mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-25 23:11:02 +08:00
清理过期文章
This commit is contained in:
parent
eb425f3ab2
commit
bb22fac27f
@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Microsoft loves Linux -- for Azure's sake
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Scott Guthrie, executive vice president, Microsoft Cloud and Enterprise group, shows how Microsoft differentiates Azure. Credit: James Niccolai/IDG News Service
|
||||
|
||||
### Microsoft adds CoreOS and Cloudera to its growing set of Azure services ###
|
||||
|
||||
Microsoft now loves Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
This was the message from Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella, standing in front of an image that read "Microsoft [heart symbol] Linux," during a Monday webcast to announce a number of services it had added to its Azure cloud, including the Cloudera Hadoop package and the CoreOS Linux distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, the company launched a marketplace portal, now in preview mode, designed to make it easier for customers to procure and manage their cloud operations.
|
||||
|
||||
Microsoft is also planning to release an Azure appliance, in conjunction with Dell, that will allow organizations to run hybrid clouds where they can easily move operations between Microsoft's Azure cloud and their own in-house version.
|
||||
|
||||
The declaration of affection for Linux indicates a growing acceptance of software that wasn't created at Microsoft, at least for the sake of making its Azure cloud platform as comprehensive as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
For decades, the company tied most of its new products and innovations to its Windows platform, and saw other OSes, such as Linux, as a competitive threat. Former CEO Steve Ballmer [once infamously called Linux a cancer][1].
|
||||
|
||||
This animosity may be evaporating as Microsoft is finding that customers want cloud services that incorporate software from other sources in addition to Microsoft. About 20 percent of the workloads run on Azure are based on Linux, Nadella admitted.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, the company considers its newest competitors to be the cloud services offered by Amazon and Google.
|
||||
|
||||
Nadella said that by early 2015, Azure will be operational in 19 regions around the world, which will provide more local coverage than either Google or Amazon.
|
||||
|
||||
He also noted that the company is investing more than $4.5 billion in data centers, which by Microsoft's estimation is twice as much as Amazon's investments and six times as much as Google's.
|
||||
|
||||
To compete, Microsoft has been adding widely-used third party software packages to Azure at a rapid clip. Nadella noted that Azure now supports all the major data integration stacks, such as those from Oracle and IBM, as well as major new entrants such as MongoDB and Hadoop.
|
||||
|
||||
The results seem to be paying off. Today Azure is generating about $4.48 billion in annual revenue for Microsoft, and we are "still at the early days," of cloud computing, Nadella said.
|
||||
|
||||
The service attracts about 10,000 new customers per week. About 2 million developers have signed on to Visual studio online since its launch. The service runs about 1.2 million SQL databases.
|
||||
|
||||
CoreOS is now actually the fifth Linux distribution that Azure offers, joining Ubuntu, CentOS, OpenSuse, and Oracle Linux (a variant of Red Hat Enterprise Linux). Customers [can also package their own Linux distributions][2] to run in Azure.
|
||||
|
||||
CoreOS was developed as [a lightweight Linux distribution][3] to be used primarily in cloud environments. Officially launched in December, CoreOS is already offered as a service by Google, Rackspace, DigitalOcean and others.
|
||||
|
||||
Cloudera is the second Hadoop distribution offered on Azure, following Hortonworks. Cloudera CEO Mike Olson joined the Microsoft executives onstage to demonstrate how easily one can use the Cloudera Hadoop software within Azure.
|
||||
|
||||
Using the new portal, Olson showed how to start up a 90-node instance of Cloudera with a few clicks. Such a deployment can be connected to an Excel spreadsheet, where the user can query the dataset using natural language.
|
||||
|
||||
Microsoft also announced a number of other services and products.
|
||||
|
||||
Azure will have a new type of virtual machine, which is being called the "G Family." These virtual machines can have up to 32 CPU cores, 450GB of working memory and 6.5TB of storage, making it in effect "the largest virtual machine in the cloud," said Scott Guthrie, who is the Microsoft executive vice president overseeing Azure.
|
||||
|
||||
This family of virtual machines is equipped to handle the much larger workloads Microsoft is anticipating its customers will want to run. It has also upped the amount of storage each virtual machine can access, to 32TB.
|
||||
|
||||
The new cloud platform appliance, available in November, will allow customers to run Azure services on-premise, which can provide a way to bridge their on-premise and cloud operations. One early customer, integrator General Dynamics, plans to use this technology to help its U.S. government customers migrate to the cloud.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.computerworld.com/article/2836315/microsoft-loves-linux-for-azures-sake.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joab Jackson][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.computerworld.com/author/Joab-Jackson/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.theregister.co.uk/2001/06/02/ballmer_linux_is_a_cancer/
|
||||
[2]:http://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/documentation/articles/virtual-machines-linux-create-upload-vhd/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.itworld.com/article/2696116/open-source-tools/coreos-linux-does-away-with-the-upgrade-cycle.html
|
||||
@ -1,28 +0,0 @@
|
||||
This is the name of Ubuntu 15.04 — And It’s Not Velociraptor
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Ubuntu 14.10 may not be out of the door yet, but attention is already turning to Ubuntu 15.04. Today it got its name: ‘[Vivid Vervet][1]’.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Announcing the monkey-themed moniker in his usual loquacious style, Mark Shuttleworth cites the ‘upstart’ and playful nature of the mascot as in tune with its own foray into the mobile space.
|
||||
|
||||
> “This is a time when every electronic thing can be an Internet thing, and that’s a chance for us to bring our platform, with its security and its long term support, to a vast and important field. In a world where almost any device can be smart, and also subverted, our shared efforts to make trusted and trustworthy systems might find fertile ground.
|
||||
|
||||
Talking of plans for the release Shuttleworth states one goal is to “show the way past a simple Internet of things, to a world of Internet things-you-can-trust.”
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.04 is due for release in April 2015. It’s not expected to arrive with either Mir or Unity 8 by default, but given the veracious speed of acceleration in ambitions, it may find its way out for testing.
|
||||
|
||||
Do you like the name? Were you hoping for velociraptor?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/10/ubuntu-15-04-named-vivid-vervet
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.markshuttleworth.com/archives/1425
|
||||
@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.04 Is Called Vivid Vervet
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Mark Shuttleworth decided on the new name for Ubuntu 15.04
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**One of Mark Shuttleworth's privileges is to decide what the code name for upcoming Ubuntu versions is. It's usually a real animal and now it's a monkey whose name starts with V and, as usual, it's probably a species you’ve never heard of before.**
|
||||
|
||||
With very few exceptions, some of the names chosen for Ubuntu releases send the older users to the Encyclopedia Britannica and the new ones to Google. Shuttleworth generally chooses animals that are less known and the names usually have something in common with the release.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, Trusty Tahr, the name of Ubuntu 14.04 LTS, followed the idea of long term support for the operating system, hence the trusty adjective. Precise Pangolin did the same for Ubuntu 12.04 LTS, and so on. Intermediary releases are not all that obvious and the Ubuntu 14.10 Utopic Unicorn is proof of that.
|
||||
|
||||
### Still thinking about the monkey whose name starts with a V? ###
|
||||
|
||||
The way the version number is chosen is pretty clear. The first part is for the year and the second one is for the month, so Ubuntu 14.10 is actually Ubuntu 2014 October. On the other hand, the names only follow a simple rule, one adjective and one animal, so the choice is rather simple. Unlike other communities, where the designation is decided by users or at least with their participation, Ubuntu is different, although it's not a singular example.
|
||||
|
||||
"Release week! Already! I wouldn't call Trusty 'vintage' just yet, but Utopic is poised to leap into the torrent stream. We've all managed to land our final touches to *buntu and are excited to bring the next wave of newness to users around the world. Glad to see the unicorn theme went down well, judging from the various desktops I see on G+."
|
||||
|
||||
"In my favourite places, the smartest thing around is a particular kind of monkey. Vexatious at times, volant and vogie at others, a vervet gets in anywhere and delights in teasing cats and dogs alike. As the upstart monkey in this business I can think of no better mascot. And so let's launch our vicenary cycle, our verist varlet, the Vivid Vervet!" says Mark Shuttleworth on his [blog][1].
|
||||
|
||||
So, there you have it, Ubuntu 15.04, the operating system that is scheduled to arrive in April 2015, will be called Vivid Vervet. I won't keep you anymore for details, I'm sure you are already looking up the vervet on Wikipedia.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Ubuntu-15-04-Is-Called-Vivid-Vervet-462621.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://www.markshuttleworth.com/archives/1425
|
||||
@ -1,190 +0,0 @@
|
||||
9 ASCII Games You'll Want to Play Again and Again
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Modern Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) offer exceptional gaming capabilities, and have contributed to the trend of astonishing leaps in graphics fidelity. There is not a year that has gone by without a game being released that makes significant advances in technical graphics wizardry. Computer graphics have been advancing at a staggering pace. At the current rate of progress, in the next 10 years it may not be possible to distinguish computer graphics from reality.
|
||||
|
||||
Personally, these developments do not overly interest me. I find little fascination playing games that focus so much on the visuals they neglect the essential elements. Too often the storyline and game play has been compromised for visual quality. Most of my favourite games are somewhat deficient in the graphics department. Gameplay is always king in my eyes.
|
||||
|
||||
Linux has an excellent library of free games many of which are released under an open source license. The vast majority of these games are aesthetically pleasing. Popular games often have full motion video, vector graphics, 3D graphics, realistic 3D rendering, animation, texturing, a physics engine, and much more. Early computer games did not have these graphic techniques. The earliest video games were text games or text-based games that used text characters rather than vector or bitmapped graphics.
|
||||
|
||||
Text-based games often receive little coverage in the Linux press. However, there are some real ASCII gems out there waiting to be explored which are immensely addictive and great fun to play.
|
||||
|
||||
The idiom 'don't judge a book by its cover' can be extended to 'don't judge a computer game by its graphics'. Whilst the games featured in this article have extremely basic graphics, they have many redeeming qualities beyond evoking fond memories of the early days of computer gaming.
|
||||
|
||||
There are no fancy graphics here, just great gameplay coupled with the urge of always having just one more play.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The first game in this roundup is UnNetHack, a fork of NetHack, originally based on the hugely popular roguelike game NetHack. NetHack was first released in 1987, and is considered by many gamers to be one of the best gaming experiences the computing world offers.
|
||||
|
||||
UnNetHack adds a number of enhancements to NetHack, such as additional monsters, more levels, a few new objects, additional dangers, more challenging gameplay, and most importantly more entertainment than vanilla NetHack. It offers a tutorial to help new players get started.
|
||||
|
||||
Be warned, UnNetHack is fiendishly addictive.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [sourceforge.net/apps/trac/unnethack][1]
|
||||
- Authors: Patric Mueller
|
||||
- License: Nethack General Public License
|
||||
- Version Number: 5.1.0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Empire is a simulation of a full-scale war between two emperors, the computer and you. Naturally, there is only room for one, so the object of the game is to destroy the other. The computer plays by the same rules that you do.
|
||||
|
||||
This game is the ancestor of all the multiplayer 4X simulations out there, including Civilization and Master of Orion. The classic game from the 1980s uses text mode graphical output, drawing your units, cities and the world in color. Commands are issued using the keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||
The world on which the game takes place is a square rectangle containing cities, land, and water. Cities are used to build armies, planes, and ships which can move across the world destroying enemy pieces, exploring, and capturing more cities. The objective of the game is to destroy all the enemy pieces, and capture all the cities.
|
||||
|
||||
The game starts by assigning you one city and the computer one city. Cities can produce new pieces. Every city that you own produces more pieces for you according to the cost of the desired piece. The typical play of the game is to issue the Automove command until you decide to do something special. During movement in each round, the player is prompted to move each piece that does not otherwise have an assigned function.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [www.catb.org/~esr/vms-empire][2]
|
||||
- Authors: Chuck Simmons, Eric S. Raymond
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.12
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Intricacy is an addictive, open source, networked, video puzzle game. It is written in Haskell, using the Curses and SDL libraries.
|
||||
|
||||
Intricacy runs directly from the command-line, and provides a turn-based, abstract puzzle game where the players need to pick locks, simply by coordinating a couple of tools in order to manipulate the lock’s mechanism. Constructing and solving difficult puzzles within certain strict design constraints is both challenging and good fun.
|
||||
|
||||
The catch is that you will be able to pick locks that are designed by other players. It has multi-platform support, with binaries for both Linux and Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [mbays.freeshell.org/intricacy][3]
|
||||
- Authors: Chuck Simmons, Eric S. Raymond
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.2.6.3
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
XorCurses is a puzzle game set inside a series of mazes. It is a remake of XOR by Astral Software, a game published in 1987 and released on the popular home computers of the day including the Commodore 64, ZX Spectrum, Atari ST, and Amiga. XOR is a pure puzzle game with no random or arcade elements.
|
||||
|
||||
In some respects, XorCurses is a regression from the graphics of the old 8 bit computers as it uses even more simplistic graphics, with coloured ASCII characters instead of pixel based graphics.
|
||||
|
||||
XorCurses attempts to faithfully recreate that game for Linux, with particular attention placed on the behaviour of the objects within the original game.
|
||||
|
||||
The basic premise of Xor is to roam around a series of mazes collecting all of the blue masks and then finding the exit. You have two player-shields to aid you and you can use either one at any time and switch between them. The first few levels are easy to progress, but the rest are progressively harder to solve. A particularly challenging and difficult puzzle game that will keep you engaged for hours.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [www.jwm-art.net/dark.php?p=XorCurses][4]
|
||||
- Authors: James W. Morris
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.2.2
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Goblin Hack is an open source roguelike OpenGL-based smooth-scrolling ASCII graphics game. The game is inspired by the likes of NetHack, but faster with fewer keys.
|
||||
|
||||
Goblin Hack has a simple interface that appears to appeal to players of all ages, and fires their imagination in today's world of over-rendered games.
|
||||
|
||||
Players can choose one of several classes before being thrown into the first floor of a randomized, ongoing dungeon.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [goblinhack.sourceforge.net][5]
|
||||
- Authors: Neil McGill
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.18
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Curse of War is a fast-paced real time strategy game released under an open source license. It is implemented using C and ncurses. There is also an SDL version available.
|
||||
|
||||
The core game mechanics turns out to be quite close to WWI-WWII type of warfare, however, there is no explicit reference to any historical period.
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike most real time strategy games, in Curse of War players do not control units, but instead they concentrate on high-level strategic planning: Building infrastructure, securing resources, and moving armies.
|
||||
|
||||
A multiplayer mode is available. Computer opponents differ in personality, and it affects the way they fight.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [a-nikolaev.github.io/curseofwar][6]
|
||||
- Authors: Alexey Nikolaev
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.2.0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Brogue is an open source Roguelike game for Mac OS X, Windows, Linux, iOS and Android.
|
||||
|
||||
Brogue is a direct descendant of Rogue, a dungeon crawling video game first developed by Michael Toy and Glenn Wichman around 1980. Unlike other popular modern roguelikes, Brogue favors simplicity over complexity, while trying to ensure that the interactions between components are interesting and varied.
|
||||
|
||||
Your goal is to travel to the 26th subterranean floor of the dungeon, retrieve the Amulet of Yendor and return with it to the surface. For the truly skillful who desire further challenge, depths below 26 contain three lumenstones each, items which confer an increased score upon victory.
|
||||
|
||||
Brogue is a challenging game, but still great fun to play. Try not to be disheartened by the difficulty of the game; with some application, Brogue will become very addictive.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [sites.google.com/site/broguegame][7]
|
||||
- Authors: Brian Walker
|
||||
- License: GNU Affero GPL
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.7.3
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
DiabloRL is a roguelike "unmake" of the popular Blizzard game Diablo 1 classic RPG to a turn-based ASCII roguelike.
|
||||
|
||||
The game was created for the 7 Day Roguelike Competition, but has since been expanded with magic items, spells, more classes and levels, as well as fast travelling to known locations, and high scores.
|
||||
|
||||
DiabloRL gives you a choice of classes, the Warrior, Rogue, or Sorcerer. Each of these has different starting and maximum stats, as well as completely different play styles.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [diablo.chaosforge.org][8]
|
||||
- Authors: Kornel Kisielewicz, Chris Johnson and Mel'nikova Anastasia
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.5.0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cataclysm is an open source post-apocalyptic roguelike, set in the countryside of fictional New England after a devastating plague of monsters and zombies. It is a continuation of Whale's original Cataclysm, which expands it with numerous new creatures, buildings, gameplay mechanics and many other features.
|
||||
|
||||
While some have described it as a "zombie game", there's far more to Cataclysm than that. Struggle to survive in a harsh, persistent, procedurally generated world. Scavenge the remnants of a dead civilization for for food, equipment, or, if you're lucky, a vehicle with a full tank of gas to get you the hell out of Dodge. Fight to defeat or escape from a wide variety of powerful monstrosities, from zombies to giant insects to killer robots and things far stranger and deadlier, and against the others like yourself, that want what you have...
|
||||
|
||||
Cataclysm is very different from most roguelikes in many ways. Rather than being set in a vertical, linear dungeon, it is set in an unbounded, 3D world. This means that exploration plays a much bigger role than in most roguelikes, and the game is much less linear. As the map is so huge, it is actually completely persistant between games. If you die, and start a new character, your new game will be set in the same game world as your last. Like in many roguelikes, you will be able to loot the dead bodies of previous characters; unlike most roguelikes, you will also be able to retrace their steps completely, and any dramatic changes made to the world will persist into your next game.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [en.cataclysmdda.com][9]
|
||||
- Authors: Kevin Granade
|
||||
- License: Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.A
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20140621060017503/9ASCIIGames.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://sourceforge.net/apps/trac/unnethack/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.catb.org/~esr/vms-empire/
|
||||
[3]:http://mbays.freeshell.org/intricacy/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.jwm-art.net/dark.php?p=XorCurses
|
||||
[5]:http://goblinhack.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[6]:http://a-nikolaev.github.io/curseofwar/
|
||||
[7]:https://sites.google.com/site/broguegame/
|
||||
[8]:http://diablo.chaosforge.org/
|
||||
[9]:http://en.cataclysmdda.com/
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Translating by instdio
|
||||
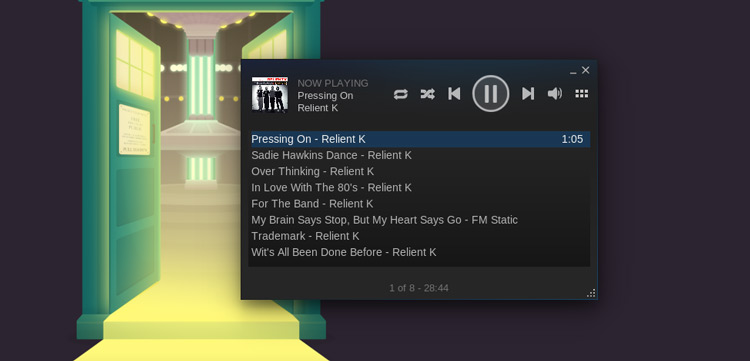
How To Use Steam Music Player on Ubuntu Desktop
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux Administration: A Smart Career Choice
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> This is a good year for IT professionals with a number of new jobs in emerging technologies like Big Data and Analytics, and Social Mobile Analytics and Cloud (SMAC) as employers look to strengthen their technological force.
|
||||
|
||||
If we were to believe the reports by [Dice.com][1] and Linux foundation released in mid Feb, 2014, this year will be a high octane year for Linux professionals and aspirants particularly. Thus it only makes sense to be future-ready and find out about the details of career opportunities such as that of a Linux administrator.
|
||||
|
||||
Dice.com, the leading job site for tech professionals and Linux Foundation did a comprehensive survey to find out about the advantage Linux professionals have in the current technology landscape. The findings were heavily skewed in favor of those who are looking for a good job opportunity on Linux platform.
|
||||
|
||||
While seventy seven percent of hiring managers surveyed consider hiring Linux talent as one of their top priorities (up from 70 percent in 2013), 64 percent of professionals chose to work with Linux owing to its ubiquitous nature in the present day technology infrastructure. More than nine in ten recruitment manager is planning to hire a Linux professional in the next six months. This demand is surely going to translate in form of a lot of interview calls from employers. Most hiring managers also agree to the fact that it is rather difficult to find experienced professionals, and those who have the right mix of skills, knowledge, certifications and experience are being aggressively recruited.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why Linux administration? ###
|
||||
|
||||
The findings of this report make it clear that Linux professionals are amongst the most sought after in the current tech market. However, a more interesting finding of the report is that amongst all the skills, the hiring managers are most actively seeking system administration, with 58 percent confirming they were on look out of professionals with good system administration skills. The reason is quite simple. There aren’t too many good system administrators out there, which is also driving the salaries of system admins northwards.
|
||||
Getting started in Linux administration
|
||||
|
||||
Armed with all this data, it wouldn’t come as surprise if you decide right away to pursue a career in Linux administration. So, how do you become a pro Linux system admin? Well, the right mix of certification, education and experience will obviously land you the perfect Linux job, but if you are clueless about a place to start, then a degree in computers is what you should be looking at. This could be B.Tech with Computer Science or IT as specialisation or Bachelors in Computer Application or even a Bachelor in Science with IT as specialisation will do. This would actually make you familiar with the various aspects of computer science as a subject, likes of programming, hardware, and software. This understanding would come handy in the advancement of your career, when you climb the next ladder through certifications.
|
||||
|
||||
### Certifications ###
|
||||
|
||||
It is widely believed that IT certifications do help one in career advancement. However, it ultimately boils down to selecting the right certification to gain the maximum RoI. There are many Linux based certifications, the most famous of which is Red Hat Certification Program, which teaches general Linux related skills along with specific system administration skills.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the vendor sponsored certifications, there is a vendor-independent Linux Professional Institute Certification offered by Linux Professional Institute, a non-profit organisation based in Toronto, Canada.
|
||||
|
||||
These exams can be taken by anyone irrespective of their nationalities. The LPI programs have three level hierarchies that include LPIC-1: Junior Level Linux Administration, LPIC-2: Advanced Level Linux Administration and LPIC 3: Senior Level Linux Administration. In order to be considered seriously for any system administrator job opportunity in one must possess at least one of the above described certifications. The LPI also has partnerships with SUSE, which is the vendor for a famous enterprise operating system going by the same name. CompTIA, which is a global IT certification agency also provided a Linux+ certification which was phased out after an agreement between LPI and CompTIA.
|
||||
|
||||
### Salaries and Benefits ###
|
||||
|
||||
The compensations for Linux administrators are generally on the higher side. As per PayScale, the annual median salary is around INR 3 lacs for entry level professionals (as updated on 27th March, 2014). With experience, there is an exponential increase in the salary levels as individuals with 5+ years of experience getting annual packages in seven figures.
|
||||
Well, with the grass being greener for Linux professionals this year, you won’t get a better opportunity or time for pursuing career as a Linux system administrator.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.opensourceforu.com/2014/04/career-overview-linux-administrator/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://dice.com/
|
||||
@ -1,141 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Install Google Docs on Linux with Grive Tools
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Google Drive is two years old now and Google’s cloud storage solution seems to be still going strong thanks to its integration with Google Docs and Gmail. There’s one thing still missing though: a lack of an official Linux client. Apparently Google has had one floating around their offices for a while now, however it’s not seen the light of day on any Linux system.
|
||||
|
||||
Thankfully, there is an alternative solution using Grive Tools. We’ve covered Grive once before when it was in its infancy, but it’s received a fair few upgrades since then thanks to Grive Tools and is now compatible with Fedora and OpenSUSE to cover a better selection of distros. Over the course of this tutorial, we’ll show you how to set up Grive Tools and get it syncing files to and from Google Drive on a regular basis, so your work is always perfectly backed up. With the death of Ubuntu One, it’s a great alternative to Canonical’s own cloud storage solution.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Accesss your backed up Linux files from anywhere with an internet connection by making use of the Drive connection
|
||||
|
||||
### Resources ###
|
||||
|
||||
A Google account
|
||||
|
||||
- [Grive Tools][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### Step-by-step ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 01 Ubuntu repository ####
|
||||
|
||||
Grive Tools is not included in Ubuntu or Ubuntu-based distros yet, so you’ll need to add a third-party repository to access it. Add this with:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:thefanclub/grive-tools
|
||||
|
||||
Follow this up with the usual sudo apt-get update before we continue.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 02 Ubuntu install ####
|
||||
|
||||
After the apt-get update, Grive Tools will appear in the software centre. If you want to go there and install it you can, however as we already have a terminal open we might as well use:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install grive-tools
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 03 Fedora dependencies ####
|
||||
|
||||
You’ll need to install some specific dependencies for OpenSUSE, Fedora and other RHEL-based distros. In Fedora specifically, open a terminal and install them with:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install json-c json-c-devel qt-devel boost-devel openssl-devel libxslt libcurl libcurl-devel
|
||||
|
||||
The same packages will need to be installed on the other distros.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 04 Grive package ####
|
||||
|
||||
Grive is not in the repositories of any of
|
||||
these distros, however binaries exist if you won’t want to build it from source. Go to RPMSEEK.com and search for Grive; look out for the version for your distro and download it.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 05 Install the download ####
|
||||
|
||||
Once downloaded, install the package; you can either do it graphical or install with:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install grive-tools-1.9.noarch.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
After that, go to the Resources link for Grive Tools and locate the Fedora package on the website: download this binary and install it alongside Grive.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 06 Start the setup ####
|
||||
|
||||
The method to actually get Grive and Grive Tools working on both systems is basically the same, so we’ll cover both at once while mentioning any extras that need to be done for a specific distro. The first thing you’ll need to do is look for Grive Setup in your list of programs.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 07 Log into your account ####
|
||||
|
||||
If you haven’t already created a Google account, you’ll need to get one sorted now before continuing. Otherwise, click Next to bring up a browser that will point you towards Google and ask you to log in. Make sure you’re logged in to the correct email address before continuing.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 08 Connect your account ####
|
||||
|
||||
You’ll be asked if the specific info it can look at is okay – you’ll need to confirm to continue, otherwise it can’t download or sync your Drive data. It will then give you a code to paste into a pop-up that launched when the browser opened.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 09 Code input ####
|
||||
|
||||
Press Next for Grive to accept the code. It will automatically open up a new Google Drive window and show your files being synced straight to your PC. This may take a while depending on how much you have stored on your account.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 10 Desktop notifications ####
|
||||
|
||||
Once the sync is complete, search again for Grive in your programs and look for Google Drive Indicator. Click on this and it will automatically launch a Dropbox-style toolbar notifier for Google Drive. This is also similar to the kind of notifier on desktops with an official client.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 11 Access Google Drive ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can quick access the contents of your Google Drive by finding the app of the same name in your program list. It links straight to your folder for ease of access, so you can add it to favourites or quick bar if you wish. There’s also an option to open it from the notifier.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 12 Drive options ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can access syncing options from the indicator to make sure Grive works as you want it to. Access them by clicking on the toolbar icon and select preferences. A couple of options you’d probably want checked are ‘Start Drive when computer turns on’, and ‘On screen notifications’.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 13 Auto-syncing ####
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike the official clients, you cannot select which folders do and do not get synced on your client. Depending on how you plan to use it, you can turn on Auto-sync so that everything is synced up and down at all times, or you can turn it off and sync manually when everything is ready.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 14 Large file tip ####
|
||||
|
||||
Google Drive – not just Grive – always seems to have issues with uploading larger files. We suggest splitting them up into smaller files using split on a compressed file to make them all a specific size. You can do it in a terminal with:
|
||||
|
||||
split -b 500m file.mp4 newfilename
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 15 File types ####
|
||||
|
||||
One of the major things you may have noticed is which documents have and have not been downloaded by Grive. On the official clients, links will be added that can let you jump straight to pure Google Docs files, while files that are actually DOC, ODF or PDF will be downloaded outright to the system. Only the latter files are downloaded with Grive as they’re purely stored in the cloud on Drive. The upside is they’re properly stored locally and will still sync between the cloud and other systems.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 16 Location ####
|
||||
|
||||
Very simply, the Google Drive folder is kept in the home folder under Google Drive. If you’re using standard GNOME it’s actually opening the files in the GNOME file manager; for some reason it also does that in Unity and any non-GNOME desktop environment.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 17 Backup to Grive ####
|
||||
|
||||
One of the benefits of cloud storage for files is that the storage itself is off-site and difficult to lose. This makes it ideal for backing up other important documents and settings. The simplest and quickest way to do this is to periodically copy a file over to the Drive folder and watch it upload.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 18 Better backup ####
|
||||
|
||||
This is not the most efficient way to backup such files though; fortunately Linux comes with many tools to back up data that also includes backup scheduling thanks to cron. We’ll be using luckyBackup for this: find it in your package manager and install it.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 19 Set up the backup ####
|
||||
|
||||
Click Add to create a new task and name it however you wish. Keep the Type setting to ‘Backup Source inside Destination’, choose your Source and finally set the Destination as the Google Drive folder. Click OK to save it, followed by the checkbox next to the task to activate it.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 20 First backup ####
|
||||
|
||||
Click Run at the top to do the first backup operation. It will print out a verbose list of the files and operations and will inform you once it’s finished, along with any errors that occurred along the way. If you have automatic sync on, it will start uploading the backed up files to Drive.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 21 Timed backup ####
|
||||
|
||||
Click Done to return to the main menu. Click Profile followed by Schedule to bring up the scheduling dialog. The schedules are done by profiles, which can all contain a number of different backup tasks. Click Add to start creating a schedule for our Drive backup.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 22 To schedule ####
|
||||
|
||||
The schedule creates a cron job, so you can set it to occur on specific days of the week or specific months of the year and at what time the backup should occur. You can have it do so every hour at a specific minute past the hour if you need it to back up so frequently.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 23 Reverse backup ####
|
||||
|
||||
Google Drive helpfully keeps a record of past versions of files on its servers; however they do not extend forever. If you’re backing up or saving to the cloud you may want to consider creating a backup of the Drive files to your PC or network as well.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 24 Driven ####
|
||||
|
||||
While there are no official tools for Linux just yet, Grive and Grive Tools at least enable you to emulate what they should be relatively well. Look out for updates to Drive and Grive Tools to see if any new functions would work well for you.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxuser.co.uk/tutorials/install-google-docs-on-linux-with-grive-tools
|
||||
|
||||
原文作者:Rob Zwetsloot
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.thefanclub.co.za/
|
||||
@ -1,101 +0,0 @@
|
||||
luoyutiantan
|
||||
Shellshock: How to protect your Unix, Linux and Mac servers
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Summary**: The Unix/Linux Bash security hole can be deadly to your servers. Here's what you need to worry about, how to see if you can be attacked, and what to do if your shields are down.
|
||||
|
||||
The only thing you have to fear with [Shellshock, the Unix/Linux Bash security hole][1], is fear itself. Yes, Shellshock can serve as a highway for worms and malware to hit your Unix, Linux, and Mac servers, but you can defend against it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you don't patch and defend yourself against Shellshock today, you may have lost control of your servers by tomorrow.
|
||||
|
||||
However, Shellshock is not as bad as [HeartBleed][2]. Not yet, anyway.
|
||||
|
||||
While it's true that the [Bash shell][3] is the default command interpreter on most Unix and Linux systems and all Macs — the majority of Web servers — for an attacker to get to your system, there has to be a way for him or her to actually get to the shell remotely. So, if you're running a PC without [ssh][4], [rlogin][5], or another remote desktop program, you're probably safe enough.
|
||||
|
||||
A more serious problem is faced by devices that use embedded Linux — such as routers, switches, and appliances. If you're running an older, no longer supported model, it may be close to impossible to patch it and will likely be vulnerable to attacks. If that's the case, you should replace as soon as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
The real and present danger is for servers. According to the National Institute of Standards (NIST), [Shellshock scores a perfect 10][6] for potential impact and exploitability. [Red Hat][7] reports that the most common attack vectors are:
|
||||
|
||||
- **httpd (Your Web server)**: CGI [Common-Gateway Interface] scripts are likely affected by this issue: when a CGI script is run by the web server, it uses environment variables to pass data to the script. These environment variables can be controlled by the attacker. If the CGI script calls Bash, the script could execute arbitrary code as the httpd user. mod_php, mod_perl, and mod_python do not use environment variables and we believe they are not affected.
|
||||
- **Secure Shell (SSH)**: It is not uncommon to restrict remote commands that a user can run via SSH, such as rsync or git. In these instances, this issue can be used to execute any command, not just the restricted command.
|
||||
- **dhclient**: The [Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Client (dhclient)][8] is used to automatically obtain network configuration information via DHCP. This client uses various environment variables and runs Bash to configure the network interface. Connecting to a malicious DHCP server could allow an attacker to run arbitrary code on the client machine.
|
||||
- **[CUPS][9] (Linux, Unix and Mac OS X's print server)**: It is believed that CUPS is affected by this issue. Various user-supplied values are stored in environment variables when cups filters are executed.
|
||||
- **sudo**: Commands run via sudo are not affected by this issue. Sudo specifically looks for environment variables that are also functions. It could still be possible for the running command to set an environment variable that could cause a Bash child process to execute arbitrary code.
|
||||
- **Firefox**: We do not believe Firefox can be forced to set an environment variable in a manner that would allow Bash to run arbitrary commands. It is still advisable to upgrade Bash as it is common to install various plug-ins and extensions that could allow this behavior.
|
||||
- **Postfix**: The Postfix [mail] server will replace various characters with a ?. While the Postfix server does call Bash in a variety of ways, we do not believe an arbitrary environment variable can be set by the server. It is however possible that a filter could set environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
So much for Red Hat's thoughts. Of these, the Web servers and SSH are the ones that worry me the most. The DHCP client is also troublesome, especially if, as it the case with small businesses, your external router doubles as your Internet gateway and DHCP server.
|
||||
|
||||
Of these, Web server attacks seem to be the most common by far. As Florian Weimer, a Red Hat security engineer, wrote: "[HTTP requests to CGI scripts][10] have been identified as the major attack vector." Attacks are being made against systems [running both Linux and Mac OS X][11].
|
||||
|
||||
Jaime Blasco, labs director at [AlienVault][12], a security management services company, ran a [honeypot][13] looking for attackers and found "[several machines trying to exploit the Bash vulnerability][14]. The majority of them are only probing to check if systems are vulnerable. On the other hand, we found two worms that are actively exploiting the vulnerability and installing a piece of malware on the system."
|
||||
|
||||
Other security researchers have found that the malware is the usual sort. They typically try to plant distributed denial of service (DDoS) IRC bots and attempt to guess system logins and passwords using a list of poor passwords such as 'root', 'admin', 'user', 'login', and '123456.'
|
||||
|
||||
So, how do you know if your servers can be attacked? First, you need to check to see if you're running a vulnerable version of Bash. To do that, run the following command from a Bash shell:
|
||||
|
||||
env x='() { :;}; echo vulnerable' bash -c "echo this is a test"
|
||||
|
||||
If you get the result:
|
||||
|
||||
*vulnerable this is a test*
|
||||
|
||||
Bad news, your version of Bash can be hacked. If you see:
|
||||
|
||||
*bash: warning: x: ignoring function definition attempt bash: error importing function definition for `x' this is a test*
|
||||
|
||||
You're good. Well, to be more exact, you're as protected as you can be at the moment.
|
||||
|
||||
While all major Linux distributors have released patches that stop most attacks — [Apple has not released a patch yet][15] — it has been discovered that "[patches shipped for this issue are incomplete][16]. An attacker can provide specially-crafted environment variables containing arbitrary commands that will be executed on vulnerable systems under certain conditions." While it's unclear if these attacks can be used to hack into a system, it is clear that they can be used to crash them, thanks to a null-pointer exception.
|
||||
|
||||
Patches to fill-in the [last of the Shellshock security hole][17] are being worked on now. In the meantime, you should update your servers as soon as possible with the available patches and keep an eye open for the next, fuller ones.
|
||||
|
||||
In the meantime, if, as is likely, you're running the Apache Web server, there are some [Mod_Security][18] rules that can stop attempts to exploit Shellshock. These rules, created by Red Hat, are:
|
||||
|
||||
Request Header values:
|
||||
SecRule REQUEST_HEADERS "^\(\) {" "phase:1,deny,id:1000000,t:urlDecode,status:400,log,msg:'CVE-2014-6271 - Bash Attack'"
|
||||
|
||||
SERVER_PROTOCOL values:
|
||||
SecRule REQUEST_LINE "\(\) {" "phase:1,deny,id:1000001,status:400,log,msg:'CVE-2014-6271 - Bash Attack'"
|
||||
|
||||
GET/POST names:
|
||||
SecRule ARGS_NAMES "^\(\) {" "phase:2,deny,id:1000002,t:urlDecode,t:urlDecodeUni,status:400,log,msg:'CVE-2014-6271 - Bash Attack'"
|
||||
|
||||
GET/POST values:
|
||||
SecRule ARGS "^\(\) {" "phase:2,deny,id:1000003,t:urlDecode,t:urlDecodeUni,status:400,log,msg:'CVE-2014-6271 - Bash Attack'"
|
||||
|
||||
File names for uploads:
|
||||
SecRule FILES_NAMES "^\(\) {" "phase:2,deny,id:1000004,t:urlDecode,t:urlDecodeUni,status:400,log,msg:'CVE-2014-6271 - Bash Attack'"
|
||||
|
||||
It is vital that you patch your servers as soon as possible, even with the current, incomplete ones, and to set up defenses around your Web servers. If you don't, you could come to work tomorrow to find your computers completely compromised. So get out there and start patching!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.zdnet.com/shellshock-how-to-protect-your-unix-linux-and-mac-servers-7000034072/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.zdnet.com/meet-the-team/us/steven-j-vaughan-nichols/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.zdnet.com/unixlinux-bash-critical-security-hole-uncovered-7000034021/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.zdnet.com/heartbleed-serious-openssl-zero-day-vulnerability-revealed-7000028166
|
||||
[3]:http://www.gnu.org/software/bash/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.openbsd.org/cgi-bin/man.cgi?query=ssh&sektion=1
|
||||
[5]:http://unixhelp.ed.ac.uk/CGI/man-cgi?rlogin
|
||||
[6]:http://web.nvd.nist.gov/view/vuln/detail?vulnId=CVE-2014-7169
|
||||
[7]:http://www.redhat.com/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.isc.org/downloads/dhcp/
|
||||
[9]:https://www.cups.org/
|
||||
[10]:http://seclists.org/oss-sec/2014/q3/650
|
||||
[11]:http://www.zdnet.com/first-attacks-using-shellshock-bash-bug-discovered-7000034044/
|
||||
[12]:http://www.alienvault.com/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.sans.org/security-resources/idfaq/honeypot3.php
|
||||
[14]:http://www.alienvault.com/open-threat-exchange/blog/attackers-exploiting-shell-shock-cve-2014-6721-in-the-wild
|
||||
[15]:http://apple.stackexchange.com/questions/146849/how-do-i-recompile-bash-to-avoid-the-remote-exploit-cve-2014-6271-and-cve-2014-7
|
||||
[16]:https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1141597#c27
|
||||
[17]:http://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2014-7169
|
||||
[18]:http://www.inmotionhosting.com/support/website/modsecurity/what-is-modsecurity-and-why-is-it-important
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user