mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
commit
c2300091b4
@ -1,249 +0,0 @@
|
||||
DockerChen翻译中
|
||||
|
||||
# A Practical Guide to Nmap (Network Security Scanner) in Kali Linux
|
||||
|
||||
In the second Kali Linux article, the network tool known as ‘[nmap][30]‘ will be discussed. While nmap isn’t a Kali only tool, it is one of the most [useful network mapping tools][29] in Kali.
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Kali Linux Installation Guide for Beginners – Part 1][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap, short for Network Mapper, is maintained by Gordon Lyon (more about Mr. Lyon here: [http://insecure.org/fyodor/][28]) and is used by many security professionals all over the world.
|
||||
|
||||
The utility works in both Linux and Windows and is command line (CLI) driven. However for those a little more timid of the command line, there is a wonderful graphical frontend for nmap called zenmap.
|
||||
|
||||
It is strongly recommended that individuals learn the CLI version of nmap as it provides much more flexibility when compared to the zenmap graphical edition.
|
||||
|
||||
What purpose does nmap server? Great question. Nmap allows for an administrator to quickly and thoroughly learn about the systems on a network, hence the name, Network MAPper or nmap.
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap has the ability to quickly locate live hosts as well as services associated with that host. Nmap’s functionality can be extended even further with the Nmap Scripting Engine, often abbreviated as NSE.
|
||||
|
||||
This scripting engine allows administrators to quickly create a script that can be used to determine if a newly discovered vulnerability exists on their network. Many scripts have been developed and included with most nmap installs.
|
||||
|
||||
A word of caution – nmap is a commonly used by people with both good and bad intentions. Extreme caution should be taken to ensure that you aren’t using nmap against systems that permission has not be explicitlyprovided in a written/legal agreement. Please use caution when using the nmap tool.
|
||||
|
||||
#### System Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Kali Linux][3] (nmap is available in other operating systems and functions similar to this guide).
|
||||
2. Another computer and permission to scan that computer with nmap – This is often easily done with software such as [VirtualBox][2] and the creation of a virtual machine.
|
||||
1. For a good machine to practice with, please read about Metasploitable 2
|
||||
2. Download for MS2 [Metasploitable2][1]
|
||||
3. A valid working connection to a network or if using virtual machines, a valid internal network connection for the two machines.
|
||||
|
||||
### Kali Linux – Working with Nmap
|
||||
|
||||
The first step to working with nmap is to log into the Kali Linux machine and if desired, start a graphical session (This first article in this series installed [Kali Linux with the Enlightenment Desktop Environment][27]).
|
||||
|
||||
During the installation, the installer would have prompted the user for a ‘root‘ user password which will be needed to login. Once logged in to the Kali Linux machine, using the command ‘startx‘ the Enlightenment Desktop Environment can be started – it is worth noting that nmap doesn’t require a desktop environment to run.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# startx
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][26]
|
||||
|
||||
Start Desktop Environment in Kali Linux
|
||||
|
||||
Once logged into Enlightenment, a terminal window will need to be opened. By clicking on the desktop background, a menu will appear. Navigating to a terminal can be done as follows: Applications -> System ->‘Xterm‘ or ‘UXterm‘ or ‘Root Terminal‘.
|
||||
|
||||
The author is a fan of the shell program called ‘[Terminator][25]‘ but this may not show up in a default install of Kali Linux. All shell programs listed will work for the purposes of nmap.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][24]
|
||||
|
||||
Launch Terminal in Kali Linux
|
||||
|
||||
Once a terminal has been launched, the nmap fun can begin. For this particular tutorial, a private network with a Kali machine and a Metasploitable machine was created.
|
||||
|
||||
This made things easier and safer since the private network range would ensure that scans remained on safe machines and prevents the vulnerable Metasploitable machine from being compromised by someone else.
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, both of the machines are on a private 192.168.56.0 /24 network. The Kali machine has an IP address of 192.168.56.101 and the Metasploitable machine to be scanned has an IP address of 192.168.56.102.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s say though that the IP address information was unavailable. A quick nmap scan can help to determine what is live on a particular network. This scan is known as a ‘Simple List’ scan hence the `-sL` arguments passed to the nmap command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nmap -sL 192.168.56.0/24
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][23]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap – Scan Network for Live Hosts
|
||||
|
||||
Sadly, this initial scan didn’t return any live hosts. Sometimes this is a factor of the way certain Operating Systems handle [port scan network traffic][22].
|
||||
|
||||
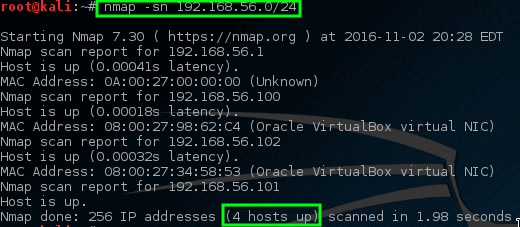
Not to worry though, there are some tricks that nmap has available to try to find these machines. This next trick will tell nmap to simply try to ping all the addresses in the 192.168.56.0/24 network.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nmap -sn 192.168.56.0/24
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][21]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap – Ping All Connected Live Network Hosts
|
||||
|
||||
This time nmap returns some prospective hosts for scanning! In this command, the `-sn` disables nmap’s default behavior of attempting to port scan a host and simply has nmap try to ping the host.
|
||||
|
||||
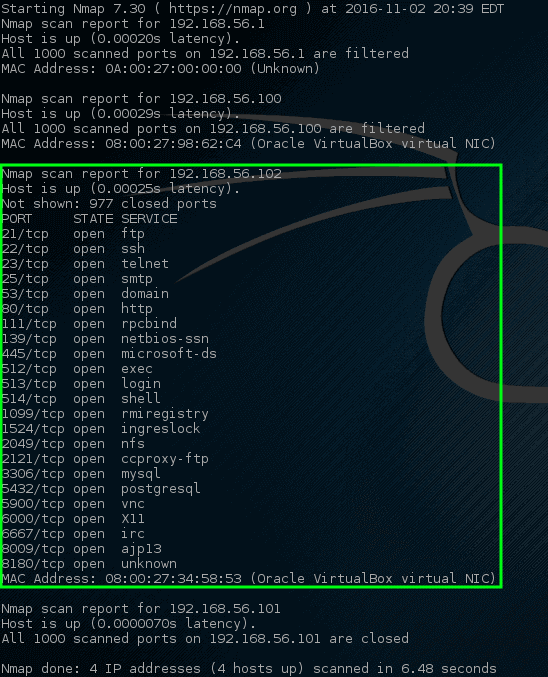
Let’s try letting nmap port scan these specific hosts and see what turns up.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nmap 192.168.56.1,100-102
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][20]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap – Network Ports Scan on Host
|
||||
|
||||
Wow! This time nmap hit a gold mine. This particular host has quite a bit of [open network ports][19].
|
||||
|
||||
These ports all indicate some sort of listening service on this particular machine. Recalling from earlier, the 192.168.56.102 IP address is assigned to the metasploitable vulnerable machine hence why there are so many [open ports on this host][18].
|
||||
|
||||
Having this many ports open on most machines is highly abnormal so it may be a wise idea to investigate this machine a little closer. Administrators could track down the physical machine on the network and look at the machine locally but that wouldn’t be much fun especially when nmap could do it for us much quicker!
|
||||
|
||||
This next scan is a service scan and is often used to try to determine what [service may be listening on a particular port][17] on a machine.
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap will probe all of the open ports and attempt to banner grab information from the services running on each port.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nmap -sV 192.168.56.102
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][16]
|
||||
|
||||
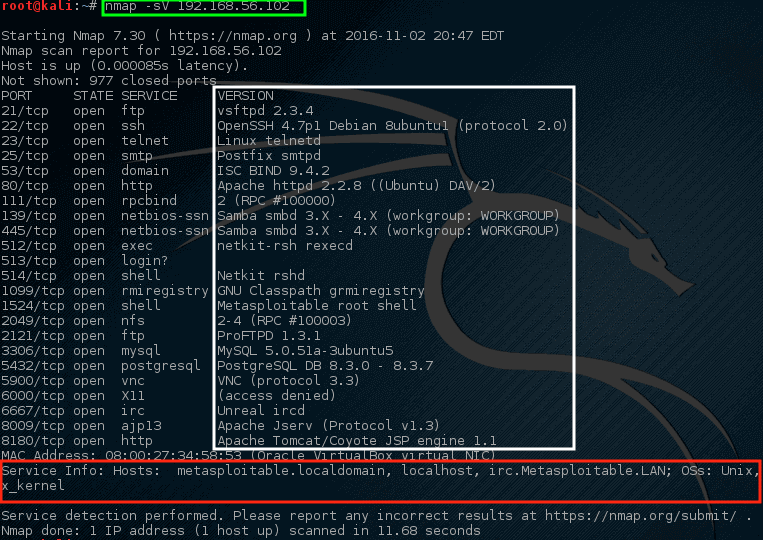
Nmap – Scan Network Services Listening of Ports
|
||||
|
||||
Notice this time nmap provided some suggestions on what nmap thought might be running on this particular port (highlighted in the white box). Also nmap also tried to [determine information about the operating system][15]running on this machine as well as its hostname (with great success too!).
|
||||
|
||||
Looking through this output should raise quite a few concerns for a network administrator. The very first line claims that VSftpd version 2.3.4 is running on this machine! That’s a REALLY old version of VSftpd.
|
||||
|
||||
Searching through ExploitDB, a serious vulnerability was found back in 2011 for this particular version (ExploitDB ID – 17491).
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s have nmap take a closer look at this particular port and see what can be determined.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nmap -sC 192.168.56.102 -p 21
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][14]
|
||||
|
||||
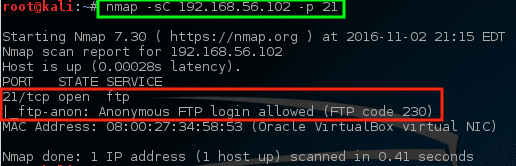
Nmap – Scan Particular Post on Machine
|
||||
|
||||
With this command, nmap was instructed to run its default script (-sC) on the FTP port (-p 21) on the host. While it may or may not be an issue, nmap did find out that [anonymous FTP login is allowed][13] on this particular server.
|
||||
|
||||
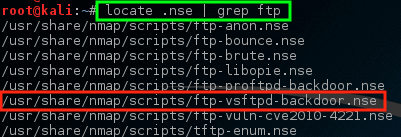
This paired with the earlier knowledge about VSftd having an old vulnerability should raise some concern though. Let’s see if nmap has any scripts that attempt to check for the VSftpd vulnerability.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# locate .nse | grep ftp
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][12]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap – Scan VSftpd Vulnerability
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that nmap has a NSE script already built for the VSftpd backdoor problem! Let’s try running this script against this host and see what happens but first it may be important to know how to use the script.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nmap --script-help=ftp-vsftd-backdoor.nse
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][11]
|
||||
|
||||
Learn Nmap NSE Script Usage
|
||||
|
||||
Reading through this description, it is clear that this script can be used to attempt to see if this particular machine is vulnerable to ExploitDB issue identified earlier.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s run the script and see what happens.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
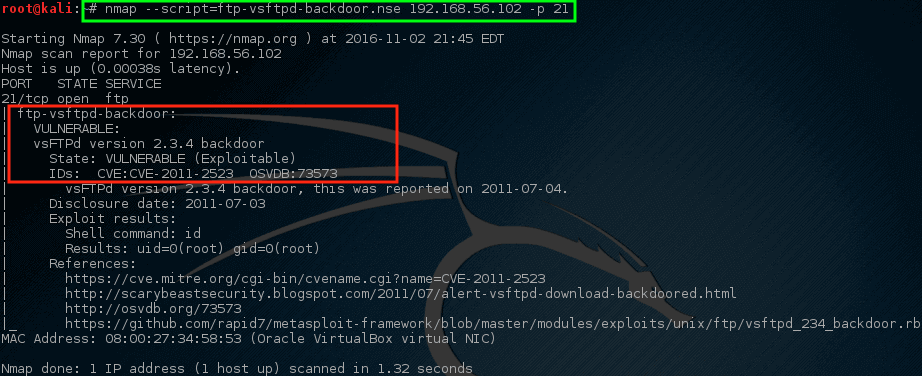
# nmap --script=ftp-vsftpd-backdoor.nse 192.168.56.102 -p 21
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][10]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap – Scan Host for Vulnerable
|
||||
|
||||
Yikes! Nmap’s script returned some dangerous news. This machine is likely a good candidate for a serious investigation. This doesn’t mean that the machine is compromised and being used for horrible/terrible things but it should bring some concerns to the network/security teams.
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap has the ability to be extremely selective and extremely quite. Most of what has been done so far has attempted to keep nmap’s network traffic moderately quiet however scanning a personally owned network in this fashion can be extremely time consuming.
|
||||
|
||||
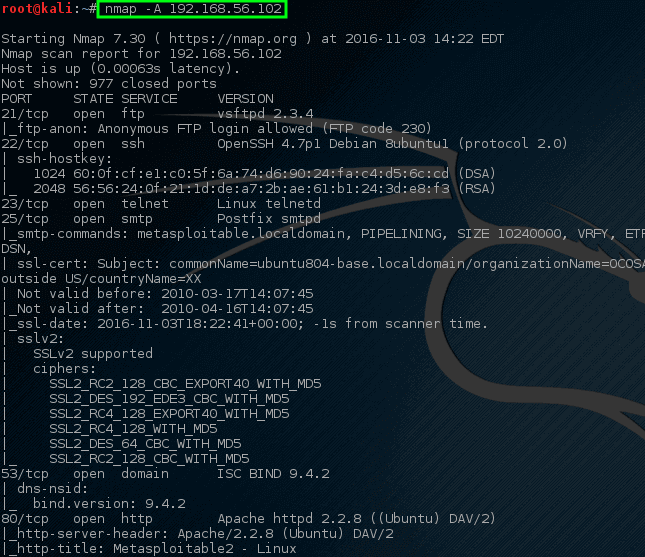
Nmap has the ability to do a much more aggressive scan that will often yield much of the same information but in one command instead of several. Let’s take a look at the output of an aggressive scan (Do note – an aggressive scan can set off [intrusion detection/prevention systems][9]!).
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nmap -A 192.168.56.102
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap – Complete Network Scan on Host
|
||||
|
||||
Notice this time, with one command, nmap has returned a lot of the information it returned earlier about the open ports, services, and configurations running on this particular machine. Much of this information can be used to help determine [how to protect this machine][7] as well as to evaluate what software may be on a network.
|
||||
|
||||
This was just a short, short list of the many useful things that nmap can be used to find on a host or network segment. It is strongly urged that individuals continue to [experiment with nmap][6] in a controlled manner on a network that is owned by the individual (Do not practice by scanning other entities!).
|
||||
|
||||
There is a official guide on Nmap Network Scanning by author Gordon Lyon, available from Amazon.
|
||||
|
||||
<center style="border: 0px; font-style: inherit; font-variant: inherit; font-weight: inherit; font-stretch: inherit; font-size: inherit; line-height: inherit; font-family: inherit; vertical-align: baseline;">[
|
||||

|
||||
][5]</center>
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/nmap-network-security-scanner-in-kali-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Rob Turner][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/robturner/
|
||||
[1]:https://sourceforge.net/projects/metasploitable/files/Metasploitable2/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-virtualbox-on-redhat-centos-fedora/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/kali-linux-installation-guide
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/kali-linux-installation-guide
|
||||
[5]:http://amzn.to/2eFNYrD
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/nmap-command-examples/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/security-and-hardening-centos-7-guide/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Scan-Network-Host.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/protect-apache-using-mod_security-and-mod_evasive-on-rhel-centos-fedora/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Scan-Host-for-Vulnerable.png
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Learn-NSE-Script.png
|
||||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Scan-Service-Vulnerability.png
|
||||
[13]:http://www.tecmint.com/setup-ftp-anonymous-logins-in-linux/
|
||||
[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Scan-Particular-Port-on-Host.png
|
||||
[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/commands-to-collect-system-and-hardware-information-in-linux/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Scan-Network-Services-Ports.png
|
||||
[17]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-linux-processes-memory-ram-cpu-usage/
|
||||
[18]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-open-ports-in-linux/
|
||||
[19]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-open-ports-in-linux/
|
||||
[20]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Scan-for-Ports-on-Hosts.png
|
||||
[21]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Ping-All-Network-Live-Hosts.png
|
||||
[22]:http://www.tecmint.com/audit-network-performance-security-and-troubleshooting-in-linux/
|
||||
[23]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Scan-Network.png
|
||||
[24]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Launch-Terminal-in-Kali-Linux.png
|
||||
[25]:http://www.tecmint.com/terminator-a-linux-terminal-emulator-to-manage-multiple-terminal-windows/
|
||||
[26]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Start-Desktop-Environment-in-Kali-Linux.png
|
||||
[27]:http://www.tecmint.com/kali-linux-installation-guide
|
||||
[28]:http://insecure.org/fyodor/
|
||||
[29]:http://www.tecmint.com/bcc-best-linux-performance-monitoring-tools/
|
||||
[30]:http://www.tecmint.com/nmap-command-examples/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,261 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# 一份关于在Kali Linux下使用Nmap(网络安全扫描器)的实用指南
|
||||
在这第二篇Kali Linux文章中, 将讨论称为‘[nmap][30]‘的网络工具。虽然nmap不是Kali下唯一的一个工具,但它是最[有用的网络映射工具][29]之一。
|
||||
|
||||
1. [第一部分-为初学者准备的Kali Linux安装指南][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap,是Network Mapper的缩写,由Gordon Lyon维护(更多关于Mr. Lyon的信息在这里: [http://insecure.org/fyodor/][28]) ,并被世界各地许多的安全专业人员使用。
|
||||
|
||||
这个工具在Linux和Windows都能使用,并且是用命令行驱动的。相对于那些令人害怕的命令行,对于nmap,在这里有一个美妙的图形化前端叫做zenmap。
|
||||
|
||||
强烈建议个人去学习nmap的CLI版本,因为与图形化版本zenmap相比,它提供了更多的灵活性。
|
||||
|
||||
nmap服务器的目的是什么?很好的问题。Nmap允许管理员快速彻底地了解网络上的系统,因此,它的名字叫Network MAPper或者nmap。
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap能够快速找到活动的主机和与该主机相关联的服务。Nmap的功能还可以进一步被扩展,通过结合Nmap脚本引擎,通常缩写为NSE。
|
||||
|
||||
此脚本引擎允许管理员快速创建可用于确定其网络上是否存在新发现的漏洞的脚本。许多脚本已经被开发并且包含在大多数的nmap安装中。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
提醒一句- nmap是被有好的和坏的意图的人共同使用的。应该非常小心,以确保你不使用nmap对系统的权限没有明确提供在书面/法律协议上进行攻击。请在使用nmap工具的时候注意!
|
||||
|
||||
#### 系统要求
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Kali Linux][3] (nmap可以用于其他操作系统并且功能也和这个指南里面讲的类似).
|
||||
2. 有另一台计算机并且装有nmap的计算机有权限扫描它-这通常很容易通过软件来实现,例如[VirtualBox][2],可以创建虚拟机.
|
||||
1. 想要有一个好的机器来联系,请阅读Metasploitable 2
|
||||
2. 下载MS2 [Metasploitable2][1]
|
||||
3. 一个与网络有效的工作连接或者是使用虚拟机,就可以为这两台计算机建立有效的内部网络连接
|
||||
|
||||
### Kali Linux – 使用Nmap
|
||||
|
||||
The first step to working with nmap is to log into the Kali Linux machine and if desired, start a graphical session (This first article in this series installed [Kali Linux with the Enlightenment Desktop Environment][27]).
|
||||
使用nmap的第一步是登录Kali Linux,如果需要,就启动一个图形会话(本系列的第一篇文章安装了[Kali Linux with Enlightenment桌面环境] [27])。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在安装过程中,安装程序将提示用户输入需要登录的“root”用户和密码。 一旦登录到Kali Linux机器,使用命令'startx'就可以启动Enlightenment桌面环境 - 值得注意的是nmap不需要运行桌面环境。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# startx
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][26]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在Kali Linux中启动桌面环境
|
||||
|
||||
一旦登录启用,将需要打开终端窗口。 通过点击桌面背景,将会出现一个菜单。 导航到终端可以进行如下操作:应用程序 - >系统 - >'Xterm'或'UXterm'或'根终端'。
|
||||
|
||||
作者是shell程序的粉丝叫'[Terminator] [25]',但是这可能不会显示在Kali Linux的默认安装中。 列出的所有shell程序都出于使用nmap的目的。
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][24]
|
||||
|
||||
在Kali Linux下启动终端
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
一旦终端启动,nmap的乐趣就开始了。 对于这个特定的教程,创建了一个具有Kali机器和Metasploitable机器的专用网络。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这会使事情变得更容易和更安全,因为私有的网络范围将确保扫描保持在安全的机器上,防止易受攻击的Metasploitable机器被其他人攻击。
|
||||
|
||||
在此示例中,这两台计算机都位于专用的192.168.56.0 / 24网络上。 Kali机器的IP地址为192.168.56.101,要扫描的Metasploitable机器的IP地址为192.168.56.102。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
虽然IP地址信息不可用,但是 快速nmap扫描可以帮助确定在特定网络上存在什么, 此扫描称为“Simple List”扫描,因此将`-sL`参数传递给nmap命令。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nmap -sL 192.168.56.0/24
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][23]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap – 扫描网络上的存活主机
|
||||
|
||||
悲伤的是,这个初始扫描没有返回任何活主机。 有时,这是某些操作系统处理[端口扫描网络流量] [22]的一个因素。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
不用担心,在这里有一些技巧可以使nmap尝试找到这些机器。 下一个技巧会告诉nmap只是尝试ping 192.168.56.0/24网络中的所有地址。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nmap -sn 192.168.56.0/24
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][21]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap – Ping所有已连接的活动网络主机
|
||||
这个时间nmap会返回一些潜在的主机来进行扫描! 在此命令中,`-sn`禁用nmap的尝试端口扫描主机的默认行为,只是让nmap尝试ping主机。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
让我们尝试让nmap端口扫描这些特定的主机,看看会出现什么。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nmap 192.168.56.1,100-102
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][20]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap – 在主机上扫描网络端口
|
||||
|
||||
哇! 这一次nmap挖到了一个金矿。 这个特定的主机有相当多的[开放网络端口] [19]。
|
||||
|
||||
这些端口都指代在此特定机器上的某种监听服务。 从早期回忆,192.168.56.102的IP地址会分配给性易受攻击的机器,因此这就是为什么会有这么多[开放端口在这个主机上] [18]。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在大多数机器上打开这个端口是非常不正常的,所以它可能是一个明智的想法,因为可以非常紧密地调查这台机器。 管理员可以跟踪网络上的物理机器,并在本地查看这台机器,但这不会很有趣,特别是当nmap可以做到我们更快!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
下一个扫描是服务扫描,通常用于尝试确定机器上什么[服务在特定的端口被监听] [17]。
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap将探测所有打开的端口,并尝试从每个端口上运行的服务中获取信息。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nmap -sV 192.168.56.102
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][16]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap – 扫描网络服务监听端口
|
||||
|
||||
请注意这次nmap提供了一些关于nmap在特定端口运行的建议(在白框中突出显示),而且nmap也试图[确认这个操作系统的信息][15]运行在这台机器上和它的主机名(也非常成功!)。
|
||||
Notice this time nmap provided some suggestions on what nmap thought might be running on this particular port (highlighted in the white box). Also nmap also tried to [determine information about the operating system][15]running on this machine as well as its hostname (with great success too!).
|
||||
|
||||
查看这个输出,应该引起网络管理员相当多的关注。 第一行声称VSftpd版本2.3.4正在这台机器上运行! 这是一个真正的旧版本的VSftpd。
|
||||
|
||||
通过查找ExploitDB,一个非常严重的漏洞是在2001被发现,这是一个特别的版本(ExploitDB ID – 17491)。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们使用nmap更加清楚的查看这个特别的端口并且看看可以确认什么东西。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nmap -sC 192.168.56.102 -p 21
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][14]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap – 扫描机器上的特定邮件
|
||||
|
||||
使用此命令,让nmap在主机上的FTP端口(-p 21)上运行其默认脚本(-sC)。 虽然它可能是也可能不是一个问题,但是nmap确实发现[匿名FTP登录是允许的] [13]在这个特定的服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
这与早先有关具有旧漏洞的VSftd的知识相匹配,应该引起一些关注。 让我们看看nmap是否有任何脚本来试图检查VSftpd漏洞。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# locate .nse | grep ftp
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][12]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap – 扫描VSftpd漏洞
|
||||
|
||||
注意nmap有一个NSE脚本已经用来处理VSftpd后门问题! 让我们尝试对这个主机运行这个脚本,看看会发生什么,但首先知道如何使用脚本可能是很重要的。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nmap --script-help=ftp-vsftd-backdoor.nse
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][11]
|
||||
|
||||
了解Nmap NSE脚本使用情况
|
||||
|
||||
通过这个描述,很明显,这个脚本可以用来试图查看这个特定的机器是否容易受到先前识别的ExploitDB问题。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们运行这个脚本,看看会发生什么。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nmap --script=ftp-vsftpd-backdoor.nse 192.168.56.102 -p 21
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][10]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap – 扫描易受攻击的主机
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Yikes! Nmap的脚本返回了一些危险的消息。 这台机器可能是一个很好的候选者,之后可以进行更加详细的调查。 这并不意味着机器缺乏抵抗力和可以被用于做一些可怕/糟糕的事情,但它应该给网络/安全团队带来一些关注。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap具有极高的选择性和极高的能力。 到目前为止已经做的大多数尝试保持nmap的网络流量适度保持平稳,然而以这种方式扫描个人拥有的网络可能是非常耗时的。
|
||||
Nmap有能力做一个更积极的扫描,往往会产生大部分相同的信息,但在一个命令,而不是几个。 让我们来看看积极的扫描的输出(注意 - 积极的扫描可以被关闭[入侵检测/预防系统][9]!).
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nmap -A 192.168.56.102
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap – 在主机上完成网络扫描
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
注意这一次,使用一个命令,nmap返回了很多关于在这台特定机器上运行的开放端口,服务和配置的信息。 这些信息中的大部分可用于帮助确定[如何保护本机] [7]以及评估网络上可能存在的软件。
|
||||
|
||||
这只是nmap可用于在主机或网段上找到的许多有用事情的简短列表。 强烈敦促个人在个人拥有的网络上继续[以nmap] [6]进行实验。(不要通过扫描其他实体练习!)。
|
||||
|
||||
有一个关于Nmap网络扫描的官方指南,作者Gordon Lyon,可从亚马逊上获得。
|
||||
|
||||
<center style="border: 0px; font-style: inherit; font-variant: inherit; font-weight: inherit; font-stretch: inherit; font-size: inherit; line-height: inherit; font-family: inherit; vertical-align: baseline;">[
|
||||

|
||||
][5]</center>
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/nmap-network-security-scanner-in-kali-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Rob Turner][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[DockerChen](https://github.com/DockerChen)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/robturner/
|
||||
[1]:https://sourceforge.net/projects/metasploitable/files/Metasploitable2/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-virtualbox-on-redhat-centos-fedora/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/kali-linux-installation-guide
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/kali-linux-installation-guide
|
||||
[5]:http://amzn.to/2eFNYrD
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/nmap-command-examples/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/security-and-hardening-centos-7-guide/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Scan-Network-Host.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/protect-apache-using-mod_security-and-mod_evasive-on-rhel-centos-fedora/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Scan-Host-for-Vulnerable.png
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Learn-NSE-Script.png
|
||||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Scan-Service-Vulnerability.png
|
||||
[13]:http://www.tecmint.com/setup-ftp-anonymous-logins-in-linux/
|
||||
[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Scan-Particular-Port-on-Host.png
|
||||
[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/commands-to-collect-system-and-hardware-information-in-linux/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Scan-Network-Services-Ports.png
|
||||
[17]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-linux-processes-memory-ram-cpu-usage/
|
||||
[18]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-open-ports-in-linux/
|
||||
[19]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-open-ports-in-linux/
|
||||
[20]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Scan-for-Ports-on-Hosts.png
|
||||
[21]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Ping-All-Network-Live-Hosts.png
|
||||
[22]:http://www.tecmint.com/audit-network-performance-security-and-troubleshooting-in-linux/
|
||||
[23]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Nmap-Scan-Network.png
|
||||
[24]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Launch-Terminal-in-Kali-Linux.png
|
||||
[25]:http://www.tecmint.com/terminator-a-linux-terminal-emulator-to-manage-multiple-terminal-windows/
|
||||
[26]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Start-Desktop-Environment-in-Kali-Linux.png
|
||||
[27]:http://www.tecmint.com/kali-linux-installation-guide
|
||||
[28]:http://insecure.org/fyodor/
|
||||
[29]:http://www.tecmint.com/bcc-best-linux-performance-monitoring-tools/
|
||||
[30]:http://www.tecmint.com/nmap-command-examples/
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user