mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-25 23:11:02 +08:00
Translated 20190205 Install Apache, MySQL, PHP (LAMP) Stack On Ubuntu 18.04 LTS (#20790)
Co-authored-by: frstlis <48125063@qq.com>
This commit is contained in:
parent
39834abcbf
commit
cb17643b57
@ -1,443 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: (stevenzdg988)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
[#]: subject: (Install Apache, MySQL, PHP (LAMP) Stack On Ubuntu 18.04 LTS)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://www.ostechnix.com/install-apache-mysql-php-lamp-stack-on-ubuntu-18-04-lts/)
|
||||
[#]: author: (SK https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/)
|
||||
|
||||
Install Apache, MySQL, PHP (LAMP) Stack On Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**LAMP** stack is a popular, open source web development platform that can be used to run and deploy dynamic websites and web-based applications. Typically, LAMP stack consists of Apache webserver, MariaDB/MySQL databases, PHP/Python/Perl programming languages. LAMP is the acronym of **L** inux, **M** ariaDB/ **M** YSQL, **P** HP/ **P** ython/ **P** erl. This tutorial describes how to install Apache, MySQL, PHP (LAMP stack) in Ubuntu 18.04 LTS server.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Apache, MySQL, PHP (LAMP) Stack On Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
|
||||
|
||||
For the purpose of this tutorial, we will be using the following Ubuntu testbox.
|
||||
|
||||
* **Operating System** : Ubuntu 18.04.1 LTS Server Edition
|
||||
* **IP address** : 192.168.225.22/24
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Install Apache web server
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, update Ubuntu server using commands:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt update
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt upgrade
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, install Apache web server:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install apache2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Check if Apache web server is running or not:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl status apache2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output would be:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
● apache2.service - The Apache HTTP Server
|
||||
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/apache2.service; enabled; vendor preset: en
|
||||
Drop-In: /lib/systemd/system/apache2.service.d
|
||||
└─apache2-systemd.conf
|
||||
Active: active (running) since Tue 2019-02-05 10:48:03 UTC; 1min 5s ago
|
||||
Main PID: 2025 (apache2)
|
||||
Tasks: 55 (limit: 2320)
|
||||
CGroup: /system.slice/apache2.service
|
||||
├─2025 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
|
||||
├─2027 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
|
||||
└─2028 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
|
||||
|
||||
Feb 05 10:48:02 ubuntuserver systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server...
|
||||
Feb 05 10:48:03 ubuntuserver apachectl[2003]: AH00558: apache2: Could not reliably
|
||||
Feb 05 10:48:03 ubuntuserver systemd[1]: Started The Apache HTTP Server.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Congratulations! Apache service is up and running!!
|
||||
|
||||
##### 1.1 Adjust firewall to allow Apache web server
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the apache web browser can’t be accessed from remote systems if you have enabled the UFW firewall in Ubuntu 18.04 LTS. You must allow the http and https ports by following the below steps.
|
||||
|
||||
First, list out the application profiles available on your Ubuntu system using command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo ufw app list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Available applications:
|
||||
Apache
|
||||
Apache Full
|
||||
Apache Secure
|
||||
OpenSSH
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, Apache and OpenSSH applications have installed UFW profiles. You can list out information about each profile and its included rules using “ **ufw app info “Profile Name”** command.
|
||||
|
||||
Let us look into the **“Apache Full”** profile. To do so, run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo ufw app info "Apache Full"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Profile: Apache Full
|
||||
Title: Web Server (HTTP,HTTPS)
|
||||
Description: Apache v2 is the next generation of the omnipresent Apache web
|
||||
server.
|
||||
|
||||
Ports:
|
||||
80,443/tcp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As you see, “Apache Full” profile has included the rules to enable traffic to the ports **80** and **443** :
|
||||
|
||||
Now, run the following command to allow incoming HTTP and HTTPS traffic for this profile:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo ufw allow in "Apache Full"
|
||||
Rules updated
|
||||
Rules updated (v6)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you don’t want to allow https traffic, but only http (80) traffic, run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo ufw app info "Apache"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 1.2 Test Apache Web server
|
||||
|
||||
Now, open your web browser and access Apache test page by navigating to **<http://localhost/>** or **<http://IP-Address/>**.
|
||||
|
||||
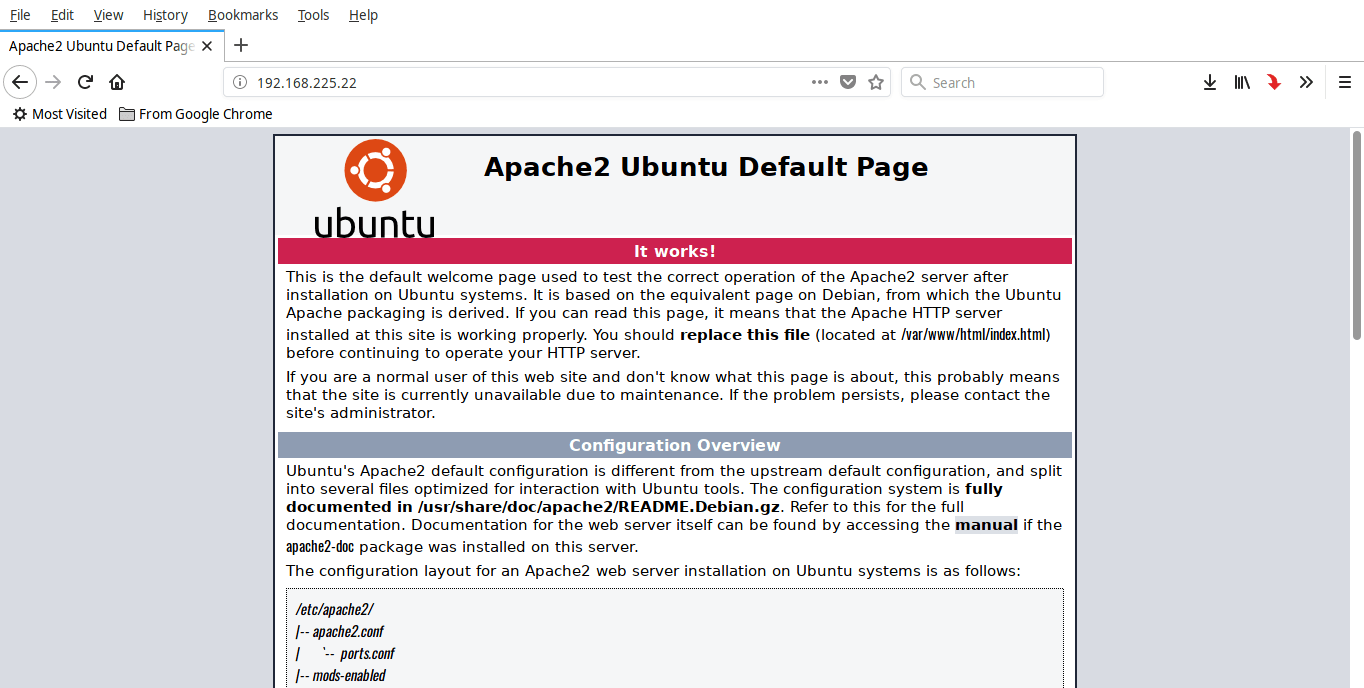
|
||||
|
||||
If you are see a screen something like above, you are good to go. Apache server is working!
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Install MySQL
|
||||
|
||||
To install MySQL On Ubuntu, run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install mysql-server
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Verify if MySQL service is running or not using command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl status mysql
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample output:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
● mysql.service - MySQL Community Server
|
||||
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mysql.service; enabled; vendor preset: enab
|
||||
Active: active (running) since Tue 2019-02-05 11:07:50 UTC; 17s ago
|
||||
Main PID: 3423 (mysqld)
|
||||
Tasks: 27 (limit: 2320)
|
||||
CGroup: /system.slice/mysql.service
|
||||
└─3423 /usr/sbin/mysqld --daemonize --pid-file=/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
|
||||
|
||||
Feb 05 11:07:49 ubuntuserver systemd[1]: Starting MySQL Community Server...
|
||||
Feb 05 11:07:50 ubuntuserver systemd[1]: Started MySQL Community Server.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Mysql is running!
|
||||
|
||||
##### 2.1 Setup database administrative user (root) password
|
||||
|
||||
By default, MySQL **root** user password is blank. You need to secure your MySQL server by running the following script:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You will be asked whether you want to setup **VALIDATE PASSWORD plugin** or not. This plugin allows the users to configure strong password for database credentials. If enabled, It will automatically check the strength of the password and enforces the users to set only those passwords which are secure enough. **It is safe to leave this plugin disabled**. However, you must use a strong and unique password for database credentials. If don’t want to enable this plugin, just press any key to skip the password validation part and continue the rest of the steps.
|
||||
|
||||
If your answer is **Yes** , you will be asked to choose the level of password validation.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Securing the MySQL server deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
Connecting to MySQL using a blank password.
|
||||
|
||||
VALIDATE PASSWORD PLUGIN can be used to test passwords
|
||||
and improve security. It checks the strength of password
|
||||
and allows the users to set only those passwords which are
|
||||
secure enough. Would you like to setup VALIDATE PASSWORD plugin?
|
||||
|
||||
Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No y
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The available password validations are **low** , **medium** and **strong**. Just enter the appropriate number (0 for low, 1 for medium and 2 for strong password) and hit ENTER key.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
There are three levels of password validation policy:
|
||||
|
||||
LOW Length >= 8
|
||||
MEDIUM Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, and special characters
|
||||
STRONG Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, special characters and dictionary file
|
||||
|
||||
Please enter 0 = LOW, 1 = MEDIUM and 2 = STRONG:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, enter the password for MySQL root user. Please be mindful that you must use password for mysql root user depending upon the password policy you choose in the previous step. If you didn’t enable the plugin, just use any strong and unique password of your choice.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Please set the password for root here.
|
||||
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
|
||||
Re-enter new password:
|
||||
|
||||
Estimated strength of the password: 50
|
||||
Do you wish to continue with the password provided?(Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once you entered the password twice, you will see the password strength (In our case it is **50** ). If it is OK for you, press Y to continue with the provided password. If not satisfied with password length, press any other key and set a strong password. I am OK with my current password, so I chose **y**.
|
||||
|
||||
For the rest of questions, just type **y** and hit ENTER. This will remove anonymous user, disallow root user login remotely and remove test database.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
|
||||
Success.
|
||||
|
||||
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from
|
||||
'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at
|
||||
the root password from the network.
|
||||
|
||||
Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
|
||||
Success.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that
|
||||
anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing,
|
||||
and should be removed before moving into a production
|
||||
environment.
|
||||
|
||||
Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
|
||||
- Dropping test database...
|
||||
Success.
|
||||
|
||||
- Removing privileges on test database...
|
||||
Success.
|
||||
|
||||
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes
|
||||
made so far will take effect immediately.
|
||||
|
||||
Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
|
||||
Success.
|
||||
|
||||
All done!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it. Password for MySQL root user has been set.
|
||||
|
||||
##### 2.2 Change authentication method for MySQL root user
|
||||
|
||||
By default, MySQL root user is set to authenticate using the **auth_socket** plugin in MySQL 5.7 and newer versions on Ubuntu. Even though it enhances the security, it will also complicate things when you access your database server using any external programs, for example phpMyAdmin. To fix this issue, you need to change authentication method from **auth_socket** to **mysql_native_password**. To do so, login to your MySQL prompt using command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mysql
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following command at the mysql prompt to find the current authentication method for all mysql user accounts:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
SELECT user,authentication_string,plugin,host FROM mysql.user;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample output:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
+------------------|-------------------------------------------|-----------------------|-----------+
|
||||
| user | authentication_string | plugin | host |
|
||||
+------------------|-------------------------------------------|-----------------------|-----------+
|
||||
| root | | auth_socket | localhost |
|
||||
| mysql.session | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE | mysql_native_password | localhost |
|
||||
| mysql.sys | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE | mysql_native_password | localhost |
|
||||
| debian-sys-maint | *F126737722832701DD3979741508F05FA71E5BA0 | mysql_native_password | localhost |
|
||||
+------------------|-------------------------------------------|-----------------------|-----------+
|
||||
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
As you see, mysql root user uses `auth_socket` plugin for authentication.
|
||||
|
||||
To change this authentication to **mysql_native_password** method, run the following command at mysql prompt. Don’t forget to replace **“password”** with a strong and unique password of your choice. If you have enabled VALIDATION plugin, make sure you have used a strong password based on the current policy requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'password';
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Update the changes using command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now check again if the authentication method is changed or not using command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
SELECT user,authentication_string,plugin,host FROM mysql.user;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||
![][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Good! Now the myql root user can authenticate using password to access mysql shell.
|
||||
|
||||
Exit from the mysql prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
exit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3\. Install PHP
|
||||
|
||||
To install PHP, run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install php libapache2-mod-php php-mysql
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After installing PHP, create **info.php** file in the Apache root document folder. Usually, the apache root document folder will be **/var/www/html/** or **/var/www/** in most Debian based Linux distributions. In Ubuntu 18.04 LTS, it is **/var/www/html/**.
|
||||
|
||||
Let us create **info.php** file in the apache root folder:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo vi /var/www/html/info.php
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Add the following lines:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<?php
|
||||
phpinfo();
|
||||
?>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Press ESC key and type **:wq** to save and quit the file. Restart apache service to take effect the changes.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 3.1 Test PHP
|
||||
|
||||
Open up your web browser and navigate to **<http://IP-address/info.php>** URL.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the php test page now.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Usually, when a user requests a directory from the web server, Apache will first look for a file named **index.html**. If you want to change Apache to serve php files rather than others, move **index.php** to first position in the **dir.conf** file as shown below
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/dir.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the contents of the above file.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<IfModule mod_dir.c>
|
||||
DirectoryIndex index.html index.cgi index.pl index.php index.xhtml index.htm
|
||||
</IfModule>
|
||||
|
||||
# vim: syntax=apache ts=4 sw=4 sts=4 sr noet
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Move the “index.php” file to first. Once you made the changes, your **dir.conf** file will look like below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<IfModule mod_dir.c>
|
||||
DirectoryIndex index.php index.html index.cgi index.pl index.xhtml index.htm
|
||||
</IfModule>
|
||||
|
||||
# vim: syntax=apache ts=4 sw=4 sts=4 sr noet
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Press **ESC** key and type **:wq** to save and close the file. Restart Apache service to take effect the changes.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 3.2 Install PHP modules
|
||||
|
||||
To improve the functionality of PHP, you can install some additional PHP modules.
|
||||
|
||||
To list the available PHP modules, run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-cache search php- | less
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample output:**
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Use the arrow keys to go through the result. To exit, type **q** and hit ENTER key.
|
||||
|
||||
To find the details of any particular php module, for example **php-gd** , run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-cache show php-gd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To install a php module run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install php-gd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To install all modules (not necessary though), run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install php*
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Do not forget to restart Apache service after installing any php module. To check if the module is loaded or not, open info.php file in your browser and check if it is present.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, you might want to install any database management tools to easily manage databases via a web browser. If so, install phpMyAdmin as described in the following link.
|
||||
|
||||
Congratulations! We have successfully setup LAMP stack in Ubuntu 18.04 LTS server.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.ostechnix.com/install-apache-mysql-php-lamp-stack-on-ubuntu-18-04-lts/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[stevenzdg988](https://github.com/stevenzdg988)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7
|
||||
[2]: http://www.ostechnix.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/mysql-1.png
|
||||
[3]: http://www.ostechnix.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/mysql-2.png
|
||||
[4]: http://www.ostechnix.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/php-modules.png
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,443 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: (stevenzdg988)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
[#]: subject: (Install Apache, MySQL, PHP (LAMP) Stack On Ubuntu 18.04 LTS)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://www.ostechnix.com/install-apache-mysql-php-lamp-stack-on-ubuntu-18-04-lts/)
|
||||
[#]: author: (SK https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/)
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 安装 Apache,MySQL,PHP(LAMP)套件
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**LAMP** 套件是一种流行的开源 Web 开发平台,可用于运行和部署动态网站和基于 Web 的应用程序。 通常,LAMP 套件由 Apache Web 服务器,MariaDB/MySQL 数据库,PHP/Python/Perl 程序设计(脚本)语言组成。 LAMP 是 **L**inux,**M**ariaDB/**M**YSQL,**P**HP/**P**ython/**P**erl 的缩写。 本教程描述了如何在 Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 服务器中安装 Apache,MySQL,PHP(LAMP套件)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 上安装 Apache,MySQL,PHP(LAMP)套件
|
||||
|
||||
就本教程而言,我们将使用以下 Ubuntu 测试项。
|
||||
|
||||
* **操作系统**:Ubuntu 18.04.1 LTS Server Edition
|
||||
* **IP 地址** :192.168.225.22/24
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. 安装 Apache Web 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
首先,利用下面命令更新 Ubuntu 服务器:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt update
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt upgrade
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后,安装 Apache Web 服务器(命令如下):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install apache2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
检查 Apache Web 服务器是否已经运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl status apache2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
输出结果大概是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
● apache2.service - The Apache HTTP Server
|
||||
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/apache2.service; enabled; vendor preset: en
|
||||
Drop-In: /lib/systemd/system/apache2.service.d
|
||||
└─apache2-systemd.conf
|
||||
Active: active (running) since Tue 2019-02-05 10:48:03 UTC; 1min 5s ago
|
||||
Main PID: 2025 (apache2)
|
||||
Tasks: 55 (limit: 2320)
|
||||
CGroup: /system.slice/apache2.service
|
||||
├─2025 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
|
||||
├─2027 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
|
||||
└─2028 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
|
||||
|
||||
Feb 05 10:48:02 ubuntuserver systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server...
|
||||
Feb 05 10:48:03 ubuntuserver apachectl[2003]: AH00558: apache2: Could not reliably
|
||||
Feb 05 10:48:03 ubuntuserver systemd[1]: Started The Apache HTTP Server.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
祝贺你! Apache 服务已经启动并运行了!!
|
||||
|
||||
##### 1.1 调整防火墙允许 Apache Web 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,如果您已在 Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 中启用 UFW 防火墙,则无法从远程系统访问 Apache Web 服务器。 必须按照以下步骤开启 `http` 和 `https` 端口。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,使用以下命令列出 Ubuntu 系统上可用的应用程序配置文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo ufw app list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
输出结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Available applications:
|
||||
Apache
|
||||
Apache Full
|
||||
Apache Secure
|
||||
OpenSSH
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如你所见,Apache 和 OpenSSH 应用程序已安装 UFW 配置文件。你可以使用 “**ufw app info “Profile Name”**” 命令列出有关每个配置文件及其包含的规则的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们研究一下 **“Apache Full”** 配置文件。 为此,请运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo ufw app info "Apache Full"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
输出结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Profile: Apache Full
|
||||
Title: Web Server (HTTP,HTTPS)
|
||||
Description: Apache v2 is the next generation of the omnipresent Apache web
|
||||
server.
|
||||
|
||||
Ports:
|
||||
80,443/tcp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如你所见,“Apache Full” 配置文件包含了启用经由端口 **80** 和 **443** 的传输规则:
|
||||
|
||||
现在,运行以下命令配置允许 HTTP 和 HTTPS 传入通信:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo ufw allow in "Apache Full"
|
||||
Rules updated
|
||||
Rules updated (v6)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果您不想允许 `https` 通信,而只允许 `http(80)` 通信,请运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo ufw app info "Apache"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 1.2 测试 Apache Web 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
现在,打开 Web 浏览器并导航到 **<http://localhost/>** 或 **<http://IP-Address/>** 来访问 Apache 测试页。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果看到上面类似的显示内容,那就成功了。 Apache 服务器正在工作!
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 安装 MySQL
|
||||
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 安装 MySQL 请运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install mysql-server
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下命令验证 MySQL 服务是否正在运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl status mysql
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**输出结果:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
● mysql.service - MySQL Community Server
|
||||
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mysql.service; enabled; vendor preset: enab
|
||||
Active: active (running) since Tue 2019-02-05 11:07:50 UTC; 17s ago
|
||||
Main PID: 3423 (mysqld)
|
||||
Tasks: 27 (limit: 2320)
|
||||
CGroup: /system.slice/mysql.service
|
||||
└─3423 /usr/sbin/mysqld --daemonize --pid-file=/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
|
||||
|
||||
Feb 05 11:07:49 ubuntuserver systemd[1]: Starting MySQL Community Server...
|
||||
Feb 05 11:07:50 ubuntuserver systemd[1]: Started MySQL Community Server.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
MySQL 正在运行!
|
||||
|
||||
##### 2.1 配置数据库管理用户(root)密码
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,MySQL **root** 用户密码为空。您需要通过运行以下脚本使你的 MySQL 服务器安全:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
系统将询问你是否要安装 **VALIDATE PASSWORD plugin(密码验证插件)**。该插件允许用户为数据库配置强密码凭据。如果启用,它将自动检查密码的强度并强制用户设置足够安全的密码。 **禁用此插件是安全的**。但是,必须为数据库使用唯一的强密码凭据。如果不想启用此插件,只需按任意键即可跳过密码验证部分,然后继续其余步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
如果回答是 **是**,则会要求您选择密码验证级别。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Securing the MySQL server deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
Connecting to MySQL using a blank password.
|
||||
|
||||
VALIDATE PASSWORD PLUGIN can be used to test passwords
|
||||
and improve security. It checks the strength of password
|
||||
and allows the users to set only those passwords which are
|
||||
secure enough. Would you like to setup VALIDATE PASSWORD plugin?
|
||||
|
||||
Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No y
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可用的密码验证有 **low(低)** , **medium(中)** and **strong(强)**。只需输入适当的数字(0表示低,1表示中,2表示强密码)并按 ENTER 键。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
There are three levels of password validation policy:
|
||||
|
||||
LOW Length >= 8
|
||||
MEDIUM Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, and special characters
|
||||
STRONG Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, special characters and dictionary file
|
||||
|
||||
Please enter 0 = LOW, 1 = MEDIUM and 2 = STRONG:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在,输入 MySQL root 用户的密码。请注意,必须根据上一步中选择的密码策略,为 Mysql root 用户使用密码。如果你未启用该插件,则只需使用你选择的任意强度且唯一的密码即可。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Please set the password for root here.
|
||||
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
|
||||
Re-enter new password:
|
||||
|
||||
Estimated strength of the password: 50
|
||||
Do you wish to continue with the password provided?(Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
两次输入密码后,您将看到密码强度(在此示例情况下为**50**)。如果您确定可以,请按 Y 继续提供的密码。如果对密码长度不满意,请按其他任意键并设置一个强密码。我现在的密码可以,所以我选择了**y**。
|
||||
|
||||
对于其余的问题,只需键入**y**并按 Enter。这将删除匿名用户,禁止 root 用户远程登录并删除 `test`(测试)数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
|
||||
Success.
|
||||
|
||||
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from
|
||||
'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at
|
||||
the root password from the network.
|
||||
|
||||
Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
|
||||
Success.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that
|
||||
anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing,
|
||||
and should be removed before moving into a production
|
||||
environment.
|
||||
|
||||
Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
|
||||
- Dropping test database...
|
||||
Success.
|
||||
|
||||
- Removing privileges on test database...
|
||||
Success.
|
||||
|
||||
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes
|
||||
made so far will take effect immediately.
|
||||
|
||||
Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
|
||||
Success.
|
||||
|
||||
All done!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
以上就是为 MySQL root 用户设置密码。
|
||||
|
||||
##### 2.2 更改 MySQL 超级用户的身份验证方法
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,Ubuntu 系统的 MySQL root 用户为 MySQL 5.7 版本使用插件 **auth_socket** 和更新版本设置身份验证。 尽管它增强了安全性,但是当您使用任何外部程序(例如 phpMyAdmin)访问数据库服务器时,也会变得更困难。 要解决此问题,您需要将身份验证方法从 **auth_socket** 更改为 **mysql_native_password**。 为此,请使用以下命令登录到您的 MySQL 提示符下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mysql
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 MySQL 提示符下运行以下命令,找到所有 MySQL 当前用户帐户的身份验证方法:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
SELECT user,authentication_string,plugin,host FROM mysql.user;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**输出结果:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
+------------------|-------------------------------------------|-----------------------|-----------+
|
||||
| user | authentication_string | plugin | host |
|
||||
+------------------|-------------------------------------------|-----------------------|-----------+
|
||||
| root | | auth_socket | localhost |
|
||||
| mysql.session | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE | mysql_native_password | localhost |
|
||||
| mysql.sys | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE | mysql_native_password | localhost |
|
||||
| debian-sys-maint | *F126737722832701DD3979741508F05FA71E5BA0 | mysql_native_password | localhost |
|
||||
+------------------|-------------------------------------------|-----------------------|-----------+
|
||||
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
如你所见,Mysql root 用户使用 `auth_socket` 插件进行身份验证。
|
||||
|
||||
要将此身份验证更改为 **mysql_native_password** 方法,请在 Mysql 提示符下运行以下命令。 别忘了用你选择的强大唯一密码替换 **“password”**。 如果已启用 VALIDATION 插件,请确保已根据当前策略要求使用了强密码。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'password';
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下命令更新数据库:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用命令再次检查身份验证方法是否已更改:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
SELECT user,authentication_string,plugin,host FROM mysql.user;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
输出结果:
|
||||
|
||||
![][3]
|
||||
|
||||
好!Myql root 用户就可以使用密码进行身份验证来访问 `mysql shell`。
|
||||
|
||||
从 Mysql 提示符下退出:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
exit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3\. 安装 PHP
|
||||
|
||||
安装 PHP 请运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install php libapache2-mod-php php-mysql
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装 PHP 后,在 Apache 文档根目录中创建 **info.php** 文件。通常,在大多数基于 Debian 的 Linux 发行版中,Apache 文档根目录为 **/var/www/html/** 或 **/var/www/**。Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 系统下,文档根目录是 **/var/www/html/**。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Apache 根目录中创建 **info.php** 文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo vi /var/www/html/info.php
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在此文件中编辑如下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<?php
|
||||
phpinfo();
|
||||
?>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后按下 ESC 键并且输入 **:wq** 保存并退出此文件。重新启动 Apache 服务使更改生效。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 3.1 测试 PHP
|
||||
|
||||
打开 Web 浏览器,然后导航到 URL **<http://IP地址/info.php>**。
|
||||
|
||||
你就将看到 `php` 测试页面。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
通常,当用户向 Web 服务器发出请求时,Apache 首先会在文档根目录中查找名为 **index.html** 的文件。如果您想将 Apache 更改为 `php` 文件提供服务而不是其他文件,请将 **dir.conf** 配置文件中的 **index.php** 移至第一个位置,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/dir.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上面的配置文件 (**dir.conf**) 内容如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<IfModule mod_dir.c>
|
||||
DirectoryIndex index.html index.cgi index.pl index.php index.xhtml index.htm
|
||||
</IfModule>
|
||||
|
||||
# vim: syntax=apache ts=4 sw=4 sts=4 sr noet
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将 **“index.php”** 移动到最前面。更改后,**dir.conf** 文件内容看起来如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<IfModule mod_dir.c>
|
||||
DirectoryIndex index.php index.html index.cgi index.pl index.xhtml index.htm
|
||||
</IfModule>
|
||||
|
||||
# vim: syntax=apache ts=4 sw=4 sts=4 sr noet
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后按下 ESC 键并且输入 **:wq** 保存并关闭此文件。重新启动 Apache 服务使更改生效。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 3.2 安装 PHP 模块
|
||||
|
||||
为了增加 PHP 的功能,可以安装一些其他的 PHP 模块。
|
||||
|
||||
要列出可用的 PHP 模块,请运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-cache search php- | less
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**输出结果:**
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
使用方向键浏览结果。要退出,请输入**q** 并按下 ENTER 键。
|
||||
|
||||
要查找任意 `php` 模块的详细信息,例如 **php-gd**,请运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-cache show php-gd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装 `php` 模块请运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install php-gd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装所有的模块(虽然没有必要),请运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install php*
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装任何 `php` 模块后,请不要忘记重新启动 Apache 服务。要检查模块是否已加载,请在浏览器中打开 `info.php` 文件并检查是否存在。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,您可能需要安装数据库管理工具,以通过 Web 浏览器轻松管理数据库。如果是这样,请按照以下链接中的说明安装 `phpMyAdmin`。
|
||||
|
||||
祝贺你!我们已经在 Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 服务器中成功配置了 LAMP 套件。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.ostechnix.com/install-apache-mysql-php-lamp-stack-on-ubuntu-18-04-lts/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[stevenzdg988](https://github.com/stevenzdg988)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7
|
||||
[2]: http://www.ostechnix.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/mysql-1.png
|
||||
[3]: http://www.ostechnix.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/mysql-2.png
|
||||
[4]: http://www.ostechnix.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/php-modules.png
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user