mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-30 02:40:11 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject into new
This commit is contained in:
commit
c4dc60bcbd
published
20140805 How to Install Cinnamon Desktop on Ubuntu.md20171124 How do groups work on Linux.md20180201 Here are some amazing advantages of Go that you dont hear much about.md20180516 Manipulating Directories in Linux.md20180730 7 Python libraries for more maintainable code.md20180824 [Solved] -sub process usr bin dpkg returned an error code 1- Error in Ubuntu.md20180828 A Cat Clone With Syntax Highlighting And Git Integration.md20180828 How to Play Windows-only Games on Linux with Steam Play.md20180917 Linux tricks that can save you time and trouble.md
sources/tech
20180828 A Cat Clone With Syntax Highlighting And Git Integration.md20180917 4 scanning tools for the Linux desktop.md20180921 Clinews - Read News And Latest Headlines From Commandline.md20180928 10 handy Bash aliases for Linux.md20180928 A Free And Secure Online PDF Conversion Suite.md20180928 How to Install Popcorn Time on Ubuntu 18.04 and Other Linux Distributions.md20180928 Using Grails with jQuery and DataTables.md20180928 What containers can teach us about DevOps.md
translated/tech
@ -1,29 +1,31 @@
|
||||
# 如何在 Ubuntu 上安装 Cinnamon 桌面环境
|
||||
如何在 Ubuntu 上安装 Cinnamon 桌面环境
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
**这篇教程将会为你展示如何在 Ubuntu 上安装 Cinnamon 桌面环境**
|
||||
> 这篇教程将会为你展示如何在 Ubuntu 上安装 Cinnamon 桌面环境。
|
||||
|
||||
[Cinnamon][1]是 [Linux Mint][2] 的默认桌面环境。不同于 Ubuntu 的 Unity 桌面环境,Cinnamon 通过底部面板和应用菜单等查看桌面信息的方式更加传统和优雅。由于 Cinnamon 桌面以及它类 Windows 的用户界面,许多桌面用户[相较于 Ubuntu 更喜欢 Linux Mint][3]。
|
||||
[Cinnamon][1] 是 [Linux Mint][2] 的默认桌面环境。不同于 Ubuntu 的 Unity 桌面环境,Cinnamon 是一个更加传统而优雅的桌面环境,其带有底部面板和应用菜单。由于 Cinnamon 桌面以及它类 Windows 的用户界面,许多桌面用户[相较于 Ubuntu 更喜欢 Linux Mint][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
现在你无需[安装 Linux Mint][4] 就能够体验到 Cinnamon了。在这篇教程,我将会展示给你 **如何在 Ubuntu 18.04,16.04 和 14.04 上安装 Cinnamon**。
|
||||
现在你无需[安装 Linux Mint][4] 就能够体验到 Cinnamon了。在这篇教程,我将会展示给你如何在 Ubuntu 18.04,16.04 和 14.04 上安装 Cinnamon。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 上安装 Cinnamon 之前,有一些事情需要你注意。有时候,安装的额外桌面环境可能会与你当前的桌面环境有冲突。可能导致会话,应用程序或功能等的崩溃。这就是为什么你需要在做这个决定时谨慎一点的原因。
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 上安装 Cinnamon 之前,有一些事情需要你注意。有时候,安装的额外桌面环境可能会与你当前的桌面环境有冲突。可能导致会话、应用程序或功能等的崩溃。这就是为什么你需要在做这个决定时谨慎一点的原因。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在 Ubuntu 上安装 Cinnamon 桌面环境
|
||||
|
||||
![如何在 Ubuntu 上安装 Cinnamon 桌面环境][5]
|
||||
|
||||
过去有一系列 Cinnamon team 为 Ubuntu 提供的官方 PPA,但现在都已经失效了。不过不用担心,还有一个非官方的 PPA,而且它运行的很完美。这个 PPA 里包含了最新的 Cinnamon 版本。
|
||||
过去有 Cinnamon 团队为 Ubuntu 提供的一系列的官方 PPA,但现在都已经失效了。不过不用担心,还有一个非官方的 PPA,而且它运行的很完美。这个 PPA 里包含了最新的 Cinnamon 版本。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository
|
||||
ppa:embrosyn/cinnamon
|
||||
sudo apt update && sudo apt install cinnamon
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下载的大小大概是 150 MB(如果我没记错的话)。这其中提供的 Nemo(Cinnamon 的文件管理器,基于Nautilus)和 Cinnamon 控制中心。这些东西提供了一个更加接近于 Linux Mint 的感觉。
|
||||
下载的大小大概是 150 MB(如果我没记错的话)。这其中提供的 Nemo(Cinnamon 的文件管理器,基于 Nautilus)和 Cinnamon 控制中心。这些东西提供了一个更加接近于 Linux Mint 的感觉。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 上使用 Cinnamon 桌面环境
|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon安装完成后,退出当前会话,在登陆界面,点击用户名旁边的 Ubuntu 符号:
|
||||
Cinnamon 安装完成后,退出当前会话,在登录界面,点击用户名旁边的 Ubuntu 符号:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -31,11 +33,11 @@ Cinnamon安装完成后,退出当前会话,在登陆界面,点击用户名
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在你应该已经登陆到有着 Cinnamon 桌面环境的 Ubuntu 中了。你还可以通过同样的方式再回到 Unity 桌面。这里有一张以 Cinnamon 做为桌面环境的 Ubuntu 桌面截图。
|
||||
现在你应该已经登录到有着 Cinnamon 桌面环境的 Ubuntu 中了。你还可以通过同样的方式再回到 Unity 桌面。这里有一张以 Cinnamon 做为桌面环境的 Ubuntu 桌面截图。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
看起来是不是像极了 Linux Mint。此外,我并没有发现任何有关 Cinnamon 和 Unity 的兼容性问题。在 Unity 和 Cinnamon 来回切换,他们也依旧工作的很完美。
|
||||
看起来是不是像极了 Linux Mint。此外,我并没有发现任何有关 Cinnamon 和 Unity 的兼容性问题。在 Unity 和 Cinnamon 来回切换,它们也依旧工作的很完美。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 从 Ubuntu 卸载 Cinnamon
|
||||
|
||||
@ -43,14 +45,12 @@ Cinnamon安装完成后,退出当前会话,在登陆界面,点击用户名
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt-get install ppa-purge
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成之后,使用下面的命令去移除 PPA:
|
||||
安装完成之后,使用下面的命令去移除该 PPA:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo ppa-purge ppa:embrosyn/cinnamon
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
更多的信息,我建议你去阅读 [如何从 Linux 移除 PPA][6] 这篇文章。
|
||||
@ -64,7 +64,7 @@ via: https://itsfoss.com/install-cinnamon-on-ubuntu/
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[dianbanjiu](https://github.com/dianbanjiu)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
132
published/20171124 How do groups work on Linux.md
Normal file
132
published/20171124 How do groups work on Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
|
||||
“用户组”在 Linux 上到底是怎么工作的?
|
||||
========
|
||||
|
||||
嗨!就在上周,我还自认为对 Linux 上的用户和组的工作机制了如指掌。我认为它们的关系是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 每个进程都属于一个用户(比如用户 `julia`)
|
||||
2. 当这个进程试图读取一个被某个组所拥有的文件时, Linux 会
|
||||
a. 先检查用户`julia` 是否有权限访问文件。(LCTT 译注:此处应该是指检查文件的所有者是否就是 `julia`)
|
||||
b. 检查 `julia` 属于哪些组,并进一步检查在这些组里是否有某个组拥有这个文件或者有权限访问这个文件。
|
||||
3. 如果上述 a、b 任一为真(或者“其它”位设为有权限访问),那么这个进程就有权限访问这个文件。
|
||||
|
||||
比如说,如果一个进程被用户 `julia` 拥有并且 `julia` 在`awesome` 组,那么这个进程就能访问下面这个文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
r--r--r-- 1 root awesome 6872 Sep 24 11:09 file.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然而上述的机制我并没有考虑得非常清楚,如果你硬要我阐述清楚,我会说进程可能会在**运行时**去检查 `/etc/group` 文件里是否有某些组拥有当前的用户。
|
||||
|
||||
### 然而这并不是 Linux 里“组”的工作机制
|
||||
|
||||
我在上个星期的工作中发现了一件有趣的事,事实证明我前面的理解错了,我对组的工作机制的描述并不准确。特别是 Linux **并不会**在进程每次试图访问一个文件时就去检查这个进程的用户属于哪些组。
|
||||
|
||||
我在读了《[Linux 编程接口][1]》这本书的第九章(“进程资格”)后才恍然大悟(这本书真是太棒了),这才是组真正的工作方式!我意识到之前我并没有真正理解用户和组是怎么工作的,我信心满满的尝试了下面的内容并且验证到底发生了什么,事实证明现在我的理解才是对的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 用户和组权限检查是怎么完成的
|
||||
|
||||
现在这些关键的知识在我看来非常简单! 这本书的第九章上来就告诉我如下事实:用户和组 ID 是**进程的属性**,它们是:
|
||||
|
||||
* 真实用户 ID 和组 ID;
|
||||
* 有效用户 ID 和组 ID;
|
||||
* 保存的 set-user-ID 和保存的 set-group-ID;
|
||||
* 文件系统用户 ID 和组 ID(特定于 Linux);
|
||||
* 补充的组 ID;
|
||||
|
||||
这说明 Linux **实际上**检查一个进程能否访问一个文件所做的组检查是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
* 检查一个进程的组 ID 和补充组 ID(这些 ID 就在进程的属性里,**并不是**实时在 `/etc/group` 里查找这些 ID)
|
||||
* 检查要访问的文件的访问属性里的组设置
|
||||
* 确定进程对文件是否有权限访问(LCTT 译注:即文件的组是否是以上的组之一)
|
||||
|
||||
通常当访问控制的时候使用的是**有效**用户/组 ID,而不是**真实**用户/组 ID。技术上来说当访问一个文件时使用的是**文件系统**的 ID,它们通常和有效用户/组 ID 一样。(LCTT 译注:这句话针对 Linux 而言。)
|
||||
|
||||
### 将一个用户加入一个组并不会将一个已存在的进程(的用户)加入那个组
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一个有趣的例子:如果我创建了一个新的组:`panda` 组并且将我自己(`bork`)加入到这个组,然后运行 `groups` 来检查我是否在这个组里:结果是我(`bork`)竟然不在这个组?!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
bork@kiwi~> sudo addgroup panda
|
||||
Adding group `panda' (GID 1001) ...
|
||||
Done.
|
||||
bork@kiwi~> sudo adduser bork panda
|
||||
Adding user `bork' to group `panda' ...
|
||||
Adding user bork to group panda
|
||||
Done.
|
||||
bork@kiwi~> groups
|
||||
bork adm cdrom sudo dip plugdev lpadmin sambashare docker lxd
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`panda` 并不在上面的组里!为了再次确定我们的发现,让我们建一个文件,这个文件被 `panda` 组拥有,看看我能否访问它。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ touch panda-file.txt
|
||||
$ sudo chown root:panda panda-file.txt
|
||||
$ sudo chmod 660 panda-file.txt
|
||||
$ cat panda-file.txt
|
||||
cat: panda-file.txt: Permission denied
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
好吧,确定了,我(`bork`)无法访问 `panda-file.txt`。这一点都不让人吃惊,我的命令解释器并没有将 `panda` 组作为补充组 ID,运行 `adduser bork panda` 并不会改变这一点。
|
||||
|
||||
### 那进程一开始是怎么得到用户的组的呢?
|
||||
|
||||
这真是个非常令人困惑的问题,对吗?如果进程会将组的信息预置到进程的属性里面,进程在初始化的时候怎么取到组的呢?很明显你无法给你自己指定更多的组(否则就会和 Linux 访问控制的初衷相违背了……)
|
||||
|
||||
有一点还是很清楚的:一个新的进程是怎么从我的命令行解释器(`/bash/fish`)里被**执行**而得到它的组的。(新的)进程将拥有我的用户 ID(`bork`),并且进程属性里还有很多组 ID。从我的命令解释器里执行的所有进程是从这个命令解释器里 `fork()` 而来的,所以这个新进程得到了和命令解释器同样的组。
|
||||
|
||||
因此一定存在一个“第一个”进程来把你的组设置到进程属性里,而所有由此进程而衍生的进程将都设置这些组。而那个“第一个”进程就是你的<ruby>登录程序<rt>login shell</rt></ruby>,在我的笔记本电脑上,它是由 `login` 程序(`/bin/login`)实例化而来。登录程序以 root 身份运行,然后调用了一个 C 的库函数 —— `initgroups` 来设置你的进程的组(具体来说是通过读取 `/etc/group` 文件),因为登录程序是以 root 运行的,所以它能设置你的进程的组。
|
||||
|
||||
### 让我们再登录一次
|
||||
|
||||
好了!假如说我们正处于一个登录程序中,而我又想刷新我的进程的组设置,从我们前面所学到的进程是怎么初始化组 ID 的,我应该可以通过再次运行登录程序来刷新我的进程组并启动一个新的登录命令!
|
||||
|
||||
让我们试试下边的方法:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo login bork
|
||||
$ groups
|
||||
bork adm cdrom sudo dip plugdev lpadmin sambashare docker lxd panda
|
||||
$ cat panda-file.txt # it works! I can access the file owned by `panda` now!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
当然,成功了!现在由登录程序衍生的程序的用户是组 `panda` 的一部分了!太棒了!这并不会影响我其他的已经在运行的登录程序(及其子进程),如果我真的希望“所有的”进程都能对 `panda` 组有访问权限。我必须完全的重启我的登录会话,这意味着我必须退出我的窗口管理器然后再重新登录。(LCTT 译注:即更新进程树的树根进程,这里是窗口管理器进程。)
|
||||
|
||||
### newgrp 命令
|
||||
|
||||
在 Twitter 上有人告诉我如果只是想启动一个刷新了组信息的命令解释器的话,你可以使用 `newgrp`(LCTT 译注:不启动新的命令解释器),如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo addgroup panda
|
||||
sudo adduser bork panda
|
||||
newgrp panda # starts a new shell, and you don't have to be root to run it!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以用 `sg panda bash` 来完成同样的效果,这个命令能启动一个`bash` 登录程序,而这个程序就有 `panda` 组。
|
||||
|
||||
### seduid 将设置有效用户 ID
|
||||
|
||||
其实我一直对一个进程如何以 `setuid root` 的权限来运行意味着什么有点似是而非。现在我知道了,事实上所发生的是:`setuid` 设置了
|
||||
“有效用户 ID”! 如果我(`julia`)运行了一个 `setuid root` 的进程( 比如 `passwd`),那么进程的**真实**用户 ID 将为 `julia`,而**有效**用户 ID 将被设置为 `root`。
|
||||
|
||||
`passwd` 需要以 root 权限来运行,但是它能看到进程的真实用户 ID 是 `julia` ,是 `julia` 启动了这个进程,`passwd` 会阻止这个进程修改除了 `julia` 之外的用户密码。
|
||||
|
||||
### 就是这些了!
|
||||
|
||||
在《[Linux 编程接口][1]》这本书里有很多 Linux 上一些功能的罕见使用方法以及 Linux 上所有的事物到底是怎么运行的详细解释,这里我就不一一展开了。那本书棒极了,我上面所说的都在该书的第九章,这章在 1300 页的书里只占了 17 页。
|
||||
|
||||
我最爱这本书的一点是我只用读 17 页关于用户和组是怎么工作的内容,而这区区 17 页就能做到内容完备、详实有用。我不用读完所有的 1300 页书就能得到有用的东西,太棒了!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://jvns.ca/blog/2017/11/20/groups/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Julia Evans][a]
|
||||
译者:[DavidChen](https://github.com/DavidChenLiang)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://jvns.ca/
|
||||
[1]:http://man7.org/tlpi/
|
||||
@ -1,65 +1,58 @@
|
||||
你没听说过的 Go 语言惊人优点
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
=========
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
来自 [https://github.com/ashleymcnamara/gophers][1] 的图稿
|
||||
*来自 [https://github.com/ashleymcnamara/gophers][1] 的图稿*
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中,我将讨论为什么你需要尝试一下 Go,以及应该从哪里学起。
|
||||
在这篇文章中,我将讨论为什么你需要尝试一下 Go 语言,以及应该从哪里学起。
|
||||
|
||||
Golang 是可能是最近几年里你经常听人说起的编程语言。尽管它在 2009 年已经发布,但它最近才开始流行起来。
|
||||
Go 语言是可能是最近几年里你经常听人说起的编程语言。尽管它在 2009 年已经发布了,但它最近才开始流行起来。
|
||||
|
||||
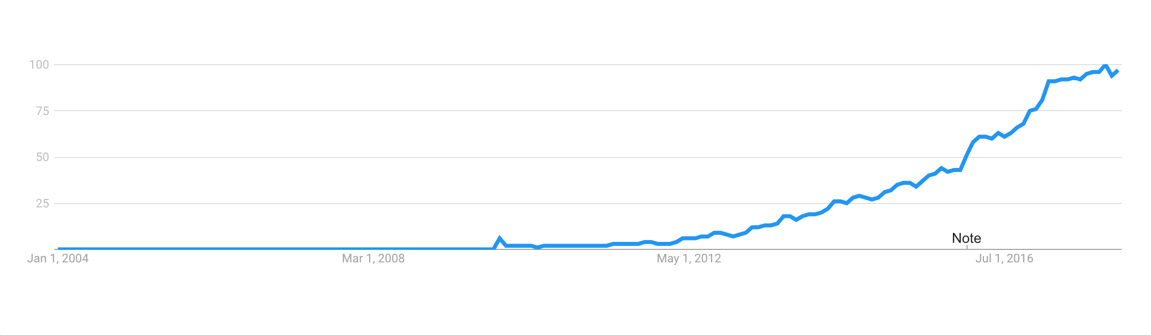
|
||||
|
||||
根据 Google 趋势,Golang 语言非常流行。
|
||||
*根据 Google 趋势,Go 语言非常流行。*
|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章不会讨论一些你经常看到的 Golang 的主要特性。
|
||||
这篇文章不会讨论一些你经常看到的 Go 语言的主要特性。
|
||||
|
||||
相反,我想向您介绍一些相当小众但仍然很重要的功能。在您决定尝试Go后,您才会知道这些功能。
|
||||
相反,我想向您介绍一些相当小众但仍然很重要的功能。只有在您决定尝试 Go 语言后,您才会知道这些功能。
|
||||
|
||||
这些都是表面上没有体现出来的惊人特性,但它们可以为您节省数周或数月的工作量。而且这些特性还可以使软件开发更加愉快。
|
||||
|
||||
阅读本文不需要任何语言经验,所以不比担心 Golang 对你来说是新的事物。如果你想了解更多,可以看看我在底部列出的一些额外的链接,。
|
||||
阅读本文不需要任何语言经验,所以不必担心你还不了解 Go 语言。如果你想了解更多,可以看看我在底部列出的一些额外的链接。
|
||||
|
||||
我们将讨论以下主题:
|
||||
|
||||
* GoDoc
|
||||
|
||||
* 静态代码分析
|
||||
|
||||
* 内置的测试和分析框架
|
||||
|
||||
* 竞争条件检测
|
||||
|
||||
* 学习曲线
|
||||
|
||||
* 反射(Reflection)
|
||||
|
||||
* Opinionatedness(专制独裁的 Go)
|
||||
|
||||
* 反射
|
||||
* Opinionatedness
|
||||
* 文化
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,这个列表不遵循任何特定顺序来讨论。
|
||||
|
||||
### GoDoc
|
||||
|
||||
Golang 非常重视代码中的文档,简洁也是如此。
|
||||
Go 语言非常重视代码中的文档,所以也很简洁。
|
||||
|
||||
[GoDoc][4] 是一个静态代码分析工具,可以直接从代码中创建漂亮的文档页面。GoDoc 的一个显着特点是它不使用任何其他的语言,如 JavaDoc,PHPDoc 或 JSDoc 来注释代码中的结构,只需要用英语。
|
||||
[GoDoc][4] 是一个静态代码分析工具,可以直接从代码中创建漂亮的文档页面。GoDoc 的一个显著特点是它不使用任何其他的语言,如 JavaDoc、PHPDoc 或 JSDoc 来注释代码中的结构,只需要用英语。
|
||||
|
||||
它使用从代码中获取的尽可能多的信息来概述、构造和格式化文档。它有多而全的功能,比如:交叉引用,代码示例以及一个指向版本控制系统仓库的链接。
|
||||
它使用从代码中获取的尽可能多的信息来概述、构造和格式化文档。它有多而全的功能,比如:交叉引用、代码示例,并直接链接到你的版本控制系统仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
而你需要做的只有添加一些好的,像 `// MyFunc transforms Foo into Bar` 这样子的注释,而这些注释也会反映在的文档中。你甚至可以添加一些通过网络接口或者在本地可以实际运行的 [代码示例][5]。
|
||||
而你需要做的只有添加一些像 `// MyFunc transforms Foo into Bar` 这样子的老牌注释,而这些注释也会反映在的文档中。你甚至可以添加一些通过网络界面或者在本地可以实际运行的 [代码示例][5]。
|
||||
|
||||
GoDoc 是 Go 的唯一文档引擎,供整个社区使用。这意味着用 Go 编写的每个库或应用程序都具有相同的文档格式。从长远来看,它可以帮你在浏览这些文档时节省大量时间。
|
||||
GoDoc 是 Go 的唯一文档引擎,整个社区都在使用。这意味着用 Go 编写的每个库或应用程序都具有相同的文档格式。从长远来看,它可以帮你在浏览这些文档时节省大量时间。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,这是我最近一个小项目的 GoDoc 页面:[pullkee — GoDoc][6]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 静态代码分析
|
||||
|
||||
Go 严重依赖于静态代码分析。例子包括 godoc 文档,gofmt 代码格式化,golint 代码风格统一,等等。
|
||||
Go 严重依赖于静态代码分析。例如用于文档的 [godoc][7],用于代码格式化的 [gofmt][8],用于代码风格的 [golint][9],等等。
|
||||
|
||||
其中有很多甚至全部包含在类似 [gometalinter][10] 的项目中,这些将它们全部组合成一个实用程序。
|
||||
它们是如此之多,甚至有一个总揽了它们的项目 [gometalinter][10] ,将它们组合成了单一的实用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
这些工具通常作为独立的命令行应用程序实现,并可轻松与任何编码环境集成。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -67,21 +60,21 @@ Go 严重依赖于静态代码分析。例子包括 godoc 文档,gofmt 代码
|
||||
|
||||
创建自己的分析器非常简单,因为 Go 有专门的内置包来解析和加工 Go 源码。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以从这个链接中了解到更多相关内容: [GothamGo Kickoff Meetup: Go Static Analysis Tools by Alan Donovan][11].
|
||||
你可以从这个链接中了解到更多相关内容: [GothamGo Kickoff Meetup: Alan Donovan 的 Go 静态分析工具][11]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 内置的测试和分析框架
|
||||
|
||||
您是否曾尝试为一个从头开始的 Javascript 项目选择测试框架?如果是这样,你可能会明白经历这种分析瘫痪的斗争。您可能也意识到您没有使用其中 80% 的框架。
|
||||
您是否曾尝试为一个从头开始的 JavaScript 项目选择测试框架?如果是这样,你或许会理解经历这种<ruby>过度分析<rt>analysis paralysis</rt></ruby>的痛苦。您可能也意识到您没有使用其中 80% 的框架。
|
||||
|
||||
一旦您需要进行一些可靠的分析,问题就会重复出现。
|
||||
|
||||
Go 附带内置测试工具,旨在简化和提高效率。它为您提供了最简单的 API,并做出最小的假设。您可以将它用于不同类型的测试,分析,甚至可以提供可执行代码示例。
|
||||
Go 附带内置测试工具,旨在简化和提高效率。它为您提供了最简单的 API,并做出最小的假设。您可以将它用于不同类型的测试、分析,甚至可以提供可执行代码示例。
|
||||
|
||||
它可以开箱即用地生成持续集成友好的输出,而且它的用法很简单,只需运行 `go test`。当然,它还支持高级功能,如并行运行测试,跳过标记代码,以及其他更多功能。
|
||||
它可以开箱即用地生成便于持续集成的输出,而且它的用法很简单,只需运行 `go test`。当然,它还支持高级功能,如并行运行测试,跳过标记代码,以及其他更多功能。
|
||||
|
||||
### 竞争条件检测
|
||||
|
||||
您可能已经了解了 Goroutines,它们在 Go 中用于实现并发代码执行。如果你未曾了解过,[这里][12]有一个非常简短的解释。
|
||||
您可能已经听说了 Goroutine,它们在 Go 中用于实现并发代码执行。如果你未曾了解过,[这里][12]有一个非常简短的解释。
|
||||
|
||||
无论具体技术如何,复杂应用中的并发编程都不容易,部分原因在于竞争条件的可能性。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -93,13 +86,13 @@ Go 附带内置测试工具,旨在简化和提高效率。它为您提供了
|
||||
|
||||
### 学习曲线
|
||||
|
||||
您可以在一个晚上学习所有 Go 的语言功能。我是认真的。当然,还有标准库,以及不同,更具体领域的最佳实践。但是两个小时就足以让你自信地编写一个简单的 HTTP 服务器或命令行应用程序。
|
||||
您可以在一个晚上学习**所有**的 Go 语言功能。我是认真的。当然,还有标准库,以及不同的,更具体领域的最佳实践。但是两个小时就足以让你自信地编写一个简单的 HTTP 服务器或命令行应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
Golang 拥有[出色的文档][14],大部分高级主题已经在博客上进行了介绍:[The Go Programming Language Blog][15]。
|
||||
Go 语言拥有[出色的文档][14],大部分高级主题已经在他们的博客上进行了介绍:[Go 编程语言博客][15]。
|
||||
|
||||
比起 Java(以及 Java 家族的语言),Javascript,Ruby,Python 甚至 PHP,你可以更轻松地把 Go 语言带到你的团队中。由于环境易于设置,您的团队在完成第一个生产代码之前需要进行的投资要小得多。
|
||||
比起 Java(以及 Java 家族的语言)、Javascript、Ruby、Python 甚至 PHP,你可以更轻松地把 Go 语言带到你的团队中。由于环境易于设置,您的团队在完成第一个生产代码之前需要进行的投资要小得多。
|
||||
|
||||
### 反射(Reflection)
|
||||
### 反射
|
||||
|
||||
代码反射本质上是一种隐藏在编译器下并访问有关语言结构的各种元信息的能力,例如变量或函数。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -107,19 +100,19 @@ Golang 拥有[出色的文档][14],大部分高级主题已经在博客上进
|
||||
|
||||
此外,Go [没有实现一个名为泛型的概念][16],这使得以抽象方式处理多种类型更具挑战性。然而,由于泛型带来的复杂程度,许多人认为不实现泛型对语言实际上是有益的。我完全同意。
|
||||
|
||||
根据 Go 的理念(这是一个单独的主题),您应该努力不要过度设计您的解决方案。这也适用于动态类型编程。尽可能坚持使用静态类型,并在确切知道要处理的类型时使用接口(interfaces)。接口在 Go 中非常强大且无处不在。
|
||||
根据 Go 的理念(这是一个单独的主题),您应该努力不要过度设计您的解决方案。这也适用于动态类型编程。尽可能坚持使用静态类型,并在确切知道要处理的类型时使用<ruby>接口<rt>interface</rt></ruby>。接口在 Go 中非常强大且无处不在。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,仍然存在一些情况,你无法知道你处理的数据类型。一个很好的例子是 JSON。您可以在应用程序中来回转换所有类型的数据。字符串,缓冲区,各种数字,嵌套结构等。
|
||||
但是,仍然存在一些情况,你无法知道你处理的数据类型。一个很好的例子是 JSON。您可以在应用程序中来回转换所有类型的数据。字符串、缓冲区、各种数字、嵌套结构等。
|
||||
|
||||
为了解决这个问题,您需要一个工具来检查运行时的数据并根据其类型和结构采取不同行为。反射(Reflect)可以帮到你。Go 拥有一流的反射包,使您的代码能够像 Javascript 这样的语言一样动态。
|
||||
为了解决这个问题,您需要一个工具来检查运行时的数据并根据其类型和结构采取不同行为。<ruby>反射<rt>Reflect</rt></ruby>可以帮到你。Go 拥有一流的反射包,使您的代码能够像 Javascript 这样的语言一样动态。
|
||||
|
||||
一个重要的警告是知道你使用它所带来的代价 - 并且只有知道在没有更简单的方法时才使用它。
|
||||
一个重要的警告是知道你使用它所带来的代价 —— 并且只有知道在没有更简单的方法时才使用它。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在这里阅读更多相关信息: [反射的法则 — Go 博客][18].
|
||||
|
||||
您还可以在此处阅读 JSON 包源码中的一些实际代码: [src/encoding/json/encode.go — Source Code][19]
|
||||
|
||||
### Opinionatedness
|
||||
### Opinionatedness(专制独裁的 Go)
|
||||
|
||||
顺便问一下,有这样一个单词吗?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -127,9 +120,9 @@ Golang 拥有[出色的文档][14],大部分高级主题已经在博客上进
|
||||
|
||||
这有时候基本上让我卡住了。我需要花时间思考这些事情而不是编写代码并满足用户。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我应该注意到我完全可以得到这些惯例的来源,它总是来源于你或者你的团队。无论如何,即使是一群经验丰富的 Javascript 开发人员也可以轻松地发现自己拥有完全不同的工具和范例的大部分经验,以实现相同的结果。
|
||||
首先,我应该注意到我完全知道这些惯例的来源,它总是来源于你或者你的团队。无论如何,即使是一群经验丰富的 Javascript 开发人员也很容易发现他们在实现相同的结果时,而大部分的经验却是在完全不同的工具和范例上。
|
||||
|
||||
这导致整个团队中分析的瘫痪,并且使得个体之间更难以相互协作。
|
||||
这导致整个团队中出现过度分析,并且使得个体之间更难以相互协作。
|
||||
|
||||
嗯,Go 是不同的。即使您对如何构建和维护代码有很多强烈的意见,例如:如何命名,要遵循哪些结构模式,如何更好地实现并发。但你只有一个每个人都遵循的风格指南。你只有一个内置在基本工具链中的测试框架。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -141,11 +134,11 @@ Golang 拥有[出色的文档][14],大部分高级主题已经在博客上进
|
||||
|
||||
人们说,每当你学习一门新的口语时,你也会沉浸在说这种语言的人的某些文化中。因此,您学习的语言越多,您可能会有更多的变化。
|
||||
|
||||
编程语言也是如此。无论您将来如何应用新的编程语言,它总能给的带来新的编程视角或某些特别的技术。
|
||||
编程语言也是如此。无论您将来如何应用新的编程语言,它总能给你带来新的编程视角或某些特别的技术。
|
||||
|
||||
无论是函数式编程,模式匹配(pattern matching)还是原型继承(prototypal inheritance)。一旦你学会了它们,你就可以随身携带这些编程思想,这扩展了你作为软件开发人员所拥有的问题解决工具集。它们也改变了你阅读高质量代码的方式。
|
||||
无论是函数式编程,<ruby>模式匹配<rt>pattern matching</rt></ruby>还是<ruby>原型继承<rt>prototypal inheritance</rt></ruby>。一旦你学会了它们,你就可以随身携带这些编程思想,这扩展了你作为软件开发人员所拥有的问题解决工具集。它们也改变了你阅读高质量代码的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
而 Go 在方面有一项了不起的财富。Go 文化的主要支柱是保持简单,脚踏实地的代码,而不会产生许多冗余的抽象概念,并将可维护性放在首位。大部分时间花费在代码的编写工作上,而不是在修补工具和环境或者选择不同的实现方式上,这也是 Go文化的一部分。
|
||||
而 Go 在这方面有一项了不起的财富。Go 文化的主要支柱是保持简单,脚踏实地的代码,而不会产生许多冗余的抽象概念,并将可维护性放在首位。大部分时间花费在代码的编写工作上,而不是在修补工具和环境或者选择不同的实现方式上,这也是 Go 文化的一部分。
|
||||
|
||||
Go 文化也可以总结为:“应当只用一种方法去做一件事”。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -161,12 +154,11 @@ Go 文化也可以总结为:“应当只用一种方法去做一件事”。
|
||||
|
||||
这不是 Go 的所有惊人的优点的完整列表,只是一些被人低估的特性。
|
||||
|
||||
请尝试一下从 [Go 之旅(A Tour of Go)][20]来开始学习 Go,这将是一个令人惊叹的开始。
|
||||
请尝试一下从 [Go 之旅][20] 来开始学习 Go,这将是一个令人惊叹的开始。
|
||||
|
||||
如果您想了解有关 Go 的优点的更多信息,可以查看以下链接:
|
||||
|
||||
* [你为什么要学习 Go? - Keval Patel][2]
|
||||
|
||||
* [告别Node.js - TJ Holowaychuk][3]
|
||||
|
||||
并在评论中分享您的阅读感悟!
|
||||
@ -175,30 +167,16 @@ Go 文化也可以总结为:“应当只用一种方法去做一件事”。
|
||||
|
||||
不断为您的工作寻找最好的工具!
|
||||
|
||||
* * *
|
||||
|
||||
If you like this article, please consider following me for more, and clicking on those funny green little hands right below this text for sharing. 👏👏👏
|
||||
|
||||
Check out my [Github][21] and follow me on [Twitter][22]!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
Software Engineer and Traveler. Coding for fun. Javascript enthusiast. Tinkering with Golang. A lot into SOA and Docker. Architect at Velvica.
|
||||
|
||||
------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
via: https://medium.freecodecamp.org/here-are-some-amazing-advantages-of-go-that-you-dont-hear-much-about-1af99de3b23a
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kirill Rogovoy][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/imquanquan)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[imquanquan](https://github.com/imquanquan)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:
|
||||
[a]:https://twitter.com/krogovoy
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/ashleymcnamara/gophers
|
||||
[2]:https://medium.com/@kevalpatel2106/why-should-you-learn-go-f607681fad65
|
||||
[3]:https://medium.com/@tjholowaychuk/farewell-node-js-4ba9e7f3e52b
|
||||
181
published/20180516 Manipulating Directories in Linux.md
Normal file
181
published/20180516 Manipulating Directories in Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,181 @@
|
||||
在 Linux 上操作目录
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> 让我们继续学习一下 Linux 文件系统的树形结构,并展示一下如何在其中创建你的目录。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不熟悉本系列(以及 Linux),[请查看我们的第一部分][1]。在那篇文章中,我们贯穿了 Linux 文件系统的树状结构(或者更确切地说是<ruby>文件层次结构标准<rt>File Hierarchy Standard</rt></ruby>,FHS)。我建议你仔细阅读,确保你理解自己能安全的做哪些操作。因为这一次,我将向你展示目录操作的魅力。
|
||||
|
||||
### 新建目录
|
||||
|
||||
在破坏之前,先让我们来创建。首先,打开一个终端窗口并使用命令 `mkdir` 创建一个新目录,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir <directoryname>
|
||||
```
|
||||
如果你只输入了目录名称,该目录将显示在您当前所在目录中。如果你刚刚打开一个终端,你当前位置为你的家目录。在这个例子中,我们展示了将要创建的目录与你当前所处位置的关系:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ pwd # 告知你当前所在位置(参见第一部分)
|
||||
/home/<username>
|
||||
$ mkdir newdirectory # 创建 /home/<username>/newdirectory
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(注:你不用输入 `#` 后面的文本。`#` 后面的文本为注释内容,用于解释发生了什么。它会被 shell 忽略,不会被执行)。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在当前位置中已经存在的某个目录下创建新的目录,方法是在命令行中指定它:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir Documents/Letters
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这将在 `Documents` 目录中创建 `Letters` 目录。
|
||||
|
||||
你还可以在路径中使用 `..` 在当前目录的上一级目录中创建目录。假设你进入刚刚创建的 `Documents/Letters/` 目录,并且想要创建`Documents/Memos/` 目录。你可以这样做:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd Documents/Letters # 进入到你刚刚创建的 Letters/ 目录
|
||||
mkdir ../Memos
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
同样,以上所有内容都是相对于你当前的位置做的。这就是使用了相对路径。
|
||||
|
||||
你还可以使用目录的绝对路径:这意味着告诉 `mkdir` 命令将目录放在和根目录(`/`)有关的位置:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir /home/<username>/Documents/Letters
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的命令中将 `<username>` 更改为你的用户名,这相当于从你的主目录执行 `mkdir Documents/Letters`,通过使用绝对路径你可以在目录树中的任何位置完成这项工作。
|
||||
|
||||
无论你使用相对路径还是绝对路径,只要命令成功执行,`mkdir` 将静默的创建新目录,而没有任何明显的反馈。只有当遇到某种问题时,`mkdir`才会在你敲下回车键后打印一些反馈。
|
||||
|
||||
与大多数其他命令行工具一样,`mkdir` 提供了几个有趣的选项。 `-p` 选项特别有用,因为它允许你嵌套创建目录,即使目录不存在也可以。例如,要在 `Documents/` 中创建一个目录存放写给妈妈的信,你可以这样做:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir -p Documents/Letters/Family/Mom
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`mkdir` 会创建 `Mom/` 之上的整个目录分支,并且也会创建 `Mom/` 目录,无论其上的目录在你敲入该命令时是否已经存在。
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以用空格来分隔目录名,来同时创建几个目录:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir Letters Memos Reports
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这将在当前目录下创建目录 `Letters`、`Memos` 和 `Reports`。
|
||||
|
||||
### 目录名中可怕的空格
|
||||
|
||||
……这带来了目录名称中关于空格的棘手问题。你能在目录名中使用空格吗?是的你可以。那么建议你使用空格吗?不,绝对不建议。空格使一切变得更加复杂,并且可能是危险的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
假设您要创建一个名为 `letters mom/` 的目录。如果你不知道如何更好处理,你可能会输入:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir letters mom
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
但这是错误的!错误的!错误的!正如我们在上面介绍的,这将创建两个目录 `letters/` 和 `mom/`,而不是一个目录 `letters mom/`。
|
||||
|
||||
得承认这是一个小麻烦:你所要做的就是删除这两个目录并重新开始,这没什么大不了。
|
||||
|
||||
可是等等!删除目录可是个危险的操作。想象一下,你使用图形工具[Dolphin][2] 或 [Nautilus][3] 创建了目录 `letters mom/`。如果你突然决定从终端删除目录 `letters mom`,并且您在同一目录下有另一个名为 `letters` 的目录,并且该目录中包含重要的文档,结果你为了删除错误的目录尝试了以下操作:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
rmdir letters mom
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你将会有删除目录 letters 的风险。这里说“风险”,是因为幸运的是`rmdir` 这条用于删除目录的指令,有一个内置的安全措施,如果你试图删除一个非空目录时,它会发出警告。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,下面这个:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
rm -Rf letters mom
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(注:这是删除目录及其内容的一种非常标准的方式)将完全删除 `letters/` 目录,甚至永远不会告诉你刚刚发生了什么。)
|
||||
|
||||
`rm` 命令用于删除文件和目录。当你将它与选项 `-R`(递归删除)和 `-f`(强制删除)一起使用时,它会深入到目录及其子目录中,删除它们包含的所有文件,然后删除子目录本身,然后它将删除所有顶层目录中的文件,再然后是删除目录本身。
|
||||
|
||||
`rm -Rf` 是你必须非常小心处理的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
我的建议是,你可以使用下划线来代替空格,但如果你仍然坚持使用空格,有两种方法可以使它们起作用。您可以使用单引号或双引号,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir 'letters mom'
|
||||
mkdir "letters dad"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
或者,你可以转义空格。有些字符对 shell 有特殊意义。正如你所见,空格用于在命令行上分隔选项和参数。 “分离选项和参数”属于“特殊含义”范畴。当你想让 shell 忽略一个字符的特殊含义时,你需要转义,你可以在它前面放一个反斜杠(`\`)如:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir letters\ mom
|
||||
mkdir letter\ dad
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
还有其他特殊字符需要转义,如撇号或单引号(`'`),双引号(`“`)和&符号(`&`):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir mom\ \&\ dad\'s\ letters
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我知道你在想什么:如果反斜杠有一个特殊的含义(即告诉 shell 它必须转义下一个字符),这也使它成为一个特殊的字符。然后,你将如何转义转义字符(`\`)?
|
||||
|
||||
事实证明,你转义任何其他特殊字符都是同样的方式:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir special\\characters
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这将生成一个名为 `special\characters/` 的目录。
|
||||
|
||||
感觉困惑?当然。这就是为什么你应该避免在目录名中使用特殊字符,包括空格。
|
||||
|
||||
以防误操作你可以参考下面这个记录特殊字符的列表。(LCTT 译注:此处原文链接丢失。)
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
* 使用 `mkdir <directory name>` 创建新目录。
|
||||
* 使用 `rmdir <directory name>` 删除目录(仅在目录为空时才有效)。
|
||||
* 使用 `rm -Rf <directory name>` 来完全删除目录及其内容 —— 请务必谨慎使用。
|
||||
* 使用相对路径创建相对于当前目录的目录: `mkdir newdir`。
|
||||
* 使用绝对路径创建相对于根目录(`/`)的目录: `mkdir /home/<username>/newdir`。
|
||||
* 使用 `..` 在当前目录的上级目录中创建目录: `mkdir ../newdir`。
|
||||
* 你可以通过在命令行上使用空格分隔目录名来创建多个目录: `mkdir onedir twodir threedir`。
|
||||
* 同时创建多个目录时,你可以混合使用相对路径和绝对路径: `mkdir onedir twodir /home/<username>/threedir`。
|
||||
* 在目录名称中使用空格和特殊字符真的会让你很头疼,你最好不要那样做。
|
||||
|
||||
有关更多信息,您可以查看 `mkdir`、`rmdir` 和 `rm` 的手册:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
man mkdir
|
||||
man rmdir
|
||||
man rm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
要退出手册页,请按键盘 `q` 键。
|
||||
|
||||
### 下次预告
|
||||
|
||||
在下一部分中,你将学习如何创建、修改和删除文件,以及你需要了解的有关权限和特权的所有信息!
|
||||
|
||||
通过 Linux 基金会和 edX 免费提供的[“Introduction to Linux”][4]课程了解有关Linux的更多信息。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.linux.com/blog/learn/2018/5/manipulating-directories-linux
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Paul Brown][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[way-ww](https://github.com/way-ww)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.linux.com/users/bro66
|
||||
[1]:https://linux.cn/article-9798-1.html
|
||||
[2]:https://userbase.kde.org/Dolphin
|
||||
[3]:https://projects-old.gnome.org/nautilus/screenshots.html
|
||||
[4]:https://training.linuxfoundation.org/linux-courses/system-administration-training/introduction-to-linux
|
||||
@ -1,80 +1,84 @@
|
||||
这 7 个 Python 库让你写出更易维护的代码
|
||||
让 Python 代码更易维护的七种武器
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
> 检查你的代码的质量,通过这些外部库使其更易维护。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> 可读性很重要。
|
||||
> — [Python 之禅(The Zen of Python)][1], Tim Peters
|
||||
> — <ruby>[Python 之禅][1]<rt>The Zen of Python</rt></ruby>,Tim Peters
|
||||
|
||||
尽管很多项目一开始的时候就有可读性和编码标准的要求,但随着项目进入“维护模式”,这些要求都会变得虎头蛇尾。然而,在代码库中保持一致的代码风格和测试标准能够显著减轻维护的压力,也能确保新的开发者能够快速了解项目的情况,同时能更好地保持应用程序的运行良好。
|
||||
随着软件项目进入“维护模式”,对可读性和编码标准的要求很容易落空(甚至从一开始就没有建立过那些标准)。然而,在代码库中保持一致的代码风格和测试标准能够显著减轻维护的压力,也能确保新的开发者能够快速了解项目的情况,同时能更好地全程保持应用程序的质量。
|
||||
|
||||
使用外部库来检查代码的质量不失为保护项目未来可维护性的一个好方法。以下会推荐一些我们最喜爱的[检查代码][2](包括检查 PEP 8 和其它代码风格错误)的库,用它们来强制保持代码风格一致,并确保在项目成熟时有一个可接受的测试覆盖率。
|
||||
|
||||
### 检查你的代码风格
|
||||
|
||||
使用外部库来检查代码运行情况不失为保护项目未来可维护性的一个好方法。以下会推荐一些我们最喜爱的[检查代码][2](包括检查 PEP 8 和其它代码风格错误)的库,用它们来强制保持代码风格一致,并确保在项目成熟时有一个可接受的测试覆盖率。
|
||||
[PEP 8][3] 是 Python 代码风格规范,它规定了类似行长度、缩进、多行表达式、变量命名约定等内容。尽管你的团队自身可能也会有稍微不同于 PEP 8 的代码风格规范,但任何代码风格规范的目标都是在代码库中强制实施一致的标准,使代码的可读性更强、更易于维护。下面三个库就可以用来帮助你美化代码。
|
||||
|
||||
[PEP 8][3]是Python代码风格规范,规定了行长度,缩进,多行表达式、变量命名约定等内容。尽管你的团队自身可能也会有不同于 PEP 8 的代码风格规范,但任何代码风格规范的目标都是在代码库中强制实施一致的标准,使代码的可读性更强、更易于维护。下面三个库就可以用来帮助你美化代码。
|
||||
#### 1、 Pylint
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1\. Pylint
|
||||
[Pylint][4] 是一个检查违反 PEP 8 规范和常见错误的库。它在一些流行的[编辑器和 IDE][5] 中都有集成,也可以单独从命令行运行。
|
||||
|
||||
[Pylint][4] 是一个检查违反 PEP 8 规范和常见错误的库。它在一些流行的编辑器和 IDE 中都有集成,也可以单独从命令行运行。
|
||||
|
||||
执行 `pip install pylint`安装 Pylint 。然后运行 `pylint [options] path/to/dir` 或者 `pylint [options] path/to/module.py` 就可以在命令行中使用 Pylint,它会向控制台输出代码中违反规范和出现错误的地方。
|
||||
执行 `pip install pylint` 安装 Pylint 。然后运行 `pylint [options] path/to/dir` 或者 `pylint [options] path/to/module.py` 就可以在命令行中使用 Pylint,它会向控制台输出代码中违反规范和出现错误的地方。
|
||||
|
||||
你还可以使用 `pylintrc` [配置文件][6]来自定义 Pylint 对哪些代码错误进行检查。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2\. Flake8
|
||||
#### 2、 Flake8
|
||||
|
||||
对 [Flake8][7] 的描述是“将 PEP 8、Pyflakes(类似 Pylint)、McCabe(代码复杂性检查器)、第三方插件整合到一起,以检查 Python 代码风格和质量的一个 Python 工具”。
|
||||
[Flake8][7] 是“将 PEP 8、Pyflakes(类似 Pylint)、McCabe(代码复杂性检查器)和第三方插件整合到一起,以检查 Python 代码风格和质量的一个 Python 工具”。
|
||||
|
||||
执行 `pip install flake8` 安装 flake8 ,然后执行 `flake8 [options] path/to/dir` 或者 `flake8 [options] path/to/module.py` 可以查看报出的错误和警告。
|
||||
|
||||
和 Pylint 类似,Flake8 允许通过[配置文件][8]来自定义检查的内容。它有非常清晰的文档,包括一些有用的[提交钩子][9],可以将自动检查代码纳入到开发工作流程之中。
|
||||
|
||||
Flake8 也允许集成到一些流行的编辑器和 IDE 当中,但在文档中并没有详细说明。要将 Flake8 集成到喜欢的编辑器或 IDE 中,可以搜索插件(例如 [Sublime Text 的 Flake8 插件][10])。
|
||||
Flake8 也可以集成到一些流行的编辑器和 IDE 当中,但在文档中并没有详细说明。要将 Flake8 集成到喜欢的编辑器或 IDE 中,可以搜索插件(例如 [Sublime Text 的 Flake8 插件][10])。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3\. Isort
|
||||
#### 3、 Isort
|
||||
|
||||
[Isort][11] 这个库能将你在项目中导入的库按字母顺序,并将其[正确划分为不同部分][12](例如标准库、第三方库,自建的库等)。这样提高了代码的可读性,并且可以在导入的库较多的时候轻松找到各个库。
|
||||
[Isort][11] 这个库能将你在项目中导入的库按字母顺序排序,并将其[正确划分为不同部分][12](例如标准库、第三方库、自建的库等)。这样提高了代码的可读性,并且可以在导入的库较多的时候轻松找到各个库。
|
||||
|
||||
执行 `pip install isort` 安装 isort,然后执行 `isort path/to/module.py` 就可以运行了。文档中还提供了更多的配置项,例如通过配置 `.isort.cfg` 文件来决定 isort 如何处理一个库的多行导入。
|
||||
执行 `pip install isort` 安装 isort,然后执行 `isort path/to/module.py` 就可以运行了。[文档][13]中还提供了更多的配置项,例如通过[配置][14] `.isort.cfg` 文件来决定 isort 如何处理一个库的多行导入。
|
||||
|
||||
和 Flake8、Pylint 一样,isort 也提供了将其与流行的[编辑器和 IDE][15] 集成的插件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 共享代码风格
|
||||
### 分享你的代码风格
|
||||
|
||||
每次文件发生变动之后都用命令行手动检查代码是一件痛苦的事,你可能也不太喜欢通过运行 IDE 中某个插件来实现这个功能。同样地,你的同事可能会用不同的代码检查方式,也许他们的编辑器中也没有安装插件,甚至自己可能也不会严格检查代码和按照警告来更正代码。总之,你共享的代码库将会逐渐地变得混乱且难以阅读。
|
||||
每次文件发生变动之后都用命令行手动检查代码是一件痛苦的事,你可能也不太喜欢通过运行 IDE 中某个插件来实现这个功能。同样地,你的同事可能会用不同的代码检查方式,也许他们的编辑器中也没有那种插件,甚至你自己可能也不会严格检查代码和按照警告来更正代码。总之,你分享出来的代码库将会逐渐地变得混乱且难以阅读。
|
||||
|
||||
一个很好的解决方案是使用一个库,自动将代码按照 PEP 8 规范进行格式化。我们推荐的三个库都有不同的自定义级别来控制如何格式化代码。其中有一些设置较为特殊,例如 Pylint 和 Flake8 ,你需要先行测试,看看是否有你无法忍受蛋有不能修改的默认配置。
|
||||
一个很好的解决方案是使用一个库,自动将代码按照 PEP 8 规范进行格式化。我们推荐的三个库都有不同的自定义级别来控制如何格式化代码。其中有一些设置较为特殊,例如 Pylint 和 Flake8 ,你需要先行测试,看看是否有你无法忍受但又不能修改的默认配置。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4\. Autopep8
|
||||
#### 4、 Autopep8
|
||||
|
||||
[Autopep8][16] 可以自动格式化指定的模块中的代码,包括重新缩进行,修复缩进,删除多余的空格,并重构常见的比较错误(例如布尔值和 `None` 值)。你可以查看文档中完整的[更正列表][17]。
|
||||
[Autopep8][16] 可以自动格式化指定的模块中的代码,包括重新缩进行、修复缩进、删除多余的空格,并重构常见的比较错误(例如布尔值和 `None` 值)。你可以查看文档中完整的[更正列表][17]。
|
||||
|
||||
运行 `pip install --upgrade autopep8` 安装 autopep8。然后执行 `autopep8 --in-place --aggressive --aggressive <filename>` 就可以重新格式化你的代码。`aggressive` 标记的数量表示 auotopep8 在代码风格控制上有多少控制权。在这里可以详细了解 [aggressive][18] 选项。
|
||||
运行 `pip install --upgrade autopep8` 安装 Autopep8。然后执行 `autopep8 --in-place --aggressive --aggressive <filename>` 就可以重新格式化你的代码。`aggressive` 选项的数量表示 Auotopep8 在代码风格控制上有多少控制权。在这里可以详细了解 [aggressive][18] 选项。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5\. Yapf
|
||||
#### 5、 Yapf
|
||||
|
||||
[Yapf][19] 是另一种有自己的[配置项][20]列表的重新格式化代码的工具。它与 autopep8 的不同之处在于它不仅会指出代码中违反 PEP 8 规范的地方,还会对没有违反 PEP 8 但代码风格不一致的地方重新格式化,旨在令代码的可读性更强。
|
||||
[Yapf][19] 是另一种有自己的[配置项][20]列表的重新格式化代码的工具。它与 Autopep8 的不同之处在于它不仅会指出代码中违反 PEP 8 规范的地方,还会对没有违反 PEP 8 但代码风格不一致的地方重新格式化,旨在令代码的可读性更强。
|
||||
|
||||
执行`pip install yapf` 安装 Yapf,然后执行 `yapf [options] path/to/dir` 或 `yapf [options] path/to/module.py` 可以对代码重新格式化。
|
||||
执行 `pip install yapf` 安装 Yapf,然后执行 `yapf [options] path/to/dir` 或 `yapf [options] path/to/module.py` 可以对代码重新格式化。[定制选项][20]的完整列表在这里。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6\. Black
|
||||
#### 6、 Black
|
||||
|
||||
[Black][21] 在代码检查工具当中算是比较新的一个。它与 autopep8 和 Yapf 类似,但限制较多,没有太多的自定义选项。这样的好处是你不需要去决定使用怎么样的代码风格,让 black 来给你做决定就好。你可以在这里查阅 black 的[自定义选项][22]以及[如何在配置文件中对其进行设置][23]。
|
||||
[Black][21] 在代码检查工具当中算是比较新的一个。它与 Autopep8 和 Yapf 类似,但限制较多,没有太多的自定义选项。这样的好处是你不需要去决定使用怎么样的代码风格,让 Black 来给你做决定就好。你可以在这里查阅 Black [有限的自定义选项][22]以及[如何在配置文件中对其进行设置][23]。
|
||||
|
||||
Black 依赖于 Python 3.6+,但它可以格式化用 Python 2 编写的代码。执行 `pip install black` 安装 black,然后执行 `black path/to/dir` 或 `black path/to/module.py` 就可以使用 black 优化你的代码。
|
||||
Black 依赖于 Python 3.6+,但它可以格式化用 Python 2 编写的代码。执行 `pip install black` 安装 Black,然后执行 `black path/to/dir` 或 `black path/to/module.py` 就可以使用 Black 优化你的代码。
|
||||
|
||||
### 检查你的测试覆盖率
|
||||
|
||||
如果你正在进行测试工作,你需要确保提交到代码库的新代码都已经测试通过,并且不会降低测试覆盖率。虽然测试覆盖率不是衡量测试有效性和充分性的唯一指标,但它是确保项目遵循基本测试标准的一种方法。对于计算测试覆盖率,我们推荐使用 Coverage 这个库。
|
||||
如果你正在进行编写测试,你需要确保提交到代码库的新代码都已经测试通过,并且不会降低测试覆盖率。虽然测试覆盖率不是衡量测试有效性和充分性的唯一指标,但它是确保项目遵循基本测试标准的一种方法。对于计算测试覆盖率,我们推荐使用 Coverage 这个库。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 7\. Coverage
|
||||
#### 7、 Coverage
|
||||
|
||||
[Coverage][24] 有数种显示测试覆盖率的方式,包括将结果输出到控制台或 HTML 页面,并指出哪些具体哪些地方没有被覆盖到。你可以通过配置文件自定义 Coverage 检查的内容,让你更方便使用。
|
||||
[Coverage][24] 有数种显示测试覆盖率的方式,包括将结果输出到控制台或 HTML 页面,并指出哪些具体哪些地方没有被覆盖到。你可以通过[配置文件][25]自定义 Coverage 检查的内容,让你更方便使用。
|
||||
|
||||
执行 `pip install coverage` 安装 Converage 。然后执行 `coverage [path/to/module.py] [args]` 可以运行程序并查看输出结果。如果要查看哪些代码行没有被覆盖,执行 `coverage report -m` 即可。
|
||||
|
||||
持续集成(Continuous integration, CI)是在合并和部署代码之前自动检查代码风格错误和测试覆盖率最小值的过程。很多免费或付费的工具都可以用于执行这项工作,具体的过程不在本文中赘述,但 CI 过程是令代码更易读和更易维护的重要步骤,关于这一部分可以参考 [Travis CI][26] 和 [Jenkins][27]。
|
||||
### 持续集成工具
|
||||
|
||||
<ruby>持续集成<rt>Continuous integration</rt></ruby>(CI)是在合并和部署代码之前自动检查代码风格错误和测试覆盖率最小值的过程。很多免费或付费的工具都可以用于执行这项工作,具体的过程不在本文中赘述,但 CI 过程是令代码更易读和更易维护的重要步骤,关于这一部分可以参考 [Travis CI][26] 和 [Jenkins][27]。
|
||||
|
||||
以上这些只是用于检查 Python 代码的各种工具中的其中几个。如果你有其它喜爱的工具,欢迎在评论中分享。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -85,7 +89,7 @@ via: https://opensource.com/article/18/7/7-python-libraries-more-maintainable-co
|
||||
作者:[Jeff Triplett][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[HankChow](https://github.com/HankChow)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,12 @@
|
||||
[已解决] Ubuntu 中的 “sub process usr bin dpkg returned an error code 1” 错误
|
||||
怎样解决 Ubuntu 中的 “sub process usr bin dpkg returned an error code 1” 错误
|
||||
======
|
||||
如果你在 Ubuntu Linux 上安装软件时遇到 “sub process usr bin dpkg returned an error code 1”,请按照以下步骤进行修复。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 和其他基于 Debian 的发行版中的一个常见问题是已经损坏的包。你尝试更新系统或安装新软件包时遇到类似 “Sub-process /usr/bin/dpkg returned an error code” 的错误。
|
||||
> 如果你在 Ubuntu Linux 上安装软件时遇到 “sub process usr bin dpkg returned an error code 1”,请按照以下步骤进行修复。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 和其他基于 Debian 的发行版中的一个常见问题是已经损坏的包。你尝试更新系统或安装新软件包时会遇到类似 “Sub-process /usr/bin/dpkg returned an error code” 的错误。
|
||||
|
||||
这就是前几天发生在我身上的事。我试图在 Ubuntu 中安装一个电台程序时,它给我了这个错误:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Unpacking python-gst-1.0 (1.6.2-1build1) ...
|
||||
Selecting previously unselected package radiotray.
|
||||
@ -30,11 +32,11 @@ E: Sub-process /usr/bin/dpkg returned an error code (1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这里最后三行非常重要。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Errors were encountered while processing:
|
||||
polar-bookshelf
|
||||
E: Sub-process /usr/bin/dpkg returned an error code (1)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
它告诉我 polar-bookshelf 包引发了问题。这可能对你如何修复这个错误至关重要。
|
||||
@ -45,59 +47,59 @@ E: Sub-process /usr/bin/dpkg returned an error code (1)
|
||||
|
||||
让我们尝试修复这个损坏的错误包。我将展示几种你可以逐一尝试的方法。最初的那些易于使用,几乎不用动脑子。
|
||||
|
||||
你应该尝试运行 sudo apt update,接着尝试安装新的包或尝试升级这里讨论的每个包。
|
||||
在试了这里讨论的每一种方法之后,你应该尝试运行 `sudo apt update`,接着尝试安装新的包或升级。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 方法 1:重新配包数据库
|
||||
|
||||
你可以尝试的第一种方法是重新配置包数据库。数据库可能在安装包时损坏了。重新配置通常可以解决问题。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo dpkg --configure -a
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 方法 2:强制安装
|
||||
|
||||
如果是之前中断安装的包,你可以尝试强制安装。
|
||||
如果是之前包安装过程被中断,你可以尝试强制安装。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt-get install -f
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 方法3:尝试删除有问题的包
|
||||
|
||||
如果这不是你的问题,你可以尝试手动删除包。请不要在 Linux Kernels(以 linux- 开头的软件包)中执行此操作。
|
||||
如果这不是你的问题,你可以尝试手动删除包。但不要对 Linux 内核包(以 linux- 开头)执行此操作。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt remove
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 方法 4:删除有问题的包中的信息文件
|
||||
|
||||
这应该是你最后的选择。你可以尝试从 /var/lib/dpkg/info 中删除与相关软件包关联的文件。
|
||||
这应该是你最后的选择。你可以尝试从 `/var/lib/dpkg/info` 中删除与相关软件包关联的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
**你需要了解一些基本的 Linux 命令来了解发生了什么以及如何对应你的问题**
|
||||
|
||||
就我而言,我在 polar-bookshelf 中遇到问题。所以我查找了与之关联的文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ls -l /var/lib/dpkg/info | grep -i polar-bookshelf
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2324811 Aug 14 19:29 polar-bookshelf.list
|
||||
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2822824 Aug 10 04:28 polar-bookshelf.md5sums
|
||||
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 113 Aug 10 04:28 polar-bookshelf.postinst
|
||||
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 84 Aug 10 04:28 polar-bookshelf.postrm
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在我需要做的就是删除这些文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo mv /var/lib/dpkg/info/polar-bookshelf.* /tmp
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 sudo apt update,接着你应该就能像往常一样安装软件了。
|
||||
使用 `sudo apt update`,接着你应该就能像往常一样安装软件了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 哪种方法适合你(如果有效)?
|
||||
|
||||
我希望这篇快速文章可以帮助你修复 “E: Sub-process /usr/bin/dpkg returned an error code (1)” 的错误
|
||||
我希望这篇快速文章可以帮助你修复 “E: Sub-process /usr/bin/dpkg returned an error code (1)” 的错误。
|
||||
|
||||
如果它对你有用,是那种方法?你是否设法使用其他方法修复此错误?如果是,请分享一下以帮助其他人解决此问题。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -108,7 +110,7 @@ via: https://itsfoss.com/dpkg-returned-an-error-code-1/
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,161 @@
|
||||
Bat:一种具有语法高亮和 Git 集成的 Cat 类命令
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在类 UNIX 系统中,我们使用 `cat` 命令去打印和连接文件。使用 `cat` 命令,我们能将文件目录打印到到标准输出,合成几个文件为一个目标文件,还有追加几个文件到目标文件中。今天,我偶然发现一个具有相似作用的命令叫做 “Bat” ,它是 `cat` 命令的一个克隆版,具有一些例如语法高亮、 Git 集成和自动分页等非常酷的特性。在这个简略指南中,我们将讲述如何在 Linux 中安装和使用 `bat` 命令。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装
|
||||
|
||||
Bat 可以在 Arch Linux 的默认软件源中获取。 所以你可以使用 `pacman` 命令在任何基于 arch 的系统上来安装它。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo pacman -S bat
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 Debian、Ubuntu、Linux Mint 等系统中,从其[发布页面][1]下载 **.deb** 文件,然后用下面的命令来安装。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install gdebi
|
||||
$ sudo gdebi bat_0.5.0_amd64.deb
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
对于其他系统,你也许需要从软件源编译并安装。确保你已经安装了 Rust 1.26 或者更高版本。
|
||||
|
||||
然后运行以下命令来安装 Bat:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cargo install bat
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
或者,你可以从 [Linuxbrew][2] 软件包管理中来安装它。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ brew install bat
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### bat 命令的使用
|
||||
|
||||
`bat` 命令的使用与 `cat` 命令的使用非常相似。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `bat` 命令创建一个新的文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat > file.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `bat` 命令来查看文件内容,只需要:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat file.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你能同时查看多个文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat file1.txt file2.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将多个文件的内容合并至一个单独文件中:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt > document.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
就像我之前提到的那样,除了浏览和编辑文件以外,`bat` 命令有一些非常酷的特性。
|
||||
|
||||
`bat` 命令支持大多数编程和标记语言的<ruby>语法高亮<rt>syntax highlighting</rt></ruby>。比如,下面这个例子。我将使用 `cat` 和 `bat` 命令来展示 `reverse.py` 的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
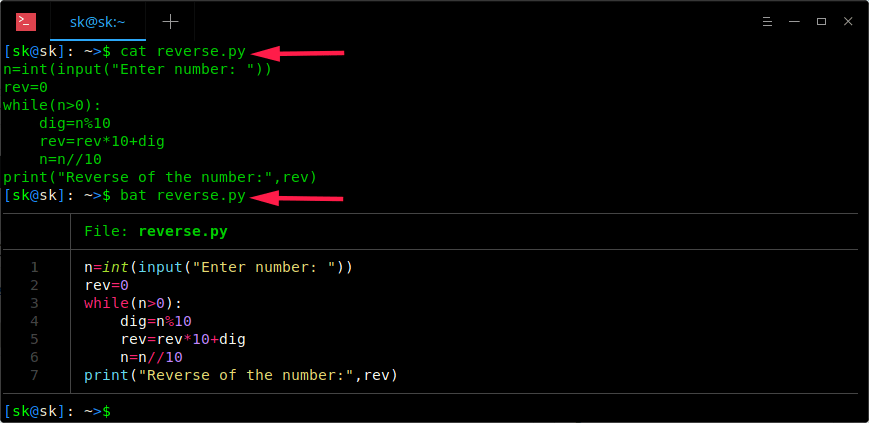
|
||||
|
||||
你注意到区别了吗? `cat` 命令以纯文本格式显示文件的内容,而 `bat` 命令显示了语法高亮和整齐的文本对齐格式。更好了不是吗?
|
||||
|
||||
如果你只想显示行号(而没有表格)使用 `-n` 标记。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat -n reverse.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
另一个 `bat` 命令中值得注意的特性是它支持<ruby>自动分页<rt>automatic paging</rt></ruby>。 它的意思是当文件的输出对于屏幕来说太大的时候,`bat` 命令自动将自己的输出内容传输到 `less` 命令中,所以你可以一页一页的查看输出内容。
|
||||
|
||||
让我给你看一个例子,使用 `cat` 命令查看跨多个页面的文件的内容时,提示符会快速跳至文件的最后一页,你看不到内容的开头和中间部分。
|
||||
|
||||
看一下下面的输出:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
正如你所看到的,`cat` 命令显示了文章的最后一页。
|
||||
|
||||
所以你也许需要去将使用 `cat` 命令的输出传输到 `less` 命令中去从开头一页一页的查看内容。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cat reverse.py | less
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以使用回车键去一页一页的查看输出。然而当你使用 `bat` 命令时这些都是不必要的。`bat` 命令将自动传输跨越多个页面的文件的输出。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat reverse.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在按下回车键去往下一页。
|
||||
|
||||
`bat` 命令也支持 <ruby>Git 集成<rt>**GIT integration**</rt></ruby>,这样您就可以轻松查看/编辑 Git 存储库中的文件。 它与 Git 连接可以显示关于索引的修改。(看左栏)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 定制 Bat
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不喜欢默认主题,你也可以修改它。Bat 同样有修改它的选项。
|
||||
|
||||
若要显示可用主题,只需运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat --list-themes
|
||||
1337
|
||||
DarkNeon
|
||||
Default
|
||||
GitHub
|
||||
Monokai Extended
|
||||
Monokai Extended Bright
|
||||
Monokai Extended Light
|
||||
Monokai Extended Origin
|
||||
TwoDark
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
要使用其他主题,例如 TwoDark,请运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat --theme=TwoDark file.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想永久改变主题,在你的 shells 启动文件中加入 `export BAT_THEME="TwoDark"`。
|
||||
|
||||
`bat` 还可以选择修改输出的外观。使用 `--style` 选项来修改输出外观。仅显示 Git 的更改和行号但不显示网格和文件头,请使用 `--style=numbers,changes`。
|
||||
|
||||
更多详细信息,请参阅 Bat 项目的 GitHub 库(链接在文末)。
|
||||
|
||||
最好,这就是目前的全部内容了。希望这篇文章会帮到你。更多精彩文章即将到来,敬请关注!
|
||||
|
||||
干杯!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.ostechnix.com/bat-a-cat-clone-with-syntax-highlighting-and-git-integration/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[z52527](https://github.com/z52527)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/sharkdp/bat/releases
|
||||
[2]:https://www.ostechnix.com/linuxbrew-common-package-manager-linux-mac-os-x/
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
|
||||
如何使用 Steam Play 在 Linux 上玩仅限 Windows 的游戏
|
||||
======
|
||||
Steam 的新实验功能允许你在 Linux 上玩仅限 Windows 的游戏。以下是如何在 Steam 中使用此功能。
|
||||
|
||||
你已经听说过这个消息。游戏发行平台[ Steam 正在实现一个 WINE 分支来允许你玩仅在 Windows 上的游戏][1]。对于 Linux 用户来说,这绝对是一个好消息,因为我们抱怨 Linux 的游戏数量不足。
|
||||
> Steam 的新实验功能允许你在 Linux 上玩仅限 Windows 的游戏。以下是如何在 Steam 中使用此功能。
|
||||
|
||||
你已经听说过这个消息。游戏发行平台 [Steam 正在复刻一个 WINE 分支来允许你玩仅限于 Windows 上的游戏][1]。对于 Linux 用户来说,这绝对是一个好消息,因为我们总抱怨 Linux 的游戏数量不足。
|
||||
|
||||
这个新功能仍处于测试阶段,但你现在可以在 Linux 上试用它并在 Linux 上玩仅限 Windows 的游戏。让我们看看如何做到这一点。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,20 +15,19 @@ Steam 的新实验功能允许你在 Linux 上玩仅限 Windows 的游戏。以
|
||||
|
||||
安装了 Steam 并且你已登录到 Steam 帐户,就可以了解如何在 Steam Linux 客户端中启用 Windows 游戏。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤 1:进入帐户设置
|
||||
|
||||
运行 Steam 客户端。在左上角,单击 Steam,然后单击 Settings。
|
||||
运行 Steam 客户端。在左上角,单击 “Steam”,然后单击 “Settings”。
|
||||
|
||||
![Enable steam play beta on Linux][4]
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤 2:选择加入测试计划
|
||||
|
||||
在“设置”中,从左侧窗口中选择“帐户”,然后单击 “Beta participation” 下的 “CHANGE” 按钮。
|
||||
在“Settings”中,从左侧窗口中选择“Account”,然后单击 “Beta participation” 下的 “CHANGE” 按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
![Enable beta feature in Steam Linux][5]
|
||||
|
||||
你应该在此处选择 Steam Beta Update。
|
||||
你应该在此处选择 “Steam Beta Update”。
|
||||
|
||||
![Enable beta feature in Steam Linux][6]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -37,32 +37,29 @@ Steam 的新实验功能允许你在 Linux 上玩仅限 Windows 的游戏。以
|
||||
|
||||
下载好 Steam 新的测试版更新后,它将重新启动。到这里就差不多了。
|
||||
|
||||
再次进入“设置”。你现在可以在左侧窗口看到新的 Steam Play 选项。单击它并选中复选框:
|
||||
再次进入“Settings”。你现在可以在左侧窗口看到新的 “Steam Play” 选项。单击它并选中复选框:
|
||||
|
||||
* Enable Steam Play for supported titles (你可以玩列入白名单的 Windows 游戏)
|
||||
* Enable Steam Play for all titles (你可以尝试玩所有仅限 Windows 的游戏)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
![Play Windows games on Linux using Steam Play][7]
|
||||
|
||||
我不记得 Steam 是否会再次重启,但我想这是微不足道的。你现在应该可以在 Linux 上看到安装仅限 Windows 的游戏的选项了。
|
||||
我不记得 Steam 是否会再次重启,但我想这无所谓。你现在应该可以在 Linux 上看到安装仅限 Windows 的游戏的选项了。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,我的 Steam 库中有 Age of Empires,正常情况下这个在 Linux 中没有。但我在 Steam Play 测试版启用所有 Windows 游戏后,现在我可以选择在 Linux 上安装 Age of Empires 了。
|
||||
比如,我的 Steam 库中有《Age of Empires》,正常情况下这个在 Linux 中没有。但我在 Steam Play 测试版启用所有 Windows 游戏后,现在我可以选择在 Linux 上安装《Age of Empires》了。
|
||||
|
||||
![Install Windows-only games on Linux using Steam][8]
|
||||
现在可以在 Linux 上安装仅限 Windows 的游戏
|
||||
|
||||
*现在可以在 Linux 上安装仅限 Windows 的游戏*
|
||||
|
||||
### 有关 Steam Play 测试版功能的信息
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 上使用 Steam Play 测试版玩仅限 Windows 的游戏有一些事情你需要知道并且牢记。
|
||||
|
||||
* If you have games downloaded on Windows via Steam, you can save some download data by [sharing Steam game files between Linux and Windows][12].
|
||||
* 目前,[只有 27 个 Steam Play 中的 Windows 游戏被列入白名单][9]。这些白名单游戏在 Linux 上无缝运行。
|
||||
* 你可以使用 Steam Play 测试版尝试任何 Windows 游戏,但它可能无法一直运行。有些游戏有时会崩溃,而某些游戏可能根本无法运行。
|
||||
* 目前,[只有 27 个 Steam Play 中的 Windows 游戏被列入白名单][9]。这些白名单游戏可以在 Linux 上无缝运行。
|
||||
* 你可以使用 Steam Play 测试版尝试任何 Windows 游戏,但它可能不是总能运行。有些游戏有时会崩溃,而某些游戏可能根本无法运行。
|
||||
* 在测试版中,你无法 Steam 商店中看到适用于 Linux 的 Windows 限定游戏。你必须自己尝试游戏或参考[这个社区维护的列表][10]以查看该 Windows 游戏的兼容性状态。你也可以通过填写[此表][11]来为列表做出贡献。
|
||||
* 如果你通过 Steam 在 Windows 上下载游戏,那么可以通过[在 Linux 和 Windows 之间共享 Steam 游戏文件][12]来保存一些下载数据。
|
||||
|
||||
* 如果你在 Windows 中通过 Steam 下载了游戏,你可以[在 Linux 和 Windows 之间共享 Steam 游戏文件][12]来节省下载的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
我希望本教程能帮助你在 Linux 上运行仅限 Windows 的游戏。你期待在 Linux 上玩哪些游戏?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -73,12 +70,12 @@ via: https://itsfoss.com/steam-play/
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:https://itsfoss.com/steam-play-proton/
|
||||
[1]:https://linux.cn/article-10054-1.html
|
||||
[2]:https://4bds6hergc-flywheel.netdna-ssl.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/play-windows-games-on-linux-featured.jpeg
|
||||
[3]:https://itsfoss.com/install-steam-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
[4]:https://4bds6hergc-flywheel.netdna-ssl.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/enable-steam-play-beta.jpeg
|
||||
@ -89,4 +86,4 @@ via: https://itsfoss.com/steam-play/
|
||||
[9]:https://steamcommunity.com/games/221410
|
||||
[10]:https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1DcZZQ4HL_Ol969UbXJmFG8TzOHNnHoj8Q1f8DIFe8-8/htmlview?sle=true#
|
||||
[11]:https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSeefaYQduMST_lg0IsYxZko8tHLKe2vtVZLFaPNycyhY4bidQ/viewform
|
||||
[12]:https://itsfoss.com/share-steam-files-linux-windows/
|
||||
[12]:https://linux.cn/article-8027-1.html
|
||||
@ -1,14 +1,15 @@
|
||||
让你提高效率的 Linux 技巧
|
||||
======
|
||||
想要在 Linux 命令行工作中提高效率,你需要使用一些技巧。
|
||||
|
||||
> 想要在 Linux 命令行工作中提高效率,你需要使用一些技巧。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
巧妙的 Linux 命令行技巧能让你节省时间、避免出错,还能让你记住和复用各种复杂的命令,专注在需要做的事情本身,而不是做事的方式。以下介绍一些好用的命令行技巧。
|
||||
巧妙的 Linux 命令行技巧能让你节省时间、避免出错,还能让你记住和复用各种复杂的命令,专注在需要做的事情本身,而不是你要怎么做。以下介绍一些好用的命令行技巧。
|
||||
|
||||
### 命令编辑
|
||||
|
||||
如果要对一个已输入的命令进行修改,可以使用 ^a(ctrl + a)或 ^e(ctrl + e)将光标快速移动到命令的开头或命令的末尾。
|
||||
如果要对一个已输入的命令进行修改,可以使用 `^a`(`ctrl + a`)或 `^e`(`ctrl + e`)将光标快速移动到命令的开头或命令的末尾。
|
||||
|
||||
还可以使用 `^` 字符实现对上一个命令的文本替换并重新执行命令,例如 `^before^after^` 相当于把上一个命令中的 `before` 替换为 `after` 然后重新执行一次。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -59,11 +60,11 @@ alias show_dimensions='xdpyinfo | grep '\''dimensions:'\'''
|
||||
|
||||
### 冻结、解冻终端界面
|
||||
|
||||
^s(ctrl + s)将通过执行流量控制命令 XOFF 来停止终端输出内容,这会对 PuTTY 会话和桌面终端窗口产生影响。如果误输入了这个命令,可以使用 ^q(ctrl + q)让终端重新响应。所以只需要记住^q 这个组合键就可以了,毕竟这种情况并不多见。
|
||||
`^s`(`ctrl + s`)将通过执行流量控制命令 XOFF 来停止终端输出内容,这会对 PuTTY 会话和桌面终端窗口产生影响。如果误输入了这个命令,可以使用 `^q`(`ctrl + q`)让终端重新响应。所以只需要记住 `^q` 这个组合键就可以了,毕竟这种情况并不多见。
|
||||
|
||||
### 复用命令
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 提供了很多让用户复用命令的方法,其核心是通过历史缓冲区收集执行过的命令。复用命令的最简单方法是输入 `!` 然后接最近使用过的命令的开头字母;当然也可以按键盘上的向上箭头,直到看到要复用的命令,然后按 Enter 键。还可以先使用 `history` 显示命令历史,然后输入 `!` 后面再接命令历史记录中需要复用的命令旁边的数字。
|
||||
Linux 提供了很多让用户复用命令的方法,其核心是通过历史缓冲区收集执行过的命令。复用命令的最简单方法是输入 `!` 然后接最近使用过的命令的开头字母;当然也可以按键盘上的向上箭头,直到看到要复用的命令,然后按回车键。还可以先使用 `history` 显示命令历史,然后输入 `!` 后面再接命令历史记录中需要复用的命令旁边的数字。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
!! <== 复用上一条命令
|
||||
@ -129,7 +130,7 @@ $ rm -i <== 请求确认
|
||||
$ unalias rm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果已经将 `rm -i` 默认设置为 `rm` 的别名,但你希望在删除文件之前不必进行确认,则可以将 `unalias` 命令放在一个启动文件(例如 ~/.bashrc)中。
|
||||
如果已经将 `rm -i` 默认设置为 `rm` 的别名,但你希望在删除文件之前不必进行确认,则可以将 `unalias` 命令放在一个启动文件(例如 `~/.bashrc`)中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 sudo
|
||||
|
||||
@ -151,8 +152,6 @@ md () { mkdir -p "$@" && cd "$1"; }
|
||||
|
||||
使用 Linux 命令行是在 Linux 系统上工作最有效也最有趣的方法,但配合命令行技巧和巧妙的别名可以让你获得更好的体验。
|
||||
|
||||
加入 [Facebook][1] 和 [LinkedIn][2] 上的 Network World 社区可以和我们一起讨论。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3305811/linux/linux-tricks-that-even-you-can-love.html
|
||||
@ -160,7 +159,7 @@ via: https://www.networkworld.com/article/3305811/linux/linux-tricks-that-even-y
|
||||
作者:[Sandra Henry-Stocker][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[HankChow](https://github.com/HankChow)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,170 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by z52527
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
A Cat Clone With Syntax Highlighting And Git Integration
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In Unix-like systems, we use **‘cat’** command to print and concatenate files. Using cat command, we can print the contents of a file to the standard output, concatenate several files into the target file, and append several files into the target file. Today, I stumbled upon a similar utility named **“Bat”** , a clone to the cat command, with some additional cool features such as syntax highlighting, git integration and automatic paging etc. In this brief guide, we will how to install and use Bat command in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Bat is available in the default repositories of Arch Linux. So, you can install it using pacman on any arch-based systems.
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo pacman -S bat
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint systems, download the **.deb** file from the [**Releases page**][1] and install it as shown below.
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install gdebi
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo gdebi bat_0.5.0_amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For other systems, you may need to compile and install from source. Make sure you have installed Rust 1.26 or higher.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Then, run the following command to install Bat:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cargo install bat
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can install it using [**Linuxbrew**][2] package manager.
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ brew install bat
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Bat command Usage
|
||||
|
||||
The Bat command’s usage is very similar to cat command.
|
||||
|
||||
To create a new file using bat command, do:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat > file.txt
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To view the contents of a file using bat command, just do:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat file.txt
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also view multiple files at once:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat file1.txt file2.txt
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To append the contents of the multiple files in a single file:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt > document.txt
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Like I already mentioned, apart from viewing and editing files, the Bat command has some additional cool features though.
|
||||
|
||||
The bat command supports **syntax highlighting** for large number of programming and markup languages. For instance, look at the following example. I am going to display the contents of the **reverse.py** file using both cat and bat commands.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Did you notice the difference? Cat command shows the contents of the file in plain text format, whereas bat command shows output with syntax highlighting, order number in a neat tabular column format. Much better, isn’t it?
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to display only the line numbers (not the tabular column), use **-n** flag.
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat -n reverse.py
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample output:**
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Another notable feature of Bat command is it supports **automatic paging**. That means if output of a file is too large for one screen, the bat command automatically pipes its own output to **less** command, so you can view the output page by page.
|
||||
|
||||
Let me show you an example. When you view the contents of a file which spans multiple pages using cat command, the prompt quickly jumps to the last page of the file, and you do not see the content in the beginning or in the middle.
|
||||
|
||||
Have a look at the following output:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, the cat command displays last page of the file.
|
||||
|
||||
So, you may need to pipe the output of the cat command to **less** command to view it’s contents page by page from the beginning.
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cat reverse.py | less
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, you can view output page by page by hitting the ENTER key. However, it is not necessary if you use bat command. The bat command will automatically pipe the output of a file which spans multiple pages.
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat reverse.py
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample output:**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now hit the ENTER key to go to the next page.
|
||||
|
||||
The bat command also supports **GIT integration** , so you can view/edit the files in your Git repository without much hassle. It communicates with git to show modifications with respect to the index (see left side bar).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Customizing Bat**
|
||||
|
||||
If you don’t like the default themes, you can change it too. Bat has option for that too.
|
||||
|
||||
To list the available themes, just run:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat --list-themes
|
||||
1337
|
||||
DarkNeon
|
||||
Default
|
||||
GitHub
|
||||
Monokai Extended
|
||||
Monokai Extended Bright
|
||||
Monokai Extended Light
|
||||
Monokai Extended Origin
|
||||
TwoDark
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To use a different theme, for example TwoDark, run:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bat --theme=TwoDark file.txt
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to make the theme permanent, use `export BAT_THEME="TwoDark"` in your shells startup file.
|
||||
|
||||
Bat also have the option to control the appearance of the output. To do so, use the `--style` option. To show only Git changes and line numbers but no grid and no file header, use `--style=numbers,changes`.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, refer the Bat project GitHub Repository (Link at the end).
|
||||
|
||||
And, that’s all for now. Hope this was useful. More good stuffs to come. Stay tuned!
|
||||
|
||||
Cheers!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.ostechnix.com/bat-a-cat-clone-with-syntax-highlighting-and-git-integration/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/sharkdp/bat/releases
|
||||
[2]:https://www.ostechnix.com/linuxbrew-common-package-manager-linux-mac-os-x/
|
||||
@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by way-ww
|
||||
|
||||
4 scanning tools for the Linux desktop
|
||||
======
|
||||
Go paperless by driving your scanner with one of these open source applications.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
While the paperless world isn't here quite yet, more and more people are getting rid of paper by scanning documents and photos. Having a scanner isn't enough to do the deed, though. You need software to drive that scanner.
|
||||
|
||||
But the catch is many scanner makers don't have Linux versions of the software they bundle with their devices. For the most part, that doesn't matter. Why? Because there are good scanning applications available for the Linux desktop. They work with a variety of scanners and do a good job.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take a look at four simple but flexible open source Linux scanning tools. I've used each of these tools (and even wrote about three of them [back in 2014][1]) and found them very useful. You might, too.
|
||||
|
||||
### Simple Scan
|
||||
|
||||
One of my longtime favorites, [Simple Scan][2] is small, quick, efficient, and easy to use. If you've seen it before, that's because Simple Scan is the default scanner application on the GNOME desktop, as well as for a number of Linux distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
Scanning a document or photo takes one click. After scanning something, you can rotate or crop it and save it as an image (JPEG or PNG only) or as a PDF. That said, Simple Scan can be slow, even if you scan documents at lower resolutions. On top of that, Simple Scan uses a set of global defaults for scanning, like 150dpi for text and 300dpi for photos. You need to go into Simple Scan's preferences to change those settings.
|
||||
|
||||
If you've scanned something with more than a couple of pages, you can reorder the pages before you save. And if necessary—say you're submitting a signed form—you can email from within Simple Scan.
|
||||
|
||||
### Skanlite
|
||||
|
||||
In many ways, [Skanlite][3] is Simple Scan's cousin in the KDE world. Skanlite has few features, but it gets the job done nicely.
|
||||
|
||||
The software has options that you can configure, including automatically saving scanned files, setting the quality of the scan, and identifying where to save your scans. Skanlite can save to these image formats: JPEG, PNG, BMP, PPM, XBM, and XPM.
|
||||
|
||||
One nifty feature is the software's ability to save portions of what you've scanned to separate files. That comes in handy when, say, you want to excise someone or something from a photo.
|
||||
|
||||
### Gscan2pdf
|
||||
|
||||
Another old favorite, [gscan2pdf][4] might be showing its age, but it still packs a few more features than some of the other applications mentioned here. Even so, gscan2pdf is still comparatively light.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to saving scans in various image formats (JPEG, PNG, and TIFF), gscan2pdf also saves them as PDF or [DjVu][5] files. You can set the scan's resolution, whether it's black and white or color, and paper size before you click the Scan button. That beats going into gscan2pdf's preferences every time you want to change any of those settings. You can also rotate, crop, and delete pages.
|
||||
|
||||
While none of those features are truly killer, they give you a bit more flexibility.
|
||||
|
||||
### GIMP
|
||||
|
||||
You probably know [GIMP][6] as an image-editing tool. But did you know you can use it to drive your scanner?
|
||||
|
||||
You'll need to install the [XSane][7] scanner software and the GIMP XSane plugin. Both of those should be available from your Linux distro's package manager. From there, select File > Create > Scanner/Camera. From there, click on your scanner and then the Scan button.
|
||||
|
||||
If that's not your cup of tea, or if it doesn't work, you can combine GIMP with a plugin called [QuiteInsane][8]. With either plugin, GIMP becomes a powerful scanning application that lets you set a number of options like whether to scan in color or black and white, the resolution of the scan, and whether or not to compress results. You can also use GIMP's tools to touch up or apply effects to your scans. This makes it great for scanning photos and art.
|
||||
|
||||
### Do they really just work?
|
||||
|
||||
All of this software works well for the most part and with a variety of hardware. I've used them with several multifunction printers that I've owned over the years—whether connecting using a USB cable or over wireless.
|
||||
|
||||
You might have noticed that I wrote "works well for the most part" in the previous paragraph. I did run into one exception: an inexpensive Canon multifunction printer. None of the software I used could detect it. I had to download and install Canon's Linux scanner software, which did work.
|
||||
|
||||
What's your favorite open source scanning tool for Linux? Share your pick by leaving a comment.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/9/linux-scanner-tools
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Scott Nesbitt][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/scottnesbitt
|
||||
[1]: https://opensource.com/life/14/8/3-tools-scanners-linux-desktop
|
||||
[2]: https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/simple-scan
|
||||
[3]: https://www.kde.org/applications/graphics/skanlite/
|
||||
[4]: http://gscan2pdf.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[5]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DjVu
|
||||
[6]: http://www.gimp.org/
|
||||
[7]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scanner_Access_Now_Easy#XSane
|
||||
[8]: http://sourceforge.net/projects/quiteinsane/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
translating----geekpi
|
||||
|
||||
Clinews – Read News And Latest Headlines From Commandline
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
116
sources/tech/20180928 10 handy Bash aliases for Linux.md
Normal file
116
sources/tech/20180928 10 handy Bash aliases for Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,116 @@
|
||||
10 handy Bash aliases for Linux
|
||||
======
|
||||
Get more efficient by using condensed versions of long Bash commands.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
How many times have you repeatedly typed out a long command on the command line and wished there was a way to save it for later? This is where Bash aliases come in handy. They allow you to condense long, cryptic commands down to something easy to remember and use. Need some examples to get you started? No problem!
|
||||
|
||||
To use a Bash alias you've created, you need to add it to your .bash_profile file, which is located in your home folder. Note that this file is hidden and accessible only from the command line. The easiest way to work with this file is to use something like Vi or Nano.
|
||||
|
||||
### 10 handy Bash aliases
|
||||
|
||||
1. How many times have you needed to unpack a .tar file and couldn't remember the exact arguments needed? Aliases to the rescue! Just add the following to your .bash_profile file and then use **untar FileName** to unpack any .tar file.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alias untar='tar -zxvf '
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Want to download something but be able to resume if something goes wrong?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alias wget='wget -c '
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Need to generate a random, 20-character password for a new online account? No problem.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alias getpass="openssl rand -base64 20"
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Downloaded a file and need to test the checksum? We've got that covered too.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alias sha='shasum -a 256 '
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. A normal ping will go on forever. We don't want that. Instead, let's limit that to just five pings.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alias ping='ping -c 5'
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
6. Start a web server in any folder you'd like.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alias www='python -m SimpleHTTPServer 8000'
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
7. Want to know how fast your network is? Just download Speedtest-cli and use this alias. You can choose a server closer to your location by using the **speedtest-cli --list** command.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alias speed='speedtest-cli --server 2406 --simple'
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
8. How many times have you needed to know your external IP address and had no idea how to get that info? Yeah, me too.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alias ipe='curl ipinfo.io/ip'
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
9. Need to know your local IP address?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alias ipi='ipconfig getifaddr en0'
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
10. Finally, let's clear the screen.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alias c='clear'
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, Bash aliases are a super-easy way to simplify your life on the command line. Want more info? I recommend a quick Google search for "Bash aliases" or a trip to GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/9/handy-bash-aliases
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Patrick H.Mullins][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/pmullins
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
||||
A Free And Secure Online PDF Conversion Suite
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We are always in search for a better and more efficient solution that can make our lives more convenient. That is why when you are working with PDF documents you need a fast and reliable tool that you can use in every situation. Therefore, we wanted to introduce you to **EasyPDF** Online PDF Suite for every occasion. The promise behind this tool is that it can make your PDF management easier and we tested it to check that claim.
|
||||
|
||||
But first, here are the most important things you need to know about EasyPDF:
|
||||
|
||||
* EasyPDF is free and anonymous online PDF Conversion Suite.
|
||||
* Convert PDF to Word, Excel, PowerPoint, AutoCAD, JPG, GIF and Text.
|
||||
* Create PDF from Word, PowerPoint, JPG, Excel files and many other formats.
|
||||
* Manipulate PDFs with PDF Merge, Split and Compress.
|
||||
* OCR conversion of scanned PDFs and images.
|
||||
* Upload files from your device or the Cloud (Google Drive and DropBox).
|
||||
* Available on Windows, Linux, Mac, and smartphones via any browser.
|
||||
* Multiple languages supported.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### EasyPDF User Interface
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
One of the first things that catches your eye is the sleek user interface which gives the tool clean and functional environment in where you can work comfortably. The whole experience is even better because there are no ads on a website at all.
|
||||
|
||||
All different types of conversions have their dedicated menu with a simple box to add files, so you don’t have to wonder about what you need to do.
|
||||
|
||||
Most websites aren’t optimized to work well and run smoothly on mobile phones, but EasyPDF is an exception from that rule. It opens almost instantly on smartphone and is easy to navigate. You can also add it as the shortcut on your home screen from the **three dots menu** on the Chrome app.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Functionality
|
||||
|
||||
Apart from looking nice, EasyPDF is pretty straightforward to use. You **don’t need to register** or leave an **email** to use the tool. It is completely anonymous. Additionally, it doesn’t put any limitations to the number or size of files for conversion. No installation required either! Cool, yeah?
|
||||
|
||||
You choose a desired conversion format, for example, PDF to Word. Select the PDF file you want to convert. You can upload a file from the device by either drag & drop or selecting the file from the folder. There is also an option to upload a document from [**Google Drive**][1] or [**Dropbox**][2].
|
||||
|
||||
After you choose the file, press the Convert button to start the conversion process. You won’t wait for a long time to get your file because conversion will finish in a minute. If you have some more files to convert, remember to download the file before you proceed further. If you don’t download the document first, you will lose it.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For a different type of conversion, return to the homepage.
|
||||
|
||||
The currently available types of conversions are:
|
||||
|
||||
* **PDF to Word** – Convert PDF documents to Word documents
|
||||
|
||||
* **PDF to PowerPoint** – Convert PDF documents to PowerPoint Presentations
|
||||
|
||||
* **PDF to Excel** – Convert PDF documents to Excel documents
|
||||
|
||||
* **PDF Creation** – Create PDF documents from any type of file (E.g text, doc, odt)
|
||||
|
||||
* **Word to PDF** – Convert Word documents to PDF documents
|
||||
|
||||
* **JPG to PDF** – Convert JPG images to PDF documents
|
||||
|
||||
* **PDF to AutoCAD** – Convert PDF documents to .dwg format (DWG is native format for CAD packages)
|
||||
|
||||
* **PDF to Text** – Convert PDF documents to Text documents
|
||||
|
||||
* **PDF Split** – Split PDF files into multiple parts
|
||||
|
||||
* **PDF Merge** – Merge multiple PDF files into one
|
||||
|
||||
* **PDF Compress** – Compress PDF documents
|
||||
|
||||
* **PDF to JPG** – Convert PDF documents to JPG images
|
||||
|
||||
* **PDF to PNG** – Convert PDF documents to PNG images
|
||||
|
||||
* **PDF to GIF** – Convert PDF documents to GIF files
|
||||
|
||||
* **OCR Online** –
|
||||
|
||||
Convert scanned paper documents
|
||||
|
||||
to editable files (E.g Word, Excel, Text)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Want to give it a try? Great! Click the following link and start converting!
|
||||
|
||||
[][https://easypdf.com/]
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion
|
||||
|
||||
EasyPDF lives up to its name and enables easier PDF management. As far as I tested EasyPDF service, It offers out of the box conversion feature completely **FREE!** It is fast, secure and reliable. You will find the quality of services most satisfying without having to pay anything or leaving your personal data like email address. Give it a try and who knows maybe you will find your new favorite PDF tool.
|
||||
|
||||
And, that’s all for now. More good stuffs to come. Stay tuned!
|
||||
|
||||
Cheers!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.ostechnix.com/easypdf-a-free-and-secure-online-pdf-conversion-suite/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]: https://www.ostechnix.com/how-to-mount-google-drive-locally-as-virtual-file-system-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]: https://www.ostechnix.com/install-dropbox-in-ubuntu-18-04-lts-desktop/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,233 @@
|
||||
Translating by dianbanjiu How to Install Popcorn Time on Ubuntu 18.04 and Other Linux Distributions
|
||||
======
|
||||
**Brief: This tutorial shows you how to install Popcorn Time on Ubuntu and other Linux distributions. Some handy Popcorn Time tips have also been discussed.**
|
||||
|
||||
[Popcorn Time][1] is an open source [Netflix][2] inspired [torrent][3] streaming application for Linux, Mac and Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
With the regular torrents, you have to wait for the download to finish before you could watch the videos.
|
||||
|
||||
[Popcorn Time][4] is different. It uses torrent underneath but allows you to start watching the videos (almost) immediately. It’s like you are watching videos on streaming websites like YouTube or Netflix. You don’t have to wait for the download to finish here.
|
||||
|
||||
![Popcorn Time in Ubuntu Linux][5]
|
||||
Popcorn Time
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to watch movies online without those creepy ads, Popcorn Time is a good alternative. Keep in mind that the streaming quality depends on the number of available seeds.
|
||||
|
||||
Popcorn Time also provides a nice user interface where you can browse through available movies, tv-series and other contents. If you ever used [Netflix on Linux][6], you will find it’s somewhat a similar experience.
|
||||
|
||||
Using torrent to download movies is illegal in several countries where there are strict laws against piracy. In countries like the USA, UK and West European you may even get legal notices. That said, it’s up to you to decide if you want to use it or not. You have been warned.
|
||||
(If you still want to take the risk and use Popcorn Time, you should use a VPN service like [Ivacy][7] that has been specifically designed for using Torrents and protecting your identity. Even then it’s not always easy to avoid the snooping authorities.)
|
||||
|
||||
Some of the main features of Popcorn Time are:
|
||||
|
||||
* Watch movies and TV Series online using Torrent
|
||||
* A sleek user interface lets you browse the available movies and TV series
|
||||
* Change streaming quality
|
||||
* Bookmark content for watching later
|
||||
* Download content for offline viewing
|
||||
* Ability to enable subtitles by default, change the subtitles size etc
|
||||
* Keyboard shortcuts to navigate through Popcorn Time
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### How to install Popcorn Time on Ubuntu and other Linux Distributions
|
||||
|
||||
I am using Ubuntu 18.04 in this tutorial but you can use the same instructions for other Linux distributions such as Linux Mint, Debian, Manjaro, Deepin etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s see how to install Popcorn time on Linux. It’s really easy actually. Simply follow the instructions and copy paste the commands I have mentioned.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 1: Download Popcorn Time
|
||||
|
||||
You can download Popcorn Time from its official website. The download link is present on the homepage itself.
|
||||
|
||||
[Get Popcorn Time](https://popcorntime.sh/)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2: Install Popcorn Time
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have downloaded Popcorn Time, it’s time to use it. The downloaded file is a tar file that consists of an executable among other files. While you can extract this tar file anywhere, the [Linux convention is to install additional software in][8] /[opt directory.][8]
|
||||
|
||||
Create a new directory in /opt:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo mkdir /opt/popcorntime
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now go to the Downloads directory.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd ~/Downloads
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Extract the downloaded Popcorn Time files into the newly created /opt/popcorntime directory.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo tar Jxf Popcorn-Time-* -C /opt/popcorntime
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 3: Make Popcorn Time accessible for everyone
|
||||
|
||||
You would want every user on your system to be able to run Popcorn Time without sudo access, right? To do that, you need to create a [symbolic link][9] to the executable in /usr/bin directory.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ln -sf /opt/popcorntime/Popcorn-Time /usr/bin/Popcorn-Time
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 4: Create desktop launcher for Popcorn Time
|
||||
|
||||
So far so good. But you would also like to see Popcorn Time in the application menu, add it to your favorite application list etc.
|
||||
|
||||
For that, you need to create a desktop entry.
|
||||
|
||||
Open a terminal and create a new file named popcorntime.desktop in /usr/share/applications.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use any [command line based text editor][10]. Ubuntu has [Nano][11] installed by default so you can use that.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo nano /usr/share/applications/popcorntime.desktop
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Insert the following lines here:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[Desktop Entry]
|
||||
Version = 1.0
|
||||
Type = Application
|
||||
Terminal = false
|
||||
Name = Popcorn Time
|
||||
Exec = /usr/bin/Popcorn-Time
|
||||
Icon = /opt/popcorntime/popcorn.png
|
||||
Categories = Application;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you used Nano editor, save it using shortcut Ctrl+X. When asked for saving, enter Y and then press enter again to save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
We are almost there. One last thing to do here is to have the correct icon for Popcorn Time. For that, you can download a Popcorn Time icon and save it as popcorn.png in /opt/popcorntime directory.
|
||||
|
||||
You can do that using the command below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo wget -O /opt/popcorntime/popcorn.png https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/d/df/Pctlogo.png
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it. Now you can search for Popcorn Time and click on it to launch it.
|
||||
|
||||
![Popcorn Time installed on Ubuntu][12]
|
||||
Search for Popcorn Time in Menu
|
||||
|
||||
On the first launch, you’ll have to accept the terms and conditions.
|
||||
|
||||
![Popcorn Time in Ubuntu Linux][13]
|
||||
Accept the Terms of Service
|
||||
|
||||
Once you do that, you can enjoy the movies and TV shows.
|
||||
|
||||
![Watch movies on Popcorn Time][14]
|
||||
|
||||
Well, that’s all you needed to install Popcorn Time on Ubuntu or any other Linux distribution. You can start watching your favorite movies straightaway.
|
||||
|
||||
However, if you are interested, I would suggest reading these Popcorn Time tips to get more out of it.
|
||||
|
||||
[![][15]][16]
|
||||
![][17]
|
||||
|
||||
### 7 Tips for using Popcorn Time effectively
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you have installed Popcorn Time, I am going to tell you some nifty Popcorn Time tricks. I assure you that it will enhance your experience with Popcorn Time multiple folds.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1\. Use advanced settings
|
||||
|
||||
Always have the advanced settings enabled. It gives you more options to tweak Popcorn Time. Go to the top right corner and click on the gear symbol. Click on it and check advanced settings on the next screen.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 2\. Watch the movies in VLC or other players
|
||||
|
||||
Did you know that you can choose to watch a file in your preferred media player instead of the default Popcorn Time player? Of course, that media player should have been installed in the system.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you may ask why would one want to use another player. And my answer is because other players like VLC has hidden features which you might not find in the Popcorn Time player.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if a file has very low volume, you can use VLC to enhance the audio by 400 percent. You can also [synchronize incoherent subtitles with VLC][18]. You can switch between media players before you start to play a file:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 3\. Bookmark movies and watch it later
|
||||
|
||||
Just browsing through movies and TV series but don’t have time or mood to watch those? No issues. You can add the movies to the bookmark and can access these bookmarked videos from the Favorites tab. This enables you to create a list of movies you would watch later.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 4\. Check torrent health and seed information
|
||||
|
||||
As I had mentioned earlier, your viewing experience in Popcorn Times depends on torrent speed. Good thing is that Popcorn time shows the health of the torrent file so that you can be aware of the streaming speed.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see a green/yellow/red dot on the file. Green means there are plenty of seeds and the file will stream easily. Yellow means a medium number of seeds, streaming should be okay. Red means there are very few seeds available and the streaming will be poor or won’t work at all.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 5\. Add custom subtitles
|
||||
|
||||
If you need subtitles and it is not available in your preferred language, you can add custom subtitles downloaded from external websites. Get the .srt files and use it inside Popcorn Time:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This is where VLC comes handy as you can [download subtitles automatically with VLC][19].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6\. Save the files for offline viewing
|
||||
|
||||
When Popcorn Times stream a content, it downloads it and store temporarily. When you close the app, it’s cleaned out. You can change this behavior so that the downloaded file remains there for your future use.
|
||||
|
||||
In the advanced settings, scroll down a bit. Look for Cache directory. You can change this to some other directory like Downloads. This way, even if you close Popcorn Time, the file will be available for viewing.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 7\. Drag and drop external torrent files to play immediately
|
||||
|
||||
I bet you did not know about this one. If you don’t find a certain movie on Popcorn Time, download the torrent file from your favorite torrent website. Open Popcorn Time and just drag and drop the torrent file in Popcorn Time. It will start playing the file, depending upon seeds. This way, you don’t need to download the entire file before watching it.
|
||||
|
||||
When you drag and drop the torrent file in Popcorn Time, it will give you the option to choose which video file should it play. If there are subtitles in it, it will play automatically or else, you can add external subtitles.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
There are plenty of other features in Popcorn Time. But I’ll stop with my list here and let you explore Popcorn Time on Ubuntu Linux. I hope you find these Popcorn Time tips and tricks useful.
|
||||
|
||||
I am repeating again. Using Torrents is illegal in many countries. If you do that, take precaution and use a VPN service. If you are looking for my recommendation, you can go for [Swiss-based privacy company ProtonVPN][20] (of [ProtonMail][21] fame). Singapore based [Ivacy][7] is another good option. If you think these are expensive, you can look for [cheap VPN deals on It’s FOSS Shop][22].
|
||||
|
||||
Note: This article contains affiliate links. Please read our [affiliate policy][23].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://itsfoss.com/popcorn-time-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]: https://popcorntime.sh/
|
||||
[2]: https://netflix.com/
|
||||
[3]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Torrent_file
|
||||
[4]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Popcorn_Time
|
||||
[5]: https://4bds6hergc-flywheel.netdna-ssl.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/popcorn-time-linux.jpeg
|
||||
[6]: https://itsfoss.com/netflix-firefox-linux/
|
||||
[7]: https://billing.ivacy.com/page/23628
|
||||
[8]: http://tldp.org/LDP/Linux-Filesystem-Hierarchy/html/opt.html
|
||||
[9]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Symbolic_link
|
||||
[10]: https://itsfoss.com/command-line-text-editors-linux/
|
||||
[11]: https://itsfoss.com/nano-3-release/
|
||||
[12]: https://4bds6hergc-flywheel.netdna-ssl.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/popcorn-time-ubuntu-menu.jpg
|
||||
[13]: https://4bds6hergc-flywheel.netdna-ssl.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/popcorn-time-ubuntu-license.jpeg
|
||||
[14]: https://4bds6hergc-flywheel.netdna-ssl.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/popcorn-time-watch-movies.jpeg
|
||||
[15]: https://ivacy.postaffiliatepro.com/accounts/default1/vdegzkxbw/7f82d531.png
|
||||
[16]: https://billing.ivacy.com/page/23628/7f82d531
|
||||
[17]: http://ivacy.postaffiliatepro.com/scripts/vdegzkxiw?aff=23628&a_bid=7f82d531
|
||||
[18]: https://itsfoss.com/how-to-synchronize-subtitles-with-movie-quick-tip/
|
||||
[19]: https://itsfoss.com/download-subtitles-automatically-vlc-media-player-ubuntu/
|
||||
[20]: https://protonvpn.net/?aid=chmod777
|
||||
[21]: https://itsfoss.com/protonmail/
|
||||
[22]: https://shop.itsfoss.com/search?utf8=%E2%9C%93&query=vpn
|
||||
[23]: https://itsfoss.com/affiliate-policy/
|
||||
544
sources/tech/20180928 Using Grails with jQuery and DataTables.md
Normal file
544
sources/tech/20180928 Using Grails with jQuery and DataTables.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,544 @@
|
||||
Using Grails with jQuery and DataTables
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
Learn to build a Grails-based data browser that lets users visualize complex tabular data.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
I’m a huge fan of [Grails][1]. Granted, I’m mostly a data person who likes to explore and analyze data using command-line tools. But even data people sometimes need to _look at_ the data, and sometimes using data means having a great data browser. With Grails, [jQuery][2], and the [DataTables jQuery plugin][3], we can make really nice tabular data browsers.
|
||||
|
||||
The [DataTables website][3] offers a lot of decent “recipe-style” documentation that shows how to put together some fine sample applications, and it includes the necessary JavaScript, HTML, and occasional [PHP][4] to accomplish some pretty spiffy stuff. But for those who would rather use Grails as their backend, a bit of interpretation is necessary. Also, the sample application data used is a single flat table of employees of a fictional company, so the complexity of dealing with table relations serves as an exercise for the reader.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, we’ll fill those two gaps by creating a Grails application with a slightly more complex data structure and a DataTables browser. In doing so, we’ll cover Grails criteria, which are [Groovy][5] -fied Java Hibernate criteria. I’ve put the code for the application on [GitHub][6] , so this article is oriented toward explaining the nuances of the code.
|
||||
|
||||
For prerequisites, you will need Java, Groovy, and Grails environments set up. With Grails, I tend to use a terminal window and [Vim][7], so that’s what’s used here. To get a modern Java, I suggest downloading and installing the [Open Java Development Kit][8] (OpenJDK) provided by your Linux distro (which should be Java 8, 9, 10 or 11; at the time of writing, I’m working with Java 8). From my point of view, the best way to get up-to-date Groovy and Grails is to use [SDKMAN!][9].
|
||||
|
||||
Readers who have never tried Grails will probably need to do some background reading. As a starting point, I recommend [Creating Your First Grails Application][10].
|
||||
|
||||
### Getting the employee browser application
|
||||
|
||||
As mentioned above, I’ve put the source code for this sample employee browser application on [GitHub][6]. For further explanation, the application **embrow** was built using the following commands in a Linux terminal window:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd Projects
|
||||
grails create-app com.nuevaconsulting.embrow
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The domain classes and unit tests are created as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
grails create-domain-class com.nuevaconsulting.embrow.Position
|
||||
grails create-domain-class com.nuevaconsulting.embrow.Office
|
||||
grails create-domain-class com.nuevaconsulting.embrow.Employeecd embrowgrails createdomaincom.grails createdomaincom.grails createdomaincom.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The domain classes built this way have no attributes, so they must be edited as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
The Position domain class:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
package com.nuevaconsulting.embrow
|
||||
|
||||
class Position {
|
||||
|
||||
String name
|
||||
int starting
|
||||
|
||||
static constraints = {
|
||||
name nullable: false, blank: false
|
||||
starting nullable: false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}com.Stringint startingstatic constraintsnullableblankstarting nullable
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The Office domain class:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
package com.nuevaconsulting.embrow
|
||||
|
||||
class Office {
|
||||
|
||||
String name
|
||||
String address
|
||||
String city
|
||||
String country
|
||||
|
||||
static constraints = {
|
||||
name nullable: false, blank: false
|
||||
address nullable: false, blank: false
|
||||
city nullable: false, blank: false
|
||||
country nullable: false, blank: false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And the Employee domain class:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
package com.nuevaconsulting.embrow
|
||||
|
||||
class Employee {
|
||||
|
||||
String surname
|
||||
String givenNames
|
||||
Position position
|
||||
Office office
|
||||
int extension
|
||||
Date hired
|
||||
int salary
|
||||
static constraints = {
|
||||
surname nullable: false, blank: false
|
||||
givenNames nullable: false, blank: false
|
||||
: false
|
||||
office nullable: false
|
||||
extension nullable: false
|
||||
hired nullable: false
|
||||
salary nullable: false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that whereas the Position and Office domain classes use predefined Groovy types String and int, the Employee domain class defines fields that are of type Position and Office (as well as the predefined Date). This causes the creation of the database table in which instances of Employee are stored to contain references, or foreign keys, to the tables in which instances of Position and Office are stored.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can generate the controllers, views, and various other test components:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
-all com.nuevaconsulting.embrow.Position
|
||||
grails generate-all com.nuevaconsulting.embrow.Office
|
||||
grails generate-all com.nuevaconsulting.embrow.Employeegrails generateall com.grails generateall com.grails generateall com.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, you have a basic create-read-update-delete (CRUD) application ready to go. I’ve included some base data in the **grails-app/init/com/nuevaconsulting/BootStrap.groovy** to populate the tables.
|
||||
|
||||
If you run the application with the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
grails run-app
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
you will see the following screen in the browser at **<http://localhost:8080/:>**
|
||||
|
||||
![Embrow home screen][12]
|
||||
|
||||
The Embrow application home screen
|
||||
|
||||
Clicking on the link for the OfficeController gives you a screen that looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
![Office list][14]
|
||||
|
||||
The office list
|
||||
|
||||
Note that this list is generated by the **OfficeController index** method and displayed by the view `office/index.gsp`.
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, clicking on the **EmployeeController** gives a screen that looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
![Employee controller][16]
|
||||
|
||||
The employee controller
|
||||
|
||||
Ok, that’s pretty ugly—what’s with the Position and Office links?
|
||||
|
||||
Well, the views generated by the `generate-all` commands above create an **index.gsp** file that uses the Grails <f:table/> tag that by default shows the class name ( **com.nuevaconsulting.embrow.Position** ) and the persistent instance identifier ( **30** ). This behavior can be customized to yield something better looking, and there is some pretty neat stuff with the autogenerated links, the autogenerated pagination, and the autogenerated sortable columns.
|
||||
|
||||
But even when it's fully cleaned up, this employee browser offers limited functionality. For example, what if you want to find all employees whose position includes the text “dev”? What if you want to combine columns for sorting so that the primary sort key is a surname and the secondary sort key is an office name? Or what if you want to export a sorted subset to a spreadsheet or PDF to email to someone who doesn’t have access to the browser?
|
||||
|
||||
The jQuery DataTables plugin provides this kind of extra functionality and allows you to create a full-fledged tabular data browser.
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating the employee browser view and controller methods
|
||||
|
||||
In order to create an employee browser based on jQuery DataTables, you must complete two tasks:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create a Grails view that incorporates the HTML and JavaScript required to enable the DataTables
|
||||
|
||||
2. Add a method to the Grails controller to handle the new view
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### The employee browser view
|
||||
|
||||
In the directory **embrow/grails-app/views/employee** , start by making a copy of the **index.gsp** file, calling it **browser.gsp** :
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd Projects
|
||||
cd embrow/grails-app/views/employee
|
||||
cp gsp browser.gsp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, you want to customize the new **browser.gsp** file to add the relevant jQuery DataTables code.
|
||||
|
||||
As a rule, I like to grab my JavaScript and CSS from a content provider when feasible; to do so in this case, after the line:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<title><g:message code="default.list.label" args="[entityName]" /></title>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
insert the following lines:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-2.2.4.min.js" integrity="sha256-BbhdlvQf/xTY9gja0Dq3HiwQF8LaCRTXxZKRutelT44=" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
|
||||
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.10.16/css/jquery.dataTables.css">
|
||||
<script type="text/javascript" charset="utf8" src="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.10.16/js/jquery.dataTables.js"></script>
|
||||
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="https://cdn.datatables.net/scroller/1.4.4/css/scroller.dataTables.min.css">
|
||||
<script type="text/javascript" charset="utf8" src="https://cdn.datatables.net/scroller/1.4.4/js/dataTables.scroller.min.js"></script>
|
||||
<script type="text/javascript" charset="utf8" src="https://cdn.datatables.net/buttons/1.5.1/js/dataTables.buttons.min.js"></script>
|
||||
<script type="text/javascript" charset="utf8" src="https://cdn.datatables.net/buttons/1.5.1/js/buttons.flash.min.js"></script>
|
||||
<script type="text/javascript" charset="utf8" src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jszip/3.1.3/jszip.min.js"></script>
|
||||
<script type="text/javascript" charset="utf8" src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/pdfmake/0.1.32/pdfmake.min.js"></script>
|
||||
<script type="text/javascript" charset="utf8" src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/pdfmake/0.1.32/vfs_fonts.js"></script>
|
||||
<script type="text/javascript" charset="utf8" src="https://cdn.datatables.net/buttons/1.5.1/js/buttons.html5.min.js"></script>
|
||||
<script type="text/javascript" charset="utf8" src="https://cdn.datatables.net/buttons/1.5.1/js/buttons.print.min.js "></script>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, remove the code that provided the data pagination in **index.gsp** :
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<div id="list-employee" class="content scaffold-list" role="main">
|
||||
<h1><g:message code="default.list.label" args="[entityName]" /></h1>
|
||||
<g:if test="${flash.message}">
|
||||
<div class="message" role="status">${flash.message}</div>
|
||||
</g:if>
|
||||
<f:table collection="${employeeList}" />
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="pagination">
|
||||
<g:paginate total="${employeeCount ?: 0}" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and insert the code that materializes the jQuery DataTables.
|
||||
|
||||
The first part to insert is the HTML that creates the basic tabular structure of the browser. For the application where DataTables talks to a database backend, provide only the table headers and footers; the DataTables JavaScript takes care of the table contents.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<div id="employee-browser" class="content" role="main">
|
||||
<h1>Employee Browser</h1>
|
||||
<table id="employee_dt" class="display compact" style="width:99%;">
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th>Surname</th>
|
||||
<th>Given name(s)</th>
|
||||
<th>Position</th>
|
||||
<th>Office</th>
|
||||
<th>Extension</th>
|
||||
<th>Hired</th>
|
||||
<th>Salary</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tfoot>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th>Surname</th>
|
||||
<th>Given name(s)</th>
|
||||
<th>Position</th>
|
||||
<th>Office</th>
|
||||
<th>Extension</th>
|
||||
<th>Hired</th>
|
||||
<th>Salary</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tfoot>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, insert a JavaScript block, which serves three primary functions: It sets the size of the text boxes shown in the footer for column filtering, it establishes the DataTables table model, and it creates a handler to do the column filtering.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<g:javascript>
|
||||
$('#employee_dt tfoot th').each( function() {javascript
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The code below handles sizing the filter boxes at the bottoms of the table columns:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
var title = $(this).text();
|
||||
if (title == 'Extension' || title == 'Hired')
|
||||
$(this).html('<input type="text" size="5" placeholder="' + title + '?" />');
|
||||
else
|
||||
$(this).html('<input type="text" size="15" placeholder="' + title + '?" />');
|
||||
});titletitletitletitletitle
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, define the table model. This is where all the table options are provided, including the scrolling, rather than paginated, nature of the interface, the cryptic decorations to be provided according to the dom string, the ability to export data to CSV and other formats, as well as where the Ajax connection to the server is established. Note that the URL is created with a Groovy GString call to the Grails **createLink()** method, referring to the **browserLister** action in the **EmployeeController**. Also of interest is the definition of the columns of the table. This information is sent across to the back end, which queries the database and returns the appropriate records.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
var table = $('#employee_dt').DataTable( {
|
||||
"scrollY": 500,
|
||||
"deferRender": true,
|
||||
"scroller": true,
|
||||
"dom": "Brtip",
|
||||
"buttons": [ 'copy', 'csv', 'excel', 'pdf', 'print' ],
|
||||
"processing": true,
|
||||
"serverSide": true,
|
||||
"ajax": {
|
||||
"url": "${createLink(controller: 'employee', action: 'browserLister')}",
|
||||
"type": "POST",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"columns": [
|
||||
{ "data": "surname" },
|
||||
{ "data": "givenNames" },
|
||||
{ "data": "position" },
|
||||
{ "data": "office" },
|
||||
{ "data": "extension" },
|
||||
{ "data": "hired" },
|
||||
{ "data": "salary" }
|
||||
]
|
||||
});
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, monitor the filter columns for changes and use them to apply the filter(s).
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
table.columns().every(function() {
|
||||
var that = this;
|
||||
$('input', this.footer()).on('keyup change', function(e) {
|
||||
if (that.search() != this.value && 8 < e.keyCode && e.keyCode < 32)
|
||||
that.search(this.value).draw();
|
||||
});
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And that’s it for the JavaScript. This completes the changes to the view code.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
});
|
||||
</g:javascript>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a screenshot of the UI this view creates:
|
||||
|
||||
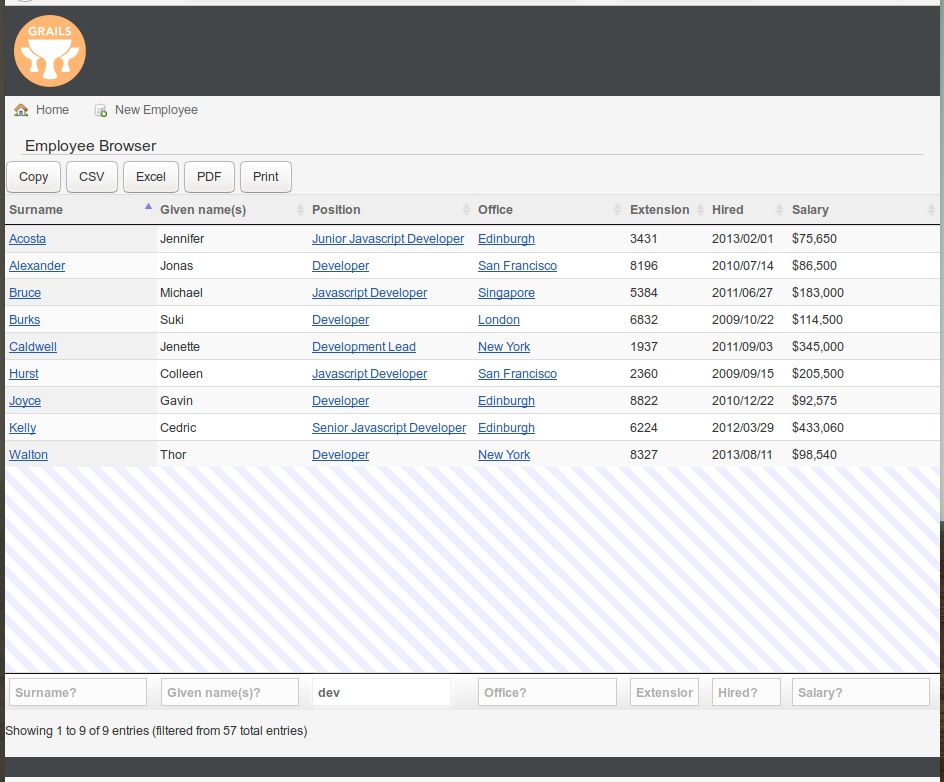
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s another screenshot showing the filtering and multi-column sorting at work (looking for employees whose positions include the characters “dev”, ordering first by office, then by surname):
|
||||
|
||||
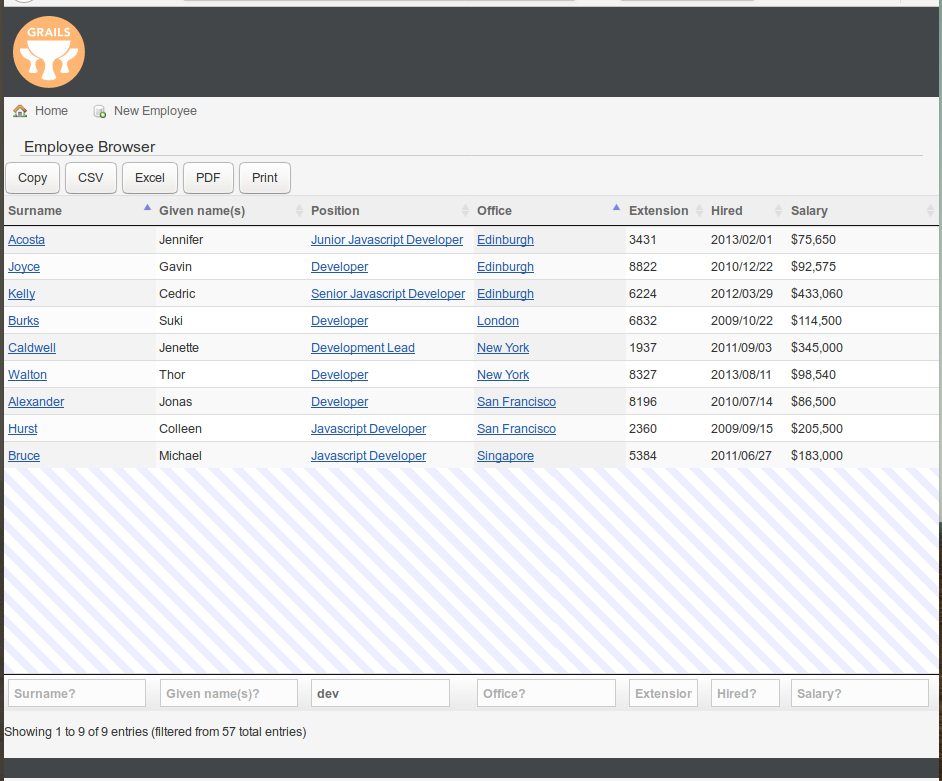
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s another screenshot, showing what happens when you click on the CSV button:
|
||||
|
||||
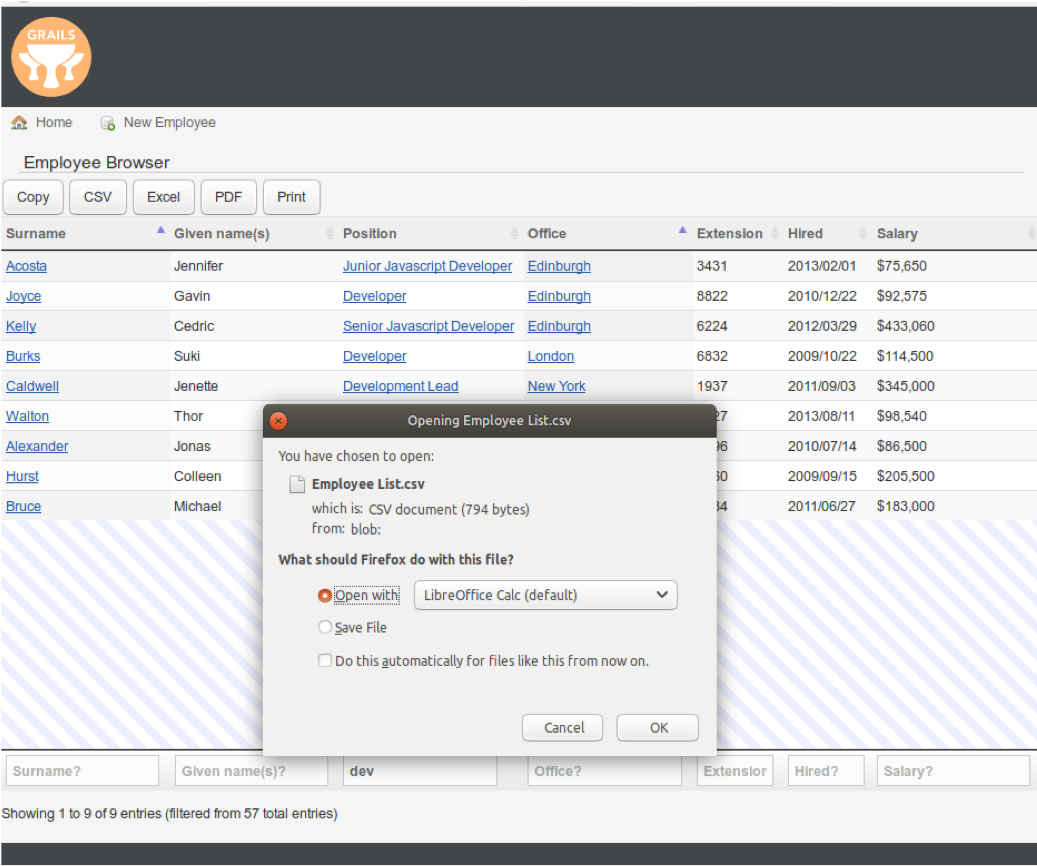
|
||||
|
||||
And finally, here’s a screenshot showing the CSV data opened in LibreOffice:
|
||||
|
||||
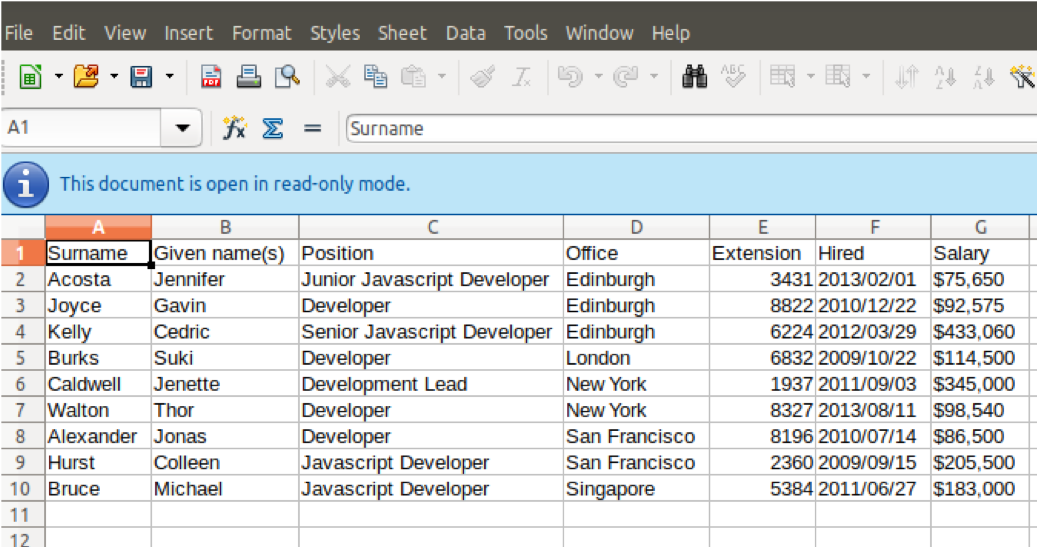
|
||||
|
||||
Ok, so the view part looked pretty straightforward; therefore, the controller action must do all the heavy lifting, right? Let’s see…
|
||||
|
||||
#### The employee controller browserLister action
|
||||
|
||||
Recall that we saw this string
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
"${createLink(controller: 'employee', action: 'browserLister')}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
as the URL used for the Ajax calls from the DataTables table model. [createLink() is the method][17] behind a Grails tag that is used to dynamically generate a link as the HTML is preprocessed on the Grails server. This ends up generating a link to the **EmployeeController** , located in
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
embrow/grails-app/controllers/com/nuevaconsulting/embrow/EmployeeController.groovy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and specifically to the controller method **browserLister()**. I’ve left some print statements in the code so that the intermediate results can be seen in the terminal window where the application is running.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
def browserLister() {
|
||||
// Applies filters and sorting to return a list of desired employees
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
First, print out the parameters passed to **browserLister()**. I usually start building controller methods with this code so that I’m completely clear on what my controller is receiving.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
println "employee browserLister params $params"
|
||||
println()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, process those parameters to put them in a more usable shape. First, the jQuery DataTables parameters, a Groovy map called **jqdtParams** :
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
def jqdtParams = [:]
|
||||
params.each { key, value ->
|
||||
def keyFields = key.replace(']','').split(/\[/)
|
||||
def table = jqdtParams
|
||||
for (int f = 0; f < keyFields.size() - 1; f++) {
|
||||
def keyField = keyFields[f]
|
||||
if (!table.containsKey(keyField))
|
||||
table[keyField] = [:]
|
||||
table = table[keyField]
|
||||
}
|
||||
table[keyFields[-1]] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
println "employee dataTableParams $jqdtParams"
|
||||
println()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, the column data, a Groovy map called **columnMap** :
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
def columnMap = jqdtParams.columns.collectEntries { k, v ->
|
||||
def whereTerm = null
|
||||
switch (v.data) {
|
||||
case 'extension':
|
||||
case 'hired':
|
||||
case 'salary':
|
||||
if (v.search.value ==~ /\d+(,\d+)*/)
|
||||
whereTerm = v.search.value.split(',').collect { it as Integer }
|
||||
break
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if (v.search.value ==~ /[A-Za-z0-9 ]+/)
|
||||
whereTerm = "%${v.search.value}%" as String
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
[(v.data): [where: whereTerm]]
|
||||
}
|
||||
println "employee columnMap $columnMap"
|
||||
println()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, a list of all column names, retrieved from **columnMap** , and a corresponding list of how those columns should be ordered in the view, Groovy lists called **allColumnList** and **orderList** , respectively:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
def allColumnList = columnMap.keySet() as List
|
||||
println "employee allColumnList $allColumnList"
|
||||
def orderList = jqdtParams.order.collect { k, v -> [allColumnList[v.column as Integer], v.dir] }
|
||||
println "employee orderList $orderList"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We’re going to use Grails’ implementation of Hibernate criteria to actually carry out the selection of elements to be displayed as well as their ordering and pagination. Criteria requires a filter closure; in most examples, this is given as part of the creation of the criteria instance itself, but here we define the filter closure beforehand. Note in this case the relatively complex interpretation of the “date hired” filter, which is treated as a year and applied to establish date ranges, and the use of **createAlias** to allow us to reach into related classes Position and Office:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
def filterer = {
|
||||
createAlias 'position', 'p'
|
||||
createAlias 'office', 'o'
|
||||
|
||||
if (columnMap.surname.where) ilike 'surname', columnMap.surname.where
|
||||
if (columnMap.givenNames.where) ilike 'givenNames', columnMap.givenNames.where
|
||||
if (columnMap.position.where) ilike 'p.name', columnMap.position.where
|
||||
if (columnMap.office.where) ilike 'o.name', columnMap.office.where
|
||||
if (columnMap.extension.where) inList 'extension', columnMap.extension.where
|
||||
if (columnMap.salary.where) inList 'salary', columnMap.salary.where
|
||||
if (columnMap.hired.where) {
|
||||
if (columnMap.hired.where.size() > 1) {
|
||||
or {
|
||||
columnMap.hired.where.each {
|
||||
between 'hired', Date.parse('yyyy/MM/dd',"${it}/01/01" as String),
|
||||
Date.parse('yyyy/MM/dd',"${it}/12/31" as String)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
between 'hired', Date.parse('yyyy/MM/dd',"${columnMap.hired.where[0]}/01/01" as String),
|
||||
Date.parse('yyyy/MM/dd',"${columnMap.hired.where[0]}/12/31" as String)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, it’s time to apply the foregoing. The first step is to get a total count of all the Employee instances, required by the pagination code:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
def recordsTotal = Employee.count()
|
||||
println "employee recordsTotal $recordsTotal"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, apply the filter to the Employee instances to get the count of filtered results, which will always be less than or equal to the total number (again, this is for the pagination code):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
def c = Employee.createCriteria()
|
||||
def recordsFiltered = c.count {
|
||||
filterer.delegate = delegate
|
||||
filterer()
|
||||
}
|
||||
println "employee recordsFiltered $recordsFiltered"
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have those two counts, you can get the actual filtered instances using the pagination and ordering information as well.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
def orderer = Employee.withCriteria {
|
||||
filterer.delegate = delegate
|
||||
filterer()
|
||||
orderList.each { oi ->
|
||||
switch (oi[0]) {
|
||||
case 'surname': order 'surname', oi[1]; break
|
||||
case 'givenNames': order 'givenNames', oi[1]; break
|
||||
case 'position': order 'p.name', oi[1]; break
|
||||
case 'office': order 'o.name', oi[1]; break
|
||||
case 'extension': order 'extension', oi[1]; break
|
||||
case 'hired': order 'hired', oi[1]; break
|
||||
case 'salary': order 'salary', oi[1]; break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
maxResults (jqdtParams.length as Integer)
|
||||
firstResult (jqdtParams.start as Integer)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To be completely clear, the pagination code in JTables manages three counts: the total number of records in the data set, the number resulting after the filters are applied, and the number to be displayed on the page (whether the display is scrolling or paginated). The ordering is applied to all the filtered records and the pagination is applied to chunks of those filtered records for display purposes.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, process the results returned by the orderer, creating links to the Employee, Position, and Office instance in each row so the user can click on these links to get all the detail on the relevant instance:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
def dollarFormatter = new DecimalFormat('$##,###.##')
|
||||
def employees = orderer.collect { employee ->
|
||||
['surname': "<a href='${createLink(controller: 'employee', action: 'show', id: employee.id)}'>${employee.surname}</a>",
|
||||
'givenNames': employee.givenNames,
|
||||
'position': "<a href='${createLink(controller: 'position', action: 'show', id: employee.position?.id)}'>${employee.position?.name}</a>",
|
||||
'office': "<a href='${createLink(controller: 'office', action: 'show', id: employee.office?.id)}'>${employee.office?.name}</a>",
|
||||
'extension': employee.extension,
|
||||
'hired': employee.hired.format('yyyy/MM/dd'),
|
||||
'salary': dollarFormatter.format(employee.salary)]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And finally, create the result you want to return and give it back as JSON, which is what jQuery DataTables requires.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
def result = [draw: jqdtParams.draw, recordsTotal: recordsTotal, recordsFiltered: recordsFiltered, data: employees]
|
||||
render(result as JSON)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it.
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re familiar with Grails, this probably seems like more work than you might have originally thought, but there’s no rocket science here, just a lot of moving parts. However, if you haven’t had much exposure to Grails (or to Groovy), there’s a lot of new stuff to understand—closures, delegates, and builders, among other things.
|
||||
|
||||
In that case, where to start? The best place is to learn about Groovy itself, especially [Groovy closures][18] and [Groovy delegates and builders][19]. Then go back to the reading suggested above on Grails and Hibernate criteria queries.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusions
|
||||
|
||||
jQuery DataTables make awesome tabular data browsers for Grails. Coding the view isn’t too tricky, but the PHP examples provided in the DataTables documentation take you only so far. In particular, they aren’t written with Grails programmers in mind, nor do they explore the finer details of using elements that are references to other classes (essentially lookup tables).
|
||||
|
||||
I’ve used this approach to make a couple of data browsers that allow the user to select which columns to view and accumulate record counts, or just to browse the data. The performance is good even in million-row tables on a relatively modest VPS.
|
||||
|
||||
One caveat: I have stumbled upon some problems with the various Hibernate criteria mechanisms exposed in Grails (see my other GitHub repositories), so care and experimentation is required. If all else fails, the alternative approach is to build SQL strings on the fly and execute them instead. As of this writing, I prefer to work with Grails criteria, unless I get into messy subqueries, but that may just reflect my relative lack of experience with subqueries in Hibernate.
|
||||
|
||||
I hope you Grails programmers out there find this interesting. Please feel free to leave comments or suggestions below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/9/using-grails-jquery-and-datatables
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Chris Hermansen][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/clhermansen
|
||||
[1]: https://grails.org/
|
||||
[2]: https://jquery.com/
|
||||
[3]: https://datatables.net/
|
||||
[4]: http://php.net/
|
||||
[5]: http://groovy-lang.org/
|
||||
[6]: https://github.com/monetschemist/grails-datatables
|
||||
[7]: https://www.vim.org/
|
||||
[8]: http://openjdk.java.net/
|
||||
[9]: http://sdkman.io/
|
||||
[10]: http://guides.grails.org/creating-your-first-grails-app/guide/index.html
|
||||
[11]: https://opensource.com/file/410061
|
||||
[12]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/screen_1.png (Embrow home screen)
|
||||
[13]: https://opensource.com/file/410066
|
||||
[14]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/screen_2.png (Office list screenshot)
|
||||
[15]: https://opensource.com/file/410071
|
||||
[16]: https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/uploads/screen3.png (Employee controller screenshot)
|
||||
[17]: https://gsp.grails.org/latest/ref/Tags/createLink.html
|
||||
[18]: http://groovy-lang.org/closures.html
|
||||
[19]: http://groovy-lang.org/dsls.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
||||
What containers can teach us about DevOps
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
The use of containers supports the three pillars of DevOps practices: flow, feedback, and continual experimentation and learning.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
One can argue that containers and DevOps were made for one another. Certainly, the container ecosystem benefits from the skyrocketing popularity of DevOps practices, both in design choices and in DevOps’ use by teams developing container technologies. Because of this parallel evolution, the use of containers in production can teach teams the fundamentals of DevOps and its three pillars: [The Three Ways][1].
|
||||
|
||||
### Principles of flow
|
||||
|
||||
**Container flow**
|
||||
|
||||
A container can be seen as a silo, and from inside, it is easy to forget the rest of the system: the host node, the cluster, the underlying infrastructure. Inside the container, it might appear that everything is functioning in an acceptable manner. From the outside perspective, though, the application inside the container is a part of a larger ecosystem of applications that make up a service: the web API, the web app user interface, the database, the workers, and caching services and garbage collectors. Teams put constraints on the container to limit performance impact on infrastructure, and much has been done to provide metrics for measuring container performance because overloaded or slow container workloads have downstream impact on other services or customers.
|
||||
|
||||
**Real-world flow**
|
||||
|
||||
This lesson can be applied to teams functioning in a silo as well. Every process (be it code release, infrastructure creation or even, say, manufacturing of [Spacely’s Sprockets][2]), follows a linear path from conception to realization. In technology, this progress flows from development to testing to operations and release. If a team working alone becomes a bottleneck or introduces a problem, the impact is felt all along the entire pipeline. A defect passed down the line destroys productivity downstream. While the broken process within the scope of the team itself may seem perfectly correct, it has a negative impact on the environment as a whole.
|
||||
|
||||
**DevOps and flow**
|
||||
|
||||
The first way of DevOps, principles of flow, is about approaching the process as a whole, striving to comprehend how the system works together and understanding the impact of issues on the entire process. To increase the efficiency of the process, pain points and waste are identified and removed. This is an ongoing process; teams must continually strive to increase visibility into the process and find and fix trouble spots and waste.
|
||||
|
||||
> “The outcomes of putting the First Way into practice include never passing a known defect to downstream work centers, never allowing local optimization to create global degradation, always seeking to increase flow, and always seeking to achieve a profound understanding of the system (as per Deming).”
|
||||
|
||||
–Gene Kim, [The Three Ways: The Principles Underpinning DevOps][3], IT Revolution, 25 Apr. 2017
|
||||
|
||||
### Principles of feedback
|
||||
|
||||
**Container feedback**
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to limiting containers to prevent impact elsewhere, many products have been created to monitor and trend container metrics in an effort to understand what they are doing and notify when they are misbehaving. [Prometheus][4], for example, is [all the rage][5] for collecting metrics from containers and clusters. Containers are excellent at separating applications and providing a way to ship an environment together with the code, sometimes at the cost of opacity, so much is done to try to provide rapid feedback so issues can be addressed promptly within the silo.
|
||||
|
||||
**Real-world feedback**
|
||||
|
||||
The same is necessary for the flow of the system. From inception to realization, an efficient process quickly provides relevant feedback to identify when there is an issue. The key words here are “quick” and “relevant.” Burying teams in thousands of irrelevant notifications make it difficult or even impossible to notice important events that need immediate action, and receiving even relevant information too late may allow small, easily solved issues to move downstream and become bigger problems. Imagine [if Lucy and Ethel][6] had provided immediate feedback that the conveyor belt was too fast—there would have been no problem with the chocolate production (though that would not have been nearly as funny).
|
||||
|
||||
**DevOps and feedback**
|
||||
|
||||
The Second Way of DevOps, principles of feedback, is all about getting relevant information quickly. With immediate, useful feedback, problems can be identified as they happen and addressed before impact is felt elsewhere in the development process. DevOps teams strive to “optimize for downstream” and immediately move to fix problems that might impact other teams that come after them. As with flow, feedback is a continual process to identify ways to quickly get important data and act on problems as they occur.
|
||||
|
||||
> “Creating fast feedback is critical to achieving quality, reliability, and safety in the technology value stream.”
|
||||
|
||||
–Gene Kim, et al., The DevOps Handbook: How to Create World-Class Agility, Reliability, and Security in Technology Organizations, IT Revolution Press, 2016
|
||||
|
||||
### Principles of continual experimentation and learning
|
||||
|
||||
**Container continual experimentation and learning**
|
||||
|
||||
It is a bit more challenging applying operational learning to the Third Way of DevOps:continual experimentation and learning. Trying to salvage what we can grasp of the very edges of the metaphor, containers make development easy, allowing developers and operations teams to test new code or configurations locally and safely outside of production and incorporate discovered benefits into production in a way that was difficult in the past. Changes can be radical and still version-controlled, documented, and shared quickly and easily.
|
||||
|
||||
**Real-world continual experimentation and learning**
|
||||
|
||||
For example, consider this anecdote from my own experience: Years ago, as a young, inexperienced sysadmin (just three weeks into the job), I was asked to make changes to an Apache virtual host running the website of the central IT department for a university. Without an easy-to-use test environment, I made a configuration change to the production site that I thought would accomplish the task and pushed it out. Within a few minutes, I overheard coworkers in the next cube:
|
||||
|
||||
“Wait, is the website down?”
|
||||
|
||||
“Hrm, yeah, it looks like it. What the heck?”
|
||||
|
||||
There was much eye-rolling involved.
|
||||
|
||||
Mortified (the shame is real, folks), I sunk down as far as I could into my seat and furiously tried to back out the changes I’d introduced. Later that same afternoon, the director of the department—the boss of my boss’s boss—appeared in my cube to talk about what had happened. “Don’t worry,” she told me. “We’re not mad at you. It was a mistake and now you have learned.”
|
||||
|
||||
In the world of containers, this could have been easily changed and tested on my own laptop and the broken configuration identified by more skilled team members long before it ever made it into production.
|
||||
|
||||
**DevOps continual experimentation and learning**
|
||||
|
||||
A real culture of experimentation promotes the individual’s ability to find where a change in the process may be beneficial, and to test that assumption without the fear of retaliation if they fail. For DevOps teams, failure becomes an educational tool that adds to the knowledge of the individual and organization, rather than something to be feared or punished. Individuals in the DevOps team dedicate themselves to continuous learning, which in turn benefits the team and wider organization as that knowledge is shared.
|
||||
|
||||
As the metaphor completely falls apart, focus needs to be given to a specific point: The other two principles may appear at first glance to focus entirely on process, but continual learning is a human task—important for the future of the project, the person, the team, and the organization. It has an impact on the process, but it also has an impact on the individual and other people.
|
||||
|
||||
> “Experimentation and risk-taking are what enable us to relentlessly improve our system of work, which often requires us to do things very differently than how we’ve done it for decades.”
|
||||
|
||||
–Gene Kim, et al., [The Phoenix Project: A Novel about IT, DevOps, and Helping Your Business Win][7], IT Revolution Press, 2013
|
||||
|
||||
### Containers can teach us DevOps
|
||||
|
||||
Learning to work effectively with containers can help teach DevOps and the Three Ways: principles of flow, principles of feedback, and principles of continuous experimentation and learning. Looking holistically at the application and infrastructure rather than putting on blinders to everything outside the container teaches us to take all parts of the system and understand their upstream and downstream impacts, break out of silos, and work as a team to increase global performance and deep understanding of the entire system. Working to provide timely and accurate feedback teaches us to create effective feedback patterns within our organizations to identify problems before their impact grows. Finally, providing a safe environment to try new ideas and learn from them teaches us to create a culture where failure represents a positive addition to our knowledge and the ability to take big chances with educated guesses can result in new, elegant solutions to complex problems.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/9/containers-can-teach-us-devops
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Chris Hermansen][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/clhermansen
|
||||
[1]: https://itrevolution.com/the-three-ways-principles-underpinning-devops/
|
||||
[2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Jetsons
|
||||
[3]: http://itrevolution.com/the-three-ways-principles-underpinning-devops
|
||||
[4]: https://prometheus.io/
|
||||
[5]: https://opensource.com/article/18/9/prometheus-operational-advantage
|
||||
[6]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8NPzLBSBzPI
|
||||
[7]: https://itrevolution.com/book/the-phoenix-project/
|
||||
@ -1,152 +0,0 @@
|
||||
"组"在 Linux 上到底是怎么工作的?
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
你好!就在上周,我还自认为对 Linux 上的用户和组的工作机制了如指掌。我认为它们的关系是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 每个进程都属于一个用户( 比如用户`julia`)
|
||||
|
||||
2. 当这个进程试图读取一个被某个组所拥有的文件时, Linux 会 a)先检查用户`julia` 是否有权限访问文件。(LCTT译注:检查文件的所有者是否就是`julia`) b)检查`julia` 属于哪些组,并进一步检查在这些组里是否有某个组拥有这个文件或者有权限访问这个文件。
|
||||
|
||||
3. 如果上述a,b任一为真( 或者`其他`位设为有权限访问),那么这个进程就有权限访问这个文件。
|
||||
|
||||
比如说,如果一个进程被用户`julia`拥有并且`julia` 在`awesome`组,那么这个进程就能访问下面这个文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
r--r--r-- 1 root awesome 6872 Sep 24 11:09 file.txt
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然而上述的机制我并没有考虑得非常清楚,如果你硬要我阐述清楚,我会说进程可能会在**运行时**去检查`/etc/group` 文件里是否有某些组拥有当前的用户。
|
||||
|
||||
### 然而这并不是Linux 里“组”的工作机制
|
||||
|
||||
我在上个星期的工作中发现了一件有趣的事,事实证明我前面的理解错了,我对组的工作机制的描述并不准确。特别是Linux**并不会**在进程每次试图访问一个文件时就去检查这个进程的用户属于哪些组。
|
||||
|
||||
我在读了[The Linux Programming
|
||||
Interface][1]这本书的第九章后才恍然大悟(这本书真是太棒了。)这才是组真正的工作方式!我意识到之前我并没有真正理解用户和组是怎么工作的,我信心满满的尝试了下面的内容并且验证到底发生了什么,事实证明现在我的理解才是对的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 用户和组权限检查是怎么完成的
|
||||
|
||||
现在这些关键的知识在我看来非常简单! 这本书的第九章上来就告诉我如下事实:用户和组ID是**进程的属性**,它们是:
|
||||
|
||||
* 真实用户ID和组ID;
|
||||
|
||||
* 有效用户ID和组ID;
|
||||
|
||||
* 被保存的set-user-ID和被保存的set-group-ID;
|
||||
|
||||
* 文件系统用户ID和组ID(特定于 Linux);
|
||||
|
||||
* 增补的组ID;
|
||||
|
||||
这说明Linux**实际上**检查一个进程能否访问一个文件所做的组检查是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
* 检查一个进程的组ID和补充组ID(这些ID就在进程的属性里,**并不是**实时在`/etc/group`里查找这些ID)
|
||||
|
||||
* 检查要访问的文件的访问属性里的组设置
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* 确定进程对文件是否有权限访问(LCTT 译注:即文件的组是否是以上的组之一)
|
||||
|
||||
通常当访问控制的时候使用的是**有效**用户/组ID,而不是**真实**用户/组ID。技术上来说当访问一个文件时使用的是**文件系统**ID,他们实际上和有效用户/组ID一样。(LCTT译注:这句话针对 Linux 而言。)
|
||||
|
||||
### 将一个用户加入一个组并不会将一个已存在的进程(的用户)加入那个组
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一个有趣的例子:如果我创建了一个新的组:`panda` 组并且将我自己(bork)加入到这个组,然后运行`groups` 来检查我是否在这个组里:结果是我(bork)竟然不在这个组?!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
bork@kiwi~> sudo addgroup panda
|
||||
Adding group `panda' (GID 1001) ...
|
||||
Done.
|
||||
bork@kiwi~> sudo adduser bork panda
|
||||
Adding user `bork' to group `panda' ...
|
||||
Adding user bork to group panda
|
||||
Done.
|
||||
bork@kiwi~> groups
|
||||
bork adm cdrom sudo dip plugdev lpadmin sambashare docker lxd
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`panda`并不在上面的组里!为了再次确定我们的发现,让我们建一个文件,这个文件被`panda`组拥有,看看我能否访问它。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ touch panda-file.txt
|
||||
$ sudo chown root:panda panda-file.txt
|
||||
$ sudo chmod 660 panda-file.txt
|
||||
$ cat panda-file.txt
|
||||
cat: panda-file.txt: Permission denied
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
好吧,确定了,我(bork)无法访问`panda-file.txt`。这一点都不让人吃惊,我的命令解释器并没有`panda` 组作为补充组ID,运行`adduser bork panda`并不会改变这一点。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 那进程一开始是怎么得到用户的组的呢?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这真是个非常令人困惑的问题,对吗?如果进程会将组的信息预置到进程的属性里面,进程在初始化的时候怎么取到组的呢?很明显你无法给你自己指定更多的组(否则就会和Linux访问控制的初衷相违背了。。。)
|
||||
|
||||
有一点还是很清楚的:一个新的进程是怎么从我的命令行解释器(/bash/fish)里被**执行**而得到它的组的。(新的)进程将拥有我的用户 ID(bork),并且进程属性里还有很多组ID。从我的命令解释器里执行的所有进程是从这个命令解释器里`复刻`而来的,所以这个新进程得到了和命令解释器同样的组。
|
||||
|
||||
因此一定存在一个“第一个”进程来把你的组设置到进程属性里,而所有由此进程而衍生的进程将都设置这些组。而那个“第一个”进程就是你的**登录命令**,在我的笔记本电脑上,它是由‘登录’程序(`/bin/login`)实例化而来。` 登录程序` 以root身份运行,然后调用了一个 C 的库函数-`initgroups`来设置你的进程的组(具体来说是通过读取`/etc/group` 文件),因为登录程序是以root运行的,所以它能设置你的进程的组。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 让我们再登录一次
|
||||
|
||||
好了!既然我们的`login shell`正在运行,而我又想刷新我的进程的组设置,从我们前面所学到的进程是怎么初始化组ID的,我应该可以通过再次运行`login` 程序来刷新我的进程组并启动一个新的`login shell`!
|
||||
|
||||
让我们试试下边的方法:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo login bork
|
||||
$ groups
|
||||
bork adm cdrom sudo dip plugdev lpadmin sambashare docker lxd panda
|
||||
$ cat panda-file.txt # it works! I can access the file owned by `panda` now!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
当然,成功了!现在由登录程序衍生的程序的用户是组`panda`的一部分了!太棒了!这并不会影响我其他的已经在运行的登录程序(及其子进程),如果我真的希望“所有的”进程都能对`panda`
|
||||
组有访问权限。我必须完全的重启我的登陆会话,这意味着我必须退出我的窗口管理器然后再重新`login`。(LCTT译注:即更新进程树的树根进程,这里是窗口管理器进程。)
|
||||
|
||||
### newgrp命令
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在 Twitter 上有人告诉我如果只是想启动一个刷新了组信息的命令解释器的话,你可以使用`newgrp`(LCTT译注:不启动新的命令解释器),如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo addgroup panda
|
||||
sudo adduser bork panda
|
||||
newgrp panda # starts a new shell, and you don't have to be root to run it!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以用`sg panda bash` 来完成同样的效果,这个命令能启动一个`bash` 登录程序,而这个程序就有`panda` 组。
|
||||
|
||||
### seduid 将设置有效用户 ID
|
||||
|
||||
其实我一直对一个进程如何以`setuid root`的权限来运行意味着什么有点似是而非。现在我知道了,事实上所发生的是:setuid 设置了`有效用户ID`! 如果我('julia')运行了一个`setuid root` 的进程( 比如`passwd`),那么进程的**真实**用户 ID 将为`julia`,而**有效**用户 ID 将被设置为`root`。
|
||||
|
||||
`passwd` 需要以root权限来运行,但是它能看到进程的真实用户ID是`julia` ,是`julia`启动了这个进程,`passwd`会阻止这个进程修改除了`julia`之外的用户密码。
|
||||
|
||||
### 就是这些了!
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux Programming Interface 这本书里有很多Linux上一些功能的罕见使用方法以及Linux上所有的事物到底是怎么运行的详细解释,这里我就不一一展开了。那本书棒极了,我上面所说的都在该书的第九章,这章在1300页的书里只占了17页。
|
||||
|
||||
我最爱这本书的一点是我只用读17页关于用户和组是怎么工作的内容,而这区区17页就能做到内容完备,详实有用。我不用读完所有的1300页书就能得到有用的东西,太棒了!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://jvns.ca/blog/2017/11/20/groups/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Julia Evans ][a]
|
||||
译者:[DavidChen](https://github.com/DavidChenLiang)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://jvns.ca/
|
||||
[1]:http://man7.org/tlpi/
|
||||
@ -1,166 +0,0 @@
|
||||
在Linux上操作目录
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你不熟悉本系列(以及Linux),[请查看我们的第一部分][1]。在那篇文章中,我们通过Linux文件系统的树状结构,或者更确切地说以文件层次结构标准工作。我建议你仔细阅读,确保你理解自己能安全的做哪些操作。因为这一次,我将向你展示目录操作的魅力。
|
||||
|
||||
### 新建目录
|
||||
|
||||
在操作变得具有破坏性之前,让我们发挥创意创造。首先,打开一个终端窗口并使用命令mkdir创建一个新目录,如下所示:
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir <directoryname>
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
如果你只输入了目录名称,该目录将显示在您当前所在目录中。如果你刚刚打开一个终端,你当前位置为你的家目录。下面这个例子,我们展示了将要创建的目录与你当前所处位置的关系:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ pwd #This tells you where you are now -- see our first tutorial
|
||||
/home/<username>
|
||||
$ mkdir newdirectory #Creates /home/<username>/newdirectory
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(注 你不用输入#后面的文本。#后面的文本为注释内容,用于解释发生了什么。它会被shell忽略,不会被执行).
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在当前位置中已经存在的某个目录下创建新的目录,方法是在命令行中指定它:
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir Documents/Letters
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
这将在Documents目录中创建Letters目录。
|
||||
|
||||
你还可以在路径中使用..在当前目录的上一级目录中创建目录。假设你进入刚刚创建的Documents/Letters/目录,并且想要创建Documents/Memos/目录。你可以这样做:
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd Documents/Letters # Move into your recently created Letters/ directory
|
||||
mkdir ../Memos
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
同样,以上所有内容都是相对于你当前的位置做的。这就是使用了相对路径。
|
||||
你还可以使用目录的绝对路径:这意味着告诉mkdir命令将目录放在和根目录(/)有关的位置:
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir /home/<username>/Documents/Letters
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
在上面的命令中将<username>更改为你的用户名,这相当于从你的主目录执行mkdir Documents / Letters,通过使用绝对路径你可以在目录树中的任何位置完成这项工作。
|
||||
|
||||
无论你使用相对路径还是绝对路径,只要命令成功执行,mkdir将静默的创建新目录,而没有任何明显的反馈。只有当遇到某种问题时,mkdir才会在你敲下[Enter]后打印一些反馈。
|
||||
|
||||
与大多数其他命令行工具一样,mkdir提供了几个有趣的选项。 -p选项特别有用,因为它允许你创建嵌套目录,即使目录不存在也可以。例如,要在Documents /中创建一个目录存放写给妈妈的信,你可以这样做:
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir -p Documents/Letters/Family/Mom
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
And `mkdir` will create the whole branch of directories above _Mom/_ and also the directory _Mom/_ for you, regardless of whether any of the parent directories existed before you issued the command.
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以用空格来分隔目录名,来同时创建几个目录:
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir Letters Memos Reports
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
这将在当前目录下创建目录Letters,Memos和Reports。
|
||||
|
||||
### 目录名中可怕的空格
|
||||
|
||||
... 这带来了目录名称中关于空格的棘手问题。你能在目录名中使用空格吗?是的你可以。那么建议你使用空格吗?不,绝对不是。空格使一切变得更加复杂,并且可能是危险的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
假设您要创建一个名为letters mom的目录。如果你不知道如何更好处理,你可能会输入:
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir letters mom
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
但这是错误的!错误的!错误的!正如我们在上面介绍的,这将创建两个目录letters和mom,而不是一个目录letters mom。
|
||||
|
||||
得承认这是一个小麻烦:你所要做的就是删除这两个目录并重新开始,这没什么大不了。
|
||||
|
||||
可是等等!删除目录可是个危险的操作。想象一下,你确实使用图形工具[Dolphin][2]或[Nautilus][3]创建了目录letters mom。如果你突然决定从终端删除目录letters mom,并且您在同一目录下有另一个名为letters的目录,并且该目录中包含重要的文档,结果你为了删除错误的目录尝试了以下操作:
|
||||
```
|
||||
rmdir letters mom
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
你将会有风险删除目录letters。这里说“风险”,是因为幸运的是rmdir这条用于删除目录的指令,有一个内置的安全措施,如果你试图删除一个非空目录时,它会发出警告。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,下面这个:
|
||||
```
|
||||
rm -Rf letters mom
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
(注 这是删除目录及其内容的一种非常标准的方式)将完全删除letters目录,甚至永远不会告诉你刚刚发生了什么。
|
||||
|
||||
rm命令用于删除文件和目录。当你将它与选项-R(递归删除)和-f(强制删除)一起使用时,它会深入到目录及其子目录中,删除它们包含的所有文件,然后删除子目录本身,然后它将删除所有顶层目录中的文件,再然后是删除目录本身。
|
||||
|
||||
`rm -Rf` 是你必须非常小心处理的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
我的建议是,你可以使用下划线来代替空格,但如果你仍然坚持使用空格,有两种方法可以使它们起作用。您可以使用单引号或双引号,如下所示:
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir 'letters mom'
|
||||
mkdir "letters dad"
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
或者,你可以转义空格。有些字符对shell有特殊意义。正如你所见,空格用于在命令行上分隔选项和参数。 “分离选项和参数”属于“特殊含义”范畴。当你想让shell忽略一个字符的特殊含义时,你需要转义,你可以在它前面放一个反斜杠(\)如:
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir letters\ mom
|
||||
mkdir letter\ dad
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
还有其他特殊字符需要转义,如撇号或单引号('),双引号(“)和&符号(&):
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir mom\ \&\ dad\'s\ letters
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
我知道你在想什么:如果反斜杠有一个特殊的含义(即告诉shell它必须转义下一个字符),这也使它成为一个特殊的字符。然后,你将如何转义转义字符(\)?
|
||||
|
||||
事实证明,你转义任何其他特殊字符都是同样的方式:
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir special\\characters
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
这将生成一个名为special\characters的目录。
|
||||
|
||||
感觉困惑?当然。这就是为什么你应该避免在目录名中使用特殊字符,包括空格。
|
||||
|
||||
以防误操作你可以参考下面这个记录特殊字符的列表。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
* 使用 `mkdir <directory name>` 创建新目录。
|
||||
* 使用 `rmdir <directory name>` 删除目录(仅在目录为空时才有效)。
|
||||
* 使用 `rm -Rf <directory name>` 来完全删除目录及其内容 - 请务必谨慎使用。
|
||||
* 使用相对路径创建相对于当前目录的目录: `mkdir newdir.`.
|
||||
* 使用绝对路径创建相对于根目录(`/`)的目录: `mkdir /home/<username>/newdir`
|
||||
* 使用 `..` 在当前目录的上级目录中创建目录: `mkdir ../newdir`
|
||||
* 你可以通过在命令行上使用空格分隔目录名来创建多个目录: `mkdir onedir twodir threedir`
|
||||
* 同时创建多个目录时,你可以混合使用相对路径和绝对路径: `mkdir onedir twodir /home/<username>/threedir`
|
||||
* 在目录名称中使用空格和特殊字符真的会让你很头疼,你最好不要那样做。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
有关更多信息,您可以查看`mkdir`, `rmdir` 和 `rm`的手册:
|
||||
```
|
||||
man mkdir
|
||||
man rmdir
|
||||
man rm
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
要退出手册页,请按键盘[q]键。
|
||||
|
||||
### 下次预告
|
||||
|
||||
在下一部分中,你将学习如何创建,修改和删除文件,以及你需要了解的有关权限和特权的所有信息!
|
||||
|
||||
通过Linux Foundation和edX免费提供的["Introduction to Linux" ][4]课程了解有关Linux的更多信息。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.linux.com/blog/learn/2018/5/manipulating-directories-linux
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Paul Brown][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[way-ww](https://github.com/way-ww)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.linux.com/users/bro66
|
||||
[1]:https://www.linux.com/blog/learn/intro-to-linux/2018/4/linux-filesystem-explained
|
||||
[2]:https://userbase.kde.org/Dolphin
|
||||
[3]:https://projects-old.gnome.org/nautilus/screenshots.html
|
||||
[4]:https://training.linuxfoundation.org/linux-courses/system-administration-training/introduction-to-linux
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
用于Linux桌面的4个扫描工具
|
||||
======
|
||||
使用其中一个开源软件驱动扫描仪来实现无纸化办公。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
尽管无纸化世界还没有到来,但越来越多的人通过扫描文件和照片来摆脱纸张的束缚。不过,仅仅拥有一台扫描仪还不足够。你还需要软件来驱动扫描仪。
|
||||
|
||||
然而问题是许多扫描仪制造商没有将Linux版本的软件与他们的设备适配在一起。不过在大多数情况下,即使没有也没多大关系。因为在linux桌面上已经有很好的扫描软件了。它们能够与许多扫描仪配合很好的完成工作。
|
||||
|
||||
现在就让我们看看四个简单又灵活的开源Linux扫描工具。我已经使用过了下面这些工具(甚至[早在2014年][1]写过关于其中三个工具的文章)并且觉得它们非常有用。希望你也会这样认为。
|
||||
|
||||
### Simple Scan
|
||||
|
||||
这是我最喜欢的一个软件之一,[Simple Scan][2]小巧,迅速,高效,且易于使用。如果你以前见过它,那是因为Simple Scan是GNOME桌面上的默认扫描程序应用程序,也是许多Linux发行版的默认扫描程序。
|
||||
|
||||
你只需单击一下就能扫描文档或照片。扫描过某些内容后,你可以旋转或裁剪它并将其另存为图像(仅限JPEG或PNG格式)或PDF格式。也就是说Simple Scan可能会很慢,即使你用较低分辨率来扫描文档。最重要的是,Simple Scan在扫描时会使用一组全局的默认值,例如150dpi用于文本,300dpi用于照片。你需要进入Simple Scan的首选项才能更改这些设置。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你扫描的内容超过了几页,还可以在保存之前重新排序页面。如果有必要的话 - 假如你正在提交已签名的表格 - 你可以使用Simple Scan来发送电子邮件。
|
||||
|
||||
### Skanlite
|
||||
|
||||
从很多方面来看,[Skanlite][3]是Simple Scan在KDE世界中的表兄弟。虽然Skanlite功能很少,但它可以出色的完成工作。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以自己配置这个软件的选项,包括自动保存扫描文件,设置扫描质量以及确定扫描保存位置。 Skanlite可以保存为以下图像格式:JPEG,PNG,BMP,PPM,XBM和XPM。
|
||||
|
||||
其中一个很棒的功能是Skanlite能够将你扫描的部分内容保存到单独的文件中。当你想要从照片中删除某人或某物时,这就派上用场了。
|
||||
|
||||
### Gscan2pdf
|
||||
|
||||
这是我另一个最爱的老软件,[gscan2pdf][4]可能会显得很老旧了,但它仍然包含一些比这里提到的其他软件更好的功能。即便如此,gscan2pdf仍然显得很轻便。
|
||||
|
||||
除了以各种图像格式(JPEG,PNG和TIFF)保存扫描外,gscan2pdf还将它们保存为PDF或[DjVu][5]文件。你可以在单击“扫描”按钮之前设置扫描的分辨率,无论是黑白,彩色还是纸张大小,每当你想要更改任何这些设置时,这都会进入gscan2pdf的首选项。你还可以旋转,裁剪和删除页面。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然这些都不是真正的杀手级功能,但它们会给你带来更多的灵活性。
|
||||
|
||||
### GIMP
|
||||
|
||||
你大概会知道[GIMP][6]是一个图像编辑工具。但是你恐怕不知道可以用它来驱动你的扫描仪吧。
|
||||
|
||||
你需要安装[XSane][7]扫描软件和GIMP XSane插件。这两个应该都可以从你的Linux发行版的包管理器中获得。在软件里,选择文件>创建>扫描仪/相机。单击扫描仪,然后单击扫描按钮即可进行扫描。
|
||||
|
||||
如果这不是你想要的,或者它不起作用,你可以将GIMP和一个叫作[QuiteInsane][8]的插件结合起来。使用任一插件,都能使GIMP成为一个功能强大的扫描软件,它可以让你设置许多选项,如是否扫描彩色或黑白,扫描的分辨率,以及是否压缩结果等。你还可以使用GIMP的工具来修改或应用扫描后的效果。这使得它非常适合扫描照片和艺术品。
|
||||
|
||||
### 它们真的能够工作吗?
|
||||
|
||||
所有的这些软件在大多数时候都能够在各种硬件上运行良好。我将它们与我过去几年来拥有的多台多功能打印机一起使用 - 无论是使用USB线连接还是通过无线连接。
|
||||
|
||||
你可能已经注意到我在前一段中写过“大多数时候运行良好”。这是因为我确实遇到过一个例外:一个便宜的canon多功能打印机。我使用的软件都没有检测到它。最后我不得不下载并安装canon的Linux扫描仪软件才使它工作。
|
||||
|
||||
你最喜欢的Linux开源扫描工具是什么?发表评论,分享你的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/18/9/linux-scanner-tools
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Scott Nesbitt][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
|
||||
译者:[way-ww](https://github.com/way-ww)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/scottnesbitt
|
||||
[1]: https://opensource.com/life/14/8/3-tools-scanners-linux-desktop
|
||||
[2]: https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/simple-scan
|
||||
[3]: https://www.kde.org/applications/graphics/skanlite/
|
||||
[4]: http://gscan2pdf.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[5]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DjVu
|
||||
[6]: http://www.gimp.org/
|
||||
[7]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scanner_Access_Now_Easy#XSane
|
||||
[8]: http://sourceforge.net/projects/quiteinsane/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user