mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-04 22:00:34 +08:00
Merge remote-tracking branch 'upup/master'
This commit is contained in:
commit
bd9554b730
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
[bazz222222222]
|
||||
How to secure SSH login with one-time passwords on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
As someone says, security is a not a product, but a process. While SSH protocol itself is cryptographically secure by design, someone can wreak havoc on your SSH service if it is not administered properly, be it weak passwords, compromised keys or outdated SSH client.
|
||||
@ -177,4 +178,4 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/secure-ssh-login-one-time-passwords-linux.html
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-force-ssh-login-via-public-key-authentication.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/two-factor-authentication-ssh-login-linux.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~mgk25/otpw.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~mgk25/otpw.html
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,166 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by ictlyh
|
||||
How to set up NTP server in CentOS
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is used to synchronize system clocks of different hosts over network. All managed hosts can synchronize their time with a designated time server called an NTP server. An NTP server on the other hand synchronizes its own time with any public NTP server, or any server of your choice. The system clocks of all NTP-managed devices are synchronized to the millisecond precision.
|
||||
|
||||
In a corporate environment, if they do not want to open up their firewall for NTP traffic, it is necessary to set up in-house NTP server, and let employees use the internal server as opposed to public NTP servers. In this tutorial, we will describe how to configure a CentOS system as an NTP server. Before going into the detail, let's go over the concept of NTP first.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why Do We Need NTP? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Due to manufacturing variances, all (non-atomic) clocks do not run at the exact same speed. Some clocks tend to run faster, while some run slower. So over a large timeframe, the time of one clock gradually drifts from another, causing what is known as "clock drift" or "time drift". To minimize the effect of clock drift, the hosts using NTP should periodically communicate with a designated NTP server to keep their clock in sync.
|
||||
|
||||
Time synchrony across different hosts is important for things like scheduled backup, [intrusion detection][1] logging, [distributed job scheduling ][2]or transaction bookkeeping. It may even be required as part of regulatory compliance.
|
||||
|
||||
### NTP Hierarchy ###
|
||||
|
||||
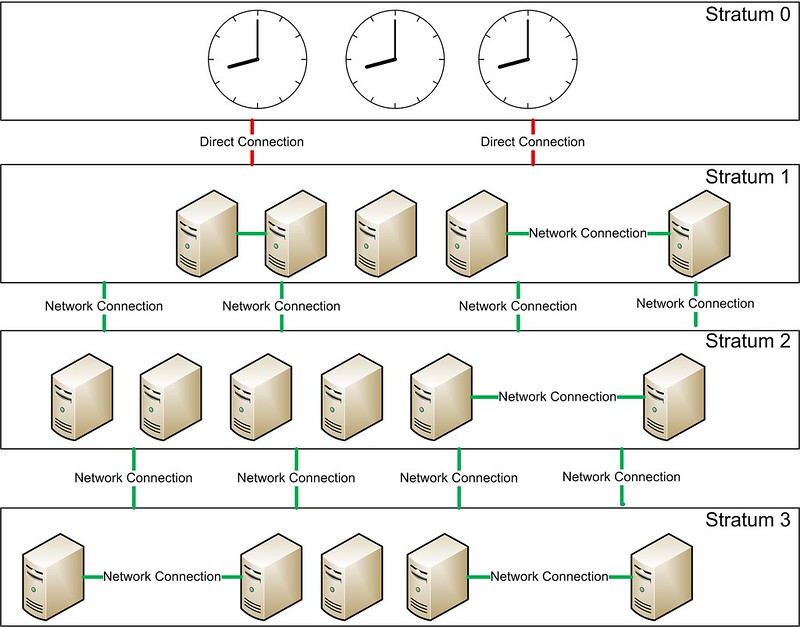
NTP clocks are organized in a layered hierarchy. Each level of the hierarchy is called a *stratum*. The notion of stratum describes how many NTP hops away a machine is from an authoritative time source.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Stratum 0 is populated with clocks that have virtually no time drifts, such as atomic clocks. These clocks cannot be directly used over the network. Stratum N (N > 1) servers synchronize their time against Stratum N-1 servers. Stratum N clocks may be connected with each other over network.
|
||||
|
||||
NTP supports up to 15 stratums in the hierarchy. Stratum 16 is considered unsynchronized and unusable.
|
||||
|
||||
### Preparing CentOS Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's proceed to set up an NTP server on CentOS.
|
||||
|
||||
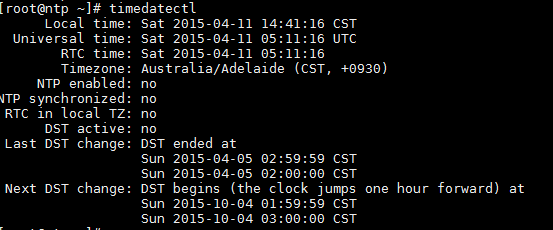
First of all, we need to make sure that the time zone of the server is set up correctly. In CentOS 7, we can use the timedatectl command to view and change the server time zone (e.g., "Australia/Adelaide")
|
||||
|
||||
# timedatectl list-timezones | grep Australia
|
||||
# timedatectl set-timezone Australia/Adelaide
|
||||
# timedatectl
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Go ahead and set up necessary software using yum.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install ntp
|
||||
|
||||
Then we will add the global NTP servers to synchronize time with.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/ntp.conf
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
server 0.oceania.pool.ntp.org
|
||||
server 1.oceania.pool.ntp.org
|
||||
server 2.oceania.pool.ntp.org
|
||||
server 3.oceania.pool.ntp.org
|
||||
|
||||
By default, NTP server logs are saved in /var/log/messages. If you want to use a custom log file, that can be specified as well.
|
||||
|
||||
logfile /var/log/ntpd.log
|
||||
|
||||
If you opt for a custom log file, make sure to change its ownership and SELinux context.
|
||||
|
||||
# chown ntp:ntp /var/log/ntpd.log
|
||||
# chcon -t ntpd_log_t /var/log/ntpd.log
|
||||
|
||||
Now initiate NTP service and make sure it's added to startup.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart ntp
|
||||
# systemctl enable ntp
|
||||
|
||||
### Verifying NTP Server Clock ###
|
||||
|
||||
We can use the ntpq command to check how the local server's clock is synchronized via NTP.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The following table explains the output columns.
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
<table id="content">
|
||||
<tbody><tr>
|
||||
<td>remote</td>
|
||||
<td>The sources defined at ntp.conf. '*' indicates the current and best source; '+' indicates that these sources are available as NTP source. Sources with - are considered unusable.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>refid</td>
|
||||
<td>The IP address of the clock with which the remote server clock is synchronized with.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>st</td>
|
||||
<td>Stratum</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>t</td>
|
||||
<td>Type. 'u' is for unicast. Other values may include local, multicast, broadcast.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>when</td>
|
||||
<td>The time elapsed (in seconds) since the last contact with the server.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>poll</td>
|
||||
<td>Polling frequency with the server in seconds.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>reach</td>
|
||||
<td>An octal value that indicates whether there are any errors in communication with the server. The value 377 indicates 100% success.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>delay</td>
|
||||
<td>The round trip time between our server and the remote server.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>offset</td>
|
||||
<td>The time difference between our server and the remote server in milliseconds.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>jitter</td>
|
||||
<td>The average time difference in milliseconds between two samples.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody></table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Controlling Access to NTP Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default, NTP server allows incoming queries from all hosts. If you want to filter incoming NTP synchronization connections, you could add a rule in your firewall to filter the traffic.
|
||||
|
||||
# iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p udp --dport 123 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
# iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 123 -j DROP
|
||||
|
||||
The rule will allow NTP traffic (on port UDP/123) from 192.168.1.0/24, and deny traffic from all other networks. You can update the rule to match your requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuring NTP Clients ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Linux ####
|
||||
|
||||
NTP client hosts need the ntpdate package to synchronize time against the server. The package can be easily installed using yum or apt-get. After installing the package, run the command with the IP address of the server.
|
||||
|
||||
# ntpdate <server-IP-address>
|
||||
|
||||
The command is identical for RHEL and Debian based systems.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Windows ####
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using Windows, look for 'Internet Time' under Date and Time settings.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. Cisco Devices ####
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to synchronize the time of a Cisco device, you can use the following command from the global configuration mode.
|
||||
|
||||
# ntp server <server-IP-address>
|
||||
|
||||
NTP enabled devices from other vendors have their own parameters for Internet time. Please check the documentation of the device if you want to synchronize its time with the NTP server.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
To sum up, NTP is a protocol that keeps the clocks across all your hosts in sync. We have demonstrated how we can set up an NTP server, and let NTP enabled devices synchronize their time against the server.
|
||||
|
||||
Hope this helps.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/setup-ntp-server-centos.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-compile-and-install-snort-from-source-code-on-ubuntu.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-install-hdfs-and-hadoop-using.html
|
||||
165
translated/tech/20150427 How to set up NTP server in CentOS.md
Normal file
165
translated/tech/20150427 How to set up NTP server in CentOS.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
|
||||
如何在 CentOS 中设置 NTP 服务器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
网络时间协议(NTP)用来同步网络上不同主机的系统时间。所有托管的主机都可以和一个指定的被称为 NTP 服务器的时间服务器同步它们的时间。另一方面一个 NTP 服务器将它的时间和任何公共 NTP 服务器,或者你选定的服务器同步。NTP 托管的所有系统时钟都同步精确到毫秒级。
|
||||
|
||||
在一个协作环境中,如果他们不想为 NTP 传输打开防火墙,就有必要设置一个内部 NTP 服务器,然后让员工使用内部服务器而不是公共 NTP 服务器。在这个指南中,我们会介绍如何将一个 CentOS 系统配置为 NTP 服务器。在介绍详细内容之前,让我们先来简单了解一下 NTP 的概念。
|
||||
|
||||
### 为什么我们需要 NTP? ###
|
||||
|
||||
由于制造工艺多种多样,所有的(非原子)时钟并不按照完全一致的速度行走。有一些时钟走的比较快而有一些走的比较慢。因此经过很长一段时间以后,一个时钟的时间慢慢的偏移于其它,导致有名的 “时钟漂移” 或 “时间漂移”。为了最小化时钟漂移的影响,使用 NTP 的主机应该周期性地和指定的 NTP 服务器交互以保持它们的时钟同步。
|
||||
|
||||
在不同的主机之间进行时间同步对于计划备份、[干扰检测][1]日志、[分布式任务调度][2]或者事务订单管理来说是很重要的事情。它甚至可能要求作为日常任务的一部分。
|
||||
|
||||
### NTP 层次 ###
|
||||
|
||||
NTP 时钟以层次模型组织。层级中的每层被称为一个 *stratum*。stratum 的概念说明了一台机器到授权的时间源有多少 NTP 跳。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Stratum 0 由没有时间漂移的时钟组成,例如原子时钟。这种时钟不能在网络上直接使用。Stratum N (N > 1) 层服务器从 Stratum N-1 层服务器同步时间。Stratum N 时钟可能通过网络和彼此互联。
|
||||
|
||||
NTP 支持多达 15 stratums 的层级。Stratum 16 被认为是没有同步不能使用的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 准备 CentOS 服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在让我们来开始在 CentOS 上设置 NTP 服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们需要保证正确设置了服务器的时区。在 CentOS 7 中,我们可以使用 timedatectl 命令查看和更改服务器的时区(比如,"Australia/Adelaide")
|
||||
|
||||
# timedatectl list-timezones | grep Australia
|
||||
# timedatectl set-timezone Australia/Adelaide
|
||||
# timedatectl
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
继续并使用 yum 安装需要的软件
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install ntp
|
||||
|
||||
然后我们会添加全球 NTP 服务器用于同步时间。
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/ntp.conf
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
server 0.oceania.pool.ntp.org
|
||||
server 1.oceania.pool.ntp.org
|
||||
server 2.oceania.pool.ntp.org
|
||||
server 3.oceania.pool.ntp.org
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,NTP 服务器的日志保存在 /var/log/messages。如果你希望使用自定义的日志文件,那也可以指定。
|
||||
|
||||
logfile /var/log/ntpd.log
|
||||
|
||||
如果你选择自定义日志文件,确保更改了它的属主和 SELinux 环境。
|
||||
|
||||
# chown ntp:ntp /var/log/ntpd.log
|
||||
# chcon -t ntpd_log_t /var/log/ntpd.log
|
||||
|
||||
现在初始化 NTP 服务并确保把它添加到了随机启动。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart ntp
|
||||
# systemctl enable ntp
|
||||
|
||||
### 验证 NTP Server 时钟 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以使用 ntpq 命令来检查本地服务器的时钟如何通过 NTP 同步。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
下面的表格解释了输出列。
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
<table id="content">
|
||||
<tbody><tr>
|
||||
<td>remote</td>
|
||||
<td>源在 ntp.conf 中定义。‘*’ 表示当前使用的最好的源;‘+’ 表示可作为 NTP 源的源;‘-’ 标记的源是不可用的。</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>refid</td>
|
||||
<td>和远程服务器时钟同步的时钟的 IP 地址。</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>st</td>
|
||||
<td>Stratum</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>t</td>
|
||||
<td>类型。 'u' 表示单播(unicast)。其它值包括本地(local)、多播(multicast)、广播(broadcast)。</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>when</td>
|
||||
<td>自从上次和服务器交互经过的时间(以秒数计)。</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>poll</td>
|
||||
<td>和服务器的轮询频率,以秒数计。</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>reach</td>
|
||||
<td>表示和服务器交互是否有任何错误的十进制数。值 337 表示 100% 成功。</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>delay</td>
|
||||
<td>服务器和远程服务器来回的时间。</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>offset</td>
|
||||
<td>我们服务器和远程服务器的时间差异,以毫秒数计。</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>jitter</td>
|
||||
<td>两个例子之间平局时间差异,以毫秒数计。</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody></table>
|
||||
|
||||
### 控制到 NTP 服务器的访问 ###
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,NTP 服务器允许来自所有主机的查询。如果你想过滤进来的 NTP 同步连接,你可以在你的防火墙中添加规则过滤流量。
|
||||
|
||||
# iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p udp --dport 123 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
# iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 123 -j DROP
|
||||
|
||||
该规则允许从 192.168.1.0/24 来的 NTP 流量(端口 UDP/123),任何其它网络的流量会被截停。你可以根据需要更改规则。
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置 NTP 客户端 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Linux ####
|
||||
|
||||
NTP 客户端主机需要 ntpupdate 软件包和服务器同步时间。可以轻松地使用 yum 或 apt-get 安装这个软件包。安装完软件包之后,用服务器的 IP 地址运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# ntpdate <server-IP-address>
|
||||
|
||||
基于 RHEL 和 Debian 的系统命令都相同。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Windows ####
|
||||
|
||||
如果你正在使用 Windows,在日期和时间设置(Date and Time settings)下查找网络时间(Internet Time)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. Cisco 设备 ####
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想和 Cisco 设备同步时间,你可以在全局配置模式下使用下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# ntp server <server-IP-address>
|
||||
|
||||
其它有支持 NTP 的卖家有自己的参数用于网络时间。如果你想将设备和 NTP服务器同步时间,请查看设备的说明文档。
|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
总而言之,NTP 是在你的所有主机上同步时钟的一个协议。我们已经介绍了如何设置 NTP 服务器并使支持 NTP 的设备和服务器同步时间。
|
||||
|
||||
希望能对你有所帮助
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/setup-ntp-server-centos.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-compile-and-install-snort-from-source-code-on-ubuntu.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-install-hdfs-and-hadoop-using.html
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user