mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-15 01:50:08 +08:00
[翻译完成] How to Install Elastic Stack on CentOS 7
This commit is contained in:
parent
e613255276
commit
bccffb50bd
@ -1,564 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by Flowsnow!
|
||||
|
||||
How to Install Elastic Stack on CentOS 7
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
### On this page
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Step 1 - Prepare the Operating System][1]
|
||||
2. [Step 2 - Install Java][2]
|
||||
3. [Step 3 - Install and Configure Elasticsearch][3]
|
||||
4. [Step 4 - Install and Configure Kibana with Nginx][4]
|
||||
5. [Step 5 - Install and Configure Logstash][5]
|
||||
6. [Step 6 - Install and Configure Filebeat on the CentOS Client][6]
|
||||
7. [Step 7 - Install and Configure Filebeat on the Ubuntu Client][7]
|
||||
8. [Step 8 - Testing][8]
|
||||
9. [Reference][9]
|
||||
|
||||
**Elasticsearch** is an open source search engine based on Lucene, developed in Java. It provides a distributed and multitenant full-text search engine with an HTTP Dashboard web-interface (Kibana). The data is queried, retrieved and stored with a JSON document scheme. Elasticsearch is a scalable search engine that can be used to search for all kind of text documents, including log files. Elasticsearch is the heart of the 'Elastic Stack' or ELK Stack.
|
||||
|
||||
**Logstash** is an open source tool for managing events and logs. It provides real-time pipelining for data collections. Logstash will collect your log data, convert the data into JSON documents, and store them in Elasticsearch.
|
||||
|
||||
**Kibana** is an open source data visualization tool for Elasticsearch. Kibana provides a pretty dashboard web interface. It allows you to manage and visualize data from Elasticsearch. It's not just beautiful, but also powerful.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I will show you how to install and configure Elastic Stack on a CentOS 7 server for monitoring server logs. Then I'll show you how to install 'Elastic beats' on a CentOS 7 and a Ubuntu 16 client operating system.
|
||||
|
||||
**Prerequisite**
|
||||
|
||||
* CentOS 7 64 bit with 4GB of RAM - elk-master
|
||||
* CentOS 7 64 bit with 1 GB of RAM - client1
|
||||
* Ubuntu 16 64 bit with 1GB of RAM - client2
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1 - Prepare the Operating System
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, we will disable SELinux on the CentOS 7 server. Edit the SELinux configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
vim /etc/sysconfig/selinux
|
||||
|
||||
Change SELINUX value from enforcing to disabled.
|
||||
|
||||
SELINUX=disabled
|
||||
|
||||
Then reboot the server.
|
||||
|
||||
reboot
|
||||
|
||||
Login to the server again and check the SELinux state.
|
||||
|
||||
getenforce
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure the result is disabled.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2 - Install Java
|
||||
|
||||
Java is required for the Elastic stack deployment. Elasticsearch requires Java 8, it is recommended to use the Oracle JDK 1.8\. I will install Java 8 from the official Oracle rpm package.
|
||||
|
||||
Download Java 8 JDK with the wget command.
|
||||
|
||||
wget --no-cookies --no-check-certificate --header "Cookie: gpw_e24=http:%2F%2Fwww.oracle.com%2F; oraclelicense=accept-securebackup-cookie" "http://download.oracle.com/otn-pub/java/jdk/8u77-b02/jdk-8u77-linux-x64.rpm"
|
||||
|
||||
Then install it with this rpm command;
|
||||
|
||||
rpm -ivh jdk-8u77-linux-x64.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, check java JDK version to ensure that it is working properly.
|
||||
|
||||
java -version
|
||||
|
||||
You will see Java version of the server.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3 - Install and Configure Elasticsearch
|
||||
|
||||
In this step, we will install and configure Elasticsearch. I will install Elasticsearch from an rpm package provided by elastic.co and configure it to run on localhost (to make the setup secure and ensure that it is not reachable from the outside).
|
||||
|
||||
Before installing Elasticsearch, add the elastic.co key to the server.
|
||||
|
||||
rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
|
||||
|
||||
Next, download Elasticsearch 5.1 with wget and then install it.
|
||||
|
||||
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-5.1.1.rpm
|
||||
rpm -ivh elasticsearch-5.1.1.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
Elasticsearch is installed. Now go to the configuration directory and edit the elasticsaerch.yml configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
cd /etc/elasticsearch/
|
||||
vim elasticsearch.yml
|
||||
|
||||
Enable memory lock for Elasticsearch by removing a comment on line 40\. This disables memory swapping for Elasticsearch.
|
||||
|
||||
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
|
||||
|
||||
In the 'Network' block, uncomment the network.host and http.port lines.
|
||||
|
||||
network.host: localhost
|
||||
http.port: 9200
|
||||
|
||||
Save the file and exit the editor.
|
||||
|
||||
Now edit the elasticsearch.service file for the memory lock configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service
|
||||
|
||||
Uncomment LimitMEMLOCK line.
|
||||
|
||||
LimitMEMLOCK=infinity
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
Edit the sysconfig configuration file for Elasticsearch.
|
||||
|
||||
vim /etc/sysconfig/elasticsearch
|
||||
|
||||
Uncomment line 60 and make sure the value is 'unlimited'.
|
||||
|
||||
MAX_LOCKED_MEMORY=unlimited
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
The Elasticsearch configuration is finished. Elasticsearch will run on the localhost IP address on port 9200, we disabled memory swapping for it by enabling mlockall on the CentOS server.
|
||||
|
||||
Reload systemd, enable Elasticsearch to start at boot time, then start the service.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
|
||||
sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch
|
||||
sudo systemctl start elasticsearch
|
||||
|
||||
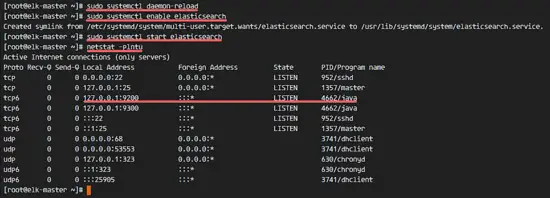
Wait a second for Eelasticsearch to start, then check the open ports on the server, make sure 'state' for port 9200 is 'LISTEN'.
|
||||
|
||||
netstat -plntu
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][10]
|
||||
|
||||
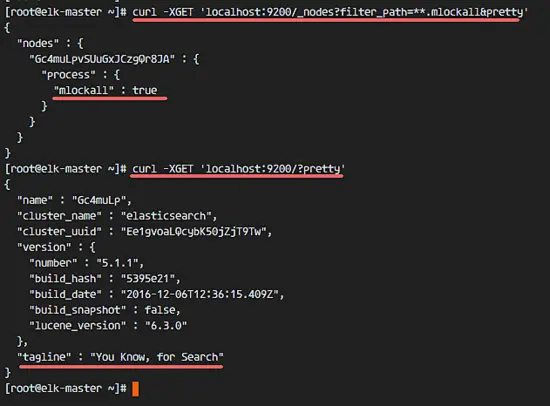
Then check the memory lock to ensure that mlockall is enabled, and check that Elasticsearch is running with the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/_nodes?filter_path=**.mlockall&pretty'
|
||||
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/?pretty'
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the results below.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][11]
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4 - Install and Configure Kibana with Nginx
|
||||
|
||||
In this step, we will install and configure Kibana with a Nginx web server. Kibana will listen on the localhost IP address and Nginx acts as a reverse proxy for the Kibana application.
|
||||
|
||||
Download Kibana 5.1 with wget, then install it with the rpm command:
|
||||
|
||||
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
|
||||
rpm -ivh kibana-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
Now edit the Kibana configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
vim /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
|
||||
|
||||
Uncomment the configuration lines for server.port, server.host and elasticsearch.url.
|
||||
|
||||
server.port: 5601
|
||||
server.host: "localhost"
|
||||
elasticsearch.url: "http://localhost:9200"
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
Add Kibana to run at boot and start it.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo systemctl enable kibana
|
||||
sudo systemctl start kibana
|
||||
|
||||
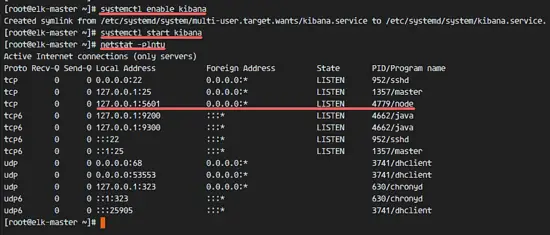
Kibana will run on port 5601 as node application.
|
||||
|
||||
netstat -plntu
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][12]
|
||||
|
||||
The Kibana installation is finished. Now we need to install Nginx and configure it as reverse proxy to be able to access Kibana from the public IP address.
|
||||
|
||||
Nginx is available in the Epel repository, install epel-release with yum.
|
||||
|
||||
yum -y install epel-release
|
||||
|
||||
Next, install the Nginx and httpd-tools package.
|
||||
|
||||
yum -y install nginx httpd-tools
|
||||
|
||||
The httpd-tools package contains tools for the web server, we will use htpasswd basic authentication for Kibana.
|
||||
|
||||
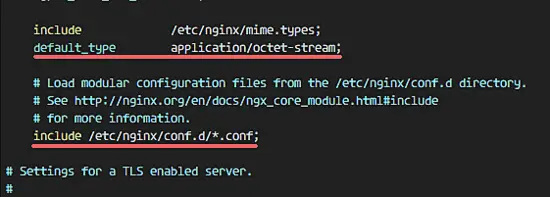
Edit the Nginx configuration file and remove the **'server { }**' block, so we can add a new virtual host configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
cd /etc/nginx/
|
||||
vim nginx.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Remove the server { } block.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][13]
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
Now we need to create a new virtual host configuration file in the conf.d directory. Create the new file 'kibana.conf' with vim.
|
||||
|
||||
vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/kibana.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Paste the configuration below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 80;
|
||||
|
||||
server_name elk-stack.co;
|
||||
|
||||
auth_basic "Restricted Access";
|
||||
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.kibana-user;
|
||||
|
||||
location / {
|
||||
proxy_pass http://localhost:5601;
|
||||
proxy_http_version 1.1;
|
||||
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
|
||||
proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade';
|
||||
proxy_set_header Host $host;
|
||||
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
Then create a new basic authentication file with the htpasswd command.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo htpasswd -c /etc/nginx/.kibana-user admin
|
||||
TYPE YOUR PASSWORD
|
||||
|
||||
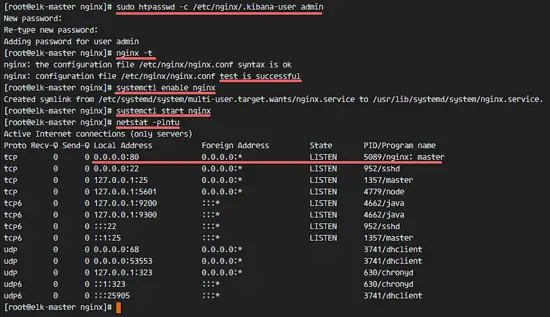
Test the Nginx configuration and make sure there is no error. Then add Nginx to run at the boot time and start Nginx.
|
||||
|
||||
nginx -t
|
||||
systemctl enable nginx
|
||||
systemctl start nginx
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][14]
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 5 - Install and Configure Logstash
|
||||
|
||||
In this step, we will install Logsatash and configure it to centralize server logs from clients with filebeat, then filter and transform the Syslog data and move it into the stash (Elasticsearch).
|
||||
|
||||
Download Logstash and install it with rpm.
|
||||
|
||||
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-5.1.1.rpm
|
||||
rpm -ivh logstash-5.1.1.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
Generate a new SSL certificate file so that the client can identify the elastic server.
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the tls directory and edit the openssl.cnf file.
|
||||
|
||||
cd /etc/pki/tls
|
||||
vim openssl.cnf
|
||||
|
||||
Add a new line in the '[ v3_ca ]' section for the server identification.
|
||||
|
||||
[ v3_ca ]
|
||||
|
||||
# Server IP Address
|
||||
subjectAltName = IP: 10.0.15.10
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
Generate the certificate file with the openssl command.
|
||||
|
||||
openssl req -config /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf -x509 -days 3650 -batch -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/pki/tls/private/logstash-forwarder.key -out /etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt
|
||||
|
||||
The certificate files can be found in the '/etc/pki/tls/certs/' and '/etc/pki/tls/private/' directories.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we will create new configuration files for Logstash. We will create a new 'filebeat-input.conf' file to configure the log sources for filebeat, then a 'syslog-filter.conf' file for syslog processing and the 'output-elasticsearch.conf' file to define the Elasticsearch output.
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the logstash configuration directory and create the new configuration files in the 'conf.d' subdirectory.
|
||||
|
||||
cd /etc/logstash/
|
||||
vim conf.d/filebeat-input.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Input configuration: paste the configuration below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
input {
|
||||
beats {
|
||||
port => 5443
|
||||
ssl => true
|
||||
ssl_certificate => "/etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt"
|
||||
ssl_key => "/etc/pki/tls/private/logstash-forwarder.key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
Create the syslog-filter.conf file.
|
||||
|
||||
vim conf.d/syslog-filter.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Paste the configuration below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
filter {
|
||||
if [type] == "syslog" {
|
||||
grok {
|
||||
match => { "message" => "%{SYSLOGTIMESTAMP:syslog_timestamp} %{SYSLOGHOST:syslog_hostname} %{DATA:syslog_program}(?:\[%{POSINT:syslog_pid}\])?: %{GREEDYDATA:syslog_message}" }
|
||||
add_field => [ "received_at", "%{@timestamp}" ]
|
||||
add_field => [ "received_from", "%{host}" ]
|
||||
}
|
||||
date {
|
||||
match => [ "syslog_timestamp", "MMM d HH:mm:ss", "MMM dd HH:mm:ss" ]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We use a filter plugin named '**grok**' to parse the syslog files.
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
Create the output configuration file 'output-elasticsearch.conf'.
|
||||
|
||||
vim conf.d/output-elasticsearch.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Paste the configuration below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
output {
|
||||
elasticsearch { hosts => ["localhost:9200"]
|
||||
hosts => "localhost:9200"
|
||||
manage_template => false
|
||||
index => "%{[@metadata][beat]}-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
|
||||
document_type => "%{[@metadata][type]}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
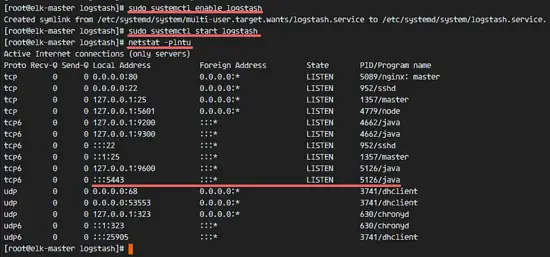
Finally add logstash to start at boot time and start the service.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo systemctl enable logstash
|
||||
sudo systemctl start logstash
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][15]
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 6 - Install and Configure Filebeat on the CentOS Client
|
||||
|
||||
Beats are data shippers, lightweight agents that can be installed on the client nodes to send huge amounts of data from the client machine to the Logstash or Elasticsearch server. There are 4 beats available, 'Filebeat' for 'Log Files', 'Metricbeat' for 'Metrics', 'Packetbeat' for 'Network Data' and 'Winlogbeat' for the Windows client 'Event Log'.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I will show you how to install and configure 'Filebeat' to transfer data log files to the Logstash server over an SSL connection.
|
||||
|
||||
Login to the client1 server. Then copy the certificate file from the elastic server to the client1 server.
|
||||
|
||||
ssh root@client1IP
|
||||
|
||||
Copy the certificate file with the scp command.
|
||||
|
||||
scp root@elk-serverIP:~/logstash-forwarder.crt .
|
||||
TYPE elk-server password
|
||||
|
||||
Create a new directory and move certificate file to that directory.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo mkdir -p /etc/pki/tls/certs/
|
||||
mv ~/logstash-forwarder.crt /etc/pki/tls/certs/
|
||||
|
||||
Next, import the elastic key on the client1 server.
|
||||
|
||||
rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
|
||||
|
||||
Download Filebeat and install it with rpm.
|
||||
|
||||
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
|
||||
rpm -ivh filebeat-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
Filebeat has been installed, go to the configuration directory and edit the file 'filebeat.yml'.
|
||||
|
||||
cd /etc/filebeat/
|
||||
vim filebeat.yml
|
||||
|
||||
In the paths section on line 21, add the new log files. We will add two files '/var/log/secure' for ssh activity and '/var/log/messages' for the server log.
|
||||
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- /var/log/secure
|
||||
- /var/log/messages
|
||||
|
||||
Add a new configuration on line 26 to define the syslog type files.
|
||||
|
||||
document-type: syslog
|
||||
|
||||
Filebeat is using Elasticsearch as the output target by default. In this tutorial, we will change it to Logshtash. Disable Elasticsearch output by adding comments on the lines 83 and 85.
|
||||
|
||||
Disable elasticsearch output.
|
||||
|
||||
#-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------
|
||||
#output.elasticsearch:
|
||||
# Array of hosts to connect to.
|
||||
# hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
|
||||
|
||||
Now add the new logstash output configuration. Uncomment the logstash output configuration and change all value to the configuration that is shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
output.logstash:
|
||||
# The Logstash hosts
|
||||
hosts: ["10.0.15.10:5443"]
|
||||
bulk_max_size: 1024
|
||||
ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt"]
|
||||
template.name: "filebeat"
|
||||
template.path: "filebeat.template.json"
|
||||
template.overwrite: false
|
||||
|
||||
Save the file and exit vim.
|
||||
|
||||
Add Filebeat to start at boot time and start it.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo systemctl enable filebeat
|
||||
sudo systemctl start filebeat
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 7 - Install and Configure Filebeat on the Ubuntu Client
|
||||
|
||||
Connect to the server by ssh.
|
||||
|
||||
ssh root@ubuntu-clientIP
|
||||
|
||||
Copy the certificate file to the client with the scp command.
|
||||
|
||||
scp root@elk-serverIP:~/logstash-forwarder.crt .
|
||||
|
||||
Create a new directory for the certificate file and move the file to that directory.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo mkdir -p /etc/pki/tls/certs/
|
||||
mv ~/logstash-forwarder.crt /etc/pki/tls/certs/
|
||||
|
||||
Add the elastic key to the server.
|
||||
|
||||
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
|
||||
Download the Filebeat .deb package and install it with the dpkg command.
|
||||
|
||||
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-5.1.1-amd64.deb
|
||||
dpkg -i filebeat-5.1.1-amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the filebeat configuration directory and edit the file 'filebeat.yml' with vim.
|
||||
|
||||
cd /etc/filebeat/
|
||||
vim filebeat.yml
|
||||
|
||||
Add the new log file paths in the paths configuration section.
|
||||
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- /var/log/auth.log
|
||||
- /var/log/syslog
|
||||
|
||||
Set the document type to syslog.
|
||||
|
||||
document-type: syslog
|
||||
|
||||
Disable elasticsearch output by adding comments to the lines shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
#-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------
|
||||
#output.elasticsearch:
|
||||
# Array of hosts to connect to.
|
||||
# hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
|
||||
|
||||
Enable logstash output, uncomment the configuration and change the values as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
output.logstash:
|
||||
# The Logstash hosts
|
||||
hosts: ["10.0.15.10:5443"]
|
||||
bulk_max_size: 1024
|
||||
ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt"]
|
||||
template.name: "filebeat"
|
||||
template.path: "filebeat.template.json"
|
||||
template.overwrite: false
|
||||
|
||||
Save the file and exit vim.
|
||||
|
||||
Add Filebeat to start at boot time and start it.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo systemctl enable filebeat
|
||||
sudo systemctl start filebeat
|
||||
|
||||
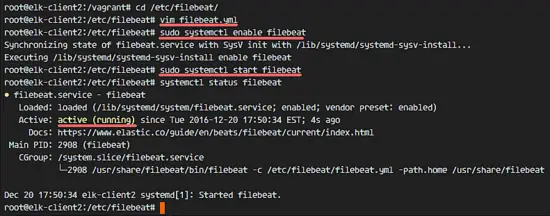
Check the service status.
|
||||
|
||||
systemctl status filebeat
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][16]
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 8 - Testing
|
||||
|
||||
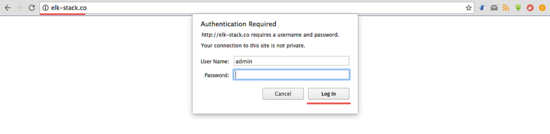
Open your web browser and visit the elastic stack domain that you used in the Nginx configuration, mine is 'elk-stack.co'. Login as admin user with your password and press Enter to log in to the Kibana dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][17]
|
||||
|
||||
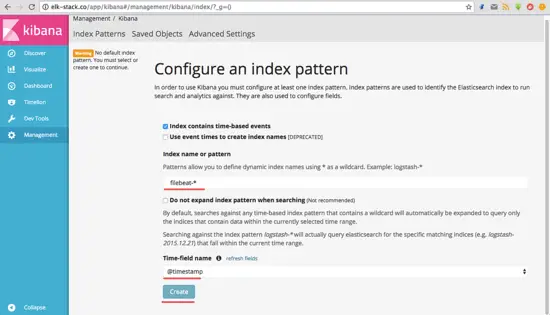
Create a new default index 'filebeat-*' and click on the 'Create' button.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][18]
|
||||
|
||||
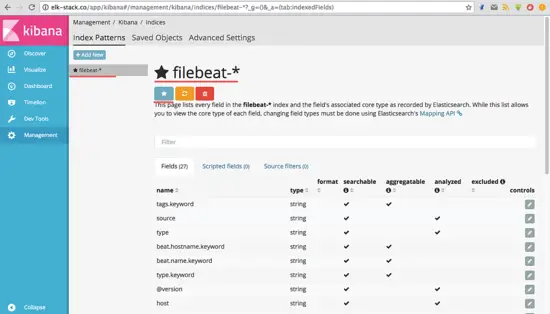
Th default index has been created. If you have multiple beats on the elastic stack, you can configure the default beat with just one click on the 'star' button.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][19]
|
||||
|
||||
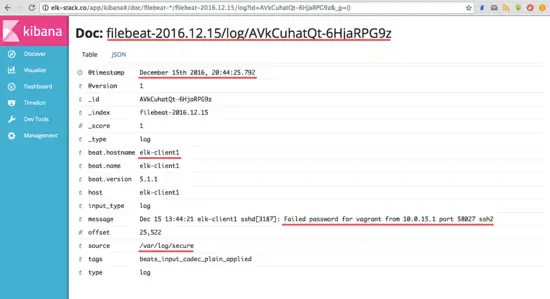
Go to the '**Discover**' menu and you will see all the log file from the elk-client1 and elk-client2 servers.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][20]
|
||||
|
||||
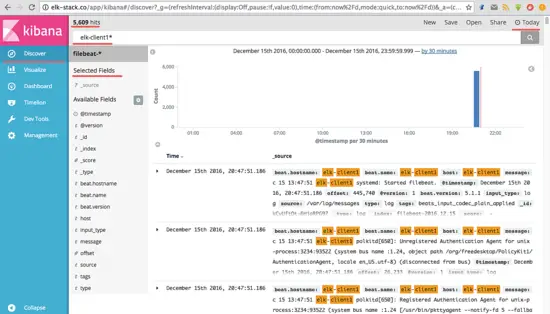
An example of JSON output from the elk-client1 server log for an invalid ssh login.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][21]
|
||||
|
||||
And there is much more that you can do with Kibana dashboard, just play around with the available options.
|
||||
|
||||
Elastic Stack has been installed on a CentOS 7 server. Filebeat has been installed on a CentOS 7 and a Ubuntu client.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Muhammad Arul][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/
|
||||
[1]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-nbspprepare-the-operating-system
|
||||
[2]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-install-java
|
||||
[3]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-install-and-configure-elasticsearch
|
||||
[4]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-install-and-configure-kibana-with-nginx
|
||||
[5]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-install-and-configure-logstash
|
||||
[6]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-install-and-configure-filebeat-on-the-centos-client
|
||||
[7]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-install-and-configure-filebeat-on-the-ubuntu-client
|
||||
[8]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-testing
|
||||
[9]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#reference
|
||||
[10]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/1.png
|
||||
[11]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/2.png
|
||||
[12]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/3.png
|
||||
[13]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/4.png
|
||||
[14]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/5.png
|
||||
[15]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/6.png
|
||||
[16]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/12.png
|
||||
[17]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/7.png
|
||||
[18]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/8.png
|
||||
[19]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/9.png
|
||||
[20]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/10.png
|
||||
[21]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/11.png
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,644 @@
|
||||
如何在CentOS 7 上安装 Elastic Stack
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
### 本页
|
||||
|
||||
1. [步骤1 - 准备操作系统][1]
|
||||
2. [步骤2 - 安装 Java][2]
|
||||
3. [步骤3 - 安装和配置 Elasticsearch][3]
|
||||
4. [步骤4 - 安装和配置 Kibana 和 Nginx][4]
|
||||
5. [步骤5 - 安装和配置 Logstash][5]
|
||||
6. [步骤6 - 在 CentOS 客户端上安装并配置 Filebeat][6]
|
||||
7. [步骤7 - 在 Ubuntu 客户端上安装并配置 Filebeat][7]
|
||||
8. [步骤8 - 测试][8]
|
||||
9. [参考][9]
|
||||
|
||||
**Elasticsearch** 是基于Lucene由Java开发的开源搜索引擎。它提供了一个分布式,多租户(译者注:多租户是指多租户技术,是一种软件架构技术,用来探讨与实现如何在多用户的环境下共用相同的系统或程序组件,并且仍可确保各用户间数据的隔离性。)的全文搜索引擎,并带有 HTTP 仪表盘的web界面(Kibana)。数据会被Elasticsearch查询,检索并且使用JSON文档方案存储。Elasticsearch 是一个可扩展的搜索引擎,可用于搜索所有类型的文本文档,包括日志文件。Elasticsearch 是‘Elastic Stack‘的核心,“Elastic Stack”也被称为“ELK Stack”。
|
||||
|
||||
**Logstash** 是用于管理事件和日志的开源工具。它为数据收集提供实时传递途径。 Logstash将收集您的日志数据,将数据转换为JSON文档,并将其存储在Elasticsearch中。
|
||||
|
||||
**Kibana** 是Elasticsearch的开源数据可视化工具。Kibana提供了一个漂亮的仪表盘Web界面。 你可以用它来管理和可视化来自Elasticsearch的数据。 它不仅美丽,而且强大。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我将向您展示如何在CentOS 7服务器上安装和配置 Elastic Stack以监视服务器日志。 然后,我将向您展示如何在操作系统为 CentOS 7和Ubuntu 16的客户端上安装“Elastic beats”。
|
||||
|
||||
**前提条件**
|
||||
|
||||
* 64位的CentOS 7,4GB 内存 - elk 主控机
|
||||
* 64位的CentOS 7 ,1 GB 内存 - 客户端1
|
||||
* 64位的Ubuntu 16 ,1GB 内存 - 客户端2
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤1 - 准备操作系统
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我们将禁用CentOS 7服务器上的SELinux。 编辑SELinux配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vim /etc/sysconfig/selinux
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将 SELINUX 的值从 enforcing 改成 disabled 。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
SELINUX=disabled
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后从起服务器
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
reboot
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
再次登录服务器并检查SELinux状态。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
getenforce
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
确保结果是disabled。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤2 - 安装 Java
|
||||
|
||||
部署Elastic stack依赖于Java,Elasticsearch 需要Java 8 版本,推荐使用Oracle JDK 1.8 。我将从官方的Oracle rpm包安装Java 8。
|
||||
|
||||
使用wget命令下载Java 8 的JDK。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
wget --no-cookies --no-check-certificate --header "Cookie: gpw_e24=http:%2F%2Fwww.oracle.com%2F; oraclelicense=accept-securebackup-cookie" "http://download.oracle.com/otn-pub/java/jdk/8u77-b02/jdk-8u77-linux-x64.rpm"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后使用rpm命令安装
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
rpm -ivh jdk-8u77-linux-x64.rpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最后,检查java JDK版本,确保它正常工作。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
java -version
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您将看到服务器的Java版本。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤3 - 安装和配置 Elasticsearch
|
||||
|
||||
在此步骤中,我们将安装和配置Elasticsearch。 从elastic.co网站提供的rpm包安装Elasticsearch,并将其配置在本地主机上运行(确保安装程序安全,而且不能从外部访问)。
|
||||
|
||||
在安装Elasticsearch之前,将elastic.co添加到服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,使用wget下载Elasticsearch 5.1,然后安装它。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-5.1.1.rpm
|
||||
rpm -ivh elasticsearch-5.1.1.rpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Elasticsearch 已经安装好了。 现在进入配置目录编辑elasticsaerch.yml 配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd /etc/elasticsearch/
|
||||
vim elasticsearch.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
去掉第40行的注释,启用Elasticsearch 的内存锁。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在“Network”块中,取消注释network.host和http.port行。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
network.host: localhost
|
||||
http.port: 9200
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存文件并退出编辑器。
|
||||
|
||||
现在编辑elasticsearch.service文件获取内存锁配置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
去掉第60行的注释,确保该值为“unlimited”。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
MAX_LOCKED_MEMORY=unlimited
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
Elasticsearch 配置到此结束。Elasticsearch 将在本机的9200端口运行,我们通过在 CentOS 服务器上启用mlockall来禁用内存交换。重新加载systemd,将 Elasticsearch 置为启动,然后启动服务。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
|
||||
sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch
|
||||
sudo systemctl start elasticsearch
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
等待 Eelasticsearch 启动成功,然后检查服务器上打开的端口,确保9200端口的状态是“LISTEN”
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
netstat -plntu
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
![Check elasticsearch running on port 9200] [10]
|
||||
|
||||
然后检查内存锁以确保启用mlockall,并使用以下命令检查Elasticsearch是否正在运行。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/_nodes?filter_path=**.mlockall&pretty'
|
||||
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/?pretty'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
会看到如下结果。
|
||||
|
||||
![Check memory lock elasticsearch and check status] [11]
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤4 - 安装和配置 Kibana 和 Nginx
|
||||
|
||||
In this step, we will install and configure Kibana with a Nginx web server. Kibana will listen on the localhost IP address and Nginx acts as a reverse proxy for the Kibana application.
|
||||
|
||||
下载Kibana 5.1与wget,然后使用rpm命令安装:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
|
||||
rpm -ivh kibana-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
编辑 Kibana 配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vim /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
去掉配置文件中 server.port, server.host 和 elasticsearch.url 这三行的注释。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
server.port: 5601
|
||||
server.host: "localhost"
|
||||
elasticsearch.url: "http://localhost:9200"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
将 Kibana 设为开机启动,并且启动Kibana 。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo systemctl enable kibana
|
||||
sudo systemctl start kibana
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Kibana将作为节点应用程序运行在端口5601上。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
netstat -plntu
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
![Kibana running as node application on port 5601] [12]
|
||||
|
||||
Kibana 安装到此结束。 现在我们需要安装Nginx并将其配置为反向代理,以便能够从公共IP地址访问Kibana。
|
||||
|
||||
Nginx在Epel资源库中可以找到,用yum安装epel-release。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
yum -y install epel-release
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后安装 Nginx 和 httpd-tools 这两个包。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
yum -y install nginx httpd-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
httpd-tools软件包包含Web服务器的工具,可以为Kibana添加htpasswd基础认证。
|
||||
|
||||
编辑Nginx配置文件并删除'server {}'块,这样我们可以添加一个新的虚拟主机配置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd /etc/nginx/
|
||||
vim nginx.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
删除server { }块。
|
||||
|
||||
![Remove Server Block on Nginx configuration] [13]
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们需要在conf.d目录中创建一个新的虚拟主机配置文件。 用vim创建新文件'kibana.conf'。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/kibana.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
复制下面的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 80;
|
||||
|
||||
server_name elk-stack.co;
|
||||
|
||||
auth_basic "Restricted Access";
|
||||
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.kibana-user;
|
||||
|
||||
location / {
|
||||
proxy_pass http://localhost:5601;
|
||||
proxy_http_version 1.1;
|
||||
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
|
||||
proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade';
|
||||
proxy_set_header Host $host;
|
||||
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
然后使用htpasswd命令创建一个新的基本认证文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo htpasswd -c /etc/nginx/.kibana-user admin
|
||||
TYPE YOUR PASSWORD
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
测试Nginx配置,确保没有错误。 然后设定Nginx开机启动并启动Nginx。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
nginx -t
|
||||
systemctl enable nginx
|
||||
systemctl start nginx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
![Add nginx virtual host configuration for Kibana Application] [14]
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤5 - 安装和配置 Logstash
|
||||
|
||||
在此步骤中,我们将安装Logstash并将其配置为:从配置了filebeat的logstash客户端集中服务器的日志,然后过滤和转换Syslog数据并将其移动到存储中心(Elasticsearch)中。
|
||||
|
||||
下载Logstash并使用rpm进行安装。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-5.1.1.rpm
|
||||
rpm -ivh logstash-5.1.1.rpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
生成新的SSL证书文件,以便客户端可以识别 elastic 服务端。
|
||||
|
||||
进入tls目录并编辑openssl.cnf文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd /etc/pki/tls
|
||||
vim openssl.cnf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在“[v3_ca]”部分添加新行,以获取服务器标识。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[ v3_ca ]
|
||||
|
||||
# Server IP Address
|
||||
subjectAltName = IP: 10.0.15.10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
使用openssl命令生成证书文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
openssl req -config /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf -x509 -days 3650 -batch -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/pki/tls/private/logstash-forwarder.key -out /etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
证书文件可以在'/etc/pki/tls/certs/'和'/etc/pki/tls/private/' 目录中找到。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,我们会为Logstash创建新的配置文件。创建一个新的“filebeat-input.conf”文件来配置filebeat的日志源,然后创建一个“syslog-filter.conf”配置文件来处理syslog,再创建一个“output-elasticsearch.conf”文件来定义输出日志数据到Elasticsearch。
|
||||
|
||||
转到logstash配置目录,并在”conf.d“子目录中创建新的配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd /etc/logstash/
|
||||
vim conf.d/filebeat-input.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
输入配置:粘贴以下配置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
input {
|
||||
beats {
|
||||
port => 5443
|
||||
ssl => true
|
||||
ssl_certificate => "/etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt"
|
||||
ssl_key => "/etc/pki/tls/private/logstash-forwarder.key"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
创建 syslog-filter.conf 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vim conf.d/syslog-filter.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
粘贴以下配置
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
filter {
|
||||
if [type] == "syslog" {
|
||||
grok {
|
||||
match => { "message" => "%{SYSLOGTIMESTAMP:syslog_timestamp} %{SYSLOGHOST:syslog_hostname} %{DATA:syslog_program}(?:\[%{POSINT:syslog_pid}\])?: %{GREEDYDATA:syslog_message}" }
|
||||
add_field => [ "received_at", "%{@timestamp}" ]
|
||||
add_field => [ "received_from", "%{host}" ]
|
||||
}
|
||||
date {
|
||||
match => [ "syslog_timestamp", "MMM d HH:mm:ss", "MMM dd HH:mm:ss" ]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用名为“grok”的过滤器插件来解析syslog文件。
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
创建输出配置文件 “output-elasticsearch.conf“。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vim conf.d/output-elasticsearch.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
粘贴以下配置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
output {
|
||||
elasticsearch { hosts => ["localhost:9200"]
|
||||
hosts => "localhost:9200"
|
||||
manage_template => false
|
||||
index => "%{[@metadata][beat]}-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
|
||||
document_type => "%{[@metadata][type]}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,将logstash设定为开机启动并且启动服务。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo systemctl enable logstash
|
||||
sudo systemctl start logstash
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
![Logstash started on port 5443 with SSL Connection] [15]
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤6 - 在 CentOS 客户端上安装并配置 Filebeat
|
||||
|
||||
Beat作为数据发送人的角色,是一种可以安装在客户端节点上的轻量级代理,将大量数据从客户机发送到Logstash或Elasticsearch服务器。有4中beat,“Filebeat” 用于发送“日志文件”,“Metricbeat” 用于发送“指标”,“Packetbeat” 用于发送”网络数据“,”Winlogbeat“用于发送Windows客户端的“事件日志”。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我将向您展示如何安装和配置“Filebeat”,通过SSL连接将数据日志文件传输到Logstash服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
登录到客户端1的服务器上。 然后将证书文件从elastic 服务器复制到客户端1的服务器上。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ssh root@client1IP
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用scp命令拷贝证书文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
scp root@elk-serverIP:~/logstash-forwarder.crt .
|
||||
TYPE elk-server password
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个新的目录,将证书移动到这个目录中。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo mkdir -p /etc/pki/tls/certs/
|
||||
mv ~/logstash-forwarder.crt /etc/pki/tls/certs/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,在客户端1服务器上导入 elastic 密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下载 Filebeat 并且用rpm命令安装。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
|
||||
rpm -ivh filebeat-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Filebeat已经安装好了,请转到配置目录并编辑“filebeat.yml”文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd /etc/filebeat/
|
||||
vim filebeat.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在第21行的路径部分,添加新的日志文件。 我们将创建两个文件,”/var/log/secure“文件用于ssh活动,“/var/log/secure”文件服务器日志。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- /var/log/secure
|
||||
- /var/log/messages
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在第26行添加一个新配置来定义syslog类型的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
document-type: syslog
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Filebeat默认使用Elasticsearch作为输出目标。 在本教程中,我们将其更改为Logshtash。 在83行和85行添加注释来禁用 Elasticsearch 输出。
|
||||
|
||||
禁用 Elasticsearch 输出。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------
|
||||
#output.elasticsearch:
|
||||
# Array of hosts to connect to.
|
||||
# hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在添加新的logstash输出配置。 去掉logstash输出配置的注释,并将所有值更改为下面配置中的值。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
output.logstash:
|
||||
# The Logstash hosts
|
||||
hosts: ["10.0.15.10:5443"]
|
||||
bulk_max_size: 1024
|
||||
ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt"]
|
||||
template.name: "filebeat"
|
||||
template.path: "filebeat.template.json"
|
||||
template.overwrite: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存文件并退出vim。
|
||||
|
||||
将 Filebeat 设定为开机启动并启动。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo systemctl enable filebeat
|
||||
sudo systemctl start filebeat
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤7 - 在 Ubuntu 客户端上安装并配置 Filebeat
|
||||
|
||||
使用ssh连接到服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ssh root@ubuntu-clientIP
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用scp命令拷贝证书文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
scp root@elk-serverIP:~/logstash-forwarder.crt .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个新的目录,将证书移动到这个目录中。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo mkdir -p /etc/pki/tls/certs/
|
||||
mv ~/logstash-forwarder.crt /etc/pki/tls/certs/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在服务器上导入 elastic 密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下载 Filebeat .deb 包并且使用dpkg命令进行安装。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-5.1.1-amd64.deb
|
||||
dpkg -i filebeat-5.1.1-amd64.deb
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
转到配置目录并编辑“filebeat.yml”文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd /etc/filebeat/
|
||||
vim filebeat.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在路径配置部分添加新的日志文件路径。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- /var/log/auth.log
|
||||
- /var/log/syslog
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
设定document type配置为 syslog 。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
document-type: syslog
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将下列几行注释掉,禁用输出到 Elasticsearch。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------
|
||||
#output.elasticsearch:
|
||||
# Array of hosts to connect to.
|
||||
# hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启用logstash输出,去掉以下配置的注释并且按照如下所示更改值。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
output.logstash:
|
||||
# The Logstash hosts
|
||||
hosts: ["10.0.15.10:5443"]
|
||||
bulk_max_size: 1024
|
||||
ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt"]
|
||||
template.name: "filebeat"
|
||||
template.path: "filebeat.template.json"
|
||||
template.overwrite: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出vim。
|
||||
|
||||
将 Filebeat 设定为开机启动并启动。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo systemctl enable filebeat
|
||||
sudo systemctl start filebeat
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
检查服务状态。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
systemctl status filebeat
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
![Filebeat is running on the client Ubuntu] [16]
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤8 - 测试
|
||||
|
||||
打开您的网络浏览器,并访问您在Nginx中配置的elastic stack域,我的是“elk-stack.co”。 使用管理员密码登录,然后按Enter键登录Kibana仪表盘。
|
||||
|
||||
![Login to the Kibana Dashboard with Basic Auth] [17]
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个新的默认索引”filebeat- *“,然后点击'创建'按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
![Create First index filebeat for Kibana] [18]
|
||||
|
||||
默认索引已创建。 如果elastic stack上有多个beat,您可以在“星形”按钮上点击一下即可配置默认beat。
|
||||
|
||||
![Filebeat index as default index on Kibana Dashboard] [19]
|
||||
|
||||
转到 “**Discover**” 菜单,您就可以看到elk-client1和elk-client2服务器上的所有日志文件。
|
||||
|
||||
![Discover all Log Files from the Servers] [20]
|
||||
|
||||
来自elk-client1服务器日志中的无效ssh登录的JSON输出示例。
|
||||
|
||||
![JSON output for Failed SSH Login] [21]
|
||||
|
||||
使用其他的选项,你可以使用Kibana仪表盘做更多的事情。
|
||||
|
||||
Elastic Stack已安装在CentOS 7服务器上。 Filebeat已安装在CentOS 7和Ubuntu客户端上。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Muhammad Arul][a]
|
||||
译者:[Flowsnow](https://github.com/Flowsnow)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/
|
||||
[1]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-nbspprepare-the-operating-system
|
||||
[2]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-install-java
|
||||
[3]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-install-and-configure-elasticsearch
|
||||
[4]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-install-and-configure-kibana-with-nginx
|
||||
[5]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-install-and-configure-logstash
|
||||
[6]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-install-and-configure-filebeat-on-the-centos-client
|
||||
[7]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-install-and-configure-filebeat-on-the-ubuntu-client
|
||||
[8]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#step-testing
|
||||
[9]: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/#reference
|
||||
[10]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/1.png
|
||||
[11]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/2.png
|
||||
[12]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/3.png
|
||||
[13]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/4.png
|
||||
[14]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/5.png
|
||||
[15]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/6.png
|
||||
[16]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/12.png
|
||||
[17]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/7.png
|
||||
[18]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/8.png
|
||||
[19]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/9.png
|
||||
[20]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/10.png
|
||||
[21]: https://www.howtoforge.com/images/how-to-install-elastic-stack-on-centos-7/big/11.png
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user