mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-25 23:11:02 +08:00
[Translated] tech/RHCE/Part 7 - Setting Up NFS Server with Kerberos-based Authentication for Linux Clients.md
This commit is contained in:
parent
05a15d7a87
commit
b6b80a6daa
@ -1,189 +0,0 @@
|
||||
ictlyh Translating
|
||||
Setting Up NFS Server with Kerberos-based Authentication for Linux Clients – Part 7
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In the last article of this series, we reviewed [how to set up a Samba share over a network][1] that may consist of multiple types of operating systems. Now, if you need to set up file sharing for a group of Unix-like clients you will automatically think of the Network File System, or NFS for short.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
RHCE Series: Setting Up NFS Server with Kerberos Authentication – Part 7
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we will walk you through the process of using Kerberos-based authentication for NFS shares. It is assumed that you already have set up a NFS server and a client. If not, please refer to [install and configure NFS server][2] – which will list the necessary packages that need to be installed and explain how to perform initial configurations on the server before proceeding further.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, you will want to configure both [SELinux][3] and [firewalld][4] to allow for file sharing through NFS.
|
||||
|
||||
The following example assumes that your NFS share is located in /nfs in box2:
|
||||
|
||||
# semanage fcontext -a -t public_content_rw_t "/nfs(/.*)?"
|
||||
# restorecon -R /nfs
|
||||
# setsebool -P nfs_export_all_rw on
|
||||
# setsebool -P nfs_export_all_ro on
|
||||
|
||||
(where the -P flag indicates persistence across reboots).
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, don’t forget to:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Create NFS Group and Configure NFS Share Directory ####
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create a group called nfs and add the nfsnobody user to it, then change the permissions of the /nfs directory to 0770 and its group owner to nfs. Thus, nfsnobody (which is mapped to the client requests) will have write permissions on the share) and you won’t need to use no_root_squash in the /etc/exports file.
|
||||
|
||||
# groupadd nfs
|
||||
# usermod -a -G nfs nfsnobody
|
||||
# chmod 0770 /nfs
|
||||
# chgrp nfs /nfs
|
||||
|
||||
2. Modify the exports file (/etc/exports) as follows to only allow access from box1 using Kerberos security (sec=krb5).
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: that the value of anongid has been set to the GID of the nfs group that we created previously:
|
||||
|
||||
**exports – Add NFS Share**
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
/nfs box1(rw,sec=krb5,anongid=1004)
|
||||
|
||||
3. Re-export (-r) all (-a) the NFS shares. Adding verbosity to the output (-v) is a good idea since it will provide helpful information to troubleshoot the server if something goes wrong:
|
||||
|
||||
# exportfs -arv
|
||||
|
||||
4. Restart and enable the NFS server and related services. Note that you don’t have to enable nfs-lock and nfs-idmapd because they will be automatically started by the other services on boot:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart rpcbind nfs-server nfs-lock nfs-idmap
|
||||
# systemctl enable rpcbind nfs-server
|
||||
|
||||
#### Testing Environment and Other Prerequisites ####
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide we will use the following test environment:
|
||||
|
||||
- Client machine [box1: 192.168.0.18]
|
||||
- NFS / Kerberos server [box2: 192.168.0.20] (also known as Key Distribution Center, or KDC for short).
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: that Kerberos service is crucial to the authentication scheme.
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, the NFS server and the KDC are hosted in the same machine for simplicity, although you can set them up in separate machines if you have more available. Both machines are members of the `mydomain.com` domain.
|
||||
|
||||
Last but not least, Kerberos requires at least a basic schema of name resolution and the [Network Time Protocol][5] service to be present in both client and server since the security of Kerberos authentication is in part based upon the timestamps of tickets.
|
||||
|
||||
To set up name resolution, we will use the /etc/hosts file in both client and server:
|
||||
|
||||
**host file – Add DNS for Domain**
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
192.168.0.18 box1.mydomain.com box1
|
||||
192.168.0.20 box2.mydomain.com box2
|
||||
|
||||
In RHEL 7, chrony is the default software that is used for NTP synchronization:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install chrony
|
||||
# systemctl start chronyd
|
||||
# systemctl enable chronyd
|
||||
|
||||
To make sure chrony is actually synchronizing your system’s time with time servers you may want to issue the following command two or three times and make sure the offset is getting nearer to zero:
|
||||
|
||||
# chronyc tracking
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Synchronize Server Time with Chrony
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing and Configuring Kerberos ###
|
||||
|
||||
To set up the KDC, install the following packages on both server and client (omit the server package in the client):
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install krb5-server krb5-workstation pam_krb5
|
||||
|
||||
Once it is installed, edit the configuration files (/etc/krb5.conf and /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl) and replace all instances of example.com (lowercase and uppercase) with `mydomain.com` as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, enable Kerberos through the firewall and start / enable the related services.
|
||||
|
||||
**Important**: nfs-secure must be started and enabled on the client as well:
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=kerberos
|
||||
# systemctl start krb5kdc kadmin nfs-secure
|
||||
# systemctl enable krb5kdc kadmin nfs-secure
|
||||
|
||||
Now create the Kerberos database (please note that this may take a while as it requires a some level of entropy in your system. To speed things up, I opened another terminal and ran ping -f localhost for 30-45 seconds):
|
||||
|
||||
# kdb5_util create -s
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Create Kerberos Database
|
||||
|
||||
Next, using the kadmin.local tool, create an admin principal for root:
|
||||
|
||||
# kadmin.local
|
||||
# addprinc root/admin
|
||||
|
||||
And add the Kerberos server to the database:
|
||||
|
||||
# addprinc -randkey host/box2.mydomain.com
|
||||
|
||||
Same with the NFS service for both client (box1) and server (box2). Please note that in the screenshot below I forgot to do it for box1 before quitting:
|
||||
|
||||
# addprinc -randkey nfs/box2.mydomain.com
|
||||
# addprinc -randkey nfs/box1.mydomain.com
|
||||
|
||||
And exit by typing quit and pressing Enter:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Add Kerberos to NFS Server
|
||||
|
||||
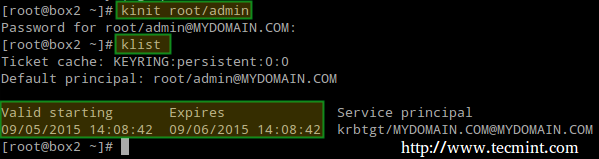
Then obtain and cache Kerberos ticket-granting ticket for root/admin:
|
||||
|
||||
# kinit root/admin
|
||||
# klist
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Cache Kerberos
|
||||
|
||||
The last step before actually using Kerberos is storing into a keytab file (in the server) the principals that are authorized to use Kerberos authentication:
|
||||
|
||||
# kdadmin.local
|
||||
# ktadd host/box2.mydomain.com
|
||||
# ktadd nfs/box2.mydomain.com
|
||||
# ktadd nfs/box1.mydomain.com
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, mount the share and perform a write test:
|
||||
|
||||
# mount -t nfs4 -o sec=krb5 box2:/nfs /mnt
|
||||
# echo "Hello from Tecmint.com" > /mnt/greeting.txt
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Mount NFS Share
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s now unmount the share, rename the keytab file in the client (to simulate it’s not present) and try to mount the share again:
|
||||
|
||||
# umount /mnt
|
||||
# mv /etc/krb5.keytab /etc/krb5.keytab.orig
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Mount Unmount Kerberos NFS Share
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can use the NFS share with Kerberos-based authentication.
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we have explained how to set up NFS with Kerberos authentication. Since there is much more to the topic than we can cover in a single guide, feel free to check the online [Kerberos documentation][6] and since Kerberos is a bit tricky to say the least, don’t hesitate to drop us a note using the form below if you run into any issue or need help with your testing or implementation.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/setting-up-nfs-server-with-kerberos-based-authentication/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/setup-samba-file-sharing-for-linux-windows-clients/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/configure-nfs-server/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/selinux-essentials-and-control-filesystem-access/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/firewalld-rules-for-centos-7/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-ntp-server-in-centos/
|
||||
[6]:http://web.mit.edu/kerberos/krb5-1.12/doc/admin/admin_commands/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
|
||||
第七部分 - 在 Linux 客户端配置基于 Kerberos 身份验证的 NFS 服务器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在本系列的前一篇文章,我们回顾了[如何在可能包括多种类型操作系统的网络上配置 Samba 共享][1]。现在,如果你需要为一组类-Unix 客户端配置文件共享,很自然的你会想到网络文件系统,或简称 NFS。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
RHCE 系列:第七部分 - 设置使用 Kerberos 进行身份验证的 NFS 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中我们会介绍配置基于 Kerberos 身份验证的 NFS 共享的整个流程。假设你已经配置好了一个 NFS 服务器和一个客户端。如果还没有,可以参考 [安装和配置 NFS 服务器][2] - 它列出了需要安装的依赖软件包并解释了在进行下一步之前如何在服务器上进行初始化配置。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,你可能还需要配置 [SELinux][3] 和 [firewalld][4] 以允许通过 NFS 进行文件共享。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的例子假设你的 NFS 共享目录在 box2 的 /nfs:
|
||||
|
||||
# semanage fcontext -a -t public_content_rw_t "/nfs(/.*)?"
|
||||
# restorecon -R /nfs
|
||||
# setsebool -P nfs_export_all_rw on
|
||||
# setsebool -P nfs_export_all_ro on
|
||||
|
||||
(其中 -P 标记指示重启持久有效)。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,别忘了:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 创建 NFS 组并配置 NFS 共享目录 ####
|
||||
|
||||
1. 新建一个名为 nfs 的组并给它添加用户 nfsnobody,然后更改 /nfs 目录的权限为 0770,组属主为 nfs。于是,nfsnobody(对应请求用户)在共享目录有写的权限,你就不需要在 /etc/exports 文件中使用 no_root_squash(译者注:设为 root_squash 意味着在访问 NFS 服务器上的文件时,客户机上的 root 用户不会被当作 root 用户来对待)。
|
||||
|
||||
# groupadd nfs
|
||||
# usermod -a -G nfs nfsnobody
|
||||
# chmod 0770 /nfs
|
||||
# chgrp nfs /nfs
|
||||
|
||||
2. 像下面那样更改 export 文件(/etc/exports)只允许从 box1 使用 Kerberos 安全验证的访问(sec=krb5)。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:anongid 的值设置为之前新建的组 nfs 的 GID:
|
||||
|
||||
**exports – 添加 NFS 共享**
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
/nfs box1(rw,sec=krb5,anongid=1004)
|
||||
|
||||
3. 再次 exprot(-r)所有(-a)NFS 共享。为输出添加详情(-v)是个好主意,因为它提供了发生错误时解决问题的有用信息:
|
||||
|
||||
# exportfs -arv
|
||||
|
||||
4. 重启并启用 NFS 服务器以及相关服务。注意你不需要启动 nfs-lock 和 nfs-idmapd,因为系统启动时其它服务会自动启动它们:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart rpcbind nfs-server nfs-lock nfs-idmap
|
||||
# systemctl enable rpcbind nfs-server
|
||||
|
||||
#### 测试环境和其它前提要求 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇指南中我们使用下面的测试环境:
|
||||
|
||||
- 客户端机器 [box1: 192.168.0.18]
|
||||
- NFS / Kerberos 服务器 [box2: 192.168.0.20] (也称为密钥分发中心,简称 KDC)。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:Kerberos 服务是至关重要的认证方案。
|
||||
|
||||
正如你看到的,为了简便,NFS 服务器和 KDC 在同一台机器上,当然如果你有更多可用机器你也可以把它们安装在不同的机器上。两台机器都在 `mydomain.com` 域。
|
||||
|
||||
最后同样重要的是,Kerberos 要求客户端和服务器中至少有一个域名解析的基本模式和[网络时间协议][5]服务,因为 Kerberos 身份验证的安全一部分基于时间戳。
|
||||
|
||||
为了配置域名解析,我们在客户端和服务器中编辑 /etc/hosts 文件:
|
||||
|
||||
**host 文件 – 为域添加 DNS**
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
192.168.0.18 box1.mydomain.com box1
|
||||
192.168.0.20 box2.mydomain.com box2
|
||||
|
||||
在 RHEL 7 中,chrony 是用于 NTP 同步的默认软件:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install chrony
|
||||
# systemctl start chronyd
|
||||
# systemctl enable chronyd
|
||||
|
||||
为了确保 chrony 确实在和时间服务器同步你系统的时间,你可能要输入下面的命令两到三次,确保时间偏差尽可能接近 0:
|
||||
|
||||
# chronyc tracking
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
用 Chrony 同步服务器时间
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装和配置 Kerberos ###
|
||||
|
||||
要设置 KDC,首先在客户端和服务器安装下面的软件包(客户端不需要 server 软件包):
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install krb5-server krb5-workstation pam_krb5
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后,编辑配置文件(/etc/krb5.conf 和 /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl),像下面那样用 `mydomain.com` 替换所有 example.com。
|
||||
|
||||
下一步,确保 Kerberos 能功过防火墙并启动/启用相关服务。
|
||||
|
||||
**重要**:客户端也必须启动和启用 nfs-secure:
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=kerberos
|
||||
# systemctl start krb5kdc kadmin nfs-secure
|
||||
# systemctl enable krb5kdc kadmin nfs-secure
|
||||
|
||||
现在创建 Kerberos 数据库(请注意这可能会需要一点时间,因为它会和你的系统进行多次交互)。为了加速这个过程,我打开了另一个终端并运行了 ping -f localhost 30 到 45 秒):
|
||||
|
||||
# kdb5_util create -s
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建 Kerberos 数据库
|
||||
|
||||
下一步,使用 kadmin.local 工具为 root 创建管理权限:
|
||||
|
||||
# kadmin.local
|
||||
# addprinc root/admin
|
||||
|
||||
添加 Kerberos 服务器到数据库:
|
||||
|
||||
# addprinc -randkey host/box2.mydomain.com
|
||||
|
||||
在客户端(box1)和服务器(box2)上对 NFS 服务同样操作。请注意下面的截图中在退出前我忘了在 box1 上进行操作:
|
||||
|
||||
# addprinc -randkey nfs/box2.mydomain.com
|
||||
# addprinc -randkey nfs/box1.mydomain.com
|
||||
|
||||
输入 quit 和回车键退出:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
添加 Kerberos 到 NFS 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
为 root/admin 获取和缓存票据授权票据(ticket-granting ticket):
|
||||
|
||||
# kinit root/admin
|
||||
# klist
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
缓存 Kerberos
|
||||
|
||||
真正使用 Kerberos 之前的最后一步是保存被授权使用 Kerberos 身份验证的规则到一个密钥表文件(在服务器中):
|
||||
|
||||
# kdadmin.local
|
||||
# ktadd host/box2.mydomain.com
|
||||
# ktadd nfs/box2.mydomain.com
|
||||
# ktadd nfs/box1.mydomain.com
|
||||
|
||||
最后,挂载共享目录并进行一个写测试:
|
||||
|
||||
# mount -t nfs4 -o sec=krb5 box2:/nfs /mnt
|
||||
# echo "Hello from Tecmint.com" > /mnt/greeting.txt
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
挂载 NFS 共享
|
||||
|
||||
现在让我们卸载共享,在客户端中重命名密钥表文件(模拟它不存在)然后试着再次挂载共享目录:
|
||||
|
||||
# umount /mnt
|
||||
# mv /etc/krb5.keytab /etc/krb5.keytab.orig
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
挂载/卸载 Kerberos NFS 共享
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以使用基于 Kerberos 身份验证的 NFS 共享了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中我们介绍了如何设置带 Kerberos 身份验证的 NFS。和我们在这篇指南中介绍的相比,该主题还有很多相关内容,可以在 [Kerberos 手册][6] 查看,另外至少可以说 Kerberos 有一点棘手,如果你在测试或实现中遇到了任何问题或需要帮助,别犹豫在下面的评论框中告诉我们吧。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/setting-up-nfs-server-with-kerberos-based-authentication/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](http://www.mutouxiaogui.cn/blog/)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/setup-samba-file-sharing-for-linux-windows-clients/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/configure-nfs-server/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/selinux-essentials-and-control-filesystem-access/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/firewalld-rules-for-centos-7/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-ntp-server-in-centos/
|
||||
[6]:http://web.mit.edu/kerberos/krb5-1.12/doc/admin/admin_commands/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user