mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-25 23:11:02 +08:00
[Translated]20150824 Mhddfs--Combine Several Smaller Partition into One Large Virtual Storage.md
This commit is contained in:
parent
73ae192667
commit
c8652ceaca
@ -1,187 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by GOLinux!
|
||||
Mhddfs – Combine Several Smaller Partition into One Large Virtual Storage
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Let’s assume that you have 30GB of movies and you have 3 drives each 20 GB in size. So how will you store?
|
||||
|
||||
Obviously you can split your videos in two or three different volumes and store them on the drive manually. This certainly is not a good idea, it is an exhaustive work which requires manual intervention and a lots of your time.
|
||||
|
||||
Another solution is to create a [RAID array of disk][1]. The RAID has always remained notorious for loss of storage reliability and usable disk space. Another solution is mhddfs.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Mhddfs – Combine Multiple Partitions in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
mhddfs is a driver for Linux that combines several mount points into one virtual disk. It is a fuse based driver, which provides a easy solution for large data storage. It combines all small file systems to create a single big virtual filesystem which contains every particle of its member filesystem including files and free spaces.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Why you need Mhddfs? ####
|
||||
|
||||
All your storage devices creates a single virtual pool and it can be mounted right at the boot. This small utility takes care of, which drive is full and which is empty and to write data to what drive, intelligently. Once you create virtual drives successfully, you can share your virtual filesystem using [SAMBA][2]. Your client will always see a huge drive and lots of free space.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features of Mhddfs ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Get attributes of the file system and system information.
|
||||
- Set attributes of the file system.
|
||||
- Create, Read, Remove and write Directories and files.
|
||||
- Support for file locks and Hardlinks on single device.
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
<table cellspacing="0" border="0">
|
||||
<colgroup width="472"></colgroup>
|
||||
<colgroup width="491"></colgroup>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="29" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: black; font-size: large;">Pros of mhddfs</span></b></td>
|
||||
<td align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: black; font-size: large;">Cons of mhddfs</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Perfect for home users.</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;">mhddfs driver is not built in the Linux Kernel</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Simple to run.</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Required lots of processing power during runtime</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> No evidence of Data loss</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> No redundancy solution.</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Do not split the file.</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Hardlinks moving not supported</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Add new files to the combined virtual filesystem.</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: medium;"> </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Manage the location where these files are saved.</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: medium;"> </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> Extended file attributes</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: medium;"> </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation of Mhddfs in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian and portable to alike systems, you can install mhddfs package using following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update && apt-get install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Install Mhddfs on Debian based Systems
|
||||
|
||||
On RHEL/CentOS Linux systems, you need to turn on [epel-repository][3] and then execute the below command to install mhddfs package.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora 22+ systems, you may get it by dnf package manger as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
# dnf install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Install Mhddfs on Fedora
|
||||
|
||||
If incase, mhddfs package isn’t available from epel repository, then you need to resolve following dependencies to install and compile it from source as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
- FUSE header files
|
||||
- GCC
|
||||
- libc6 header files
|
||||
- uthash header files
|
||||
- libattr1 header files (optional)
|
||||
|
||||
Next, download the latest source package simply as suggested below and compile it.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://mhddfs.uvw.ru/downloads/mhddfs_0.1.39.tar.gz
|
||||
# tar -zxvf mhddfs*.tar.gz
|
||||
# cd mhddfs-0.1.39/
|
||||
# make
|
||||
|
||||
You should be able to see binary mhddfs in the current directory. Move it to /usr/bin/ and /usr/local/bin/ as root.
|
||||
|
||||
# cp mhddfs /usr/bin/
|
||||
# cp mhddfs /usr/local/bin/
|
||||
|
||||
All set, mhddfs is ready to be used.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I use Mhddfs? ###
|
||||
|
||||
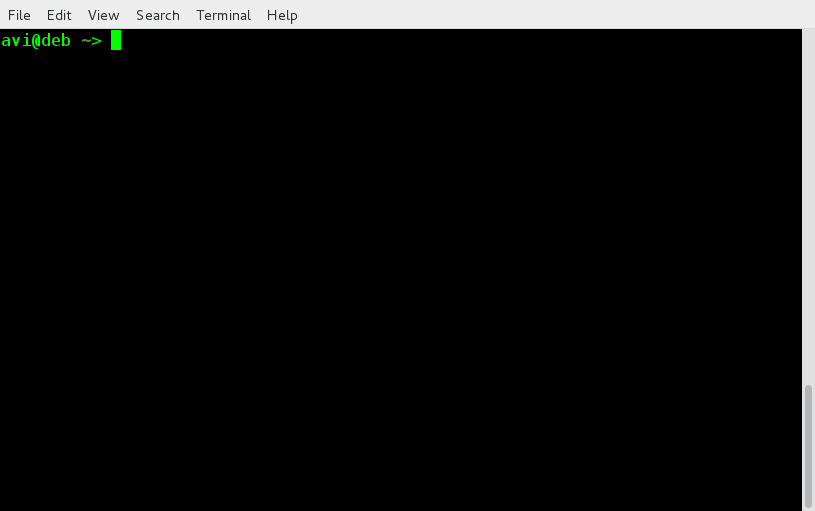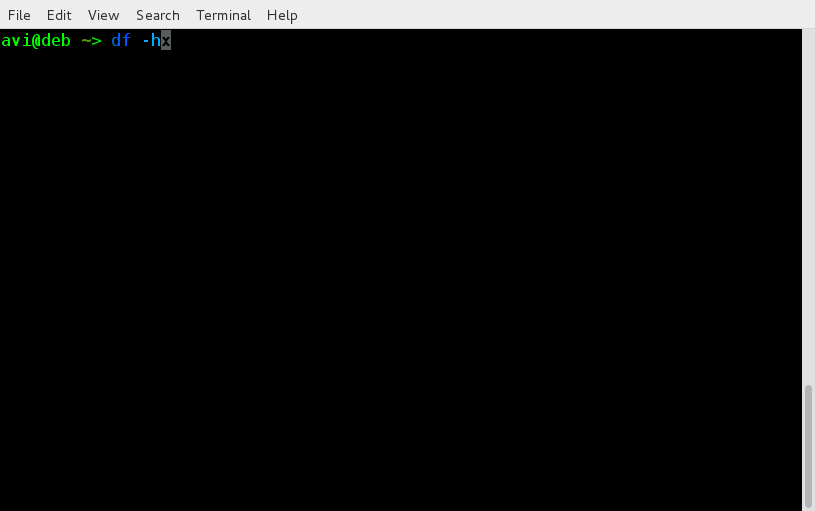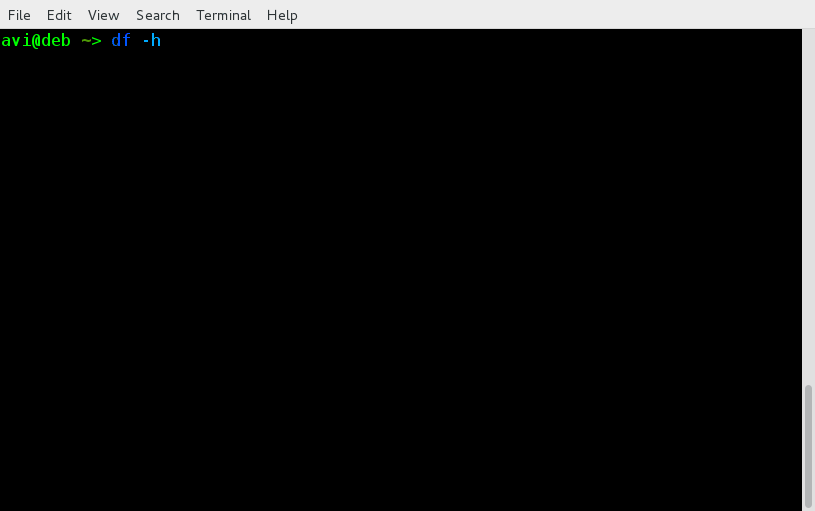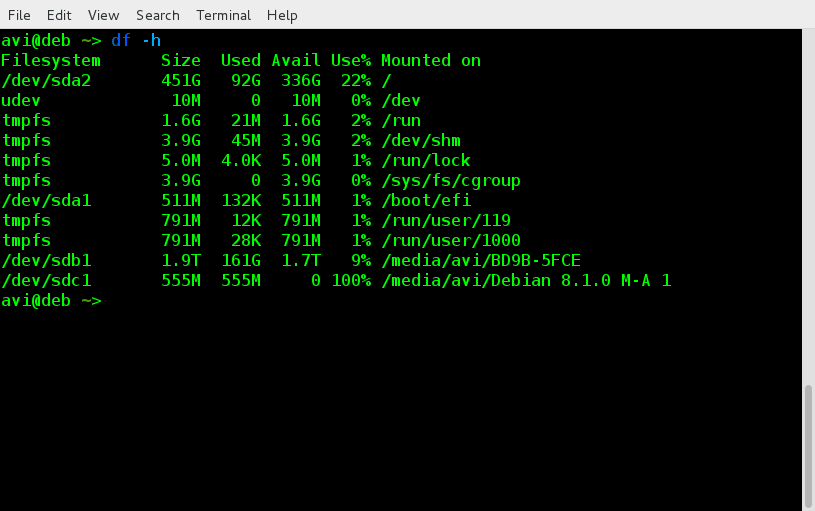
1. Lets see all the HDD mounted to my system currently.
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample Output**
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
|
||||
|
||||
/dev/sda1 511M 132K 511M 1% /boot/efi
|
||||
/dev/sda2 451G 92G 336G 22% /
|
||||
/dev/sdb1 1.9T 161G 1.7T 9% /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE
|
||||
/dev/sdc1 555M 555M 0 100% /media/avi/Debian 8.1.0 M-A 1
|
||||
|
||||
Notice the ‘Mount Point‘ name here, which we will be using later.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Create a directory `/mnt/virtual_hdd` where all these all file system will be grouped together as,
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir /mnt/virtual_hdd
|
||||
|
||||
3. And then mount all the file-systems. Either as root or as a user who is a member of FUSE group.
|
||||
|
||||
# mhddfs /boot/efi, /, /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE/, /media/avi/Debian\ 8.1.0\ M-A\ 1/ /mnt/virtual_hdd -o allow_other
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Mount All File System in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: We are used mount Point names here of all the HDDs. Obviously the mount point in your case will be different. Also notice “-o allow_other” option makes this Virtual file system visible to all others and not only the person who created it.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Now run “df -h” see all the filesystems. It should contain the one you created just now.
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Verify Virtual File System Mount
|
||||
|
||||
You can perform all the option to the Virtual File System you created as you would have done to a Mounted Drive.
|
||||
|
||||
5. To create this Virtual File system on every system boot, you should add the below line of code (in your case it should be different, depending upon your mount point), at the end of /etc/fstab file as root.
|
||||
|
||||
mhddfs# /boot/efi, /, /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE/, /media/avi/Debian\ 8.1.0\ M-A\ 1/ /mnt/virtual_hdd fuse defaults,allow_other 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
6. If at any point of time you want to add/remove a new drive to Virtual_hdd, you may mount a new drive, copy the contents of mount point /mnt/virtual_hdd, un-mount the volume, Eject the Drive you want to remove and/or mount the new drive you want to include, Mount the overall filesystem under Virtual_hdd using mhddfs command and you should be done.
|
||||
|
||||
#### How do I Un-Mount Virtual_hdd? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Unmounting virtual_hdd is as easy as,
|
||||
|
||||
# umount /mnt/virtual_hdd
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Unmount Virtual Filesystem
|
||||
|
||||
Notice it is umount and not unmount. A lot of user type it wrong.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I am working on another post you people will love to read. Till then stay tuned and connected to Tecmint. Provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments below. Like and share us and help us get spread.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/combine-partitions-into-one-in-linux-using-mhddfs/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/understanding-raid-setup-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/mount-filesystem-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-enable-epel-repository-for-rhel-centos-6-5/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,183 @@
|
||||
Mhddfs——将多个小分区合并成一个大的虚拟存储
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
让我们假定你有30GB的电影,并且你有3个驱动器,每个的大小为20GB。那么,你会怎么来存放东西呢?
|
||||
|
||||
很明显,你可以将你的视频分割成2个或者3个不同的卷,并将它们手工存储到驱动器上。这当然不是一个好主意,它成了一项费力的工作,它需要你手工干预,而且花费你大量时间。
|
||||
|
||||
另外一个解决方案是创建一个[RAID磁盘阵列][1]。然而,RAID在缺乏存储可靠性,磁盘空间可用性差等方面声名狼藉。另外一个解决方案,就是mhddfs。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Mhddfs——在Linux中合并多个分区
|
||||
|
||||
mhddfs是一个用于Linux的驱动,它可以将多个挂载点合并到一个虚拟磁盘中。它是一个基于FUSE的驱动,提供了一个用于大数据存储的简单解决方案。它将所有小文件系统合并,以创建一个单一的大虚拟文件系统,该文件系统包含其成员文件系统的所有颗粒,包括文件和空闲空间。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 你为什么需要Mhddfs? ####
|
||||
|
||||
你所有存储设备创建了一个单一的虚拟池,它可以在启动时被挂载。这个小工具可以智能地照看并处理哪个驱动器满了,哪个驱动器空着,将数据写到哪个驱动器中。当你成功创建虚拟驱动器后,你可以使用[SAMBA][2]来共享你的虚拟文件系统。你的客户端将在任何时候都看到一个巨大的驱动器和大量的空闲空间。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Mhddfs特性 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 获取文件系统属性和系统信息。
|
||||
- 设置文件系统属性。
|
||||
- 创建、读取、移除和写入目录和文件。
|
||||
- 支持文件锁和单一设备上的硬链接。
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
<table cellspacing="0" border="0">
|
||||
<colgroup width="472"></colgroup>
|
||||
<colgroup width="491"></colgroup>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="29" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: black; font-size: large;">mhddfs的优点</span></b></td>
|
||||
<td align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: black; font-size: large;">mhddfs的缺点</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 适合家庭用户</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;">mhddfs驱动没有内建在Linux内核中 </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 运行简单</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 运行时需要大量处理能力</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 没有明显的数据丢失</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 没有冗余解决方案</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 不分割文件</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 不支持移动硬链接</span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 添加新文件到合并的虚拟文件系统</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: medium;"> </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 管理文件保存的位置</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: medium;"> </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: black; font-size: medium;"> 扩展文件属性</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="left" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: medium;"> </span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux中安装Mhddfs ###
|
||||
|
||||
在Debian及其类似的移植系统中,你可以使用下面的命令来安装mhddfs包。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update && apt-get install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
安装Mhddfs到基于Debian的系统中
|
||||
|
||||
在RHEL/CentOS Linux系统中,你需要开启[epel仓库][3],然后执行下面的命令来安装mhddfs包。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||
在Fedora 22及以上系统中,你可以通过dnf包管理来获得它,就像下面这样。
|
||||
|
||||
# dnf install mhddfs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
安装Mhddfs到Fedora
|
||||
|
||||
如果万一mhddfs包不能从epel仓库获取到,那么你需要解决下面的依赖,然后像下面这样来编译源码并安装。
|
||||
|
||||
- FUSE头文件
|
||||
- GCC
|
||||
- libc6头文件
|
||||
- uthash头文件
|
||||
- libattr1头文件(可选)
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,只需从下面建议的地址下载最新的源码包,然后编译。
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://mhddfs.uvw.ru/downloads/mhddfs_0.1.39.tar.gz
|
||||
# tar -zxvf mhddfs*.tar.gz
|
||||
# cd mhddfs-0.1.39/
|
||||
# make
|
||||
|
||||
你应该可以在当前目录中看到mhddfs的二进制文件,以root身份将它移动到/usr/bin/和/usr/local/bin/中。
|
||||
|
||||
# cp mhddfs /usr/bin/
|
||||
# cp mhddfs /usr/local/bin/
|
||||
|
||||
一切搞定,mhddfs已经可以用了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 我怎么使用Mhddfs? ###
|
||||
|
||||
1.让我们看看当前所有挂载到我们系统中的硬盘。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
**样例输出**
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
|
||||
|
||||
/dev/sda1 511M 132K 511M 1% /boot/efi
|
||||
/dev/sda2 451G 92G 336G 22% /
|
||||
/dev/sdb1 1.9T 161G 1.7T 9% /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE
|
||||
/dev/sdc1 555M 555M 0 100% /media/avi/Debian 8.1.0 M-A 1
|
||||
|
||||
注意这里的‘挂载点’名称,我们后面会使用到它们。
|
||||
|
||||
2.创建目录‘/mnt/virtual_hdd’,在这里,所有这些文件系统将被组成组。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir /mnt/virtual_hdd
|
||||
|
||||
3.然后,挂载所有文件系统。你可以通过root或者FUSE组中的某个成员来完成。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# mhddfs /boot/efi, /, /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE/, /media/avi/Debian\ 8.1.0\ M-A\ 1/ /mnt/virtual_hdd -o allow_other
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
在Linux中挂载所有文件系统
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:这里我们使用了所有硬盘的挂载点名称,很明显,你的挂载点名称会有所不同。也请注意“-o allow_other”选项可以让这个虚拟文件系统让其它所有人可见,而不仅仅是创建它的人。
|
||||
|
||||
4.现在,运行“df -h”来看看所有文件系统。它应该包含了你刚才创建的那个。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
验证虚拟文件系统挂载
|
||||
|
||||
你可以像对已挂在的驱动器那样给虚拟文件系统部署所有的选项。
|
||||
|
||||
5.要在每次系统启动创建这个虚拟文件系统,你应该以root身份添加下面的这行代码(在你那里会有点不同,取决于你的挂载点)到/etc/fstab文件的末尾。
|
||||
|
||||
mhddfs# /boot/efi, /, /media/avi/BD9B-5FCE/, /media/avi/Debian\ 8.1.0\ M-A\ 1/ /mnt/virtual_hdd fuse defaults,allow_other 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
6.如果在任何时候你想要添加/移除一个新的驱动器到/从虚拟硬盘,你可以挂载一个新的驱动器,拷贝/mnt/vritual_hdd的内容,卸载卷,弹出你要移除的的驱动器并/或挂载你要包含的新驱动器。使用mhddfs命令挂载全部文件系统到Virtual_hdd下,这样就全部搞定了。
|
||||
#### 我怎么卸载Virtual_hdd? ####
|
||||
|
||||
卸载virtual_hdd相当简单,就像下面这样
|
||||
|
||||
# umount /mnt/virtual_hdd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
卸载虚拟文件系统
|
||||
|
||||
注意,是umount,而不是unmount,很多用户都输错了。
|
||||
|
||||
到现在为止全部结束了。我正在写另外一篇文章,你们一定喜欢读的。到那时,请保持连线到Tecmint。请在下面的评论中给我们提供有用的反馈吧。请为我们点赞并分享,帮助我们扩散。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/combine-partitions-into-one-in-linux-using-mhddfs/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/understanding-raid-setup-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/mount-filesystem-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-enable-epel-repository-for-rhel-centos-6-5/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user