mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-25 23:11:02 +08:00
Merge remote-tracking branch 'lcct/master'
This commit is contained in:
commit
c980a0c515
@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
|
||||
修复Ubuntu 14.04中各种更新错误
|
||||
Ubuntu 更新错误修复大全
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu更新中,谁没有碰见个错误?在Ubuntu和其它基于Ubuntu的Linux发行版中,更新错误很常见,也为数不少。这些错误出现的原因多种多样,修复起来也很简单。在本文中,我们将见到Ubuntu中各种类型频繁发生的更新错误以及它们的修复方法。
|
||||
在Ubuntu更新中,谁没有碰见个错误?在Ubuntu和其它基于Ubuntu的Linux发行版中,更新错误是一个共性的错误,也经常发生。这些错误出现的原因多种多样,修复起来也很简单。在本文中,我们将见到Ubuntu中各种类型频繁发生的更新错误以及它们的修复方法。
|
||||
|
||||
### 合并列表问题 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,7 +38,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
下载仓库信息失败的另外一种类型是由于PPA过时导致的。通常,当你运行更新管理器,并看到这样的错误时:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可以运行sudo apt-get update来查看哪个PPA更新失败,你可以把它从源列表中删除。你可以按照这个截图指南来[修复下载仓库信息失败错误][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -48,7 +48,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
该错误很容易修复,只需修改软件源为主服务器即可。转到软件和更新,在那里你可以修改下载服务器为主服务器:
|
||||
该错误很容易修复,只需修改软件源为主服务器即可。转到“软件和更新”,在那里你可以修改下载服务器为主服务器:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -78,7 +78,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在这里查找到更多详细内容[加载共享库时发生错误][6]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 无法获取锁/var/cache/apt/archives/lock ###
|
||||
### 无法获取锁 /var/cache/apt/archives/lock ###
|
||||
|
||||
在另一个程序在使用APT时,会发生该错误。假定你正在Ubuntu软件中心安装某个东西,然后你又试着在终端中运行apt。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -135,7 +135,7 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-update-errors-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,21 +1,22 @@
|
||||
Linux中用于监控网络、磁盘使用、开机时间、平均负载和内存使用率的shell脚本
|
||||
一个Linux中用于监控的简易shell脚本
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
系统管理员的任务真的很艰难,因为他/她必须监控服务器、用户、日志,还得创建备份,等等等等。对于大多数重复性的任务,大多数管理员都会写一个自动化脚本来日复一日重复这些任务。这里,我们已经写了一个shell脚本给大家,用来自动化完成系统管理员所要完成的常规任务,这可能在多数情况下,尤其是对于新手而言十分有用,他们能通过该脚本获取到大多数的他们想要的信息,包括系统、网络、用户、负载、内存、主机、内部IP、外部IP、开机时间等。
|
||||
系统管理员的任务真的很艰难,因为他/她必须监控服务器、用户、日志,还得创建备份,等等等等。对于大多数重复性的任务,大多数管理员都会写一个自动化脚本来日复一日地重复这些任务。这里,我们已经写了一个shell脚本给大家,用来自动化完成系统管理员所要完成的常规任务,这可能在多数情况下,尤其是对于新手而言十分有用,他们能通过该脚本获取到大多数的他们想要的信息,包括系统、网络、用户、负载、内存、主机、内部IP、外部IP、开机时间等。
|
||||
|
||||
我们已经注意并进行了格式化输出(在一定程度上哦)。此脚本不包含任何恶意内容,并且它能以普通用户帐号运行。事实上,我们也推荐你以普通用户运行该脚本,而不是root。
|
||||
|
||||
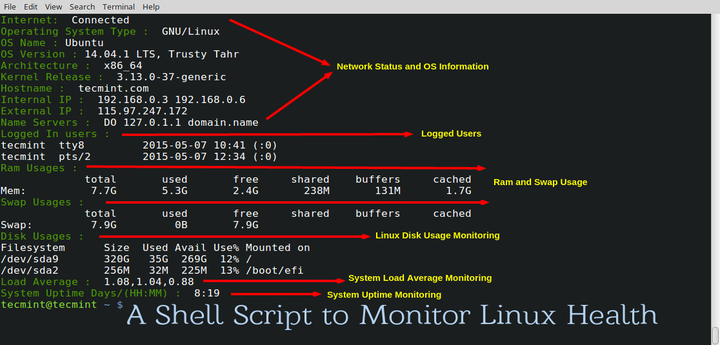
|
||||
监控Linux系统健康的Shell脚本
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过给Tecmint和脚本作者合适的积分,获得自由使用/修改/再分发下面代码的权利。我们已经试着在一定程度上自定义了输出结果,除了要求的输出内容外,其它内容都不会生成。我们也已经试着使用了那些Linux系统中通常不使用的变量,这些变量可能也是自由代码。
|
||||
*监控Linux系统健康的Shell脚本*
|
||||
|
||||
在保留Tecmint和脚本作者应得荣誉的前提下,可以自由使用/修改/再分发下面代码。我们已经试着在一定程度上自定义了输出结果,除了要求的输出内容外,其它内容都不会生成。我们也已经试着使用了那些Linux系统中通常不使用的变量,这些变量应该是可以随便用的。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 最小系统要求 ####
|
||||
|
||||
你所需要的一切,就是一台正常运转的Linux盒子。
|
||||
你所需要的一切,就是一台正常运转的Linux机器。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 依赖性 ####
|
||||
|
||||
对于一个标准的Linux发行版,使用此包时没有任何依赖。此外,该脚本不需要root权限来执行。但是,如果你想要安装,则必须输入一次root密码。
|
||||
对于一个标准的Linux发行版,使用此软件包不需任何依赖。此外,该脚本不需要root权限来执行。但是,如果你想要安装,则必须输入一次root密码。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 安全性 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,16 +31,16 @@ Linux中用于监控网络、磁盘使用、开机时间、平均负载和内存
|
||||
|
||||
强烈建议你以普通用户身份安装该脚本,而不是root。安装过程中会询问root密码,并且在需要的时候安装必要的组件。
|
||||
|
||||
要安装`“tecmint_monitor.sh”`脚本,只需像下面这样使用-i(安装)选项就可以了。
|
||||
要安装“`tecmint_monitor.sh`”脚本,只需像下面这样使用-i(安装)选项就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
/tecmint_monitor.sh -i
|
||||
./tecmint_monitor.sh -i
|
||||
|
||||
在提示你输入root密码时输入该密码。如果一切顺利,你会看到像下面这样的安装成功信息。
|
||||
|
||||
Password:
|
||||
Congratulations! Script Installed, now run monitor Command
|
||||
|
||||
安装完毕后,你可以通过在任何位置,以任何用户调用命令`‘monitor’`来运行该脚本。如果你不喜欢安装,你需要在每次运行时输入路径。
|
||||
安装完毕后,你可以在任何位置,以任何用户调用命令`‘monitor’`来运行该脚本。如果你不喜欢安装,你需要在每次运行时输入路径。
|
||||
|
||||
# ./Path/to/script/tecmint_monitor.sh
|
||||
|
||||
@ -49,7 +50,7 @@ Linux中用于监控网络、磁盘使用、开机时间、平均负载和内存
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
你一运行命令,就会获得下面这些各种各样和系统相关的信息:
|
||||
你运行命令就会获得下面这些各种各样和系统相关的信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- 互联网连通性
|
||||
- 操作系统类型
|
||||
@ -78,9 +79,9 @@ Linux中用于监控网络、磁盘使用、开机时间、平均负载和内存
|
||||
|
||||
### 小结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
该脚本在一些机器上可以开机即用,这一点我已经检查过。相信对于你而言,它也会正常工作。如果你们发现了什么毛病,可以在评论中告诉我。这个脚本还不是结束,这仅仅是个开始。从这里开始,你可以将它提升到任何等级。如果你想要编辑脚本,将它带入一个更深的层次,尽管随意去做吧,别忘了给我们合适的积分,也别忘了把你更新后的脚本拿出来和我们分享哦,这样,我们也能通过给你合适的积分来更新此文。
|
||||
该脚本在一些机器上可以开机即用,这一点我已经检查过。相信对于你而言,它也会正常工作。如果你们发现了什么毛病,可以在评论中告诉我。这个脚本还不完善,这仅仅是个开始。从这里开始,你可以将它改进到任何程度。如果你想要编辑脚本,将它带入一个更深的层次,尽管随意去做吧,别忘了给我们应的的荣誉,也别忘了把你更新后的脚本拿出来和我们分享哦,这样,我们也会更新此文来给你应得的荣誉。
|
||||
|
||||
别忘了和我们分享你的想法或者脚本,我们会在这儿帮助你。谢谢你们给予的所有挚爱。保持连线,不要走开哦。
|
||||
别忘了和我们分享你的想法或者脚本,我们会在这儿帮助你。谢谢你们给予的所有挚爱。继续浏览,不要走开哦。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -88,7 +89,7 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-server-health-monitoring-script/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
|
||||
基础的Docker容器网络命令
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
各位好,今天我们将学习一些Docker容器的基础命令。Docker 是一个开源项目,提供了一个可以打包、装载和运行任何应用的轻量级容器的开放平台。它没有语言支持、框架和打包系统的限制,从小型的家用电脑到高端服务器,在何时何地都可以运行。它可以使部署和扩展web应用程序、数据库和后端服务像搭积木一样容易,而不依赖特定技术栈或提供商。Docker适用于网络环境,它正应用于数据中心、ISP和越来越多的网络服务。
|
||||
|
||||
因此,这里有一些你在管理Docker容器的时候会用到的一些命令。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 找到Docker接口 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Docker默认会创建一个名为docker0的网桥接口作为连接外部世界的基础。运行中的docker容器直接连接到网桥接口docker0。默认上,docker会分配172.17.42.1/16给docker0,它是所有运行中的容器ip地址的子网。找到Docker接口的ip地址非常简单。要找出docker0网桥接口和连接到网桥上的docker容器,我们可以在安装了docker的终端或者shell中运行ip命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# ip a
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 得到Docker容器的ip地址 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如我们上面读到的,docker在宿主机中创建了一个叫docker0的网桥接口。在我们创建一个新的docker容器时,它自动被默认分配了一个在该子网范围内的ip地址。因此,要检测运行中的Docker容器的ip地址,我们需要进入一个正在运行的容器并用下面的命令检查ip地址。首先,我们运行一个新的容器并进入其中。如果你已经有一个正在运行的容器,你可以跳过这个步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run -it ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们可以运行ip a来得到容器的ip地址了。
|
||||
|
||||
# ip a
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 映射暴露的端口 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要映射配置在Dockerfile的暴露端口到宿主机的高位端口,我们只需用下面带上-P标志的命令。这会打开docker容器的随机端口并映射到Dockerfile中定义的端口。下面是使用-P来打开/暴露定义的端口的例子。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run -itd -P httpd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令会映射容器的端口到 httpd 容器的 Dockerfile 中定义的80端口上。我们用下面的命令来查看正在运行的容器暴露的端口。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker ps
|
||||
|
||||
并且可以用下面的curl命令来检查。
|
||||
|
||||
# curl http://localhost:49153
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 映射到特定的端口上 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们也可以映射暴露端口或者docker容器端口到我们指定的端口上。要实现这个,我们用-p标志来定义我们所需的端口。这里是我们的一个例子。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run -itd -p 8080:80 httpd
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令会映射(宿主机的)8080端口到(容器的)80上。我们可以运行curl来检查这点。
|
||||
|
||||
# curl http://localhost:8080
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 创建自己的网桥 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要给容器创建一个自定义的IP地址,在本篇中我们会创建一个名为br0的新网桥。要分配需要的ip地址,我们需要在运行docker的宿主机中运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# stop docker.io
|
||||
# ip link add br0 type bridge
|
||||
# ip addr add 172.30.1.1/20 dev br0
|
||||
# ip link set br0 up
|
||||
# docker -d -b br0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建完docker网桥之后,我们要让docker的守护进程知道它。
|
||||
|
||||
# echo 'DOCKER_OPTS="-b=br0"' >> /etc/default/docker
|
||||
# service docker.io start
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
到这里,桥接后的接口将会分配给容器在桥接子网内的新ip地址。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 链接到另外一个容器上 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以用Docker将一个容器连接到另外一个上。我们可以在不同的容器上运行不同的程序,并且相互连接或链接。链接允许容器间相互连接并从一个容器上安全地传输信息给另一个容器。要做到这个,我们可以使用--link标志。首先,我们使用--name标志来标示training/postgres镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run -d --name db training/postgres
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
完成之后,我们将容器db与training/webapp链接来形成新的叫web的容器。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run -d -P --name web --link db:db training/webapp python app.py
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Docker网络很神奇也好玩,我们可以对docker容器做很多事情。我们可以把玩这些简单而基础的docker网络命令。docker的网络是非常先进的,我们可以用它做很多事情。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你有任何的问题、建议、反馈请在下面的评论栏写下来以便于我们我们可以提升或者更新文章的内容。谢谢! 玩得开心!:-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/networking-commands-docker-containers/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
|
||||
如何使用xkill命令傻点Linux进程/未响应的程序
|
||||
如何使用xkill命令杀掉Linux进程/未响应的程序
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
我们如何在Linux中杀掉一个资源/进程?很明显我们会找出资源的pid然后用kill命令。
|
||||
|
||||
更准确一点,我们可以找到资源(这里就是terminal)的PID:
|
||||
说的更明白一点,我们可以找到某个资源(比如terminal)的PID:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps -A | grep -i terminal
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,7 +15,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
kill命令会发送一个信号给该pid的进程。
|
||||
|
||||
另外一个方法是我们可以使用pkill命令,它可以基于进程的名字或者其他的属性来杀掉进程。同样我们要杀掉一个叫terminal的进程可以这么做:
|
||||
另外一个方法是我们可以使用pkill命令,它可以基于进程的名字或者其他的属性来杀掉进程。同样我们要杀掉一个叫terminal的进程可以这么做:
|
||||
|
||||
$ pkill terminal
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,15 +23,15 @@ kill命令会发送一个信号给该pid的进程。
|
||||
|
||||
pkill看上去更加容易上手,因为你你不用找出进程的pid。但是如果你要对系统做更好的控制,那么没有什么可以打败'kill'。使用kill命令可以更好地审视你要杀掉的进程。
|
||||
|
||||
我们已经有一篇覆盖了[kill、pkill和killall命令][1]间细节的指导了。
|
||||
我们已经有一篇覆盖了[kill、pkill和killall命令][1]细节的指导了。
|
||||
|
||||
对于那些运行X Server的人而言,有另外一个工具称为xkill可以将进程从X Window中杀掉而不必传递它的名字或者pid。
|
||||
|
||||
xkill工具强制X server关闭于它客户端之间的联系,这可以让X resource关闭这个客户端。xkill是X11工具集中一个非常容易上手的杀掉无用窗口的工具。
|
||||
xkill工具强制X server关闭与它的客户程序之间的联系,其结果就是X resource关闭了这个客户程序。xkill是X11工具集中一个非常容易上手的杀掉无用窗口的工具。
|
||||
|
||||
它支持的选项如在同时运行多个X Server时使用-display选项后面跟上显示号连接到指定的X server,使用-all(并不建议)杀掉所有在屏幕上的所遇顶层窗口,同时将帧(-frame)也计算在内。
|
||||
它支持的选项如在同时运行多个X Server时使用-display选项后面跟上显示号连接到指定的X server,使用-all(并不建议)杀掉所有在屏幕上的所有顶层窗口,以及帧(-frame)参数。
|
||||
|
||||
要得到所有的客户端你可以运行:
|
||||
要列出所有的客户程序你可以运行:
|
||||
|
||||
$ xlsclients
|
||||
|
||||
@ -46,12 +47,11 @@ xkill工具强制X server关闭于它客户端之间的联系,这可以让X re
|
||||
|
||||
如果后面没有跟上资源id,xkill会将鼠标指针变成一个特殊符号,类似于“X”。只需在你要杀掉的窗口上点击,它就会杀掉它与server端的通信,这个程序就被杀掉了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
$ xkill
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
使用xkill杀掉进程
|
||||
*使用xkill杀掉进程*
|
||||
|
||||
需要注意的是xkill并不能保证它的通信会被成功杀掉/退出。大多数程序会在与服务端的通信被关闭后杀掉。然而仍有少部分会继续运行。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ xkill工具强制X server关闭于它客户端之间的联系,这可以让X re
|
||||
|
||||
**我需要在linux命令行中使用xkill么**
|
||||
|
||||
不是,你不必在命令行中运行xkill。你可以设置一个快捷键,并用它来调用xkill。
|
||||
不是,你不必非在命令行中运行xkill。你可以设置一个快捷键,并用它来调用xkill。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是如何在典型的gnome3桌面中设置键盘快捷键。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -71,13 +71,13 @@ xkill工具强制X server关闭于它客户端之间的联系,这可以让X re
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Gnome 设置
|
||||
*Gnome 设置*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
添加快捷键
|
||||
*添加快捷键*
|
||||
|
||||
下次你要杀掉X资源只要用组合键就行了(Ctrl+Alt+Shift+x),你看到你的鼠标变成x了。点击想要杀掉的x资源就行了。
|
||||
下次你要杀掉一个X资源只要用组合键就行了(Ctrl+Alt+Shift+x),你看到你的鼠标变成x了。点击想要杀掉的x资源就行了。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -85,9 +85,9 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/kill-processes-unresponsive-programs-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-kill-a-process-in-linux/
|
||||
[1]:https://linux.cn/article-2116-1.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
|
||||
Tickr Is An Open-Source RSS News Ticker for Linux Desktops
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Latest! Latest! Read all about it!**
|
||||
|
||||
Alright, so the app we’re highlighting today isn’t quite the binary version of an old newspaper seller — but it is a great way to have the latest news brought to you, on your desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
Tick is a GTK-based news ticker for the Linux desktop that scrolls the latest headlines and article titles from your favourite RSS feeds in horizontal strip that you can place anywhere on your desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
Call me Joey Calamezzo; I put mine on the bottom TV news station style.
|
||||
|
||||
“Over to you, sub-heading.”
|
||||
|
||||
### RSS — Remember That? ###
|
||||
|
||||
“Thanks paragraph ending.”
|
||||
|
||||
In an era of push notifications, social media, and clickbait, cajoling us into reading the latest mind-blowing, humanity saving listicle ASAP, RSS can seem a bit old hat.
|
||||
|
||||
For me? Well, RSS lives up to its name of Really Simple Syndication. It’s the easiest, most manageable way to have news come to me. I can manage and read stuff when I want; there’s no urgency to view lest the tweet vanish into the stream or the push notification vanish.
|
||||
|
||||
The beauty of Tickr is in its utility. You can have a constant stream of news trundling along the bottom of your screen, which you can passively glance at from time to time.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
There’s no pressure to ‘read’ or ‘mark all read’ or any of that. When you see something you want to read you just click it to open it in a web browser.
|
||||
|
||||
### Setting it Up ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Although Tickr is available to install from the Ubuntu Software Centre it hasn’t been updated for a long time. Nowhere is this sense of abandonment more keenly felt than when opening the unwieldy and unintuitive configuration panel.
|
||||
|
||||
To open it:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Right click on the Tickr bar
|
||||
1. Go to Edit > Preferences
|
||||
1. Adjust the various settings
|
||||
|
||||
Row after row of options and settings, few of which seem to make sense at first. But poke and prod around and you’ll controls for pretty much everything, including:
|
||||
|
||||
- Set scrolling speed
|
||||
- Choose behaviour when mousing over
|
||||
- Feed update frequency
|
||||
- Font, including font sizes and color
|
||||
- Separator character (‘delineator’)
|
||||
- Position of Tickr on screen
|
||||
- Color and opacity of Tickr bar
|
||||
- Choose how many articles each feed displays
|
||||
|
||||
One ‘quirk’ worth mentioning is that pressing the ‘Apply’ only updates the on-screen Tickr to preview changes. For changes to take effect when you exit the Preferences window you need to click ‘OK’.
|
||||
|
||||
Getting the bar to sit flush on your display can also take a fair bit of tweaking, especially on Unity.
|
||||
|
||||
Press the “full width button” to have the app auto-detect your screen width. By default when placed at the top or bottom it leaves a 25px gap (the app was created back in the days of GNOME 2.x desktops). After hitting the top or bottom buttons just add an extra 25 pixels to the input box compensate for this.
|
||||
|
||||
Other options available include: choose which browser articles open in; whether Tickr appears within a regular window frame; whether a clock is shown; and how often the app checks feed for articles.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Adding Feeds ####
|
||||
|
||||
Tickr comes with a built-in list of over 30 different feeds, ranging from technology blogs to mainstream news services.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can select as many of these as you like to show headlines in the on screen ticker. If you want to add your own feeds you can: –
|
||||
|
||||
1. Right click on the Tickr bar
|
||||
1. Go to File > Open Feed
|
||||
1. Enter Feed URL
|
||||
1. Click ‘Add/Upd’ button
|
||||
1. Click ‘OK (select)’
|
||||
|
||||
To set how many items from each feed shows in the ticker change the “Read N items max per feed” in the other preferences window.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Tickr in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS and Up ###
|
||||
|
||||
So that’s Tickr. It’s not going to change the world but it will keep you abreast of what’s happening in it.
|
||||
|
||||
To install it in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS or later head to the Ubuntu Software Centre but clicking the button below.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Click to install Tickr form the Ubuntu Software Center][1]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/06/tickr-open-source-desktop-rss-news-ticker
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:apt://tickr
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
wyangsun翻译中
|
||||
How to Create Own Online Shopping Store Using “OpenCart” in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In the Internet world we are doing everything using a computer. Electronic Commerce aka e-commerce is one one of them. E-Commerce is nothing new and it started in the early days of ARPANET, where ARPANET used to arrange sale between students of Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Stanford Artificial Intelligence Laboratory.
|
||||
@ -222,4 +223,4 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/create-e-commerce-online-shopping-store-using-openca
|
||||
[1]:http://demo.opencart.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://demo.opencart.com/admin/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.opencart.com/index.php?route=download/download/
|
||||
[4]:http://secure.hostgator.com/%7Eaffiliat/cgi-bin/affiliates/clickthru.cgi?id=tecmint
|
||||
[4]:http://secure.hostgator.com/%7Eaffiliat/cgi-bin/affiliates/clickthru.cgi?id=tecmint
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
||||
How to Clear RAM Memory Cache, Buffer and Swap Space on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Like any other operating system, GNU/Linux has implemented a memory management efficiently and even more than that. But if any process is eating away your memory and you want to clear it, Linux provides a way to flush or clear ram cache.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### How to Clear Cache in Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Every Linux System has three options to clear cache without interrupting any processes or services.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Clear PageCache only.
|
||||
|
||||
# sync; echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
|
||||
|
||||
2. Clear dentries and inodes.
|
||||
|
||||
# sync; echo 2 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
|
||||
|
||||
3. Clear PageCache, dentries and inodes.
|
||||
|
||||
# sync; echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
|
||||
|
||||
Explanation of above command.
|
||||
|
||||
sync will flush the file system buffer. Command Separated by `“;”` run sequentially. The shell wait for each command to terminate before executing the next command in the sequence. As mentioned in kernel documentation, writing to drop_cache will clean cache without killing any application/service, [command echo][1] is doing the job of writing to file.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have to clear the disk cache, the first command is safest in enterprise and production as `“...echo 1 > ….”` will clear the PageCache only. It is not recommended to use third option above `“...echo 3 >”` in production until you know what you are doing, as it will clear PageCache, dentries and inodes.
|
||||
|
||||
**Is it a good idea to free Buffer and Cache in Linux that might be used by Linux Kernel?**
|
||||
|
||||
When you are applying various settings and want to check, if it is actually implemented specially on I/O-extensive benchmark, then you may need to clear buffer cache. You can drop cache as explained above without rebooting the System i.e., no downtime required.
|
||||
|
||||
Linux is designed in such a way that it looks into disk cache before looking onto the disk. If it finds the resource in the cache, then the request doesn’t reach the disk. If we clean the cache, the disk cache will be less useful as the OS will look for the resource on the disk.
|
||||
|
||||
Moreover it will also slow the system for a few seconds while the cache is cleaned and every resource required by OS is loaded again in the disk-cache.
|
||||
|
||||
Now we will be creating a shell script to auto clear RAM cache daily at 2PM via a cron scheduler task. Create a shell script clearcache.sh and add the following lines.
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
# Note, we are using "echo 3", but it is not recommended in production instead use "echo 1"
|
||||
echo "echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches"
|
||||
|
||||
Set execute permission on the clearcache.sh file.
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod 755 clearcache.sh
|
||||
|
||||
Now you may call the script whenever you required to clear ram cache.
|
||||
|
||||
Now set a cron to clear RAM cache everyday at 2PM. Open crontab for editing.
|
||||
|
||||
# crontab -e
|
||||
|
||||
Append the below line, save and exit to run it at 2PM daily.
|
||||
|
||||
0 3 * * * /path/to/clearcache.sh
|
||||
|
||||
For more details on how to cron a job you may like to check our article on [11 Cron Scheduling Jobs][2].
|
||||
|
||||
**Is it good idea to auto clear RAM cache on production server?**
|
||||
|
||||
No! it is not. Think of a situation when you have scheduled the script to clear ram cache everyday at 2PM. Everyday at 2PM the script is executed and it flushes your RAM cache. One day for whatsoever reason, may be more than expected users are online on your website and seeking resource from your server.
|
||||
|
||||
At the same time scheduled script run and clears everything in cache. Now all the user are fetching data from disk. It will result in server crash and corrupt the database. So clear ram-cache only when required,and known your foot steps, else you are a Cargo Cult System Administrator.
|
||||
|
||||
#### How to Clear Swap Space in Linux? ####
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to clear Swap space, you may like to run the below command.
|
||||
|
||||
# swapoff -a && swapon -a
|
||||
|
||||
Also you may add above command to a cron script above, after understanding all the associated risk.
|
||||
|
||||
Now we will be combining both above commands into one single command to make a proper script to clear RAM Cache and Swap Space.
|
||||
|
||||
# echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches && swapoff -a && swapon -a && printf '\n%s\n' 'Ram-cache and Swap Cleared'
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
su -c 'echo 3 >/proc/sys/vm/drop_caches' && swapoff -a && swapon -a && printf '\n%s\n' 'Ram-cache and Swap Cleared'
|
||||
|
||||
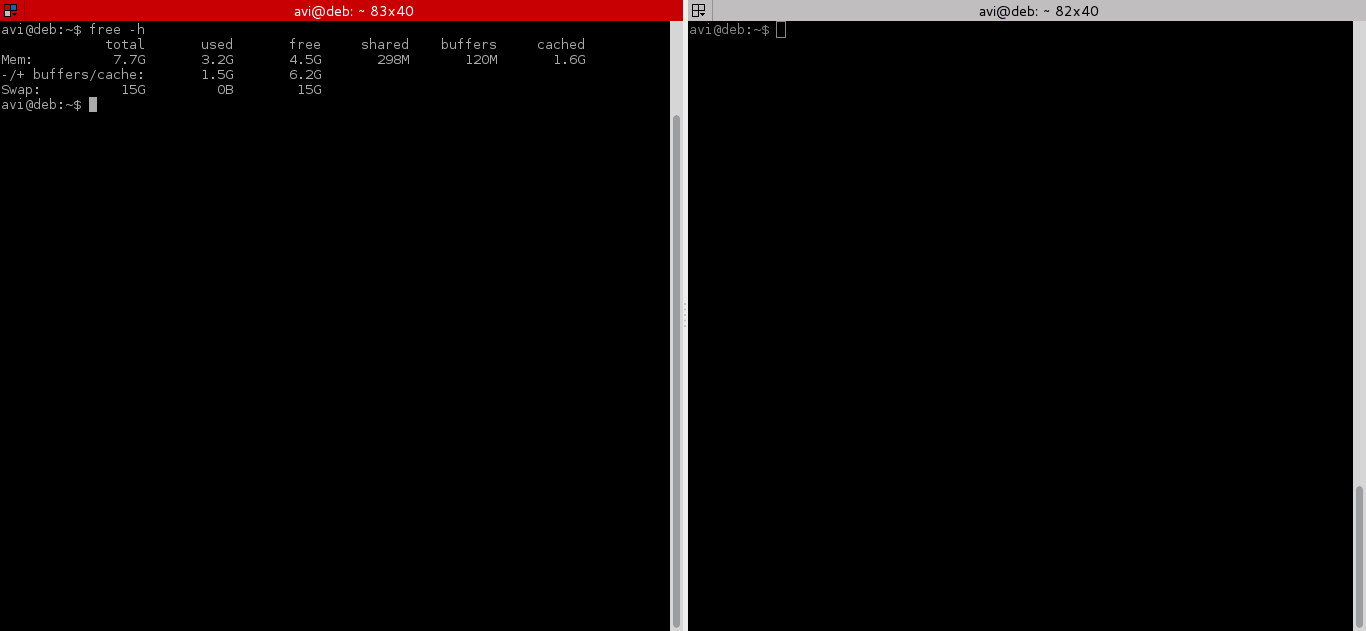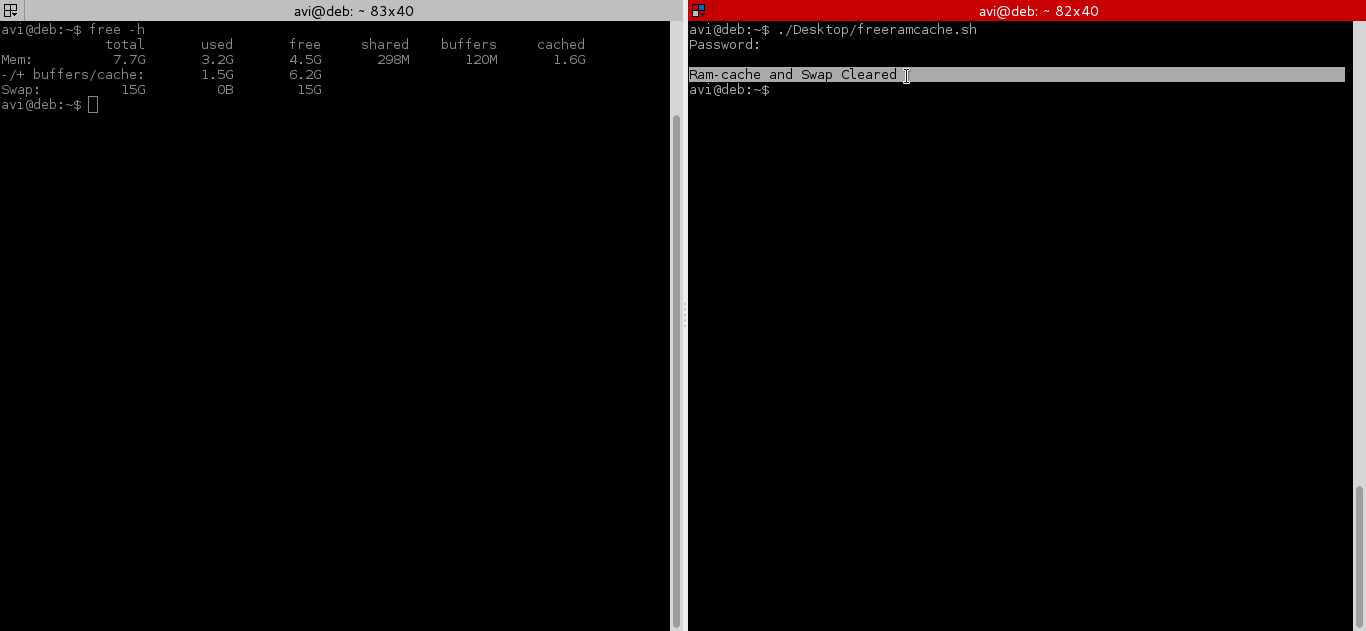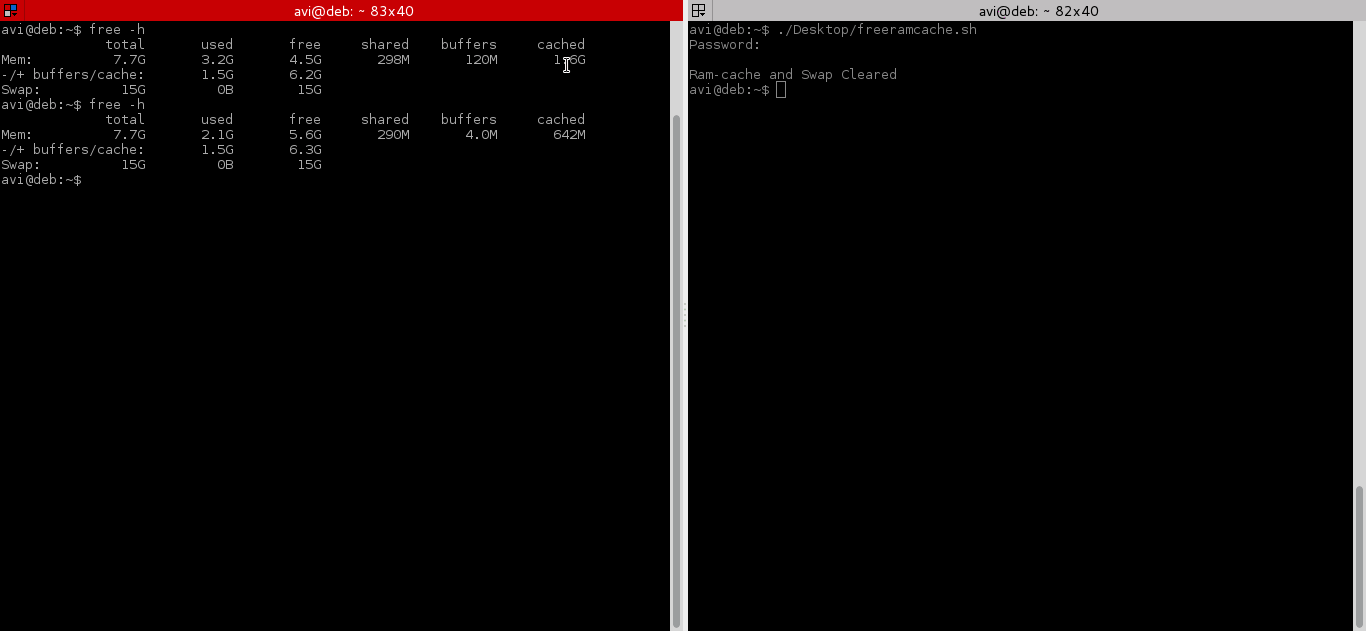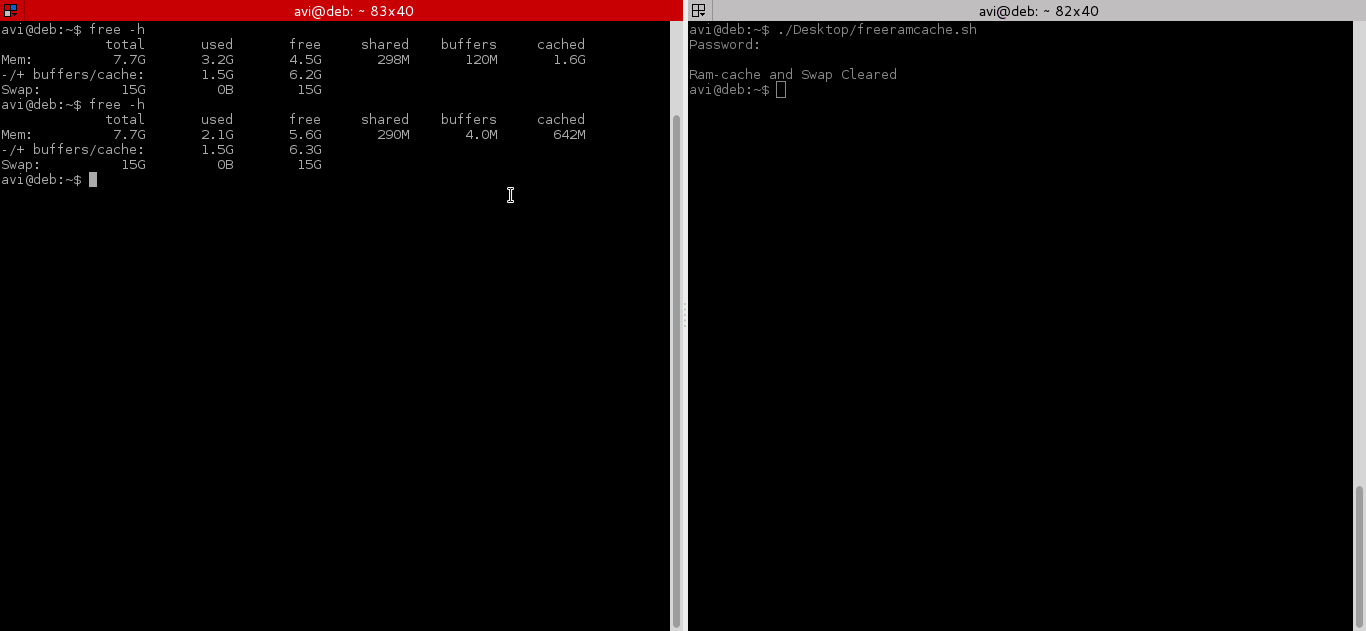
After testing both above command, we will run command “free -h” before and after running the script and will check cache.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now, if you liked the article, don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments to let us know, what you think is it a good idea to clear ram cache and buffer in production and Enterprise?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/clear-ram-memory-cache-buffer-and-swap-space-on-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/echo-command-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/11-cron-scheduling-task-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
|
||||
How to Install nginx and google pagespeed on Ubuntu 15.04 (Vivid Vervet)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Nginx (engine-x) is a open source and high performance HTTP server, reverse proxy and IMAP/POP3 proxy server. The outstanding features of Nginx are: stability, rich feature set, simple configuration and low resource consumption. Nginx is being used by some of the largest websites on the internet and is gaining more and more popularity in the webmaster community. This tutorials shows how to build a nginx .deb package for Ubuntu 15.04 from source that has Google pagespeed module compiled in.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Pagespeed is a web server module developed by Google to speed up a website response times, optimize html and reduce the page load time. ngx_pagespeed features include :
|
||||
|
||||
- Image optimization: stripping meta-data, dynamic resizing, recompression.
|
||||
- CSS & JavaScript minification, concatenation, inlining, and outlining.
|
||||
- Small resource inlining.
|
||||
- Deferring image and JavaScript loading.
|
||||
- HTML rewriting.
|
||||
- Cache lifetime extension.
|
||||
|
||||
see more [https://developers.google.com/speed/pagespeed/module/][1].
|
||||
|
||||
### Prerequisites ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Server 15.04 64 bit
|
||||
root privileges
|
||||
|
||||
What we will do in this tutorial :
|
||||
|
||||
- Install the prerequisite packages.
|
||||
- Installing nginx with ngx_pagespeed.
|
||||
- Testing.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install the prerequisite packages ####
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install dpkg-dev build-essential zlib1g-dev libpcre3 libpcre3-dev
|
||||
|
||||
#### Installing nginx with ngx_pagespeed ####
|
||||
|
||||
**Step 1 - Adding nginx repository**
|
||||
|
||||
vim /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx.list
|
||||
|
||||
add the line:
|
||||
|
||||
deb http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu/ trusty nginx
|
||||
deb-src http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu/ trusty nginx
|
||||
|
||||
Update your repository:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
note : if you get the messege : GPG error [...] NO_PUBKEY [...] bla bla
|
||||
|
||||
please add the the key:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys KEYNUMBER
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
**Step 2 - Download nginx 1.8 from ubuntu repository**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo su
|
||||
cd ~
|
||||
mkdir -p ~/new/nginx_source/
|
||||
cd ~/new/nginx_source/
|
||||
apt-get source nginx
|
||||
apt-get build-dep nginx
|
||||
|
||||
**Step 3 - Download Pagespeed**
|
||||
|
||||
cd ~
|
||||
mkdir -p ~/new/ngx_pagespeed/
|
||||
cd ~/new/ngx_pagespeed/
|
||||
ngx_version=1.9.32.3
|
||||
wget https://github.com/pagespeed/ngx_pagespeed/archive/release-${ngx_version}-beta.zip
|
||||
unzip release-${ngx_version}-beta.zip
|
||||
|
||||
cd ngx_pagespeed-release-1.9.32.3-beta/
|
||||
wget https://dl.google.com/dl/page-speed/psol/${ngx_version}.tar.gz
|
||||
tar -xzf 1.9.32.3.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
**Step 4 - Configure nginx to build with Pagespeed**
|
||||
|
||||
cd ~/new/nginx_source/nginx-1.8.0/debin/
|
||||
vim rules
|
||||
|
||||
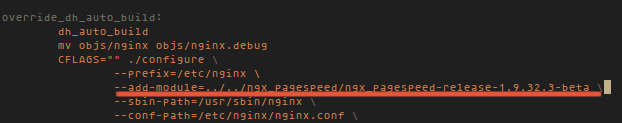
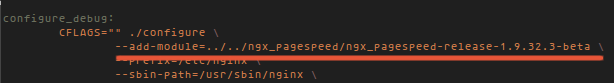
add the module under CFLAGS `.configure` :
|
||||
|
||||
--add-module=../../ngx_pagespeed/ngx_pagespeed-release-1.9.32.3-beta \
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Step 5 - Build nginx package and Install**
|
||||
|
||||
cd ~/new/nginx_source/nginx-1.8.0/
|
||||
dpkg-buildpackage -b
|
||||
|
||||
The dpkg-buildpackage command will build the nginx.deb under ~/new/ngix_source/ Once package building is complete, please look in the directory:
|
||||
|
||||
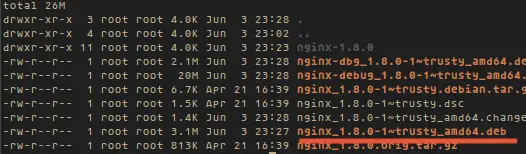
cd ~/new/ngix_source/
|
||||
ls
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
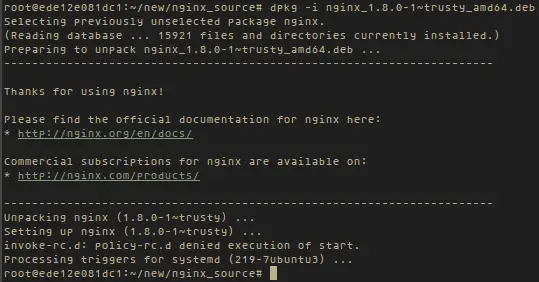
And then install nginx.
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg -i nginx_1.8.0-1~trusty_amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Testing ####
|
||||
|
||||
Run nginx -V to see the ngx_pagespeed was builted with nginx.
|
||||
|
||||
nginx -V
|
||||
|
||||
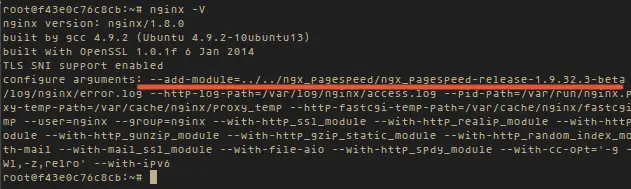
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
The nginx web server there is a stable and fast open source http server that supports a variety of modules for optimization. One of these modules is the 'PageSpeed module' which is developed by google. Unlike apache, nginx modules are not dynamically loadable, so you have to select the desired modules before you build the nginx package.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-nginx-and-google-pagespeed-on-ubuntu-15-04/#step-build-nginx-package-and-install
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Muhammad Arul
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://developers.google.com/speed/pagespeed/module/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,435 @@
|
||||
How to Manipulate Filenames Having Spaces and Special Characters in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
We come across files and folders name very regularly. In most of the cases file/folder name are related to the content of the file/folder and starts with number and characters. Alpha-Numeric file name are pretty common and very widely used, but this is not the case when we have to deal with file/folder name that has special characters in them.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: We can have files of any type but for simplicity and easy implementation we will be dealing with Text file (.txt), throughout the article.
|
||||
|
||||
Example of most common file names are:
|
||||
|
||||
abc.txt
|
||||
avi.txt
|
||||
debian.txt
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Example of numeric file names are:
|
||||
|
||||
121.txt
|
||||
3221.txt
|
||||
674659.txt
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Example of Alpha-Numeric file names are:
|
||||
|
||||
eg84235.txt
|
||||
3kf43nl2.txt
|
||||
2323ddw.txt
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Examples of file names that has special character and is not very common:
|
||||
|
||||
#232.txt
|
||||
#bkf.txt
|
||||
#bjsd3469.txt
|
||||
#121nkfd.txt
|
||||
-2232.txt
|
||||
-fbjdew.txt
|
||||
-gi32kj.txt
|
||||
--321.txt
|
||||
--bk34.txt
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
One of the most obvious question here is – who on earth create/deal with files/folders name having a Hash `(#)`, a semi-colon `(;)`, a dash `(-)` or any other special character.
|
||||
|
||||
I Agree to you, that such file names are not common still your shell should not break/give up when you have to deal with any such file names. Also speaking technically every thing be it folder, driver or anything else is treated as file in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### Dealing with file that has dash (-) in it’s name ###
|
||||
|
||||
Create a file that starts with a dash `(-)`, say -abx.txt.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch -abc.txt
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sample Output ####
|
||||
|
||||
touch: invalid option -- 'b'
|
||||
Try 'touch --help' for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
The reason for above error, that shell interprets anything after a dash `(-)`, as option, and obviously there is no such option, hence is the error.
|
||||
|
||||
To resolve such error, we have to tell the Bash shell (yup this and most of the other examples in the article is for BASH) not to interpret anything after special character (here dash), as option.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two ways to resolve this error as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch -- -abc.txt [Option #1]
|
||||
$ touch ./-abc.txt [Option #2]
|
||||
|
||||
You may verify the file thus created by both the above ways by running commands ls or [ls -l][1] for long listing.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls -l
|
||||
|
||||
total 0
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 avi avi 0 Jun 8 11:05 -abc.txt
|
||||
|
||||
To edit the above file you may do:
|
||||
|
||||
$ nano -- -abc.txt
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ nano ./-abc.txt
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: You may replace nano with any other editor of your choice say vim as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ vim -- -abc.txt
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ vim ./-abc.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly to move such file you have to do:
|
||||
|
||||
$ mv -- -abc.txt -a.txt
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ mv -- -a.txt -abc.txt
|
||||
|
||||
and to Delete this file, you have to do:
|
||||
|
||||
$ rm -- -abc.txt
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ rm ./-abc.txt
|
||||
|
||||
If you have lots of files in a folder the name of which contains dash, and you want to delete all of them at once, do as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ rm ./-*
|
||||
|
||||
**Important to Note:**
|
||||
|
||||
1. The same rule as discussed above follows for any number of hypen in the name of the file and their occurrence. Viz., -a-b-c.txt, ab-c.txt, abc-.txt, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
2. The same rule as discussed above follows for the name of the folder having any number of hypen and their occurrence, except the fact that for deleting the folder you have to use ‘rm -rf‘ as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ rm -rf -- -abc
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ rm -rf ./-abc
|
||||
|
||||
### Dealing with files having HASH (#) in the name ###
|
||||
|
||||
The symbol `#` has a very different meaning in BASH. Anything after a `#` is interpreted as comment and hence neglected by BASH.
|
||||
|
||||
**Understand it using examples:**
|
||||
|
||||
create a file #abc.txt.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch #abc.txt
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sample Output ####
|
||||
|
||||
touch: missing file operand
|
||||
Try 'touch --help' for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
The reason for above error, that Bash is interpreting #abc.txt a comment and hence ignoring. So the [command touch][2] has been passed without any file Operand, and hence is the error.
|
||||
|
||||
To resolve such error, you may ask BASH not to interpret # as comment.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch ./#abc.txt
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ touch '#abc.txt'
|
||||
|
||||
and verify the file just created as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls -l
|
||||
|
||||
total 0
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 avi avi 0 Jun 8 12:14 #abc.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Now create a file the name of which contains # anywhere except at the begging.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch ./a#bc.txt
|
||||
$ touch ./abc#.txt
|
||||
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ touch 'a#bc.txt'
|
||||
$ touch 'abc#.txt'
|
||||
|
||||
Run ‘ls -l‘ to verify it:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls -l
|
||||
|
||||
total 0
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 avi avi 0 Jun 8 12:16 a#bc.txt
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 avi avi 0 Jun 8 12:16 abc#.txt
|
||||
|
||||
What happens when you create two files (say a and #bc) at once:
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch a.txt #bc.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Verify the file just created:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls -l
|
||||
|
||||
total 0
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 avi avi 0 Jun 8 12:18 a.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Obvious from the above example it only created file ‘a‘ and file ‘#bc‘ has been ignored. To execute the above situation successfully we can do,
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch a.txt ./#bc.txt
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ touch a.txt '#bc.txt'
|
||||
|
||||
and verify it as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls -l
|
||||
|
||||
total 0
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 avi avi 0 Jun 8 12:20 a.txt
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 avi avi 0 Jun 8 12:20 #bc.txt
|
||||
|
||||
You can move the file as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ mv ./#bc.txt ./#cd.txt
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ mv '#bc.txt' '#cd.txt'
|
||||
|
||||
Copy it as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cp ./#cd.txt ./#de.txt
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ cp '#cd.txt' '#de.txt'
|
||||
|
||||
You may edit it as using your choice of editor as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ vi ./#cd.txt
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ vi '#cd.txt'
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
$ nano ./#cd.txt
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ nano '#cd.txt'
|
||||
|
||||
And Delete it as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ rm ./#bc.txt
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ rm '#bc.txt'
|
||||
|
||||
To delete all the files that has hash (#) in the file name, you may use:
|
||||
|
||||
# rm ./#*
|
||||
|
||||
### Dealing with files having semicolon (;) in its name ###
|
||||
|
||||
In case you are not aware, semicolon acts as a command separator in BASH and perhaps other shell as well. Semicolon lets you execute several command in one go and acts as separator. Have you ever deal with any file name having semicolon in it? If not here you will.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a file having semi-colon in it.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch ;abc.txt
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sample Output ####
|
||||
|
||||
touch: missing file operand
|
||||
Try 'touch --help' for more information.
|
||||
bash: abc.txt: command not found
|
||||
|
||||
The reason for above error, that when you run the above command BASH interpret touch as a command but could not find any file operand before semicolon and hence it reports error. It also reports another error that ‘abc.txt‘ command not found, only because after semicolon BASH was expecting another command and ‘abc.txt‘, is not a command.
|
||||
|
||||
To resolve such error, tell BASH not to interpret semicolon as command separator, as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch ./';abc.txt'
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ touch ';abc.txt'
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: We have enclosed the file name with single quote ''. It tells BASH that ; is a part of file name and not command separator.
|
||||
|
||||
Rest of the action (viz., copy, move, delete) on the file and folder having semicolon in its name can be carried out straight forward by enclosing the name in single quote.
|
||||
|
||||
### Dealing with other special characters in file/folder name ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Plus Sign (+) in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
Don’t requires anything extra, just do it normal way, as simple file name as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch +12.txt
|
||||
|
||||
#### Dollar sign ($) in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
You have to enclose file name in single quote, as we did in the case of semicolon. Rest of the things are straight forward..
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch '$12.txt'
|
||||
|
||||
#### Percent (%) in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
You don’t need to do anything differently, treat it as normal file.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch %12.txt
|
||||
|
||||
#### Asterisk (*) in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
Having Asterisk in file name don’t change anything and you can continue using it as normal file.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch *12.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Note: When you have to delete a file that starts with *, Never use following commands to delete such files.
|
||||
|
||||
$ rm *
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ rm -rf *
|
||||
|
||||
Instead use,
|
||||
|
||||
$ rm ./*.txt
|
||||
|
||||
#### Exclamation mark (!) in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
Just Enclose the file name in single quote and rest of the things are same.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch '!12.txt'
|
||||
|
||||
#### At Sign (@) in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
Nothing extra, treat a filename having At Sign as nonrmal file.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch '@12.txt'
|
||||
|
||||
#### ^ in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
No extra attention required. Use a file having ^ in filename as normal file.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch ^12.txt
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ampersand (&) in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
Filename should be enclosed in single quotes and you are ready to go.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch '&12.txt'
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parentheses () in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
If the file name has Parenthesis, you need to enclose filename with single quotes.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch '(12.txt)'
|
||||
|
||||
#### Braces {} in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
No Extra Care needed. Just treat it as just another file.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch {12.txt}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Chevrons <> in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
A file name having Chevrons must be enclosed in single quotes.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch '<12.txt>'
|
||||
|
||||
#### Square Brackets [ ] in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
Treat file name having Square Brackets as normal files and you need not take extra care of it.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch [12.txt]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Under score (_) in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
They are very common and don’t require anything extra. Just do what you would have done with a normal file.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch _12.txt
|
||||
|
||||
#### Equal-to (=) in File name ####
|
||||
|
||||
Having an Equal-to sign do not change anything, you can use it as normal file.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch =12.txt
|
||||
|
||||
#### Dealing with back slash (\) ####
|
||||
|
||||
Backslash tells shell to ignore the next character. You have to enclose file name in single quote, as we did in the case of semicolon. Rest of the things are straight forward.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch '\12.txt'
|
||||
|
||||
#### The Special Case of Forward Slash ####
|
||||
|
||||
You cannot create a file the name of which includes a forward slash (/), until your file system has bug. There is no way to escape a forward slash.
|
||||
|
||||
So if you can create a file such as ‘/12.txt’ or ‘b/c.txt’ then either your File System has bug or you have Unicode support, which lets you create a file with forward slash. In this case the forward slash is not a real forward slash but a Unicode character that looks alike a forward slash.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Question Mark (?) in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
Again, an example where you don’t need to put any special attempt. A file name having Question mark can be treated in the most general way.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch ?12.txt
|
||||
|
||||
#### Dot Mark (.) in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
The files starting with dot `(.)` are very special in Linux and are called dot files. They are hidden files generally a configuration or system files. You have to use switch ‘-a‘ or ‘-A‘ with ls command to view such files.
|
||||
|
||||
Creating, editing, renaming and deleting of such files are straight forward.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch .12.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Note: In Linux you may have as many dots `(.)` as you need in a file name. Unlike other system dots in file name don’t means to separate name and extension. You can create a file having multiple dots as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.txt
|
||||
|
||||
and check it as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls -l
|
||||
|
||||
total 0
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 avi avi 0 Jun 8 14:32 1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.txt
|
||||
|
||||
#### Comma (,) in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can have comma in a file name, as many as you want and you Don’t requires anything extra. Just do it normal way, as simple file name.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch ,12.txt
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ touch ,12,.txt
|
||||
|
||||
#### Colon (:) in File name ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can have colon in a file name, as many as you want and you Don’t requires anything extra. Just do it normal way, as simple file name.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch :12.txt
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ touch :12:.txt
|
||||
|
||||
#### Having Quotes (single and Double) in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
To have quotes in file name, we have to use the rule of exchange. I.e, if you need to have single quote in file name, enclose the file name with double quotes and if you need to have double quote in file name, enclose it with single quote.
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch "15'.txt"
|
||||
|
||||
and
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch '15”.txt'
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tilde (~) in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
Some Editors in Linux like emacs create a backup file of the file being edited. The backup file has the name of the original file plus a tilde at the end of the file name. You can have a file that name of which includes tilde, at any location simply as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch ~1a.txt
|
||||
or
|
||||
$touch 2b~.txt
|
||||
|
||||
#### White Space in file name ####
|
||||
|
||||
Create a file the name of which has space between character/word, say “hi my name is avishek.txt”.
|
||||
|
||||
It is not a good idea to have file name with spaces and if you have to distinct readable name, you should use, underscore or dash. However if you have to create such a file, you have to use backward slash which ignores the next character to it. To create above file we have to do it this way..
|
||||
|
||||
$ touch hi\ my\ name\ is\ avishek.txt
|
||||
|
||||
hi my name is avishek.txt
|
||||
|
||||
I have tried covering all the scenario you may come across. Most of the above implementation are explicitly for BASH Shell and may not work in other shell.
|
||||
|
||||
If you feel that I missed something (that is very common and human nature), you may include your suggestion in the comments below. Keep Connected, Keep Commenting. Stay Tuned and connected! Like and share us and help us get spread!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/manage-linux-filenames-with-special-characters/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/15-basic-ls-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/8-pratical-examples-of-linux-touch-command/
|
||||
233
sources/tech/20150610 How to secure your Linux server.md
Normal file
233
sources/tech/20150610 How to secure your Linux server.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,233 @@
|
||||
How to secure your Linux server
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> A server is made up of so many different components that makes it hard to offer one solution for everyone's needs. This articles tries to cover some useful tips and tricks to help you keep your server and users protected.
|
||||
|
||||
No doubt improving server security is one of the most important things system administrators should always look for. This of course has been a topic of many different articles, blogs and forum threads.
|
||||
|
||||
A server is made up of so many different components that makes it hard to offer one solution for everyone’s needs. This articles tries to cover some useful tips and tricks to help you keep your server and users protected.
|
||||
|
||||
There are a few things that every system administrator should know and there is no way to talk about security without mentioning:
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep your system **up to date**
|
||||
- Change passwords frequently – use numeric, alphabetical and non-alphabetical symbols
|
||||
- Give users the **minimum** permissions they need to do their job.
|
||||
- Install only packages that you really need
|
||||
|
||||
Here comes the more interesting part:
|
||||
|
||||
### Change default SSH port ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing that I would like to change when setting up a new server is the default SSH port. This simple change can save your server from thousands of brute force attempts.
|
||||
|
||||
To change the default SSH port, open your sshd_config:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||
|
||||
Find the following line:
|
||||
|
||||
#Port 22
|
||||
|
||||
The “#” symbol means that this line is a comment. Remove the # symbol then change the port to a number of your choice. The port number should not be larger than 65535. Make sure not to use any port already used by your system or other services. You can see a list of commonly used ports in [Wikipedia][1]. For the purpose of this article I will use:
|
||||
|
||||
Port 16543
|
||||
|
||||
Now save the file and close it for a moment.
|
||||
|
||||
Next important step is to:
|
||||
|
||||
### Use SSH Keys ###
|
||||
|
||||
It is extremely important to use SSH keys when accessing the server over SSH. This adds additional protection and ensure that only people who have the key can access the server.
|
||||
|
||||
To generate SSH key on your local computer run:
|
||||
|
||||
ssh-keygen -t rsa
|
||||
|
||||
You will receive an output asking you to setup the file name where the key should be written as well as setup a password:
|
||||
|
||||
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
|
||||
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa): my_key
|
||||
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
|
||||
Enter same passphrase again:
|
||||
Your identification has been saved in my_key.
|
||||
Your public key has been saved in my_key.pub.
|
||||
The key fingerprint is:
|
||||
SHA256:MqD/pzzTRsCjZb6mpfjyrr5v1pJLBcgprR5tjNoI20A
|
||||
|
||||
When compete, you will have two files:
|
||||
|
||||
my_key
|
||||
|
||||
my_key.pub
|
||||
|
||||
Now copy the my_key.pub to ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
|
||||
|
||||
cp my_key.pub ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
|
||||
|
||||
Now upload your key on the server by using:
|
||||
|
||||
scp -P16543 authorized_keys user@yourserver-ip:/home/user/.ssh/
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can access the server from the same local machine without having to enter any password.
|
||||
|
||||
### Disable password authentication for SSH ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we have SSH keys, it is safe to disable the password authentication for SSH. Open again the sshd_config file and set the following changes:
|
||||
|
||||
ChallengeResponseAuthentication no
|
||||
PasswordAuthentication no
|
||||
UsePAM no
|
||||
|
||||
### Disable Root login ###
|
||||
|
||||
The next important step is to disable direct access with root user. Instead you should use sudo or su to perform administrative jobs. To do this you will need to add a new user that has root privileges. To do this you will need to edit the sudoers file located in:
|
||||
|
||||
/etc/sudoers/
|
||||
|
||||
You may edit that file with command such as **visudo**. I would recommend you using this command as it will check the file for any syntax errors prior closing the file. This is useful if you have wrongly edited the file.
|
||||
|
||||
Now to give root privileges to a user. For the purpose of this tutorial I will use user **sysadmin**. Make sure you are using an existing user on your system when you edit your own file. Now find the following line:
|
||||
|
||||
root ALL=(ALL) ALL
|
||||
|
||||
Copy that line and paste it below. In the new line change “root” with “sysadmin”. You should now have these two lines:
|
||||
|
||||
root ALL=(ALL) ALL
|
||||
sysadmin ALL=(ALL) ALL
|
||||
|
||||
I would like to explain what each of the options in the above line represents:
|
||||
|
||||
(1) root (2)ALL=(3)(ALL) (4)ALL
|
||||
|
||||
(1) User
|
||||
|
||||
(2) Terminal from which user can use sudo
|
||||
|
||||
(3) Which users User may act as
|
||||
|
||||
(4) Which commands he may use
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You can use this settings to give access to users to some of the system tools.
|
||||
|
||||
At this point it is safe to save your file.
|
||||
|
||||
To disable direct root access over SSH open again the **sshd_config** file and find the following line:
|
||||
|
||||
#PermitRootLogin yes
|
||||
|
||||
and change it to:
|
||||
|
||||
PermitRootLogin no
|
||||
|
||||
Now save the file and restart the sshd daemon so the changes can take effect. Simply run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo /etc/init.d/sshd restart
|
||||
|
||||
### Setup firewall ###
|
||||
|
||||
A firewall can help you block incoming and outgoing ports as well as block brute force login attempts. I like using SCF (Config Server Firewall) as it a powerful solution that uses iptables, it’s easy to manage and has a web interface for people who don’t like typing too many commands.
|
||||
|
||||
To install CSF access your server and navigate to:
|
||||
|
||||
cd /usr/local/src/
|
||||
|
||||
Then execute the following commands as root:
|
||||
|
||||
wget https://download.configserver.com/csf.tgz
|
||||
tar -xzf csf.tgz
|
||||
csf
|
||||
sh install.sh
|
||||
|
||||
You will need to wait for the installer to finish its job. We will edit CSF configuration by editing:
|
||||
|
||||
/etc/csf/csf.conf
|
||||
|
||||
By default CSF will be started in testing mode. You will need to set it to product by changing the “TESTING” value to 0
|
||||
|
||||
TESTING = "0"
|
||||
|
||||
Next thing you can edit are the allowed ports on your server. For that purpose find the following section of the csf.conf file and modify the ports per your needs:
|
||||
|
||||
# Allow incoming TCP ports
|
||||
TCP_IN = "20,21,25,53,80,110,143,443,465,587,993,995,16543"
|
||||
# Allow outgoing TCP ports
|
||||
TCP_OUT = "20,21,22,25,53,80,110,113,443,587,993,995,16543"
|
||||
# Allow incoming UDP ports
|
||||
UDP_IN = "20,21,53"
|
||||
# Allow outgoing UDP ports
|
||||
# To allow outgoing traceroute add 33434:33523 to this list
|
||||
UDP_OUT = "20,21,53,113,123"
|
||||
|
||||
Setup these per your requirements. I would recommend you using only the ports you need and avoiding allowing huge ranges of ports. Additionally you can avoid using the unsecured services unsecured ports. For example instead of allowing the default SMTP port 25 you can only allow ports 465 and 587 for outgoing emails.
|
||||
|
||||
**IMPORTANT**: Do not forget to allow your customized SSH port.
|
||||
|
||||
It is important to allow your IP address so it will never get blocked. Such IP addresses can be defined in:
|
||||
|
||||
/etc/csf/csf.ignore
|
||||
|
||||
The blocked IP address will appear in:
|
||||
|
||||
/etc/csf/csf.deny
|
||||
|
||||
When you have finished making changes – restart csf with:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo /etc/init.d/csf restart
|
||||
|
||||
Just to show you how useful CSF is I will show you part of csf.deny on one of my servers:
|
||||
|
||||
211.216.48.205 # lfd: (sshd) Failed SSH login from 211.216.48.205 (KR/Korea, Republic of/-): 5 in the last 3600 secs - Fri Mar 6 00:30:35 2015
|
||||
103.41.124.53 # lfd: (sshd) Failed SSH login from 103.41.124.53 (HK/Hong Kong/-): 5 in the last 3600 secs - Fri Mar 6 01:06:46 2015
|
||||
103.41.124.42 # lfd: (sshd) Failed SSH login from 103.41.124.42 (HK/Hong Kong/-): 5 in the last 3600 secs - Fri Mar 6 01:59:04 2015
|
||||
103.41.124.26 # lfd: (sshd) Failed SSH login from 103.41.124.26 (HK/Hong Kong/-): 5 in the last 3600 secs - Fri Mar 6 02:48:26 2015
|
||||
109.169.74.58 # lfd: (sshd) Failed SSH login from 109.169.74.58 (GB/United Kingdom/mail2.algeos.com): 5 in the last 3600 secs - Fri Mar 6 03:49:03 2015
|
||||
|
||||
The IP addresses that performed the brute force login attempt got blocked and they will not bother me again.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Lock accounts ####
|
||||
|
||||
In case an account is not going to be used for a long period of time you can lock it in order to prevent access to it. You can do this with:
|
||||
|
||||
passwd -l accountName
|
||||
|
||||
Account can still be used by the root user.
|
||||
|
||||
### Know your services ###
|
||||
|
||||
The whole idea of a server is to provide access to different services. Limit those to only the ones you need and disable the unused ones. This will not only free some resources, but will make your server a little bit more secured. For example if you are running a headless server you will definitely not need X display or a desktop environment. If there are no Windows network shares, you can safely disable Samba.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the commands below to see which services are started upon system boot:
|
||||
|
||||
chkconfig --list | grep "3:on"
|
||||
|
||||
If your system runs with **systemd**:
|
||||
|
||||
systemctl list-unit-files --type=service | grep enabled
|
||||
|
||||
To disable a service you can use commands such as:
|
||||
|
||||
chkconfig service off
|
||||
systemctl disable service
|
||||
|
||||
In the above example change “service” with the name of the actual service you wish to stop. Here is an example:
|
||||
|
||||
chkconfig httpd off
|
||||
systemctl disable httpd
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
This article was meant to cover some of the general security steps you can take to start securing your server. You can always take additional actions to increase the server protection. Remember that it is your responsibility to keep your server secured and make the wise decision while doing it. Unfortunately there is no easy way to do this and the “perfect” setup requires lots of time and tests until you achieve the desired result.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxveda.com/2015/06/03/secure-linux-server/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Marin Todorow][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxveda.com/author/marin_todorov/
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Port_%28computer_networking%29#Common_port_numbers
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,212 @@
|
||||
Nishita Agarwal Shares Her Interview Experience on Linux ‘iptables’ Firewall
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Nishita Agarwal, a frequent Tecmint Visitor shared her experience (Question and Answer) with us regarding the job interview she had just given in a privately owned hosting company in Pune, India. She was asked a lot of questions on a variety of topics however she is an expert in iptables and she wanted to share those questions and their answer (she gave) related to iptables to others who may be going to give interview in near future.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
All the questions and their Answer are rewritten based upon the memory of Nishita Agarwal.
|
||||
|
||||
> “Hello Friends! My name is **Nishita Agarwal**. I have Pursued Bachelor Degree in Technology. My area of Specialization is UNIX and Variants of UNIX (BSD, Linux) fascinates me since the time I heard it. I have 1+ years of experience in storage. I was looking for a job change which ended with a hosting company in Pune, India.”
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the collection of what I was asked during the Interview. I’ve documented only those questions and their answer that were related to iptables based upon my memory. Hope this will help you in cracking your Interview.
|
||||
|
||||
**1. Have you heard of iptables and firewall in Linux? Any idea of what they are and for what it is used?**
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : I’ve been using iptables for quite long time and I am aware of both iptables and firewall. Iptables is an application program mostly written in C Programming Language and is released under GNU General Public License. Written for System administration point of view, the latest stable release if iptables 1.4.21.iptables may be considered as firewall for UNIX like operating system which can be called as iptables/netfilter, more accurately. The Administrator interact with iptables via console/GUI front end tools to add and define firewall rules into predefined tables. Netfilter is a module built inside of kernel that do the job of filtering.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Firewalld is the latest implementation of filtering rules in RHEL/CentOS 7 (may be implemented in other distributions which I may not be aware of). It has replaced iptables interface and connects to netfilter.
|
||||
|
||||
**2. Have you used some kind of GUI based front end tool for iptables or the Linux Command Line?**
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Though I have used both the GUI based front end tools for iptables like Shorewall in conjugation of [Webmin][1] in GUI and Direct access to iptables via console.And I must admit that direct access to iptables via Linux console gives a user immense power in the form of higher degree of flexibility and better understanding of what is going on in the background, if not anything other. GUI is for novice administrator while console is for experienced.
|
||||
|
||||
**3. What are the basic differences between between iptables and firewalld?**
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : iptables and firewalld serves the same purpose (Packet Filtering) but with different approach. iptables flush the entire rules set each time a change is made unlike firewalld. Typically the location of iptables configuration lies at ‘/etc/sysconfig/iptables‘ whereas firewalld configuration lies at ‘/etc/firewalld/‘, which is a set of XML files.Configuring a XML based firewalld is easier as compared to configuration of iptables, however same task can be achieved using both the packet filtering application ie., iptables and firewalld. Firewalld runs iptables under its hood along with it’s own command line interface and configuration file that is XML based and said above.
|
||||
|
||||
**4. Would you replace iptables with firewalld on all your servers, if given a chance?**
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : I am familiar with iptables and it’s working and if there is nothing that requires dynamic aspect of firewalld, there seems no reason to migrate all my configuration from iptables to firewalld.In most of the cases, so far I have never seen iptables creating an issue. Also the general rule of Information technology says “why fix if it is not broken”. However this is my personal thought and I would never mind implementing firewalld if the Organization is going to replace iptables with firewalld.
|
||||
|
||||
**5. You seems confident with iptables and the plus point is even we are using iptables on our server.**
|
||||
|
||||
What are the tables used in iptables? Give a brief description of the tables used in iptables and the chains they support.
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Thanks for the recognition. Moving to question part, There are four tables used in iptables, namely they are:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> - Nat Table
|
||||
> - Mangle Table
|
||||
> - Filter Table
|
||||
> - Raw Table
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Nat Table : Nat table is primarily used for Network Address Translation. Masqueraded packets get their IP address altered as per the rules in the table. Packets in the stream traverse Nat Table only once. ie., If a packet from a jet of Packets is masqueraded they rest of the packages in the stream will not traverse through this table again. It is recommended not to filter in this table. Chains Supported by NAT Table are PREROUTING Chain, POSTROUTING Chain and OUTPUT Chain.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Mangle Table : As the name suggests, this table serves for mangling the packets. It is used for Special package alteration. It can be used to alter the content of different packets and their headers. Mangle table can’t be used for Masquerading. Supported chains are PREROUTING Chain, OUTPUT Chain, Forward Chain, INPUT Chain, POSTROUTING Chain.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Filter Table : Filter Table is the default table used in iptables. It is used for filtering Packets. If no rules are defined, Filter Table is taken as default table and filtering is done on the basis of this table. Supported Chains are INPUT Chain, OUTPUT Chain, FORWARD Chain.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Raw Table : Raw table comes into action when we want to configure packages that were exempted earlier. It supports PREROUTING Chain and OUTPUT Chain.
|
||||
|
||||
**6. What are the target values (that can be specified in target) in iptables and what they do, be brief!**
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Following are the target values that we can specify in target in iptables:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> - ACCEPT : Accept Packets
|
||||
> - QUEUE : Paas Package to user space (place where application and drivers reside)
|
||||
> - DROP : Drop Packets
|
||||
> - RETURN : Return Control to calling chain and stop executing next set of rules for the current Packets in the chain.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**7. Lets move to the technical aspects of iptables, by technical I means practical.**
|
||||
|
||||
How will you Check iptables rpm that is required to install iptables in CentOS?.
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : iptables rpm are included in standard CentOS installation and we do not need to install it separately. We can check the rpm as:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # rpm -qa iptables
|
||||
>
|
||||
> iptables-1.4.21-13.el7.x86_64
|
||||
>
|
||||
> If you need to install it, you may do yum to get it.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # yum install iptables-services
|
||||
|
||||
**8. How to Check and ensure if iptables service is running?**
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : To check the status of iptables, you may run the following command on the terminal.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # service status iptables [On CentOS 6/5]
|
||||
> # systemctl status iptables [On CentOS 7]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> If it is not running, the below command may be executed.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> ---------------- On CentOS 6/5 ----------------
|
||||
> # chkconfig --level 35 iptables on
|
||||
> # service iptables start
|
||||
>
|
||||
> ---------------- On CentOS 7 ----------------
|
||||
> # systemctl enable iptables
|
||||
> # systemctl start iptables
|
||||
>
|
||||
> We may also check if the iptables module is loaded or not, as:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # lsmod | grep ip_tables
|
||||
|
||||
**9. How will you review the current Rules defined in iptables?**
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The current rules in iptables can be review as simple as:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # iptables -L
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Sample Output
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
|
||||
> target prot opt source destination
|
||||
> ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
|
||||
> ACCEPT icmp -- anywhere anywhere
|
||||
> ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere
|
||||
> ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere state NEW tcp dpt:ssh
|
||||
> REJECT all -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
|
||||
> target prot opt source destination
|
||||
> REJECT all -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
|
||||
> target prot opt source destination
|
||||
|
||||
**10. How will you flush all iptables rules or a particular chain?**
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : To flush a particular iptables chain, you may use following commands.
|
||||
>
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # iptables --flush OUTPUT
|
||||
>
|
||||
> To Flush all the iptables rules.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # iptables --flush
|
||||
|
||||
**11. Add a rule in iptables to accept packets from a trusted IP Address (say 192.168.0.7)**
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The above scenario can be achieved simply by running the below command.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.0.7 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
>
|
||||
> We may include standard slash or subnet mask in the source as:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.0.7/24 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
> # iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.0.7/255.255.255.0 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
|
||||
**12. How to add rules to ACCEPT, REJECT, DENY and DROP ssh service in iptables.**
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Hoping ssh is running on port 22, which is also the default port for ssh, we can add rule to iptables as:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> To ACCEPT tcp packets for ssh service (port 22).
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # iptables -A INPUT -s -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
>
|
||||
> To REJECT tcp packets for ssh service (port 22).
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # iptables -A INPUT -s -p tcp --dport 22 -j REJECT
|
||||
>
|
||||
> To DENY tcp packets for ssh service (port 22).
|
||||
>
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # iptables -A INPUT -s -p tcp --dport 22 -j DENY
|
||||
>
|
||||
> To DROP tcp packets for ssh service (port 22).
|
||||
>
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # iptables -A INPUT -s -p tcp --dport 22 -j DROP
|
||||
|
||||
**13. Let me give you a scenario. Say there is a machine the local ip address of which is 192.168.0.6. You need to block connections on port 21, 22, 23, and 80 to your machine. What will you do?**
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Well all I need to use is the ‘multiport‘ option with iptables followed by port numbers to be blocked and the above scenario can be achieved in a single go as.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.0.6 -p tcp -m multiport --dport 21,22,23,80 -j DROP
|
||||
>
|
||||
> The written rules can be checked using the below command.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # iptables -L
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
|
||||
> target prot opt source destination
|
||||
> ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
|
||||
> ACCEPT icmp -- anywhere anywhere
|
||||
> ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere
|
||||
> ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere state NEW tcp dpt:ssh
|
||||
> REJECT all -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
|
||||
> DROP tcp -- 192.168.0.6 anywhere multiport dports ssh,telnet,http,webcache
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
|
||||
> target prot opt source destination
|
||||
> REJECT all -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
|
||||
> target prot opt source destination
|
||||
|
||||
**Interviewer** : That’s all I wanted to ask. You are a valuable employee we won’t like to miss. I will recommend your name to the HR. If you have any question you may ask me.
|
||||
|
||||
As a candidate I don’t wanted to kill the conversation hence keep asking about the projects I would be handling if selected and what are the other openings in the company. Not to mention HR round was not difficult to crack and I got the opportunity.
|
||||
|
||||
Also I would like to thank Avishek and Ravi (whom I am a friend since long) for taking the time to document my interview.
|
||||
|
||||
Friends! If you had given any such interview and you would like to share your interview experience to millions of Tecmint readers around the globe? then send your questions and answers to admin@tecmint.com or you may submit your interview experience using following form.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Share Your Interview Experience][2]
|
||||
|
||||
Thank you! Keep Connected. Also let me know if I could have answered a question more correctly than what I did.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-firewall-iptables-interview-questions-and-answers/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-webmin-web-based-system-administration-tool-for-rhel-centos-fedora/
|
||||
[2]:https://docs.google.com/a/tecmint.com/forms/d/1jfu1Kg8_qToqvyi6pOT1HQb0dAFvRE-Yc_aOkj0RoSg/viewform
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
|
||||
watch - Repeat Linux / Unix Commands Regular Intervals
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A server administrator needs to maintain the system and keep it updated and safe. A number of intrusion attempts may happen every day. There are some other activities that maintain their log. These logs are updated regularly. In order to check these updates, the commands are executed repeatedly. For example, for simply reading a file, commands like head, tail, cat etc are used. These commands need to be executed repeatedly. The watch command can be used to repeat a command at regular intervals.
|
||||
|
||||
### Watch Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
Watch is a simple command, with a few options. The basic syntax of watch command is:
|
||||
|
||||
watch [-dhvt] [-n <seconds>] [--differences[=cumulative]] [--help] [--interval=<seconds>] [--no-title] [--version] <command>
|
||||
|
||||
Watch command runs the command specified to it after every 2 seconds by default. This time is counted between the completion of command and beginning of next execution. As a simple example, watch command can be used to watch the log updates, The updates are appended at the end of the file, so tail command can be used with watch to see the updates to the file. This command continues to run until you hit CTRL + C to return to the prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
### Examples ###
|
||||
|
||||
> Keep an eye on errors/notices/warning being generated at run time every couple of seconds.
|
||||
|
||||
watch tail /var/log/messages
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> Keep an eye on disk usage after specified time interval.
|
||||
|
||||
watch df -h
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> It is very important for administrators to keep an eye on high I/O wait causing disk operations especially the Mysql transactions.
|
||||
|
||||
watch mysqladmin processlist
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> Keep an eye on server load and uptime at runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
watch uptime
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> Keep an eye on queue size for Exim at the time a cron is run to send notices to subscribers.
|
||||
|
||||
watch exim -bpc
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 1) Iteration delay ###
|
||||
|
||||
watch [-n <seconds>] <command>
|
||||
|
||||
The default interval between the commands can be changed with -n switch. The following command will run the tail command after 5 seconds:
|
||||
|
||||
watch -n 5 date
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2) Successive output comparison ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you use -d option with watch command, it will highlight the differences between the first command output to every next command output cumulatively.
|
||||
|
||||
watch [-d or --differences[=cumulative]] <command>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example1 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s see the successive time outputs extracted using following watch command and observe how the difference is highlighted.
|
||||
|
||||
watch -n 15 -d date
|
||||
|
||||
First time date is capture when command is executed, the next iteration will be repeated after 15 seconds.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Upon the execution of next iteration, it can be seen that all output is exactly same except the seconds have increased from 14 to 29 which is highlighted.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Example 2 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s experience in difference between two successive outputs of “uptime” command repeated by watch.
|
||||
|
||||
watch -n 20 -d uptime
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now the difference between the time is highlighted as well as the three load snapshots as well.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3) Output without title ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you don’t want to display extra details about the iteration delay and actual command run by watch then –t switch can be used.
|
||||
|
||||
watch [-t or --no-title] <command>
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s see the output of following command as an example.
|
||||
|
||||
watch -t date
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Watch help ###
|
||||
|
||||
Brief details of the watch command can be found by typing the following command in SSH.
|
||||
|
||||
watch -h [or --help]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Watch version ###
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following command in SSH terminal to check the version of watch.
|
||||
|
||||
watch -v [--version]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**BUGS**
|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately, upon terminal resize, the screen will not be correctly repainted until the next scheduled update. All --differences highlight-ing is lost on that update as well.
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
Watch is a very powerful utility for system administrators because it can be used to monitor, logs, operations, performance and throughput of the system at run time. One can easily format and delay the output of watch utility. Any Linux command / utility or script and be supplied to watch for desired and continuous output.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-watch-command/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aun Raza][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunrz/
|
||||
@ -1,106 +0,0 @@
|
||||
关于Docker容器的基础网络命令
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
各位好,今天我们将学习一些Docker容器的基础命令。Docker是一个提供了开放平台来打包、发布并以一个轻量级容器运行任意程序的开放平台。它没有语言支持、框架或者打包系统的限制,可在任何时间、任何地方在小到家用电脑大到高端服务器上运行。这使得在部署和扩展网络应用、数据库和终端服务时不依赖于特定的栈或者提供商。Docker注定是用于网络的如它正应用于数据中心、ISP和越来越多的网络服务。
|
||||
|
||||
因此,这里有一些你在管理Docker容器的时候会用到的一些命令。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 找到Docker接口 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Docker默认会创建一个名为docker0的网桥接口来连接外部的世界。docker容器运行时直接连接到网桥接口docker0。默认上,docker会分配172.17.42.1/16给docker0,它是所有运行容器ip地址的子网。得到Docker接口的ip地址非常简单。要找出docker0网桥接口和连接到网桥上的docker容器,我们可以在终端或者安装了docker的shell中运行ip命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# ip a
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 得到Docker容器的ip地址 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如我们上面读到的,docker在主机中创建了一个叫docker0的网桥接口。如我们创建一个心的docker容器一样,它自动被默认分配了一个在子网范围内的ip地址。因此,要检测运行中的Docker容器的ip地址,我们需要进入一个正在运行的容器并用下面的命令检查ip地址。首先,我们运行一个新的容器并进入。如果你已经有一个正在运行的容器,你可以跳过这个步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run -it ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们可以运行ip a来得到容器的ip地址了。
|
||||
|
||||
# ip a
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 映射暴露的端口 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要映射配置在Dockerfile的暴露端口,我们只需用下面带上-P标志的命令。这会打开docker容器的随机端口并映射到Dockerfile中定义的端口。下面是使用-P来打开/映射定义的端口的例子。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run -itd -P httpd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令会映射Dockerfile中定义的httpd 80端口到容器的端口上。我们用下面的命令来查看正在运行的容器暴露的端口。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker ps
|
||||
|
||||
并且可以用下面的curl命令来检查。
|
||||
|
||||
# curl http://localhost:49153
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 映射到特定的端口上 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们也可以映射暴露端口或者docker容器端口到我们指定的端口上。要实现这个,我们用-p标志来定义我们的需要。这里是我们的一个例子。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run -itd -p 8080:80 httpd
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令会映射8080端口到80上。我们可以运行curl来检查这点。
|
||||
|
||||
# curl http://localhost:8080
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 创建自己的网桥 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要给容器创建一个自定义的IP地址,在本篇中我们会创建一个名为bro的新网桥。要分配需要的ip地址,我们需要在运行docker的主机中运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# stop docker.io
|
||||
# ip link add br0 type bridge
|
||||
# ip addr add 172.30.1.1/20 dev br0
|
||||
# ip link set br0 up
|
||||
# docker -d -b br0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建完docker网桥之后,我们要让docker的守护进程知道它。
|
||||
|
||||
# echo 'DOCKER_OPTS="-b=br0"' >> /etc/default/docker
|
||||
# service docker.io start
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
到这里,桥接后的接口将会分配给容器新的在桥接子网内的ip地址。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 链接到另外一个容器上 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以用Dokcer连接一个容器到另外一个上。我们可以在不容的容器上运行不同的程序,并且相互连接或链接。链接允许容器间相互连接并安全地从一个容器上传输信息给另一个容器。要做到这个,我们可以使用--link标志。首先,我们使用--name标志来表示training/postgres镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run -d --name db training/postgres
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
完成之后,我们将容器db与training/webapp链接来形成新的叫web的容器。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run -d -P --name web --link db:db training/webapp python app.py
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Docker网络很神奇也好玩,因为有我们可以对docker容器做很多事情。这里有些简单和基础的我们可以把玩docker网络命令。docker的网络是非常高级的。我们可以用它做很多事情。如果你有任何的问题、建议、反馈请在下面的评论栏写下来以便于我们我们可以提升或者更新文章的内容。谢谢! 玩得开心!:-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/networking-commands-docker-containers/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu 15.04下安装Android Studio
|
||||
PS 原MD文件有大段重复并且排版错误,译者已修复
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Android Studio是官方为了Android应用开发者而发布的IDE,它基于IntelliJ的IDEA。
|
||||
|
||||
### Android Studio的功能 ###
|
||||
|
||||
灵活的基于Gradle的建构系统
|
||||
|
||||
针对不同手机编译多个版本的apk
|
||||
|
||||
代码模板功能构建出各种常用的应用
|
||||
|
||||
支持拖动编辑主题的富布局编辑器
|
||||
|
||||
lint工具可以捕捉到应用的性能、可用性、版本冲突或者其他问题
|
||||
|
||||
代码混淆和应用签名功能
|
||||
|
||||
内置 Google Cloud Platform 的支持,可以轻易的融入Google Cloud Messaging 和 App Engine支持
|
||||
|
||||
还有更多
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 15.04 上安装 Android Studio ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开terminal,输入以下命令
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:paolorotolo/android-studio
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install android-studio
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如果要把Android Studio添加到启动栏,你需要如下操作
|
||||
|
||||
打开Android Studio,点击Configure选择Create Desktop Entry,这样Android Studio应该在dash中创建快捷方式了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 截图 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/install-android-studio-on-ubuntu-15-04.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ruchi][a]
|
||||
译者:[NearTan](https://github.com/NearTan)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user