mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-27 02:30:10 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of git@github.com:LCTT/TranslateProject.git
This commit is contained in:
commit
c6126bf0f8
published
20151012 How To Use iPhone In Antergos Linux.md20151027 How To Show Desktop In GNOME 3.md
RHCE
Part 4 - Using Shell Scripting to Automate Linux System Maintenance Tasks.mdPart 5 - How to Manage System Logs (Configure, Rotate and Import Into Database) in RHEL 7.md
The history of Android
sources
news
share
20150824 Great Open Source Collaborative Editing Tools.md20150901 5 best open source board games to play online.md20151104 Optimize Web Delivery with these Open Source Tools.md
talk
20150820 LinuxCon's surprise keynote speaker Linus Torvalds muses about open-source software.md20150820 Why did you start using Linux.md20150824 LinuxCon exclusive--Mark Shuttleworth says Snappy was born long before CoreOS and the Atomic Project.md20150910 The Free Software Foundation--30 years in.md20150916 Italy's Ministry of Defense to Drop Microsoft Office in Favor of LibreOffice.md20150929 A Slick New Set-Up Wizard Is Coming To Ubuntu and Ubuntu Touch.md20151012 The Brief History Of Aix HP-UX Solaris BSD And LINUX.md20151023 Ubuntu 15.10 Codenamed Wily Werewolf Review.md20151028 10 Things To Do After Installing Ubuntu 15.10 'Wily Werewolf'.md20151028 Here are the 9 New Ubuntu 15.10 Features You Should Know.md20151105 Linus Torvalds Lambasts Open Source Programmers over Insecure Code.md
tech
20150806 Installation Guide for Puppet on Ubuntu 15.04.md20150831 How to switch from NetworkManager to systemd-networkd on Linux.md20151027 How To Install Retro Terminal In Linux.md20151104 How to Install Pure-FTPd with TLS on FreeBSD 10.2.md20151104 How to Install Redis Server on CentOS 7.md20151104 How to Install SQLite 3.9.1 with JSON Support on Ubuntu 15.04.md20151104 How to Setup Pfsense Firewall and Basic Configuration.md20151105 How to Manage Your To-Do Lists in Ubuntu Using Go For It Application.md20151105 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change default Java version on Linux.md20151105 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to find which shell I am using on Linux.md20151105 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install Ubuntu desktop behind a proxy.md
LFCS
Part 10 - LFCS--Understanding and Learning Basic Shell Scripting and Linux Filesystem Troubleshooting.mdPart 2 - LFCS--How to Install and Use vi or vim as a Full Text Editor.mdPart 3 - LFCS--How to Archive or Compress Files and Directories Setting File Attributes and Finding Files in Linux.mdPart 4 - LFCS--Partitioning Storage Devices Formatting Filesystems and Configuring Swap Partition.mdPart 5 - LFCS--How to Mount or Unmount Local and Network Samba and NFS Filesystems in Linux.mdPart 6 - LFCS--Assembling Partitions as RAID Devices – Creating & Managing System Backups.mdPart 7 - LFCS--Managing System Startup Process and Services SysVinit Systemd and Upstart.mdPart 8 - LFCS--Managing Users and Groups File Permissions and Attributes and Enabling sudo Access on Accounts.mdPart 9 - LFCS--Linux Package Management with Yum RPM Apt Dpkg Aptitude and Zypper.md
Learn with Linux
translated/tech
@ -1,22 +1,22 @@
|
||||
如何在Antergos Linux中使用iPhone
|
||||
如何在 Antergos Linux 中使用 iPhone
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在Arch Linux中使用iPhone遇到麻烦了么?iPhone和Linux从来都没有集成的很好。本教程中,我会向你展示如何在Antergos Linux中使用iPhone,对于同样基于Arch的的Linux发行版如Manjaro也应该同样管用。
|
||||
在Arch Linux中使用iPhone遇到麻烦了么?iPhone和Linux从来都没有很好地集成。本教程中,我会向你展示如何在Antergos Linux中使用iPhone,对于同样基于Arch的的Linux发行版如Manjaro也应该同样管用。
|
||||
|
||||
我最近购买了一台全新的iPhone 6S,当我连接到Antergos Linux中要拷贝一些照片时,它完全没有检测到它。我看见iPhone正在被充电并且我已经允许了iPhone“信任这台电脑”,但是还是完全没有检测到。我尝试运行dmseg但是没有关于iPhone或者Apple的信息。有趣的是我已经安装了[libimobiledevice][1]。这个可以可以解决[iPhone在Ubuntu中的挂载问题][2]。
|
||||
我最近购买了一台全新的iPhone 6S,当我连接到Antergos Linux中要拷贝一些照片时,它完全没有检测到它。我看见iPhone正在被充电并且我已经允许了iPhone“信任这台电脑”,但是还是完全没有检测到。我尝试运行`dmseg`但是没有关于iPhone或者Apple的信息。有趣的是我当我安装好了[libimobiledevice][1],这个就可以解决[iPhone在Ubuntu中的挂载问题][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
我会向你展示如何在Antergos中使用运行iOS 9的iPhone 6S。这会有更多的命令行,但是我假设你用的是ArchLinux,并不惧怕使用终端(也不应该惧怕)、
|
||||
我会向你展示如何在Antergos中使用运行iOS 9的iPhone 6S。这会有更多的命令行,但是我假设你用的是ArchLinux,并不惧怕使用终端(也不应该惧怕)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Arch Linux中挂载iPhone ###
|
||||
|
||||
**第一步**:如果已经插入拔下你的iPhone
|
||||
**第一步**:如果已经插入,请拔下你的iPhone。
|
||||
|
||||
**第二步**:现在,打开终端输入下面的命令来安装必要的包。不要担心如果它们已经安装过了。
|
||||
**第二步**:现在,打开终端输入下面的命令来安装必要的包。如果它们已经安装过了也没有关系。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo pacman -Sy ifuse usbmuxd libplist libimobiledevice
|
||||
|
||||
**第三步**: 这些库和程序安装完成后,重启系统
|
||||
**第三步**: 这些库和程序安装完成后,重启系统。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo reboot
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,11 +24,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir ~/iPhone
|
||||
|
||||
**第五步**:解锁你的手机并插入,如果询问是否允许,请允许。
|
||||
**第五步**:解锁你的手机并插入,如果询问是否信任该计算机,请允许信任。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**第六步**: 验证这时iPhone已经被机器识别了。
|
||||
**第六步**: 看看这时iPhone是否已经被机器识别了。
|
||||
|
||||
dmesg | grep -i iphone
|
||||
|
||||
@ -46,7 +46,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
ifuse ~/iPhone
|
||||
|
||||
由于我们在家目录中创建了挂载目录,你不需要root权限就可以在家目录中看见。如果命令成功了,你就不会看见输出。
|
||||
由于我们在家目录中创建了挂载目录,你不需要root权限就可以在家目录中看见。如果命令成功了,你就不会看见任何输出。
|
||||
|
||||
回到Files看下iPhone是否已经识别。对于我而言,在Antergos中看上去这样:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -62,7 +62,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 对你有用么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
我知道这并不是非常方便和理想,iPhone应该像其他USB其他usb设备那样但是事情并不总是像人们想的那样。好事是一点小的DIY就能解决这个问题带来了一点成就感(至少对我而言)。我必须要说的是Antergos应该修复这个问题让iPhone可以默认挂载。
|
||||
我知道这并不是非常方便和理想,iPhone应该像其他USB设备那样工作,但是事情并不总是像人们想的那样。好的是一点小的DIY就能解决这个问题带来了一点成就感(至少对我而言)。我必须要说的是Antergos应该修复这个问题让iPhone可以默认挂载。
|
||||
|
||||
这个技巧对你有用么?如果你有任何问题或者建议,欢迎留下评论。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/iphone-antergos-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 在GNOME 3 中添加显示桌面的快捷键 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我在本教程的使用的是GNOME 3.18的[Antergos Linux][2]但是这些步骤对于任何GNOME 3版本的Linux发行版都适用。同时也使用了[Numix主题][3]作为默认主题。因此你也许不会看到平常的GNOME图标。但是我相信步骤是一目了然的,很容易就能理解。
|
||||
我在本教程的使用的是带有GNOME 3.18的[Antergos Linux][2],但是这些步骤对于任何GNOME 3版本的Linux发行版都适用。同时,Antergos也使用了[Numix主题][3]作为默认主题。因此你也许不会看到平常的GNOME图标。但是我相信步骤是一目了然的,很容易就能理解。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第一步 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -34,7 +34,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第四步 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在“Hide all normla windows”上面点击一下。你会看到它变成了**New accelerator**。现在无论你按下哪个键,他都会被指定为显示桌面。
|
||||
在“Hide all normla windows”上面点击一下。你会看到它变成了**New accelerator**。现在无论你按下哪个键,它都会被指定为显示桌面的快捷键。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不小心按下了错误的组合键,只要按下退格它就会被禁用。再次点击并使用需要的组合键。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,7 +42,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第五步 ####
|
||||
|
||||
一旦设置了组合键,只要关闭系统设置。没有保存设置因为更改是立即生效的。在本例中,我使用Ctrl+Super+D来与我在Ubuntu Unity中的使用习惯保持一致。
|
||||
一旦设置了组合键,只要关闭系统设置。不用保存设置因为更改是立即生效的。在本例中,我使用Ctrl+Super+D来与我在Ubuntu Unity中的使用习惯保持一致。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -61,4 +61,4 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/show-desktop-gnome-3/
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.gnome.org/gnome-3/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/tag/antergos/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/install-numix-ubuntu/
|
||||
[3]:https://linux.cn/article-3281-1.html
|
||||
@ -1,20 +1,20 @@
|
||||
第四部分 - 使用 Shell 脚本自动化 Linux 系统维护任务
|
||||
RHCE 系列(四): 使用 Shell 脚本自动化 Linux 系统维护任务
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
之前我听说高效系统管理员/工程师的其中一个特点是懒惰。一开始看起来很矛盾,但作者接下来解释了其中的原因:
|
||||
之前我听说高效的系统管理员的一个特点是懒惰。一开始看起来很矛盾,但作者接下来解释了其中的原因:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
RHCE 系列:第四部分 - 自动化 Linux 系统维护任务
|
||||
*RHCE 系列:第四部分 - 自动化 Linux 系统维护任务*
|
||||
|
||||
如果一个系统管理员花费大量的时间解决问题以及做重复的工作,你就应该怀疑他这么做是否正确。换句话说,一个高效的系统管理员/工程师应该制定一个计划使得尽量花费少的时间去做重复的工作,以及通过使用该系列中第三部分 [使用 Linux 工具集监视系统活动报告][1] 介绍的工具预见问题。因此,尽管看起来他/她没有做很多的工作,但那是因为 shell 脚本帮助完成了他的/她的大部分任务,这也就是本章我们将要探讨的东西。
|
||||
如果一个系统管理员花费大量的时间解决问题以及做重复的工作,你就应该怀疑他这么做是否正确。换句话说,一个高效的系统管理员/工程师应该制定一个计划使得其尽量花费少的时间去做重复的工作,以及通过使用本系列中第三部分 [使用 Linux 工具集监视系统活动报告][1] 介绍的工具来预见问题。因此,尽管看起来他/她没有做很多的工作,但那是因为 shell 脚本帮助完成了他的/她的大部分任务,这也就是本章我们将要探讨的东西。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 shell 脚本? ###
|
||||
|
||||
简单的说,shell 脚本就是一个由 shell 一步一步执行的程序,而 shell 是在 Linux 内核和端用户之间提供接口的另一个程序。
|
||||
简单的说,shell 脚本就是一个由 shell 一步一步执行的程序,而 shell 是在 Linux 内核和最终用户之间提供接口的另一个程序。
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,RHEL 7 中用户使用的 shell 是 bash(/bin/bash)。如果你想知道详细的信息和历史背景,你可以查看 [维基页面][2]。
|
||||
默认情况下,RHEL 7 中用户使用的 shell 是 bash(/bin/bash)。如果你想知道详细的信息和历史背景,你可以查看这个[维基页面][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
关于这个 shell 提供的众多功能的介绍,可以查看 **man 手册**,也可以从 ([Bash 命令][3])下载 PDF 格式。除此之外,假设你已经熟悉 Linux 命令(否则我强烈建议你首先看一下 **Tecmint.com** 中的文章 [从新手到系统管理员指南][4] )。现在让我们开始吧。
|
||||
关于这个 shell 提供的众多功能的介绍,可以查看 **man 手册**,也可以从 ([Bash 命令][3])处下载 PDF 格式。除此之外,假设你已经熟悉 Linux 命令(否则我强烈建议你首先看一下 **Tecmint.com** 中的文章 [从新手到系统管理员指南][4] )。现在让我们开始吧。
|
||||
|
||||
### 写一个脚本显示系统信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ RHCE 系列:第四部分 - 自动化 Linux 系统维护任务
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
# RHCE 系列第四部分事例脚本
|
||||
# RHCE 系列第四部分示例脚本
|
||||
# 该脚本会返回以下这些系统信息:
|
||||
# -主机名称:
|
||||
echo -e "\e[31;43m***** HOSTNAME INFORMATION *****\e[0m"
|
||||
@ -67,9 +67,9 @@ RHCE 系列:第四部分 - 自动化 Linux 系统维护任务
|
||||
|
||||
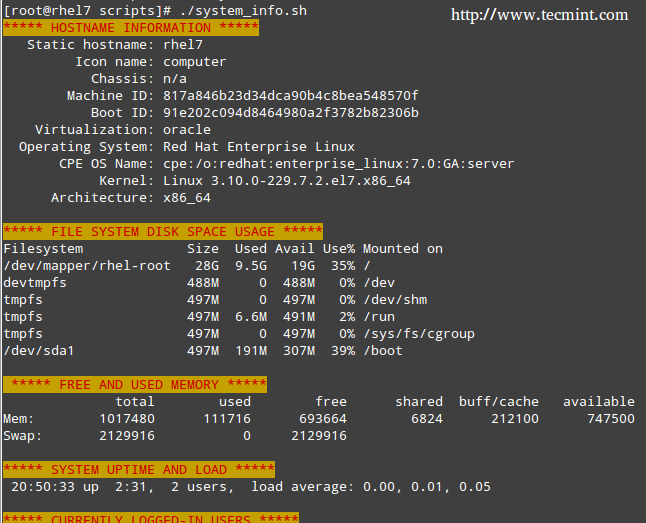
|
||||
|
||||
服务器监视 Shell 脚本
|
||||
*服务器监视 Shell 脚本*
|
||||
|
||||
该功能用以下命令提供:
|
||||
颜色功能是由以下命令提供的:
|
||||
|
||||
echo -e "\e[COLOR1;COLOR2m<YOUR TEXT HERE>\e[0m"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -79,13 +79,13 @@ RHCE 系列:第四部分 - 自动化 Linux 系统维护任务
|
||||
|
||||
你想使其自动化的任务可能因情况而不同。因此,我们不可能在一篇文章中覆盖所有可能的场景,但是我们会介绍使用 shell 脚本可以使其自动化的三种典型任务:
|
||||
|
||||
**1)** 更新本地文件数据库, 2) 查找(或者删除)有 777 权限的文件, 以及 3) 文件系统使用超过定义的阀值时发出警告。
|
||||
1) 更新本地文件数据库, 2) 查找(或者删除)有 777 权限的文件, 以及 3) 文件系统使用超过定义的阀值时发出警告。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们在脚本目录中新建一个名为 `auto_tasks.sh` 的文件并添加以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
# 自动化任务事例脚本:
|
||||
# 自动化任务示例脚本:
|
||||
# -更新本地文件数据库:
|
||||
echo -e "\e[4;32mUPDATING LOCAL FILE DATABASE\e[0m"
|
||||
updatedb
|
||||
@ -123,16 +123,16 @@ RHCE 系列:第四部分 - 自动化 Linux 系统维护任务
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
查找 777 权限文件的 Shell 脚本
|
||||
*查找 777 权限文件的 Shell 脚本*
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 Cron ###
|
||||
|
||||
想更进一步提高效率,你不会想只是坐在你的电脑前手动执行这些脚本。相反,你会使用 cron 来调度这些任务周期性地执行,并把结果通过邮件发动给预定义的接收者或者将它们保存到使用 web 浏览器可以查看的文件中。
|
||||
想更进一步提高效率,你不会想只是坐在你的电脑前手动执行这些脚本。相反,你会使用 cron 来调度这些任务周期性地执行,并把结果通过邮件发动给预先指定的接收者,或者将它们保存到使用 web 浏览器可以查看的文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的脚本(filesystem_usage.sh)会运行有名的 **df -h** 命令,格式化输出到 HTML 表格并保存到 **report.html** 文件中:
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
# Sample script to demonstrate the creation of an HTML report using shell scripting
|
||||
# 演示使用 shell 脚本创建 HTML 报告的示例脚本
|
||||
# Web directory
|
||||
WEB_DIR=/var/www/html
|
||||
# A little CSS and table layout to make the report look a little nicer
|
||||
@ -177,7 +177,7 @@ RHCE 系列:第四部分 - 自动化 Linux 系统维护任务
|
||||
|
||||
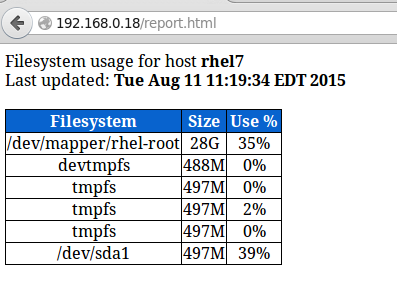
|
||||
|
||||
服务器监视报告
|
||||
*服务器监视报告*
|
||||
|
||||
你可以添加任何你想要的信息到那个报告中。添加下面的 crontab 条目在每天下午的 1:30 运行该脚本:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -193,12 +193,12 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/using-shell-script-to-automate-linux-system-maintena
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-performance-monitoring-and-file-system-statistics-reports/
|
||||
[1]:https://linux.cn/article-6512-1.html
|
||||
[2]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bash_%28Unix_shell%29
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/pdf/bash.pdf
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/60-commands-of-linux-a-guide-from-newbies-to-system-administrator/
|
||||
@ -1,26 +1,24 @@
|
||||
第五部分 - 如何在 RHEL 7 中管理系统日志(配置、旋转以及导入到数据库)
|
||||
RHCE 系列(五):如何在 RHEL 7 中管理系统日志(配置、轮换以及导入到数据库)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
为了确保你的 RHEL 7 系统安全,你需要通过查看日志文件监控系统中发生的所有活动。这样,你就可以检测任何不正常或有潜在破坏的活动并进行系统故障排除或者其它恰当的操作。
|
||||
为了确保你的 RHEL 7 系统安全,你需要通过查看日志文件来监控系统中发生的所有活动。这样,你就可以检测到任何不正常或有潜在破坏的活动并进行系统故障排除或者其它恰当的操作。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
(译者注:[日志旋转][9]是系统管理中归档每天产生的日志文件的自动化过程)
|
||||
|
||||
RHCE 考试 - 第五部分:使用 Rsyslog 和 Logrotate 管理系统日志
|
||||
*RHCE 考试 - 第五部分:使用 Rsyslog 和 Logrotate 管理系统日志*
|
||||
|
||||
在 RHEL 7 中,[rsyslogd][1] 守护进程负责系统日志,它从 /etc/rsyslog.conf(该文件指定所有系统日志的默认路径)和 /etc/rsyslog.d 中的所有文件(如果有的话)读取配置信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### Rsyslogd 配置 ###
|
||||
|
||||
快速浏览一下 [rsyslog.conf][2] 会是一个好的开端。该文件分为 3 个主要部分:模块(rsyslong 按照模块化设计),全局指令(用于设置 rsyslogd 守护进程的全局属性),以及规则。正如你可能猜想的,最后一个部分指示获取,显示以及在哪里保存什么的日志(也称为选择子),这也是这篇博文关注的重点。
|
||||
快速浏览一下 [rsyslog.conf][2] 会是一个好的开端。该文件分为 3 个主要部分:模块(rsyslong 按照模块化设计),全局指令(用于设置 rsyslogd 守护进程的全局属性),以及规则。正如你可能猜想的,最后一个部分指示记录或显示什么以及在哪里保存(也称为选择子(selector)),这也是这篇文章关注的重点。
|
||||
|
||||
rsyslog.conf 中典型的一行如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Rsyslogd 配置
|
||||
*Rsyslogd 配置*
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的图片中,我们可以看到一个选择子包括了一个或多个用分号分隔的设备:优先级(Facility:Priority)对,其中设备描述了消息类型(参考 [RFC 3164 4.1.1 章节][3] 查看 rsyslog 可用的完整设备列表),优先级指示它的严重性,这可能是以下几种之一:
|
||||
在上面的图片中,我们可以看到一个选择子包括了一个或多个用分号分隔的“设备:优先级”(Facility:Priority)对,其中设备描述了消息类型(参考 [RFC 3164 4.1.1 章节][3],查看 rsyslog 可用的完整设备列表),优先级指示它的严重性,这可能是以下几种之一:
|
||||
|
||||
- debug
|
||||
- info
|
||||
@ -31,7 +29,7 @@ Rsyslogd 配置
|
||||
- alert
|
||||
- emerg
|
||||
|
||||
尽管自身并不是一个优先级,关键字 none 意味着指定设备没有任何优先级。
|
||||
尽管 none 并不是一个优先级,不过它意味着指定设备没有任何优先级。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:给定一个优先级表示该优先级以及之上的消息都应该记录到日志中。因此,上面例子中的行指示 rsyslogd 守护进程记录所有优先级为 info 以及以上(不管是什么设备)的除了属于 mail、authpriv、以及 cron 服务(不考虑来自这些设备的消息)的消息到 /var/log/messages。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,7 +45,7 @@ Rsyslogd 配置
|
||||
|
||||
#### 创建自定义日志文件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
要把所有的守护进程消息记录到 /var/log/tecmint.log,我们需要在 rsyslog.conf 或者 /etc/rsyslog.d 目录中的单独文件(易于管理)添加下面一行:
|
||||
要把所有的守护进程消息记录到 /var/log/tecmint.log,我们需要在 rsyslog.conf 或者 /etc/rsyslog.d 目录中的单独文件(这样易于管理)添加下面一行:
|
||||
|
||||
daemon.* /var/log/tecmint.log
|
||||
|
||||
@ -55,19 +53,19 @@ Rsyslogd 配置
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart rsyslog
|
||||
|
||||
在随机重启两个守护进程之前和之后查看自定义日志的内容:
|
||||
在随便重启两个守护进程之前和之后查看下自定义日志的内容:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建自定义日志文件
|
||||
*创建自定义日志文件*
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个自学练习,我建议你重点关注设备和优先级,添加额外的消息到已有的日志文件或者像上面那样创建一个新的日志文件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 Logrotate 旋转日志 ###
|
||||
### 使用 Logrotate 轮换日志 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了防止日志文件无限制增长,logrotate 工具用于旋转、压缩、移除或者通过电子邮件发送日志,从而减轻管理会产生大量日志文件系统的困难。
|
||||
为了防止日志文件无限制增长,logrotate 工具用于轮换、压缩、移除或者通过电子邮件发送日志,从而减轻管理会产生大量日志文件系统的困难。(译者注:[日志轮换][9](rotate)是系统管理中归档每天产生的日志文件的自动化过程)
|
||||
|
||||
Logrotate 作为一个 cron 作业(/etc/cron.daily/logrotate)每天运行,并从 /etc/logrotate.conf 和 /etc/logrotate.d 中的文件(如果有的话)读取配置信息。
|
||||
Logrotate 作为一个 cron 任务(/etc/cron.daily/logrotate)每天运行,并从 /etc/logrotate.conf 和 /etc/logrotate.d 中的文件(如果有的话)读取配置信息。
|
||||
|
||||
对于 rsyslog,即使你可以在主文件中为指定服务包含设置,为每个服务创建单独的配置文件能帮助你更好地组织设置。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -75,27 +73,27 @@ Logrotate 作为一个 cron 作业(/etc/cron.daily/logrotate)每天运行,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Logrotate 配置
|
||||
*Logrotate 配置*
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的例子中,logrotate 会为 /var/log/wtmp 进行以下操作:尝试每个月旋转一次,但至少文件要大于 1MB,然后用 0664 权限、用户 root、组 utmp 创建一个新的日志文件。下一步只保存一个归档日志,正如旋转指令指定的:
|
||||
在上面的例子中,logrotate 会为 /var/log/wtmp 进行以下操作:尝试每个月轮换一次,但至少文件要大于 1MB,然后用 0664 权限、用户 root、组 utmp 创建一个新的日志文件。下一步只保存一个归档日志,正如轮换指令指定的:
|
||||
|
||||
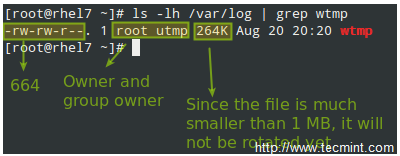
|
||||
|
||||
每月 Logrotate 日志
|
||||
*每月 Logrotate 日志*
|
||||
|
||||
让我们再来看看 /etc/logrotate.d/httpd 中的另一个例子:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
旋转 Apache 日志文件
|
||||
*轮换 Apache 日志文件*
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在 logrotate 的 man 手册([man logrotate][4] 和 [man logrotate.conf][5])中阅读更多有关它的设置。为了方便你的阅读,本文还提供了两篇文章的 PDF 格式。
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个系统工程师,很可能由你决定多久按照什么格式保存一次日志,取决于你是否有一个单独的分区/逻辑卷给 /var。否则,你真的要考虑删除旧日志以节省存储空间。另一方面,根据你公司和客户内部的政策,为了以后的安全审核,你可能被迫要保留多个日志。
|
||||
作为一个系统工程师,很可能由你决定多久按照什么格式保存一次日志,这取决于你是否有一个单独的分区/逻辑卷给 `/var`。否则,你真的要考虑删除旧日志以节省存储空间。另一方面,根据你公司和客户内部的政策,为了以后的安全审核,你可能必须要保留多个日志。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 保存日志到数据库 ####
|
||||
|
||||
当然检查日志可能是一个很繁琐的工作(即使有类似 grep 工具和正则表达式的帮助)。因为这个原因,rsyslog 允许我们把它们导出到数据库(OTB 支持的关系数据库管理系统包括 MySQL、MariaDB、PostgreSQL 和 Oracle)。
|
||||
当然检查日志可能是一个很繁琐的工作(即使有类似 grep 工具和正则表达式的帮助)。因为这个原因,rsyslog 允许我们把它们导出到数据库(OTB 支持的关系数据库管理系统包括 MySQL、MariaDB、PostgreSQL 和 Oracle 等)。
|
||||
|
||||
指南的这部分假设你已经在要管理日志的 RHEL 7 上安装了 MariaDB 服务器和客户端:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -104,10 +102,9 @@ Logrotate 配置
|
||||
|
||||
然后使用 `mysql_secure_installation` 工具为 root 用户设置密码以及其它安全考量:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
保证 MySQL 数据库安全
|
||||
*保证 MySQL 数据库安全*
|
||||
|
||||
注意:如果你不想用 MariaDB root 用户插入日志消息到数据库,你也可以配置用另一个用户账户。如何实现的介绍已经超出了本文的范围,但在 [MariaDB 知识][6] 中有详细解析。为了简单在这篇指南中我们会使用 root 账户。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -117,7 +114,7 @@ Logrotate 配置
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
保存服务器日志到数据库
|
||||
*保存服务器日志到数据库*
|
||||
|
||||
最后,添加下面的行到 /etc/rsyslog.conf:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -132,18 +129,18 @@ Logrotate 配置
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 SQL 语法查询日志 ####
|
||||
|
||||
现在执行一些会改变日志的操作(例如停止和启动服务),然后登陆到你的 DB 服务器并使用标准的 SQL 命令显示和查询日志:
|
||||
现在执行一些会改变日志的操作(例如停止和启动服务),然后登录到你的数据库服务器并使用标准的 SQL 命令显示和查询日志:
|
||||
|
||||
USE Syslog;
|
||||
SELECT ReceivedAt, Message FROM SystemEvents;
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在数据库中查询日志
|
||||
*在数据库中查询日志*
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中我们介绍了如何设置系统日志,如果旋转日志以及为了简化查询如何重定向消息到数据库。我们希望这些技巧能对你准备 [RHCE 考试][8] 和日常工作有所帮助。
|
||||
在这篇文章中我们介绍了如何设置系统日志,如果轮换日志以及为了简化查询如何重定向消息到数据库。我们希望这些技巧能对你准备 [RHCE 考试][8] 和日常工作有所帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
正如往常,非常欢迎你的反馈。用下面的表单和我们联系吧。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -153,7 +150,7 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/manage-linux-system-logs-using-rsyslogd-and-logrotat
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](http://www.mutouxiaogui.cn/blog/)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -165,5 +162,5 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/manage-linux-system-logs-using-rsyslogd-and-logrotat
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/pdf/logrotate.conf.pdf
|
||||
[6]:https://mariadb.com/kb/en/mariadb/create-user/
|
||||
[7]:https://github.com/sematext/rsyslog/blob/master/plugins/ommysql/createDB.sql
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-setup-and-configure-static-network-routing-in-rhel/
|
||||
[8]:https://linux.cn/article-6451-1.html
|
||||
[9]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Log_rotation
|
||||
@ -1,48 +1,48 @@
|
||||
The history of Android
|
||||
安卓编年史(6)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
T-Mobile G1
|
||||
T-Mobile供图
|
||||
|
||||
*T-Mobile G1 [T-Mobile供图]*
|
||||
|
||||
### 安卓1.0——谷歌系app和实体硬件的引入 ###
|
||||
|
||||
到了2008年10月,安卓1.0已经准备好发布,这个系统在[T-Mobile G1][1](又以HTC Dream为人周知)上初次登台。G1进入了被iPhone 3G和[Nokia 1680 classic][2]所主宰的市场。(这些手机并列获得了2008年[销量最佳手机][3]称号,各自卖出了350万台。)G1的销量数字已难以获得,但T-Mobile宣称截至2009年4月该设备的销量突破了100万台。无论从哪方面来说这在竞争中都处于落后地位。
|
||||
到了2008年10月,安卓1.0已经准备好发布,这个系统在[T-Mobile G1][1](又以HTC Dream为人周知)上初次登台。G1进入了被iPhone 3G和[Nokia 1680 classic][2]所主宰的市场。(这些手机并列获得了2008年[销量最佳手机][3]称号,各自卖出了350万台。)G1的具体销量数字已难以获得,但T-Mobile宣称截至2009年4月该设备的销量突破了100万台。无论从哪方面来说这在竞争中都处于落后地位。
|
||||
|
||||
G1拥有单核528Mhz的ARM 11处理器,一个Adreno 130的GPU,192MB内存,以及多达256MB的存储空间供给系统以及应用使用。它有一块3.2英寸,320x480分辨率的显示屏,被布置在一个含有实体全键盘的滑动结构之上。所以尽管安卓软件的确走过了很长的一段路,硬件也是的。时至今日,我们可以在厂商的一个手表中得到比这更好的参数:最新的[三星智能手表][4]拥有512MB内存以及1GHz的双核处理器。
|
||||
G1拥有单核528Mhz的ARM 11处理器,一个Adreno 130的GPU,192MB内存,以及多达256MB的存储空间提供给系统以及应用使用。它有一块3.2英寸、320x480分辨率的显示屏,被布置在一个含有实体全键盘的滑动结构之上。所以尽管安卓软件的确走过了很长的一段路,硬件也是的。时至今日,我们可以在一个厂商提供手表中得到比这更好的参数:最新的[三星智能手表][4]拥有512MB内存以及1GHz的双核处理器。
|
||||
|
||||
当iPhone有着最少数量的按键的时候,G1确实完全相反的,按键几乎支持每个硬件控制。它有拨通和挂断按钮,home键,后退,以及菜单键,一个相机快门键,音量控制键,一个轨迹球,当然,还有50个键盘按钮。未来安卓设备将会慢慢离开按键多多的界面设计,几乎每部新旗舰都在减少按键的数量。
|
||||
当iPhone有着最少数量的按键的时候,G1确实完全相反的,按键几乎支持每个硬件控制。它有拨通和挂断按钮,home键,后退,以及菜单键,一个相机快门键,音量控制键,一个轨迹球,当然,还有50个键盘按键。未来安卓设备将会慢慢离开按键多多的界面设计,几乎每部新旗舰都在减少按键的数量。
|
||||
|
||||
但是这是第一次,人们见到了运行在实机上的安卓,而不是跑在一个令人沮丧的慢吞吞的模拟器上。安卓1.0没有iPhone那样顺滑流畅,闪亮耀眼,或拥有那么多的新闻报道。它也不像Windows Mobile 6.5那样才华横溢。但这仍然是个好的开始。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
安卓1.0和0.9的默认应用列表。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
安卓1.0的核心与两个月前发布的beta版本相比看起来并没有什么引人注目的不同,但消费者产品带来了不少应用,包括一套完整的谷歌系应用。日历,电子邮件,Gmail,即时通讯,市场,设置,语音拨号,以及YouTube都是全新登场。那时候,音乐是智能手机上占据主宰地位的媒体类型,其王者是iTunes音乐商店。谷歌没有自家的音乐服务,所以它选择了亚马逊并绑定了亚马逊MP3商店。
|
||||
*安卓1.0和0.9的默认应用列表。[Ron Amadeo供图]*
|
||||
|
||||
安卓最重要的新增是谷歌商店的首次登场,叫做“安卓市场Beta”。与此同时大部分公司满足于将它们的软件目录称作一些不同的“应用商店”——意思是一个出售应用的商店,并且只出售应用——谷歌明显有着更大的野心。它搭配了一个更为通用的名字,“安卓市场”。这个名字的想法是安卓市场不仅仅拥有应用,还拥有一切你的安卓设备所需要的东西。
|
||||
安卓1.0的核心与两个月前发布的beta版本相比看起来并没有什么引人注目的不同,但这个消费产品带来了不少应用,包括一套完整的谷歌系应用。日历,电子邮件,Gmail,即时通讯,市场,设置,语音拨号,以及YouTube都是全新登场。那时候,音乐是智能手机上占据主宰地位的媒体类型,其王者是iTunes音乐商店。谷歌没有自家的音乐服务,所以它选择了亚马逊并绑定了亚马逊MP3商店。
|
||||
|
||||
安卓最重要的新增内容是首次登场的谷歌商店,叫做“安卓市场Beta”。与此同时大部分公司满足于将它们的软件目录称作各种“应用商店”——意思是一个出售应用的商店,并且只出售应用——谷歌明显有着更大的野心。它搭配了一个更为通用的名字,“安卓市场”。这个名字的想法是安卓市场不仅仅拥有应用,还拥有一切你的安卓设备所需要的东西。
|
||||
|
||||
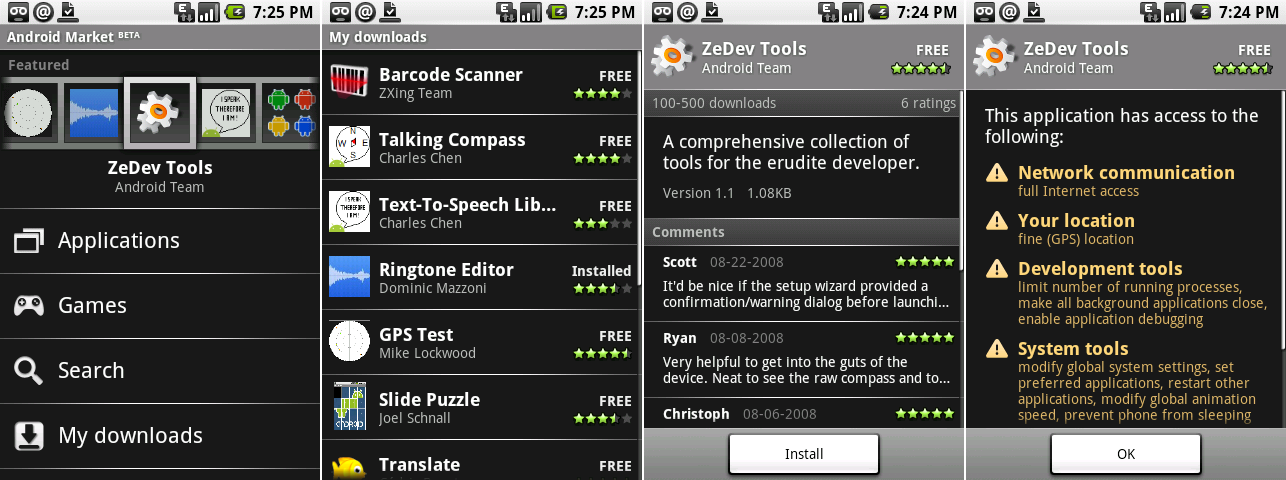
|
||||
第一个安卓市场客户端。截图展示了主页,“我的下载”,一个应用页面,以及一个应用权限页面。
|
||||
[Google][5]供图
|
||||
|
||||
那时候,安卓市场只提供应用和游戏,开发者们甚至还不能为它们收费。苹果的App Store相对与安卓市场有4个月的先发优势,但是谷歌的主要差异化在于安卓的商店几乎是完全开放的。在iPhone上,应用受制于苹果的审查,必须遵循设计和技术指南。潜在的新应用不允许在功能上复制已有应用。在安卓市场,开发者可以自由地做任何想做的,包括开发替代已有的应用。控制的缺失会转变成祝福同时也是诅咒。它允许开发者革新已有的功能,但同时意味着甚至是毫无价值的垃圾应用也被允许进入市场。
|
||||
*第一个安卓市场客户端。截图展示了主页,“我的下载”,一个应用页面,以及一个应用权限页面。[[Google][5]供图]*
|
||||
|
||||
现在,这个客户端是又一个不再能够和谷歌服务器通讯的应用。幸运的是,它也是在因特网上被[真正记录][6]的为数不多的早期安卓应用之一。主页提供了通向一般区域的连接,像应用,游戏,搜索,以及下载,顶部有横向滚动显示的特色应用图标。搜索结果和“我的下载”页面以滚动列表的方式显示应用,显示应用名,开发者,费用(在那时都是免费的),以及评分。单独的应用页面展示了一个简短的描述,安装数,用户评论和评分,以及最重要的安装按钮。早期的安卓市场不支持图片,开发者唯一能使用的区域是应用描述,还有着500字的限制。这使得类似维护一个更新日志变的十分困难,因为只有描述的位置可以供其使用。
|
||||
那时候,安卓市场只提供应用和游戏,开发者们甚至还不能为它们收费。苹果的App Store相对与安卓市场有4个月的先发优势,但是谷歌的主要差异化在于安卓的商店几乎是完全开放的。在iPhone上,应用受制于苹果的审查,必须遵循设计和技术指南。潜在的新应用不允许在功能上复制已有应用。在安卓市场,开发者可以自由地做任何想做的,包括开发替代已有的应用。控制的缺失导致福祸相依。它允许开发者革新已有的功能,但同时意味着甚至是毫无价值的垃圾应用也被允许进入市场。
|
||||
|
||||
时至今日,这个安卓市场的客户端是又一个不再能够和谷歌服务器通讯的应用。幸运的是,它也是在因特网上被[真正记录][6]的为数不多的早期安卓应用之一。主页提供了通向一般区域的连接,像应用,游戏,搜索,以及下载,顶部有横向滚动显示的特色应用图标。搜索结果和“我的下载”页面以滚动列表的方式显示应用,显示应用名,开发者,费用(在那时都是免费的),以及评分。单独的应用页面展示了一个简短的描述,安装数,用户评论和评分,以及最重要的安装按钮。早期的安卓市场不支持图片,开发者唯一能使用的区域是应用描述,还有着500字的限制。这使得类似维护一个更新日志变的十分困难,因为只有描述的位置可以供其使用。
|
||||
|
||||
就在安装之前,安卓市场显示了应用所需要的权限。这是苹果直至2012年之前都避免做的,那年一个iOS应用被发现在用户不知情的情况下[将完整的通讯录上传][7]到云端。权限显示给出了一个完整的应用用到的权限列表,尽管这个版本强迫用户同意应用权限。界面有个“OK”按钮,但是除了后退按钮没有办法取消。
|
||||
|
||||
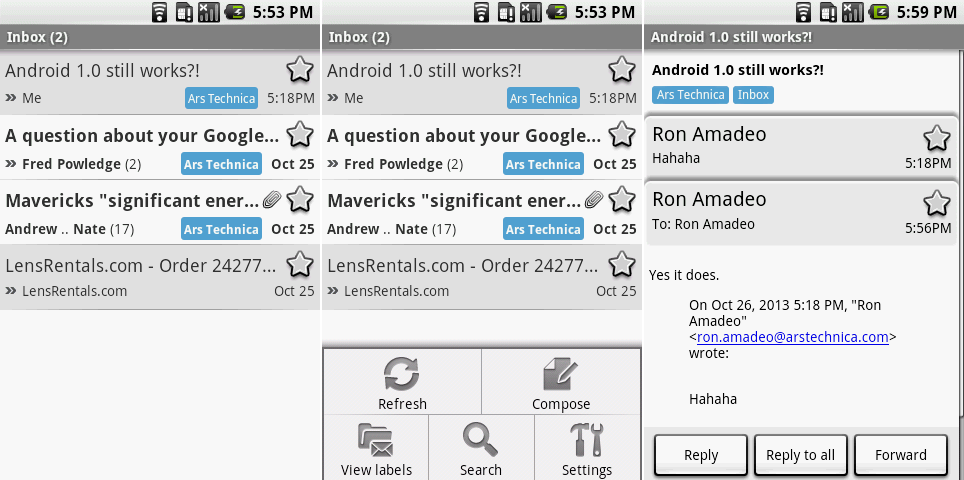
|
||||
Gmail展示收件箱,打开菜单的收件箱。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
下一个重要的应用也许就是Gmail。大多数基本的功能此时已经准备好了。未读邮件以加粗显示,标签是个有颜色的标记。在收件箱中每封独立邮件显示着主题,发件人,以及一个会话中的回复数。Gmail加星标志也在这里——快速点击即可给邮件加星或取消。一如往常,对于早期版本的安卓,菜单里有收件箱视图应有的所有按钮。但是,一旦打开了一封邮件,界面看起来就更加的现代了,“回复”和“转发”按钮永久固定在了屏幕底部。各个独立回复可以点击它们来展开和收缩。
|
||||
*Gmail展示收件箱,打开菜单的收件箱。[Ron Amadeo供图]*
|
||||
|
||||
下一个重要的应用也许就是Gmail。大多数基本的功能此时已经准备好了。未读邮件以加粗显示,标签是个有颜色的标记。在收件箱中每封独立邮件显示着主题,发件人,以及一个会话中的回复数。Gmail加星标志也在这里——快速点击即可给邮件加星或取消。一如往常,对于早期版本的安卓,菜单里有收件箱视图应有的所有按钮。但是,一旦打开了一封邮件,界面看起来就更加的现代了,“回复”和“转发”按钮永久固定在了屏幕底部。单独回复可以点击它们来展开和收缩。
|
||||
|
||||
圆角,阴影,以及气泡图标给了整个应用“卡通”的外表,但是这是个好的开始。安卓的功能第一哲学真正从此开始:Gmail支持标签,邮件会话,搜索,以及邮件推送。
|
||||
|
||||
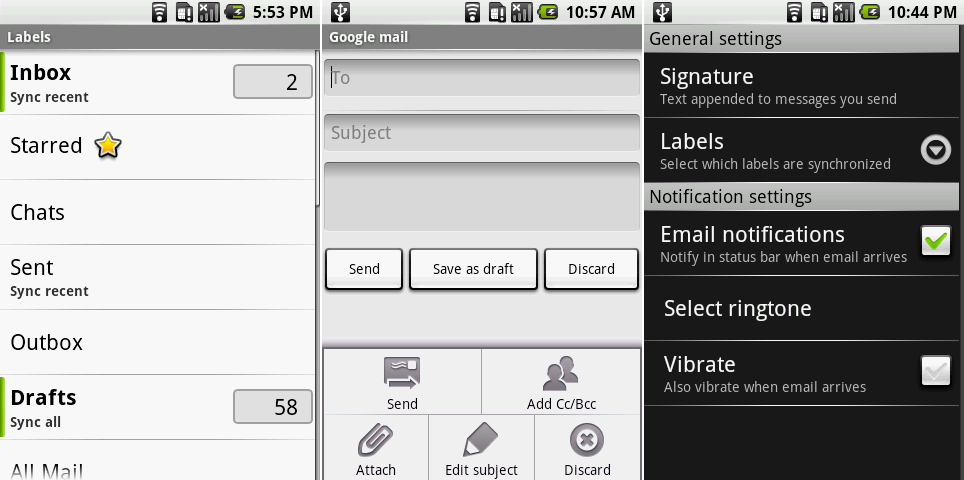
|
||||
Gmail在安卓1.0的标签视图,写邮件界面,以及设置。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
*Gmail在安卓1.0的标签视图,写邮件界面,以及设置。[Ron Amadeo供图]*
|
||||
|
||||
但是如果你认为Gmail很丑,电子邮件应用又拉低了下限。它没有分离的收件箱或文件夹视图——所有东西都糊在一个界面。应用呈现给你一个文件夹列表,点击一个文件夹会以内嵌的方式展开内容。未读邮件左侧有条绿色的线指示,这就是电子邮件应用的界面。这个应用支持IMAP和POP3,但是没有Exchange。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/6/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,90 +1,90 @@
|
||||
安卓编年史
|
||||
安卓编年史(7)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
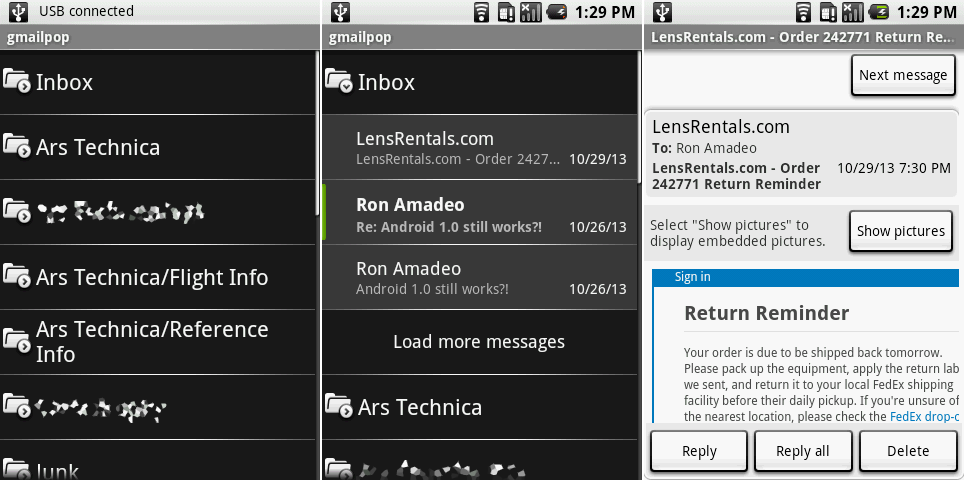
|
||||
电子邮件应用的所有界面。前两张截图展示了标签/收件箱结合的视图,最后一张截图展示了一封邮件。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
邮件视图是——令人惊讶的!——白色。安卓的电子邮件应用从历史角度来说算是个打了折扣的Gmail应用,你可以在这里看到紧密的联系。读邮件以及写邮件视图几乎没有任何修改地就从Gmail那里直接取过来使用。
|
||||
*电子邮件应用的所有界面。前两张截图展示了标签/收件箱结合的视图,最后一张截图展示了一封邮件。 [Ron Amadeo供图]*
|
||||
|
||||
邮件视图是——令人惊讶的!居然是白色。安卓的电子邮件应用从历史角度来说算是个打了折扣的Gmail应用,你可以在这里看到紧密的联系。读邮件以及写邮件视图几乎没有任何修改地就从Gmail那里直接取过来使用。
|
||||
|
||||
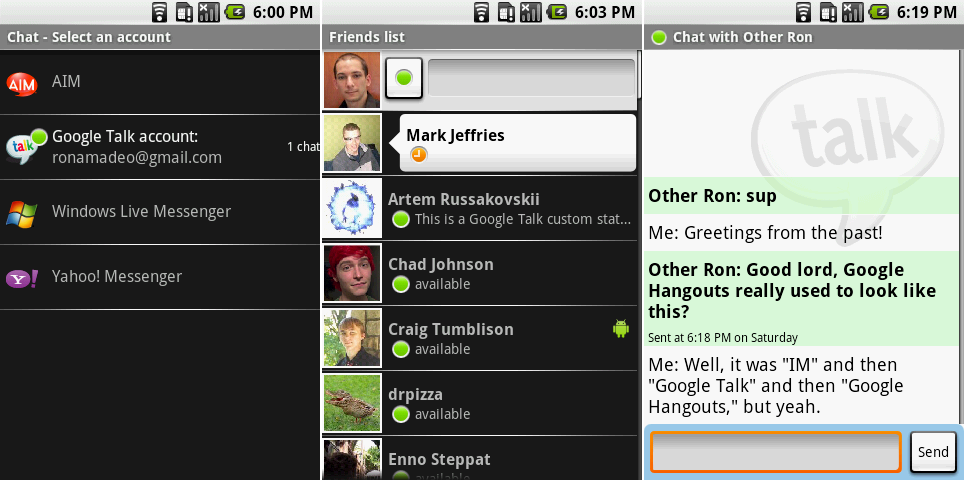
|
||||
即时通讯应用。截图展示了服务提供商选择界面,朋友列表,以及一个对话。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
在Google Hangouts之前,甚至是Google Talk之前,就有“IM”——安卓1.0带来的唯一一个即时通讯客户端。令人惊奇的是,它支持多种IM服务:用户可以从AIM,Google Talk,Windows Live Messenger以及Yahoo中挑选。还记得操作系统开发者什么时候关心过互通性吗?
|
||||
*即时通讯应用。截图展示了服务提供商选择界面,朋友列表,以及一个对话。[Ron Amadeo供图]*
|
||||
|
||||
朋友列表是聊天中带有白色聊天气泡的黑色背景界面。状态用一个带颜色的圆形来指示,右侧的小安卓机器人指示出某人正在使用移动设备。IM应用相比Google Hangouts远比它有沟通性,这真是十分神奇的。绿色代表着某人正在使用设备并且已经登录,黄色代表着他们登录了但处于空闲状态,红色代表他们手动设置状态为忙,不想被打扰,灰色表示离线。现在Hangouts只显示用户是否打开了应用。
|
||||
在Google Hangouts之前,甚至是Google Talk之前,就有了“IM”——安卓1.0带来的唯一一个即时通讯客户端。令人惊奇的是,它支持多种IM服务:用户可以从AIM,Google Talk,Windows Live Messenger以及Yahoo中挑选。还记得操作系统开发者什么时候关心过互通性吗?
|
||||
|
||||
朋友列表是黑色背景界面,如果在聊天中则带有白色聊天气泡。状态用一个带颜色的圆形来指示,右侧的小安卓机器人指示出某人正在使用移动设备。IM应用相比Google Hangouts远比它有沟通性,这真是十分神奇的。绿色代表着某人正在使用设备并且已经登录,黄色代表着他们登录了但处于空闲状态,红色代表他们手动设置状态为忙,不想被打扰,灰色表示离线。现在Hangouts只显示用户是否打开了应用。
|
||||
|
||||
聊天对话界面明显基于信息应用,聊天的背景从白色和蓝色被换成了白色和绿色。但是没人更改信息输入框的颜色,所以加上橙色的高亮效果,界面共使用了白色,绿色,蓝色和橙色。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
安卓1.0上的YouTube。截图展示了主界面,打开菜单的主界面,分类界面,视频播放界面。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
YouTube仅仅以G1的320p屏幕和3G网络速度可能不会有今天这样的移动意识,但谷歌的视频服务在安卓1.0上就被置入发布了。主界面看起来就像是安卓市场调整过的版本,顶部带有一个横向滚动选择部分,下面有垂直滚动分类列表。谷歌的一些分类选择还真是奇怪:“最热门”和“最多观看”有什么区别?
|
||||
*安卓1.0上的YouTube。截图展示了主界面,打开菜单的主界面,分类界面,视频播放界面。[Ron Amadeo供图]*
|
||||
|
||||
一个谷歌没有意识到YouTube最终能达到多庞大的标志——有一个视频分类是“最近更新”。在今天,每分钟有[100小时时长的视频][1]上传到Youtube上,如果这个分类能正常工作的话,它会是一个快速滚动的视频列表,快到以至于变为一片无法阅读的模糊。
|
||||
以G1的320p屏幕和3G网络速度,YouTube可能不会有今天这样的手机上的表现,但谷歌的视频服务在安卓1.0上就被置入发布了。主界面看起来就像是安卓市场调整过的版本,顶部带有一个横向滚动选择部分,下面有垂直滚动分类列表。谷歌的一些分类选择还真是奇怪:“最热门”和“最多观看”有什么区别?
|
||||
|
||||
菜单含有搜索,喜爱,分类,设置。设置(没有图片)是有史以来最简陋的,只有个清除搜索历史的选项。分类都是一样的平淡,仅仅是个黑色的文本列表。
|
||||
这是一个谷歌没有意识到YouTube最终能达到多庞大的标志——有一个视频分类是“最近更新”。在今天,每分钟有[100小时时长的视频][1]上传到Youtube上,如果这个分类能正常工作的话,它会是一个快速滚动的视频列表,快到以至于变为一片无法阅读的模糊。
|
||||
|
||||
菜单含有搜索,喜爱,分类,设置。设置(没有该图片)是有史以来最简陋的,只有个清除搜索历史的选项。分类都是一样的平淡,仅仅是个黑色的文本列表。
|
||||
|
||||
最后一张截图展示了视频播放界面,只支持横屏模式。尽管自动隐藏的播放控制有个进度条,但它还是很奇怪地包含了后退和前进按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
YouTube的视频菜单,描述页面,评论。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
每个视频的更多选项可以通过点击菜单按钮来打开。在这里你可以把视频标记为喜爱,查看详细信息,以及阅读评论。所有的这些界面,和视频播放一样,是锁定横屏模式的。
|
||||
*YouTube的视频菜单,描述页面,评论。[Ron Amadeo供图]*
|
||||
|
||||
每个视频的更多选项可以通过点击菜单按钮来打开。在这里你可以把视频标记为“喜爱”,查看详细信息,以及阅读评论。所有的这些界面,和视频播放一样,是锁定横屏模式的。
|
||||
|
||||
然而“共享”不会打开一个对话框,它只是向Gmail邮件中加入了视频的链接。想要把链接通过短信或即时消息发送给别人是不可能的。你可以阅读评论,但是没办法评价他们或发表自己的评论。你同样无法给视频评分或赞。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
相机应用的拍照界面,菜单,照片浏览模式。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
在实体机上跑上真正的安卓意味着相机功能可以正常运作,即便那里没什么太多可关注的。左边的黑色方块是相机的界面,原本应该显示取景器图像,但SDK的截图工具没办法捕捉下来。G1有个硬件实体的拍照键(还记得吗?),所以相机没必要有个屏幕上的快门键。相机没有曝光,白平衡,或HDR设置——你可以拍摄照片,仅此而已。
|
||||
*相机应用的拍照界面,菜单,照片浏览模式。[Ron Amadeo供图]*
|
||||
|
||||
在实体机上跑真正的安卓意味着相机功能可以正常运作,即便那里没什么太多可关注的。左边的黑色方块是相机的界面,原本应该显示取景器图像,但SDK的截图工具没办法捕捉下来。G1有个硬件实体的拍照键(还记得吗?),所以相机没必要有个屏幕上的快门键。相机没有曝光,白平衡,或HDR设置——你可以拍摄照片,仅此而已。
|
||||
|
||||
菜单按钮显示两个选项:跳转到相册应用和带有两个选项的设置界面。第一个设置选项是是否给照片加上地理标记,第二个是在每次拍摄后显示提示菜单,你可以在上面右边看到截图。同样的,你目前还只能拍照——还不支持视频拍摄。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
日历的月视图,打开菜单的周视图,日视图,以及日程。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
*日历的月视图,打开菜单的周视图,日视图,以及日程。[Ron Amadeo供图]*
|
||||
|
||||
就像这个时期的大多数应用一样,日历的主命令界面是菜单。菜单用来切换视图,添加新事件,导航至当天,选择要显示的日程,以及打开设置。菜单扮演着每个单独按钮的入口的作用。
|
||||
|
||||
月视图不能显示约会事件的文字。每个日期旁边有个侧边,约会会显示为侧边上的绿色部分,通过位置来表示约会是在一天中的什么时候。周视图同样不能显示预约文字——G1的320×480的显示屏像素还不够密——所以你会在日历中看到一个带有颜色指示条的白块。唯一一个显示文字的是日程和日视图。你可以用滑动来切换日期——左右滑动切换周和日,上下滑动切换月份和日程。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
设置主界面,无线设置,关于页面的底部。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
安卓1.0最终带来了设置界面。这个界面是个带有文字的黑白界面,粗略地分为各个部分。每个列表项边的下箭头让人误以为点击它会展开折叠的更多东西,但是触摸列表项的任何位置只会加载下一屏幕。所有的界面看起来确实无趣,都差不多一样,但是嘿,这可是设置啊。
|
||||
*设置主界面,无线设置,关于页面的底部。[Ron Amadeo供图]*
|
||||
|
||||
任何带有开/关状态的选项都使用了卡通风的复选框。安卓1.0最初的复选框真是奇怪——就算是在“未选中”状态时,它们还是有个灰色的勾选标记在里面。安卓把勾选标记当作了灯泡,打开时亮起来,关闭的时候变得黯淡,但这不是复选框的工作方式。然而我们最终还是见到了“关于”页面。安卓1.0运行Linux内核2.6.25版本。
|
||||
安卓1.0最终带来了设置界面。这个界面是个带有文字的黑白界面,粗略地分为各个部分。每个列表项边上的下箭头让人误以为点击它会展开折叠的更多东西,但是触摸列表项的任何位置只会加载下一屏幕。所有的界面看起来确实无趣,都差不多一样,但是嘿,这可是设置啊。
|
||||
|
||||
任何带有开/关状态的选项都使用了卡通风格的复选框。安卓1.0最初的复选框真是奇怪——就算是在“未选中”状态时,它们还是有个灰色的勾选标记在里面。安卓把勾选标记当作了灯泡,打开时亮起来,关闭的时候变得黯淡,但这不是复选框的工作方式。然而我们最终还是见到了“关于”页面。安卓1.0运行Linux内核2.6.25版本。
|
||||
|
||||
设置界面意味着我们终于可以打开安全设置并更改锁屏。安卓1.0只有两种风格,安卓0.9那样的灰色方形锁屏,以及需要你在9个点组成的网格中画出图案的图形解锁。像这样的滑动图案相比PIN码更加容易记忆和输入,尽管它没有增加多少安全性。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
语音拨号,图形锁屏,电池低电量警告,时间设置。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
语音功能和语音拨号一同来到了1.0。这个特性以各种功能实现在AOSP徘徊了一段时间,然而它是一个简单的拨打号码和联系人的语音命令应用。语音拨号是个和谷歌未来的语音产品完全无关的应用,但是,它的工作方式和非智能机上的语音拨号一样。
|
||||
*语音拨号,图形锁屏,电池低电量警告,时间设置。[Ron Amadeo供图]*
|
||||
|
||||
语音功能和语音拨号一同来到了1.0。这个特性以各种功能实现在AOSP徘徊了一段时间,然而它是一个简单的拨打号码和联系人的语音命令应用。语音拨号是个和谷歌未来的语音产品完全无关的应用,它的工作方式和非智能机上的语音拨号一样。
|
||||
|
||||
关于最后一个值得注意的,当电池电量低于百分之十五的时候会触发低电量弹窗。这是个有趣的图案,它把电源线错误的一端插入手机。谷歌,那可不是(现在依然不是)手机应该有的充电方式。
|
||||
|
||||
安卓1.0是个伟大的开头,但是功能上仍然有许多缺失。实体键盘和大量硬件按钮被强制要求配备,因为不带有十字方向键或轨迹球的安卓设备依然不被允许销售。另外,基本的智能手机功能比如自动旋转依然缺失。内置应用不可能像今天这样通过安卓市场来更新。所有的谷歌系应用和系统交织在一起。如果谷歌想要升级一个单独的应用,需要通过运营商推送整个系统的更新。安卓依然还有许多工作要做。
|
||||
安卓1.0是个伟大的开端,但是功能上仍然有许多缺失。强制配备了实体键盘和大量硬件按钮,因为不带有十字方向键或轨迹球的安卓设备依然不被允许销售。另外,基本的智能手机功能比如自动旋转依然缺失。内置应用不可能像今天这样通过安卓市场来更新。所有的谷歌系应用和系统交织在一起。如果谷歌想要升级一个单独的应用,需要通过运营商推送整个系统的更新。安卓依然还有许多工作要做。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安卓1.1——第一个真正的增量更新 ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
安卓1.1的所有新特性:语音搜索,安卓市场付费应用支持,谷歌纵横,设置中的新“系统更新”选项。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
安卓1.0发布四个半月后,2009年2月,安卓在安卓1.1中得到了它的第一个公开更新。系统方面没有太多变化,谷歌向1.1中添加新东西现如今也都已被关闭。谷歌语音搜索是安卓向云端语音搜索的第一个突击,它在应用抽屉里有自己的图标。尽管这个应用已经不能与谷歌服务器通讯,你可以[在iPhone上][2]看到它以前是怎么工作的。它还没有语音操作,但你可以说出想要搜索的,结果会显示在一个简单的谷歌搜索中。
|
||||
*安卓1.1的所有新特性:语音搜索,安卓市场付费应用支持,谷歌纵横,设置中的新“系统更新”选项。[Ron Amadeo供图]*
|
||||
|
||||
安卓市场添加了对付费应用的支持,但是就像beta客户端中一样,这个版本的安卓市场不再能够连接Google Play服务器。我们最多能够看到分类界面,你可以在免费应用,付费应用和全部应用中选择。
|
||||
安卓1.0发布四个半月后,2009年2月,安卓在安卓1.1中得到了它的第一个公开更新。系统方面没有太多变化,谷歌向1.1中添加的新东西现如今也都已被关闭。谷歌语音搜索是安卓向云端语音搜索的第一个突击,它在应用抽屉里有自己的图标。尽管这个应用已经不能与谷歌服务器通讯,你可以[在iPhone上][2]看到它以前是怎么工作的。它还没有语音操作,但你可以说出想要搜索的,结果会显示在一个简单的谷歌搜索中。
|
||||
|
||||
安卓市场添加了对付费应用的支持,但是就像beta客户端中一样,这个版本的安卓市场已经不能连接Google Play服务器。我们最多能够看到分类界面,你可以在免费应用、付费应用和全部应用中选择。
|
||||
|
||||
地图添加了[谷歌纵横][3],一个向朋友分享自己位置的方法。纵横在几个月前为了支持Google+而被关闭并且不再能够工作。地图菜单里有个纵横的选项,但点击它现在只会打开一个带载入中圆圈的画面,并永远停留在这里。
|
||||
|
||||
安卓世界的系统更新来得更加迅速——或者至少是一条在运营商和OEM推送之前获得更新的途径——谷歌向“关于手机”界面添加了检查系统更新按钮。
|
||||
安卓世界的系统更新来得更加迅速——或者至少是一条在运营商和OEM推送之前获得更新的途径——谷歌也在“关于手机”界面添加了检查系统更新按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -98,7 +98,7 @@ Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/7/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu Software Centre To Be Replaced in 16.04 LTS
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The USC Will Be Replaced
|
||||
|
||||
**The Ubuntu Software Centre is to be replaced in Ubuntu 16.04 LTS.**
|
||||
|
||||
Users of the Xenial Xerus desktop will find that the familiar (and somewhat cumbersome) Ubuntu Software Centre is no longer available.
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME’s [Software application][1] will – according to current plans – take its place as the default and package management utility on the Unity 7-based desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME Software
|
||||
|
||||
New plugins will be created to support the Software Centre’s ratings, reviews and paid app features as a result of the switch.
|
||||
|
||||
The decisions were taken at a recent desktop Sprint held at Canonical HQ in London.
|
||||
|
||||
“We are more confident in our ability to add support for Snaps to GNOME Software Centre (sic) than we are to Ubuntu Software Centre. And so, right now, it looks like we will be replacing [the USC] with GNOME Software Centre”, explains Ubuntu desktop manager Will Cooke at the Ubuntu Online Summit.
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME 3.18 stack will also be included in Ubuntu 16.04, with select app updates to GNOME 3.20 apps taken ‘as and when it makes sense’, adds Will Cooke.
|
||||
|
||||
We recently ran a poll on Twitter asking how you install software on Ubuntu. The results suggest that few of you will mourn the passing of the incumbent Software Centre…
|
||||
|
||||
注:投票项目
|
||||
Which of these do you use to install software on #Ubuntu?
|
||||
|
||||
- Software Centre
|
||||
- Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
### Other Apps Being Dropped in Ubuntu 16.04 ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Ubuntu Software Centre is not the only app set to be given the heave-ho in Xenial Xerus.
|
||||
|
||||
Disc burning utility Brasero and instant messaging app **Empathy** are also to be removed from the default install image.
|
||||
|
||||
Neither app is considered to be under active development, and with the march of laptops lacking optical drives and web and mobile-based chat services, they may also be seen as increasingly obsolete.
|
||||
|
||||
If you do have use for them don’t panic: both Brasero and Empathy will **still be available to install on Ubuntu from the archives**.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s not all removals and replacements as one new desktop app is set be included by default: GNOME Calendar.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/11/the-ubuntu-software-centre-is-being-replace-in-16-04-lts
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sam Tran][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/111008502832304483939?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Software
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
cygmris is translating...
|
||||
Great Open Source Collaborative Editing Tools
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In a nutshell, collaborative writing is writing done by more than one person. There are benefits and risks of collaborative working. Some of the benefits include a more integrated / co-ordinated approach, better use of existing resources, and a stronger, united voice. For me, the greatest advantage is one of the most transparent. That's when I need to take colleagues' views. Sending files back and forth between colleagues is inefficient, causes unnecessary delays and leaves people (i.e. me) unhappy with the whole notion of collaboration. With good collaborative software, I can share notes, data and files, and use comments to share thoughts in real-time or asynchronously. Working together on documents, images, video, presentations, and tasks is made less of a chore.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Translating by H-mudcup
|
||||
5 best open source board games to play online
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
I have always had a fascination with board games, in part because they are a device of social interaction, they challenge the mind and, most importantly, they are great fun to play. In my misspent youth, myself and a group of friends gathered together to escape the horrors of the classroom, and indulge in a little escapism. The time provided an outlet for tension and rivalry. Board games help teach diplomacy, how to make and break alliances, bring families and friends together, and learn valuable lessons.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,195 @@
|
||||
Optimize Web Delivery with these Open Source Tools
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Web proxy software forwards HTTP requests without modifying traffic in any way. They can be configured as a transparent proxy with no client-side configuration required. They can also be used as a reverse proxy front-end to websites; here the cache serves an unlimited number of clients for one or some web servers.
|
||||
|
||||
Web proxies are versatile tools. They have a wide variety of uses, from caching web, DNS and other lookups, to speeding up the delivery of a web server / reducing bandwidth consumption. Web proxy software can also harden security by filtering traffic and anonymizing connections, and offer media-range limitations. This software is used by high-profile, high-traffic websites such as The New York Times, The Guardian, and social media and content sites such as Twitter, Facebook, and Wikipedia.
|
||||
|
||||
Web caches have become a vital mechanism for optimising the amount of data that is delivered in a given period of time. Good web caches also help to minimise latency, serving pages as quickly as possible. This helps to prevent the end user from becoming impatient having to wait for content to be delivered. Web caches optimise the data flow between client and server. They also help to converse bandwidth by caching frequently-delivered content. If you need to reduce server load and improve delivery speed of your content, it is definitely worth exploring the benefits offered by web cache software.
|
||||
|
||||
To provide an insight into the quality of software available for Linux, I feature below 5 excellent open source web proxy tools. Some of the them are full-featured; a couple of them have very modest resource needs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Squid ###
|
||||
|
||||
Squid is a high-performance open source proxy caching server and web cache daemon. It supports FTP, Internet Gopher, HTTPS, TLS, and SSL. It handles all requests in a single, non-blocking, I/O-driven process over IPv4 or IPv6.
|
||||
|
||||
Squid consists of a main server program squid, a Domain Name System lookup program dnsserver, some optional programs for rewriting requests and performing authentication, together with some management and client tools.
|
||||
|
||||
Squid offers a rich access control, authorization and logging environment to develop web proxy and content serving applications.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Web proxy:
|
||||
- Caching to reduce access time and bandwidth use
|
||||
- Keeps meta data and especially hot objects cached in RAM
|
||||
- Caches DNS lookups
|
||||
- Supports non-blocking DNS lookups
|
||||
- Implements negative chacking of failed requests
|
||||
- Squid caches can be arranged in a hierarchy or mesh for additional bandwidth savings
|
||||
- Enforce site-usage policies with extensive access controls
|
||||
- Anonymize connections, such as disabling or changing specific header fields in a client's HTTP request
|
||||
- Reverse proxy
|
||||
- Media-range limitations
|
||||
- Supports SSL
|
||||
- Support for IPv6
|
||||
- Error Page Localization - error pages presented by Squid may now be localized per-request to match the visitors local preferred language
|
||||
- Connection Pinning (for NTLM Auth Passthrough) - a workaround which permits Web servers to use Microsoft NTLM Authentication instead of HTTP standard authentication through a web proxy
|
||||
- Quality of Service (QoS) Flow support
|
||||
- Select a TOS/Diffserv value to mark local hits
|
||||
- Select a TOS/Diffserv value to mark peer hits
|
||||
- Selectively mark only sibling or parent requests
|
||||
- Allows any HTTP response towards clients to have the TOS value of the response coming from the remote server preserved
|
||||
- Mask certain bits in the TOS received from the remote server, before copying the value to the TOS send towards clients
|
||||
- SSL Bump (for HTTPS Filtering and Adaptation) - Squid-in-the-middle decryption and encryption of CONNECT tunneled SSL traffic, using configurable client- and server-side certificates
|
||||
- eCAP Adaptation Module support
|
||||
- ICAP Bypass and Retry enhancements - ICAP is now extended with full bypass and dynamic chain routing to handle multiple adaptation services.
|
||||
- ICY streaming protocol support - commonly known as SHOUTcast multimedia streams
|
||||
- Dynamic SSL Certificate Generation
|
||||
- Support for the Internet Content Adaptation Protocol (ICAP)
|
||||
- Full request logging
|
||||
- Anonymize connections
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [www.squid-cache.org][1]
|
||||
- Developer: National Laboratory for Applied Networking Research (NLANR) and Internet volunteers
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 4.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
### Privoxy ###
|
||||
|
||||
Privoxy (Privacy Enhancing Proxy) is a non-caching Web proxy with advanced filtering capabilities for enhancing privacy, modifying web page data and HTTP headers, controlling access, and removing ads and other obnoxious Internet junk. Privoxy has a flexible configuration and can be customized to suit individual needs and tastes. It supports both stand-alone systems and multi-user networks.
|
||||
|
||||
Privoxy uses the concept of actions in order to manipulate the data stream between the browser and remote sites.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Highly configurable - completely personalize your installation
|
||||
- Ad blocking
|
||||
- Cookie management
|
||||
- Supports "Connection: keep-alive". Outgoing connections can be kept alive independently from the client
|
||||
- Supports IPv6
|
||||
- Tagging which allows to change the behaviour based on client and server headers
|
||||
- Run as an "intercepting" proxy
|
||||
- Sophisticated actions and filters for manipulating both server and client headers
|
||||
- Can be chained with other proxies
|
||||
- Integrated browser-based configuration and control utility. Browser-based tracing of rule and filter effects. Remote toggling
|
||||
- Web page filtering (text replacements, removes banners based on size, invisible "web-bugs" and HTML annoyances, etc)
|
||||
- Modularized configuration that allows for standard settings and user settings to reside in separate files, so that installing updated actions files won't overwrite individual user settings
|
||||
- Support for Perl Compatible Regular Expressions in the configuration files, and a more sophisticated and flexible configuration syntax
|
||||
- GIF de-animation
|
||||
- Bypass many click-tracking scripts (avoids script redirection)
|
||||
- User-customizable HTML templates for most proxy-generated pages (e.g. "blocked" page)
|
||||
- Auto-detection and re-reading of config file changes
|
||||
- Most features are controllable on a per-site or per-location basis
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [www.privoxy.org][2]
|
||||
- Developer: Fabian Keil (lead developer), David Schmidt, and many other contributors
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 3.4.2
|
||||
|
||||
### Varnish Cache ###
|
||||
|
||||
Varnish Cache is a web accelerator written with performance and flexibility in mind. It's modern architecture offers significantly better performance. It typically speeds up delivery with a factor of 300 - 1000x, depending on your architecture. Varnish stores web pages in memory so the web servers do not have to create the same web page repeatedly. The web server only recreates a page when it is changed. When content is served from memory this happens a lot faster then anything.
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally Varnish can serve web pages much faster then any application server is capable of - giving the website a significant speed enhancement.
|
||||
|
||||
For a cost-effective configuration, Varnish Cache uses between 1-16GB and a SSD disk.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Modern design
|
||||
- VCL - a very flexible configuration language. The VCL configuration is translated to C, compiled, loaded and executed giving flexibility and speed
|
||||
- Load balancing using both a round-robin and a random director, both with a per-backend weighting
|
||||
- DNS, Random, Hashing and Client IP based Directors
|
||||
- Load balance between multiple backends
|
||||
- Support for Edge Side Includes including stitching together compressed ESI fragments
|
||||
- Heavily threaded
|
||||
- URL rewriting
|
||||
- Cache multiple vhosts with a single Varnish
|
||||
- Log data is stored in shared memory
|
||||
- Basic health-checking of backends
|
||||
- Graceful handling of "dead" backends
|
||||
- Administered by a command line interface
|
||||
- Use In-line C to extend Varnish
|
||||
- Can be used on the same system as Apache
|
||||
- Run multiple Varnish on the same system
|
||||
- Support for HAProxy's PROXY protocol. This is a protocol adds a small header on each incoming TCP connection that describes who the real client is, added by (for example) an SSL terminating process
|
||||
- Warm and cold VCL states
|
||||
- Plugin support with Varnish Modules, called VMODs
|
||||
- Backends defined through VMODs
|
||||
- Gzip Compression and Decompression
|
||||
- HTTP Streaming Pass & Fetch
|
||||
- Saint and Grace mode. Saint Mode allows for unhealthy backends to be blacklisted for a period of time, preventing them from serving traffic when using Varnish as a load balancer. Grace mode allows Varnish to serve an expired version of a page or other asset in cases where Varnish is unable to retrieve a healthy response from the backend
|
||||
- Experimental support for Persistent Storage, without LRU eviction
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [www.varnish-cache.org][3]
|
||||
- Developer: Varnish Software
|
||||
- License: FreeBSD
|
||||
- Version Number: 4.1.0
|
||||
|
||||
### Polipo ###
|
||||
|
||||
Polipo is an open source caching HTTP proxy which has modest resource needs.
|
||||
|
||||
It listens to requests for web pages from your browser and forwards them to web servers, and forwards the servers’ replies to your browser. In the process, it optimises and cleans up the network traffic. It is similar in spirit to WWWOFFLE, but the implementation techniques are more like the ones ones used by Squid.
|
||||
|
||||
Polipo aims at being a compliant HTTP/1.1 proxy. It should work with any web site that complies with either HTTP/1.1 or the older HTTP/1.0.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- HTTP 1.1, IPv4 & IPv6, traffic filtering and privacy-enhancement
|
||||
- Uses HTTP/1.1 pipelining if it believes that the remote server supports it, whether the incoming requests are pipelined or come in simultaneously on multiple connections
|
||||
- Cache the initial segment of an instance if the download has been interrupted, and, if necessary, complete it later using Range requests
|
||||
- Upgrade client requests to HTTP/1.1 even if they come in as HTTP/1.0, and up- or downgrade server replies to the client's capabilities
|
||||
- Complete support for IPv6 (except for scoped (link-local) addresses)
|
||||
- Use as a bridge between the IPv4 and IPv6 Internets
|
||||
- Content-filtering
|
||||
- Can use a technique known as Poor Man's Multiplexing to reduce latency
|
||||
- SOCKS 4 and SOCKS 5 protocol support
|
||||
- HTTPS proxying
|
||||
- Behaves as a transparent proxy
|
||||
- Run Polipo together with Privoxy or tor
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [www.pps.univ-paris-diderot.fr/~jch/software/polipo/][4]
|
||||
- Developer: Juliusz Chroboczek, Christopher Davis
|
||||
- License: MIT License
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.1.1
|
||||
|
||||
### Tinyproxy ###
|
||||
|
||||
Tinyproxy is a lightweight open source web proxy daemon. It is designed to be fast and yet small. It is useful for cases such as embedded deployments where a full featured HTTP proxy is required, but the system resources for a larger proxy are unavailable.
|
||||
|
||||
Tinyproxy is very useful in a small network setting, where a larger proxy would either be too resource intensive, or a security risk. One of the key features of Tinyproxy is the buffering connection concept. In effect, Tinyproxy will buffer a high speed response from a server, and then relay it to a client at the highest speed the client will accept. This feature greatly reduces the problems with sluggishness on the net.
|
||||
|
||||
Features:
|
||||
|
||||
- Easy to modify
|
||||
- Anonymous mode - allows specification of individual HTTP headers that should be allowed through, and which should be blocked
|
||||
- HTTPS support - Tinyproxy allows forwarding of HTTPS connections without modifying traffic in any way through the CONNECT method
|
||||
- Remote monitoring - access proxy statistics from afar, letting you know exactly how busy the proxy is
|
||||
- Load average monitoring - configure software to refuse connections after the server load reaches a certain point
|
||||
- Access control - configure to only allow connections from certain subnets or IP addresses
|
||||
- Secure - run without any special privileges, thus minimizing the chance of system compromise
|
||||
- URL based filtering - allows domain and URL-based black- and whitelisting
|
||||
- Transparent proxying - configure as a transparent proxy, so that a proxy can be used without any client-side configuration
|
||||
- Proxy chaining - use an upstream proxy server for outbound connections, instead of direct connections to the target server, creating a so-called proxy chain
|
||||
- Privacy features - restrict both what data comes to your web browser from the HTTP server (e.g., cookies), and to restrict what data is allowed through from your web browser to the HTTP server (e.g., version information)
|
||||
- Small footprint - the memory footprint is about 2MB with glibc, and the CPU load increases linearly with the number of simultaneous connections (depending on the speed of the connection). Tinyproxy can be run on an old machine without affecting performance
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [banu.com/tinyproxy][5]
|
||||
- Developer: Robert James Kaes and contributors
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.8.3
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20151101020309690/WebDelivery.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.squid-cache.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.privoxy.org/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.varnish-cache.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.pps.univ-paris-diderot.fr/%7Ejch/software/polipo/
|
||||
[5]:https://banu.com/tinyproxy/
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
LinuxCon's surprise keynote speaker Linus Torvalds muses about open-source software
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> In a broad-ranging question and answer session, Linus Torvalds, Linux's founder, shared his thoughts on the current state of open source and Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
**SEATTLE** -- [LinuxCon][1] attendees got an early Christmas present when the Wednesday morning "surprise" keynote speaker turned out to be Linux's founder, Linus Torvalds.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Jim Zemlin and Linus Torvalds shooting the breeze at LinuxCon in Seattle. -- sjvn
|
||||
|
||||
Jim Zemlin, the Linux Foundation's executive director, opened the question and answer session by quoting from a recent article about Linus, "[Torvalds may be the most influential individual economic force][2] of the past 20 years. ... Torvalds has, in effect, been as instrumental in retooling the production lines of the modern economy as Henry Ford was 100 years earlier."
|
||||
|
||||
Torvalds replied, "I don't think I'm all that powerful, but I'm glad to get all the credit for open source." For someone who's arguably been more influential on technology than Bill Gates, Steve Jobs, or Larry Ellison, Torvalds remains amusingly modest. That's probably one reason [Torvalds, who doesn't suffer fools gladly][3], remains the unchallenged leader of Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
It also helps that he doesn't take himself seriously, except when it comes to code quality. Zemlin reminded him that he was also described in the same article as being "5-feet, ho-hum tall with a paunch, ... his body type and gait resemble that of Tux, the penguin mascot of Linux." Torvald's reply was to grin and say "What is this? A roast?" He added that 5'8" was a perfectly good height.
|
||||
|
||||
More seriously, Zemlin asked Torvalds what he thought about the current excitement over containers. Indeed, at times LinuxCon has felt like DockerCon. Torvalds replied, "I'm glad that the kernel is far removed from containers and other buzzwords. We only care about just the kernel. I'm so focused on the kernel I really don't care. I don't get involved in the politics above the kernel and I'm really happy that I don't know."
|
||||
|
||||
Moving on, Zemlin asked Torvalds what he thought about the demand from the Internet of Things (IoT) for an even smaller Linux kernel. "Everyone has always wished for a smaller kernel," Torvalds said. "But, with all the modules it's still tens of MegaBytes in size. It's shocking that it used to fit into a MB. We'd like it to be mean lean, mean IT machine again."
|
||||
|
||||
But, "Torvalds continued, "It's hard to get rid of unnecessary fat. Things tend to grow. Realistically I don't think we can get down to the sizes we were 20 years ago."
|
||||
|
||||
As for security, the next topic, Torvalds said, "I'm at odds with the security community. They tend to see technology as black and white. If it's not security they don't care at all about it." The truth is "security is bugs. Most of the security issues we've had in the kernel hasn't been that big. Most of them have been really stupid and then some clever person takes advantage of it."
|
||||
|
||||
The bottom line is, "We'll never get rid of bugs so security will never be perfect. We do try to be really careful about code. With user space we have to be very strict." But, "Bugs happen and all you can do is mitigate them. Open source is doing fairly well, but anyone who thinks we'll ever be completely secure is foolish."
|
||||
|
||||
Zemlin concluded by asking Torvalds where he saw Linux ten years from now. Torvalds replied that he doesn't look at it this way. "I'm plodding, pedestrian, I look ahead six months, I don't plan 10 years ahead. I think that's insane."
|
||||
|
||||
Sure, "companies plan ten years, and their plans use open source. Their whole process is very forward thinking. But I'm not worried about 10 years ahead. I look to the next release and the release beyond that."
|
||||
|
||||
For Torvalds, who works at home where "the FedEx guy is no longer surprised to find me in my bathrobe at 2 in the afternoon," looking ahead a few months works just fine. And so do all the businesses -- both technology-based Amazon, Google, Facebook and more mainstream, WalMart, the New York Stock Exchange, and McDonalds -- that live on Linux every day.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.zdnet.com/article/linus-torvalds-muses-about-open-source-software/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.zdnet.com/meet-the-team/us/steven-j-vaughan-nichols/
|
||||
[1]:http://events.linuxfoundation.org/events/linuxcon-north-america
|
||||
[2]:http://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2015-06-16/the-creator-of-linux-on-the-future-without-him
|
||||
[3]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/linus-torvalds-finds-gnome-3-4-to-be-a-total-user-experience-design-failure/
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
KevinSJ translating
|
||||
Why did you start using Linux?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> In today's open source roundup: What got you started with Linux? Plus: IBM's Linux only Mainframe. And why you should skip Windows 10 and go with Linux
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,92 +0,0 @@
|
||||
LinuxCon exclusive: Mark Shuttleworth says Snappy was born long before CoreOS and the Atomic Project
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Mark Shuttleworth at LinuxCon Credit: Swapnil Bhartiya
|
||||
|
||||
> Mark Shuttleworth, founder of Canonical and Ubuntu, made a surprise visit at LinuxCon. I sat down with him for a video interview and talked about Ubuntu on IBM’s new LinuxONE systems, Canonical’s plans for containers, open source in the enterprise space and much more.
|
||||
|
||||
### You made a surprise entry during the keynote. What brought you to LinuxCon? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Mark Shuttleworth**: I am here at LinuxCon to support IBM and Canonical in their announcement of Ubuntu on their new Linux-only super-high-end mainframe LinuxONE. These are the biggest machines in the world, purpose-built to run only Linux. And we will be bringing Ubuntu to them, which is a real privilege for us and is going to be incredible for developers.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Swapnil Bhartiya
|
||||
|
||||
Mark Shuttleworth and Swapnil Bhartiya, mandatory selfie at LinuxCon
|
||||
|
||||
### Only Red Hat and SUSE were supported on it. Why was Ubuntu missing from the mainframe scene? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Mark**: Ubuntu has always been about developers. It has been about enabling the free software platform from where it is collaboratively built to be available at no cost to developers in the world, so they are limited only by their imagination—not by money, not by geography.
|
||||
|
||||
There was an incredible story told today about a 12-year-old kid who started out with Ubuntu; there are incredible stories about people building giant businesses with Ubuntu. And for me, being able to empower people, whether they come from one part of the world or another to express their ideas on free software, is what Ubuntu is all about. It's been a journey for us essentially, going to the platforms those developers care about, and just in the last year, we suddenly saw a flood of requests from companies who run mainframes, who are using Ubuntu for their infrastructure—70% of OpenStack deployments are on Ubuntu. Those same people said, “Look, there is the mainframe, and we like to unleash it and think of it as a region in the cloud.” So when IBM started talking to us, saying that they have this project in the works, it felt like a very natural fit: You are going to be able to take your Ubuntu laptop, build code there and ship it straight to every cloud, every virtualization environment, every bare metal in every architecture including the mainframe, and that's going to be beautiful.
|
||||
|
||||
### Will Canonical be offering support for these systems? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Mark**: Yes. Ubuntu on z Systems is going to be completely supported. We will make long-term commitments to that. The idea is to bring together scale-out-fast cloud-like workloads, which is really born on Ubuntu; 70% of workloads on Amazon and other public clouds run on Ubuntu. Now you can think of running that on a mainframe if that makes sense to you.
|
||||
|
||||
We are going to provide exactly the same platform that we do on the cloud, and we are going to provide that on the mainframe as well. We are also going to expose it to the OpenStack API so you can consume it on a mainframe with exactly the same tools and exactly the same processes that you would consume on a laptop, or OpenStack or public cloud resources. So all of the things that Ubuntu builds to make your life easy as a developer are going to be available across that full range of platforms and systems, and all of that is commercially supported.
|
||||
|
||||
### Canonical is doing a lot of things: It is into enterprise, and it’s in the consumer space with mobile and desktop. So what is the core focus of Canonical now? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Mark**: The trick for us is to enable the reuse of specifically the same parts [of our technology] in as many useful ways as possible. So if you look at the work that we do at z Systems, it's absolutely defined by the work that we do on the cloud. We want to deliver exactly the same libraries on exactly the same date for the mainframe as we do for public clouds and for x86, ARM and Power servers today.
|
||||
|
||||
We don't allow Ubuntu or our focus to fragment very dramatically because we don't allow different products managers to find Ubuntu in different ways in different environments. We just want to bring that standard experience that developers love to this new environment.
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly if you look at the work we are doing on IoT [Internet of Things], Snappy Ubuntu is the heart of the phone. It’s the phone without the GUI. So the definitions, the tools, the kernels, the mechanisms are shared across those projects. So we are able to multiply the impact of the work. We have an incredible community, and we try to enable the community to do things that they want to do that we can’t do. So that's why we have so many buntus, and it's kind of incredible for me to see what they do with that.
|
||||
|
||||
We also see the community climbing in. We see hundreds of developers working with Snappy for IoT, and we see developers working with Snappy on mobile, for personal computing as convergence becomes real. And, of course, there is the cloud server story: 70% of the world is Ubuntu, so there is a huge audience. We don't have to do all the work that we do; we just have to be open and willing to, kind of, do the core infrastructure and then reuse it as efficiently as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
### Is Snappy a response to Atomic or CoreOS? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Mark**: Snappy as a project was born four years ago when we started working on the phone, which was long before the CoreOS, long before Atomic. I think the principles of atomicity, transactionality are beautiful, but remember: We needed to build the same things for the phone. And with Snappy, we have the ability to deliver transactional updates to any of these systems—phones, servers and cloud devices.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, it feels a little different because in order to provide those guarantees, we have to shape the system in such a way that we can guarantee the guarantees. And that's why Snappy is snappy; it's a new thing. It's not based on an old packaging system. Though we will keep both of them: All Snaps for us that Canonical makes, the core snaps that define the OS, are all built from Debian packages. They are two different faces of the same coin for us, and developers will use them as tools. We use the right tools for the job.
|
||||
|
||||
There are couple of key advantages for Snappy over CoreOS and Atomic, and the main one is this: We took the view that we wanted the base idea to be extensible. So with Snappy, the core operating system is tiny. You make all the choices, and you take all the decisions about things you want to bolt on that: you want to bolt on Docker; you want to bolt on Kubernete; you want to bolt on Mesos; you want to bolt on Lattice from Pivotal; you want to bolt on OpenStack. Those are the things you choose to add with Snappy. Whereas with Atomic and CoreOS, it's one blob and you have to do it exactly the way they want you to do it. You have to live with the versions of software and the choices they make.
|
||||
|
||||
Whereas with Snappy, we really preserve this idea of the choices you have got in Ubuntu are now transactionally available on Snappy systems. That makes the core much smaller, and it gives you the choice of different container systems, different container management systems, different cloud infrastructure systems or different apps of every description. I think that's the winning idea. In fullness of time, people will realize that they wanted to make those choices themselves; they just want Canonical to do the work of providing the updates in a really efficient manner.
|
||||
|
||||
### There is so much competition in the container space with Docker, Rocket and many other players. Where will Canonical stand amid this competition? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Mark**: Canonical is focused on platform tools, and we see things like the Rocket and Docker as things super-useful for developers; we just make sure that those work best on Ubuntu. Docker, for years, ran only Ubuntu because we work very closely with them, and we are glad now that it's available everywhere else. But if you look at the numbers, the vast majority of Docker containers are on Ubuntu. Because we work really hard, as developers, you get the best experience with all of these tools on Ubuntu. We don't want to try and control everything, and it’s great for us to have those guys competing.
|
||||
|
||||
I think in the end people will see that there is really two kinds of containers. 1) There are cases where a container is just like a VM machine. It feels like a whole machine, it runs all processes, all the logs and cron jobs are there. It's like a VM, just that it's much cheaper, much lighter, much faster, and that's LXD. 2) And then there would be process containers, which are like Docker or Rocket; they are there to run a specific application very fast. I think we lead the world in general machine container story, which is our hypervisor LXD, and I think Docker leads the story when it comes to applications containers, process containers. And those two work together really beautifully.
|
||||
|
||||
### Microsoft and Canonical are working together on LXD? Can you tell us about this engagement? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Mark: LXD is two things. First, it's an implementation on top of Canonical's work on the kernel so that you can start to create full machine containers on any host. But it's also a REST API. That’s the transitions from LXC to LXD. We got a daemon there so you can talk to the daemon over the network, if it's listening on the network, and says tell me about the containers on that machine, tell me about the file systems on that machine, the networks on that machine, start or stop the container.
|
||||
|
||||
So LXD becomes a distributed hypervisor effectively. Very interestingly, last week Microsoft announced that they like REST API. It is very clean, very simple, very well engineered, and they are going to implement the same API for Windows machines. It's completely cross-platform, which means you will be able to talk to any machine—Linux or Windows. So it gives you very clean and simple APIs to talk about containers on any host on the network.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, we have led the work in [OpenStack to bind LXD to Nova][1], which is the control system to compute in OpenStack, so that's how we create a whole cloud with OpenStack API with the individual VMs being actually containers, so much denser, much faster, much lighter, much cheaper.
|
||||
|
||||
### Open Source is becoming a norm in the enterprise segment. What do you think is driving the adoption of open source in the enterprise? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Mark**: The reason why open source has become so popular in the enterprise is because it enables them to go faster. We are all competing at some level, and if you can't make progress because you have to call up some vendor, you can't dig in and help yourself go faster, then you feel frustrated. And given the choice between frustration and at least the ability to dig into a problem, enterprises over time will always choose to give themselves the ability to dig in and help themselves. So that is why open source is phenomenal.
|
||||
|
||||
I think it goes a bit deeper than that. I think people have started to realize as much as we compete, 99% of what we need to do is shared, and there is something meaningful about contributing to something that is shared. As I have seen Ubuntu go from something that developers love, to something that CIOs love that developers love Ubuntu. As that happens, it's not a one-way ticket. They often want to say how can we help contribute to make this whole thing go faster.
|
||||
|
||||
We have always seen a curve of complexity, and open source has traditionally been higher up on the curve of complexity and therefore considered threatening or difficult or too uncertain for people who are not comfortable with the complexity. What's wonderful to me is that many open source projects have identified that as a blocker for their own future. So in Ubuntu we have made user experience, design and “making it easy” a first-class goal. We have done the same for OpenStack. With Ubuntu tools for OpenStack anybody can build an OpenStack cloud in an hour, and if you want, that cloud can run itself, scale itself, manage itself, can deal with failures. It becomes something you can just fire up and forget, which also makes it really cheap. It also makes it something that's not a distraction, and so by making open source easier and easier, we are broadening its appeal to consumers and into the enterprise and potentially into the government.
|
||||
|
||||
### How open are governments to open source? Can you tell us about the utilization of open source by governments, especially in the U.S.? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Mark**: I don't track the usage in government, but part of government utilization in the modern era is the realization that how untrustworthy other governments might be. There is a desire for people to be able to say, “Look, I want to review or check and potentially self-build all the things that I depend on.” That's a really important mission. At the end of the day, some people see this as a game where maybe they can get something out of the other guy. I see it as a game where we can make a level playing field, where everybody gets to compete. I have a very strong interest in making sure that Ubuntu is trustworthy, which means the way we build it, the way we run it, the governance around it is such that people can have confidence in it as an independent thing.
|
||||
|
||||
### You are quite vocal about freedom, privacy and other social issues on Google+. How do you see yourself, your company and Ubuntu playing a role in making the world a better place? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Mark**: The most important thing for us to do is to build confidence in trusted platforms, platforms that are freely available but also trustworthy. At any given time, there will always be people who can make arguments about why they should have access to something. But we know from history that at the end of the day, due process of law, justice, doesn't depend on the abuse of privacy, abuse of infrastructure, the abuse of data. So I am very strongly of the view that in the fullness of time, all of the different major actors will come to the view that their primary interest is in having something that is conceptually trustworthy. This isn't about what America can steal from Germany or what China can learn in Russia. This is about saying we’re all going to be able to trust our infrastructure; that's a generational journey. But I believe Ubuntu can be right at the center of people's thinking about that.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.itworld.com/article/2973116/linux/linuxcon-exclusive-mark-shuttleworth-says-snappy-was-born-long-before-coreos-and-the-atomic-project.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Swapnil Bhartiya][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.itworld.com/author/Swapnil-Bhartiya/
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/HypervisorSupportMatrix
|
||||
@ -1,149 +0,0 @@
|
||||
The Free Software Foundation: 30 years in
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Welcome back, folks, to a new Six Degrees column. As usual, please send your thoughts on this piece to the comment box and your suggestions for future columns to [my inbox][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Now, I have to be honest with you all, this column went a little differently than I expected.
|
||||
|
||||
A few weeks ago when thinking what to write, I mused over the notion of a piece about the [Free Software Foundation][2] celebrating its 30 year anniversary and how relevant and important its work is in today's computing climate.
|
||||
|
||||
To add some meat I figured I would interview [John Sullivan][3], executive director of the FSF. My plan was typical of many of my pieces: thread together an interesting narrative and quote pieces of the interview to give it color.
|
||||
|
||||
Well, that all went out the window when John sent me a tremendously detailed, thoughtful, and descriptive interview. I decided therefore to present it in full as the main event, and to add some commentary throughout. Thus, this is quite a long column, but I think it paints a fascinating picture of a fascinating organization. I recommend you grab a cup of something delicious and settle in for a solid read.
|
||||
|
||||
### The sands of change ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Free Software Foundation was founded in 1985. To paint a picture of what computing was like back then, the [Amiga 1000][4] was released, C++ was becoming a dominant language, [Aldus PageMaker][5] was announced, and networking was just starting to grow. Oh, and that year [Careless Whisper][6] by Wham! was a major hit.
|
||||
|
||||
Things have changed a lot in 30 years. Back in 1985 the FSF was primarily focused on building free pieces of software that were primarily useful to nerdy computer people. These days we have software, services, social networks, and more to consider.
|
||||
|
||||
I first wanted to get a sense of what John feels are most prominent risks to software freedom today.
|
||||
|
||||
"I think there's widespread agreement on the biggest risks for computer user freedom today, but maybe not on the names for them."
|
||||
|
||||
"The first is what we might as well just call 'tiny computers everywhere.' The free software movement has succeeded to the point where laptops, desktops, and servers can run fully free operating systems doing anything users of proprietary systems can do. There are still a few holes, but they'll be closed. The challenge that remains in this area is to cut through the billion dollar marketing budgets and legal regimes working against us to actually get the systems into users hands."
|
||||
|
||||
"However, we have a serious problem on the set of computers whose primary common trait is that they are very small. Even though a car is not especially small, the computers in it are, so I include that form factor in this category, along with phones, tablets, glasses, watches, and so on. While these computers often have a basis in free software—for example, using the kernel Linux along with other free software like Android or GNU—their primary uses are to run proprietary applications and be shims for services that replace local computing with computing done on a server over which the user has no control. Since these devices serve vital functions, with some being primary means of communication for huge populations, some sitting very close to our bodies and our actual vital functions, some bearing responsibility for our physical safety, it is imperative that they run fully free systems under their users' control. Right now, they don't."
|
||||
|
||||
John feels the risk here is not just the platforms and form factors, but the services integrates into them.
|
||||
|
||||
"The services many of these devices talk to are the second major threat we face. It does us little good booting into a free system if we do our actual work and entertainment on companies' servers running software we have no access to at all. The point of free software is that we can see, modify, and share code. The existence of those freedoms even for nontechnical users provides a shield that prevents companies from controlling us. None of these freedoms exist for users of Facebook or Salesforce or Google Docs. Even more worrisome, we see a trend where people are accepting proprietary restrictions imposed on their local machines in order to have access to certain services. Browsers—including Firefox—are now automatically installing a DRM plugin in order to appease Netflix and other video giants. We need to work harder at developing free software decentralized replacements for media distribution that can actually empower users, artists, and user-artists, and for other services as well. For Facebook we have GNU social, pump.io, Diaspora, Movim, and others. For Salesforce, we have CiviCRM. For Google Docs, we have Etherpad. For media, we have GNU MediaGoblin. But all of these projects need more help, and many services don't have any replacement contenders yet."
|
||||
|
||||
It is interesting that John mentions finding free software equivalents for common applications and services today. The FSF maintains a list of "High Priority Projects" that are designed to fill this gap. Unfortunately the capabilities of these projects varies tremendously and in an age where social media is so prominent, the software is only part of the problem: the real challenge is getting people to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
This all begs the question of where the FSF fit in today's modern computing world. I am a fan of the FSF. I think the work they do is valuable and I contribute financially to support it too. They are an important organization for building an open computing culture, but all organizations need to grow, adjust, and adapt, particularly ones in the technology space.
|
||||
|
||||
I wanted to get a better sense of what the FSF is doing today that it wasn't doing at it's inception.
|
||||
|
||||
"We're speaking to a much larger audience than we were 30 years ago, and to a much broader audience. It's no longer just hackers and developers and researchers that need to know about free software. Everyone using a computer does, and it's quickly becoming the case that everyone uses a computer."
|
||||
|
||||
John went on to provide some examples of these efforts.
|
||||
|
||||
"We're doing coordinated public advocacy campaigns on issues of concern to the free software movement. Earlier in our history, we expressed opinions on these things, and took action on a handful, but in the last ten years we've put more emphasis on formulating and carrying out coherent campaigns. We've made especially significant noise in the area of Digital Restrictions Management (DRM) with Defective by Design, which I believe played a role in getting iTunes music off DRM (now of course, Apple is bringing DRM back with Apple Music). We've made attractive and useful introductory materials for people new to free software, like our [User Liberation animated video][7] and our [Email Self-Defense Guide][8].
|
||||
|
||||
We're also endorsing hardware that [respects users' freedoms][9]. Hardware distributors whose devices have been certified by the FSF to contain and require only free software can display a logo saying so. Expanding the base of free software users and the free software movement has two parts: convincing people to care, and then making it possible for them to act on that. Through this initiative, we encourage manufacturers and distributors to do the right thing, and we make it easy for users who have started to care about free software to buy what they need without suffering through hours and hours of research. We've certified a home WiFi router, 3D printers, laptops, and USB WiFi adapters, with more on the way.
|
||||
|
||||
We're collecting all of the free software we can find in our [Free Software Directory][10]. We still have a long way to go on this—we're at only about 15,500 packages right now, and we can imagine many improvements to the design and function of the site—but I think this resource has great potential for helping users find the free software they need, especially users who aren't yet using a full GNU/Linux system. With the dangers inherent in downloading random programs off the Internet, there is a definite need for a curated collection like this. It also happens to provide a wealth of machine-readable data of use to researchers.
|
||||
|
||||
We're acting as the fiscal sponsor for several specific free software projects, enabling them to raise funds for development. Most of these projects are part of GNU (which we continue to provide many kinds of infrastructure for), but we also sponsor [Replicant][11], a fully free fork of Android designed to give users the free-est mobile devices currently possible.
|
||||
|
||||
We're helping developers use free software licenses properly, and we're following up on complaints about companies that aren't following the terms of the GPL. We help them fix their mistakes and distribute properly. RMS was in fact doing similar work with the precursors of the GPL very early on, but it's now an ongoing part of our work.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of the specific things the FSF does now it wasn't doing 30 years ago, but the vision is little changed from the original paperwork—we aim to create a world where everything users want to do on any computer can be done using free software; a world where users control their computers and not the other way around."
|
||||
|
||||
### A cult of personality ###
|
||||
|
||||
There is little doubt in anyone's minds about the value the FSF brings. As John just highlighted, its efforts span not just the creation and licensing of free software, but also recognizing, certifying, and advocating a culture of freedom in technology.
|
||||
|
||||
The head of the FSF is the inimitable Richard M. Stallman, commonly referred to as RMS.
|
||||
|
||||
RMS is a curious character. He has demonstrated an unbelievable level of commitment to his ideas, philosophy, and ethical devotion to freedom in software.
|
||||
|
||||
While he is sometimes mocked online for his social awkwardness, be it things said in his speeches, his bizarre travel requirements, or other sometimes cringeworthy moments, RMS's perspectives on software and freedom are generally rock-solid. He takes a remarkably consistent approach to his perspectives and he is clearly a careful thinker about not just his own thoughts but the wider movement he is leading. My only criticism is that I think from time to time he somewhat over-eggs the pudding with the voracity of his words. But hey, given his importance in our world, I would rather take an extra egg than no pudding for anyone. O.K., I get that the whole pudding thing here was strained...
|
||||
|
||||
So RMS is a key part of the FSF, but the organization is also much more than that. There are employees, a board, and many contributors. I was curious to see how much of a role RMS plays these days in the FSF. John shared this with me.
|
||||
|
||||
"RMS is the FSF's President, and does that work without receiving a salary from the FSF. He continues his grueling global speaking schedule, advocating for free software and computer user freedom in dozens of countries each year. In the course of that, he meets with government officials as well as local activists connected with all varieties of social movements. He also raises funds for the FSF and inspires many people to volunteer."
|
||||
|
||||
"In between engagements, he does deep thinking on issues facing the free software movement, and anticipates new challenges. Often this leads to new articles—he wrote a 3-part series for Wired earlier this year about free software and free hardware designs—or new ideas communicated to the FSF's staff as the basis for future projects."
|
||||
|
||||
As we delved into the cult of personality, I wanted to tap John's perspectives on how wide the free software movement has grown.
|
||||
|
||||
I remember being at the [Open Source Think Tank][12] (an event that brings together execs from various open source organizations) and there was a case study where attendees were asked to recommend license choice for a particular project. The vast majority of break-out groups recommended the Apache Software License (APL) over the GNU Public License (GPL).
|
||||
|
||||
This stuck in my mind as since then I have noticed that many companies seem to have opted for open licenses other than the GPL. I was curious to see if John had noticed a trend towards the APL as opposed to the GPL.
|
||||
|
||||
"Has there been? I'm not so sure. I gave a presentation at FOSDEM a few years ago called 'Is Copyleft Being Framed?' that showed some of the problems with the supposed data behind claims of shifts in license adoption. I'll be publishing an article soon on this, but here's some of the major problems:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Free software license choices do not exist in a vacuum. The number of people choosing proprietary software licenses also needs to be considered in order to draw the kinds of conclusions that people want to draw. I find it much more likely that lax permissive license choices (such as the Apache License or 3-clause BSD) are trading off with proprietary license choices, rather than with the GPL.
|
||||
- License counters often, ironically, don't publish the software they use to collect that data as free software. That means we can't inspect their methods or reproduce their results. Some people are now publishing the code they use, but certainly any that don't should be completely disregarded. Science has rules.
|
||||
- What counts as a thing with a license? Are we really counting an app under the APL that makes funny noises as 1:1 with GNU Emacs under GPLv3? If not, how do we decide which things to treat as equals? Are we only looking at software that actually works? Are we making sure not to double- and triple- count programs that exist on multiple hosting sites, and what about ports for different OSes?
|
||||
|
||||
The question is interesting to ponder, but every conclusion I've seen so far has been extremely premature in light of the actual data. I'd much rather see a survey of developers asking about why they chose particular licenses for their projects than any more of these attempts to programmatically ascertain the license of programs and then ascribe human intentions on to patterns in that data.
|
||||
|
||||
Copyleft is as vital as it ever was. Permissively licensed software is still free software and on-face a good thing, but it is contingent and needs an accompanying strong social commitment to not incorporate it in proprietary software. If free software's major long-term impact is enabling businesses to more efficiently make products that restrict us, then we have achieved nothing for computer user freedom."
|
||||
|
||||
### Rising to new challenges ###
|
||||
|
||||
30 years is an impressive time for any organization to be around, and particularly one with such important goals that span so many different industries, professions, governments, and cultures.
|
||||
|
||||
As I started to wrap up the interview I wanted to get a better sense of what the FSF's primary function is today, 30 years after the mission started.
|
||||
|
||||
"I think the FSF is in a very interesting position of both being a steady rock and actively pushing the envelope."
|
||||
|
||||
"We have core documents like the [Free Software Definition][13], the [GNU General Public License][14], and the [list we maintain of free and nonfree software licenses][15], which have been keystones in the construction of the world of free software we have today. People place a great deal of trust in us to stay true to the principles outlined in those documents, and to apply them correctly and wisely in our assessments of new products or practices in computing. In this role, we hold the ladder for others to climb. As a 501(c)(3) charity held legally accountable to the public interest, and about 85% funded by individuals, we have the right structure for this."
|
||||
|
||||
"But we also push the envelope. We take on challenges that others say are too hard. I guess that means we also build ladders? Or maybe I should stop with the metaphors."
|
||||
|
||||
While John may not be great with metaphors (like I am one to talk), the FSF is great at setting a mission and demonstrating a devout commitment to it. This mission starts with a belief that free software should be everywhere.
|
||||
|
||||
"We are not satisfied with the idea that you can get a laptop that works with free software except for a few components. We're not satisfied that you can have a tablet that runs a lot of free software, and just uses proprietary software to communicate with networks and to accelerate video and to take pictures and to check in on your flight and to call an Über and to.. Well, we are happy about some such developments for sure, but we are also unhappy about the suggestion that we should be fully content with them. Any proprietary software on a system is both an injustice to the user and inherently a threat to users' security. These almost-free things can be stepping stones on the way to a free world, but only if we keep our feet moving."
|
||||
|
||||
In the early years of the FSF, we actually had to get a free operating system written. This has now been done by GNU and Linux and many collaborators, although there is always more software to write and bugs to fix. So while the FSF does still sponsor free software development in specific areas, there are thankfully many other organizations also doing this."
|
||||
|
||||
A key part of the challenge John is referring to is getting the right hardware into the hands of the right people.
|
||||
|
||||
"What we have been focusing on now are the challenges I highlighted in the first question. We are in desperate need of hardware in several different areas that fully supports free software. We have been talking a lot at the FSF about what we can do to address this, and I expect us to be making some significant moves to both increase our support for some of the projects already out there—as we having been doing to some extent through our Respects Your Freedom certification program—and possibly to launch some projects of our own. The same goes for the network service problem. I think we need to tackle them together, because having full control over the mobile components has great potential for changing how we relate to services, and decentralizing more and more services will in turn shape the mobile components."
|
||||
|
||||
I hope folks will support the FSF as we work to grow and tackle these challenges. Hardware is expensive and difficult, as is making usable, decentralized, federated replacements for network services. We're going to need the resources and creativity of a lot of people. But, 30 years ago, a community rallied around RMS and the concept of copyleft to write an entire operating system. I've spent my last 12 years at the FSF because I believe we can rise to the new challenges in the same way."
|
||||
|
||||
### Final thoughts ###
|
||||
|
||||
In reading John's thoughtful responses to my questions, and in knowing various FSF members, the one sense that resonates for me is the sheer level of passion that is alive and kicking in the FSF. This is not an organization that has got bored or disillusioned with its mission. Its passion and commitment is as voracious as it has ever been.
|
||||
|
||||
While I don't always agree with the FSF and I sometimes think its approach is a little one-dimensional at times, I have been and will continue to be a huge fan and supporter of its work. The FSF represent the ethical heartbeat of much of the free software and open source work that happens across the world. It represents a world view that is pretty hard to the left, but I believe its passion and conviction helps to bring people further to the right a little closer to the left too.
|
||||
|
||||
Sure, RMS can be odd, somewhat hardline, and a little sensational, but he is precisely the kind of leader that is valuable in a movement that encapsulates a mixture of technology, ethics, and culture. We need an RMS in much the same way we need a Torvalds, a Shuttleworth, a Whitehurst, and a Zemlin. These different people bring together mixture of perspectives that ultimately maps to technology that can be adaptable to almost any set of use cases, ethics, and ambitions.
|
||||
|
||||
So, in closing, I want to thank the FSF for its tremendous efforts, and I wish the FSF and its fearless leaders, one Richard M. Stallman and one John Sullivan, another 30 years of fighting the good fight. Go get 'em!
|
||||
|
||||
> This article is part of Jono Bacon's Six Degrees column, where he shares his thoughts and perspectives on culture, communities, and trends in open source.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://opensource.com/business/15/9/free-software-foundation-30-years
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jono Bacon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://opensource.com/users/jonobacon
|
||||
[1]:Welcome back, folks, to a new Six Degrees column. As usual, please send your thoughts on this piece to the comment box and your suggestions for future columns to my inbox.
|
||||
[2]:http://www.fsf.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://twitter.com/johns_fsf/
|
||||
[4]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amiga_1000
|
||||
[5]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adobe_PageMaker
|
||||
[6]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=izGwDsrQ1eQ
|
||||
[7]:http://fsf.org/
|
||||
[8]:http://emailselfdefense.fsf.org/
|
||||
[9]:http://fsf.org/ryf
|
||||
[10]:http://directory.fsf.org/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.replicant.us/
|
||||
[12]:http://www.osthinktank.com/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.fsf.org/about/what-is-free-software
|
||||
[14]:http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html
|
||||
[15]:http://www.gnu.org/licenses/licenses.en.html
|
||||
@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Italy's Ministry of Defense to Drop Microsoft Office in Favor of LibreOffice
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
>**LibreItalia's Italo Vignoli [reports][1] that the Italian Ministry of Defense is about to migrate to the LibreOffice open-source software for productivity and adopt the Open Document Format (ODF), while moving away from proprietary software products.**
|
||||
|
||||
The movement comes in the form of a [collaboration][1] between Italy's Ministry of Defense and the LibreItalia Association. Sonia Montegiove, President of the LibreItalia Association, and Ruggiero Di Biase, Rear Admiral and General Executive Manager of Automated Information Systems of the Ministry of Defense in Italy signed an agreement for a collaboration to adopt the LibreOffice office suite in all of the Ministry's offices.
|
||||
|
||||
While the LibreItalia non-profit organization promises to help the Italian Ministry of Defense with trainers for their offices across the country, the Ministry will start the implementation of the LibreOffice software on October 2015 with online training courses for their staff. The entire transition process is expected to be completed by the end of year 2016\. An Italian law lets officials find open source software alternatives to well-known commercial software.
|
||||
|
||||
"Under the agreement, the Italian Ministry of Defense will develop educational content for a series of online training courses on LibreOffice, which will be released to the community under Creative Commons, while the partners, LibreItalia, will manage voluntarily the communication and training of trainers in the Ministry," says Italo Vignoli, Honorary President of LibreItalia.
|
||||
|
||||
### The Ministry of Defense will adopt the Open Document Format (ODF)
|
||||
|
||||
The initiative will allow the Italian Ministry of Defense to be independent from proprietary software applications, which are aimed at individual productivity, and adopt open source document format standards like Open Document Format (ODF), which is used by default in the LibreOffice office suite. The project follows similar movements already made by governments of other European countries, including United Kingdom, France, Spain, Germany, and Holland.
|
||||
|
||||
It would appear that numerous other public institutions all over Italy are using open source alternatives, including the Italian Region Emilia Romagna, Galliera Hospital in Genoa, Macerata, Cremona, Trento and Bolzano, Perugia, the municipalities of Bologna, ASL 5 of Veneto, Piacenza and Reggio Emilia, and many others. AGID (Agency for Digital Italy) welcomes this project and hopes that other public institutions will do the same.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/italy-s-ministry-of-defense-to-drop-microsoft-office-in-favor-of-libreoffice-491850.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Marius Nestor][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/marius-nestor
|
||||
[1]:http://www.libreitalia.it/accordo-di-collaborazione-tra-associazione-libreitalia-onlus-e-difesa-per-ladozione-del-prodotto-libreoffice-quale-pacchetto-di-produttivita-open-source-per-loffice-automation/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.libreitalia.it/chi-siamo/
|
||||
@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
|
||||
A Slick New Set-Up Wizard Is Coming To Ubuntu and Ubuntu Touch
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Canonical aims to 'seduce and reassure' those unfamiliar with the OS by making a good first impression
|
||||
|
||||
**The Ubuntu installer is set to undergo a dramatic makeover.**
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu will modernise its out-of-the-box experience (OOBE) to be easier and quicker to complete, look more ‘seductive’ to new users, and better present the Ubuntu brand through its design.
|
||||
|
||||
Ubiquity, the current Ubuntu installer, has largely remained unchanged since its [introduction back in 2010][1].
|
||||
|
||||
### First Impressions Are Everything ###
|
||||
|
||||
Since the first thing most users see when trying Ubuntu for the first time is an installer (or set-up wizard, depending on device) the design team feel it’s “one of the most important categories of software usability”.
|
||||
|
||||
“It essentially says how easy your software is to use, as well as introducing the user into your brand through visual design and tone of voice, which can convey familiarity and trust within your product.”
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical’s new OOBE designs show a striking departure from the current look of the Ubiquity installer used by the Ubuntu desktop, and presents a refined approach to the way mobile users ‘set up’ a new Ubuntu Phone.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Old design (left) and the new proposed design
|
||||
|
||||
Detailing the designs in [new blog post][2], the Canonical Design team say the aim of the revamp is to create a consistent out-of-the-box experience across Ubuntu devices.
|
||||
|
||||
To do this it groups together “common first experiences found on the mobile, tablet and desktop” and unifies the steps and screens between each, something they say moves the OS closer to “achieving a seamless convergent platform.”
|
||||
|
||||
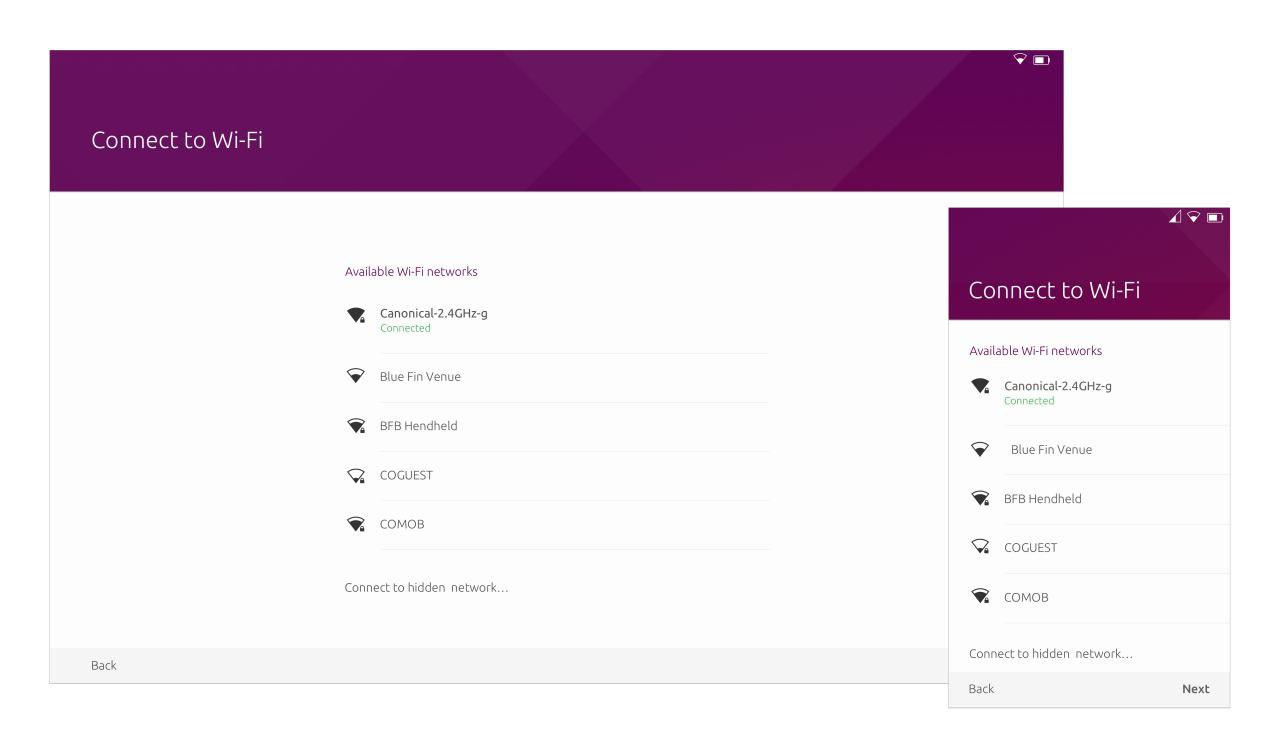
|
||||
|
||||
New Ubuntu installer on desktop/tablet (left) and phone
|
||||
|
||||
Implementation of the new ‘OOBE’ has already begun’ according to Canonical, though as of writing there’s no firm word on when a revamped installer may land on either desktop or phone images.
|
||||
|
||||
With the march to ‘desktop’ convergence now in full swing, and a(nother) stack of design changes set to hit the mobile build in lieu of the first Ubuntu Phone that ‘transforms’ in to a PC, chances are you won’t have to wait too long to try it out.
|
||||
|
||||
**What do you think of the designs? How would you go about improving the Ubuntu set-up experience? Let us know in the comments below.**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/09/new-look-ubuntu-installer-coming-soon
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2010/09/ubuntu-10-10s-installer-slideshow-oozes-class
|
||||
[2]:http://design.canonical.com/wp-content/uploads/Convergence.jpg
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
zpl1025 translating
|
||||
The Brief History Of Aix, HP-UX, Solaris, BSD, And LINUX
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
@ -98,4 +99,4 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/brief-history-aix-hp-ux-solaris-bsd-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/pirat9/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/ken-thompson-unix-systems-father/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.unixmen.com/dennis-m-ritchie-father-c-programming-language/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.unixmen.com/dennis-m-ritchie-father-c-programming-language/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,68 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.10, Codenamed Wily Werewolf, Review
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The problem we have with reviewing Ubuntu on any occasion, is readers consistently expect to read of a revolutionary new release, every 6 months. If you’re expecting Ubuntu 15.10 to be just that, then you may want to click out of this review right now. It’s important to clarify that this is nothing negative towards 15.10 as a release, but it is a maintenance release and not a release which purports to introduce a great deal of new software.
|
||||
|
||||
With that opening disclaimer out of the way, let’s take a look at what 15.10 does offer.
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux kernel 4.2 ###
|
||||
|
||||
The biggest change you will find with Ubuntu 15.10 is the kernel branch has been upgraded to **Linux 4.2**.
|
||||
|
||||
This is long overdue for Ubuntu. It feels like it has been lagging behind other distributions by sticking with the 3.x branch of Linux for the entirety of the 15.04 cycle.
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re going to be installing Ubuntu 15.10 on new hardware, then you will benefit greatly from the Linux kernel upgrade to 4.x branch as there is loads of updates which directly improve performance on new hardware. Support for AMDGPU kernel DRM is included, which is a boon for owners of recent Radeon graphics cards. The latest iteration of the driver will reside alongside the current Radeon DRM drivers, which was already in the kernel in addition to the usual open-source driver offerings.
|
||||
|
||||
Support for Intel Broxton is also included in Linux 4.2, albeit Ubuntu 15.10 users are probably going to get nothing out of this update, yet it’s still worthy of a mention we think. There are also some erroneous updates for Skylake CPU’s. Finally, there is a host of code updates and fixes for Ext4 filesystems.
|
||||
|
||||
That pretty much rounds out the Linux kernel 4.2 updates. So what else is new? Let’s take a closer look at the software that you may be more familiar with and get more excited about.
|
||||
|
||||
### Software ###
|
||||
|
||||
LibreOffice has been upgraded to 5.0.1.2, a major update for LibreOffice users. Firefox on the version that we tested is sitting at 41.0.2. By the time you read this, it will most-likely be updated again and you may see a newer version be pushed out through the Ubuntu Repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
On the desktop front, a vanilla Ubuntu installation will see you running Unity 7.3.2 while GNOME sits at 3.8. On the KDE end, a Plasma 5 desktop will see you running version 5.4.2. For the alternative desktop-environments, XFCE has been upgraded to the latest revision, 4.12 while the version of MATE includes 1.10.
|
||||
|
||||
### User Experience/Screenshots ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.10 as a operating system for Review is pretty lackluster. There’s nothing new as such and there’s nothing we can really say that is going to change your opinion from its predecessor, 15.04. Therefore, we recommend you to upgrade either out of habit and according to your regular upgrade schedule rather than out of a specific necessity for a specific feature of this release. Because there is really nothing that could possibly differentiate it from the older, yet still very stable 15.04 release. But if you’re going to stick with 15.04 for a little longer, we do recommend that you look at [upgrading the kernel to the latest 4.2 branch][2]. It is worth it.
|
||||
|
||||
If you really want a reason to upgrade? Linux kernel 4.2 would be our sole reason for taking Ubuntu 15.10 into consideration.
|
||||
|
||||
### Looking Ahead ###
|
||||
|
||||
What we really look forward to is the release of Ubuntu 16.04. We have been promised over and over again for several releases that Mir will be the default display server included in Ubuntu. We still see releases pushed out that rely on X.org. It has resulted in us adopting a “yeah right” attitude as we have become accustomed to the usual delay announcements.
|
||||
|
||||
We are hopeful that Mir Developers can push out a working version in time for the release of 16.04 next year. As precaution though, we urge you to not get too excited because it may very well not happen.
|
||||
|
||||
It remains much the same with Unity 8. It’s most certainly a possibility, but we can’t guarantee that it will be included in 16.04, yet we remain hopeful.
|
||||
|
||||
As we’ve mentioned for this release, there’s nothing really ground-breaking with this release. In fact, it has been much the same story for the last couple of releases of Ubuntu Linux. It is in dire need of a distribution-wide reboot. Developers and Ubuntu users alike are positive that Mir and Unity 8 will be the two primary packages that may just provide the popular, yet ailing, distribution the reboot that it needs.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/ubuntu-15-10-codenamed-wily-werewolf-review/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Chris Jones][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/chris/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/how-to-install-linux-kernel-4-2-3/
|
||||
@ -1,194 +0,0 @@
|
||||
10 Things To Do After Installing Ubuntu 15.10 'Wily Werewolf'
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Yesterday Ubuntu 15.10 was made [available to download][1] with some new features, improvements and updated apps. If you've upgraded to Ubuntu 15.10 then this article is going to show you 10 things/tweaks that you need to do to make your Ubuntu more handy and fruitful.
|
||||
|
||||
### What's New In Ubuntu 15.10? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.10 codenamed 'Wily Werewolf' was released yesterday with new features, improvements, fixes and updated apps. Read our complete article to know more stuff added with Ubuntu 15.10.
|
||||
|
||||
### Things To Do After Installing Ubuntu 15.10 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.10 is shipping with new features that are activated by default, no need to tweak for anyone. But, changes made in the last release of Ubuntu 15.04, were not activated by default and so in Ubuntu 15.10. Other than those changes you need to install useful/must have applications. So first tweak our newly installed Wily Werewolf.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Update Ubuntu 15.10 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Before you use the system and any app first check for updates. Updating the system is necessary to keep the OS more stable and secure. Updates also adds new features in the system. Although there won't be larger size of updates after you within some days of release as all the packages are already to their newest versions.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Tweak Ubuntu 15.10 ####
|
||||
|
||||
One of things to notice is that the tweaks that were presented in the last Ubuntu release are not activated by default. Those are still at your wish, if you want go ahead and activate them. For example, Always Show Menus, Where to show menu, in the window's title bar or in the menu bar.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Set Menus Position ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default in Ubuntu 15.10, the menu are set to show in the menu bar which is sometimes uneasy to reach to but you can set the menus to show in the window's title bar. Go to **Settings >> Appearances >> Behavior >> in the window's title bar**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
3. Install Unity Tweak Tool
|
||||
|
||||
To tweak system more install Unity Tweak Tool, It has more options than the default system settings. You can change theme, icons, workspaces settings and many more. Check the screenshot below -
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Install Firewall To Block Harmful Incoming/Outgoing Connections ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
One of the favorite ways of hackers to get access to individuals' system is to scan for the open ports and attack through them. A firewall protect your system from such attacks by blocking harmful incoming/outgoing connections.
|
||||
|
||||
UFW stands ofr Uncomplicated Firewall. As the name suggests it's the most easy to use firewall you ever used. Just install and switch it on. Configure firewall rules, block particular ports etc. easily. To know all about UFW and how to use all of its features read our following article -
|
||||
|
||||
[Install UFW Firewall In Linux And Secure Computer From Harmful Incoming/Outgoing Connections][2]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install UFW Firewall ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install ufw
|
||||
Install Graphical Interface
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install gufw
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Install Graphics Drivers ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you're a game lover or you play HD videos or do video editing kind of things then you need to have proprietary drivers installed available for your hardware for better graphics performance.
|
||||
|
||||
To install graphics driver -
|
||||
|
||||
Go to **Settings >> Software & Updates >> Additional Drivers**
|
||||
|
||||
It will search for the latest drivers available for you hardware.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Install VLC & Media Codecs For More Media Support ###
|
||||
|
||||
VLC supports most file formats so it's better to use VLC to escape the error while playing audio files.
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes you play a mp3 and it does not play. To solve this problem, Ubuntu gives an option while you're installing Ubuntu to install all the necessary media codecs. If you checked that then don't worry, if you haven't then do the following -
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install vlc
|
||||
Install Media Codecs
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install ubuntu-restricted-extras
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Configure Cloud Storage ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud storage are very useful to share files across your local devices like, Mobile to PC or Laptops and vice-versa. User can easily install Storages like, Dropbox, Copy, Gdrive (Using Grive) etc.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Dropbox ####
|
||||
|
||||
To install Dropbox, download Dropbox installation client first.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Dropbox][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Download Dropbox for your system architecture. To check whether your system is 64-Bit or 32-Bit
|
||||
|
||||
Goto **Settings >> Details**
|
||||
|
||||
Open the downloaded .deb file with Ubuntu Software Center and click install.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
When installed search Dropbox in Ubuntu dash and open it. It's just an installation client, so now this will install Dropbox app. Once the download competes you'll have the app asking for your Dropbox credentials. Enter your email id and password and login. All of your cloud files will be synced in your Ubuntu desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Enhance Look By Installing Themes ###
|
||||
|
||||
The default two themes are not too much attractive. You can download and install cool themes from our Linux Themes Page.
|
||||
|
||||
[][4]
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
[][6]
|
||||
|
||||
[][7]
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download More Themes][8]
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Install & Configure Email Client ###
|
||||
|
||||
Email clients are very useful because you can check for new emails without opening up web browser. Ubuntu 15.10 comes with Thunderbird email client, one of the most popular email clients, supports multiple email accounts and desktop notifications.
|
||||
|
||||
Thunderbird is simple to configure. Just use your email id and password to login and sync your emails right into your desktop/laptop.
|
||||
|
||||
If you don't want to use Thunderbird then check out our article [Top 4 Open Source Email Clients For Linux][9]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Take The Poll ###
|
||||
|
||||
After you have upgraded to Ubuntu 15.10, configure all the necessary or must have apps. Please take the poll to tell us what you like the most in Ubuntu 15.10 'Wily Werewolf'.
|
||||
|
||||
注:投票项目
|
||||
What Do You Like The Most In Ubuntu 15.10?
|
||||
|
||||
- Linux Kernel 4.2
|
||||
- Unity Improvements
|
||||
- Steam Controller Support
|
||||
- Ubuntu Make
|
||||
- Persistent Network Interface Names
|
||||
- New Wallpapers
|
||||
- Other? Please Comment Below
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/10-things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-1510-wily-werewolf
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Mohd Sohail][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://in.linkedin.com/in/mohdsohail
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/linux/ubuntu-1510-wily-werewolf-released-with-new-features-and-improvements-download-now
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/linux/install-ufw-firewall-in-linux-and-secure-computer-from-harmful-incoming-outgoing-connections
|
||||
[3]:https://db.tt/CbUWY1ca
|
||||
[4]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/linux-themes/arc-dark-red-cinnamon-install-in-ubuntu-and-derivatives
|
||||
[5]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/linux-themes/windows-8-gtk3-modern-ui-09-install-in-ubuntu-linux
|
||||
[6]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/linux-themes/ubuntu-touch-unity-17-install-in-ubuntu-gtk
|
||||
[7]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/linux-themes/numixdarkred-cinnamon-021-install-in-ubuntulinux-mint
|
||||
[8]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/linux-themes.html
|
||||
[9]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/linux/top-5-open-source-email-clients-for-linux
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
[13]:
|
||||
[14]:
|
||||
[15]:
|
||||
[16]:
|
||||
[17]:
|
||||
[18]:
|
||||
[19]:
|
||||
[20]:
|
||||
[21]:
|
||||
[22]:
|
||||
[23]:
|
||||
[24]:
|
||||
[25]:
|
||||
[26]:
|
||||
[27]:
|
||||
[28]:
|
||||
[29]:
|
||||
[30]:
|
||||
[31]:
|
||||
[32]:
|
||||
[33]:
|
||||
[34]:
|
||||
[35]:
|
||||
[36]:
|
||||
[37]:
|
||||
[38]:
|
||||
[39]:
|
||||
[40]:
|
||||
[41]:
|
||||
[42]:
|
||||
[43]:
|
||||
[44]:
|
||||
[45]:
|
||||
[46]:
|
||||
[47]:
|
||||
[48]:
|
||||
[49]:
|
||||
[50]:
|
||||
@ -1,109 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Here are the 9 New Ubuntu 15.10 Features You Should Know
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The stable edition of Ubuntu 15.10 wily werewolf is just released by canonical few days a ago and it now available to download and install on your computer. Lets take a look at the features that are implemented in the new release of ubuntu 15.10 and see what important packages have been updated.
|
||||
|
||||
Watch – A quick video about “What’s new in Ubuntu 15.10“, thanks to [linuxscoop][1] for making this video.
|
||||
|
||||
注:youtube 视频
|
||||
<iframe width="720" height="405" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/VoeCcCQuJrM?feature=oembed&wmode=opaque" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
Below we are can mention the new features of Ubuntu 15.10 Wily Werewolf
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux kernel 4.2 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.10 ships with linux kernel 4.2. This introduces lots of changes, like support for the new AMD GPU driver, NCQ TRIM handling, queue spinlocks, F2FS per-file encryption and lots of new and updated drivers.
|
||||
|
||||
### Unity 7.3.2 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unity as the main desktop of ubuntu 15.10 has been updated to version 7.3.2. it comes with bug fixes, polish and small usability improvements. The following we can mention the features of Unity 7.3.2:
|
||||
|
||||
- Allows drag and drop apps from the Dash to the desktop to create shortcuts
|
||||
- Page up/down keyboard navigation works as scroll in the Dash
|
||||
- Dash title & BFB tooltip is updated based on your privacy settings
|
||||
- Session exit buttons now have a click effect
|
||||
- Fix to prevent ‘shutdown’ of computer when screen is locked
|
||||
- Active app icons now show unfolded when launcher accordion triggered
|
||||
- Fix for full screen menubar
|
||||
- Fixes issues with ‘show desktop’ that caused window decoration for two windows of same app to vanish
|
||||
- Dash: Non-expandable category headers skipped in keyboard navigation
|
||||
- Dash: Non-expandable category headers are no longer highlighted on mouse over
|
||||
- Dash: screenreader and KeyNav fixes
|
||||
- New setting to control the show-now delay (when pressing Alt key)
|
||||
- Logic tweak to stop adjacent menu opening when moving from an indicator icon to its menu
|
||||
|
||||
### GNOME 3.16 stack ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Another important changes for this release, the most of the packages from the GNOME stack updated to version 3.16.x. This is a good thing since these packages do come with lots of improvements.Unfortunately, the nautilus file manager for Ubuntu 15.10 is still in version 3.14 and Gedit text editor file still dating from 3.10.
|
||||
|
||||
### Introduce GNOME Overlay Scrollbars ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In Ubuntu 15.10, Ubuntu developers have decided to implement the GNOME Overlay scrollbars, it replacement of Unity’s overlay scrollbars for GTK3 applications. That’s no different than before, but it does serve as a stark and regular reminder of how much easier it is to use scrollbars that are always present in a predicable spot and wider than the pinpoint tip of a mouse cursor.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu Make ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Make, a command-line utility that allows you to download the latest version of popular developer tools easier on Ubuntu, now supports even more platforms, frameworks and services, including a full Android development environment.
|
||||
|
||||
### Persistent Network Interface Names ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu developer also introduces stateless persistent network interface names in Ubuntu 15.10. This means that naming the network interfaces like eth0 or eth1 will be a thing of the past and that new more comprehensive names will be used. Also, the names will remain valid even after a restart or if the hardware is removed.
|
||||
|
||||
### Steam Controller Support ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In this release, Ubuntu Developer also add support for the Steam Controller in Ubuntu 15.10. For now, the updated Steam package seems to be available only for Ubuntu 15.10, but it’s possible that the patch will be backported to other supported distributions. This means that Ubuntu 15.10 users will be able to plug the new controller, open Steam, and just play without having to read and apply any kind of advice from tutorials.
|
||||
|
||||
### New Default Wallpaper ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.10 bring a new default wallpaper, the wallpaper desaign concept adopted from origami and it called suru. A new set of community sourced wallpapers are also included.
|
||||
|
||||
### Core Applications Updates ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.10 updates the core applications. among them:
|
||||
|
||||
- Firefox 41
|
||||
- Chromium 45
|
||||
- LibreOffice 5.0.2
|
||||
- Totem (aka ‘Videos’) 3.16
|
||||
- Nautilus (aka ‘Files’) 3.14.2
|
||||
- Rhythmbox 3.2.1
|
||||
- GNOME Terminal 3.16
|
||||
- Eye of GNOME 3.16
|
||||
- Empathy 3.12.10
|
||||
- Shotwell 0.22
|
||||
|
||||
Download Ubuntu 15.10 Final Release
|
||||
|
||||
The image of Ubuntu 15.10 ready to download and install. it available in 64-bit and 32-bit, the both can download from the official ISO downloads page by hitting the link below
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Ubuntu 15.10][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ubuntuportal.com/2015/10/ubuntu-15-10.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ncode][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ubuntuportal.com/author/ncode/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.youtube.com/user/linuxscoop
|
||||
[2]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/15.10/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
Linus Torvalds Lambasts Open Source Programmers over Insecure Code
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linus Torvalds's latest rant underscores the high expectations the Linux developer places on open source programmers—as well the importance of security for Linux kernel code.
|
||||
|
||||
Torvalds is the unofficial "benevolent dictator" of the Linux kernel project. That means he gets to decide which code contributions go into the kernel, and which ones land in the reject pile.
|
||||
|
||||
On Oct. 28, open source coders whose work did not meet Torvalds's expectations faced an [angry rant][1]. "Christ people," Torvalds wrote about the code. "This is just sh*t."
|
||||
|
||||
He went on to call the coders "just incompetent and out to lunch."
|
||||
|
||||
What made Torvalds so angry? He believed the code could have been written more efficiently. It could have been easier for other programmers to understand and would run better through a compiler, the program that translates human-readable code into the binaries that computers understand.
|
||||
|
||||
Torvalds posted his own substitution for the code in question and suggested that the programmers should have written it his way.
|
||||
|
||||
Torvalds has a history of lashing out against people with whom he disagrees. It stretches back to 1991, when he famously [flamed Andrew Tanenbaum][2]—whose Minix operating system he later described as a series of "brain-damages." No doubt this latest criticism of fellow open source coders will go down as another example of Torvalds's confrontational personality.
|
||||
|
||||
But Torvalds may also have been acting strategically during this latest rant. "I want to make it clear to *everybody* that code like this is completely unacceptable," he wrote, suggesting that his goal was to send a message to all Linux programmers, not just vent his anger at particular ones.
|
||||
|
||||
Torvalds also used the incident as an opportunity to highlight the security concerns that arise from poorly written code. Those are issues dear to open source programmers' hearts in an age when enterprises are finally taking software security seriously, and demanding top-notch performance from their code in this regard. Lambasting open source programmers who write insecure code thus helps Linux's image.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/110415/linus-torvalds-lambasts-open-source-programmers-over-inse
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Christopher Tozzi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://thevarguy.com/author/christopher-tozzi
|
||||
[1]:http://lkml.iu.edu/hypermail/linux/kernel/1510.3/02866.html
|
||||
[2]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tanenbaum%E2%80%93Torvalds_debate
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Translating by ZTinoZ
|
||||
Installation Guide for Puppet on Ubuntu 15.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Hi everyone, today in this article we'll learn how to install puppet to manage your server infrastructure running ubuntu 15.04. Puppet is an open source software configuration management tool which is developed and maintained by Puppet Labs that allows us to automate the provisioning, configuration and management of a server infrastructure. Whether we're managing just a few servers or thousands of physical and virtual machines to orchestration and reporting, puppet automates tasks that system administrators often do manually which frees up time and mental space so sysadmins can work on improving other aspects of your overall setup. It ensures consistency, reliability and stability of the automated jobs processed. It facilitates closer collaboration between sysadmins and developers, enabling more efficient delivery of cleaner, better-designed code. Puppet is available in two solutions configuration management and data center automation. They are **puppet open source and puppet enterprise**. Puppet open source is a flexible, customizable solution available under the Apache 2.0 license, designed to help system administrators automate the many repetitive tasks they regularly perform. Whereas puppet enterprise edition is a proven commercial solution for diverse enterprise IT environments which lets us get all the benefits of open source puppet, plus puppet apps, commercial-only enhancements, supported modules and integrations, and the assurance of a fully supported platform. Puppet uses SSL certificates to authenticate communication between master and agent nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Translating by Ping
|
||||
|
||||
How to switch from NetworkManager to systemd-networkd on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In the world of Linux, adoption of [systemd][1] has been a subject of heated controversy, and the debate between its proponents and critics is still going on. As of today, most major Linux distributions have adopted systemd as a default init system.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
FSSlc translating
|
||||
|
||||
How To Install Retro Terminal In Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
@ -71,4 +73,4 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/cool-retro-term/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/tag/antergos/
|
||||
[3]:https://manjaro.github.io/
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/Swordfish90/cool-retro-term
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,154 @@
|
||||
How to Install Pure-FTPd with TLS on FreeBSD 10.2
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
FTP or File Transfer Protocol is application layer standard network protocol used to transfer file from the client to the server, after user logged in to the FTP server over the TCP-Network, such as internet. FTP has been round long time ago, much longer then P2P Program, or World Wide Web, and until this day it was a primary method for sharing file with other over the internet and it it remain very popular even today. FTP provide an secure transmission, that protect username, password and encrypt the content with SSL/TLS.
|
||||
|
||||
Pure-FTPd is free FTP Server with strong and focus on the software security. It was great choice for you if you want to provide a fast, secure, lightweight with feature rich FTP Services. Pure-FTPd can be install on variety of Unix-like operating system, include Linux and FreeBSD. Pure-FTPd is created by Frank Dennis in 2001, based on Troll-FTPd, and until now is actively developed by a team led by Dennis.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial we will provide about installation and configuration of "**Pure-FTPd**" with Unix-like operating system FreeBSD 10.2.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1 - Update system ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing you must do is to install and update the freebsd repository, please connect to your server with SSH and then type command below as sudo/root :
|
||||
|
||||
freebsd-update fetch
|
||||
freebsd-update install
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2 - Install Pure-FTPd ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can install Pure-FTPd from the ports method, but in this tutorial we will install from the freebsd repository with "**pkg**" command. So, now let's install :
|
||||
|
||||
pkg install pure-ftpd
|
||||
|
||||
Once installation is finished, please add pure-ftpd to the start at the boot time with sysrc command below :
|
||||
|
||||
sysrc pureftpd_enable=yes
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3 - Configure Pure-FTPd ###
|
||||
|
||||
Configuration file for Pure-FTPd is located at directory "/usr/local/etc/", please go to the directory and copy the sample configuration for pure-ftpd to "**pure-ftpd.conf**".
|
||||
|
||||
cd /usr/local/etc/
|
||||
cp pure-ftpd.conf.sample pure-ftpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Now edit the file configuration with nano editor :
|
||||
|
||||
nano -c pure-ftpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Note : -c option to show line number on nano.
|
||||
|
||||
Go to line 59 and change the value of "VerboseLog" to "**yes**". This option is allow you as administrator to see the log all command used by the users.
|
||||
|
||||
VerboseLog yes
|
||||
|
||||
And now look at line 126 "PureDB" for virtual-users configuration. Virtual users is a simple mechanism to store a list of users, with their password, name, uid, directory, etc. It's just like /etc/passwd. But it's not /etc/passwd. It's a different file and only for FTP. In this tutorial we will store the list of user to the file "**/usr/local/etc/pureftpd.passwd**" and "**/usr/local/etc/pureftpd.pdb**". Please uncomment that line and change the path for the file to "/usr/local/etc/pureftpd.pdb".
|
||||
|
||||
PureDB /usr/local/etc/pureftpd.pdb
|
||||
|
||||
Next, uncomment on the line 336 "**CreateHomeDir**", this option make you easy to add the virtual users, allow automatically create home directories if they are missing.
|
||||
|
||||
CreateHomeDir yes
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, start pure-ftpd with service command :
|
||||
|
||||
service pure-ftpd start
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4 - Adding New Users ###
|
||||
|
||||
At this step FTP server is started without error, but you can not log in to the FTP Server, because the default configuration of pure-ftpd is disabled for anonymous users. We need to create new users with home directory, and then give it the password for login.
|
||||
|
||||
On thing you must do befere you add new user to pure-ftpd virtual-user is to create a system user for this, lets create new system user "**vftp**" and the default group is same as username, with home directory "**/home/vftp/**".
|
||||
|
||||
pw useradd vftp -s /sbin/nologin -w no -d /home/vftp \
|
||||
-c "Virtual User Pure-FTPd" -m
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can add the new user for the FTP Server with "**pure-pw**" command. For an example here, we will create new user named "**akari**", so please see command below :
|
||||
|
||||
pure-pw useradd akari -u vftp -g vftp -d /home/vftp/akari
|
||||
Password: TYPE YOUR PASSWORD
|
||||
|
||||
that command will create user "**akari**" and the data stored at the file "**/usr/local/etc/pureftpd.passwd**", not at /etc/passwd file, so this means is that you can easily create FTP-only accounts without messing up your system accounts.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, you must generate the PureDB user database with this command :
|
||||
|
||||
pure-pw mkdb
|
||||
|
||||
Now restart the pure-ftpd services and try connect with user "akari" :
|
||||
|
||||
service pure-ftpd restart
|
||||
|
||||
Trying to connect with user akari :
|
||||
|
||||
ftp SERVERIP
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE :**
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to add new user again, you can use "**pure-pw**" command. And if you want to delete the current user, you can use this :
|
||||
|
||||
pure-pw userdel useryouwanttodelete
|
||||
pure-pw mkdb
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 5 - Add SSL/TLS to Pure-FTPd ###
|
||||
|
||||
Pure-FTPd supports encryption using TLS security mechanisms. To support for TLS/SSL, make sure the OpenSSL library is already installed on your freebsd system.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you must generate new "**self-signed certificate**" on the directory "**/etc/ssl/private**". Before you generate the certificate, please create new directory there called "private".
|
||||
|
||||
cd /etc/ssl/
|
||||
mkdir private
|
||||
cd private/
|
||||
|
||||
Now generate "self-signed certificate" with openssl command below :
|
||||
|
||||
openssl req -x509 -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -sha256 -keyout \
|
||||
/etc/ssl/private/pure-ftpd.pem \
|
||||
-out /etc/ssl/private/pure-ftpd.pem
|
||||
|
||||
FILL ALL WITH YOUR PERSONAL INFO.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, change the certificate permission :
|
||||
|
||||
chmod 600 /etc/ssl/private/*.pem
|
||||
|
||||
Once the certifcate is generated, Edit the pure-ftpd configuration file :
|
||||
|
||||
nano -c /usr/local/etc/pure-ftpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Uncomment on line **423** to enable the TLS :
|
||||
|
||||
TLS 1
|
||||
|
||||
And line **439** for the certificate file path :
|
||||
|
||||
CertFile /etc/ssl/private/pure-ftpd.pem
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit, then restart the pure-ftpd services :
|
||||
|
||||
service pure-ftpd restart
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's test the Pure-FTPd that work with TLS/SSL. I'm here use "**FileZilla**" to connect to the FTP Server, and use user "**akari**" that have been created.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Pure-FTPd with TLS on FreeBSD 10.2 successfully.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
FTP or File Transfer Protocol is standart protocol used to transfer file between users and the server. One of the best, lightweight and secure FTP Server Software is Pure-FTPd. It is secure and support for TLS/SSL encryption mechanism. Pure-FTPd is easy to to install and configure, you can manage the user with virtual user support, and it is make you as sysadmin is easy to manage the user if you have a much user ftp server.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-pure-ftpd-tls-freebsd-10-2/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arul][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arulm/
|
||||
236
sources/tech/20151104 How to Install Redis Server on CentOS 7.md
Normal file
236
sources/tech/20151104 How to Install Redis Server on CentOS 7.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,236 @@
|
||||
How to Install Redis Server on CentOS 7
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Hi everyone, today Redis is the subject of our article, we are going to install it on CentOS 7. Build sources files, install the binaries, create and install files. After installing its components, we will set its configuration as well as some operating system parameters to make it more reliable and faster.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Redis server
|
||||
|
||||
Redis is an open source multi-platform data store written in ANSI C, that uses datasets directly from memory achieving extremely high performance. It supports various programming languages, including Lua, C, Java, Python, Perl, PHP and many others. It is based on simplicity, about 30k lines of code that do "few" things, but do them well. Despite you work on memory, persistence may exist and it has a fairly reasonable support for high availability and clustering, which does good in keeping your data safe.
|
||||
|
||||
### Building Redis ###
|
||||
|
||||
There is no official RPM package available, we need to build it from sources, in order to do this you will need install Make and GCC.
|
||||
|
||||
Install GNU Compiler Collection and Make with yum if it is not already installed
|
||||
|
||||
yum install gcc make
|
||||
|
||||
Download the tarball from [redis download page][1].
|
||||
|
||||
curl http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-3.0.4.tar.gz -o redis-3.0.4.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Extract the tarball contents
|
||||
|
||||
tar zxvf redis-3.0.4.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Enter Redis the directory we have extracted
|
||||
|
||||
cd redis-3.0.4
|
||||
|
||||
Use Make to build the source files
|
||||
|
||||
make
|
||||
|
||||
### Install ###
|
||||
|
||||
Enter on the src directory
|
||||
|
||||
cd src
|
||||
|
||||
Copy Redis server and client to /usr/local/bin
|
||||
|
||||
cp redis-server redis-cli /usr/local/bin
|
||||
|
||||
Its good also to copy sentinel, benchmark and check as well.
|
||||
|
||||
cp redis-sentinel redis-benchmark redis-check-aof redis-check-dump /usr/local/bin
|
||||
|
||||
Make Redis config directory
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir /etc/redis
|
||||
|
||||
Create a working and data directory under /var/lib/redis
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir -p /var/lib/redis/6379
|
||||
|
||||
#### System parameters ####
|
||||
|
||||
In order to Redis work correctly you need to set some kernel options
|
||||
|
||||
Set the vm.overcommit_memory to 1, which means always, this will avoid data to be truncated, take a look [here][2] for more.
|
||||
|
||||
sysctl -w vm.overcommit_memory=1
|
||||
|
||||
Change the maximum of backlog connections some value higher than the value on tcp-backlog option of redis.conf, which defaults to 511. You can find more on sysctl based ip networking "tunning" on [kernel.org][3] website.
|
||||
|
||||
sysctl -w net.core.somaxconn=512.
|
||||
|
||||
Disable transparent huge pages support, that is known to cause latency and memory access issues with Redis.
|
||||
|
||||
echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled
|
||||
|
||||
### redis.conf ###
|
||||
|
||||
Redis.conf is the Redis configuration file, however you will see the file named as 6379.conf here, where the number is the same as the network port is listening to. This name is recommended if you are going to run more than one Redis instance.
|
||||
|
||||
Copy sample redis.conf to **/etc/redis/6379.conf**.
|
||||
|
||||
cp redis.conf /etc/redis/6379.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Now edit the file and set at some of its parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/redis/6379.conf
|
||||
|
||||
#### daemonize ####
|
||||
|
||||
Set daemonize to no, systemd need it to be in foreground, otherwise Redis will suddenly die.
|
||||
|
||||
daemonize no
|
||||
|
||||
#### pidfile ####
|
||||
|
||||
Set the pidfile to redis_6379.pid under /var/run.
|
||||
|
||||
pidfile /var/run/redis_6379.pid
|
||||
|
||||
#### port ####
|
||||
|
||||
Change the network port if you are not going to use the default
|
||||
|
||||
port 6379
|
||||
|
||||
#### loglevel ####
|
||||
|
||||
Set your loglevel.
|
||||
|
||||
loglevel notice
|
||||
|
||||
#### logfile ####
|
||||
|
||||
Set the logfile to /var/log/redis_6379.log
|
||||
|
||||
logfile /var/log/redis_6379.log
|
||||
|
||||
#### dir ####
|
||||
|
||||
Set the directory to /var/lib/redis/6379
|
||||
|
||||
dir /var/lib/redis/6379
|
||||
|
||||
### Security ###
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some actions that you can take to enforce the security.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Unix sockets ####
|
||||
|
||||
In many cases, the client application resides on the same machine as the server, so there is no need to listen do network sockets. If this is the case you may want to use unix sockets instead, for this you need to set the **port** option to 0, and then enable unix sockets with the following options.
|
||||
|
||||
Set the path to the socket file
|
||||
|
||||
unixsocket /tmp/redis.sock
|
||||
|
||||
Set restricted permission to the socket file
|
||||
|
||||
unixsocketperm 700
|
||||
|
||||
Now, to have access with redis-cli you should use the -s flag pointing to the socket file
|
||||
|
||||
redis-cli -s /tmp/redis.sock
|
||||
|
||||
#### requirepass ####
|
||||
|
||||
You may need remote access, if so, you should use a password, that will be required before any operation.
|
||||
|
||||
requirepass "bTFBx1NYYWRMTUEyNHhsCg"
|
||||
|
||||
#### rename-command ####
|
||||
|
||||
Imagine the output of the next command. Yes, it will dump the configuration of the server, so you should deny access to this kind information whenever is possible.
|
||||
|
||||
CONFIG GET *
|
||||
|
||||
To restrict, or even disable this and other commands by using the **rename-command**. You must provide a command name and a replacement. To disable, set the replacement string to "" (blank), this is more secure as it will prevent someone from guessing the command name.
|
||||
|
||||
rename-command FLUSHDB "FLUSHDB_MY_SALT_G0ES_HERE09u09u"
|
||||
rename-command FLUSHALL ""
|
||||
rename-command CONFIG "CONFIG_MY_S4LT_GO3S_HERE09u09u"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Access through unix sockets with password and command changes
|
||||
|
||||
#### Snapshots ####
|
||||
|
||||
By default Redis will periodically dump its datasets to **dump.rdb** on the data directory we set. You can configure how often the rdb file will be updated by the save command, the first parameter is a timeframe in seconds and the second is a number of changes performed on the data file.
|
||||
|
||||
Every 15 hours if there was at least 1 key change
|
||||
|
||||
save 900 1
|
||||
|
||||
Every 5 hours if there was at least 10 key changes
|
||||
|
||||
save 300 10
|
||||
|
||||
Every minute if there was at least 10000 key changes
|
||||
|
||||
save 60 10000
|
||||
|
||||
The **/var/lib/redis/6379/dump.rdb** file contains a dump of the dataset on memory since last save. Since it creates a temporary file and then replace the original file, there is no problem of corruption and you can always copy it directly without fear.
|
||||
|
||||
### Starting at boot ###
|
||||
|
||||
You may use systemd to add Redis to the system startup
|
||||
|
||||
Copy sample init_script to /etc/init.d, note also the number of the port on the script name
|
||||
|
||||
cp utils/redis_init_script /etc/init.d/redis_6379
|
||||
|
||||
We are going to use systemd, so create a unit file named redis_6379.service under **/etc/systems/system**
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/systemd/system/redis_6379.service
|
||||
|
||||
Put this content, try man systemd.service for details
|
||||
|
||||
[Unit]
|
||||
Description=Redis on port 6379
|
||||
|
||||
[Service]
|
||||
Type=forking
|
||||
ExecStart=/etc/init.d/redis_6379 start
|
||||
ExecStop=/etc/init.d/redis_6379 stop
|
||||
|
||||
[Install]
|
||||
WantedBy=multi-user.target
|
||||
|
||||
Now add the memory overcommit and maximum backlog options we have set before to the **/etc/sysctl.conf** file.
|
||||
|
||||
vm.overcommit_memory = 1
|
||||
|
||||
net.core.somaxconn=512
|
||||
|
||||
For the transparent huge pages support there is no sysctl directive, so you can put the command at the end of /etc/rc.local
|
||||
|
||||
echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
That's enough to start, with these settings you will be able to deploy Redis server for many simpler scenarios, however there is many options on redis.conf for more complex environments. On some cases, you may use [replication][4] and [Sentinel][5] to provide high availability, [split the data][6] across servers, create a cluster of servers. Thanks for reading!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/storage/install-redis-server-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Carlos Alberto][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/carlosal/
|
||||
[1]:http://redis.io/download
|
||||
[2]:https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/vm/overcommit-accounting
|
||||
[3]:https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/networking/ip-sysctl.txt
|
||||
[4]:http://redis.io/topics/replication
|
||||
[5]:http://redis.io/topics/sentinel
|
||||
[6]:http://redis.io/topics/partitioning
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
|
||||
How to Install SQLite 3.9.1 with JSON Support on Ubuntu 15.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Hello and welcome to our today's article on SQLite which is the most widely deployed SQL database engine in the world that comes with zero-configuration, that means no setup or administration needed. SQLite is public-domain software package that provides relational database management system, or RDBMS that is used to store user-defined records in large tables. In addition to data storage and management, database engine process complex query commands that combine data from multiple tables to generate reports and data summaries.
|
||||
|
||||
SQLite is very small and light weight that does not require a separate server process or system to operate. It is available on UNIX, Linux, Mac OS-X, Android, iOS and Windows which is being used in various software applications like Opera, Ruby On Rails, Adobe System, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome and Skype.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1) Basic Requirements: ###
|
||||
|
||||
There is are no such complex complex requirements for the installation of SQLite as it mostly comes support all major cross platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
So, let's login to your Ubuntu server with sudo or root credentials using your CLI or Secure Shell. Then update your system so that your operating system is upto date with latest packages.
|
||||
|
||||
In ubuntu, the below command is to be used for system update.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
If you are starting to deploy SQLite on on a fresh Ubuntu, then make sure that you have installed some basic system management utilities like wget, make, unzip, gcc.
|
||||
|
||||
To install wget, make and gcc packages on ubuntu, you use the below command, then press "Y" to allow and proceed with installation of these packages.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install wget make gcc
|
||||
|
||||
### 2) Download SQLite ###
|
||||
|
||||
To download the latest package of SQLite, you can refer to their official [SQLite Download Page][1] as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can copy the link of its resource package and download it on ubuntu server using the wget utility command.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget https://www.sqlite.org/2015/sqlite-autoconf-3090100.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After downloading is complete, extract the package and change your current directory to the extracted SQLite folder by using the below command as shown.
|
||||
|
||||
# tar -zxvf sqlite-autoconf-3090100.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
### 3) Installing SQLite ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now we are going to install and configure the SQLite package that we downloaded. So, to compile and install SQLite on ubuntu run the configuration script within the same directory where your have extracted the SQLite package as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
root@ubuntu-15:~/sqlite-autoconf-3090100# ./configure –prefix=/usr/local
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once the package is configuration is done under the mentioned prefix, then run the below command make command to compile the package.
|
||||
|
||||
root@ubuntu-15:~/sqlite-autoconf-3090100# make
|
||||
source='sqlite3.c' object='sqlite3.lo' libtool=yes \
|
||||
DEPDIR=.deps depmode=none /bin/bash ./depcomp \
|
||||
/bin/bash ./libtool --tag=CC --mode=compile gcc -DPACKAGE_NAME=\"sqlite\" -DPACKAGE_TARNAME=\"sqlite\" -DPACKAGE_VERSION=\"3.9.1\" -DPACKAGE_STRING=\"sqlite\ 3.9.1\" -DPACKAGE_BUGREPORT=\"http://www.sqlite.org\" -DPACKAGE_URL=\"\" -DPACKAGE=\"sqlite\" -DVERSION=\"3.9.1\" -DSTDC_HEADERS=1 -DHAVE_SYS_TYPES_H=1 -DHAVE_SYS_STAT_H=1 -DHAVE_STDLIB_H=1 -DHAVE_STRING_H=1 -DHAVE_MEMORY_H=1 -DHAVE_STRINGS_H=1 -DHAVE_INTTYPES_H=1 -DHAVE_STDINT_H=1 -DHAVE_UNISTD_H=1 -DHAVE_DLFCN_H=1 -DLT_OBJDIR=\".libs/\" -DHAVE_FDATASYNC=1 -DHAVE_USLEEP=1 -DHAVE_LOCALTIME_R=1 -DHAVE_GMTIME_R=1 -DHAVE_DECL_STRERROR_R=1 -DHAVE_STRERROR_R=1 -DHAVE_POSIX_FALLOCATE=1 -I. -D_REENTRANT=1 -DSQLITE_THREADSAFE=1 -DSQLITE_ENABLE_FTS3 -DSQLITE_ENABLE_RTREE -g -O2 -c -o sqlite3.lo sqlite3.c
|
||||
|
||||
After running make command, to complete the installation of SQLite on ubuntu run the 'make install' command as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
# make install
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4) Testing SQLite Installation ###
|
||||
|
||||
To confirm the successful installation of SQLite 3.9, run the below command in your command line interface.
|
||||
|
||||
# sqlite3
|
||||
|
||||
You will the SQLite verion after running the above command as shown.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 5) Using SQLite ###
|
||||
|
||||
SQLite is very handy to use. To get the detailed information about its usage, simply run the below command in the SQLite console.
|
||||
|
||||
sqlite> .help
|
||||
|
||||
So here is the list of all its available commands, with their description that you can get help to start using SQLite.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now in this last section , we make use of few SQLite commands to create a new database using the SQLite3 command line interface.
|
||||
|
||||
To to create a new database run the below command.
|
||||
|
||||
# sqlite3 test.db
|
||||
|
||||
To create a table within the new database run the below command.
|
||||
|
||||
sqlite> create table memos(text, priority INTEGER);
|
||||
|
||||
After creating the table, insert some data using the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
sqlite> insert into memos values('deliver project description', 15);
|
||||
sqlite> insert into memos values('writing new artilces', 100);
|
||||
|
||||
To view the inserted data from the table , run the below command.
|
||||
|
||||
sqlite> select * from memos;
|
||||
deliver project description|15
|
||||
writing new artilces|100
|
||||
|
||||
to exit from the sqlite3 type the below command.
|
||||
|
||||
sqlite> .exit
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this article you learned the installation of latest version of SQLite 3.9.1 which enables the recently JSON1 support in its 3.9.0 version and so on. Its is an amazing library that gets embedded inside the application that makes use of it to keep the resources much efficient and lighter. We hope you find this article much helpful, feel free to get back to us if you find any difficulty.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/install-sqlite-json-ubuntu-15-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kashif Siddique][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/kashifs/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.sqlite.org/download.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,266 @@
|
||||
How to Setup Pfsense Firewall and Basic Configuration
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In this article our focus is Pfsense setup, basic configuration and overview of features available in the security distribution of FreeBSD. In this tutorial we will run network wizard for basic setting of firewall and detailed overview of services. After the [installation process][1] following snapshot shows the IP addresses of WAN/LAN and different options for the management of Pfsense firewall.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After setup , following window appear which shows the url for configuration of Pfsense.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Open above given URL in the browser and login with username **admin** and password **pfsense**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After successful login, following wizard appears for the basic setting of Pfsense firewall. However setup wizard option can be bypassed and user can run it from the **System** menu from the web interface.
|
||||
|
||||
Click on the **Next** button to start basic configuration process on Pfsense firewall.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Setting hostname, domain and DNS addresses is shown in the following figure.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Setting time zone is shown in the below given snapshot.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next window shows setting for the WAN interface. By defaults Pfsense firewall block bogus and private networks.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Setting LAN IP address which is used to access the Pfsense web interface for further configuration.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
By default password for web interface is "pfsense". Enter new password for admin user on the following window to access the web interface for further configuration.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Click on the "reload" button which is shown below. It applies the setting and redirect firewall user to main dashboard of Pfsense.
|
||||
|
||||
 and status of ethernet/wireless interfaces etc.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Menu detail ###
|
||||
|
||||
PFsense consist of System, interfaces, firewall,services,vpn,status,diagnostics and help menus.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### System Menu ###
|
||||
|
||||
Sub menus of **System** is given below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the **Advanced** sub menu user can perform following operations.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Configuration of web interface
|
||||
1. Firewall/Nat setting
|
||||
1. Networking setting
|
||||
1. System tuneables setting
|
||||
1. Notification setting
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the **Cert manager** sub menu, firewall administrator generates certificates for CA and users.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the **Firmware** sub menu, user can update Pfsense firmware manually/automatically. User can take full backup of Pfsense configurations.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the **General Setup** sub menu, user can change basic setting such as hostname and domain etc.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As menu title indicates, user can enable/disable high availability feature from this sub menu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Packages sub menu provides package manager facility in the web interface for Pfsense .
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
User can perform gateway and route management using **Routing** sub menu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Setup Wizard** sub menu opens following window which start basic configuration of Pfsense.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Management of user can be done from the **User manager** sub menu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Interfaces Menu ###
|
||||
|
||||
This menu is used for the assignment of interfaces (LAN/WAN), VLAN setting,wireless and GRE configuration etc.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Firewall Menu ###
|
||||
|
||||
Firewall is the main and core part of Pfsense distribution and it provides following features.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Aliases**
|
||||
|
||||
Aliases are defined for real hosts, networks or ports and they can be used to minimize the number of changes.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**NAT (Network Address Translation)**
|
||||
|
||||
NAT binds a specific internal address to a specific external address. Incoming traffic from the Internet to the specified IP will be directed toward the associated internal IP.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Firewall Rules**
|
||||
|
||||
Firewall rules control what traffic is allowed to enter an interface on the firewall. After traffic is passed on the interface, it enters an entry in the state table is created.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Schedules**
|
||||
|
||||
Firewall rules can be scheduled so that they are only active at certain times of day or on certain specific days or days of the week.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Traffic Shaper**
|
||||
|
||||
Traffic shaping is the control of computer network traffic in order to optimize performance and lower latency.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Virtual IPs**
|
||||
|
||||
Virtual IPs add knowledge of additional IP addresses to the firewall that are different from the firewall's real interface addresses.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Services Menu ###
|
||||
|
||||
Services menu shows services which are provided by the Pfsense distribution along firewall.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
New program/software installed for some specific service is also shown in this menu such as snort. By default following services are listed in services menu.
|
||||
|
||||
**Captive portal**
|
||||
|
||||
The captive portal functionality in Pfsense allows securing a network by requiring a username and password entered on a portal page.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**DHCP Relay**
|
||||
|
||||
The DHCP Relay daemon will relay DHCP requests between broadcast domains for IPv4 DHCP.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**DHCP Server**
|
||||
|
||||
User can run DHCP service on the firewall for the network devices.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**DNS Forwarder/Resolver/Dynamic DNS**
|
||||
|
||||
DNS different services can be configured on the Pfsense firewall.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**IGMP Proxy**
|
||||
|
||||
User can configure IGMP on the Pfsense firewall from services menu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Load Balancer**
|
||||
|
||||
Load Balancing is one of the important feature which is also supported by the Pfsense firewall.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)**
|
||||
|
||||
Pfsense supports all versions of snmp for remote management of firewall.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Wake on Lan**
|
||||
|
||||
Using this feature packet sent to a workstation on a locally connected network which will power on a workstation.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### VPN Menu ###
|
||||
|
||||
It is one of the most important feature of Pfsense. Its supports following types of vpn configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
**VPN IPsec**
|
||||
|
||||
IPsec is a standard for providing security to IP protocols via encryption and/or authentication.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**L2TP IPsec**
|
||||
|
||||
L2TP/IPsec is a common VPN type that wraps L2TP, an insecure tunneling protocol, inside a secure channel built using transport mode IPsec.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**OpenVPN**
|
||||
|
||||
OpenVPN is an Open Source VPN server and client that is supported on pfSense.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Status Menu**
|
||||
|
||||
It shows the status of services provided by Pfsense such as dhcp server, ipsec and load balancer etc.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Diagnostic Menu**
|
||||
|
||||
This menu helps administrator/user for the rectification of Pfsense issues or problems.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Help Menu**
|
||||
|
||||
This menu provides links for different useful resources such as FreeBSD handbook,developer wiki, paid support and pfsense book.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this article our focus was on the basic configuration and features set of Pfsense distribution. It is based on FreeBSD distribution and widely used due to security and stability features. In our future articles on Pfsense, our focus will be on the basic firewall rules setting, snort (IDS/IPS) and IPSEC VPN configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/firewall/pfsense-setup-basic-configuration/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[nido][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/naveeda/
|
||||
[1]:http://linoxide.com/firewall/install-pfsense-firewall/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
How to Manage Your To-Do Lists in Ubuntu Using Go For It Application
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Task management is arguably one of the most important and challenging part of professional as well as personal life. Professionally, as you assume more and more responsibility, your performance is directly related to or affected with your ability to manage the tasks you’re assigned.
|
||||
|
||||
If your job involves working on a computer, then you’ll be happy to know that there are various applications available that claim to make task management easy for you. While most of them cater to Windows users, there are many options available on Linux, too. In this article we will discuss one such application: Go For It.
|
||||
|
||||
### Go For It ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Go For It][1] (GFI) is developed by Manuel Kehl, who describes it as a “a simple and stylish productivity app, featuring a to-do list, merged with a timer that keeps your focus on the current task.” The timer feature, specifically, is interesting, as it also makes sure that you take a break from your current task and relax for sometime before proceeding further.
|
||||
|
||||
### Download and Installation ###
|
||||
|
||||
Users of Debian-based systems, like Ubuntu, can easily install the app by running the following commands in terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:mank319/go-for-it
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install go-for-it
|
||||
|
||||
Once done, you can execute the application by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
go-for-it
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage and Configuration ###
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how the GFI interface looks when you run the app for the very first time:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, the interface consists of three tabs: To-Do, Timer, and Done. While the To-Do tab contains a list of tasks (the 4 tasks shown in the image above are there by default – you can delete them by clicking on the rectangular box in front of them), the Timer tab contains task timer, while Done contains a list of tasks that you’ve finished successfully. Right at the bottom is a text box where you can enter the task text and click “+” to add it to the list above.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, I added a task named “MTE-research-work” to the list and selected it by clicking on it in the list – see the screenshot below:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Then I selected the Timer tab. Here I could see a 25-minute timer for the active task which was “MTE-reaserch-work.”
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Of course, you can change the timer value and set to any time you want. I, however, didn’t change the value and clicked the Start button present below to start the task timer. Once 60 seconds were left, GFI issued a notification indicating the same.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
And once the time was up, I was asked to take a break of five minutes.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once those five minutes were over, I could again start the task timer for my task.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
When you’re done with your task, you can click the Done button in the Timer tab. The task is then removed from the To-Do tab and listed in the Done tab.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
GFI also allows you to tweak some of its settings. For example, the settings window shown below contains options to tweak the default task duration, break duration, and reminder time.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It’s worth mentioning that GFI stores the to-do lists in the Todo.txt format which simplifies synchronization with mobile devices and makes it possible for you to edit tasks using other frontends – read more about it [here][2].
|
||||
|
||||
You can also see the GFI app in action in the video below.
|
||||
|
||||
注:youtube 视频
|
||||
<iframe frameborder="0" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/mnw556C9FZQ?autoplay=1&autohide=2&border=1&wmode=opaque&enablejsapi=1&controls=1&showinfo=0" id="youtube-iframe"></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
As you have observed, GFI is an easy to understand and simple to use task management application. Although it doesn’t offer a plethora of features, it does what it claims – the timer integration is especially useful. If you’re looking for a basic, open-source task management tool for Linux, Go For It is worth trying.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/to-do-lists-ubuntu-go-for-it/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Himanshu Arora][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/himanshu/
|
||||
[1]:http://manuel-kehl.de/projects/go-for-it/
|
||||
[2]:http://todotxt.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change default Java version on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: When I am trying to run a Java program on Linux, I am getting the following error. Looks like the Java program is compiled for a different Java version than the default Java program installed on my Linux. How can I switch the default Java version on Linux?
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: com/xmodulo/hmon/gui/NetConf : Unsupported major.minor version 51.0
|
||||
|
||||
When a Java program is compiled, the build environment sets a "target" which is the oldest JRE version the program can support. If you run the Java program on a Linux system which does not meet the lowest JRE version requirement, you will encounter the following error while starting the program.
|
||||
|
||||
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: com/xmodulo/hmon/gui/NetConf : Unsupported major.minor version 51.0
|
||||
|
||||
For example, in this case the program is compiled for Java JRE 1.7 but the system only has Java JRE 1.6.
|
||||
|
||||
To solve this problem, you need to change the default Java version you are using to Java JRE 1.7 or higher (assuming that such JRE is already installed).
|
||||
|
||||
First, **check available Java versions** on your Linux system by using update-alternatives command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo update-alternatives --display java
|
||||
|
||||
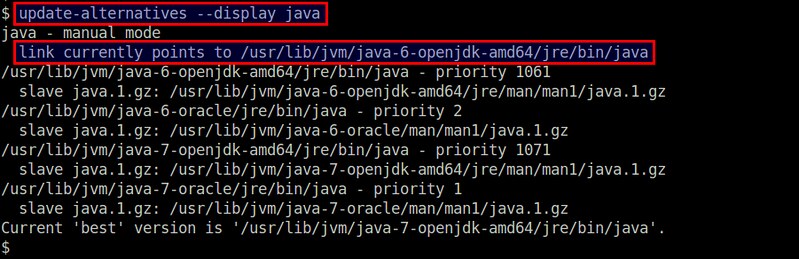
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, there are four different Java versions that are installed: OpenJDK JRE 1.6, Oracle Java JRE 1.6, OpenJDK JRE 1.7 and Oracle Java JRE 1.7. The default Java version is currently set to OpenJDK JRE 1.6.
|
||||
|
||||
If the necessary Java JRE is not installed, you can always install it using [these instructions][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Now that there are suitable candidates to change to, you can **switch the default Java version** among available Java JREs by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo update-alternatives --config java
|
||||
|
||||
When prompted, select the Java version you would like to use. In this example, we choose Oracle Java JRE 1.7.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now you can verify the default Java version as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ java -version
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Finally, if you defined JAVA_HOME environment variable somewhere, update the variable according to the newly set default Java version.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/change-default-java-version-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-java-runtime-linux.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
|
||||
translation by strugglingyouth
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to find which shell I am using on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I often change between different shells at the command line. Is there a quick and easy way to find out which shell I am currently in? Also how can I find out the version of the shell?
|
||||
|
||||
### Find out Which Shell You are In ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are different ways to tell what shell you are currently in. The easiest way to find that out is by using special shell parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
For one, [a special parameter named "$$"][1] denotes the PID of the current instance of the shell you are running. This parameter is read-only and cannot be modified. So the following command will also show you the name of the shell you are running:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps -p $$
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
PID TTY TIME CMD
|
||||
21666 pts/4 00:00:00 bash
|
||||
|
||||
The above command works across all available shells.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are not using csh, another way to find out the current shell is to use an special shell parameter called "$$", which denotes the name of the shell or shell script that is currently running. This is one of the Bash special parameters, but available in other shells as well, such as sh, zsh, tcsh or dash. Using echo command to print out its value will tell you the name of the shell you are currently in.
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo $0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
bash
|
||||
|
||||
Don't be confused with a separate environment variable called $SHELL, which is set to the full path to your default shell. As such, this variable is not necessarily point to the current shell you are using. For example, $SHELL remains the same even if you invoke a different shell within a terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo $SHELL
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
/bin/shell
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Thus to find out the current shell, you should use either $$ or $0, but not $SHELL.
|
||||
|
||||
### Find out the Version of the Shell You are Using ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once you know which shell you are in, you may want to find out what version of the shell it is. For that, type the name of your shell followed by "--version" at the command line. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
**For** bash **shell**:
|
||||
|
||||
$ bash --version
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
GNU bash, version 4.3.30(1)-release (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)
|
||||
Copyright (C) 2013 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
|
||||
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later
|
||||
|
||||
This is free software; you are free to change and redistribute it.
|
||||
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
|
||||
|
||||
**For** zsh **shell**:
|
||||
|
||||
$ zsh --version
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
zsh 5.0.7 (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)
|
||||
|
||||
**For** tcsh **shell**:
|
||||
$ tcsh --version
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
tcsh 6.18.01 (Astron) 2012-02-14 (x86_64-unknown-linux) options wide,nls,dl,al,kan,rh,nd,color,filec
|
||||
|
||||
For some shells, you can also use shell-specific variables (e.g., $BASH_VERSION or $ZSH_VERSION).
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo $BASH_VERSION
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
4.3.8(1)-release
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/which-shell-am-i-using.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/process-id-pid-shell-script.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install Ubuntu desktop behind a proxy
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: My computer is connected to a corporate network sitting behind an HTTP proxy. When I try to install Ubuntu desktop on the computer from a CD-ROM drive, the installation hangs and never finishes while trying to retrieve files, which is presumably due to the proxy. However, the problem is that Ubuntu installer never asks me to configure proxy during installation procedure. Then how can I install Ubuntu desktop behind a proxy?
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike Ubuntu server, installation of Ubuntu desktop is pretty much auto-pilot, not leaving much room for customization, such as custom disk partitioning, manual network settings, package selection, etc. While such simple, one-shot installation is considered user-friendly, it leaves much to be desired for those users looking for "advanced installation mode" to customize their Ubuntu desktop installation.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, one big problem of the default Ubuntu desktop installer is the absense of proxy settings. If your computer is connected behind a proxy, you will notice that Ubuntu installation gets stuck while preparing to download files.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This post describes how to get around the limitation of Ubuntu **installer and install Ubuntu desktop when you are behind a proxy**.
|
||||
|
||||
The basic idea is as follows. Instead of starting with Ubuntu installer directly, boot into live Ubuntu desktop first, configure proxy settings, and finally launch Ubuntu installer manually from live desktop. The following is the step by step procedure.
|
||||
|
||||
After booting from Ubuntu desktop CD/DVD or USB, click on "Try Ubuntu" on the first welcome screen.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once you boot into live Ubuntu desktop, click on Settings icon in the left.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Go to Network menu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Configure proxy settings manually.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, open a terminal.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enter a root session by typing the following:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo su
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, type the following command as the root.
|
||||
|
||||
# ubiquity gtk_ui
|
||||
|
||||
This will launch GUI-based Ubuntu installer as follows.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Proceed with the rest of installation.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-ubuntu-desktop-behind-proxy.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Translating by Xuanwo
|
||||
|
||||
Part 10 - LFCS: Understanding & Learning Basic Shell Scripting and Linux Filesystem Troubleshooting
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The Linux Foundation launched the LFCS certification (Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin), a brand new initiative whose purpose is to allow individuals everywhere (and anywhere) to get certified in basic to intermediate operational support for Linux systems, which includes supporting running systems and services, along with overall monitoring and analysis, plus smart decision-making when it comes to raising issues to upper support teams.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Translating by Xuanwo
|
||||
|
||||
Part 2 - LFCS: How to Install and Use vi/vim as a Full Text Editor
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A couple of months ago, the Linux Foundation launched the LFCS (Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin) certification in order to help individuals from all over the world to verify they are capable of doing basic to intermediate system administration tasks on Linux systems: system support, first-hand troubleshooting and maintenance, plus intelligent decision-making to know when it’s time to raise issues to upper support teams.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Translating by Xuanwo
|
||||
|
||||
Part 3 - LFCS: How to Archive/Compress Files & Directories, Setting File Attributes and Finding Files in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Recently, the Linux Foundation started the LFCS (Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin) certification, a brand new program whose purpose is allowing individuals from all corners of the globe to have access to an exam, which if approved, certifies that the person is knowledgeable in performing basic to intermediate system administration tasks on Linux systems. This includes supporting already running systems and services, along with first-level troubleshooting and analysis, plus the ability to decide when to escalate issues to engineering teams.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Translating by Xuanwo
|
||||
|
||||
Part 4 - LFCS: Partitioning Storage Devices, Formatting Filesystems and Configuring Swap Partition
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Last August, the Linux Foundation launched the LFCS certification (Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin), a shiny chance for system administrators to show, through a performance-based exam, that they can perform overall operational support of Linux systems: system support, first-level diagnosing and monitoring, plus issue escalation – if needed – to other support teams.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Translating by Xuanwo
|
||||
|
||||
Part 5 - LFCS: How to Mount/Unmount Local and Network (Samba & NFS) Filesystems in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The Linux Foundation launched the LFCS certification (Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin), a brand new program whose purpose is allowing individuals from all corners of the globe to get certified in basic to intermediate system administration tasks for Linux systems, which includes supporting running systems and services, along with overall monitoring and analysis, plus smart decision-making when it comes to raising issues to upper support teams.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Translating by Xuanwo
|
||||
|
||||
Part 6 - LFCS: Assembling Partitions as RAID Devices – Creating & Managing System Backups
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Recently, the Linux Foundation launched the LFCS (Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin) certification, a shiny chance for system administrators everywhere to demonstrate, through a performance-based exam, that they are capable of performing overall operational support on Linux systems: system support, first-level diagnosing and monitoring, plus issue escalation, when required, to other support teams.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Translating by Xuanwo
|
||||
|
||||
Part 7 - LFCS: Managing System Startup Process and Services (SysVinit, Systemd and Upstart)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A couple of months ago, the Linux Foundation announced the LFCS (Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin) certification, an exciting new program whose aim is allowing individuals from all ends of the world to get certified in performing basic to intermediate system administration tasks on Linux systems. This includes supporting already running systems and services, along with first-hand problem-finding and analysis, plus the ability to decide when to raise issues to engineering teams.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Translating by Xuanwo
|
||||
|
||||
Part 8 - LFCS: Managing Users & Groups, File Permissions & Attributes and Enabling sudo Access on Accounts
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Last August, the Linux Foundation started the LFCS certification (Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin), a brand new program whose purpose is to allow individuals everywhere and anywhere take an exam in order to get certified in basic to intermediate operational support for Linux systems, which includes supporting running systems and services, along with overall monitoring and analysis, plus intelligent decision-making to be able to decide when it’s necessary to escalate issues to higher level support teams.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Translating by Xuanwo
|
||||
|
||||
Part 9 - LFCS: Linux Package Management with Yum, RPM, Apt, Dpkg, Aptitude and Zypper
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Last August, the Linux Foundation announced the LFCS certification (Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin), a shiny chance for system administrators everywhere to demonstrate, through a performance-based exam, that they are capable of succeeding at overall operational support for Linux systems. A Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin has the expertise to ensure effective system support, first-level troubleshooting and monitoring, including finally issue escalation, when needed, to engineering support teams.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,126 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translated by KnightJoker
|
||||
|
||||
用Linux学习:使用这些Linux应用来征服你的数学
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章是[用Linux学习][1]系列的一部分:
|
||||
|
||||
- [用Linux学习: 学习类型][2]
|
||||
- [用Linux学习: 物理模拟][3]
|
||||
- [用Linux学习: 学习音乐][4]
|
||||
- [用Linux学习: 两个地理应用程序][5]
|
||||
- [用Linux学习: 用这些Linux应用来征服你的数学][6]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Linux提供了大量的教育软件和许多优秀的工具来帮助所有年龄段的学生学习和练习各种各样的话题,常常以交互的方式。与Linux一起学习这一系列的文章则为这些各种各样的教育软件和应用提供了一个介绍。
|
||||
|
||||
数学是计算机的核心。如果有人用精益求精和纪律来预期一个伟大的操作系统,比如GNU/ Linux,那么这将是数学。如果你在寻求一些数学应用程序,那么你将不会感到失望。Linux提供了很多优秀的工具使得数学看起来和你曾经做过的一样令人畏惧,但实际上他们会简化你使用它的方式。
|
||||
### Gnuplot ###
|
||||
|
||||
Gnuplot 是一个适用于不同平台的命令行脚本化和多功能的图形工具。尽管它的名字,并不是GNU操作系统的一部分。也没有免费授权,但它是免费软件(这意味着它受版权保护,但免费使用)。
|
||||
|
||||
要在Ubuntu系统(或者衍生系统)上安装 `gnuplot`,输入:
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gnuplot gnuplot-x11
|
||||
|
||||
进入一个终端窗口。启动该程序,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
gnuplot
|
||||
|
||||
你会看到一个简单的命令行界面:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在其中您可以直接开始输入函数。绘图命令将绘制一个曲线图。
|
||||
|
||||
输入内容,例如,
|
||||
|
||||
plot sin(x)/x
|
||||
|
||||
随着`gnuplot的`提示,将会打开一个新的窗口,图像便会在里面呈现。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你也可以在线这个图设置不同的属性,比如像这样指定“title”
|
||||
|
||||
plot sin(x) title 'Sine Function', tan(x) title 'Tangent'
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
使用`splot`命令,你可以给的东西更深入一点并且绘制3D图形
|
||||
|
||||
splot sin(x*y/20)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这个窗口有几个基本的配置选项,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
但是`gnuplot`的真正力量在于在它的命令行和脚本功能,`gnuplot`广泛完整的文档可在这里找到,并在[Duke大学网站][8]上面看见这个了不起的教程[7]的原始版本。
|
||||
|
||||
### Maxima ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Maxima][9]是从Macsyma原始资料开发的一个计算机代数系统,根据它的 SourceForge 页面,
|
||||
|
||||
> “Maxima是符号和数值的表达,包括微分,积分,泰勒级数,拉普拉斯变换,常微分方程,线性方程组,多项式,集合,列表,向量,矩阵和张量系统的操纵系统。Maxima通过精确的分数,任意精度的整数和可变精度浮点数产生高精度的计算结果。Maxima可以二维和三维中绘制函数和数据。“
|
||||
|
||||
你将会获得二进制包用于大多数Ubuntu衍生系统的Maxima以及它的图形界面中,插入所有包,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install maxima xmaxima wxmaxima
|
||||
|
||||
在终端窗口中,Maxima是一个没有太多UI的命令行工具,但如果你开始wxmaxima,你会进入一个简单但功能强大的图形用户界面。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可以开始输入这个来简单的一个开始。(提示:如果你想计算一个表达式,使用“Shift + Enter”回车后会增加更多的方法)
|
||||
|
||||
Maxima可以用于一些简单的问题,因此也可以作为一个计算器,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
以及一些更复杂的问题,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
它使用`gnuplot`使得绘制简单,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
或者绘制一些复杂的图形.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
(它需要gnuplot-X11的包,来显示它们。)
|
||||
|
||||
除了美化一些图形,Maxima也尽可能用latex格式导出它们,或者通过右键是捷菜单进行一些突出的操作.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
然而其主菜单还是提供了大量压倒性的功能,当然Maxima的功能远不止如此,这里也有一个广泛使用的在线文档。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
数学不是一个简单的学科,这些在Linux上的优秀软件也没有使得数学更加简单,但是这些应用使得使用数学变得更加的简单和工程化。以上两种应用都只是介绍一下Linux的所提供的。如果你是认真从事数学和需要更多的功能与丰富的文档,那你更应该看看这些Mathbuntu项目。
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-linux-maths/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[KnightJoker](https://github.com/KnightJoker/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/attilaorosz/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/series/learn-with-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-to-type-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-physics-simulation/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-learning-music/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-geography-apps/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-linux-maths/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.gnuplot.info/documentation.html
|
||||
[8]:http://people.duke.edu/~hpgavin/gnuplot.html
|
||||
[9]:http://maxima.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[10]:http://maxima.sourceforge.net/documentation.html
|
||||
[11]:http://www.mathbuntu.org/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
|
||||
|
||||
如何在 Linux 终端下创建新的文件系统/分区
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 中创建分区或新的文件系统通常意味着一件事:安装 Gnome Parted 分区编辑器(GParted)。对于大多数 Linux 用户而言,这是唯一的办法。不过,你是否考虑过在终端创建这些分区和文件系统?当然可以!以下就是方法!
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 CFdisk 创建一个基本的 Linux 分区 ###
|
||||
|
||||
以下是如何在命令行中创建一个基本的 Linux 分区的正确方案。要做的第一件事就是先打开你的终端。若你已打开,你需要找到你想要创建分区的磁盘。这可以使用一个简单的命令来找到。
|
||||
|
||||
lsblk
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
一旦你运行了 `lsblk`,你应该会看到当前系统上每个磁盘的详细列表。看看这个列表,然后找出你想要使用的磁盘。在本文中,我将使用 `sdb` 来进行演示。
|
||||
|
||||
在终端输入这个命令。它会显示一个功能强大的基于终端的分区编辑程序。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo cfdisk /dev/sdb
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 使用在 `lsblk` 命令输出的你想要使用的磁盘来替换 `sdb`。
|
||||
|
||||
当输入此命令后,你将进入分区编辑器中,然后访问你想改变的磁盘。
|
||||
|
||||
Since hard drive partitions are different, depending on a user’s needs, this part of the guide will go over **how to set up a split Linux home/root system layout**.
|
||||
|
||||
由于磁盘分区的不同,这取决于用户的需求,这部分的指南将在 **如何建立一个分布的 Linux home/root 文件分区**。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,需要创建根分区。这需要根据磁盘的字节数来进行分割。我测试的磁盘是 32 GB。
|
||||
|
||||
在 CFdisk 中使用键盘上的方向键选择需要分配的空间。你找到后,请使用箭头键选择 [ NEW ],然后按 Enter 键。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
该程序会要求你输入分区大小。一旦你指定好大小后,按 Enter 键。这将被称为根分区(或 /dev/sdb1)。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来该创建用户分区(/dev/sdb2)了。你需要在 CFdisk 中再选择一些空闲分区。使用箭头选择 [ NEW ] 选项,然后按 Enter 键。输入你用户分区的大小,然后按 Enter 键来创建它。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最后,需要创建交换分区。像前两次一样,先找一些空闲分区,并使用箭头选择 [ NEW ] 选项。之后,算下你 Linux 想使用多大的交换分区。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 交换分区通常和计算机的内存差不多大。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在,交换分区被创建了,该指定其类型。使用上下箭头来选择它。之后,使用左右箭头选择 [ TYPE ] 。找到 Linux swap 选项,然后按 Enter 键。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
所有分区创建后。然后就是将其写入到磁盘。使用右箭头键,选择 [ WRITE ] 选项,然后按 Enter 键。这将直接将新创建的分布写入到磁盘中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 mkfs 创建文件系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
有时候,你并不需要一个完整的分区,你只想要创建一个文件系统而已。你可以在终端直接使用 `mkfs` 命令来实现。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
首先,找出你要使用的磁盘。在终端输入 `lsblk` 找出来。它会打印出列表,之后只要找到你想制作文件系统的分区或盘符。
|
||||
|
||||
在这个例子中,我将使用 `/dev/sdb1` 的第一个分区。只对 `/dev/sdb` 使用 mkfs(将会使用整个分区)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
要在一个特定的分区上创建新文件系统,只需输入
|
||||
|
||||
sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
|
||||
|
||||
在终端。应当指出的是,`mkfs.ext4` 可以将你指定的任何文件系统改变。
|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
虽然使用图形工具编辑文件系统和分区更容易,但终端可以说是更有效的。终端的加载速度更快,点击几个按钮即可。GParted 和其它工具一样,它也是一个完整的工具。我希望在本教程的帮助下,你会明白如何在终端中高效的编辑文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
你是否更喜欢使用基于终端的方法在 Linux 上编辑分区?为什么或为什么不?在下面告诉我们!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/create-file-systems-partitions-terminal-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Derrik Diener][a]
|
||||
译者:[strugglingyouth](https://github.com/strugglingyouth)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/derrikdiener/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user