mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-26 21:30:55 +08:00
yangmingming translating
This commit is contained in:
parent
636d5c0226
commit
bdea55a328
@ -1,121 +0,0 @@
|
||||
yangmingming translating
|
||||
# How to Start Linux Command in Background and Detach Process in Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, we shall bring to light a simple yet important concept in [process handling in a Linux system][8], that is how to completely detach a process from its controlling terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
When a process is associated with a terminal, two problems might occur:
|
||||
|
||||
1. your controlling terminal is filled with so much output data and error/diagnostic messages.
|
||||
2. in the event that the terminal is closed, the process together with its child processes will be terminated.
|
||||
|
||||
To deal with these two issues, you need to totally detach a process from a controlling terminal. Before we actually move to solve the problem, let us briefly cover how to run processes in the background.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Start a Linux Process or Command in Background
|
||||
|
||||
If a process is already in execution, such as the [tar command example][7] below, simply press `Ctrl+Z` to stop it then enter the command `bg` to continue with its execution in the background as a job.
|
||||
|
||||
You can view all your background jobs by typing `jobs`. However, its stdin, stdout, stderr are still joined to the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ tar -czf home.tar.gz .
|
||||
$ bg
|
||||
$ jobs
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Run Linux Command in Background
|
||||
|
||||
You can as well run a process directly from the background using the ampersand, `&` sign.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ tar -czf home.tar.gz . &
|
||||
$ jobs
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
Start Linux Process in Background
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the example below, although the [tar command][4] was started as a background job, an error message was still sent to the terminal meaning the process is still connected to the controlling terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ tar -czf home.tar.gz . &
|
||||
$ jobs
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[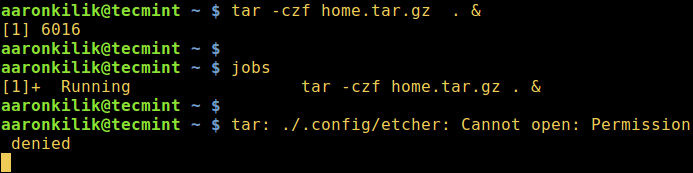][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Linux Process Running in Background Message
|
||||
|
||||
### Keep Linux Processes Running After Exiting Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
We will use disown command, it is used after the a process has been launched and put in the background, it’s work is to remove a shell job from the shell’s active list jobs, therefore you will not use `fg`, `bg` commands on that particular job anymore.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, when you close the controlling terminal, the job will not hang or send a SIGHUP to any child jobs.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s take a look at the below example of using diswon bash built-in function.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo rsync Templates/* /var/www/html/files/ &
|
||||
$ jobs
|
||||
$ disown -h %1
|
||||
$ jobs
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[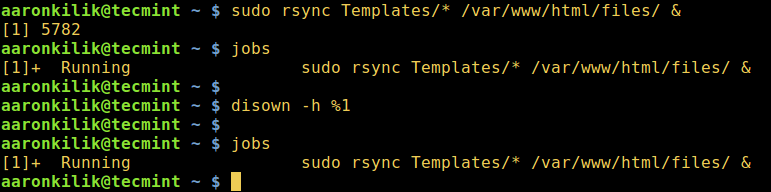][2]
|
||||
|
||||
Keep Linux Process Running After Closing Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use `nohup` command, which also enables a process to continue running in the background when a user exits a shell.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ nohup tar -czf iso.tar.gz Templates/* &
|
||||
$ jobs
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Put Linux Process in Background After Closing Shell
|
||||
|
||||
### Detach a Linux Processes From Controlling Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, to completely detach a process from a controlling terminal, use the command format below, this is more effective for graphical user interface (GUI) applications such as firefox:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ firefox </dev/null &>/dev/null &
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In Linux, /dev/null is a special device file which writes-off (gets rid of) all data written to it, in the command above, input is read from, and output is sent to /dev/null.
|
||||
|
||||
As a concluding remark, provided a process is connected to a controlling terminal, as a user, you will see several output lines of the process data as well as error messages on your terminal. Again, when you close the a controlling terminal, your process and child processes will be terminated.
|
||||
|
||||
Importantly, for any questions or remarks on the subject, reach us by using the comment form below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/run-linux-command-process-in-background-detach-process/#
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Put-Linux-Process-in-Background.png
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Keep-Linux-Processes-Running.png
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Linux-Process-Running-in-Background-Message.png
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/18-tar-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Start-Linux-Process-in-Background.png
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Run-Linux-Command-in-Background.png
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/18-tar-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/monitor-linux-processes-and-set-process-limits-per-user/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
|
||||
# 如何在后台运行 Linux 命令并且在终端分离进程
|
||||
|
||||
在本指南中,我们将会阐明一个在 [Linux 系统中进程管理][8]的简单但是重要的概念,那就是如何从它的控制终端完全分离一个进程。
|
||||
|
||||
当一个进程和终端关联,两个问题有可能发生:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 你的控制终端充满了很多输出数据或者错误和诊断信息
|
||||
2. 如果发生终端关闭的情况,进程连同它的子进程都将会终止
|
||||
|
||||
为了解决上面两个问题,你需要从一个控制终端完全分离一个进程。在我们实际上解决这个问题之前,让我们先简要的介绍一下,如何在后台运行一个进程。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在后台开始一个 Linux 进程或者命令行
|
||||
|
||||
如果一个进程已经运行,例如下面的[tar 命令行的例子][7],简单的按下 `Ctrl+Z` 就可以停止前台运行,然后输入命令 `bg` 就可以继续其后台运行的作业了。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过输入 `jobs` 查看所有的后台作业。但是,标准输入、标准输出和标准错误依旧掺杂到控制台中。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ tar -czf home.tar.gz .
|
||||
$ bg
|
||||
$ jobs
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][6]
|
||||
|
||||
在后台运行 Linux 命令
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以直接在前台使用符号 `&` 运行一个进程
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ tar -czf home.tar.gz . &
|
||||
$ jobs
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
在后台开始一个 Linux 进程
|
||||
|
||||
看一下下面的这个例子,虽然 [tar 命令][4]是作为一个后台任务开始的,但是错误信息依旧发送到终端,意思也就是说,进程依旧和控制终端关联在一起。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ tar -czf home.tar.gz . &
|
||||
$ jobs
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][3]
|
||||
|
||||
运行在后台的 Linux 进程信息
|
||||
|
||||
### 退出控制台之后,保持 Linux 进程的运行
|
||||
|
||||
我们将使用 disown 命令,它在一个进程已经运行并且被放在后台之后使用,它的作用是从 shell 的活动的任务列表中移走一个 shell 任务,因此,在特定的任务中,你将再也不能使用 `fg` 、 `bg` 命令了。
|
||||
|
||||
而且,当你关闭控制控制终端,这个任务将不会暂停或者向任何一个子任务发送 SIGHUP 信号。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们看一下先下面的这个使用 bash 中内置函数——disown 的例子。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo rsync Templates/* /var/www/html/files/ &
|
||||
$ jobs
|
||||
$ disown -h %1
|
||||
$ jobs
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][2]
|
||||
|
||||
关闭终端之后,保持 Linux 进程运行
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以使用 `nohup` 命令,这个命令也可以在用户退出 shell 之后保证进程在后台继续运行。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ nohup tar -czf iso.tar.gz Templates/* &
|
||||
$ jobs
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[][1]
|
||||
|
||||
关闭 shell 之后把 Linux 进程至于后台
|
||||
|
||||
### 从控制终端分离一个 Linux 进程
|
||||
|
||||
因此,为了彻底从控制终端分离一个程序,对于图形用户界面 (GUI) 例如 firefox 来说,使用下面的命令行格式会更有效:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ firefox </dev/null &>/dev/null &
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 上,/dev/null 是一个特殊的文件设备,它会忽略所有的写在它上面的数据,上面的命令,输入来源于并且输出发送至都是 /dev/null。
|
||||
|
||||
作为结束语,提供了一个连接控制终端的进程,作为一个用户,你将会在你的终端上看到这个进程数据的许多行输出,也包含错误信息。同样,当你关闭一个控制终端,你的进程和子进程都将会终止。
|
||||
|
||||
重要的是,对于这个主题任何的问题或者观点,通过下面的评论联系我们。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/run-linux-command-process-in-background-detach-process/#
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[yangmingming](https://github.com/yangmingming)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Put-Linux-Process-in-Background.png
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Keep-Linux-Processes-Running.png
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Linux-Process-Running-in-Background-Message.png
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/18-tar-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Start-Linux-Process-in-Background.png
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Run-Linux-Command-in-Background.png
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/18-tar-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/monitor-linux-processes-and-set-process-limits-per-user/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user