mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-25 23:11:02 +08:00
Complete translating of 20170307 Assign Read-Write Access to a User on Specific Directory in Linux.md
This commit is contained in:
parent
28321209be
commit
c28b629bff
@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
|
|||||||
Translating by Ping
|
给用户赋予指定目录的读写权限
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Assign Read/Write Access to a User on Specific Directory in Linux
|
|
||||||
============================================================
|
============================================================
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In a previous article, we showed you how to [create a shared directory in Linux][3]. Here, we will describe how to give read/write access to a user on a specific directory in Linux.
|
在上篇文章中我们向您展示了如何在Linux上[创建一个共享目录][3]。这次,我们会为您介绍如何将Linux上指定目录的读写权限赋予用户。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
There are two possible methods of doing this: the first is [using ACLs (Access Control Lists)][4] and the second is [creating user groups to manage file permissions][5], as explained below.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For the purpose of this tutorial, we will use following setup.
|
有两种方法可以实现这个目标:第一种是 [使用 ACLs (访问控制列表)][4] ,第二种是[创建用户组来管理文件权限][5],下面会一一介绍。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
为了完成这个教程,我们将使用以下设置。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
Operating system: CentOS 7
|
Operating system: CentOS 7
|
||||||
@ -17,34 +17,34 @@ Test user: tecmint
|
|||||||
Filesystem type: Ext4
|
Filesystem type: Ext4
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Make sure all commands are executed as root user or use the the [sudo command][6] with equivalent privileges.
|
请确认所有的命令都是使用root用户执行的,或者使用 [sudo 命令][6] 来享受与之同样的权限。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Let’s start by creating the directory called `reports` using the mkdir command:
|
让我们开始吧!下面,先使用 mkdir 命令来创建一个名为 `reports` 的目录。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
# mkdir -p /shares/project1/reports
|
# mkdir -p /shares/project1/reports
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Using ACL to Give Read/Write Access to User on Directory
|
### 使用ACL来为用户赋予目录的读写权限
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Important: To use this method, ensure that your Linux filesystem type (such as Ext3 and Ext4, NTFS, BTRFS) support ACLs.
|
重要提示:打算使用此方法的话,您需要确认您的Linux文件系统类型(如 Ext3 and Ext4, NTFS, BTRFS)支持 ACLs.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
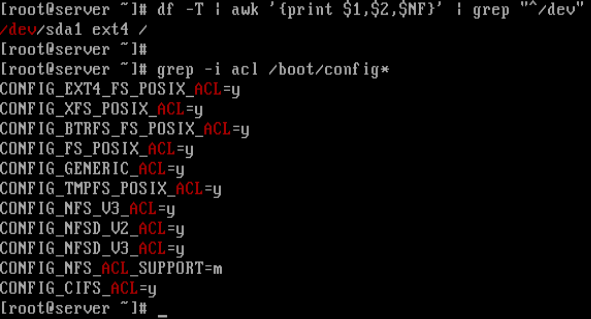
1. First, [check the current file system type][7] on your system, and also whether the kernel supports ACL as follows:
|
1. 首先, 依照以下命令在您的系统中[检查当前文件系统类型][7],并且查看内核是否支持ACL:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
# df -T | awk '{print $1,$2,$NF}' | grep "^/dev"
|
# df -T | awk '{print $1,$2,$NF}' | grep "^/dev"
|
||||||
# grep -i acl /boot/config*
|
# grep -i acl /boot/config*
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
From the screenshot below, the filesystem type is Ext4 and the kernel supports POSIX ACLs as indicated by the CONFIG_EXT4_FS_POSIX_ACL=y option.
|
从下方的截屏可以看到,文件系统类型是 Ext4,并且从 CONFIG_EXT4_FS_POSIX_ACL=y 选项可以发现内核是支持 POSIX ACLs 的。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[
|
[
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
][8]
|
][8]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Check Filesystem Type and Kernel ACL Support
|
查看文件系统类型和内核的ACL支持。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
2. Next, check if the file system (partition) is mounted with ACL option or not:
|
2. 接下来,查看文件系统(分区)挂载时是否使用了ACL选项。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
# tune2fs -l /dev/sda1 | grep acl
|
# tune2fs -l /dev/sda1 | grep acl
|
||||||
@ -53,16 +53,16 @@ Check Filesystem Type and Kernel ACL Support
|
|||||||

|

|
||||||
][9]
|
][9]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Check Partition ACL Support
|
查看分区是否支持ACL
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
From the above output, we can see that default mount option already has support for ACL. If in case it’s not enabled, you can enable it for the particular partition (/dev/sda3 for this case):
|
通过上边的输出可以发现,默认的挂载项目中已经对ACL进行了支持。如果发现结果不如所愿,你可以通过以下命令对指定分区(此例中使用/dev/sda3)开启ACL的支持。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
# mount -o remount,acl /
|
# mount -o remount,acl /
|
||||||
# tune2fs -o acl /dev/sda3
|
# tune2fs -o acl /dev/sda3
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
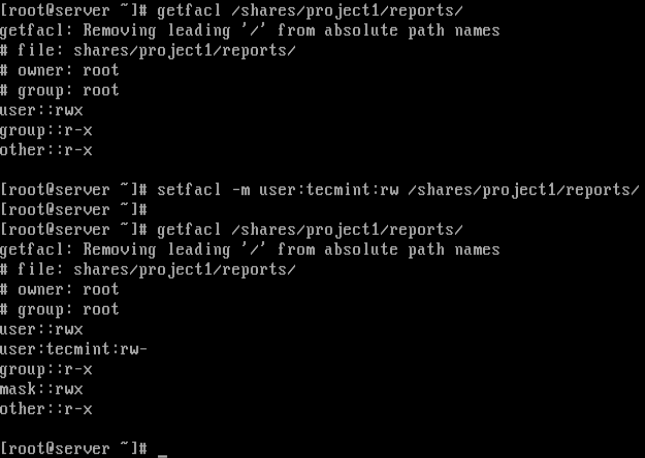
3. Now, its time to assign a read/write access to a user `tecmint` to a specific directory called `reports`by running the following commands.
|
3. 现在是时候指定目录 `reports` 的读写权限分配给名为 `tecmint` 的用户了,依照以下命令执行即可。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
# getfacl /shares/project1/reports # Check the default ACL settings for the directory
|
# getfacl /shares/project1/reports # Check the default ACL settings for the directory
|
||||||
@ -73,66 +73,67 @@ From the above output, we can see that default mount option already has support
|
|||||||
|

|
||||||
][10]
|
][10]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Give Read/Write Access to Directory Using ACL
|
通过ACL对指定目录赋予读写权限
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In the screenshot above, the user `tecmint` now has read/write (rw) permissions on directory /shares/project1/reports as seen from the output of the second getfacl command.
|
在上方的截屏中,通过输出结果的第二行getfacl命令可以发现,用户 `tecmint` 已经成功的被赋予了 /shares/project1/reports 目录的读写权限。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For more information about ACL lists, do check out our following guides.
|
如果想要获取ACL列表的更多信息。可以在下方查看我们的其他指南。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. [How to Use ACLs (Access Control Lists) to Setup Disk Quotas for Users/Groups][1]
|
1. [How to Use ACLs (Access Control Lists) to Setup Disk Quotas for Users/Groups][1]
|
||||||
2. [How to Use ACLs (Access Control Lists) to Mount Network Shares][2]
|
2. [How to Use ACLs (Access Control Lists) to Mount Network Shares][2]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now let’s see the second method of assigning read/write access to a directory.
|
现在我们来看看如何使用第二种方法来为目录赋予读写权限。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Using Groups to Give Read/Write Access to User on Directory
|
### 使用用户组来为用户赋予指定目录的读写权限
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. If the user already has a default user group (normally with same name as username), simply change the group owner of the directory.
|
1. 如果用户已经拥有了默认的用户组(通常组名与用户名相同),就可以简单的通过变更文件夹的所属用户组来完成。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
# chgrp tecmint /shares/project1/reports
|
# chgrp tecmint /shares/project1/reports
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Alternatively, create a new group for multiple users (who will be given read/write permissions on a specific directory), as follows. However, this will c[reate a shared directory][11]:
|
另外,我们也可以通过以下方法为多个用户(需要赋予指定目录读写权限的)新建一个用户组。如此一来,也就[创建了一个共享目录][11]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
# groupadd projects
|
# groupadd projects
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
2. Then add the user `tecmint` to the group `projects` as follows:
|
2. 接下来将用户 `tecmint` 添加到 `projects` 组中:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
# usermod -aG projects tecmint # add user to projects
|
# usermod -aG projects tecmint # add user to projects
|
||||||
# groups tecmint # check users groups
|
# groups tecmint # check users groups
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
3. Change the group owner of the directory to projects:
|
3. 将目录的所属用户组变更为 projects:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
# chgrp projects /shares/project1/reports
|
# chgrp projects /shares/project1/reports
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
4. Now set read/write access for the group members:
|
4. 现在,给组成员设置读写权限。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
# chmod -R 0760 /shares/projects/reports
|
# chmod -R 0760 /shares/projects/reports
|
||||||
# ls -l /shares/projects/ #check new permissions
|
# ls -l /shares/projects/ #check new permissions
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
That’s it! In this tutorial, we showed you how to give read/write access to a user on a specific directory in Linux. If any issues, do ask via the comment section below.
|
|
||||||
|
好了!这篇教程中,我们向您展示了如何在Linux中将指定目录的读写权限赋予用户。若有疑问,请在留言区中提问。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
作者简介:
|
作者简介:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
|
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,未来的 Linux 系统管理员和网络开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/give-read-write-access-to-directory-in-linux/
|
via: http://www.tecmint.com/give-read-write-access-to-directory-in-linux/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||||
译者:[ChrisLeeGit](https://github.com/chrisleegit)
|
译者:[Mr-Ping](http://www.mr-ping.com)
|
||||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user