. Is this a big deal? Yes and no. Yes, because Xmir will be a major change to the sub-systems of Ubuntu. No, because Xmir must be faultless when released -- otherwise, the backlash will knock Canonical back so far in the past that they'll have a hard time recovering in the eyes of the Linux community.
|
||||
|
||||
Beyond Xmir, the biggest change from .04 to .10 is the much-maligned inclusion of Smart Scopes. What are Smart Scopes? Let me explain it in the simplest terms as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
When you open your browser and begin typing a string of characters, you know how that browser will make suggestions for you based on search terms, location, and history? Smart Scopes brings that same functionality to the desktop. I've run some tests on it, and it's pretty incredible. Search for nearly anything, and it will return results based on a number of criteria. Want to know the location of a restaurant in your area? I conducted a search for my favorite Mexican restaurant, Bazos, and an entry appeared in Smart Scopes (**Figure A**). Click the entry to get the address or open that entry in a web browser to get more information (and even reviews).
|
||||
|
||||
**Figure A**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**My favorite place to eat listed in Smart Scopes.**
|
||||
|
||||
I get it, there are people out there suffering from apoplectic fits of terror because Smart Scopes is an invasion of privacy. This is no different than what your web browser is doing. So, unless you constantly run your web browser in Incognito mode, all those search strings are saved and compared anyway. And the truth is, why wouldn't you want your search results based on your preferences and behavior instead of some generic algorithm? Personally, I don't mind my search results being quantified and qualified, so long as it constantly refines the search results based on my needs.
|
||||
|
||||
Smart Scopes isn't limited to seeking out search results from the network. You'll be happily searching for anything and everything on your local (or locally attached) drives as well. With this inclusion, Smart Scopes becomes one of the single most powerful search tools available.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, if you don't like Smart Scopes, you can turn them off. Here's how:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Click the Settings launcher
|
||||
1. Select Security & Privacy
|
||||
1. In the Search tab, turn Include online search results to Off (**Figure B**)
|
||||
|
||||
**Figure B**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**It's easy to turn off the Smart Scopes feature.**
|
||||
|
||||
With all of that said, let's step away from the arguments for or against search privacy and let me explain exactly why Ubuntu 13.10 is the perfect desktop for nearly any user.
|
||||
|
||||
The install was fresh from the latest daily build. During the installation, I included third-party software, updates, and was even able to authenticated to my UbuntuOne account. The install was incredibly simple (as most modern Linux distributions are), and at first login, everything was smooth.
|
||||
|
||||
What initially struck me about Ubuntu 13.10 is how everything worked out of the box. There was no need to install codecs to listen or view various multi-media files, flash worked, and everything was ready for average, daily computer use. You could work on office documents, set up your email account... you name it. But that has become the standard operating procedure for Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
So, what's different? Honestly, not much. However, what little difference there is should go a long way with the average user. Probably the single most important thing I've found is that a lot of the little quirks and oddities are gone. There are no longer any strange errors that randomly pop up to cause confusion and disdain among new users. Windows don't artifact or stall, the Dash is very responsive (as is Smart Scopes), and the compositing is smooth and effortless against your CPU. Also, the bug is resolved that plagued the Dash when trying to use the arrow keys to navigate through search results.
|
||||
|
||||
## Ubuntu 13.10 just works ##
|
||||
|
||||
I would go as far to say that Ubuntu has done to the desktop what Apple did with hardware/software -- it developed a clean, solid convergence of pieces to create a cohesive whole. Although that whole has ruffled some feathers, Ubuntu 13.10 should go a long way to smooth them out. How is that possible, considering how many users have turned their back (thanks to [the Wayland kerfuffle][1])?
|
||||
|
||||
Outside of Smart Scopes, there are no major changes. There's little excitement on the desktop -- it's still the same old look and feel. Oh sure, there are tiny tweaks here and there, but overall, 13.10 and 13.04 look the same at first blush. Under the hood? Same thing. You'll find a new kernel (3.11) and a few other tweaks, but nothing to cause the cheerleaders of the world to frustratingly toss their pompoms in the air.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, Ubuntu 13.10 is a refinement of something that was already there and polished. There are no show stopping or curtain call worthy new features -- just countless tweaks here and there that make the whole system run smooth and fast.
|
||||
|
||||
The final release of Saucy Salamander is set for October 17, 2013. You can get a copy of the [daily build][2] or wait for the release date. Either way, you're going to get a solid, reliable platform that just works.
|
||||
What are your thoughts about Saucy Salamander? Share your opinion in the discussion thread below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.techrepublic.com/blog/linux-and-open-source/ubuntu-1310-it-just-works/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.techrepublic.com/blog/linux-and-open-source/the-canonical-conundrum-why-the-ubuntu-hate/
|
||||
[2]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/daily-live/current/
|
||||
@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu Mobile icon theme sees new icons
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Unity 8, Web Browser App, Friends App, Ubuntu SDK are pieces of the upcoming Ubuntu converged, pieces that are gradually forming the whole,--the convergence-enabled Ubuntu--, with a constantly-maintained vigorous development covering all the pieces via a consistent uniform development energy.
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu Mobile** is a fancy icon theme used by Ubuntu Touch, icon theme presently containing relevant icons for used actions and applications, progressively being expanded to cover the Ubuntu Touch's needs.
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Mobile has been updated to another release, adding new icons, among which icons located under the actions category.
|
||||
|
||||
`Add-to-call`, `browser-timeline`, `calendar`, `calendar-today`, `dropdown-menu`, `external-link`, `media-playlist-repeat`, `media-playlist-shuffle`, `navigation-menu`, `new-event`, `remove-from-call` are among the newly-introduced icons`, new icons increasing the available actions and buttons of the growing and growing Ubuntu Mobile theme.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Mobile (while being used in Ubuntu Touch by default) is [available][1] for installation via Ubuntu 13.10's Ubuntu Software Center.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/ubuntu-mobile-icon-theme-sees-new-icons
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:apt://ubuntu-mobile-icons
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
VirtualBox 4.3 comes with New Multi-Touch Support, virtual cam and more
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Oracle announced [the release of VirtualBox 4.3][1], this is a major release that comes with important new features, devices support and improvements. According to the announcement, “*Oracle VM VirtualBox 4.3 adds a unique virtual multi-touch interface to support touch-based operating systems, and other new virtual devices and utilities, including webcam devices and a session recording facility. This release also builds on previous releases with support for the latest Microsoft, Apple, Linux and Oracle Solaris operating systems, new virtual devices, and improved networking functionality.* “
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
What`s new in VirtualBox 4.3:
|
||||
|
||||
- **New operating system platform support**: Oracle VM VirtualBox 4.3 supports the input device features, of the latest platforms such as Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2 and Mac OS X 10.9 in a virtual environment. For Windows 8.1, the new release can also simulate a 10 point multi-touch device. Additionally, improved 3D acceleration accommodates the translucent effects in the latest Linux distributions from Ubuntu and Fedora, and enhanced multi-monitor support allows users with multiple screens to use them from within the virtual environment.
|
||||
- **New devices and management utilities**: A new virtual USB webcam device enables video conferencing applications such as Skype or Google Hangouts to run in virtual machines. New recording session capabilities allow users to record part, or all, of a virtual machine session using a new video-capture facility. For easy playback, movies are created in WebM format by a range of movie-players.
|
||||
- **Networking improvements**: A new Network Address Translation (NAT) option allows virtual machines to talk to each other on the same host, and communicate with the outside world. IPv6 is now offered across Bridged, Host-only, Internal and the new NAT networking modes. In addition, the remote display server built-in to Oracle VM VirtualBox can accommodate RDP connections over IPv4 and IPv6 networks.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation: ##
|
||||
|
||||
For Ubuntu, Fedora, LinuxMint, Debian, Open Suse and Mandriva, You can download the new release and the Guest additions pack from [this Link][2] . (You need to download the package related to your distro version)
|
||||
|
||||
For Ubuntu via repository:
|
||||
|
||||
To start the installation, first open a terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
Copy and paste the following in to your command-line. Press Enter to download and install key from Oracle. Type user password and press Enter to continue:
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget -q http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/debian/oracle_vbox.asc -O- | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
|
||||
After Oracle’s Public Key has been downloaded and installed successfully you will see an OK message in the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
Now run this command to add VirtualBox to your repository:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/debian raring contrib" >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/virtualbox.list'
|
||||
|
||||
When prompted, input password and press Enter.
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, run the combined command below to update your system and install VirtualBox.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install virtualbox-4.3
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/virtualbox-4-3-released/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.oracle.com/us/corporate/press/2033376?rssid=rss_ocom_pr
|
||||
[2]:http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/server-storage/virtualbox/downloads/index.html?ssSourceSiteId=ocomen#vboxhttp://
|
||||
@ -1,265 +0,0 @@
|
||||
翻译中 Luox
|
||||
di – Disk Information Utility, Better Than df
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
If you are a Linux command line user, you would have definitely used the df command to check disk usage for file systems. Though df is a popular command but still it does not provide some advanced features like actual disk space that is available to a user, various useful display formats etc. There is another command line utility available that not only provides these advanced features but also all the features that df provides. In this article, we will discuss the disk information utility — **di**.
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE** – If you want to more about df, check out [the df command tutorial][1].
|
||||
|
||||
### di – The Disk Information Utility ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It is evident from this snapshot of di’s manual page that this utility provides some valuable features and hence makes it worth using. Lets try out some practical examples of this utility.
|
||||
|
||||
### Testing Environment ###
|
||||
|
||||
- OS – Ubuntu 13.04
|
||||
- Shell – Bash 4.2.45
|
||||
- Application – di 4.30
|
||||
|
||||
### A Brief Tutorial ###
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some of the examples of di utility :
|
||||
|
||||
**1. The Default Output**
|
||||
|
||||
By default di command produces output in human readable format.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example :
|
||||
|
||||
$ di
|
||||
Filesystem Mount Size Used Avail %Used fs Type
|
||||
/dev/sda6 / 28.1G 20.2G 6.5G 77% ext4
|
||||
udev /dev 1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% devtmpfs
|
||||
tmpfs /run 300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
|
||||
So you can see that the disk usage figures are displayed in gigabytes (G) and Megabytes(M). This is definitely better than the default output that df produces.
|
||||
|
||||
**2. Print All Fields Like Mount Points, Special Device Names etc Using – A Option**
|
||||
|
||||
The option -A can be used to print mount points, special device names etc at full length.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example :
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -A
|
||||
Mount fs Type Filesystem
|
||||
Options
|
||||
Size Used Free %Used %Free
|
||||
Size Used Avail %Used %Free
|
||||
Size Used Avail %Used
|
||||
Inodes Iused Ifree %Iused
|
||||
/ ext4 /dev/sda6
|
||||
rw,errors=remount-ro
|
||||
28.1G 20.2G 8.0G 72% 28%
|
||||
28.1G 21.6G 6.5G 77% 23%
|
||||
26.7G 20.2G 6.5G 75%
|
||||
1884160 389881 1494279 21%
|
||||
/dev devtmpfs udev
|
||||
rw,mode=0755
|
||||
1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% 100%
|
||||
1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% 100%
|
||||
1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0%
|
||||
381805 571 381234 0%
|
||||
/run tmpfs tmpfs
|
||||
rw,noexec,nosuid,size=10%,mode=0755
|
||||
300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% 100%
|
||||
300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% 100%
|
||||
300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0%
|
||||
384191 549 383642 0%
|
||||
|
||||
So you can see that all the fields — that can also be used for debugging purposes — are printed in the output.
|
||||
|
||||
**3. Print All Mounted Devices Using -a Option**
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example :
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -a
|
||||
Filesystem Mount Size Used Avail %Used fs Type
|
||||
/dev/sda6 / 28.1G 20.2G 6.5G 77% ext4
|
||||
udev /dev 1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% devtmpfs
|
||||
devpts /dev/pts 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% devpts
|
||||
proc /proc 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% proc
|
||||
binfmt_misc /proc/sys/fs/bi 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% binfmt_misc
|
||||
tmpfs /run 300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /run/lock 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /run/shm 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /run/user 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
gvfsd-fuse /run/user/himan 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% fuse.gvfsd-fuse
|
||||
sysfs /sys 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% sysfs
|
||||
none /sys/fs/cgroup 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /sys/fs/fuse/co 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% fusectl
|
||||
none /sys/kernel/deb 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% debugfs
|
||||
none /sys/kernel/sec 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% securityfs
|
||||
|
||||
So you can see that all the information related to all the mounted devices was printed.
|
||||
|
||||
**4. Print Comma Separated Values Through -c Option**
|
||||
|
||||
The option -c can be used to print command separated values enclosed with double quotes.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example :
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -c
|
||||
s,m,b,u,v,p,T
|
||||
/dev/sda6,/,"28.1G","20.2G","6.5G",77%,ext4
|
||||
udev,/dev,"1.5G","0.0G","1.5G",0%,devtmpfs
|
||||
tmpfs,/run,"300.2M","0.9M","299.3M",0%,tmpfs
|
||||
|
||||
So you can see that the comma separated values were printed in the output.
|
||||
|
||||
**5. Print Size In Gigabytes Through -g Option**
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example :
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -g
|
||||
Filesystem Mount Gibis Used Avail %Used fs Type
|
||||
/dev/sda6 / 28.1 20.2 6.5 77% ext4
|
||||
udev /dev 1.5 0.0 1.5 0% devtmpfs
|
||||
tmpfs /run 0.3 0.0 0.3 0% tmpfs
|
||||
|
||||
So you can see that all the size related values were printed in gigabytes.
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly you can use -k and -m options to display the size in kilobytes and megabytes respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
**6. Display Information Related To Specific File-system Type Through -I Option**
|
||||
|
||||
Suppose you want to display disk information related to only tmpfs filesystems. Here is how you can do it through -I option :
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -I tmpfs
|
||||
Filesystem Mount Size Used Avail %Used fs Type
|
||||
tmpfs /run 300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /run/lock 5.0M 0.0M 5.0M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /run/shm 1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /run/user 100.0M 0.0M 100.0M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
none /sys/fs/cgroup 0.0M 0.0M 0.0M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
|
||||
So you can see that information related to only tmpfs type file systems was displayed in the output.
|
||||
|
||||
**7. Skip The Header Line In Output Through -n Option**
|
||||
|
||||
If you are trying to parse the output of this command through a script (or a program) and want the di command to skip the display of header line then it can be made possible through -n option.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example :
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -n
|
||||
/dev/sda6 / 28.1G 20.2G 6.5G 77% ext4
|
||||
udev /dev 1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% devtmpfs
|
||||
tmpfs /run 300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
|
||||
So you can see that the header line was not displayed in the output.
|
||||
|
||||
**8. Print A Totals Line Below The List Of Filesystems Through -t Option**
|
||||
|
||||
If it is desired to display the totals of all the relevant columns, use -t option.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example :
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -t
|
||||
Filesystem Mount Size Used Avail %Used fs Type
|
||||
/dev/sda6 / 28.1G 20.2G 6.5G 77% ext4
|
||||
udev /dev 1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% devtmpfs
|
||||
tmpfs /run 300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
Total 29.9G 20.2G 8.3G 72%
|
||||
|
||||
Observe that the last row consists of the totals of values for all file systems.
|
||||
|
||||
**9. Sort The Output Through -s Option**
|
||||
|
||||
The option -s can be used to sort the output of this command.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how you can reverse sort the output :
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -sr
|
||||
Filesystem Mount Size Used Avail %Used fs Type
|
||||
tmpfs /run 300.2M 0.9M 299.3M 0% tmpfs
|
||||
udev /dev 1.5G 0.0G 1.5G 0% devtmpfs
|
||||
/dev/sda6 / 28.1G 20.2G 6.5G 77% ext4
|
||||
|
||||
So you can use the sub-option ‘r’ along with -s to reverse sort the output.
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, you can do several other types of sorts using -s option. Here is an excerpt from the man page for your reference:
|
||||
|
||||
-s sort-type
|
||||
Use sort-type to sort the output. The out‐
|
||||
put of di is normally sorted by mount
|
||||
point. The following sort flags may be
|
||||
used to change the sort order: m – by mount
|
||||
point (default); n – leave unsorted (as it
|
||||
appears in the mount table); s – by special
|
||||
device name; t – by filesystem type; r -
|
||||
reverse the sort order.
|
||||
|
||||
These sort options may be combined in any
|
||||
order. e.g.: di -stsrm – by type, special,
|
||||
reversed mount; di -strsrm – by type,
|
||||
reversed special, mount.
|
||||
|
||||
**10. Specify Output Format Strings Through -f Option**
|
||||
|
||||
You can specify the output format string through a combination of -f option and a sub-option.
|
||||
|
||||
For instance, to print the name of the mount point, use -fm.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example :
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -fm
|
||||
Mount
|
||||
/
|
||||
/dev
|
||||
/run
|
||||
|
||||
So you can see that only mount names were printed in the output.
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, to print file system type, use -ft.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example :
|
||||
|
||||
$ di -ft
|
||||
fsType
|
||||
ext4
|
||||
devtmpf
|
||||
tmpfs
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to have a quick look then here is a snapshot of other formatting options available :
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For complete set of options, refer to the [man page of di command][2].
|
||||
|
||||
### Download/Install ###
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some of the important links related to di command :
|
||||
|
||||
- [Home Page][3]
|
||||
- [Download Link][4]
|
||||
|
||||
The command line utility di can also be downloaded and installed through command line by using apt, yum etc. Ubuntu users can download this command from Ubuntu Software Centre too.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pros ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Provides many advanced features
|
||||
- OS independent
|
||||
|
||||
### Cons ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Does not come pre-installed on most of the Linux distributions
|
||||
- Lots of option to learn
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
To conclude, di command provides some very useful features over and above what df command provides. If you are looking for a df-like but advanced disk information related command line utility then di is the ideal choice. Try it out, it does what it promises.
|
||||
|
||||
**Have you ever tried di or any other df-like utility? Share your experience with us.**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://mylinuxbook.com/di-a-disk-information-utility/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.expertslogin.com/linux-command/linux-df-command/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.manpagez.com/man/1/di/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.gentoo.com/di/
|
||||
[4]:http://freecode.com/projects/diskinfo
|
||||
@ -1,50 +0,0 @@
|
||||
‘Polari’ – An Awesome New IRC App for GNOME
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
You have to hand it to the GNOME designers and developers: their work in creating a coherent, integrated set of apps for the desktop is showing true promise.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*The latest build of Polari in action.*
|
||||
|
||||
In fact, they’ve barely sat still over the last couple of years, creating app after app.
|
||||
|
||||
There are now dedicated apps for Music, Video and Photos; a virtual machine manager in the shape of Boxes; the Maps, Weather & Notes tools are all looking fantastic. And the new GNOME Software Store? Design wise it knocks Ubuntu’s aged offering out of the park!
|
||||
|
||||
But it seems that the GNOME app gurus aren’t done yet. Work has recently begun on a new GNOME 3 IRC app called ‘Polari’.
|
||||
|
||||
(As an aside, it’s a testament to the focus within the GNOME development community on putting users first that the one tool they likely use most often to communicate is one of the last to get the GNOME app treatment.)
|
||||
|
||||
## Polari – Planned Features ##
|
||||
|
||||
It’s not fixed in a dusty coding tome that all IRC clients have to resemble something from an 80s sci-fi movie, or be intimidating to the general user. Even in today’s world of instant communications via social networks, IRC remains a great way for people to chat.
|
||||
|
||||
To this end, if [Polari][1] (expect a name change further down the line) had a slogan it would be “*An IRC client for dummies*.”
|
||||
|
||||
On the features n’ functionality front Polari aims to offer:
|
||||
|
||||
- Easy connection to IRC servers & rooms
|
||||
- Clearly see mentions & notifications
|
||||
- Support GNOME 3 notifications
|
||||
- Integration with Contacts, the GNOME contacts app
|
||||
- History & transcript features
|
||||
- Link previews
|
||||
- File transfers
|
||||
|
||||
Developer-orientated features have also been mooted, including integrated support for Pastebin & Bugzilla.
|
||||
|
||||
So when can you try it? Not quite yet. Development of Polari is still in its early stages, but, if you’re willing to build it from Git (requires GNOME 3.10) you’ll find that it’s already capable of handling the basics, including delivering notifications for mentions.
|
||||
|
||||
For code-compiling-phobes Polari is expected to feature (most likely as an app preview) in GNOME 3.12, due next year.
|
||||
|
||||
- [More about Polari][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/10/gnome-irc-app-polari-in-development
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://git.gnome.org/browse/polari
|
||||
[2]:https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Polari
|
||||
@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
|
||||
"Performance, refinement, maintainability, technical debt, improving quality" and "we’re going to keep racing forward" to characterize Ubuntu 14.04's development cycle
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 was released yesterday, Ubuntu 13.10 allowing users to utilize an up-to-date optimized Ubuntu release with gains in agility, fluidity and an overall solid look & feel.
|
||||
|
||||
Starting of today, the natural flow of the developers is Ubuntu 14.04-centric, version being an LTS and, therefore, receiving a special treatment following Ubuntu's values and strategies.
|
||||
|
||||
**Mark Shuttleworth** [announced][1] hours ago the new name of Ubuntu 14.04 LTS, Trusty Tahr, interesting article presenting the focus on the 14.04 LTS version, too.
|
||||
|
||||
Among the to-be-followed directions, Mark Shuttleworth talked about and listed performance, refinement, maintainability and technical debt, while adopting a more conservative approach in creating, shaping and delivering Trusty, "it would be entirely appropriate for us to make **conservative choices**".
|
||||
|
||||
The conservative nature of Ubuntu 14.04's development is natural, the next LTS will feature five years of support, while pleasing both users and companies interested in the most stable Ubuntu experience.
|
||||
|
||||
Moreover, Ubuntu 14.04 LTS is to witness:
|
||||
|
||||
- "we will be providing OpenStack I, J and K on 14.04 for LTS deployments"
|
||||
- "on the desktop, 13.10 has benefited greatly from the fact that it has a team just focused on improving quality. We’ll do the same again and more for 14.04"
|
||||
- "on the mobile front, we’re going to keep racing forward, the platform is too new for an LTS"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The in-depth decisions about what, where, how, when related to Ubuntu 14.04 LTS are to be planned, discussed and refined in the upcoming [virtual Ubuntu Developer][2] Summit, video-session based event happening during **November 19th - November 21st **2013, event fully open for participation and completely open to interested users, third-party developers and teams seeking to learn about all Ubuntu layers and areas directly as presented by Ubuntu developers, designers, leaders, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 14.04 LTS will not feature convergence capabilities, yet, the work continues with vigorous plans and according features in the 14.04 cycle, too, "we won’t get there in one cycle but given the pace of improvement of the phone and tablet in the last month I think **it’s going to be a fantastic cycle there"**.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/performance-refinement-maintainability-technical-debt-improving-quality-and-we%E2%80%99re-going-keep-racing
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.markshuttleworth.com/archives/1295
|
||||
[2]:http://uds.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
||||
Linus Torvalds 十句精彩语录 —— 来自 LinuxCon Europe 大会上的主旨发言
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Linus Torvalds 和 Linus Torvalds 在 Edinburgh举行的 LinuxCon Europe 大会主席台上*
|
||||
|
||||
今天, Linux创始人 Linus Torvalds 坐在了在Edinburgh举办的[LinuxCon Europe][1]大会主席台上,
|
||||
陪同他的是来自Intel公司linux主管和开源技术专家 Dirk Hohndel, 二人一起探讨linux的现在和未来,并且回答了来自社区的问题。讨论的话题很广泛,包括即将发布的3.12版内核, 内核维护者的理想性格,
|
||||
还有能让 Linus 熬夜去解决的一些问题,linux桌面游戏, 等等。
|
||||
|
||||
以下是linus的十句精彩语录, 来自周三早上的主旨演讲, 按大会上发言时的顺序排列。
|
||||
|
||||
1. Linus 很满意当前内核版本三个月时间的发布周期,因为这样的话,开发者可以充分利用该时间段构建新的特性。即使他们错过了合并的窗口期, 等到下一次机会的到来,三个月的等待时间也不算很长, 他们也就不必急于提交代码了。
|
||||
**不必担心你的代码。确保代码运行良好,并得到精心设计就行了。不要担心期限问题。**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. 快速变更的步调还允许开发人员快速合并他们的代码, 然后继续前进。
|
||||
|
||||
**“开发者在注意力持续时间问题上,有点类似于迟钝的林地动物。”**
|
||||
|
||||
**3. “对于一个维护者来说,最重要的不在于你是不是一个优秀的工程师, 而在于你得负责任, 别人可以指望你, 7天的每一个24小时, 一年52个星期都是如此”。**
|
||||
|
||||
年轻的开发者想成为一名维护人员是比较困难的。要经过数年时间的观察期,让社区信任你, 注意到你确实坚守在这里。那即是说,只要你能证明自己是可信赖的,想成为一名维护者还是容易的(因为你经受住了时间的考验),毕竟这是一份棘手的工作
|
||||
4. Dirk:“是什么让你熬夜?”
|
||||
Linus: 代码中的Bug,还有其他一些技术问题, 不过这些问题并不难解决。
|
||||
|
||||
**“技术上的东西,可以这么说,即使你做了蠢事,但都是可以解决的。**
|
||||
5. 真正让Linus熬夜的是与开发进度有关的社交性问题。
|
||||
|
||||
**有时候情绪来了,可能好几天都比较有压力。 我也有脾气, 这对我来说没什么…… 。 但是其他人倾向于陷入到问题里边。结果浪费好几周时间,而且这些问题都挺让人纠结的。**
|
||||
|
||||
6.当提到说服大公司继续贡献内核代码并且使用开源软件, linus持达尔文观点。他们要么从开源获益,要么就得承受经济上的损失。
|
||||
|
||||
**我从事开源,因为有乐趣而且开源行得通……。 跟开源社区合作的公司会花费更少的时间并且使工作更有成效。**
|
||||
|
||||
**7. 如果你有一家公司, 对内核的微小的改动会给你带来竞争优势, 你很可能就要面对经济上的问题。最好还是考虑一下生产廉价的高质量的硬件好了。**
|
||||

|
||||
*Linux 创始人 Linux Torvalds 回答现场观众的提问,2013 LinuxCon Europe大会。*
|
||||
8. 有关linux桌面版的现状,linus有几点要谈。linux桌面仍然可以改善。但是各个发行版之间的内讧已然是个问题。
|
||||
|
||||
**我写linux就是因为想让它在桌面上跑…… 我希望人们可以一起努力…… 把登陆界面搞得更漂亮一点**
|
||||
9. Linus说, Valve’s Steam有助于linux桌面版的开发,这是个极好的机会。他们要为打算运行游戏的Linux发行版制定一个标准。
|
||||
|
||||
**这是标准化的最好的模式。标准不是说人们就坐在房间里,写啊写。标准能够带来市场效益才称得上成功。**
|
||||
10. 针对多样性, linus说他希望看到内核社区的发展壮大, 有来自不同地区的更多的女性和开发者参与到其中。
|
||||
|
||||
**女性太少了。但是我并不担心。过去我们就讨论过来自日本的开发者太少的问题。这是可以解决,只是时间问题。**
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxfoundation.org/news-media/blogs/browse/2013/10/10-best-quotes-linus-torvalds-keynote-linuxcon-europe
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/l3b2w1) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://events.linuxfoundation.org/events/linuxcon-europe
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
云端服务管理工具 Juju GUI 0.11版发布
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
坚如磐石的桌面、光鲜靓丽的手机、高端大气上档次的云管理工具,这三样东西一直是 Canonical 公司的立足之本,高速发展、大气的决策、热衷创新 —— 这些来自市场的认可使得这家公司与戴尔、惠普以及 OpenStack 基金会等组织成为高级合作伙伴,同时它在 IT 世界中扮演着传播新鲜事物和现代主义思想的角色。
|
||||
|
||||
[Juju][2] 是 Ubuntu 旗下的一款工具,可以对云端的服务进行快速可靠的布署,包括可以扩展云端业务,因此管理员可以很容易地布署 Wordpress 博客系统、MongoDB 大系统管理系统、Ceph 分布式文件系统等。
|
||||
|
||||
用户可以通过命令行和图形界面使用 Juju,图形界面被称为“Juju GUI”。
|
||||
|
||||
[Juju GUI][3]界面基于网页,精美、对用户友好、直观,用户可以通过网页简单的操作完成复杂的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
Juju GUI 已经[升级到][4] **0.11版**,下面介绍一下新版本涉及的功能、修复、优化:
|
||||
|
||||
- 支持 charms 的升级、降级
|
||||
- 可以显示两个节点的关联
|
||||
- 大量减少 GUI 的大小,加快布署的进度
|
||||
- 优化服务定位功能
|
||||
- 增加红三角标记,用于标记 charms 和 bundles
|
||||
- 删除有缺陷的操作(如添加己存在的单元)
|
||||
- 为单元提供精确的链接地址
|
||||
- 其他一些改进这里就不说了
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Juju GUI 长什么样?试试[https://jujucharms.com/sidebar/][5]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/cloud-tool-juju-gui-011-released-new-features-and-enhancements
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.canonical.com/
|
||||
[2]:https://juju.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[3]:https://launchpad.net/juju-gui
|
||||
[4]:http://jujugui.wordpress.com/2013/10/18/0-11-0-juju-gui-release/
|
||||
[5]:https://jujucharms.com/sidebar/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
每日Ubuntu小技巧——怎样修改你的计算机名字
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
本文又是一篇为Ubuntu新用户和新手准备的文章,将会指导你怎样在使用Ubuntu时轻松更改你的计算机名字,许多用户从来不会考虑在Ubuntu更改计算机名字或者主机名,那是他们最不用考虑担心的事情。
|
||||
|
||||
许多用户会使用安装Ubuntu过程中创建或设定的名字,但是对于想要知道怎么更改名字的新用户,可以继续接下来的学习。本文不是为Ubuntu专家所准备,是为那些刚刚开始使用Ubuntu的初学者用户。
|
||||
|
||||
那么,为什么你又想要更改你的计算机名字?如果除了想要学习怎样操作,你没有一个好的理由,那么就不要学了,反之,如果你有一个好的理由或者想要学习怎样操作,那么请继续。
|
||||
|
||||
按下 **Ctrl – Alt – T** 组合键,打开终端。
|
||||
当终端打开,输入下列命令,使用gedit编辑hostname文件
|
||||
|
||||
sudo gedit /etc/hostname
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,无论旧的计算机名字是什么,换一个新的吧。例如,如果你想要你的计算机名字为“RDOMNU”,先删除文件内容,输入 **RDOMNU**,然后保存文件。
|
||||
|
||||
然后,输入下列命令来打开hosts文件
|
||||
|
||||
sudo gedit /etc/hosts
|
||||
|
||||
更改第二行箭头标记位置的值,使它与你刚才输入的计算机名字相符,完成后保存文件。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
就是这样!重启你的计算机,然后你的机器将会显示新的名字。这就是怎么改变Ubuntu机器的名字。
|
||||
|
||||
试一试吧!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/10/daily-ubuntu-tips-change-computer-name/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Vic___](https://blog.csdn.net/Vic___) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
|
||||
如何在手机上安装Ubuntu Touch 13.10
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Ubuntu Touch 13.10是Canonical公司针对手机出的一款新的操作系统,但它不是那么容易装到你的手机上相比安装到桌面上**
|
||||
**buntu Touch 13.10是Canonical公司针对手机新推出的一款操作系统,但是相对于桌面而言,安装到手机并不是那么容易。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Canonical提供了安装Ubuntu Touch 13.10所有必要的工具。这是一个非常好的消息,因为手动安装操作系统可是相当麻烦的。
|
||||
Canonical提供了安装Ubuntu Touch 13.10所有必要的工具。这真是个好消息,因为手动安装操作系统可是相当麻烦的。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,此操作系统并非可用于任何手机上。因开发原因,Canonical限制其只能使用在Nexus 4设备上(代号金枪鱼和灰鲭鲨) ,而且手机必须已被解锁。
|
||||
首先提醒,此操作系统并非任何手机都能使用。因开发原因,Canonical限制其只能使用在Nexus 4设备上(代号金枪鱼和灰鲭鲨) ,而且手机必须已被解锁。
|
||||
|
||||
要安装工具,你将需要在终端输入几个简单的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ Canonical提供了安装Ubuntu Touch 13.10所有必要的工具。这是一个
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install phablet-tools android-tools-adb android-tools-fastboot
|
||||
|
||||
用户还必须确保他们的手机已被设置成开发使用。进入“设置项/关于手机”,点击“软件版本”7次。一条短消息会告诉你是否执行了正确的步骤。
|
||||
用户还必须确保他们的手机已被设置成开发使用。进入“设置项/关于手机”,点击“软件版本”7次。如果你操作正确,将会收到一条提示消息。
|
||||
|
||||
你必须从新菜单——“开发者选项”中启用USB调试,该菜单通过前面的方法已被解锁。在手机上勾选该选项时,会出现一条消息,通知用户正在配对。同意,那么你准备得差不多了。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,18 +26,18 @@ Canonical提供了安装Ubuntu Touch 13.10所有必要的工具。这是一个
|
||||
|
||||
adb restore backup.ab
|
||||
|
||||
最后的命令应该关乎到一切,你应该使用sudo运行,以确保正确执行该命令。打开一个终端,输入以下命令:
|
||||
最后的命令至关重要,你应该使用sudo运行,以确保正确执行该命令。打开一个终端,输入以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
phablet-flash ubuntu-system --no-backup
|
||||
|
||||
运行过程中应该没有任何问题,设备将最终引导到Ubuntu Touch。不要停止终端和不要中断的此过程。
|
||||
运行过程中应该没有任何问题,设备将最终引导到Ubuntu Touch。不要停止终端也不要中断此过程。
|
||||
|
||||
以上就是你需要遵照的简单步骤,这些步骤在所支持的设备上应该没有任何问题地运作。
|
||||
以上就是你需要遵照的简单步骤,这样,在所支持的设备上运作应该没有任何问题了。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
来源于: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Install-Ubuntu-Touch-13-10-On-Your-Phone-392828.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[coolpigs](https://github.com/coolpigs) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[coolpigs](https://github.com/coolpigs) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,134 +1,130 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 安装Apache和SSL
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu 13.10 下安装支持SSL的Apache
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
通过这个简短的教程,让我来给你展示如何安装Apache与SSL的支持.以下是我的试验机的详细说明:
|
||||
|
||||
### 系统信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
root@ubuntu-unixmen:~# ifconfig
|
||||
|
||||
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:b8:b4:87
|
||||
|
||||
inet addr:10.1.1.110 Bcast:10.1.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
|
||||
|
||||
inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:feb8:b487/64 Scope:Link
|
||||
|
||||
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
|
||||
|
||||
RX packets:1738 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
|
||||
|
||||
TX packets:69 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
|
||||
|
||||
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
|
||||
|
||||
RX bytes:168845 (168.8 KB) TX bytes:9767 (9.7 KB)
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
root@ubuntu-unixmen:~# cat /etc/issue
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 \n \l
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装apache ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
通过这个简短的教程,让我来指导你如何安装支持SSL的Apache.以下是我的试验机的详细说明:
|
||||
|
||||
### 系统信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
root@ubuntu-unixmen:~# ifconfig
|
||||
|
||||
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:b8:b4:87
|
||||
|
||||
inet addr:10.1.1.110 Bcast:10.1.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
|
||||
|
||||
inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:feb8:b487/64 Scope:Link
|
||||
|
||||
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
|
||||
|
||||
RX packets:1738 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
|
||||
|
||||
TX packets:69 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
|
||||
|
||||
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
|
||||
|
||||
RX bytes:168845 (168.8 KB) TX bytes:9767 (9.7 KB)
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
root@ubuntu-unixmen:~# cat /etc/issue
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 \n \l
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装apache ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install apache2 apache2-doc apache2-utils
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Reading package lists... Done
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Building dependency tree
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Reading state information... Done
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The following extra packages will be installed:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
apache2-bin apache2-data libapr1 libaprutil1 libaprutil1-dbd-sqlite3 libaprutil1-ldap ssl-cert
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### apache测试页面 ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
打开浏览器,转到http://ip-address/.你应该会看到类似以下的信息.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建目录 ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个名为**ssl**的目录
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
sudo mkdir /etc/apache2/ssl
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建一个自签名凭证 ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/apache2/ssl/apache.key -out /etc/apache2/ssl/apache.crt
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key.......................................................................................+++....................................+++writing new private key to '/etc/apache2/ssl/apache.key'-----You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporatedinto your certificate request.What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blankFor some fields there will be a default value,If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.-----Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 开启Apache SSL模块 ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
运行以下命令开启ssl模块
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
$ a2enmod ssl
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Considering dependency setenvif for ssl:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Module setenvif already enabled
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Considering dependency mime for ssl:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Module mime already enabled
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Considering dependency socache_shmcb for ssl:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Enabling module socache_shmcb.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Enabling module ssl
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
编辑 **/etc/apache2/sites-enabled/default-ssl.conf** 文件,
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost 10.1.1.110:443>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ServerName www.unixmen.com:443
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
SSLEngine on
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
SSLCertificateFile /etc/apache2/ssl/apache.crt
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/apache2/ssl/apache.key
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 启动Apache缺省ssl的虚拟主机: ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
a2ensite default-ssl
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Enabling site default-ssl.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To activate the new configuration, you need to run:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
service apache2 reload
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 重启Apache: ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
sudo service apache2 restart
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
###测试SSL连接###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
打开浏览器,转到**https://IP-address**.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
完成了.再见!
|
||||
|
||||
You’re done. Cheers!
|
||||
"完成了.再见!"
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成,尽情享用!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/install-apache-ssl-ubuntu-13-10/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
235
translated/The Linux Kernel/03 The Linux Kernel--Drivers.md
Executable file
235
translated/The Linux Kernel/03 The Linux Kernel--Drivers.md
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,235 @@
|
||||
03 Linux : 驱动
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
驱动是使内核能够交流和处理硬件或协议(规则和标准)的小程序。没有驱动程序,内核不知道如何与硬件交流或者处理协议(内核实际上先发送指令给BIOS然后BIOS传给硬件) 。 Linux内核代码在驱动程序文件夹中以源代码的形式包含了许多驱动程序。 驱动文件夹中的每个文件夹会在下面说明。在配置和编译内核时,它有助于了解驱动程序。否则,用户可能会在编译时加入不必要的或者遗留重要的驱动。驱动代码通常会包含一行注释行来指出驱动的目的。 比如,tc的驱动代码,有一行的注释说是用于TURBOchannel总线。由于这些文档,用户应该看驱动前几行的注释来了解它们的目的。
|
||||
|
||||
有几个术语应该已经知道所以以下信息是可以理解的。一个I / O设备指的是输入/输出设备。调制解调器和网卡就是这样的例子,他们发送和接收数据。监视器是一个输出设备 - 只有信息出来。键盘,鼠标和游戏杆是数据输入系统。存储设备存储数据。这方面的例子包括SD卡、硬盘、光盘、存储卡等等。 CPU (也称为处理器)是计算机的“大脑”或“心脏” 。如果没有这一块处理芯片,电脑无法运作。 主板是一块连接板上不同组件的印刷线路板。主板和各个组件的一台计算机不可缺少的功能。许多计算机用户说主板是电脑的心脏(主板上有CPU ) 。该主板包含了用于连接外设的端口。外设包括输入,输出和存储设备。总线上主板的电路并且它连接着连接外设。网络设备处理两台或多台计算机之间的连接。端口是用户可以插入另外一台设备或一根电缆的设备。例如,用户将插入一根火线记忆棒插入一个火线端口;以太网电缆插入入一个以太网端口。光碟的读取是利用激光从可以散射或反射的激光的反射面上读出。一个常见的光盘是DVD 。许多系统是32位或者64位系统,这指的是寄存器的,地址总线或数据总线的位数。例如,在一块64位的主板上,数据总线(组件之间的银线)有64根并排到目的的线。存储器地址以位(0和1)的形式在存储器中编址。因此,一个32位存储地址包含32位的0和1来表示存储器上的某处地址。
|
||||
|
||||
许多驱动程序是通用驱动程序这意味着一个通用键盘驱动可以使内核可以处理几乎所有的键盘。然而,有些驱动是专用驱动。像苹果和Commodore分别为苹果电脑和Amiga系统制造了专门的硬件。 Linux内核中已经包含了许多诸如智能手机、苹果、Amiga系统、PS3、Android平板,和许多其他设备的驱动程序。
|
||||
|
||||
注意有些设备不在本目录中。比如,射频驱动在net和media文件夹下。
|
||||
|
||||
**accessibility** - 这些驱动提供支持一些辅助设备。在Linux 3.9.4中,这个文件夹中只有一个驱动就是盲文设备驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
**acpi** - 高级配置和电源接口(ACPI)驱动用来管理电源使用。
|
||||
|
||||
**amba** - 高级微控制器总线架构(AMBA)是与片上系统(SoC)的管理和互连的协议。SoC是一块包含许多或所有必要的计算机组件的芯片。这里的AMBA驱动让内核能够运行在这上面。
|
||||
|
||||
**ata** - 该目录包含PATA和SATA设备的驱动程序。串行ATA(SATA)是一种连接主机总线适配器到像硬盘那样的存储器的计算机总线接口。并行ATA(PATA)用于连接存储设备,如硬盘驱动器,软盘驱动器,光盘驱动器的标准。PATA就是我们所说的IDE。
|
||||
|
||||
**atm** - 异步通信模式(ATM)是一种通信标准。这里有各种接到PCI桥的驱动(他们连接到PCI总线)和以太网控制器(控制以太网通信的集成电路芯片)。
|
||||
|
||||
**auxdisplay** - 这个文件夹提供了三个驱动。LCD帧缓存驱动、LCD控制器驱动和一个LCD驱动。这些驱动管理液晶显示器。液晶显示器会在按压时显示波纹。注意:按压会损害屏幕,所以请不要用力戳LCD显示屏。
|
||||
|
||||
**base** - 这是个重要的目录包含了固件、系统总线、虚拟化能力等基本的驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
**bcma** - 这些驱动是用于使用基于AMBA协议的总线协议。AMBA是由博通公司开发。
|
||||
|
||||
**block** - 这些驱动提供对块设备的支持,像软驱、SCSI磁带、TCP块设备等等。
|
||||
|
||||
**bluetooth** - 蓝牙是一种安全的无线个人区域网络标准(PANs)。蓝牙驱动就在这个文件夹,它允许系统使用不同的蓝牙设备。例如,一个蓝牙鼠标缺少电缆,并且计算机有一个电子狗(小型USB接收器)。Linux系统必须能够知道进入电子狗的信号。否则,蓝牙设备无法工作。
|
||||
|
||||
**bus** - 这个目录包含了三个驱动。一个转换ocp接口协议到scp协议。一个是设备间的互联驱动,第三个是用于处理互联中的错误处理。
|
||||
|
||||
**cdrom** - rom(只读GB盘)。GD光盘是1.2GB容量的光盘。这像一个更大的CD或者更小的DVD。GD通常用于世嘉游戏机中。
|
||||
|
||||
**char** - 字符设备驱动就在这里。字符设备每次传输数据传输一个字符。这个文件夹里的驱动包括打印机,PS3闪存驱动、东芝SMM驱动和随机数发生器驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
**clk** - 这些驱动用于系统时钟。
|
||||
|
||||
**clocksource** - 这些驱动使用时钟作为定时器。
|
||||
|
||||
**connector** - 这些驱动使内核知道当进程fork并使用proc连接器更改UID(用户ID),GID(组ID),和SID(会话ID)。内核需要知道什么时候进程fork(CPU中运行多个任务)并执行。否则,内核可能会低效管理资源。
|
||||
|
||||
**cpufreq** - 这些驱动改变CPU的电源功率。
|
||||
|
||||
**cpuidle** - 这些驱动用来管理空闲的CPU。一些系统使用多个CPU,那么其中一个会尝试保持空闲。
|
||||
|
||||
**crypto** - 这些驱动提供加密功能。
|
||||
|
||||
**dca** - 直接缓存访问驱动允许内核访问CPU缓存。CPU缓存就像CPU内置的RAM。CPU缓存的速度比RAM更快。然而,CPU缓存的容量比RAM小得多。CPU在这个缓存系统上存储了最重要的和执行的代码。
|
||||
|
||||
**devfreq** - 这个驱动程序提供了一个通用的动态电压和频率调整(DVFS)框架,可以根据需要改变CPU频率来节约能源。这就是所谓的CPU节流。
|
||||
|
||||
**dio** - 数字输入/输出总线驱动允许内核可以使用DIO总线。
|
||||
|
||||
**dma** - 直接内存访问(DMA)驱动允许设备无需CPU访问内存。这减少了CPU的负载。
|
||||
|
||||
**edac** - 错误检测和校正驱动帮助减少和纠正错误。
|
||||
|
||||
**eisa** - 扩展工业标准结构总线驱动提供内核对EISA总线的支持。
|
||||
|
||||
**extcon** - 外部连接器驱动用于检测设备插入时的变化。例如,extcon会检测用户是否插入了USB驱动器。
|
||||
|
||||
**firewire** - 这些驱动用于控制苹果制造的类似于USB的火线设备。
|
||||
|
||||
**firmware** - 这些驱动用于和像BIOS(计算机的基本输入输出系统固件)这样的设备的固件通信。BIOS用于启动操作系统和控制硬件与设备的固件。一些BIOS允许用户超频CPU。超频是使CPU运行在一个更快的速度。CPU速度以MHz(百万赫兹)或GHz衡量。一个3.7 GHz的CPU的的速度明显快于一个700Mhz的处理器。
|
||||
|
||||
**gpio** - 通用输入/输出(GPIO)是由用户控制行为的芯片的管脚。这里的驱动就是控制GPIO。
|
||||
|
||||
**gpu** - 直接渲染管理(DRM)。VGA是640*480的模拟计算机显示器或是简化的分辨率标准。GPU是图形处理器。DRM是一个Unix渲染系统。
|
||||
|
||||
**hid** - 这驱动用于对USB人机界面设备的支持。
|
||||
|
||||
**hsi** - 这个驱动用于内核可以访问像Nokia N900这样的蜂窝式调制解调器。
|
||||
|
||||
**hv** - 这个驱动用于提供Linux中的键值对(KVP)功能。
|
||||
|
||||
**hwmon** - 硬件监控驱动用于内核读取硬件传感器上的信息。比如,CPU上有个温度传感器。那么内核就可以追踪温度的变化并相应地调节风扇的速度。
|
||||
|
||||
**hwspinlock** - 硬件自旋锁驱动允许系统同时使用两个或者更多的处理器而不是使用一个处理器上的两个或更多的核心。
|
||||
|
||||
**i2c** - I2C驱动可以使计算机用I2C协议处理主板上的低速外设。系统管理总线(SMBus)驱动管理SMBus,这是一种用于轻量级通信的two-wire总线。
|
||||
|
||||
**ide** - 这些驱动用来处理像CDROM和硬盘这些PATA/IDE设备。
|
||||
|
||||
**idle** - 这个驱动用来处理空闲的Intel处理器。
|
||||
|
||||
**iio** - 工业I/O核心驱动程序用来处理AD或DA转换器。
|
||||
|
||||
**infiniband** - Infiniband是在企业数据中心和一些超级计算机中使用的一中高性能的端口。这个目录中的驱动用来支持Infiniband硬件。
|
||||
|
||||
**input** - 耳机按钮,和许多其他的驱动。如今的操纵杆使用USB端口,但是在1980年代和1990年代,操纵杆是插在gameport中。
|
||||
|
||||
**iommu** - 输入/输出内存管理单元(IOMMU)驱动用来管理内存管理单元中的IOMMU。IOMMU连接DMA IO 总线到内存上。IOMMU是设备在没有CPU帮助下直接访问内存的桥梁。这有助于减少处理器的负载。
|
||||
|
||||
**ipack** - Ipack代表的是IndustryPack。 这个驱动是一个虚拟总线,允许在载体和夹板之间操作。
|
||||
|
||||
**irqchip** - 这些驱动程序允许硬件的中断请求(IRQ)发送到处理器,暂时停止一个正在运行的程序而去运行一个特殊的程序(称为一个中断处理程序)。
|
||||
|
||||
**isdn** - 这些驱动用于支持综合业务数字网(ISDN),这是用于同步数字传输语音、视频、数据和其他网络服务使用传统电话网络的电路的通信标准。
|
||||
|
||||
**leds** - 用于LED的驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
**lguest** - lguest用于管理客户机系统的中断。中断是CPU被重要任务打断的硬件或软件信号。CPU接着给硬件或软件一些处理资源。
|
||||
|
||||
**macintosh** - 苹果设备的驱动在这个文件夹里。
|
||||
|
||||
**mailbox** - 这个文件夹(pl320-pci)中的驱动用于管理邮箱系统的连接。
|
||||
|
||||
**md** - 多设备驱动用于支持磁盘阵列,一种多块硬盘间共享或复制数据的系统。
|
||||
|
||||
**media** - 媒体驱动提供了对收音机、调谐器、视频捕捉卡、DVB标准的数字电视等等的支持。驱动还提供了对不同通过USB或火线端口插入的多媒体设备的支持。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**memory** - 只是支持内存的重要驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
**memstick** - 这个驱动用于支持Sony记忆棒。
|
||||
|
||||
**message** - 这些驱动用于运行LSI Fusion MPT(一种消息传递技术)固件的LSI PCI芯片/适配器。LSI大规模集成,这代表每片芯片上集成了几万晶体管、
|
||||
|
||||
**mfd** - 多用途设备(MFD)驱动提供了对可以提供诸如电子邮件、传真、复印机、扫描仪、打印机功能的多用途设备的支持。这里的驱动还给MFD设备提供了一个通用多媒体通信端口(MCP)层。
|
||||
|
||||
**misc** - 这个目录包含了不适合在其他目录的各种驱动。就像光线传感器驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
**mmc** - MMC卡驱动用于处理用于MMC标准的闪存卡。
|
||||
|
||||
**mtd** - 内存技术设备(MTD)驱动程序用于Linux和闪存的交互,这就就像一层闪存转换层。其他块和字符驱动程序不会以闪存设备的操作方式来做映射。尽管USB记忆卡和SD卡是闪存设备,但它们不使用这个驱动,因为他们隐藏在系统的块设备接口后。这个驱动用于新型闪存设备的通用闪存驱动器驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
**net** - 网络驱动提供像AppleTalk、TCP和其他的网络协议。这些驱动也提供对调制解调器、USB 2.0的网络设备、和射频设备的支持。
|
||||
|
||||
**nfc** - 这个驱动是德州仪器的共享传输层之间的接口和NCI核心。
|
||||
|
||||
**ntb** - 不透明的桥接驱动提供了在PCIe系统的不透明桥接。PCIe是一种高速扩展总线标准。
|
||||
|
||||
**nubus** - NuBus是一种32位并行计算总线。用于支持苹果设备。
|
||||
|
||||
**of** - 此驱动程序提供设备树中创建,访问和解释程序的OF助手。设备树是一种数据结构,用于描述硬件。
|
||||
|
||||
**oprofile** - 这个驱动用于从驱动到用户空间进程(运行在用户态下的应用)评测整个系统。这帮助开发人员找到性能问题
|
||||
|
||||
**parisc** - 这些驱动用于HP生产的PA-RISC架构设备。PA-RISC是一种特殊指令集的处理器。
|
||||
|
||||
**parport** - 并口驱动提供了Linux下的并口支持。
|
||||
|
||||
**pci** - 这些驱动提供了PCI总线服务。
|
||||
|
||||
**pcmcia** - 这些事笔记本主板驱动
|
||||
|
||||
**pinctrl** - 这些驱动用来处理引脚控制设备。引脚控制器可以禁用或启用I/O设备。
|
||||
|
||||
**platform** -这个文件夹包含了不同的计算机平台的驱动像Acer、Dell、Toshiba、IBM、Intel、Chrombooks等等。
|
||||
|
||||
**pnp** - 即插即用驱动允许用户在插入一个像USB的设备后可以立即使用而不必手动配置设备。
|
||||
|
||||
**power** - 电源驱动是内核可以测量电池电量,检测充电器,和电源管理。
|
||||
|
||||
**pps** - Pulse-Per-Second驱动用来控制电流脉冲速率。这用于计时。
|
||||
|
||||
**ps3** - 这是Sony的游戏控制台驱动- PlayStation3。
|
||||
**ptp** - 图片传输协议(PTP)驱动支持一种从数码相机中传输图片的协议。
|
||||
|
||||
**pwm** - 脉宽调制(PWM)驱动用于控制设备的电流脉冲。主要用于控制像CPU风扇。
|
||||
|
||||
**rapidio** - RapidIO驱动用于管理RapidIO架构,它是一种高性能分组交换,用于电路板上交互芯片的交互技术,也用于互相使用底板的电路板。
|
||||
|
||||
**regulator** - 校准驱动用于校准电流、温度、或其他可能系统存在的校准硬件。
|
||||
|
||||
**remoteproc** - 这些驱动用来管理远程处理器。
|
||||
|
||||
**rpmsg** - 这个驱动用来控制支持大量驱动的远程处理器通讯总线(rpmsg)。这些总线提供消息传递设施,促进客户端驱动程序编写自己的连接协议消息。
|
||||
|
||||
**rtc** - 实时时钟(RTC)驱动使内核可以读取时钟。
|
||||
|
||||
**s390** - 用于31/32位的大型机架构的驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
**sbus** - 用于管理基于SPARC的总线驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
**scsi** - 允许内核使用SCSI标准外围设备。例如,Linux将在与SCSI硬件传输数据时使用SCSI驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
**sfi** -简单固件接口(SFI)驱动允许固件发送信息表给操作系统。这些表的数据称为SFI表。
|
||||
|
||||
**sh** - 该驱动用于支持SuperHway总线。
|
||||
|
||||
**sn** - 该驱动用于支持IOC3串口。
|
||||
|
||||
**spi** - 这些驱动处理串行设备接口总线(SPI),它是一个在在全双工下运行的同步串行数据链路标准,。全双工是指两个设备可以同一时间同时发送和接收信息。双工指的是双向通信。设备在主/从模式下通信(取决于设备配置)。
|
||||
|
||||
**ssb** - ssb(Sonics Silicon Backplane)驱动提供对在不同博通芯片和嵌入式设备上使用的迷你总线的支持。
|
||||
|
||||
**staging** - 该目录含有许多子目录。这里所有的驱动还需要在加入主内核前经过更多的开发工作。
|
||||
|
||||
**target** - SCSI设备驱动
|
||||
|
||||
**tc** - 这些驱动用于TURBOchannel,TURBOchannel是数字设备公司开发的32位开放总线。这主要用于DEC工作站。
|
||||
|
||||
**thermal** - thermal驱动使CPU保持较低温度。
|
||||
|
||||
**tty** - tty驱动用于管理物理终端连接。
|
||||
|
||||
**uio** - 该驱动允许用户编译运行在用户空间而不是内核空间的驱动。这使用户驱动不会导致内核崩溃。
|
||||
|
||||
**usb** - USB设备允许内核使用USB端口。闪存驱动和记忆卡已经包含了固件和控制器,所以这些驱动程序允许内核使用USB接口和与USB设备。
|
||||
|
||||
**uwb** - Ultra-WideBand驱动用来管理短距离,高带宽通信的超低功耗的射频设备
|
||||
|
||||
**vfio** - 允许设备访问用户空间的VFIO驱动
|
||||
|
||||
**vhost** - 这是用于宿主内核中的virtio服务器驱动。用于虚拟化中
|
||||
|
||||
**video** - 这是用来管理显卡和监视器的视频驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
**virt** - 这些驱动用来虚拟化。
|
||||
|
||||
**virtio** - 这个驱动用来在虚拟PCI设备上使用virtio设备。用于虚拟化中。
|
||||
|
||||
**vlynq** - 这个驱动控制着由德州仪器开发的专有接口。这些都是宽带产品,像WLAN和调制解调器,VOIP处理器,音频和数字媒体信号处理芯片。
|
||||
|
||||
**vme** - WMEbus最初是为摩托罗拉68000系列处理器开发的总线标准
|
||||
|
||||
**w1** - 这些驱动用来控制one-wire总线。
|
||||
|
||||
**watchdog** - 该驱动管理看门狗定时器,这是一个可以用来检测和恢复异常的定时器。
|
||||
|
||||
**xen** - 该驱动是Xen管理程序系统。这是个允许用户运行多个操作系统在一台计算机的软件或硬件。这意味着xen的代码将允许用户在同一时间的一台计算机上运行两个或更多的Linux系统。用户也可以在Linux上运行Windows、Solaris、FreeBSD、或其他操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
**zorro** - 该驱动提供Zorro Amiga总线支持。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-drivers.4205/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user