mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-06 01:20:12 +08:00
[Translated] 20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure a static IP address on CentOS 7.md
This commit is contained in:
parent
90a7fe5921
commit
bc15e937a6
@ -1,79 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by GOLinux ...
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure a static IP address on CentOS 7
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: On CentOS 7, I want to switch from DHCP to static IP address configuration with one of my network interfaces. What is a proper way to assign a static IP address to a network interface permanently on CentOS or RHEL 7?
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to set up a static IP address on a network interface in CentOS 7, there are several different ways to do it, varying depending on whether or not you want to use Network Manager for that.
|
||||
|
||||
Network Manager is a dynamic network control and configuration system that attempts to keep network devices and connections up and active when they are available). CentOS/RHEL 7 comes with Network Manager service installed and enabled by default.
|
||||
|
||||
To verify the status of Network Manager service:
|
||||
|
||||
$ systemctl status NetworkManager.service
|
||||
|
||||
To check which network interface is managed by Network Manager, run:
|
||||
|
||||
$ nmcli dev status
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If the output of nmcli shows "connected" for a particular interface (e.g., enp0s3 in the example), it means that the interface is managed by Network Manager. You can easily disable Network Manager for a particular interface, so that you can configure it on your own for a static IP address.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are **two different ways to assign a static IP address to a network interface on CentOS 7**. We will be configuring a network interface named enp0s3.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure a Static IP Address without Network Manager ###
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts directory, and locate its configuration file (ifcfg-enp0s3). Create it if not found.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Open the configuration file and edit the following variables:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the above, "NM_CONTROLLED=no" indicates that this interface will be set up using this configuration file, instead of being managed by Network Manager service. "ONBOOT=yes" tells the system to bring up the interface during boot.
|
||||
|
||||
Save changes and restart the network service using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart network.service
|
||||
|
||||
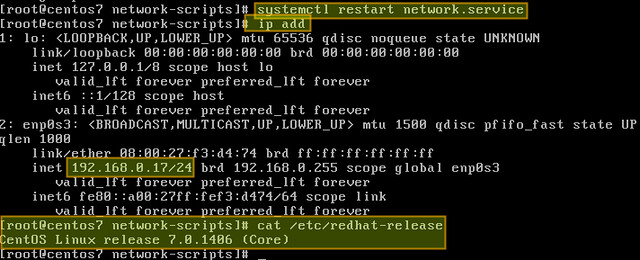
Now verify that the interface has been properly configured:
|
||||
|
||||
# ip add
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure a Static IP Address with Network Manager ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to use Network Manager to manage the interface, you can use nmtui (Network Manager Text User Interface) which provides a way to configure Network Manager in a terminal environment.
|
||||
|
||||
Before using nmtui, first set "NM_CONTROLLED=yes" in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3.
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's install nmtui as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install NetworkManager-tui
|
||||
|
||||
Then go ahead and edit the Network Manager configuration of enp0s3 interface:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmtui edit enp0s3
|
||||
|
||||
The following screen will allow us to manually enter the same information that is contained in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3.
|
||||
|
||||
Use the arrow keys to navigate this screen, press Enter to select from a list of values (or fill in the desired values), and finally click OK at the bottom right:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Finally, restart the network service.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart network.service
|
||||
|
||||
and you're ready to go.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/configure-static-ip-address-centos7.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答——如何为CentOS 7配置静态IP地址
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**:在CentOS 7上,我想要将我其中一个网络接口从DHCP改为静态IP地址配置,如何才能永久为CentOS或RHEL 7上的网络接口分配静态IP地址?
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要为CentOS 7中的某个网络接口设置静态IP地址,有几种不同的方法,这取决于你是否想要使用网络管理器。
|
||||
|
||||
网络管理器是一个动态的网络控制与配置系统,它用于在网络设备可用时保持设备和连接开启并激活。默认情况下,CentOS/RHEL 7安装有网络管理器,并处于启用状态。
|
||||
|
||||
使用下面的命令来验证网络管理器服务的状态:
|
||||
|
||||
$ systemctl status NetworkManager.service
|
||||
|
||||
运行以下命令来检查受网络管理器管理的网络接口:
|
||||
|
||||
$ nmcli dev status
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果某个接口的nmcli的输出结果是“已连接”(如本例中的enp0s3),这就是说该接口受网络管理器管理。你可以轻易地为某个特定接口禁用网络管理器,以便你可以自己为它配置一个静态IP地址。
|
||||
|
||||
下面将介绍**在CentOS 7上为网络接口配置静态IP地址的两种方式**,在例子中我们将对名为enp0s3的网络接口进行配置。
|
||||
|
||||
### 不使用网络管理配置静态IP地址 ###
|
||||
|
||||
进入/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts目录,找到该接口的配置文件(ifcfg-enp0s3)。如果没有,请创建一个。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
打开配置文件并编辑以下变量:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在上图中,“NM_CONTROLLED=no”表示该接口将通过该配置进行设置,而不是通过网络管理器进行管理。“ONBOOT=yes”告诉我们,系统将在启动时开启该接口。
|
||||
|
||||
保存修改并使用以下命令来重启网络服务:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart network.service
|
||||
|
||||
现在验证接口是否配置正确:
|
||||
|
||||
# ip add
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 使用网络管理器配置静态IP地址 ###
|
||||
如果你想要使用网络管理器来管理该接口,你可以使用nmtui(网络管理器文本用户界面),它提供了在终端环境中配置配置网络管理器的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
在使用nmtui之前,首先要在/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3中设置“NM_CONTROLLED=yes”。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,请按以下方式安装nmtui。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install NetworkManager-tui
|
||||
|
||||
然后继续去编辑enp0s3接口的网络管理器配置:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmtui edit enp0s3
|
||||
|
||||
在下面的屏幕中,我们可以手动输入与/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3中所包含的内容相同的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
使用箭头键在屏幕中导航,按回车选择值列表中的内容(或填入想要的内容),最后点击屏幕底部右侧的确定按钮。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最后,重启网络服务。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart network.service
|
||||
|
||||
好了,现在一切就绪。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/configure-static-ip-address-centos7.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user