mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-28 23:20:10 +08:00
Merge pull request #9587 from MjSeven/master
20170706 Docker Guide Dockerizing Python Django Application.md 翻译完毕
This commit is contained in:
commit
ca6338e289
@ -1,450 +0,0 @@
|
||||
MjSeven is translating
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Docker Guide: Dockerizing Python Django Application
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
### On this page
|
||||
|
||||
1. [What we will do?][6]
|
||||
|
||||
2. [Step 1 - Install Docker-ce][7]
|
||||
|
||||
3. [Step 2 - Install Docker-compose][8]
|
||||
|
||||
4. [Step 3 - Configure Project Environment][9]
|
||||
1. [Create a New requirements.txt file][1]
|
||||
|
||||
2. [Create the Nginx virtual host file django.conf][2]
|
||||
|
||||
3. [Create the Dockerfile][3]
|
||||
|
||||
4. [Create Docker-compose script][4]
|
||||
|
||||
5. [Configure Django project][5]
|
||||
|
||||
5. [Step 4 - Build and Run the Docker image][10]
|
||||
|
||||
6. [Step 5 - Testing][11]
|
||||
|
||||
7. [Reference][12]
|
||||
|
||||
Docker is an open-source project that provides an open platform for developers and sysadmins to build, package, and run applications anywhere as a lightweight container. Docker automates the deployment of applications inside software containers.
|
||||
|
||||
Django is a web application framework written in python that follows the MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture. It is available for free and released under an open source license. It is fast and designed to help developers get their application online as quickly as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I will show you step-by-step how to create a docker image for an existing Django application project in Ubuntu 16.04\. We will learn about dockerizing a python Django application, and then deploy the application as a container to the docker environment using a docker-compose script.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to deploy our python Django application, we need additional docker images. We need an nginx docker image for the web server and PostgreSQL image for the database.
|
||||
|
||||
### What we will do?
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install Docker-ce
|
||||
|
||||
2. Install Docker-compose
|
||||
|
||||
3. Configure Project Environment
|
||||
|
||||
4. Build and Run
|
||||
|
||||
5. Testing
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1 - Install Docker-ce
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, we will install docker-ce community edition from the docker repository. We will install docker-ce community edition and docker-compose that support compose file version 3.
|
||||
|
||||
Before installing docker-ce, install docker dependencies needed using the apt command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt install -y \
|
||||
apt-transport-https \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
curl \
|
||||
software-properties-common
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now add the docker key and repository by running commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository \
|
||||
"deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
|
||||
$(lsb_release -cs) \
|
||||
stable"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[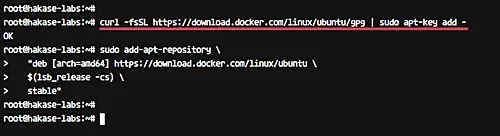][14]
|
||||
|
||||
Update the repository and install docker-ce.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt update
|
||||
sudo apt install -y docker-ce
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After the installation is complete, start the docker service and enable it to launch every time at system boot.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
systemctl start docker
|
||||
systemctl enable docker
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we will add a new user named 'omar' and add it to the docker group.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
useradd -m -s /bin/bash omar
|
||||
usermod -a -G docker omar
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[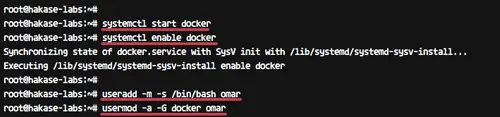][15]
|
||||
|
||||
Login as the omar user and run docker command as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
su - omar
|
||||
docker run hello-world
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure you get the hello-world message from Docker.
|
||||
|
||||
[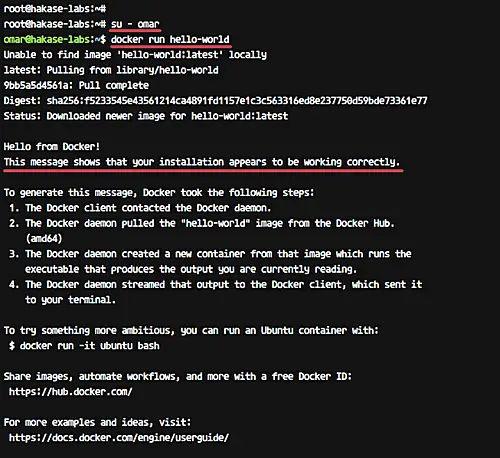][16]
|
||||
|
||||
Docker-ce installation has been completed.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2 - Install Docker-compose
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, we will be using the latest docker-compose support for compose file version 3\. We will install docker-compose manually.
|
||||
|
||||
Download the latest version of docker-compose using curl command to the '/usr/local/bin' directory and make it executable using chmod.
|
||||
|
||||
Run commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo curl -L https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.21.0/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m) -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
|
||||
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now check the docker-compose version.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker-compose version
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And make sure you get the latest version of the docker-compose 1.21.
|
||||
|
||||
[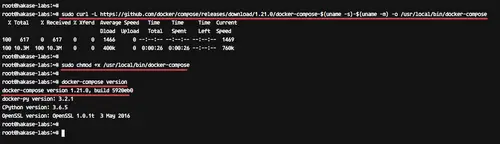][17]
|
||||
|
||||
The docker-compose latest version that supports compose file version 3 has been installed.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3 - Configure Project Environment
|
||||
|
||||
In this step, we will configure the python Django project environment. We will create new directory 'guide01' and make it as the main directory for our project files, such as a Dockerfile, Django project, nginx configuration file etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Login to the 'omar' user.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
su - omar
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
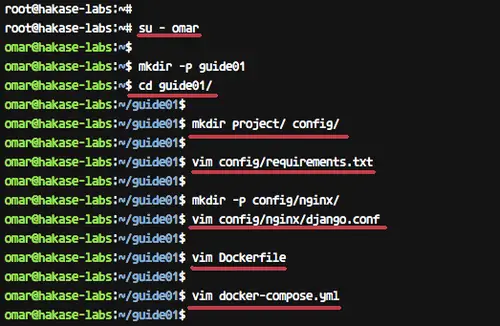
Create new directory 'guide01' and go to the directory.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir -p guide01
|
||||
cd guide01/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now inside the 'guide01' directory, create new directories 'project' and 'config'.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir project/ config/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note:
|
||||
|
||||
* Directory 'project': All our python Django project files will be placed in that directory.
|
||||
|
||||
* Directory 'config': Directory for the project configuration files, including nginx configuration file, python pip requirements file etc.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a New requirements.txt file
|
||||
|
||||
Next, create new file 'requirements.txt' inside the 'config' directory using vim command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vim config/requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Paste the configuration below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Django==2.0.4
|
||||
gunicorn==19.7.0
|
||||
psycopg2==2.7.4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create the Nginx virtual host file django.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Under the config directory, create the 'nginx' configuration directory and add the virtual host configuration file django.conf.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir -p config/nginx/
|
||||
vim config/nginx/django.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Paste the following configuration there.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
upstream web {
|
||||
ip_hash;
|
||||
server web:8000;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# portal
|
||||
server {
|
||||
location / {
|
||||
proxy_pass http://web/;
|
||||
}
|
||||
listen 8000;
|
||||
server_name localhost;
|
||||
|
||||
location /static {
|
||||
autoindex on;
|
||||
alias /src/static/;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create the Dockerfile
|
||||
|
||||
Create new 'Dockerfile' inside the 'guide01' directory.
|
||||
|
||||
Run the command below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vim Dockerfile
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now paste Dockerfile script below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
FROM python:3.5-alpine
|
||||
ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED 1
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apk update && \
|
||||
apk add --virtual build-deps gcc python-dev musl-dev && \
|
||||
apk add postgresql-dev bash
|
||||
|
||||
RUN mkdir /config
|
||||
ADD /config/requirements.txt /config/
|
||||
RUN pip install -r /config/requirements.txt
|
||||
RUN mkdir /src
|
||||
WORKDIR /src
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
Note:
|
||||
|
||||
We want to build the Docker images for our Django project based on Alpine Linux, the smallest size of Linux. Our Django project will run Alpine Linux with python 3.5 installed on top of it and add the postgresql-dev package for the PostgreSQL database support. And then we will install all python packages listed on the 'requirements.txt' file using python pip command, and create new '/src' for our project.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create Docker-compose script
|
||||
|
||||
Create the 'docker-compose.yml' file under the 'guide01' directory using [vim][18] command below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vim docker-compose.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Paste the following configuration there.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
version: '3'
|
||||
services:
|
||||
db:
|
||||
image: postgres:10.3-alpine
|
||||
container_name: postgres01
|
||||
nginx:
|
||||
image: nginx:1.13-alpine
|
||||
container_name: nginx01
|
||||
ports:
|
||||
- "8000:8000"
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- ./project:/src
|
||||
- ./config/nginx:/etc/nginx/conf.d
|
||||
depends_on:
|
||||
- web
|
||||
web:
|
||||
build: .
|
||||
container_name: django01
|
||||
command: bash -c "python manage.py makemigrations && python manage.py migrate && python manage.py collectstatic --noinput && gunicorn hello_django.wsgi -b 0.0.0.0:8000"
|
||||
depends_on:
|
||||
- db
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- ./project:/src
|
||||
expose:
|
||||
- "8000"
|
||||
restart: always
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
Note:
|
||||
|
||||
With this docker-compose file script, we will create three services. Create the database service named 'db' using the PostgreSQL alpine Linux, create the 'nginx' service using the Nginx alpine Linux again, and create our python Django container using the custom docker images generated from our Dockerfile.
|
||||
|
||||
[][19]
|
||||
|
||||
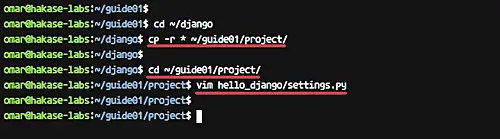
### Configure Django project
|
||||
|
||||
Copy your Django project files to the 'project' directory.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd ~/django
|
||||
cp -r * ~/guide01/project/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the 'project' directory and edit the application setting 'settings.py'.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd ~/guide01/project/
|
||||
vim hello_django/settings.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note:
|
||||
|
||||
We will deploy simple Django application called 'hello_django' app.
|
||||
|
||||
On the 'ALLOW_HOSTS' line, add the service name 'web'.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ALLOW_HOSTS = ['web']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now change the database settings. We will be using the PostgreSQL database that runs as a service named 'db' with default user and password.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
DATABASES = {
|
||||
'default': {
|
||||
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.postgresql_psycopg2',
|
||||
'NAME': 'postgres',
|
||||
'USER': 'postgres',
|
||||
'HOST': 'db',
|
||||
'PORT': 5432,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And for the 'STATIC_ROOT' configuration directory, add this line to the end of the line of the file.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
STATIC_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'static/')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
[][20]
|
||||
|
||||
Now we're ready to build and run the Django project under the docker container.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4 - Build and Run the Docker image
|
||||
|
||||
In this step, we want to build a Docker image for our Django project using the configuration on the 'guide01' directory.
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the 'guide01' directory.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd ~/guide01/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
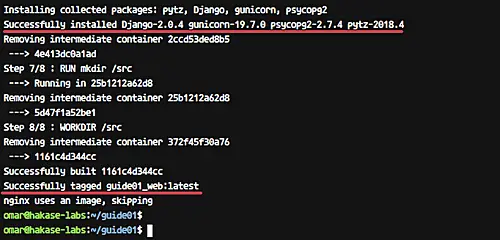
Now build the docker images using the docker-compose command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker-compose build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][21]
|
||||
|
||||
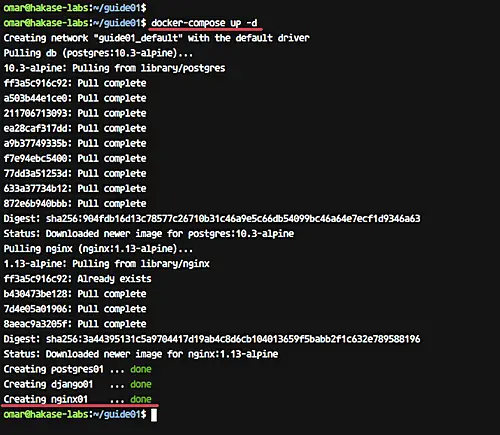
Start all services inside the docker-compose script.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker-compose up -d
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wait for some minutes for Docker to build our Python image and download the nginx and postgresql docker images.
|
||||
|
||||
[][22]
|
||||
|
||||
And when it's complete, check running container and list docker images on the system using following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker-compose ps
|
||||
docker-compose images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And now you will get three containers running and list of Docker images on the system as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
[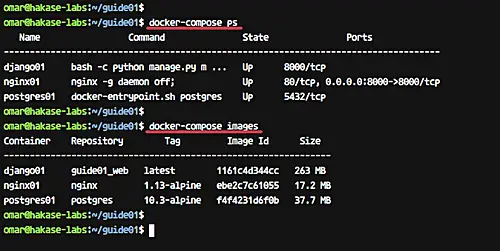][23]
|
||||
|
||||
Our Python Django Application is now running inside the docker container, and docker images for our service have been created.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 5 - Testing
|
||||
|
||||
Open your web browser and type the server address with port 8000, mine is: http://ovh01:8000/
|
||||
|
||||
Now you will get the default Django home page.
|
||||
|
||||
[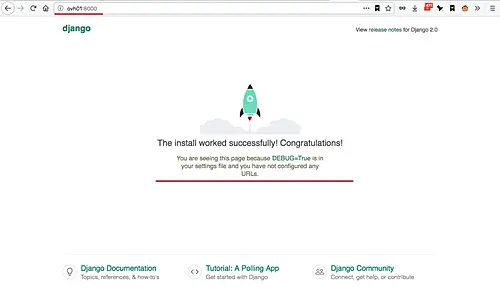][24]
|
||||
|
||||
Next, test the admin page by adding the '/admin' path on the URL.
|
||||
|
||||
http://ovh01:8000/admin/
|
||||
|
||||
And you will see the Django admin login page.
|
||||
|
||||
[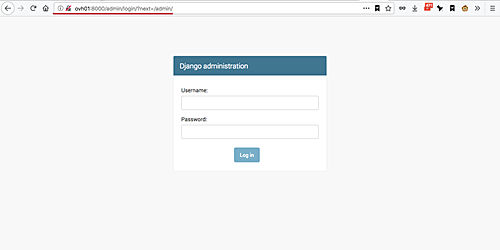][25]
|
||||
|
||||
The Dockerizing Python Django Application has been completed successfully.
|
||||
|
||||
### Reference
|
||||
|
||||
* [https://docs.docker.com/][13]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Muhammad Arul][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#create-a-new-requirementstxt-file
|
||||
[2]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#create-the-nginx-virtual-host-file-djangoconf
|
||||
[3]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#create-the-dockerfile
|
||||
[4]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#create-dockercompose-script
|
||||
[5]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#configure-django-project
|
||||
[6]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#what-we-will-do
|
||||
[7]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#step-install-dockerce
|
||||
[8]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#step-install-dockercompose
|
||||
[9]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#step-configure-project-environment
|
||||
[10]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#step-build-and-run-the-docker-image
|
||||
[11]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#step-testing
|
||||
[12]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#reference
|
||||
[13]:https://docs.docker.com/
|
||||
[14]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/1.png
|
||||
[15]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/2.png
|
||||
[16]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/3.png
|
||||
[17]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/4.png
|
||||
[18]:https://www.howtoforge.com/vim-basics
|
||||
[19]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/5.png
|
||||
[20]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/6.png
|
||||
[21]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/7.png
|
||||
[22]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/8.png
|
||||
[23]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/9.png
|
||||
[24]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/10.png
|
||||
[25]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/11.png
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,415 @@
|
||||
Docker 指南:Docker 化 Python Django 应用程序
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
### 目录
|
||||
|
||||
1. [我们要做什么?][6]
|
||||
|
||||
2. [步骤 1 - 安装 Docker-ce][7]
|
||||
|
||||
3. [步骤 2 - 安装 Docker-compose][8]
|
||||
|
||||
4. [步骤 3 - 配置项目环境][9]
|
||||
1. [创建一个新的 requirements.txt 文件][1]
|
||||
|
||||
2. [创建 Nginx 虚拟主机文件 django.conf][2]
|
||||
|
||||
3. [创建 Dockerfile][3]
|
||||
|
||||
4. [创建 Docker-compose 脚本][4]
|
||||
|
||||
5. [配置 Django 项目][5]
|
||||
|
||||
5. [步骤 4 - 构建并运行 Docker 镜像][10]
|
||||
|
||||
6. [步骤 5 - 测试][11]
|
||||
|
||||
7. [参考][12]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Docker 是一个开源项目,为开发人员和系统管理员提供了一个开放平台,作为一个轻量级容器,它可以在任何地方构建,打包和运行应用程序。Docker 在软件容器中自动部署应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
Django 是一个用 Python 编写的 Web 应用程序框架,遵循 MVC(模型-视图-控制器)架构。它是免费的,并在开源许可下发布。它速度很快,旨在帮助开发人员尽快将他们的应用程序上线。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我将逐步向你展示在 Ubuntu 16.04 如何为现有的 Django 应用程序创建 docker 镜像。我们将学习如何 docker 化一个 Python Django 应用程序,然后使用一个 docker-compose 脚本将应用程序作为容器部署到 docker 环境。
|
||||
|
||||
为了部署我们的 Python Django 应用程序,我们需要其他 docker 镜像:一个用于 Web 服务器的 nginx docker 镜像和用于数据库的 PostgreSQL 镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
### 我们要做什么?
|
||||
|
||||
1. 安装 Docker-ce
|
||||
|
||||
2. 安装 Docker-compose
|
||||
|
||||
3. 配置项目环境
|
||||
|
||||
4. 构建并运行
|
||||
|
||||
5. 测试
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 1 - 安装 Docker-ce
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我们将重 docker 仓库安装 docker-ce 社区版。我们将安装 docker-ce 社区版和 docker-compose,其支持 compose 文件版本 3(to 校正者:此处不太明白具体意思)。
|
||||
|
||||
在安装 docker-ce 之前,先使用 apt 命令安装所需的 docker 依赖项。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt install -y \
|
||||
apt-transport-https \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
curl \
|
||||
software-properties-common
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在通过运行以下命令添加 docker 密钥和仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository \
|
||||
"deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
|
||||
$(lsb_release -cs) \
|
||||
stable"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][14]
|
||||
|
||||
更新仓库并安装 docker-ce。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt update
|
||||
sudo apt install -y docker-ce
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后,启动 docker 服务并使其能够在每次系统引导时启动。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
systemctl start docker
|
||||
systemctl enable docker
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接着,我们将添加一个名为 'omar' 的新用户并将其添加到 docker 组。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
useradd -m -s /bin/bash omar
|
||||
usermod -a -G docker omar
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][15]
|
||||
|
||||
以 omar 用户身份登录并运行 docker 命令,如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
su - omar
|
||||
docker run hello-world
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
确保你能从 Docker 获得 hello-world 消息。
|
||||
|
||||
[][16]
|
||||
|
||||
Docker-ce 安装已经完成。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 2 - 安装 Docker-compose
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我们将使用最新的 docker-compose 支持 compose 文件版本 3。我们将手动安装 docker-compose。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 curl 命令将最新版本的 docker-compose 下载到 `/usr/local/bin` 目录,并使用 chmod 命令使其有执行权限。
|
||||
|
||||
运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo curl -L https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.21.0/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m) -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
|
||||
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在检查 docker-compose 版本。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker-compose version
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
确保你安装的是最新版本的 docker-compose 1.21。
|
||||
|
||||
[][17]
|
||||
|
||||
已安装支持 compose 文件版本 3 的 docker-compose 最新版本。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 3 - 配置项目环境
|
||||
|
||||
在这一步中,我们将配置 Python Django 项目环境。我们将创建新目录 'guide01',并使其成为我们项目文件的主目录,例如 Dockerfile,Django 项目,nginx 配置文件等。
|
||||
|
||||
登录到 'omar' 用户。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
su - omar
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个新目录 'guide01',并进入目录。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir -p guide01
|
||||
cd guide01/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在在 'guide01' 目录下,创建两个新目录 'project' 和 'config'。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir project/ config/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意:
|
||||
|
||||
* 'project' 目录:我们所有的 python Django 项目文件都将放在该目录中。
|
||||
|
||||
* 'config' 目录:项目配置文件的目录,包括 nginx 配置文件,python pip requirements 文件等。
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建一个新的 requirements.txt 文件
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,使用 vim 命令在 'config' 目录中创建一个新的 requirements.txt 文件
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vim config/requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
粘贴下面的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Django==2.0.4
|
||||
gunicorn==19.7.0
|
||||
psycopg2==2.7.4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建 Dockerfile
|
||||
|
||||
在 'guide01' 目录下创建新文件 'Dockerfile'。
|
||||
|
||||
运行以下命令。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vim Dockerfile
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在粘贴下面的 Dockerfile 脚本。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
FROM python:3.5-alpine
|
||||
ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED 1
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apk update && \
|
||||
apk add --virtual build-deps gcc python-dev musl-dev && \
|
||||
apk add postgresql-dev bash
|
||||
|
||||
RUN mkdir /config
|
||||
ADD /config/requirements.txt /config/
|
||||
RUN pip install -r /config/requirements.txt
|
||||
RUN mkdir /src
|
||||
WORKDIR /src
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:
|
||||
|
||||
我们想要为我们的 Django 项目构建基于 Alpine Linux 的 Docker 镜像,Alpine 是最小的 Linux 版本。我们的 Django 项目将运行在带有 Python3.5 的 Alpine Linux 上,并添加 postgresql-dev 包以支持 PostgreSQL 数据库。然后,我们将使用 python pip 命令安装在 'requirements.txt' 上列出的所有 Python 包,并为我们的项目创建新目录 '/src'。
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建 Docker-compose 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
使用 [vim][18] 命令在 'guide01' 目录下创建 'docker-compose.yml' 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vim docker-compose.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
粘贴以下配置内容。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
version: '3'
|
||||
services:
|
||||
db:
|
||||
image: postgres:10.3-alpine
|
||||
container_name: postgres01
|
||||
nginx:
|
||||
image: nginx:1.13-alpine
|
||||
container_name: nginx01
|
||||
ports:
|
||||
- "8000:8000"
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- ./project:/src
|
||||
- ./config/nginx:/etc/nginx/conf.d
|
||||
depends_on:
|
||||
- web
|
||||
web:
|
||||
build: .
|
||||
container_name: django01
|
||||
command: bash -c "python manage.py makemigrations && python manage.py migrate && python manage.py collectstatic --noinput && gunicorn hello_django.wsgi -b 0.0.0.0:8000"
|
||||
depends_on:
|
||||
- db
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- ./project:/src
|
||||
expose:
|
||||
- "8000"
|
||||
restart: always
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:
|
||||
|
||||
使用这个 docker-compose 文件脚本,我们将创建三个服务。使用 PostgreSQL alpine Linux 创建名为 'db' 的数据库服务,再次使用 Nginx alpine Linux 创建 'nginx' 服务,并使用从 Dockerfile 生成的自定义 docker 镜像创建我们的 python Django 容器。
|
||||
|
||||
[][19]
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置 Django 项目
|
||||
|
||||
将 Django 项目文件复制到 'project' 目录。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd ~/django
|
||||
cp -r * ~/guide01/project/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
进入 'project' 目录并编辑应用程序设置 'settings.py'。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd ~/guide01/project/
|
||||
vim hello_django/settings.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意:
|
||||
|
||||
我们将部署名为 'hello_django' 的简单 Django 应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
在 'ALLOW_HOSTS' 行中,添加服务名称 'web'。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ALLOW_HOSTS = ['web']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在更改数据库设置,我们将使用 PostgreSQL 数据库,'db' 数据库作为服务运行,使用默认用户和密码。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
DATABASES = {
|
||||
'default': {
|
||||
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.postgresql_psycopg2',
|
||||
'NAME': 'postgres',
|
||||
'USER': 'postgres',
|
||||
'HOST': 'db',
|
||||
'PORT': 5432,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
至于 'STATIC_ROOT' 配置目录,将此行添加到文件行的末尾。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
STATIC_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'static/')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
[][20]
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们准备在 docker 容器下构建和运行 Django 项目。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 4 - 构建并运行 Docker 镜像
|
||||
|
||||
在这一步中,我们想要使用 'guide01' 目录中的配置为我们的 Django 项目构建一个 Docker 镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
进入 'guide01' 目录。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd ~/guide01/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在使用 docker-compose 命令构建 docker 镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker-compose build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][21]
|
||||
|
||||
启动 docker-compose 脚本中的所有服务。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker-compose up -d
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
等待几分钟让 Docker 构建我们的 Python 镜像并下载 nginx 和 postgresql docker 镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
[][22]
|
||||
|
||||
完成后,使用以下命令检查运行容器并在系统上列出 docker 镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker-compose ps
|
||||
docker-compose images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你将在系统上运行三个容器并列出 Docker 镜像,如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
[][23]
|
||||
|
||||
我们的 Python Django 应用程序现在在 docker 容器内运行,并且已经创建了为我们服务的 docker 镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 5 - 测试
|
||||
|
||||
打开 Web 浏览器并使用端口 8000 键入服务器地址,我的是:http://ovh01:8000/
|
||||
|
||||
现在你将获得默认的 Django 主页。
|
||||
|
||||
[][24]
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,通过在 URL 上添加 “/admin” 路径来测试管理页面。
|
||||
|
||||
http://ovh01:8000/admin/
|
||||
|
||||
然后你将会看到 Django admin 登录页面。
|
||||
|
||||
[][25]
|
||||
|
||||
Docker 化 Python Django 应用程序已成功完成。
|
||||
|
||||
### 参考
|
||||
|
||||
* [https://docs.docker.com/][13]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Muhammad Arul][a]
|
||||
译者:[MjSeven](https://github.com/MjSeven)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#create-a-new-requirementstxt-file
|
||||
[2]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#create-the-nginx-virtual-host-file-djangoconf
|
||||
[3]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#create-the-dockerfile
|
||||
[4]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#create-dockercompose-script
|
||||
[5]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#configure-django-project
|
||||
[6]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#what-we-will-do
|
||||
[7]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#step-install-dockerce
|
||||
[8]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#step-install-dockercompose
|
||||
[9]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#step-configure-project-environment
|
||||
[10]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#step-build-and-run-the-docker-image
|
||||
[11]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#step-testing
|
||||
[12]:https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/docker-guide-dockerizing-python-django-application/#reference
|
||||
[13]:https://docs.docker.com/
|
||||
[14]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/1.png
|
||||
[15]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/2.png
|
||||
[16]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/3.png
|
||||
[17]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/4.png
|
||||
[18]:https://www.howtoforge.com/vim-basics
|
||||
[19]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/5.png
|
||||
[20]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/6.png
|
||||
[21]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/7.png
|
||||
[22]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/8.png
|
||||
[23]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/9.png
|
||||
[24]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/10.png
|
||||
[25]:https://www.howtoforge.com/images/docker_guide_dockerizing_python_django_application/big/11.png
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user