mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-13 22:30:37 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject
This commit is contained in:
commit
c0806fa06d
@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
|
||||
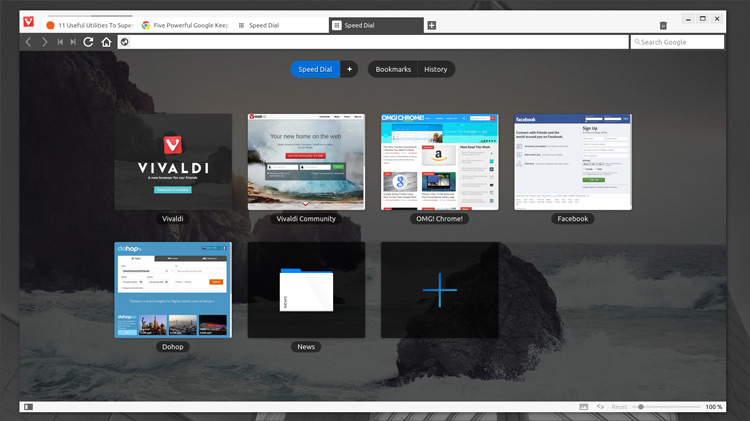
Meet Vivaldi — A New Web Browser Built for Power Users
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**A brand new web browser has arrived this week that aims to meet the needs of power users — and it’s already available for Linux.**
|
||||
|
||||
Vivaldi is the name of this new browser and it has been launched as a tech preview (read: a beta without the responsibility) for 64-bit Linux machines, Windows and Mac. It is built — shock — on the tried-and-tested open-source frameworks of Chromium, Blink and Google’s open-source V8 JavaScript engine (among other projects).
|
||||
|
||||
Does the world really want another browser? Vivaldi, the brain child of former Opera Software CEO Jon von Tetzchner, is less concerned about want and more about need.
|
||||
|
||||
Vivaldi is being built with the sort of features that keyboard preferring tab addicts need. It is not being pitched at users who find Firefox perplexing or whose sole criticism of Chrome is that it moved the bookmarks button.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s not tacky marketing spiel either. Despite the ‘technical preview’ badge it comes with, Vivaldi is already packed with features that demonstrate its power user slant.
|
||||
|
||||
Plenty of folks feel left behind and underserved by the simplified, paired back offerings other software companies are producing. Vivaldi, even at this early juncture, looks well placed to succeed in winning them over.
|
||||
|
||||
### Vivaldi Features ###
|
||||
|
||||
A few of Vivaldi’s key features already present include:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Quick Commands** (Ctrl + Q) is an in-app HUD that lets you quickly filter through settings, options and features, be it opening a bookmark or hiding the status bar, using your keyboard. No clicks needed.
|
||||
|
||||
**Tab Stacks** let you clean up your workspace by grouping separate tabs into one, and then using a keyboard command or the tab preview picker to switch between them.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
A collapsible **side panel** that houses extra features (just like old Opera) including a (not yet working) mail client, contacts, bookmarks browser and note taking section that lets you take and annotate screenshots.
|
||||
|
||||
A bunch of other features are on offer too, including customizable keyboard shortcuts, a tabs bar that can be set on any edge of the browser (or hidden entirely), privacy options and a speed dial with folders.
|
||||
|
||||
### Opera Mark II ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
It’s not a leap to see Vivaldi as the true successor to Opera post-Presto (Opera’s old, proprietary rendering engine). Opera (which also pushed out a minor new update today) has split out many of its “power user” features as it chases a lighter, more manageable set of features.
|
||||
|
||||
Vivaldi wants to pick up the baggage Opera has been so keen to offload. And while that might not help it grab marketshare it will see it grab the attention of power users, many of whom will no doubt already be using Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### Download ###
|
||||
|
||||
Interested in taking it for a spin? You can. Vivaldi is available to download for Windows, Mac and 64-bit Linux distributions. On the latter you have a choice of Debian or RPM installer.
|
||||
|
||||
Bear in mind that it’s not finished and that more features (including extensions, sync and more) are planned for future builds.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Vivaldi Tech Preview for Linux][1]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/01/vivaldi-web-browser-linux-download-power-users
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:https://vivaldi.com/#Download
|
||||
153
sources/talk/20150128 The top 10 rookie open source projects.md
Normal file
153
sources/talk/20150128 The top 10 rookie open source projects.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,153 @@
|
||||
The top 10 rookie open source projects
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Black Duck presents its Open Source Rookies of the Year -- the 10 most exciting, active new projects germinated by the global open source community
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Open Source Rookies of the Year ###
|
||||
|
||||
Each year sees the start of thousands of new open source projects. Only a handful gets real traction. Some projects gain momentum by building on existing, well-known technologies; others truly break new ground. Many projects are created to solve a simple development problem, while others begin with loftier intentions shared by like-minded developers around the world.
|
||||
|
||||
Since 2009, the open source software logistics company Black Duck has identified the [Open Source Rookies of the Year][1], based on activity tracked by its [Open Hub][2] (formerly Ohloh) site. This year, we're delighted to present 10 winners and two honorable mentions for 2015, selected from thousands of open source projects. Using a weighted scoring system, points were awarded based on project activity, the pace of commits, and several other factors.
|
||||
|
||||
Open source has become the industry's engine of innovation. This year, for example, growth in projects related to Docker containerization trumped every other rookie area -- and not coincidentally reflected the most exciting area of enterprise technology overall. At the very least, the projects described here provide a window on what the global open source developer community is thinking, which is fast becoming a good indicator of where we're headed.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2015 Open Source Rookie of the Year: DebOps ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[DebOps][3] is a collection of [Ansible][4] playbooks and roles, scalable from one container to an entire data center. Founder Maciej Delmanowski open-sourced DebOps to ensure his work outlived his current work environment and could grow in strength and depth from outside contributors.
|
||||
|
||||
DebOps began at a small university in Poland that ran its own data center, where everything was configured by hand. Crashes sometimes led to days of downtime -- and Delmanowski realized that a configuration management system was needed. Starting with a Debian base, DebOps is a group of Ansible playbooks that configure an entire data infrastructure. The project has been implemented in many different working environments, and the founders plan to continue supporting and improving it as time goes on.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2015 Open Source Rookie of the Year: Code Combat ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The traditional pen-and-paper way of learning falls short for technical subjects. Games, however, are all about engagement -- which is why the founders of [CodeCombat][5] went about creating a multiplayer programming game to teach people how to code.
|
||||
|
||||
At its inception, CodeCombat was an idea for a startup, but the founders decided to create an open source project instead. The idea blossomed within the community, and the project gained contributors at a steady rate. A mere two months after its launch, the game was accepted into Google’s Summer of Code. The game reaches a broad audience and is available in 45 languages. CodeCombat hopes to become the standard for people who want to learn to code and have fun at the same time.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2015 Open Source Rookie of the Year: Storj ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Storj][6] is a peer-to-peer cloud storage network that implements end-to-end encryption, enabling users to transfer and share data without reliance on a third party. Based on bitcoin blockchain technology and peer-to-peer protocols, Storj provides secure, private, and encrypted cloud storage.
|
||||
|
||||
Opponents of cloud-based data storage worry about cost efficiencies and vulnerability to attack. Intended to address both concerns, Storj is a private cloud storage marketplace where space is purchased and traded via Storjcoin X (SJCX). Files uploaded to Storj are shredded, encrypted, and stored across the community. File owners are the sole individuals who possess keys to the encrypted information.
|
||||
|
||||
The proof of concept for this decentralized cloud storage marketplace was first presented at the Texas Bitcoin Conference Hackathon in 2014. After winning first place in the hackathon, the project founders and leaders used open forums, Reddit, bitcoin forums, and social media to grow an active community, now an essential part of the Storj decision-making process.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2015 Open Source Rookie of the Year: Neovim ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Since its inception in 1991, Vim has been a beloved text editor adopted by millions of software developers. [Neovim][6] is the next generation.
|
||||
|
||||
The software development ecosystem has experienced exponential growth and innovation over the past 23 years. Neovim founder Thiago de Arruda knew that Vim was lacking in modern-day features and development speed. Although determined to preserve the signature features of Vim, the community behind Neovim seeks to improve and evolve the technology of its favorite text editor. Crowdfunding initially enabled de Arruda to focus six uninterrupted months on launching this endeavor. He credits the Neovim community for supporting the project and for inspiring him to continue contributing.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2015 Open Source Rookie of the Year: CockroachDB ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Former Googlers are bringing a big-company data solution to open source in the form of [CockroachDB][8], a scalable, geo-replicated, transactional data store.
|
||||
|
||||
To maintain the terabytes of data transacted over its global online properties, Google developed Spanner. This powerful tool provides Google with scalability, survivability, and transactionality -- qualities that the team behind CockroachDB is serving up to the open source community. Like an actual cockroach, CockroachDB can survive without its head, tolerating the failure of any node. This open source project has a devoted community of experienced contributors, actively cultivated by the founders via social media, GitHub, networking, conferences, and meet-ups.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2015 Open Source Rookie of the Year: Kubernetes ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In introducing containerized software development to the open source community, [Docker][9] has become the backbone of a strong, innovative set of tools and technologies. [Kubernetes][10], which Google introduced last June, is an open source container management tool used to accelerate development and simplify operations.
|
||||
|
||||
Google has been using containers for years in its internal operations. At the summer 2014 DockerCon, the Internet giant open-sourced Kubernetes, which was developed to meet the needs of the exponentially growing Docker ecosystem. Through collaborations with other organizations and projects, such as Red Hat and CoreOS, Kubernetes project managers have grown their project to be the No. 1 downloaded tool on the Docker Hub. The Kubernetes team hopes to expand the project and grow the community, so software developers can spend less time managing infrastructure and more time building the apps they want.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2015 Open Source Rookie of the Year: Open Bazaar ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[OpenBazaar][11] is a decentralized marketplace for trading with anyone using bitcoin. The proof of concept for OpenBazaar was born at a hackathon, where its founders combined BitTorent, bitcoin, and traditional financial server methodologies to create a censorship-resistant trading platform. The OpenBazaar team sought new members, and before long they were able to expand the OpenBazaar community immensely. The table stakes of OpenBazaar -- transparency and a common goal to revolutionize trade and commerce -- are helping founders and contributors work toward a real-world, uncontrolled, and decentralized marketplace.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2015 Open Source Rookie of the Year: IPFS ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[IPFS (InterPlanetary File System)][12] is a global, versioned, peer-to-peer file system.It synthesizes many of the ideas behind Git, BitTorrent, and HTTP to bring a new data and data structure transport protocol to the open Web.
|
||||
|
||||
Open source is known for developing simple solutions to complex problems that result in many innovations, but these powerful projects represent only one slice of the open source community. IFPS belong to a more radical group whose proof of concept seems daring, outrageous, and even unattainable -- in this case, a peer-to-peer distributed file system that seeks to connect all computing devices. This possible HTTP replacement maintains a community through multiple mediums, including the Git community and an IRC channel that has more than 100 current contributors. This “crazy” idea will be available for alpha testing in 2015.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2015 Open Source Rookie of the Year: cAdvisor ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[cAdvisor (Container Advisor)][13] is a daemon that collects, aggregates, processes, and exports information about running containers, providing container users with an understanding of resource usage and performance characteristics. For each container, cAdvisor keeps resource isolation parameters, historical resource usage, histograms of complete historical resource usage, and network statistics. This data is exported by container and across machines.
|
||||
|
||||
cAdvisor can run on most Linux distros and supports many container types, including Docker. It has become the de facto monitoring agent for containers, has been integrated into many systems, and is one of the most downloaded images on the Docker Hub. The team hopes to grow cAdvisor to understand application performance more deeply and to integrate this information into clusterwide systems.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2015 Open Source Rookie of the Year: Terraform ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Terraform][14] provides a common configuration to launch infrastructure, from physical and virtual servers to email and DNS providers. The idea is to encompass everything from custom in-house solutions to services offered by public cloud platforms. Once launched, Terraform enables ops to change infrastructure safely and efficiently as the configuration evolves.
|
||||
|
||||
Working at a devops company, Terraform.io's founders identified a pain point in codifying the knowledge required to build a complete data center, from plugged-in servers to a fully networked and functional data center. Infrastructure is described using a high-level configuration syntax, which allows a blueprint of your data center to be versioned and treated as you would any other code. Sponsorship from the well-respected open source company HashiCorp helped launch the project.
|
||||
|
||||
### Honorable mention: Docker Fig ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Fig][15] provides fast, isolated development environments using [Docker][16]. It moves the configuration required to orchestrate Docker into a simple fig.yml file. It handles all the work of building and running containers and forwarding their ports, as well as sharing volumes and linking them.
|
||||
|
||||
Orchard formed Fig last year to create a new system of tools to make Docker work. It was developed as a way of setting up development environments with Docker, enabling users to define the exact environment for their apps, while also running databases and caches inside Docker. Fig solved a major pain point for developers. Docker fully supports this open source project and [recently purchased Orchard][17] to expand the reach of Fig.
|
||||
|
||||
### Honorable mention: Drone ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Drone][18] is a Continuous Integration platform built on Docker and [written in Go][19]. The Drone project grew out of frustration with existing available technologies and processes for setting up development environments.
|
||||
|
||||
Drone provides a simple approach to automated testing and continuous delivery: Simply pick a Docker image tailored to your needs, connect GitHub, and commit. Drone uses Docker containers to provision isolated testing environments, giving every project complete control over its stack without the burden of traditional server administration. The community behind Drone is 100 contributors strong and hopes to bring this project to the enterprise and to mobile app development.
|
||||
|
||||
### Open source rookies ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- [Open Source Rookies of the 2014 Year][20]
|
||||
- [InfoWorld's 2015 Technology of the Year Award winners][21]
|
||||
- [Bossies: The Best of Open Source Software Awards][22]
|
||||
- [15 essential open source tools for Windows admins][23]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.infoworld.com/article/2875439/open-source-software/the-top-10-rookie-open-source-projects.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Black Duck Software][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.infoworld.com/author/Black-Duck-Software/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.blackducksoftware.com/open-source-rookies
|
||||
[2]:https://www.openhub.net/
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/debops/debops
|
||||
[4]:http://www.infoworld.com/article/2612397/data-center/review--ansible-orchestration-is-a-veteran-unix-admin-s-dream.html
|
||||
[5]:https://codecombat.com/
|
||||
[6]:http://storj.io/
|
||||
[7]:http://neovim.org/
|
||||
[8]:https://github.com/cockroachdb/cockroach
|
||||
[9]:http://www.infoworld.com/resources/16373/application-virtualization/the-beginners-guide-to-docker
|
||||
[10]:http://kubernetes.io/
|
||||
[11]:https://openbazaar.org/
|
||||
[12]:http://ipfs.io/
|
||||
[13]:https://github.com/google/cadvisor
|
||||
[14]:https://www.terraform.io/
|
||||
[15]:http://www.fig.sh/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.infoworld.com/resources/16373/application-virtualization/the-beginners-guide-to-docker
|
||||
[17]:http://www.infoworld.com/article/2608546/application-virtualization/docker-acquires-orchard-in-a-sign-of-rising-ambitions.html
|
||||
[18]:https://drone.io/
|
||||
[19]:http://www.infoworld.com/article/2683845/google-go/164121-Fast-guide-to-Go-programming.html
|
||||
[20]:https://www.blackducksoftware.com/open-source-rookies
|
||||
[21]:http://www.infoworld.com/article/2871935/application-development/infoworlds-2015-technology-of-the-year-award-winners.html
|
||||
[22]:http://www.infoworld.com/article/2688104/open-source-software/article.html
|
||||
[23]:http://www.infoworld.com/article/2854954/microsoft-windows/15-essential-open-source-tools-for-windows-admins.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
How To Monitor Access Point Signal Strength With wifi-linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
As a python geek I love exploring new python tools on github that target the linux users. Today I discovered a simple application written in python programming language that can be used to monitor access point signal strength.
|
||||
|
||||
I have been experimenting for about two hours with **wifi-linux** and it works great but I would like to see some unittests in the near future from the author as the command **plot** is not working on my machine and is also causing some errors.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is wifi-linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
According to the official readme.md file on author's github account wifi-linux is a very simple python script which collects RSSI information about wifi access points around you and draws graphics showing RSSI activity.
|
||||
|
||||
The author states that the program also draws RSSI activity graphic and this can be generated with the command plot but unfortunetly it is not working for me. wifi-linux supports other commands such as **bp** to add a breakpoint, **print** to print some statistics and **start changer**.
|
||||
|
||||
The wifi-linux application has the folowing dependencies:
|
||||
|
||||
- dbus-python
|
||||
- gnuplot-py
|
||||
|
||||
So first we have to install all the package dependencies for our project in order to run it in our linux machine.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install pakages required by wifi-linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
I tried to install python-dbus by using the pip tool which is used to manage python packages but it did not work and the reason for this is that pip looks for setup.py, which dbus-python doesn't have. So the following command is not going to work.
|
||||
|
||||
pip install dbus-python
|
||||
|
||||
And to make sure it does not work give it a try. It is a very high probability that you will get the following error displayed on your console.
|
||||
|
||||
IOError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: '/tmp/pip_build_oltjano/dbus-python/setup.py'
|
||||
|
||||
How did I manage to solve this problem? It is very simple. I installed the the system package for the Python DBUS bindings using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install python-dbus
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will work only in machines that make use of the apt-get package manager such as Debian and Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
Then the second dependency we have to take care is the gnuplot-py. Download it, extract using the tar utility and then run setup.py install to install the python package.
|
||||
|
||||
First step is to download gnuplot-py.
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://prdownloads.sourceforge.net/gnuplot-py/gnuplot-py-1.8.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Then use the tar utility to extract it.
|
||||
|
||||
tar xvf gnuplot-py-1.8.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Then use the cd command to change directory.
|
||||
|
||||
cd gnuplot-py-1.8
|
||||
|
||||
Once there then run the following command to install the package gunplot-py on your system.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo setup.py install
|
||||
|
||||
Once the installation is finished you are ready to run the wifi-linux on your machine. Just download it and use the following command to run the script.
|
||||
|
||||
Download wifi-linux on your local machine by using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
wget https://github.com/dixel/wifi-linux/archive/master.zip
|
||||
|
||||
Extract the master.zip archive and then use the following command to run the python script list_rsssi.py
|
||||
|
||||
python list_rssi.py
|
||||
|
||||
The following screenshot shows wifi-linux in action.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Then the command **bp** is executed to add a breakpoint like shown below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The command **print** can be used to display stats on the console of your machine. An example of its usage is shown below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/monitor-access-point-signal-strength-wifi-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Oltjano Terpollari][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/oltjano/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,137 @@
|
||||
Linux Basics: How To Check If A Package Is Installed Or Not In Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you’re managing Debian or Ubuntu servers, probably, you may use **dpkg** or **apt-get** commands often. These two commands are used to install, remove, update packages.
|
||||
|
||||
In this brief tutorial, let us see how to check if a package is installed or not in DEB based systems.
|
||||
|
||||
To check whether a particular package for example firefox, is installed or not using command:
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg -s firefox
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||
Package: firefox
|
||||
Status: install ok installed
|
||||
Priority: optional
|
||||
Section: web
|
||||
Installed-Size: 93339
|
||||
Maintainer: Ubuntu Mozilla Team <ubuntu-mozillateam@lists.ubuntu.com>
|
||||
Architecture: amd64
|
||||
Version: 35.0+build3-0ubuntu0.14.04.2
|
||||
Replaces: kubuntu-firefox-installer
|
||||
Provides: gnome-www-browser, iceweasel, www-browser
|
||||
Depends: lsb-release, libasound2 (>= 1.0.16), libatk1.0-0 (>= 1.12.4), libc6 (>= 2.17), libcairo2 (>= 1.2.4), libdbus-1-3 (>= 1.0.2), libdbus-glib-1-2 (>= 0.78), libfontconfig1 (>= 2.9.0), libfreetype6 (>= 2.2.1), libgcc1 (>= 1:4.1.1), libgdk-pixbuf2.0-0 (>= 2.22.0), libglib2.0-0 (>= 2.37.3), libgtk2.0-0 (>= 2.24.0), libpango-1.0-0 (>= 1.22.0), libpangocairo-1.0-0 (>= 1.14.0), libstartup-notification0 (>= 0.8), libstdc++6 (>= 4.6), libx11-6, libxcomposite1 (>= 1:0.3-1), libxdamage1 (>= 1:1.1), libxext6, libxfixes3, libxrender1, libxt6
|
||||
Recommends: xul-ext-ubufox, libcanberra0, libdbusmenu-glib4, libdbusmenu-gtk4
|
||||
Suggests: ttf-lyx
|
||||
Conffiles:
|
||||
/etc/firefox/syspref.js 09e457e65435a1a043521f2bd19cd2a1
|
||||
/etc/apport/blacklist.d/firefox ee63264f847e671832d42255912ce144
|
||||
/etc/apport/native-origins.d/firefox 7c26b75c7c2b715c89cc6d85338252a4
|
||||
/etc/apparmor.d/usr.bin.firefox f54f7a43361c7ecfa3874abca2f292cf
|
||||
Description: Safe and easy web browser from Mozilla
|
||||
Firefox delivers safe, easy web browsing. A familiar user interface,
|
||||
enhanced security features including protection from online identity theft,
|
||||
and integrated search let you get the most out of the web.
|
||||
Xul-Appid: {ec8030f7-c20a-464f-9b0e-13a3a9e97384}
|
||||
|
||||
As you see in the above output, the firefox is installed.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, you can do the same using **dpkg-query** command. This command displays the decent output, and ofcourse, you can wild cards too.
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg-query -l firefox
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||
Desired=Unknown/Install/Remove/Purge/Hold
|
||||
| Status=Not/Inst/Conf-files/Unpacked/halF-conf/Half-inst/trig-aWait/Trig-pend
|
||||
|/ Err?=(none)/Reinst-required (Status,Err: uppercase=bad)
|
||||
||/ Name Version Architecture Description
|
||||
+++-====================================-=======================-=======================-=============================================================================
|
||||
ii firefox 35.0+build3-0ubuntu0.14 amd64 Safe and easy web browser from Mozilla
|
||||
|
||||
To list all installed package in your system, enter the following command
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg --get-selections
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||
abiword install
|
||||
abiword-common install
|
||||
accountsservice install
|
||||
acl install
|
||||
adduser install
|
||||
alsa-base install
|
||||
alsa-utils install
|
||||
anacron install
|
||||
app-install-data install
|
||||
apparmor install
|
||||
.
|
||||
.
|
||||
.
|
||||
zeitgeist install
|
||||
zeitgeist-core install
|
||||
zeitgeist-datahub install
|
||||
zenity install
|
||||
zenity-common install
|
||||
zip install
|
||||
zlib1g:amd64 install
|
||||
zlib1g:i386 install
|
||||
|
||||
The above might be very long depending upon the number of packages you have installed on your system.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also filter through **grep** to get results for the exact package you need. For example, I want to see which gcc packages are already installed on my system using **dpkg** command:
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg --get-selections | grep gcc
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||
gcc install
|
||||
gcc-4.8 install
|
||||
gcc-4.8-base:amd64 install
|
||||
gcc-4.8-base:i386 install
|
||||
gcc-4.9-base:amd64 install
|
||||
gcc-4.9-base:i386 install
|
||||
libgcc-4.8-dev:amd64 install
|
||||
libgcc1:amd64 install
|
||||
libgcc1:i386 install
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, you can find location of the files within a package using the parameter “**-L**”.
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg -L gcc-4.8
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||
/.
|
||||
/usr
|
||||
/usr/share
|
||||
/usr/share/doc
|
||||
/usr/share/doc/gcc-4.8-base
|
||||
/usr/share/doc/gcc-4.8-base/README.Bugs
|
||||
/usr/share/doc/gcc-4.8-base/NEWS.html
|
||||
/usr/share/doc/gcc-4.8-base/quadmath
|
||||
/usr/share/doc/gcc-4.8-base/quadmath/changelog.gz
|
||||
/usr/share/doc/gcc-4.8-base/gcc
|
||||
.
|
||||
.
|
||||
.
|
||||
/usr/bin/x86_64-linux-gnu-gcc-4.8
|
||||
/usr/bin/x86_64-linux-gnu-gcc-ar-4.8
|
||||
/usr/bin/x86_64-linux-gnu-gcov-4.8
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. Hope this short tutorial will useful for you.
|
||||
|
||||
Good day!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/linux-basics-check-package-installed-not-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user